Abstract
The Y-Balance Test (YBT) is a dynamic balance assessment commonly used in sports medicine. In this research we explore how data from a wearable sensor can provide further insights from YBT performance. We do this in a Case-Based Reasoning (CBR) framework where the assessment of similarity on the wearable sensor data is the key challenge. The assessment of similarity on time-series data is not a new topic in CBR research; however the focus here is on working as close to the raw time-series as possible so that no information is lost. We report results on two aspects, the assessment of YBT performance and the insights that can be drawn from comparisons between pre- and post- injury performance.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
This dataset is available at http://mlg.ucd.ie/ybt.
- 2.
- 3.
Similarity computation with DTW between two time-series of unequal length is handled by padding the shorter time-series with zeroes.
- 4.
Edit Distance and Wagner-Fischer measures requires no size matching as it handles the unequal length of the sequences.
References
Aha, D.W., Bankert, R.L.: A comparative evaluation of sequential feature selection algorithms. In: Fisher, D., Lenz, H.J. (eds.) Learning from Data. LNS, vol. 112, pp. 199–206. Springer, New York (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4612-2404-4_19
Bregón, A., Simón, M.A., Rodríguez, J.J., Alonso, C., Pulido, B., Moro, I.: Early fault classification in dynamic systems using case-based reasoning. In: Marín, R., Onaindía, E., Bugarín, A., Santos, J. (eds.) CAEPIA 2005. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 4177, pp. 211–220. Springer, Heidelberg (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/11881216_23
Ding, H., Trajcevski, G., Scheuermann, P., Wang, X., Keogh, E.: Querying and mining of time series data. Proc. VLDB Endow. 1(2), 1542–1552 (2008)
Doherty, C., Bleakley, C.M., Hertel, J., Caulfield, B., Ryan, J., Delahunt, E.: Laboratory measures of postural control during the star excursion balance test after acute first-time lateral ankle sprain. J. Athl. Train. 50(6), 651–664 (2015)
Elsayed, A., Hijazi, M.H.A., Coenen, F., García-Fiñana, M., Sluming, V., Zheng, Y.: Time series case based reasoning for image categorisation. In: Ram, A., Wiratunga, N. (eds.) ICCBR 2011. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 6880, pp. 423–436. Springer, Heidelberg (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-23291-6_31
Gribble, P.A., Hertel, J., Plisky, P.: Using the star excursion balance test to assess dynamic postural-control deficits and outcomes in lower extremity injury: a literature and systematic review. J. Athl. Train. 47(3), 339–357 (2012)
Herrington, L., Hatcher, J., Hatcher, A., McNicholas, M.: A comparison of star excursion balance test reach distances between ACL deficient patients and asymptomatic controls. Knee 16(2), 149–152 (2009)
Howell, D.R., Lynall, R.C., Buckley, T.A., Herman, D.C.: Neuromuscular control deficits and the risk of subsequent injury after a concussion: a scoping review. Sports Med. 48(5), 1097–1115 (2018)
Johnston, W., O’Reilly, M., Dolan, K., Reid, N., Coughlan, G., Caulfield, B.: Objective classification of dynamic balance using a single wearable sensor. In: 4th International Congress on Sport Sciences Research and Technology Support 2016, Porto, Portugal, 7–9 November 2016, pp. 15–24. SCITEPRESS-Science and Technology Publications (2016)
Johnston, W., O’Reilly, M., Argent, R., Caulfield, B.: Reliability, validity and utility of inertial sensor systems for postural control assessment in sport science and medicine applications: a systematic review. Sports Med. 49, 783–818 (2019)
Johnston, W., O’Reilly, M., Coughlan, G.F., Caulfield, B.: Inter-session test-retest reliability of the quantified Y balance test. In: 6th International Congress on Sports Sciences Research and Technology Support, pp. 63–70 (2018)
