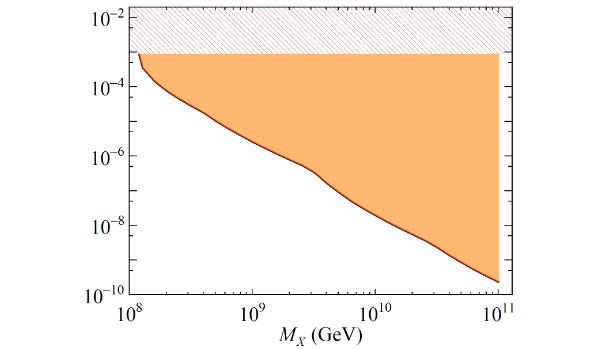
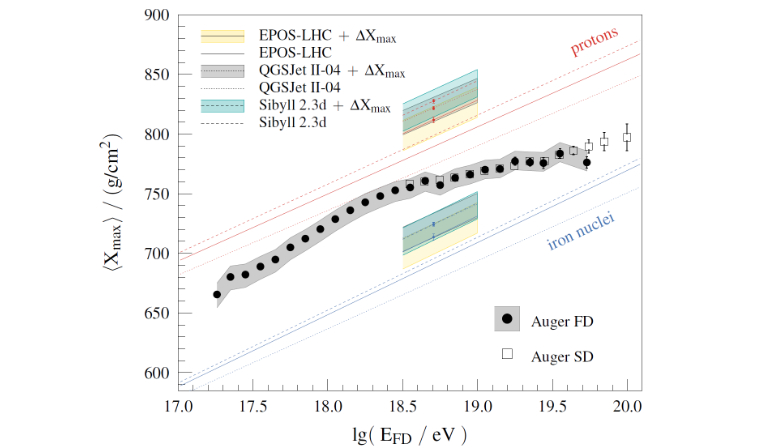
The Pierre Auger Observatory is located on the vast plain known as the Pampa Amarilla (yellow prairie) in western Argentina. It studies the highest-energy particles in the Universe, which hit the Earth from all directions, so-called cosmic rays. Cosmic rays with low to moderate energies are well understood, while those with extremely high energies remain highly mysterious. By detecting and studying these rare particles, the Pierre Auger Observatory is tackling the enigmas of their origin and existence.
The Observatory is a hybrid detector, employing two independent methods to detect and study high-energy cosmic rays. One technique detects high energy particles through their interaction with water placed in surface detector tanks. The other technique tracks the development of air showers by observing ultraviolet light emitted high in the Earth's atmosphere. The hybrid nature of the Pierre Auger Observatory provides for two independent ways to see cosmic rays.