0.引言
因笔者课题涉及点云处理,需要通过PCL进行点云数据一系列处理分析,查阅现有网络资料,对常用PCL点云曲面重建进行代码实现,本文记录曲面重建实现过程。
1.CloudCompare界面设计重建(reconstruct)按钮
(1)设计.ui文件
①设计按钮

②编译.ui

(2)修改mainwindow.h文件
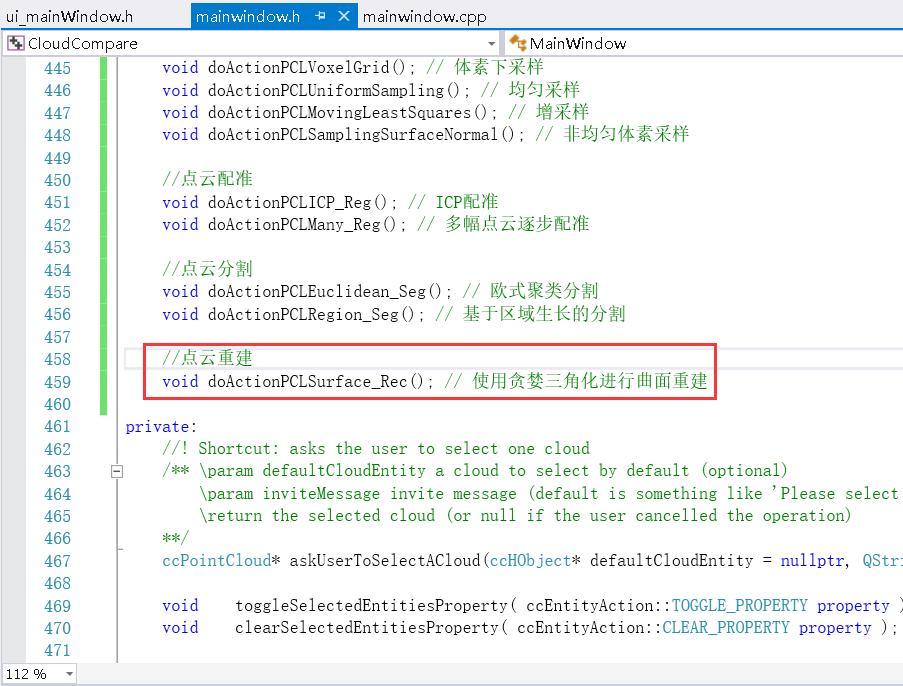
//点云重建
void doActionPCLSurface_Rec(); // 使用贪婪三角化进行曲面重建
(3)修改mainwindow.cpp文件
①添加头文件

#include <pcl/filters/radius_outlier_removal.h>
#include <pcl/filters/voxel_grid.h>
#include <pcl/filters/statistical_outlier_removal.h>
#include <pcl/surface/mls.h>
#include <pcl/features/normal_3d.h>
#include <pcl/surface/gp3.h>
②添加实现代码

//使用贪婪三角化进行曲面重建
void MainWindow::doActionPCLSurface_Rec()
{
}
③添加信号槽函数

onnect(m_UI->actionSurface_Rec, &QAction::triggered, this, &MainWindow::doActionPCLSurface_Rec);//使用贪婪三角化进行曲面重建
(4)生成

