+ * Input: arr[] = {1, 2, 3, 5}
+ * Output: 4
+ * Explanation: The missing number from 1 to 5 is 4
+ *
+ * Approach:
+ * XOR has certain properties
+ * Assume a1 ^ a2 ^ a3 ^ …^ an = a and a1 ^ a2 ^ a3 ^ …^ an-1 = b
+ * Then a ^ b = an
+ * Using this property, the missing element can be found. Calculate XOR of all the natural number from 1 to n and store it as a.
+ * Now calculate XOR of all the elements of the array and store it as b.
+ * The missing number will be a ^ b.
+ * ^ is XOR operator.
+ *
+ * Algorithm:
+ * Create two variables a = 0 and b = 0
+ * Run a loop from 1 to n with i as counter.
+ * For every index update a as a = a ^ i
+ * Now traverse the array from start to end.
+ * For every index update b as b = b ^ array[i]
+ * Print the missing number as a ^ b.
+ *
+ * Compelxity Analysis:
+ * Time Complexity: O(n).
+ * Only one traversal of array is needed.
+ * Space Complexity: O(1).
+ * No extra space is needed
+ *
+ * Bitwise operations are incredibly simple and thus usually faster than arithmetic operations.
+ */
+
+public class FindMissingNumber {
+
+ public static long missingNumber(int[] nums, int n) {
+ System.out.println("time start");
+
+ long naturalNumberXOR = 1;
+ long arrayXOR = nums[0];
+
+ for (int i = 2; i <= n + 1; i++) {
+ naturalNumberXOR = naturalNumberXOR ^ i;
+ }
+
+ for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
+ arrayXOR = arrayXOR ^ nums[i];
+ }
+ System.out.println("time end");
+ return naturalNumberXOR ^ arrayXOR;
+
+
+ }
+
+
+ public static long missingNumberUsingSUm(int[] nums, int n) {
+ System.out.println("time start");
+ long naturalNumberSum = 1;
+ long arraySum = nums[0];
+
+ naturalNumberSum = (n * (n + 1)) / 2; //Summation formula GUass's formula
+
+
+ for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
+ arraySum = arraySum + nums[i];
+ }
+ System.out.println("time end");
+ return naturalNumberSum - arraySum;
+
+ }
+
+ public static void main(String args[]) {
+ int[] nums = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9, 10};
+ System.out.println("Missing Number:" + missingNumberUsingSUm(nums, 10));
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/arrays/InversionCountInArray_MergeSort.html b/src/main/java/com/arrays/InversionCountInArray_MergeSort.html
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..f516ebb8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/com/arrays/InversionCountInArray_MergeSort.html
@@ -0,0 +1,2475 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
Inversion Count for an array indicates – how far (or close) the array is from being sorted. If array is already sorted then inversion count is 0. If array is sorted in reverse order that inversion count is the maximum.
+Formally speaking, two elements a[i] and a[j] form an inversion if a[i] > a[j] and i < j
+
Example:
+
+Input: arr[] = {8, 4, 2, 1}
+Output: 6
+
+Explanation: Given array has six inversions:
+(8,4), (4,2),(8,2), (8,1), (4,1), (2,1).
+
+
+Input: arr[] = {3, 1, 2}
+Output: 2
+
+Explanation: Given array has two inversions:
+(3, 1), (3, 2)
+
+
+
+METHOD 1 (Simple)
+
+
METHOD 2(Enhance Merge Sort)
+
+- Approach:
+Suppose the number of inversions in the left half and right half of the array (let be inv1 and inv2), what kinds of inversions are not accounted for in Inv1 + Inv2? The answer is – the inversions that need to be counted during the merge step. Therefore, to get a number of inversions, that needs to be added a number of inversions in the left subarray, right subarray and merge().
+
+How to get number of inversions in merge()?
+In merge process, let i is used for indexing left sub-array and j for right sub-array. At any step in merge(), if a[i] is greater than a[j], then there are (mid – i) inversions. because left and right subarrays are sorted, so all the remaining elements in left-subarray (a[i+1], a[i+2] … a[mid]) will be greater than a[j]
+
+The complete picture:
+
+- Algorithm:
+
+- The idea is similar to merge sort, divide the array into two equal or almost equal halves in each step until the base case is reached.
+- Create a function merge that counts the number of inversions when two halves of the array are merged, create two indices i and j, i is the index for first half and j is an index of the second half. if a[i] is greater than a[j], then there are (mid – i) inversions. because left and right subarrays are sorted, so all the remaining elements in left-subarray (a[i+1], a[i+2] … a[mid]) will be greater than a[j].
+- Create a recursive function to divide the array into halves and find the answer by summing the number of inversions is the first half, number of inversion in the second half and the number of inversions by merging the two.
+- The base case of recursion is when there is only one element in the given half.
+- Print the answer
+
+
+-
+Implementation:
+
+
C++
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ #include <bits/stdc++.h>
+ using namespace std;
+
+ int _mergeSort(int arr[], int temp[], int left, int right);
+ int merge(int arr[], int temp[], int left, int mid, int right);
+
+
+
+ int mergeSort(int arr[], int array_size)
+ {
+ int temp[array_size];
+ return _mergeSort(arr, temp, 0, array_size - 1);
+ }
+
+
+
+ int _mergeSort(int arr[], int temp[], int left, int right)
+ {
+ int mid, inv_count = 0;
+ if (right > left) {
+
+
+
+ mid = (right + left) / 2;
+
+
+
+
+ inv_count += _mergeSort(arr, temp, left, mid);
+ inv_count += _mergeSort(arr, temp, mid + 1, right);
+
+
+ inv_count += merge(arr, temp, left, mid + 1, right);
+ }
+ return inv_count;
+ }
+
+
+
+ int merge(int arr[], int temp[], int left,
+ int mid, int right)
+ {
+ int i, j, k;
+ int inv_count = 0;
+
+ i = left;
+ j = mid;
+ k = left;
+ while ((i <= mid - 1) && (j <= right)) {
+ if (arr[i] <= arr[j]) {
+ temp[k++] = arr[i++];
+ }
+ else {
+ temp[k++] = arr[j++];
+
+
+
+ inv_count = inv_count + (mid - i);
+ }
+ }
+
+
+
+ while (i <= mid - 1)
+ temp[k++] = arr[i++];
+
+
+
+ while (j <= right)
+ temp[k++] = arr[j++];
+
+
+ for (i = left; i <= right; i++)
+ arr[i] = temp[i];
+
+ return inv_count;
+ }
+
+
+ int main()
+ {
+ int arr[] = { 1, 20, 6, 4, 5 };
+ int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
+ int ans = mergeSort(arr, n);
+ cout << " Number of inversions are " << ans;
+ return 0;
+ }
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
C
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ #include <stdio.h>
+
+ int _mergeSort(int arr[], int temp[], int left, int right);
+ int merge(int arr[], int temp[], int left, int mid, int right);
+
+
+
+ int mergeSort(int arr[], int array_size)
+ {
+ int* temp = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * array_size);
+ return _mergeSort(arr, temp, 0, array_size - 1);
+ }
+
+
+
+ int _mergeSort(int arr[], int temp[], int left, int right)
+ {
+ int mid, inv_count = 0;
+ if (right > left) {
+
+
+ mid = (right + left) / 2;
+
+
+
+ inv_count += _mergeSort(arr, temp, left, mid);
+ inv_count += _mergeSort(arr, temp, mid + 1, right);
+
+
+ inv_count += merge(arr, temp, left, mid + 1, right);
+ }
+ return inv_count;
+ }
+
+
+
+ int merge(int arr[], int temp[], int left, int mid, int right)
+ {
+ int i, j, k;
+ int inv_count = 0;
+
+ i = left;
+ j = mid;
+ k = left;
+ while ((i <= mid - 1) && (j <= right)) {
+ if (arr[i] <= arr[j]) {
+ temp[k++] = arr[i++];
+ }
+ else {
+ temp[k++] = arr[j++];
+
+
+ inv_count = inv_count + (mid - i);
+ }
+ }
+
+
+
+ while (i <= mid - 1)
+ temp[k++] = arr[i++];
+
+
+
+ while (j <= right)
+ temp[k++] = arr[j++];
+
+
+ for (i = left; i <= right; i++)
+ arr[i] = temp[i];
+
+ return inv_count;
+ }
+
+
+ int main(int argv, char** args)
+ {
+ int arr[] = { 1, 20, 6, 4, 5 };
+ printf(" Number of inversions are %d \n", mergeSort(arr, 5));
+ getchar();
+ return 0;
+ }
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
Java
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ import java.util.Arrays;
+
+ public class GFG {
+
+
+
+ private static int mergeAndCount(int[] arr, int l, int m, int r)
+ {
+
+
+ int[] left = Arrays.copyOfRange(arr, l, m + 1);
+
+
+ int[] right = Arrays.copyOfRange(arr, m + 1, r + 1);
+
+ int i = 0, j = 0, k = l, swaps = 0;
+
+ while (i < left.length && j < right.length) {
+ if (left[i] <= right[j])
+ arr[k++] = left[i++];
+ else {
+ arr[k++] = right[j++];
+ swaps += (m + 1) - (l + i);
+ }
+ }
+
+
+ while (i < left.length)
+ arr[k++] = left[i++];
+
+
+ while (j < right.length)
+ arr[k++] = right[j++];
+
+ return swaps;
+ }
+
+
+ private static int mergeSortAndCount(int[] arr, int l, int r)
+ {
+
+
+
+ int count = 0;
+
+ if (l < r) {
+ int m = (l + r) / 2;
+
+
+
+
+
+ count += mergeSortAndCount(arr, l, m);
+
+
+ count += mergeSortAndCount(arr, m + 1, r);
+
+
+ count += mergeAndCount(arr, l, m, r);
+ }
+
+ return count;
+ }
+
+
+ public static void main(String[] args)
+ {
+ int[] arr = { 1, 20, 6, 4, 5 };
+
+ System.out.println(mergeSortAndCount(arr, 0, arr.length - 1));
+ }
+ }
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
Python3
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ def mergeSort(arr, n):
+
+
+ temp_arr = [0]*n
+ return _mergeSort(arr, temp_arr, 0, n-1)
+
+
+
+ def _mergeSort(arr, temp_arr, left, right):
+
+
+
+
+ inv_count = 0
+
+
+
+
+ if left < right:
+
+
+
+
+ mid = (left + right)//2
+
+
+
+ inv_count += _mergeSort(arr, temp_arr, left, mid)
+
+
+
+ inv_count += _mergeSort(arr, temp_arr, mid + 1, right)
+
+
+
+ inv_count += merge(arr, temp_arr, left, mid, right)
+ return inv_count
+
+
+ def merge(arr, temp_arr, left, mid, right):
+ i = left
+ j = mid + 1
+ k = left
+ inv_count = 0
+
+
+
+
+ while i <= mid and j <= right:
+
+
+
+ if arr[i] <= arr[j]:
+ temp_arr[k] = arr[i]
+ k += 1
+ i += 1
+ else:
+
+ temp_arr[k] = arr[j]
+ inv_count += (mid-i + 1)
+ k += 1
+ j += 1
+
+
+ while i <= mid:
+ temp_arr[k] = arr[i]
+ k += 1
+ i += 1
+
+
+ while j <= right:
+ temp_arr[k] = arr[j]
+ k += 1
+ j += 1
+
+
+ for loop_var in range(left, right + 1):
+ arr[loop_var] = temp_arr[loop_var]
+
+ return inv_count
+
+
+
+ arr = [1, 20, 6, 4, 5]
+ n = len(arr)
+ result = mergeSort(arr, n)
+ print("Number of inversions are", result)
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
C#
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ using System;
+ public class Test {
+
+
+
+ static int mergeSort(int[] arr, int array_size)
+ {
+ int[] temp = new int[array_size];
+ return _mergeSort(arr, temp, 0, array_size - 1);
+ }
+
+
+
+ static int _mergeSort(int[] arr, int[] temp, int left, int right)
+ {
+ int mid, inv_count = 0;
+ if (right > left) {
+
+
+ mid = (right + left) / 2;
+
+
+
+ inv_count += _mergeSort(arr, temp, left, mid);
+ inv_count += _mergeSort(arr, temp, mid + 1, right);
+
+
+ inv_count += merge(arr, temp, left, mid + 1, right);
+ }
+ return inv_count;
+ }
+
+
+
+ static int merge(int[] arr, int[] temp, int left, int mid, int right)
+ {
+ int i, j, k;
+ int inv_count = 0;
+
+ i = left;
+ j = mid;
+ k = left;
+ while ((i <= mid - 1) && (j <= right)) {
+ if (arr[i] <= arr[j]) {
+ temp[k++] = arr[i++];
+ }
+ else {
+ temp[k++] = arr[j++];
+
+
+ inv_count = inv_count + (mid - i);
+ }
+ }
+
+
+
+ while (i <= mid - 1)
+ temp[k++] = arr[i++];
+
+
+
+ while (j <= right)
+ temp[k++] = arr[j++];
+
+
+ for (i = left; i <= right; i++)
+ arr[i] = temp[i];
+
+ return inv_count;
+ }
+
+
+ public static void Main()
+ {
+ int[] arr = new int[] { 1, 20, 6, 4, 5 };
+ Console.Write("Number of inversions are " + mergeSort(arr, 5));
+ }
+ }
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Output:
+Number of inversions are 5
+
+- Complexity Analysis:
+
+- Time Complexity: O(n log n), The algorithm used is divide and conquer, So in each level one full array traversal is needed and there are log n levels so the time complexity is O(n log n).
+- Space Compelxity:O(1), No extra space is required.
+
+
+
+
Note that above code modifies (or sorts) the input array. If we want to count only inversions then we need to create a copy of original array and call mergeSort() on copy.
+
+
You may like to see.
+Count inversions in an array | Set 2 (Using Self-Balancing BST)
+Counting Inversions using Set in C++ STL
+Count inversions in an array | Set 3 (Using BIT)
+
+References:
+http://www.cs.umd.edu/class/fall2009/cmsc451/lectures/Lec08-inversions.pdf
+http://www.cp.eng.chula.ac.th/~piak/teaching/algo/algo2008/count-inv.htm
+
Please write comments if you find any bug in the above program/algorithm or other ways to solve the same problem.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/arrays/InversionCountInArray_MergeSort.java b/src/main/java/com/arrays/InversionCountInArray_MergeSort.java
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..f108c436
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/com/arrays/InversionCountInArray_MergeSort.java
@@ -0,0 +1,87 @@
+package com.arrays;
+
+import java.util.Arrays;
+
+/**
+ * Inversion Count : For an array, inversion count indicates how far (or close) the array is from being sorted.
+ * If array is already sorted then inversion count is 0. If array is sorted in reverse order that inversion count is the maximum.
+ * Formally, two elements a[i] and a[j] form an inversion if a[i] > a[j] and i < j.
+ *
+ *
+ * Algorithm:
+ * The idea is similar to merge sort, divide the array into two equal or almost equal halves in each step until the base case is reached.
+ * Create a function merge that counts the number of inversions when two halves of the array are merged,
+ * create two indices i and j, i is the index for first half and j is an index of the second half.
+ * if a[i] is greater than a[j], then there are (mid – i) inversions. because left and right subarrays are sorted, so all the remaining elements in left-subarray (a[i+1], a[i+2] … a[mid]) will be greater than a[j].
+ * Create a recursive function to divide the array into halves and find the answer by summing the number of inversions is the first half, number of inversion in the second half and the number of inversions by merging the two.
+ * The base case of recursion is when there is only one element in the given half.
+ * Print the answer
+ *
+ *
+ * Complexity Analysis:
+ * Time Complexity: O(n log n), The algorithm used is divide and conquer,
+ * So in each level one full array traversal is needed and there are log n levels so the time complexity is O(n log n).
+ * Space Compelxity:O(1), No extra space is required.
+ */
+public class InversionCountInArray_MergeSort {
+
+ // Merge two sorted subarrays arr[low .. mid] and arr[mid + 1 .. high]
+ public static int merge(int[] arr, int start, int mid, int end) {
+ // Left subarray
+ int[] left = Arrays.copyOfRange(arr, start, mid + 1);
+
+ // Right subarray
+ int[] right = Arrays.copyOfRange(arr, mid + 1, end + 1);
+
+ int leftCursor = 0, rightCursor = 0, current = start, swaps = 0;
+
+ while (leftCursor < left.length && rightCursor < right.length) {
+ if (left[leftCursor] <= right[rightCursor])
+ arr[current++] = left[leftCursor++];
+ else {
+ arr[current++] = right[rightCursor++];
+ swaps += mid + 1 - leftCursor; /**important*/
+ }
+ }
+
+ // Fill from the rest of the left subarray
+ while (leftCursor < left.length)
+ arr[current++] = left[leftCursor++];
+
+ // Fill from the rest of the right subarray
+ while (rightCursor < right.length)
+ arr[current++] = right[rightCursor++];
+
+ return swaps;
+ }
+
+ // Sort array arr [low..high] using auxiliary array aux[]
+ public static int mergeSort(int[] arr, int low, int high) {
+ // Base case
+ if (high == low) { // if run size == 1
+ return 0;
+ }
+
+ // find mid point
+ int mid = (low + high) / 2;
+ int inversionCount = 0;
+
+ // recursively split runs into two halves until run size == 1,
+ // then merge them and return back up the call chain
+
+ inversionCount += mergeSort(arr, low, mid); // split / merge left half
+ inversionCount += mergeSort(arr, mid + 1, high); // split / merge right half
+ inversionCount += merge(arr, low, mid, high); // merge the two half runs
+
+ return inversionCount;
+ }
+
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ int[] arr = {1, 9, 6, 4, 5};
+ int[] aux = Arrays.copyOf(arr, arr.length);
+
+ // get inversion count by performing merge sort on arr
+ System.out.println("Inversion count is " +
+ mergeSort(arr, 0, arr.length - 1));
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/arrays/LongestConsecutiveSubsequence.java b/src/main/java/com/arrays/LongestConsecutiveSubsequence.java
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..2a8f17cd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/com/arrays/LongestConsecutiveSubsequence.java
@@ -0,0 +1,61 @@
+package com.arrays;
+
+import java.util.HashSet;
+
+/**
+ * Given an unsorted array of integers,
+ * find the length of the longest consecutive elements sequence.
+ *
+ * For example, given [100, 4, 200, 1, 3, 2],
+ * the longest consecutive elements sequence should be [1, 2, 3, 4]. Its length is 4.
+ *
+ * Because it requires O(n) complexity,
+ * we can not solve the problem by sorting the array first. Sorting takes at least O(nlogn) time.
+ *
+ * We can use a HashSet to add and remove elements.
+ * The add, remove and contains methods have constant time complexity O(1).
+ */
+public class LongestConsecutiveSubsequence {
+
+ public static int longestConsecutive(int[] nums) {
+
+ /** Add all the elements of array to Set */
+ HashSet set = new HashSet<>();
+ for (int num : nums)
+ set.add(num);
+
+ int result = 0;
+
+ /** Iterate over each element in array */
+ for (int num : nums) {
+ int count = 1;
+
+ /** calculate previous element to current element to see if present in set */
+ int down = num - 1;
+ while (set.contains(down)) {
+ set.remove(down);
+ down--;
+ count++;
+ }
+
+ /** calculate next element to current element to see if present in set */
+ int up = num + 1;
+ while (set.contains(up)) {
+ set.remove(up);
+ up++;
+ count++;
+ }
+
+ /** update the result if current counter is bigger than result */
+ result = Math.max(result, count);
+ }
+
+ return result;
+ }
+
+ public static void main(String args[]) {
+ int nums[] = {1, 5, 4, 100, 200, 2, 3};
+ int result = longestConsecutive(nums);
+ System.out.println("longestConsecutive : " + result);
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/arrays/MaxSumSubArray_KadaneAlgo_DynamicProgram.html b/src/main/java/com/arrays/MaxSumSubArray_KadaneAlgo_DynamicProgram.html
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..3eab7092
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/com/arrays/MaxSumSubArray_KadaneAlgo_DynamicProgram.html
@@ -0,0 +1,2919 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Kadane's Algorithm in Java. | JavaByPatel
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Kadane's Algorithm in Java to find Largest Sum Contiguous Subarray.
+
+
Kadane's Algorithm in Java. Kadane's Algorithm to solve maximum sum subarray problem.
+
+
The maximum subarray problem is the task of finding the contiguous subarray within a one-dimensional array of numbers which has the largest sum.
+
+

+
+
Lets see what is expected output from given input,
+
Case 1:
Input:
{3, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, 2, 0, 0, 0}
Output:
start index :0
End index :0
Sum :3
Case 2:
Input:
{-1, 3, -5, 4, 6, -1, 2, -7, 13, -3}
Output:
start index :3
End index :8
Sum :17
Case 3:
Input:
{-2,-3,4,-1,-2,1,5,-3}
Output:
start index :2
End index :6
Sum :7
Case 4:
Input:
{-1,3,-5,4,6,-1,2,-7,13,-3}
Output:
start index :3
End index :8
Sum :17
Case 5:
Input:
{-1}
Output:
start index :0
End index :0
Sum :-1
Case 6:
Input:
{-6,-2,-3,-4,-1,-5,-5}
Output:
start index :4
End index :4
Sum :-1
+
+
+Algorithm: How to find maximum subarray sequence?
+
+
+
0 element Array
+
If there is no element present in array then we can say that,
+
in this case, startIndex = -1, endIndex = -1 and
+
maxSum = -1 (or any other suitable notation for no element present)
+
+
+
+
1 element Array
+
If array is having only one element, then that single element is the highest in array
+
as that is the only element present in array,
+
in this case, startIndex = 0, endIndex = 0 and maxSum = arr[0];
+
+
Now, lets look for array having length greater than 1.
+
Before iterating the array, we first check array length and if it is greater then 0,
+
then only proceed else return startIndex = -1, endIndex = -1 and maxSum = -1.
+
+
Lets take one variable for storing sum and initialize it to 0;
+
int tempSum = 0;
+
+
Lets start a loop from 0 to length of array,
+
we will pick the first element of array and check,
+
+
+ tempSum = tempSum + array[i];
+
If tempSum is less then 0,
+
It means there is no point in including or considering this element in maximum
+
sum sub array search as including this element will bring the tempSum to less then 0,
+
So ignore the element and go ahead for searching next element.
+
+
If tempSum is greater then 0,
+
It means there is a chance that including or considering this element can lead to
+
maximum sum sub array, as including this element is not bringing tempSum to less then 0,
+
So consider this element and go ahead for searching next element.
+
+
However, considering this element is not guaranteed to form a maximum sub array
+
as it can decrease the total sum which is not less then 0.
+
+
Eg: if the array is {4, -2}
+
So initially, when considering element at position 0.
+
we will get tempSum = 4 and it is greater then 0, so we are including it,
+
+
Now lets see element at position 1, we will get tempSum = 2 (4 + -2 = -2),
+
In this case tempSum = 2, which is not less then 0, so should we consider this????
+
we should consider this and give a try because chances are there that we may get
+
higher element at next position(Eg array: {4, -2, 4})
+
but in our case we don't have element at position 2, so what to do in this case,
+
+
So what we will do is we will take 2 variables,
+
1. maxSumTillNow, which will store max sum till now encountered.
+
2. tempSum, which will store max sum till now encountered and also take risk of
+
adding next element which may or may not increase the maxSumTillNow.
+
+
Lets try to map this variables in our example,
+
In 1st iteration, for arr[0]
+
maxSumTillNow=4
+
tempSum=4
+
+
In 2nd iteration, for arr[1]
+
maxSumTillNow=4
+
tempSum=2
+
+
So our maxSumTillNow will reflect the maximum sub array sum.
+
+
+
+
+
Lets see example {4, -2, 6},
+
+
In 1st iteration, for arr[0]
+
maxSumTillNow=4
+
tempSum=4
+
+
In 2nd iteration, for arr[1]
+
maxSumTillNow=4
+
tempSum=2
+
+
In 3rd iteration, for arr[2]
+
maxSumTillNow=4
+
tempSum=8
+
+
In this case, our tempSum is greater then maxSumTillNow and maxSumTillNow is stale,
+
so what we will do in this situation is,
+
when tempSum > maxSumTillNow, then we will re initialize maxSumTillNow = tempSum;
+
and maxSumTillNow gets updated.
+
Now when maxSumTillNow gets updated, obviously we have to update
+
startIndex and endIndex as new element get added to maxSumTillNow.
+
+
So by looking at this example, do we need to update start index when we include element 6?
+
Lets see example from start {4, -2, 6},
+
+ In 1st iteration, for arr[0]
+
maxSumTillNow=4
+
tempSum=4
+
startIndex = 0
+
endIndex = 0
+
+ In 2nd iteration, for arr[1]
+
maxSumTillNow=4
+
tempSum=2
+
startIndex = 0
+
endIndex = 0
+
+ In 3rd iteration, for arr[2]
+
maxSumTillNow=8
+
(in this case tempSum > maxSumTillNow, so maxSumTillNow is updated to
+
value of tempSum)
+
tempSum=8
+
startIndex = 0
+
endIndex = 2
+
+
We can see from above example, when our tempSum > maxSumTillNow,
+
we are including a new element in our chain, so our chain start element will remain same,
+
that is we don't need to update start index at this point but we need to update endIndex to
+
index position of new element added.
+
+
So when we will update startIndex then????
+
+
+
+
Let see one more example {4, -2, 6, -10, 8, 1},
+
+
In 1st iteration, for arr[0]
+
maxSumTillNow=4
+
tempSum=4
+
startIndex = 0
+
endIndex = 0
+
+
In 2nd iteration, for arr[1]
+
maxSumTillNow=4
+
tempSum=2
+
startIndex = 0
+
endIndex = 0
+
+
In 3rd iteration, for arr[2]
+
maxSumTillNow=8
+
tempSum=8
+
startIndex = 0
+
endIndex = 2
+
+
In 4th iteration, for arr[3]
+
maxSumTillNow=8
+
tempSum=-2
+
startIndex = ?
+
endIndex = ?
+
+
Now, when we encounter that our result was going good and next element when checked
is making tempSum to -2 that is tempSum < 0,
+
So in this case it is sure including this element(-10) in chain before this element(4, -2, 6)
will make the result negative, so not include this element in consideration and simply ignore
this element and keep our variables as it is without modification.
+
+
So our variables will be,
+
+
maxSumTillNow=8
+
tempSum=-2
+
startIndex = 0
+
endIndex = 2
+
+
we can see from this, that there forms 2 chain,
+
one chain is before -10 that is (4, -2, 6) and
+
one chain is after -10 that is (8, 1)
+
+
and -10 when included with before chain or after chain will surely decrease the result.
+
Now question is which chain contains maximum sub array sum, before -10 or after -10?
+
+
Till now we have seen before chain and we got maxSumTillNow=8 and variables as,
+
maxSumTillNow=8
+
startIndex = 0
+
endIndex = 2
+
+
Now, we will start exploring after chain, so before exploring after chain,
+
we have to reset variable tempSum to 0 as we are starting the things again.
+
+
So when tempSum<0, we will reset tempSum to 0.
+
Also, keeping existing startIndex = 0 and endIndex = 2 intact, we need to explore next chain.
+
+
So we have to take one more variable as tempStartIndex.
+
tempStartIndex holds new start index of new chain that we are going to explore.
+
+
When we found that new chain sum is greater then chain we already explored,
at that time we will update startIndex to tempStartIndex.
+
+
Also, when we observe tempSum<0, at that time we will initialize
tempStartIndex = i(currentIndex) + 1,
+
because next max chain we can get, can be formed excluding current element and start from
+
next index.
+
+
In 5th iteration, for arr[4]
maxSumTillNow=8
tempSum=8(from -2, reseted to 0 and now included element 8)
startIndex = 0
endIndex = 2
tempStartIndex = 4
In 6th iteration, for arr[5]
maxSumTillNow=8
tempSum=9
we can see in this step,
tempSum>maxSumTillNow, so we have to update maxSumTillNow as we got new chain
+
starting from tempStartIndex and ending at i(curent index)
+
So we will update variable startIndex to tempStartIndex value as that is the starting
place where we started exploring new chain.
also, we will update variable endIndex to i(current index of loop).
also, we will update variable maxSumTillNow to tempSum.
So the new variables are,
maxSumTillNow=9
tempSum=9
startIndex = 4
endIndex = 5
tempStartIndex = 4
+
+
+Program to find the largest sum contiguous subarray in Java
+In this program, instead of using 3 variables that we are interested in
+maxSumTillNow, startIndex. and endIndex, we are using result array whose,
+result[0] will represent startIndex,
+result[1] will represent endIndex,
+result[2] will represent maxSumTillNow
+
+
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 | package algo.kadane;
public class MaximumSubArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {-1,3,-5,4,6,-1,2,-7,13,-3};
int[] result = findMaxSumIndex(arr);
System.out.println("start index :"+result[0]);
System.out.println("End index :"+result[1]);
System.out.println("Sum :"+result[2]);
}
private static int[] findMaxSumIndex(int[] arr){
int[] result = new int[3];
int maxSumTillNow = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int tempStartIndex = 0;
int tempSum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
tempSum = tempSum + arr[i];
if(tempSum > maxSumTillNow){
maxSumTillNow = tempSum;
result[0] = tempStartIndex;
result[1] = i;
result[2] = maxSumTillNow;
}
if(tempSum<0){
tempSum = 0;
tempStartIndex = i + 1;
}
}
return result;
}
}
|
+
+Time Complexity:
+
+
The runtime complexity of Kadane's algorithm is O(n) as we are iterating the array containing n elements only once.
+
+
+
+Enjoy !!!!
+
+
+
+If you find any issue in post or face any error while implementing, Please comment.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
Related Posts :
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ * The arrival and departure time of several trains are provided.
+ * Two disparate arrays are given: one with all the arrival times and another with the departure time in 24 hours clock.
+ * Write a program to find the minimum number of platforms needed in a given railway station.
+ *
+ * Solution:
+ *
+ * Clue: The minimum number of platforms is nothing but the maximum number of trains that rest in the given railway station
+ * from the time limit between the arrival of the first train to the departure of the last train.
+ * Input: arr[] = {9:00, 9:40, 9:50, 11:00, 15:00, 18:00}
+ * dep[] = {9:10, 12:00, 11:20, 11:30, 19:00, 20:00}
+ * Output: 3
+ * There are at-most three trains at a time (time between 9:40 to 11:00)
+ *
+ * Sort the timing values given in both the arrays and later check the count of trains at every given time of arrival and departure.
+ * The maximum number of trains in the process is taken as the output.
+ *
+ * arr[] = {9:00, 9:40, 9:50, 11:00, 15:00, 18:00}
+ * dep[] = {9:10, 12:00, 11:20, 11:30, 19:00, 20:00}
+ *
+ * Time complexity is O(n + nlog n). n = traverse the array of n elements + nlogn (for sorting the array)
+ * Space Complexity: O(1).
+ * As no extra space is required.
+ *
+ * dynamic programming is used to conserve memory.
+ */
+public class MinimumPlatforms_Greedy {
+
+ // Returns minimum number of platforms required
+ static int findPlatform(int arr[], int dep[], int n) {
+
+ //Edge case for input.
+ if (arr.length==0){
+ return 0;
+ }
+ if(dep.length==0){
+ return arr.length;
+ }
+
+ /**important*/
+ // Sort arrival and departure arrays
+ Arrays.sort(arr);
+ Arrays.sort(dep);
+
+ // max_platforms_so_far indicates number of platforms needed at a time
+ int max_platforms_so_far = 1, needed_platforms = 1;
+ int i = 1, j = 0;
+
+ // Similar to merge in merge sort to process all events in sorted order
+ while (i < n && j < n) { /** end the loop when any one iterator completes any one array.*/
+ // If next event in sorted order is arrival,
+ // increment count of platforms needed
+ if (arr[i] <= dep[j]) { /**means one more train came before any train could depart so increment the max_platfroms */
+ max_platforms_so_far++;
+ i++;
+
+ // Update result if needed
+ if (max_platforms_so_far > needed_platforms)
+ needed_platforms = max_platforms_so_far;
+ }
+
+ // Else decrement count of platforms needed
+ else {
+ max_platforms_so_far--;
+ j++;
+ }
+ }
+
+ return needed_platforms;
+ }
+
+ // Driver program to test methods of graph class
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ int arr[] = {900, 940, 950, 1100, 1500, 1800};
+ int dep[] = {910, 1200, 1120, 1130, 1900, 2000};
+ int n = arr.length;
+ System.out.println("Minimum Number of Platforms Required = "
+ + findPlatform(arr, dep, n));
+ }
+}
+
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/arrays/SearchInRotatedSortedArray_BitonicArray.adoc b/src/main/java/com/arrays/SearchInRotatedSortedArray_BitonicArray.adoc
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..f91316d1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/com/arrays/SearchInRotatedSortedArray_BitonicArray.adoc
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+image::../../../images/SearchInRotatedSortedArray.png[]
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/arrays/SearchInRotatedSortedArray_BitonicArray.java b/src/main/java/com/arrays/SearchInRotatedSortedArray_BitonicArray.java
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..f107e2ae
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/com/arrays/SearchInRotatedSortedArray_BitonicArray.java
@@ -0,0 +1,49 @@
+package com.arrays;
+
+/**
+ * An array is called Bitonic if it is comprises of an increasing sequence of integers followed immediately
+ * by a decreasing sequence of integers.
+ * Given a bitonic array A of N distinct integers. Find a element X in it.
+ *
+ * You may assume no duplicate exists in the array.
+ */
+public class SearchInRotatedSortedArray_BitonicArray {
+
+ public static int search(int[] nums, int target) {
+ int left = 0;
+ int right = nums.length - 1;
+
+ while (left <= right) {
+
+ int mid = (left + right) / 2;
+ if (target == nums[mid])
+ return mid;
+
+ /** update left and right
+ left will always move forward and right will always shrink*/
+ if (nums[left] <= nums[mid]) { /** first half = left -> mid */
+ if (nums[left] <= target && target < nums[mid]) { /** target is between left and mid so means left at right position and need
+ to update right as right will always shrink/move backward it will be mid-1 */
+ right = mid - 1;
+ } else {
+ left = mid + 1;
+ }
+ } else { /** second half = mid -> right */
+ if (nums[mid] < target && target <= nums[right]) { /** target is between mid and right so means right is at correct position and need
+ to update left as left will always move forward it will be mid+1 */
+ left = mid + 1;
+ } else {
+ right = mid - 1;
+ }
+ }
+
+ }
+
+ return -1;
+ }
+
+ public static void main(String args[]) {
+ int[] arr = {4, 5, 6, 7, 0, 1, 2};
+ System.out.println("Element found at index : " + search(arr, 7));
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/arrays/SortArrayOf0s1s2s_DutchNationalFlagAlgo.html b/src/main/java/com/arrays/SortArrayOf0s1s2s_DutchNationalFlagAlgo.html
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..3dc6ebd2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/com/arrays/SortArrayOf0s1s2s_DutchNationalFlagAlgo.html
@@ -0,0 +1,552 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+dutch flag problem Archives | Algorithms and Me
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
Skip to content
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
Dutch National Flag Problem
+
Given an array with 0s,1s and 2s, sort array in increasing order. Another way to phrase this problem is sort balls with three different colors : red, blue and white, where balls of each color are placed together. This is typically know as Dutch national flag problem and algorithm to solve it is called Dutch national flag problem. Example:
+ A = [0,1,0,1,1,2,0,2,0,1]
+Output = [0,0,0,0,1,1,1,1,2,2]
+
+ A = [R,B,B,W,B,R,W,B,B]
+Output = [R,R,W,W,B,B,B,B]
+
+This problem can be asked as design question, as let’s say you have to design a robot. All this robot does is : it see three empty buckets and a bucket full of colored balls (red, blue and white). Design an instruction set for this robot that it fill each empty buckets with one color. It’s the same problem as Dutch National Flag problem.
+
Count to sort an array of 0s,1s and 2s
+We have already seen a similar problem before as Segregate 0s and 1s in an array. We explored how to count elements and re-write them again on to the array.
+
Let’s apply the same method for this problem. Take an array of three integers, index store corresponding count for that number. E.g count[0] stores count of 0 and count[1] stores count of 1. Scan through the array and count each element. At last, re-write those numbers back on to array starting from index 0, according to their count. For example, if there are 4 zeros, then starting from 0 indexes, write 4 zeros, followed by 1s and then by 2.
+
Complexity of counting method is O(n), notice that we scan array twice, first time for counts and second time for writing on array.
+
Dutch national flag problem : algorithm
+
+- Start with three pointers :
reader, low and high.
+reader and low are initialized as 0 and high is initialized as last element of array as size-1.- reader will be used to scan the array while low and high will be used to swap elements to their desired positions.
+- Starting with current position of reader, follow below steps, keep in mind we need 0 at start of array
+
+- If element at index
reader is 0, swap element at reader with element at low and increment low and reader by 1.
+- If element at
reader is 1, do not swap and increment reader by 1.
+- If element at
reader is 2, swap element at reader with element at high and decrease high by 1
+
+
+
+
Actually, three pointers divide array into four parts. Red, white, unknown and Blue. Every element is taken from unknown part and put into its right place. So all three other parts expand while unknown part shrinks.
+
Let’s take an example and see how dutch national flag algorithm works.
+
First step, initialize reader, low and high.
+

+
Element at reader is 0, hence swap element at reader and low,also increment reader and low.
+

+
Follow the same step, check element at reader again, it’s 1, hence, just move reader by one.
+

+
Element at reader is now 2, swap element at reader with element at high and decrease high by 1.
+

+
Element at reader is 1, just increment reader.
+

+
Element at reader is now 2, swap element at reader with element at high and decrease high by 1.
+

+
Element at reader is 1, just increment reader.
+

+
Element at reader is 1, just increment reader.
+

+
Element at reader 0, hence swap element at reader and low,also increment reader and low.
+

+
Element at reader 0, hence swap element at reader and low,also increment reader and low.
+

+
Element at reader is now 2, swap element at reader with element at high and decrease high by 1.
+

+
Here, high becomes less than reader, we can stop as array is already sorted.
+
Dutch national flag problem implementation
+
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 | package com.company;
/**
* Created by sangar on 5.1.18.
*/
public class DutchNationalFlag {
public static void swap(int[] input, int i, int j){
int temp = input[i];
input[i] = input[j];
input[j] = temp;
}
public static void dutchNationalFalgAlgorithm(int [] input){
int reader = 0;
int low = 0;
int high = input.length - 1;
while(reader <= high){
if(input[reader] == 0){
swap(input, reader, low);
reader++;
low++;
}
else if(input[reader] == 1){
reader++;
}
else if(input[reader] == 2){
swap(input, reader, high);
high--;
}
else{
System.out.println("Bad input");
break;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] input = {2,2,1,1,0,0,0,1,1,2};
dutchNationalFalgAlgorithm(input);
for(int i=0; i<input.length; i++){
System.out.print(" " + input[i]);
}
}
}
|
+
Complexity of Dutch National Flag algorithm is O(n), however, we scan the array only once.
+
Please share if you have some suggestions or comments. Sharing is caring.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
This website uses cookies to improve your experience. We'll assume you're ok with this, but you can opt-out if you wish. Cookie settingsACCEPT Privacy & Cookies Policy
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/arrays/SortArrayOf0s1s2s_DutchNationalFlagAlgo.java b/src/main/java/com/arrays/SortArrayOf0s1s2s_DutchNationalFlagAlgo.java
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..2bbfee7a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/com/arrays/SortArrayOf0s1s2s_DutchNationalFlagAlgo.java
@@ -0,0 +1,101 @@
+package com.arrays;
+
+/**
+Dutch National Flag Algorithm, or 3-way Partitioning
+
+Sort an array of 0s, 1s and 2s
+Given an array A[] consisting 0s, 1s and 2s.
+The task is to write a function that sorts the given array.
+The functions should put all 0s first, then all 1s and all 2s in last.
+https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/sort-an-array-of-0s-1s-and-2s/
+
+Examples:
+
+Input: {0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2}
+Output: {0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 2}
+
+Input: {0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 2, 1, 2, 0, 0, 0, 1}
+Output: {0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2}
+
+Simplest Solution
+Count the number of 0’s, 1’s and 2’s. After Counting, put all 0’s first, then 1’s and lastly 2’s in the array.
+We traverse the array two times. Time complexity will be O(n).
+
+ Dutch national flag problem : algorithm
+ Start with three pointers : reader, low and high.
+ reader and low are initialized as 0 and high is initialized as last element of array as size-1.
+ reader will be used to scan the array while low and high will be used to swap elements to their desired positions.
+ Starting with current position of reader, follow below steps, keep in mind we need 0 at start of array
+ If element at index reader is 0, swap element at reader with element at low and increment low and reader by 1.
+ If element at reader is 1, do not swap and increment reader by 1.
+ If element at reader is 2, swap element at reader with element at high and decrease high by 1
+
+ Actually, three pointers divide array into four parts. Red, white, unknown and Blue.
+ Every element is taken from unknown part and put into its right place.
+ So all three other parts expand while unknown part shrinks.
+
+Best Solution
+https://algorithmsandme.com/dutch-national-flag-problem/
+*/
+
+
+public class SortArrayOf0s1s2s_DutchNationalFlagAlgo {
+
+ public static void swap(int[] input, int i, int j){
+ int temp = input[i];
+ input[i] = input[j];
+ input[j] = temp;
+ }
+
+ public static void dutchNationalFalgAlgorithm(int [] input){
+
+ //initialize all variables
+ int reader = 0;
+ int low = 0;
+ int high = input.length - 1;
+
+ while(reader <= high){
+ /*
+ input always holds a permutation of the
+ original data with input(0..(lo-1)) =0,
+ input(lo..(reader-1))=1, input(reader..hi) is
+ untouched, and input((hi+1)..(input.length-1)) = 2
+ */
+ if(input[reader] == 0){
+ /*When element at reader is 0, swap
+ element at reader with element at index
+ low and increment reader and low*/
+ swap(input, reader, low);
+ reader++;
+ low++;
+ }
+ else if(input[reader] == 1){
+ /* if element at reader is just
+ increment reader by 1 */
+ reader++;
+ }
+ else if(input[reader] == 2){
+ /* If element at reader is 2, swap
+ element at reader with element at
+ high and decrease high by 1 */
+ swap(input, reader, high);
+ high--;
+ }
+ else{
+ System.out.println("Bad input");
+ break;
+ }
+ }
+
+ }
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ int[] input = {2,2,1,1,0,0,0,1,1,2};
+
+ dutchNationalFalgAlgorithm(input);
+
+ for(int i=0; i prices[i - 1])
+ maxprofit += prices[i] - prices[i - 1];
+ }
+ return maxprofit;
+ }
+
+ public static void main (String args[]){
+ int[] price = {100,60,120,110,90,200};
+ int maxProfit= maxProfit(price);
+ System.out.println(maxProfit);
+
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/arrays/TripletSumInArray_Sorting_TwoPointerAlgo.java b/src/main/java/com/arrays/TripletSumInArray_Sorting_TwoPointerAlgo.java
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..2316ea20
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/com/arrays/TripletSumInArray_Sorting_TwoPointerAlgo.java
@@ -0,0 +1,66 @@
+package com.arrays;
+
+import java.util.Arrays;
+
+/**
+ * This method uses the method of Sorting and Two-pointer Technique to solve the above problem.
+ * This execution will involve O(n2)) time complexity and O(1) space complexity.
+ */
+
+
+/**
+ * 1. Sort all element of array
+ * 2. Run loop from i=0 to n-2.
+ * Initialize two index variables l=i+1 and r=n-1
+ * 4. while (l < r)
+ * Check sum of arr[i], arr[l], arr[r] is
+ * given sum or not if sum is 'sum', then print
+ * the triplet and do l++ and r--.
+ * 5. If sum is less than given sum then l++
+ * 6. If sum is greater than given sum then r--
+ * 7. If not exist in array then print not found.
+ */
+
+/**
+ * Complexity Analysis:
+ * Time Complexity: O(n2).
+ * Use of a nested loop (one for iterating , other for two-pointer technique) brings the time complexity to O(n2).
+ * Auxiliary Space: O(1).
+ * As no use of additional data structure is used.
+ */
+
+public class TripletSumInArray_Sorting_TwoPointerAlgo {
+
+ public static void find_all_triplets(int[] arr, int sum) {
+
+ /**sort array elements*/
+ Arrays.sort(arr); /**important*/
+
+ int n = arr.length;
+ int left;
+ int right;
+ for (int i = 0; i < n - 2; i++) {
+ left = i + 1; //cursor starting from front
+ right = n - 1; // cursor starting from end
+ while (left < right) {
+ int tempSum = arr[i] + arr[left] + arr[right];
+ if (tempSum == sum) {
+ System.out.println("triplet:{" + arr[i] + "," + arr[left] + "," + arr[right] + "}");
+ left++;
+ right--;
+ } else if (tempSum < sum) {
+ left++;
+ } else {
+ right--;
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+
+ public static void main(String args[]) {
+ int arr[] = {1, 7, 4, 3, 4, 5, 2};
+ int sum = 9;
+ find_all_triplets(arr, sum);
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/arrays/WildCardMatching.adoc b/src/main/java/com/arrays/WildCardMatching.adoc
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..fe1b513e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/com/arrays/WildCardMatching.adoc
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+image::../../../images/WildCardMatching.png[]
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/arrays/WildCardMatching.html b/src/main/java/com/arrays/WildCardMatching.html
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..2f834ef3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/com/arrays/WildCardMatching.html
@@ -0,0 +1,109 @@
+ Wildcard Matching in C++ - ProDeveloperTutorial.com Given an input string (s) and a pattern (p), implement wildcard pattern matching with support for ‘?’ and ‘*’.
'?' Matches any single character.
+
+'*' Matches any sequence of characters (including the empty sequence).
The matching should cover the entire input string .
Example 1:
+
+Input:
+s = "aa"
+p = "a"
+Output: false
+Explanation: "a" does not match the entire string "aa".
+
Example 2:
+
+Input:
+s = "aa"
+p = "*"
+Output: true
+Explanation: '*' matches any sequence.
+
Example 3:
+
+Input:
+s = "cb"
+p = "?a"
+Output: false
+Explanation: '?' matches 'c', but the second letter is 'a', which does not match 'b'.
+
Example 4:
+
+Input:
+s = "adceb"
+p = "*a*b"
+Output: true
+Explanation: The first '*' matches the empty sequence, while the second '*' matches the substring "dce".
+
Example 5:
+
+Input:
+s = "acdcb"
+p = "a*c?b"
+Output: false
+
Before going through the solution, I recommend you to read a similar problem of “regular expression matching”.
This problem can be solved using Dynamic Programming. We shall be taking a Boolean array and update it according to the below 2 formulas. At the end of the array, we shall get the result.
Formula:
1. boolean_array[i][j] = boolean_array[i-1][j-1] if the value at boolean_array[i][j] is a character or a “?”.
+
+2. boolean_array[i][j] = boolean_array[i][j-1] || boolean_array[i-1][j] if the value at at boolean_array[i][j] is “*”.
To understand the problem better we shall take an example and solve step by step.
In our example,
String = “xaylmz”
+
+Pattern = “x?y*z”
The initial Boolean array will be as shown below:

boolean_array [0][0] = True. Because consider an empty string and an empty pattern, they both will match. Hence true.
boolean_array [0][1] = False. Because the pattern is “x” and the string is “null”. They will not match. Hence false.
With the same analysis, the whole column will become false as shown below.

Now, boolean_array [1][0] = False. Because the pattern is “null” and the string is “x”. They will not match. Hence the whole row will be false.

Now, boolean_array [1][1] = True. Because the pattern is “x” and string is also “x”. This matches our first condition. Value of boolean_array [1][1] = boolean_array [0][0], which is true.
Now, boolean_array [1][2] = False. Because the pattern is “x?” and the string is “x”. This matches our first condition. Value of boolean_array [1][2] = boolean_array [0][1], which is False.
Now, boolean_array [1][3] = False. Because the pattern is “y” and string is “x”. Hence is false.
Now, boolean_array [1][4] = False. Since the pattern is “*”, we look at the value at left and top, [represented in purple], since both are false, the result is false.
Now, boolean_array [1][5] = False. Since the pattern is “z” and string is “x”, false.

Once we solve all the index, finally we get the value “true” as shown in green color in below image.

Solution in C++
+#include<iostream>
+#include<vector>
+
+using namespace std;
+
+bool isMatch(string str, string pattern)
+{
+ bool bool_array [str.size()+1] [pattern.size()+1];
+
+ //initialize boolean array to false.
+ for (int i = 0; i <= str.size(); ++i)
+ {
+ for (int j = 0; j <= pattern.size(); ++j)
+ {
+ bool_array[i][j] = 0;
+ }
+ }
+
+ // base case
+ bool_array[0][0] = true;
+
+
+ for (int i = 1; i <= str.size(); i++)
+ {
+ for (int j = 1; j <= pattern.size(); j++)
+ {
+ if (str[i-1] == pattern[j-1] || pattern[j-1] == '?')
+ bool_array[i][j] = bool_array[i-1][j-1];
+
+ else if (pattern[j-1] == '*')
+ bool_array[i][j] = bool_array[i][j-1] || bool_array[i-1][j];
+ }
+ }
+
+ return bool_array[str.size()][pattern.size()];
+}
+
+int main()
+{
+ string str = "xaylmz";
+ string pattern = "x?y*z";
+
+ bool result = isMatch(str, pattern);
+
+ if(result)
+ cout<<" The pattern and string matches"<<endl;
+ else
+ cout<<" The pattern and string does not match"<<endl;
+
+ return 0;
+}Output:
The pattern and string matches
About The Author

