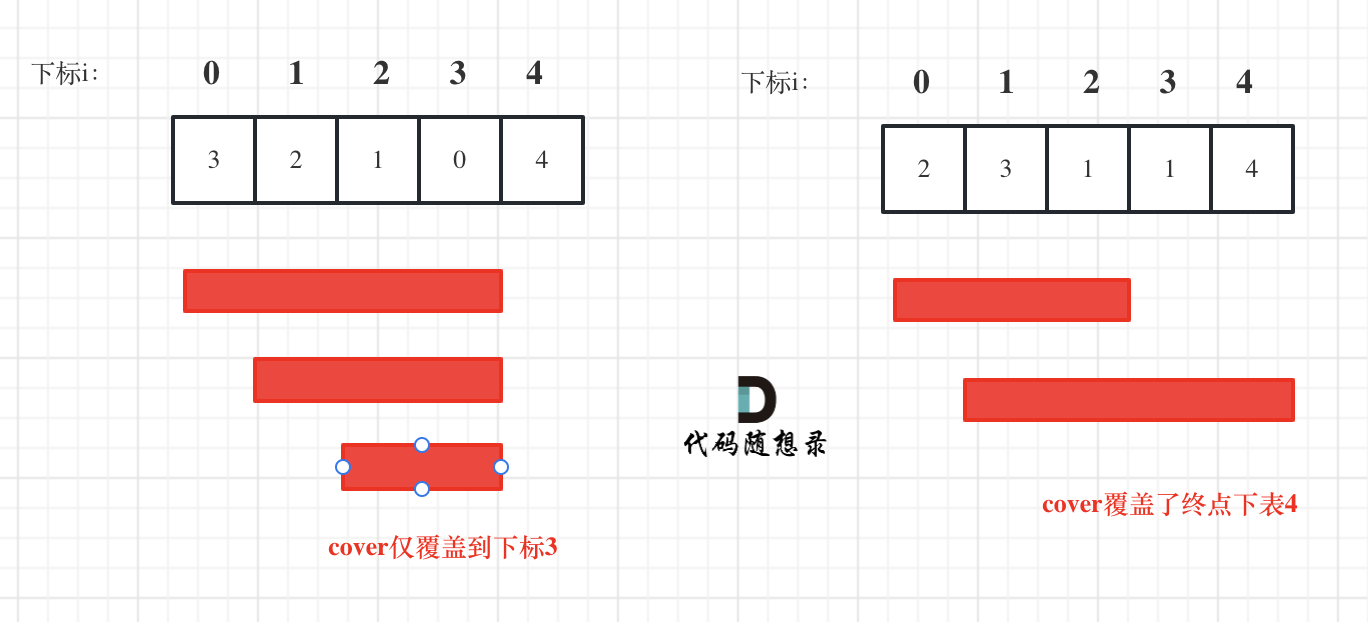
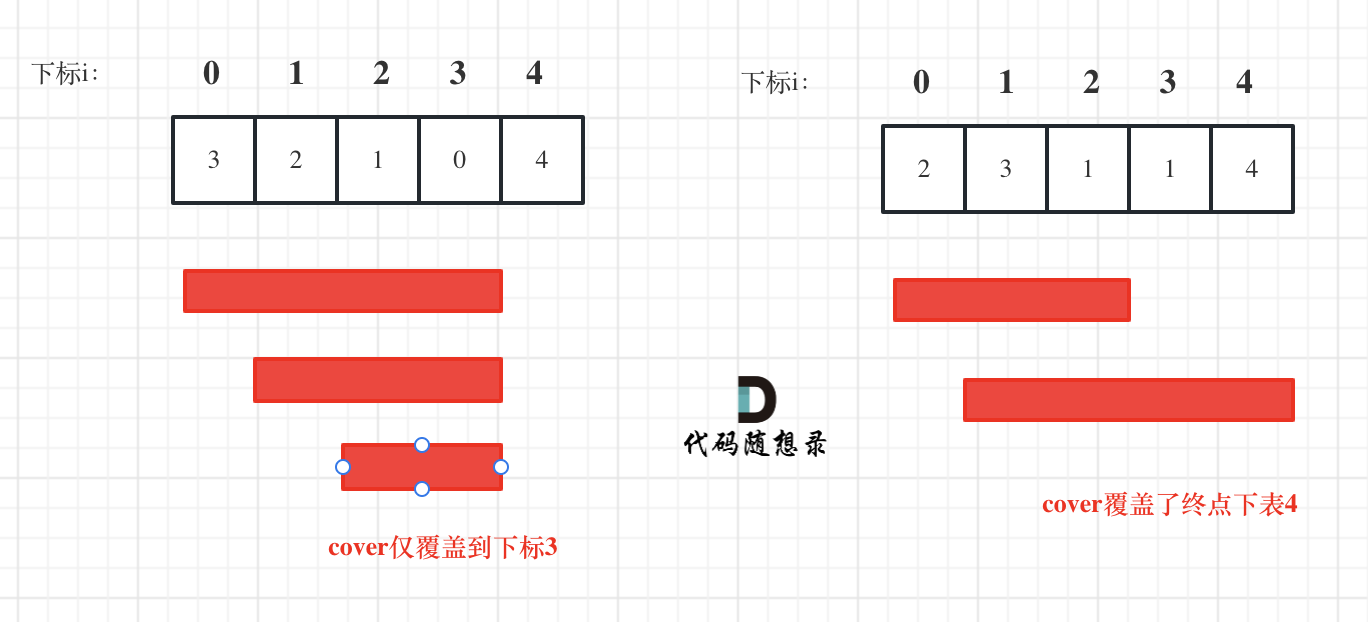
& nums, int val) {
- int leftIndex = 0;
- int rightIndex = nums.size() - 1;
- while (leftIndex <= rightIndex) {
- // 找左边等于val的元素
- while (leftIndex <= rightIndex && nums[leftIndex] != val){
- ++leftIndex;
- }
- // 找右边不等于val的元素
- while (leftIndex <= rightIndex && nums[rightIndex] == val) {
- -- rightIndex;
- }
- // 将右边不等于val的元素覆盖左边等于val的元素
- if (leftIndex < rightIndex) {
- nums[leftIndex++] = nums[rightIndex--];
- }
- }
- return leftIndex; // leftIndex一定指向了最终数组末尾的下一个元素
- }
-};
-```
## 相关题目推荐
@@ -160,7 +129,24 @@ public:
## 其他语言版本
### Java:
-
+```java
+class Solution {
+ public int removeElement(int[] nums, int val) {
+ // 暴力法
+ int n = nums.length;
+ for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
+ if (nums[i] == val) {
+ for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
+ nums[j - 1] = nums[j];
+ }
+ i--;
+ n--;
+ }
+ }
+ return n;
+ }
+}
+```
```java
class Solution {
public int removeElement(int[] nums, int val) {
@@ -253,8 +239,47 @@ class Solution:
```
+``` python 3
+# 相向双指针法
+# 时间复杂度 O(n)
+# 空间复杂度 O(1)
+class Solution:
+ def removeElement(self, nums: List[int], val: int) -> int:
+ n = len(nums)
+ left, right = 0, n - 1
+ while left <= right:
+ while left <= right and nums[left] != val:
+ left += 1
+ while left <= right and nums[right] == val:
+ right -= 1
+ if left < right:
+ nums[left] = nums[right]
+ left += 1
+ right -= 1
+ return left
+
+```
+
### Go:
+```go
+// 暴力法
+// 时间复杂度 O(n^2)
+// 空间复杂度 O(1)
+func removeElement(nums []int, val int) int {
+ size := len(nums)
+ for i := 0; i < size; i ++ {
+ if nums[i] == val {
+ for j := i + 1; j < size; j ++ {
+ nums[j - 1] = nums[j]
+ }
+ i --
+ size --
+ }
+ }
+ return size
+}
+```
```go
// 快慢指针法
// 时间复杂度 O(n)
@@ -297,7 +322,6 @@ func removeElement(nums []int, val int) int {
right--
}
}
- fmt.Println(nums)
return left
}
```
@@ -467,7 +491,29 @@ public class Solution {
}
```
-
-
-  -
+###Dart:
+```dart
+int removeElement(List nums, int val) {
+ //相向双指针法
+ var left = 0;
+ var right = nums.length - 1;
+ while (left <= right) {
+ //寻找左侧的val,将其被右侧非val覆盖
+ if (nums[left] == val) {
+ while (nums[right] == val&&left<=right) {
+ right--;
+ if (right < 0) {
+ return 0;
+ }
+ }
+ nums[left] = nums[right--];
+ } else {
+ left++;
+ }
+ }
+ //覆盖后可以将0至left部分视为所需部分
+ return left;
+}
+
+```
+
diff --git "a/problems/0028.\345\256\236\347\216\260strStr.md" "b/problems/0028.\345\256\236\347\216\260strStr.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 8d0cc52559..ef8a6c58e6
--- "a/problems/0028.\345\256\236\347\216\260strStr.md"
+++ "b/problems/0028.\345\256\236\347\216\260strStr.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+###Dart:
+```dart
+int removeElement(List nums, int val) {
+ //相向双指针法
+ var left = 0;
+ var right = nums.length - 1;
+ while (left <= right) {
+ //寻找左侧的val,将其被右侧非val覆盖
+ if (nums[left] == val) {
+ while (nums[right] == val&&left<=right) {
+ right--;
+ if (right < 0) {
+ return 0;
+ }
+ }
+ nums[left] = nums[right--];
+ } else {
+ left++;
+ }
+ }
+ //覆盖后可以将0至left部分视为所需部分
+ return left;
+}
+
+```
+
diff --git "a/problems/0028.\345\256\236\347\216\260strStr.md" "b/problems/0028.\345\256\236\347\216\260strStr.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 8d0cc52559..ef8a6c58e6
--- "a/problems/0028.\345\256\236\347\216\260strStr.md"
+++ "b/problems/0028.\345\256\236\347\216\260strStr.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
> 在一个串中查找是否出现过另一个串,这是KMP的看家本领。
@@ -108,7 +106,7 @@ next数组就是一个前缀表(prefix table)。
如动画所示:
-
+
动画里,我特意把 子串`aa` 标记上了,这是有原因的,大家先注意一下,后面还会说到。
@@ -149,11 +147,11 @@ next数组就是一个前缀表(prefix table)。
这就是前缀表,那为啥就能告诉我们 上次匹配的位置,并跳过去呢?
