DCLK1: Difference between revisions
Appearance
Content deleted Content added
Tom.Reding (talk | contribs) m CS1 maintenance: vauthors/veditors or enumerate multiple authors/editors; WP:GenFixes on, added underlinked tag using AWB |
Added wikilink |
||
| (19 intermediate revisions by 15 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Protein-coding gene in the species Homo sapiens}} |
|||
{{Underlinked|date=May 2016}} |
|||
{{cs1 config|name-list-style=vanc}} |
|||
{{Infobox_gene}} |
{{Infobox_gene}} |
||
''' |
'''Doublecortin-like kinase protein 1''' ('''DCLK1''')<ref name="pmid9747029">{{cite journal | vauthors = Omori Y, Suzuki M, Ozaki K, Harada Y, Nakamura Y, Takahashi E, Fujiwara T | title = Expression and chromosomal localization of KIAA0369, a putative kinase structurally related to Doublecortin | journal = J Hum Genet | volume = 43 | issue = 3 | pages = 169–77 |date=Oct 1998 | pmid = 9747029 | doi = 10.1007/s100380050063 | doi-access = free }}</ref><ref name="pmid10036192">{{cite journal | vauthors = Sossey-Alaoui K, Srivastava AK | title = DCAMKL1, a brain-specific transmembrane protein on 13q12.3 that is similar to doublecortin (DCX) | journal = Genomics | volume = 56 | issue = 1 | pages = 121–6 |date=May 1999 | pmid = 10036192 | doi = 10.1006/geno.1998.5718 }}</ref><ref name=ding2023>{{cite journal|vauthors=Ding L, Weygant N, Ding C, Lai Y, Li H|title=DCLK1 and tuft cells: Immune-related functions and implications for cancer immunotherapy|journal=Critical Reviews in Oncology and Hematology|volume=191|id=Art. No. 104118|year=2023|doi=10.1016/j.critrevonc.2023.104118|pmid=37660932}}</ref><ref name="entrez">{{cite web | title = Entrez Gene: DCAMKL1 doublecortin and CaM kinase-like 1| url = https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=9201|access-date=30 May 2024|date=7 April 2024|website=Gene|publisher=National Library of Medicine}}</ref> is an [[enzyme]] that in humans is encoded by the ''DCLK1'' [[gene]].<ref name="pmid9747029"/><ref name="pmid10036192"/><ref name="entrez"/> Its C-terminal domain in rats is expressed independently from an alternative transcript, ''cpg16'', and can function alone as a [[serine/threonine protein kinase]] that is [[cyclic AMP]] dependent.<ref>{{cite journal|vauthors=Silverman MA, Benard O, Jaaro H, Rattner A, Citri Y, Seger R|title=CPG16, a novel protein serine/threonine kinase downstream of cAMP-dependent protein kinase|journal=Journal of Biological Chemistry|year=1999|volume=274|issue=5|pages=2631-2636|doi-access=free|pmid=9915791|doi=10.1074/jbc.274.5.2631}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors=Lin PT, Gleeson JG, Corbo JC |title=DCAMKL1 encodes a protein kinase with homology to doublecortin that regulates microtubule polymerization. |journal=J. Neurosci. |volume=20 |issue= 24 |pages= 9152–61 |year= 2001 |pmid= 11124993 |doi= 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-24-09152.2000|pmc=6773030 |display-authors=etal|doi-access=free }}</ref> |
||
DCLK1 expression is a marker for [[tuft cells]], a type of chemosensory cell of the intestinal epithelium.<ref name=ding2023/><ref>{{cite journal|vauthors=Gerbe F, Legraverend C, Jay P|title=The intestinal epithelium tuft cells: specification and function|journal=Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences|volume=69|pages=2907-2917|year=2012|issue=17|pmid=22527717|pmc=3417095|doi=10.1007/s00018-012-0984-7|doi-access=free}}</ref> |
|||
<!-- The PBB_Summary template is automatically maintained by Protein Box Bot. See Template:PBB_Controls to Stop updates. --> |
|||
{{PBB_Summary |
|||
| section_title = |
|||
| summary_text = |
|||
}} |
|||
==References== |
==References== |
||
| Line 14: | Line 11: | ||
==Further reading== |
==Further reading== |
||
{{refbegin | 2}} |
{{refbegin | 2}} |
||
| ⚫ | *{{cite journal | vauthors=Nagase T, Ishikawa K, Nakajima D |title=Prediction of the coding sequences of unidentified human genes. VII. The complete sequences of 100 new cDNA clones from brain which can code for large proteins in vitro. |journal=DNA Res. |volume=4 |issue= 2 |pages= 141–50 |year= 1997 |pmid= 9205841 |doi=10.1093/dnares/4.2.141 |display-authors=etal|doi-access=free }} |
||
{{PBB_Further_reading |
|||
| citations = |
|||
| ⚫ | *{{cite journal | vauthors=Nagase T, Ishikawa K, Nakajima D |title=Prediction of the coding sequences of unidentified human genes. VII. The complete sequences of 100 new cDNA clones from brain which can code for large proteins in vitro. |journal=DNA Res. |volume=4 |issue= 2 |pages= 141–50 |year= 1997 |pmid= 9205841 |doi=10.1093/dnares/4.2.141 |display-authors=etal}} |