Daily we discuss about competitive programming questions, join us at: Telegram Channel Facebook PageFacebook Group
+ * Input:
+ * s = "cb"
+ * p = "?a"
+ * Output: false
+ * Explanation: '?' matches 'c', but the second letter is 'a', which does not match 'b'.
+ *
+ * Time complexity of above solution is O(m x n). Auxiliary space used is also O(m x n).
+ * where m = length of pattern
+ * n = length of String
+ */
+
+public class WildCardMatching {
+
+ public boolean isMatch(String s, String p) {
+ char[] str = s.toCharArray();
+ char[] pattern = p.toCharArray();
+
+ //replace multiple * with one *
+ //e.g a**b***c --> a*b*c
+ int writeIndex = 0;
+ boolean isFirst = true;
+ for (int i = 0; i < pattern.length; i++) {
+ if (pattern[i] == '*') {
+ if (isFirst) {
+ pattern[writeIndex++] = pattern[i];
+ isFirst = false;
+ }
+ } else {
+ pattern[writeIndex++] = pattern[i];
+ isFirst = true;
+ }
+ }
+
+ boolean T[][] = new boolean[str.length + 1][pattern.length + 1];
+
+ if (writeIndex > 0 && pattern[0] == '*') {
+ T[0][1] = true;
+ }
+
+ // base case
+ T[0][0] = true;
+
+ /**
+ * Rules
+ * 1) if the value at boolean_array[i][j] is a matching character or a “?”.
+ * boolean_array[i][j] = boolean_array[i-1][j-1] (means diagonal)
+ *
+ * 2) if the value at at boolean_array[i][j] is “*”.
+ * boolean_array[i][j] = boolean_array[i][j-1] || boolean_array[i-1][j] (means one one left or one on top whichever is true)
+ */
+
+ for (int i = 1; i <= str.length; i++) {
+ for (int j = 1; j <= pattern.length; j++)
+ if (pattern[j - 1] == '?' || str[i - 1] == pattern[j - 1]) {
+ T[i][j] = T[i - 1][j - 1]; //diagonal
+ } else if (pattern[j - 1] == '*') {
+ T[i][j] = T[i - 1][j] || T[i][j - 1];
+ }
+ }
+
+ return T[str.length][pattern.length];
+ }
+
+
+ public static void main(String args[]) {
+ WildCardMatching wcm = new WildCardMatching();
+ System.out.println(wcm.isMatch("xbylmz", "x?y*z"));
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/ctci/arraysandstrings/CheckPermutation.java b/src/main/java/com/ctci/arraysandstrings/CheckPermutation.java
deleted file mode 100644
index dbf7c795..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/ctci/arraysandstrings/CheckPermutation.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,67 +0,0 @@
-package com.ctci.arraysandstrings;
-
-import java.util.Arrays;
-
-/**
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 19/11/2018
- */
-public class CheckPermutation {
-
- /**
- * Checks if {@code s1} is a permutation of {@code s2}.
- *
- * @param s1
- * @param s2
- * @return
- */
- private static boolean isOnePermutationOfOther(String s1, String s2) {
- if (s1.length() != s2.length()) {
- return false;
- }
-
- char[] c1 = s1.toCharArray();
- char[] c2 = s2.toCharArray();
- Arrays.sort(c1);
- Arrays.sort(c2);
-
- return Arrays.equals(c1, c2);
- }
-
- /**
- * Checks if {@code s1} is a permutation of {@code s2}.
- *
- * @param s1
- * @param s2
- * @return
- */
- private static boolean isOnePermutationOfOtherGivenThatStringsContainOnlyAscii(String s1, String s2) {
- if (s1.length() != s2.length()) {
- return false;
- }
-
- int[] chars = new int[128]; // assuming strings contain only ASCII characters
-
- for (int i = 0; i < s1.length(); i++) {
- chars[s1.charAt(i)]++;
- }
-
- for (int i = 0; i < s2.length(); i++) {
- chars[s2.charAt(i)]--;
- if (chars[s2.charAt(i)] < 0) {
- return false;
- }
- }
- return true;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(isOnePermutationOfOther("ram", "mar"));
- System.out.println(isOnePermutationOfOther("rama", "mar"));
- System.out.println(isOnePermutationOfOther("rama", "marA"));
- System.out.println("-------");
- System.out.println(isOnePermutationOfOtherGivenThatStringsContainOnlyAscii("ram", "mar"));
- System.out.println(isOnePermutationOfOtherGivenThatStringsContainOnlyAscii("rama", "mar"));
- System.out.println(isOnePermutationOfOtherGivenThatStringsContainOnlyAscii("rama", "marA"));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/ctci/arraysandstrings/IsUnique.java b/src/main/java/com/ctci/arraysandstrings/IsUnique.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 895d16b3..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/ctci/arraysandstrings/IsUnique.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,51 +0,0 @@
-package com.ctci.arraysandstrings;
-
-/**
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 18/11/2018
- */
-public class IsUnique {
-
- private static boolean hasAllUniqueCharacters(String str) {
- if (str == null || str.length() > 128) return false;
-
- boolean[] charSet = new boolean[128]; // assuming the string contains only ASCII characters
- for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
- int charVal = str.charAt(i);
- if (charSet[charVal]) {
- return false;
- }
- charSet[charVal] = true;
- }
- return true;
- }
-
- private static boolean hasAllUniqueCharactersWhenStringContainsAllLowercase(String s) {
- int checker = 0;
- for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
- int charValue = s.charAt(i) - 'a';
- if ((checker & (1 << charValue)) > 0) {
- return false;
- }
- checker |= (1 << charValue);
- }
- return true;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- String s = "ram";
- System.out.println(hasAllUniqueCharacters(s));
- s = "rama";
- System.out.println(hasAllUniqueCharacters(s));
- s = "ramA";
- System.out.println(hasAllUniqueCharacters(s));
- System.out.println("-------");
- s = "ram";
- System.out.println(hasAllUniqueCharactersWhenStringContainsAllLowercase(s));
- s = "rama";
- System.out.println(hasAllUniqueCharactersWhenStringContainsAllLowercase(s));
- // not working as the input contains different cases
- s = "ramA";
- System.out.println(hasAllUniqueCharactersWhenStringContainsAllLowercase(s));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/ctci/arraysandstrings/OneAway.java b/src/main/java/com/ctci/arraysandstrings/OneAway.java
deleted file mode 100644
index f5345ed7..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/ctci/arraysandstrings/OneAway.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,70 +0,0 @@
-package com.ctci.arraysandstrings;
-
-/**
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 24/11/2018
- */
-public class OneAway {
-
- /**
- * Checks if two strings are only one edit away, that is, by inserting, deleting, or editing
- * at max one character in {@code s1} it becomes same as {@code s2}.
- *
- * @param s1
- * @param s2
- * @return
- */
- private static boolean isOneEditAway(String s1, String s2) {
- if (s1.length() == s2.length()) {
- return isOneCharacterDiffAtMax(s1, s2);
- } else if (s1.length() < s2.length()) {
- return checkForMaxOneInsertOrDeleteInS1(s1, s2);
- } else {
- return checkForMaxOneInsertOrDeleteInS1(s1, s2);
- }
- }
-
- private static boolean isOneCharacterDiffAtMax(String s1, String s2) {
- boolean foundDiff = false;
- for (int i = 0; i < s1.length(); i++) {
- if (s1.charAt(i) != s2.charAt(i)) {
- if (foundDiff) {
- return false; // means we already found a difference earlier
- }
- foundDiff = true;
- }
- }
- return true;
- }
-
- private static boolean checkForMaxOneInsertOrDeleteInS1(String s1, String s2) {
- int i = 0;
- int j = 0;
- int s1Len = s1.length();
- int s2Len = s2.length();
- if (Math.abs(s1Len - s2Len) > 1) return false;
-
- while (i < s1Len && j < s2Len) {
- if (s1.charAt(i) != s2.charAt(j)) {
- if (s1Len > s2Len) {
- i++;
- } else {
- j++;
- }
- continue;
- }
- i++;
- j++;
- }
- return Math.abs(i - j) <= 1; // check whether difference in two strings is not more than 1
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println("pale, ple: " + isOneEditAway("pale", "ple"));
- System.out.println("pales,pale: " + isOneEditAway("pales", "pale"));
- System.out.println("pale, bale: " + isOneEditAway("pale", "bale"));
- System.out.println("pale, bake: " + isOneEditAway("pale", "bake"));
- System.out.println("ram, rama: " + isOneEditAway("ram", "rama"));
- System.out.println("ram, ramaaaaaaa: " + isOneEditAway("ram", "ramaaaaaaa"));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/ctci/arraysandstrings/PalindromePermutation.java b/src/main/java/com/ctci/arraysandstrings/PalindromePermutation.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 0ab21095..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/ctci/arraysandstrings/PalindromePermutation.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,103 +0,0 @@
-package com.ctci.arraysandstrings;
-
-import java.util.HashMap;
-import java.util.Map;
-
-/**
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 21/11/2018
- */
-public class PalindromePermutation {
-
- /**
- * This method exploits the fact that a palindrome will contain at most
- * one character with odd counts. All other characters should be of even
- * counts.
- *
- * @param str input string
- * @return {@code true} if {@code str} is a permutation of a palindrome
- */
- private static boolean isPermutationOfPalindrome(String str) {
- Map charCounts = new HashMap<>();
- Integer freq;
- int oddCounts = 0; // keep count of odds so that we don't have to loop through the hashmap the second time
- for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
- char c = str.charAt(i);
- if (c != 32) {
- freq = charCounts.get(c) == null ? 0 : charCounts.get(c);
- if ((freq + 1) % 2 == 1) {
- oddCounts++;
- } else {
- oddCounts--;
- }
- charCounts.put(c, freq + 1);
- }
- }
- return oddCounts <= 1;
- }
-
-
- /**
- * This approach sets a bit in a number based on the character in the string and
- * then un-sets the bit if it sees the character again. Finally, checks if the
- * bitVector has at most one bit set only.
- *
- * @param str input string
- * @return {@code true} if {@code str} is a permutation of a palindrome
- */
- private static boolean isPermutationOfPalindromeViaBits(String str) {
- int bitVector = 0;
- int index;
-
- for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
- index = getIndex(str.charAt(i));
- if (index != -1) {
- bitVector = toggleBitAt(bitVector, index);
- }
- }
- return (bitVector & (bitVector - 1)) == 0;
- }
-
- /**
- * Calculates the index to set the bit according to the character {@code c}.
- *
- * @param c
- * @return the index to set the bit as per the character {@code c}
- */
- private static int getIndex(char c) {
- char a = 'a';
- char z = 'z';
-
- // assuming string contains only lowercase characters
- if (c < a || c > z) {
- return -1;
- }
-
- return c - a;
- }
-
- /**
- * Toggles the bit at index {@code index} in {@code bitVector}.
- *
- * @param bitVector
- * @param index
- * @return the resulting {@code bitVector} after toggling the bit
- */
- private static int toggleBitAt(int bitVector, int index) {
- return bitVector ^ (1 << index);
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(isPermutationOfPalindrome("tactc oapapa"));
- System.out.println(isPermutationOfPalindrome("maam"));
- System.out.println(isPermutationOfPalindrome("maa m"));
- System.out.println(isPermutationOfPalindrome("rammmar"));
- System.out.println(isPermutationOfPalindrome("rammmara"));
- System.out.println("---------");
- System.out.println(isPermutationOfPalindromeViaBits("tactc oapapa"));
- System.out.println(isPermutationOfPalindromeViaBits("maam"));
- System.out.println(isPermutationOfPalindromeViaBits("maa m"));
- System.out.println(isPermutationOfPalindromeViaBits("rammmar"));
- System.out.println(isPermutationOfPalindromeViaBits("rammmara"));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/ctci/arraysandstrings/RotateMatrix.java b/src/main/java/com/ctci/arraysandstrings/RotateMatrix.java
deleted file mode 100644
index de43c56b..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/ctci/arraysandstrings/RotateMatrix.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,16 +0,0 @@
-package com.ctci.arraysandstrings;
-
-/**
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-01-20
- */
-public class RotateMatrix {
-
- public static void rotateImage(int[][] pixels) {
-
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
-
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/ctci/arraysandstrings/StringCompression.java b/src/main/java/com/ctci/arraysandstrings/StringCompression.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 5c2df955..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/ctci/arraysandstrings/StringCompression.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,39 +0,0 @@
-package com.ctci.arraysandstrings;
-
-/**
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 24/11/2018
- */
-public class StringCompression {
-
- /**
- * Compresses the string {@code s} such that a string {@code aabccccaaa} becomes {@code a2b1c4a3}.
- * Also, if the compressed string is not shorter than the original, returns the original string.
- *
- * @param str input string containing only a-z characters, both cases
- * @return which ever is the shorter string
- */
- private static String compressString(String str) {
- StringBuilder compressedSb = new StringBuilder();
- int countConsecutive = 0;
- for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
- countConsecutive++;
-
- /* If next character is different than current, append this char to result. */
- if (i + 1 >= str.length() || str.charAt(i) != str.charAt(i + 1)) {
- compressedSb.append(str.charAt(i));
- compressedSb.append(countConsecutive);
- countConsecutive = 0;
- }
- }
- return compressedSb.length() < str.length() ? compressedSb.toString() : str;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println("aabccccaaa: " + compressString("aabccccaaa"));
- System.out.println("aabccccAAAA: " + compressString("aabccccAAAA"));
- System.out.println("abcd: " + compressString("abcd"));
- System.out.println("a: " + compressString("a"));
- System.out.println("aabcccccccccccccccccccccccccaaa: " + compressString("aabcccccccccccccccccccccccccaaa"));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/ctci/arraysandstrings/StringRotation.java b/src/main/java/com/ctci/arraysandstrings/StringRotation.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 0c03e94f..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/ctci/arraysandstrings/StringRotation.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,39 +0,0 @@
-package com.ctci.arraysandstrings;
-
-/**
- * Assume you have a method isSubString which checks if one word is a substring of another. Given two
- * strings, S1 and S2, write code to check if S2 is a rotation of S1 using only one call to isSubString
- * (e.g., "waterbottle" is a rotation of" erbottlewat").
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-01-22
- */
-public class StringRotation {
-
- private static boolean isStringRotation(String s1, String s2) {
- if (s1.length() != s2.length()) {
- return false;
- }
- s2 = s2 + s2;
- return isSubString(s1, s2);
- }
-
- /**
- * Given method in question.
- *
- * @param s1 first string
- * @param s2 second string
- * @return {@code true} if s1 is a substring of s2 or else {@code false}
- */
- private static boolean isSubString(String s1, String s2) {
- return s2.contains(s1);
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(isStringRotation("waterbottle", "erbottlewat")); // true
- System.out.println(isStringRotation("rampatra", "atraramp")); // true
- System.out.println(isStringRotation("rampatra", "arampata")); // false
- System.out.println(isStringRotation("rampatra", "arampat")); // false
- System.out.println(isStringRotation("", "")); // true
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/ctci/arraysandstrings/URLify.java b/src/main/java/com/ctci/arraysandstrings/URLify.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 712829ac..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/ctci/arraysandstrings/URLify.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,43 +0,0 @@
-package com.ctci.arraysandstrings;
-
-/**
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 19/11/2018
- */
-public class URLify {
-
- /**
- * We space encode the string such that all spaces in the string are replaced with '%20'. The string {@code str}
- * contains extra spaces to accommodate the extra characters.
- *
- * @param str string with spaces
- * @return string with spaces replaced with %20
- */
- private static String urlify(String str) {
- char[] chars = str.toCharArray();
- int curr = chars.length - 1; // we will start backwards so that we don't have to worry about characters we overwrite
- int insertIndex = curr;
-
- // move the curr pointer to the last character which isn't a space
- while (chars[curr] == 32) {
- curr--;
- }
-
- while (curr >= 0) {
- if (chars[curr] == 32) {
- chars[insertIndex--] = '0';
- chars[insertIndex--] = '2';
- chars[insertIndex--] = '%';
- } else {
- chars[insertIndex--] = chars[curr];
- }
- curr--;
- }
- return String.valueOf(chars);
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(urlify("Mr John Smith "));
- System.out.println(urlify("Mr Ram Patra "));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/ctci/arraysandstrings/ZeroMatrix.java b/src/main/java/com/ctci/arraysandstrings/ZeroMatrix.java
deleted file mode 100644
index f73d8760..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/ctci/arraysandstrings/ZeroMatrix.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,78 +0,0 @@
-package com.ctci.arraysandstrings;
-
-import java.util.ArrayList;
-import java.util.List;
-
-/**
- * Write an algorithm such that if an element in an MxN matrix is 0, its entire row
- * and column are set to 0.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-01-20
- */
-public class ZeroMatrix {
-
- private static void zeroMatrix(int[][] matrix) {
- // keep count of which rows and columns have a number zero
- List rowsToZero = new ArrayList<>();
- List colsToZero = new ArrayList<>();
-
- for (int i = 0; i < matrix.length; i++) {
- for (int j = 0; j < matrix[0].length; j++) {
- if (matrix[i][j] == 0) {
- rowsToZero.add(i);
- colsToZero.add(j);
- }
- }
- }
-
- makeRowColumnZero(matrix, rowsToZero, colsToZero);
- }
-
- private static void makeRowColumnZero(int[][] matrix, List rows, List cols) {
- for (int row : rows) {
- // make entire row zero
- for (int c = 0; c < matrix[0].length; c++) {
- matrix[row][c] = 0;
- }
- }
- for (int col : cols) {
- // make entire column zero
- for (int r = 0; r < matrix.length; r++) {
- matrix[r][col] = 0;
- }
- }
- }
-
- private static void printMatrix(int[][] matrix) {
- for (int i = 0; i < matrix.length; i++) {
- for (int j = 0; j < matrix[0].length; j++) {
- System.out.print(matrix[i][j]);
- if (j + 1 >= matrix[0].length) {
- System.out.println();
- }
- }
- }
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- int[][] m = new int[][]{{0, 1, 2}, {3, 4, 5}, {6, 7, 8}};
- printMatrix(m);
- zeroMatrix(m);
- System.out.println("---");
- printMatrix(m);
- System.out.println("---");
- m = new int[][]{{1, 0, 2}, {3, 4, 5}, {6, 7, 8}};
- printMatrix(m);
- zeroMatrix(m);
- System.out.println("---");
- printMatrix(m);
- System.out.println("---");
- m = new int[][]{{1, 2, 0}, {3, 4, 5}, {6, 7, 8}};
- printMatrix(m);
- zeroMatrix(m);
- System.out.println("---");
- printMatrix(m);
- System.out.println("---");
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/ctci/bitmanipulation/BinaryToString.java b/src/main/java/com/ctci/bitmanipulation/BinaryToString.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 895c354a..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/ctci/bitmanipulation/BinaryToString.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,48 +0,0 @@
-package com.ctci.bitmanipulation;
-
-/**
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-03-16
- */
-public class BinaryToString {
-
- /**
- * Given a real number between 0 and 1 (e.g., 0.72) that is passed in as a double, print the binary representation.
- * If the number cannot be represented accurately in binary with at most 32 characters, print "ERROR."
- *
- * @param realNum a real number between 0 and 1 (for ex. 0.75)
- * @return binary string of the real number
- * @see how to convert decimal fraction to binary
- */
- private static String decimalFractionToBinaryString(double realNum) {
- if (realNum <= 0 || realNum >= 1) {
- return "ERROR";
- }
-
- int binaryBit;
- StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
- sb.append("0.");
-
- while (realNum > 0) {
- if (sb.length() == 32) {
- return "ERROR";
- }
- realNum = realNum * 2;
- // the binary bit is the whole number part (left to the decimal)
- binaryBit = (int) realNum;
- // we only have to take the part after the decimal (right to the decimal) for the next iteration
- if (binaryBit == 1) {
- realNum -= 1;
- }
- sb.append(binaryBit);
- }
- return sb.toString();
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(decimalFractionToBinaryString(0.625));
- System.out.println(decimalFractionToBinaryString(0.75));
- System.out.println(decimalFractionToBinaryString(0.72));
- System.out.println(decimalFractionToBinaryString(0.10));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/ctci/bitmanipulation/Conversion.java b/src/main/java/com/ctci/bitmanipulation/Conversion.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 5a4c7575..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/ctci/bitmanipulation/Conversion.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,63 +0,0 @@
-package com.ctci.bitmanipulation;
-
-/**
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-03-17
- */
-public class Conversion {
-
- /**
- * Write a function to determine the number of bits you would need to flip to convert
- * integer A to integer B.
- * Example:
- * Input: 29 (or: 11101), 15 (or: 01111)
- * Output: 2
- *
- * @param a
- * @param b
- * @return the number of bits to flip
- */
- private static int getNoOfBitsToFlipToConvertAToB(int a, int b) {
- return countSetBits(a ^ b);
- }
-
- private static int countSetBits(int n) {
- int count = 0;
- while (n > 0) {
- if ((n & 1) == 1) {
- count++;
- }
- n >>>= 1;
- }
- return count;
- }
-
- /**
- * In this approach, we first take the xor of both the integers (which sets the bits at positions where the bits
- * in a and b are different). We then unset the least significant bit in each iteration (c & (c - 1)) and count the
- * number of iterations to find the bits to flip.
- *
- * @param a
- * @param b
- * @return the number of bits to flip
- */
- private static int getNoOfBitsToFlipToConvertAToBWithoutRightShift(int a, int b) {
- int count = 0;
- for (int c = a ^ b; c != 0; c = c & (c - 1)) {
- count++;
- }
- return count;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(getNoOfBitsToFlipToConvertAToB(5, 7));
- System.out.println(getNoOfBitsToFlipToConvertAToB(5, 5));
- System.out.println(getNoOfBitsToFlipToConvertAToB(29, 15));
-
- System.out.println("---");
-
- System.out.println(getNoOfBitsToFlipToConvertAToBWithoutRightShift(5, 7));
- System.out.println(getNoOfBitsToFlipToConvertAToBWithoutRightShift(5, 5));
- System.out.println(getNoOfBitsToFlipToConvertAToBWithoutRightShift(29, 15));
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/ctci/bitmanipulation/Debugger.java b/src/main/java/com/ctci/bitmanipulation/Debugger.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 6782036b..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/ctci/bitmanipulation/Debugger.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,30 +0,0 @@
-package com.ctci.bitmanipulation;
-
-/**
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-03-17
- */
-public class Debugger {
-
- /**
- * If after un-setting the least significant bit in n, it becomes 0 then it implies that it has only set bit. This
- * can also imply that n is a power of 2.
- *
- * @param n input integer
- * @return {@code true} if n has only set bit, {@code false} otherwise.
- */
- private static boolean hasOneSetBit(int n) {
- // edge case
- if (n == 0) {
- return false;
- }
- return (n & (n - 1)) == 0; // (n & (n - 1)) un-sets the least significant bit
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(hasOneSetBit(0));
- System.out.println(hasOneSetBit(2));
- System.out.println(hasOneSetBit(16));
- System.out.println(hasOneSetBit(10));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/ctci/bitmanipulation/DrawLine.java b/src/main/java/com/ctci/bitmanipulation/DrawLine.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 3eb2be0c..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/ctci/bitmanipulation/DrawLine.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,109 +0,0 @@
-package com.ctci.bitmanipulation;
-
-import java.util.Arrays;
-
-/**
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-03-21
- */
-public class DrawLine {
-
- /**
- * A monochrome screen is stored as a single array of bytes, allowing eight consecutive pixels to be stored
- * in one byte. The screen has width w, where w is divisible by 8 (that is, no byte will be split across rows).
- * The height of the screen, of course, can be derived from the length of the array and the width. Implement a
- * function that draws a horizontal line from (xl, y) to ( x2, y).
- *
- * The method signature should look something like:
- * {@code drawline(byte[] screen, int width, int xl, int x2, int y)}
- *
- * Approach:
- * First, find the numbers in which all bits has to be set. Next, find the starting number and apply the mask
- * created from the starting offset. Do the same with the ending number.
- *
- * @param screen
- * @param width
- * @param x1
- * @param x2
- * @param y
- */
- private static void drawLine(byte[] screen, int width, int x1, int x2, int y) {
- int startOffset = x1 % 8;
- int startFullByte = x1 / 8;
- if (startOffset != 0) {
- startFullByte++;
- }
- int endOffset = x2 % 8;
- int endFullByte = x2 / 8;
- if (endOffset != 7) {
- endFullByte--;
- }
-
- // all bits have to be set in in-between numbers
- for (int i = startFullByte; i <= endFullByte; i++) {
- screen[width / 8 * y + i] |= (byte) 0xff;
- }
-
- /* 0xff is an integer literal which is like 000...11111111 (32 bits) but when we
- cast it to a byte, we get rid of the initial 24 bits */
- byte startByteMask = (byte) (0xff >> startOffset);
- byte endByteMask = (byte) ~(0xff >> endOffset + 1);
-
- if (x1 / 8 == x2 / 8) { // if starting and ending both lie in the same byte
- screen[width / 8 * y + (x1 / 8)] |= (startByteMask & endByteMask);
- } else {
- screen[width / 8 * y + (startFullByte - 1)] |= startByteMask; // only specific bits set in the starting number
- screen[width / 8 * y + (endFullByte + 1)] |= endByteMask; // only specific bits set in the ending number
- }
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- /*
- Consider the below screen with width 32 as an example:
-
- byte[] screen = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12};
-
- This screen has a width of 32 so you can assume the screen would be looking like:
-
- 9 10 11 12
- 5 6 7 8
- 1 2 3 4
-
- x-axis is 5-20 (5th position to 20th position)
- y-axis is 1
-
- which means our line would lie in numbers 5, 6, and 7
-
- so if you visualize these numbers in bits, it would be like:
-
- 00000101 00000110 00000111
- ^ ^
- and after drawing the line, the bits would become:
-
- 00000111 11111111 11111111
-
- and in the output we would see:
-
- 7, -1, -1 instead of 5, 6, 7
- */
- byte[] screen = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12};
- System.out.println("Input: " + Arrays.toString(screen));
- drawLine(screen, 32, 5, 20, 1);
- System.out.println("Output: " + Arrays.toString(screen));
- System.out.println("---");
- screen = new byte[]{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12};
- System.out.println("Input: " + Arrays.toString(screen));
- drawLine(screen, 32, 0, 5, 1);
- System.out.println("Output: " + Arrays.toString(screen));
- System.out.println("---");
- screen = new byte[]{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12};
- System.out.println("Input: " + Arrays.toString(screen));
- drawLine(screen, 32, 3, 7, 1);
- System.out.println("Output: " + Arrays.toString(screen));
- System.out.println("---");
- screen = new byte[]{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12};
- System.out.println("Input: " + Arrays.toString(screen));
- drawLine(screen, 16, 0, 7, 0);
- System.out.println("Output: " + Arrays.toString(screen));
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/ctci/bitmanipulation/FlipBitToWin.java b/src/main/java/com/ctci/bitmanipulation/FlipBitToWin.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 4424f7ab..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/ctci/bitmanipulation/FlipBitToWin.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,53 +0,0 @@
-package com.ctci.bitmanipulation;
-
-/**
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-03-16
- */
-public class FlipBitToWin {
-
- /**
- * You have an integer and you can flip exactly one bit from a O to a 1. Write code to find the length of the
- * longest sequence of 1s you could create.
- * Example:
- * Input: 1775 (or: 11011101111)
- * Output: 8
- *
- * Approach:
- * We just walk through the integer tracking the current 1s sequence length and the previous 1s sequence length.
- * When we see a zero, update previous length as follows:
- * - If the next bit is a 1, previous Length should be set to current Length.
- * - If the next bit is a 0, then we can't merge these sequences together. So, set previous Length to 0.
- *
- * @param n an integer
- * @return the longest sequence of set bits in {@code n} by flipping only one zero bit
- */
- private static int findLongestSequence(int n) {
- // if all bits are set, return the total number of bits in an integer
- if (n == ~0) {
- return Integer.BYTES * 8;
- }
-
- int prevOnesLen = 0;
- int currOnesLen = 0;
- int maxOnesLen = 0;
-
- while (n > 0) {
- // if the current bit is 0, reset the currOnesLen
- if ((n & 1) == 0) {
- prevOnesLen = (n & 2) == 0 ? 0 : currOnesLen; // if the next bit is also 0, set prevOnesLen to 0
- currOnesLen = 0;
- } else {
- currOnesLen++;
- }
- n >>>= 1;
- maxOnesLen = Math.max(maxOnesLen, prevOnesLen + 1 + currOnesLen);
- }
- return maxOnesLen;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println("Longest seq in " + Integer.toBinaryString(125) + " is " + findLongestSequence(125));
- System.out.println("Longest seq in " + Integer.toBinaryString(1275) + " is " + findLongestSequence(1275));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/ctci/bitmanipulation/Insertion.java b/src/main/java/com/ctci/bitmanipulation/Insertion.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 3230d86f..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/ctci/bitmanipulation/Insertion.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,49 +0,0 @@
-package com.ctci.bitmanipulation;
-
-/**
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-03-14
- */
-public class Insertion {
-
- /**
- * You are given two 32-bit numbers, N and M, and two bit positions, startIndex and endIndex. Write a method to
- * insert M into N such that M starts at bit startIndex and ends at bit endIndex. You can assume that the bits
- * startIndex through endIndex have enough space to fit all of M. That is, if M = 10011, you can assume that there
- * are at least 5 bits between j and i. You would not, for example, have startIndex = 3 and endIndex = 2, because
- * M could not fully fit between bit 3 and bit 2.
- *
- * EXAMPLE
- * Input: N = 10000000000, M = 10011, startIndex = 6, endIndex = 2
- * Output: 10001001100
- *
- * @param n
- * @param m
- * @param startIndex
- * @param endIndex
- * @return
- */
- private static int insertMIntoN(int n, int m, int startIndex, int endIndex) {
- // create a mask with only one bit set
- int mask = 1;
- // shift the set bit so that it starts with endIndex
- mask <<= endIndex;
-
- // unset the bits in 'n' from endIndex to startIndex
- for (int i = endIndex; i <= startIndex; i++) {
- n = n & ~mask; // ~mask will make the bit at ith index 0 but the rest of the bits will be 1
- mask <<= 1;
- }
-
- // shift 'm' so that it lines up with bits from startIndex to endIndex
- m <<= endIndex;
-
- // finally, return the xor of both as we know that 0 ^ a = a
- return n ^ m;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(insertMIntoN(Integer.parseInt("10000000000", 2), Integer.parseInt("10011", 2), 6, 2)));
- System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(insertMIntoN(Integer.parseInt("10110110111", 2), Integer.parseInt("11101", 2), 7, 3)));
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/ctci/bitmanipulation/NextNumber.java b/src/main/java/com/ctci/bitmanipulation/NextNumber.java
deleted file mode 100644
index ec817c13..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/ctci/bitmanipulation/NextNumber.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,124 +0,0 @@
-package com.ctci.bitmanipulation;
-
-/**
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-03-17
- */
-public class NextNumber {
-
- private static class NextLargerAndSmallerNumber {
- int nextLarger;
- int nextSmaller;
- }
-
- /**
- * Given a positive integer, print the next smallest and the next largest number that have the same number of
- * 1 bits in their binary representation.
- *
- * @param n a positive integer.
- * @return an object containing the next larger and next smaller number containing the identical set bits.
- */
- private static NextLargerAndSmallerNumber getNextLargerAndSmallerNumber(int n) {
- NextLargerAndSmallerNumber result = new NextLargerAndSmallerNumber();
- result.nextLarger = getNextLarger(n);
- result.nextSmaller = getNextSmaller(n);
- return result;
- }
-
- private static int getNextLarger(int n) {
- int rightmostNonTrailingZero = 0;
- int noOfZeros = 0;
- int noOfOnes = 0;
- int temp = n;
-
- /* Count the number of zeros and ones until the rightmost non-trailing zero
- For example, see below:
-
- n = 10110110011110
- ^
- */
- while ((temp & 1) == 0 && temp != 0) {
- noOfZeros++;
- temp >>>= 1;
- }
-
- while ((temp & 1) == 1 && temp != 0) {
- noOfOnes++;
- temp >>>= 1;
- }
-
- if (noOfZeros + noOfOnes == 31 || noOfZeros + noOfOnes == 0) {
- return -1;
- }
-
- /* Flip the bit and then shift all the 1s to the right end and then fill with 0s until the bit pattern '01.
- For example, consider the above number:
- n = 10110110011110 (original)
- ^
- n = 10110110111110 (after flip bit)
- ^
- next larger = 10110110100111 (the 1s are shifted to the right end and 0s to the left but before the rightmostNonTrailingZero)
- ^
- */
- rightmostNonTrailingZero = noOfOnes + noOfZeros;
- n |= 1 << rightmostNonTrailingZero; // set the rightmost non-trailing zero
- n &= ~((1 << rightmostNonTrailingZero) - 1); // unset all bits until rightmost non-trailing zero
- n |= (1 << noOfOnes - 1) - 1; // set (noOfOnes - 1) bits from the right
-
- return n;
- }
-
- private static int getNextSmaller(int n) {
- int rightmostNonTrailingOne = 0;
- int noOfZeros = 0;
- int noOfOnes = 0;
- int temp = n;
-
- while ((temp & 1) == 1 && temp != 0) {
- noOfOnes++;
- temp >>>= 1;
- }
-
- if (temp == 0) {
- return -1;
- }
-
- while ((temp & 1) == 0 && temp != 0) {
- noOfZeros++;
- temp >>>= 1;
- }
-
- rightmostNonTrailingOne = noOfZeros + noOfOnes;
- n &= ~(1 << rightmostNonTrailingOne); // unset the rightmost non-trailing one
- n |= (1 << rightmostNonTrailingOne - 1); // set all the bits until rightmost non-trailing one
- n &= ~((1 << noOfZeros - 1) - 1); // unset (noOfZeros - 1) bits from the right
-
- return n;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- NextLargerAndSmallerNumber of0 = getNextLargerAndSmallerNumber(0);
- System.out.println("Next larger of 0: " + of0.nextLarger);
- System.out.println("Next smaller of 0: " + of0.nextSmaller);
-
- NextLargerAndSmallerNumber of2 = getNextLargerAndSmallerNumber(2);
- System.out.println("Next larger of 2: " + of2.nextLarger);
- System.out.println("Next smaller of 2: " + of2.nextSmaller);
-
- NextLargerAndSmallerNumber of5 = getNextLargerAndSmallerNumber(5);
- System.out.println("Next larger of 5: " + of5.nextLarger);
- System.out.println("Next smaller of 5: " + of5.nextSmaller);
-
- NextLargerAndSmallerNumber of7 = getNextLargerAndSmallerNumber(7);
- System.out.println("Next larger of 7: " + of7.nextLarger);
- System.out.println("Next smaller of 7: " + of7.nextSmaller);
-
- NextLargerAndSmallerNumber of8 = getNextLargerAndSmallerNumber(8);
- System.out.println("Next larger of 8: " + of8.nextLarger);
- System.out.println("Next smaller of 8: " + of8.nextSmaller);
-
- NextLargerAndSmallerNumber of15 = getNextLargerAndSmallerNumber(15);
- System.out.println("Next larger of 15: " + of15.nextLarger);
- System.out.println("Next smaller of 15: " + of15.nextSmaller);
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/ctci/bitmanipulation/PairwiseSwap.java b/src/main/java/com/ctci/bitmanipulation/PairwiseSwap.java
deleted file mode 100644
index a1219d47..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/ctci/bitmanipulation/PairwiseSwap.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,40 +0,0 @@
-package com.ctci.bitmanipulation;
-
-/**
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-03-18
- */
-public class PairwiseSwap {
-
- /**
- * Write a program to swap odd and even bits in an integer with as few instructions as
- * possible (e.g., bit O and bit 1 are swapped, bit 2 and bit 3 are swapped, and so on).
- *
- * Approach:
- * Shift the odd bits to the left, shift the even bits to the right, and finally, OR both the results.
- * Note: You can operate on only odd bits or only even bits by using the appropriate masks, for e.g.,
- * 0x55555555 for odd bits and 0xaaaaaaaa for even bits.
- *
- * @param n an input integer.
- * @return an integer with even and odd bits swapped.
- */
- private static int swapBits(int n) {
- return ((n & 0x55555555) << 1) | ((n & 0xaaaaaaaa) >>> 1);
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println("Input: " + Integer.toBinaryString(1569) +
- "\nOutput: " + Integer.toBinaryString(swapBits(1569)));
-
- assert Integer.toBinaryString(swapBits(1569)).equals("100100010010");
-
- System.out.println("Input: " + Integer.toBinaryString(2680) +
- "\nOutput: " + Integer.toBinaryString(swapBits(2680)));
-
- assert Integer.toBinaryString(swapBits(2680)).equals("10110110100");
-
- // fyi
- System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(0x55555555));
- System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(0xaaaaaaaa));
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/ctci/linkedlists/DeleteMiddleNode.java b/src/main/java/com/ctci/linkedlists/DeleteMiddleNode.java
deleted file mode 100644
index c4b4052e..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/ctci/linkedlists/DeleteMiddleNode.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,65 +0,0 @@
-package com.ctci.linkedlists;
-
-/**
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-01-27
- */
-public class DeleteMiddleNode {
-
- /**
- * Implement an algorithm to delete a node in the middle (i.e., any node but the first and last node, not
- * necessarily the exact middle) of a singly linked list, given only access to that node.
- *
- * EXAMPLE
- * Input: the node c from the linked list a->b->c->d->e->f
- * Result: nothing is returned, but the new linked list looks like a->b->d->e->f
- *
- * @param middle the node to be deleted
- */
- private static void deleteMiddleNode(Node middle) {
- if (middle == null || middle.next == null) {
- return;
- }
- // copy the data from the next node over to the middle node, and then to delete the next node
- Node next = middle.next;
- middle.val = next.val;
- middle.next = next.next;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Node l1 = new Node(1);
- l1.next = new Node(2);
- l1.next.next = new Node(3);
- l1.next.next.next = new Node(4);
- l1.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);
- l1.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(6);
- l1.print();
- deleteMiddleNode(l1.next.next);
- l1.print();
-
- System.out.println("----");
-
- l1 = new Node(1);
- l1.next = new Node(2);
- l1.next.next = new Node(3);
- l1.print();
- deleteMiddleNode(l1.next);
- l1.print();
-
- System.out.println("----");
-
- l1 = new Node(1);
- l1.next = new Node(3);
- l1.print();
- deleteMiddleNode(l1);
- l1.print();
-
- System.out.println("----");
-
- l1 = new Node(1);
- l1.next = new Node(3);
- l1.print();
- deleteMiddleNode(l1.next);
- l1.print();
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/ctci/linkedlists/Intersection.java b/src/main/java/com/ctci/linkedlists/Intersection.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 4665fe43..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/ctci/linkedlists/Intersection.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,104 +0,0 @@
-package com.ctci.linkedlists;
-
-/**
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-02-02
- */
-public class Intersection {
-
- /**
- * Given two (singly) linked lists, determine if the two lists intersect. Return the intersecting node. Note that
- * the intersection is defined based on reference, not value. That is, if the kth node of the first linked list is
- * the exact same node (by reference) as the jth node of the second linked list, then they are intersecting.
- *
- * @param n1
- * @param n2
- * @return the intersecting node, {@code null} otherwise.
- */
- private static Node findIntersectingNode(Node n1, Node n2) {
- Node curr1 = n1;
- Node curr2 = n2;
- int len1 = 1;
- int len2 = 1;
-
- /* Calculate the length of both linked lists */
- while (curr1 != null && curr1.next != null) {
- len1++;
- curr1 = curr1.next;
- }
- while (curr2 != null && curr2.next != null) {
- len2++;
- curr2 = curr2.next;
- }
-
- // if different tail nodes, they don't intersect
- if (curr1 != curr2) {
- return null;
- }
-
- curr1 = n1;
- curr2 = n2;
-
- /* Get rid of the extra nodes from the longer list */
- if (len1 > len2) {
- for (int i = 0; i < len1 - len2; i++) {
- curr1 = curr1.next;
- }
- }
- if (len2 > len1) {
- for (int i = 0; i < len2 - len1; i++) {
- curr2 = curr2.next;
- }
- }
-
- // move both pointers until you have a collision
- while (curr1 != curr2) {
- curr1 = curr1.next;
- curr2 = curr2.next;
- }
-
- // return either
- return curr1;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Node l1 = new Node(1);
- l1.next = new Node(2);
- l1.next.next = new Node(3);
- l1.next.next.next = new Node(4);
- l1.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);
- l1.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);
- Node l2 = new Node(1);
- l2.next = new Node(4);
- l2.next.next = new Node(2);
- l2.next.next.next = new Node(3);
- l2.next.next.next.next = l1.next.next.next;
- l1.print();
- l2.print();
- System.out.println(findIntersectingNode(l1, l2).val); // may throw NPE, not handling for the sake of simplicity
-
- System.out.println("----");
-
- l1 = new Node(1);
- l2 = l1;
- l1.print();
- l2.print();
- System.out.println(findIntersectingNode(l1, l2).val); // may throw NPE, not handling for the sake of simplicity
-
- System.out.println("----");
-
- l1 = new Node(1);
- l1.next = new Node(2);
- l1.next.next = new Node(3);
- l1.next.next.next = new Node(4);
- l1.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);
- l1.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);
- l2 = new Node(1);
- l2.next = new Node(4);
- l2.next.next = new Node(2);
- l2.next.next.next = new Node(3);
- l1.print();
- l2.print();
- System.out.println(findIntersectingNode(l1, l2));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/ctci/linkedlists/KthToLastElement.java b/src/main/java/com/ctci/linkedlists/KthToLastElement.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 8fff3f9d..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/ctci/linkedlists/KthToLastElement.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,88 +0,0 @@
-package com.ctci.linkedlists;
-
-/**
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 21/11/2018
- */
-public class KthToLastElement {
-
- /**
- * Finds the kth node from the end in a linked list.
- *
- * @param head is the reference to the head of the linked list
- * @param k is the position of element from the end
- * @return the Kth node from the end
- */
- private static Node getKthToLastElement(Node head, int k) {
- Node slow = head;
- Node fast = head;
- int i = 0;
-
- // forward the fast reference k times
- while (i < k) {
- if (fast == null) return null; // k is out of bounds
- fast = fast.next;
- i++;
- }
-
- while (fast != null) {
- slow = slow.next;
- fast = fast.next;
- }
- return slow;
- }
-
- /**
- * This approach is recursive and it just prints the kth to last node instead
- * of returning the node.
- *
- * @param head starting node of the linklist
- * @param k kth to last node to print
- * @return the index of the kth to last node
- */
- private static int printKthToLastElement(Node head, int k) {
- if (head == null) {
- return 0;
- }
- int index = printKthToLastElement(head.next, k) + 1;
- if (index == k) {
- System.out.println(head.val);
- }
- return index;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Node l1 = new Node(1);
- l1.next = new Node(6);
- l1.next.next = new Node(3);
- l1.next.next.next = new Node(4);
- l1.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);
- l1.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(7);
- l1.print();
- System.out.println("k=2: " + getKthToLastElement(l1, 2).val); // NPE check is omitted intentionally to keep it simple
- System.out.print("k=2: ");
- printKthToLastElement(l1, 2);
-
- Node l2 = new Node(1);
- l2.next = new Node(6);
- l2.next.next = new Node(2);
- l2.next.next.next = new Node(3);
- l2.next.next.next.next = new Node(4);
- l2.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(7);
- l2.print();
- System.out.println("k=1: " + getKthToLastElement(l2, 1).val);
- System.out.print("k=1: ");
- printKthToLastElement(l2, 1);
-
- Node l3 = new Node(1);
- l3.next = new Node(6);
- l3.next.next = new Node(3);
- l3.next.next.next = new Node(3);
- l3.next.next.next.next = new Node(4);
- l3.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(7);
- l3.print();
- System.out.println("k=6: " + getKthToLastElement(l3, 6).val);
- System.out.print("k=6: ");
- printKthToLastElement(l3, 6);
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/ctci/linkedlists/LoopDetection.java b/src/main/java/com/ctci/linkedlists/LoopDetection.java
deleted file mode 100644
index d0a9a110..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/ctci/linkedlists/LoopDetection.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,67 +0,0 @@
-package com.ctci.linkedlists;
-
-/**
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-02-03
- */
-public class LoopDetection {
-
- /**
- * Given a circular linked list, implement an algorithm that returns the node at the beginning of the loop.
- * DEFINITION
- * Circular linked list: A (corrupt) linked list in which a node's next pointer points to an earlier node, so
- * as to make a loop in the linked list.
- * EXAMPLE
- * Input: A -> B -> C -> D -> E -> C [the same C as earlier]
- * Output: C
- *
- * See {@link com.rampatra.linkedlists.DetectAndRemoveLoop} for a slightly more complex problem.
- *
- * @param head the starting node of the linked list
- * @return the {@code Node} where the loop starts, {@code null} otherwise.
- */
- private static Node findLoopStartNode(Node head) {
- Node slow = head;
- Node fast = head;
-
- while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
- slow = slow.next;
- fast = fast.next.next;
- if (slow == fast) {
- break;
- }
- }
-
- /* Error check - no meeting point, and therefore no loop */
- if (fast == null || fast.next == null) {
- return null;
- }
-
- /* Move slow to Head. Keep fast at Meeting Point. Each are k steps from the
- * Loop Start. If they move at the same pace, they must meet at Loop Start. */
- slow = head;
- while (slow != fast) {
- slow = slow.next;
- fast = fast.next;
- }
-
- /* You can return either as now both point to the start of the loop */
- return fast;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- /*
- * 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 -> 6
- * ^ |
- * |_________|
- */
- Node l1 = new Node(1);
- l1.next = new Node(2);
- l1.next.next = new Node(3);
- l1.next.next.next = new Node(4);
- l1.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);
- l1.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(6);
- l1.next.next.next.next.next.next = l1.next.next.next;
- System.out.println(findLoopStartNode(l1).val);
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/ctci/linkedlists/Node.java b/src/main/java/com/ctci/linkedlists/Node.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 5c0d1ec3..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/ctci/linkedlists/Node.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,23 +0,0 @@
-package com.ctci.linkedlists;
-
-/**
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 21/11/2018
- */
-class Node {
- int val;
- Node next;
-
- Node(int val) {
- this.val = val;
- }
-
- public void print() {
- Node curr = this;
- while (curr.next != null) {
- System.out.print(curr.val + "->");
- curr = curr.next;
- }
- System.out.println(curr.val);
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/ctci/linkedlists/Palindrome.java b/src/main/java/com/ctci/linkedlists/Palindrome.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 57bb184d..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/ctci/linkedlists/Palindrome.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,107 +0,0 @@
-package com.ctci.linkedlists;
-
-import java.util.Stack;
-
-/**
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-02-02
- */
-public class Palindrome {
-
- /**
- * Checks whether a Linked List is palindrome by using a stack.
- *
- * @param head starting node of the linked list.
- * @return {@code true} if linked list palindrome, {@code false} otherwise.
- */
- private static boolean isPalindrome(Node head) {
- Node curr = head;
- Stack stack = new Stack<>();
- // pop all elements into stack
- while (curr != null) {
- stack.push(curr.val);
- curr = curr.next;
- }
- curr = head;
- // as stack contains the elements in reverse order, pop and compare with the list one by one
- while (curr != null) {
- if (curr.val != stack.pop()) {
- return false;
- }
- curr = curr.next;
- }
- return true;
- }
-
- /**
- * This is a similar approach like above but a bit faster as we are not iterating the entire list twice.
- *
- * @param head starting node of the linked list.
- * @return {@code true} if linked list palindrome, {@code false} otherwise.
- */
- private static boolean isPalindromeOptimized(Node head) {
- Node slow = head;
- Node fast = head;
- Stack stack = new Stack<>();
-
- // push half of the elements into the stack
- while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
- stack.push(slow.val);
- slow = slow.next;
- fast = fast.next.next;
- }
-
- // linked list has odd number of elements, so forward the slow reference by one
- if (fast != null) {
- slow = slow.next;
- }
-
- while (slow != null) {
- if (slow.val != stack.pop()) {
- return false;
- }
- slow = slow.next;
- }
- return true;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
-
- Node l1 = new Node(1);
- l1.next = new Node(2);
- l1.next.next = new Node(3);
- l1.next.next.next = new Node(3);
- l1.next.next.next.next = new Node(2);
- l1.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(1);
- l1.print();
- System.out.println(isPalindrome(l1));
- System.out.println(isPalindromeOptimized(l1));
- System.out.println("------");
-
- l1 = new Node(1);
- l1.next = new Node(2);
- l1.next.next = new Node(3);
- l1.next.next.next = new Node(2);
- l1.next.next.next.next = new Node(1);
- l1.print();
- System.out.println(isPalindrome(l1));
- System.out.println(isPalindromeOptimized(l1));
- System.out.println("------");
-
- l1 = new Node(0);
- l1.next = new Node(2);
- l1.next.next = new Node(3);
- l1.next.next.next = new Node(3);
- l1.next.next.next.next = new Node(0);
- l1.print();
- System.out.println(isPalindrome(l1));
- System.out.println(isPalindromeOptimized(l1));
- System.out.println("------");
-
- l1 = new Node(1);
- l1.print();
- System.out.println(isPalindrome(l1));
- System.out.println(isPalindromeOptimized(l1));
-
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/ctci/linkedlists/Partition.java b/src/main/java/com/ctci/linkedlists/Partition.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 8876a424..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/ctci/linkedlists/Partition.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,93 +0,0 @@
-package com.ctci.linkedlists;
-
-/**
- * Write code to partition a linked list around a value x, such that all nodes less than x come before all
- * nodes greater than or equal to x. If x is contained within the list, the values of x only need to be
- * after the elements less than x (see below). The partition element x can appear anywhere in the "right
- * partition"; it does not need to appear between the left and right partitions.
- *
- * EXAMPLE:
- * Input: 3 -> 5 -> 8 -> 5 -> 10 -> 2 -> 1 [partition=5]
- * Output: 3 -> 1 -> 2 -> 10 -> 5 -> 5 -> 8
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-01-28
- */
-public class Partition {
-
- private static Node partition(Node head, int x) {
- Node leftPartitionHead = null;
- Node leftPartitionCurr = null;
- Node rightPartitionHead = null;
- Node rightPartitionCurr = null;
- Node curr = head;
-
- while (curr != null) {
- if (curr.val < x) {
- if (leftPartitionHead == null) {
- leftPartitionHead = curr;
- leftPartitionCurr = curr;
- } else {
- leftPartitionCurr.next = curr;
- leftPartitionCurr = leftPartitionCurr.next;
- }
- } else {
- if (rightPartitionHead == null) {
- rightPartitionHead = curr;
- rightPartitionCurr = curr;
- } else {
- rightPartitionCurr.next = curr;
- rightPartitionCurr = rightPartitionCurr.next;
- }
- }
- curr = curr.next;
- }
-
- if (leftPartitionCurr != null) leftPartitionCurr.next = rightPartitionHead;
- if (rightPartitionCurr != null) rightPartitionCurr.next = null;
-
- return leftPartitionHead;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Node l1 = new Node(3);
- l1.next = new Node(5);
- l1.next.next = new Node(8);
- l1.next.next.next = new Node(5);
- l1.next.next.next.next = new Node(10);
- l1.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(2);
- l1.next.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(1);
- l1.print();
- l1.print();
-
- System.out.println("----");
-
- l1 = new Node(1);
- l1.next = new Node(2);
- l1.next.next = new Node(3);
- l1.print();
- l1.print();
-
- System.out.println("----");
-
- l1 = new Node(3);
- l1.next = new Node(2);
- l1.next.next = new Node(1);
- l1.print();
- l1.print();
-
- System.out.println("----");
-
- l1 = new Node(1);
- l1.print();
- l1.print();
-
- System.out.println("----");
-
- l1 = null;
- l1.print();
- l1.print();
-
- System.out.println("----");
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/ctci/linkedlists/RemoveDuplicates.java b/src/main/java/com/ctci/linkedlists/RemoveDuplicates.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 31029188..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/ctci/linkedlists/RemoveDuplicates.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,88 +0,0 @@
-package com.ctci.linkedlists;
-
-import java.util.HashSet;
-import java.util.Set;
-
-/**
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 21/11/2018
- */
-public class RemoveDuplicates {
-
- /**
- * Removes duplicates in an unsorted linked list by using additional memory
- * and two references.
- *
- * If asked not to use any additional memory then you can
- * loop through the list for each node and check for repeated elements but bear
- * in mind that the time complexity of this would be O(n^2) where n is the number
- * of nodes in the linked list.
- *
- * @param head reference to the head of the linked list
- */
- private static void removeDuplicatesFromUnsortedList(Node head) {
- Set valuesInList = new HashSet<>();
- Node curr = head;
- Node prev = curr;
- while (curr != null) {
- if (valuesInList.contains(curr.val)) {
- prev.next = curr.next;
- }
- valuesInList.add(curr.val);
- prev = curr;
- curr = curr.next;
- }
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Node l1 = new Node(1);
- l1.next = new Node(2);
- l1.next.next = new Node(3);
- l1.next.next.next = new Node(4);
- l1.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);
- l1.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);
- System.out.print("With dups: ");
- l1.print();
- removeDuplicatesFromUnsortedList(l1);
- System.out.print("Without dups: ");
- l1.print();
-
- Node l2 = new Node(1);
- l2.next = new Node(1);
- l2.next.next = new Node(2);
- l2.next.next.next = new Node(3);
- l2.next.next.next.next = new Node(4);
- l2.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);
- System.out.print("\nWith dups: ");
- l2.print();
- removeDuplicatesFromUnsortedList(l2);
- System.out.print("Without dups: ");
- l2.print();
-
- Node l3 = new Node(1);
- l3.next = new Node(2);
- l3.next.next = new Node(3);
- l3.next.next.next = new Node(3);
- l3.next.next.next.next = new Node(4);
- l3.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);
- System.out.print("\nWith dups: ");
- l3.print();
- removeDuplicatesFromUnsortedList(l3);
- System.out.print("Without dups: ");
- l3.print();
-
- Node l4 = new Node(1);
- System.out.print("\nWith dups: ");
- l4.print();
- removeDuplicatesFromUnsortedList(l4);
- System.out.print("Without dups: ");
- l4.print();
-
- Node l5 = null;
- System.out.print("\nWith dups: ");
- l5.print();
- removeDuplicatesFromUnsortedList(l5);
- System.out.print("Without dups: ");
- l5.print();
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/ctci/linkedlists/SumLists.java b/src/main/java/com/ctci/linkedlists/SumLists.java
deleted file mode 100644
index befdfc3e..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/ctci/linkedlists/SumLists.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,86 +0,0 @@
-package com.ctci.linkedlists;
-
-/**
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-01-31
- */
-public class SumLists {
-
- /**
- * You have two numbers represented by a linked list, where each node contains a single digit. The digits are
- * stored in reverse order, such that the 1's digit is at the head of the list (or in other words, the least
- * significant digit is stored at the head of the list). Write a function that adds the two numbers and returns
- * the sum as a linked list.
- *
- * EXAMPLE
- * Input: (7-> 1 -> 6) + (5 -> 9 -> 2).That is, 617 + 295.
- * Output: 2 -> 1 -> 9. That is, 912.
- *
- * @param num1
- * @param num2
- * @return
- */
- private static Node sumLists(Node num1, Node num2) {
- int carry = 0;
- int sum;
- Node sumList = null, curr = null;
- while (num1 != null || num2 != null) {
- sum = ((num1 == null) ? 0 : num1.val) + ((num2 == null) ? 0 : num2.val) + carry;
- carry = sum / 10;
- if (sumList == null) {
- sumList = new Node(sum % 10);
- curr = sumList;
- } else {
- curr.next = new Node(sum % 10);
- curr = curr.next;
- }
- if (num1 != null) num1 = num1.next;
- if (num2 != null) num2 = num2.next;
- }
- if (carry != 0) {
- curr.next = new Node(carry);
- }
- return sumList;
- }
-
- // TODO: After doing reverseListRecursive
- private static Node sumListsWithMostSignificantDigitAtHead(Node n1, Node n2) {
- return null;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Node l1 = new Node(9);
- l1.next = new Node(9);
- l1.next.next = new Node(9);
-
- Node l2 = new Node(9);
- l2.next = new Node(9);
- l2.next.next = new Node(9);
-
- l1.print();
- l2.print();
- sumLists(l1, l2).print();
- System.out.println("-----------");
-
- l1 = new Node(9);
- l1.next = new Node(9);
-
- l2 = new Node(9);
- l2.next = new Node(9);
- l2.next.next = new Node(9);
-
- l1.print();
- l2.print();
- sumLists(l1, l2).print();
- System.out.println("-----------");
-
- l1 = null;
- l2 = new Node(9);
- l2.next = new Node(9);
- l2.next.next = new Node(8);
-
- l1.print();
- l2.print();
- sumLists(l1, l2).print();
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/ctci/recursionanddp/FibonacciNumber.java b/src/main/java/com/ctci/recursionanddp/FibonacciNumber.java
deleted file mode 100644
index caa4d095..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/ctci/recursionanddp/FibonacciNumber.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,64 +0,0 @@
-package com.ctci.recursionanddp;
-
-/**
- * The fabled fibonacci numbers problem with three different solutions.
- * The {@link FibonacciNumber#fibonacciBottomUpOptimized(int)} version is the most optimized among all w.r.t space
- * and time. See {@link com.rampatra.dynamicprogramming.FibonacciNumbers} for Fibonacci series.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-02-26
- */
-public class FibonacciNumber {
-
- private static int fibonacciTopDown(int n, int[] memo) {
- if (n == 0 || n == 1) return n;
-
- if (memo[n] != 0) {
- return memo[n];
- } else {
- memo[n] = fibonacciTopDown(n - 1, memo) + fibonacciTopDown(n - 2, memo);
- return memo[n];
- }
- }
-
- private static int fibonacciBottomUp(int n) {
- if (n == 0 || n == 1) return n;
-
- int[] memo = new int[n + 1];
- memo[1] = 1;
- for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
- memo[i] = memo[i - 1] + memo[i - 2];
- }
- return memo[n];
- }
-
- private static int fibonacciBottomUpOptimized(int n) {
- if (n == 0 || n == 1) return n;
-
- int a = 0;
- int b = 1;
- int res = a + b;
-
- for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
- res = a + b;
- a = b;
- b = res;
- }
-
- return res;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(fibonacciTopDown(4, new int[5]));
- System.out.println(fibonacciBottomUp(4));
- System.out.println(fibonacciBottomUpOptimized(4));
- System.out.println("---");
- System.out.println(fibonacciTopDown(5, new int[6]));
- System.out.println(fibonacciBottomUp(5));
- System.out.println(fibonacciBottomUpOptimized(5));
- System.out.println("---");
- System.out.println(fibonacciTopDown(10, new int[11]));
- System.out.println(fibonacciBottomUp(10));
- System.out.println(fibonacciBottomUpOptimized(10));
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/ctci/stacksandqueues/QueueViaStacks.java b/src/main/java/com/ctci/stacksandqueues/QueueViaStacks.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 271fd8e4..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/ctci/stacksandqueues/QueueViaStacks.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,61 +0,0 @@
-package com.ctci.stacksandqueues;
-
-import java.util.NoSuchElementException;
-import java.util.Stack;
-
-/**
- * Implement a queue using two stacks. No other data structures to be used.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-02-06
- */
-public class QueueViaStacks {
-
- private Stack stackFront = new Stack<>();
- private Stack stackRear = new Stack<>();
-
- private T add(T item) {
- return stackRear.push(item);
- }
-
- private T remove() {
- if (stackFront.empty() && stackRear.empty()) {
- throw new NoSuchElementException();
- } else if (!stackFront.empty()) {
- return stackFront.pop();
- } else {
- while (!stackRear.empty()) {
- stackFront.push(stackRear.pop());
- }
- return stackFront.pop();
- }
- }
-
- private void print() {
- Stack tempStack = new Stack<>();
- while (!stackFront.empty()) {
- tempStack.push(stackFront.pop());
- }
- System.out.print("[");
- tempStack.forEach(item -> System.out.print(item + ","));
- stackRear.forEach(item -> System.out.print(item + ","));
- System.out.println("]");
- while (!tempStack.empty()) {
- stackFront.push(tempStack.pop());
- }
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- QueueViaStacks queue = new QueueViaStacks<>();
- queue.add(1);
- queue.add(2);
- queue.add(3);
- queue.print();
- queue.remove();
- queue.print();
- queue.remove();
- queue.print();
- queue.remove();
- queue.print();
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/ctci/stacksandqueues/SortStack.java b/src/main/java/com/ctci/stacksandqueues/SortStack.java
deleted file mode 100644
index b94c68fb..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/ctci/stacksandqueues/SortStack.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,48 +0,0 @@
-package com.ctci.stacksandqueues;
-
-import java.util.Arrays;
-import java.util.Stack;
-
-/**
- * Write a program to sort a stack such that the smallest items are on the top. You can use an additional temporary
- * stack, but you may not copy the elements into any other data structure (such as an array). The stack supports the
- * following operations: push, pop, peek, and isEmpty.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-02-08
- */
-public class SortStack {
-
- private static void sortStack(Stack stack) {
- Stack tempStack = new Stack<>();
- while (!stack.empty()) {
- tempStack.push(stack.pop());
- }
- while (!tempStack.empty()) {
- Integer item = tempStack.pop();
- if (stack.empty()) {
- stack.push(item);
- } else {
- while (!stack.empty() && item > stack.peek()) {
- tempStack.push(stack.pop());
- }
- stack.push(item);
- }
- }
- }
-
- private static void printStack(Stack stack) {
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(stack.toArray()));
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Stack unsortedStack = new Stack<>();
- unsortedStack.push(2);
- unsortedStack.push(5);
- unsortedStack.push(1);
- unsortedStack.push(3);
- printStack(unsortedStack);
- sortStack(unsortedStack);
- printStack(unsortedStack);
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/ctci/stacksandqueues/StackMin.java b/src/main/java/com/ctci/stacksandqueues/StackMin.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 0a5d2d59..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/ctci/stacksandqueues/StackMin.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,62 +0,0 @@
-package com.ctci.stacksandqueues;
-
-import com.sun.tools.javac.util.Assert;
-
-import java.util.Stack;
-
-/**
- * How would you design a stack which, in addition to push and pop, has a function min
- * which returns the minimum element? Push, pop and min should all operate in 0(1) time.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-02-04
- */
-public class StackMin {
-
- // the main stack to do push, pop, and min operations
- private static Stack stack = new Stack<>();
- // another stack to store the mins (needed to make min() call O(1))
- private static Stack minStack = new Stack<>();
-
- private static int push(int item) {
- minPush(item);
- return stack.push(item);
- }
-
- private static int pop() {
- minPop(stack.peek());
- return stack.pop();
- }
-
- private static int min() {
- return minStack.peek();
- }
-
- private static void minPush(int item) {
- if (minStack.empty() || item <= minStack.peek()) {
- minStack.push(item);
- }
- }
-
- private static void minPop(int item) {
- if (item == minStack.peek()) {
- minStack.pop();
- }
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- push(2);
- push(5);
- push(1);
- push(1);
- push(6);
- push(8);
- Assert.check(min() == 1);
- pop();
- pop();
- pop();
- Assert.check(min() == 1);
- pop();
- Assert.check(min() == 2);
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/ctci/stacksandqueues/StackOfPlates.java b/src/main/java/com/ctci/stacksandqueues/StackOfPlates.java
deleted file mode 100644
index f001c4e4..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/ctci/stacksandqueues/StackOfPlates.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,80 +0,0 @@
-package com.ctci.stacksandqueues;
-
-import java.util.ArrayList;
-import java.util.Collection;
-import java.util.EmptyStackException;
-import java.util.List;
-import java.util.Stack;
-
-/**
- * Imagine a (literal) stack of plates. If the stack gets too high, it might topple. Therefore, in real life, we
- * would likely start a new stack when the previous stack exceeds some threshold. Implement a data structure
- * SetOfStacks that mimics this. SetOfStacks should be composed of several stacks and should create a new stack once
- * the previous one exceeds capacity. SetOfStacks.push() and SetOfStacks. pop() should behave identically to a single
- * stack (that is, pop() should return the same values as it would if there were just a single stack).
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-02-08
- */
-public class StackOfPlates {
-
- private static final int capacity = 3;
- private static List> stackList = new ArrayList<>();
-
- private static int push(int item) {
- return getLastStack().push(item);
- }
-
- private static int pop() {
- Stack lastStack = stackList.get(stackList.size() - 1);
- if (lastStack == null || (stackList.size() == 1 && lastStack.empty())) {
- throw new EmptyStackException();
- } else if (lastStack.empty()) {
- stackList.remove(stackList.size() - 1);
- return pop();
- } else {
- return lastStack.pop();
- }
- }
-
- private static Stack getLastStack() {
- if (stackList.size() == 0 || isFull(stackList.get(stackList.size() - 1))) {
- stackList.add(new Stack<>());
- }
- return stackList.get(stackList.size() - 1);
- }
-
- private static boolean isFull(Stack stack) {
- return stack.size() >= capacity;
- }
-
- private static void print() {
- System.out.print("[");
- stackList.stream().flatMap(Collection::stream).forEach(System.out::print);
- System.out.println("]");
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- push(1);
- push(2);
- print();
- push(3);
- print();
- push(4);
- push(5);
- print();
- push(6);
- push(7);
- print();
- pop();
- print();
- pop();
- pop();
- pop();
- print();
- pop();
- pop();
- pop();
- print();
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/ctci/treesandgraphs/BuildOrder.java b/src/main/java/com/ctci/treesandgraphs/BuildOrder.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 6d64e48a..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/ctci/treesandgraphs/BuildOrder.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,144 +0,0 @@
-package com.ctci.treesandgraphs;
-
-import java.util.ArrayList;
-import java.util.HashMap;
-import java.util.HashSet;
-import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
-import java.util.List;
-import java.util.Map;
-import java.util.Set;
-import java.util.stream.Stream;
-
-/**
- * You are given a list of projects and a list of dependencies (which is a list of pairs of projects, where the second
- * project is dependent on the first project). All of a project's dependencies must be built before the project is. Find
- * a build order that will allow the projects to be built. If there is no valid build order, return an error.
- * EXAMPLE
- * Input: projects: a, b, c, d, e, f and dependencies: (a, d), (f, b), (b, d), (f, a), (d, c)
- * Output: f, e, a, b, d, c
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-02-21
- */
-public class BuildOrder {
-
- private class Project {
- String name;
- Set dependencies = new HashSet<>();
-
- Project(String name) {
- this.name = name;
- }
-
- @Override
- public String toString() {
- return name;
- }
- }
-
- private final Map projects = new HashMap<>();
-
- private void addProjects(Stream projectNames) {
- projectNames.forEach(name -> projects.put(name, new Project(name)));
- }
-
- /**
- * Adds a directed edge from {@code projectName2} to {@code ProjectName1}. This means {@code projectName2} is
- * dependent on {@code projectName1}, i.e, {@code projectName1} has to be built before {@code projectName2}.
- *
- * @param projectName1 name of project 1
- * @param projectName2 name of project 2
- */
- private void addDependency(String projectName1, String projectName2) {
- Project p1 = projects.get(projectName1);
- Project p2 = projects.get(projectName2);
-
- if (p1 == null) {
- p1 = new Project(projectName1);
- projects.put(projectName1, p1);
- }
- if (p2 == null) {
- p2 = new Project(projectName2);
- projects.put(projectName2, p2);
- }
-
- p2.dependencies.add(p1);
- }
-
- /**
- * Determines the order in which the projects need to be built.
- * Time complexity: TODO
- *
- * @return a list of projects in the order they should be built, the first project should be built first and so on.
- */
- private List getBuildOrder() {
- Map projectsBuilt = new LinkedHashMap<>(); // linked hashmap is needed to maintain the insertion order
-
- while (projectsBuilt.size() != projects.size()) {
- // find the projects which are not dependent on any project
- Set nextProjectsToBuild = getProjectsWithNoDependencies(projectsBuilt);
-
- // if there are no further independent projects to build, then we can't proceed further
- if (nextProjectsToBuild.size() == 0) {
- throw new IllegalStateException("Error: Projects can't be built.");
- }
- nextProjectsToBuild.forEach(p -> projectsBuilt.put(p.name, p));
-
- // once a project is built, remove the dependencies from all other projects dependent on this
- removeDependency(nextProjectsToBuild);
- }
-
- return new ArrayList<>(projectsBuilt.values());
- }
-
- private Set getProjectsWithNoDependencies(Map alreadyBuildProjects) {
- Set unBuiltProjectsWithZeroDependencies = new HashSet<>();
-
- for (Map.Entry entry : projects.entrySet()) {
- if (entry.getValue().dependencies.size() == 0 && alreadyBuildProjects.get(entry.getKey()) == null) {
- unBuiltProjectsWithZeroDependencies.add(entry.getValue());
- }
- }
-
- return unBuiltProjectsWithZeroDependencies;
- }
-
- private void removeDependency(Set newlyBuiltProjects) {
- projects.forEach((n, p) -> p.dependencies.removeAll(newlyBuiltProjects));
- }
-
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- /* test case 1
-
- ––––––––––– b
- | ↑
- ↓ |
- f <–– a <–– d <–– c
-
- Note: Project "a" is dependent on "f", and project "d" is dependent on "a", and so on.
-
- */
- BuildOrder buildOrder = new BuildOrder();
- buildOrder.addProjects(Stream.of("a", "b", "c", "d", "e", "f"));
- buildOrder.addDependency("a", "d");
- buildOrder.addDependency("f", "b");
- buildOrder.addDependency("b", "d");
- buildOrder.addDependency("f", "a");
- buildOrder.addDependency("d", "c");
- System.out.println(buildOrder.getBuildOrder());
-
- // test case 2
- buildOrder = new BuildOrder();
- buildOrder.addProjects(Stream.of("a", "b", "c", "d", "e", "f", "g"));
- buildOrder.addDependency("d", "g");
- buildOrder.addDependency("f", "b");
- buildOrder.addDependency("f", "c");
- buildOrder.addDependency("f", "a");
- buildOrder.addDependency("c", "a");
- buildOrder.addDependency("b", "a");
- buildOrder.addDependency("b", "e");
- buildOrder.addDependency("a", "e");
- System.out.println(buildOrder.getBuildOrder());
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/ctci/treesandgraphs/CheckBalanced.java b/src/main/java/com/ctci/treesandgraphs/CheckBalanced.java
deleted file mode 100644
index d7658cd8..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/ctci/treesandgraphs/CheckBalanced.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,81 +0,0 @@
-package com.ctci.treesandgraphs;
-
-/**
- * Implement a function to check if a binary tree is balanced. For the purposes of this question, a balanced
- * tree is defined to be a tree such that the heights of the two subtrees of any node never differ by more than one.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-02-16
- */
-public class CheckBalanced {
-
- /**
- * Checks whether its left and right child are balanced, if yes then continues down the
- * tree or else stops and returns {@code false}. Time complexity: O(n log n) since each
- * node is touched once per node above it. Space complexity: O(h) where, h is the height
- * of the tree.
- *
- * @param node reference to the node for which the balanced property needs to be checked
- * @return {@code true} if balanced, {@code false} otherwise
- */
- private static boolean isBalanced(TreeNode node) {
- if (node == null) return true;
-
- boolean isBalanced = (height(node.left) - height(node.right)) <= 1;
-
- /* Note: isBalanced is first checked below as there is no point is checking the left and right child
- if the current node itself is not balanced. And, as '&&' is a short circuit operator, it won't evaluate
- the rest of the conditions if the first condition is false. */
- return isBalanced && isBalanced(node.left) && isBalanced(node.right);
- }
-
- private static int height(TreeNode node) {
- if (node == null) return -1;
-
- return Math.max(height(node.left), height(node.right)) + 1;
- }
-
- /**
- * This approach is a slight modification to the above {@link CheckBalanced#height(TreeNode)} method where
- * while calculating the height we also check whether the difference between the left and right child heights
- * is more than 1. If yes, we return an error code, which in this case, is {@code Integer.MIN_VALUE}.
- * Time complexity: O(n). Space complexity: O(h) where, h is the height of the tree.
- *
- * @param node reference to the node for which the balanced property needs to be checked
- * @return the height of the tree if it's balance, {@code Integer.MIN_VALUE} otherwise
- */
- private static int checkHeightAndBalance(TreeNode node) {
- if (node == null) return -1;
-
- int leftHeight = checkHeightAndBalance(node.left);
- int rightHeight = checkHeightAndBalance(node.right);
-
- if (leftHeight == Integer.MIN_VALUE || rightHeight == Integer.MIN_VALUE || !(leftHeight - rightHeight <= 1)) {
- return Integer.MIN_VALUE;
- }
-
- return Math.max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1;
- }
-
- public static boolean isBalancedOptimized(TreeNode node) {
- return checkHeightAndBalance(node) != Integer.MIN_VALUE;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- TreeNode treeRoot = new TreeNode(1);
- treeRoot.left = new TreeNode(2);
- treeRoot.right = new TreeNode(3);
- System.out.println("Height: " + height(treeRoot));
- System.out.println("Is Balance: " + isBalanced(treeRoot));
- System.out.println("Is Balance Optimized: " + isBalancedOptimized(treeRoot));
-
- treeRoot = new TreeNode(1);
- treeRoot.left = new TreeNode(2);
- treeRoot.right = new TreeNode(3);
- treeRoot.left.left = new TreeNode(4);
- treeRoot.left.left.left = new TreeNode(5);
- System.out.println("Height: " + height(treeRoot));
- System.out.println("Is Balance: " + isBalanced(treeRoot));
- System.out.println("Is Balance Optimized: " + isBalancedOptimized(treeRoot));
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/ctci/treesandgraphs/CheckSubtree.java b/src/main/java/com/ctci/treesandgraphs/CheckSubtree.java
deleted file mode 100644
index a49f1b74..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/ctci/treesandgraphs/CheckSubtree.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,96 +0,0 @@
-package com.ctci.treesandgraphs;
-
-/**
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-02-24
- */
-public class CheckSubtree {
-
- private static boolean isT2SubtreeOfT1(TreeNode t1, TreeNode t2) {
- if (t1 == null) {
- return false;
- } else if (t2 == null) {
- return true;
- }
-
- if (t1.val == t2.val) {
- if (matchTree(t1, t2)) {
- return true;
- }
- }
- return isT2SubtreeOfT1(t1.left, t2) || isT2SubtreeOfT1(t1.right, t2);
- }
-
- private static boolean matchTree(TreeNode a, TreeNode b) {
- if (a == null && b == null) {
- return true;
- } else if (a == null) {
- return false;
- } else if (b == null) {
- return true;
- } else if (a.val != b.val) {
- return false;
- } else {
- return matchTree(a.left, b.left) && matchTree(a.right, b.right);
- }
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- /*
- The BST looks like:
-
- 4
- / \
- 2 8
- / \ / \
- 1 3 6 9
- /
- 0
-
- */
- TreeNode treeRoot = new TreeNode(4);
- treeRoot.left = new TreeNode(2);
- treeRoot.right = new TreeNode(8);
- treeRoot.left.left = new TreeNode(1);
- treeRoot.left.right = new TreeNode(3);
- treeRoot.left.left.left = new TreeNode(0);
- treeRoot.right.left = new TreeNode(6);
- treeRoot.right.right = new TreeNode(9);
- System.out.println(isT2SubtreeOfT1(treeRoot, treeRoot));
- System.out.println(isT2SubtreeOfT1(treeRoot, treeRoot.left));
- System.out.println(isT2SubtreeOfT1(treeRoot, treeRoot.right));
-
- /*
- The sub-tree:
-
- 8
- /
- 6
- */
- TreeNode treeRoot2 = new TreeNode(8);
- treeRoot2.left = new TreeNode(6);
- System.out.println(isT2SubtreeOfT1(treeRoot, treeRoot2));
-
- /*
- The sub-tree:
-
- 2
- /
- 1
- */
- TreeNode treeRoot3 = new TreeNode(2);
- treeRoot3.left = new TreeNode(1);
- System.out.println(isT2SubtreeOfT1(treeRoot, treeRoot3));
-
- /*
- The sub-tree:
-
- 8
- /
- 9
- */
- TreeNode treeRoot4 = new TreeNode(8);
- treeRoot4.left = new TreeNode(9);
- System.out.println(isT2SubtreeOfT1(treeRoot, treeRoot4));
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/ctci/treesandgraphs/FirstCommonAncestor.java b/src/main/java/com/ctci/treesandgraphs/FirstCommonAncestor.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 38977be3..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/ctci/treesandgraphs/FirstCommonAncestor.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,103 +0,0 @@
-package com.ctci.treesandgraphs;
-
-/**
- * Design an algorithm and write code to find the first common ancestor of two nodes in a binary
- * tree. Avoid storing additional nodes in a data structure. Also, for this question, the tree node
- * does NOT have access to its parent node. NOTE: This is not necessarily a binary search tree.
- *
- * First Common Ancestor or the Least/Lowest Common Ancestor of two nodes is a node which is the
- * closest to both of the nodes.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-02-24
- */
-public class FirstCommonAncestor {
-
- /**
- * We recurse through the entire tree with a function called findFCA(TreeNode root, TreeNode TreeNode a, TreeNode b).
- * This function returns values as follows:
- * - Returns p, if root's subtree includes p (and not q).
- * - Returns q, if root's subtree includes q (and not p).
- * - Returns null, if neither p nor q are in root's subtree.
- * - Else, returns the common ancestor of p and q.
- *
- * See {@link com.rampatra.trees.LeastCommonAncestorInBT} for a better answer.
- *
- * @param root
- * @param a
- * @param b
- * @return the least common ancestor node
- */
- private static TreeNode findFCA(TreeNode root, TreeNode a, TreeNode b) {
- if (root == null) { // validation
- return null;
- }
- if (root == a && root == b) { // optimization
- return root;
- }
-
- TreeNode left = findFCA(root.left, a, b);
- if (left != null && left != a && left != b) {
- return left;
- }
-
- TreeNode right = findFCA(root.right, a, b);
- if (right != null && right != a && right != b) {
- return right;
- }
-
- /* One node is found on the left subtree and other on the
- right one. This means current node is the ancestor. */
- if (left != null && right != null) {
- return root;
- } else if (root == a || root == b) {
- return root;
- } else {
- return left == null ? right : left;
- }
- }
-
- private static class TreeNode {
- int val;
- TreeNode left;
- TreeNode right;
-
- TreeNode(int val) {
- this.val = val;
- }
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- /*
- The binary tree looks like:
-
- 4
- / \
- 5 8
- / \ / \
- 1 3 2 9
- / \
- 0 7
-
- */
- TreeNode treeRoot = new TreeNode(4);
- treeRoot.left = new TreeNode(5);
- treeRoot.right = new TreeNode(8);
- treeRoot.left.left = new TreeNode(1);
- treeRoot.left.right = new TreeNode(3);
- treeRoot.left.left.left = new TreeNode(0);
- treeRoot.right.left = new TreeNode(2);
- treeRoot.right.right = new TreeNode(9);
- treeRoot.right.left.right = new TreeNode(7);
-
- System.out.println("FCA of 0 and 7 is: " + findFCA(treeRoot, treeRoot.left.left.left, treeRoot.right.left.right).val);
- System.out.println("FCA of 0 and 9 is: " + findFCA(treeRoot, treeRoot.left.left.left, treeRoot.right.right).val);
- System.out.println("FCA of 0 and 1 is: " + findFCA(treeRoot, treeRoot.left.left.left, treeRoot.left.left).val);
- System.out.println("FCA of 1 and 2 is: " + findFCA(treeRoot, treeRoot.left.left, treeRoot.right.left).val);
- System.out.println("FCA of 1 and 7 is: " + findFCA(treeRoot, treeRoot.left.left, treeRoot.right.left.right).val);
- System.out.println("FCA of 4 and 7 is: " + findFCA(treeRoot, treeRoot, treeRoot.right.left.right).val);
- System.out.println("FCA of 5 and 2 is: " + findFCA(treeRoot, treeRoot.left, treeRoot.right.left).val);
- System.out.println("FCA of 7 and 9 is: " + findFCA(treeRoot, treeRoot.right.left.right, treeRoot.right.right).val);
- System.out.println("FCA of 7 and 10 is: " + findFCA(treeRoot, treeRoot.right.left.right, new TreeNode(10)).val); // this use case does not work with the above algorithm
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/ctci/treesandgraphs/FirstCommonAncestorWithParentAccess.java b/src/main/java/com/ctci/treesandgraphs/FirstCommonAncestorWithParentAccess.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 5aa453cf..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/ctci/treesandgraphs/FirstCommonAncestorWithParentAccess.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,115 +0,0 @@
-package com.ctci.treesandgraphs;
-
-/**
- * Design an algorithm and write code to find the first common ancestor of two nodes in a binary
- * tree. Avoid storing additional nodes in a data structure. Also, for this question, the tree node
- * has access to its parent node. NOTE: This is not necessarily a binary search tree.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-02-23
- */
-public class FirstCommonAncestorWithParentAccess {
-
- /**
- * This is a simple approach where we start with two references, one pointing to {@code node a} and another
- * pointing to {@code node b}. We move the reference pointing to the deeper node upwards, if required, so that
- * both the references are at the same depth from root. After both the references are at same depth, we simply
- * move both the references upwards until they merge. The node at which they merge is our LCA.
- *
- * @param a
- * @param b
- * @return the least common ancestor node
- */
- private static TreeNode findLCA(TreeNode a, TreeNode b) {
- if (a == null || b == null) {
- return null;
- }
-
- int depthA = depth(a);
- int depthB = depth(b);
- /* be little careful when both nodes are at same depth, have the checks such that
- shallow and deeper references point to different nodes */
- TreeNode shallowNode = depthA < depthB ? a : b;
- TreeNode deeperNode = depthB > depthA ? b : a;
-
- // move deeper node reference upwards so that both the references are at same depth
- deeperNode = goUpBy(deeperNode, Math.abs(depthA - depthB));
-
- while (shallowNode != deeperNode && shallowNode != null && deeperNode != null) {
- shallowNode = shallowNode.parent;
- deeperNode = deeperNode.parent;
- }
-
- return shallowNode;
- }
-
- private static int depth(TreeNode node) {
- int d = 0;
- while (node != null && node.parent != null) {
- d++;
- node = node.parent;
- }
- return d;
- }
-
- private static TreeNode goUpBy(TreeNode node, int levelsUp) {
- int c = 0;
- while (node != null && c < levelsUp) {
- node = node.parent;
- c++;
- }
- return node;
- }
-
- private static class TreeNode {
- int val;
- TreeNode parent;
- TreeNode left;
- TreeNode right;
-
- TreeNode(int val) {
- this.val = val;
- }
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- /*
- The binary tree looks like:
-
- 4
- / \
- 5 8
- / \ / \
- 1 3 2 9
- / \
- 0 7
-
- */
- TreeNode treeRoot = new TreeNode(4);
- treeRoot.left = new TreeNode(5);
- treeRoot.left.parent = treeRoot;
- treeRoot.right = new TreeNode(8);
- treeRoot.right.parent = treeRoot;
- treeRoot.left.left = new TreeNode(1);
- treeRoot.left.left.parent = treeRoot.left;
- treeRoot.left.right = new TreeNode(3);
- treeRoot.left.right.parent = treeRoot.left;
- treeRoot.left.left.left = new TreeNode(0);
- treeRoot.left.left.left.parent = treeRoot.left.left;
- treeRoot.right.left = new TreeNode(2);
- treeRoot.right.left.parent = treeRoot.right;
- treeRoot.right.right = new TreeNode(9);
- treeRoot.right.right.parent = treeRoot.right;
- treeRoot.right.left.right = new TreeNode(7);
- treeRoot.right.left.right.parent = treeRoot.right.left;
-
- System.out.println("FCA of 0 and 7 is: " + findLCA(treeRoot.left.left.left, treeRoot.right.left.right).val);
- System.out.println("FCA of 0 and 9 is: " + findLCA(treeRoot.left.left.left, treeRoot.right.right).val);
- System.out.println("FCA of 0 and 1 is: " + findLCA(treeRoot.left.left.left, treeRoot.left.left).val);
- System.out.println("FCA of 1 and 2 is: " + findLCA(treeRoot.left.left, treeRoot.right.left).val);
- System.out.println("FCA of 1 and 7 is: " + findLCA(treeRoot.left.left, treeRoot.right.left.right).val);
- System.out.println("FCA of 4 and 7 is: " + findLCA(treeRoot, treeRoot.right.left.right).val);
- System.out.println("FCA of 5 and 2 is: " + findLCA(treeRoot.left, treeRoot.right.left).val);
- System.out.println("FCA of 7 and 9 is: " + findLCA(treeRoot.right.left.right, treeRoot.right.right).val);
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/ctci/treesandgraphs/GraphNode.java b/src/main/java/com/ctci/treesandgraphs/GraphNode.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 573cccf3..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/ctci/treesandgraphs/GraphNode.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,17 +0,0 @@
-package com.ctci.treesandgraphs;
-
-import java.util.HashSet;
-import java.util.Set;
-
-/**
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-03-21
- */
-public class GraphNode {
- int value;
- Set adjacent = new HashSet<>();
-
- GraphNode(int value) {
- this.value = value;
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/ctci/treesandgraphs/ListOfDepths.java b/src/main/java/com/ctci/treesandgraphs/ListOfDepths.java
deleted file mode 100644
index fd5287dc..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/ctci/treesandgraphs/ListOfDepths.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,99 +0,0 @@
-package com.ctci.treesandgraphs;
-
-import java.util.ArrayList;
-import java.util.List;
-
-/**
- * Given a binary tree, design an algorithm which creates a linked list of all the nodes
- * at each depth (e.g., if you have a tree with depth D, you'll have D linked lists).
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-02-16
- */
-public class ListOfDepths {
-
- /**
- * This approach visits the root node, adds all its children to a list, then iterates
- * that list, and repeats the same process until all nodes are visited.
- *
- * @param root the root node of the tree
- * @return list of nodes at each depth, where depth starts from 0
- */
- private static List> listOfDepths(TreeNode root) {
- List> listOfDepths = new ArrayList<>();
- List listOfNodesAtCurrentDepth = new ArrayList<>();
-
- if (root != null) {
- listOfNodesAtCurrentDepth.add(root);
- }
-
- while (listOfNodesAtCurrentDepth.size() > 0) {
- listOfDepths.add(listOfNodesAtCurrentDepth); // add current depth
- List listOfNodesAtPreviousDepth = listOfNodesAtCurrentDepth; // make current depth as previous
- /* make current depth as the new depth to be processed considering
- the nodes from the previous depth as parents */
- listOfNodesAtCurrentDepth = new ArrayList<>();
-
- for (TreeNode node : listOfNodesAtPreviousDepth) {
- if (node.left != null) {
- listOfNodesAtCurrentDepth.add(node.left);
- }
- if (node.right != null) {
- listOfNodesAtCurrentDepth.add(node.right);
- }
- }
- }
-
- return listOfDepths;
- }
-
- /**
- * This is a recursive approach where we pass the depth of each node in the call. We use a
- * list {@code listOfDepths} to keep track of all the depths.
- *
- * @param node
- * @param depth
- * @param listOfDepths
- * @return list of nodes at each depth, where depth starts from 0
- */
- private static List> listOfDepths(TreeNode node, int depth, List> listOfDepths) {
- if (node == null) return null;
-
- List listOfNodesAtDepth;
- if (depth == listOfDepths.size()) {
- listOfNodesAtDepth = new ArrayList<>();
- listOfDepths.add(listOfNodesAtDepth);
- } else {
- listOfNodesAtDepth = listOfDepths.get(depth);
- }
-
- listOfNodesAtDepth.add(node);
-
- listOfDepths(node.left, depth + 1, listOfDepths);
- listOfDepths(node.right, depth + 1, listOfDepths);
-
- return listOfDepths;
- }
-
- private static void printAllDepths(List> listOfDepths) {
- for (int i = 0; i < listOfDepths.size(); i++) {
- System.out.print("Depth " + i + ": ");
- listOfDepths.get(i).forEach(node -> System.out.print("->" + node.val));
- System.out.println();
- }
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- TreeNode treeRoot = new TreeNode(1);
- treeRoot.left = new TreeNode(2);
- treeRoot.right = new TreeNode(3);
- treeRoot.left.left = new TreeNode(4);
- treeRoot.left.right = new TreeNode(5);
- treeRoot.right.left = new TreeNode(6);
- treeRoot.right.right = new TreeNode(7);
-
- printAllDepths(listOfDepths(treeRoot));
- System.out.println("-----");
- printAllDepths(listOfDepths(treeRoot, 0, new ArrayList<>()));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/ctci/treesandgraphs/MinimalTree.java b/src/main/java/com/ctci/treesandgraphs/MinimalTree.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 4d18faf7..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/ctci/treesandgraphs/MinimalTree.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,43 +0,0 @@
-package com.ctci.treesandgraphs;
-
-/**
- * Given a sorted (increasing order) array with unique integer elements, write
- * an algorithm to create a binary search tree with minimal height.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-02-15
- */
-public class MinimalTree {
-
- private static TreeNode constructBSTWithMinimalHeight(int[] arr, int start, int end) {
- if (start > end) return null;
-
- int mid = (start + end) / 2;
- TreeNode root = new TreeNode(arr[mid]);
- root.left = constructBSTWithMinimalHeight(arr, start, mid - 1);
- root.right = constructBSTWithMinimalHeight(arr, mid + 1, end);
- return root;
- }
-
- private static void inOrderTraversal(TreeNode node) {
- if (node == null) return;
-
- inOrderTraversal(node.left);
- System.out.print("->" + node.val);
- inOrderTraversal(node.right);
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- TreeNode root = constructBSTWithMinimalHeight(new int[]{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7}, 0, 6);
- inOrderTraversal(root);
- System.out.println();
- root = constructBSTWithMinimalHeight(new int[]{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8}, 0, 7);
- inOrderTraversal(root);
- System.out.println();
- root = constructBSTWithMinimalHeight(new int[]{1, 2}, 0, 1);
- inOrderTraversal(root);
- System.out.println();
- root = constructBSTWithMinimalHeight(new int[]{1}, 0, 0);
- inOrderTraversal(root);
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/ctci/treesandgraphs/RouteBetweenNodes.java b/src/main/java/com/ctci/treesandgraphs/RouteBetweenNodes.java
deleted file mode 100644
index b849b8c8..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/ctci/treesandgraphs/RouteBetweenNodes.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,94 +0,0 @@
-package com.ctci.treesandgraphs;
-
-import java.util.ArrayDeque;
-import java.util.HashMap;
-import java.util.HashSet;
-import java.util.Map;
-import java.util.Queue;
-import java.util.Set;
-
-/**
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-03-21
- */
-public class RouteBetweenNodes {
-
- class Graph {
-
- private final Map nodes = new HashMap<>();
-
- /**
- * Adds an edge from a node with value {@code v1} to another node with value {@code v2}.
- * Note: This code doesn't work for nodes having duplicate values.
- *
- * @param v1
- * @param v2
- */
- void addEdge(int v1, int v2) {
- GraphNode n1 = nodes.get(v1);
- GraphNode n2 = nodes.get(v2);
-
- if (n1 == null) {
- n1 = new GraphNode(v1);
- nodes.put(v1, n1);
- }
- if (n2 == null) {
- n2 = new GraphNode(v2);
- nodes.put(v2, n2);
- }
-
- n1.adjacent.add(n2); // as it is a directed graph
- }
-
- /**
- * Checks for a path from a node with value {@code v1} to another node with value {@code v2} in a breadth-first
- * manner. Note: This code doesn't work for nodes having duplicate values.
- *
- * @param v1 the value of the first node or starting node.
- * @param v2 the value of the ending node.
- * @return {@code true} if path exists, {@code false} otherwise.
- */
- boolean isRoutePresent(int v1, int v2) {
- Queue queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
- Set visited = new HashSet<>();
-
- GraphNode n1 = nodes.get(v1);
- GraphNode n2 = nodes.get(v2);
-
- if (n1 == null || n2 == null) {
- return false;
- }
-
- queue.add(n1);
-
- while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
- GraphNode n = queue.poll();
-
- if (visited.contains(n)) {
- continue;
- }
- if (n.adjacent.contains(n2)) {
- return true;
- }
- queue.addAll(n.adjacent);
- visited.add(n);
- }
-
- return false;
- }
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Graph g = new RouteBetweenNodes().new Graph();
- g.addEdge(1, 2);
- g.addEdge(2, 3);
- g.addEdge(4, 5);
- g.addEdge(5, 6);
- System.out.println("Route exists from 1 to 2: " + g.isRoutePresent(1, 2));
- System.out.println("Route exists from 2 to 5: " + g.isRoutePresent(2, 5));
- System.out.println("Route exists from 1 to 3: " + g.isRoutePresent(1, 3));
- System.out.println("Route exists from 4 to 6: " + g.isRoutePresent(4, 6));
- System.out.println("Route exists from 6 to 4: " + g.isRoutePresent(6, 4));
- System.out.println("Route exists from 6 to 5: " + g.isRoutePresent(6, 5));
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/ctci/treesandgraphs/Successor.java b/src/main/java/com/ctci/treesandgraphs/Successor.java
deleted file mode 100644
index d37488bd..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/ctci/treesandgraphs/Successor.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,98 +0,0 @@
-package com.ctci.treesandgraphs;
-
-/**
- * Write an algorithm to find the "next" node (i.e., in-order successor) of a given node
- * in a binary search tree. You may assume that each node has a link to its parent.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-02-17
- */
-public class Successor {
-
- /**
- * To get the inorder successor what this method does is that it checks if the right child of the input node
- * is null and if not, gets the leftmost child of the right child. And, if the right child of the input
- * node is null, it checks all the parents until it finds the next successor.
- *
- * @param node
- * @return
- */
- private static TreeNode getInOrderSuccessor(TreeNode node) {
- if (node == null) return null;
-
- if (node.right != null) {
- return getLeftmostNode(node.right);
- } else {
- TreeNode curr = node;
-
- while (curr != null) {
- if (curr.parent != null && curr.parent.left == curr) {
- return curr.parent;
- }
- curr = curr.parent;
- }
- }
- return null;
- }
-
- private static TreeNode getLeftmostNode(TreeNode node) {
- TreeNode curr = node;
- while (curr != null && curr.left != null) {
- curr = curr.left;
- }
- return curr;
- }
-
- private static class TreeNode {
- int val;
- TreeNode parent;
- TreeNode left;
- TreeNode right;
-
- TreeNode(int val) {
- this.val = val;
- }
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- /*
- The binary search tree looks like:
-
- 4
- / \
- 2 8
- / \ / \
- 1 3 6 9
- / \
- 0 7
-
- */
- TreeNode treeRoot = new TreeNode(4);
- treeRoot.left = new TreeNode(2);
- treeRoot.left.parent = treeRoot;
- treeRoot.right = new TreeNode(8);
- treeRoot.right.parent = treeRoot;
- treeRoot.left.left = new TreeNode(1);
- treeRoot.left.left.parent = treeRoot.left;
- treeRoot.left.right = new TreeNode(3);
- treeRoot.left.right.parent = treeRoot.left;
- treeRoot.left.left.left = new TreeNode(0);
- treeRoot.left.left.left.parent = treeRoot.left.left;
- treeRoot.right.left = new TreeNode(6);
- treeRoot.right.left.parent = treeRoot.right;
- treeRoot.right.right = new TreeNode(9);
- treeRoot.right.right.parent = treeRoot.right;
- treeRoot.right.left.right = new TreeNode(7);
- treeRoot.right.left.right.parent = treeRoot.right.left;
-
- System.out.println("InOrder successor of 0 is: " + getInOrderSuccessor(treeRoot.left.left.left).val);
- System.out.println("InOrder successor of 1 is: " + getInOrderSuccessor(treeRoot.left.left).val);
