Prince-Bishopric of Verden: Difference between revisions
Sync modified notice of move discussion on Talk:Verden (state) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<noinclude>{{User:RMCD bot/subject notice|1=Prince-Bishopric of Verden|2=Talk:Verden (state)#Requested move July 2022}} |
<noinclude>{{User:RMCD bot/subject notice|1=Prince-Bishopric of Verden|2=Talk:Verden (state)#Requested move 20 July 2022}} |
||
</noinclude>{{Infobox country |
</noinclude>{{Infobox country |
||
|conventional_long_name = Prince-Bishopric of Verden<br>Principality of Verden |
|conventional_long_name = Prince-Bishopric of Verden<br>Principality of Verden |
||
Revision as of 13:03, 21 July 2022
A request that this article title be changed to Prince-Bishopric of Verden is under discussion. Please do not move this article until the discussion is closed. |
Prince-Bishopric of Verden Principality of Verden (Hoch)Stift Verden (1180–1648) Fürstentum Verden (1648–1807/10) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1180–1807/10 | |||||||||
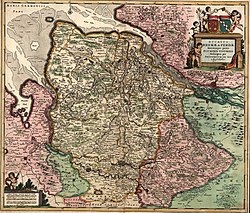 The territory of Verden (pink, below right) around 1655 | |||||||||
| Status | State of the Holy Roman Empire (until 1806) | ||||||||
| Capital | Verden (seat of chapter), Rotenburg (residence of pr.-bishops since 1195)¹ | ||||||||
| Common languages | German, Low German | ||||||||
| Religion | Catholic Church till the 1550s, then Lutheranism | ||||||||
| Government | Principality | ||||||||
| Ruler | |||||||||
• 1395–1398 | Prince-Bishop Dietrich | ||||||||
• 1398–1399 | Prince-Bishop Conrad II | ||||||||
• 1623–29, 1635–45 | Administrator Frederick II | ||||||||
• 1630–1631 | Prince-Bishop Francis | ||||||||
• 1631–1634 | Admin. John Frederick | ||||||||
| Historical era | Middle Ages | ||||||||
• Break-up of Saxony | 1180 | ||||||||
15 May 1648 | |||||||||
• Disestablished | 1807/10 1807 | ||||||||
1815 | |||||||||
| Area | |||||||||
| 1806[1] | 730 km2 (280 sq mi) | ||||||||
| Population | |||||||||
• 1806[1] | 20,000 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
1: Rotenburg castle was built in 1195, this may have been when the diocese had effectively acquired territorial power as prince-bishopric. | |||||||||
The Prince-Bishopric of Verden (Template:Lang-de) was an ecclesiastical principality of the Holy Roman Empire that was located in what is today the state of Lower Saxony in Germany. Verden (Template:IPA-de) had been a diocese of the Catholic Church since the middle of the 8th century. The state was disestablished in 1648. The territory was managed by secular lords on behalf of the Bishop of Verden. As a Prince-Bishopric of the Empire, the territory of the state was not identical with that of the bishopric, but was located within its boundaries and made up about a quarter of the diocesan area. The territory was referred to at the time as Stift Verden or Hochstift Verden, roughly equating to Prince-Bishopric of Verden. By the terms of the Peace of Westphalia, the Prince-Bishopric was disestablished and a new entity was established — the Principality of Verden (also known as the Duchy of Verden).
Location
The territory of the Prince-Bishopric of Verden covered the eastern part of the present district of Verden (its border ran between Langwedel and Etelsen), the southern part of the district of Rotenburg (Wümme) and parts of the districts of Harburg and the Heath district (Heidekreis).
History
Foundation
The Diocese of Verden was founded around 800 in Verden upon Aller as a suffragan in the ecclesiastical province of Mainz.[citation needed] The first nine or ten bishops were Scots (Irish) or Englishmen, and include Saint Erlulph.[2] Originally held in personal union with Amorbach Abbey in the Odenwald, by the 9th century the bishopric had become a political football for the regional nobility. For example, the Amelungs promoted their favourite monks from Corvey Abbey to the episcopal throne.
