Key Facts
Webb is an International Collaboration
including NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA), and the Canadian Space Agency (CSA).
The NASA Goddard Space Flight Center managed the development effort. The main industrial partner is Northrop Grumman; the Space Telescope Science Institute operates Webb after launch. Thousands of scientists, engineers and technicians from 14 countries, 29 U.S. states, and Washington, D.C. contributed to the design, build, test, integration, launch, commissioning and operations of Webb.
The International Team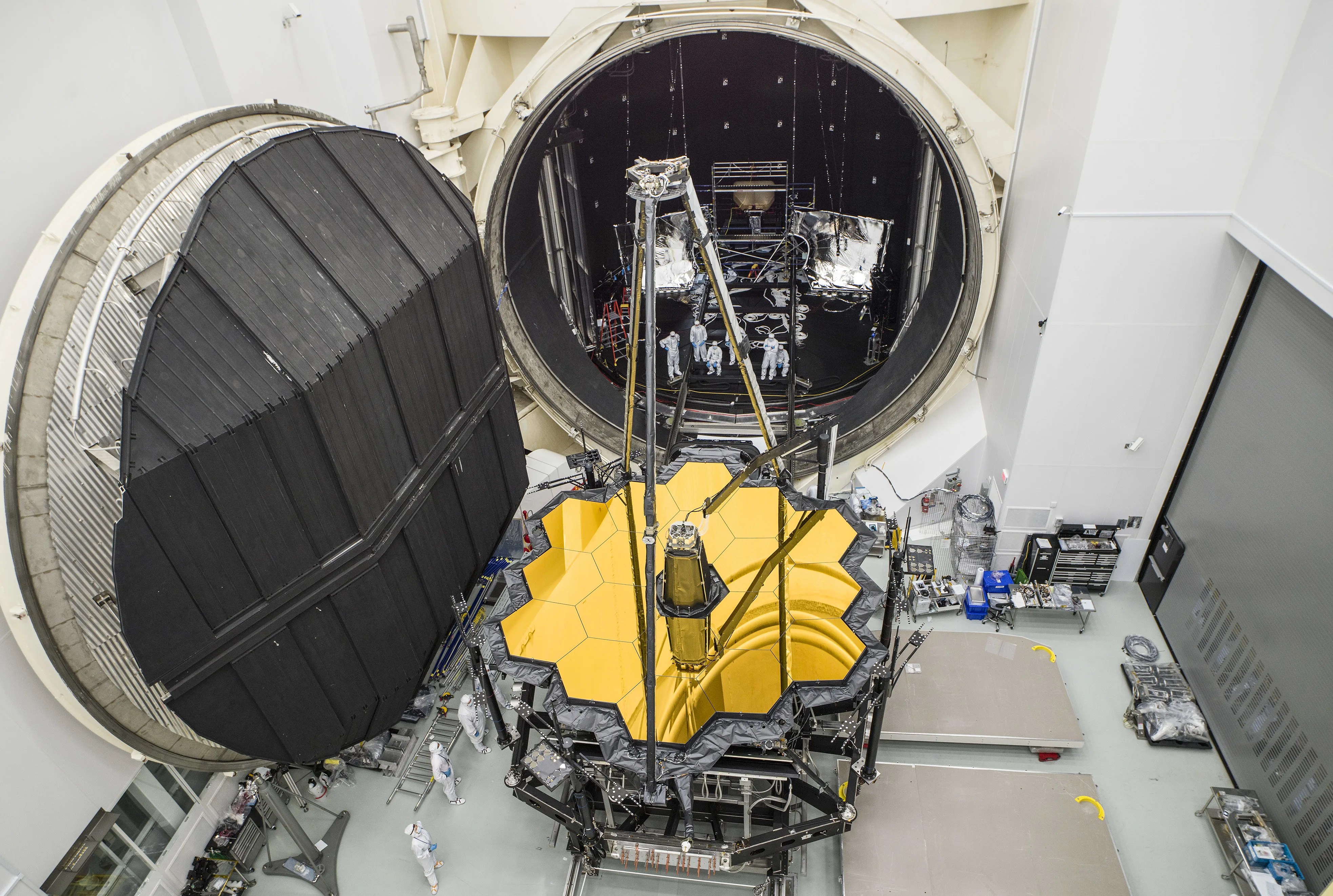
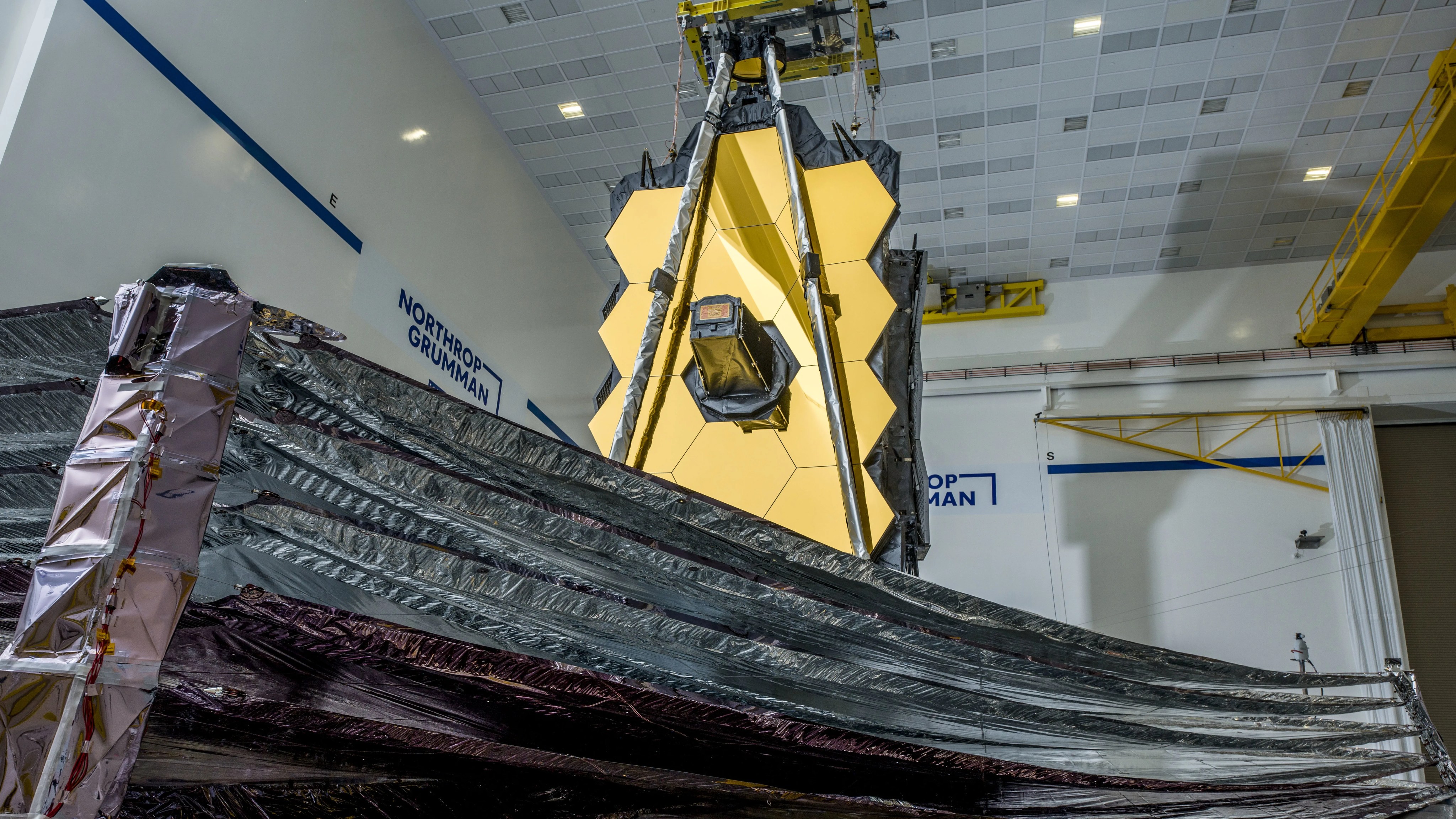
Webb is the largest telescope ever placed in space.