- System.out.println("InOrder successor of 2 is: " + getInOrderSuccessor(treeRoot.left).val);
- System.out.println("InOrder successor of 3 is: " + getInOrderSuccessor(treeRoot.left.right).val);
- System.out.println("InOrder successor of 4 is: " + getInOrderSuccessor(treeRoot).val);
- System.out.println("InOrder successor of 6 is: " + getInOrderSuccessor(treeRoot.right.left).val);
- System.out.println("InOrder successor of 7 is: " + getInOrderSuccessor(treeRoot.right.left.right).val);
- System.out.println("InOrder successor of 8 is: " + getInOrderSuccessor(treeRoot.right).val);
- System.out.println("InOrder successor of 9 is: " + getInOrderSuccessor(treeRoot.right.right));
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/ctci/treesandgraphs/TreeNode.java b/src/main/java/com/ctci/treesandgraphs/TreeNode.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 3fe24210..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/ctci/treesandgraphs/TreeNode.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,15 +0,0 @@
-package com.ctci.treesandgraphs;
-
-/**
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-02-15
- */
-public class TreeNode {
- public int val;
- public TreeNode left;
- public TreeNode right;
-
- public TreeNode(int val) {
- this.val = val;
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/ctci/treesandgraphs/ValidateBST.java b/src/main/java/com/ctci/treesandgraphs/ValidateBST.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 0170cdfe..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/ctci/treesandgraphs/ValidateBST.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,101 +0,0 @@
-package com.ctci.treesandgraphs;
-
-import java.util.ArrayList;
-import java.util.List;
-
-/**
- * Implement a function to check if a binary tree is a binary search tree.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-02-17
- */
-public class ValidateBST {
-
- private static boolean isBST(TreeNode node) {
- return isBST(node, new ArrayList<>());
- }
-
- /**
- * This method exploits the fact that the inorder traversal of a binary search tree
- * results in the values being sorted in ascending order. Here, we have used a list
- * but if you see closely we use this list to only compare with the previous element.
- * Ergo, we can use an instance/class variable to store just the last element. This
- * will be a good optimization for space.
- *
- * Time Complexity: O(n) as we touch all the nodes in the tree.
- * Space Complexity: O(n) as we use a list to store all the elements in the tree. If we
- * had used just a instance/class variable, the space complexity would have been O(log n)
- * as there can be up to O(log n) recursive calls as we may recurse up to the depth of
- * the tree. Note, the tree has to balanced though.
- *
- * @param node
- * @param values
- * @return
- */
- private static boolean isBST(TreeNode node, List values) {
- if (node == null) return true;
-
- isBST(node.left, values);
- if (values.isEmpty() || node.val > values.get(values.size() - 1)) {
- values.add(node.val);
- } else {
- return false;
- }
- isBST(node.right, values);
-
- return true;
- }
-
- private static boolean isBSTApproach2(TreeNode node) {
- return isBSTApproach2(node, Integer.MIN_VALUE, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
- }
-
- /**
- * This approach exploits the condition that all left nodes must be less than or equal to
- * the current node, which must be less than all the right nodes.
- *
- * Time Complexity: O(n) as we touch all the nodes in the tree.
- * Space Complexity: O(log n) as there are up to O(log n) recursive calls on the stack
- * as we may recurse up to the depth fo the tree. Note, the tree has to be balanced though.
- *
- * @param node
- * @param min
- * @param max
- * @return
- */
- private static boolean isBSTApproach2(TreeNode node, int min, int max) {
- if (node == null) return true;
-
- if (node.val < min || node.val > max) {
- return false;
- }
-
- return isBSTApproach2(node.left, min, node.val) && isBSTApproach2(node.right, node.val + 1, max);
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- TreeNode treeRoot = new TreeNode(1);
- treeRoot.left = new TreeNode(2);
- treeRoot.right = new TreeNode(3);
- System.out.println("Is BST Approach 1: " + isBST(treeRoot));
- System.out.println("Is BST Approach 2: " + isBSTApproach2(treeRoot));
-
- treeRoot = new TreeNode(2);
- treeRoot.left = new TreeNode(1);
- treeRoot.right = new TreeNode(3);
- System.out.println("Is BST Approach 1: " + isBST(treeRoot));
- System.out.println("Is BST Approach 2: " + isBSTApproach2(treeRoot));
-
- treeRoot = new TreeNode(4);
- treeRoot.left = new TreeNode(2);
- treeRoot.right = new TreeNode(8);
- treeRoot.left.left = new TreeNode(1);
- treeRoot.left.right = new TreeNode(3);
- treeRoot.left.left.left = new TreeNode(0);
- treeRoot.right.left = new TreeNode(6);
- treeRoot.right.right = new TreeNode(9);
- treeRoot.right.left.right = new TreeNode(7);
- System.out.println("Is BST Approach 1: " + isBST(treeRoot));
- System.out.println("Is BST Approach 2: " + isBSTApproach2(treeRoot));
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/design/LRUCache.java b/src/main/java/com/design/LRUCache.java
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..3b18ee23
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/com/design/LRUCache.java
@@ -0,0 +1,92 @@
+package com.design;
+
+import com.linkedlist.model.DoublyLLNode;
+
+import java.util.HashMap;
+
+/**
+ * Design and implement a data structure for Least Recently Used (LRU) cache, which supports get and put.
+ * The key to solve this problem is using a double linked list which enables us to quickly move nodes.
+ *
+ * The LRU cache is a hash table of keys and double linked nodes.
+ * The hash table makes the time of get() to be O(1). The list of double linked nodes make the nodes adding/removal operations O(1).
+ *
+ * By analyzing the get and put, we can summarize there are 2 basic operations:
+ * 1) removeNode(Node t), 2) offerNode(Node t).
+ *
+ */
+class LRUCache {
+ DoublyLLNode head;
+ DoublyLLNode tail;
+ HashMap map = null;
+ int cap = 0;
+
+ public LRUCache(int capacity) {
+ this.cap = capacity;
+ this.map = new HashMap<>();
+ }
+
+ public int get(int key) {
+ if(map.get(key)==null){
+ return -1;
+ }
+
+ //move to tail
+ DoublyLLNode t = map.get(key);
+
+ removeDoublyLLNode(t);
+ offerDoublyLLNode(t);
+
+ return t.value;
+ }
+
+ public void put(int key, int value) {
+ if(map.containsKey(key)){
+ DoublyLLNode t = map.get(key);
+ t.value = value;
+
+ //move to tail
+ removeDoublyLLNode(t);
+ offerDoublyLLNode(t);
+ }else{
+ if(map.size()>=cap){
+ //delete head
+ map.remove(head.key);
+ removeDoublyLLNode(head);
+ }
+
+ //add to tail
+ DoublyLLNode DoublyLLNode = new DoublyLLNode(key, value);
+ offerDoublyLLNode(DoublyLLNode);
+ map.put(key, DoublyLLNode);
+ }
+ }
+
+ private void removeDoublyLLNode(DoublyLLNode n){
+ if(n.prev!=null){
+ n.prev.next = n.next;
+ }else{
+ head = n.next;
+ }
+
+ if(n.next!=null){
+ n.next.prev = n.prev;
+ }else{
+ tail = n.prev;
+ }
+ }
+
+ private void offerDoublyLLNode(DoublyLLNode n){
+ if(tail!=null){
+ tail.next = n;
+ }
+
+ n.prev = tail;
+ n.next = null;
+ tail = n;
+
+ if(head == null){
+ head = tail;
+ }
+ }
+}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/design/LowLevelDesign.java b/src/main/java/com/design/LowLevelDesign.java
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..11059607
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/com/design/LowLevelDesign.java
@@ -0,0 +1,79 @@
+package com.design;
+
+import javax.jms.Message;
+import javax.jms.MessageListener;
+import javax.jms.TextMessage;
+
+/**
+ * This design uses Strategy Pattern
+ *
+ * Strategy pattern and the open closed principle
+ * According to the strategy pattern, the behaviour of a class should be encapsulated
+ * using interfaces and should not be inherited.
+ * This is compatible with the open closed principle,
+ */
+
+public class LowLevelDesign {
+
+ MessageProcessor processor;
+
+ class MessageConsumer implements MessageListener{
+
+ @JMSListener
+ public void onMessage(Message message){
+ if (message instanceof TextMessage){
+ processor = new MessageProcessor();
+ MessageParser mp = new swiftParser();
+ processor.setParser(mp);
+ processor.process(message);
+ }
+ if (message instanceof BytesMessage){
+
+ }
+
+
+ }
+
+ }
+
+ class MessageProcessor {
+
+ MessageParser parser;
+
+ public void setParser(MessageParser p){
+ this.parser = p;
+ }
+
+ public void process(Message message){
+ parser.parse(message);
+ }
+
+ }
+
+ interface MessageParser{
+ void parse(Message message);
+ }
+
+ class SwiftParser implements MessageParser{
+
+ @Override
+ public void parse(Message message) {
+
+ }
+ }
+ class JsonParser implements MessageParser{
+
+ @Override
+ public void parse(Message message) {
+
+ }
+ }
+ class XMLParser implements MessageParser{
+
+ @Override
+ public void parse(Message message) {
+
+ }
+ }
+
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/design/OnlineBookingSystem.java b/src/main/java/com/design/OnlineBookingSystem.java
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..b80ebe6f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/com/design/OnlineBookingSystem.java
@@ -0,0 +1,99 @@
+package com.design;
+
+// Java code skeleton to design an online hotel
+// booking system.
+
+enum RoomStatus {
+ EMPTY,
+ NOT_EMPTY;
+ }
+
+enum RoomType {
+ SINGLE,
+ DOUBLE,
+ TRIPLE;
+}
+
+enum PaymentStatus {
+ PAID,
+ UNPAID;
+}
+
+public enum Facility {
+ LIFT;
+ POWER_BACKUP;
+ HOT_WATERR;
+ BREAKFAST_FREE;
+ SWIMMING_POOL;
+}
+
+class User {
+
+ int userId;
+ String name;
+ Date dateOfBirth;
+ String mobNo;
+ String emailId;
+ String sex;
+}
+
+// For the room in any hotel
+class Room {
+
+ int roomId; // roomNo
+ int hotelId;
+ RoomType roomType;
+ RoomStatus roomStatus;
+}
+
+class Hotel {
+
+ int hotelId;
+ String hotelName;
+ Adress adress;
+
+ // hotel contains the list of rooms
+ List rooms;
+ float rating;
+ Facilities facilities;
+}
+
+// a new booking is created for each booking
+// done by any user
+class Booking {
+ int bookingId;
+ int userId;
+ int hotelId;
+
+ // We are assuming that in a single
+ // booking we can book only the rooms
+ // of a single hotel
+ List bookedRooms;
+
+ int amount;
+ PaymentStatus status_of_payment;
+ Date bookingTime;
+ Duration duration;
+}
+
+class Address {
+
+ String city;
+ String pinCode;
+ String state;
+ String streetNo;
+ String landmark;
+}
+
+class Duration {
+
+ Date from;
+ Date to;
+
+}
+
+class Facilities {
+
+ List facilitiesList;
+}
+
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/design/OnlineReaderSystem.java b/src/main/java/com/design/OnlineReaderSystem.java
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..20ede4d3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/com/design/OnlineReaderSystem.java
@@ -0,0 +1,372 @@
+package com.design;
+
+import java.util.HashMap;
+
+/*
+ * This class represents the system
+ */
+
+class OnlineReaderSystem {
+ private Library library;
+ private UserManager userManager;
+ private Display display;
+ private Book activeBook;
+ private User activeUser;
+
+ public OnlineReaderSystem()
+ {
+ userManager = new UserManager();
+ library = new Library();
+ display = new Display();
+ }
+
+ public Library getLibrary()
+ {
+ return library;
+ }
+
+ public UserManager getUserManager()
+ {
+ return userManager;
+ }
+
+ public Display getDisplay()
+ {
+ return display;
+ }
+
+ public Book getActiveBook()
+ {
+ return activeBook;
+ }
+
+ public void setActiveBook(Book book)
+ {
+ activeBook = book;
+ display.displayBook(book);
+ }
+
+ public User getActiveUser()
+ {
+ return activeUser;
+ }
+
+ public void setActiveUser(User user)
+ {
+ activeUser = user;
+ display.displayUser(user);
+ }
+}
+
+/*
+ * We then implement separate classes to handle the user
+ * manager, the library, and the display components
+ */
+
+/*
+ * This class represents the Library which is responsible
+ * for storing and searching the books.
+ */
+class Library {
+ private HashMap books;
+
+ public Library()
+ {
+ books = new HashMap();
+ }
+
+ public Boolean addBook(int id, String details, String title)
+ {
+ if (books.containsKey(id)) {
+ return false;
+ }
+ Book book = new Book(id, details, title);
+ books.put(id, book);
+ return true;
+ }
+
+ public Boolean addBook(Book book)
+ {
+ if (books.containsKey(book.getId())) {
+ return false;
+ }
+
+ books.put(book.getId(), book);
+ return true;
+ }
+
+ public boolean remove(Book b)
+ {
+ return remove(b.getId());
+ }
+
+ public boolean remove(int id)
+ {
+ if (!books.containsKey(id)) {
+ return false;
+ }
+ books.remove(id);
+ return true;
+ }
+
+ public Book find(int id)
+ {
+ return books.get(id);
+ }
+}
+
+/*
+ * This class represents the UserManager which is responsible
+ * for managing the users, their membership etc.
+ */
+
+class UserManager {
+ private HashMap users;
+
+ public UserManager()
+ {
+ users = new HashMap();
+ }
+ public Boolean addUser(int id, String details, String name)
+ {
+ if (users.containsKey(id)) {
+ return false;
+ }
+ User user = new User(id, details, name);
+ users.put(id, user);
+ return true;
+ }
+
+ public Boolean addUser(User user)
+ {
+ if (users.containsKey(user.getId())) {
+ return false;
+ }
+
+ users.put(user.getId(), user);
+ return true;
+ }
+
+ public boolean remove(User u)
+ {
+ return remove(u.getId());
+ }
+
+ public boolean remove(int id)
+ {
+ if (users.containsKey(id)) {
+ return false;
+ }
+ users.remove(id);
+ return true;
+ }
+
+ public User find(int id)
+ {
+ return users.get(id);
+ }
+}
+
+/*
+ * This class represents the Display, which is responsible
+ * for displaying the book, it's pages and contents. It also
+ * shows the current user. * It provides the method
+ * turnPageForward, turnPageBackward, refreshPage etc.
+ */
+
+class Display {
+ private Book activeBook;
+ private User activeUser;
+ private int pageNumber = 0;
+
+ public void displayUser(User user)
+ {
+ activeUser = user;
+ refreshUsername();
+ }
+
+ public void displayBook(Book book)
+ {
+ pageNumber = 0;
+ activeBook = book;
+
+ refreshTitle();
+ refreshDetails();
+ refreshPage();
+ }
+
+ public void turnPageForward()
+ {
+ pageNumber++;
+ System.out.println("Turning forward to page no " +
+ pageNumber + " of book having title " +
+ activeBook.getTitle());
+ refreshPage();
+ }
+
+ public void turnPageBackward()
+ {
+ pageNumber--;
+ System.out.println("Turning backward to page no " +
+ pageNumber + " of book having title " +
+ activeBook.getTitle());
+ refreshPage();
+ }
+
+ public void refreshUsername()
+ {
+ /* updates username display */
+ System.out.println("User name " + activeUser.getName() +
+ " is refreshed");
+ }
+
+ public void refreshTitle()
+ {
+ /* updates title display */
+ System.out.println("Title of the book " +
+ activeBook.getTitle() + " refreshed");
+ }
+
+ public void refreshDetails()
+ {
+ /* updates details display */
+ System.out.println("Details of the book " +
+ activeBook.getTitle() + " refreshed");
+ }
+
+ public void refreshPage()
+ {
+ /* updated page display */
+ System.out.println("Page no " + pageNumber + " refreshed");
+ }
+}
+
+/*
+ * The classes for User and Book simply hold data and
+ * provide little functionality.
+ * This class represents the Book which is a simple POJO
+ */
+
+class Book {
+ private int bookId;
+ private String details;
+ private String title;
+
+ public Book(int id, String details, String title)
+ {
+ bookId = id;
+ this.details = details;
+ this.title = title;
+ }
+
+ public int getId()
+ {
+ return bookId;
+ }
+
+ public void setId(int id)
+ {
+ bookId = id;
+ }
+
+ public String getDetails()
+ {
+ return details;
+ }
+
+ public void setDetails(String details)
+ {
+ this.details = details;
+ }
+
+ public String getTitle()
+ {
+ return title;
+ }
+
+ public void setTitle(String title)
+ {
+ this.title = title;
+ }
+}
+
+/*
+ * This class represents the User which is a simple POJO
+ */
+
+class User {
+ private int userId;
+ private String name;
+ private String details;
+
+ public void renewMembership()
+ {
+ }
+
+ public User(int id, String details, String name)
+ {
+ this.userId = id;
+ this.details = details;
+ this.name = name;
+ }
+
+ public int getId()
+ {
+ return userId;
+ }
+
+ public void setId(int id)
+ {
+ userId = id;
+ }
+
+ public String getDetails()
+ {
+ return details;
+ }
+
+ public void setDetails(String details)
+ {
+ this.details = details;
+ }
+
+ public String getName()
+ {
+ return name;
+ }
+
+ public void setName(String name)
+ {
+ this.name = name;
+ }
+}
+
+// This class is used to test the Application
+
+public class AppTest {
+
+ public static void main(String[] args)
+ {
+
+ OnlineReaderSystem onlineReaderSystem = new OnlineReaderSystem();
+
+ Book dsBook = new Book(1, "It contains Data Structures", "Ds");
+ Book algoBook = new Book(2, "It contains Algorithms", "Algo");
+
+ onlineReaderSystem.getLibrary().addBook(dsBook);
+ onlineReaderSystem.getLibrary().addBook(algoBook);
+
+ User user1 = new User(1, " ", "Ram");
+ User user2 = new User(2, " ", "Gopal");
+
+ onlineReaderSystem.getUserManager().addUser(user1);
+ onlineReaderSystem.getUserManager().addUser(user2);
+
+ onlineReaderSystem.setActiveBook(algoBook);
+ onlineReaderSystem.setActiveUser(user1);
+
+ onlineReaderSystem.getDisplay().turnPageForward();
+ onlineReaderSystem.getDisplay().turnPageForward();
+ onlineReaderSystem.getDisplay().turnPageBackward();
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/graph/DijkstraShortestPath.java b/src/main/java/com/graph/DijkstraShortestPath.java
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..78e9020d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/com/graph/DijkstraShortestPath.java
@@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
+//package com.graph;
+//
+//public class DijkstraShortestPath {
+//
+//
+// public static void main(String args[]){
+// Graph graph = new Graph<>(false);
+// /*graph.addEdge(0, 1, 4);
+// graph.addEdge(1, 2, 8);
+// graph.addEdge(2, 3, 7);
+// graph.addEdge(3, 4, 9);
+// graph.addEdge(4, 5, 10);
+// graph.addEdge(2, 5, 4);
+// graph.addEdge(1, 7, 11);
+// graph.addEdge(0, 7, 8);
+// graph.addEdge(2, 8, 2);
+// graph.addEdge(3, 5, 14);
+// graph.addEdge(5, 6, 2);
+// graph.addEdge(6, 8, 6);
+// graph.addEdge(6, 7, 1);
+// graph.addEdge(7, 8, 7);*/
+//
+// graph.addEdge(1, 2, 5);
+// graph.addEdge(2, 3, 2);
+// graph.addEdge(1, 4, 9);
+// graph.addEdge(1, 5, 3);
+// graph.addEdge(5, 6, 2);
+// graph.addEdge(6, 4, 2);
+// graph.addEdge(3, 4, 3);
+//
+// DijkstraShortestPath dsp = new DijkstraShortestPath();
+// Vertex sourceVertex = graph.getVertex(1);
+// Map,Integer> distance = dsp.shortestPath(graph, sourceVertex);
+// System.out.print(distance);
+// }
+//}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/arraysandsorting/InsertionSort1.java b/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/arraysandsorting/InsertionSort1.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 6fd03542..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/arraysandsorting/InsertionSort1.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,48 +0,0 @@
-package com.hackerrank.algorithms.arraysandsorting;
-
-import java.util.Scanner;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- * User: rampatra
- * Date: 3/1/15
- * Time: 8:58 PM
- * To change this template go to Preferences | IDE Settings | File and Code Templates
- */
-public class InsertionSort1 {
-
- static void insertIntoSorted(int[] ar) {
- int V = ar[ar.length - 1], i = ar.length - 2;
-
- for (; i >= 0; i--) {
- if (V < ar[i]) {
- ar[i + 1] = ar[i];
- } else {
- break;
- }
- printArray(ar);
- }
-
- ar[i + 1] = V;
- printArray(ar);
- }
-
- /* Tail starts here */
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
- int s = in.nextInt();
- int[] ar = new int[s];
- for (int i = 0; i < s; i++) {
- ar[i] = in.nextInt();
- }
- insertIntoSorted(ar);
- }
-
- private static void printArray(int[] ar) {
- for (int n : ar) {
- System.out.print(n + " ");
- }
- System.out.println("");
- }
-
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/arraysandsorting/InsertionSort2.java b/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/arraysandsorting/InsertionSort2.java
deleted file mode 100644
index cd710eb9..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/arraysandsorting/InsertionSort2.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,46 +0,0 @@
-package com.hackerrank.algorithms.arraysandsorting;
-
-import java.util.Scanner;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- * User: rampatra
- * Date: 3/1/15
- * Time: 9:42 PM
- * To change this template go to Preferences | IDE Settings | File and Code Templates
- */
-public class InsertionSort2 {
-
- static void insertionSortPart2(int[] ar) {
- for (int i = 1; i < ar.length; i++) {
- int V = ar[i], j;
- /**
- * keep shifting no.s to right until
- * right place for insertion(of V) is found
- */
- for (j = i - 1; j >= 0 && ar[j] > V; j--) {
- ar[j + 1] = ar[j];
- }
- ar[j + 1] = V;
- printArray(ar);
- }
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
- int s = in.nextInt();
- int[] ar = new int[s];
- for (int i = 0; i < s; i++) {
- ar[i] = in.nextInt();
- }
- insertionSortPart2(ar);
-
- }
-
- private static void printArray(int[] ar) {
- for (int n : ar) {
- System.out.print(n + " ");
- }
- System.out.println("");
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/arraysandsorting/IntroTutorial.java b/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/arraysandsorting/IntroTutorial.java
deleted file mode 100644
index aeb8ea5f..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/arraysandsorting/IntroTutorial.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,35 +0,0 @@
-package com.hackerrank.algorithms.arraysandsorting;
-
-import java.util.Arrays;
-import java.util.Scanner;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- * User: rampatra
- * Date: 3/1/15
- * Time: 3:38 PM
- * To change this template go to Preferences | IDE Settings | File and Code Templates
- */
-public class IntroTutorial {
- static int search(int searchVal, int[] arr) {
- return Arrays.binarySearch(arr, searchVal);
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
-
- int searchVal = in.nextInt();
- int arrSize = in.nextInt();
- int[] arr = new int[arrSize];
- // as nextInt() doesn't read new line character
- in.nextLine();
- String next = in.nextLine();
- String[] next_split = next.split(" ");
-
- for (int _a_i = 0; _a_i < arrSize; _a_i++) {
- arr[_a_i] = Integer.parseInt(next_split[_a_i]);
- }
-
- System.out.print(search(searchVal, arr));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/arraysandsorting/LoopInvariant.java b/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/arraysandsorting/LoopInvariant.java
deleted file mode 100644
index dd12ee7e..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/arraysandsorting/LoopInvariant.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,44 +0,0 @@
-package com.hackerrank.algorithms.arraysandsorting;
-
-import java.util.Scanner;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- * User: rampatra
- * Date: 3/2/15
- * Time: 3:26 PM
- * To change this template go to Preferences | IDE Settings | File and Code Templates
- */
-public class LoopInvariant {
-
- public static void insertionSort(int[] A) {
- for (int i = 1; i < A.length; i++) {
- int value = A[i];
- int j = i - 1;
- while (j >= 0 && A[j] > value) {
- A[j + 1] = A[j];
- j = j - 1;
- }
- A[j + 1] = value;
- }
-
- printArray(A);
- }
-
-
- static void printArray(int[] ar) {
- for (int n : ar) {
- System.out.print(n + " ");
- }
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
- int n = in.nextInt();
- int[] ar = new int[n];
- for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
- ar[i] = in.nextInt();
- }
- insertionSort(ar);
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/arraysandsorting/QuickSort1.java b/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/arraysandsorting/QuickSort1.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 0753f812..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/arraysandsorting/QuickSort1.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,43 +0,0 @@
-package com.hackerrank.algorithms.arraysandsorting;
-
-import java.util.Scanner;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- * User: rampatra
- * Date: 3/2/15
- * Time: 5:13 PM
- * To change this template go to Preferences | IDE Settings | File and Code Templates
- */
-public class QuickSort1 {
-
- static void partition(int[] ar) {
- int pivot = ar[0], j = 0;
- int[] arCopy = ar.clone();
-
- for (int i = 0; i < arCopy.length; i++) {
- if (arCopy[i] < pivot) ar[j++] = arCopy[i];
- }
- for (int i = 0; i < arCopy.length; i++) {
- if (arCopy[i] >= pivot) ar[j++] = arCopy[i];
- }
- printArray(ar);
- }
-
- static void printArray(int[] ar) {
- for (int n : ar) {
- System.out.print(n + " ");
- }
- System.out.println("");
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
- int n = in.nextInt();
- int[] ar = new int[n];
- for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
- ar[i] = in.nextInt();
- }
- partition(ar);
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/arraysandsorting/QuickSort2.java b/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/arraysandsorting/QuickSort2.java
deleted file mode 100644
index b9b1dcba..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/arraysandsorting/QuickSort2.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,62 +0,0 @@
-package com.hackerrank.algorithms.arraysandsorting;
-
-import java.util.Scanner;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- * User: rampatra
- * Date: 3/3/15
- * Time: 1:05 PM
- * To change this template go to Preferences | IDE Settings | File and Code Templates
- */
-public class QuickSort2 {
-
- static int partition(int[] a, int start, int end) {
-
- int pivot = start, temp;
-
- for (int i = start + 1; i <= end; i++) {
- // maintains the relative positioning of elements in each partition
- if (a[i] < a[pivot]) {
- start++;
- temp = a[i];
- int j;
- for (j = i; j > start; j--) {
- a[j] = a[j - 1];
- }
- a[j] = temp;
- }
- }
-
- temp = a[pivot];
- while (pivot < start) {
- a[pivot] = a[pivot + 1];
- pivot++;
- }
- a[pivot] = temp;
-
- return pivot;
- }
-
- static void quickSort(int[] ar, int start, int end) {
- if (start < end) {
- int p = partition(ar, start, end);
- quickSort(ar, start, p - 1);
- quickSort(ar, p + 1, end);
- for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) {
- System.out.print(ar[i] + " ");
- }
- System.out.println();
- }
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
- int n = in.nextInt();
- int[] ar = new int[n];
- for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
- ar[i] = in.nextInt();
- }
- quickSort(ar, 0, n - 1);
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/arraysandsorting/RunningTime.java b/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/arraysandsorting/RunningTime.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 27a0bd77..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/arraysandsorting/RunningTime.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,43 +0,0 @@
-package com.hackerrank.algorithms.arraysandsorting;
-
-import java.util.Scanner;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- * User: rampatra
- * Date: 3/2/15
- * Time: 5:02 PM
- * To change this template go to Preferences | IDE Settings | File and Code Templates
- */
-public class RunningTime {
- static void insertionSortPart2(int[] ar) {
- int c = 0;
- for (int i = 1; i < ar.length; i++) {
- int V = ar[i], j;
- for (j = i - 1; j >= 0 && ar[j] > V; j--, c++) {
- ar[j + 1] = ar[j];
- }
- ar[j + 1] = V;
- //printArray(ar);
- }
- System.out.print(c);
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
- int s = in.nextInt();
- int[] ar = new int[s];
- for (int i = 0; i < s; i++) {
- ar[i] = in.nextInt();
- }
- insertionSortPart2(ar);
-
- }
-
- private static void printArray(int[] ar) {
- for (int n : ar) {
- System.out.print(n + " ");
- }
- System.out.println("");
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/implementation/CavityMap.java b/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/implementation/CavityMap.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 0bc4a052..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/implementation/CavityMap.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,30 +0,0 @@
-package com.hackerrank.algorithms.implementation;
-
-import java.util.Scanner;
-
-/**
- * Created by rampatra on 08/05/2016.
- */
-public class CavityMap {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
- int n = in.nextInt();
- String grid[] = new String[n];
- for (int grid_i = 0; grid_i < n; grid_i++) {
- grid[grid_i] = in.next();
- }
- for (int i = 1; i < n - 1; i++) {
- for (int j = 1; j < n - 1; j++) {
- if (Character.getNumericValue(grid[i].charAt(j)) > Character.getNumericValue(grid[i].charAt(j - 1))
- && Character.getNumericValue(grid[i].charAt(j)) > Character.getNumericValue(grid[i].charAt(j + 1))
- && Character.getNumericValue(grid[i].charAt(j)) > Character.getNumericValue(grid[i - 1].charAt(j))
- && Character.getNumericValue(grid[i].charAt(j)) > Character.getNumericValue(grid[i + 1].charAt(j))) {
- grid[i] = grid[i].substring(0, j) + "X" + grid[i].substring(j + 1);
- }
- }
- }
- for (int grid_i = 0; grid_i < n; grid_i++) {
- System.out.println(grid[grid_i]);
- }
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/implementation/ExtraLongFactorials.java b/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/implementation/ExtraLongFactorials.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 230a18aa..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/implementation/ExtraLongFactorials.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,19 +0,0 @@
-package com.hackerrank.algorithms.implementation;
-
-import java.math.BigInteger;
-import java.util.Scanner;
-
-/**
- * Created by rampatra on 29/05/2016.
- */
-public class ExtraLongFactorials {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
- int n = in.nextInt();
- BigInteger res = BigInteger.ONE;
- for (int i = n; i > 0; i--) {
- res = res.multiply(BigInteger.valueOf(i));
- }
- System.out.println(res);
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/implementation/GridSearch.java b/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/implementation/GridSearch.java
deleted file mode 100644
index a317913c..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/implementation/GridSearch.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,68 +0,0 @@
-package com.hackerrank.algorithms.implementation;
-
-import java.util.Scanner;
-
-/**
- * Created by rampatra on 02/05/2016.
- */
-public class GridSearch {
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
- int t = in.nextInt();
- for (int a0 = 0; a0 < t; a0++) {
- int R = in.nextInt();
- int C = in.nextInt();
- String G[] = new String[R];
- for (int G_i = 0; G_i < R; G_i++) {
- G[G_i] = in.next();
- }
- int r = in.nextInt();
- int c = in.nextInt();
- String P[] = new String[r];
- for (int P_i = 0; P_i < r; P_i++) {
- P[P_i] = in.next();
- }
-
- // create 2D array for grid
- int grid[][] = new int[R][C];
- for (int i = 0; i < R; i++) {
- for (int j = 0; j < C; j++) {
- grid[i][j] = Character.getNumericValue(G[i].charAt(j));
- }
- }
-
- // create 2D array for pattern to be searched in grid
- int pattern[][] = new int[r][c];
- for (int i = 0; i < r; i++) {
- for (int j = 0; j < c; j++) {
- pattern[i][j] = Character.getNumericValue(P[i].charAt(j));
- }
- }
-
- // search logic
- outerLoop:
- for (int G_i = 0; G_i < R; G_i++) {
- for (int G_j = 0; G_j < C; G_j++) {
- innerLoop:
- for (int P_i = 0; P_i < r && G_i + P_i < R; P_i++) {
- for (int P_j = 0; P_j < c && G_j + P_j < C; P_j++) {
- if (grid[G_i + P_i][G_j + P_j] != pattern[P_i][P_j]) {
- break innerLoop;
- } else if (P_i == r - 1 && P_j == c - 1) {
- System.out.println("YES");
- break outerLoop;
- }
- }
-
- }
- if (R - G_i < r) { // no. of rows left in grid less than no. of rows in pattern
- System.out.println("NO");
- break outerLoop;
- }
- }
- }
- }
- }
-}
-
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/implementation/TheTimeInWords.java b/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/implementation/TheTimeInWords.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 4915014b..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/implementation/TheTimeInWords.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,38 +0,0 @@
-package com.hackerrank.algorithms.implementation;
-
-import java.util.Scanner;
-
-/**
- * Created by rampatra on 29/05/2016.
- */
-public class TheTimeInWords {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
- int h = in.nextInt();
- int m = in.nextInt();
- String timeInWords;
- String[] words = {"", "one", "two", "three", "four", "five", "six", "seven", "eight", "nine", "ten",
- "eleven", "twelve", "thirteen", "fourteen", "fifteen", "sixteen", "seventeen", "eighteen",
- "nineteen", "twenty", "twenty one", "twenty two", "twenty three", "twenty four", "twenty five", "twenty six",
- "twenty seven", "twenty eight", "twenty nine"};
-
- if (m == 0) {
- timeInWords = words[h] + " o' clock";
- } else if (m == 1) {
- timeInWords = words[m] + " minute past " + words[h];
- } else if (m == 15) {
- timeInWords = "quarter past " + words[h];
- } else if (m < 30) {
- timeInWords = words[m] + " minutes past " + words[h];
- } else if (m == 30) {
- timeInWords = "half past " + words[h];
- } else if (m == 45) {
- timeInWords = "quarter to " + words[(h == 12) ? h - 11 : h + 1];
- } else if (60 - m == 1) {
- timeInWords = words[60 - m] + " minute to " + words[(h == 12) ? h - 11 : h + 1];
- } else {
- timeInWords = words[60 - m] + " minutes to " + words[(h == 12) ? h - 11 : h + 1];
- }
- System.out.println(timeInWords);
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/recursion/RecursiveDigitSum.java b/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/recursion/RecursiveDigitSum.java
deleted file mode 100644
index cd9cae21..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/recursion/RecursiveDigitSum.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,60 +0,0 @@
-package com.hackerrank.algorithms.recursion;
-
-import java.io.BufferedWriter;
-import java.io.FileWriter;
-import java.io.IOException;
-import java.util.Scanner;
-
-/**
- * Recursive Digit Sum Problem.
- *
- * @link https://www.hackerrank.com/challenges/recursive-digit-sum/problem
- * @author rpatra16
- * @since 06/11/2018
- */
-public class RecursiveDigitSum {
-
- /**
- * Finds the recursive digit sum of n.
- *
- * @param n number
- * @param k the number would be repeated k times
- * @return recursive sum of the digits
- */
- private static int superDigit(String n, int k) {
- if (n.length() == 1 && k == 0) {
- return Integer.parseInt(n);
- }
-
- Long sum = 0L;
- char[] num = n.toCharArray();
- for (int i = 0; i < num.length; i++) {
- sum += Long.parseLong(String.valueOf(num[i]));
- }
-
- if (k != 0) sum *= k;
-
- return superDigit(sum.toString(), 0);
- }
-
- private static final Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
-
- public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
- BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(System.getenv("OUTPUT_PATH")));
-
- String[] nk = scanner.nextLine().split(" ");
-
- String n = nk[0];
-
- int k = Integer.parseInt(nk[1]);
-
- int result = superDigit(n, k);
-
- bufferedWriter.write(String.valueOf(result));
- bufferedWriter.newLine();
-
- bufferedWriter.close();
-
- scanner.close();
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/strings/AlternatingCharacters.java b/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/strings/AlternatingCharacters.java
deleted file mode 100644
index c81f5c22..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/strings/AlternatingCharacters.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,37 +0,0 @@
-package com.hackerrank.algorithms.strings;
-
-import java.util.Scanner;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 10/22/15
- * @time: 9:24 AM
- */
-public class AlternatingCharacters {
-
- public static int countDeletions(String s) {
- int count = 0, index = 0;
- for (int i = 1; i < s.length(); i++) {
- if (s.charAt(i) == s.charAt(index)) {
- count++;
- } else {
- index = i;
- }
- }
- return count;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
- int t = Integer.parseInt(in.nextLine());
- String[] input = new String[t];
- for (int i = 0; i < t; i++) {
- input[i] = in.nextLine();
- }
- for (int i = 0; i < t; i++) {
- System.out.println(countDeletions(input[i]));
- }
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/strings/MakingAnagrams.java b/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/strings/MakingAnagrams.java
deleted file mode 100644
index b218c04e..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/strings/MakingAnagrams.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,53 +0,0 @@
-package com.hackerrank.algorithms.strings;
-
-import java.util.Arrays;
-
-/**
- * @author rampatra
- * @version 28/09/2016
- */
-public class MakingAnagrams {
-
- /**
- * Find number of characters to be deleted to make {@param a}
- * and {@param b} anagrams.
- * See: https://www.hackerrank.com/challenges/making-anagrams
- *
- * @param a
- * @param b
- * @return
- */
- public static int makeAnagrams(String a, String b) {
-
- int i = 0, j = 0, c = 0;
- char[] s1 = a.toCharArray();
- char[] s2 = b.toCharArray();
- Arrays.sort(s1);
- Arrays.sort(s2);
-
- while (i < s1.length || j < s2.length) {
- if (i >= s1.length) {
- c++;
- j++;
- } else if (j >= s2.length) {
- c++;
- i++;
- } else if (s1[i] < s2[j]) {
- c++;
- i++;
- } else if (s1[i] > s2[j]) {
- c++;
- j++;
- } else {
- i++;
- j++;
- }
- }
-
- return c;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(makeAnagrams("abc", "cde"));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/strings/PalindromeIndex.java b/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/strings/PalindromeIndex.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 294c4dd2..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/strings/PalindromeIndex.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,54 +0,0 @@
-package com.hackerrank.algorithms.strings;
-
-import java.util.Scanner;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- * User: rampatra
- * Date: 3/18/15
- * Time: 12:27 PM
- * To change this template go to Preferences | IDE Settings | File and Code Templates
- */
-public class PalindromeIndex {
-
- static int makePalindrome(String s) {
- int index = -1, l = s.length();
- if (isPalindrome(s)) {
- return -1;
- }
- for (int i = 0; i < l; i++) {
- StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(s);
- sb.deleteCharAt(i);
- String str = sb.toString();
- if (isPalindrome(str)) {
- return i;
- }
- }
- return index;
- }
-
- static boolean isPalindrome(String s) {
- int l = s.length(), i, j;
- for (i = 0, j = l - 1; i < l / 2; i++, j--) {
- if ((int) s.charAt(i) != (int) s.charAt(j)) {
- return false;
- }
- }
- return true;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
-
- int t = in.nextInt();
- String s[] = new String[t];
-
- for (int i = 0; i < t; i++) {
- s[i] = in.next();
- }
-
- for (int i = 0; i < t; i++) {
- System.out.println(makePalindrome(s[i]));
- }
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/strings/Pangram.java b/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/strings/Pangram.java
deleted file mode 100644
index fa98b4fd..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/strings/Pangram.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,42 +0,0 @@
-package com.hackerrank.algorithms.strings;
-
-import java.util.Scanner;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 10/22/15
- * @time: 8:47 AM
- */
-public class Pangram {
-
- public static String isPangram(String s) {
-
- char c;
- s = s.replaceAll("\\s+", "");
- s = s.toUpperCase();
- int[] alphabets = new int[26];
-
- // check if all alphabets are present only once
- for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
- c = s.charAt(i);
- if (alphabets[c - 65] == 0) {
- alphabets[c - 65] = 1;
- }
- }
-
- // check if all alphabets are present in string at least once
- for (int i = 0; i < alphabets.length; i++) {
- if (alphabets[i] == 0) return "not pangram";
- }
-
- return "pangram";
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
- String s = in.nextLine();
- System.out.println(isPangram(s));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/strings/TwoStrings.java b/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/strings/TwoStrings.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 779a148b..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/strings/TwoStrings.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,40 +0,0 @@
-package com.hackerrank.algorithms.strings;
-
-import java.util.Scanner;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 10/22/15
- * @time: 10:08 AM
- */
-public class TwoStrings {
-
- public static String isSubstringInBoth(String[] a) {
- char[] alphabets = new char[]{'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g', 'h', 'i', 'j', 'k', 'l', 'm', 'n', 'o', 'p',
- 'q', 'r', 's', 't', 'u', 'v', 'x', 'y', 'z'};
-
- for (int i = 0; i < alphabets.length; i++) {
- if (a[0].indexOf(alphabets[i]) != -1 && a[1].indexOf(alphabets[i]) != -1) return "YES";
- }
-
- return "NO";
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
-
- int t = Integer.parseInt(in.nextLine());
- String[][] input = new String[t][2];
-
- for (int i = 0; i < t; i++) {
- input[i][0] = in.nextLine();
- input[i][1] = in.nextLine();
- }
-
- for (int i = 0; i < t; i++) {
- System.out.println(isSubstringInBoth(input[i]));
- }
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/warmup/FlippingBits.java b/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/warmup/FlippingBits.java
deleted file mode 100644
index e335efe1..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/warmup/FlippingBits.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,32 +0,0 @@
-package com.hackerrank.algorithms.warmup;
-
-import java.util.Scanner;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- * User: rampatra
- * Date: 2/28/15
- * Time: 12:41 PM
- * To change this template go to Preferences | IDE Settings | File and Code Templates
- */
-public class FlippingBits {
-
- static long flipBits(long i) {
- return i ^ 4294967295l;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
-
- int t = Integer.parseInt(in.nextLine());
- long[] in_ar = new long[t];
-
- for (int i = 0; i < t; i++) {
- in_ar[i] = in.nextLong();
- }
-
- for (long i : in_ar) {
- System.out.println(flipBits(i));
- }
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/warmup/LonelyInteger.java b/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/warmup/LonelyInteger.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 666b3fa0..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/warmup/LonelyInteger.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,50 +0,0 @@
-package com.hackerrank.algorithms.warmup;
-
-import java.util.HashMap;
-import java.util.Map;
-import java.util.Scanner;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- * User: rampatra
- * Date: 2/28/15
- * Time: 12:16 PM
- * To change this template go to Preferences | IDE Settings | File and Code Templates
- */
-public class LonelyInteger {
-
- static int lonelyInteger(int[] a) {
-
- Map map = new HashMap<>();
- for (int i : a) {
- map.put(i, map.get(i) == null ? 1 : map.get(i) + 1);
- }
-
- for (Map.Entry entry : map.entrySet()) {
- if (entry.getValue() == 1) {
- return entry.getKey();
- }
- }
-
- return 1;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
- int res;
-
- int _a_size = Integer.parseInt(in.nextLine());
- int[] _a = new int[_a_size];
- int _a_item;
- String next = in.nextLine();
- String[] next_split = next.split(" ");
-
- for (int _a_i = 0; _a_i < _a_size; _a_i++) {
- _a_item = Integer.parseInt(next_split[_a_i]);
- _a[_a_i] = _a_item;
- }
-
- res = lonelyInteger(_a);
- System.out.println(res);
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/warmup/LoveLetterMystery.java b/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/warmup/LoveLetterMystery.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 8855498c..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/warmup/LoveLetterMystery.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,37 +0,0 @@
-package com.hackerrank.algorithms.warmup;
-
-import java.util.Scanner;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- * User: rampatra
- * Date: 3/17/15
- * Time: 3:22 PM
- * To change this template go to Preferences | IDE Settings | File and Code Templates
- */
-public class LoveLetterMystery {
- static int calcPalindromeSteps(String s) {
- int steps = 0, length = s.length(), a, b;
- for (int i = 0, j = length - 1; i < length / 2; i++, j--) {
- if ((a = (int) s.charAt(i)) != (b = (int) s.charAt(j))) {
- steps += Math.abs(a - b);
- }
- }
- return steps;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
-
- int t = in.nextInt();
- String s[] = new String[t];
-
- for (int i = 0; i < t; i++) {
- s[i] = in.next();
- }
-
- for (int i = 0; i < t; i++) {
- System.out.println(calcPalindromeSteps(s[i]));
- }
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/warmup/MaximizingXor.java b/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/warmup/MaximizingXor.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 2b0cc0ab..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/warmup/MaximizingXor.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,38 +0,0 @@
-package com.hackerrank.algorithms.warmup;
-
-import java.util.Scanner;
-import java.util.TreeSet;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- * User: rampatra
- * Date: 3/7/15
- * Time: 11:07 AM
- * To change this template go to Preferences | IDE Settings | File and Code Templates
- */
-public class MaximizingXor {
-
- static int maxXor(int l, int r) {
- TreeSet res = new TreeSet();
- for (int i = l; i <= r; i++) {
- for (int j = i; j <= r; j++) {
- res.add(i ^ j);
- }
- }
- return (int) res.last();
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
- int res;
- int _l;
- _l = Integer.parseInt(in.nextLine());
-
- int _r;
- _r = Integer.parseInt(in.nextLine());
-
- res = maxXor(_l, _r);
- System.out.println(res);
-
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/warmup/UtopianTree.java b/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/warmup/UtopianTree.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 43e455c2..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/algorithms/warmup/UtopianTree.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,40 +0,0 @@
-package com.hackerrank.algorithms.warmup;
-
-import java.util.Scanner;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- * User: rampatra
- * Date: 3/1/15
- * Time: 3:07 PM
- * To change this template go to Preferences | IDE Settings | File and Code Templates
- */
-public class UtopianTree {
- static int calcHeight(int growthCycles) {
- int h = 1;
-
- for (int i = 1; i <= growthCycles; i++) {
- if (i % 2 != 0)
- h *= 2;
- else
- h += 1;
- }
-
- return h;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
-
- int t = in.nextInt();
- int n[] = new int[t];
-
- for (int i = 0; i < t; i++) {
- n[i] = in.nextInt();
- }
-
- for (int i = 0; i < t; i++) {
- System.out.println(calcHeight(n[i]));
- }
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/bitmanipulation/CounterGame.java b/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/bitmanipulation/CounterGame.java
deleted file mode 100644
index b2a03e21..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/bitmanipulation/CounterGame.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,54 +0,0 @@
-package com.hackerrank.bitmanipulation;
-
-import java.math.BigInteger;
-import java.util.Scanner;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 6/24/15
- * @time: 12:03 PM
- */
-public class CounterGame {
-
- public static boolean isPowerOf2(BigInteger n) {
- return !n.equals(BigInteger.ZERO) && (n.and(n.subtract(BigInteger.ONE))).equals(BigInteger.ZERO);
- }
-
- public static BigInteger nextLowerPowerOf2(BigInteger n) {
- BigInteger p = BigInteger.ONE;
- while (p.compareTo(n) == -1) {
- p = p.shiftLeft(1);
- }
- return (n.compareTo(BigInteger.ONE) == 1) ? p.shiftRight(1) : n; // check for n = 0 or 1;
- }
-
- public static String computeWinner(BigInteger n) {
- boolean louiseTurn = true;
- while (!n.equals(BigInteger.ONE)) {
- if (isPowerOf2(n)) {
- n = n.shiftRight(1);
- } else {
- n = n.subtract(nextLowerPowerOf2(n));
- }
- louiseTurn = !louiseTurn;
- }
- return (louiseTurn) ? "Richard" : "Louise";
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
-
- int t = Integer.parseInt(in.nextLine());
- BigInteger[] in_ar = new BigInteger[t];
-
- for (int i = 0; i < t; i++) {
- in_ar[i] = in.nextBigInteger();
- }
-
- for (BigInteger i : in_ar) {
- System.out.println(computeWinner(i));
- }
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/bitmanipulation/Solution.java b/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/bitmanipulation/Solution.java
deleted file mode 100644
index d07b9f37..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/bitmanipulation/Solution.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,63 +0,0 @@
-package com.hackerrank.bitmanipulation;
-
-import java.io.BufferedReader;
-import java.io.IOException;
-import java.io.InputStreamReader;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 6/24/15
- * @time: 10:25 PM
- */
-public class Solution {
- private final static byte BITS;
- private final static long[] BIT_COUNT_TO_BIT;
-
- static {
- BITS = 32;
- BIT_COUNT_TO_BIT = new long[BITS + 1];
- BIT_COUNT_TO_BIT[0] = 1;
- for (byte i = 1; i <= BITS; i++) {
- BIT_COUNT_TO_BIT[i] = ((BIT_COUNT_TO_BIT[i - 1] - 1L) << 1) + (1L << (i - 1)) + 1L;
- }
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
- StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
- BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
- for (short T = Short.parseShort(br.readLine()); T > 0; T--) {
- String[] temp = br.readLine().split(" ");
- int A = Integer.parseInt(temp[0]);
- int B = Integer.parseInt(temp[1]);
- long bits = bitCountToNum(B) - bitCountToNum(A) + getHammingWeight(A);
- bits += (A < 0 && B >= 0) ? BIT_COUNT_TO_BIT[BITS] - 1L : 0;
- sb.append(bits + "\n");
- }
- System.out.print(sb);
- }
-
- //Bit count in number
- private static int getHammingWeight(int n) {
- byte count = 0;
- while (n != 0) {
- count++;
- n &= n - 1;
- }
- return count;
- }
-
- //Bit count to number, inclusive
- private static long bitCountToNum(int n) {
- long count = 0;
- for (byte b = BITS; n != 0; ) {
- int x = 1 << --b;
- if ((n & x) != 0) {
- n &= ~x;
- count += BIT_COUNT_TO_BIT[b] + n;
- }
- }
- return count;
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/bitmanipulation/TwosCompliment.java b/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/bitmanipulation/TwosCompliment.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 0bfdc29f..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/bitmanipulation/TwosCompliment.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,36 +0,0 @@
-package com.hackerrank.bitmanipulation;
-
-import java.util.Scanner;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 6/24/15
- * @time: 10:25 PM
- */
-public class TwosCompliment {
-
- public static long countSetBitsInRange(int start, int end) {
- int count = 0;
- for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) {
- count += Integer.bitCount(i);
- }
- return count;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
-
- int t = Integer.parseInt(in.nextLine());
- String[][] in_ar = new String[t][2];
-
- for (int i = 0; i < t; i++) {
- in_ar[i] = in.nextLine().split(" ");
- }
-
- for (String[] i : in_ar) {
- System.out.println(countSetBitsInRange(Integer.parseInt(i[0]), Integer.parseInt(i[1])));
- }
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/contests/SwappingInAnArray.java b/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/contests/SwappingInAnArray.java
deleted file mode 100644
index d21866d8..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/contests/SwappingInAnArray.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,75 +0,0 @@
-package com.hackerrank.contests;
-
-import java.io.BufferedWriter;
-import java.io.FileWriter;
-import java.io.IOException;
-import java.util.Scanner;
-
-/**
- * @author rpatra16
- * @since 04/11/2018
- */
-public class SwappingInAnArray {
-
- /**
- * The problem asks if we can sort the array with only one swap.
- *
- * @param a array to sort
- * @return 0 if already sorted, 1 if it can be sorted with one swap, -1 otherwise
- */
- static int swapToSort(int[] a) {
- int swaps = 0;
- for (int i=0; i < a.length-1; i++) {
- int swapIndex = i;
- for (int j = i + 1; j < a.length; j++) {
- if (a[i] > a[j]) {
- swapIndex = j;
- }
- }
- if (swapIndex != i) {
- swap(a, i, swapIndex);
- swaps++;
- i--;
- }
- }
- if (swaps > 1) {
- return -1;
- } else {
- return swaps;
- }
- }
-
- private static void swap(int[] a, int i, int j) {
- int temp = a[i];
- a[i] = a[j];
- a[j] = temp;
- }
-
- private static final Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
-
- public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
- BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(System.getenv("OUTPUT_PATH")));
-
- int n = scanner.nextInt();
- scanner.skip("(\r\n|[\n\r\u2028\u2029\u0085])?");
-
- int[] a = new int[n];
-
- String[] aItems = scanner.nextLine().split(" ");
- scanner.skip("(\r\n|[\n\r\u2028\u2029\u0085])?");
-
- for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
- int aItem = Integer.parseInt(aItems[i]);
- a[i] = aItem;
- }
-
- int result = swapToSort(a);
-
- bufferedWriter.write(String.valueOf(result));
- bufferedWriter.newLine();
-
- bufferedWriter.close();
-
- scanner.close();
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/interviewpreparation/arrays/DS2DArrayProblem.java b/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/interviewpreparation/arrays/DS2DArrayProblem.java
deleted file mode 100644
index ba7a2fe6..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/interviewpreparation/arrays/DS2DArrayProblem.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,55 +0,0 @@
-package com.hackerrank.interviewpreparation.arrays;
-
-import java.io.BufferedWriter;
-import java.io.FileWriter;
-import java.io.IOException;
-import java.util.Scanner;
-
-/**
- * @author rpatra16
- * @since 31/10/2018
- */
-public class DS2DArrayProblem {
-
- private static final Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
-
- private static int hourglassSum(int[][] arr) {
- int maxSum = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
- int hourglassSum;
- for (int i = 0; i < arr.length - 2; i++) {
- for (int j = 0; j < arr[0].length - 2; j++) {
- hourglassSum = arr[i][j] + arr[i][j + 1] + arr[i][j + 2] + arr[i + 1][j + 1] +
- arr[i + 2][j] + arr[i + 2][j + 1] + arr[i + 2][j + 2];
- if (hourglassSum > maxSum) {
- maxSum = hourglassSum;
- }
- }
- }
- return maxSum;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
- BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(System.getenv("OUTPUT_PATH")));
-
- int[][] arr = new int[6][6];
-
- for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
- String[] arrRowItems = scanner.nextLine().split(" ");
- scanner.skip("(\r\n|[\n\r\u2028\u2029\u0085])?");
-
- for (int j = 0; j < 6; j++) {
- int arrItem = Integer.parseInt(arrRowItems[j]);
- arr[i][j] = arrItem;
- }
- }
-
- int result = hourglassSum(arr);
-
- bufferedWriter.write(String.valueOf(result));
- bufferedWriter.newLine();
-
- bufferedWriter.close();
-
- scanner.close();
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/interviewpreparation/arrays/NewYearChaos.java b/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/interviewpreparation/arrays/NewYearChaos.java
deleted file mode 100644
index a065be9d..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/interviewpreparation/arrays/NewYearChaos.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,56 +0,0 @@
-package com.hackerrank.interviewpreparation.arrays;
-
-import java.util.Scanner;
-
-/**
- * @author rpatra16
- * @since 02/11/2018
- */
-public class NewYearChaos {
-
- /**
- * To solve this question, we just need to count the number of persons
- * that overtake a particular person.
- *
- * @param q the queue
- */
- private static void minimumBribes(int[] q) {
- int bribes = 0;
- for (int i = q.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
- if (q[i] - i - 1 > 2) {
- System.out.println("Too chaotic");
- return;
- }
- for (int j = Math.max(0, q[i] - 2); j < i; j++) {
- if (q[j] > q[i]) bribes++;
- }
- }
- System.out.println(bribes);
- }
-
- private static final Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- int t = scanner.nextInt();
- scanner.skip("(\r\n|[\n\r\u2028\u2029\u0085])?");
-
- for (int tItr = 0; tItr < t; tItr++) {
- int n = scanner.nextInt();
- scanner.skip("(\r\n|[\n\r\u2028\u2029\u0085])?");
-
- int[] q = new int[n];
-
- String[] qItems = scanner.nextLine().split(" ");
- scanner.skip("(\r\n|[\n\r\u2028\u2029\u0085])?");
-
- for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
- int qItem = Integer.parseInt(qItems[i]);
- q[i] = qItem;
- }
-
- minimumBribes(q);
- }
-
- scanner.close();
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/interviewpreparation/greedyalgorithmns/LuckBalance.java b/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/interviewpreparation/greedyalgorithmns/LuckBalance.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 3cf74165..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/interviewpreparation/greedyalgorithmns/LuckBalance.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,77 +0,0 @@
-package com.hackerrank.interviewpreparation.greedyalgorithmns;
-
-import java.io.BufferedWriter;
-import java.io.FileWriter;
-import java.io.IOException;
-import java.util.ArrayList;
-import java.util.Collections;
-import java.util.List;
-import java.util.Scanner;
-
-/**
- * @author rpatra16
- * @since 04/11/2018
- */
-public class LuckBalance {
-
- /**
- * For the full question, please see: https://www.hackerrank.com/challenges/luck-balance/
- *
- * @param k
- * @param contests
- * @return
- */
- private static int luckBalance(int k, int[][] contests) {
- int lucks = 0;
- List lucksForImportantContests = new ArrayList<>();
- for (int i = 0; i < contests.length; i++) {
- if (contests[i][1] == 1) {
- lucksForImportantContests.add(contests[i][0]);
- } else {
- lucks += contests[i][0];
- }
- }
- lucksForImportantContests.sort(Collections.reverseOrder());
- for (int i = 0; i < lucksForImportantContests.size(); i++) {
- if (i < k) { // can lose at most k of the important contests
- lucks += lucksForImportantContests.get(i);
- } else {
- lucks -= lucksForImportantContests.get(i);
- }
- }
- return lucks;
- }
-
- private static final Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
-
- public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
- BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(System.getenv("OUTPUT_PATH")));
-
- String[] nk = scanner.nextLine().split(" ");
-
- int n = Integer.parseInt(nk[0]);
-
- int k = Integer.parseInt(nk[1]);
-
- int[][] contests = new int[n][2];
-
- for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
- String[] contestsRowItems = scanner.nextLine().split(" ");
- scanner.skip("(\r\n|[\n\r\u2028\u2029\u0085])?");
-
- for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++) {
- int contestsItem = Integer.parseInt(contestsRowItems[j]);
- contests[i][j] = contestsItem;
- }
- }
-
- int result = luckBalance(k, contests);
-
- bufferedWriter.write(String.valueOf(result));
- bufferedWriter.newLine();
-
- bufferedWriter.close();
-
- scanner.close();
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/interviewpreparation/greedyalgorithmns/MinimumAbsoluteDifference.java b/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/interviewpreparation/greedyalgorithmns/MinimumAbsoluteDifference.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 6cff867b..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/interviewpreparation/greedyalgorithmns/MinimumAbsoluteDifference.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,59 +0,0 @@
-package com.hackerrank.interviewpreparation.greedyalgorithmns;
-
-import java.io.BufferedWriter;
-import java.io.FileWriter;
-import java.io.IOException;
-import java.util.Arrays;
-import java.util.Scanner;
-
-/**
- * @author rpatra16
- * @since 04/11/2018
- */
-public class MinimumAbsoluteDifference {
-
- /**
- * Finds the minimum absolute difference in the array.
- *
- * @param a input array
- * @return the minimum absolute difference between any two different elements in the array a
- */
- static int minimumAbsoluteDifference(int[] a) {
- int minDiff = Integer.MAX_VALUE, diff;
- Arrays.sort(a);
- for (int i = 0; i < a.length - 1; i++) {
- if ((diff = Math.abs(a[i] - a[i + 1])) < minDiff) {
- minDiff = diff;
- }
- }
- return minDiff;
- }
-
- private static final Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
-
- public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
- BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(System.getenv("OUTPUT_PATH")));
-
- int n = scanner.nextInt();
- scanner.skip("(\r\n|[\n\r\u2028\u2029\u0085])?");
-
- int[] arr = new int[n];
-
- String[] arrItems = scanner.nextLine().split(" ");
- scanner.skip("(\r\n|[\n\r\u2028\u2029\u0085])?");
-
- for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
- int arrItem = Integer.parseInt(arrItems[i]);
- arr[i] = arrItem;
- }
-
- int result = minimumAbsoluteDifference(arr);
-
- bufferedWriter.write(String.valueOf(result));
- bufferedWriter.newLine();
-
- bufferedWriter.close();
-
- scanner.close();
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/interviewpreparation/warmup/JumpingClouds.java b/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/interviewpreparation/warmup/JumpingClouds.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 36cab3dc..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/interviewpreparation/warmup/JumpingClouds.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,58 +0,0 @@
-package com.hackerrank.interviewpreparation.warmup;
-
-import java.io.BufferedWriter;
-import java.io.FileWriter;
-import java.io.IOException;
-import java.util.Scanner;
-
-/**
- * @author rpatra16
- * @since 31/10/2018
- */
-public class JumpingClouds {
-
- private static final Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
-
- private static int jumpingOnClouds(int[] c) {
- int jumps = 0;
- int i = 0;
- while (i < c.length) {
- if (((i + 2) < c.length) && c[i + 2] != 1) {
- i += 2;
- } else if (((i + 1) < c.length) && c[i + 1] != 1) {
- i += 1;
- }
- jumps++;
- if (i == c.length - 1) {
- break;
- }
- }
- return jumps;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
- BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(System.getenv("OUTPUT_PATH")));
-
- int n = scanner.nextInt();
- scanner.skip("(\r\n|[\n\r\u2028\u2029\u0085])?");
-
- int[] c = new int[n];
-
- String[] cItems = scanner.nextLine().split(" ");
- scanner.skip("(\r\n|[\n\r\u2028\u2029\u0085])?");
-
- for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
- int cItem = Integer.parseInt(cItems[i]);
- c[i] = cItem;
- }
-
- int result = jumpingOnClouds(c);
-
- bufferedWriter.write(String.valueOf(result));
- bufferedWriter.newLine();
-
- bufferedWriter.close();
-
- scanner.close();
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/interviewpreparation/warmup/RepeatedString.java b/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/interviewpreparation/warmup/RepeatedString.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 63b4ffba..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/interviewpreparation/warmup/RepeatedString.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,56 +0,0 @@
-package com.hackerrank.interviewpreparation.warmup;
-
-import java.io.BufferedWriter;
-import java.io.FileWriter;
-import java.io.IOException;
-import java.util.Scanner;
-
-/**
- * Repeated String problem.
- *
- * @author rpatra16
- * @since 29/10/2018
- */
-public class RepeatedString {
-
- private static final Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
-
- private static long repeatedString(String s, long n) {
- int extraLetters;
- long totalCount = 0, count = 0, stringLength = s.length();
- // count the no of a in non-repeated string
- for (int i = 0; i < stringLength; i++) {
- if (s.charAt(i) == 'a') {
- count++;
- }
- }
- totalCount += (n / stringLength * count);
- extraLetters = (int) (n % stringLength);
- // count the no of a in the remainder of the string
- for (int i = 0; i < extraLetters; i++) {
- if (s.charAt(i) == 'a') {
- totalCount++;
- }
- }
- return totalCount;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
- BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(System.getenv("OUTPUT_PATH")));
-
- String s = scanner.nextLine();
-
- long n = scanner.nextLong();
- scanner.skip("(\r\n|[\n\r\u2028\u2029\u0085])?");
-
- long result = repeatedString(s, n);
-
- bufferedWriter.write(String.valueOf(result));
- bufferedWriter.newLine();
-
- bufferedWriter.close();
-
- scanner.close();
- }
-}
-
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/java/advanced/JavaVisitorPattern.java b/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/java/advanced/JavaVisitorPattern.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 5f91e9b5..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/java/advanced/JavaVisitorPattern.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,226 +0,0 @@
-package com.hackerrank.java.advanced;
-
-import java.util.*;
-
-/**
- * Level: Medium
- * Problem Link: https://www.hackerrank.com/challenges/java-vistor-pattern/
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-06-22
- */
-enum Color {
- RED, GREEN
-}
-
-abstract class Tree {
-
- private int value;
- private Color color;
- private int depth;
-
- public Tree(int value, Color color, int depth) {
- this.value = value;
- this.color = color;
- this.depth = depth;
- }
-
- public int getValue() {
- return value;
- }
-
- public Color getColor() {
- return color;
- }
-
- public int getDepth() {
- return depth;
- }
-
- public abstract void accept(TreeVis visitor);
-
-
-}
-
-class TreeNode extends Tree {
-
- private ArrayList children = new ArrayList<>();
-
- public TreeNode(int value, Color color, int depth) {
- super(value, color, depth);
- }
-
- public void accept(TreeVis visitor) {
- visitor.visitNode(this);
-
- for (Tree child : children) {
- child.accept(visitor);
- }
- }
-
- public void addChild(Tree child) {
- children.add(child);
- }
-}
-
-class TreeLeaf extends Tree {
-
- public TreeLeaf(int value, Color color, int depth) {
- super(value, color, depth);
- }
-
- public void accept(TreeVis visitor) {
- visitor.visitLeaf(this);
- }
-}
-
-abstract class TreeVis {
- public abstract int getResult();
-
- public abstract void visitNode(TreeNode node);
-
- public abstract void visitLeaf(TreeLeaf leaf);
-
-}
-
-class SumInLeavesVisitor extends TreeVis {
- int nodeSum = 0;
- int leafSum = 0;
-
- public int getResult() {
- //implement this
- return leafSum;
- }
-
- public void visitNode(TreeNode node) {
- //implement this
- //nodeSum += node.getValue();
- }
-
- public void visitLeaf(TreeLeaf leaf) {
- //implement this
- leafSum += leaf.getValue();
- }
-}
-
-class ProductOfRedNodesVisitor extends TreeVis {
- int prodOfRedNodesAndLeaves = 1;
- private final int M = 1000000007;
-
- public int getResult() {
- //implement this
- return prodOfRedNodesAndLeaves;
- }
-
- public void visitNode(TreeNode node) {
- //implement this
- if (node.getColor() == Color.RED) {
- prodOfRedNodesAndLeaves *= (node.getValue() % M);
- }
- }
-
- public void visitLeaf(TreeLeaf leaf) {
- //implement this
- if (leaf.getColor() == Color.RED) {
- prodOfRedNodesAndLeaves *= (leaf.getValue() % M);
- }
- }
-}
-
-class FancyVisitor extends TreeVis {
- int sumOfNodesAtEvenDepth = 0;
- int sumOfGreenLeaves = 0;
-
- public int getResult() {
- //implement this
- return Math.abs(sumOfNodesAtEvenDepth - sumOfGreenLeaves);
- }
-
- public void visitNode(TreeNode node) {
- //implement this
- if (node.getDepth() % 2 == 0) {
- sumOfNodesAtEvenDepth += node.getValue();
- }
- }
-
- public void visitLeaf(TreeLeaf leaf) {
- //implement this
- if (leaf.getColor() == Color.GREEN) {
- sumOfGreenLeaves += leaf.getValue();
- }
- }
-}
-
-public class JavaVisitorPattern {
-
- public static Tree solve() {
- //read the tree from STDIN and return its root as a return value of this function
- Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
-
- int numOfNodes = s.nextInt();
- int[] nodeValues = new int[numOfNodes];
- int[] nodeColors = new int[numOfNodes];
- Map> parentToChildMap = new HashMap<>();
- Map childToParentMap = new HashMap<>();
-
- for (int i = 0; i < numOfNodes; i++) {
- nodeValues[i] = s.nextInt();
- }
- for (int i = 0; i < numOfNodes; i++) {
- nodeColors[i] = s.nextInt();
- }
- for (int i = 0; i < numOfNodes - 1; i++) {
- int parentIndex = s.nextInt();
- int childIndex = s.nextInt();
-
- Set children = parentToChildMap.get(parentIndex - 1) != null ? parentToChildMap.get(parentIndex - 1) : new HashSet<>();
- children.add(childIndex - 1);
- parentToChildMap.put(parentIndex - 1, children);
- childToParentMap.put(childIndex - 1, parentIndex - 1);
- }
-
- List nodes = new ArrayList<>(numOfNodes);
- for (int i = 0; i < numOfNodes; i++) {
-
- int depth = childToParentMap.get(i) == null ? -1 : nodes.get(childToParentMap.get(i)).getDepth();
-
- if (parentToChildMap.get(i) != null) {
- nodes.add(new TreeNode(nodeValues[i], nodeColors[i] == 0 ? Color.RED : Color.GREEN, depth + 1));
- } else {
- nodes.add(new TreeLeaf(nodeValues[i], nodeColors[i] == 0 ? Color.RED : Color.GREEN, depth + 1));
- }
- }
-
-
- for (Map.Entry> entry : parentToChildMap.entrySet()) {
-
- TreeNode parent = (TreeNode) nodes.get(entry.getKey());
-
- for (Integer childIndex : entry.getValue()) {
- parent.addChild(nodes.get(childIndex));
- }
- }
-
- return nodes.get(0);
- }
-
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Tree root = solve();
- SumInLeavesVisitor vis1 = new SumInLeavesVisitor();
- ProductOfRedNodesVisitor vis2 = new ProductOfRedNodesVisitor();
- FancyVisitor vis3 = new FancyVisitor();
-
- root.accept(vis1);
- root.accept(vis2);
- root.accept(vis3);
-
- int res1 = vis1.getResult();
- int res2 = vis2.getResult();
- int res3 = vis3.getResult();
-
- System.out.println(res1);
- System.out.println(res2);
- System.out.println(res3);
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/java/bignumber/BigDecimal.java b/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/java/bignumber/BigDecimal.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 7e1b804e..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/java/bignumber/BigDecimal.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,40 +0,0 @@
-package com.hackerrank.java.bignumber;
-
-import java.util.Arrays;
-import java.util.List;
-import java.util.Scanner;
-
-/**
- * Problem Link: https://www.hackerrank.com/challenges/java-bigdecimal/
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-06-22
- */
-class BigDecimal {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- //Input
- Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
- int n = sc.nextInt();
- String[] s = new String[n + 2];
- for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
- s[i] = sc.next();
- }
- sc.close();
-
- //Write your code here
- s = Arrays.copyOfRange(s, 0, s.length - 2);
- List input = Arrays.asList(s);
- Arrays.sort(s, (s1, s2) -> {
- int compare = new java.math.BigDecimal(s2).compareTo(new java.math.BigDecimal(s1));
- if (compare == 0) {
- return Integer.compare(input.indexOf(s1), input.indexOf(s2));
- }
- return compare;
- });
-
- //Output
- for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
- System.out.println(s[i]);
- }
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/java/oops/JavaInheritance.java b/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/java/oops/JavaInheritance.java
deleted file mode 100644
index b8d0d9e4..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/java/oops/JavaInheritance.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,30 +0,0 @@
-package com.hackerrank.java.oops;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 7/19/15
- * @time: 3:36 PM
- */
-public class JavaInheritance {
-
- public void JavaInheritance() {
-
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
-
- }
-}
-
-
-class Arithmetic {
-
-}
-
-class Adder extends Arithmetic {
- int add(int a, int b) {
- return a + b;
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/projecteuler/MultiplesOf3and5.java b/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/projecteuler/MultiplesOf3and5.java
deleted file mode 100644
index f56da78e..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/projecteuler/MultiplesOf3and5.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,20 +0,0 @@
-package com.hackerrank.projecteuler;
-
-import java.util.Scanner;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 1/1/16
- * @time: 8:48 AM
- */
-public class MultiplesOf3and5 {
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
-
- int t = Integer.parseInt(in.nextLine());
-
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/tutorials/ctci/QueuesWithTwoStacks.java b/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/tutorials/ctci/QueuesWithTwoStacks.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 333ecd1d..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/tutorials/ctci/QueuesWithTwoStacks.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,56 +0,0 @@
-package com.hackerrank.tutorials.ctci;
-
-import java.util.Scanner;
-import java.util.Stack;
-
-/**
- * Question: https://www.hackerrank.com/challenges/ctci-queue-using-two-stacks
- * Level: Medium
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @version 07/10/2016
- */
-public class QueuesWithTwoStacks {
-
- public static class MyQueue {
- Stack stackNewestOnTop = new Stack();
- Stack stackOldestOnTop = new Stack();
-
- public void enqueue(T value) { // Push onto newest stack
- stackNewestOnTop.push(value);
- }
-
- public T peek() {
- return stackOldestOnTop.isEmpty() ? stackNewestOnTop.firstElement() : stackOldestOnTop.peek();
- }
-
- public T dequeue() {
- if (stackOldestOnTop.isEmpty()) {
- while (!stackNewestOnTop.isEmpty()) {
- stackOldestOnTop.push(stackNewestOnTop.pop());
- }
- }
- return stackOldestOnTop.pop();
- }
- }
-
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- MyQueue queue = new MyQueue<>();
-
- Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
- int n = scan.nextInt();
-
- for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
- int operation = scan.nextInt();
- if (operation == 1) { // enqueue
- queue.enqueue(scan.nextInt());
- } else if (operation == 2) { // dequeue
- queue.dequeue();
- } else if (operation == 3) { // print/peek
- System.out.println(queue.peek());
- }
- }
- scan.close();
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/tutorials/ctci/RansomNote.java b/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/tutorials/ctci/RansomNote.java
deleted file mode 100644
index b0d45c75..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/hackerrank/tutorials/ctci/RansomNote.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,70 +0,0 @@
-package com.hackerrank.tutorials.ctci;
-
-import java.util.HashMap;
-import java.util.Map;
-import java.util.Scanner;
-
-/**
- * Question: https://www.hackerrank.com/challenges/ctci-ransom-note
- * Level: Easy
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @version 30/09/2016
- */
-public class RansomNote {
-
- Map magazineMap;
- Map noteMap;
-
- public RansomNote(String magazine, String note) {
-
- magazineMap = new HashMap<>();
- noteMap = new HashMap<>();
- String[] magazineWords = magazine.split(" ");
- String[] noteWords = note.split(" ");
- Integer c;
-
- for (int i = 0; i < magazineWords.length; i++) {
- if ((c = magazineMap.get(magazineWords[i])) == null) {
- magazineMap.put(magazineWords[i], 1);
- } else {
- magazineMap.put(magazineWords[i], c + 1);
- }
- }
-
- for (int i = 0; i < noteWords.length; i++) {
- if ((c = noteMap.get(noteWords[i])) == null) {
- noteMap.put(noteWords[i], 1);
- } else {
- noteMap.put(noteWords[i], c + 1);
- }
- }
- }
-
- public boolean solve() {
- for (Map.Entry entry : noteMap.entrySet()) {
- if (magazineMap.get(entry.getKey()) == null || magazineMap.get(entry.getKey()) - entry.getValue() < 0) {
- return false;
- }
- }
- return true;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
- int m = scanner.nextInt();
- int n = scanner.nextInt();
-
- // Eat whitespace to beginning of next line
- scanner.nextLine();
-
- RansomNote s = new RansomNote(scanner.nextLine(), scanner.nextLine());
- scanner.close();
-
- if (s.solve()) {
- System.out.println("Yes");
- } else {
- System.out.println("No");
- }
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/heaps/FindMedianFromDataStream.java b/src/main/java/com/heaps/FindMedianFromDataStream.java
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..8c46d39a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/com/heaps/FindMedianFromDataStream.java
@@ -0,0 +1,59 @@
+package com.heaps;
+
+import java.util.Collections;
+import java.util.Comparator;
+import java.util.PriorityQueue;
+
+/**
+ * Median is the middle value in an ordered integer list.
+ * If the size of the list is even, there is no middle value. So the median is the mean of the two middle value.
+ *
+ * First of all, it seems that the best time complexity we can get for this problem is O(log(n)) of add() and O(1) of getMedian().
+ * This data structure seems highly likely to be a tree.
+ * O(log(n)) of add() and O(1) of getMedian()
+ */
+class FindMedianFromDataStream {
+
+ PriorityQueue minHeap = null;
+ PriorityQueue maxHeap = null;
+
+ /**
+ * initialize your data structure here.
+ */
+ public FindMedianFromDataStream() {
+ minHeap = new PriorityQueue<>();
+ maxHeap = new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.reverseOrder());
+ }
+
+ public void addNum(int num) {
+ minHeap.offer(num); /** Step 1- Each element is first added to minHeap First */
+ maxHeap.offer(minHeap.poll()); /** Step 2- Minimum element is poped put and offered to MaxHeap .
+ This assures all the elements in minHeap are greater than maxHeap */
+
+ if (minHeap.size() < maxHeap.size()) { /** Step 3- The two heaps need to be laod balanced */
+ minHeap.offer(maxHeap.poll());
+ }
+ }
+
+ public double findMedian() {
+ if (minHeap.size() > maxHeap.size()) { /** Odd num of total elements */
+ return minHeap.peek();
+ } else {
+ return (minHeap.peek() + maxHeap.peek()) / 2.0; /** Even num of total elements */
+ }
+ }
+
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ FindMedianFromDataStream stream = new FindMedianFromDataStream();
+
+ stream.addNum(2);
+ stream.addNum(5);
+ stream.addNum(8);
+ stream.addNum(18);
+ stream.addNum(20);
+ stream.addNum(28);
+
+ System.out.println("Median " + stream.findMedian());
+ }
+}
+
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/heaps/FindMedianFromDataStream.jpg b/src/main/java/com/heaps/FindMedianFromDataStream.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..0ea46f22
Binary files /dev/null and b/src/main/java/com/heaps/FindMedianFromDataStream.jpg differ
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/heaps/KthLargestElement.java b/src/main/java/com/heaps/KthLargestElement.java
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..4e253650
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/com/heaps/KthLargestElement.java
@@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
+package com.heaps;
+
+import java.util.PriorityQueue;
+
+/**
+
+Link to priority Queue -
+https://onedrive.live.com/redir?resid=26052E8C3C647484%21105&page=Edit&wd=target%28Queue.one%7C71d394a6-f4c4-41dd-b56a-e1878e78a88a%2FPriorityQueue%7C27bf58ff-75e1-4c3a-aa71-2823e1ff846b%2F%29&wdorigin=703
+
+An Efficient Solution is to use Min Heap of size k to store k largest elements of the stream.
+The k’th largest element is always at root and can be found in O(1) time.
+
+Time complexity of finding the k’th largest element is O(Logk).
+
+ */
+public class KthLargestElement {
+
+ public static int findKthLargest(int arr[], int k) {
+ PriorityQueue minHeap = new PriorityQueue<>();
+ for (int num : arr) {
+ minHeap.add(num);
+ if (minHeap.size() > k) {
+
+ //this will remove the element from root since its minHeap it will remove minimum element.
+ //this will rearrange the elements back in proper heap with min element on root.
+ minHeap.remove();
+ }
+ }
+ return minHeap.remove();
+ }
+
+ public static void main(String args[]) {
+ int arr[] = {10, 70, 20, 30, 50, 80};
+ int result = findKthLargest(arr, 2);
+ System.out.println(result);
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/heaps/KthSmallestElement.java b/src/main/java/com/heaps/KthSmallestElement.java
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..5cca239e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/com/heaps/KthSmallestElement.java
@@ -0,0 +1,46 @@
+package com.heaps;
+
+import java.util.PriorityQueue;
+
+
+/*
+
+Example:
+
+int[] A = { 1, 2, 10, 20, 40, 32, 44, 51, 6 };
+
+K=4. 4th smallest element in given array: 10
+
+Approach: (Kth Smallest Element)
+ Use min-Heap. (Click here to read about Priority Queue).
+ Insert all the elements in the Priority Queue.
+ Extract K elements from the priority queue.
+ The last element (kth) extracted with be the kth smallest element in the array.
+
+Link to priority Queue -
+https://onedrive.live.com/redir?resid=26052E8C3C647484%21105&page=Edit&wd=target%28Queue.one%7C71d394a6-f4c4-41dd-b56a-e1878e78a88a%2FPriorityQueue%7C27bf58ff-75e1-4c3a-aa71-2823e1ff846b%2F%29
+
+
+*/
+public class KthSmallestElement {
+
+ public static int findKthSmallest(int arr[], int k) {
+ PriorityQueue minHeap = new PriorityQueue<>();
+ for (int num : arr) {
+ minHeap.add(num);
+ }
+ int n = -1;
+ while(k>0){
+ n = minHeap.poll();
+ k--;
+ }
+
+ return n;
+ }
+
+ public static void main(String args[]) {
+ int arr[] = {10, 70, 20, 30, 50, 80};
+ int result = findKthSmallest(arr, 5);
+ System.out.println(result);
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/arrays/BuySellStocks.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/arrays/BuySellStocks.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 4d4ba02b..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/arrays/BuySellStocks.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,67 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.arrays;
-
-/**
- * Level: Easy
- * Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock/
- * Description:
- * Say you have an array for which the ith element is the price of a given stock on day i.
- *
- * If you were only permitted to complete at most one transaction (i.e., buy one and sell one share of the stock),
- * design an algorithm to find the maximum profit.
- *
- * Note that you cannot sell a stock before you buy one.
- *
- * Example 1:
- *
- * Input: [7,1,5,3,6,4]
- * Output: 5
- * Explanation: Buy on day 2 (price = 1) and sell on day 5 (price = 6), profit = 6-1 = 5.
- * Not 7-1 = 6, as selling price needs to be larger than buying price.
- *
- * Example 2:
- *
- * Input: [7,6,4,3,1]
- * Output: 0
- * Explanation: In this case, no transaction is done, i.e. max profit = 0.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-04-23
- */
-public class BuySellStocks {
-
- /**
- * Time complexity: O(n)
- * where,
- * n = no. of stock prices
- *
- * Runtime: 0 ms.
- *
- * @param prices
- * @return
- */
- public static int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
- int profit = 0;
- int buyPrice = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
-
- for (int i = 0; i < prices.length; i++) {
- if (prices[i] < buyPrice) {
- buyPrice = prices[i];
- } else if (prices[i] - buyPrice > profit) {
- profit = prices[i] - buyPrice;
- }
- }
-
- return profit;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
-
- System.out.println(maxProfit(new int[]{7, 1, 5, 3, 6, 4}));
- System.out.println(maxProfit(new int[]{7, 1, 5, 0, 6, 4}));
- System.out.println(maxProfit(new int[]{4, 3, 2, 1}));
-
- // edge cases
- System.out.println(maxProfit(new int[]{}));
- System.out.println(maxProfit(new int[]{1}));
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/arrays/BuySellStocksII.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/arrays/BuySellStocksII.java
deleted file mode 100644
index d215246e..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/arrays/BuySellStocksII.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,94 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.arrays;
-
-/**
- * Level: Easy
- * Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock-ii/
- * Description:
- * Say you have an array for which the ith element is the price of a given stock on day i.
- *
- * Design an algorithm to find the maximum profit. You may complete as many transactions as you
- * like (i.e., buy one and sell one share of the stock multiple times).
- *
- * Note: You may not engage in multiple transactions at the same time (i.e., you must sell the stock
- * before you buy again).
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-04-23
- */
-public class BuySellStocksII {
-
- /**
- * The key point is we need to consider every peak immediately following a valley to maximize the profit. In case
- * we skip one of the peaks (trying to obtain more profit), we will end up losing the profit over one of the
- * transactions leading to an overall lesser profit.
- * Read this to learn more.
- *
- * Time complexity: O(n)
- * where,
- * n = no. of stock prices
- *
- * Runtime: 0 ms.
- *
- * @param prices
- * @return
- */
- public static int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
- int valley;
- int peak;
- int maxProfit = 0;
-
- for (int i = 0; i < prices.length; i++) {
- while (i < prices.length - 1 && prices[i] > prices[i + 1]) {
- i++;
- }
- valley = i;
-
- while (i < prices.length - 1 && prices[i] < prices[i + 1]) {
- i++;
- }
- peak = i;
-
- maxProfit += prices[peak] - prices[valley];
- }
-
- return maxProfit;
- }
-
- /**
- * This solution follows the logic used in the above approach {@link #maxProfit(int[])}, but with only a slight
- * variation. In this case, instead of looking for every peak following a valley, we can simply go on crawling over
- * the slope and keep on adding the profit obtained from every consecutive transaction.
- * In the end, we will be using the peaks and valleys effectively, but we need not track the costs corresponding to
- * the peaks and valleys along with the maximum profit, but we can directly keep on adding the difference between the
- * consecutive numbers of the array if the second number is larger than the first one, and at the total sum we obtain
- * will be the maximum profit. This approach will simplify the solution.
- *
- * Time complexity: O(n)
- * where,
- * n = no. of stock prices
- *
- * @param prices
- * @return
- */
- public static int maxProfitSimplified(int[] prices) {
- int maxProfit = 0;
- for (int i = 1; i < prices.length; i++) {
- if (prices[i] > prices[i - 1]) {
- maxProfit += prices[i] - prices[i - 1];
- }
- }
- return maxProfit;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(maxProfit(new int[]{7, 1, 5, 3, 6, 4}));
- System.out.println(maxProfit(new int[]{1, 2, 3, 4, 5}));
- System.out.println(maxProfit(new int[]{7, 6, 4, 3, 1}));
-
- System.out.println("----");
-
- System.out.println(maxProfitSimplified(new int[]{7, 1, 5, 3, 6, 4}));
- System.out.println(maxProfitSimplified(new int[]{1, 2, 3, 4, 5}));
- System.out.println(maxProfitSimplified(new int[]{7, 6, 4, 3, 1}));
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/arrays/CanPlaceFlowers.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/arrays/CanPlaceFlowers.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 916499ac..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/arrays/CanPlaceFlowers.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,68 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.arrays;
-
-
-import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertFalse;
-import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertTrue;
-
-/**
- * Level: Easy
- * Problem Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/can-place-flowers/
- * Problem Description:
- * Suppose you have a long flowerBed in which some of the plots are planted and some are not. However, flowers cannot
- * be planted in adjacent plots - they would compete for water and both would die.
- *
- * Given a flowerBed (represented as an array containing 0 and 1, where 0 means empty and 1 means not empty), and a
- * number n, return if n new flowers can be planted in it without violating the no-adjacent-flowers rule.
- *
- * Example 1:
- * Input: flowerBed = [1,0,0,0,1], n = 1
- * Output: True
- *
- * Example 2:
- * Input: flowerBed = [1,0,0,0,1], n = 2
- * Output: False
- *
- * Note:
- * The input array won't violate no-adjacent-flowers rule.
- * The input array size is in the range of [1, 20000].
- * n is a non-negative integer which won't exceed the input array size.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-07-24
- */
-public class CanPlaceFlowers {
-
- /**
- * Time Complexity: O(n)
- * Space Complexity: O(1)
- * Runtime: 1 ms.
- *
- * @param flowerBed
- * @param n
- * @return
- */
- public static boolean canPlaceFlowers(int[] flowerBed, int n) {
- int i = 0, count = 0;
- while (i < flowerBed.length) {
- if (flowerBed[i] == 0 && (i == 0 || flowerBed[i - 1] == 0) && (i == flowerBed.length - 1 || flowerBed[i + 1] == 0)) {
- flowerBed[i++] = 1;
- count++;
- }
- if (count >= n)
- return true;
- i++;
- }
- return false;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- assertTrue(canPlaceFlowers(new int[]{0}, 0));
- assertTrue(canPlaceFlowers(new int[]{0}, 1));
- assertTrue(canPlaceFlowers(new int[]{1}, 0));
- assertFalse(canPlaceFlowers(new int[]{1}, 1));
- assertTrue(canPlaceFlowers(new int[]{1, 0, 0, 0, 1}, 1));
- assertFalse(canPlaceFlowers(new int[]{1, 0, 0, 0, 1}, 2));
- assertFalse(canPlaceFlowers(new int[]{1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1}, 2));
- assertTrue(canPlaceFlowers(new int[]{1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0}, 2));
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/arrays/FindTheCelebrity.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/arrays/FindTheCelebrity.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 1b15d996..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/arrays/FindTheCelebrity.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,105 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.arrays;
-
-import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
-
-/**
- * Level: Medium
- * Problem Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/find-the-celebrity/
- * Problem Description:
- * Suppose you are at a party with n people (labeled from 0 to n - 1) and among them, there may exist one celebrity.
- * The definition of a celebrity is that all the other n - 1 people know him/her but he/she does not know any of them.
- *
- * Now you want to find out who the celebrity is or verify that there is not one. The only thing you are allowed to do
- * is to ask questions like: "Hi, A. Do you know B?" to get information of whether A knows B. You need to find out the
- * celebrity (or verify there is not one) by asking as few questions as possible (in the asymptotic sense).
- *
- * You are given a helper function bool knows(a, b) which tells you whether A knows B. Implement a
- * function int findCelebrity(n). There will be exactly one celebrity if he/she is in the party. Return the celebrity's
- * label if there is a celebrity in the party. If there is no celebrity, return -1.
- *
- * Example 1:
- *
- * Input: graph = [
- * [1,1,0],
- * [0,1,0],
- * [1,1,1]
- * ]
- * Output: 1
- * Explanation: There are three persons labeled with 0, 1 and 2. graph[i][j] = 1 means person i knows person j, otherwise
- * graph[i][j] = 0 means person i does not know person j. The celebrity is the person labeled as 1 because both 0 and 2
- * know him but 1 does not know anybody.
- *
- *
- * Example 2:
- *
- * Input: graph = [
- * [1,0,1],
- * [1,1,0],
- * [0,1,1]
- * ]
- * Output: -1
- * Explanation: There is no celebrity.
- *
- *
- * Note: The directed graph is represented as an adjacency matrix, which is an n x n matrix where a[i][j] = 1 means
- * person i knows person j while a[i][j] = 0 means the contrary. Remember that you won't have direct access to the
- * adjacency matrix.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-08-04
- */
-public class FindTheCelebrity {
-
- private int[][] knowsMatrix;
-
- FindTheCelebrity(int[][] knowsMatrix) {
- this.knowsMatrix = knowsMatrix;
- }
-
- public boolean knows(int a, int b) {
- return knowsMatrix[a][b] == 1;
- }
-
- /**
- * Time Complexity: O(n)
- * Space Complexity: O(1)
- * Runtime: 6 ms.
- *
- * @param n
- * @return
- */
- public int findCelebrity(int n) {
- int celebrityIndex = 0;
-
- for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
- // if a person doesn't know another person then he maybe a celebrity
- if (!knows(i, celebrityIndex)) {
- celebrityIndex = i;
- }
- }
-
- for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
- // verify whether the celebrity only knows himself and all other people know the celebrity
- if ((knows(celebrityIndex, i) && i != celebrityIndex) || !knows(i, celebrityIndex)) {
- return -1;
- }
- }
-
- return celebrityIndex;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- FindTheCelebrity findTheCelebrity = new FindTheCelebrity(new int[][]{
- {1, 1, 0},
- {0, 1, 0},
- {1, 1, 1}});
-
- assertEquals(1, findTheCelebrity.findCelebrity(3));
-
- findTheCelebrity = new FindTheCelebrity(new int[][]{
- {1, 0},
- {0, 1}});
-
- assertEquals(-1, findTheCelebrity.findCelebrity(2));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/arrays/InsertInterval.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/arrays/InsertInterval.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 52155f19..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/arrays/InsertInterval.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,78 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.arrays;
-
-import java.util.Arrays;
-
-/**
- * Level: Hard
- * Problem Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/insert-interval/
- * Problem Description:
- * Given a set of non-overlapping intervals, insert a new interval into the intervals (merge if necessary).
- *
- * You may assume that the intervals were initially sorted according to their start times.
- *
- * Example 1:
- * Input: intervals = [[1,3],[6,9]], newInterval = [2,5]
- * Output: [[1,5],[6,9]]
- *
- * Example 2:
- * Input: intervals = [[1,2],[3,5],[6,7],[8,10],[12,16]], newInterval = [4,8]
- * Output: [[1,2],[3,10],[12,16]]
- * Explanation: Because the new interval [4,8] overlaps with [3,5],[6,7],[8,10].
- *
- * Companies: LinkedIn.
- * Related: {@link MergeIntervals}.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-07-23
- */
-public class InsertInterval {
-
- /**
- * Time Complexity: O(n)
- * Space Complexity: O(n)
- * Runtime: 2 ms.
- *
- * @param intervals
- * @param newInterval
- * @return
- */
- public static int[][] insert(int[][] intervals, int[] newInterval) {
- if (intervals.length == 0 && newInterval.length == 0) {
- return new int[][]{};
- } else if (intervals.length == 0) {
- return new int[][]{newInterval};
- }
-
- int[][] mergedIntervals = new int[intervals.length + 1][2];
- int j = 0;
-
- for (int i = 0; i < intervals.length; i++) {
- if (newInterval == null || newInterval[0] > intervals[i][1]) { // newInterval is after the ith interval
- mergedIntervals[j++] = intervals[i];
- } else if (newInterval[1] < intervals[i][0]) { // newInterval is before the ith interval
- mergedIntervals[j++] = newInterval;
- mergedIntervals[j++] = intervals[i];
- newInterval = null;
- } else { // if overlapping
- newInterval[0] = Math.min(newInterval[0], intervals[i][0]);
- newInterval[1] = Math.max(newInterval[1], intervals[i][1]);
- }
- }
-
- if (newInterval != null) {
- mergedIntervals[j++] = newInterval;
- }
-
- return Arrays.copyOfRange(mergedIntervals, 0, j);
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(Arrays.deepToString(insert(new int[][]{}, new int[]{})));
- System.out.println(Arrays.deepToString(insert(new int[][]{}, new int[]{5, 7})));
- System.out.println(Arrays.deepToString(insert(new int[][]{{1, 5}}, new int[]{0, 0})));
- System.out.println(Arrays.deepToString(insert(new int[][]{{1, 5}}, new int[]{2, 3})));
- System.out.println(Arrays.deepToString(insert(new int[][]{{2, 5}, {6, 7}, {8, 9}}, new int[]{0, 1})));
- System.out.println(Arrays.deepToString(insert(new int[][]{{1, 3}, {6, 9}}, new int[]{2, 5})));
- System.out.println(Arrays.deepToString(insert(new int[][]{{1, 2}, {3, 5}, {6, 7}, {8, 10}, {12, 16}}, new int[]{4, 8})));
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/arrays/MajorityElement.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/arrays/MajorityElement.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 2ccdd116..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/arrays/MajorityElement.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,47 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.arrays;
-
-/**
- * Level: Easy
- * Problem Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/majority-element/
- * Problem Description:
- * Given an array of size n, find the majority element. The majority element is the element
- * that appears more than ⌊ n/2 ⌋ times. You may assume that the array is non-empty and the
- * majority element always exist in the array.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-04-27
- */
-public class MajorityElement {
-
- /**
- * Time complexity: O(n)
- * Runtime: 1 ms.
- *
- * @param nums
- * @return
- */
- public static int majorityElement(int[] nums) {
- int count = 1;
- int majElem = nums[0];
-
- for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
- if (count <= 0) {
- majElem = nums[i];
- count = 0;
- }
- if (majElem == nums[i]) {
- count++;
- } else {
- count--;
- }
- }
-
- return majElem;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(majorityElement(new int[]{10, 9, 9, 9, 10}));
- System.out.println(majorityElement(new int[]{2, 3, 2, 2, 3, 2}));
- System.out.println(majorityElement(new int[]{2, 3, 2, 2, 2, 3}));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/arrays/MergeIntervals.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/arrays/MergeIntervals.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 58f56ebc..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/arrays/MergeIntervals.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,78 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.arrays;
-
-import java.util.Arrays;
-import java.util.Comparator;
-
-/**
- * Level: Medium
- * Problem Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/merge-intervals/
- * Problem Description:
- *
- * Given a collection of intervals, merge all overlapping intervals.
- *
- * Example 1:
- * Input: [[1,3],[2,6],[8,10],[15,18]]
- * Output: [[1,6],[8,10],[15,18]]
- * Explanation: Since intervals [1,3] and [2,6] overlaps, merge them into [1,6].
- *
- * Example 2:
- * Input: [[1,4],[4,5]]
- * Output: [[1,5]]
- * Explanation: Intervals [1,4] and [4,5] are considered overlapping.
- *
- * Companies: LinkedIn
