Abstract
Rehabilitation for the most common symptoms such as dementia is brain training, and it is thought that this type of training is highly compatible to digitalization and applications.
In this paper, we propose an application using sliding block puzzles for prevention of MCI. This will include an editing function that acquires image data, divides it into 3 * 3 or 4 * 4 and creates questions. The function determines whether the image is portrait or landscape and resizes the image accordingly. It also changes the color and brightness of the image in consideration of the user’s vision.
Therefore, this proposed application is operated with intuitive movement using touch and slide operation on a tablet terminal. Intuitive operations such as touch and slide are easily understood by anyone without instruction.
As with the conventional sliding block puzzle, the user will slide the panel using the space of one frame to arrange the panel in the desired order. It is thought that the cerebral blood flow is activated by the user performing such an activity. Since the sliding block puzzle requires the memory of a goal, the arrangement of figures and special awareness, we believe that it will suppress the progress of dementia.
You have full access to this open access chapter, Download conference paper PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
1 Introduction
According to the 2017 Senior Citizens White Paper (Japan), under future statistics for the number of dementia patients and prevalence for those 65 and over, senior citizens with dementia were over 4.62 million (approximately 1 in 7 senior citizens over 65), but in 2025 it is estimated that this will increase to 1 out of 5.
A lifestyle that can activate the brain through physical exercise is effective to prevent dementia. Rehabilitation for the most common symptoms of dementia is brain training, and it is thought that this type of training is highly compatible to digitalization and applications.
In Japan, smartphones outnumbered PCs within households at 75.1% vs 72.5% respectively in 2017. Therefore, we believed it was necessary to create an application that used a tablet terminal that was similar to a smartphone and easy for users to operate. A tablet terminal is considered best suited for the medical and nursing care fields such as rehabilitation, because it has a larger screen and is easier to operate than a smartphone.
Mild cognitive impairment (MCI) refers to a condition in which cognitive function is impaired, but the individual is living independently.
MCI is said to develop into dementia in a few years, but early detection and appropriate measures and treatment may delay the onset of dementia. Currently, no complete prevention or radical cure for dementia has been found.
We propose a rehabilitation application system using sliding block puzzles for prevention of MCI. This will include an editing function that acquires image data, divides it into 3 * 3 or 4 * 4 and creates questions. The function determines whether the image is portrait or landscape and resizes the image accordingly. It also changes the color and brightness of the image in consideration of the user’s vision.
The proposed application is operated with intuitive movement using touch and slide operation on a tablet terminal. Intuitive operations such as touch and slide are easily understood by anyone without instruction.
As with the conventional sliding block puzzle, the user will slide the panel using the space of one frame to arrange the panel in the desired order. It is thought that the cerebral blood flow is activated by the user performing such an activity. Since the sliding block puzzle requires the memory of a goal, the arrangement of figures and special awareness, we believe that it will suppress the progress of dementia.
2 Dementia
Characteristics of dementia
The characteristics of dementia are roughly divided into the following three
-
Obstacles are less apparent
In Alzheimer’s disease, a typical form of dementia, the accumulation of amyloid β protein in the brain destroys cranial nerves, and impairs intellectual functions such as language, thinking, memory, action, learning, and attention. The symptoms are self-contained and often inconspicuous in appearance.
-
The person himself cannot fully recognize the disability
As explained earlier, dementia often does not allow the person himself to recognize the disability because the symptoms are often inconspicuous in appearance. In addition, it is difficult to confront one’s inability to do what one has always been able to do before because symptoms may suddenly occur, and it is often the case that they are not easily motivated for rehabilitation and consultation.
-
Symptoms are more likely to appear in daily life and social activities at home than in consultation and hospitalization
Many of the typical symptoms are manifested in intellectual functions, and are likely to occur in daily life and social activities (workplace, shopping, use of transportation, procedures at government offices and banks, etc.). Therefore, unless family and doctors around them encounter the scene, they often cannot fully recognize the disability.
Mild cognitive impairment (MCI)
MCI is considered to be a pre-dementia stage and has received attention in recent years. Although it is associated with a decline in cognitive function, it is not currently considered dementia nor does it cause heavy difficulty in everyday life.
Currently, there is no complete prevention or radical cure for dementia.
MCI is a situation with a high rate of developing into dementia if it is not addressed, and is often said to be the pre-dementia stage or the middle point between a healthy state and dementia.
However, there are also those with MCI who do not develop dementia but recover to a healthy state. In addition, early stage recognition and proper measures and treatment can slow progression of dementia.