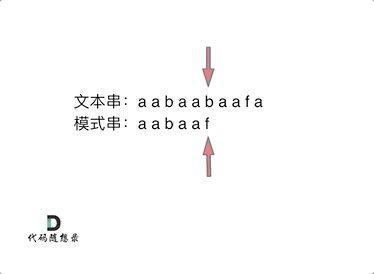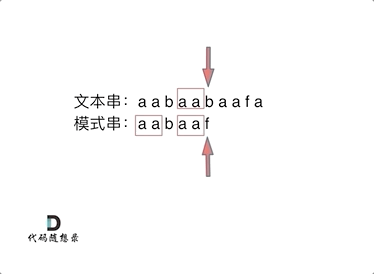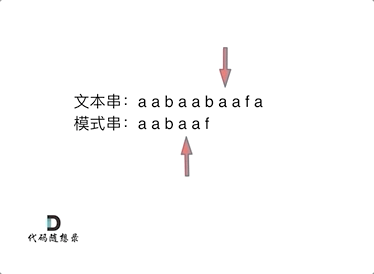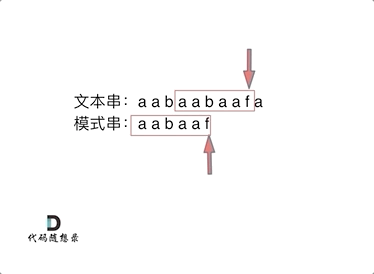
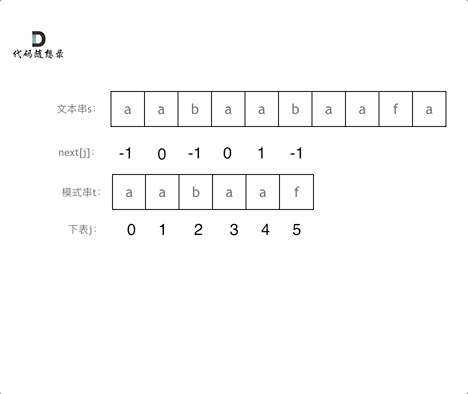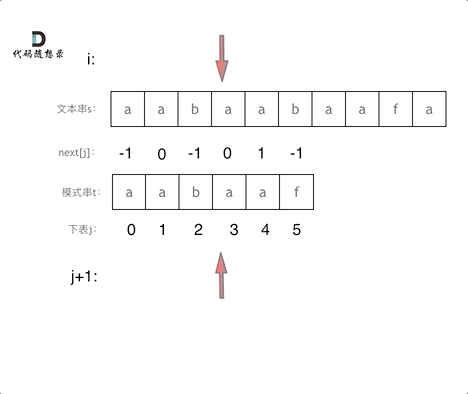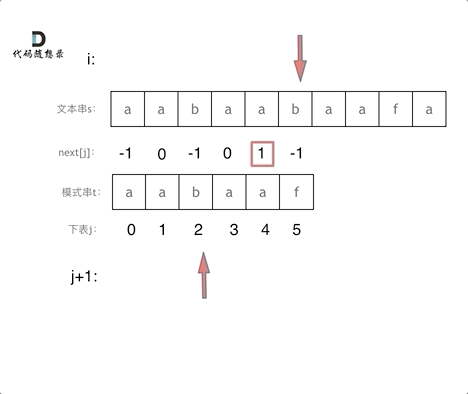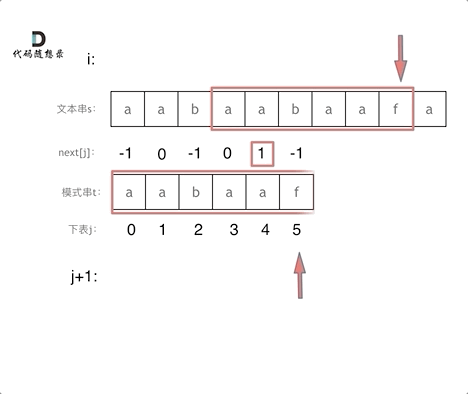
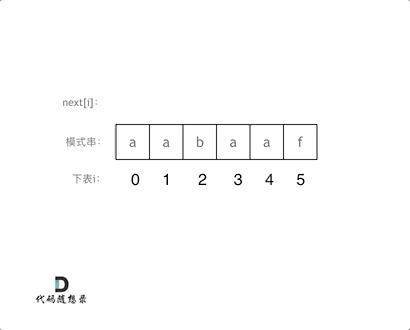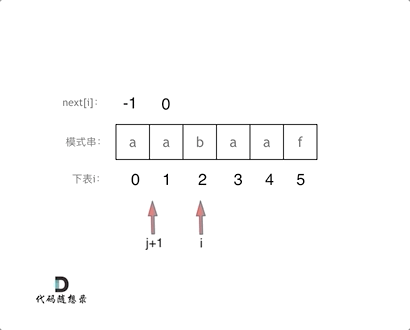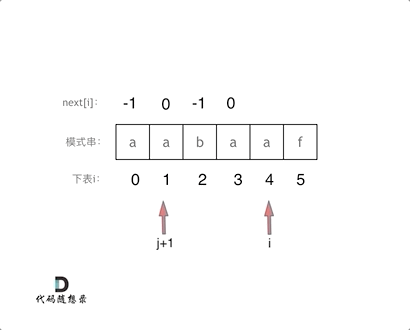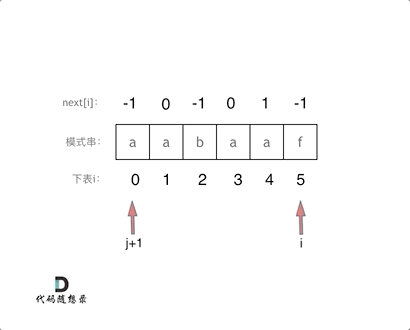
回顾一下,刚刚匹配的过程在下标5的地方遇到不匹配,模式串是指向f,如图:
- +
+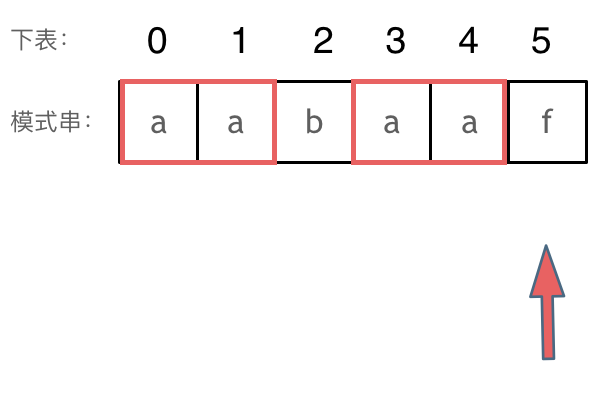 然后就找到了下标2,指向b,继续匹配:如图:
-
然后就找到了下标2,指向b,继续匹配:如图:
- +
+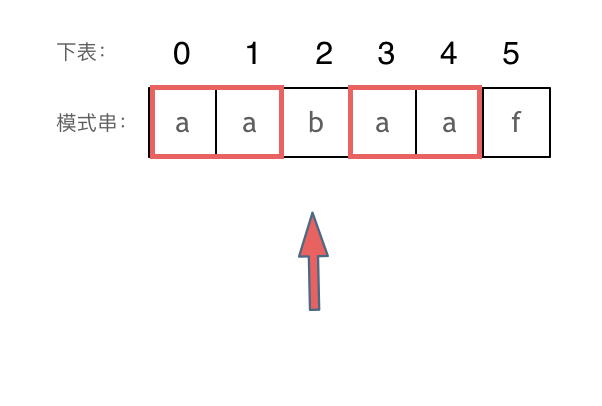 以下这句话,对于理解为什么使用前缀表可以告诉我们匹配失败之后跳到哪里重新匹配 非常重要!
@@ -169,15 +167,15 @@ next数组就是一个前缀表(prefix table)。
如图:
-
以下这句话,对于理解为什么使用前缀表可以告诉我们匹配失败之后跳到哪里重新匹配 非常重要!
@@ -169,15 +167,15 @@ next数组就是一个前缀表(prefix table)。
如图:
- +
+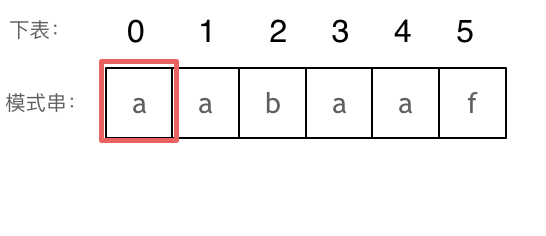 长度为前1个字符的子串`a`,最长相同前后缀的长度为0。(注意字符串的**前缀是指不包含最后一个字符的所有以第一个字符开头的连续子串**;**后缀是指不包含第一个字符的所有以最后一个字符结尾的连续子串**。)
-
长度为前1个字符的子串`a`,最长相同前后缀的长度为0。(注意字符串的**前缀是指不包含最后一个字符的所有以第一个字符开头的连续子串**;**后缀是指不包含第一个字符的所有以最后一个字符结尾的连续子串**。)
- +
+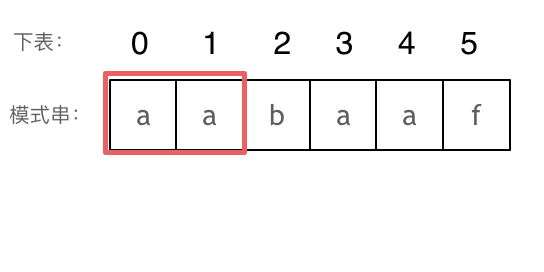 长度为前2个字符的子串`aa`,最长相同前后缀的长度为1。
-
长度为前2个字符的子串`aa`,最长相同前后缀的长度为1。
- +
+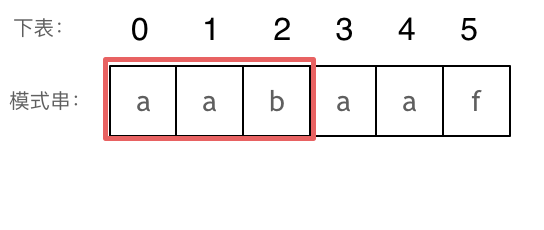 长度为前3个字符的子串`aab`,最长相同前后缀的长度为0。
@@ -187,13 +185,13 @@ next数组就是一个前缀表(prefix table)。
长度为前6个字符的子串`aabaaf`,最长相同前后缀的长度为0。
那么把求得的最长相同前后缀的长度就是对应前缀表的元素,如图:
-
长度为前3个字符的子串`aab`,最长相同前后缀的长度为0。
@@ -187,13 +185,13 @@ next数组就是一个前缀表(prefix table)。
长度为前6个字符的子串`aabaaf`,最长相同前后缀的长度为0。
那么把求得的最长相同前后缀的长度就是对应前缀表的元素,如图:
- +
+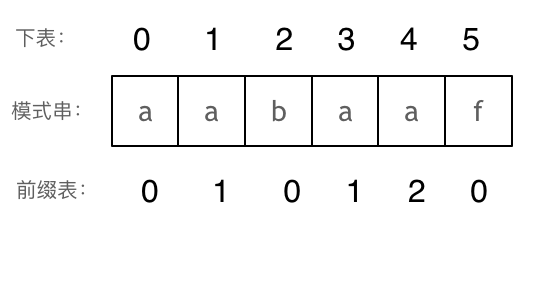 可以看出模式串与前缀表对应位置的数字表示的就是:**下标i之前(包括i)的字符串中,有多大长度的相同前缀后缀。**
再来看一下如何利用 前缀表找到 当字符不匹配的时候应该指针应该移动的位置。如动画所示:
-
+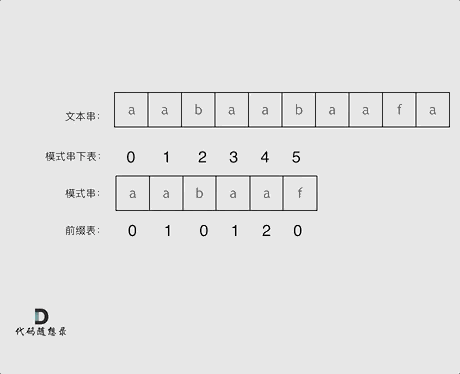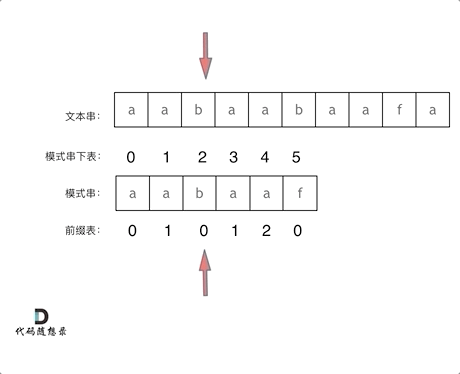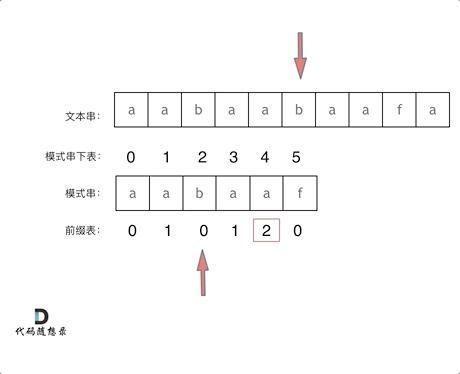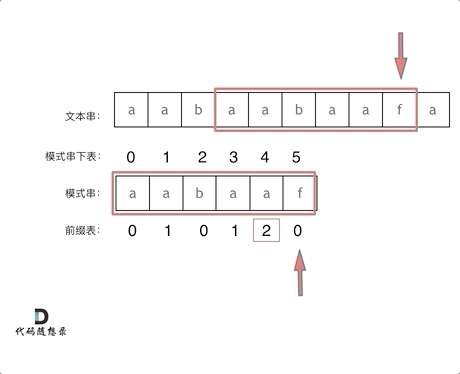
找到的不匹配的位置, 那么此时我们要看它的前一个字符的前缀表的数值是多少。
@@ -227,7 +225,7 @@ next数组就可以是前缀表,但是很多实现都是把前缀表统一减
匹配过程动画如下:
-
+
### 时间复杂度分析
@@ -334,7 +332,7 @@ void getNext(int* next, const string& s){
代码构造next数组的逻辑流程动画如下:
-
+
得到了next数组之后,就要用这个来做匹配了。
@@ -564,6 +562,38 @@ public:
## 其他语言版本
### Java:
+```Java
+class Solution {
+ /**
+ 牺牲空间,换取最直白的暴力法
+ 时间复杂度 O(n * m)
+ 空间 O(n + m)
+ */
+ public int strStr(String haystack, String needle) {
+ // 获取 haystack 和 needle 的长度
+ int n = haystack.length(), m = needle.length();
+ // 将字符串转换为字符数组,方便索引操作
+ char[] s = haystack.toCharArray(), p = needle.toCharArray();
+
+ // 遍历 haystack 字符串
+ for (int i = 0; i < n - m + 1; i++) {
+ // 初始化匹配的指针
+ int a = i, b = 0;
+ // 循环检查 needle 是否在当前位置开始匹配
+ while (b < m && s[a] == p[b]) {
+ // 如果当前字符匹配,则移动指针
+ a++;
+ b++;
+ }
+ // 如果 b 等于 m,说明 needle 已经完全匹配,返回当前位置 i
+ if (b == m) return i;
+ }
+
+ // 如果遍历完毕仍未找到匹配的子串,则返回 -1
+ return -1;
+ }
+}
+```
```Java
class Solution {
@@ -1424,7 +1454,67 @@ public int[] GetNext(string needle)
}
```
-
可以看出模式串与前缀表对应位置的数字表示的就是:**下标i之前(包括i)的字符串中,有多大长度的相同前缀后缀。**
再来看一下如何利用 前缀表找到 当字符不匹配的时候应该指针应该移动的位置。如动画所示:
-
+
找到的不匹配的位置, 那么此时我们要看它的前一个字符的前缀表的数值是多少。
@@ -227,7 +225,7 @@ next数组就可以是前缀表,但是很多实现都是把前缀表统一减
匹配过程动画如下:
-
+
### 时间复杂度分析
@@ -334,7 +332,7 @@ void getNext(int* next, const string& s){
代码构造next数组的逻辑流程动画如下:
-
+
得到了next数组之后,就要用这个来做匹配了。
@@ -564,6 +562,38 @@ public:
## 其他语言版本
### Java:
+```Java
+class Solution {
+ /**
+ 牺牲空间,换取最直白的暴力法
