Laboratory of Nitrogen-Containing Compounds
Development of new methods for the synthesis and structural modification of various nitrogen-containing heterocyclic compounds of a number of oxadiazole, imidazotriazine and glycoluryl, as well as the study of their properties to yield pharmacologically active compounds or functional organic materials.
- Subtle organic synthesis
- IR spectroscopy
- UV spectroscopy
- X-ray diffraction analysis
- Thin-layer chromatography
- Mass spectrometry
- Column chromatography
Research directions
Development of methods for the synthesis and transformation of glycoluryl derivatives (bicyclic bisureas)
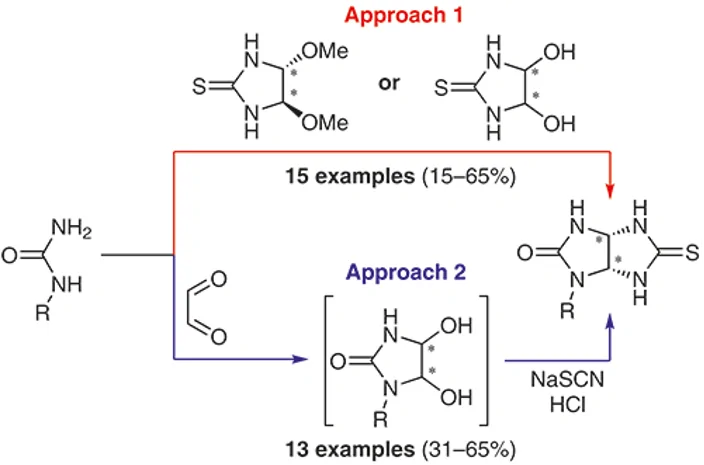
Glycolurils belong to the class of highly demanded nitrogen-containing heterocyclic systems with pronounced anxiolytic and antidepressant effects. Thanks to the development of this area, the laboratory staff developed and introduced the drug Mebikar (Adaptol) into medical practice.
Currently, research is continuing on the directed synthesis and transformation of various glycoluryl derivatives and their thio- and selenium-containing analogues.
Development of methods for the synthesis and transformation of condensed heterocyclic systems based on imidazothiazolotriazine
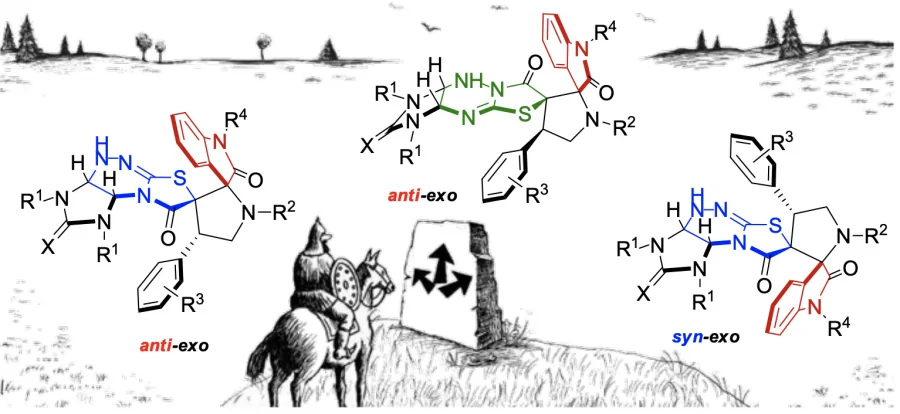
Within the framework of this direction, the development of diastereoselective methods for the synthesis and transformation of polycondensated heterocyclic systems based on imidazothiazolotriazine with pronounced antitumor and fungicidal effects is carried out.