||
*{{cite journal | vauthors=Matsumoto N, Pilz DT, Ledbetter DH |title=Genomic structure, chromosomal mapping, and expression pattern of human DCAMKL1 (KIAA0369), a homologue of DCX (XLIS). |journal=Genomics |volume=56 |issue= 2 |pages= 179–83 |year= 1999 |pmid= 10051403 |doi= 10.1006/geno.1998.5673 }} |
*{{cite journal | vauthors=Matsumoto N, Pilz DT, Ledbetter DH |title=Genomic structure, chromosomal mapping, and expression pattern of human DCAMKL1 (KIAA0369), a homologue of DCX (XLIS). |journal=Genomics |volume=56 |issue= 2 |pages= 179–83 |year= 1999 |pmid= 10051403 |doi= 10.1006/geno.1998.5673 }} |
||
*{{cite journal | vauthors= |
*{{cite journal | vauthors=Burgess HA, Reiner O |title=Alternative splice variants of doublecortin-like kinase are differentially expressed and have different kinase activities. |journal=J. Biol. Chem. |volume=277 |issue= 20 |pages= 17696–705 |year= 2002 |pmid= 11884394 |doi= 10.1074/jbc.M111981200 |doi-access= free }} |
||
*{{cite journal | vauthors= |
*{{cite journal | vauthors=Kim MH, Derewenda U, Devedjiev Y |title=Purification and crystallization of the N-terminal domain from the human doublecortin-like kinase. |journal=Acta Crystallogr. D |volume=59 |issue= Pt 3 |pages= 502–5 |year= 2003 |pmid= 12595708 |doi=10.1107/S0907444903000027 |bibcode=2003AcCrD..59..502K |display-authors=etal}} |
||
*{{cite journal | vauthors=Kim MH, |
*{{cite journal | vauthors=Kim MH, Cierpicki T, Derewenda U |title=The DCX-domain tandems of doublecortin and doublecortin-like kinase. |journal=Nat. Struct. Biol. |volume=10 |issue= 5 |pages= 324–33 |year= 2003 |pmid= 12692530 |doi= 10.1038/nsb918 |s2cid=10173864 |display-authors=etal}} |
||
*{{cite journal | vauthors= |
*{{cite journal | vauthors=Seet LF, Liu N, Hanson BJ, Hong W |title=Endofin recruits TOM1 to endosomes. |journal=J. Biol. Chem. |volume=279 |issue= 6 |pages= 4670–9 |year= 2004 |pmid= 14613930 |doi= 10.1074/jbc.M311228200 |doi-access= free }} |
||
*{{cite journal | vauthors= |
*{{cite journal | vauthors=Ballif BA, Villén J, Beausoleil SA |title=Phosphoproteomic analysis of the developing mouse brain. |journal=Mol. Cell. Proteomics |volume=3 |issue= 11 |pages= 1093–101 |year= 2005 |pmid= 15345747 |doi= 10.1074/mcp.M400085-MCP200 |display-authors=etal|doi-access=free }} |
||
*{{cite journal | vauthors=Ballif BA, Villén J, Beausoleil SA |title=Phosphoproteomic analysis of the developing mouse brain. |journal=Mol. Cell Proteomics |volume=3 |issue= 11 |pages= 1093–101 |year= 2005 |pmid= 15345747 |doi= 10.1074/mcp.M400085-MCP200 |display-authors=etal}} |
|||
}} |
|||
{{refend}} |
{{refend}} |
||
== External links == |
|||
* {{PDBe-KB2|O15075|Serine/threonine-protein kinase DCLK1}} |
|||
{{PDB Gallery|geneid=9201}} |
{{PDB Gallery|geneid=9201}} |
||
{{Serine/threonine-specific protein kinases}} |
{{Serine/threonine-specific protein kinases}} |
||
{{Enzymes}} |
{{Enzymes}} |
||
{{Portal bar| |
{{Portal bar|Biology|border=no}} |
||
<!-- The PBB_Controls template provides controls for Protein Box Bot, please see Template:PBB_Controls for details. --> |
|||
{{PBB_Controls |
|||
| update_page = yes |
|||
| require_manual_inspection = no |
|||
| update_protein_box = yes |
|||
| update_summary = yes |
|||
| update_citations = yes |
|||
}} |
|||
[[Category:EC 2.7.11]] |
[[Category:EC 2.7.11]] |
||
Latest revision as of 22:48, 30 May 2024
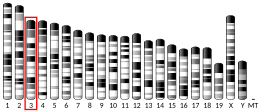
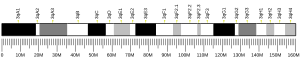
Doublecortin-like kinase protein 1 (DCLK1)[5][6][7][8] is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DCLK1 gene.[5][6][8] Its C-terminal domain in rats is expressed independently from an alternative transcript, cpg16, and can function alone as a serine/threonine protein kinase that is cyclic AMP dependent.[9][10]
DCLK1 expression is a marker for tuft cells, a type of chemosensory cell of the intestinal epithelium.[7][11]
References
[edit]- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000133083 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000027797 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ a b Omori Y, Suzuki M, Ozaki K, Harada Y, Nakamura Y, Takahashi E, Fujiwara T (Oct 1998). "Expression and chromosomal localization of KIAA0369, a putative kinase structurally related to Doublecortin". J Hum Genet. 43 (3): 169–77. doi:10.1007/s100380050063. PMID 9747029.