+ 时间复杂度 O(n * m)
+ 空间 O(n + m)
+ */
+ public int strStr(String haystack, String needle) {
+ // 获取 haystack 和 needle 的长度
+ int n = haystack.length(), m = needle.length();
+ // 将字符串转换为字符数组,方便索引操作
+ char[] s = haystack.toCharArray(), p = needle.toCharArray();
+
+ // 遍历 haystack 字符串
+ for (int i = 0; i < n - m + 1; i++) {
+ // 初始化匹配的指针
+ int a = i, b = 0;
+ // 循环检查 needle 是否在当前位置开始匹配
+ while (b < m && s[a] == p[b]) {
+ // 如果当前字符匹配,则移动指针
+ a++;
+ b++;
+ }
+ // 如果 b 等于 m,说明 needle 已经完全匹配,返回当前位置 i
+ if (b == m) return i;
+ }
+
+ // 如果遍历完毕仍未找到匹配的子串,则返回 -1
+ return -1;
+ }
+}
+```
```Java
class Solution {
@@ -1424,7 +1454,67 @@ public int[] GetNext(string needle)
}
```
-
-
-  -
+### C:
+
+> 前缀表统一右移和减一
+
+```c
+
+int *build_next(char* needle, int len) {
+
+ int *next = (int *)malloc(len * sizeof(int));
+ assert(next); // 确保分配成功
+
+ // 初始化next数组
+ next[0] = -1; // next[0] 设置为 -1,表示没有有效前缀匹配
+ if (len <= 1) { // 如果模式串长度小于等于 1,直接返回
+ return next;
+ }
+ next[1] = 0; // next[1] 设置为 0,表示第一个字符没有公共前后缀
+
+ // 构建next数组, i 从模式串的第三个字符开始, j 指向当前匹配的最长前缀长度
+ int i = 2, j = 0;
+ while (i < len) {
+ if (needle[i - 1] == needle[j]) {
+ j++;
+ next[i] = j;
+ i++;
+ } else if (j > 0) {
+ // 如果不匹配且 j > 0, 回退到次长匹配前缀的长度
+ j = next[j];
+ } else {
+ next[i] = 0;
+ i++;
+ }
+ }
+ return next;
+}
+
+int strStr(char* haystack, char* needle) {
+
+ int needle_len = strlen(needle);
+ int haystack_len = strlen(haystack);
+
+ int *next = build_next(needle, needle_len);
+
+ int i = 0, j = 0; // i 指向主串的当前起始位置, j 指向模式串的当前匹配位置
+ while (i <= haystack_len - needle_len) {
+ if (haystack[i + j] == needle[j]) {
+ j++;
+ if (j == needle_len) {
+ free(next);
+ next = NULL
+ return i;
+ }
+ } else {
+ i += j - next[j]; // 调整主串的起始位置
+ j = j > 0 ? next[j] : 0;
+ }
+ }
+
+ free(next);
+ next = NULL;
+ return -1;
+}
+```
+
diff --git "a/problems/0031.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\216\222\345\210\227.md" "b/problems/0031.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\216\222\345\210\227.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 3cfb673a29..4bbf20fbb8
--- "a/problems/0031.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\216\222\345\210\227.md"
+++ "b/problems/0031.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\216\222\345\210\227.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+### C:
+
+> 前缀表统一右移和减一
+
+```c
+
+int *build_next(char* needle, int len) {
+
+ int *next = (int *)malloc(len * sizeof(int));
+ assert(next); // 确保分配成功
+
+ // 初始化next数组
+ next[0] = -1; // next[0] 设置为 -1,表示没有有效前缀匹配
+ if (len <= 1) { // 如果模式串长度小于等于 1,直接返回
+ return next;
+ }
+ next[1] = 0; // next[1] 设置为 0,表示第一个字符没有公共前后缀
+
+ // 构建next数组, i 从模式串的第三个字符开始, j 指向当前匹配的最长前缀长度
+ int i = 2, j = 0;
+ while (i < len) {
+ if (needle[i - 1] == needle[j]) {
+ j++;
+ next[i] = j;
+ i++;
+ } else if (j > 0) {
+ // 如果不匹配且 j > 0, 回退到次长匹配前缀的长度
+ j = next[j];
+ } else {
+ next[i] = 0;
+ i++;
+ }
+ }
+ return next;
+}
+
+int strStr(char* haystack, char* needle) {
+
+ int needle_len = strlen(needle);
+ int haystack_len = strlen(haystack);
+
+ int *next = build_next(needle, needle_len);
+
+ int i = 0, j = 0; // i 指向主串的当前起始位置, j 指向模式串的当前匹配位置
+ while (i <= haystack_len - needle_len) {
+ if (haystack[i + j] == needle[j]) {
+ j++;
+ if (j == needle_len) {
+ free(next);
+ next = NULL
+ return i;
+ }
+ } else {
