Abstract
Monte Carlo simulation is used to investigate the
fluctuations in the Xe proportional electroluminescence (EL) yield 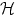 (also
known as secondary scintillation) produced by sub-ionization primary
electrons drifting in the gas under appropriate electric fields, comparing
pure Xe gas with Xe doped with CH4 or CF4. The work is modeled on
gas detectors of the gas proportional-scintillation type, where
amplification is achieved through the production of EL under a
charge-multiplication free regime. The addition of the molecular gases to Xe
reduces electron diffusion, a desirable effect in large size detectors where
primary electrons drift across a long absorption/drift region. However, the
presence of the molecules reduces
(also
known as secondary scintillation) produced by sub-ionization primary
electrons drifting in the gas under appropriate electric fields, comparing
pure Xe gas with Xe doped with CH4 or CF4. The work is modeled on
gas detectors of the gas proportional-scintillation type, where
amplification is achieved through the production of EL under a
charge-multiplication free regime. The addition of the molecular gases to Xe
reduces electron diffusion, a desirable effect in large size detectors where
primary electrons drift across a long absorption/drift region. However, the
presence of the molecules reduces 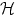 and increases its fluctuations. In the
case of CF4, the effects are very strong due to significant electron
attachment in the EL field range, ruling out CF4 as an acceptable
additive. The addition of CH4 affects
and increases its fluctuations. In the
case of CF4, the effects are very strong due to significant electron
attachment in the EL field range, ruling out CF4 as an acceptable
additive. The addition of CH4 affects 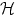 and its fluctuations to a much
lower extent, and CH4 concentrations lower than ∼1% may be an
appropriate choice. In addition, Monte Carlo calculations in pure Xe under
cylindrical geometry in a regime below charge multiplication have shown that
fluctuations in the EL yield
and its fluctuations to a much
lower extent, and CH4 concentrations lower than ∼1% may be an
appropriate choice. In addition, Monte Carlo calculations in pure Xe under
cylindrical geometry in a regime below charge multiplication have shown that
fluctuations in the EL yield 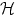 are an order of magnitude higher than for
planar geometry. For both geometries, though, the fluctuations have a
negligible effect on the energy resolution, and variations of the anode
radius in cylindrical geometry or grid parallelism in planar geometry may be
a more significant cause of concern.
are an order of magnitude higher than for
planar geometry. For both geometries, though, the fluctuations have a
negligible effect on the energy resolution, and variations of the anode
radius in cylindrical geometry or grid parallelism in planar geometry may be
a more significant cause of concern.