Synthesis of energy-intensive heterocyclic systems based on furoxane derivatives
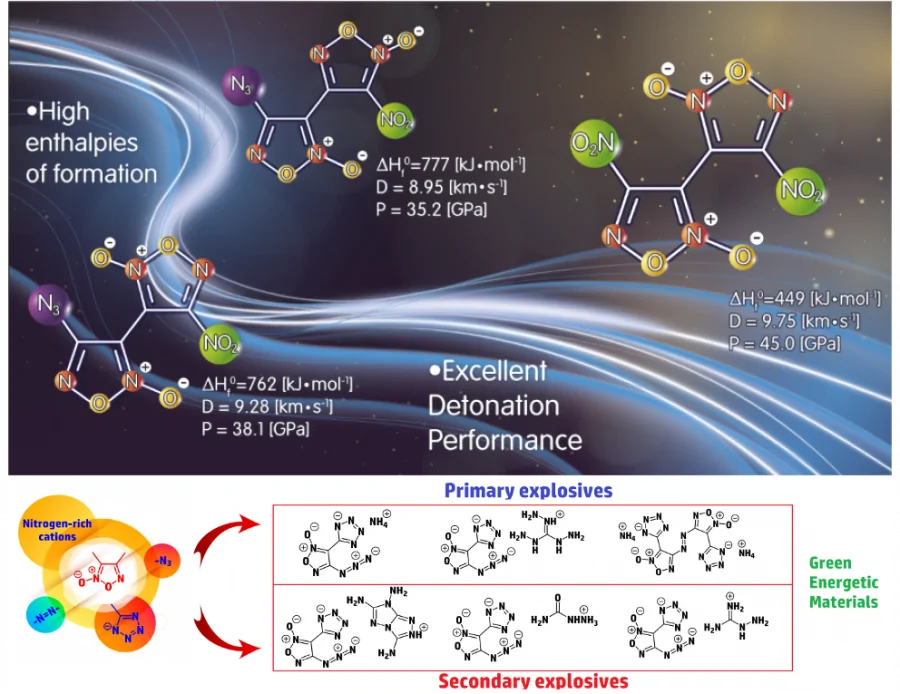
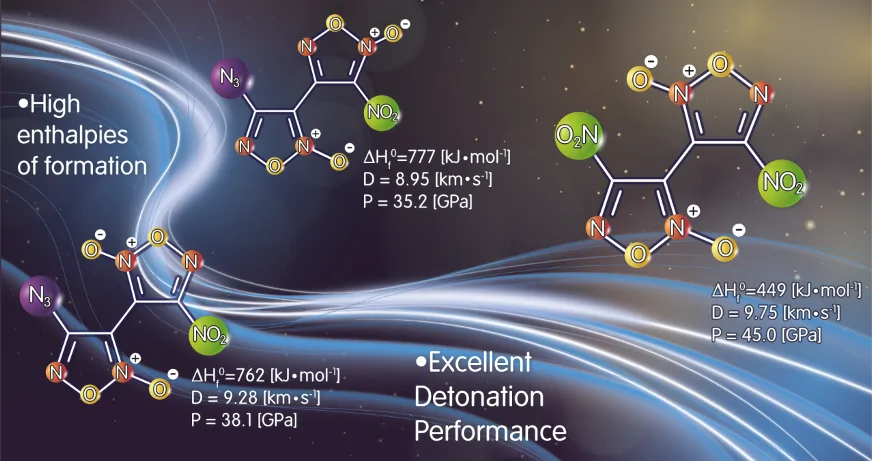
Furoxanes have a high density and positive enthalpy of formation. In addition, the furoxane cycle contains two "active" oxygen atoms in its composition, which makes it possible to consider these compounds as components of various energy-intensive compositions.
The combination of the furoxane cycle together with other explosive nitrogen-oxygen groups opens the way to obtaining promising environmentally friendly high-energy materials.
Synthesis of pharmacologically oriented systems based on oxadiazole derivatives
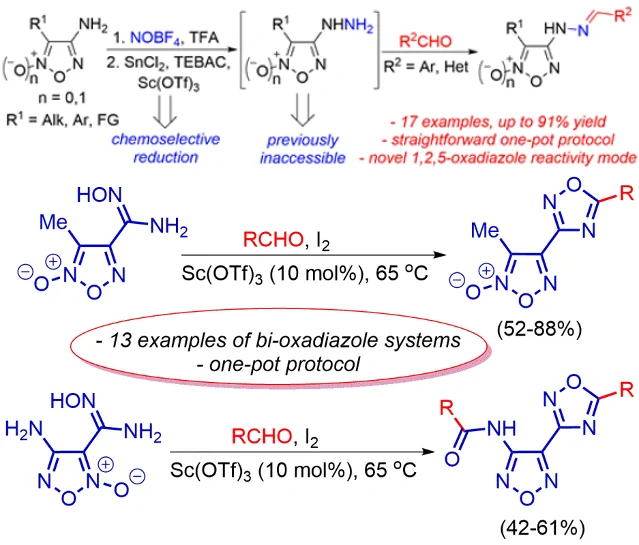
Within the framework of this direction, new methods are being developed for the synthesis of potentially pharmacologically active heterocyclic structures based on oxadiazole derivatives, primarily 1,2,5-oxadiazole (furazane) and 1,2,5-oxadiazole-2-oxide (furoxane).
Furoxane derivatives belong primarily to the class of exogenous nitric oxide (NO) donors, which determines their pharmacological profile as antiplatelet and antitumor agents.