+ i += j - next[j]; // 调整主串的起始位置
+ j = j > 0 ? next[j] : 0;
+ }
+ }
+
+ free(next);
+ next = NULL;
+ return -1;
+}
+```
+
diff --git "a/problems/0031.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\216\222\345\210\227.md" "b/problems/0031.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\216\222\345\210\227.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 3cfb673a29..4bbf20fbb8
--- "a/problems/0031.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\216\222\345\210\227.md"
+++ "b/problems/0031.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\216\222\345\210\227.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
@@ -69,7 +67,7 @@
以求1243为例,流程如图:
- +
+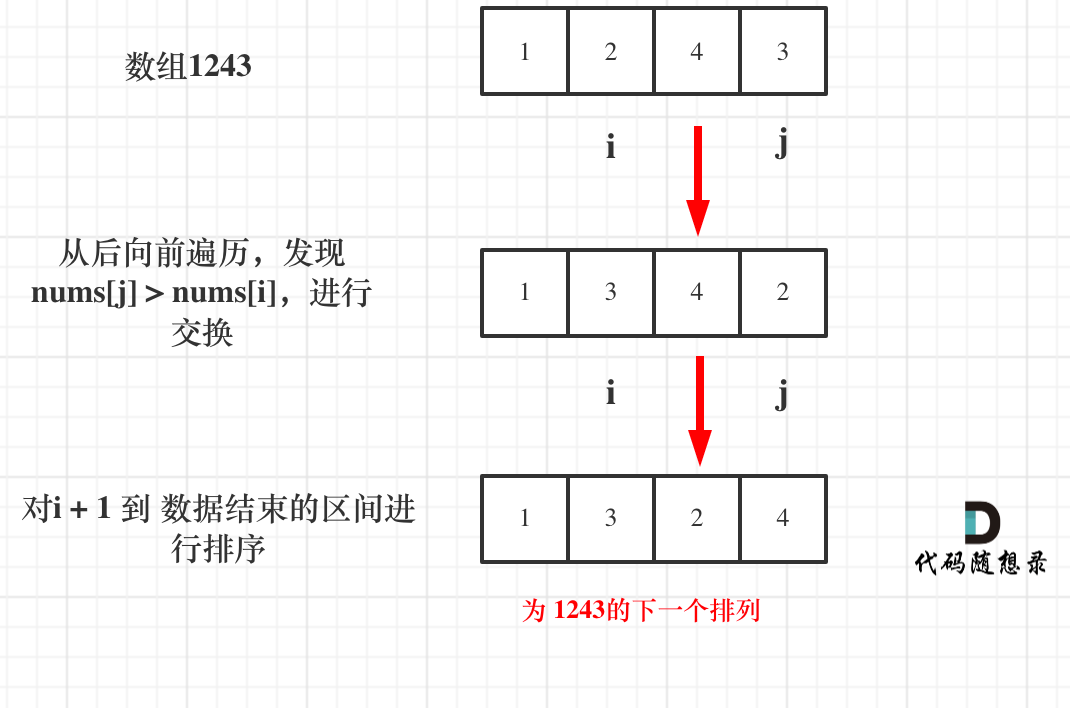 对应的C++代码如下:
@@ -268,8 +266,4 @@ var nextPermutation = function(nums) {
```
-
对应的C++代码如下:
@@ -268,8 +266,4 @@ var nextPermutation = function(nums) {
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0034.\345\234\250\346\216\222\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\344\270\255\346\237\245\346\211\276\345\205\203\347\264\240\347\232\204\347\254\254\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\222\214\346\234\200\345\220\216\344\270\200\344\270\252\344\275\215\347\275\256.md" "b/problems/0034.\345\234\250\346\216\222\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\344\270\255\346\237\245\346\211\276\345\205\203\347\264\240\347\232\204\347\254\254\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\222\214\346\234\200\345\220\216\344\270\200\344\270\252\344\275\215\347\275\256.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 22936fef13..37248e4819
--- "a/problems/0034.\345\234\250\346\216\222\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\344\270\255\346\237\245\346\211\276\345\205\203\347\264\240\347\232\204\347\254\254\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\222\214\346\234\200\345\220\216\344\270\200\344\270\252\344\275\215\347\275\256.md"
+++ "b/problems/0034.\345\234\250\346\216\222\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\344\270\255\346\237\245\346\211\276\345\205\203\347\264\240\347\232\204\347\254\254\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\222\214\346\234\200\345\220\216\344\270\200\344\270\252\344\275\215\347\275\256.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0034.\345\234\250\346\216\222\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\344\270\255\346\237\245\346\211\276\345\205\203\347\264\240\347\232\204\347\254\254\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\222\214\346\234\200\345\220\216\344\270\200\344\270\252\344\275\215\347\275\256.md" "b/problems/0034.\345\234\250\346\216\222\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\344\270\255\346\237\245\346\211\276\345\205\203\347\264\240\347\232\204\347\254\254\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\222\214\346\234\200\345\220\216\344\270\200\344\270\252\344\275\215\347\275\256.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 22936fef13..37248e4819
--- "a/problems/0034.\345\234\250\346\216\222\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\344\270\255\346\237\245\346\211\276\345\205\203\347\264\240\347\232\204\347\254\254\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\222\214\346\234\200\345\220\216\344\270\200\344\270\252\344\275\215\347\275\256.md"