Johnston, W., et al.: Association of dynamic balance with sports-related concussion: a prospective cohort study. Am. J. Sports Med. 47(1), 197–205 (2019)
Keogh, E., Kasetty, S.: On the need for time series data mining benchmarks. In: Proceedings of the Eighth ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining - KDD 2002 (2002)
Keogh, E.J., Pazzani, M.J.: Scaling up dynamic time warping for datamining applications. In: Proceedings of the Sixth ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining - KDD 2000 (2000)
Keogh, E.J., Pazzani, M.J.: Derivative dynamic time warping. In: Proceedings of the 2001 SIAM International Conference on Data Mining, pp. 1–11. SIAM (2001)
Lin, J., Keogh, E., Lonardi, S., Chiu, B.: A symbolic representation of time series, with implications for streaming algorithms. In: Proceedings of the 8th ACM SIGMOD Workshop on Research Issues in Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery - DMKD 2003 (2003)
Mahato, V., O’Reilly, M., Cunningham, P.: A comparison of \(k\)-NN methods for time series classification and regression. In: Brennan, R., Beel, J., Byrne, R., Debattista, J., Junior, A.C. (eds.) 2018 Proceedings for the 26th AIAI Irish Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Cognitive Science. CEUR Workshop Proceedings, vol. 2259, pp. 102–113. CEUR-WS.org (2018). http://ceur-ws.org/Vol-2259/aics_11.pdf
Mitsa, T.: Temporal Data Mining, pp. 99–102. Chapman & Hall, London (2010)
Montani, S., Bottrighi, A., Leonardi, G., Portinale, L.: A CBR-based, closed-loop architecture for temporal abstractions configuration. Comput. Intell. 25(3), 235–249 (2009)
Montani, S., Leonardi, G., Bottrighi, A., Portinale, L., Terenziani, P.: Supporting flexible, efficient, and user-interpretable retrieval of similar time series. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 25(3), 677–689 (2013)
Newell, A., et al.: The knowledge level. Artif. Intell. 18(1), 87–127 (1982)
Penta, K.K., Khemani, D.: Satellite health monitoring using CBR framework. In: Funk, P., González Calero, P.A. (eds.) ECCBR 2004. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 3155, pp. 732–747. Springer, Heidelberg (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-28631-8_53
Sakoe, H., Chiba, S.: Dynamic programming algorithm optimization for spoken word recognition. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 26(1), 43–49 (1978)
Schäfer, P., Högqvist, M.: SFA: a symbolic Fourier approximation and index for similarity search in high dimensional datasets. In: Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Extending Database Technology, pp. 516–527. ACM (2012)
Shahar, Y.: A framework for knowledge-based temporal abstraction. Artif. Intell. 90(1–2), 79–133 (1997)
Wagner, R.A., Fischer, M.J.: The string-to-string correction problem. J. ACM 21(1), 168–173 (1974)
Yujian, L., Bo, L.: A normalized Levenshtein distance metric. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 29(6), 1091–1095 (2007)
Acknowledgments
This publication has resulted from research supported in part by a grant from Science Foundation Ireland (SFI) under Grant Number 16/RC/3872 and is co-funded under the European Regional Development Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Appendix
Appendix
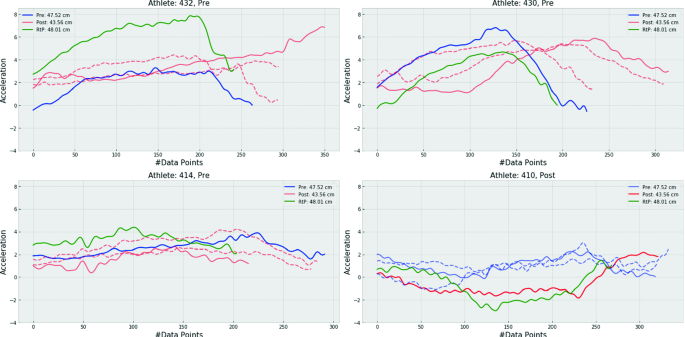
See Fig. 10.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Mahato, V., Johnston, W., Cunningham, P. (2019). Scoring Performance on the Y-Balance Test. In: Bach, K., Marling, C. (eds) Case-Based Reasoning Research and Development. ICCBR 2019. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11680. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-29249-2_19
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-29249-2_19
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-29248-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-29249-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)