3 Proposal
In this paper, we propose a brain training application using sliding block puzzles to prevent MCI for rehabilitation of dementia. Most popular smartphones have a screen size of 6 in. or less. Smartphone screens are small for elderly people, and characters may be difficult to see, so we propose an application recommended for use on a tablet-type terminal with a size of about 10 in. These are as easy to carry as smartphones and can also be used anywhere.
Using the same operation as the conventional sliding block puzzle, the user would slide the panel using the space for one frame to arrange the panel in the desired arrangement. The cerebral blood flow is activated when the user performs a finger motion such as a slide.
It stimulates the frontal lobe, which controls memory, as the user predicts in which direction the moving panels can be moved to attain the desired arrangement. The user must shift the position of the panels in the sliding block puzzle while remembering the original shape.
The spatial recognition function of the frontal lobe is stimulated as the user comes up with the procedure to attain the correct answer by grasping the position of the panels. To complete the puzzle, the target memory, the arrangement of figures, and the ability to grasp the space is needed, so it is thought that it will prevent the progression of dementia and prevent MCI.
A terminal equipped with a camera and capable of touch panel operation can be used to create new puzzles from captured images.
The image used as a puzzle does not need to be prepared in advance, and it is possible to resize an image from the tablet terminal or the size of the image file owned by the user.
We believe that it would be effective for rehabilitation and prevention because not only can the number of puzzles could be increased, but also images taken of places familiar to the person can be easily used.
4 Implementation
We propose a brain training application using sliding block puzzles. Introduce an editing function that acquires image data in the application, divides it into 3 × 3 or 4 × 4 and creates questions.
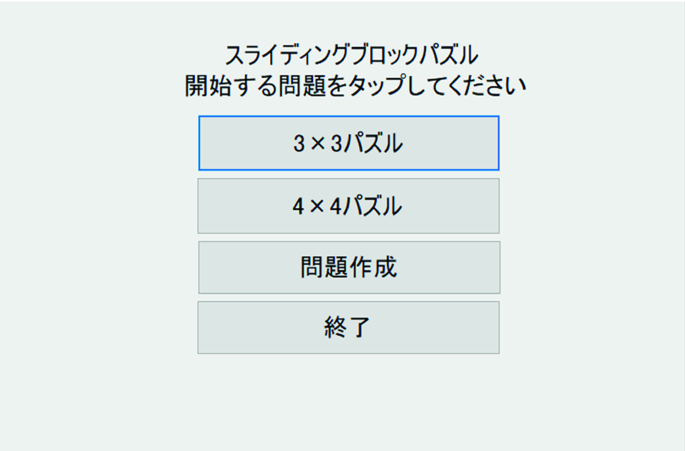
When adjusting image data, determine whether the image is portrait or landscape and resize the image to fit the screen. Creates questions’s function can Change the color and brightness of the image base on user’s vision. Tapping the desired mode on the screen shown in Fig. 1 to change to be figure. Instead of starting the puzzle immediately the application will show the figure for the user first to memorize the completed figure.
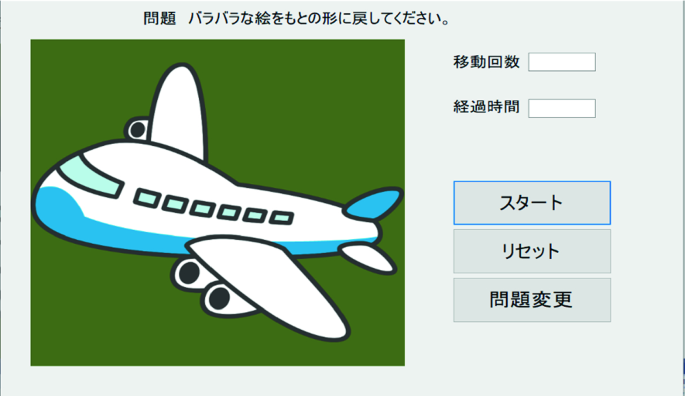
In Fig. 2, a problem as an example is prepared instead of a photographed image.
If you want to change the question, tap on the “Question change” at the bottom right of Fig. 2 to change to another question. Question will changes randomly.
To avoid facing difficult problems, the user can tap ‘question change’ botton to finish by himself even the questions is not yet finished. You can adjust the brightness of the image with the “brightness function” for older people to see easies.