- * Related: {@link InsertInterval}.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-07-22
- */
-public class MergeIntervals {
-
- /**
- * Time complexity: O(n log n)
- * Space complexity: O(n)
- * Runtime: 6 ms
- *
- * @param intervals a list of intervals, may not be sorted
- * @return a list of intervals, with overlapping intervals merged
- */
- public static int[][] merge(int[][] intervals) {
- // some validations
- if (intervals.length == 0) return new int[0][2];
-
- // we first sort the intervals based on their start times
- Arrays.sort(intervals, new IntervalComparator());
-
- int[][] mergedIntervals = new int[intervals.length][2];
- int lastMergedIndex = 0;
- mergedIntervals[lastMergedIndex] = intervals[0];
-
- for (int i = 1; i < intervals.length; i++) {
- if (isOverlap(mergedIntervals[lastMergedIndex], intervals[i])) {
- // if two intervals overlap, then merge the two
- mergedIntervals[lastMergedIndex] = new int[]{Math.min(mergedIntervals[lastMergedIndex][0], intervals[i][0]),
- Math.max(mergedIntervals[lastMergedIndex][1], intervals[i][1])};
- } else {
- mergedIntervals[++lastMergedIndex] = intervals[i];
- }
- }
-
- return Arrays.copyOfRange(mergedIntervals, 0, lastMergedIndex + 1);
- }
-
- private static boolean isOverlap(int[] interval1, int[] interval2) {
- return interval1[0] <= interval2[0] && interval1[1] >= interval2[0];
- }
-
- private static class IntervalComparator implements Comparator {
- @Override
- public int compare(int[] interval1, int[] interval2) {
- return interval1[0] - interval2[0];
- }
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(Arrays.deepToString(merge(new int[][]{{1, 3}, {2, 6}, {8, 10}, {15, 18}})));
- System.out.println(Arrays.deepToString(merge(new int[][]{{1, 4}, {4, 5}})));
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/arrays/MergeSortedArray.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/arrays/MergeSortedArray.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 975db8ec..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/arrays/MergeSortedArray.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,86 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.arrays;
-
-import java.util.Arrays;
-
-/**
- * Level: Easy
- * Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/merge-sorted-array/
- * Description:
- * Given two sorted integer arrays nums1 and nums2, merge nums2 into nums1 as one sorted array.
- *
- * Note:
- * The number of elements initialized in nums1 and nums2 are m and n respectively.
- * You may assume that nums1 has enough space (size that is greater or equal to m + n) to hold
- * additional elements from nums2.
- *
- * Example:
- * Input:
- * nums1 = [1,2,3,0,0,0], m = 3
- * nums2 = [2,5,6], n = 3
- * Output: [1,2,2,3,5,6]
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-04-26
- */
-public class MergeSortedArray {
-
- /**
- * Time complexity: O(m*n)
- * Runtime: 1 ms.
- *
- * @param nums1
- * @param m
- * @param nums2
- * @param n
- */
- public static void mergeSimple(int[] nums1, int m, int[] nums2, int n) {
- int i = 0;
-
- for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
- // find the index where the element from nums2 need to be inserted
- while (i < m + j && nums1[i] < nums2[j]) {
- i++;
- }
- // copy elements from i+1th position to one position right
- for (int k = m + j; k > i; k--) { // note: replacing this with System.arraycopy() gives a 0 ms runtime
- nums1[k] = nums1[k - 1];
- }
- nums1[i] = nums2[j];
- }
- }
-
- /**
- * Time complexity: O(m+n)
- * Runtime: 0 ms.
- *
- * @param nums1
- * @param m
- * @param nums2
- * @param n
- */
- public static void merge(int[] nums1, int m, int[] nums2, int n) {
- for (int i = m + n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
- if (m == 0) {
- nums1[i] = nums2[--n];
- } else if (n == 0) { // we ran out of nums2 elements so there is nothing left to merge
- return;
- } else if (nums1[m - 1] > nums2[n - 1]) {
- nums1[i] = nums1[--m];
- } else {
- nums1[i] = nums2[--n];
- }
- }
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- int[] nums1 = {1, 2, 3, 0, 0, 0};
- int[] nums2 = {4, 5, 6};
- merge(nums1, 3, nums2, 3);
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(nums1));
-
- nums1 = new int[]{4, 5, 6, 0, 0, 0};
- nums2 = new int[]{1, 2, 3};
- merge(nums1, 3, nums2, 3);
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(nums1));
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/arrays/NumberOfIslands.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/arrays/NumberOfIslands.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 04ac6831..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/arrays/NumberOfIslands.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,107 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.arrays;
-
-import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
-
-/**
- * Level: Medium
- * Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/number-of-islands/
- * Description:
- * Given a 2d grid map of '1's (land) and '0's (water), count the number of islands. An island is surrounded by water
- * and is formed by connecting adjacent lands horizontally or vertically. You may assume all four edges of the grid
- * are all surrounded by water.
- *
- * Example 1:
- * Input:
- * 11110
- * 11010
- * 11000
- * 00000
- * Output: 1
- *
- * Example 2:
- * Input:
- * 11000
- * 11000
- * 00100
- * 00011
- * Output: 3
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-08-07
- */
-public class NumberOfIslands {
-
- /**
- * The idea is simple and straightforward. Once we encounter land ('1' in grid) we drown the island or change the
- * neighboring '1's to '0's. Therefore, the number of '1's we encounter, we can say that we have that many islands.
- *
- * Time Complexity: O(n)
- * Space Complexity: O(n)
- * Runtime: 1 ms.
- *
- * @param grid
- * @return
- */
- public static int numIslands(char[][] grid) {
- int count = 0;
-
- for (int i = 0; i < grid.length; i++) {
- for (int j = 0; j < grid[0].length; j++) {
- if (grid[i][j] == '1') {
- drownTheIsland(grid, i, j);
- count++;
- }
- }
- }
-
- return count;
- }
-
- private static void drownTheIsland(char[][] grid, int i, int j) {
- if (i < 0 || j < 0 || i >= grid.length || j >= grid[0].length || grid[i][j] == '0') {
- return;
- }
-
- grid[i][j] = '0';
-
- drownTheIsland(grid, i, j + 1);
- drownTheIsland(grid, i, j - 1);
- drownTheIsland(grid, i + 1, j);
- drownTheIsland(grid, i - 1, j);
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- assertEquals(1, numIslands(new char[][]{
- {'1', '1', '1', '1', '0'},
- {'1', '1', '0', '1', '0'},
- {'1', '1', '0', '0', '0'},
- {'0', '0', '0', '0', '0'}
- }));
-
- assertEquals(2, numIslands(new char[][]{
- {'1', '1', '1', '1', '0'},
- {'1', '1', '0', '1', '0'},
- {'1', '1', '0', '0', '0'},
- {'0', '0', '0', '1', '0'}
- }));
-
- assertEquals(1, numIslands(new char[][]{
- {'1', '1', '1', '1', '1'},
- {'1', '1', '1', '1', '1'},
- {'1', '1', '1', '1', '1'},
- {'1', '1', '1', '1', '1'}
- }));
-
- assertEquals(1, numIslands(new char[][]{
- {'1'}
- }));
-
- assertEquals(0, numIslands(new char[][]{
- {'0'}
- }));
-
- assertEquals(0, numIslands(new char[][]{
- {}
- }));
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/arrays/PascalsTriangle.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/arrays/PascalsTriangle.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 5f32d69f..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/arrays/PascalsTriangle.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,53 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.arrays;
-
-import java.util.ArrayList;
-import java.util.List;
-
-/**
- * Level: Easy
- * Problem: https://leetcode.com/problems/pascals-triangle/
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-04-20
- */
-public class PascalsTriangle {
-
- /**
- * Time complexity: O(numRows^2)
- * Space complexity: O(numRows^2)
- *
- * Runtime: 0 ms.
- *
- * @param numRows
- * @return
- */
- public static List> generatePascalsTriangle(int numRows) {
- List> pascalsTriangle = new ArrayList<>();
-
- if (numRows == 0) return pascalsTriangle;
-
- List firstRow = new ArrayList<>();
- firstRow.add(1);
- pascalsTriangle.add(firstRow);
-
- List prevRow;
- for (int i = 1; i < numRows; i++) {
- prevRow = pascalsTriangle.get(i - 1);
-
- List currRow = new ArrayList<>();
- currRow.add(1);
- for (int j = 0; j < prevRow.size() - 1; j++) {
- currRow.add(prevRow.get(j) + prevRow.get(j + 1));
- }
- currRow.add(1);
-
- pascalsTriangle.add(currRow);
- }
-
- return pascalsTriangle;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(generatePascalsTriangle(5));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/arrays/RemoveDuplicates.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/arrays/RemoveDuplicates.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 57eba5ad..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/arrays/RemoveDuplicates.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,62 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.arrays;
-
-import java.util.Arrays;
-
-/**
- * Level: Easy
- * Problem Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-array/
- * Problem Description:
- * Given a sorted array nums, remove the duplicates in-place such that each element appear only once and return the new length.
- *
- * Do not allocate extra space for another array, you must do this by modifying the input array in-place with O(1) extra memory.
- * Example 1:
- *
- * Given nums = [1,1,2]
- *
- * Your function should return length = 2, with the first two elements of nums being 1 and 2 respectively.
- *
- * NOTE: It doesn't matter what you leave beyond the returned length.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-04-24
- */
-public class RemoveDuplicates {
-
- /**
- * This removes the duplicates from the array in-place.
- *
- * Time complexity: O(n)
- * where,
- * n = no. of elements in the array
- *
- * Runtime: 1 ms.
- *
- * @param nums
- * @return
- */
- public static int removeDuplicatesInSortedArray(int[] nums) {
- int insertIndex = 0;
-
- for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
- if (nums[i] != nums[i - 1]) {
- nums[++insertIndex] = nums[i];
- }
- }
-
- return insertIndex + 1;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- int[] arr = new int[]{1, 1, 2};
- System.out.println(removeDuplicatesInSortedArray(arr));
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
-
- arr = new int[]{0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4};
- System.out.println(removeDuplicatesInSortedArray(arr));
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
-
- arr = new int[]{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
- System.out.println(removeDuplicatesInSortedArray(arr));
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/arrays/RotateArray.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/arrays/RotateArray.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 91475160..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/arrays/RotateArray.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,93 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.arrays;
-
-import java.util.Arrays;
-
-/**
- * Level: Easy
- * Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/rotate-array/
- * Description:
- * Given an array, rotate the array to the right by k steps, where k is non-negative.
- *
- * Example 1:
- * Input: [1,2,3,4,5,6,7] and k = 3
- * Output: [5,6,7,1,2,3,4]
- * Explanation:
- * rotate 1 steps to the right: [7,1,2,3,4,5,6]
- * rotate 2 steps to the right: [6,7,1,2,3,4,5]
- * rotate 3 steps to the right: [5,6,7,1,2,3,4]
- *
- * Example 2:
- * Input: [-1,-100,3,99] and k = 2
- * Output: [3,99,-1,-100]
- * Explanation:
- * rotate 1 steps to the right: [99,-1,-100,3]
- * rotate 2 steps to the right: [3,99,-1,-100]
- *
- * Note:
- * Try to come up as many solutions as you can, there are at least 3 different ways to solve this problem.
- * Could you do it in-place with O(1) extra space?
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-04-20
- */
-public class RotateArray {
-
- /**
- * Time complexity: O(n)
- * where,
- * n = no. of elements in the array
- *
- * Runtime: 0 ms.
- *
- * @param nums
- * @param k
- */
- public static void rotate(int[] nums, int k) {
-
- if (k > nums.length) {
- k = k % nums.length;
- }
-
- reverse(nums, 0, nums.length);
- reverse(nums, 0, k);
- reverse(nums, k, nums.length);
- }
-
- private static void reverse(int[] nums, int start, int end) {
- int temp;
- for (int i = start, j = end - 1; i < j; i++, j--) {
- temp = nums[i];
- nums[i] = nums[j];
- nums[j] = temp;
- }
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- // normal case
- int[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7};
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
- rotate(arr, 3);
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
-
- // edge cases
- arr = new int[]{1, 2};
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
- rotate(arr, 2);
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr)); // should be [1, 2]
-
- arr = new int[]{1, 2};
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
- rotate(arr, 3);
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr)); // should be [2, 1]
-
- arr = new int[]{1, 2, 3};
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
- rotate(arr, 4);
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr)); // should be [3, 1, 2]
-
- arr = new int[]{1};
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
- rotate(arr, 2);
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/arrays/ShortestWordDistance.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/arrays/ShortestWordDistance.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 5cd0c821..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/arrays/ShortestWordDistance.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,71 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.arrays;
-
-import com.leetcode.hashtables.ShortestWordDistanceII;
-
-import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
-
-/**
- * Level: Easy
- * Problem Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/shortest-word-distance/
- * Problem Description:
- * Given a list of words and two words word1 and word2, return the shortest distance between these two words in the
- * list of words.
- *
- * Example 1:
- * Assume that words = ["practice", "makes", "perfect", "coding", "makes"].
- * Given word1 = "coding", word2 = "practice", return 3.
- * Given word1 = "makes", word2 = "coding", return 1.
- *
- * Note: You may assume that word1 does not equal to word2, and word1 and word2 are both in the list.
- *
- * Lastly, for a more complex variant, see {@link ShortestWordDistanceII}.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-07-31
- */
-public class ShortestWordDistance {
-
- /**
- * Time Complexity:
- * Space Complexity:
- * Runtime: 1 ms.
- *
- * @param words
- * @param word1
- * @param word2
- * @return
- */
- public static int findShortestDistance(String[] words, String word1, String word2) {
- int indexWord1 = -1;
- int indexWord2 = -1;
- int minDistance = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
-
- for (int i = 0; i < words.length; i++) {
- if (words[i].equals(word1)) {
- indexWord1 = i;
- } else if (words[i].equals(word2)) {
- indexWord2 = i;
- }
- if (indexWord1 != -1 && indexWord2 != -1) {
- minDistance = Math.min(minDistance, Math.abs(indexWord1 - indexWord2));
- }
- }
-
- return minDistance;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- assertEquals(3, findShortestDistance(new String[]{"practice", "makes", "perfect", "coding", "makes"},
- "practice", "coding"));
- assertEquals(3, findShortestDistance(new String[]{"practice", "makes", "perfect", "coding", "makes"},
- "coding", "practice"));
- assertEquals(1, findShortestDistance(new String[]{"practice", "makes", "perfect", "coding", "makes"},
- "makes", "coding"));
- assertEquals(1, findShortestDistance(new String[]{"practice", "makes", "perfect", "coding", "makes"},
- "makes", "perfect"));
- assertEquals(0, findShortestDistance(new String[]{"practice", "makes", "perfect", "coding", "makes"},
- "perfect", "perfect"));
- assertEquals(0, findShortestDistance(new String[]{"practice", "makes", "perfect", "coding", "makes"},
- "makes", "makes"));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/arrays/ShortestWordDistanceIII.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/arrays/ShortestWordDistanceIII.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 0d404633..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/arrays/ShortestWordDistanceIII.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,80 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.arrays;
-
-import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
-
-/**
- * Level: Easy
- * Problem Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/shortest-word-distance-iii/
- * Problem Description:
- * This is a follow-up problem of {@link ShortestWordDistance}. The only difference is that now word1 could be the
- * same as word2.
- *
- * Given a list of words and two words word1 and word2, return the shortest distance between these two words in the list.
- * word1 and word2 may be the same and they represent two individual words in the list.
- *
- * For example,
- * Assume that words = ["practice", "makes", "perfect", "coding", "makes"].
- * Given word1 = “makes”, word2 = “coding”, return 1.
- * Given word1 = "makes", word2 = "makes", return 3.
- *
- * Note: You may assume word1 and word2 are both in the list. If they are same then it's guaranteed that there are
- * two occurrences of the same.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-07-31
- */
-public class ShortestWordDistanceIII {
-
- /**
- * Time Complexity:
- * Space Complexity:
- * TODO
- *
- * @param words
- * @param word1
- * @param word2
- * @return
- */
- public static int findShortestDistance(String[] words, String word1, String word2) {
- int indexWord1 = -1;
- int indexWord2 = -1;
- int minDistance = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
-
- for (int i = 0; i < words.length; i++) {
- if (words[i].equals(word1)) {
- // if both words are same and the first index is already set then do nothing
- if (word1.equals(word2) && indexWord1 != -1) {
-
- } else {
- indexWord1 = i;
- }
- }
- if (words[i].equals(word2)) {
- // if both words are same and i is same as first index then it implies its the
- // first occurrence, skip and continue look for the second occurrence
- if (word1.equals(word2) && i == indexWord1) {
- continue;
- }
- indexWord2 = i;
- }
- if (indexWord1 != -1 && indexWord2 != -1) {
- minDistance = Math.min(minDistance, Math.abs(indexWord1 - indexWord2));
- }
- }
-
- return minDistance;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- assertEquals(3, findShortestDistance(new String[]{"practice", "makes", "perfect", "coding", "makes"},
- "makes", "makes"));
- assertEquals(3, findShortestDistance(new String[]{"practice", "makes", "perfect", "coding", "makes"},
- "coding", "practice"));
- assertEquals(3, findShortestDistance(new String[]{"practice", "makes", "perfect", "coding", "makes"},
- "practice", "coding"));
- assertEquals(1, findShortestDistance(new String[]{"practice", "makes", "perfect", "coding", "makes"},
- "makes", "coding"));
- assertEquals(1, findShortestDistance(new String[]{"practice", "makes", "perfect", "coding", "makes"},
- "makes", "perfect"));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/arrays/SparseMatrixMultiplication.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/arrays/SparseMatrixMultiplication.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 78c884e4..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/arrays/SparseMatrixMultiplication.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,87 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.arrays;
-
-import java.util.Arrays;
-
-import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
-
-/**
- * Level: Medium
- * Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/sparse-matrix-multiplication/
- * Description:
- * Given two sparse matrices A and B, return the result of AB.
- *
- * You may assume that A's column number is equal to B's row number.
- *
- * Example:
- *
- * Input:
- *
- * A = [
- * [ 1, 0, 0],
- * [-1, 0, 3]
- * ]
- *
- * B = [
- * [ 7, 0, 0 ],
- * [ 0, 0, 0 ],
- * [ 0, 0, 1 ]
- * ]
- *
- * Output:
- *
- * | 1 0 0 | | 7 0 0 | | 7 0 0 |
- * AB = | -1 0 3 | x | 0 0 0 | = | -7 0 3 |
- * | 0 0 1 |
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-08-09
- */
-public class SparseMatrixMultiplication {
-
- /**
- * Time Complexity: O(Arow * Acol * Bcol)
- * Space Complexity: O(Arow * Bcol)
- *
- * @param A
- * @param B
- * @return
- */
- public static int[][] multiply(int[][] A, int[][] B) {
- int[][] AB = new int[A.length][B[0].length];
-
- for (int Bcol = 0; Bcol < B[0].length; Bcol++) {
- for (int Arow = 0; Arow < A.length; Arow++) {
- int sum = 0;
- for (int Acol = 0; Acol < A[0].length; Acol++) {
- sum += A[Arow][Acol] * B[Acol][Bcol];
- }
- AB[Arow][Bcol] = sum;
- }
- }
-
- return AB;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- assertEquals(Arrays.deepToString(new int[][]{
- {7, 0, 0},
- {-7, 0, 3}
- }), Arrays.deepToString(multiply(new int[][]{
- {1, 0, 0},
- {-1, 0, 3}
- }, new int[][]{
- {7, 0, 0},
- {0, 0, 0},
- {0, 0, 1}
- })));
-
- assertEquals(Arrays.deepToString(new int[][]{
- {0}
- }), Arrays.deepToString(multiply(new int[][]{
- {0, 1}
- }, new int[][]{
- {1},
- {0}
- })));
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/arrays/ValidTriangleNumber.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/arrays/ValidTriangleNumber.java
deleted file mode 100644
index cdbfb0c5..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/arrays/ValidTriangleNumber.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,117 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.arrays;
-
-import java.util.Arrays;
-
-import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
-
-/**
- * Level: Medium
- * Problem Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/valid-triangle-number/
- * Problem Description:
- * Given an array consists of non-negative integers, your task is to count the number of triplets chosen from the array
- * that can make triangles if we take them as side lengths of a triangle.
- *
- * Example 1:
- * Input: [2,2,3,4]
- * Output: 3
- * Explanation:
- * Valid combinations are:
- * 2,3,4 (using the first 2)
- * 2,3,4 (using the second 2)
- * 2,2,3
- *
- * Note:
- * - The length of the given array won't exceed 1000.
- * - The integers in the given array are in the range of [0, 1000].
- * - Triangle Property: Sum of any 2 sides must be greater than the 3rd side.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-08-07
- */
-public class ValidTriangleNumber {
-
- /**
- * Time complexity : O(n^2 log n). In worst case, the inner loop will take n log n (binary search applied n times).
- * Space complexity : O(log n). Sorting takes O(log n) space.
- * Runtime: 13 ms.
- *
- * @param nums
- * @return
- */
- public static int triangleNumberUsingBinarySearch(int[] nums) {
- int noOfTriangles = 0;
-
- Arrays.sort(nums);
-
- for (int i = 0; i < nums.length - 2; i++) {
- int k = i + 2;
- for (int j = i + 1; j < nums.length - 1; j++) {
- k = binarySearch(nums, k, nums.length - 1, nums[i] + nums[j]);
- if (k - j - 1 > 0) {
- noOfTriangles += k - j - 1;
- }
- }
- }
-
- return noOfTriangles;
- }
-
- private static int binarySearch(int[] nums, int low, int high, int num) {
- while (low <= high) {
- int mid = (low + high) / 2;
- if (nums[mid] < num) {
- low = mid + 1;
- } else {
- high = mid - 1;
- }
- }
-
- return low;
- }
-
- /**
- * The concept is simple. For each pair (i,j), find the value of k such that nums[i] + nums[j] > nums[k] (as per
- * triangle property). Once we find k then we can form k- j - 1 triangles.
- *
- * Time Complexity: O(n^2) Loop of k and j will be executed O(n^2) times in total, because, we do
- * not reinitialize the value of k for a new value of j chosen(for the same i). Thus, the complexity
- * will be O(n^2 + n^2) = O(n^2).
- * Space Complexity: O(log n). Sorting takes O(log n) space.
- * Runtime: 5 ms.
- *
- * @param nums
- * @return
- */
- public static int triangleNumber(int[] nums) {
- int noOfTriangles = 0;
- Arrays.sort(nums);
-
- for (int i = 0; i < nums.length - 2; i++) {
- int k = i + 2;
- for (int j = i + 1; j < nums.length - 1; j++) {
- while (k < nums.length && nums[i] + nums[j] > nums[k]) {
- k++;
- }
- if (k - j - 1 > 0) {
- noOfTriangles += k - j - 1;
- }
- }
- }
-
- return noOfTriangles;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- assertEquals(0, triangleNumberUsingBinarySearch(new int[]{}));
- assertEquals(0, triangleNumberUsingBinarySearch(new int[]{1}));
- assertEquals(3, triangleNumberUsingBinarySearch(new int[]{2, 2, 3, 4}));
- assertEquals(0, triangleNumberUsingBinarySearch(new int[]{0, 1, 0, 1}));
- assertEquals(7, triangleNumberUsingBinarySearch(new int[]{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}));
-
- assertEquals(0, triangleNumber(new int[]{}));
- assertEquals(0, triangleNumber(new int[]{1}));
- assertEquals(3, triangleNumber(new int[]{2, 2, 3, 4}));
- assertEquals(0, triangleNumber(new int[]{0, 1, 0, 1}));
- assertEquals(7, triangleNumber(new int[]{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}));
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/arrays/binarysearch/PowXN.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/arrays/binarysearch/PowXN.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 3591c50e..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/arrays/binarysearch/PowXN.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,85 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.arrays.binarysearch;
-
-import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
-
-/**
- * Level: Medium
- * Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/powx-n/
- * Description:
- * Implement pow(x, n), which calculates x raised to the power n (x^n).
- *
- * Example 1:
- * Input: 2.00000, 10
- * Output: 1024.00000
- *
- * Example 2:
- * Input: 2.10000, 3
- * Output: 9.26100
- *
- * Example 3:
- * Input: 2.00000, -2
- * Output: 0.25000
- * Explanation: 2^-2 = 1/22 = 1/4 = 0.25
- *
- * Note:
- * -100.0 < x < 100.0
- * n is a 32-bit signed integer, within the range [−231, 231 − 1]
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-08-19
- */
-public class PowXN {
-
- /**
- * In this approach we iterate n times and keep multiplying x with x.
- * Runtime: Time limit exceeded.
- *
- * @param x
- * @param n
- * @return
- */
- public static double myPowNaive(double x, int n) {
- if (n == 0) {
- return 1;
- }
- double res = x;
- int absN = Math.abs(n);
- for (int i = 1; i < absN; i++) {
- res *= x;
- }
- return n < 0 ? 1 / res : res;
- }
-
-
- /**
- * In this approach, we iterate log n times. We omit half of n each time. When n is odd, we store whatever product
- * we have calculated so far in the final result.
- *
- * Runtime: 1 ms.
- *
- * @param x
- * @param n
- * @return
- */
- public static double myPow(double x, int n) {
- double res = 1;
- long absN = Math.abs((long) n); // used a long so that `absN / 2` doesn't overflow
-
- while (absN > 0) {
- if (absN % 2 == 1) res *= x; // store whatever we have calculated so far in the final result
- x *= x;
- absN /= 2;
- }
- return n < 0 ? 1 / res : res;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- assertEquals(1024.0, myPowNaive(2.0, 10));
- assertEquals(0.25, myPowNaive(2.0, -2));
- assertEquals(0.0, myPowNaive(0.00001, 2147483647));
-
- assertEquals(1024.0, myPow(2.0, 10));
- assertEquals(0.25, myPow(2.0, -2));
- assertEquals(0.0, myPow(0.00001, 2147483647));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/arrays/binarysearch/SearchInsertPosition.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/arrays/binarysearch/SearchInsertPosition.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 2f13214a..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/arrays/binarysearch/SearchInsertPosition.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,64 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.arrays.binarysearch;
-
-import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
-
-/**
- * Level: Easy
- * Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/search-insert-position/
- * Description:
- * Given a sorted array and a target value, return the index if the target is found. If not, return the index where it
- * would be if it were inserted in order.
- *
- * You may assume no duplicates in the array.
- *
- * Example 1:
- * Input: [1,3,5,6], 5
- * Output: 2
- *
- * Example 2:
- * Input: [1,3,5,6], 2
- * Output: 1
- *
- * Example 3:
- * Input: [1,3,5,6], 7
- * Output: 4
- *
- * Example 4:
- * Input: [1,3,5,6], 0
- * Output: 0
- *
- * Similar question: {@link SmallestLetterGreaterThanTarget}.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-08-19
- */
-public class SearchInsertPosition {
-
- /**
- * Runtime: 0 ms.
- *
- * @param nums
- * @param target
- * @return
- */
- public static int searchInsert(int[] nums, int target) {
- int low = 0;
- int high = nums.length - 1;
- while (low <= high) {
- int mid = low + (high - low) / 2;
- if (nums[mid] == target) {
- return mid;
- } else if (nums[mid] < target) {
- low = mid + 1;
- } else {
- high = mid - 1;
- }
- }
- return low;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- assertEquals(2, searchInsert(new int[]{1, 2}, 3));
- assertEquals(1, searchInsert(new int[]{1, 3, 5, 6}, 2));
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/arrays/binarysearch/SmallestLetterGreaterThanTarget.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/arrays/binarysearch/SmallestLetterGreaterThanTarget.java
deleted file mode 100644
index e44dc339..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/arrays/binarysearch/SmallestLetterGreaterThanTarget.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,87 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.arrays.binarysearch;
-
-import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
-
-/**
- * Level: Easy
- * Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/find-smallest-letter-greater-than-target/
- * Description:
- * Given a list of sorted characters letters containing only lowercase letters, and given a target letter target, find
- * the smallest element in the list that is larger than the given target.
- *
- * Letters also wrap around. For example, if the target is target = 'z' and letters = ['a', 'b'], the answer is 'a'.
- *
- * Examples:
- *
- * Input:
- * letters = ["c", "f", "j"]
- * target = "a"
- * Output: "c"
- *
- * Input:
- * letters = ["c", "f", "j"]
- * target = "c"
- * Output: "f"
- *
- * Input:
- * letters = ["c", "f", "j"]
- * target = "d"
- * Output: "f"
- *
- * Input:
- * letters = ["c", "f", "j"]
- * target = "g"
- * Output: "j"
- *
- * Input:
- * letters = ["c", "f", "j"]
- * target = "j"
- * Output: "c"
- *
- * Input:
- * letters = ["c", "f", "j"]
- * target = "k"
- * Output: "c"
- *
- * Note:
- * - letters has a length in range [2, 10000].
- * - letters consists of lowercase letters, and contains at least 2 unique letters.
- * - target is a lowercase letter.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-08-19
- */
-public class SmallestLetterGreaterThanTarget {
-
- /**
- * Runtime: 0 ms.
- *
- * @param letters
- * @param target
- * @return
- */
- public static char nextGreatestLetter(char[] letters, char target) {
- int low = 0, hi = letters.length - 1;
- while (low <= hi) {
- int mid = low + (hi - low) / 2;
- if (letters[mid] <= target) {
- low = mid + 1;
- } else {
- hi = mid - 1;
- }
- }
- return letters[low % letters.length];
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- assertEquals('a', nextGreatestLetter(new char[]{'a'}, 'z'));
- assertEquals('b', nextGreatestLetter(new char[]{'a', 'b'}, 'a'));
- assertEquals('b', nextGreatestLetter(new char[]{'a', 'b', 'c'}, 'a'));
- assertEquals('a', nextGreatestLetter(new char[]{'a', 'b', 'c'}, 'z'));
- assertEquals('c', nextGreatestLetter(new char[]{'c', 'f', 'j'}, 'a'));
- assertEquals('f', nextGreatestLetter(new char[]{'c', 'f', 'j'}, 'c'));
- assertEquals('f', nextGreatestLetter(new char[]{'c', 'f', 'j'}, 'd'));
- assertEquals('b', nextGreatestLetter(new char[]{'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g', 'h', 'j', 'k', 'l',
- 'm', 'n', 'o', 'p', 'q', 'r', 's', 't', 'u', 'v', 'w', 'x', 'y', 'z'}, 'a'));
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/arrays/binarysearch/SqrtX.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/arrays/binarysearch/SqrtX.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 0dde1308..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/arrays/binarysearch/SqrtX.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,62 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.arrays.binarysearch;
-
-import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
-
-/**
- * Level: Easy
- * Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/sqrtx/
- * Description:
- * Implement int sqrt(int x).
- *
- * Compute and return the square root of x, where x is guaranteed to be a non-negative integer.
- *
- * Since the return type is an integer, the decimal digits are truncated and only the integer part
- * of the result is returned.
- *
- * Example 1:
- * Input: 4
- * Output: 2
- *
- * Example 2:
- * Input: 8
- * Output: 2
- * Explanation: The square root of 8 is 2.82842..., and since
- * the decimal part is truncated, 2 is returned.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-08-19
- */
-public class SqrtX {
-
- /**
- * Runtime: 1 ms.
- *
- * @param x
- * @return
- */
- public static int mySqrt(int x) {
- if (x == 0 || x == 1) {
- return x;
- }
- long low = 1;
- long high = x / 2;
-
- while (low <= high) {
- long mid = low + (high - low) / 2;
- if (mid * mid == x) {
- return (int) mid;
- } else if (mid * mid < x) {
- low = mid + 1;
- } else {
- high = mid - 1;
- }
- }
- return (int) high;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- assertEquals(2, mySqrt(8));
- assertEquals(3, mySqrt(9));
- assertEquals(46339, mySqrt(2147395599));
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/design/AllOne.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/design/AllOne.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 51f771d7..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/design/AllOne.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,125 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.design;
-
-import java.util.HashMap;
-import java.util.HashSet;
-import java.util.Map;
-import java.util.Set;
-
-import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
-
-/**
- * Level: Hard
- * Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/all-oone-data-structure/
- * Description:
- * Implement a data structure supporting the following operations:
- * Inc(Key) - Inserts a new key with value 1. Or increments an existing key by 1. Key is guaranteed to be a non-empty
- * string.
- * Dec(Key) - If Key's value is 1, remove it from the data structure. Otherwise decrements an existing key by 1. If
- * the key does not exist, this function does nothing. Key is guaranteed to be a non-empty string.
- * GetMaxKey() - Returns one of the keys with maximal value. If no element exists, return an empty string "".
- * GetMinKey() - Returns one of the keys with minimal value. If no element exists, return an empty string "".
- *
- * Challenge: Perform all these in O(1) time complexity.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-08-11
- */
-public class AllOne {
-
-
-
- Map keyToValMap;
- Map> valToKeyMap;
-
- /**
- * Initialize your data structure here.
- */
- public AllOne() {
- keyToValMap = new HashMap<>();
- valToKeyMap = new HashMap<>();
- }
-
- /**
- * Inserts a new key with value 1. Or increments an existing key by 1.
- */
- public void inc(String key) {
-
- }
-
- /**
- * Decrements an existing key by 1. If Key's value is 1, remove it from the data structure.
- */
- public void dec(String key) {
-
- }
-
- /**
- * Returns one of the keys with maximal value.
- */
- public String getMaxKey() {
- return null;
- }
-
- /**
- * Returns one of the keys with Minimal value.
- */
- public String getMinKey() {
- return null;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- AllOne allOne = new AllOne();
- allOne.inc("r");
- allOne.inc("r");
- allOne.dec("r");
- allOne.inc("a");
- allOne.inc("b");
- allOne.inc("b");
- assertEquals("b", allOne.getMaxKey());
- assertEquals("a", allOne.getMinKey());
-
- allOne = new AllOne();
- allOne.dec("hello");
- assertEquals("", allOne.getMaxKey());
-
- allOne = new AllOne();
- allOne.inc("a");
- allOne.inc("b");
- allOne.inc("b");
- allOne.inc("b");
- allOne.inc("b");
- allOne.dec("b");
- allOne.dec("b");
- assertEquals("b", allOne.getMaxKey());
- assertEquals("a", allOne.getMinKey());
-
- allOne = new AllOne();
- allOne.inc("hello");
- allOne.inc("hello");
- assertEquals("hello", allOne.getMaxKey());
- assertEquals("hello", allOne.getMinKey());
- allOne.inc("leet");
- assertEquals("hello", allOne.getMaxKey());
- assertEquals("leet", allOne.getMinKey());
-
- allOne = new AllOne();
- allOne.inc("a");
- allOne.inc("b");
- allOne.inc("b");
- allOne.inc("c");
- allOne.inc("c");
- allOne.inc("c");
- allOne.dec("b");
- allOne.dec("b");
- assertEquals("a", allOne.getMinKey());
- allOne.dec("a");
- assertEquals("c", allOne.getMaxKey());
- //assertEquals("c", allOne.getMinKey());
-
- allOne = new AllOne();
- allOne.inc("hello");
- allOne.dec("hello");
- assertEquals("", allOne.getMaxKey());
- assertEquals("", allOne.getMinKey());
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/design/DesignHitCounter.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/design/DesignHitCounter.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 62133196..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/design/DesignHitCounter.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,117 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.design;
-
-import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
-
-/**
- * Level: Medium
- * Problem Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/design-hit-counter/
- * Problem Description:
- * Design a hit counter which counts the number of hits received in the past 5 minutes.
- *
- * Each function accepts a timestamp parameter (in seconds granularity) and you may assume that calls are being made
- * to the system in chronological order (ie, the timestamp is monotonically increasing). You may assume that the
- * earliest timestamp starts at 1.
- *
- * It is possible that several hits arrive roughly at the same time.
- *
- * Example:
- *
- * HitCounter counter = new HitCounter();
- *
- * // hit at timestamp 1.
- * counter.hit(1);
- *
- * // hit at timestamp 2.
- * counter.hit(2);
- *
- * // hit at timestamp 3.
- * counter.hit(3);
- *
- * // get hits at timestamp 4, should return 3.
- * counter.getHits(4);
- *
- * // hit at timestamp 300.
- * counter.hit(300);
- *
- * // get hits at timestamp 300, should return 4.
- * counter.getHits(300);
- *
- * // get hits at timestamp 301, should return 3.
- * counter.getHits(301);
- *
- * Follow up:
- * What if the number of hits per second could be very large? Does your design scale?
- *
- * Runtime: 42 ms (better than ~98%).
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-08-04
- */
-public class DesignHitCounter {
-
- private int[] timestamps;
- private int[] hits;
-
- /**
- * Initialize your data structure here.
- */
- public DesignHitCounter() {
- this.timestamps = new int[300];
- this.hits = new int[300];
- }
-
- /**
- * Record a hit.
- *
- * @param timestamp - The current timestamp (in seconds granularity).
- */
- public void hit(int timestamp) {
- int bucket = timestamp % 300;
- if (timestamps[bucket] == timestamp) {
- hits[bucket]++;
- } else {
- timestamps[bucket] = timestamp;
- hits[bucket] = 1;
- }
- }
-
- /**
- * Return the number of hits in the past 5 minutes.
- *
- * @param timestamp - The current timestamp (in seconds granularity).
- */
- public int getHits(int timestamp) {
- int totalHits = 0;
- for (int i = 0; i < 300; i++) {
- if (timestamp - 300 < timestamps[i]) {
- totalHits += hits[i];
- }
- }
- return totalHits;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- DesignHitCounter counter = new DesignHitCounter();
-
- // hit at timestamp 1.
- counter.hit(1);
-
- // hit at timestamp 2.
- counter.hit(2);
-
- // hit at timestamp 3.
- counter.hit(3);
-
- // get hits at timestamp 4, should return 3.
- assertEquals(3, counter.getHits(4));
-
- // hit at timestamp 300.
- counter.hit(300);
-
- // get hits at timestamp 300, should return 4.
- assertEquals(4, counter.getHits(300));
-
- // get hits at timestamp 301, should return 3.
- assertEquals(3, counter.getHits(301));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/design/InsertDeleteGetRandom.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/design/InsertDeleteGetRandom.java
deleted file mode 100644
index a6c2f376..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/design/InsertDeleteGetRandom.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,106 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.design;
-
-import java.util.*;
-
-import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
-
-/**
- * Level: Medium
- * Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/insert-delete-getrandom-o1/
- * Description:
- * Design a data structure that supports all following operations in average O(1) time.
- *
- * insert(val): Inserts an item val to the set if not already present.
- * remove(val): Removes an item val from the set if present.
- * getRandom: Returns a random element from current set of elements. Each element must have the same probability of
- * being returned.
- *
- * Example:
- *
- * // Init an empty set.
- * RandomizedSet randomSet = new RandomizedSet();
- *
- * // Inserts 1 to the set. Returns true as 1 was inserted successfully.
- * randomSet.insert(1);
- *
- * // Returns false as 2 does not exist in the set.
- * randomSet.remove(2);
- *
- * // Inserts 2 to the set, returns true. Set now contains [1,2].
- * randomSet.insert(2);
- *
- * // getRandom should return either 1 or 2 randomly.
- * randomSet.getRandom();
- *
- * // Removes 1 from the set, returns true. Set now contains [2].
- * randomSet.remove(1);
- *
- * // 2 was already in the set, so return false.
- * randomSet.insert(2);
- *
- * // Since 2 is the only number in the set, getRandom always return 2.
- * randomSet.getRandom();
- *
- * Runtime: 54 ms.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-08-20
- */
-public class LRUCache {
-
- private LinkedHashMap cache;
-
- public LRUCache(int capacity) {
- this.cache = new LinkedHashMap(capacity, 0.75f, true) {
- @Override
- protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry eldest) {
- return size() > capacity;
- }
- };
- }
-
- public int get(int key) {
- Integer val = cache.get(key);
- return val == null ? -1 : val;
- }
-
- public void put(int key, int value) {
- cache.put(key, value);
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- LRUCache cache = new LRUCache(2);
- cache.put(1,1);
- cache.put(2,2);
- cache.put(1,1);
- cache.put(3,3);
- assertEquals(1, cache.get(1));
- assertEquals(-1, cache.get(2));
- assertEquals(3, cache.get(3));
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/dynamicprogramming/MaximumProductSubArray.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/dynamicprogramming/MaximumProductSubArray.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 781cad13..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/dynamicprogramming/MaximumProductSubArray.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,62 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.dynamicprogramming;
-
-import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
-
-/**
- * Level: Medium
- * Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-product-subarray/
- * Description:
- * Given an integer array nums, find the contiguous subarray within an array (containing at least one number) which
- * has the largest product.
- *
- * Example 1:
- * Input: [2,3,-2,4]
- * Output: 6
- * Explanation: [2,3] has the largest product 6.
- *
- * Example 2:
- * Input: [-2,0,-1]
- * Output: 0
- * Explanation: The result cannot be 2, because [-2,-1] is not a subarray.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-08-18
- */
-public class MaximumProductSubArray {
-
- /**
- * The approach is similar to {@link MaximumSubArray} where we update maxUntilIndex only if multiplying the current
- * number to the product of of all numbers until index produces a larger product and if not make maxUntilIndex the
- * current number. The only twist here is that we keep two such variables, one for max and one for min, and that's
- * because the product of two negatives gives us a positive number.
- *
- * Runtime: 1 ms.
- *
- * @param nums
- * @return
- */
- public static int maxProduct(int[] nums) {
- int maxProd = nums[0];
- int maxUntilIndex = nums[0];
- int minUntilIndex = nums[0];
-
- for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
- if (nums[i] >= 0) {
- maxUntilIndex = Math.max(nums[i], maxUntilIndex * nums[i]);
- minUntilIndex = Math.min(nums[i], minUntilIndex * nums[i]);
- } else {
- int prevMaxUntilIndex = maxUntilIndex;
- maxUntilIndex = Math.max(nums[i], minUntilIndex * nums[i]); // when current number is -ve then multiply with minUntilIndex to get the max as product of two negatives is a positive
- minUntilIndex = Math.min(nums[i], prevMaxUntilIndex * nums[i]);
- }
-
- maxProd = Math.max(maxProd, maxUntilIndex);
- }
-
- return maxProd;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- assertEquals(24, maxProduct(new int[]{-2, 3, -4}));
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/dynamicprogramming/MaximumSubArray.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/dynamicprogramming/MaximumSubArray.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 90a28c93..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/dynamicprogramming/MaximumSubArray.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,104 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.dynamicprogramming;
-
-/**
- * Level: Easy
- * Problem Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-subarray
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-04-26
- */
-public class MaximumSubArray {
-
- /**
- * Time complexity: O(n)
- * Runtime: 0 ms.
- *
- * @param nums
- * @return
- */
- public static int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {
- if (nums.length == 0) {
- return 0;
- }
-
- int consecutiveSum = nums[0];
- int maxSum = nums[0];
-
- for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
- consecutiveSum += nums[i];
-
- /* if the current number is larger than the summation of all the
- previous numbers then start from current number */
- if (nums[i] > consecutiveSum) {
- consecutiveSum = nums[i];
- }
-
- if (consecutiveSum > maxSum) {
- maxSum = consecutiveSum;
- }
- }
-
- return maxSum;
- }
-
-
- /**
- * Divide and Conquer approach.
- * Time complexity: O(n log n). See Master's Theorem to understand how.
- * Runtime: 1 ms.
- *
- * @param nums
- * @return
- */
- public static int maxSubArrayDivideAndConquer(int[] nums) {
- return maxSubArrayDivideAndConquer(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
- }
-
- public static int maxSubArrayDivideAndConquer(int[] nums, int start, int end) {
- if (start == end) {
- return nums[start];
- }
-
- int mid = start + (end - start) / 2;
- int leftSASum = maxSubArrayDivideAndConquer(nums, start, mid);
- int rightSASum = maxSubArrayDivideAndConquer(nums, mid + 1, end);
-
- int leftSum = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
- int rightSum = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
-
- // compute consecutive sum from mid towards start
- int sum = 0;
- for (int i = mid; i >= start; i--) {
- sum += nums[i];
- if (sum > leftSum) {
- leftSum = sum;
- }
- }
-
- // compute consecutive sum from mid towards end
- sum = 0;
- for (int i = mid + 1; i <= end; i++) {
- sum += nums[i];
- if (sum > rightSum) {
- rightSum = sum;
- }
- }
-
- // return the max of left sub-array, right sub-array, and the consecutive sum between start and end via mid
- return Math.max(Math.max(leftSASum, rightSASum), leftSum + rightSum);
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(maxSubArray(new int[]{3}));
- System.out.println(maxSubArray(new int[]{-3}));
- System.out.println(maxSubArray(new int[]{-2, 1, -3, 4, -1, 2, 1, -5, 4}));
- System.out.println(maxSubArray(new int[]{4, -5, 1, 2, -1, 4, -3, 1, -2}));
-
- System.out.println("----");
-
- System.out.println(maxSubArrayDivideAndConquer(new int[]{3}));
- System.out.println(maxSubArrayDivideAndConquer(new int[]{-3}));
- System.out.println(maxSubArrayDivideAndConquer(new int[]{-2, 1, -3, 4, -1, 2, 1, -5, 4}));
- System.out.println(maxSubArrayDivideAndConquer(new int[]{4, -5, 1, 2, -1, 4, -3, 1, -2}));
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/dynamicprogramming/PaintHouse.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/dynamicprogramming/PaintHouse.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 5692b0d8..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/dynamicprogramming/PaintHouse.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,52 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.dynamicprogramming;
-
-/**
- * Level: Easy
- * Problem Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/paint-house/
- * Problem Description:
- * There are a row of n houses, each house can be painted with one of the three colors: red, blue or green. The cost
- * of painting each house with a certain color is different. You have to paint all the houses such that no two adjacent
- * houses have the same color. The cost of painting each house with a certain color is represented by a n x 3 cost matrix.
- *
- * For example, costs[0][0] is the cost of painting house 0 with color red; costs[1][2] is the cost of painting
- * house 1 with color green, and so on... Find the minimum cost to paint all houses.
- *
- * Companies: LinkedIn.
- * Related: {@link PaintHouseII}.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-07-23
- */
-public class PaintHouse {
-
- /**
- * Runtime: 1 ms.
- *
- * @param costs of coloring the houses with red, blue, and green respectively. 1st row represents house 1, 2nd row
- * house 2 and so on
- * @return the minimum cost to paint all houses such that no two adjacent houses are of same color
- */
- public static int minCost(int[][] costs) {
- if (costs == null || costs.length == 0) return 0;
-
- for (int i = 1; i < costs.length; i++) {
- costs[i][0] += Math.min(costs[i - 1][1], costs[i - 1][2]);
- costs[i][1] += Math.min(costs[i - 1][0], costs[i - 1][2]);
- costs[i][2] += Math.min(costs[i - 1][0], costs[i - 1][1]);
- }
-
- int lastRow = costs.length - 1;
- return Math.min(Math.min(costs[lastRow][0], costs[lastRow][1]), costs[lastRow][2]);
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(minCost(new int[][]{
- }));
-
- System.out.println(minCost(new int[][]{
- {2, 3, 4},
- {5, 7, 6},
- {8, 7, 2}
- }));
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/dynamicprogramming/PaintHouseII.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/dynamicprogramming/PaintHouseII.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 431ce612..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/dynamicprogramming/PaintHouseII.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,120 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.dynamicprogramming;
-
-import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
-
-/**
- * Level: Hard
- * Problem Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/paint-house-ii/
- * Problem Description:
- * There are a row of n houses, each house can be painted with one of the m colors.
- * The cost of painting each house with a certain color is different.
- * You have to paint all the houses such that no two adjacent houses have the same color.
- *
- * The cost of painting each house with a certain color is represented by a n x m cost matrix.
- *
- * For example, costs[0][0] is the cost of painting house 0 with color 0;
- * costs[1][2] is the cost of painting house 1 with color 2, and so on...
- * Find the minimum cost to paint all houses.
- *
- * Note: All costs are positive integers.
- *
- * Follow up: Could you solve it in O(n * m) runtime? // TODO
- *
- * Companies: LinkedIn.
- * Related: {@link PaintHouse}.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-07-24
- */
-public class PaintHouseII {
-
- /**
- * The approach is similar to {@link PaintHouse} but slightly complex as the number of colors are arbitrary
- * instead of the 3 fixed colors. So, we use two additional for loops to cycle through all the colors.
- * Time Complexity: O(n * m * m)
- * Space Complexity: O(1)
- *
- * @param costs the costs of coloring the house, each row represents the cost of coloring a particular
- * house with different colors
- * @return the minimum cost to paint all houses such that no two adjacent houses are of same color
- */
- public static int minCost(int[][] costs) {
- if (costs == null || costs.length == 0) return 0;
-
- for (int i = 1; i < costs.length; i++) {
- for (int j = 0; j < costs[0].length; j++) {
- int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
- // loop through all colors for the previous house except the color of the current house
- for (int k = 0; k < costs[0].length; k++) {
- if (k != j) {
- min = Math.min(costs[i - 1][k], min);
- }
- }
- costs[i][j] += min;
- }
- }
-
- int minCost = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
- for (int i = 0; i < costs[0].length; i++) {
- minCost = Math.min(costs[costs.length - 1][i], minCost);
- }
-
- return minCost;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- assertEquals(0, minCost(new int[][]{}));
-
- assertEquals(10, minCost(new int[][]{
- {2, 3, 4},
- {5, 7, 6},
- {8, 7, 2}
- }));
-
- assertEquals(10, minCost(new int[][]{{10, 30, 20}}));
-
- assertEquals(3, minCost(new int[][]{{1, 1, 1},
- {1, 1, 1},
- {1, 1, 1}}));
-
- assertEquals(5, minCost(new int[][]{{1, 2, 3},
- {3, 2, 1},
- {2, 2, 2},
- {3, 1, 2}}));
-
- assertEquals(10, minCost(new int[][]{{17, 2, 17},
- {16, 16, 5},
- {14, 3, 19}}));
-
- assertEquals(5, minCost(new int[][]{{1, 5, 3},
- {2, 9, 4}}));
-
- assertEquals(8, minCost(new int[][]{{8}}));
-
- assertEquals(143, minCost(new int[][]{{12, 1, 19},
- {15, 1, 10},
- {3, 11, 10},
- {9, 3, 10},
- {4, 8, 7},
- {4, 18, 2},
- {16, 6, 6},
- {3, 3, 6},
- {10, 18, 16},
- {5, 4, 8},
- {5, 3, 16},
- {11, 8, 19},
- {18, 15, 18},
- {16, 4, 15},
- {10, 7, 13},
- {11, 10, 14},
- {3, 9, 8},
- {5, 2, 2},
- {3, 2, 5},
- {2, 19, 14},
- {17, 3, 6},
- {6, 4, 17},
- {5, 15, 19},
- {2, 14, 14},
- {19, 4, 16}}));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/graphs/GraphValidTree.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/graphs/GraphValidTree.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 15950143..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/graphs/GraphValidTree.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,131 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.graphs;
-
-import java.util.ArrayList;
-import java.util.List;
-
-import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertFalse;
-import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertTrue;
-
-/**
- * Level: Medium
- * Problem Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/graph-valid-tree/
- * Problem Description:
- * Given n nodes labeled from 0 to n-1 and a list of undirected edges (each edge is a pair of nodes), write a function
- * to check whether these edges make up a valid tree.
- *
- * Example 1:
- * Input: n = 5, and edges = [[0,1], [0,2], [0,3], [1,4]]
- * Output: true
- *
- * Example 2:
- * Input: n = 5, and edges = [[0,1], [1,2], [2,3], [1,3], [1,4]]
- * Output: false
- *
- * Note: you can assume that no duplicate edges will appear in edges. Since all edges are undirected, [0,1] is the
- * same as [1,0] and thus will not appear together in edges.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-08-05
- */
-public class GraphValidTree {
-
- /**
- *
- * @param n
- * @param edges
- * @return
- */
- public static boolean isValidTree(int n, int[][] edges) {
- List> adjacencyList = new ArrayList<>(n);
-
- for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
- adjacencyList.add(new ArrayList<>());
- }
-
- for (int i = 0; i < edges.length; i++) {
- adjacencyList.get(edges[i][0]).add(edges[i][1]);
- }
-
- boolean[] visited = new boolean[n];
-
- if (hasCycle(adjacencyList, 0, -1, visited)) {
- return false;
- }
-
- for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
- if (!visited[i]) {
- return false;
- }
- }
-
- return true;
- }
-
- private static boolean hasCycle(List> adjacencyList, int node1, int exclude, boolean[] visited) {
- visited[node1] = true;
-
- for (int i = 0; i < adjacencyList.get(node1).size(); i++) {
- int node2 = adjacencyList.get(node1).get(i);
-
- if ((visited[node2] && exclude != node2) || (!visited[node2] && hasCycle(adjacencyList, node2, node1, visited))) {
- return true;
- }
- }
-
- return false;
- }
-
-
- /**
- * Union-find algorithm: We keep all connected nodes in one set in the union operation and in find operation we
- * check whether two nodes belong to the same set. If yes then there's a cycle and if not then no cycle.
- *
- * Good articles on union-find:
- * - https://www.hackerearth.com/practice/notes/disjoint-set-union-union-find/
- * - https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wU6udHRIkcc
- *
- * @param n
- * @param edges
- * @return
- */
- public static boolean isValidTreeUsingUnionFind(int n, int[][] edges) {
- int[] roots = new int[n];
-
- for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
- roots[i] = i;
- }
-
- for (int i = 0; i < edges.length; i++) {
- // find operation
- if (roots[edges[i][0]] == roots[edges[i][1]]) {
- return false;
- }
- // union operation
- roots[edges[i][1]] = findRoot(roots, roots[edges[i][0]]); // note: we can optimize this even further by
- // considering size of each side and then join the side with smaller size to the one with a larger size (weighted union).
- // We can use another array called size to keep count of the size or we can use the same root array with
- // negative values, i.e, negative resembles that the node is pointing to itself and the number will represent
- // the size. For example, roots = [-2, -1, -1, 0] means that node 3 is pointing to node 0 and node 0 is pointing
- // to itself and is has 2 nodes under it including itself.
- }
-
- return edges.length == n - 1;
- }
-
- private static int findRoot(int[] roots, int node) {
- while (roots[node] != node) {
- node = roots[node];
- }
- return node;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- assertTrue(isValidTree(5, new int[][]{{0, 1}, {0, 2}, {0, 3}, {1, 4}}));
- assertFalse(isValidTree(5, new int[][]{{0, 1}, {1, 2}, {2, 3}, {1, 3}, {1, 4}}));
- assertFalse(isValidTree(3, new int[][]{{0, 1}, {1, 2}, {2, 0}}));
-
- assertTrue(isValidTreeUsingUnionFind(5, new int[][]{{0, 1}, {0, 2}, {0, 3}, {1, 4}}));
- assertFalse(isValidTreeUsingUnionFind(5, new int[][]{{0, 1}, {1, 2}, {2, 3}, {1, 3}, {1, 4}}));
- assertFalse(isValidTreeUsingUnionFind(3, new int[][]{{0, 1}, {1, 2}, {2, 0}}));
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/graphs/WordLadder.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/graphs/WordLadder.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 61e706ce..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/graphs/WordLadder.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,121 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.graphs;
-
-
-import javafx.util.Pair;
-
-import java.util.*;
-
-import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
-
-/**
- * Level: Medium
- * Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/word-ladder/
- * Description:
- * Given two words (beginWord and endWord), and a dictionary's word list, find the length of shortest transformation
- * sequence from beginWord to endWord, such that:
- *
- * Only one letter can be changed at a time. Each transformed word must exist in the word list. Note that beginWord
- * is not a transformed word.
- *
- * Note:
- * - Return 0 if there is no such transformation sequence.
- * - All words have the same length.
- * - All words contain only lowercase alphabetic characters.
- * - You may assume no duplicates in the word list.
- * - You may assume beginWord and endWord are non-empty and are not the same.
- *
- * Example 1:
- * Input:
- * beginWord = "hit",
- * endWord = "cog",
- * wordList = ["hot","dot","dog","lot","log","cog"]
- *
- * Output: 5
- *
- * Explanation: As one shortest transformation is "hit" -> "hot" -> "dot" -> "dog" -> "cog",
- * return its length 5.
- *
- * Example 2:
- * Input:
- * beginWord = "hit"
- * endWord = "cog"
- * wordList = ["hot","dot","dog","lot","log"]
- *
- * Output: 0
- *
- * Explanation: The endWord "cog" is not in wordList, therefore no possible transformation.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-08-15
- */
-public class WordLadder {
-
- /**
- * Runtime: 79 ms.
- *
- * @param beginWord
- * @param endWord
- * @param wordList
- * @return
- */
- public static int ladderLength(String beginWord, String endWord, List wordList) {
- int L = beginWord.length();
- Map> transformedToOriginalWordMap = new HashMap<>();
- Queue> queue = new LinkedList<>();
-
- wordList.forEach(word -> {
- String transformedWord;
- for (int i = 0; i < L; i++) {
- transformedWord = word.substring(0, i) + "*" + word.substring(i + 1, L);
- transformedToOriginalWordMap.putIfAbsent(transformedWord, new HashSet<>());
- transformedToOriginalWordMap.get(transformedWord).add(word);
- }
- }
- );
-
- Set visited = new HashSet<>();
- queue.add(new Pair<>(beginWord, 1));
- visited.add(beginWord);
-
- while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
- Pair currPair = queue.poll();
- String word = currPair.getKey();
- Integer level = currPair.getValue();
-
- if (word.equals(endWord)) {
- return level;
- }
-
- String transformedWord;
- for (int i = 0; i < L; i++) {
- transformedWord = word.substring(0, i) + "*" + word.substring(i + 1, L);
-
- for (String originalWord : transformedToOriginalWordMap.getOrDefault(transformedWord, Collections.emptySet())) {
- if (!visited.contains(originalWord)) {
- queue.add(new Pair<>(originalWord, level + 1));
- visited.add(originalWord);
- }
- }
- }
- }
-
- return 0;
- }
-
- /**
- * TODO: Optimized both end BFS solution
- *
- * @param beginWord
- * @param endWord
- * @param wordList
- * @return
- */
- public static int ladderLengthOptimized(String beginWord, String endWord, List wordList) {
- return -1;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- assertEquals(5, ladderLength("hit", "cog", Arrays.asList("hot", "dot", "dog", "lot", "log", "cog")));
- assertEquals(0, ladderLength("hit", "cog", Arrays.asList("hot", "dot", "dog", "lot", "log")));
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/graphs/WordLadderII.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/graphs/WordLadderII.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 8265c259..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/graphs/WordLadderII.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,152 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.graphs;
-
-import javafx.util.Pair;
-
-import java.util.*;
-
-import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
-
-/**
- * Level: Hard
- * Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/word-ladder-ii/
- * Description:
- * Given two words (beginWord and endWord), and a dictionary's word list, find all shortest transformation sequence(s)
- * from beginWord to endWord, such that:
- *
- * Only one letter can be changed at a time
- * Each transformed word must exist in the word list. Note that beginWord is not a transformed word.
- *
- * Note:
- * - Return an empty list if there is no such transformation sequence.
- * - All words have the same length.
- * - All words contain only lowercase alphabetic characters.
- * - You may assume no duplicates in the word list.
- * - You may assume beginWord and endWord are non-empty and are not the same.
- *
- * Example 1:
- * Input:
- * beginWord = "hit",
- * endWord = "cog",
- * wordList = ["hot","dot","dog","lot","log","cog"]
- *
- * Output:
- * [
- * ["hit","hot","dot","dog","cog"],
- * ["hit","hot","lot","log","cog"]
- * ]
- *
- *
- * Example 2:
- * Input:
- * beginWord = "hit"
- * endWord = "cog"
- * wordList = ["hot","dot","dog","lot","log"]
- *
- * Output: []
- * Explanation: The endWord "cog" is not in wordList, therefore no possible transformation.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-08-15
- */
-public class WordLadderII {
-
- /**
- * The approach is same as {@link WordLadder}. We calculate the {@code minDistance} from start to end word and also
- * keep a map of words and its adjacent words (i.e, with only character difference). After we are done calculating
- * the {@code mindistance}, we perform a dfs on the map upto depth {@code minDistance} and if the last word at this
- * depth is equal to the end word then we add all words to the result.
- *
- * @param beginWord
- * @param endWord
- * @param wordList
- * @return
- */
- public static List> findLadders(String beginWord, String endWord, List wordList) {
- int L = beginWord.length();
- List> ladders = new LinkedList<>();
- Map> transformedToOriginalWordMap = new HashMap<>();
- Queue> queue = new LinkedList<>();
-
- wordList.forEach(word -> {
- String transformedWord;
- for (int i = 0; i < L; i++) {
- transformedWord = word.substring(0, i) + "*" + word.substring(i + 1, L);
- transformedToOriginalWordMap.putIfAbsent(transformedWord, new HashSet<>());
- transformedToOriginalWordMap.get(transformedWord).add(word);
- }
- }
- );
-
- int minDistance = -1;
- Set visited = new HashSet<>();
- queue.add(new Pair<>(beginWord, 1));
- visited.add(beginWord);
-
- HashMap> connectedNodes = new HashMap<>();
-
- while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
- Pair currPair = queue.poll();
- String word = currPair.getKey();
- Integer level = currPair.getValue();
-
- if (word.equals(endWord) && minDistance == -1) {
- minDistance = level - 1;
- }
-
- String transformedWord;
- for (int i = 0; i < L; i++) {
- transformedWord = word.substring(0, i) + "*" + word.substring(i + 1, L);
-
- for (String originalWord : transformedToOriginalWordMap.getOrDefault(transformedWord, Collections.emptySet())) {
- if (!visited.contains(originalWord)) {
- queue.add(new Pair<>(originalWord, level + 1));
- visited.add(originalWord);
- }
-
- if (!word.equals(originalWord)) {
- connectedNodes.putIfAbsent(word, new HashSet<>());
- connectedNodes.get(word).add(originalWord);
- }
- }
- }
- }
-
- dfs(ladders, new LinkedHashSet<>(), connectedNodes, beginWord, endWord, 0, minDistance);
-
- return ladders;
- }
-
- /**
- * Perform dfs on the map which contains words and its adjacent words.
- *
- * @param ladders
- * @param ladder
- * @param connectedNodes
- * @param startNode
- * @param endNode
- * @param distance
- * @param minDistance
- */
- private static void dfs(List> ladders, Set ladder, Map> connectedNodes,
- String startNode, String endNode, int distance, int minDistance) {
- if (distance == minDistance && startNode.equals(endNode)) {
- ladder.add(endNode);
- ladders.add(new ArrayList<>(ladder));
- return;
- } else if (distance > minDistance) {
- return;
- }
-
- ladder.add(startNode);
- for (String nextNode : connectedNodes.getOrDefault(startNode, new HashSet<>())) {
- if (!ladder.contains(nextNode)) {
- dfs(ladders, new LinkedHashSet<>(ladder), connectedNodes, nextNode, endNode, distance + 1, minDistance);
- }
- }
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- assertEquals("[[hit, hot, lot, log, cog], [hit, hot, dot, dog, cog]]", findLadders("hit", "cog", Arrays.asList("hot", "dot", "dog", "lot", "log", "cog")).toString());
- // TODO Fix this test case System.out.println(findLadders("cet", "ism", Arrays.asList("kid", "tag", "pup", "ail", "tun", "woo", "erg", "luz", "brr", "gay", "sip", "kay", "per", "val", "mes", "ohs", "now", "boa", "cet", "pal", "bar", "die", "war", "hay", "eco", "pub", "lob", "rue", "fry", "lit", "rex", "jan", "cot", "bid", "ali", "pay", "col", "gum", "ger", "row", "won", "dan", "rum", "fad", "tut", "sag", "yip", "sui", "ark", "has", "zip", "fez", "own", "ump", "dis", "ads", "max", "jaw", "out", "btu", "ana", "gap", "cry", "led", "abe", "box", "ore", "pig", "fie", "toy", "fat", "cal", "lie", "noh", "sew", "ono", "tam", "flu", "mgm", "ply", "awe", "pry", "tit", "tie", "yet", "too", "tax", "jim", "san", "pan", "map", "ski", "ova", "wed", "non", "wac", "nut", "why", "bye", "lye", "oct", "old", "fin", "feb", "chi", "sap", "owl", "log", "tod", "dot", "bow", "fob", "for", "joe", "ivy", "fan", "age", "fax", "hip", "jib", "mel", "hus", "sob", "ifs", "tab", "ara", "dab", "jag", "jar", "arm", "lot", "tom", "sax", "tex", "yum", "pei", "wen", "wry", "ire", "irk", "far", "mew", "wit", "doe", "gas", "rte", "ian", "pot", "ask", "wag", "hag", "amy", "nag", "ron", "soy", "gin", "don", "tug", "fay", "vic", "boo", "nam", "ave", "buy", "sop", "but", "orb", "fen", "paw", "his", "sub", "bob", "yea", "oft", "inn", "rod", "yam", "pew", "web", "hod", "hun", "gyp", "wei", "wis", "rob", "gad", "pie", "mon", "dog", "bib", "rub", "ere", "dig", "era", "cat", "fox", "bee", "mod", "day", "apr", "vie", "nev", "jam", "pam", "new", "aye", "ani", "and", "ibm", "yap", "can", "pyx", "tar", "kin", "fog", "hum", "pip", "cup", "dye", "lyx", "jog", "nun", "par", "wan", "fey", "bus", "oak", "bad", "ats", "set", "qom", "vat", "eat", "pus", "rev", "axe", "ion", "six", "ila", "lao", "mom", "mas", "pro", "few", "opt", "poe", "art", "ash", "oar", "cap", "lop", "may", "shy", "rid", "bat", "sum", "rim", "fee", "bmw", "sky", "maj", "hue", "thy", "ava", "rap", "den", "fla", "auk", "cox", "ibo", "hey", "saw", "vim", "sec", "ltd", "you", "its", "tat", "dew", "eva", "tog", "ram", "let", "see", "zit", "maw", "nix", "ate", "gig", "rep", "owe", "ind", "hog", "eve", "sam", "zoo", "any", "dow", "cod", "bed", "vet", "ham", "sis", "hex", "via", "fir", "nod", "mao", "aug", "mum", "hoe", "bah", "hal", "keg", "hew", "zed", "tow", "gog", "ass", "dem", "who", "bet", "gos", "son", "ear", "spy", "kit", "boy", "due", "sen", "oaf", "mix", "hep", "fur", "ada", "bin", "nil", "mia", "ewe", "hit", "fix", "sad", "rib", "eye", "hop", "haw", "wax", "mid", "tad", "ken", "wad", "rye", "pap", "bog", "gut", "ito", "woe", "our", "ado", "sin", "mad", "ray", "hon", "roy", "dip", "hen", "iva", "lug", "asp", "hui", "yak", "bay", "poi", "yep", "bun", "try", "lad", "elm", "nat", "wyo", "gym", "dug", "toe", "dee", "wig", "sly", "rip", "geo", "cog", "pas", "zen", "odd", "nan", "lay", "pod", "fit", "hem", "joy", "bum", "rio", "yon", "dec", "leg", "put", "sue", "dim", "pet", "yaw", "nub", "bit", "bur", "sid", "sun", "oil", "red", "doc", "moe", "caw", "eel", "dix", "cub", "end", "gem", "off", "yew", "hug", "pop", "tub", "sgt", "lid", "pun", "ton", "sol", "din", "yup", "jab", "pea", "bug", "gag", "mil", "jig", "hub", "low", "did", "tin", "get", "gte", "sox", "lei", "mig", "fig", "lon", "use", "ban", "flo", "nov", "jut", "bag", "mir", "sty", "lap", "two", "ins", "con", "ant", "net", "tux", "ode", "stu", "mug", "cad", "nap", "gun", "fop", "tot", "sow", "sal", "sic", "ted", "wot", "del", "imp", "cob", "way", "ann", "tan", "mci", "job", "wet", "ism", "err", "him", "all", "pad", "hah", "hie", "aim", "ike", "jed", "ego", "mac", "baa", "min", "com", "ill", "was", "cab", "ago", "ina", "big", "ilk", "gal", "tap", "duh", "ola", "ran", "lab", "top", "gob", "hot", "ora", "tia", "kip", "han", "met", "hut", "she", "sac", "fed", "goo", "tee", "ell", "not", "act", "gil", "rut", "ala", "ape", "rig", "cid", "god", "duo", "lin", "aid", "gel", "awl", "lag", "elf", "liz", "ref", "aha", "fib", "oho", "tho", "her", "nor", "ace", "adz", "fun", "ned", "coo", "win", "tao", "coy", "van", "man", "pit", "guy", "foe", "hid", "mai", "sup", "jay", "hob", "mow", "jot", "are", "pol", "arc", "lax", "aft", "alb", "len", "air", "pug", "pox", "vow", "got", "meg", "zoe", "amp", "ale", "bud", "gee", "pin", "dun", "pat", "ten", "mob")));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/hashtables/ContainsDuplicates.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/hashtables/ContainsDuplicates.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 7b12311b..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/hashtables/ContainsDuplicates.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,49 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.hashtables;
-
-import java.util.Arrays;
-import java.util.HashSet;
-import java.util.Set;
-
-/**
- * Level: Easy
- * Problem Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/contains-duplicate/
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-04-24
- */
-public class ContainsDuplicates {
-
- public static boolean containsDuplicates(int[] nums) {
- Set numSet = new HashSet<>();
- for (int num : nums) {
- if (!numSet.add(num)) {
- return true;
- }
- }
- return false;
- }
-
- /**
- * Runtime: 5 ms.
- *
- * @param nums
- * @return
- */
- public static boolean containsDuplicatesWithoutSet(int[] nums) {
- Arrays.sort(nums);
- for (int i = 0; i < nums.length - 1; i++) {
- if (nums[i] == nums[i + 1]) {
- return true;
- }
- }
- return false;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(containsDuplicates(new int[]{1, 2, 3, 1}));
- System.out.println(containsDuplicates(new int[]{1, 2, 3, 4}));
-
- System.out.println(containsDuplicatesWithoutSet(new int[]{1, 2, 3, 1}));
- System.out.println(containsDuplicatesWithoutSet(new int[]{1, 2, 3, 4}));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/hashtables/IsomorphicStrings.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/hashtables/IsomorphicStrings.java
deleted file mode 100644
index f9a7f4eb..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/hashtables/IsomorphicStrings.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,104 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.hashtables;
-
-import java.util.HashMap;
-import java.util.Map;
-
-import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertFalse;
-import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertTrue;
-
-/**
- * Level: Easy
- * Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/isomorphic-strings/
- * Description:
- * Given two strings s and t, determine if they are isomorphic.
- *
- * Two strings are isomorphic if the characters in s can be replaced to get t.
- *
- * All occurrences of a character must be replaced with another character while preserving the order of characters. No
- * two characters may map to the same character but a character may map to itself.
- *
- * Example 1:
- * Input: s = "egg", t = "add"
- * Output: true
- *
- * Example 2:
- * Input: s = "foo", t = "bar"
- * Output: false
- *
- * Example 3:
- * Input: s = "paper", t = "title"
- * Output: true
- *
- * Note:
- * You may assume both s and t have the same length.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-08-11
- */
-public class IsomorphicStrings {
-
- /**
- * Time Complexity:
- * Space Complexity:
- * Runtime: 8 ms.
- *
- * @param s
- * @param t
- * @return
- */
- public static boolean isIsomorphic(String s, String t) {
-
- Map sToTCharMap = new HashMap<>();
- Map tToSCharMap = new HashMap<>();
-
- for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
- char chFromS = s.charAt(i);
- char chFromT = t.charAt(i);
- if (sToTCharMap.get(chFromS) == null && tToSCharMap.get(chFromT) == null) {
- sToTCharMap.put(chFromS, chFromT);
- tToSCharMap.put(chFromT, chFromS);
- }
- Character mappedChFromSToT = sToTCharMap.get(chFromS);
- if (mappedChFromSToT == null || mappedChFromSToT != chFromT) {
- return false;
- }
- }
-
- return true;
- }
-
- /**
- * Time Complexity:
- * Space Complexity:
- * Runtime: 3 ms.
- *
- * @param s
- * @param t
- * @return
- */
- public static boolean isIsomorphicWithoutMaps(String s, String t) {
- int[] charMap = new int[512];
- for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
- char chFromS = s.charAt(i);
- char chFromT = t.charAt(i);
- if (charMap[chFromS] != charMap[chFromT + 256]) {
- return false;
- }
- charMap[chFromS] = charMap[chFromT + 256] = i + 1;
- }
-
- return true;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- assertTrue(isIsomorphic("egg", "add"));
- assertFalse(isIsomorphic("foo", "bar"));
- assertTrue(isIsomorphic("paper", "title"));
- assertFalse(isIsomorphic("ab", "aa"));
-
- assertTrue(isIsomorphicWithoutMaps("egg", "add"));
- assertFalse(isIsomorphicWithoutMaps("foo", "bar"));
- assertTrue(isIsomorphicWithoutMaps("paper", "title"));
- assertFalse(isIsomorphicWithoutMaps("ab", "aa"));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/hashtables/MyHashMap.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/hashtables/MyHashMap.java
deleted file mode 100644
index cf13c344..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/hashtables/MyHashMap.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,105 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.hashtables;
-
-/**
- * Level: Learning cards
- * Problem Link: https://leetcode.com/explore/learn/card/hash-table/182/practical-applications/1140/
- * Runtime: https://leetcode.com/submissions/detail/224928756/
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-04-25
- */
-public class MyHashMap {
-
- class Entry {
- int key;
- int value;
- Entry next;
-
- Entry(int key, int value) {
- this.key = key;
- this.value = value;
- }
- }
-
- private final int SIZE = 10000;
- private final Entry[] entries;
-
- /**
- * Initialize your data structure here.
- */
- public MyHashMap() {
- entries = new Entry[SIZE];
- }
-
- /**
- * value will always be non-negative.
- */
- public void put(int key, int value) {
- int bucket = key % SIZE;
- Entry entry = entries[bucket];
-
- if (entry == null) {
- entries[bucket] = new Entry(key, value);
- } else {
- while (entry.next != null && entry.key != key) {
- entry = entry.next;
- }
-
- if (entry.key == key) {
- entry.value = value;
- } else {
- entry.next = new Entry(key, value);
- }
- }
- }
-
- /**
- * Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped, or -1 if this map contains no mapping for the key
- */
- public int get(int key) {
- int bucket = key % SIZE;
- Entry entry = entries[bucket];
- while (entry != null) {
- if (entry.key == key) {
- return entry.value;
- }
- entry = entry.next;
- }
- return -1;
- }
-
- /**
- * Removes the mapping of the specified value key if this map contains a mapping for the key
- */
- public void remove(int key) {
- int bucket = key % SIZE;
- Entry entry = entries[bucket];
-
- if (entry != null && entry.key == key) {
- entries[bucket] = entry.next;
- return;
- }
-
- Entry curr = new Entry(0, 0);
- curr.next = entry;
-
- while (curr.next != null && curr.next.key != key) {
- curr = curr.next;
- }
-
- if (curr.next != null) {
- curr.next = curr.next.next;
- }
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- MyHashMap map = new MyHashMap();
- map.put(1, 2);
- System.out.println("1 -> " + map.get(1));
- map.put(1, 4);
- System.out.println("1 -> " + map.get(1));
- map.remove(1);
- System.out.println("1 -> " + map.get(1));
- System.out.println("5 -> " + map.get(5));
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/hashtables/MyHashSet.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/hashtables/MyHashSet.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 3c13d488..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/hashtables/MyHashSet.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,93 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.hashtables;
-
-/**
- * Level: Learning Cards
- * Problem Link: https://leetcode.com/explore/learn/card/hash-table/182/practical-applications/1139/
- * Runtime: https://leetcode.com/submissions/detail/224872991/
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-04-24
- */
-public class MyHashSet {
-
- private final int SIZE = 10000;
- private final Entry[] entries;
-
- class Entry {
- int key;
- Entry next;
-
- Entry(int key) {
- this.key = key;
- }
- }
-
- /**
- * Initialize your data structure here.
- */
- public MyHashSet() {
- entries = new Entry[SIZE];
- }
-
- public void add(int key) {
- if (contains(key)) return;
-
- Entry newEntry = new Entry(key);
- int bucket = key % SIZE;
-
- newEntry.next = entries[bucket];
- entries[bucket] = newEntry;
- }
-
- public void remove(int key) {
- int bucket = key % SIZE;
- Entry entry = entries[bucket];
-
- if (entry != null && entry.key == key) {
- entries[bucket] = entry.next;
- return;
- }
-
- Entry curr = new Entry(0);
- curr.next = entry;
-
- while (curr.next != null && curr.next.key != key) {
- curr = curr.next;
- }
-
- if (curr.next != null) {
- curr.next = curr.next.next;
- }
- }
-
- /**
- * Returns true if this set contains the specified element
- */
- public boolean contains(int key) {
- int bucket = key % SIZE;
- Entry entry = entries[bucket];
-
- while (entry != null) {
- if (entry.key == key) {
- return true;
- }
- entry = entry.next;
- }
-
- return false;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- MyHashSet set = new MyHashSet();
- set.add(1);
- set.add(2);
- set.add(3);
- System.out.println(set.contains(1));
- System.out.println(set.contains(2));
- set.remove(2);
- System.out.println(set.contains(2));
- System.out.println(set.contains(3));
- set.remove(3);
- System.out.println(set.contains(3));
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/hashtables/RepeatedDnaSequence.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/hashtables/RepeatedDnaSequence.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 7674273d..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/hashtables/RepeatedDnaSequence.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,89 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.hashtables;
-
-import java.util.*;
-
-import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
-
-/**
- * Level: Medium
- * Problem Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/repeated-dna-sequences/submissions/
- * Problem Description:
- * All DNA is composed of a series of nucleotides abbreviated as A, C, G, and T, for example: "ACGAATTCCG". When
- * studying DNA, it is sometimes useful to identify repeated sequences within the DNA.
- *
- * Write a function to find all the 10-letter-long sequences (substrings) that occur more than once in a DNA molecule.
- *
- * Example:
- * Input: s = "AAAAACCCCCAAAAACCCCCCAAAAAGGGTTT"
- * Output: ["AAAAACCCCC", "CCCCCAAAAA"]
- *
- * TODO: Figure another method which would have a better runtime.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-07-29
- */
-public class RepeatedDnaSequence {
-
- /**
- * Rabin-Karp Algorithm: https://brilliant.org/wiki/rabin-karp-algorithm/
- * Following Rabin-Karp's approach let's you avoid spurious hits (worst case scenario) but once the hash matches,
- * you will have to compare and check the string you're searching. I tried to just rely on the hash and few test
- * cases failed for me (https://leetcode.com/submissions/detail/247342702/).
- *
- * Time Complexity:
- * Space Complexity:
- * Runtime: 38 ms.
- *
- * @param s
- * @return
- */
- public static List findRepeatedDnaSequences(String s) {
- if (s.length() < 10) return new ArrayList<>();
-
- Set repeatedSequences = new HashSet<>();
- Map> hashToStringMap = new HashMap<>();
- long hashOfSequence = computeHash(s);
- hashToStringMap.put(hashOfSequence, new HashSet() {{
- add(s.substring(0, 10));
- }});
-
- long pow = (long) Math.pow(4, 9);
-
- for (int i = 10; i < s.length(); i++) {
- hashOfSequence = (hashOfSequence - (pow * (s.charAt(i - 10) - 'A'))) * 4 + (s.charAt(i) - 'A');
- String subString = s.substring(i - 10 + 1, i + 1);
-
- if (hashToStringMap.get(hashOfSequence) != null && hashToStringMap.get(hashOfSequence).contains(subString)) {
- repeatedSequences.add(subString);
- continue;
- }
-
- hashToStringMap.putIfAbsent(hashOfSequence, new HashSet<>());
- hashToStringMap.get(hashOfSequence).add(subString);
- }
-
- return new ArrayList<>(repeatedSequences);
- }
-
- private static long computeHash(String s) {
- long hash = 0;
- for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
- hash += (Math.pow(4, i) * (s.charAt(9 - i) - 'A'));
- }
- return hash;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- assertEquals(new ArrayList<>(),
- findRepeatedDnaSequences("AAAAACCC"));
-
- assertEquals(Arrays.asList("AAAAACCCCC", "CCCCCAAAAA"),
- findRepeatedDnaSequences("AAAAACCCCCAAAAACCCCCCAAAAAGGGTTT"));
-
- assertEquals(Collections.singletonList("AAAAAAAAAA"),
- findRepeatedDnaSequences("AAAAAAAAAAAA"));
-
- assertEquals(Collections.singletonList("BBBBBBBBBB"),
- findRepeatedDnaSequences("BBBBBBBBBBBB"));
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/hashtables/ShortestWordDistanceII.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/hashtables/ShortestWordDistanceII.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 3932cebf..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/hashtables/ShortestWordDistanceII.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,89 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.hashtables;
-
-import java.util.ArrayList;
-import java.util.HashMap;
-import java.util.List;
-import java.util.Map;
-
-import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
-
-/**
- * Level: Medium
- * Problem Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/shortest-word-distance-ii/
- * Problem Description:
- * Design a class which receives a list of words in the constructor, and implements a method that takes two words
- * word1 and word2 and return the shortest distance between these two words in the list. Your method will be called
- * repeatedly many times with different parameters. For a simpler variant, see {@link com.leetcode.arrays.ShortestWordDistance}.
- *
- * Examples:
- * Assume that words = ["practice", "makes", "perfect", "coding", "makes"].
- *
- * Input1: word1 = “coding”, word2 = “practice”
- * Output1: 3
- *
- * Input2: word1 = "makes", word2 = "coding"
- * Output2: 1
- *
- * Note: You may assume that word1 does not equal to word2, and word1 and word2 are both in the list.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-07-31
- */
-public class ShortestWordDistanceII {
-
- private String[] words;
- private Map> wordsToIndexesMap;
-
- ShortestWordDistanceII(String[] words) {
- this.words = words;
- this.wordsToIndexesMap = getWordsToIndexesMap();
- }
-
- /**
- * Runtime: 65 ms.
- *
- * @param word1
- * @param word2
- * @return
- */
- public int findShortestDistance(String word1, String word2) {
- return findShortestDistance(wordsToIndexesMap.get(word1), wordsToIndexesMap.get(word2));
- }
-
- private int findShortestDistance(List indexes1, List indexes2) {
- int minDistance = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
-
- for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < indexes1.size() && j < indexes2.size(); ) {
- if (indexes1.get(i) <= indexes2.get(j)) {
- minDistance = Math.min(minDistance, Math.abs(indexes1.get(i) - indexes2.get(j)));
- i++;
- } else if (indexes1.get(i) > indexes2.get(j)) {
- minDistance = Math.min(minDistance, Math.abs(indexes1.get(i) - indexes2.get(j)));
- j++;
- }
- }
-
- return minDistance;
- }
-
- private Map> getWordsToIndexesMap() {
- Map> wordsToIndexesMap = new HashMap<>();
-
- for (int i = 0; i < words.length; i++) {
- wordsToIndexesMap.putIfAbsent(words[i], new ArrayList<>());
- wordsToIndexesMap.get(words[i]).add(i);
- }
- return wordsToIndexesMap;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- ShortestWordDistanceII shortestWordDist = new ShortestWordDistanceII(new String[]{"practice", "makes", "perfect", "coding", "makes"});
- assertEquals(1, shortestWordDist.findShortestDistance("coding", "makes"));
- assertEquals(1, shortestWordDist.findShortestDistance("perfect", "makes"));
- assertEquals(1, shortestWordDist.findShortestDistance("practice", "makes"));
- assertEquals(1, shortestWordDist.findShortestDistance("makes", "practice"));
- assertEquals(3, shortestWordDist.findShortestDistance("coding", "practice"));
- assertEquals(0, shortestWordDist.findShortestDistance("coding", "coding"));
- assertEquals(0, shortestWordDist.findShortestDistance("makes", "makes"));
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/hashtables/TwoSumIII.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/hashtables/TwoSumIII.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 88916db0..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/hashtables/TwoSumIII.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,78 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.hashtables;
-
-import java.util.HashMap;
-import java.util.Map;
-
-import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertTrue;
-
-/**
- * Level: Easy
- * Problem Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/two-sum-iii-data-structure-design/
- * Problem Description:
- * Design and implement a TwoSum class. It should support the following operations: add and find.
- *
- * add - Add the number to an internal data structure.
- * find - Find if there exists any pair of numbers which sum is equal to the value.
- *
- * Example 1:
- * add(1); add(3); add(5);
- * find(4) -> true
- * find(7) -> false
- *
- * Example 2:
- * add(3); add(1); add(2);
- * find(3) -> true
- * find(6) -> false
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-08-03
- */
-public class TwoSumIII {
-
- Map numCount;
-
- /**
- * Initialize your data structure here.
- */
- public TwoSumIII() {
- this.numCount = new HashMap<>();
- }
-
- /**
- * Add the number to an internal data structure..
- */
- public void add(int number) {
- if (numCount.containsKey(number)) {
- numCount.put(number, 2);
- } else {
- numCount.put(number, 1);
- }
- }
-
- /**
- * Find if there exists any pair of numbers which sum is equal to the value.
- */
- public boolean find(int value) {
- for (Map.Entry entry : numCount.entrySet()) {
- int num1 = entry.getKey();
- int num2 = value - num1;
- if ((num2 == num1 && entry.getValue() == 2) || (num1 != num2 && numCount.containsKey(num2))) {
- return true;
- }
- }
- return false;
- }
-
- /**
- * Runtime: 115 ms.
- *
- * @param args
- */
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- TwoSumIII twoSumIII = new TwoSumIII();
- twoSumIII.add(0);
- twoSumIII.add(-1);
- twoSumIII.add(1);
- assertTrue(twoSumIII.find(0));
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/hashtables/slidingwindow/LongestSubstringWithKDistinctCharacters.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/hashtables/slidingwindow/LongestSubstringWithKDistinctCharacters.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 4b209b6e..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/hashtables/slidingwindow/LongestSubstringWithKDistinctCharacters.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,83 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.hashtables.slidingwindow;
-
-import java.util.HashMap;
-import java.util.Map;
-
-import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
-
-/**
- * Level: Hard
- * Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/longest-substring-with-at-most-k-distinct-characters/
- * Description:
- * Given a string, find the length of the longest substring T that contains at most k distinct characters.
- *
- * Example 1:
- * Input: s = "eceba", k = 2
- * Output: 3
- * Explanation: T is "ece" which its length is 3.
- *
- * Example 2:
- * Input: s = "aa", k = 1
- * Output: 2
- * Explanation: T is "aa" which its length is 2.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-08-09
- */
-public class LongestSubstringWithKDistinctCharacters {
-
- /**
- * Time Complexity: O(n)
- * Space Complexity: O(k), as we keep at most k characters in the hash table
- *
- * @param str
- * @param k
- * @return
- */
- public static int lengthOfLongestSubstringKDistinct(String str, int k) {
- int length = 0;
- Map letterCountInWindow = new HashMap<>();
-
- int left = 0; // start of window
- int right = 0; // end of window
-
- while (right < str.length()) {
- char ch = str.charAt(right);
-
- letterCountInWindow.put(ch, letterCountInWindow.getOrDefault(ch, 0) + 1);
-
- // when number of distinct characters in the window exceeds k:
- // - update length
- // - remove the first character in the window or reduce its count if the window has more than one of this character
- // - lastly, move the window forward
- if (letterCountInWindow.keySet().size() > k) {
- char firstChar = str.charAt(left);
- int firstCharCount = letterCountInWindow.get(firstChar);
- if (firstCharCount > 1) {
- letterCountInWindow.put(firstChar, firstCharCount - 1);
- } else {
- letterCountInWindow.remove(firstChar);
- }
- length = Math.max(length, right - left);
- left++;
- }
- right++;
- }
-
- return Math.max(length, right - left);
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- assertEquals(3, lengthOfLongestSubstringKDistinct("eceba", 2));
- assertEquals(7, lengthOfLongestSubstringKDistinct("eceeeeeba", 2));
- assertEquals(12, lengthOfLongestSubstringKDistinct("bbbeeeeebaaaaaaaaaaa", 2));
- assertEquals(2, lengthOfLongestSubstringKDistinct("abcdef", 2));
- assertEquals(1, lengthOfLongestSubstringKDistinct("a", 1));
- assertEquals(0, lengthOfLongestSubstringKDistinct("aa", 0));
- assertEquals(2, lengthOfLongestSubstringKDistinct("aa", 1));
- assertEquals(3, lengthOfLongestSubstringKDistinct("aaa", 1));
- assertEquals(3, lengthOfLongestSubstringKDistinct("aab", 2));
- assertEquals(8, lengthOfLongestSubstringKDistinct("abcabcbb", 3));
- assertEquals(5, lengthOfLongestSubstringKDistinct("pwwkew", 3));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/hashtables/slidingwindow/LongestSubstringWithoutRepeatingCharacters.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/hashtables/slidingwindow/LongestSubstringWithoutRepeatingCharacters.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 93a940e4..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/hashtables/slidingwindow/LongestSubstringWithoutRepeatingCharacters.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,128 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.hashtables.slidingwindow;
-
-import java.util.HashSet;
-import java.util.Set;
-
-import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
-
-/**
- * Level: Medium
- * Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/longest-substring-without-repeating-characters/
- * Description:
- * Given a string, find the length of the longest substring without repeating characters.
- *
- * Example 1:
- * Input: "abcabcbb"
- * Output: 3
- * Explanation: The answer is "abc", with the length of 3.
- *
- * Example 2:
- * Input: "bbbbb"
- * Output: 1
- * Explanation: The answer is "b", with the length of 1.
- *
- * Example 3:
- * Input: "pwwkew"
- * Output: 3
- * Explanation: The answer is "wke", with the length of 3.
- * Note that the answer must be a substring, "pwke" is a subsequence and not a substring.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-08-15
- */
-public class LongestSubstringWithoutRepeatingCharacters {
-
- /**
- * Sliding Window Approach (using map).
- *
- * Note:
- * If we know that the charset is rather small, we can replace the Map with an integer array as direct access table.
- *
- * Commonly used tables are:
- *
- * int[26] for Letters 'a' - 'z' or 'A' - 'Z'
- * int[128] for ASCII
- * int[256] for Extended ASCII
- *
- * Runtime: 8 ms.
- *
- * @param s
- * @return
- */
- public static int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
- int left = 0;
- int right = 0;
- int longestSubstringLen = 0;
- Set charsInWindow = new HashSet<>();
-
-
- while (right < s.length()) {
-
- if (charsInWindow.contains(s.charAt(right))) {
- while (s.charAt(left) != s.charAt(right)) {
- longestSubstringLen = Math.max(longestSubstringLen, right - left);
- charsInWindow.remove(s.charAt(left));
- left++;
- }
- left++;
- }
-
- charsInWindow.add(s.charAt(right));
- right++;
- }
-
- return Math.max(longestSubstringLen, right - left);
- }
-
- /**
- * Sliding Window Approach using int array.
- *
- * Runtime: 2 ms.
- *
- * @param s
- * @return
- */
- public static int lengthOfLongestSubstringNoMap(String s) {
- int left = 0;
- int right = 0;
- int longestSubstringLen = 0;
- int[] charsInWindow = new int[128];
-
- // keep moving forward the right pointer and adding characters to the window
- while (right < s.length()) {
-
- // once we encounter repeated characters, move the left pointer until the repeated character is removed
- if (charsInWindow[s.charAt(right)] == 1) {
- while (s.charAt(left) != s.charAt(right)) {
- longestSubstringLen = Math.max(longestSubstringLen, right - left);
- charsInWindow[s.charAt(left)] = 0;
- left++;
- }
- left++;
- }
-
- charsInWindow[s.charAt(right)] = 1;
- right++;
- }
-
- return Math.max(longestSubstringLen, right - left);
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- assertEquals(0, lengthOfLongestSubstring(""));
- assertEquals(1, lengthOfLongestSubstring(" "));
- assertEquals(1, lengthOfLongestSubstring("a"));
- assertEquals(2, lengthOfLongestSubstring("aab"));
- assertEquals(3, lengthOfLongestSubstring("abcabcbb"));
- assertEquals(1, lengthOfLongestSubstring("bbbbb"));
- assertEquals(3, lengthOfLongestSubstring("pwwkew"));
-
- assertEquals(0, lengthOfLongestSubstringNoMap(""));
- assertEquals(1, lengthOfLongestSubstringNoMap(" "));
- assertEquals(1, lengthOfLongestSubstringNoMap("a"));
- assertEquals(2, lengthOfLongestSubstringNoMap("aab"));
- assertEquals(3, lengthOfLongestSubstringNoMap("abcabcbb"));
- assertEquals(1, lengthOfLongestSubstringNoMap("bbbbb"));
- assertEquals(3, lengthOfLongestSubstringNoMap("pwwkew"));
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/hashtables/slidingwindow/MinimumWindowSubstring.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/hashtables/slidingwindow/MinimumWindowSubstring.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 5414cdc1..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/hashtables/slidingwindow/MinimumWindowSubstring.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,104 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.hashtables.slidingwindow;
-
-import java.util.HashMap;
-import java.util.Map;
-
-import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
-
-/**
- * Level: Hard
- * Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/minimum-window-substring/
- * Description:
- * Given a string S and a string T, find the minimum window in S which will contain all the characters in T in
- * complexity O(n).
- *
- * Example:
- *
- * Input: S = "ADOBECODEBANC", T = "ABC"
- * Output: "BANC"
- *
- * Note:
- * - If there is no such window in S that covers all characters in T, return the empty string "".
- * - If there is such window, you are guaranteed that there will always be only one unique minimum window in S.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-08-13
- */
-public class MinimumWindowSubstring {
-
- /**
- * Sliding Window Approach (using map).
- *
- * Note:
- * If we know that the charset is rather small, we can replace the Map with an integer array as direct access table.
- *
- * Commonly used tables are:
- *
- * int[26] for Letters 'a' - 'z' or 'A' - 'Z'
- * int[128] for ASCII
- * int[256] for Extended ASCII
- *
- * Runtime: 22 ms.
- *
- * @param s
- * @param t
- * @return
- */
- public static String minWindow(String s, String t) {
-