High Middle Ages
In 985, Emperor Otto III, represented by his mother, Empress Theophanu, granted the bishop of Verden market, minting, taxation and ban privileges in the Sturmigau – as the region of the present district of Verden and the pre-1977 district of Rotenburg was then called. These privileges formed the basis of a future prince-bishopric (Hochstift), which materialised with the carve-up of the old Duchy of Saxony in 1180. Prince-Bishop Tammo of Verden gained for about a quarter of the diocesan territory, where the see held already considerable privileges, the territorial princely power, establishing the Prince-Bishopric of Verden. In 1195 Prince-Bishop Rudolph I founded the castle of Rotenburg upon Wümme as a stronghold against the neighbouring Bremen prince-archbishops. Later the castle took on the function of a prince-episcopal Residenz.
Since the Investiture Controversy in the 11th and 12th century the cathedral chapters used to elect the Catholic bishops in the Holy Roman Empire. Thus Verden prince-bishopric was an elective monarchy of imperial immediacy within the Empire, with the monarch being the respective bishop usually elected by the chapter and confirmed by the Holy See, or exceptionally only appointed by the Holy See, which happened in increasing frequency in Verden. Papally confirmed bishops were then invested by the emperor with the princely regalia, thus the title prince-bishop.
In the early 13th century the Pope was increasingly involved by the local prince-bishops in regional affairs. From the 14th century it was hardly possible to hold out against the papal commission, which led to a strengthening of the influence of the cathedral chapter; whilst many prince-bishops were now seen as Landfremde or alien, who lacked local support because they were not elected by the chapter but only appointed by the pope.
From the early 16th century the prince-bishopric belonged to the Lower Rhenish–Westphalian Circle (colloquially: Westphalian Circle), a fiscal and military subsection of the empire. Verden sent its representatives to the diets of the empire and the Imperial Circle. At times the prince-bishops ruled in personal union the Prince-Archbishopric of Bremen. In order to maintain the two seats in the diets the sees of Bremen and Verden were never formally united in a real union. The same is true for the collectively governed Duchies of Bremen and Verden which emerged in 1648 from the secularised two prince-bishoprics.
Around 890 AD the cathedral chapter was able to effect a separation of their estate from that of the bishop, under the law of property. From 1275, it was fixed at 16 members, of whom the five eldest were responsible for ordination of priests, the five middle ones the appointment of deacons and the five youngest the appointment of sub-deacons. The provost of St. John's in Lüneburg was the 16th member and, as such, had a special status. Its members supplemented the chapter, whose dignitaries included the provost, dean, scholaster, cellarer, cantor and treasurer, independently. Towards the end of the 15th century, there were no fewer than 48 cathedral vicars (Domvikaren), led by the two episcopal vicars.
Several of the eight archdeacons were incorporated into the cathedral chapter.
While the Prince-Bishopric of Verden belonged, like the neighbouring County of Hoya, to the Westphalian Circle, other adjacent territories such as the Duchy of Brunswick-Lüneburg and Prince-Archbishopric of Bremen were part of the Lower Saxon Circle, albeit ecclesiastically having a share in the Verden diocese. Verden's secular territory in those days roughly covered what is now the eastern part of the county of Verden, the southern part of the county of Rotenburg and parts of the county of Heidekreis.
The Reformation
From 1558, a gradual change of confession to Lutheranism took place across the Verden diocesan area at different speeds depending on whether its secular rulers promoted or inhibited the Reformation. Within Verden's secular territory, the actual Hochstift, the Reformation was concluded with the enactment of a church ordinance by Administrator Eberhard von Holle, in 1568. In 1630, during the Thirty Years' War, a Roman Catholic bishop, Francis of Wartenberg, took over again as a consequence of the Edict of Restitution, but was only able to hold office until 1634. Thereafter, the Roman Catholic church was only represented there by the Apostolic Vicariate of Northern Missions.