+++ "b/problems/0034.\345\234\250\346\216\222\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\344\270\255\346\237\245\346\211\276\345\205\203\347\264\240\347\232\204\347\254\254\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\222\214\346\234\200\345\220\216\344\270\200\344\270\252\344\275\215\347\275\256.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 34. 在排序数组中查找元素的第一个和最后一个位置
@@ -233,7 +231,7 @@ class Solution {
if (index == -1) { // nums 中不存在 target,直接返回 {-1, -1}
return new int[] {-1, -1}; // 匿名数组
}
- // nums 中存在 targe,则左右滑动指针,来找到符合题意的区间
+ // nums 中存在 target,则左右滑动指针,来找到符合题意的区间
int left = index;
int right = index;
// 向左滑动,找左边界
@@ -450,7 +448,7 @@ class Solution:
return -1
index = binarySearch(nums, target)
if index == -1:return [-1, -1] # nums 中不存在 target,直接返回 {-1, -1}
- # nums 中存在 targe,则左右滑动指针,来找到符合题意的区间
+ # nums 中存在 target,则左右滑动指针,来找到符合题意的区间
left, right = index, index
# 向左滑动,找左边界
while left -1 >=0 and nums[left - 1] == target: left -=1
@@ -854,8 +852,4 @@ int* searchRange(int* nums, int numsSize, int target, int* returnSize){
}
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0035.\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\217\222\345\205\245\344\275\215\347\275\256.md" "b/problems/0035.\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\217\222\345\205\245\344\275\215\347\275\256.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 80b7e40e4a..b48910eef7
--- "a/problems/0035.\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\217\222\345\205\245\344\275\215\347\275\256.md"
+++ "b/problems/0035.\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\217\222\345\205\245\344\275\215\347\275\256.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0035.\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\217\222\345\205\245\344\275\215\347\275\256.md" "b/problems/0035.\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\217\222\345\205\245\344\275\215\347\275\256.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 80b7e40e4a..b48910eef7
--- "a/problems/0035.\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\217\222\345\205\245\344\275\215\347\275\256.md"
+++ "b/problems/0035.\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\217\222\345\205\245\344\275\215\347\275\256.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
@@ -43,7 +41,7 @@
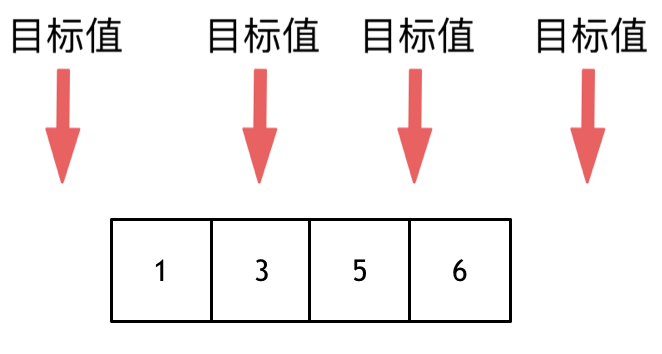
这道题目,要在数组中插入目标值,无非是这四种情况。
-
+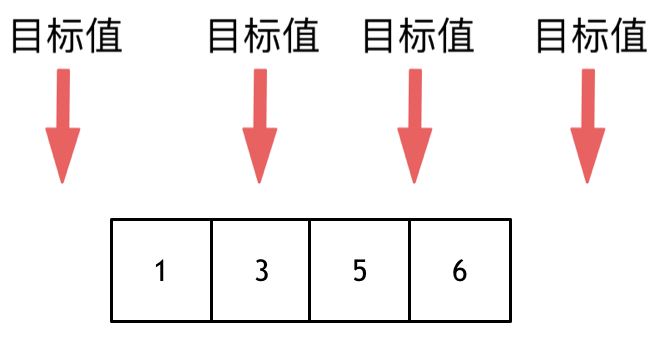
* 目标值在数组所有元素之前
* 目标值等于数组中某一个元素
@@ -84,14 +82,14 @@ public:
效率如下:
-
+
### 二分法
既然暴力解法的时间复杂度是O(n),就要尝试一下使用二分查找法。
-
+
大家注意这道题目的前提是数组是有序数组,这也是使用二分查找的基础条件。
@@ -101,7 +99,7 @@ public:
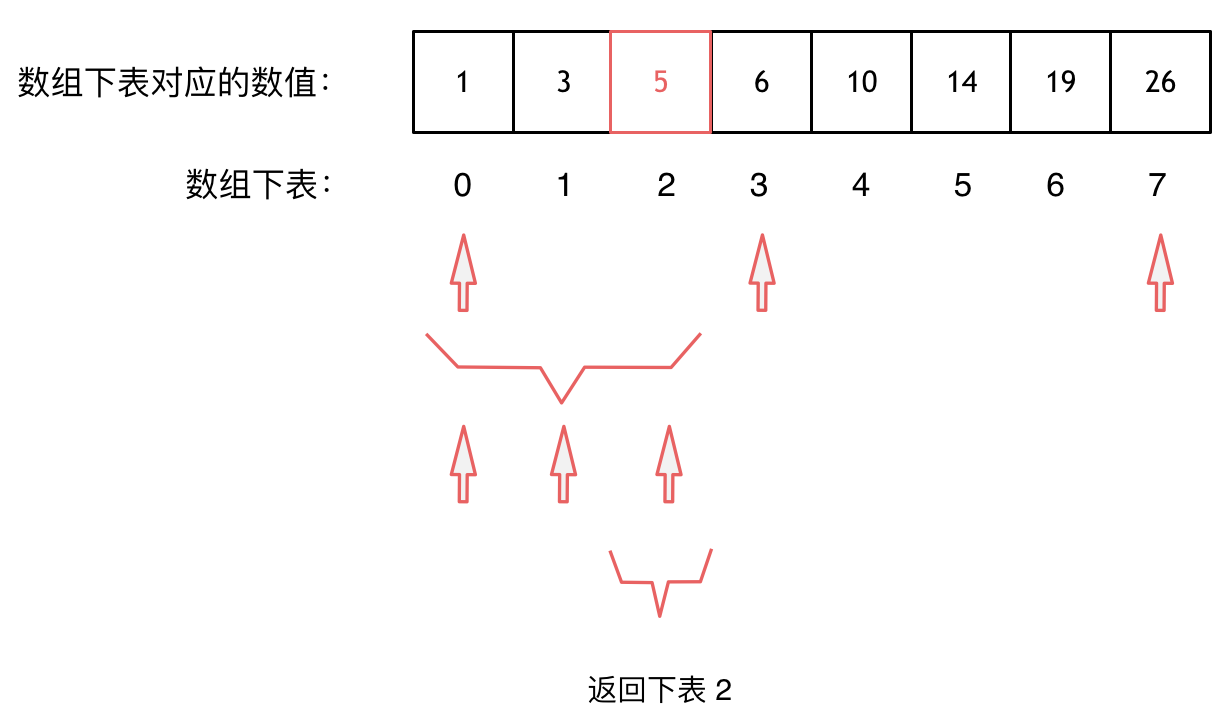
大体讲解一下二分法的思路,这里来举一个例子,例如在这个数组中,使用二分法寻找元素为5的位置,并返回其下标。
-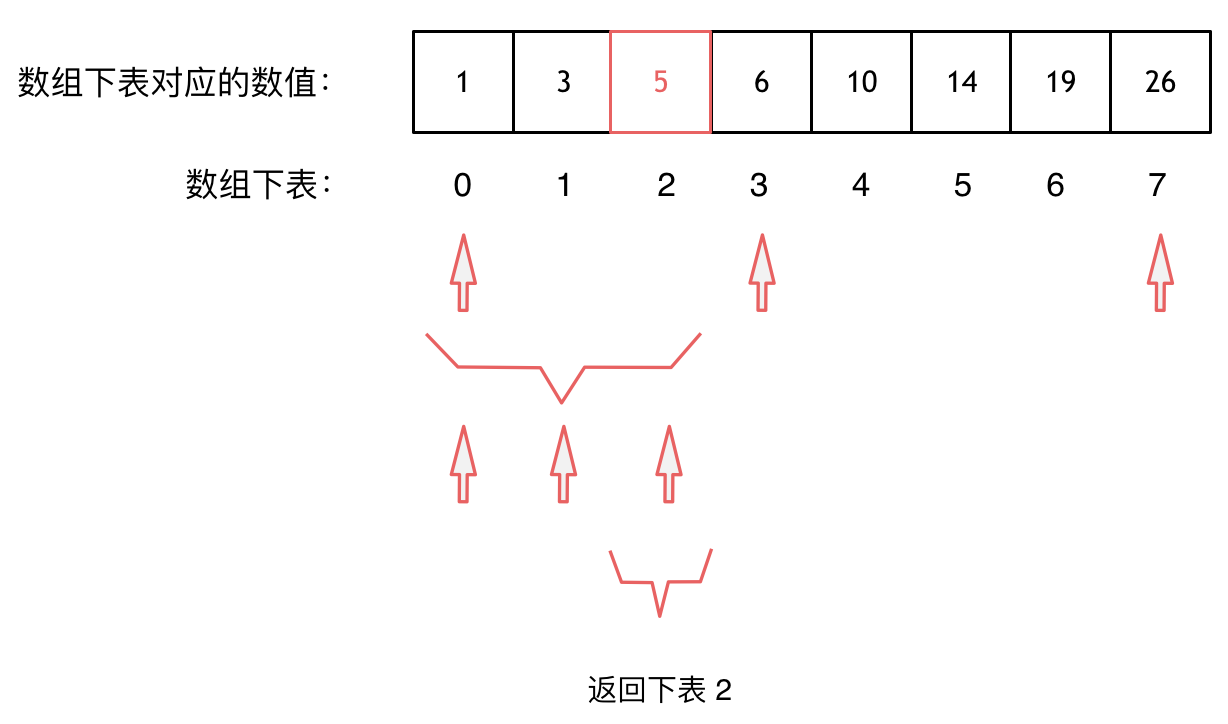
+
二分查找涉及的很多的边界条件,逻辑比较简单,就是写不好。
@@ -152,7 +150,7 @@ public:
* 空间复杂度:O(1)
效率如下:
-
+
### 二分法第二种写法
@@ -313,18 +311,18 @@ func searchInsert(nums []int, target int) int {
```rust
impl Solution {
- pub fn search_insert(nums: Vec, target: i32) -> i32 {
- let mut left = 0;
- let mut right = nums.len();
- while left < right {
+ pub fn search_insert(nums: Vec, target: i32) -> i32 {
+ use std::cmp::Ordering::{Equal, Greater, Less};
+ let (mut left, mut right) = (0, nums.len() as i32 - 1);
+ while left <= right {
let mid = (left + right) / 2;