- int left = 0; // start of window
- int right = 0; // end of window
- int begin = 0;
- int windowSize = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
- int charsInWindow = 0; // to check whether the window has all the characters in t with the required frequency
-
- // characters and their counts in t
- Map dictT = new HashMap<>();
- for (int i = 0; i < t.length(); i++) {
- char ch = t.charAt(i);
- dictT.put(ch, dictT.getOrDefault(ch, 0) + 1);
- }
-
- // characters and their counts in the window
- Map dictWindow = new HashMap<>();
-
- while (right < s.length()) {
- char rightChar = s.charAt(right);
- int rightCharCount;
- dictWindow.put(rightChar, (rightCharCount = dictWindow.getOrDefault(rightChar, 0) + 1));
-
- // once the window has a character in t with the required frequency, increment charsInWindow
- if (dictT.get(rightChar) != null && dictT.get(rightChar).equals(rightCharCount)) {
- charsInWindow++;
- }
-
- // once the window has all characters in t with required frequency then shorten the window by moving the
- // left window forward until the window no longer has all characters of t
- while (left <= right && charsInWindow == dictT.size()) {
- if (right - left < windowSize) {
- windowSize = right - left + 1;
- begin = left;
- }
-
- char leftChar = s.charAt(left);
- Integer leftCharCount = dictWindow.get(leftChar);
- dictWindow.put(leftChar, leftCharCount - 1);
-
- if (dictT.get(leftChar) != null && leftCharCount - 1 < dictT.get(leftChar)) {
- charsInWindow--;
- }
- left++;
- }
- right++;
- }
-
- return windowSize == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? "" : s.substring(begin, begin + windowSize);
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- assertEquals("BANC", minWindow("ADOBECODEBANC", "ABC"));
- assertEquals("BAC", minWindow("ADOBECODEBAC", "ABC"));
- assertEquals("ba", minWindow("bba", "ab"));
- assertEquals("baca", minWindow("acbbaca", "aba"));
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/heaps/KthLargestElementInArray.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/heaps/KthLargestElementInArray.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 2422de08..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/heaps/KthLargestElementInArray.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,143 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.heaps;
-
-import com.rampatra.base.MaxHeap;
-
-import java.util.PriorityQueue;
-
-import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
-
-/**
- * Level: Medium
- * Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/kth-largest-element-in-an-array/
- * Description:
- * Find the kth largest element in an unsorted array. Note that it is the kth largest element in the sorted order, not
- * the kth distinct element.
- *
- * Example 1:
- * Input: [3,2,1,5,6,4] and k = 2
- * Output: 5
- *
- * Example 2:
- * Input: [3,2,3,1,2,4,5,5,6] and k = 4
- * Output: 4
- *
- * Note:
- * You may assume k is always valid, 1 ≤ k ≤ array's length.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-08-19
- */
-public class KthLargestElementInArray {
-
- /**
- * Runtime: 1 ms.
- *
- * @param nums
- * @param k
- * @return
- */
- public static int findKthLargest(int[] nums, int k) {
- return heapSortUntilK(nums, k);
- }
-
- /**
- * In heapsort, after each iteration we have the max element at the end of the array. Ergo, if we run the algorithm
- * k times then we would have our kth largest element.
- *
- * @param a
- * @param k
- * @return
- */
- public static int heapSortUntilK(int[] a, int k) {
- buildMaxHeap(a);
- int count = 0;
-
- for (int i = a.length - 1; i > 0; i--) {
- if (count++ == k) {
- break;
- }
- swap(a, 0, i);
- maxHeapify(a, 0, i);
- }
-
- return a[a.length - k];
- }
-
- /**
- * Makes the array {@param a} satisfy the max heap property starting from
- * {@param index} till {@param end} position in array.
- *
- * See this {@link MaxHeap#maxHeapify} for a basic version of maxHeapify.
- *
- * Time complexity: O(log n).
- *
- * @param a
- * @param index
- * @param end
- */
- public static void maxHeapify(int[] a, int index, int end) {
- int largest = index;
- int leftIndex = 2 * index + 1;
- int rightIndex = 2 * index + 2;
-
- if (leftIndex < end && a[index] < a[leftIndex]) {
- largest = leftIndex;
- }
- if (rightIndex < end && a[largest] < a[rightIndex]) {
- largest = rightIndex;
- }
-
- if (largest != index) {
- swap(a, index, largest);
- maxHeapify(a, largest, end);
- }
- }
-
- /**
- * Converts array {@param a} in to a max heap.
- *
- * Time complexity: O(n) and is not O(n log n).
- */
- private static void buildMaxHeap(int[] a) {
- for (int i = a.length / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
- maxHeapify(a, i, a.length);
- }
- }
-
-
- /**
- * When you poll() on a PriorityQueue the smallest number in the queue is removed. Based on this property, we can
- * iterate over the entire array and in the end we would be left with the k largest element in the queue.
- *
- * @param nums
- * @param k
- * @return
- */
- public static int findKthLargestUsingPriorityQueue(int[] nums, int k) {
- PriorityQueue priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>();
-
- for (int num : nums) {
- priorityQueue.add(num);
-
- if (priorityQueue.size() > k) {
- priorityQueue.poll();
- }
- }
-
- return priorityQueue.isEmpty() ? -1 : priorityQueue.peek();
- }
-
- private static void swap(int[] a, int firstIndex, int secondIndex) {
- a[firstIndex] = a[firstIndex] + a[secondIndex];
- a[secondIndex] = a[firstIndex] - a[secondIndex];
- a[firstIndex] = a[firstIndex] - a[secondIndex];
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- assertEquals(5, findKthLargest(new int[]{3, 2, 1, 5, 6, 4}, 2));
- assertEquals(3, findKthLargest(new int[]{3, 2, 1, 5, 6, 4}, 4));
-
- assertEquals(5, findKthLargestUsingPriorityQueue(new int[]{3, 2, 1, 5, 6, 4}, 2));
- assertEquals(3, findKthLargestUsingPriorityQueue(new int[]{3, 2, 1, 5, 6, 4}, 4));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/heaps/TopKFrequentElements.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/heaps/TopKFrequentElements.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 5a684325..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/heaps/TopKFrequentElements.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,68 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.heaps;
-
-import javafx.util.Pair;
-
-import java.util.*;
-import java.util.stream.Collectors;
-
-import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
-
-/**
- * Level: Medium
- * Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/top-k-frequent-elements/
- * Description:
- * Given a non-empty array of integers, return the k most frequent elements.
- *
- * Example 1:
- * Input: nums = [1,1,1,2,2,3], k = 2
- * Output: [1,2]
- *
- * Example 2:
- * Input: nums = [1], k = 1
- * Output: [1]
- *
- * Note:
- * - You may assume k is always valid, 1 ≤ k ≤ number of unique elements.
- * - Your algorithm's time complexity must be better than O(n log n), where n is the array's size.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-08-19
- */
-public class TopKFrequentElements {
-
- /**
- * TODO: A faster approach without using Pair.
- *
- * Runtime: 51 ms.
- *
- * @param nums
- * @param k
- * @return
- */
- public static List topKFrequent(int[] nums, int k) {
- Map numCount = new HashMap<>();
- PriorityQueue> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.comparing(Pair::getValue));
-
- for (int num : nums) {
- numCount.put(num, numCount.getOrDefault(num, 0) + 1);
- }
-
- for (Map.Entry entry : numCount.entrySet()) {
- pq.add(new Pair<>(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue()));
-
- if (pq.size() > k) {
- pq.poll();
- }
- }
-
- return pq.stream().map(Pair::getKey).collect(Collectors.toList());
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- assertEquals("[2, 1]", topKFrequent(new int[]{1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 3}, 2).toString());
- assertEquals("[0]", topKFrequent(new int[]{3, 0, 1, 0}, 1).toString());
- assertEquals("[1]", topKFrequent(new int[]{1}, 1).toString());
- assertEquals("[1, 2]", topKFrequent(new int[]{1, 2}, 2).toString());
- assertEquals("[2, -1]", topKFrequent(new int[]{4, 1, -1, 2, -1, 2, 3}, 2).toString());
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/linkedlists/AddOneToNumberInList.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/linkedlists/AddOneToNumberInList.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 9f0a029c..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/linkedlists/AddOneToNumberInList.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,91 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.linkedlists;
-
-/**
- * Level: Easy
- * Problem Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/plus-one-linked-list/
- * Problem Description: Given a non-empty single linked list representing a number where the head is the
- * most significant bit, add one to the number and return a new linked list.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-06-19
- */
-public class AddOneToNumberInList {
-
-
- /**
- * Add {@code one} to the number represented by linked list {@code head}.
- *
- * @param head the starting node of the linked list
- * @return the head of the linked list after adding {@code one}
- */
- private static Node addOne(Node head) {
- Node currOrig = reverse(head);
- Node currRes = null;
- Node res = null;
-
- int sum = 1;
- int carry = 0;
- int rem;
-
- while (currOrig != null) {
- sum += carry + currOrig.val;
- rem = sum % 10;
- carry = sum / 10;
-
- if (res == null) {
- res = currRes = new Node(rem);
- } else {
- currRes.next = new Node(rem);
- currRes = currRes.next;
- }
-
- sum = 0;
- currOrig = currOrig.next;
- }
-
- if (carry != 0) {
- currRes.next = new Node(carry);
- }
-
- return reverse(res);
- }
-
- private static Node reverse(Node head) {
- Node prev = null;
- Node curr = head;
- Node next;
-
- while (curr != null) {
- next = curr.next;
- curr.next = prev;
-
- prev = curr;
- curr = next;
- }
-
- return prev;
- }
-
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Node node = new Node(9);
- node.next = new Node(9);
- node.next.next = new Node(9);
- node.print();
- addOne(node).print();
-
- System.out.println("---------");
-
- node = new Node(1);
- node.next = new Node(9);
- node.next.next = new Node(9);
- node.print();
- addOne(node).print();
-
- System.out.println("---------");
-
- node = new Node(0);
- node.print();
- addOne(node).print();
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/linkedlists/LinkedListCycleII.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/linkedlists/LinkedListCycleII.java
deleted file mode 100644
index d5fe0e50..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/linkedlists/LinkedListCycleII.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,73 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.linkedlists;
-
-/**
- * Level: Medium
- * Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii/
- * Description:
- * Given a linked list, return the node where the cycle begins. If there is no cycle, return null.
- *
- * To represent a cycle in the given linked list, we use an integer pos which represents the position (0-indexed) in
- * the linked list where tail connects to. If pos is -1, then there is no cycle in the linked list.
- *
- * Note: Do not modify the linked list.
- *
- * Example 1:
- *
- * Input: head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
- * Output: tail connects to node index 1
- * Explanation: There is a cycle in the linked list, where tail connects to the second node.
- *
- *
- * Example 2:
- *
- * Input: head = [1,2], pos = 0
- * Output: tail connects to node index 0
- * Explanation: There is a cycle in the linked list, where tail connects to the first node.
- *
- *
- * Example 3:
- *
- * Input: head = [1], pos = -1
- * Output: no cycle
- * Explanation: There is no cycle in the linked list.
- *
- * Follow-up:
- * Can you solve it without using extra space?
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-08-18
- */
-public class LinkedListCycleII {
-
- /**
- * Runtime: 0 ms.
- *
- * @param head
- * @return
- */
- public Node detectCycle(Node head) {
- Node slow = head;
- Node fast = head;
-
- while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
- slow = slow.next;
- fast = fast.next.next;
- if (slow == fast) {
- break;
- }
- }
-
- if (fast == null || fast.next == null) {
- return null;
- } else {
- slow = head;
-
- while (slow != fast) {
- slow = slow.next;
- fast = fast.next;
- }
-
- return slow;
- }
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/linkedlists/Node.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/linkedlists/Node.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 3276413f..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/linkedlists/Node.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,23 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.linkedlists;
-
-/**
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 21/11/2018
- */
-class Node {
- int val;
- Node next;
-
- Node(int val) {
- this.val = val;
- }
-
- public void print() {
- Node curr = this;
- while (curr.next != null) {
- System.out.print(curr.val + "->");
- curr = curr.next;
- }
- System.out.println(curr.val);
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/math/BestMeetingPoint.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/math/BestMeetingPoint.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 84d96fe9..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/math/BestMeetingPoint.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,141 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.math;
-
-import java.util.ArrayList;
-import java.util.Arrays;
-import java.util.List;
-
-import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
-
-/**
- * Level: Hard
- * Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/best-meeting-point/
- * Description:
- * A group of two or more people wants to meet and minimize the total travel distance. You are given a 2D grid
- * of values 0 or 1, where each 1 marks the home of someone in the group. The distance is calculated using
- * Manhattan Distance, where distance(p1, p2) = |p2.x - p1.x| + |p2.y - p1.y|.
- *
- * Example:
- *
- * Input:
- *
- * 1 - 0 - 0 - 0 - 1
- * | | | | |
- * 0 - 0 - 0 - 0 - 0
- * | | | | |
- * 0 - 0 - 1 - 0 - 0
- *
- * Output: 6
- *
- * Explanation: Given three people living at (0,0), (0,4), and (2,2):
- * The point (0,2) is an ideal meeting point, as the total travel distance
- * of 2+2+2=6 is minimal. So, return 6.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-08-07
- */
-public class BestMeetingPoint {
-
- /**
- * Time Complexity: O(k * i * j)
- * Space Complexity: O(1)
- * where,
- * k = no of homes
- * i = rows in grid
- * j = columns in grid
- *
- * So, if i = j = k then you can see that it has a O(n^3) time complexity.
- *
- * @param grid
- * @return
- */
- public static int minTotalDistanceBrutForce(int[][] grid) {
- int minDistance = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
- List> homeCoordinates = new ArrayList<>();
-
- for (int i = 0; i < grid.length; i++) {
- for (int j = 0; j < grid[0].length; j++) {
- if (grid[i][j] == 1) {
- homeCoordinates.add(Arrays.asList(i, j));
- }
- }
- }
-
- for (int i = 0; i < grid.length; i++) {
- for (int j = 0; j < grid[0].length; j++) {
- int distance = 0;
- for (int k = 0; k < homeCoordinates.size(); k++) {
- distance += Math.abs(homeCoordinates.get(k).get(0) - i) + Math.abs(homeCoordinates.get(k).get(1) - j);
- }
- minDistance = Math.min(minDistance, distance);
- }
- }
-
- return minDistance;
- }
-
- public static int minTotalDistance(int[][] grid) {
- return -1; // todo
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- assertEquals(6, minTotalDistanceBrutForce(new int[][]{
- {1,0,0,0,1},
- {0,0,0,0,0},
- {0,0,1,0,0}
- }));
-
- assertEquals(4, minTotalDistanceBrutForce(new int[][]{
- {1,0,0,0,1},
- {0,0,0,0,0},
- {0,0,0,0,0}
- }));
-
- assertEquals(1, minTotalDistanceBrutForce(new int[][]{
- {1,1,0,0,0},
- {0,0,0,0,0},
- {0,0,0,0,0}
- }));
-
- assertEquals(0, minTotalDistanceBrutForce(new int[][]{
- {1,0,0,0,0},
- {0,0,0,0,0},
- {0,0,0,0,0}
- }));
-
- assertEquals(0, minTotalDistanceBrutForce(new int[][]{
- {0,0,0,0,0},
- {0,0,0,0,0},
- {0,0,0,0,0}
- }));
-
- assertEquals(6, minTotalDistance(new int[][]{
- {1,0,0,0,1},
- {0,0,0,0,0},
- {0,0,1,0,0}
- }));
-
- assertEquals(4, minTotalDistance(new int[][]{
- {1,0,0,0,1},
- {0,0,0,0,0},
- {0,0,0,0,0}
- }));
-
- assertEquals(1, minTotalDistance(new int[][]{
- {1,1,0,0,0},
- {0,0,0,0,0},
- {0,0,0,0,0}
- }));
-
- assertEquals(0, minTotalDistance(new int[][]{
- {1,0,0,0,0},
- {0,0,0,0,0},
- {0,0,0,0,0}
- }));
-
- assertEquals(0, minTotalDistance(new int[][]{
- {0,0,0,0,0},
- {0,0,0,0,0},
- {0,0,0,0,0}
- }));
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/math/ExcelSheetColumnNumber.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/math/ExcelSheetColumnNumber.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 29e1dded..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/math/ExcelSheetColumnNumber.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,44 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.math;
-
-/**
- * Level: Easy
- * Problem Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/excel-sheet-column-number/
- * Problem Description:
- * Given a column title as appear in an Excel sheet, return its corresponding column number.
- *
- * For example:
- *
- * A -> 1
- * B -> 2
- * C -> 3
- * ...
- * Z -> 26
- * AA -> 27
- * AB -> 28
- * ...
- *
- * Example 1:
- * Input: "A"
- * Output: 1
- *
- * Example 2:
- * Input: "AB"
- * Output: 28
- *
- * Example 3:
- * Input: "ZY"
- * Output: 701
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-05-31
- */
-public class ExcelSheetColumnNumber {
-
- private static int titleToNumber(String title) {
- return 0;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
-
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/math/ReverseInteger.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/math/ReverseInteger.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 7e540778..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/math/ReverseInteger.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,62 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.math;
-
-/**
- * Level: Easy
- * Problem Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/reverse-integer/
- * Problem Description:
- * Given a 32-bit signed integer, reverse digits of an integer.
- *
- * Example 1:
- * Input: 123
- * Output: 321
- *
- * Example 2:
- * Input: -123
- * Output: -321
- *
- * Example 3:
- * Input: 120
- * Output: 21
- *
- * Note: Assume we are dealing with an environment which could only store integers within the 32-bit signed
- * integer range: [−2^31, 2^31 − 1]. For the purpose of this problem, assume that your function returns 0 when
- * the reversed integer overflows.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-05-31
- */
-public class ReverseInteger {
-
- /**
- * Reverses the input integer.
- * Time complexity: O(d)
- * where,
- * d = number of digits in num
- *
- * Runtime: 1 ms.
- *
- * @param num an integer.
- * @return the reverse of {@code num}.
- */
- private static int reverse(int num) {
- long reverse = 0;
- int pop;
-
- while (num != 0) {
- pop = num % 10;
- num = num / 10;
- reverse = reverse * 10 + pop;
- }
-
- return reverse < Integer.MIN_VALUE || reverse > Integer.MAX_VALUE ? 0 : (int) reverse;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(reverse(0));
- System.out.println(reverse(-0));
- System.out.println(reverse(123));
- System.out.println(reverse(-123));
- System.out.println(reverse(Integer.MAX_VALUE));
- System.out.println(reverse(Integer.MIN_VALUE));
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/recursion/FlattenNestListIterator.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/recursion/FlattenNestListIterator.java
deleted file mode 100644
index b443e954..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/recursion/FlattenNestListIterator.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,69 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.recursion;
-
-import java.util.ArrayList;
-import java.util.Iterator;
-import java.util.List;
-
-/**
- * Level: Medium
- * Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/flatten-nested-list-iterator/
- * Description:
- * Given a nested list of integers, implement an iterator to flatten it.
- *
- * Each element is either an integer, or a list -- whose elements may also be integers or other lists.
- *
- * Example 1:
- * Input: [[1,1],2,[1,1]]
- * Output: [1,1,2,1,1]
- * Explanation: By calling next repeatedly until hasNext returns false,
- * the order of elements returned by next should be: [1,1,2,1,1].
- *
- * Example 2:
- * Input: [1,[4,[6]]]
- * Output: [1,4,6]
- * Explanation: By calling next repeatedly until hasNext returns false,
- * the order of elements returned by next should be: [1,4,6].
- *
- * Runtime: 2 ms.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-08-12
- */
-public class FlattenNestListIterator implements Iterator {
-
- private int index;
- private List flattenedList;
-
- public FlattenNestListIterator(List nestedList) {
- index = 0;
- flattenedList = getFlattenedList(nestedList);
- }
-
- private List getFlattenedList(List nestedList) {
- List flattenedList = new ArrayList<>();
-
- for (NestedInteger nestedInteger : nestedList) {
- if (nestedInteger.isInteger()) {
- flattenedList.add(nestedInteger.getInteger());
- } else {
- flattenedList.addAll(getFlattenedList(nestedInteger.getList()));
- }
- }
-
- return flattenedList;
- }
-
- @Override
- public Integer next() {
- return flattenedList.get(index++);
- }
-
- @Override
- public boolean hasNext() {
- return index < flattenedList.size();
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- // TODO add some test cases
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/recursion/NestedInteger.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/recursion/NestedInteger.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 1bba817e..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/recursion/NestedInteger.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,46 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.recursion;
-
-import java.util.ArrayList;
-import java.util.List;
-
-/**
- * Class needed for various problems like {@link NestedListWeightSumII}, {@link FlattenNestListIterator}, etc.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-08-12
- */
-public class NestedInteger {
-
- private Integer integer;
- private List list;
-
- public NestedInteger() {
- this.list = new ArrayList<>();
- }
-
- public NestedInteger(int integer) {
- this.integer = integer;
- this.list = new ArrayList<>();
- }
-
- public boolean isInteger() {
- return this.integer != null;
- }
-
- public Integer getInteger() {
- return integer;
- }
-
- public void setInteger(Integer integer) {
- this.integer = integer;
- }
-
- public List getList() {
- return list;
- }
-
- public NestedInteger add(NestedInteger nestedInteger) {
- this.list.add(nestedInteger);
- return this;
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/recursion/NestedListWeightSum.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/recursion/NestedListWeightSum.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 1079b29f..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/recursion/NestedListWeightSum.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,57 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.recursion;
-
-import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
-
-/**
- * Level: Easy
- * Problem Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/nested-list-weight-sum/
- * Problem Description:
- * Given a nested list of integers, return the sum of all integers in the list weighted by their depth. Each element
- * is either an integer, or a list – whose elements may also be integers or other lists.
- *
- * Example 1:
- * Given the list [[1,1],2,[1,1]], return 10. (four 1’s at depth 2, one 2 at depth 1)
- *
- * Example 2:
- * Given the list [1,[4,[6]]], return 27. (one 1 at depth 1, one 4 at depth 2, and one 6 at depth 3; 1 + 42 + 63 = 27)
- *
- * Note: For a more complex variant, see {@link NestedListWeightSumII}.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-07-27
- */
-public class NestedListWeightSum {
-
- /**
- * Time Complexity: The algorithm takes O(N) time, where N is the total number of nested elements in the input
- * list. For example, the list [ [[[[1]]]], 2 ] contains 4 nested lists and 2 nested integers (11 and 22), so N=6.
- * Space Complexity: In terms of space, at most O(D) recursive calls are placed on the stack, where D is the
- * maximum level of nesting in the input. For example, D=2 for the input [[1,1],2,[1,1]], and D=3 for the
- * input [1,[4,[6]]].
- *
- * @param nestedList
- * @return
- */
- public static long nestedSum(Object[] nestedList) {
- return nestedSum(nestedList, 1);
- }
-
- private static long nestedSum(Object[] nestedList, int depth) {
- long sum = 0;
- for (int i = 0; i < nestedList.length; i++) {
- if (nestedList[i] instanceof Integer) {
- sum += ((int) nestedList[i] * depth);
- } else {
- sum += nestedSum((Object[]) nestedList[i], depth + 1);
- }
- }
- return sum;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- assertEquals(0, nestedSum(new Object[]{}));
- assertEquals(0, nestedSum(new Object[]{new Object[]{}}));
- assertEquals(10, nestedSum(new Object[]{new Object[]{1, 1}, 2, new Object[]{1, 1}}));
- assertEquals(27, nestedSum(new Object[]{1, new Object[]{4, new Object[]{6}}}));
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/recursion/NestedListWeightSumII.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/recursion/NestedListWeightSumII.java
deleted file mode 100644
index eadd121b..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/recursion/NestedListWeightSumII.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,80 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.recursion;
-
-import java.util.*;
-
-import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
-
-/**
- * Level: Medium
- * Problem Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/nested-list-weight-sum-ii/
- * Problem Description:
- * Given a nested list of integers, return the sum of all integers in the list weighted by their depth. Each element
- * is either an integer, or a list – whose elements may also be integers or other lists.
- *
- * Different from {@link NestedListWeightSum} where weight is increasing from root to leaf, now the weight is defined
- * from bottom up, i.e., the leaf level integers have weight 1, and the root level integers have the largest weight.
- *
- * Example 1:
- * Given the list [[1,1],2,[1,1]], return 8. (four 1’s at depth 1, one 2 at depth 2)
- *
- * Example 2:
- * Given the list [1,[4,[6]]], return 17. (one 1 at depth 3, one 4 at depth 2, and one 6 at depth 1; 13 + 42 + 6*1 = 17)
- *
- * Note: For a simpler variant, see {@link NestedListWeightSum}.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-07-27
- */
-public class NestedListWeightSumII {
-
- /**
- * Time Complexity:
- * Space Complexity:
- * Runtime: 1 ms.
- *
- * @param nestedList
- * @return
- */
- public static int nestedSum(List nestedList) {
- int weightedSum = 0;
- int unweightedSum = 0;
-
- while (!nestedList.isEmpty()) {
- List nextLevel = new ArrayList<>();
-
- for (NestedInteger ni : nestedList) {
- if (ni.isInteger()) {
- unweightedSum += ni.getInteger();
- } else {
- nextLevel.addAll(ni.getList());
- }
- }
-
- unweightedSum += unweightedSum; // multiplication by repetitive addition
- weightedSum = unweightedSum;
- nestedList = nextLevel;
- }
-
- return weightedSum;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- assertEquals(0, nestedSum(Collections.singletonList(new NestedInteger())));
-
- assertEquals(0, nestedSum(Collections.singletonList(new NestedInteger().add(new NestedInteger()))));
-
- // TODO: fix the test cases
- // {2, {1,1}, {1,1}}
- NestedInteger ni = new NestedInteger(2);
- ni.add(new NestedInteger().add(new NestedInteger(1)).add(new NestedInteger(1)));
- ni.add(new NestedInteger().add(new NestedInteger(1)).add(new NestedInteger(1)));
-
- assertEquals(6, nestedSum(Collections.singletonList(ni)));
-
- // {1, {4, {6}}}
- ni = new NestedInteger(1);
- ni.add(new NestedInteger(4).add(new NestedInteger(6)));
-
- assertEquals(17, nestedSum(Collections.singletonList(ni)));
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/stacks/ExclusiveTimeOfFunctions.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/stacks/ExclusiveTimeOfFunctions.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 63c61dc2..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/stacks/ExclusiveTimeOfFunctions.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,89 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.stacks;
-
-import javafx.util.Pair;
-
-import java.util.Arrays;
-import java.util.List;
-import java.util.Stack;
-
-import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
-
-/**
- * Level: Medium
- * Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/exclusive-time-of-functions/
- * Description:
- * On a single threaded CPU, we execute some functions. Each function has a unique id between 0 and N-1.
- *
- * We store logs in timestamp order that describe when a function is entered or exited.
- *
- * Each log is a string with this format: "{function_id}:{"start" | "end"}:{timestamp}". For example, "0:start:3"
- * means the function with id 0 started at the beginning of timestamp 3. "1:end:2" means the function with id 1 ended
- * at the end of timestamp 2.
- *
- * A function's exclusive time is the number of units of time spent in this function. Note that this does not include
- * any recursive calls to child functions.
- *
- * The CPU is single threaded which means that only one function is being executed at a given time unit.
- *
- * Return the exclusive time of each function, sorted by their function id.
- *
- * Input:
- * n = 2
- * logs = ["0:start:0","1:start:2","1:end:5","0:end:6"]
- * Output: [3, 4]
- * Explanation:
- * Function 0 starts at the beginning of time 0, then it executes 2 units of time and reaches the end of time 1.
- * Now function 1 starts at the beginning of time 2, executes 4 units of time and ends at time 5.
- * Function 0 is running again at the beginning of time 6, and also ends at the end of time 6, thus executing for 1 unit of time.
- * So function 0 spends 2 + 1 = 3 units of total time executing, and function 1 spends 4 units of total time executing.
- *
- *
- * Note:
- * -> 1 <= n <= 100
- * -> Two functions won't start or end at the same time.
- * -> Functions will always log when they exit.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-08-17
- */
-public class ExclusiveTimeOfFunctions {
-
- /**
- * Runtime: 18 ms.
- *
- * @param n
- * @param logs
- * @return
- */
- public static int[] exclusiveTime(int n, List logs) {
- int[] times = new int[n];
- Stack> stack = new Stack<>();
-
- for (String log : logs) {
- String[] l = log.split(":");
- int id = Integer.parseInt(l[0]);
- String operation = l[1];
- int timestamp = Integer.parseInt(l[2]);
-
- if (operation.equals("start")) {
- if (!stack.empty()) { // if there are other processes started before, calculate their time until now
- times[stack.peek().getKey()] += (timestamp - stack.peek().getValue() - 1);
- }
- stack.push(new Pair<>(id, timestamp));
- } else {
- times[id] += timestamp - stack.pop().getValue() + 1;
- if (!stack.isEmpty()) { // if there are other processes, make their start time to now
- stack.push(new Pair<>(stack.pop().getKey(), timestamp));
- }
- }
- }
-
- return times;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- assertEquals("[4]", Arrays.toString(exclusiveTime(1, Arrays.asList("0:start:0", "0:start:1", "0:end:2", "0:end:3"))));
- assertEquals("[6]", Arrays.toString(exclusiveTime(1, Arrays.asList("0:start:0", "0:start:1", "0:start:2", "0:end:3", "0:end:4", "0:end:5"))));
- assertEquals("[3, 4]", Arrays.toString(exclusiveTime(2, Arrays.asList("0:start:0", "1:start:2", "1:end:5", "0:end:6"))));
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/stacks/ReversePolishNotation.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/stacks/ReversePolishNotation.java
deleted file mode 100644
index f917099a..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/stacks/ReversePolishNotation.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,93 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.stacks;
-
-import java.util.Stack;
-
-import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
-
-/**
- * Level: Medium
- * Problem Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/evaluate-reverse-polish-notation
- * Problem Description:
- * Evaluate the value of an arithmetic expression in Reverse Polish Notation.
- *
- * Valid operators are +, -, *, /. Each operand may be an integer or another expression.
- *
- * Note:
- * Division between two integers should truncate toward zero.
- * The given RPN expression is always valid. That means the expression would always evaluate to a result and there
- * won't be any divide by zero operation.
- *
- * Example 1:
- * Input: ["2", "1", "+", "3", "*"]
- * Output: 9
- * Explanation: ((2 + 1) * 3) = 9
- *
- * Example 2:
- * Input: ["4", "13", "5", "/", "+"]
- * Output: 6
- * Explanation: (4 + (13 / 5)) = 6
- *
- * Example 3:
- * Input: ["10", "6", "9", "3", "+", "-11", "*", "/", "*", "17", "+", "5", "+"]
- * Output: 22
- * Explanation:
- * ((10 * (6 / ((9 + 3) * -11))) + 17) + 5
- * = ((10 * (6 / (12 * -11))) + 17) + 5
- * = ((10 * (6 / -132)) + 17) + 5
- * = ((10 * 0) + 17) + 5
- * = (0 + 17) + 5
- * = 17 + 5
- * = 22
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-07-27
- */
-public class ReversePolishNotation {
-
- /**
- * Time Complexity:
- * Space Complexity:
- * Runtime: 5 ms.
- *
- * @param tokens
- * @return
- */
- public static int evalRPN(String[] tokens) {
- int operand1;
- int operand2;
-
- Stack stack = new Stack<>();
-
- for (String s : tokens) {
- switch (s) {
- case "+":
- stack.push(stack.pop() + stack.pop());
- break;
- case "-":
- operand1 = stack.pop();
- operand2 = stack.pop();
- stack.push(operand2 - operand1);
- break;
- case "*":
- stack.push(stack.pop() * stack.pop());
- break;
- case "/":
- operand1 = stack.pop();
- operand2 = stack.pop();
- stack.push(operand2 / operand1);
- break;
- default:
- stack.push(Integer.parseInt(s));
- }
- }
-
- return stack.pop();
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- assertEquals(18, evalRPN(new String[]{"18"}));
- assertEquals(9, evalRPN(new String[]{"2", "1", "+", "3", "*"}));
- assertEquals(6, evalRPN(new String[]{"4", "13", "5", "/", "+"}));
- assertEquals(22, evalRPN(new String[]{"10", "6", "9", "3", "+", "-11", "*", "/", "*", "17", "+", "5", "+"}));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/strings/AnagramsInString.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/strings/AnagramsInString.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 12e7d766..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/strings/AnagramsInString.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,143 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.strings;
-
-import java.util.ArrayList;
-import java.util.Arrays;
-import java.util.List;
-
-/**
- * Level: Medium
- * Problem: https://leetcode.com/problems/find-all-anagrams-in-a-string/
- * Description:
- * Given a string s and a non-empty string p, find all the start indices of p's anagrams in s.
- *
- * Strings consists of lowercase English letters only and the length of both strings s and p will not be larger
- * than 20,100.
- *
- * The order of output does not matter.
- *
- * Example 1:
- *
- * Input:
- * s: "cbaebabacd" p: "abc"
- *
- * Output:
- * [0, 6]
- *
- * Explanation:
- * The substring with start index = 0 is "cba", which is an anagram of "abc".
- * The substring with start index = 6 is "bac", which is an anagram of "abc".
- *
- * Example 2:
- *
- * Input:
- * s: "abab" p: "ab"
- *
- * Output:
- * [0, 1, 2]
- *
- * Explanation:
- * The substring with start index = 0 is "ab", which is an anagram of "ab".
- * The substring with start index = 1 is "ba", which is an anagram of "ab".
- * The substring with start index = 2 is "ab", which is an anagram of "ab".
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-04-13
- */
-public class AnagramsInString {
-
- /**
- * Time complexity: O((n-m) * m log m)
- * where,
- * n = text length
- * m = pattern length
- *
- * @param text
- * @param pattern
- * @return
- */
- private static List findAllAnagramsInTextNaive(String text, String pattern) {
- List indexes = new ArrayList<>();
-
- int textLen = text.length();
- int patternLen = pattern.length();
-
- char[] patternChars = pattern.toCharArray();
- Arrays.sort(patternChars); // takes O(m log m) time
- String patternSorted = String.valueOf(patternChars);
-
- String subText;
- char[] subTextChars;
- String subTextSorted;
-
- for (int i = 0; i <= textLen - patternLen; i++) { // loops n-m number of times
- subText = text.substring(i, i + patternLen);
- subTextChars = subText.toCharArray();
- Arrays.sort(subTextChars); // sorts m number of characters, takes O(m log m)
- subTextSorted = String.valueOf(subTextChars);
-
- if (subTextSorted.equals(patternSorted)) { // compare m characters takes m time
- indexes.add(i);
- }
- }
- return indexes;
- }
-
- /**
- * Time complexity: O(n)
- * where,
- * n = length of text or number of characters in text
- *
- * Runtime: 6 ms.
- *
- * @param text
- * @param pattern
- * @return
- */
- private static List findAllAnagramsInText(String text, String pattern) {
- List indices = new ArrayList<>();
-
- int textLen = text.length();
- int patternLen = pattern.length();
-
- int[] textCharCountInWindow = new int[26];
- int[] patternCharCount = new int[26];
-
- for (int i = 0; i < patternLen; i++) {
- patternCharCount[pattern.charAt(i) - 'a']++;
- }
-
- for (int i = 0; i < textLen; i++) {
- textCharCountInWindow[text.charAt(i) - 'a']++;
- if (i >= patternLen) {
- textCharCountInWindow[text.charAt(i - patternLen) - 'a']--;
- }
- if (Arrays.equals(textCharCountInWindow, patternCharCount)) { // loops 26 times no matter the text/pattern length
- indices.add(i - patternLen + 1);
- }
- }
-
- return indices;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- // basic use cases
- System.out.println(findAllAnagramsInTextNaive("cbaebabacd", "abc"));
- System.out.println(findAllAnagramsInTextNaive("abab", "ab"));
- System.out.println(findAllAnagramsInTextNaive("af", "af"));
- System.out.println(findAllAnagramsInTextNaive("af", "be"));
-
- // corner case
- System.out.println(findAllAnagramsInTextNaive("", "ab"));
-
- System.out.println("-----");
-
- // basic use cases
- System.out.println(findAllAnagramsInText("cbaebabacd", "abc"));
- System.out.println(findAllAnagramsInText("abab", "ab"));
- System.out.println(findAllAnagramsInText("af", "af"));
- System.out.println(findAllAnagramsInText("af", "be"));
-
- // corner case
- System.out.println(findAllAnagramsInText("", "ab"));
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/strings/CountAndSay.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/strings/CountAndSay.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 24f41a3e..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/strings/CountAndSay.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,48 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.strings;
-
-/**
- * Level: Easy
- * Problem: https://leetcode.com/problems/count-and-say/
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-04-20
- */
-public class CountAndSay {
-
- /**
- * Time complexity:
- * Runtime: 1 ms.
- *
- * @param n
- * @return
- */
- public static String countAndSay(int n) {
- if (n == 1) return "1";
-
- String s = countAndSay(n - 1);
- StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
- int count = 0;
-
- for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
- count++;
-
- if (i + 1 >= s.length() || s.charAt(i) != s.charAt(i + 1)) {
- sb.append(count);
- sb.append(s.charAt(i));
- count = 0;
- }
- }
-
- return sb.toString();
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(countAndSay(1));
- System.out.println(countAndSay(2));
- System.out.println(countAndSay(3));
- System.out.println(countAndSay(4));
- System.out.println(countAndSay(5));
- System.out.println(countAndSay(6));
- System.out.println(countAndSay(10));
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/strings/LongestCommonPrefix.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/strings/LongestCommonPrefix.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 07bd6392..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/strings/LongestCommonPrefix.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,48 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.strings;
-
-/**
- * Level: Easy
- * Problem: https://leetcode.com/problems/longest-common-prefix/
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-04-20
- */
-public class LongestCommonPrefix {
-
- /**
- * Time complexity: O(r * c)
- * where,
- * r = no. of strings
- * c = max. no. of characters in a particular string
- *
- * Runtime: 1 ms.
- *
- * @param strs
- * @return
- */
- public static String longestCommonPrefix(String[] strs) {
- if (strs == null || strs.length == 0) return "";
-
- int row;
- for (int col = 0; col < strs[0].length(); col++) {
- for (row = 0; row < strs.length - 1; row++) {
- // once we find a different character under one column, return the characters read so far
- if (col == strs[row].length()
- || col == strs[row + 1].length()
- || strs[row].charAt(col) != strs[row + 1].charAt(col)) {
- return strs[row].substring(0, col);
- }
- }
- }
-
- return strs[0];
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(longestCommonPrefix(new String[]{}));
- System.out.println(longestCommonPrefix(new String[]{""}));
- System.out.println(longestCommonPrefix(new String[]{"a"}));
- System.out.println(longestCommonPrefix(new String[]{"flower", "flow", "flight"}));
- System.out.println(longestCommonPrefix(new String[]{"dog", "racecar", "car"}));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/strings/RansomNote.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/strings/RansomNote.java
deleted file mode 100644
index c6b66fb0..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/strings/RansomNote.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,40 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.strings;
-
-/**
- * Level: Easy
- * Problem: https://leetcode.com/problems/ransom-note/
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-04-19
- */
-public class RansomNote {
-
- /**
- * Runtime: 4 ms/a>.
- *
- * @param ransomNote
- * @param magazine
- * @return
- */
- public static boolean canConstruct(String ransomNote, String magazine) {
- char[] charCount = new char[26];
-
- for (int i = 0; i < magazine.length(); i++) {
- charCount[magazine.charAt(i) - 'a']++;
- }
-
- for (int i = 0; i < ransomNote.length(); i++) {
- if (charCount[ransomNote.charAt(i) - 'a']-- == 0) {
- return false;
- }
- }
- return true;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(canConstruct("", ""));
- System.out.println(canConstruct("a", "a"));
- System.out.println(canConstruct("ab", "ab"));
- System.out.println(canConstruct("aab", "ab"));
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/strings/ReverseStringII.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/strings/ReverseStringII.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 4a5aabd4..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/strings/ReverseStringII.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,46 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.strings;
-
-/**
- * Level: Easy
- * Problem: https://leetcode.com/problems/reverse-string-ii/
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-04-20
- */
-public class ReverseStringII {
-
- /**
- * Time complexity: O(n)
- * where,
- * n = no. of characters in string
- *
- * Runtime: 0 ms.
- *
- * @param str
- * @param k
- * @return
- */
- public static String reverseStr(String str, int k) {
- char[] chars = str.toCharArray();
- int len = str.length();
- for (int i = 0; i < len; i += 2 * k) {
- reverse(chars, i, Math.min(len, i + k));
- }
- return new String(chars);
- }
-
- private static void reverse(char[] chars, int start, int end) {
- char temp;
- for (int i = start, j = end - 1; i < j; i++, j--) {
- temp = chars[i];
- chars[i] = chars[j];
- chars[j] = temp;
- }
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(reverseStr("abcdefg", 2));
- System.out.println(reverseStr("abcdef", 2));
- System.out.println(reverseStr("abcde", 2));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/strings/ReverseVowels.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/strings/ReverseVowels.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 25518cac..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/strings/ReverseVowels.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,66 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.strings;
-
-/**
- * Level: Easy
- * Problem: https://leetcode.com/problems/reverse-vowels-of-a-string/
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-04-19
- */
-public class ReverseVowels {
-
- /**
- * Reverse only the vowels in the string {@code str}.
- *
- * Time Complexity: O(n)
- * where,
- * n = no. of characters in the string
- *
- * Runtime: 2 ms on leetcode.
- *
- * @param str
- * @return
- */
- private static String reverseVowels(String str) {
-
- char[] chars = str.toCharArray();
- char temp;
- int left = 0;
- int right = str.length() - 1;
-
- while (left < right) {
- // find the vowel from left
- while (!isVowel(chars[left]) && left < right) {
- left++;
- }
- // find the vowel from right
- while (!isVowel(chars[right]) && left < right) {
- right--;
- }
-
- if (!isVowel(chars[left]) || !isVowel(chars[right])) {
- break;
- }
-
- // swap the characters
- temp = chars[left];
- chars[left] = chars[right];
- chars[right] = temp;
-
- left++;
- right--;
- }
- return new String(chars);
- }
-
- private static boolean isVowel(char c) {
- return c == 'a' || c == 'e' || c == 'i' || c == 'o' || c == 'u' ||
- c == 'A' || c == 'E' || c == 'I' || c == 'O' || c == 'U';
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(reverseVowels("hello"));
- System.out.println(reverseVowels("a"));
- System.out.println(reverseVowels(""));
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/strings/StrStr.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/strings/StrStr.java
deleted file mode 100644
index aa3bc896..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/strings/StrStr.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,59 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.strings;
-
-/**
- * Level: Easy
- * Problem Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/implement-strstr/
- * Problem Description:
- * Implement strStr(). Return the index of the first occurrence of needle in haystack, or -1 if needle
- * is not part of haystack.
- *
- * Example 1:
- *
- * Input: haystack = "hello", needle = "ll"
- * Output: 2
- * Example 2:
- *
- * Input: haystack = "aaaaa", needle = "bba"
- * Output: -1
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-04-28
- */
-public class StrStr {
-
- /**
- * Time complexity: O(m*n)
- * where,
- * m = length of haystack
- * n = length of needle
- *
- * Runtime: 3 ms.
- *
- * @param haystack
- * @param needle
- * @return
- */
- public static int strStr(String haystack, String needle) {
- for (int i = 0; ; i++) {
- for (int j = 0; ; j++) {
- if (j == needle.length()) return i;
- if (i + j == haystack.length()) return -1;
- if (needle.charAt(j) != haystack.charAt(i + j)) break;
- }
- }
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(strStr("hello", "ll"));
- System.out.println(strStr("leet", "e"));
- System.out.println(strStr("mississippi", "issip"));
- System.out.println(strStr("mississippi", "pi"));
- System.out.println(strStr("aaaa", "bba"));
-
- // edge cases
- System.out.println(strStr("aaa", "aaaa"));
- System.out.println(strStr("aaaa", ""));
- System.out.println(strStr("", "abc"));
- System.out.println(strStr("", ""));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/strings/StringCompression.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/strings/StringCompression.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 7697f591..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/strings/StringCompression.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,15 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.strings;
-
-/**
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-04-16
- */
-public class StringCompression {
-
- private static int compress(char[] chars) {
- return -1;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/strings/UniqueCharacterInString.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/strings/UniqueCharacterInString.java
deleted file mode 100644
index da155710..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/strings/UniqueCharacterInString.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,38 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.strings;
-
-/**
- * Level: Easy
- * Problem: https://leetcode.com/problems/first-unique-character-in-a-string/
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-04-16
- */
-public class UniqueCharacterInString {
-
- /**
- * Time complexity: O(n)
- * Runtime: 7 ms on leetcode.
- *
- * @param str the input string
- * @return the index of the first non-repeating character in {@code str}, {@code -1} otherwise.
- */
- private static int findFirstUniqueCharacterInString(String str) {
- int[] charCount = new int[26];
-
- for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
- charCount[str.charAt(i) - 'a']++;
- }
-
- for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
- if (charCount[str.charAt(i) - 'a'] == 1) {
- return i;
- }
- }
- return -1;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(findFirstUniqueCharacterInString("leetcode"));
- System.out.println(findFirstUniqueCharacterInString("loveleetcode"));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/strings/ValidPalindrome.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/strings/ValidPalindrome.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 451849b6..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/strings/ValidPalindrome.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,59 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.strings;
-
-/**
- * Level: Easy
- * Problem: https://leetcode.com/problems/valid-palindrome/
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-04-19
- */
-public class ValidPalindrome {
-
- /**
- * Time complexity: O(n)
- * where,
- * n = no. of characters in the string
- *
- * Runtime: 2 ms on leetcode.
- *
- * @param str
- * @return
- */
- private static boolean isPalindrome(String str) {
- char[] chars = str.toCharArray();
- int left = 0;
- int right = chars.length - 1;
-
- while (left < right) {
- // if it's not alphanumeric then move the left pointer forward
- while (!isAlphaNumeric(chars[left]) && left < right) {
- left++;
- }
- // if it's not alphanumeric then move the right pointer backward
- while (!isAlphaNumeric(chars[right]) && left < right) {
- right--;
- }
-
- // case insensitive comparison
- if (Character.toLowerCase(chars[left]) != Character.toLowerCase(chars[right])) {
- return false;
- }
-
- left++;
- right--;
- }
-
- return true;
- }
-
- private static boolean isAlphaNumeric(char c) {
- int i = (int) c;
- return (i >= 48 && i <= 57) || (i >= 65 && i <= 90) || (i >= 97 && i <= 122);
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(isPalindrome("A man, a plan, a canal: Panama"));
- System.out.println(isPalindrome("race a car"));
- System.out.println(isPalindrome("0P"));
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/trees/BinaryTreeUpsideDown.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/trees/BinaryTreeUpsideDown.java
deleted file mode 100644
index aa43bf50..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/trees/BinaryTreeUpsideDown.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,207 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.trees;
-
-import java.util.Stack;
-
-import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
-import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertNull;
-
-/**
- * Level: Medium
- * Problem Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/binary-tree-upside-down/
- * Problem Description:
- * Given a binary tree where all the right nodes are either leaf nodes with a sibling (a left node that shares the
- * same parent node) or empty, flip it upside down and turn it into a tree where the original right nodes turned into
- * left leaf nodes. Return the new root.
- *
- * Example:
- * Input: [1,2,3,4,5]
- *
- * 1
- * / \
- * 2 3
- * / \
- * 4 5
- *
- * Output: return the root of the binary tree [4,5,2,#,#,3,1]
- *
- * 4
- * / \
- * 5 2
- * / \
- * 3 1
- *
- * Clarification:
- * Confused what [4,5,2,#,#,3,1] means? Read more below on how binary tree is serialized on OJ. The serialization of
- * a binary tree follows a level order traversal, where '#' signifies a path terminator where no node exists below.
- *
- * Here's an example:
- *
- * 1
- * / \
- * 2 3
- * /
- * 4
- * \
- * 5
- *
- * The above binary tree is serialized as [1,2,3,#,#,4,#,#,5].
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-08-04
- */
-public class BinaryTreeUpsideDown {
-
- /**
- * The solution is simple, every node (except the root) on the left of the tree would have its parent's right child
- * as it's left child and parent as its right child. That's all you have to do to flip the tree upside down.
- *
- * Time Complexity: O(h)
- * Space Complexity: O(h)
- * where,
- * h = height of the tree
- *
- * Runtime: 1 ms.
- *
- * @param root
- * @return
- */
- public static TreeNode upsideDownBinaryTreeUsingStack(TreeNode root) {
- if (root == null) return null;
-
- TreeNode curr = root;
- TreeNode currParent;
- TreeNode newRoot = null;
-
- // using stack to keep track of the parent node
- Stack stack = new Stack<>();
-
- while (curr != null) {
- stack.add(curr);
- curr = curr.left;
- }
-
- while (!stack.empty()) {
- curr = stack.pop();
- currParent = stack.empty() ? null : stack.peek();
-
- if (newRoot == null) newRoot = curr;
-
- if (currParent != null) {
- curr.left = currParent.right;
- curr.right = currParent;
- } else {
- curr.left = null;
- curr.right = null;
- }
- }
-
- return newRoot;
- }
-
- /**
- * The solution is simple, every node (except the root) on the left of the tree would have its parent's right child
- * as it's left child and parent as its right child. That's all you have to do to flip the tree upside down.
- *
- * Time Complexity: O(h)
- * Space Complexity: O(h)
- * where,
- * h = height of the tree
- *
- * Runtime: 0 ms.
- *
- * @param node
- * @return
- */
- public static TreeNode upsideDownBinaryTree(TreeNode node) {
- if (node == null || node.left == null) return node;
-
- // go to the last node on the extreme left branch
- TreeNode newRoot = upsideDownBinaryTree(node.left);
-
- // do the node changes as you backtrack
- node.left.left = node.right;
- node.left.right = node;
-
- // clean up
- node.left = null;
- node.right = null;
-
- return newRoot;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- /*
- Binary Tree
-
- 1
- / \
- 2 3
- / \
- 4 5
- */
- TreeNode tree = new TreeNode(1);
- tree.left = new TreeNode(2);
- tree.right = new TreeNode(3);
- tree.left.left = new TreeNode(4);
- tree.left.right = new TreeNode(5);
-
- /*
- Upside Down Binary Tree
-
- 4
- / \
- 5 2
- / \
- 3 1
- */
- TreeNode upsideDownTree = upsideDownBinaryTreeUsingStack(tree);
- assertEquals(4, upsideDownTree.val);
- assertEquals(5, upsideDownTree.left.val);
- assertEquals(2, upsideDownTree.right.val);
- assertEquals(1, upsideDownTree.right.right.val);
- assertEquals(3, upsideDownTree.right.left.val);
- assertNull(upsideDownTree.right.right.left);
- assertNull(upsideDownTree.right.right.right);
-
-
-
- /******************************
- *
- * Test for the recursive method
- *
- ******************************/
-
- /*
- Binary Tree
-
- 1
- / \
- 2 3
- / \
- 4 5
- */
- tree = new TreeNode(1);
- tree.left = new TreeNode(2);
- tree.right = new TreeNode(3);
- tree.left.left = new TreeNode(4);
- tree.left.right = new TreeNode(5);
-
- /*
- Upside Down Binary Tree
-
- 4
- / \
- 5 2
- / \
- 3 1
- */
- upsideDownTree = upsideDownBinaryTree(tree);
- assertEquals(4, upsideDownTree.val);
- assertEquals(5, upsideDownTree.left.val);
- assertEquals(2, upsideDownTree.right.val);
- assertEquals(1, upsideDownTree.right.right.val);
- assertEquals(3, upsideDownTree.right.left.val);
- assertNull(upsideDownTree.right.right.right);
- assertNull(upsideDownTree.right.right.left);
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/trees/BinaryTreeZigZagLevelOrderTraversal.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/trees/BinaryTreeZigZagLevelOrderTraversal.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 1a54d952..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/trees/BinaryTreeZigZagLevelOrderTraversal.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,100 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.trees;
-
-import java.util.*;
-
-import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
-
-/**
- * Level: Medium
- * Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/binary-tree-zigzag-level-order-traversal/
- * Description:
- * Given a binary tree, return the zigzag level order traversal of its nodes' values. (ie, from left to right, then
- * right to left for the next level and alternate between).
- *
- * For example:
- * Given binary tree [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
- * 3
- * / \
- * 9 20
- * / \
- * 15 7
- * return its zigzag level order traversal as:
- * [
- * [3],
- * [20,9],
- * [15,7]
- * ]
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-08-11
- */
-public class BinaryTreeZigZagLevelOrderTraversal {
-
- /**
- * Time Complexity:
- * Space Complexity:
- * Runtime: 1 ms.
- *
- * @param root
- * @return
- */
- public static List> zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode root) {
-
- int levelNo = 0;
- LinkedList currLevel = new LinkedList<>();
- List> levelOrderTraversal = new LinkedList<>();
-
- if (root == null) {
- return levelOrderTraversal;
- }
-
- Queue queue = new LinkedList<>();
- queue.add(root);
- queue.add(null);
-
- while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
-
- TreeNode treeNode = queue.poll();
-
- if (treeNode == null) {
- levelOrderTraversal.add(currLevel);
- currLevel = new LinkedList<>();
- levelNo++;
-
- if (queue.size() > 0) {
- queue.add(null);
- }
- } else {
- if (levelNo % 2 == 0) {
- currLevel.add(treeNode.val);
- } else {
- currLevel.add(0, treeNode.val);
- }
- if (treeNode.left != null) queue.add(treeNode.left);
- if (treeNode.right != null) queue.add(treeNode.right);
- }
- }
-
- return levelOrderTraversal;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- /*
- Binary Tree
-
- 1
- / \
- 2 3
- / \
- 4 5
- */
- TreeNode tree = new TreeNode(1);
- tree.left = new TreeNode(2);
- tree.right = new TreeNode(3);
- tree.left.left = new TreeNode(4);
- tree.left.right = new TreeNode(5);
-
- assertEquals("[[1], [3, 2], [4, 5]]", zigzagLevelOrder(tree).toString());
- assertEquals("[]", zigzagLevelOrder(null).toString());
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/trees/ClosestBinarySearchTreeValue.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/trees/ClosestBinarySearchTreeValue.java
deleted file mode 100644
index ca6d94b7..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/trees/ClosestBinarySearchTreeValue.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,110 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.trees;
-
-import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
-
-/**
- * Level: Easy
- * Problem Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/closest-binary-search-tree-value/
- * Problem Description:
- * Given a non-empty binary search tree and a target value, find the value in the BST that is closest to the target.
- *
- * Note:
- * - Given target value is a floating point.
- * - You are guaranteed to have only one unique value in the BST that is closest to the target.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-07-31
- */
-public class ClosestBinarySearchTreeValue {
-
- /**
- * Runtime: 0 ms.
- *
- * @param root
- * @param target
- * @return
- */
- public static int closestValue(TreeNode root, double target) {
- if (root == null) return -1;
-
- return closestValue(root, root, target);
- }
-
- private static int closestValue(TreeNode node, TreeNode closestNode, double val) {
- if (node == null) return closestNode.val;
-
- if (Math.abs(node.val - val) < Math.abs(closestNode.val - val)) {
- closestNode = node;
- }
-
- if (node.val > val) {
- return closestValue(node.left, closestNode, val);
- } else {
- return closestValue(node.right, closestNode, val);
- }
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
-
- /*
- BST looks like:
-
- 9
- / \
- 7 13
- / \ \
- 5 8 20
- / \
- 2 6
- */
- TreeNode root = new TreeNode(9);
- root.left = new TreeNode(7);
- root.right = new TreeNode(13);
- root.left.left = new TreeNode(5);
- root.left.right = new TreeNode(8);
- root.left.left.right = new TreeNode(6);
- root.left.left.left = new TreeNode(2);
- root.right.right = new TreeNode(20);
-
- assertEquals(13, closestValue(root, 15));
- assertEquals(13, closestValue(root, 13));
- assertEquals(9, closestValue(root, 9));
- assertEquals(2, closestValue(root, 2));
- assertEquals(2, closestValue(root, 1));
- assertEquals(6, closestValue(root, 6));
- assertEquals(13, closestValue(root, 11)); // tie b/w 9 and 13
-
- /*
- BST looks like:
-
- 9
- / \
- 7 13
- / \ / \
- 5 8 13 20
- */
- root = new TreeNode(9);
- root.left = new TreeNode(7);
- root.right = new TreeNode(13);
- root.left.left = new TreeNode(5);
- root.left.right = new TreeNode(8);
- root.right.left = new TreeNode(13);
- root.right.right = new TreeNode(20);
-
- assertEquals(13, closestValue(root, 15));
-
- /*
- BST looks like:
-
- 1500000000
- /
- /
- /
- 1400000000
- */
- root = new TreeNode(1500000000);
- root.left = new TreeNode(1400000000);
-
- assertEquals(1400000000, closestValue(root, -1500000000.0));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/trees/ClosestBinarySearchTreeValueII.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/trees/ClosestBinarySearchTreeValueII.java
deleted file mode 100644
index e583723a..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/trees/ClosestBinarySearchTreeValueII.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,166 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.trees;
-
-import java.util.LinkedList;
-import java.util.List;
-import java.util.Queue;
-import java.util.Stack;
-
-import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
-
-/**
- * Level: Hard
- * Problem Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/closest-binary-search-tree-value-ii/
- * Problem Description:
- * Given a non-empty binary search tree and a target value, find k values in the BST that are closest to the target.
- *
- * Note:
- * - Given target value is a floating point.
- * - You may assume k is always valid, that is: k ≤ total nodes.
- * - You are guaranteed to have only one unique set of k values in the BST that are closest to the target.
- *
- * Example:
- * Input: root = [4,2,5,1,3], target = 3.714286, and k = 2
- *
- * 4
- * / \
- * 2 5
- * / \
- * 1 3
- *
- * Output: [4,3]
- *
- * Follow up:
- * Assume that the BST is balanced, could you solve it in less than O(n) runtime (where n = total nodes)?
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-07-31
- */
-public class ClosestBinarySearchTreeValueII {
-
-
- /**
- * The idea is simple. We do the inorder traversal and keep the values less than or equal to target in a stack and
- * the values greater than target in a queue. And finally, we compare values from both stack and queue and take
- * whichever is the closest to target value each time.
- *
- * Note: We can optimize it even further in terms of space. We can get rid of the stack and queue and just fill up
- * the result list in the recursive inOrder call. Once the result list is of size k, we can compare and remove the
- * farthest value and insert the closer value. See {@link ClosestBinarySearchTreeValueII#closestKValuesOptimized(TreeNode, double, int)}.
- *
- * @param root
- * @param target
- * @param k
- * @return
- */
- public static List closestKValues(TreeNode root, double target, int k) {
- int count = 0;
- List closestKValues = new LinkedList<>();
-
- Stack predecessors = new Stack<>();
- Queue successors = new LinkedList<>();
- inOrder(root, predecessors, successors, target, k);
-
- while (count < k) {
- if (predecessors.empty()) {
- closestKValues.add(successors.poll());
- } else if (successors.isEmpty()) {
- closestKValues.add(predecessors.pop());
- } else if (Math.abs(target - predecessors.peek()) < Math.abs(target - successors.peek())) {
- closestKValues.add(predecessors.pop());
- } else {
- closestKValues.add(successors.poll());
- }
- count++;
- }
-
- return closestKValues;
- }
-
- private static void inOrder(TreeNode root, Stack predecessors, Queue successors, double target, int k) {
- if (root == null || successors.size() == k) return;
- inOrder(root.left, predecessors, successors, target, k);
- if (root.val <= target) {
- predecessors.add(root.val);
- } else {
- successors.add(root.val);
- }
- inOrder(root.right, predecessors, successors, target, k);
- }
-
-
- /**
- * This approach is similar to the above one but it doesn't use stack or queue.
- *
- * @param root
- * @param target
- * @param k
- * @return
- */
- public static List closestKValuesOptimized(TreeNode root, double target, int k) {
- LinkedList closestKValues = new LinkedList<>();
- inOrder(root, target, k, closestKValues);
- return closestKValues;
- }
-
- private static void inOrder(TreeNode root, double target, int k, LinkedList closestKValues) {
- if (root == null) return;
-
- inOrder(root.left, target, k, closestKValues);
- if (closestKValues.size() == k) {
- //if size k, add current and remove head if it's closer to target, otherwise return
- if (Math.abs(target - root.val) < Math.abs(target - closestKValues.peekFirst()))
- closestKValues.removeFirst();
- else {
- return;
- }
- }
- closestKValues.add(root.val);
- inOrder(root.right, target, k, closestKValues);
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
-
- /*
- BST looks like:
-
- 9
- / \
- 7 13
- / \ \
- 5 8 20
- / \
- 2 6
- */
- TreeNode root = new TreeNode(9);
- root.left = new TreeNode(7);
- root.right = new TreeNode(13);
- root.left.left = new TreeNode(5);
- root.left.right = new TreeNode(8);
- root.left.left.left = new TreeNode(2);
- root.left.left.right = new TreeNode(6);
- root.right.right = new TreeNode(20);
-
- assertEquals("[9, 8, 7, 6, 5]", closestKValues(root, 8.5, 5).toString());
- assertEquals("[5, 6, 7, 8, 9]", closestKValuesOptimized(root, 8.5, 5).toString());
-
- /*
- BST looks like:
-
- 9
- / \
- 7 13
- / \ / \
- 5 8 13 20
- */
- root = new TreeNode(9);
- root.left = new TreeNode(7);
- root.right = new TreeNode(13);
- root.left.left = new TreeNode(5);
- root.right.left = new TreeNode(13);
- root.left.right = new TreeNode(8);
- root.right.right = new TreeNode(20);
-
- assertEquals("[13, 13, 9, 20, 8]", closestKValues(root, 14, 5).toString());
- assertEquals("[8, 9, 13, 13, 20]", closestKValuesOptimized(root, 14, 5).toString());
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/trees/LeavesOfBinaryTree.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/trees/LeavesOfBinaryTree.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 6ca15e22..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/trees/LeavesOfBinaryTree.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,97 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.trees;
-
-import java.util.ArrayList;
-import java.util.List;
-
-import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
-
-/**
- * Level: Medium
- * Problem Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/find-leaves-of-binary-tree/
- * Problem Description:
- * Given a binary tree, collect a tree's nodes as if you were doing this: Collect and remove all leaves, repeat
- * until the tree is empty.
- *
- * Example:
- * Input: [1,2,3,4,5]
- *
- * 1
- * / \
- * 2 3
- * / \
- * 4 5
- *
- * Output: [[4,5,3],[2],[1]]
- *
- * Explanation:
- * 1. Removing the leaves [4,5,3] would result in this tree:
- * 1
- * /
- * 2
- *
- * 2. Now removing the leaf [2] would result in this tree:
- * 1
- *
- * 3. Now removing the leaf [1] would result in the empty tree:
- * []
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-08-01
- */
-public class LeavesOfBinaryTree {
-
- /**
- * THe idea is to perform a DFS and backtrack. While backtracking, check the height of the node and insert
- * the node into the list indexed by their heights.
- * Time Complexity:
- * Space Complexity:
- * Runtime: 1 ms.
- *
- * @param root
- * @return
- */
- public static List> findLeavesOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root) {
- List> levels = new ArrayList<>();
- findLeavesOfBinaryTree(root, levels);
- return levels;
- }
-
- private static int findLeavesOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root, List> levels) {
- if (root == null) return -1;
-
- int leftHeight = findLeavesOfBinaryTree(root.left, levels);
- int rightHeight = findLeavesOfBinaryTree(root.right, levels);
- int height = Math.max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1;
-
- if (height >= levels.size()) {
- levels.add(height, new ArrayList<>());
- }
- levels.get(height).add(root.val);
-
- return height;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- /*
- BST looks like:
-
- 4
- / \
- 1 7
- / \ \
- 3 8 20
- / \
- 2 6
- */
- TreeNode root = new TreeNode(4);
- root.left = new TreeNode(1);
- root.right = new TreeNode(7);
- root.left.left = new TreeNode(3);
- root.left.right = new TreeNode(8);
- root.left.left.left = new TreeNode(2);
- root.left.left.right = new TreeNode(6);
- root.right.right = new TreeNode(20);
-
- assertEquals("[[2, 6, 8, 20], [3, 7], [1], [4]]", findLeavesOfBinaryTree(root).toString());
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/trees/SecondMinNodeInBinaryTree.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/trees/SecondMinNodeInBinaryTree.java
deleted file mode 100644
index a8cddf74..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/trees/SecondMinNodeInBinaryTree.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,108 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.trees;
-
-import java.util.Stack;
-
-/**
- * Level: Easy
- * Problem Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/second-minimum-node-in-a-binary-tree/
- * Problem Description:
- * Given a non-empty special binary tree consisting of nodes with the non-negative value, where each node in this
- * tree has exactly two or zero sub-node. If the node has two sub-nodes, then this node's value is the smaller value
- * among its two sub-nodes. More formally, the property root.val = min(root.left.val, root.right.val) always holds.
- *
- * Given such a binary tree, you need to output the second minimum value in the set made of all the nodes' value in
- * the whole tree.
- *
- * If no such second minimum value exists, output -1 instead.
- *
- * Example 1:
- * Input:
- * 2
- * / \
- * 2 5
- * / \
- * 5 7
- *
- * Output: 5
- * Explanation: The smallest value is 2, the second smallest value is 5.
- *
- *
- * Example 2:
- * Input:
- * 2
- * / \
- * 2 2
- *
- * Output: -1
- * Explanation: The smallest value is 2, but there isn't any second smallest value.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-08-03
- */
-public class SecondMinNodeInBinaryTree {
-
- /**
- * Time Complexity: O(n)
- * Space Complexity: O(n)
- * Runtime: 1 ms.
- * @param root
- * @return
- */
- public static int findSecondMinimumValueIterative(TreeNode root) {
- if (root == null || (root.left == null && root.right == null)) return -1;
-
- int min = root.val;
- long secondMin = Long.MAX_VALUE;
-
- Stack stack = new Stack<>();
- stack.push(root);
-
- while (!stack.empty()) {
- TreeNode node = stack.pop();
- if (node == null) continue;
-
- if (node.val > min && node.val < secondMin) {
- secondMin = node.val;
- }
- stack.push(node.left);
- stack.push(node.right);
- }
-
- return secondMin == Long.MAX_VALUE ? -1 : (int) secondMin;
- }
-
-
- /**
- * Time Complexity:
- * Space Complexity:
- * Runtime: 0 ms.
- *
- * @param root
- * @return
- */
- public static int findSecondMinimumValue(TreeNode root) {
- // passing a long as secondMin because TreeNode can have Integer.MAX_VALUE as its value
- long ans = findSecondMinimumValue(root, root.val, Long.MAX_VALUE);
- return ans == Long.MAX_VALUE ? -1 : (int) ans;
- }
-
- private static long findSecondMinimumValue(TreeNode root, int min, long secondMin) {
- if (root == null) return Long.MAX_VALUE;
-
- if (root.val > min && root.val < secondMin) {
- return root.val;
- } else {
- return Math.min(findSecondMinimumValue(root.left, min, secondMin),
- findSecondMinimumValue(root.right, min, secondMin));
- }
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println((int) 2147483647L);
- System.out.println(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
- // TODO: A function called buildTree which would take an array like [1,1,3,1,1,3,4,3,1,1,1,3,8,4,8,3,3,1,6,2,1]
- // and return a Binary Tree
- //assertEquals(2, findSecondMinimumValue(buildTree(new int[]{1,1,3,1,1,3,4,3,1,1,1,3,8,4,8,3,3,1,6,2,1})));
- //assertEquals(2147483647, findSecondMinimumValue(buildTree(new int[]{2,2,2147483647})));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/trees/SerializeDeserializeBinaryTree.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/trees/SerializeDeserializeBinaryTree.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 690de39d..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/trees/SerializeDeserializeBinaryTree.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,179 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.trees;
-
-
-import java.util.LinkedList;
-import java.util.Queue;
-
-/**
- * Level: Hard
- * Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/serialize-and-deserialize-binary-tree/
- * Description:
- * Serialization is the process of converting a data structure or object into a sequence of bits so that it can be
- * stored in a file or memory buffer, or transmitted across a network connection link to be reconstructed later in
- * the same or another computer environment.
- *
- * Design an algorithm to serialize and deserialize a binary tree. There is no restriction on how your
- * serialization/deserialization algorithm should work. You just need to ensure that a binary tree can be serialized
- * to a string and this string can be deserialized to the original tree structure.
- *
- * Example:
- *
- * You may serialize the following tree:
- *
- * 1
- * / \
- * 2 3
- * / \
- * 4 5
- *
- * as "[1,2,3,null,null,4,5]"
- *
- * Clarification: The above format is the same as how LeetCode serializes a binary tree. You do not necessarily need
- * to follow this format, so please be creative and come up with different approaches yourself.
- *
- * Note: Do not use class member/global/static variables to store states. Your serialize and deserialize algorithms
- * should be stateless.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-08-17
- */
-public class SerializeDeserializeBinaryTree {
-
- /**
- * Runtime: 31 ms.
- *
- * @param root
- * @return
- */
- public static String serialize(TreeNode root) {
- if (root == null) {
- return "[]";
- }
-
- StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
- sb.append("[");
-
- Queue queue = new LinkedList<>();
- queue.add(root);
-
- while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
- TreeNode node = queue.poll();
-
- if (sb.length() > 1) {
- sb.append(", ");
- }
- if (node == null) {
- sb.append("null");
- continue;
- }
-
- sb.append(node.val);
-
- queue.add(node.left);
- queue.add(node.right);
- }
-
- sb.append("]");
- return removeExtraNulls(sb.toString());
- }
-
- private static String removeExtraNulls(String data) {
- int i = data.length() - 1;
- while (!(data.charAt(i) >= 48 && data.charAt(i) <= 57)) {
- i--;
- }
- return data.substring(0, i + 1) + "]";
- }
-
- /**
- *
- * @param data
- * @return
- */
- public static TreeNode deserialize(String data) {
- data = data.substring(1, data.length() - 1);
-
- if (data.length() == 0) {
- return null;
- }
-
- String[] values = data.split(", ");
-
- TreeNode root = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(values[0]));
-
- Queue queue = new LinkedList<>();
- queue.add(root);
-
- for (int i = 0; i < values.length && !queue.isEmpty(); i += 2) {
- TreeNode currNode = queue.poll();
-
- if (i + 1 < values.length && !values[i + 1].equals("null")) {
- TreeNode leftNode = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(values[i + 1]));
- currNode.left = leftNode;
- queue.add(leftNode);
- }
-
- if (i + 2 < values.length && !values[i + 2].equals("null")) {
- TreeNode rightNode = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(values[i + 2]));
- currNode.right = rightNode;
- queue.add(rightNode);
- }
- }
-
- return root;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- // TODO Convert the print statements to asserts
-
- System.out.println(serialize(new TreeNode(1)));
-
- /*
- Binary Tree
-
- 1
- / \
- 2 3
- / \
- 4 5
- */
- TreeNode tree = new TreeNode(1);
- tree.left = new TreeNode(2);
- tree.right = new TreeNode(3);
- tree.left.left = new TreeNode(4);
- tree.left.right = new TreeNode(5);
-
- System.out.println(serialize(tree));
-
- System.out.println(serialize(deserialize(serialize(tree))));
-
- System.out.println(serialize(deserialize(serialize(null))));
-
- TreeNode tree2 = new TreeNode(1);
- tree2.right = new TreeNode(2);
- tree2.right.right = new TreeNode(3);
- tree2.right.right.right = new TreeNode(4);
- tree2.right.right.right.right = new TreeNode(5);
- tree2.right.right.right.right.right = new TreeNode(6);
- tree2.right.right.right.right.right.right = new TreeNode(7);
- tree2.right.right.right.right.right.right.right = new TreeNode(8);
-
- System.out.println(serialize(tree2));
- System.out.println(serialize(deserialize(serialize(tree2))));
-
- System.out.println("---");
-
- System.out.println(serialize(deserialize("[1, 2]")));
- System.out.println(serialize(deserialize("[1, 2, 3]")));
- System.out.println(serialize(deserialize("[3, 2, 4, 1]")));
- System.out.println(serialize(deserialize("[3, 2, 4, 1, 5, 6]")));
- System.out.println(serialize(deserialize("[1, 2, 3, null, null, 4, 5]")));
- System.out.println(serialize(deserialize("[5, 2, 3, null, null, 2, 4, 3, 1]")));
-
- System.out.println(serialize(deserialize("[1, null, 2, null, 3, null, 4, null, 5]")));
- System.out.println(serialize(deserialize("[1, null, 2, null, 3, null, 4, null, 5, null, 6]")));
- System.out.println(serialize(deserialize("[1, null, 2, null, 3, null, 4, null, 5, null, 6, null, 7]")));
- System.out.println(serialize(deserialize("[1, null, 2, null, 3, null, 4, null, 5, null, 6, null, 7, null, 8]")));
- System.out.println(serialize(deserialize("[1, null, 2, null, 3, null, 4, null, 5, null, 6, null, 7, null, 8, null, 9]")));
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/trees/SymmetricTree.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/trees/SymmetricTree.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 093d9a6f..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/trees/SymmetricTree.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,117 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.trees;
-
-import java.util.LinkedList;
-import java.util.Queue;
-
-import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertTrue;
-
-/**
- * Level: Easy
- * Problem Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/symmetric-tree/
- * Problem Description:
- * Given a binary tree, check whether it is a mirror of itself (ie, symmetric around its center).
- *
- * For example, this binary tree [1,2,2,3,4,4,3] is symmetric:
- *
- * 1
- * / \
- * 2 2
- * / \ / \
- * 3 4 4 3
- *
- *
- * But the following [1,2,2,null,3,null,3] is not:
- *
- * 1
- * / \
- * 2 2
- * \ \
- * 3 3
- *
- *
- * Note:
- * Bonus points if you could solve it both recursively and iteratively.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-07-25
- */
-public class SymmetricTree {
-
- /**
- * Time Complexity: O(n) Because we traverse the entire input tree once, the total run time is O(n), where n is
- * the total number of nodes in the tree.
- * Space Complexity: O(n) The number of recursive calls is bound by the height of the tree. In the worst case, the
- * tree is linear and the height is in O(n). Therefore, space complexity due to recursive calls on the stack is
- * O(n) in the worst case.
- * Runtime: 0 ms.
- *
- * @param root
- * @return
- */
- public static boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
- if (root == null) {
- return true;
- }
-
- return isSymmetric(root.left, root.right);
- }
-
- private static boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode leftRoot, TreeNode rightRoot) {
- if (leftRoot == null && rightRoot == null) {
- return true;
- } else if (leftRoot == null || rightRoot == null) {
- return false;
- }
-
- return isSymmetric(leftRoot.left, rightRoot.right) && isSymmetric(leftRoot.right, rightRoot.left) && leftRoot.val == rightRoot.val;
- }
-
- /**
- * Time Complexity: O(n) Because we traverse the entire input tree once, the total run time is O(n), where n is the
- * total number of nodes in the tree.
- * Space Complexity: There is additional space required for the search queue. In the worst case, we have to
- * insert O(n) nodes in the queue. Therefore, space complexity is O(n).
- * Runtime: 1 ms.
- *
- * @param root
- * @return
- */
- public static boolean isSymmetricIterative(TreeNode root) {
- if (root == null || (root.left == null && root.right == null)) return true;
- if (root.left == null || root.right == null) return false;
-
- Queue queue = new LinkedList<>();
- queue.add(root.left);
- queue.add(root.right);
-
- while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
- TreeNode t1 = queue.poll();
- TreeNode t2 = queue.poll();
-
- if (t1 == null && t2 == null) continue;
- if (t1 == null || t2 == null) return false;
- if (t1.val != t2.val) return false;
-
- // enqueue left and then right child of t1 but do the opposite for t2
- queue.add(t1.left);
- queue.add(t2.right);
- queue.add(t1.right);
- queue.add(t2.left);
- }
-
- return true;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- TreeNode root = new TreeNode(1);
- root.left = new TreeNode(2);
- root.right = new TreeNode(2);
- root.left.left = new TreeNode(4);
- root.left.right = new TreeNode(3);
- root.right.left = new TreeNode(3);
- root.right.right = new TreeNode(4);
-
- assertTrue(isSymmetric(root));
- assertTrue(isSymmetricIterative(root));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/trees/TreeNode.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/trees/TreeNode.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 4c4c2569..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/trees/TreeNode.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,21 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.trees;
-
-/**
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-07-25
- */
-public class TreeNode {
-
- int val;
- TreeNode left;
- TreeNode right;
-
- public TreeNode(int val) {
- this.val = val;
- }
-
- @Override
- public String toString() {
- return val + "";
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/trie/LongestWord.java b/src/main/java/com/leetcode/trie/LongestWord.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 155ea295..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/leetcode/trie/LongestWord.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,78 +0,0 @@
-package com.leetcode.trie;
-
-import java.util.HashMap;
-import java.util.Stack;
-
-/**
- * Level: Easy
- * Problem: https://leetcode.com/problems/longest-word-in-dictionary/
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-04-10
- */
-public class LongestWord {
-
- private class TrieNode {
- char ch;
- HashMap children = new HashMap<>();
- String completeWord; // to mark a complete word in the trie data structure
-
- TrieNode(char ch) {
- this.ch = ch;
- }
- }
-
- private TrieNode root = new TrieNode('0');
-
- /**
- * Inserts {@code data} in trie.
- *
- * @param str
- */
- public void insert(String str) {
- char c;
- TrieNode curr = root;
-
- for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
- c = str.charAt(i);
- curr.children.putIfAbsent(c, new TrieNode(c));
- curr = curr.children.get(c);
- }
-
- curr.completeWord = str;
- }
-
- public String longestWord(String[] words) {
- for (int i = 0; i < words.length; i++) {
- insert(words[i]);
- }
-
- return longestWord();
- }
-
- private String longestWord() {
- String longestWord = "";
- TrieNode curr;
- Stack stack = new Stack<>();
- stack.addAll(root.children.values());
-
- while (!stack.empty()) {
- curr = stack.pop();
- if (curr.completeWord != null) {
- if (curr.completeWord.length() > longestWord.length() ||
- (curr.completeWord.length() == longestWord.length() &&
- curr.completeWord.compareTo(longestWord) < 0)) {
- longestWord = curr.completeWord;
- }
- stack.addAll(curr.children.values());
- }
- }
- return longestWord;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- LongestWord longestWord = new LongestWord();
- System.out.println(longestWord.longestWord(new String[]{"w", "wo", "wor", "worl", "world"}));
- System.out.println(longestWord.longestWord(new String[]{"a", "banana", "app", "appl", "ap", "apply", "apple"}));
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/linkedlist/DetectLoopInLinkedList_LoopInLinkedList.java b/src/main/java/com/linkedlist/DetectLoopInLinkedList_LoopInLinkedList.java
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..73347bcd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/com/linkedlist/DetectLoopInLinkedList_LoopInLinkedList.java
@@ -0,0 +1,41 @@
+package com.linkedlist;
+
+import com.linkedlist.model.Node;
+
+public class DetectLoopInLinkedList_LoopInLinkedList {
+
+ public static void main(String args[]) {
+
+ Node node1 = new Node(4);
+ Node node2 = new Node(6);
+ Node node3 = new Node(8);
+ Node node4 = new Node(12);
+ Node node5 = new Node(14);
+
+ Node startNode = node1;
+
+ node1.setNext(node2);
+ node2.setNext(node3);
+ node3.setNext(node4);
+ node4.setNext(node5);
+ node5.setNext(node2);
+
+ System.out.println("Loop:" + detectLoop(startNode));
+
+ }
+
+ private static boolean detectLoop(Node startNode) {
+ Node slowPointer = startNode; // Initially ptr1 is at starting location.
+ Node fastPointer = startNode; // Initially ptr2 is at starting location.
+
+ while (fastPointer != null && fastPointer.getNext() != null) { // If ptr2 encounters NULL, it means there is no Loop in Linked list.
+ slowPointer = slowPointer.getNext(); // ptr1 moving one node at at time
+ fastPointer = fastPointer.getNext().getNext(); // ptr2 moving two nodes at at time
+
+ if (slowPointer == fastPointer) // if ptr1 and ptr2 meets, it means linked list contains loop.
+ return true;
+ }
+ return false;
+ }
+
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/linkedlist/IntersectionOfTwoLinkedLists.java b/src/main/java/com/linkedlist/IntersectionOfTwoLinkedLists.java
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..e80cc703
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/com/linkedlist/IntersectionOfTwoLinkedLists.java
@@ -0,0 +1,71 @@
+package com.linkedlist;
+
+import com.linkedlist.model.Node;
+
+import java.util.HashSet;
+import java.util.Set;
+
+/**
+ * Write a program to find the node at which the intersection of two singly linked lists begins.
+ *
+ * For example, the following two linked lists:
+ *
+ * Input: intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
+ * Output: Reference of the node with value = 8
+ * Input Explanation: The intersected node's value is 8 (note that this must not be 0 if the two lists intersect).
+ * From the head of A, it reads as [4,1,8,4,5]. From the head of B, it reads as [5,0,1,8,4,5].
+ * There are 2 nodes before the intersected node in A; There are 3 nodes before the intersected node in B.
+ *
+ * Notes
+ * If the two linked lists have no intersection at all, return null.
+ * The linked lists must retain their original structure after the function returns.
+ * You may assume there are no cycles anywhere in the entire linked structure.
+ * Your code should preferably run in O(n) time and use only O(1) memory.
+ *
+ */
+public class IntersectionOfTwoLinkedLists {
+
+ //Approach 2: Hash Table (10ms)
+
+ /** Space -> O(n) where n is the size of first linked list as we are storing in HashSet
+ * Time -> O(n+m) as we traverse the complete list once. n size of first list & m size of second list.
+ * @param headA
+ * @param headB
+ * @return
+ */
+ public Node getIntersectionNode(Node headA, Node headB) {
+ Set nodes = new HashSet<>();
+ Node pa = headA;
+ while (pa != null) {
+ nodes.add(pa);
+ pa = pa.next;
+ }
+ if (nodes.isEmpty()) {
+ return null;
+ }
+ Node pb = headB;
+ while (pb != null) {
+ if (nodes.contains(pb)) {
+ return pb;
+ }
+ pb = pb.next;
+ }
+ return null;
+ }
+
+ //Approach 3: Two Pointers (1ms)
+
+ public Node getIntersectionNode_1(Node headA, Node headB) {
+ Node pa = headA, pb = headB;
+ while (pa != pb) {
+ pa = (pa != null) ? pa.next : headB;
+ pb = (pb != null) ? pb.next : headA;
+ }
+ return pa;
+ }
+
+
+}
+
+
+
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/linkedlist/LRUCache.adoc b/src/main/java/com/linkedlist/LRUCache.adoc
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..ff78e3b7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/com/linkedlist/LRUCache.adoc
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+image::../../../images/LRUCache.png[]
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/linkedlist/LRUCache.java b/src/main/java/com/linkedlist/LRUCache.java
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..2c29dc32
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/com/linkedlist/LRUCache.java
@@ -0,0 +1,92 @@
+package com.linkedlist;
+
+import com.linkedlist.model.DoublyLLNode;
+
+import java.util.HashMap;
+
+/**
+ * Design and implement a data structure for Least Recently Used (LRU) cache, which supports get and put.
+ * The key to solve this problem is using a double linked list which enables us to quickly move nodes.
+ *
+ * The LRU cache is a hash table of keys and double linked nodes.
+ * The hash table makes the time of get() to be O(1). The list of double linked nodes make the nodes adding/removal operations O(1).
+ *
+ * By analyzing the get and put, we can summarize there are 2 basic operations:
+ * 1) removeNode(Node t), 2) offerNode(Node t).
+ *
+ */
+class LRUCache {
+ DoublyLLNode head;
+ DoublyLLNode tail;
+ HashMap map = null;
+ int cap = 0;
+
+ public LRUCache(int capacity) {
+ this.cap = capacity;
+ this.map = new HashMap<>();
+ }
+
+ public int get(int key) {
+ if(map.get(key)==null){
+ return -1;
+ }
+
+ //move to tail
+ DoublyLLNode t = map.get(key);
+
+ removeDoublyLLNode(t);
+ offerDoublyLLNode(t);
+
+ return t.value;
+ }
+
+ public void put(int key, int value) {
+ if(map.containsKey(key)){
+ DoublyLLNode t = map.get(key);
+ t.value = value;
+
+ //move to tail
+ removeDoublyLLNode(t);
+ offerDoublyLLNode(t);
+ }else{
+ if(map.size()>=cap){
+ //delete head
+ map.remove(head.key);
+ removeDoublyLLNode(head);
+ }
+
+ //add to tail
+ DoublyLLNode DoublyLLNode = new DoublyLLNode(key, value);
+ offerDoublyLLNode(DoublyLLNode);
+ map.put(key, DoublyLLNode);
+ }
+ }
+
+ private void removeDoublyLLNode(DoublyLLNode n){
+ if(n.prev!=null){
+ n.prev.next = n.next;
+ }else{
+ head = n.next;
+ }
+
+ if(n.next!=null){
+ n.next.prev = n.prev;
+ }else{
+ tail = n.prev;
+ }
+ }
+
+ private void offerDoublyLLNode(DoublyLLNode n){
+ if(tail!=null){
+ tail.next = n;
+ }
+
+ n.prev = tail;
+ n.next = null;
+ tail = n;
+
+ if(head == null){
+ head = tail;
+ }
+ }
+}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/linkedlist/LoopInLinkedList_FloydCycleDetectionAlgo.html b/src/main/java/com/linkedlist/LoopInLinkedList_FloydCycleDetectionAlgo.html
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..6352ea01
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/com/linkedlist/LoopInLinkedList_FloydCycleDetectionAlgo.html
@@ -0,0 +1,2324 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Floyd's Cycle Detection Algorithm in Java | JavaByPatel
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Floyd's Cycle Detection Algorithm in Java. OR
Detect loop in Linked list.
+
+
Floyd's Cycle Detection Algorithm in Java. Floyd's Cycle finding algorithm helps to detect loop in linked list. How Floyd's Cycle Algorithm works.
+
+
+
Let's start with, What is Loop in Linked list?
+
+
Generally, the last node of the linked list points to NULL, which is a indication of end of list.
But in Linked list containing Loop, last node instead of pointing NULL, it points to some of the internal node/starting node/itself.
In this case, If we traverse the Linked list node one by one, our traversal will never ends as it goes in loop.
+
+Check below images for better understanding on how Linked list containing loop looks like.
+
+
+
+
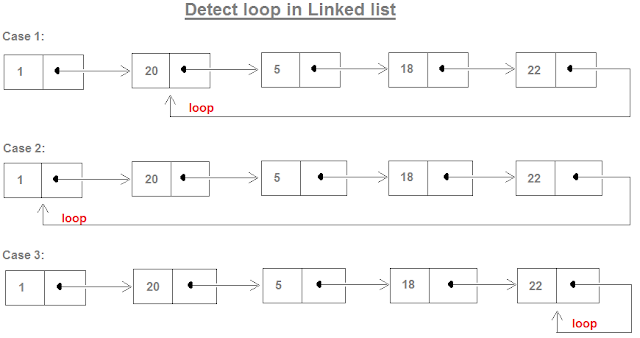
+
+Algorithm
+
+
+
Before going into detecting loop in linked list, Lets understand few basic points with help of example.
+
+
1. Jayesh and Khyati daily goes for jogging at Circular park(Park is completely circular of 1 Km).
2. Jayesh is bit lazy and jogs at "x" speed. Khyati is more energetic and jogs at 2x speed.
3. It means, when they both start from same point, and when Jayesh complete half jogging track,
+
Khyati will complete one jogging track round and reached at starting place again.
So if they both starts from common point, Jayesh running at speed "x" and Khyati running at speed "2x", Will they both meet again?
They will surely meet at the same location they started from.
Look at below image for better understanding.
+
+
+
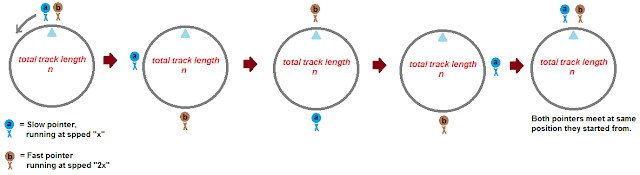
+
Now, instead of starting from same point, if the starting point for Jayesh and Khyati is different still they will meet?
+
Yes they will meet. Not at same place but at some point in track.
Look at below image for better understanding.
+
+
+
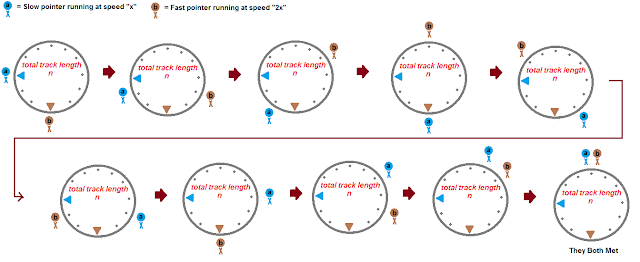
+
+
They are meeting at some point because of the circular track and speed in which both are traveling.
+
+
+
Now, If Jayesh travels at "x" speed and Khyati travels at "3x" speed, still they both will meet, but numbers of complete cycles Khyati will perform and then meet Jayesh might increase.
+
+
+
Now, Lets look at our original problem
+
+
+Detect loop in Linked list. (Floyd's Cycle detection algorithm)
+
+
So the algorithm behind identifying the loop in linked list is very similar to our jogging track example.
+
+
STEP 1: Take 2 pointers ptr1 and ptr2, both pointing at the start node initially.
+
STEP 2: Move ptr1 forward one node at a time and move ptr2 forward two nodes at same time.
+
STEP 3: ptr2 is running at double speed, so definitely it will be ahead of ptr1,
If ptr2 encounters NULL, it means there is no loop in a Linked list and stop execution.
+
If linked list contains loop, then ptr2 at some point will enter in the loop. some time later
+
ptr1 will also enter in the loop.
+
+
STEP 4: Now, when both pointers are in the loop, and if they continue to move at same speed then
+
eventually they will meet at some point.
+
(From our jogging track example, we have already seen that)
If they both meet, it means Linked list contains loop and stop execution.
+
+
+
+Java Program to Detect loop in linked list in Java.
+
+
+
package linkedlist.singly;
+
+public class DetectLoopInLinkedList{
+ private Node startNode;
+
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ DetectLoopInLinkedList detectLoopInLinkedList = new DetectLoopInLinkedList();
+
+ Node n1 = new Node(10);
+ Node n2 = new Node(20);
+ Node n3 = new Node(30);
+ Node n4 = new Node(40);
+ Node n5 = new Node(50);
+ Node n6 = new Node(60);
+ Node n7 = new Node(70);
+ Node n8 = new Node(80);
+
+ detectLoopInLinkedList.startNode = n1;
+
+ n1.setNext(n2);
+ n2.setNext(n3);
+ n3.setNext(n4);
+ n4.setNext(n5);
+ n5.setNext(n6);
+ n6.setNext(n7);
+ n7.setNext(n8);
+ n8.setNext(n6);
+
+ if(isLoopPresent(detectLoopInLinkedList.startNode)){
+ System.out.println("Loop is present in list");
+ }else{
+ System.out.println("No Loop present in list");
+ }
+ }
+
+ private static boolean isLoopPresent(Node startNode){
+ Node slowPointer = startNode; // Initially ptr1 is at starting location.
+ Node fastPointer = startNode; // Initially ptr2 is at starting location.
+
+ while(fastPointer!=null && fastPointer.getNext()!=null){ // If ptr2 encounters NULL, it means there is no Loop in Linked list.
+ slowPointer = slowPointer.getNext(); // ptr1 moving one node at at time
+ fastPointer = fastPointer.getNext().getNext(); // ptr2 moving two nodes at at time
+
+ if(slowPointer==fastPointer) // if ptr1 and ptr2 meets, it means linked list contains loop.
+ return true;
+ }
+ return false;
+ }
+
+}
+
+
+
+
public class Node{
+
+ private int data;
+ private Node next;
+
+ public Node(int data) {
+ this.data = data;
+ }
+ public int getData() {
+ return data;
+ }
+ public void setData(int data) {
+ this.data = data;
+ }
+ public Node getNext() {
+ return next;
+ }
+ public void setNext(Node next) {
+ this.next = next;
+ }
+}
+
+
+
+
+
+Why increase pointer by two while finding loop in linked list, why not 3,4,5?
+
+
So, the condition here is you cannot change the speed of ptr1, it has to move one node at a time.
+
but the choice for ptr2 to move can be 2 nodes at a time, 3 nodes at a time or any number of nodes at a time.
+
+
More the gap in which both pointers move forward, more the time they might take in worst case to meet.
+
So the lowest possible iteration in which we can find their meeting points is by moving ptr2 two nodes at a time.
+
+
+
+Identify start node of loop in linked list.
+
+
+
If the linked list is like shown below, Find a node from where loop/cycle starts.
+
(In below example, it starts at Node 5).
+
+
+
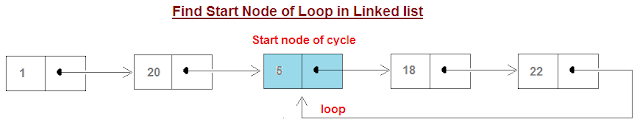
+
+
+
We just saw that, loop in a linked list can be identified by,
1. Initializing 2 pointers(tortoise, hare) at start node and then
2. Moving tortoise pointer forward 1 node at a time and moving hare pointer forward 2 nodes at same
time.
In this way, if the linked list contains loop then tortoise and hare will meet at some node in
+
loop otherwise hare will reach NULL.
Now point is, how we will come to know the start node of a loop.
+
+
STEP 1: After finding the loop, both pointers are pointing to common node that is at meeting point
+
inside loop,
+
+
STEP 2: Now, move one pointer among them(say tortoise) to the head of list, keeping hare
+
pointer at the same position that is at meeting point inside loop.
+
+
STEP 3: Start moving both pointers one node at a time. The place they both will meet is the start
+
node of the loop/cycle.
+
+
+How does the Algorithm work?
+
+
Lets understand with the help of example.
+
+
+

