Abstract
Purpose
A surgeon in a sterilized area can perform robotically assisted laparoscopic solo surgery while controlling a laparoscope-holding robot for view stabilization and a forceps robot for pulling organs. At present, no locally operated surgical assistant manipulator with a mechanical remote center of motion (RCM) is available to operate within a small space while providing a wide range of movement. The present study describes a new locally operated detachable end-effector manipulator (LODEM) with diagonal joints and multi-stage telescopic screws.
Methods
A forceps manipulator attached to commercial surgical forceps was developed. This manipulator uses RCM diagonal joints for the yaw and pitch axes, providing an intuitive pivot point and free rotation, and telescopic nested screws with multiple sliders clamp the commercial forceps for the axis of insertion. The manipulator placed above the abdominal wall using a fixed arm connected to a bed rail is motor controlled by a handheld interface with button switches for precise traction and is controlled manually for easy rough positioning.
Results
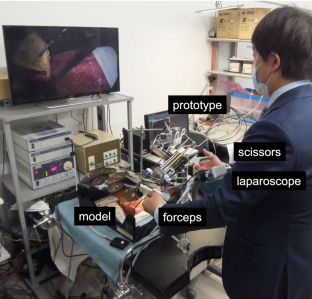
Positional accuracy at the tip with a load of 5 N was under 0.5 mm. Mechanical deflection was under 2.1 mm. The manually controlled force was under 4.4 N. Successful simulated laparoscopic cholecystectomy using the prototype manipulator to handle the target and maintain stability was performed on a surgically realistic gallbladder model.
Conclusions
A LODEM with diagonal joints and multi-stage telescopic screws was developed to facilitate minimally invasive, robotically assisted laparoscopic solo surgery by a surgeon working near the patient. This electric motor-controlled laparoscopic instrument holder by the surgeon in the surgical field could be used for such applications.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jensen KK, Andersen P, Erichsen R, Scheike T, Iversen L, Krarup P (2016) Decreased risk of surgery for small bowel obstruction after laparoscopic colon cancer surgery compared with open surgery: a nationwide cohort study. Surg Endosc 30(12):5572–5582. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-016-4930-x
Meara JG, Leather AJM, Hagander L, Alkire BC, Alonso N, Ameh EA, Bickler SW, Conteh L, Dare AJ, Davies J, Mérisier ED, El-Halabi S, Farmer PE, Gawande A, Gillies R, Greenberg SLM, Grimes CE, Gruen RL, Ismail EA, Kamara TB, Lavy C, Lundeg G, Mkandawire NC, Raykar NP, Riesel JN, Rodas E, Rose J, Roy N, Shrime MG, Sullivan R, Verguet S, Watters D, Weiser TG, Wilson IH, Yamey G, Yip W (2015) Global Surgery 2030: evidence and solutions for achieving health, welfare, and economic development. Lancet 386(9993):569–624. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(15)60160-X
Muula AS, Panulo B Jr (2007) Lost investment returns from the migration of medical doctors from Malawi. Tanzan Health Res Bull 9(1):61–64. https://doi.org/10.4314/thrb.v9i1.14295
Taylor RH, Menciassi A, Fichtinger G, Fiorini P, Dario P (2016) Medical robotics and computer-integrated Surgery. In: Siciliano B, Khatib O (eds) Springer handbook of robotics. Springer, Cham, pp 1657–1684
Guthart GS, Salisbury JJ (2000) The intuitive telesurgery system: overview and application. In: Proceedings of IEEE ICRA, pp 618–621. https://doi.org/10.1109/ROBOT.2000.844121
Tadano K, Kawashima K (2010) Development of a master–slave system with force-sensing abilities using pneumatic actuators for laparoscopic surgery. Adv Robot 24(12):1763–1783. https://doi.org/10.1163/016918610X522559
Stephan D, Sälzer H, Willeke F (2018) First experiences with the New Senhance® Telerobotic system in visceral surgery. Visc Med 34(1):31–36. https://doi.org/10.1159/000486111
Gidaro S, Buscarini M, Ruiz E, Stark M, Labruzzo A (2012) Telelap Alf-X: a novel telesurgical system for the 21st century. Surg Technol Int 22:20–25
Atallah S, Parra-Davila E, Melani AGF (2019) Assessment of the Versius surgical robotic system for dual-field synchronous transanal total mesorectal excision (taTME) in a preclinical model: Will tomorrow’s surgical robots promise newfound options? Tech Coloproctol 23:471–477. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10151-019-01992-1
Rassweiler JJ, Autorino R, Klein J, Mottrie A, Goezen AS, Stolzenburg JU, Rha KH, Schurr M, Kaouk J, Patel V, Dasgupta P, Liatsikos E (2017) Future of robotic surgery in urology. BJU Int 120(6):822–841. https://doi.org/10.1111/bju.13851
Kikuchi K, Suda K, Shibasaki S, Tanaka T, Uyama I (2021) Challenges in improving the minimal invasiveness of the surgical treatment for gastric cancer using robotic technology. Ann Gastroenterol Surg 00:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1002/ags3.12463
Gumbs AA, Crovari F, Vidal C, Henri P, Gayet B (2007) Modified robotic lightweight endoscope (ViKY) validation in vivo in a porcine model. Surg Innov 14(4):261–264. https://doi.org/10.1177/1553350607310281
Long JA, Cinquin P, Troccaz J, Voros S, Berkelman P, Descotes JL, Letoublon C, Rambeaud JJ (2007) Development of miniaturized light endoscope-holder robot for laparoscopic surgery. J Endourol 21(8):911–914. https://doi.org/10.1089/end.2006.0328
Stolzenburg JU, Franz T, Kallidonis P, Minh D, Dietel A, Hicks J, Nicolaus M, Al-Aown A, Liatsikos E (2010) Comparison of the FreeHand robotic camera holder with human assistants during endoscopic extraperitoneal radical prostatectomy. BJU Int 107(6):970–974. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-410X.2010.09656.x