- match nums[mid].cmp(&target) {
- Ordering::Less => left = mid + 1,
- Ordering::Equal => return ((left + right) / 2) as i32,
- Ordering::Greater => right = mid,
+ match nums[mid as usize].cmp(&target) {
+ Less => left = mid + 1,
+ Equal => return mid,
+ Greater => right = mid - 1,
}
}
- ((left + right) / 2) as i32
+ right + 1
}
}
```
@@ -332,6 +330,7 @@ impl Solution {
### Python
```python
+# 第一种二分法: [left, right]左闭右闭区间
class Solution:
def searchInsert(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> int:
left, right = 0, len(nums) - 1
@@ -348,6 +347,26 @@ class Solution:
return right + 1
```
+```python
+# 第二种二分法: [left, right)左闭右开区间
+class Solution:
+ def searchInsert(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> int:
+ left = 0
+ right = len(nums)
+
+ while (left < right):
+ middle = (left + right) // 2
+
+ if nums[middle] > target:
+ right = middle
+ elif nums[middle] < target:
+ left = middle + 1
+ else:
+ return middle
+
+ return right
+```
+
### JavaScript
```js
@@ -527,8 +546,4 @@ int searchInsert(int* nums, int numsSize, int target){
}
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0037.\350\247\243\346\225\260\347\213\254.md" "b/problems/0037.\350\247\243\346\225\260\347\213\254.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index d96e59dfeb..204f0cc092
--- "a/problems/0037.\350\247\243\346\225\260\347\213\254.md"
+++ "b/problems/0037.\350\247\243\346\225\260\347\213\254.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0037.\350\247\243\346\225\260\347\213\254.md" "b/problems/0037.\350\247\243\346\225\260\347\213\254.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index d96e59dfeb..204f0cc092
--- "a/problems/0037.\350\247\243\346\225\260\347\213\254.md"
+++ "b/problems/0037.\350\247\243\346\225\260\347\213\254.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
> 如果对回溯法理论还不清楚的同学,可以先看这个视频[视频来了!!带你学透回溯算法(理论篇)](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/wDd5azGIYWjbU0fdua_qBg)
@@ -20,11 +18,11 @@
数字 1-9 在每一个以粗实线分隔的 3x3 宫内只能出现一次。
空白格用 '.' 表示。
-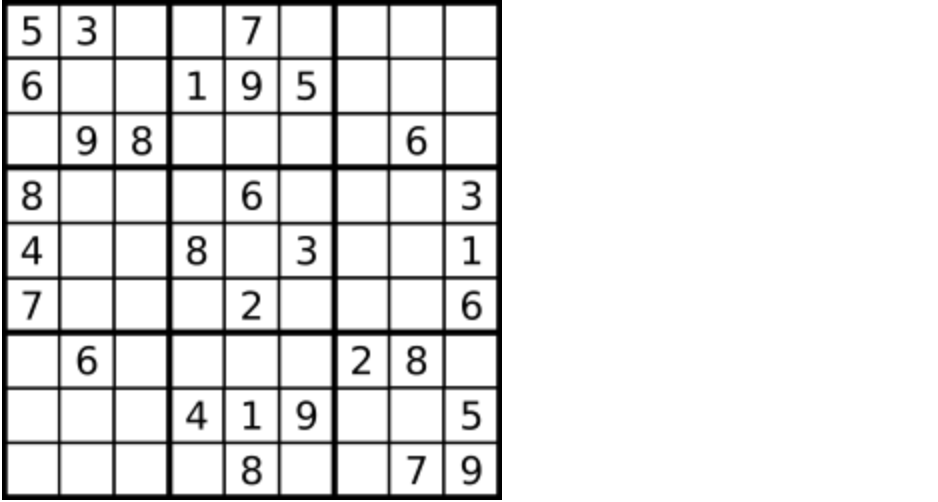
+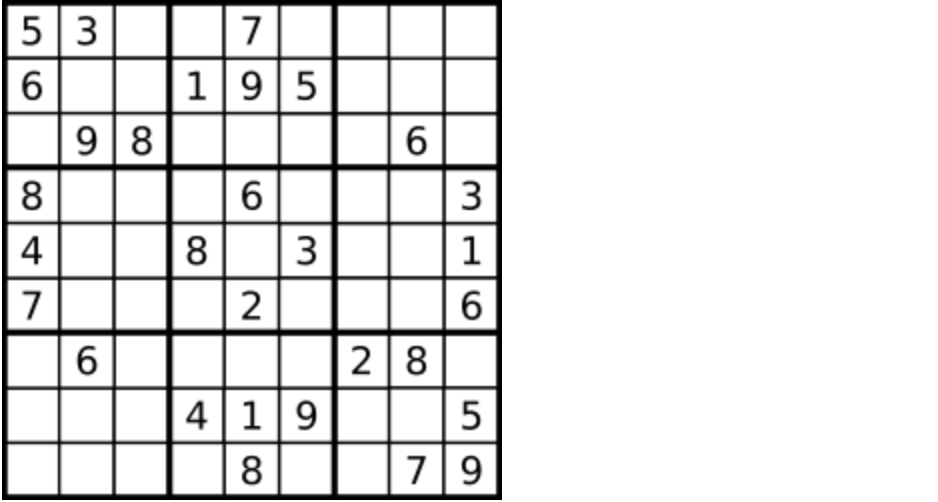
一个数独。
-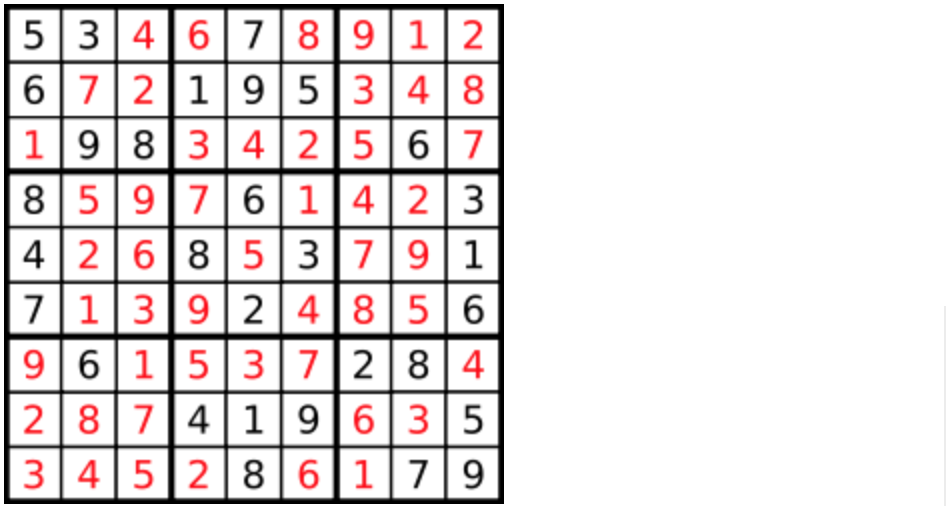
+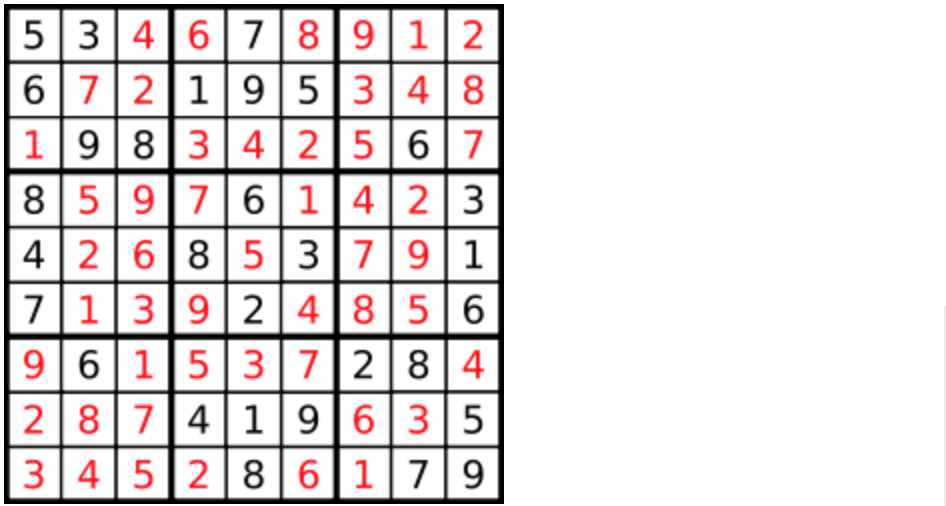
答案被标成红色。
@@ -54,7 +52,7 @@
因为这个树形结构太大了,我抽取一部分,如图所示:
-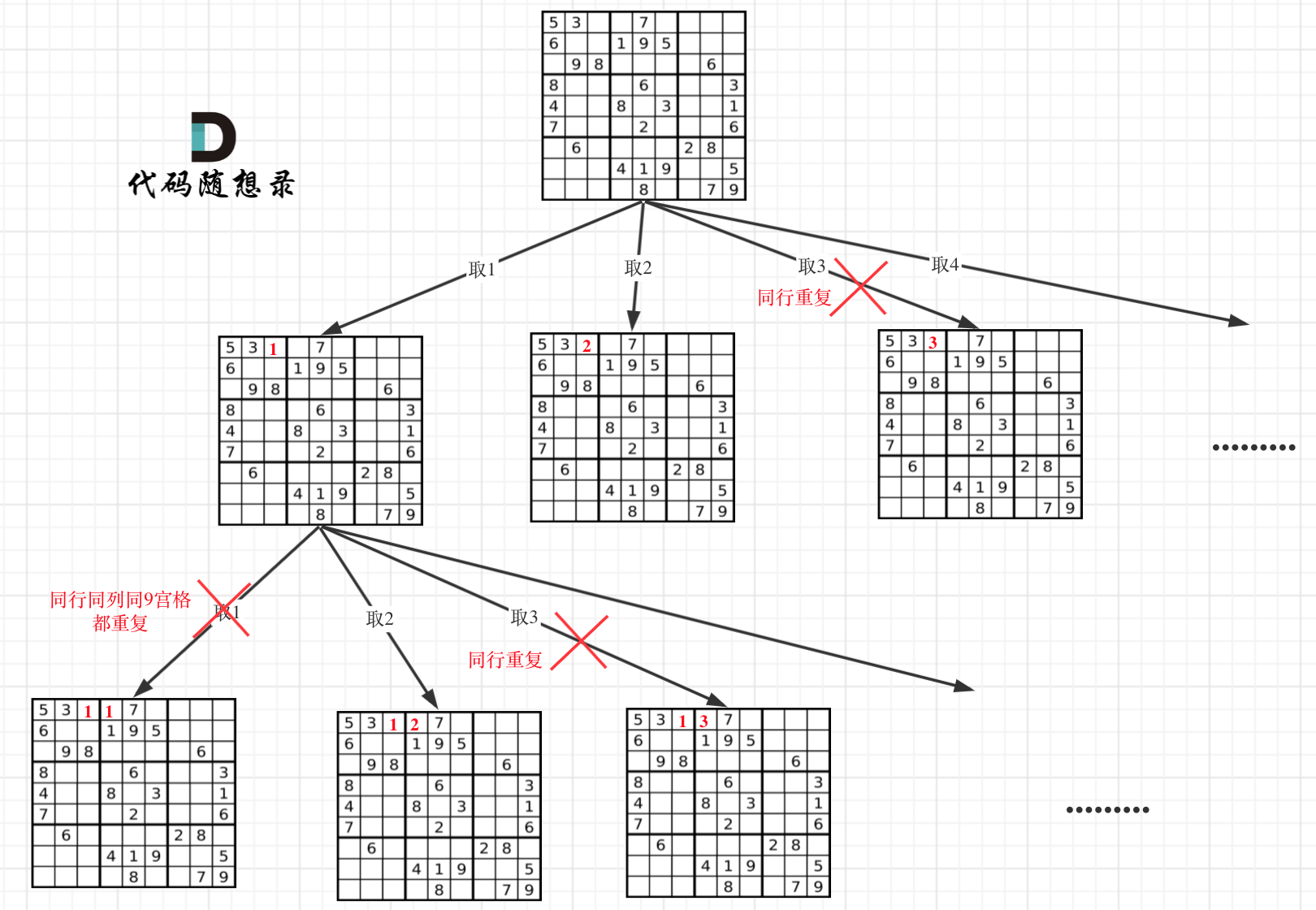
+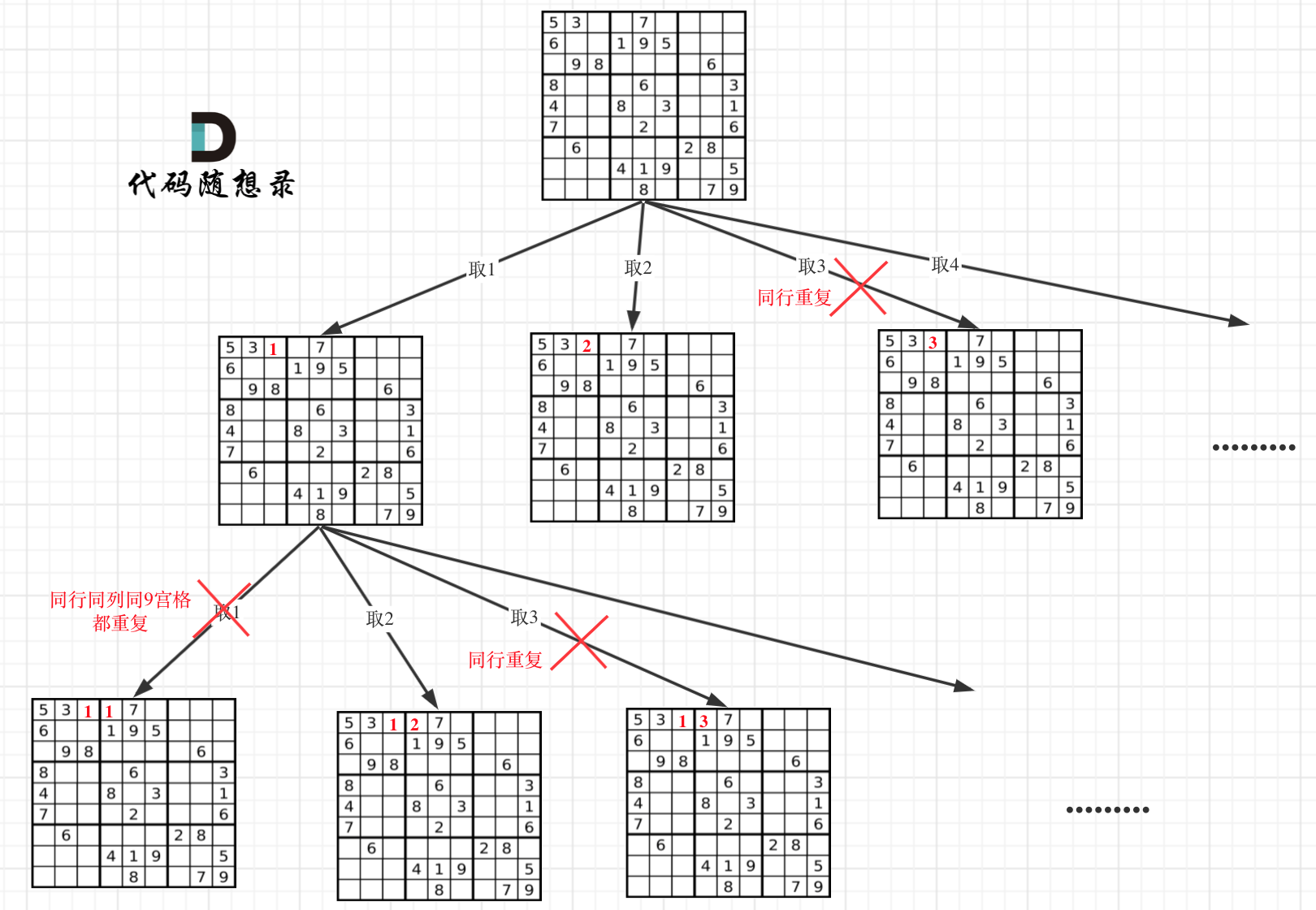
### 回溯三部曲
@@ -85,9 +83,9 @@ bool backtracking(vector>& board)
* 递归单层搜索逻辑
-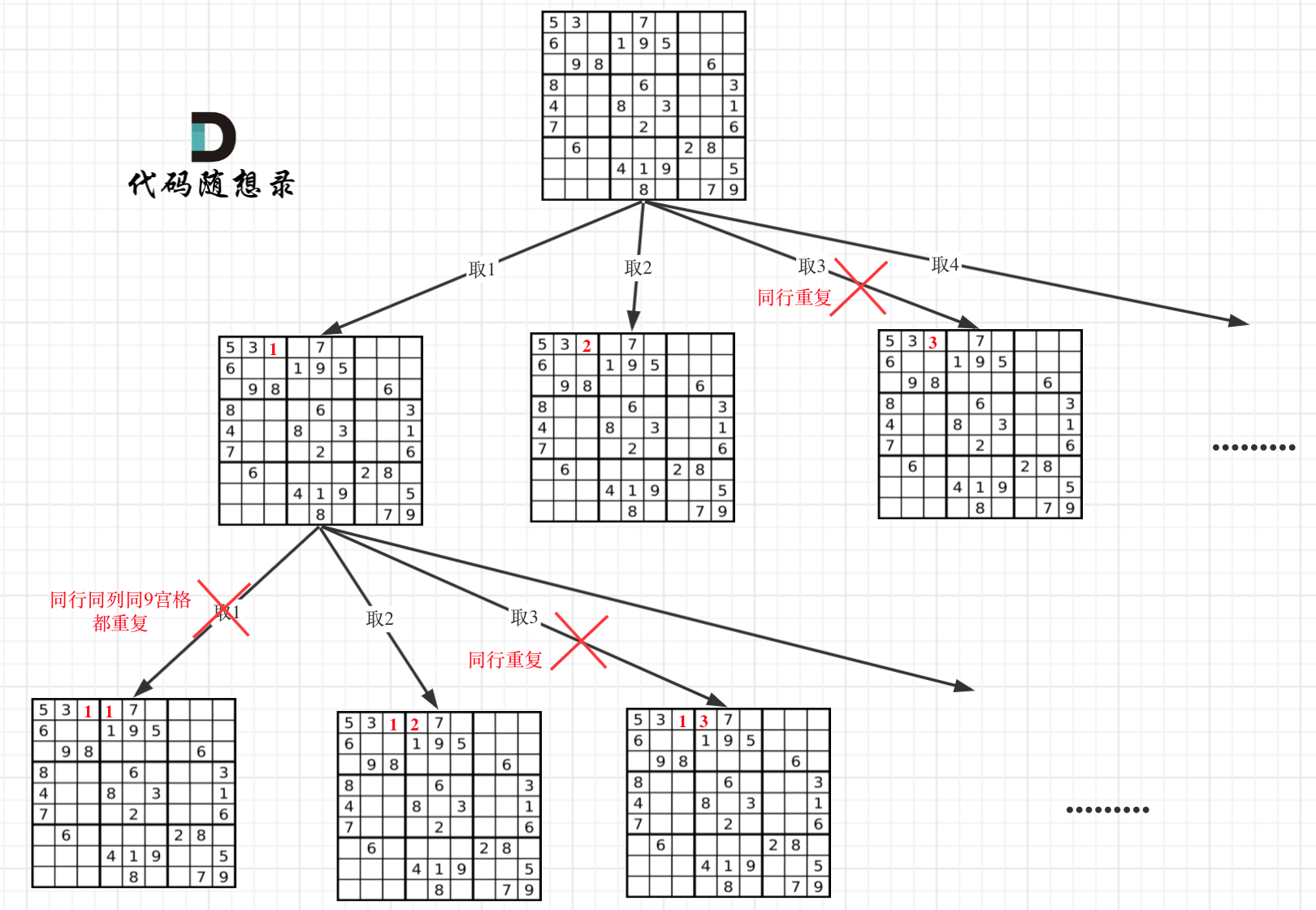
+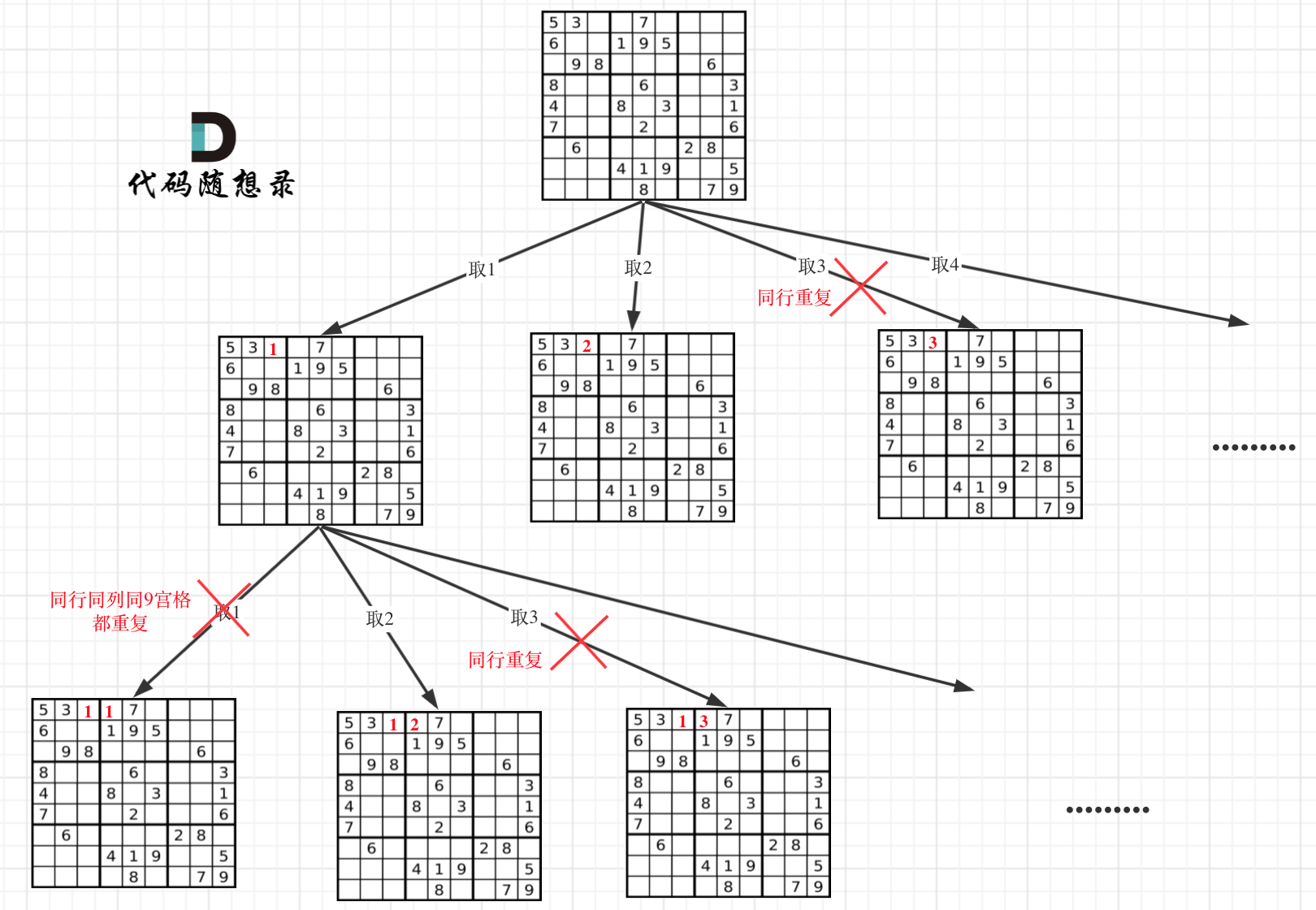
-在树形图中可以看出我们需要的是一个二维的递归(也就是两个for循环嵌套着递归)
+在树形图中可以看出我们需要的是一个二维的递归 (一行一列)
**一个for循环遍历棋盘的行,一个for循环遍历棋盘的列,一行一列确定下来之后,递归遍历这个位置放9个数字的可能性!**
@@ -224,7 +222,7 @@ public:
### Java
-
+解法一:
```java
class Solution {
public void solveSudoku(char[][] board) {
@@ -291,7 +289,73 @@ class Solution {
}
}
```
+解法二(bitmap标记)
+```
+class Solution{
+ int[] rowBit = new int[9];
+ int[] colBit = new int[9];
+ int[] square9Bit = new int[9];
+
+ public void solveSudoku(char[][] board) {
+ // 1 10 11
+ for (int y = 0; y < board.length; y++) {
+ for (int x = 0; x < board[y].length; x++) {
+ int numBit = 1 << (board[y][x] - '1');
+ rowBit[y] ^= numBit;
+ colBit[x] ^= numBit;
+ square9Bit[(y / 3) * 3 + x / 3] ^= numBit;
+ }
+ }
+ backtrack(board, 0);
+ }
+
+ public boolean backtrack(char[][] board, int n) {