2.使用贪婪三角化进行曲面重建(Surface_Rec)
(1)实现代码
typedef pcl::PointXYZ PointT;
//使用贪婪三角化进行曲面重建
void MainWindow::doActionPCLSurface_Rec() {
if (getSelectedEntities().size() != 1)
{
ccLog::Print(QStringLiteral("只能选择一个点云实体"));
return;
}
ccHObject* entity = getSelectedEntities()[0];
ccPointCloud* ccCloud = ccHObjectCaster::ToPointCloud(entity);
// ---------------------------读取数据到PCL----------------------------------
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
cloud->resize(ccCloud->size());
for (int i = 0; i < cloud->size(); ++i)
{
const CCVector3* point = ccCloud->getPoint(i);
cloud->points[i].x = point->x;
cloud->points[i].y = point->y;
cloud->points[i].z = point->z;
}
pcl::PointCloud<PointT>::Ptr cloud_downSampled(new pcl::PointCloud<PointT>);
pcl::PointCloud<PointT>::Ptr cloud_filtered(new pcl::PointCloud<PointT>);
pcl::PointCloud<PointT>::Ptr cloud_smoothed(new pcl::PointCloud<PointT>);
// 下采样,同时保持点云形状特征
pcl::VoxelGrid<PointT> downSampled; //创建滤波对象
downSampled.setInputCloud(cloud); //设置需要过滤的点云给滤波对象
downSampled.setLeafSize(0.01f, 0.01f, 0.01f); //设置滤波时创建的体素体积为1cm的立方体
downSampled.filter(*cloud_downSampled); //执行滤波处理,存储输出
// 统计滤波
pcl::StatisticalOutlierRemoval<PointT> statisOutlierRemoval; //创建滤波器对象
statisOutlierRemoval.setInputCloud(cloud_downSampled); //设置待滤波的点云
statisOutlierRemoval.setMeanK(50); //设置在进行统计时考虑查询点临近点数
statisOutlierRemoval.setStddevMulThresh(3.0); //设置判断是否为离群点的阀值:均值+1.0*标准差
statisOutlierRemoval.filter(*cloud_filtered); //滤波结果存储到cloud_filtered
// 对点云重采样
pcl::search::KdTree<PointT>::Ptr treeSampling(new pcl::search::KdTree<PointT>);
pcl::PointCloud<PointT> mls_point;
pcl::MovingLeastSquares<PointT, PointT> mls;
mls.setComputeNormals(false);
mls.setInputCloud(cloud_filtered);
mls.setPolynomialOrder(2);
mls.setPolynomialFit(false);
mls.setSearchMethod(treeSampling);
mls.setSearchRadius(0.05);
mls.process(mls_point);
// 输出重采样结果
cloud_smoothed = mls_point.makeShared();
// 法线估计
pcl::NormalEstimation<PointT, pcl::Normal> normalEstimation;
normalEstimation.setInputCloud(cloud_smoothed);
pcl::search::KdTree<PointT>::Ptr tree(new pcl::search::KdTree<PointT>);
normalEstimation.setSearchMethod(tree);
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>::Ptr normals(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>);
normalEstimation.setKSearch(10);
normalEstimation.compute(*normals);
//Triangle Projection
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointNormal>::Ptr cloud_with_normals(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointNormal>);
pcl::concatenateFields(*cloud_smoothed, *normals, *cloud_with_normals);
pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointNormal>::Ptr tree2(new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointNormal>);
tree2->setInputCloud(cloud_with_normals);
pcl::GreedyProjectionTriangulation<pcl::PointNormal> gp3;
pcl::PolygonMesh triangles;
gp3.setSearchRadius(0.1);
gp3.setMu(2.5);
gp3.setMaximumNearestNeighbors(52);
gp3.setMaximumAngle(2 * M_PI / 3);
gp3.setMinimumAngle(M_PI / 18);
gp3.setMaximumSurfaceAngle(M_PI / 4);
gp3.setNormalConsistency(false);
gp3.setInputCloud(cloud_with_normals);
gp3.setSearchMethod(tree2);
gp3.reconstruct(triangles);
ccPointCloud* newPointCloud = new ccPointCloud(QString("reconstruct_points"));
for (int i = 0; i < cloud_with_normals->size(); ++i)
{
double x = cloud_with_normals->points[i].x;
double y = cloud_with_normals->points[i].y;
double z = cloud_with_normals->points[i].z;
newPointCloud->addPoint(CCVector3(x, y, z));
}
//创建一个Mesh网格
ccMesh* mesh = new ccMesh(newPointCloud);
mesh->setName(ccCloud->getName() + "-mesh");
unsigned int v1, v2, v3; //用于接收顶点
for (int i = 0; i < triangles.polygons.size(); i++) {
v1 = triangles.polygons[i].vertices[0];
v2 = triangles.polygons[i].vertices[1];
v3 = triangles.polygons[i].vertices[2];
mesh->addTriangle(v1, v2, v3); //通过这种方式来添加三角面片
}
mesh->setTempColor(ccColor::Rgba(rand() % 255, rand() % 255, rand() % 255, 60));
mesh->showColors(true);
// ------------------------PCL->CloudCompare--------------------------------
if (ccCloud->getParent())
{
ccCloud->getParent()->addChild(mesh);
}
ccCloud->setEnabled(false);
addToDB(mesh);
refreshAll();
updateUI();
}
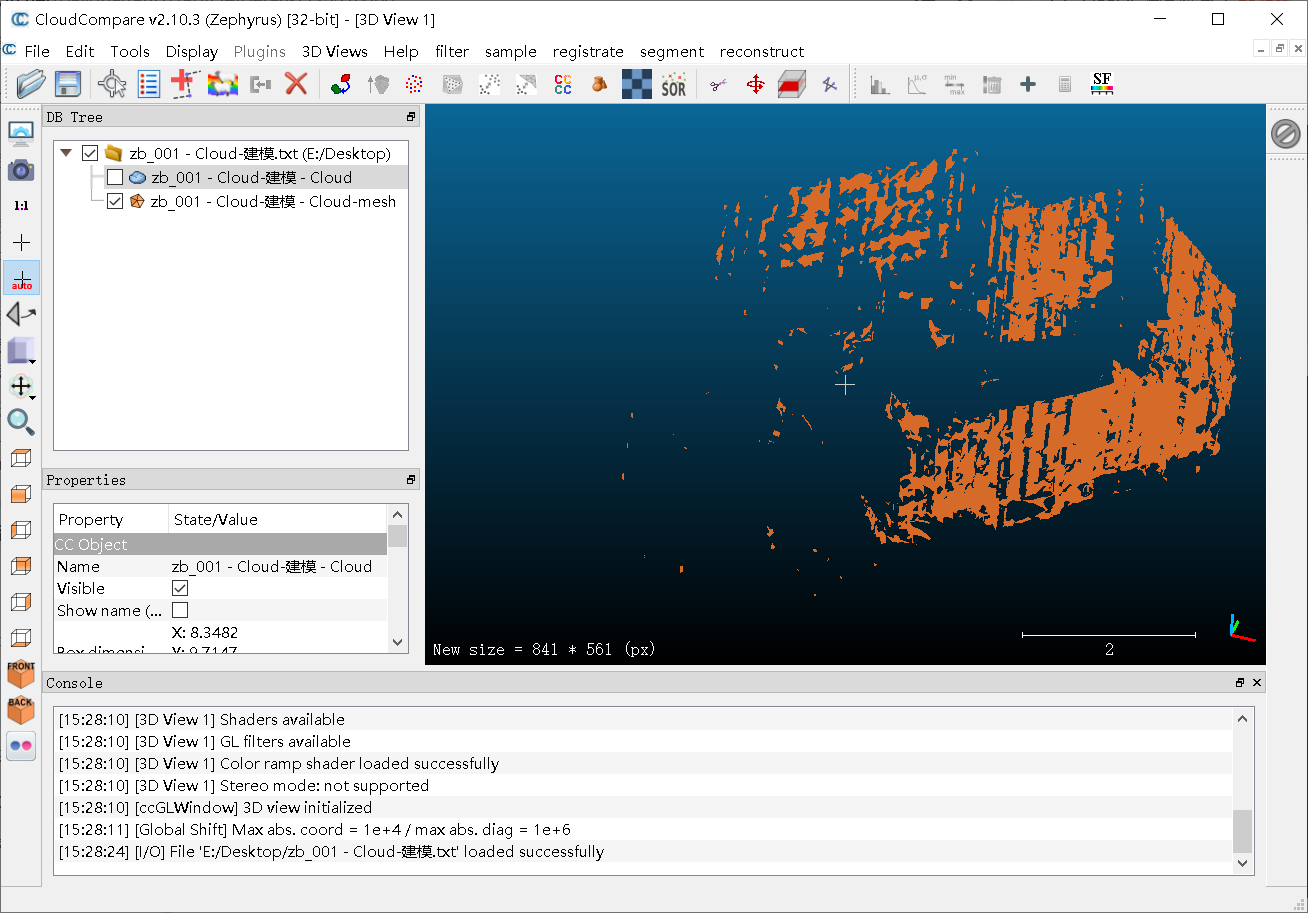
(2)重建结果
①重建前