100 times more powerful than Hubble.
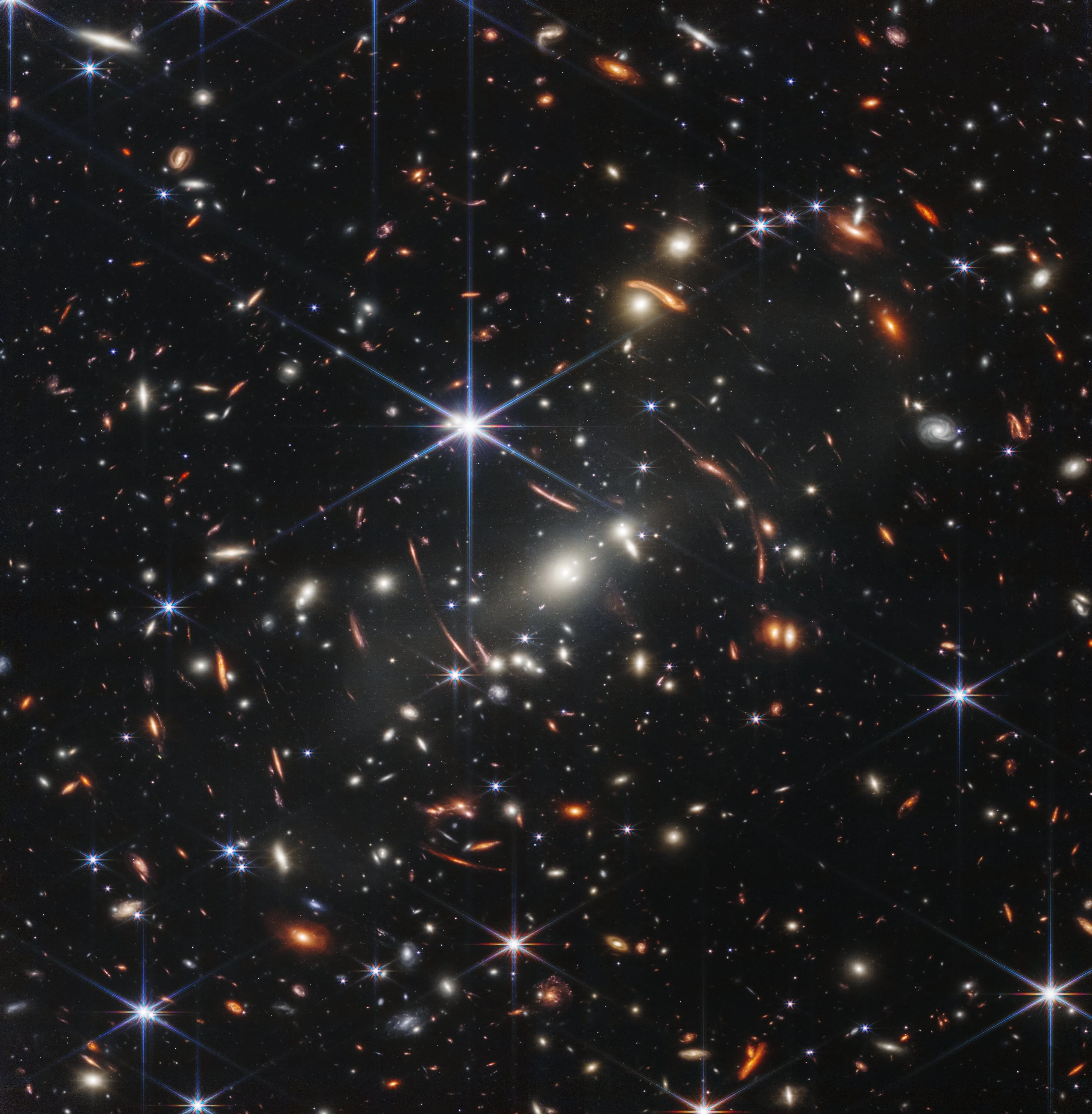
Webb is designed to look deeper into space to see the earliest stars and galaxies that formed in the universe and to look deep into nearby dust clouds to study the formation of stars and planets.