+ if (n >= 81) {
+ return true;
+ }
+
+ // 快速算出行列编号 n/9 n%9
+ int row = n / 9;
+ int col = n % 9;
+
+ if (board[row][col] != '.') {
+ return backtrack(board, n + 1);
+ }
+
+ for (char c = '1'; c <= '9'; c++) {
+ int numBit = 1 << (c - '1');
+ if (!isValid(numBit, row, col)) continue;
+ {
+ board[row][col] = c; // 当前的数字放入到数组之中,
+ rowBit[row] ^= numBit; // 第一行rowBit[0],第一个元素eg: 1 , 0^1=1,第一个元素:4, 100^1=101,...
+ colBit[col] ^= numBit;
+ square9Bit[(row / 3) * 3 + col / 3] ^= numBit;
+ }
+ if (backtrack(board, n + 1)) return true;
+ {
+ board[row][col] = '.'; // 不满足条件,回退成'.'
+ rowBit[row] &= ~numBit; // 第一行rowBit[0],第一个元素eg: 1 , 101&=~1==>101&111111110==>100
+ colBit[col] &= ~numBit;
+ square9Bit[(row / 3) * 3 + col / 3] &= ~numBit;
+ }
+ }
+ return false;
+ }
+
+ boolean isValid(int numBit, int row, int col) {
+ // 左右
+ if ((rowBit[row] & numBit) > 0) return false;
+ // 上下
+ if ((colBit[col] & numBit) > 0) return false;
+ // 9宫格: 快速算出第n个九宫格,编号[0,8] , 编号=(row / 3) * 3 + col / 3
+ if ((square9Bit[(row / 3) * 3 + col / 3] & numBit) > 0) return false;
+ return true;
+ }
+
+}
+
+```
### Python
```python
@@ -300,40 +364,56 @@ class Solution:
"""
Do not return anything, modify board in-place instead.
"""
- self.backtracking(board)
-
- def backtracking(self, board: List[List[str]]) -> bool:
- # 若有解,返回True;若无解,返回False
- for i in range(len(board)): # 遍历行
- for j in range(len(board[0])): # 遍历列
- # 若空格内已有数字,跳过
- if board[i][j] != '.': continue
- for k in range(1, 10):
- if self.is_valid(i, j, k, board):
- board[i][j] = str(k)
- if self.backtracking(board): return True
- board[i][j] = '.'
- # 若数字1-9都不能成功填入空格,返回False无解
- return False
- return True # 有解
-
- def is_valid(self, row: int, col: int, val: int, board: List[List[str]]) -> bool:
- # 判断同一行是否冲突
- for i in range(9):
- if board[row][i] == str(val):
- return False
- # 判断同一列是否冲突
- for j in range(9):
- if board[j][col] == str(val):
- return False
- # 判断同一九宫格是否有冲突
- start_row = (row // 3) * 3
- start_col = (col // 3) * 3
- for i in range(start_row, start_row + 3):
- for j in range(start_col, start_col + 3):
- if board[i][j] == str(val):
- return False
- return True
+ row_used = [set() for _ in range(9)]
+ col_used = [set() for _ in range(9)]
+ box_used = [set() for _ in range(9)]
+ for row in range(9):
+ for col in range(9):
+ num = board[row][col]
+ if num == ".":
+ continue
+ row_used[row].add(num)
+ col_used[col].add(num)
+ box_used[(row // 3) * 3 + col // 3].add(num)
+ self.backtracking(0, 0, board, row_used, col_used, box_used)
+
+ def backtracking(
+ self,
+ row: int,
+ col: int,
+ board: List[List[str]],
+ row_used: List[List[int]],
+ col_used: List[List[int]],
+ box_used: List[List[int]],
+ ) -> bool:
+ if row == 9:
+ return True
+
+ next_row, next_col = (row, col + 1) if col < 8 else (row + 1, 0)
+ if board[row][col] != ".":
+ return self.backtracking(
+ next_row, next_col, board, row_used, col_used, box_used
+ )
+
+ for num in map(str, range(1, 10)):
+ if (
+ num not in row_used[row]
+ and num not in col_used[col]
+ and num not in box_used[(row // 3) * 3 + col // 3]
+ ):
+ board[row][col] = num
+ row_used[row].add(num)
+ col_used[col].add(num)
+ box_used[(row // 3) * 3 + col // 3].add(num)
+ if self.backtracking(
+ next_row, next_col, board, row_used, col_used, box_used
+ ):
+ return True
+ board[row][col] = "."