+
+
1. Consider the distance between start node of the list and start of loop node be "p" and
+
2. Consider the distance between start of loop node and the meeting point(node) of both pointers
+
be "q".
+
3. Consider the distance between the meeting point of both pointers and the start node of the loop
+
be "r".
+
+
Tortoise pointer was moving one node at a time and hare pointer was moving 2 nodes at same time.
So we can say, when tortoise pointer has moved distance "d"
+
then hare pointer has moved distance "2d".
From the above image, the length of loop is q+r.
When tortoise and hare meet, tortoise has covered distance d = p+q and hare has covered distance 2*d = p+q+r+q
2*d = p + q + r + q
2(p+q) = p + 2q + r
2p + 2q = p + 2q + r
p = r
(It means distance from head node to the start of loop node is same as distance between meeting point of the pointers to the start of loop node)
So this shows after getting meeting point, if one pointer is placed at the beginning of the list, then moving both pointer one node at a time then they will meet at the start of loop.
+
+
+Identify start node of loop in Linked List. (in Java)
+
+
package linkedlist.singly;
+
+public class ReturnStartNodeOfLoopInLinkList {
+
+ Node startNode;
+
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+
+ ReturnStartNodeOfLoopInLinkList g = new ReturnStartNodeOfLoopInLinkList();
+
+ Node n1 = new Node(10);
+ Node n2 = new Node(20);
+ Node n3 = new Node(30);
+ Node n4 = new Node(40);
+ Node n5 = new Node(50);
+ Node n6 = new Node(60);
+ Node n7 = new Node(70);
+ Node n8 = new Node(80);
+
+ g.startNode = n1;
+
+ n1.setNext(n2);
+ n2.setNext(n3);
+ n3.setNext(n4);
+ n4.setNext(n5);
+ n5.setNext(n6);
+ n6.setNext(n7);
+ n7.setNext(n8);
+ n8.setNext(n6);
+
+ Node loopNode = g.getStartNodeOfLoopInLinklist(g.startNode);
+
+ if(loopNode==null){
+ System.out.println("Loop not present");
+ }else{
+ System.out.println("Start node of Loop is :"+loopNode.getData());
+ }
+ }
+
+ private Node getStartNodeOfLoopInLinklist(Node startNode){
+ Node tortoisePointer = startNode; // Initially ptr1 is at starting location.
+ Node harePointer = startNode; // Initially ptr2 is at starting location.
+
+ // If ptr2 encounters NULL, it means there is no Loop in Linked list.
+ while(harePointer!=null && harePointer.getNext()!=null){
+ tortoisePointer = tortoisePointer.getNext(); // ptr1 moving one node at at time
+ harePointer = harePointer.getNext().getNext(); // ptr2 moving two nodes at at time
+
+ // if ptr1 and ptr2 meets, it means linked list contains loop.
+ if(tortoisePointer==harePointer){
+
+ //After meet, moving tortoisePointer to start node of list.
+ tortoisePointer = startNode;
+
+ //Moving tortoisePointer and harePointer one node at a time till the time they meet at common point.
+ while(tortoisePointer!=harePointer){
+ tortoisePointer = tortoisePointer.getNext();
+ harePointer = harePointer.getNext();
+ }
+
+ //returning start node of loop.
+ return tortoisePointer;
+
+ }
+ }
+
+ // this condition will arise when there is no loop in list.
+ return null;
+ }
+
+}
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Remove loop in Linked list.
+
+
Removing the loop in Linked list is simple,
+
+
After identifying the loop node, we just require the previous node of loop node, So that we can set it to NULL.
+
+
For identifying the previous node of loop node, we will keep the previousPointer pointing to just previous node of loop node.
+
+
CASE 2:
+
When the meeting node of both pointers in loop is start node or root node itself, in this case by just setting previousPointer to NULL will work because previousPointer is already pointing to last node of the linked list.
+
+
CASE 1:
+
When the meeting node of both pointers in loop is in-between the linked list, in this case, first task is to identify the start of loop node in the way as we saw above and then by setting fastPointer, which is already pointing to last node of list to NULL will work.
+
+
+Program to Remove loop in linked list.
+
+
package linkedlist.singly;
+
+public class RemoveLoopInLinkList {
+
+ Node startNode;
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ RemoveLoopInLinkList g = new RemoveLoopInLinkList();
+
+ Node n1 = new Node(10);
+ Node n2 = new Node(20);
+ Node n3 = new Node(30);
+ Node n4 = new Node(40);
+ Node n5 = new Node(50);
+ Node n6 = new Node(60);
+ Node n7 = new Node(70);
+ Node n8 = new Node(80);
+
+ g.startNode = n1;
+
+ n1.setNext(n2);
+ n2.setNext(n3);
+ n3.setNext(n4);
+ n4.setNext(n5);
+ n5.setNext(n6);
+ n6.setNext(n7);
+ n7.setNext(n8);
+ n8.setNext(n6);
+
+ //Detect and Remove Loop in a Linked List
+ Node newStart = detectAndRemoveLoopInLinkedList(g.startNode);
+ g.printList(newStart);
+ }
+
+ private static Node detectAndRemoveLoopInLinkedList(Node startNode) {
+ Node slowPointer=startNode;
+ Node fastPointer=startNode;
+ Node previousPointer=null;
+
+ while(fastPointer!=null && fastPointer.getNext()!=null){
+ slowPointer = slowPointer.getNext();
+ previousPointer = fastPointer.getNext(); // For capturing just previous node of loop node for setting it to null for breaking loop.
+ fastPointer = fastPointer.getNext().getNext();
+
+ if(slowPointer==fastPointer){ // Loop identified.
+ slowPointer = startNode;
+
+ //If loop start node is starting at the root Node, then we slowpointer, fastpointer and head all point at same location.
+ //we already capture previous node, just setting it to null will work in this case.
+ if(slowPointer == fastPointer){
+ previousPointer.setNext(null);
+
+ }else{
+ // We need to first identify the start of loop node and then by setting just previous node of loop node next to null.
+ while(slowPointer.getNext()!=fastPointer.getNext()){
+ slowPointer = slowPointer.getNext();
+ fastPointer = fastPointer.getNext();
+ }
+ fastPointer.setNext(null);
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return startNode;
+ }
+
+ //Print linked list.
+ private void printList(Node startNode){
+ while(startNode!=null){
+ System.out.print(startNode.getData() + " " );
+ startNode=startNode.getNext();
+ }
+ }
+
+}
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Enjoy !!!!
+
+
+If you find any issue in post or face any error while implementing, Please comment.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
Find middle element of a linked list in Java
+
+
Given a singly linked list find middle of the linked list.
+
+
Find Nth node from last in a linked list
+
+
Lets understand the problem statement graphically and it will be more clear,
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Algorithm
+
+
There are 2 approach to get middle element of Linked list.
+
+
Approach 1:
+
+
+- Initialize the counter = 0.
+
+