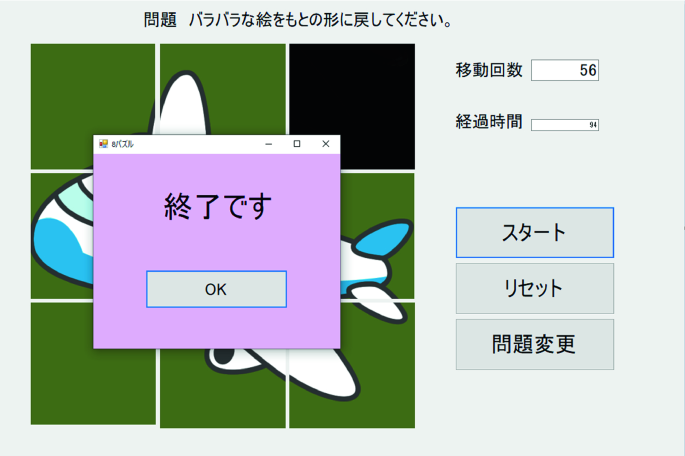
When you tap “Start”, the image will be split a part then some of it will becomes a black or empty. When you start, the timers will it is display in the elapsed time in Fig. 2 the number of puzzle movements will be displayed in Fig. 2 (Figs. 3, 4, 5, 6).
5 Additional Programs
Tap the question creation in Fig. 1 to switch to the screen in Fig. 7. Tap 3 × 3 or 4 × 4 to switch to camera mode.
Only terminals that can operate touch panels with cameras are supported.
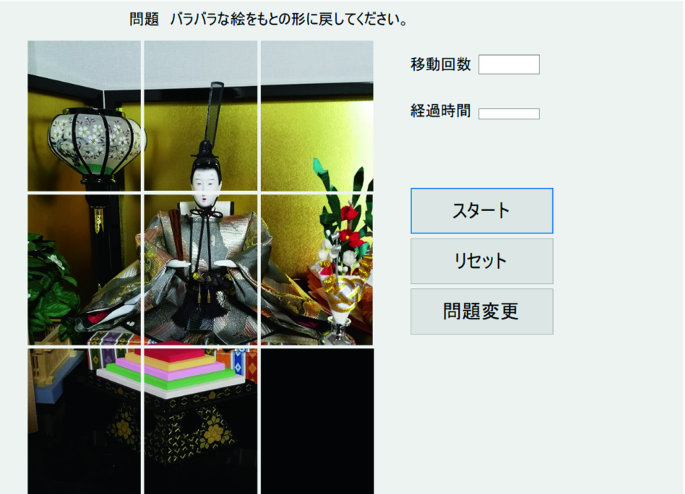
If the image is horizontal, adjust the puzzle frame horizontally, and if the image is vertical, adjust the puzzle frame vertically. The added image is added to the question file (Figs. 8, 9).
6 Result
There are comments from the user that this application is user-friendly, especially for older people. For some users with bad eyesight, it is difficult for them to see the press. In case where the application using physical press or key, such as keyboard, it is difficult to understand which press or key to press. The operation of the touch panel is considered appropriate for rehabilitation of elderly people.
For some users, their eyes were so bad that the letters were hard to see, and they didn’t know where to press. Therefore, measures such as enlarging the button and enlarging the character have been required.
There are comments from the user that the sample illustration was easy to understand. Some users do not know how to play the sliding block puzzle, so it is necessary to prepare a way how to play for the elderly. It is difficult for people with severe dementia to communication. Even if they are interested in the application, it is difficult for them to play.
7 Discussion
For rehabilitation of dementia, we proposed an application that could prevent MCI. We think that a tablet terminal with a camera can be operated intuitively, even by people with dementia.
In addition to photos taken with the camera, a problem creation function is added using image data in the terminal, and problems using family photos such as family members will be stimulating.
In addition, by collecting image data of an object of interest, such as a user’s favorite object, person, or animal, it is possible to further strengthen the thinking ability necessary for executive dysfunction by creating a problem on its own. Can be expected.
8 Conclusion
For rehabilitation of dementia, we proposed a brain training application using a sliding block puzzle that leads to the prevention of MCI. Sliding block puzzles are performed using spatial recognition ability, objective memory, figure arrangement and multiple functions to solve problems. Therefore, it can be expected that it can be used as rehabilitation. With the camera function, users can play more by adding their own problems. In the future, it will be possible to add problems other than the camera function, and to clear and clear the points and earn achievements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Sasaki, S., Takagi, H., Yokokura, S., Kuwahara, M. (2020). A Proposal of Rehabilitation Application System Using Sliding Block Puzzles for Prevention of Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI). In: Stephanidis, C., Antona, M. (eds) HCI International 2020 - Posters. HCII 2020. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 1226. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-50732-9_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-50732-9_14
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-50731-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-50732-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)