Tadano K, Kawashima K (2014) A pneumatic laparoscope holder controlled by head movement. Int J Med Robot 11(3):331–340. https://doi.org/10.1002/rcs.1606
Gillen S, Pletzer B, Heiligensetzer A, Wolf P, Kleeff J, Feussner H, Fürst A (2014) Solo-surgical laparoscopic cholecystectomy with a joystick-guided camera device: a case–control study. Surg Endosc 28(1):164–170. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-013-3142-x
Bihlmaier A (2016) Endoscope robots and automated camera guidance. In: Learning dynamic spatial relations. Springer, Wiesbaden, pp 23–71. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-658-14914-7
A-traction Inc. https://www.a-traction.co.jp/. Accessed 1 July 2021
Kawai T, Hashida J, Myongsyu S, Nishizawa Y, Nakamura T, Morita N, Murotani T, Mochizuki S (2012) Locally operated detachable end-effector manipulator for endoscopic surgery. JJSCAS 14(1):5–14. https://doi.org/10.5759/jscas.14.5
Kawai T, ShinM NY, Horise Y, Nisihkawa A, Nakamura T (2015) Mobile locally operated detachable end-effector manipulator for endoscopic surgery. Int J CARS 10(2):161–169. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-014-1062-4
Kawai T, Hayashi H, Nishizawa Y, Nishikawa A, Nakamura R, Kawahira H, Ito M, Nakamura T (2017) Compact forceps manipulator with a spherical-coordinate linear and circular telescopic rail mechanism for endoscopic surgery. Int J CARS 12(8):1345–1353. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-017-1595-4
Kawai T, Matsumoto T, Nishikawa A, Nishizawa Y, Nakamura T (2016) Bending forceps manipulator with offset distance for single-port laparoscopy. ABE 5:56–62
Sasaki A, Amemori H, Kawai T, Nishikawa A, Nishizawa Y, Nakamura T (2019) Forceps manipulator with circular ring guided rail and linear guide roller for laparoscopic surgery. In: Proceedings of EMBC: FrPOS-36.31
Han S, Kawai T, Nishikawa A, Nishizawa Y, Nakamura T (2020) Portable forceps manipulator with closed loop mechanism using gimbal-mounted parallel linkage for endoscopic surgery. JJSCAS 22(1):5–13. https://doi.org/10.5759/jscas.22.5
Sasaki A, Kawai T, Nishikawa A, Nishizawa Y, Nakamura T (2020) Forceps manipulator with diagonal joints and telescopic multi screws for laparoscopic surgery. In Proceedings of ACCAS, pp 94–95
Sasaki A, Kawai T, Nishizawa Y, Ikeda K, Tsukada Y, Sasaki T, Ito M (2020) Measurement of pulling direction and holding time for assistant’s forceps in laparoscopic colorectal surgery. In Proceedings of JSES: OS43–3
Visser H, Hijnsdijk EAM, Herder JL, Pistecky PV (2002) Forces and displacements in colon surgery. Surg Endosc 16(10):1426–1430. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-002-9003-7
Mitsuishi M, Sugita N, Yasunaka S, Hashizume M (2008) Design of a surgical robot for use inside the human body. JRSJ 26(3):242–246. https://doi.org/10.7210/jrsj.26.242
Arezzo A, Ulmer F, Weiss O, Schurr MO, Hamad M, Buess GF (2000) Experimental trial on solo surgery for minimally invasive therapy: comparison of different systems in a phantom model. Surg Endosc 14(10):955–959. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004640000106
Fukui S, Kawai T, Nishizawa Y, Nishikawa A, Nakamura T, Iwamoto N, Horise Y, Msamune K (2021) Locally operated assistant manipulators with selectable connection system for robotically assisted laparoscopic solo surgery. Int J CARS 16(4):683–693. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-021-02338-9
Mamelak AN, Danielpour M, Black KL, Hagike M, Berci G (2008) A high-definition exoscope system for neurosurgery and other microsurgical disciplines: preliminary report. Surg Innov 15(1):38–46. https://doi.org/10.1177/1553350608315954
Bosma J, Boeken Kruger A, Jaspers J (2015) A novel, intuitive instrument positioner for endoscopy, involving surgeons in design and feasibility. Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol 24(6):326–333. https://doi.org/10.3109/13645706.2015.1039547
Choi S, Choi Y, Han H, Yoon Y, Cho JY, Kwon S, Jang JS, Choi J, Kim S (2016) Solo three-incision laparoscopic cholecystectomy using a laparoscopic scope holder for acute cholecystitis. J Minim Invasive Surg 19:141–147. https://doi.org/10.7602/jmis.2016.19.4.141
Barbash GI, Glied SA (2010) New technology and health care costs–the case of robot-assisted surgery. N Engl J Med 363(8):701–704. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmp1006602
Wagner AA, Varkarakis IM, Link RE, Sullivan W, Su LM (2006) Comparison of surgical performance during laparoscopic radical prostatectomy of two robotic camera holders, EndoAssist and AESOP: a pilot study. Urology 68(1):70–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2006.02.003
Funding
The present study was supported in part by Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) KAKENHI Grant Numbers 21K03986.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest with regard to this study.
Ethical approval
This article does not describe any studies with human or animal subjects.
Informed consent
This article does not contain patient data.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file1 (MP4 1139 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sasaki, A., Kawai, T., Nishizawa, Y. et al. Surgical assistant manipulator with diagonal joints and multi-stage telescopic screws for laparoscopic solo surgery. Int J CARS 17, 487–495 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-021-02553-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-021-02553-4