- Iterate through a linked list and increment counter till you encounter null.
+- Once you got the length of linked list, say 7. Middle element of linked list is located at
(length of linked list / 2) 7/2 = 3.
+- Traverse the list again till (length of linked list / 2) and return the node at
(length of linked list / 2).
+
+
+
Approach 2:
+
We can get the middle element of linked list in one pass, lets see how,
+
+- In this approach, we take 2 pointers, fastPointer and slowPointer and initialize both to list head.
+
+

- Iterate through list and move slowPointer 1 node at a time and fastPointer 2 nodes at a time.
+- When fastPointer reaches end of list, slowPointer will be pointing to middle element of list.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Java Program to find middle element of Linked list using Approach 2
+
+
package linkedlist.singly;
+
+public class GetMiddleOfLinkedList {
+
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ new GetMiddleOfLinkList();
+ }
+
+ public GetMiddleOfLinkedList() {
+ Node startNode = new Node(10);
+ Node temp2 = new Node(20);
+ Node temp3 = new Node(30);
+ Node temp4 = new Node(40);
+ Node temp5 = new Node(50);
+ Node temp6 = new Node(60);
+ Node temp7 = new Node(70);
+ Node temp8 = new Node(80);
+
+ startNode.setNext(temp2);
+ temp2.setNext(temp3);
+ temp3.setNext(temp4);
+ temp4.setNext(temp5);
+ temp5.setNext(temp6);
+ temp6.setNext(temp7);
+ temp7.setNext(temp8);
+
+ Node temp = findMiddleNodeOfLinkedList(startNode);
+ System.out.println(temp.getData());
+ }
+
+ private Node findMiddleNodeOfLinkedList(Node startNode) {
+ if(startNode==null){
+ return startNode;
+ }
+
+ Node slowPointer = startNode;
+ Node fastPointer = startNode;
+ while(fastPointer!=null && fastPointer.getNext()!=null && fastPointer.getNext().getNext()!=null){
+ slowPointer = slowPointer.getNext();
+ fastPointer = fastPointer.getNext().getNext();
+
+ }
+ return slowPointer;
+ }
+}
+
+
+
class Node{
+ private int data;
+ private Node next;
+ public Node(int data, Node next) {
+ this.data = data;
+ this.next = next;
+ }
+ public Node(int data) {
+ this.data = data;
+ }
+ public int getData() {
+ return data;
+ }
+ public void setData(int data) {
+ this.data = data;
+ }
+ public Node getNext() {
+ return next;
+ }
+ public void setNext(Node next) {
+ this.next = next;
+ }
+}
+
+
+
+
+You may also like to see
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Enjoy !!!!
+
+
+If you find any issue in post or face any error while implementing, Please comment.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
- * TODO: Not tested.
- */
-public class CelebrityProblem {
-
- /**
- * Checks if person {@param a} knows person {@param b}.
- *
- * @param peoples
- * @param a
- * @param b
- * @return
- */
- public static boolean haveAcquaintance(int[][] peoples, int a, int b) {
- return peoples[a][b] == 1;
- }
-
- /**
- * Finds the celebrity in {@param peoples} where
- * peoples[i][j] is 1 when person i knows person j.
- *
- * Algorithm:
- * - If A knows B, then A can’t be celebrity. Discard A, but B may be celebrity.
- * - If A does not know B, then B can’t be celebrity. Discard B, but A may be celebrity.
- * - Repeat above two steps till we left with only one person.
- * Find celebrity within remaining persons by performing the below operations:
- * - Push all the celebrities into a stack.
- * - Pop off top two persons from the stack, discard one person based on return status of HaveAcquaintance(A, B).
- * - Push the remained person onto stack.
- * - Repeat step 2 and 3 until only one person remains in the stack.
- * - Check the remained person in stack does not have acquaintance with anyone else.
- *
- * @param peoples
- * @return
- */
- public static int findCelebrity(int[][] peoples) {
-
- Stack possibleCelebrities = new LinkedStack<>();
-
- for (int i = 0; i < peoples.length; i++) {
- for (int j = 0; j < peoples[0].length; j++) {
- if (haveAcquaintance(peoples, i, j)) {
- possibleCelebrities.push(j);
- }
- }
- }
-
- int firstPerson = -1, secondPerson;
- while (!possibleCelebrities.isEmpty()) {
- firstPerson = possibleCelebrities.pop();
-
- // we have found the celebrity
- if (possibleCelebrities.isEmpty()) break;
-
- secondPerson = possibleCelebrities.pop();
- if (haveAcquaintance(peoples, firstPerson, secondPerson)) {
- possibleCelebrities.push(secondPerson);
- } else {
- possibleCelebrities.push(firstPerson);
- }
- }
-
- return firstPerson;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(findCelebrity(new int[][]{{0, 0, 1, 0}, {0, 0, 1, 0}, {0, 0, 0, 0}, {0, 0, 1, 0}}));
- System.out.println(findCelebrity(new int[][]{{0, 0, 0, 1}, {0, 0, 0, 1}, {0, 0, 0, 1}, {0, 0, 0, 1}}));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/ConsecutiveElements.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/ConsecutiveElements.java
deleted file mode 100644
index f8dc151e..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/ConsecutiveElements.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,113 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 8/28/15
- * @time: 10:32 AM
- */
-public class ConsecutiveElements {
-
- /**
- * Given an unsorted array of numbers, write a function that returns true if array consists of consecutive numbers.
- *
- * Examples:
- * a) If array is {5, 2, 3, 1, 4}, then the function should return true because the array has consecutive numbers
- * from 1 to 5.
- * b) If array is {34, 23, 52, 12, 3 }, then the function should return false because the elements are not consecutive.
- * c) If the array is {7, 6, 5, 5, 3, 4}, then the function should return false because 5 and 5 are not consecutive.
- *
- * ALGORITHM:
- * The idea is to check for following two conditions. If following two conditions are true, then return true.
- * 1) max – min + 1 = n where max is the maximum element in array, min is minimum element in array and n is the number
- * of elements in array.
- * 2) All elements are distinct.
- *
- * To check if all elements are distinct, we can create a visited[] array of size n. We can map the ith element of input
- * array arr[] to visited array by using arr[i] – min as index in visited[]. So we need O(n) auxiliary space.
- *
- * @param a
- * @return
- */
- public static boolean areConsecutiveElements(int[] a) {
- int min = a[0], max = a[0];
- int[] visitedArray = new int[a.length];
-
- // find min and max element
- for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++) {
- if (a[i] < min) {
- min = a[i];
- }
- if (a[i] > max) {
- max = a[i];
- }
- }
-
- // diff of max and min should be equal to length of array
- if (a.length != max - min + 1) {
- return false;
- }
-
- // check for distinct elements
- for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
- if (visitedArray[a[i] - min] == 0) {
- visitedArray[a[i] - min] = a[i];
- } else {
- return false;
- }
- }
-
- return true;
- }
-
- /**
- * This approach is similar to {@link ConsecutiveElements#areConsecutiveElements(int[])} but
- * requires O(1) auxiliary space instead of O(n). But the only con of this method is that it modifies the original
- * input array {@param a}.
- *
- * @param a
- * @return
- */
- public static boolean areConsecutiveElementsInO1Space(int[] a) {
- int min = a[0], max = a[0];
-
- // find min and max element
- for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++) {
- if (a[i] < min) {
- min = a[i];
- }
- if (a[i] > max) {
- max = a[i];
- }
- }
-
- // diff of max and min should be equal to length of array
- if (a.length != max - min + 1) {
- return false;
- }
-
- // check for distinct elements
- for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
- if (a[Math.abs(a[i]) - min] >= 0) {
- a[Math.abs(a[i]) - min] = -(a[Math.abs(a[i]) - min]);
- } else {
- return false;
- }
- }
-
- return true;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(areConsecutiveElements(new int[]{5, 4, 3, 2, 1}));
- System.out.println(areConsecutiveElements(new int[]{67, 68, 69, 72, 70, 71}));
- System.out.println(areConsecutiveElements(new int[]{67, 68, 69, 72, 70, 71, 70}));
- System.out.println(areConsecutiveElements(new int[]{8, 5, 2, 4, 3, 1}));
- System.out.println("==============");
- System.out.println(areConsecutiveElementsInO1Space(new int[]{5, 4, 3, 2, 1}));
- System.out.println(areConsecutiveElementsInO1Space(new int[]{67, 68, 69, 72, 70, 71}));
- System.out.println(areConsecutiveElementsInO1Space(new int[]{67, 68, 69, 72, 70, 71, 70}));
- System.out.println(areConsecutiveElementsInO1Space(new int[]{8, 5, 2, 4, 3, 1}));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/CountDivisors.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/CountDivisors.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 3023dc3c..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/CountDivisors.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,35 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-/**
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 31/05/2016
- */
-public class CountDivisors {
-
- /**
- * Counts the number of integers in the range {@code begin}
- * and {@code end} that are divisible by {@code n}.
- *
- * @param begin
- * @param end
- * @param n
- * @return
- */
- private static int countDivisorsInRange(int begin, int end, int n) {
- int b = end / n + 1; // From 0 to end the integers divisible by n
- int a = begin / n + 1; // From 0 to begin the integers divisible by n
-
- if (begin % n == 0) { // "begin" is inclusive; if divisible by n then
- --a; // remove 1 from "a"
- }
- return b - a; // return integers in range
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(countDivisorsInRange(0, 0, 5));
- System.out.println(countDivisorsInRange(1, 1, 5));
- System.out.println(countDivisorsInRange(0, 1, 5));
- System.out.println(countDivisorsInRange(0, 10, 5));
- System.out.println(countDivisorsInRange(0, 2000000000, 5));
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/CountSmallerElementsOnRHS.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/CountSmallerElementsOnRHS.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 413234ec..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/CountSmallerElementsOnRHS.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,24 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-import java.util.Arrays;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 9/19/15
- * @time: 11:33 PM
- */
-public class CountSmallerElementsOnRHS {
-
- public static int[] getSmallerElementsCountOnRHSNaive(int[] a) {
- // TODO
- return null;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(getSmallerElementsCountOnRHSNaive(new int[]{12, 1, 2, 3, 0, 11, 4})));
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(getSmallerElementsCountOnRHSNaive(new int[]{5, 4, 3, 2, 1})));
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(getSmallerElementsCountOnRHSNaive(new int[]{1, 2, 3, 4, 5})));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/DistinctPairs.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/DistinctPairs.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 3ba861ab..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/DistinctPairs.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,50 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-import java.util.HashSet;
-import java.util.Set;
-
-/**
- * Level: Easy
- * Problem Description:
- * Given an array and a target sum, return the number of distinct pairs whose sum is equal to the target sum.
- *
- * For Example, given an array [1, 2, 3, 6, 7, 8, 9, 1] and a target sum of 10,
- * the 7 pairs, i.e, (1, 9), (2, 8), (3, 7), (8, 2), (9, 1), (9, 1), and (1, 9) all sum to 10 but there are only
- * three distinct pairs, i.e, (1, 9), (2, 8), and (3, 7) so the answer would be 3.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-06-03
- */
-public class DistinctPairs {
-
- /**
- * Time complexity: O(n), n = size of the array
- * Space complexity: O(n)
- *
- * @param arr
- * @param targetSum
- * @return
- */
- private static int numberOfDistinctPairs(int[] arr, int targetSum) {
- Set numSet = new HashSet<>();
- Set> pairSet = new HashSet<>();
-
- for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
- if (numSet.contains(targetSum - arr[i])) {
- Set pair = new HashSet<>();
- pair.add(arr[i]);
- pair.add(targetSum - arr[i]);
- pairSet.add(pair);
- }
- numSet.add(arr[i]);
- }
-
- return pairSet.size();
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(numberOfDistinctPairs(new int[]{1, 2, 3, 6, 7, 8, 9, 1}, 1));
- System.out.println(numberOfDistinctPairs(new int[]{1, 2, 3, 6, 7, 8, 9, 1}, 2));
- System.out.println(numberOfDistinctPairs(new int[]{1, 2, 3, 6, 7, 8, 9, 1}, 10));
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/DuplicatesInArray.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/DuplicatesInArray.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 5cb9cbe8..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/DuplicatesInArray.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,51 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-import java.util.Arrays;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 8/21/15
- */
-public class DuplicatesInArray {
-
- /**
- * Given an array of n elements which contains elements from 0 to n-1, with any of
- * these numbers appearing any number of times. Find these repeating numbers in O(n)
- * time complexity.
- *
- * For example, let n be 7 and array be {1, 2, 3, 1, 3, 6, 6}, the answer should be
- * 1, 3 and 6.
- *
- * EXPLANATION:
- * The algorithm is simple. We use index of the array to track repeating elements.
- * Once we encounter a element lets say 2 then we make the element in 2nd index -ve just
- * to mark that we have encountered 2. When we encounter 2 again and see that 2nd index
- * is already -ve we conclude that 2 is repeated.
- *
- * Similar to {@link TwoRepeatingElements#findTwoRepeatingElements(int[])}.
- *
- * @param a
- * @return
- */
- public static int[] findDuplicatesInArray(int[] a) {
- int[] duplicates = new int[a.length];
-
- for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
- if (a[Math.abs(a[i])] >= 0) {
- a[Math.abs(a[i])] = -a[Math.abs(a[i])];
- } else {
- duplicates[j++] = Math.abs(a[i]);
- }
- }
- return duplicates;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(findDuplicatesInArray(new int[]{1, 1, 2, 3, 1, 3, 6, 6})));
- // doesn't work if 0 is present in array (as -0 makes no sense but we can modify the algorithm to handle 0)
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(findDuplicatesInArray(new int[]{1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 1, 3, 6, 6})));
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(findDuplicatesInArray(new int[]{0, 0, 1, 2, 3, 1, 3, 6, 6})));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/DuplicatesInArrayWithinKDistance.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/DuplicatesInArrayWithinKDistance.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 2117d712..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/DuplicatesInArrayWithinKDistance.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,46 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-import java.util.Arrays;
-import java.util.HashSet;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 10/18/15
- */
-public class DuplicatesInArrayWithinKDistance {
-
- /**
- * Finds duplicates in an unsorted array {@code a} which are
- * only k distance apart from each other.
- *
- * @param a
- * @param k
- * @return
- */
- public static int[] findDuplicatesInArrayWithinKDistance(int[] a, int k) {
- int index = 0;
- int[] duplicates = new int[a.length];
-
- HashSet hashSet = new HashSet<>();
-
- for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
- if (hashSet.contains(a[i])) {
- duplicates[index++] = a[i];
- } else {
- hashSet.add(a[i]);
- }
-
- if (i >= k) {
- hashSet.remove(a[i - k]);
- }
- }
-
- return Arrays.copyOf(duplicates, index);
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(findDuplicatesInArrayWithinKDistance(new int[]{1, 2, 8, 1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 6, 7}, 3)));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/EqualProbabilityRandomNoGenerator.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/EqualProbabilityRandomNoGenerator.java
deleted file mode 100644
index c26d8694..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/EqualProbabilityRandomNoGenerator.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,53 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-import java.util.Random;
-import java.util.Scanner;
-
-/**
- * Given a random number generator f(n) which generates a random number
- * from {@code 0} (inclusive) to {@code n} (exclusive), design a method
- * which uses f(n) to generate non repeating random numbers from
- * {@code 0} (inclusive) to {@code n} (exclusive)?
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 8/13/15
- * @time: 1:41 PM
- */
-public class EqualProbabilityRandomNoGenerator {
-
- static int[] bucket;
- static int size;
-
- /**
- * The algorithm is to create a bucket of numbers and then to keep on
- * removing the elements from the bucket which are returned.
- *
- * @return
- */
- public static int getRandom() {
- int random = f(size--);
- int result = bucket[random];
- bucket[random] = bucket[size];
- return result;
- }
-
- public static int f(int n) {
- return new Random().nextInt(n);
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
-
- System.out.println("How many random numbers you would like to generate?");
- size = in.nextInt();
-
- bucket = new int[size];
-
- for (int i = 0; i < bucket.length; i++) {
- bucket[i] = i;
- }
- for (int i = 0; i < bucket.length; i++) {
- System.out.println(getRandom());
- }
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/EquilibriumIndex.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/EquilibriumIndex.java
deleted file mode 100644
index c943c603..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/EquilibriumIndex.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,56 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 8/22/15
- * @time: 11:56 AM
- */
-public class EquilibriumIndex {
-
- /**
- * EQUILIBRIUM INDEX of an array is an index such that the sum of elements at lower
- * indexes is equal to the sum of elements at higher indexes.
- *
- * For example, in an array A = {-7, 1, 5, 2, -4, 3, 0}
- *
- * 3 is an equilibrium index, because
- * A[0] + A[1] + A[2] = A[4] + A[5] + A[6]
- *
- * 6 is also an equilibrium index, because sum of zero elements is zero,
- * i.e., A[0] + A[1] + A[2] + A[3] + A[4] + A[5] = 0
- *
- * 7 is not an equilibrium index, because it is not a valid index of array A.
- *
- * @param a
- * @return equilibrium index of array {@param a}.
- */
- public static int getEquilibriumIndex(int[] a) {
- int totalSum = 0, leftSum = 0;
-
- for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
- totalSum += a[i];
- }
-
- for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
- totalSum -= a[i]; // totalSum now holds the right sum from ith index to end
- if (leftSum == totalSum) {
- return i; // left sum == right sum
- }
- leftSum += a[i]; // update left sum
- }
-
- return -1;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(getEquilibriumIndex(new int[]{-7, 1, 5, 2, -4, 3, 0}));
- System.out.println(getEquilibriumIndex(new int[]{-7, 1, 5, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 2, -4, 1, 3, 0}));
- System.out.println(getEquilibriumIndex(new int[]{4, 5, 2, 1, 6, 7, 8, 0, 1}));
- System.out.println(getEquilibriumIndex(new int[]{0}));
- System.out.println(getEquilibriumIndex(new int[]{0, 0, 0}));
- System.out.println(getEquilibriumIndex(new int[]{1, 1}));
- System.out.println(getEquilibriumIndex(new int[]{1, 1, 1}));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/FixedPoint.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/FixedPoint.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 99e8a333..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/FixedPoint.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,41 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 9/8/15
- * @time: 11:34 PM
- */
-public class FixedPoint {
-
- /**
- * Finds the FIXED POINT in an array {@param a} of n distinct integers sorted
- * in ascending order. If there is no fixed point it returns -1.
- * FIXED POINT in an array is an index i such that arr[i] is equal to i. Note that
- * integers in array can be negative.
- *
- * @param a
- * @return
- */
- public static int findFixedPoint(int[] a) {
- int low = 0, high = a.length - 1, mid;
- while (low <= high) {
- mid = (low + high) / 2;
- if (a[mid] == mid) {
- return mid;
- } else if (a[mid] > mid) {
- high = mid - 1;
- } else {
- low = mid + 1;
- }
- }
- return -1;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(findFixedPoint(new int[]{-10, -5, 0, 3, 7}));
- System.out.println(findFixedPoint(new int[]{0, 2, 5, 8, 17}));
- System.out.println(findFixedPoint(new int[]{-10, -5, 3, 4, 7, 9}));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/FlattenArray.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/FlattenArray.java
deleted file mode 100644
index e68c250b..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/FlattenArray.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,39 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-import java.util.ArrayList;
-import java.util.List;
-
-public class FlattenArray {
-
- /**
- * Given a nested array like [[1, 2], 3, [4]], return an array like [1, 2, 3, 4, 5].
- *
- * @param nestedArray an Object array
- * @return a list of all elements in the nestedArray but all at the same level
- */
- private static List flattenArray(Object[] nestedArray) {
- if (nestedArray == null || nestedArray.length == 0) return new ArrayList<>();
-
- List flattenedArray = new ArrayList<>();
-
- for (Object obj : nestedArray) {
- if (obj instanceof Object[]) {
- flattenedArray.addAll(flattenArray((Object[]) obj));
- } else if (obj instanceof Integer) {
- flattenedArray.add((Integer) obj);
- }
- }
-
- return flattenedArray;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(flattenArray(null));
- System.out.println(flattenArray(new Object[]{null}));
- System.out.println(flattenArray(new Object[]{new Object[]{}}));
- System.out.println(flattenArray(new Object[]{new Object[]{1, 2}}));
- System.out.println(flattenArray(new Object[]{1, 2, new Object[]{4, 5}, 6}));
- System.out.println(flattenArray(new Object[]{new Object[]{4, 5}, 1, 2, 6}));
- System.out.println(flattenArray(new Object[]{1, 2, 6, new Object[]{4, 5}}));
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/IntersectionAndUnionOf2SortedArrays.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/IntersectionAndUnionOf2SortedArrays.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 595e85a5..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/IntersectionAndUnionOf2SortedArrays.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,62 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-import java.util.Arrays;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 8/13/15
- * @time: 3:56 PM
- */
-public class IntersectionAndUnionOf2SortedArrays {
-
- /**
- * Returns a 2-D array consisting of intersection and union of
- * two sorted arrays {@param a} and {@param b} respectively.
- *
- * @param a
- * @param b
- * @return
- */
- public static int[][] getIntersectionAndUnionOf2SortedArrays(int[] a, int[] b) {
- int length = a.length + b.length, x = 0, y = 0;
- int[] intersection = new int[length], union = new int[length];
-
- for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < a.length || j < b.length; ) {
-
- // if either of the arrays runs out first
- if (i == a.length) {
- union[y++] = b[j++];
- continue;
- }
- if (j == b.length) {
- union[y++] = a[i++];
- continue;
- }
-
- if (a[i] < b[j]) {
- union[y++] = a[i++];
- } else if (a[i] > b[j]) {
- union[y++] = b[j++];
- } else {
- intersection[x++] = a[i];
- union[y++] = a[i];
- i++;
- j++;
- }
- }
-
- return new int[][]{intersection, union};
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- int[] a1 = new int[]{2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8};
- int[] a2 = new int[]{6, 7, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16};
- int[][] result = getIntersectionAndUnionOf2SortedArrays(a1, a2);
- // intersection
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(result[0]));
- // union
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(result[1]));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/InversionsInArray.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/InversionsInArray.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 1677764d..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/InversionsInArray.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,102 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-import java.util.Arrays;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 7/29/15
- * @time: 8:37 PM
- */
-public class InversionsInArray {
-
- static int inversionCount = 0;
-
- /**
- * Naive approach.
- *
- * INVERSION COUNT for an array indicates how far (or close) the array is from being
- * sorted. If array is already sorted then inversion count is 0. If array is sorted in
- * reverse order then inversion count is the maximum.
- *
- * Formally speaking, two elements a[i] and a[j] form an inversion if a[i] > a[j] and i < j.
- *
- * Example:
- * The sequence 2, 4, 1, 3, 5 has three inversions (2, 1), (4, 1), (4, 3).
- *
- * @param a
- * @return
- */
- public static int getInversionCountNaiveApproach(int[] a) {
- int count = 0;
- for (int i = 0; i < a.length - 2; i++) {
- for (int j = 1; j < a.length - 1; j++) {
- if (a[i] > a[j]) count++;
- }
- }
- return count;
- }
-
- /**
- * Optimized approach.
- *
- * Explanation: In merge() if a[i] > b[j] then all elements in array a starting
- * from i are greater than b[j] which equals to the number of inversions for
- * the two sub-arrays.
- *
- * @param a
- * @return
- * @see: http://www.geeksforgeeks.org/counting-inversions/
- */
- public static int getInversionCount(int[] a) {
- mergeSort(a);
- return inversionCount;
- }
-
- /**
- * Merge sort.
- *
- * Time complexity: O(n log n)
- * Space complexity: O(n) (also needs O(log n) stack space as it is recursive)
- *
- * @param a
- * @return
- */
- public static int[] mergeSort(int[] a) {
- if (a.length == 1) return a;
-
- int[] x = mergeSort(Arrays.copyOfRange(a, 0, a.length / 2));
- int[] y = mergeSort(Arrays.copyOfRange(a, a.length / 2, a.length));
-
- return merge(x, y);
- }
-
- /**
- * Merges two sorted arrays {@param a} and {@param b}.
- *
- * @param a
- * @param b
- * @return
- */
- public static int[] merge(int[] a, int[] b) {
- int lenA = a.length, lenB = b.length, k = 0;
- int[] sortedArray = new int[lenA + lenB];
-
- for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < lenA || j < lenB; ) {
- if (j == lenB || (i < lenA && a[i] < b[j])) {
- sortedArray[k++] = a[i++];
- } else {
- sortedArray[k++] = b[j++];
- inversionCount += lenA - i;
- }
- }
-
- return sortedArray;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(getInversionCountNaiveApproach(new int[]{2, 4, 1, 3, 5}));
- System.out.println(getInversionCount(new int[]{2, 4, 1, 3, 5}));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/KLargestElements.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/KLargestElements.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 87546e7d..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/KLargestElements.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,55 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-import com.rampatra.base.MinHeap;
-
-import java.util.Arrays;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 8/3/15
- * @time: 3:47 PM
- */
-public class KLargestElements {
-
- /**
- * Finds {@param k} largest elements in array {@param a}.
- *
- * Algorithm:
- * 1) Build a Min Heap MH of the first k elements (arr[0] to arr[k-1]) of the given array. This takes O(k) time.
- *
- * 2) For each element, after the kth element (arr[k] to arr[n-1]), compare it with root of MH.
- * ……a) If the element is greater than the root then make it root and call buildHeap for MH
- * ……b) Else ignore it.
- * This step takes (n-k) * O(k) time.
- *
- * 3) Finally, MH has k largest elements and root of the MH is the kth largest element.
- *
- * Therefore, the total time complexity of the above algorithm is: O(k) + (n-k) * O(k).
- *
- * @param a
- * @param k
- * @return
- */
- public static int[] getKLargestElements(int[] a, int k) {
-
- int[] kElements = Arrays.copyOfRange(a, 0, k);
-
- MinHeap minHeap = new MinHeap(kElements);
- minHeap.buildMinHeap();
-
- for (int i = k; i < a.length; i++) {
- if (a[i] > minHeap.findMin()) {
- minHeap.extractMin();
- minHeap.insert(a[i]);
- }
- }
-
- return minHeap.getHeap();
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(getKLargestElements(new int[]{2, 3, 4, 1, 5, 7, 9}, 3)));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/KthLargestElement.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/KthLargestElement.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 65ca77c7..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/KthLargestElement.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,63 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-import com.rampatra.sorting.MergeSort;
-import com.rampatra.base.MaxHeap;
-
-import java.util.Arrays;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 8/1/15
- * @time: 11:26 PM
- */
-public class KthLargestElement {
-
- /**
- * Naive approach.
- *
- * Time complexity: O(n log n)
- *
- * @param a
- * @param k
- * @return
- */
- public static int getKthLargestElementNaive(int[] a, int k) {
- if (k >= a.length) return -1;
-
- a = MergeSort.mergeSort(a);
-
- return a[a.length - k];
- }
-
- /**
- * Determines the kth largest element by building a max heap
- * k times removing the root each time.
- *
- * @param a
- * @param k
- * @return
- */
- public static int getKthLargestElement(int[] a, int k) {
- MaxHeap maxHeap = new MaxHeap(a);
- maxHeap.buildMaxHeap();
- while (true) {
- if (k == 1) break;
-
- maxHeap.extractMax();
- k--;
- }
-
- return maxHeap.findMax();
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- int[] ar = new int[]{2, 4, 5, 7, 1, 8, 9};
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ar));
- System.out.println(getKthLargestElementNaive(ar, 3));
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ar));
- System.out.println(getKthLargestElement(ar, 3));
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ar));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/LargestProductContiguousSubArray.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/LargestProductContiguousSubArray.java
deleted file mode 100644
index c7afb19b..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/LargestProductContiguousSubArray.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,24 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 5/28/15
- * @time: 12:44 PM
- */
-public class LargestProductContiguousSubArray {
-
- /**
- * @param a
- * @return
- */
- public static int getLargestProductContiguousSubArray(int[] a) {
- return 0;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(getLargestProductContiguousSubArray(new int[]{-2, 1, -3, 4, 5, -1, 4}));
- System.out.println(getLargestProductContiguousSubArray(new int[]{6, -3, -10, 0, 2}));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/LargestSumContiguousSubArray.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/LargestSumContiguousSubArray.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 8b34d9ef..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/LargestSumContiguousSubArray.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,60 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 5/28/15
- * @time: 12:44 PM
- */
-public class LargestSumContiguousSubArray {
-
- /**
- * Based on Kadane's Algorithm. Doesn't work when all
- * elements in array {@param a} are negative.
- *
- * @param a
- * @return
- */
- public static int getLargestSumOfContiguousSubArray(int[] a) {
- int maxSum = 0, maxSumTillIndex = 0;
-
- for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
- maxSumTillIndex += a[i]; // keep on adding elements
- if (maxSumTillIndex < 0) {
- maxSumTillIndex = 0; // once the sum is less than 0 restart adding elements from next index
- } else if (maxSumTillIndex > maxSum) {
- maxSum = maxSumTillIndex;
- }
- }
- return maxSum;
- }
-
- /**
- * Below algorithm works even when all elements in array {@param a} are negative.
- *
- * @param a
- * @return
- */
- public static int getLargestSumOfContiguousSubArrayWhenAllNosNegative(int[] a) {
- int maxSum = a[0], maxSumTillIndex = a[0];
-
- for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++) {
- maxSumTillIndex = Math.max(a[i], maxSumTillIndex + a[i]);
- maxSum = Math.max(maxSum, maxSumTillIndex);
- }
-
- return maxSum;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(getLargestSumOfContiguousSubArray(new int[]{-2, 1, -3, 4, 5, -1, 4}));
- System.out.println(getLargestSumOfContiguousSubArray(new int[]{2, -1, -3, 4, -5, 1, 4}));
- // kadane's algorithm doesn't work if all no.s are -ve
- System.out.println(getLargestSumOfContiguousSubArray(new int[]{-2, -1, -3, -4, -5, -1, -4}));
-
- System.out.println(getLargestSumOfContiguousSubArrayWhenAllNosNegative(new int[]{-2, 1, -3, 4, 5, -1, 4}));
- System.out.println(getLargestSumOfContiguousSubArrayWhenAllNosNegative(new int[]{2, -1, -3, 4, -5, 1, 4}));
- System.out.println(getLargestSumOfContiguousSubArrayWhenAllNosNegative(new int[]{-2, -1, -3, -4, -5, -1, -4}));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/LeadersInArray.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/LeadersInArray.java
deleted file mode 100644
index c2075751..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/LeadersInArray.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,45 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-import java.util.Arrays;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 7/29/15
- * @time: 12:06 PM
- */
-public class LeadersInArray {
-
- /**
- * Returns an array containing all leaders present in {@param a}.
- * An element is a LEADER if its greater than all elements to
- * the right of it in the array.
- *
- * @param a
- * @return
- */
- public static int[] getAllLeaders(int[] a) {
-
- int i = a.length - 2, j = 0;
- int[] leaders = new int[a.length];
-
- // rightmost element is always a leader
- leaders[0] = a[a.length - 1];
-
- for (; i >= 0; i--) {
- if (a[i] > leaders[j]) {
- leaders[++j] = a[i];
- }
- }
-
- // omit the extra space which aren't filled with leaders
- return Arrays.copyOfRange(leaders, 0, j + 1);
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(getAllLeaders(new int[]{16, 17, 4, 3, 5, 2})));
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(getAllLeaders(new int[]{16, 1, 4, 3, 5, 12})));
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(getAllLeaders(new int[]{16, 15, 14, 13, 12, 10})));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/LongestBitonicSubArray.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/LongestBitonicSubArray.java
deleted file mode 100644
index dc3caafb..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/LongestBitonicSubArray.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,64 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 9/18/15
- * @time: 5:10 PM
- */
-public class LongestBitonicSubArray {
-
- /**
- * Returns the length of the longest bitonic sub-array in
- * array {@param a}.
- *
- * A subarray A[i … j] is bitonic if there is a k with i <= k <= j such
- * that A[i] <= A[i + 1] ... <= A[k] >= A[k + 1] >= ... A[j – 1] > = A[j].
- *
- * @param a
- * @return
- */
- public static int getLongestBitonicSubArrayLength(int[] a) {
- int len = a.length;
- int bitonicLength;
- int[] increasingSequence = new int[len];
- int[] decreasingSequence = new int[len];
-
- increasingSequence[0] = 1; // stores the length of the increasing sequence so far
- decreasingSequence[len - 1] = 1; // stores the length of the decreasing sequence so far
-
- for (int i = 1; i < len; i++) {
- if (a[i] > a[i - 1]) {
- increasingSequence[i] = increasingSequence[i - 1] + 1;
- } else {
- increasingSequence[i] = 1;
- }
- }
-
- for (int i = len - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
- if (a[i] > a[i + 1]) {
- decreasingSequence[i] = decreasingSequence[i + 1] + 1;
- } else {
- decreasingSequence[i] = 1;
- }
- }
-
- bitonicLength = increasingSequence[0] + decreasingSequence[0] - 1;
- for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
- if ((increasingSequence[i] + decreasingSequence[i] - 1) > bitonicLength) {
- bitonicLength = increasingSequence[i] + decreasingSequence[i] - 1;
- }
- }
-
- return bitonicLength;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(getLongestBitonicSubArrayLength(new int[]{1, 2, 5, 4, 3}));
- System.out.println(getLongestBitonicSubArrayLength(new int[]{12, 4, 78, 90, 45, 23}));
- System.out.println(getLongestBitonicSubArrayLength(new int[]{10, 20, 30, 40}));
- System.out.println(getLongestBitonicSubArrayLength(new int[]{40, 30, 20, 10}));
- System.out.println(getLongestBitonicSubArrayLength(new int[]{10}));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/LongestConsecutiveSubsequence.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/LongestConsecutiveSubsequence.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 8e6a99f8..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/LongestConsecutiveSubsequence.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,80 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-import java.util.HashSet;
-import java.util.Set;
-
-/**
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 25/11/2018
- */
-public class LongestConsecutiveSubsequence {
-
- /**
- * Given an array of distinct integers, find the length of the longest sub-sequence such that
- * elements in the subsequence are consecutive integers, the consecutive numbers can be in any order.
- *
- * Examples:
- * Input: arr[] = {1, 9, 3, 10, 4, 20, 2};
- * Output: 4
- * The subsequence {1, 3, 4, 2} is the longest subsequence
- * of consecutive elements
- *
- * Input: arr[] = {36, 41, 56, 35, 44, 33, 34, 92, 43, 32, 42}
- * Output: 5
- * The subsequence {36, 35, 33, 34, 32} is the longest subsequence
- * of consecutive elements.
- *
- * NOTE: You can also sort this array and check for consecutive elements. You can take this approach if interviewer
- * asks to solve with no additional space but do bear in mind that some sorting algorithms do require extra space.
- *
- * @param arr unsorted array of non-repeating integers
- * @return the length of the longest consecutive subsequence
- */
- private static int findLengthOfLongestConsecutiveSubsequence(int[] arr) {
- int longestSubseqCount = 0;
- int subseqCount;
- int currElem;
- // add all numbers to a set to have O(1) time complexity for searching elements
- Set numSet = new HashSet<>();
- for (int n : arr) {
- numSet.add(n);
- }
-
- for (int n : arr) {
- subseqCount = 1;
- currElem = n;
- // check for the next consecutive elements
- while (numSet.contains(currElem + 1)) {
- numSet.remove(currElem);
- numSet.remove(currElem + 1);
- currElem++;
- subseqCount++;
- }
- // check for the previous consecutive elements
- while (numSet.contains(currElem - 1)) {
- numSet.remove(currElem);
- numSet.remove(currElem - 1);
- currElem--;
- subseqCount++;
- }
- // update longest counter if the length of the current subsequence is larger
- if (subseqCount > longestSubseqCount) {
- longestSubseqCount = subseqCount;
- }
- }
- return longestSubseqCount;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
-
- System.out.println("{1, 9, 3, 10, 4, 20, 2}: " +
- findLengthOfLongestConsecutiveSubsequence(new int[]{1, 9, 3, 10, 4, 20, 2}));
- System.out.println("{36, 41, 56, 35, 44, 33, 34, 92, 43, 32, 42}: " +
- findLengthOfLongestConsecutiveSubsequence(new int[]{36, 41, 56, 35, 44, 33, 34, 92, 43, 32, 42}));
- System.out.println("{1,5,8,3}: " + findLengthOfLongestConsecutiveSubsequence(new int[]{1, 5, 8, 3}));
-
- // corner cases
- System.out.println("{1}: " + findLengthOfLongestConsecutiveSubsequence(new int[]{1}));
- System.out.println("{}: " + findLengthOfLongestConsecutiveSubsequence(new int[]{}));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/MajorityElement.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/MajorityElement.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 51e5d11f..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/MajorityElement.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,62 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-/**
- * The algorithm for finding a possible candidate
- * works in O(n) which is known as Moore’s Voting Algorithm.
- * Basic idea of the algorithm is if we cancel out each
- * occurrence of an element e with all the other elements
- * that are different from e then e will exist until end
- * if it is a majority element.
- *
- * Time Complexity: O(n)
- * Auxiliary Space : O(1)
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 5/20/15
- */
-public class MajorityElement {
-
- /**
- * Uses Moore’s Voting Algorithm to
- * get a candidate for majority element.
- *
- * @param a
- * @return
- */
- public static int findCandidate(int[] a) {
- int candidate = a[0], count = 1;
- for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++) {
- if (candidate == a[i]) {
- count++;
- } else {
- count--;
- }
- if (count == 0) {
- candidate = a[i];
- count = 1;
- }
- }
- return candidate;
- }
-
- public static void majorityElement(int[] a) {
- int candidate = findCandidate(a),
- count = 0;
-
- // check if the candidate is really a majority element
- for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
- if (candidate == a[i]) {
- count++;
- }
- }
- if (count > a.length / 2) {
- System.out.print(candidate);
- } else {
- System.out.print("NONE");
- }
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- majorityElement(new int[]{1, 6, 2, 2, 2, 1, 2, 2, 7, 2});
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/MajorityElementInSortedArray.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/MajorityElementInSortedArray.java
deleted file mode 100644
index ded2db27..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/MajorityElementInSortedArray.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,72 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 7/31/15
- */
-public class MajorityElementInSortedArray {
-
- /**
- * Checks if {@code n} is a majority element in array {@code arr}
- * by performing a binary search.
- *
- * Time complexity: O(log n)
- *
- * @param arr
- * @param n
- * @return
- */
- public static boolean isMajorityElement(int[] arr, int n) {
- int l = arr.length;
- int startIndex = getFirstIndexOf(arr, n, 0, l - 1);
-
- // element not found
- if (startIndex == -1) return false;
-
- if (startIndex + l / 2 < l && arr[startIndex + l / 2] == n) {
- return true;
- } else {
- return false;
- }
-
- }
-
- /**
- * Returns the index of first occurrence of {@code n} in array {@code arr}.
- *
- * @param arr
- * @param low
- * @param high
- * @param n
- * @return
- */
- public static int getFirstIndexOf(int[] arr, int n, int low, int high) {
- if (low <= high) {
- int mid = (low + high) / 2;
- /**
- * Check if a[mid] is the first occurrence of n:
- * a[mid] is first occurrence if n is one of the following
- * is true:
- * (i) mid == 0 and a[mid] == n
- * (ii) n > a[mid-1] and a[mid] == n
- */
- if (arr[mid] == n && (mid == 0 || n > arr[mid - 1])) {
- return mid;
- } else if (n <= arr[mid]) {
- return getFirstIndexOf(arr, n, low, mid - 1);
- } else {
- return getFirstIndexOf(arr, n, mid + 1, high);
- }
- }
- return -1;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(isMajorityElement(new int[]{2, 2}, 2));
- System.out.println(isMajorityElement(new int[]{1, 2}, 2));
- System.out.println(isMajorityElement(new int[]{1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3}, 2));
- System.out.println(isMajorityElement(new int[]{1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3}, 2));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/MatrixInSpiral.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/MatrixInSpiral.java
deleted file mode 100644
index a498f39a..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/MatrixInSpiral.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,61 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-import static java.lang.System.out;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 9/9/15
- * @time: 2:55 PM
- */
-public class MatrixInSpiral {
-
- /**
- * Prints a 2D array {@param a} in spiral form (clockwise).
- *
- * @param a
- */
- public static void printMatrixInSpiral(int[][] a) {
- int row = a.length, col = a[0].length;
-
- // this loop iterates for the entire matrix
- for (int r = row, c = col, x = 0; r >= 0 && c >= 0; r--, c--, x++) {
- /**
- * Below 4 {@code for} loops print the perimeter of a matrix
- */
- // prints the top row
- for (int i = x, j = x; i < r && j < c; j++) {
- out.print(a[i][j] + " ");
- }
- // prints the right most column
- for (int i = x + 1, j = c - 1; i < r; i++) {
- out.print(a[i][j] + " ");
- }
- // prints the bottom row
- for (int i = r - 1, j = c - 2; i > x && j >= x; j--) {
- out.print(a[i][j] + " ");
- }
- // prints the left most column
- for (int i = r - 2, j = x; i > x; i--) {
- out.print(a[i][j] + " ");
- }
- }
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- printMatrixInSpiral(new int[][]{{1}, {2}});
- out.println();
- printMatrixInSpiral(new int[][]{{1, 2}, {3, 4}});
- out.println();
- printMatrixInSpiral(new int[][]{{1, 2, 3}, {4, 5, 6}});
- out.println();
- printMatrixInSpiral(new int[][]{{1, 2, 3, 4}, {5, 6, 7, 8}, {9, 10, 11, 12}});
- out.println();
- printMatrixInSpiral(new int[][]{{1, 2, 3, 4}, {5, 6, 7, 8}, {9, 10, 11, 12}, {13, 14, 15, 16}});
- out.println();
- printMatrixInSpiral(new int[][]{{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}, {7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12}, {13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18}});
- out.println();
- printMatrixInSpiral(new int[][]{{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8}, {9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16}});
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/MaxDiffWithLargerElementAfterSmallerElement.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/MaxDiffWithLargerElementAfterSmallerElement.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 04d7a9f8..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/MaxDiffWithLargerElementAfterSmallerElement.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,43 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 8/12/15
- * @time: 5:40 PM
- */
-public class MaxDiffWithLargerElementAfterSmallerElement {
-
- /**
- * Finds the difference between any two elements such that larger
- * element appears after the smaller number in array {@param a}.
- *
- * Example:
- * If array is [2, 3, 10, 6, 4, 8, 1] then returned value should be 8 (Diff between 10 and 2).
- * If array is [ 7, 9, 5, 6, 3, 2 ] then returned value should be 2 (Diff between 7 and 9).
- *
- * @param a
- * @return
- */
- public static int getMaxDiffWithLargerElementAfterSmallerElement(int[] a) {
- int minElement = a[0], maxDiff = a[1] - a[0];
-
- for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++) {
- if (a[i] < minElement) {
- minElement = a[i];
- }
- if (a[i] - minElement > maxDiff) {
- maxDiff = a[i] - minElement;
- }
- }
-
- return maxDiff;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(getMaxDiffWithLargerElementAfterSmallerElement(new int[]{2, 1, 4, 5, 10, 0}));
- System.out.println(getMaxDiffWithLargerElementAfterSmallerElement(new int[]{2, -6, 4, 5, 10, 1}));
- System.out.println(getMaxDiffWithLargerElementAfterSmallerElement(new int[]{-2, -6, -4, -5, -10, -1}));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/MaxInAllSubArrays.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/MaxInAllSubArrays.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 8061d44d..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/MaxInAllSubArrays.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,102 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-import com.rampatra.base.MaxHeap;
-
-import java.util.ArrayDeque;
-import java.util.Arrays;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 9/3/15
- * @time: 9:21 PM
- */
-public class MaxInAllSubArrays {
-
- /**
- * Naive approach.
- *
- * Finds the maximum element in each and every sub-array
- * in {@param a} of size {@param k}.
- *
- * Time complexity: O(n*k), or more precisely O((n-k) * k)
- *
- * @param a
- * @param k
- */
- public static int[] maxInAllSubArraysOfSizeKNaive(int[] a, int k) {
- int[] maxElements = new int[a.length - k + 1];
- int[] kElements;
-
- for (int i = 0; i <= a.length - k; i++) {
- kElements = Arrays.copyOfRange(a, i, i + k);
- /**
- * maxHeapify() can't be used because to call maxHeapify() on i because left(i) and right (i) should
- * already satisfy the max heap property which isn't true in this case.
- */
- MaxHeap maxHeap = new MaxHeap(kElements);
- maxHeap.buildMaxHeap();
- maxElements[i] = maxHeap.findMax();
- }
-
- return maxElements;
- }
-
- /**
- * Finds the maximum element in each and every sub-array
- * in {@param a} of size {@param k}.
- *
- * Time complexity: O(n)
- * Auxiliary Space: O(k)
- *
- * @param a
- * @param k
- * @return
- */
- public static int[] maxInAllSubArraysOfSizeK(int[] a, int k) {
- int i, j = 0;
- int[] result = new int[a.length - k + 1];
- /**
- * Create a Double Ended Queue, Qi that will store indexes of array elements
- * The queue will store indexes of useful elements in every window and it will
- * maintain decreasing order of values from front to rear in Qi, i.e,
- * arr[Qi.front[]] to arr[Qi.rear()] are sorted in decreasing order.
- */
- ArrayDeque deque = new ArrayDeque<>();
-
- for (i = 0; i < k; i++) {
- // remove smaller elements on left side of current element
- while (!deque.isEmpty() && a[i] > a[deque.peekLast()]) {
- deque.removeLast();
- }
- deque.addLast(i);
- }
-
- for (; i < a.length; i++) {
- result[j++] = a[deque.peekFirst()];
-
- // remove elements that are outside window k
- while (!deque.isEmpty() && deque.peekFirst() <= i - k) {
- deque.removeFirst();
- }
- // remove smaller elements on left side of current element
- while (!deque.isEmpty() && a[i] > a[deque.peekLast()]) {
- deque.removeLast();
- }
- deque.addLast(i);
- }
-
- // for max in last k elements
- result[j] = a[deque.peekFirst()];
-
- return result;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(maxInAllSubArraysOfSizeKNaive(new int[]{1, 2, 3, 1, 4, 5, 2, 3, 6}, 3)));
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(maxInAllSubArraysOfSizeKNaive(new int[]{8, 5, 10, 7, 9, 4, 15, 12, 90, 13}, 4)));
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(maxInAllSubArraysOfSizeK(new int[]{1, 2, 3, 1, 4, 5, 2, 3, 6}, 3)));
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(maxInAllSubArraysOfSizeK(new int[]{8, 5, 10, 7, 9, 4, 15, 12, 90, 13}, 4)));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/MaxIndexDiff.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/MaxIndexDiff.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 9eb982c4..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/MaxIndexDiff.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,59 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 9/1/15
- * @time: 10:21 PM
- */
-public class MaxIndexDiff {
-
- /**
- * Given an array arr[], find the maximum j – i such that arr[j] > arr[i].
- *
- * @param a
- * @return
- */
- public static int maxDiff(int[] a) {
- int maxDiff = -1;
- int[] leftMin = new int[a.length], rightMax = new int[a.length];
-
- /**
- * leftMin[i] holds the smallest element on left side of arr[i] including arr[i].
- * In other words, leftMin[i] stores the minimum value from (arr[0], arr[1], ... arr[i]).
- */
- leftMin[0] = a[0];
- for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++) {
- leftMin[i] = Math.min(a[i], leftMin[i - 1]);
- }
-
- /**
- * rightMax[i] holds the greatest element on right side of arr[i] including arr[i].
- * In other words, rightMax[i] stores the maximum value from (arr[i], arr[i+1], ..arr[n-1])
- */
- rightMax[a.length - 1] = a[a.length - 1];
- for (int i = a.length - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
- rightMax[i] = Math.max(a[i], rightMax[i + 1]);
- }
-
- // traverse both arrays from left to right to find maximum j - i
- for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < a.length && j < a.length; ) {
- if (rightMax[j] > leftMin[i]) {
- maxDiff = Math.max(maxDiff, j - i);
- j++;
- } else {
- i++;
- }
- }
- return maxDiff;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(maxDiff(new int[]{34, 8, 10, 3, 2, 80, 30, 33, 1}));
- System.out.println(maxDiff(new int[]{9, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 18, 0}));
- System.out.println(maxDiff(new int[]{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}));
- System.out.println(maxDiff(new int[]{6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1}));
- System.out.println(maxDiff(new int[]{10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 6, 9, 7, 5, 3}));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/MaxMinWithMinComparisons.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/MaxMinWithMinComparisons.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 23e3e99d..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/MaxMinWithMinComparisons.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,59 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-import java.util.Arrays;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 7/31/15
- * @time: 3:16 PM
- */
-public class MaxMinWithMinComparisons {
-
- /**
- * Finds the minimum and maximum number in array {@param a}
- * with minimum no. of comparisons.
- *
- * If length of array is even:
- * No. of comparisons = 1+3*(n-2)/2
- * and if length is odd:
- * No. of comparisons = 3*(n-1)/2
- *
- * @param a
- * @return
- */
- public static int[] getMaxMinWithMinComparisons(int[] a) {
- int min, max, i;
-
- if (a.length % 2 == 0) { // this is not a comparison
- if (a[0] < a[1]) { // this is a comparison
- min = a[0];
- max = a[1];
- } else {
- min = a[1];
- max = a[0];
- }
- i = 2;
- } else {
- min = max = a[0];
- i = 1;
- }
-
- for (; i < a.length - 1; i += 2) {
- if (a[i] < a[i + 1]) { // 1st comparison
- if (a[i] < min) min = a[i]; // 2nd comparison
- if (a[i + 1] > max) max = a[i + 1]; // 3rd comparison
- } else {
- if (a[i] > max) max = a[i]; // 2nd comparison
- if (a[i + 1] < min) min = a[i + 1]; // 3rd comparison
- }
- }
-
- return new int[]{min, max};
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(getMaxMinWithMinComparisons(new int[]{2, 5, 1, 6, 7, 9, 0, 8, 10})));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/MaxSpan.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/MaxSpan.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 7db17c18..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/MaxSpan.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,45 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-import com.sun.tools.javac.util.Assert;
-
-/**
- * Consider the leftmost and rightmost appearances of some value in an array. We'll say that the "span" is the
- * number of elements between the two inclusive. A single value has a span of 1. Returns the largest span found
- * in the given array.
- *
- * Examples:
- * maxSpan([1, 2, 1, 1, 3]) → 4
- * maxSpan([1, 4, 2, 1, 4, 1, 4]) → 6
- * maxSpan([1, 4, 2, 1, 4, 4, 4]) → 6
- *
- * Level: Easy
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @link https://codingbat.com/prob/p189576
- * @since 2019-01-23
- */
-public class MaxSpan {
-
- public static int maxSpan(int[] nums) {
- if (nums.length == 0) return 0;
- int largestSpan = 1;
- for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
- for (int j = nums.length - 1; j > i; j--) {
- if (nums[i] == nums[j]) {
- if (j - i + 1 > largestSpan) {
- largestSpan = j - i + 1;
- }
- }
- }
- }
- return largestSpan;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Assert.check(maxSpan(new int[]{1, 2, 1, 1, 3}) == 4);
- Assert.check(maxSpan(new int[]{1, 4, 2, 1, 4, 1, 4}) == 6);
- Assert.check(maxSpan(new int[]{1, 4, 2, 1, 4, 4, 4}) == 6);
- Assert.check(maxSpan(new int[]{1}) == 1);
- Assert.check(maxSpan(new int[]{}) == 0);
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/MaximumSizeSquareSubMatrix.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/MaximumSizeSquareSubMatrix.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 0c9c4419..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/MaximumSizeSquareSubMatrix.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,80 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 8/4/15
- * @time: 11:48 PM
- */
-public class MaximumSizeSquareSubMatrix {
-
- /**
- * Prints the maximum size square sub-matrix in {@param a} with all 1s.
- *
- * Algorithm:
- * 1) Construct a sum matrix/auxiliary matrix aux[R][C] for the given a[R][C].
- * ...a) Copy first row and first columns as it is from a[][] to aux[][]
- * ...b) For other entries, use following expressions to construct aux[][]
- * ........If a[i][j] is 1 then
- * ........aux[i][j] = min(aux[i][j-1], aux[i-1][j], aux[i-1][j-1]) + 1
- * ........Else
- * ........aux[i][j] = 0
- * 2) Find the maximum entry in aux[R][C]
- * 3) Using the value and coordinates of maximum entry in aux[i], print sub-matrix of a[][]
- *
- * @param a
- */
- public static void printMaximumSizeSquareSubMatrix(int[][] a) {
- int size = a[0].length; // no. of rows/columns
- int maxI = 0, maxJ = 0, maxSubMatrixSize = 0;
- int[][] auxMatrix = new int[size][size];
-
- // construct auxiliary matrix
- for (int i = 0, j = 0; j < size; j++) { // copy 1st row
- auxMatrix[i][j] = a[i][j];
- }
-
- for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < size; i++) { // copy 1st column
- auxMatrix[i][j] = a[i][j];
- }
-
- for (int i = 1; i < size; i++) {
- for (int j = 1; j < size; j++) {
- if (a[i][j] == 1) {
- auxMatrix[i][j] = Math.min(Math.min(auxMatrix[i - 1][j], auxMatrix[i][j - 1]), auxMatrix[i - 1][j - 1]) + 1;
- } else {
- auxMatrix[i][j] = 0;
- }
-
- if (auxMatrix[i][j] > maxSubMatrixSize) {
- maxSubMatrixSize = auxMatrix[i][j];
- maxI = i;
- maxJ = j;
- }
- }
- }
-
- // print max size sub-matrix in array 'a' from the co-ordinates in auxiliary matrix
- for (int i = maxI; i > maxI - maxSubMatrixSize; i--) {
- for (int j = maxJ; j > maxJ - maxSubMatrixSize; j--) {
- System.out.print(a[i][j]);
- }
- System.out.println();
- }
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- int[][] ar = new int[][]{{0, 1, 1, 1},
- {1, 1, 0, 1},
- {1, 0, 0, 1},
- {1, 0, 0, 1}};
- printMaximumSizeSquareSubMatrix(ar);
- int[][] ar1 = new int[][]{{0, 1, 1, 1, 0},
- {1, 1, 0, 1, 1},
- {1, 1, 1, 0, 1},
- {1, 1, 1, 1, 1},
- {1, 1, 1, 0, 0}};
- printMaximumSizeSquareSubMatrix(ar1);
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/MaximumSumNonAdjacentSubSequence.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/MaximumSumNonAdjacentSubSequence.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 9734aa29..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/MaximumSumNonAdjacentSubSequence.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,42 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 7/29/15
- * @time: 9:18 AM
- */
-public class MaximumSumNonAdjacentSubSequence {
-
- /**
- * Given an array of positive numbers, finds the maximum sum of a sub-sequence
- * with the constraint that no 2 numbers in the sub-sequence should be adjacent
- * in the array.
- *
- * Example:
- * 1) 3 2 7 10 should return 13 (sum of 3 and 10)
- * 2) 3 2 5 10 7 should return 15 (sum of 3, 5 and 7).
- *
- * Here we maintain 2 variables incl and excl which is max sum till now (satisfying the constraint)
- * including the current element and excluding the current element respectively.
- *
- * @param a
- * @return
- */
- public static int maximumSumNonAdjacentSubSequence(int[] a) {
- int incl = a[0], excl = 0, prevIncl = incl; // incl is max sum including the current element
- // and excl is max sum excluding the current element
- for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++) {
- incl = excl + a[i]; // because we have to exclude the previous element if we consider the current element
- excl = Math.max(prevIncl, excl); // we are excluding the current element so we can consider the previous element or dont
- prevIncl = incl;
- }
- return Math.max(incl, excl);
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(maximumSumNonAdjacentSubSequence(new int[]{3, 2, 7, 10}));
- System.out.println(maximumSumNonAdjacentSubSequence(new int[]{3, 2, 5, 10, 7}));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/MedianOfStream.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/MedianOfStream.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 47781bc0..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/MedianOfStream.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,81 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-import com.rampatra.base.MaxHeap;
-import com.rampatra.base.MinHeap;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 9/12/15
- * @time: 11:19 PM
- */
-public class MedianOfStream {
-
- /**
- * @param med
- * @param elem
- * @param maxHeap
- * @param minHeap
- * @return
- */
- public static int getMedianOfStream(int med, int elem, MaxHeap maxHeap, MinHeap minHeap) {
-
- switch (compare(maxHeap.getSize(), minHeap.getSize())) {
- case 0: // sizes of maxHeap and minHeap are same
- if (elem < med) {
- maxHeap.insert(elem);
- med = maxHeap.findMax();
- } else {
- minHeap.insert(elem);
- med = minHeap.findMin();
- }
- break;
- case 1: // size of maxHeap greater than minHeap
- if (elem < med) {
- minHeap.insert(maxHeap.extractMax());
- maxHeap.insert(elem);
- } else {
- minHeap.insert(elem);
- }
- med = (maxHeap.findMax() + minHeap.findMin()) / 2;
- break;
- case -1: // size of maxHeap smaller than minHeap
- if (elem < med) {
- maxHeap.insert(elem);
- } else {
- maxHeap.insert(minHeap.extractMin());
- minHeap.insert(elem);
- }
- med = (maxHeap.findMax() + minHeap.findMin()) / 2;
- break;
- }
- return med;
- }
-
- static void printMedianOfStream(int[] a) {
- int m = 0;
- MaxHeap maxHeap = new MaxHeap(a);
- MinHeap minHeap = new MinHeap(a);
-
- // calling in a loop so at to resemble a stream
- for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
- m = getMedianOfStream(m, a[i], maxHeap, minHeap);
- }
- System.out.println(m);
- }
-
- static int compare(int a, int b) {
- if (a == b) {
- return 0;
- } else {
- return a < b ? -1 : 1;
- }
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- printMedianOfStream(new int[]{5, 15, 1, 3, 2, 8, 7, 9, 10, 6, 11, 4});
- printMedianOfStream(new int[]{5, 15, 1});
- printMedianOfStream(new int[]{5, 15, 10, 20});
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/MedianOfTwoSortedArrays.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/MedianOfTwoSortedArrays.java
deleted file mode 100644
index d64ec757..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/MedianOfTwoSortedArrays.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,104 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-import java.util.Arrays;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 7/27/15
- * @time: 5:50 PM
- */
-public class MedianOfTwoSortedArrays {
-
- /**
- * Returns the median of a sorted array {@param a}.
- *
- * @param a
- * @return
- */
- public static int median(int a[]) {
- int l = a.length;
- if (l % 2 == 0) {
- return (a[l / 2] + a[l / 2 - 1]) / 2;
- } else {
- return a[l / 2];
- }
- }
-
- /**
- * Returns the median of two sorted arrays {@param a1} and {@param a2} having same length.
- * In case of any error, it returns {@code -1}.
- *
- * Example:
- *
- *
- * ar1[] = {1, 12, 15, 26, 38}
- * ar2[] = {2, 13, 17, 30, 45}
- * For above two arrays m1 = 15 and m2 = 17
- *
- * For the above ar1[] and ar2[], m1 is smaller than m2. So median is present in one of
- * the following two sub-arrays:
- *
- * [15, 26, 38] and [2, 13, 17]
- * Let us repeat the process for above two sub-arrays:
- *
- * m1 = 26 m2 = 13.
- * m1 is greater than m2. So the sub-arrays become
- *
- * [15, 26] and [13, 17]
- * Now size is 2, so median = (max(ar1[0], ar2[0]) + min(ar1[1], ar2[1]))/2
- * = (max(15, 13) + min(26, 17))/2
- * = (15 + 17)/2
- * = 16
- *
- * @param a1
- * @param a2
- * @return
- */
- public static int median(int[] a1, int[] a2) {
-
- int l1 = a1.length, l2 = a2.length, m1, m2;
-
- if (l1 != l2 || l1 <= 0) {
- return -1;
- }
-
- if (l1 == 1) {
- return (a1[0] + a2[0]) / 2;
- }
-
- if (l1 == 2) {
- return (Math.max(a1[0], a2[0]) + Math.min(a1[1], a2[1])) / 2;
- }
-
- m1 = median(a1);
- m2 = median(a2);
-
- if (m1 == m2) {
- return m1;
- }
-
- if (m1 < m2) { // median exists in a1[m1....] and a2[....m2]
- if (l1 % 2 == 0) {
- return median(Arrays.copyOfRange(a1, l1 / 2 - 1, l1), Arrays.copyOfRange(a2, 0, l2 / 2 + 1));
- } else {
- return median(Arrays.copyOfRange(a1, l1 / 2, l1), Arrays.copyOfRange(a2, 0, l2 / 2 + 1));
- }
- } else {
- if (l1 % 2 == 0) { // median exists in a1[....m1] and a2 [m2....]
- return median(Arrays.copyOfRange(a1, 0, l1 / 2 + 1), Arrays.copyOfRange(a2, l2 / 2 - 1, l2));
- } else {
- return median(Arrays.copyOfRange(a1, 0, l1 / 2 + 1), Arrays.copyOfRange(a2, l2 / 2, l2));
- }
- }
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- // test cases
- System.out.println(median(new int[]{1, 2, 3, 6}, new int[]{4, 6, 8, 9}));
- System.out.println(median(new int[]{4, 6, 8, 9}, new int[]{1, 2, 3, 6}));
- System.out.println(median(new int[]{1, 2}, new int[]{3, 4}));
- System.out.println(median(new int[]{2, 2}, new int[]{2, 2}));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/MergeArrayOfNIntoArrayOfMPlusN.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/MergeArrayOfNIntoArrayOfMPlusN.java
deleted file mode 100644
index e95c653a..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/MergeArrayOfNIntoArrayOfMPlusN.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,66 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-import java.util.Arrays;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 7/27/15
- * @time: 12:15 PM
- */
-public class MergeArrayOfNIntoArrayOfMPlusN {
-
- private static final int NA = -1;
-
- /**
- * Move non {@code NA} elements to the end of array leaving everything else unchanged.
- *
- * For example,
- * Input: {2, NA, 7, NA, NA, 10, NA};
- * Output: {2, NA, 7, NA, 2, 7, 10}
- *
- * @param arrayMPlusN
- */
- public static void moveElementsToEnd(int[] arrayMPlusN) {
- int i = arrayMPlusN.length - 1, j = i;
- for (; i >= 0; i--) {
- if (arrayMPlusN[i] != NA) {
- arrayMPlusN[j] = arrayMPlusN[i];
- j--;
- }
- }
- }
-
- /**
- * Merge {@param n} into {@param mPlusN}
- *
- * @param mPlusN
- * @param n
- */
- public static void merge(int[] mPlusN, int[] n) {
- moveElementsToEnd(mPlusN);
-
- int i = n.length, // current index in mPlusN[]
- j = 0, // current index in n[]
- k = 0; // current index in final result
-
- while (k < mPlusN.length) {
- if (j == n.length || (i < mPlusN.length && mPlusN[i] < n[j])) {
- mPlusN[k] = mPlusN[i];
- i++;
- } else {
- mPlusN[k] = n[j];
- j++;
- }
- k++;
- }
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- int[] mPlusN = {2, NA, 12, NA, NA, 14, NA};
- int[] n = {5, 7, 8, 10};
- merge(mPlusN, n);
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(mPlusN));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/MinimumDistanceBetweenTwoNos.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/MinimumDistanceBetweenTwoNos.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 48edc1a9..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/MinimumDistanceBetweenTwoNos.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,55 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 9/6/15
- * @time: 10:53 PM
- */
-public class MinimumDistanceBetweenTwoNos {
-
- /**
- * Finds the minimum distance between two no.s {@param x}
- * and {@param y} in an unsorted array {@param a} which
- * may contain duplicates.
- *
- * Note: Either of the no.s may occur first in the array.
- *
- * @param a
- * @param x
- * @param y
- * @return
- */
- public static int getMinimumDistanceBetweenTwoNos(int[] a, int x, int y) {
- int startIndex = -1, endIndex = a.length, minDiff = a.length;
-
- for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
- // find the 1st occurrence of either of the numbers
- if (startIndex == -1 && (a[i] == x || a[i] == y)) {
- startIndex = i; // holds the index of the number that occurred first in array
- } else if (a[i] == x || a[i] == y) {
- // see if it is same as the number that occurred first
- if (a[startIndex] == a[i]) {
- startIndex = i;
- } else {
- endIndex = i;
- }
- }
- // if distance is less, then update
- if (Math.abs(endIndex - startIndex) < minDiff) {
- minDiff = Math.abs(endIndex - startIndex);
- }
- }
-
- return minDiff;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(getMinimumDistanceBetweenTwoNos(new int[]{1, 2}, 1, 2));
- System.out.println(getMinimumDistanceBetweenTwoNos(new int[]{3, 4, 5}, 3, 5));
- System.out.println(getMinimumDistanceBetweenTwoNos(new int[]{3, 5, 4, 2, 6, 5, 6, 6, 5, 4, 8, 3}, 3, 6));
- System.out.println(getMinimumDistanceBetweenTwoNos(new int[]{3, 5, 4, 2, 6, 5, 6, 6, 5, 4, 8, 1, 2, 4, 3}, 3, 6));
- System.out.println(getMinimumDistanceBetweenTwoNos(new int[]{2, 5, 3, 5, 4, 4, 2, 3}, 3, 2));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/MissingAndRepeatingElements.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/MissingAndRepeatingElements.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 5fe08bf2..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/MissingAndRepeatingElements.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,46 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-import java.util.Arrays;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 9/7/15
- * @time: 10:54 AM
- */
-public class MissingAndRepeatingElements {
-
- /**
- * Finds two numbers in an unsorted array of size n with elements in range from
- * 1 to n where one number from set {1, 2, …n} is missing and one number occurs
- * twice in array.
- *
- * @param a
- * @return an array where 1st element is the repeating element and 2nd is the missing one
- */
- public static int[] findMissingAndRepeatingElements(int[] a) {
- int[] result = new int[2];
- for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
- // we use indices to mark already encountered numbers
- if (a[Math.abs(a[i]) - 1] < 0) {
- result[0] = Math.abs(a[i]); // repeating element
- } else {
- a[Math.abs(a[i]) - 1] = -a[Math.abs(a[i]) - 1];
- }
- }
- // no. is +ve means its index wasn't encountered
- for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
- if (a[i] > 0) {
- result[1] = i + 1; // missing element
- }
- }
- return result;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(findMissingAndRepeatingElements(new int[]{3, 1, 3})));
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(findMissingAndRepeatingElements(new int[]{4, 3, 6, 2, 1, 1})));
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(findMissingAndRepeatingElements(new int[]{4, 4, 6, 2, 5, 1})));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/MissingNumber.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/MissingNumber.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 6691f6db..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/MissingNumber.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,55 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 5/28/15
- * @time: 4:34 PM
- */
-
-/**
- * You are given a list of n-1 integers and these integers are in the
- * range of 1 to n. There are no duplicates in list. One of the integers
- * is missing in the list. Write an efficient code to find the missing integer.
- */
-public class MissingNumber {
-
- public static int missingNumber(int a[], int n) {
- int sum = n * (n + 1) / 2;
- int arraySum = 0;
-
- for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
- arraySum += a[i];
- }
- return sum - arraySum;
- }
-
- /**
- * Using XOR:
- * 1) XOR all the array elements, let the result of XOR be X1.
- * 2) XOR all numbers from 1 to n, let XOR be X2.
- * 3) XOR of X1 and X2 gives the missing number.
- *
- * @param a
- * @param n
- * @return
- */
- public static int missingNumberUsingXOR(int a[], int n) {
- int nXOR = 0, arrayXOR = 0;
-
- for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
- nXOR ^= i;
- }
-
- for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
- arrayXOR ^= a[i];
- }
- return nXOR ^ arrayXOR;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println("Missing No: " + missingNumber(new int[]{2, 3, 1, 4, 6, 7, 8}, 8));
- System.out.println("Missing No using XOR: " + missingNumberUsingXOR(new int[]{2, 3, 1, 4, 6, 7, 8}, 8));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/NextGreaterElement.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/NextGreaterElement.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 96c568f1..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/NextGreaterElement.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,63 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-import com.rampatra.base.LinkedStack;
-import com.rampatra.base.Stack;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 8/26/15
- * @time: 12:35 PM
- */
-public class NextGreaterElement {
-
- /**
- * Given an array, print the Next Greater Element (NGE) for every element. The Next greater Element
- * for an element x is the first greater element on the right side of x in array. Elements for which
- * no greater element exist, consider next greater element as -1.
- *
- * @param a
- * @return
- */
- public static void nextGreaterElements(int[] a) {
- int i = 0;
- Stack stack = new LinkedStack<>(); // used to store elements whose NGE is yet to be determined
-
- for (; i < a.length - 1; i++) {
- stack.push(a[i]);
-
- while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
- Integer pop = stack.pop();
- if (pop < a[i + 1]) { // NGE found for popped element
- System.out.println(pop + "->" + a[i + 1]);
- } else {
- stack.push(pop); // NGE still not found for popped element, so push it again
- break;
- }
- }
- }
-
- // no NGE for elements left in stack
- while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
- System.out.println(stack.pop() + "->" + -1);
- }
-
- // no NGE for last element
- System.out.println(a[i] + "->" + -1);
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- int[] ar = new int[]{4, 5, 2, 25};
- nextGreaterElements(ar);
- System.out.println("=========");
- ar = new int[]{11, 13, 21, 3};
- nextGreaterElements(ar);
- System.out.println("=========");
- ar = new int[]{1, 5, 3, 4, 2, 0, 11};
- nextGreaterElements(ar);
- System.out.println("=========");
- ar = new int[]{3, 6, 8, 2, 1, 5, 12, 4, 9};
- nextGreaterElements(ar);
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/NextLargerNumber.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/NextLargerNumber.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 00e00b78..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/NextLargerNumber.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,93 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-import com.rampatra.sorting.QuickSort;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 10/30/15
- * @time: 11:01 AM
- * @see: http://www.geeksforgeeks.org/find-next-greater-number-set-digits/
- */
-public class NextLargerNumber {
-
- /**
- * Finds the closest number which is larger
- * than {@param n} by using only those digits
- * present in {@param n} and using any digit
- * only once.
- *
- * @param n
- * @return
- */
- public static int findNextLargerNumber(Integer n) {
-
- String str = n.toString();
- int len = str.length();
- int[] a = new int[len];
- int minIndex;
-
- // construct int array containing all
- // digits in number {@param n}
- for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
- a[i] = Integer.parseInt(String.valueOf(str.charAt(i)));
- }
-
- // find the index where a digit is greater than its previous
- // digit (from left)
- int i = len - 1;
- while (i > 0) {
- if (a[i] > a[i - 1]) break;
- i--;
- }
-
- // digits are already in descending order, so return
- if (i <= 0) return -1;
-
- // find index of smallest no. greater than a[i-1]
- minIndex = i;
- int j = len - 1;
- while (j >= i) {
- if (a[j] < a[minIndex] && a[j] > a[i - 1]) {
- minIndex = j;
- }
- j--;
- }
-
- // swap a[i-1] with the smallest no. on the right
- // of i-1 index which is larger than a[i-1]
- swap(a, i - 1, minIndex);
-
- // sort all digits to the right of i-1 index
- QuickSort.quickSort(a, i, len - 1);
-
- // construct the no. from the int array
- StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
- for (int k = 0; k < len; k++) {
- builder.append(a[k]);
- }
-
- return Integer.parseInt(builder.toString());
- }
-
- /**
- * Swaps variables in {@param a} at {@param index1} with {@param index2}.
- *
- * @param a
- * @param index1
- * @param index2
- */
- private static void swap(int[] a, int index1, int index2) {
- int temp = a[index1];
- a[index1] = a[index2];
- a[index2] = temp;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(findNextLargerNumber(56));
- System.out.println(findNextLargerNumber(65));
- System.out.println(findNextLargerNumber(3451));
- System.out.println(findNextLargerNumber(534976));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/NthSmallestNumber.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/NthSmallestNumber.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 8f7fbaf1..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/NthSmallestNumber.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,61 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-/**
- * A Google Interview Question. For a simpler version of this question see {@link SmallestAndSecondSmallest}.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-02-01
- */
-public class NthSmallestNumber {
-
- /**
- * Given an unsorted array of integers, find the nth smallest integer in the array in most optimized way possible.
- *
- * Approach: Similar to Quick Sort where in every iteration, we choose a pivot element and shift all lesser integers
- * to left and higher integers to the right. After doing this we compare the pivot index with n and recursively call
- * the method accordingly. See {@link com.rampatra.sorting.QuickSort}.
- *
- * @param arr the input unsorted array of integers
- * @param n nth smallest integer to find
- * @param start the start index in the array to search (inclusive)
- * @param end the last index in the array to search (inclusive)
- * @return the nth smallest integer, {@code -1} if invalid input
- */
- private static int findNthSmallestNumber(int[] arr, int n, int start, int end) {
- if (arr.length == 0 || arr.length < n) {
- return -1;
- }
- int temp;
- int lastBigger = start;
- for (int i = start; i < end; i++) {
- if (arr[i] < arr[end]) {
- temp = arr[i];
- arr[i] = arr[lastBigger];
- arr[lastBigger] = temp;
- lastBigger++;
- }
- }
- temp = arr[lastBigger];
- arr[lastBigger] = arr[end];
- arr[end] = temp;
-
- if (lastBigger + 1 < n) {
- return findNthSmallestNumber(arr, n, lastBigger + 1, end);
- } else if (lastBigger + 1 > n) {
- return findNthSmallestNumber(arr, n, start, lastBigger - 1);
- } else {
- return arr[lastBigger];
- }
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(findNthSmallestNumber(new int[]{}, 3, 0, 5));
- System.out.println(findNthSmallestNumber(new int[]{0, 1}, 3, 0, 1));
- System.out.println(findNthSmallestNumber(new int[]{0, 1}, 2, 0, 1));
- System.out.println(findNthSmallestNumber(new int[]{1, 0}, 2, 0, 1));
- System.out.println(findNthSmallestNumber(new int[]{2, 3, 5, 10, 9, 4}, 3, 0, 5));
- System.out.println(findNthSmallestNumber(new int[]{2, 3, 4, 10, 9, 4}, 3, 0, 5));
- System.out.println(findNthSmallestNumber(new int[]{4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4}, 3, 0, 5));
- System.out.println(findNthSmallestNumber(new int[]{4, 8, 1, 9, 10, 2, 7, 3, 2, 6}, 3, 0, 9)); // TODO: doesn't work with duplicates currently
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/NumberOccurringOddTimes.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/NumberOccurringOddTimes.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 81656dd1..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/NumberOccurringOddTimes.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,34 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 5/20/15
- * @time: 11:09 PM
- */
-
-import com.rampatra.bits.TwoNonRepeatingElements;
-
-/**
- * Given an array of positive integers. All numbers occur
- * even number of times except one number which occurs odd
- * number of times. Find the number in O(n) time & constant space.
- *
- * See {@link TwoNonRepeatingElements} for a more
- * complex problem which is solved in a similar approach.
- */
-public class NumberOccurringOddTimes {
-
- public static int numberOccurringOddTimes(int a[]) {
- int res = a[0];
- for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++) {
- res ^= a[i];
- }
- return res;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.print(numberOccurringOddTimes(new int[]{2, 3, 3, 3, 1, 2, 1}));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/OccurrencesInSortedArray.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/OccurrencesInSortedArray.java
deleted file mode 100644
index fea37847..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/OccurrencesInSortedArray.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,85 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 8/31/15
- * @time: 2:52 PM
- */
-public class OccurrencesInSortedArray {
-
- /**
- * Finds the occurrences of {@param k} in sorted array {@param a} in
- * O(log n) time.
- *
- * @param a
- * @param k
- * @return
- */
- public static int getOccurrencesInSortedArray(int[] a, int k) {
- int firstIndex = getFirstIndexOf(a, k, 0, a.length - 1);
- // element not found
- if (firstIndex == -1) {
- return 0;
- }
- return getLastIndexOf(a, k, firstIndex, a.length - 1) - firstIndex + 1;
- }
-
- /**
- * Returns the index of first occurrence of {@param n} in array {@param a}.
- *
- * @param a
- * @param low
- * @param high
- * @param n
- * @return
- */
- public static int getFirstIndexOf(int[] a, int n, int low, int high) {
- if (low <= high) {
- int mid = (low + high) / 2;
- if (a[mid] == n && (mid == 0 || a[mid - 1] < n)) {
- return mid;
- } else if (a[mid] < n) {
- return getFirstIndexOf(a, n, mid + 1, high);
- } else {
- return getFirstIndexOf(a, n, low, mid - 1);
- }
- } else {
- return -1;
- }
- }
-
- /**
- * Returns the index of last occurrence of {@param n} in array {@param a}.
- *
- * @param a
- * @param low
- * @param high
- * @param n
- * @return
- */
- public static int getLastIndexOf(int[] a, int n, int low, int high) {
- if (low <= high) {
- int mid = (low + high) / 2;
- if (a[mid] == n && (mid == a.length - 1 || a[mid + 1] > n)) {
- return mid;
- } else if (a[mid] <= n) {
- return getLastIndexOf(a, n, mid + 1, high);
- } else {
- return getLastIndexOf(a, n, low, mid - 1);
- }
- } else {
- return -1;
- }
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(getOccurrencesInSortedArray(new int[]{1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 3}, 1));
- System.out.println(getOccurrencesInSortedArray(new int[]{1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 3}, 1));
- System.out.println(getOccurrencesInSortedArray(new int[]{1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 3}, 2));
- System.out.println(getOccurrencesInSortedArray(new int[]{1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 3}, 3));
- System.out.println(getOccurrencesInSortedArray(new int[]{1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 3}, 0));
- System.out.println(getOccurrencesInSortedArray(new int[]{1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 3}, 4));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/PairDiff.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/PairDiff.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 8fce2367..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/PairDiff.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,72 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 5/18/15
- * @time: 10:24 PM
- */
-
-import java.util.Arrays;
-import java.util.HashMap;
-import java.util.Map;
-
-/**
- * Given an array ar[] of n numbers and another number x, determine whether
- * or not there exists two elements in ar[] whose difference is exactly x.
- * This problem is similar to {@link PairSum}.
- */
-public class PairDiff {
-
- /**
- * Using sorting. If we use Merge Sort or Heap Sort
- * then (-)(nlogn) in worst case. If we use Quick Sort
- * then O(n^2) in worst case.
- *
- * @param ar
- * @param x
- * @return
- */
- static boolean pairDiff(int ar[], int x) {
- Arrays.sort(ar);
-
- int len = ar.length;
-
- for (int i = 0, j = 1; i < len && j < len; ) {
- if (i != j && ar[j] - ar[i] == x) {
- return true;
- } else if (ar[j] - ar[i] < x) {
- j++;
- } else {
- i++;
- }
- }
- return false;
- }
-
- /**
- * Using HashMap in O(n) time.
- *
- * @param ar
- * @param x
- * @param map
- * @return
- */
- static boolean pairDiff(int ar[], int x, Map map) {
- for (int i = 0; i < ar.length; i++) {
- if (map.containsKey(x + ar[i])) {
- return true;
- }
- map.put(ar[i], 1);
- }
- return false;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(pairDiff(new int[]{-3, 4, -6, 1, 1}, -4));
- System.out.println(pairDiff(new int[]{3, 1}, 2));
- System.out.println(pairDiff(new int[]{-3, 4, -6, 1, 1}, -4, new HashMap()));
- System.out.println(pairDiff(new int[]{3, 1}, 2, new HashMap()));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/PairSum.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/PairSum.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 75ce7d63..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/PairSum.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,70 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-import java.util.Arrays;
-import java.util.HashSet;
-import java.util.Set;
-
-/**
- * Given an array ar[] of n numbers and
- * another number x, determine whether or not there
- * exists two elements in ar[] whose sum is exactly x.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 5/18/15
- */
-public class PairSum {
-
- /**
- * Using sorting. If we use Merge Sort or Heap Sort
- * then (-)(nlogn) in worst case. If we use Quick Sort
- * then O(n^2) in worst case.
- *
- * @param ar
- * @param sum
- * @return
- */
- static boolean pairSum(int[] ar, int sum) {
- Arrays.sort(ar);
-
- int len = ar.length;
-
- for (int i = 0, j = len - 1; i < j; ) {
- if (ar[i] + ar[j] == sum) {
- return true;
- } else if (ar[i] + ar[j] < sum) { // approach towards larger elements
- i++;
- } else { // approach towards smaller elements
- j--;
- }
- }
- return false;
- }
-
- /**
- * Using hashmap in O(n) time.
- *
- * @param ar
- * @param sum
- * @param numSet
- * @return
- */
- static boolean pairSum(int[] ar, int sum, Set numSet) {
- for (int i = 0; i < ar.length; i++) {
- if (numSet.contains(sum - ar[i])) {
- return true;
- }
- numSet.add(ar[i]);
- }
- return false;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(pairSum(new int[]{-3, 4, -6, 1, 1}, -2));
- System.out.println(pairSum(new int[]{-3, 4, -6, 1, 1}, 5));
- System.out.println(pairSum(new int[]{-3, 4, -6, 1, 1}, 0));
- System.out.println("--------");
- System.out.println(pairSum(new int[]{-3, 4, -6, 1, 1}, -2, new HashSet<>()));
- System.out.println(pairSum(new int[]{-3, 4, -6, 1, 1}, 5, new HashSet<>()));
- System.out.println(pairSum(new int[]{-3, 4, -6, 1, 1}, 0, new HashSet<>()));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/PivotedBinarySearch.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/PivotedBinarySearch.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 2f104e6f..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/PivotedBinarySearch.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,74 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-import com.rampatra.searching.BinarySearch;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 5/31/15
- */
-public class PivotedBinarySearch {
-
- /**
- * Search an element in a sorted pivoted array {@code arr}.
- *
- * Example,
- * 1) For array [3,4,5,1,2] pivot is 5
- * 2) For array [6,7,8,5,4] pivot is 8
- *
- * @param arr
- * @param n
- * @return
- */
- public static int pivotedBinarySearch(int[] arr, int n) {
- int pivot = findPivotIndex(arr, 0, arr.length - 1);
-
- if (pivot == -1 || arr[pivot] == n) {
- return pivot;
- } else if (n < arr[0]) {
- return BinarySearch.binarySearch(arr, n, pivot + 1, arr.length - 1);
- } else {
- return BinarySearch.binarySearch(arr, n, 0, pivot - 1);
- }
- }
-
- /**
- * Finds the pivot element in array {@code arr}. Pivot element is the only
- * element for which next element to it is smaller than it.
- *
- * @param arr
- * @param low
- * @param high
- * @return the index of the pivot element in the {@code arr}.
- */
- public static int findPivotIndex(int[] arr, int low, int high) {
- if (low > high) return -1;
-
- int mid = (low + high) / 2;
-
- if (mid == 0 || mid == arr.length - 1) return -1;
-
- if (arr[mid] > arr[mid + 1] && arr[mid] > arr[mid - 1]) {
- return mid;
- } else if (arr[mid] > arr[mid - 1] && arr[mid] < arr[mid + 1]) {
- return findPivotIndex(arr, mid + 1, arr.length - 1);
- } else {
- return findPivotIndex(arr, 0, mid - 1);
- }
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println("Pivot: " + findPivotIndex(new int[]{3, 4, 5, 1, 2}, 0, 4));
- System.out.println("Index: " + pivotedBinarySearch(new int[]{3, 4, 5, 1, 2}, 5));
-
- System.out.println("Pivot: " + findPivotIndex(new int[]{1, 2, 3, 4, 5}, 0, 4));
- System.out.println("Index: " + pivotedBinarySearch(new int[]{1, 2, 3, 4, 5}, 4));
-
- System.out.println("Pivot: " + findPivotIndex(new int[]{5, 4, 3, 2, 1}, 0, 4));
- System.out.println("Index: " + pivotedBinarySearch(new int[]{5, 4, 3, 2, 1}, 4));
-
- System.out.println("Pivot: " + findPivotIndex(new int[]{5}, 0, -1));
- System.out.println("Index: " + pivotedBinarySearch(new int[]{5}, -1));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/ProductArrayPuzzle.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/ProductArrayPuzzle.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 23de1acc..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/ProductArrayPuzzle.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,71 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-import java.util.Arrays;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 8/15/15
- * @time: 9:17 PM
- */
-public class ProductArrayPuzzle {
-
- /**
- * Construct a Product Array prod[] (of same size) such that prod[i] is
- * equal to the product of all the elements of arr[] except arr[i]. Solve
- * it without division operator and in O(n).
- *
- * You can do this by taking two arrays one containing the products from
- * left to right elements and other containing the products from right to
- * left elements and then finally multiplying those two arrays gives you
- * the answer. But the auxiliary space complexity of this method is O(n)
- * as well as the space complexity is O(n).
- *
- * The below method is the optimized way to do this in O(1) auxiliary space
- * but the space complexity is O(n).
- *
- * AUXILIARY SPACE is extra space or temporary space used by the algorithm,
- * which is mostly used in algorithm where we use swapping or temporary variables.
- *
- * SPACE COMPLEXITY means total space taken by the algorithm with respect to
- * input size.Space complexity calculated by both auxiliary space and space used
- * by the input.
- *
- * For example - If we want to compare standard sorting algorithm on the basis of
- * then auxiliary space would be better criteria than space complexity. Merge sort
- * uses O(n) auxiliary space,where Insertion sort and Heap sort uses O(1) auxiliary
- * space. Merge sort requires Ω(n) but Heap sort requires only a constant amount.
- * Space complexity of all these sorting algorithm is O(n) though.
- *
- * @param a
- * @return
- */
- public static int[] getProductArray(int[] a) {
- int[] prod = new int[a.length];
-
- // prod array consists of products of the elements
- prod[0] = 1;
-
- // fill prod with products of elements from left to right excluding current element
- for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++) {
- prod[i] = a[i - 1] * prod[i - 1];
- }
-
- int temp = 1;
- // fill prod with products of elements from right to left excluding current element
- for (int i = a.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
- prod[i] *= temp;
- temp *= a[i];
- }
-
- // final prod array is the answer
- return prod;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(getProductArray(new int[]{10, 3, 5, 6, 2})));
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(getProductArray(new int[]{0, 0})));
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(getProductArray(new int[]{1})));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/ReservoirSampling.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/ReservoirSampling.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 050fb17f..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/ReservoirSampling.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,65 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-import java.util.Arrays;
-import java.util.Random;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 7/21/15
- * @time: 2:52 PM
- */
-public class ReservoirSampling {
-
- /**
- * Returns {@param k} non-repeating random numbers from {@param stream}
- * using reservoir sampling method.
- *
- * Explanation:
- * 1) Create an array reservoir[0..k-1] and copy first k items of stream[] to it.
- * 2) Now one by one consider all items from (k+1)th item to nth item.
- * a) Generate a random number from 0 to i where i is index of current item in
- * stream[]. Let the generated random number is j.
- * b) If j is in range 0 to k-1, replace reservoir[j] with arr[i].
- *
- * In the above procedure, we are computing random number for each of the indexes greater than k
- * thereby giving all items an equal probability.
- *
- * NOTE: When {@param k} is small enough we can use a simpler method as follows:
- * Create an array reservoir[] of maximum size k. One by one randomly select an
- * item from stream[0..n-1]. If the selected item is not previously selected, then
- * put it in reservoir[]. To check if an item is previously selected or not, we
- * need to search the item in reservoir[].
- * The time complexity of this algorithm will be O(k^2). This can be costly
- * if k is big. Also, this is not efficient if the input is in the form of a stream.
- *
- * @param stream
- * @param k
- * @return
- */
- public static int[] getKRandomNumbers(int[] stream, int k) {
- int i;
- int[] reservoir = new int[k];
-
- for (i = 0; i < k; i++) {
- reservoir[i] = stream[i];
- }
-
- for (; i < stream.length; i++) {
- int rand = new Random().nextInt(i);
-
- if (rand < k) {
- reservoir[rand] = stream[i];
- }
- }
-
- return reservoir;
-
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- int[] stream = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9};
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(getKRandomNumbers(stream, 4)));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/ReverseArray.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/ReverseArray.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 64550c58..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/ReverseArray.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,54 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-import java.util.Arrays;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 7/27/15
- * @time: 8:40 PM
- */
-public class ReverseArray {
-
- /**
- * Iterative method to reverse the entire array.
- *
- * @param a
- */
- public static void reverse(int[] a) {
- int temp;
- for (int i = 0, j = a.length - 1; i < j; i++, j--) {
- // swap elements
- temp = a[i];
- a[i] = a[j];
- a[j] = temp;
- }
- }
-
- /**
- * Recursive method to reverse the array elements from
- * {@param i} index to {@param j} index (both inclusive).
- *
- * @param a
- * @param i
- * @param j
- */
- public static void reverseRecursive(int[] a, int i, int j) {
- if (i > j) return;
-
- int temp = a[i];
- a[i] = a[j];
- a[j] = temp;
- reverseRecursive(a, ++i, --j);
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- int[] ar = new int[]{1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ar));
- reverse(ar);
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ar));
- reverseRecursive(ar, 0, ar.length - 1);
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ar));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/RotateArray.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/RotateArray.java
deleted file mode 100644
index f720dcf6..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/RotateArray.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,104 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-import java.util.Arrays;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 7/28/15
- * @time: 10:53 AM
- */
-public class RotateArray {
-
- /**
- * Naive approach which stores the elements to be shifted in a temp array.
- * Time complexity: O(n)
- * Space complexity: O(k)
- *
- * @param a
- * @param k
- */
- public static void rotateNaiveApproach(int[] a, int k) {
- int[] temp = new int[k];
- int i, j;
- // store elements to be shifted in temp array
- for (i = 0; i < k; i++) {
- temp[i] = a[i];
- }
- // shift elements to left
- for (j = 0; i < a.length; i++, j++) {
- a[j] = a[i];
- }
- // move elements to end
- for (i = 0; j < a.length; i++, j++) {
- a[j] = temp[i];
- }
- }
-
- /**
- * Reversal algorithm for array rotation.
- *
- * Example:
- * For arr[] = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7], k = 2 and arr.length = 7
- * A = [1, 2] and B = [3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
- * Reverse A, we get ArB = [2, 1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
- * Reverse B, we get ArBr = [2, 1, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3]
- * Reverse all, we get (ArBr)r = [3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 1, 2]
- * NOTE: Ar = Reverse of A
- * See: http://www.geeksforgeeks.org/program-for-array-rotation-continued-reversal-algorithm/
- *
- * @param a
- * @param k
- */
- public static void rotateReversal(int[] a, int k) {
- ReverseArray.reverseRecursive(a, 0, k - 1);
- ReverseArray.reverseRecursive(a, k, a.length - 1);
- ReverseArray.reverseRecursive(a, 0, a.length - 1);
- }
-
- /**
- * Juggling algorithm for array rotation.
- * See: http://www.geeksforgeeks.org/array-rotation/
- *
- * @param a
- * @param k
- */
- public static void rotateGCD(int[] a, int k) {
- int gcd = gcd(a.length, k), temp, i, j, p;
-
- for (i = 0; i < gcd; i++) {
- temp = a[i];
- j = i;
- while (true) {
- p = j + k;
- if (p >= a.length)
- p = p - a.length;
- if (p == i)
- break;
- a[j] = a[p];
- j = p;
- }
- a[j] = temp;
- }
- }
-
- public static int gcd(int a, int b) {
- if (b == 0) {
- return a;
- } else {
- return gcd(b, a % b);
- }
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- int[] ar = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7};
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ar));
- rotateNaiveApproach(ar, 2);
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ar));
- rotateGCD(ar, 2);
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ar));
- rotateReversal(ar, 2);
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ar));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/RotateMatrixBy90Degrees.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/RotateMatrixBy90Degrees.java
deleted file mode 100644
index ccff75ca..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/RotateMatrixBy90Degrees.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,58 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 8/22/15
- * @time: 4:03 PM
- */
-public class RotateMatrixBy90Degrees {
-
- /**
- * Rotates a 2-D array by 90 degrees clockwise.
- *
- * The algorithm is simple:
- * 1st row = last column
- * 2nd row = 2nd last column
- * and so on...
- *
- * @param a
- * @return
- */
- public static int[][] rotateMatrixBy90DegreesRight(int[][] a) {
- int rows = a.length, columns = a[0].length;
- int[][] rotatedMatrix = new int[columns][rows];
-
- for (int i = 0; --rows >= 0 && i < a.length; i++) {
- for (int j = 0; j < a[0].length; j++) {
- rotatedMatrix[j][rows] = a[i][j];
- }
- }
-
- return rotatedMatrix;
- }
-
- private static void print2DMatrix(int[][] a) {
- for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
- for (int j = 0; j < a[0].length; j++) {
- System.out.print(a[i][j]);
- }
- System.out.println();
- }
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- int[][] ar = new int[][]{{1, 2, 3}, {4, 5, 6}, {7, 8, 9}};
- print2DMatrix(ar);
- System.out.println("--------");
- print2DMatrix(rotateMatrixBy90DegreesRight(ar));
-
- System.out.println("========");
-
- ar = new int[][]{{1, 2, 3}, {4, 5, 6}, {7, 8, 9}, {0, 5, 7}};
- print2DMatrix(ar);
- System.out.println("--------");
- print2DMatrix(rotateMatrixBy90DegreesRight(ar));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/RotatedIndex.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/RotatedIndex.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 4478e5e3..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/RotatedIndex.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,55 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-/**
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 2019-04-04
- */
-public class RotatedIndex {
-
- private static int findIndexOfRotationPoint(String[] words) {
- return findIndexOfRotationPoint(words, 0, words.length - 1);
- }
-
- private static int findIndexOfRotationPoint(String[] words, int start, int end) {
- if (start > end) return -1;
-
- int mid = (start + end) / 2;
-
- if (mid == 0 || mid == words.length - 1) return -1;
-
- if (words[mid].compareTo(words[mid - 1]) < 0 && words[mid].compareTo(words[mid + 1]) < 0) {
- return mid;
- } else if (words[mid].compareTo(words[mid - 1]) > 0 && words[mid].compareTo(words[mid + 1]) < 0) {
- return findIndexOfRotationPoint(words, start, mid - 1);
- } else {
- return findIndexOfRotationPoint(words, mid + 1, end);
- }
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(findIndexOfRotationPoint(new String[]{
- "ptolemaic",
- "retrograde",
- "supplant",
- "undulate",
- "xenoepist",
- "asymptote", // <-- rotates here!
- "babka",
- "banoffee",
- "engender",
- "karpatka",
- "othellolagkage",
- }));
-
- System.out.println(findIndexOfRotationPoint(new String[]{}));
-
- System.out.println(findIndexOfRotationPoint(new String[]{
- "asymptote",
- "babka",
- "banoffee",
- "engender",
- "karpatka",
- "othellolagkage",
- }));
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/SearchInSorted2DArray.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/SearchInSorted2DArray.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 8ab14269..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/SearchInSorted2DArray.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,118 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-import java.util.Arrays;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 8/23/15
- * @time: 10:31 PM
- */
-public class SearchInSorted2DArray {
-
- /**
- * Searches {@param value} in a SQUARE sized 2-D array {@param a} which is sorted
- * both row wise and column wise.
- *
- * Time complexity:
- * T(n) = T(n) + T(n-1) + T(n-2) + .... + T(1)
- * T(n) = n(n+1)/2
- * T(n) = O(n^2) where n is size of 2-D array.
- *
- * Explanation:
- * Linearly searches across rows and columns until the element is found or till the last element. If
- * the element is not found in the 1st row or 1st column then we search in 2nd row and 2nd column
- * and so on.
- *
- * @param a
- * @param i
- * @param j
- * @param value
- * @return an array consisting of co-ordinates if {@param value} is found otherwise {@code new int[]{-1, -1}}.
- */
- public static int[] linearSearchNaive(int[][] a, int i, int j, int value) {
- for (int x = i; x < a.length && (a[i][x] <= value || a[x][j] <= value); x++) {
- if (a[i][x] == value) {
- return new int[]{i, x};
- } else if (a[x][j] == value) {
- return new int[]{x, j};
- }
- }
-
- if (i < a.length - 1) {
- return linearSearchNaive(a, i + 1, j + 1, value);
- } else {
- return new int[]{-1, -1};
- }
- }
-
- /**
- * More efficient way to search in a 2-D array sorted both row wise and column wise.
- *
- * Explanation:
- * We start from top right corner (we can also start from bottom left corner) and move left if current
- * element is greater than the value to be searched and bottom if current element is
- * smaller than the value to be searched.
- *
- * Time complexity: O(m+n) where m = no. of rows, n = no. of columns
- *
- * @return
- * @link http://articles.leetcode.com/2010/10/searching-2d-sorted-matrix-part-ii.html
- */
- public static int[] linearSearch(int[][] a, int value) {
- int i = 0, j = a[0].length - 1; // start from top right corner
-
- while (i < a.length && j >= 0) {
- if (a[i][j] == value) {
- return new int[]{i, j};
- } else if (a[i][j] > value) {
- j--; // move left
- } else {
- i++; // move down
- }
- }
-
- return new int[]{-1, -1};
-
- }
-
- private static void print2DMatrix(int[][] a) {
- for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
- for (int j = 0; j < a[0].length; j++) {
- System.out.print(a[i][j]);
- }
- System.out.println();
- }
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- int[][] ar = new int[][]{{1, 2, 3}, {4, 5, 6}, {7, 8, 9}};
- print2DMatrix(ar);
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(linearSearchNaive(ar, 0, 0, 1)));
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(linearSearchNaive(ar, 0, 0, 2)));
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(linearSearchNaive(ar, 0, 0, 3)));
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(linearSearchNaive(ar, 0, 0, 4)));
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(linearSearchNaive(ar, 0, 0, 5)));
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(linearSearchNaive(ar, 0, 0, 6)));
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(linearSearchNaive(ar, 0, 0, 7)));
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(linearSearchNaive(ar, 0, 0, 8)));
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(linearSearchNaive(ar, 0, 0, 9)));
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(linearSearchNaive(ar, 0, 0, 10)));
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(linearSearchNaive(ar, 0, 0, 11)));
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(linearSearchNaive(ar, 0, 0, 12)));
- System.out.println("============");
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(linearSearch(ar, 1)));
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(linearSearch(ar, 2)));
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(linearSearch(ar, 3)));
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(linearSearch(ar, 4)));
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(linearSearch(ar, 5)));
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(linearSearch(ar, 6)));
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(linearSearch(ar, 7)));
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(linearSearch(ar, 8)));
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(linearSearch(ar, 9)));
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(linearSearch(ar, 10)));
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(linearSearch(ar, 11)));
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(linearSearch(ar, 12)));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/Segregate0s1sAnd2s.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/Segregate0s1sAnd2s.java
deleted file mode 100644
index e64929f8..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/Segregate0s1sAnd2s.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,69 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-import java.util.Arrays;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 8/18/15
- * @time: 8:38 PM
- */
-public class Segregate0s1sAnd2s {
-
- /**
- * Segregates an array {@param a} consisting of only 0s, 1s and 2s. Based on
- * Dutch National Flag (DNF) problem {@see: http://www.csse.monash.edu.au/~lloyd/tildeAlgDS/Sort/Flag/}.
- *
- * @param a
- */
- public static void segregate0s1sAnd2s(int[] a) {
- // assume low points to 0 and mid to 1 and high to 2
- int low = 0, mid = 0, high = a.length - 1;
-
- while (mid <= high) {
- switch (a[mid]) {
- case 0: // mid points to 0 but it should point to 1 so swap it with low
- swap(a, low, mid);
- low++;
- mid++;
- break;
- case 1: // mid points to 1 which is correct acc. to our assumption so proceed
- mid++;
- break;
- case 2: // mid points to 2 instead of 1 so swap it with high
- swap(a, mid, high);
- high--;
- break;
- }
- }
- }
-
- private static void swap(int[] a, int index1, int index2) {
- int temp = a[index1];
- a[index1] = a[index2];
- a[index2] = temp;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- int[] ar = new int[]{0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2};
- segregate0s1sAnd2s(ar);
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ar));
-
- ar = new int[]{0, 2, 1, 1, 2, 0};
- segregate0s1sAnd2s(ar);
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ar));
-
- ar = new int[]{0, 1, 2};
- segregate0s1sAnd2s(ar);
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ar));
-
- ar = new int[]{2, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0};
- segregate0s1sAnd2s(ar);
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ar));
-
- ar = new int[]{1, 2, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0};
- segregate0s1sAnd2s(ar);
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ar));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/Segregate0sAnd1s.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/Segregate0sAnd1s.java
deleted file mode 100644
index e5f9634a..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/Segregate0sAnd1s.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,35 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-import java.util.Arrays;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 7/31/15
- * @time: 5:13 PM
- */
-public class Segregate0sAnd1s {
-
- /**
- * Segregate 0s and 1s by traversing the array only once.
- *
- * @param a
- */
- public static void segregate0sAnd1s(int[] a) {
- for (int i = 0, j = a.length - 1; i < j; i++, j--) {
- if (a[i] > a[j]) {
- // swap if a[i] > a[j]
- a[i] = a[i] + a[j];
- a[j] = a[i] - a[j];
- a[i] = a[i] - a[j];
- }
- }
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- int[] ar = new int[]{0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1};
- segregate0sAnd1s(ar);
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ar));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/SegregateEvenAndOddNos.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/SegregateEvenAndOddNos.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 8cdaf6b6..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/SegregateEvenAndOddNos.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,50 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-import java.util.Arrays;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 7/31/15
- * @time: 5:13 PM
- */
-public class SegregateEvenAndOddNos {
-
- /**
- * Segregate even and odd numbers by traversing the
- * array {@param a} only once.
- *
- * This is similar to {@link Segregate0sAnd1s}.
- *
- * @param a
- */
- public static void segregateEvenAndOddNos(int[] a) {
- for (int i = 0, j = a.length - 1; i < j; ) {
- if (a[i] % 2 != 0 && a[j] % 2 == 0) {
- // swap
- a[i] = a[i] + a[j];
- a[j] = a[i] - a[j];
- a[i] = a[i] - a[j];
- i++;
- j--;
- } else if (a[i] % 2 == 0 && a[j] % 2 == 0) {
- i++;
- } else if (a[i] % 2 != 0 && a[j] % 2 != 0) {
- j--;
- } else {
- i++;
- j--;
- }
- }
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- int[] ar = new int[]{12, 34, 45, 9, 8, 90, 3};
- segregateEvenAndOddNos(ar);
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ar));
- int[] ar1 = new int[]{34, 1, 45, 9, 8, 67, 3, 56, 78, 79, 101, 100};
- segregateEvenAndOddNos(ar1);
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ar1));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/SmallestAndSecondSmallest.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/SmallestAndSecondSmallest.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 9e683caf..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/SmallestAndSecondSmallest.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,32 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-import java.util.Arrays;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 7/30/15
- */
-public class SmallestAndSecondSmallest {
-
- private static int[] getSmallestAndSecondSmallest(int[] a) {
- int smallest = Integer.MAX_VALUE, secondSmallest = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
-
- for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
- if (a[i] < smallest) {
- secondSmallest = smallest;
- smallest = a[i];
- } else if (a[i] < secondSmallest && a[i] != smallest) { // a[i] != smallest; if numbers are repeated in array
- secondSmallest = a[i];
- }
- }
-
- return new int[]{smallest, secondSmallest};
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(getSmallestAndSecondSmallest(new int[]{100, 1, 60, -10, -80, 85, 70, -80})));
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(getSmallestAndSecondSmallest(new int[]{100, 1, 60, 10, 80, 85, 70, 0})));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/SmallestMissingNumber.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/SmallestMissingNumber.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 7b63a415..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/SmallestMissingNumber.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,56 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 8/29/15
- * @time: 12:51 PM
- */
-public class SmallestMissingNumber {
-
- /**
- * Modified Binary Search to find the smallest missing number in an array
- * {@param a} consisting of numbers between 0 to m - 1 and m > n where n is
- * length of array.
- *
- * Time complexity: O(log n)
- * Con: Doesn't work if there are repetitive elements.
- *
- * EXPLANATION:
- * In standard Binary Search, the element to be searched is compared with
- * the middle element and on the basis of comparison result, we decide whether
- * to search is over or to go to left half or right half.
- * In this method, we modify the standard Binary Search algorithm to compare the
- * middle element with its index and make decision on the basis of this comparison.
- *
- * @param a
- * @param low
- * @param high
- * @return
- */
- public static int smallestMissingNumber(int[] a, int low, int high) {
- if (low <= high) {
- int mid = (low + high) / 2;
-
- if (a[mid] == mid) {
- return smallestMissingNumber(a, mid + 1, high);
- } else if (a[mid] > mid) {
- return smallestMissingNumber(a, low, mid - 1);
- } else {
- return smallestMissingNumber(a, mid + 1, high);
- }
- } else {
- return low;
- }
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(smallestMissingNumber(new int[]{0, 1}, 0, 1));
- System.out.println(smallestMissingNumber(new int[]{0, 1, 2, 6, 9}, 0, 4));
- System.out.println(smallestMissingNumber(new int[]{4, 5, 10, 11}, 0, 3));
- System.out.println(smallestMissingNumber(new int[]{0, 4, 5, 10, 56}, 0, 4));
- System.out.println(smallestMissingNumber(new int[]{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 10}, 0, 8));
- System.out.println(smallestMissingNumber(new int[]{0, 1, 2, 3, 3}, 0, 4)); // doesn't work
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/SortedSubSequence.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/SortedSubSequence.java
deleted file mode 100644
index b6cd1b5c..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/SortedSubSequence.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,62 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 10/12/15
- */
-public class SortedSubSequence {
-
- /**
- * Finds 3 elements such that a[i] < a[j] < a[k] and i < j < k in O(n) time
- * in an array of n integers. If there are multiple such triplets, then prints any
- * one of them.
- *
- * Algorithm:
- * 1) Create an auxiliary array smaller[0..n-1]. smaller[i] should store the index of a number which is smaller than arr[i] and is on left side of arr[i]. smaller[i] should contain -1 if there is no such element.
- * 2) Create another auxiliary array greater[0..n-1]. greater[i] should store the index of a number which is greater than arr[i] and is on right side of arr[i]. greater[i] should contain -1 if there is no such element.
- * 3) Finally traverse both smaller[] and greater[] and find the index i for which both smaller[i] and greater[i] are not -1.
- *
- * @param arr
- */
- public static void printSortedSubSequenceOfSize3(int[] arr) {
- int len = arr.length, min = arr[0], max = arr[len - 1];
-
- int[] smaller = new int[len], larger = new int[len];
-
- smaller[0] = -1;
- for (int i = 1; i < len; i++) {
- if (arr[i] < min) {
- smaller[i] = -1;
- min = arr[i];
- } else {
- smaller[i] = min;
- }
- }
-
- larger[len - 1] = -1;
- for (int i = len - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
- if (arr[i] > max) {
- larger[i] = -1;
- max = arr[i];
- } else {
- larger[i] = max;
- }
- }
-
- for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
- if (smaller[i] != -1 && larger[i] != -1) {
- System.out.println(smaller[i] + "," + arr[i] + "," + larger[i]);
- break;
- }
- }
-
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- printSortedSubSequenceOfSize3(new int[]{12, 11, 10, 5, 6, 2, 30});
- printSortedSubSequenceOfSize3(new int[]{1, 2, 3, 4});
- printSortedSubSequenceOfSize3(new int[]{4, 3, 2, 1});
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/SubArrayOfSum.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/SubArrayOfSum.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 4e4f5c2e..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/SubArrayOfSum.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,49 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 9/27/15
- * @time: 7:32 PM
- */
-public class SubArrayOfSum {
-
- /**
- * Prints the sub-array in array {@param a} with sum {@param sum}.
- *
- * Algorithm: Keep on adding the elements, once the sum is larger
- * than the required sum start deleting the elements from the sum.
- * (Google Interview Question)
- *
- * @param a
- * @param sum
- */
- public static void printSubArrayOfSum(int[] a, int sum) {
- int currSum = 0, startIndex = 0;
- for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
-
- currSum += a[i];
-
- while (currSum > sum && startIndex < i) {
- currSum -= a[startIndex++];
- }
-
- if (currSum == sum) {
- System.out.println("Sub-array lies between indexes: " + startIndex + " and " + i);
- return;
- }
- }
- System.out.println("Sub-array with sum " + sum + " not found!");
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- printSubArrayOfSum(new int[]{1, 4, 20, 3, 10, 5}, 33);
- printSubArrayOfSum(new int[]{1, 4, 20, 3, 10, 5}, 38);
- printSubArrayOfSum(new int[]{1, 4, 20, 3, 10, 5}, 13);
- printSubArrayOfSum(new int[]{1, 4, 0, 0, 3, 10, 5}, 0);
- printSubArrayOfSum(new int[]{1, 4}, 0);
- printSubArrayOfSum(new int[]{1, 4}, -4);
- printSubArrayOfSum(new int[]{1, -4}, -3);
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/SubsetOfArray.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/SubsetOfArray.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 21d5ff2c..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/SubsetOfArray.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,57 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-import com.rampatra.sorting.QuickSort;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 9/4/15
- * @time: 11:28 PM
- */
-public class SubsetOfArray {
-
- /**
- * Determines if array {@param b} is a subset of array {@param a}.
- *
- * Explanation: The below method uses sorting + merge method of merge sort. Time
- * complexity is O(mlogm + nlogn) where m and n are lengths of array a and b resp.
- * You could also have used sorting + binary search but this fails when array
- * {@param b} has repeating elements for example, a={1,4,2} and b={1,4,4,2}. Time
- * complexity would be O(mlogm + nlogm).
- *
- * @param a
- * @param b
- * @return
- */
- public static boolean isSubsetOfArray(int[] a, int[] b) {
-
- QuickSort.quickSort(a);
- QuickSort.quickSort(b);
-
- int i, j;
- for (i = 0, j = 0; i < a.length && j < b.length; ) {
- if (a[i] > b[j]) {
- return false;
- } else if (a[i] == b[j]) {
- i++;
- j++;
- } else {
- i++;
- }
- }
-
- if (i < b.length) {
- return false;
- } else {
- return true;
- }
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(isSubsetOfArray(new int[]{11, 1, 13, 21, 3, 7}, new int[]{11, 3, 7, 1}));
- System.out.println(isSubsetOfArray(new int[]{1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}, new int[]{1, 2, 4}));
- System.out.println(isSubsetOfArray(new int[]{1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}, new int[]{1, 2, 2, 4}));
- System.out.println(isSubsetOfArray(new int[]{1, 4, 2}, new int[]{1, 4, 4, 2}));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/SymmetricDifference.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/SymmetricDifference.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 9ae00478..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/SymmetricDifference.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,60 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-import java.util.Arrays;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 10/20/15
- * @time: 11:34 PM
- */
-public class SymmetricDifference {
-
- /**
- * Returns the symmetric difference between array {@param a1}
- * and array {@param a2}.
- *
- * SYMMETRIC DIFFERENCE refers to the numbers which are present in
- * only one of the arrays and not both.
- *
- * @param a1
- * @param a2
- * @return
- */
- public static int[] getSymmetricDifference(int[] a1, int[] a2) {
- int index = 0;
- int[] res = new int[a1.length + a2.length];
-
- Arrays.sort(a1);
- Arrays.sort(a2);
-
- for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < a1.length || j < a2.length; ) {
- if (j >= a2.length) {
- res[index++] = a1[i];
- i++;
- } else if (i >= a1.length) {
- res[index++] = a2[j];
- j++;
- } else if (a1[i] < a2[j]) {
- res[index++] = a1[i];
- i++;
- } else if (a2[j] < a1[i]) {
- res[index++] = a2[j];
- j++;
- } else {
- i++;
- j++;
- }
- }
-
- return Arrays.copyOf(res, index);
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(getSymmetricDifference(new int[]{1, 2, 3, 4}, new int[]{2, 4, 5})));
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(getSymmetricDifference(new int[]{1, 2, 3, 4}, new int[]{5, 6, 7})));
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(getSymmetricDifference(new int[]{1, 2, 3, 4}, new int[]{5, 6, 7, 8})));
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(getSymmetricDifference(new int[]{1, 2, 3, 4}, new int[]{1, 2, 3, 4})));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/TripletOfSum.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/TripletOfSum.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 91d47649..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/TripletOfSum.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,50 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-import com.rampatra.sorting.QuickSort;
-
-import java.util.Arrays;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 9/28/15
- * @time: 10:39 PM
- */
-public class TripletOfSum {
-
- /**
- * Finds any 3 numbers in array {@param a}
- * whose sum is equal to {@param sum}.
- *
- * Time complexity: O(n^2)
- *
- * @param a
- * @param sum
- * @return
- */
- public static int[] getTripletOfSum(int[] a, int sum) {
-
- QuickSort.quickSort(a);
-
- int len = a.length;
- for (int i = 0, j = i + 1, k = len - 1; i < len - 2; i++) {
- while (j < k) {
- if (a[i] + a[j] + a[k] == sum) {
- return new int[]{a[i], a[j], a[k]};
- } else if (a[i] + a[j] + a[k] < sum) {
- j++;
- } else {
- k--;
- }
- }
- }
- return new int[]{-1};
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(getTripletOfSum(new int[]{12, 3, 4, 5, 1, 6, 9}, 24)));
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(getTripletOfSum(new int[]{12, 3, 4, 5, 1, 6, 9}, 19)));
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(getTripletOfSum(new int[]{1, 2, 3}, 6)));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/TwoElementsSumClosestToZero.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/TwoElementsSumClosestToZero.java
deleted file mode 100644
index e41a0f92..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/TwoElementsSumClosestToZero.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,46 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-import com.rampatra.sorting.QuickSort;
-
-import java.util.Arrays;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 7/30/15
- * @time: 5:44 PM
- */
-public class TwoElementsSumClosestToZero {
-
- /**
- * An array of integers is given containing both +ve and -ve numbers. You
- * need to find two elements such that their sum is closest to zero.
- *
- * @param a
- * @return
- */
- public static int[] getTwoElementsWhoseSumIsClosestToZero(int[] a) {
- QuickSort.quickSort(a);
-
- int minDiff = Math.abs(0 - (a[0] + a[a.length - 1])), n1 = a[0], n2 = a[a.length - 1];
-
- for (int i = 1, j = a.length - 2; i < j; ) {
- if (Math.abs(0 - (a[i] + a[j])) < minDiff) {
- minDiff = Math.abs(0 - (a[i] + a[j]));
- n1 = a[i];
- n2 = a[j];
- i++;
- } else {
- j--;
- }
- }
-
- return new int[]{n1, n2};
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(getTwoElementsWhoseSumIsClosestToZero(new int[]{1, 60, -10, -80, 85, 70})));
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(getTwoElementsWhoseSumIsClosestToZero(new int[]{-3, -100, -10, -80, 85, 70})));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/TwoRepeatingElements.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/TwoRepeatingElements.java
deleted file mode 100644
index a943a532..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/TwoRepeatingElements.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,100 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-import com.rampatra.bits.TwoNonRepeatingElements;
-
-import java.util.Arrays;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 8/17/15
- * @time: 7:23 PM
- */
-public class TwoRepeatingElements {
-
- /**
- * Finds the 2 repeating elements in an array {@param a} of 1 to n elements and n+2 length. This is
- * similar to {@link TwoNonRepeatingElements}.
- *
- * EXPLANATION:
- * Let the repeating numbers be X and Y, if we xor all the elements in the array and all integers from 1 to n,
- * then the result is X xor Y.
- * The 1’s in binary representation of X xor Y is corresponding to the different bits between X and Y.
- * Suppose that the kth bit of X xor Y is 1, we can xor all the elements in the array and all integers
- * from 1 to n, whose kth bits are 1. The result will be one of X and Y.
- *
- * @param a
- * @return
- */
- public static int[] getTwoRepeatingElements(int[] a) {
- int xor = a[0];
- int rightMostSetBit;
- int x = 0, y = 0;
-
- for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++) {
- xor ^= a[i];
- }
-
- for (int i = 1; i <= a.length - 2; i++) {
- xor ^= i;
- }
-
- // now xor is X xor Y, therefore find any of its set bit
- rightMostSetBit = xor & ~(xor - 1);
-
- for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
- // one number will have a set bit at that position and other wouldn't
- if ((a[i] & rightMostSetBit) == 0) {
- x ^= a[i];
- } else {
- y ^= a[i];
- }
- }
-
- for (int i = 1; i <= a.length - 2; i++) {
- // one number will have a set bit at that position and other wouldn't
- if ((i & rightMostSetBit) == 0) {
- x ^= i;
- } else {
- y ^= i;
- }
- }
-
- return new int[]{x, y};
- }
-
- /**
- * The algorithm is simple. We use index of the array to track repeating elements.
- * Once we encounter a element lets say 2 then we make the element in 2nd index -ve just
- * to mark that we have encountered 2. When we encounter 2 again and see that 2nd index
- * is already -ve we conclude that 2 is repeated.
- *
- * Similar to {@link DuplicatesInArray#findDuplicatesInArray(int[])}.
- *
- * @param a
- * @return
- */
- public static int[] findTwoRepeatingElements(int[] a) {
- int[] repeatingElements = new int[2];
-
- for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
- if (a[Math.abs(a[i])] >= 0) {
- a[Math.abs(a[i])] = -a[Math.abs(a[i])];
- } else {
- repeatingElements[j++] = Math.abs(a[i]);
- }
- }
- return repeatingElements;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(getTwoRepeatingElements(new int[]{4, 2, 4, 5, 2, 3, 1})));
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(getTwoRepeatingElements(new int[]{2, 4, 5, 2, 3, 1, 6, 7, 7})));
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(getTwoRepeatingElements(new int[]{1, 2, 1, 2})));
- System.out.println("========");
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(findTwoRepeatingElements(new int[]{4, 2, 4, 5, 2, 3, 1})));
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(findTwoRepeatingElements(new int[]{2, 4, 5, 2, 3, 1, 6, 7, 7})));
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(findTwoRepeatingElements(new int[]{1, 2, 1, 2})));
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/TwoStacksInOneArray.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/TwoStacksInOneArray.java
deleted file mode 100644
index b4e83806..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/TwoStacksInOneArray.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,93 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-import java.util.Arrays;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * Implement two stacks using a single array with efficient use of space.
- * We could do this by dividing the array into two equal halves or storing stack
- * elements alternatively in the array but that wouldn't utilize the space fully.
- * So we stored stack1's elements at one end of the array and stack2's elements at
- * the other end.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 9/21/15
- * @time: 6:18 PM
- */
-public class TwoStacksInOneArray {
-
- int[] array;
- int top1, top2, size;
-
- TwoStacksInOneArray(int size) {
- array = new int[size];
- this.size = size;
- top1 = -1;
- top2 = size;
- }
-
- void push(int stack, int item) {
- if (top1 == top2 - 1) {
- System.out.println("Stack is full");
- return;
- }
-
- if (stack == 1) {
- top1++;
- array[top1] = item;
- } else {
- top2--;
- array[top2] = item;
- }
- }
-
- int pop(int stack) {
- if (stack == 1) {
- if (top1 == -1) {
- System.out.println("Stack 1 is empty");
- return -1;
- }
- int pop = array[top1];
- top1--;
- return pop;
- } else {
- if (top2 == size) {
- System.out.println("Stack 2 is empty");
- return -1;
- }
- int pop = array[top2];
- top2++;
- return pop;
- }
- }
-
- void printStack(int stack) {
- if (stack == 1) {
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(Arrays.copyOfRange(array, 0, top1 + 1)));
- } else {
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(Arrays.copyOfRange(array, top2, size)));
- }
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- TwoStacksInOneArray twoStack = new TwoStacksInOneArray(5);
- twoStack.push(1, 3);
- twoStack.push(1, 4);
- twoStack.push(1, 5);
- twoStack.push(2, 1);
- twoStack.push(1, 6);
- twoStack.push(1, 7);
- twoStack.printStack(1);
- twoStack.pop(1);
- twoStack.pop(1);
- twoStack.pop(1);
- twoStack.pop(1);
- twoStack.pop(1);
- twoStack.pop(1);
- twoStack.printStack(2);
- twoStack.pop(2);
- twoStack.pop(2);
- twoStack.printStack(2);
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/UnsortedSubArray.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/UnsortedSubArray.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 36aa4e12..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/arrays/UnsortedSubArray.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,97 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.arrays;
-
-import java.util.Arrays;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 8/20/15
- * @time: 10:31 AM
- */
-public class UnsortedSubArray {
-
- /**
- * Finds the unsorted sub array in array {@param a} such that
- * sorting this sub array makes the entire array sorted.
- *
- * EXPLANATION:
- * 1) Find the candidate unsorted subarray
- * ...a) Scan from left to right and find the first element which is greater than the next element. Let s be the
- * index of such an element. In the above example 1, s is 3 (index of 30).
- * ...b) Scan from right to left and find the first element (first in right to left order) which is smaller than
- * the next element (next in right to left order). Let e be the index of such an element. In the above example 1,
- * e is 7 (index of 31).
- * 2) Check whether sorting the candidate unsorted subarray makes the complete array sorted or not. If not, then
- * include more elements in the subarray.
- * ...a) Find the minimum and maximum values in arr[s..e]. Let minimum and maximum values be min and max. min and
- * max for [30, 25, 40, 32, 31] are 25 and 40 respectively.
- * ...b) Find the first element (if there is any) in arr[0..s-1] which is greater than min, change s to index of
- * this element. There is no such element in above example 1.
- * ...c) Find the last element (if there is any) in arr[e+1..n-1] which is smaller than max, change e to index of
- * this element. In the above example 1, e is changed to 8 (index of 35)
- * 3) Print s and e.
- *
- * @param a
- * @return
- */
- public static int[] getUnsortedSubArray(int[] a) {
- int start = 0, end = a.length - 1, min = Integer.MAX_VALUE, max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
- int[] unsortedArray;
-
- // 1(a)
- for (int i = 0; i < a.length - 1; i++) {
- if (a[i] > a[i + 1]) {
- start = i;
- break;
- }
- }
-
- // 1(b)
- for (int i = a.length - 1; i > 0; i--) {
- if (a[i] < a[i - 1]) {
- end = i;
- break;
- }
- }
-
- // 2(a) - find min and max
- for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) {
- if (a[i] < min) {
- min = a[i];
- }
- if (a[i] > max) {
- max = a[i];
- }
- }
-
- // 2(b)
- for (int i = 0; i < start; i++) {
- if (a[i] > min) {
- start = i;
- break;
- }
- }
-
- // 2(c)
- for (int i = end + 1; i < a.length; i++) {
- if (a[i] < max) {
- end = i;
- break;
- }
- }
-
- unsortedArray = new int[end - start + 1];
- for (int i = start, j = 0; i <= end; i++, j++) {
- unsortedArray[j] = a[i];
- }
-
- return unsortedArray;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(getUnsortedSubArray(new int[]{10, 12, 20, 30, 25, 40, 32, 31, 35, 50, 60})));
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(getUnsortedSubArray(new int[]{0, 1, 15, 25, 6, 7, 30, 40, 50})));
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(getUnsortedSubArray(new int[]{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8}))); // fully sorted already
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/backtracking/KnightTour.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/backtracking/KnightTour.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 64b58918..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/backtracking/KnightTour.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,111 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.backtracking;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * A knight's tour is a sequence of moves of a knight on a chessboard such that the knight visits every square only
- * once. If the knight ends on a square that is one knight's move from the beginning square (so that it could tour the
- * board again immediately, following the same path), the tour is closed, otherwise it is open.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 10/15/15
- * @time: 11:56 PM
- * @see: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Knight%27s_tour
- * @see: RatInAMaze for a simpler version of this problem
- */
-public class KnightTour {
-
- /**
- * Determines if a move is a valid move in the given chess board.
- *
- * @param i is the row of the new move
- * @param j is the column of the new move
- * @param tour
- * @return
- */
- public static boolean isValidMove(int i, int j, int[][] tour) {
- if (i >= 0 && i < tour.length && j >= 0 && j < tour[0].length && tour[i][j] == 0) {
- return true;
- } else {
- return false;
- }
- }
-
- /**
- * Finds a valid knight's tour for a given chess board size if any
- * with the use of backtracking.
- *
- * @param i
- * @param j
- * @param xMoves
- * @param yMoves
- * @param step
- * @param tour
- * @return
- */
- public static boolean isValidKnightTour(int i, int j, int[] xMoves, int[] yMoves, int step, int[][] tour) {
-
- if (step > tour.length * tour[0].length) return true;
-
- int nextI, nextJ;
-
- for (int k = 0; k < xMoves.length; k++) {
- // next move is calculated from all possible moves
- nextI = i + xMoves[k];
- nextJ = j + yMoves[k];
-
- // if the next move is valid then we proceed otherwise we
- // try next set of moves
- if (isValidMove(nextI, nextJ, tour)) {
- tour[nextI][nextJ] = step;
- if (isValidKnightTour(nextI, nextJ, xMoves, yMoves, step + 1, tour)) {
- return true;
- } else {
- tour[nextI][nextJ] = 0; // backtrack
- }
- }
- }
-
- return false;
- }
-
-
- /**
- * Prints the knight's tour if any.
- *
- * @param i is the start row
- * @param j is the start column
- * @param boardSize is the size of the chess board
- */
- public static void printKnightTour(int i, int j, int[] boardSize) {
- if (boardSize.length < 2) return;
-
- // a 2D array for the knight's tour
- int[][] tour = new int[boardSize[0]][boardSize[1]];
- // all possible relative moves that a knight can make
- int[] xMoves = new int[]{1, 1, 2, 2, -1, -1, -2, -2};
- int[] yMoves = new int[]{-2, 2, -1, 1, -2, 2, -1, 1};
-
- tour[0][0] = 1;
-
- if (isValidKnightTour(i, j, xMoves, yMoves, 2, tour)) {
- print2DMatrix(tour);
- } else {
- System.out.println("Knight's tour doesn't exist for board size [" + boardSize[0] + "x" + boardSize[1] + "]");
- }
-
- }
-
- public static void print2DMatrix(int[][] array) {
- for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
- for (int j = 0; j < array[0].length; j++) {
- System.out.print("[" + array[i][j] + "]");
- }
- System.out.println();
- }
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- printKnightTour(0, 0, new int[]{8, 8});
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/backtracking/RatInAMaze.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/backtracking/RatInAMaze.java
deleted file mode 100644
index bb8ea749..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/backtracking/RatInAMaze.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,92 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.backtracking;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 10/18/15
- * @time: 10:39 AM
- */
-public class RatInAMaze {
-
- /**
- * @param i
- * @param j
- * @param maze
- * @return
- */
- public static boolean isValidMove(int i, int j, int[][] maze) {
- if (i >= 0 && i < maze.length && j >= 0 && j < maze[0].length && maze[i][j] == 1) {
- return true;
- } else {
- return false;
- }
- }
-
- /**
- * @param i
- * @param j
- * @param xMoves
- * @param yMoves
- * @param maze
- * @param path
- * @return
- */
- public static boolean isValidPath(int i, int j, int[] xMoves, int[] yMoves, int[][] maze, int[][] path) {
-
- if (i == maze.length - 1 && j == maze[0].length - 1) return true;
-
- int nextI, nextJ;
-
- for (int k = 0; k < xMoves.length; k++) {
- nextI = i + xMoves[k];
- nextJ = j + yMoves[k];
- if (isValidMove(nextI, nextJ, maze)) {
- path[nextI][nextJ] = 1;
- if (isValidPath(nextI, nextJ, xMoves, yMoves, maze, path)) {
- return true;
- } else {
- path[nextI][nextJ] = 0;
- }
- }
- }
- return false;
- }
-
- /**
- * @param i is the start row
- * @param j is the start column
- * @param maze is the maze in which a path has to be found (1 denotes rat can traverse and 0 denotes it cannot)
- */
- public static void printMazePath(int i, int j, int[][] maze) {
-
- int[] xMoves = {0, 1};
- int[] yMoves = {1, 0};
-
- int[][] path = new int[maze.length][maze[0].length];
-
- System.out.println("Maze");
- System.out.println("---------------");
- print2DMatrix(maze);
- System.out.println("---------------");
-
- if (isValidPath(i, j, xMoves, yMoves, maze, path)) {
- print2DMatrix(path);
- } else {
- System.out.println("No escape path found!");
- }
- }
-
- public static void print2DMatrix(int[][] array) {
- for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
- for (int j = 0; j < array[0].length; j++) {
- System.out.print("[" + array[i][j] + "]");
- }
- System.out.println();
- }
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- printMazePath(0, 0, new int[][]{{1, 1, 1, 1}, {0, 0, 1, 1}});
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/base/AVLTree.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/base/AVLTree.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 61999cd0..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/base/AVLTree.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,12 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.base;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 4/25/15
- * @time: 10:25 AM
- */
-public class AVLTree> extends Tree {
-
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/base/BinaryNode.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/base/BinaryNode.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 6e57530e..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/base/BinaryNode.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,29 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.base;
-
-/**
- * Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
- * User: rampatra
- * Date: 4/11/15
- * Time: 7:11 PM
- * To change this template go to Preferences | IDE Settings | File and Code Templates
- */
-public class BinaryNode> {
-
- public E value;
- public BinaryNode left;
- public BinaryNode right;
-
- public BinaryNode(E value, BinaryNode left, BinaryNode right) {
- this.value = value;
- this.left = left;
- this.right = right;
- }
-
- public BinaryNode(BinaryNode node) {
- if (node == null) return;
-
- this.value = node.value;
- this.left = node.left;
- this.right = node.right;
- }
-}
diff --git a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/base/BinarySearchTree.java b/src/main/java/com/rampatra/base/BinarySearchTree.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 644f1e7d..00000000
--- a/src/main/java/com/rampatra/base/BinarySearchTree.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,85 +0,0 @@
-package com.rampatra.base;
-
-import java.util.NoSuchElementException;
-
-import static java.lang.System.out;
-
-/**
- * A binary search tree is a binary tree in which every node fits a specific ordering property: all left
- * descendents <= n < all right descendents. This must be true for each node n.
- *
- * Note: The definition of a binary search tree can vary slightly with respect to equality. Under some definitions, the
- * tree cannot have duplicate values. In others, the duplicate values will be on the right or can be on either side. All
- * are valid definitions, but you should clarify this with your interviewer
- *
- * @author rampatra
- * @since 4/19/15
- * @param
- */
-public class BinarySearchTree> extends BinaryTree {
-
- /**
- * Inserts a node into the BST.
- *
- * @param value
- */
- public BinaryNode put(E value) {
- return put(root, value);
- }
-
- public BinaryNode put(BinaryNode node, E value) {
- BinaryNode newNode = new BinaryNode<>(value, null, null);
-
- if (node == null) {
- return root = new BinaryNode<>(value, null, null);
- } else {
- if (value.compareTo(node.value) < 0) {
- if (node.left == null) {
- return node.left = newNode;
- } else {
- return put(node.left, value);
- }
- } else {
- if (node.right == null) {
- return node.right = newNode;
- } else {
- return put(node.right, value);
- }
- }
- }
- }
-
-
- /**
- * Returns the node with minimum value.
- *
- * @return
- */
- public BinaryNode min() {
- return min(root);
- }
-
- public BinaryNode min(BinaryNode