- ^ a b Sossey-Alaoui K, Srivastava AK (May 1999). "DCAMKL1, a brain-specific transmembrane protein on 13q12.3 that is similar to doublecortin (DCX)". Genomics. 56 (1): 121–6. doi:10.1006/geno.1998.5718. PMID 10036192.
- ^ a b Ding L, Weygant N, Ding C, Lai Y, Li H (2023). "DCLK1 and tuft cells: Immune-related functions and implications for cancer immunotherapy". Critical Reviews in Oncology and Hematology. 191. doi:10.1016/j.critrevonc.2023.104118. PMID 37660932. Art. No. 104118.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: DCAMKL1 doublecortin and CaM kinase-like 1". Gene. National Library of Medicine. 7 April 2024. Retrieved 30 May 2024.
- ^ Silverman MA, Benard O, Jaaro H, Rattner A, Citri Y, Seger R (1999). "CPG16, a novel protein serine/threonine kinase downstream of cAMP-dependent protein kinase". Journal of Biological Chemistry. 274 (5): 2631–2636. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.5.2631. PMID 9915791.
- ^ Lin PT, Gleeson JG, Corbo JC, et al. (2001). "DCAMKL1 encodes a protein kinase with homology to doublecortin that regulates microtubule polymerization". J. Neurosci. 20 (24): 9152–61. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-24-09152.2000. PMC 6773030. PMID 11124993.
- ^ Gerbe F, Legraverend C, Jay P (2012). "The intestinal epithelium tuft cells: specification and function". Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences. 69 (17): 2907–2917. doi:10.1007/s00018-012-0984-7. PMC 3417095. PMID 22527717.
Further reading
[edit]- Nagase T, Ishikawa K, Nakajima D, et al. (1997). "Prediction of the coding sequences of unidentified human genes. VII. The complete sequences of 100 new cDNA clones from brain which can code for large proteins in vitro". DNA Res. 4 (2): 141–50. doi:10.1093/dnares/4.2.141. PMID 9205841.
- Matsumoto N, Pilz DT, Ledbetter DH (1999). "Genomic structure, chromosomal mapping, and expression pattern of human DCAMKL1 (KIAA0369), a homologue of DCX (XLIS)". Genomics. 56 (2): 179–83. doi:10.1006/geno.1998.5673. PMID 10051403.
- Burgess HA, Reiner O (2002). "Alternative splice variants of doublecortin-like kinase are differentially expressed and have different kinase activities". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (20): 17696–705. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111981200. PMID 11884394.
- Kim MH, Derewenda U, Devedjiev Y, et al. (2003). "Purification and crystallization of the N-terminal domain from the human doublecortin-like kinase". Acta Crystallogr. D. 59 (Pt 3): 502–5. Bibcode:2003AcCrD..59..502K. doi:10.1107/S0907444903000027. PMID 12595708.
- Kim MH, Cierpicki T, Derewenda U, et al. (2003). "The DCX-domain tandems of doublecortin and doublecortin-like kinase". Nat. Struct. Biol. 10 (5): 324–33. doi:10.1038/nsb918. PMID 12692530. S2CID 10173864.
- Seet LF, Liu N, Hanson BJ, Hong W (2004). "Endofin recruits TOM1 to endosomes". J. Biol. Chem. 279 (6): 4670–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M311228200. PMID 14613930.
- Ballif BA, Villén J, Beausoleil SA, et al. (2005). "Phosphoproteomic analysis of the developing mouse brain". Mol. Cell. Proteomics. 3 (11): 1093–101. doi:10.1074/mcp.M400085-MCP200. PMID 15345747.
External links
[edit]- Overview of all the structural information available in the PDB for UniProt: O15075 (Serine/threonine-protein kinase DCLK1) at the PDBe-KB.