Paper:
Cam-Like Mechanism in Intertarsal Joints of Ratites and its Design Framework
Kazuki Ito*, Sayaka Hida**, Tetsuya Kinugasa***
 , Kentaro Chiba***
, Kentaro Chiba***
 , Yu Okuda***, Miwa Ichikawa***, Tsukasa Okoshi***, Ryuji Takasaki***
, Yu Okuda***, Miwa Ichikawa***, Tsukasa Okoshi***, Ryuji Takasaki***
 , Ryota Hayashi***, Koji Yoshida***, and Koichi Osuka*
, Ryota Hayashi***, Koji Yoshida***, and Koichi Osuka*

*Graduate School of Engineering, Osaka University
2-1 Yamadaoka, Suita, Osaka 565-0871, Japan
**IHI Jet Service Co., Ltd.
1-33-3 Kichijoji-honmachi, Musashino, Tokyo 180-0004, Japan
***Okayama University of Science
1-1 Ridai-cho, Kita-ku, Okayama 700-0005, Japan
In this study, the cam-like passive mechanism, known as the engage–disengage mechanism (EDM) of the intertarsal joint of ratites, and its design principles are investigated. This mechanism operates through the interplay of a muscle and three ligaments located on the medial and lateral sides of the intertarsal joint and the articular surface morphology of the tibiotarsus. The interplay of the musculoskeletal ligamentous elements creates two stable equilibrium points when they are almost fully extended and flexed. To elucidate the EDM in the intertarsal joints of ratites, we dissected the hindlimb of an emu (Dromaius novaehollandiae) and examined anatomical features around the joint. Subsequently, we replicated the intertarsal joint of ratites using a physical model. This model consists of three-dimensional-printed ostrich bones, coil springs, and nylon strings simulating the muscle and ligaments. This model successfully replicated the EDM and facilitated the analysis of the interplay of musculoskeletal ligamentous elements. We demonstrated that the medial ligaments and the morphology of the tibiotarsal articular surface play significant roles in facilitating the execution of EDM. Furthermore, we observed that the articular surface morphology resembles a well-known cam system in engineering and is responsible for the EDM.
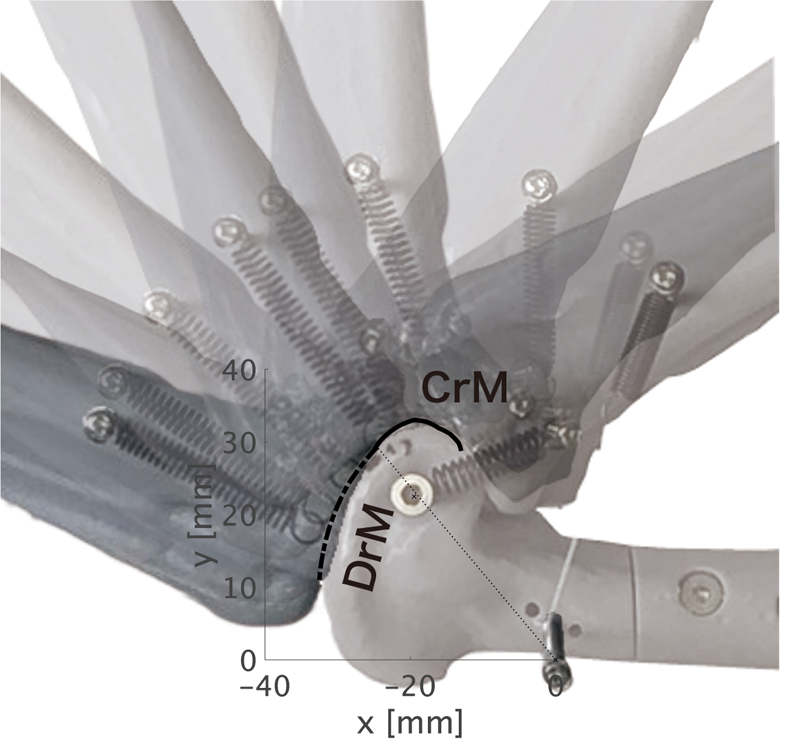
Cam surface and intertarsal joint motion
- [1] N. U. Schaller, B. Herkner, R. Villa, and P. Aerts, “The intertarsal joint of the ostrich (ıt Struthio camelus): Anatomical examination and function of passive structures in locomotion,” J. of Anatomy, Vol.214, pp. 830-847, 2009. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7580.2009.01083.x
- [2] S. M. Gatesy and A. A. Biewener, “Bipedal locomotion: effects of speed, size and limb posture in birds and humans,” J. Zool Lond, Vol.224, pp. 127-147, 1991. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7998.1991.tb04794.x
- [3] C. Bell, “Die Hand und ihre Eigenschaften (translated by F. Kottenkamp from C. Bell, “The hand, its mechanism and vital endowment as evincing design”),” Expedition der Wochenbände, Scheibele, Rieger & Sattler, 1847.
- [4] K. Langer, “Ueber die Fußgelenke der Vägel,” Denkschr Kaiser-Akad Wissenschaften Wien, Vol.16, pp. 93-130, 1859.
- [5] J. W. Hultkrantz, “Das Ellenbogengelenk und seine Mechanik,” Verlag Gustav Fischer, 1897.
- [6] H. Richter, “Die Bedeutung der federnden Gelenke oder Schnappgelenke,” Schweiz Arch Tierheilkd, Vol.64, pp. 76-87, 1922.
- [7] O. G. Aichel, “Über die Wirkung der Ligamenta collateralia nebst Bemerkungen über die sogenannten Schnappgelenke,” Zeitschrift für Anatomie und Entwicklungsgeschichte, Vol.76, pp. 1-15, 1925. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02134415
- [8] A. Palmgren, “Zur Kenntnis der sogenannten Schnappgelenke,” Z. Anat. Entwickl. Gesch., Vol.88, pp. 710-745, 1929. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02117503
- [9] R. Nickel, A. Schummer, E. Seiferle, J. Frewein, K.-H. Wille, and K. H. Wilkens, “Lehrbuch der Anatomie der Haustiere,” 6th ed., Vol.1, Paul Parey, 1992.
- [10] M. Hildebrand, “Analysis of Vertebrate Structure,” 4th ed., John Wiley & Sons, 1995.
- [11] T. McGeer, “Passive dynamic walking,” CSS-IS TR 88-02, 1988.
- [12] A. Badri-Spröwitz, A. A. Sarvestani, M. Sitti, and M. A. Daley, “BirdBot achieves energy-efficient gait with minimal control using avian-inspired leg clutching,” Science Robotics, Vol.7, No.64, Article No.eabg4055, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1126/scirobotics.abg4055
- [13] N. S. Proctor and P. K. Lynch, “Manual of Ornithology: Avian Structure and Function,” Yale University Press, 1998.
- [14] K. Ito, T. Kinugasa, K. Chiba, Y. Okuda, R. Takasaki, S. Hida, T. Okoshi, R. Hayashi, K. Yoshida, and K. Osuka, “The robotic approach to the passive interlocking mechanism in the hindlimb musculoskeletal system of ıt Crocodylus porosus,” Advanced Robotics, Vol.37, No.18, pp. 1187-1197, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1080/01691864.2023.2256375
- [15] K. Miyashita, Y. Masuda, M. Gunji, A. Fukuhara, K. Tadakuma, and M. Ishikawa, “Emergence of Swing-to-Stance Transition from Interlocking Mechanism in Horse Hindlimb,” 2020 IEEE/RSJ Int. Conf. on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), pp. 7860-7865, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1109/IROS45743.2020.9341026
 This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.
This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.