②重建后
参考资料:
[1] 来吧!我在未来等你!. CloudCompare二次开发之如何配置PCL点云库?; 2023-05-15 [accessed 2023-05-17].
[2] Tech沉思录. PCL点云使用贪婪三角化进行曲面重构; 2019-09-06 [accessed 2023-05-17].
[3] 大鱼BIGFISH. CloudCompare&PCL AlphaShape算法曲面重建; 2022-10-26 [accessed 2023-05-17].
[4] 点云侠. PCL 泊松曲面重建法(多线程加速版); 2023-02-01 [accessed 2023-05-17].
[5] 悠缘之空. PCL函数库摘要——点云曲面重建; 2021-11-07 [accessed 2023-05-17].



 本文介绍了如何在CloudCompare中通过PCL库进行点云数据处理,特别是利用贪婪三角化方法进行曲面重建的步骤。首先,文章展示了在CloudCompare界面设计重建按钮并连接信号槽函数。接着,详细阐述了点云的下采样、统计异常点去除、重采样、法线估计以及最终的贪婪三角化过程。最后,文章提供了重建前后的对比效果,并引用了多个参考资料作为学习资源。
本文介绍了如何在CloudCompare中通过PCL库进行点云数据处理,特别是利用贪婪三角化方法进行曲面重建的步骤。首先,文章展示了在CloudCompare界面设计重建按钮并连接信号槽函数。接着,详细阐述了点云的下采样、统计异常点去除、重采样、法线估计以及最终的贪婪三角化过程。最后,文章提供了重建前后的对比效果,并引用了多个参考资料作为学习资源。












 6256
6256

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?