Scapholunate ligament
| Scapholunate ligament | |
|---|---|
 | |
| From | Scaphoid |
| To | Lunate |
| TA2 | 1819 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The scapholunate ligament is a ligament of the wrist.[1]
Rupture of the scapholunate ligament causes scapholunate instability, which, if untreated, will eventually cause a predictable pattern of wrist osteoarthritis called scapholunate advanced collapse (SLAC).[2]
Anatomy
[edit]The scapholunate ligament is an intraarticular ligament binding the scaphoid and lunate bones of the wrist together. It is divided into three areas, dorsal, proximal and palmar, with the dorsal segment being the strongest part.[3] It is the main stabilizer of the scaphoid. In contrast to the scapholunate ligament, the lunotriquetral ligament is more prominent on the palmar side.
Instability
[edit]Complete rupture of this ligament leads to wrist instability. The main type of such instability is dorsal intercalated segment instability (DISI) deformity, where the lunate angulates to the posterior side of the hand.[4][5]
A dynamic scapholunate instability is where the scapholunate ligament is completely ruptured, but secondary scaphoid stabilizers are still preserved;[6] these are the scaphotrapezial (ST), scaphocapitate (SC) and radioscaphocapitate (RSC) ligaments.[6] In a static scapholunate instability, these other ligaments are ruptured as well.
Diagnosis
[edit]X-ray images indicate scapholunate ligament instability when the scapholunate distance is more than 3 mm, which is called scapholunate dissociation.[7] A static scapholunate instability is generally readily visible, but a dynamic scapholunate instability can only be seen radiographically in certain wrist positions or under certain loading conditions, such as when clenching the wrist, or loading the wrist in ulnar deviation.[6]
In order to diagnose a SLAC wrist you need a posterior anterior (PA) view X-ray, a lateral view X-ray and a fist view X-ray.[8] The fist X-ray is often made if there is no convincing Terry Thomas sign. A fist X-ray of a scapholunate ligament rupture will show a descending capitate bone. Making a fist will give pressure at the capitate, which will descend if there is a rupture in the scapholunate ligament.
The Watson's test may be used in diagnosis.
-
Static scapholunate dissociation
-
Dynamic instability: Increased scapholunate distance (between yellow lines) upon ulnar deviation of the wrist, but not otherwise.
-
Dynamic scapholunate instability visible upon clenching the wrist
-
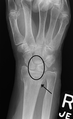
Scapholunate ligament disruption associated with a Colles' fracture
Treatment
[edit]Treatment will vary depending upon the degree of injury and can range from observation and direct ligament repair through to reconstruction.
Complications
[edit]Eventually, untreated scapholunate instability generally causes a predictable pattern of wrist osteoarthritis called scapholunate advanced collapse (SLAC).[2]
References
[edit]- ^ Mark D. Miller; Jennifer Hart; John M. MacKnight (10 July 2009). Essential Orthopaedics. Elsevier Health Sciences. pp. 305–. ISBN 978-1-4160-5473-3. Retrieved 1 November 2010.
- ^ a b Tischler, Brian T.; Diaz, Luis E.; Murakami, Akira M.; Roemer, Frank W.; Goud, Ajay R.; Arndt, William F.; Guermazi, Ali (2014). "Scapholunate advanced collapse: a pictorial review". Insights into Imaging. 5 (4): 407–417. doi:10.1007/s13244-014-0337-1. ISSN 1869-4101. PMC 4141341. PMID 24891066.
- ^ Berger, R. A. (2001). "The anatomy of the ligaments of the wrist and distal radioulnar joints". Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research. 383 (383): 32–40. doi:10.1097/00003086-200102000-00006. PMID 11210966.
- ^ Shah, CM; Stern PJ (2013). "Scapholunate advanced collapse (SLAC) and scaphoid nonunion advanced collapse (SNAC) wrist arthritis". Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 6 (1): 9–17. doi:10.1007/s12178-012-9149-4. PMC 3702758. PMID 23325545.
- ^ Omori, S; Moritomo, H; Omokawa, S; Murase, T; Sugamoto, K; Yoshikawa, H (July 2013). "In vivo 3-dimensional analysis of dorsal intercalated segment instability deformity secondary to scapholunate dissociation: a preliminary report". The Journal of Hand Surgery. 38 (7): 1346–55. doi:10.1016/j.jhsa.2013.04.004. PMID 23790423.
- ^ a b c Fairplay, Tracy; Cozzolino, Roberto; Atzei, Andrea; Luchetti, Riccardo (2013). "Current Role of Open Reconstruction of the Scapholunate Ligament". Journal of Wrist Surgery. 02 (2): 116–125. doi:10.1055/s-0033-1343092. ISSN 2163-3916. PMC 3699272. PMID 24436803.
- ^ Owen Kang and Henry Knipe; et al. "Scapholunate advanced collapse". Radiopaedia. Retrieved 5 January 2018.
- ^ Novelline, RA (2004). Squire's fundamentals of radiology, 6th Edition (6th ed.). United States of America: President and fellows of Harvard college. ISBN 0-674-01279-8.