Webb vs Hubble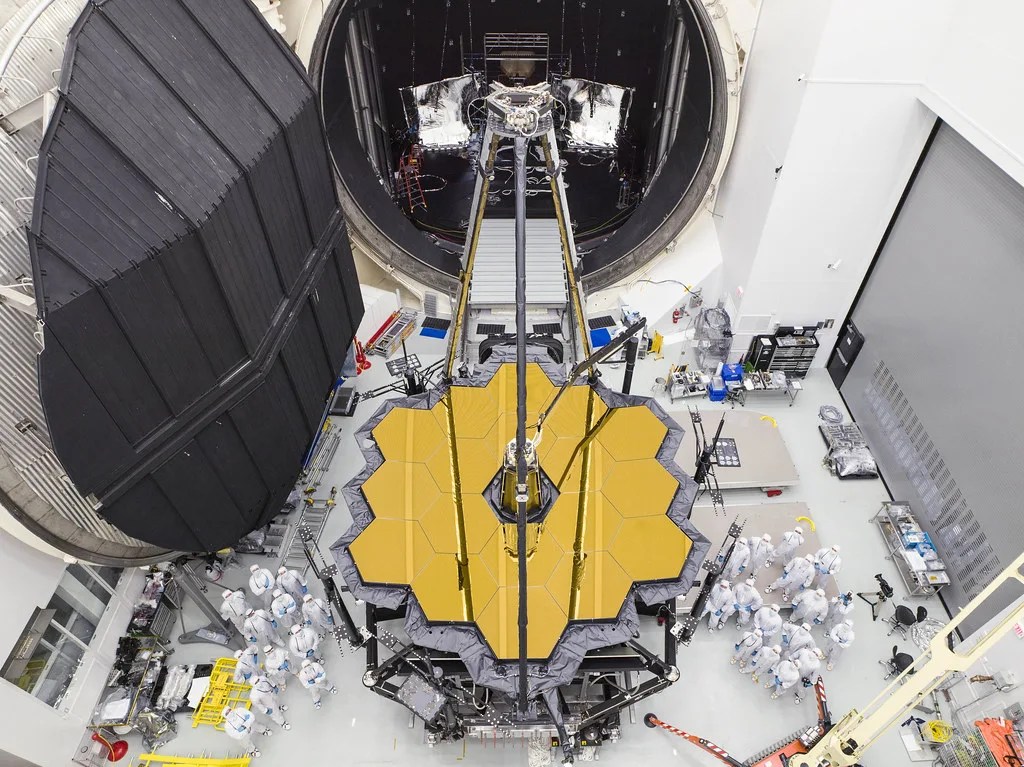
Launch and Orbit
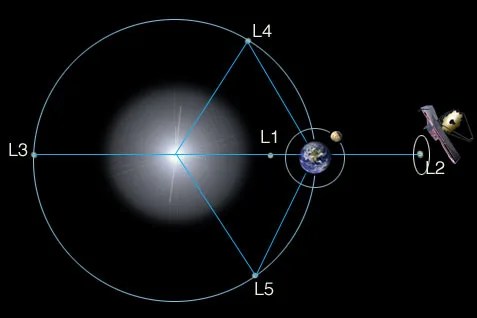
Webb was launched on Dec 25, 2021 on from French Guiana on an Arianne 5 rocket. Webb orbits the Sun 1.5 million kilometers from the Earth.

History
Who Is James Webb?
Webb was formerly known as the “Next Generation Space Telescope” (NGST); it was renamed in Sept. 2002 after a former NASA administrator.
Many believe that James E. Webb, who ran the fledgling NASA space agency from February 1961 to October 1968, did more for science than perhaps any other government official and that it is only fitting that the Next Generation Space Telescope would be named after him.