Principality of Verden
In 1648 the bishopric was finally secularised as a result of the Peace of Westphalia. It became a principality and was transferred to the Swedish crown, whereby the existence of the Stift and the bishopric came to an end. It lasted from 1648 to 1712, with a break from 1675 to 1679, ruled together in personal union with the territory of the former Prince-Archbishopric of Bremen as the Duchies of Bremen and Verden (formally the Duchy of Bremen and Principality of Verden) with their capital in Stade. For the further history see: Bremen-Verden.
In the Swedish-Brandenburg War from 1675 to 1676, Verden was conquered in a campaign by several states of the Holy Roman Empire and Denmark and remained in allied hands until the end of the war in 1679.
In 1712, Denmark conquered the state, but sold it in 1715 to the Electorate of Hanover.
With the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire in 1806, the Principality of Verden lost its importance as an Imperial Estate (Reichsstand). After its occupation and annexation during the Napoleonic Wars, it went to the Kingdom of Hanover following France's defeat. In 1823, the Principality of Verden was formally dissolved and turned into a Hanoverian administrative unit, Landdrostei Stade, along with the Duchy of Bremen and Land Hadeln, but with a participation in the administration of the estates of Verden, Bremen and Hadeln that still existed. In 1864, the first two were merged into the "Region of the Duchies of Bremen and Verden" (Landschaft der Herzogtümer Bremen und Verden) by a Hanoverian act and their area of responsibility redefined.
The new Landrostei became part of the Province of Hanover which was annexed by Prussia in 1866. On 1 April 1885, Landdrostei Stade was renamed Regierungsbezirk Stade in accordance with normal Prussian administrative practice. In 1946, the State of Hanover became part of the new post-war West German state of Lower Saxony, Regierungsbezirk Stade continuing to exist until 31 January 1978. Today, the territory of the former duchies of Bremen and Verden is only reflected in the Stade Regional Association and the Region of the Duchies of Bremen and Verden which, today, has the responsibility for territorially defined public fire insurance as part of VGH Insurance.
See also
Sources
- Gesellschaft für die Geschichte des Bistums Verden e.V.: Bistum Verden, 770 bis 1648, Editions du Signe 2001, ISBN 2-7468-0384-4
- Bernd Kappelhoff, Thomas Vogtherr: Immunität und Landesherrschaft, Beiträge zur Geschichte des Bistums Verden, Schriftenreihe des Landschaftsverbandes der ehemaligen Herzogtümer Bremen und Verden, Stade 2002, ISBN 3-931879-09-7
- Thomas Vogtherr: Chronicon episcoporum Verdensium, Die Chronik der Verdener Bischöfe, Schriftenreihe des Landschaftsverbandes der ehemaligen Herzogtümer Bremen und Verden, Stade 1997, ISBN 3-931879-03-8
- Arend Mindermann: Urkundenbuch der Bischöfe und des Domkapitels von Verden, Band 1, Von den Anfängen bis 1300, Schriftenreihe des Landschaftsverbandes der ehemaligen Herzogtümer Bremen und Verden, Stade 2001, ISBN 3-931879-07-0
- Arend Mindermann: Urkundenbuch der Bischöfe und des Domkapitels von Verden, Band 2, 1300–1380, Schriftenreihe des Landschaftsverbandes der ehemaligen Herzogtümer Bremen und Verden, Stade 2004, ISBN 3-931879-15-1
References
- ^ Köbler, Gerhard: "Historisches Lexikon der deutschen Länder. Die deutschen Territorien vom Mittelalter bis zur Gegenwart", Munich 1995, page 650
- ^ *O'Hanlon, John (1875), Lives of the Irish Saints : with special festivals, and the commemorations of holy persons, vol. 2, Dublin: J. Duffy, retrieved 2021-07-24