 +
+ +
+ 








 +
+ +
+ +
+ +
+ +
+ +
+ 










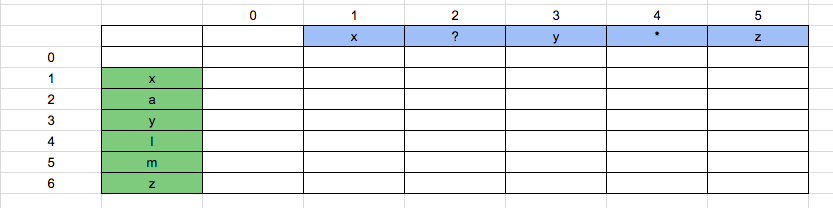
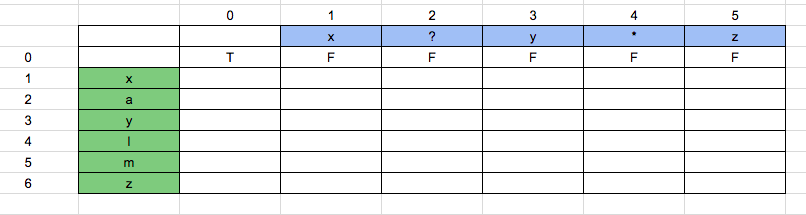
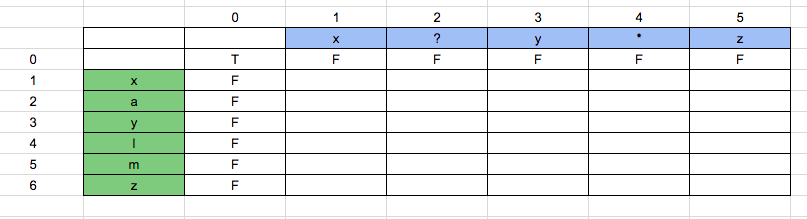
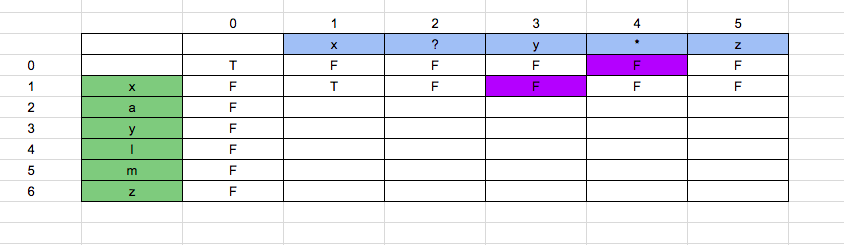
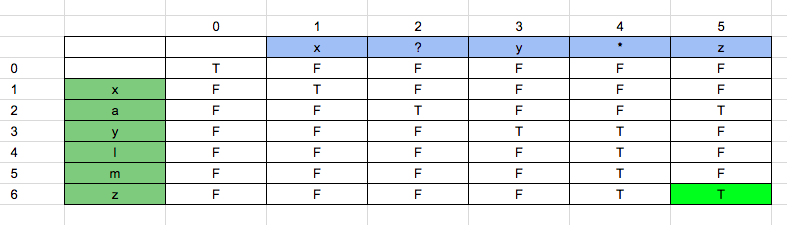










 +
+ +
+ +
+ +
+ +
+