Learn More



Innovative Technologies
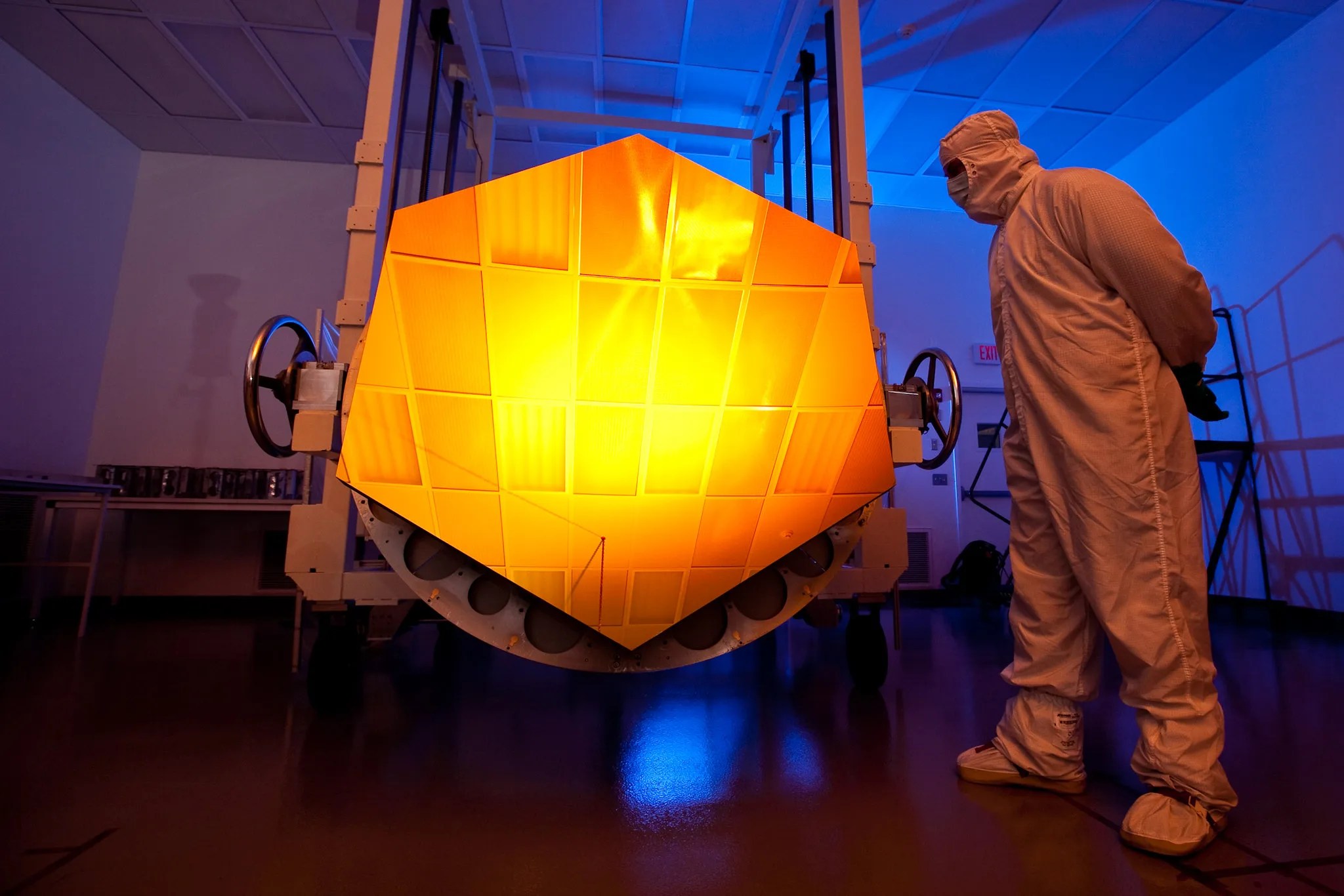
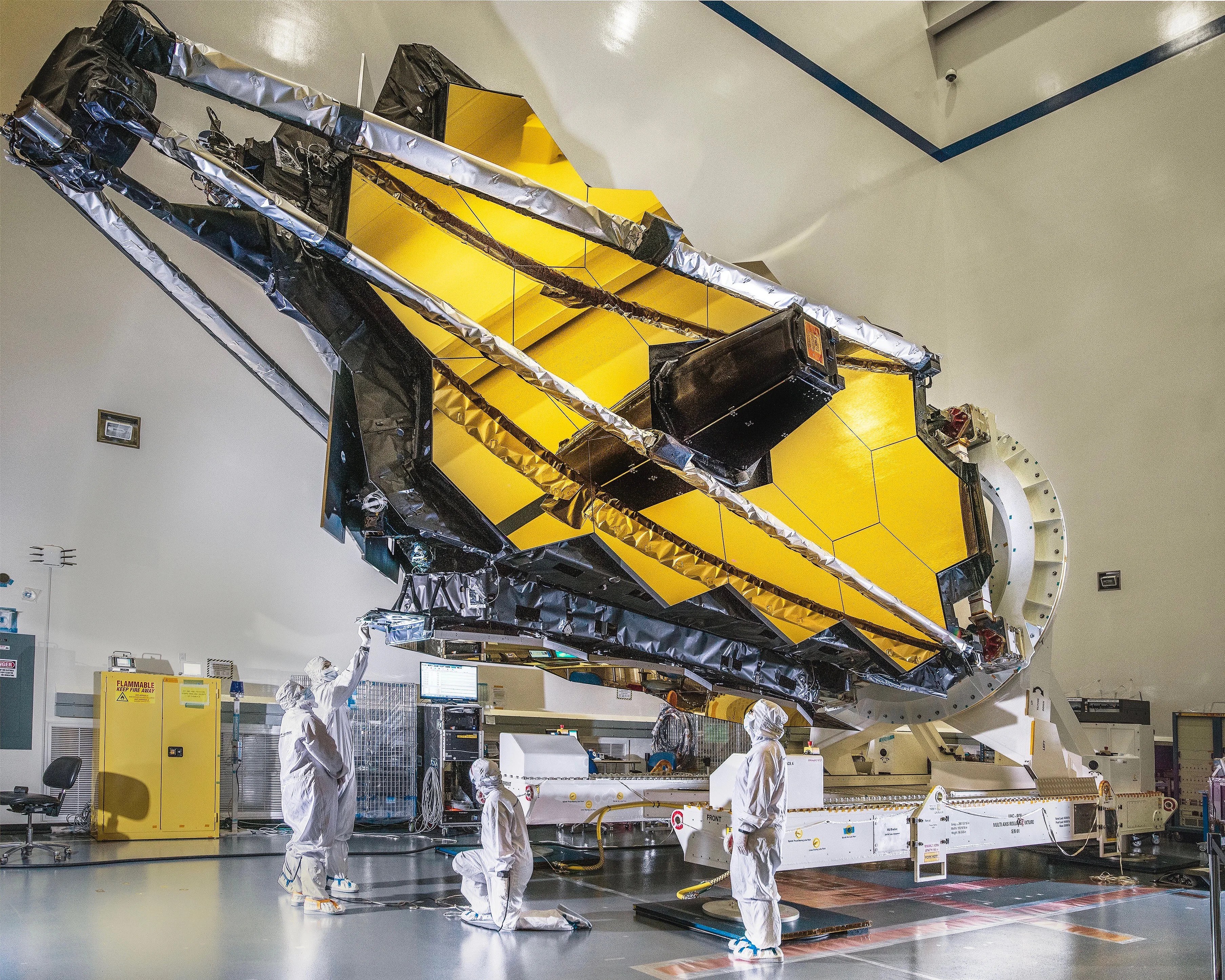
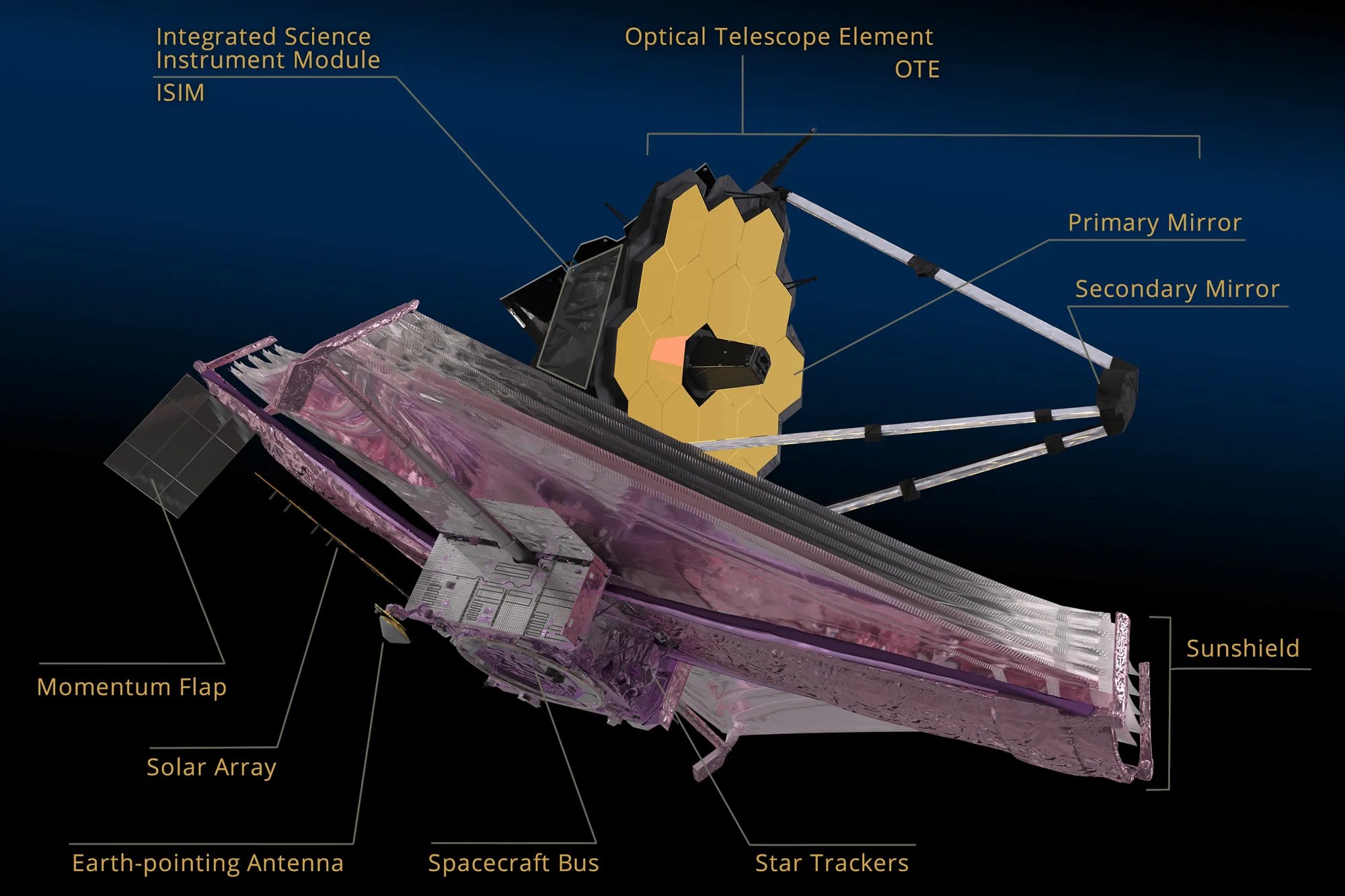
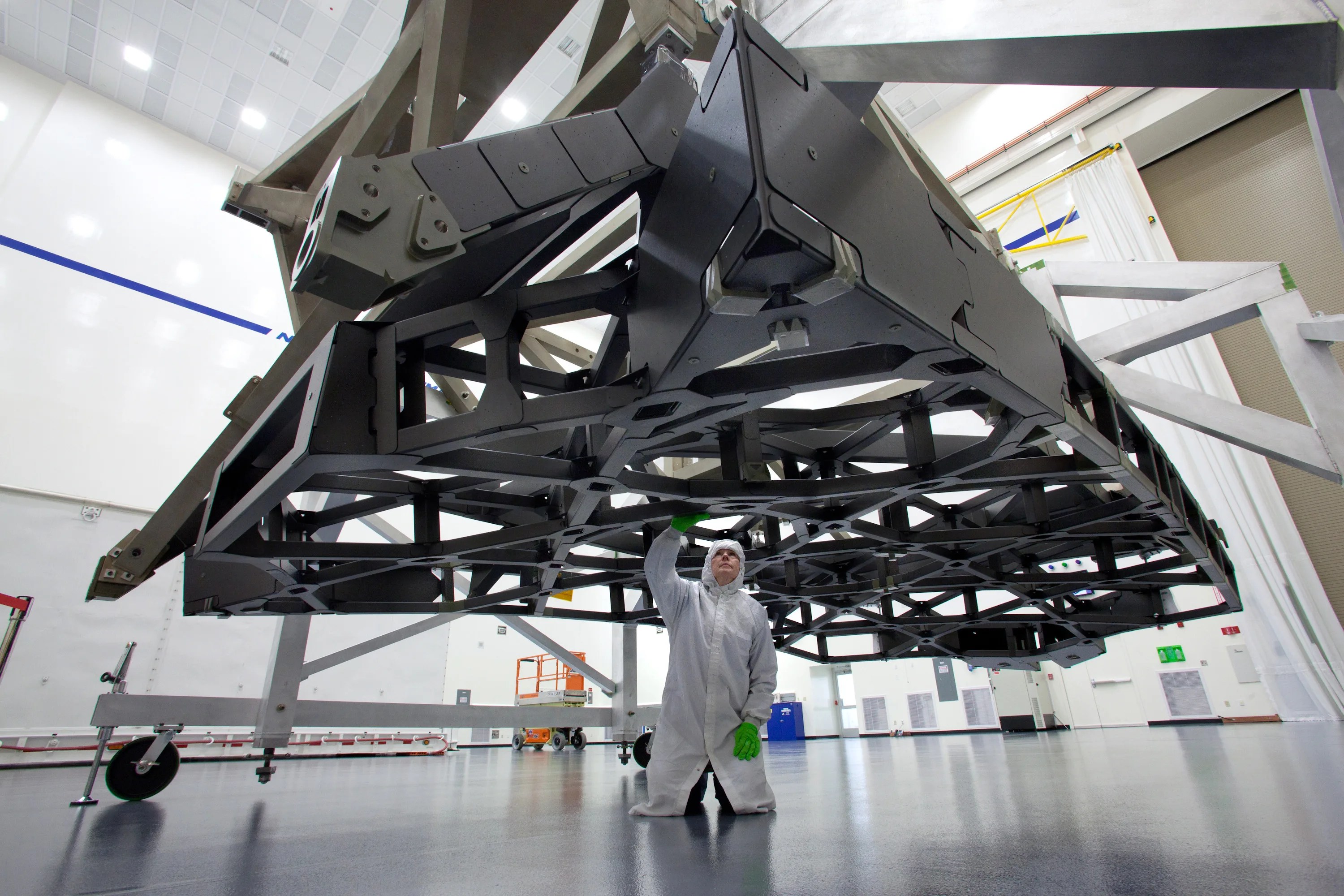
Several innovative technologies were developed for Webb. These include a primary mirror made of 18 separate segments that unfold and adjust to shape after launch. The mirrors are made of ultra-lightweight beryllium. Webb’s biggest feature is a tennis court sized five-layer sunshield that attenuates heat from the Sun more than a million times. The telescope’s four instruments – cameras and spectrometers – have detectors that are able to record extremely faint signals. One instrument (NIRSpec) has programmable microshutters, which enable observation up to 100 objects simultaneously. Webb also has a cryocooler for cooling the mid-infrared detectors of another instrument (MIRI)to a very cold 7 K to operate properly.
Innovation
Folding Deployable Mirrors
Innovation
5 layer Sunshield
Innovation
Backplane
Innovation
Microshutters
Webb Mission Overview 2023
A brief overview of the James Webb Space Telescope mission from its construction, launch, and complex unfolding, to the incredible science it achieves. Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center Producer: Michael McClare (KBRwyle)