+ row_used[row].remove(num)
+ col_used[col].remove(num)
+ box_used[(row // 3) * 3 + col // 3].remove(num)
+ return False
```
### Go
@@ -394,7 +474,7 @@ func isvalid(row, col int, k byte, board [][]byte) bool {
-### Javascript
+### JavaScript
```Javascript
var solveSudoku = function(board) {
@@ -810,8 +890,4 @@ public class Solution
}
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0039.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214.md" "b/problems/0039.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 81558cc12c..d8dac0b45b
--- "a/problems/0039.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214.md"
+++ "b/problems/0039.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0039.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214.md" "b/problems/0039.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 81558cc12c..d8dac0b45b
--- "a/problems/0039.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214.md"
+++ "b/problems/0039.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
@@ -52,7 +50,7 @@ candidates 中的数字可以无限制重复被选取。
本题搜索的过程抽象成树形结构如下:
-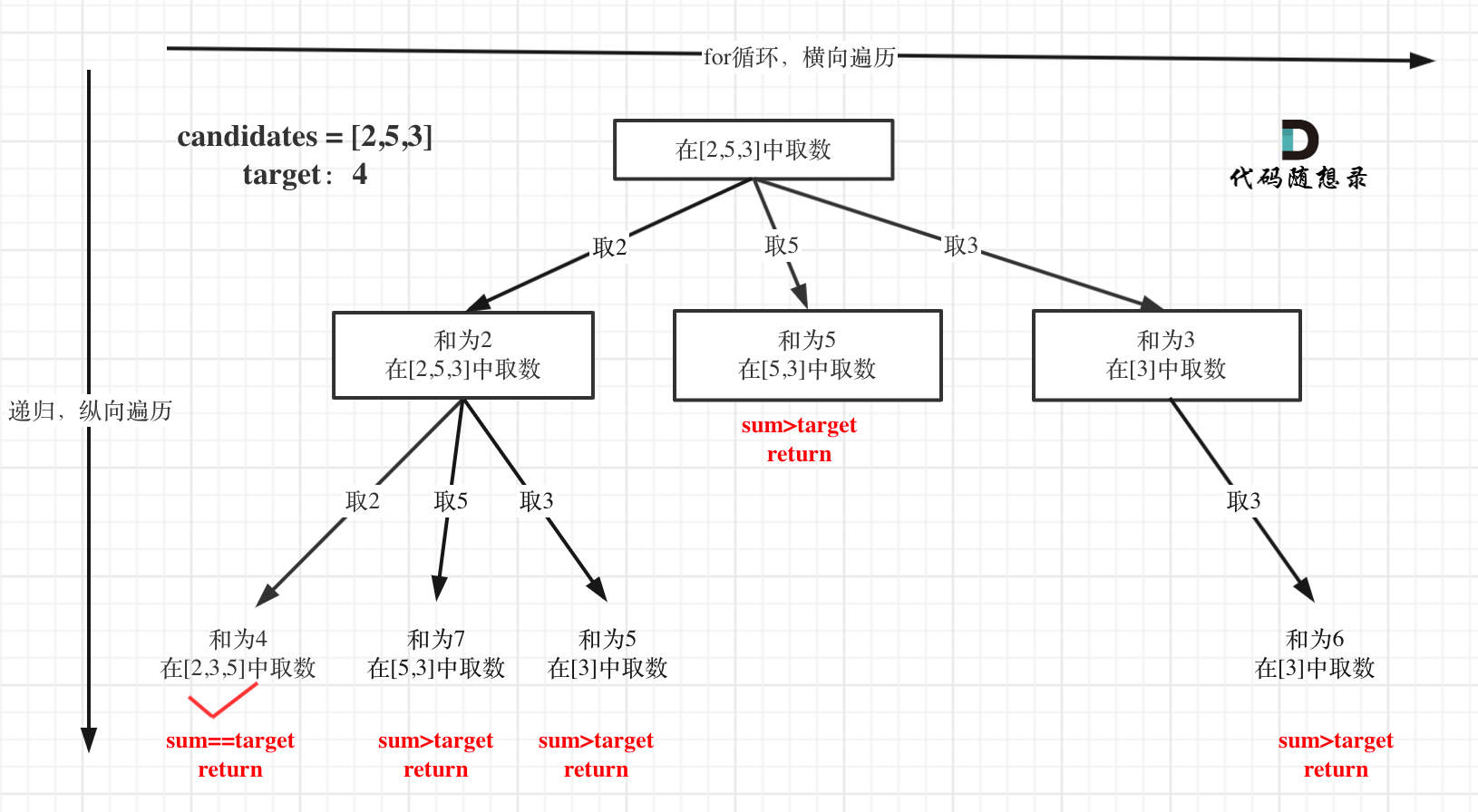
+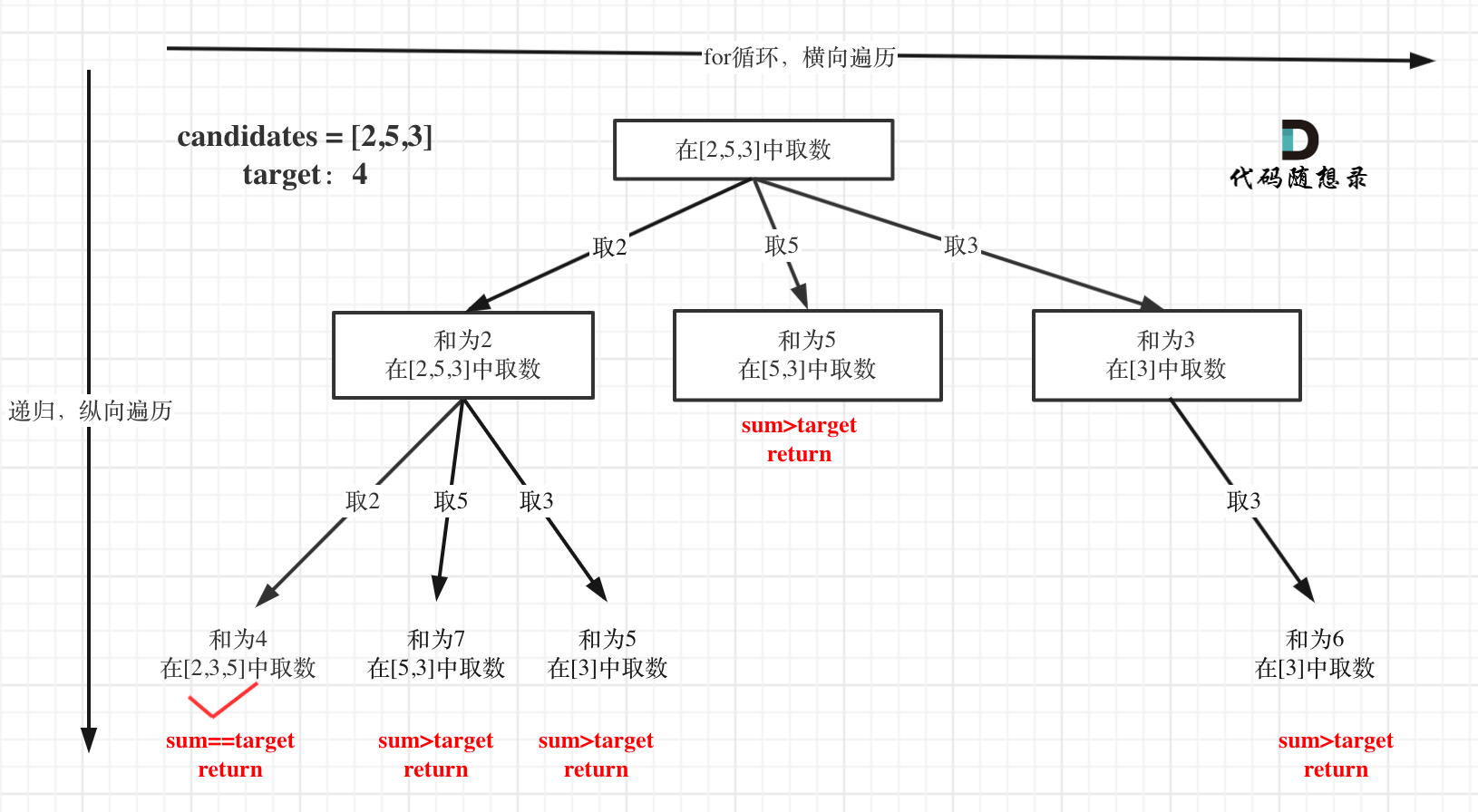
注意图中叶子节点的返回条件,因为本题没有组合数量要求,仅仅是总和的限制,所以递归没有层数的限制,只要选取的元素总和超过target,就返回!
而在[77.组合](https://programmercarl.com/0077.组合.html)和[216.组合总和III](https://programmercarl.com/0216.组合总和III.html) 中都可以知道要递归K层,因为要取k个元素的组合。
@@ -87,7 +85,7 @@ void backtracking(vector& candidates, int target, int sum, int startIndex)
在如下树形结构中:
-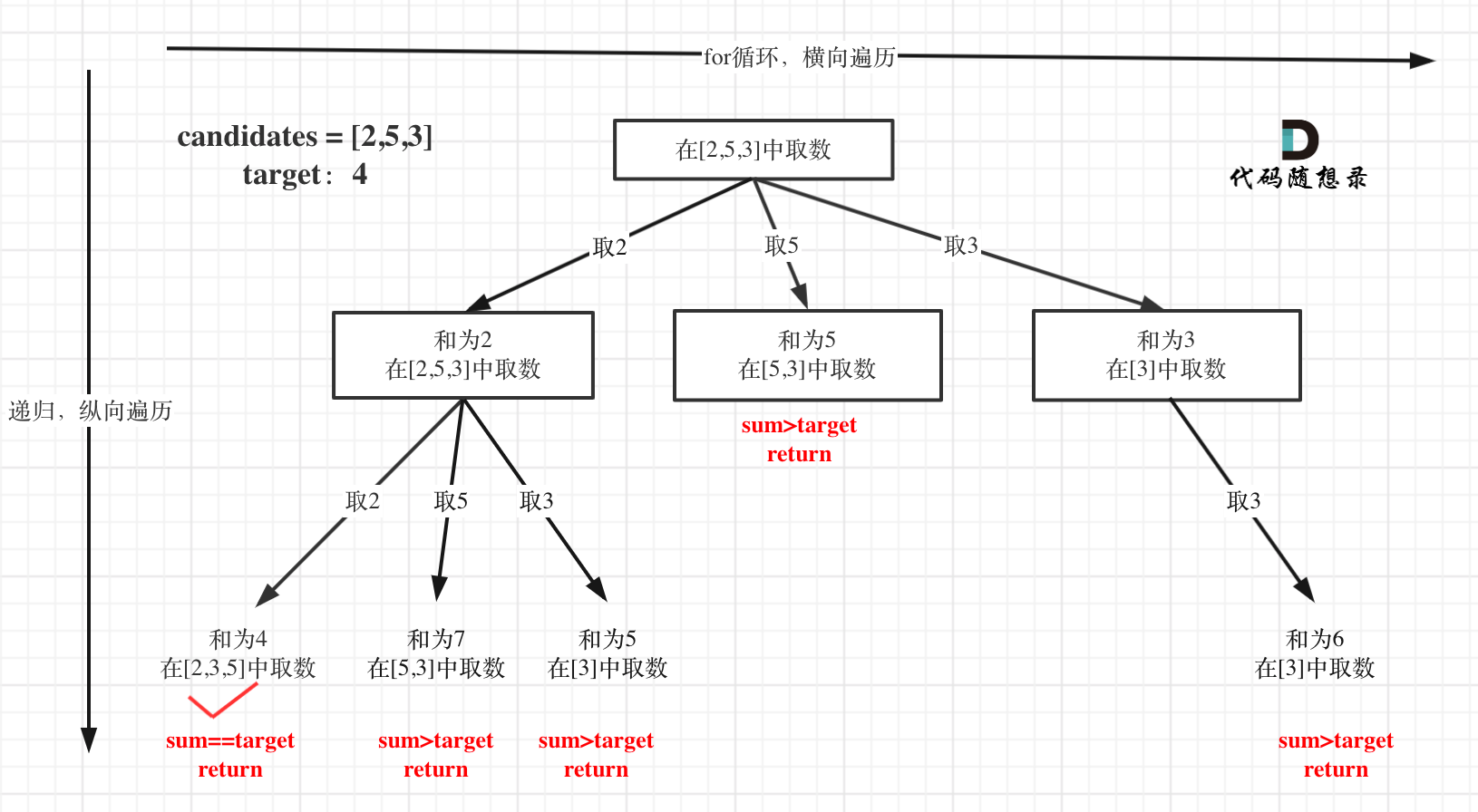
+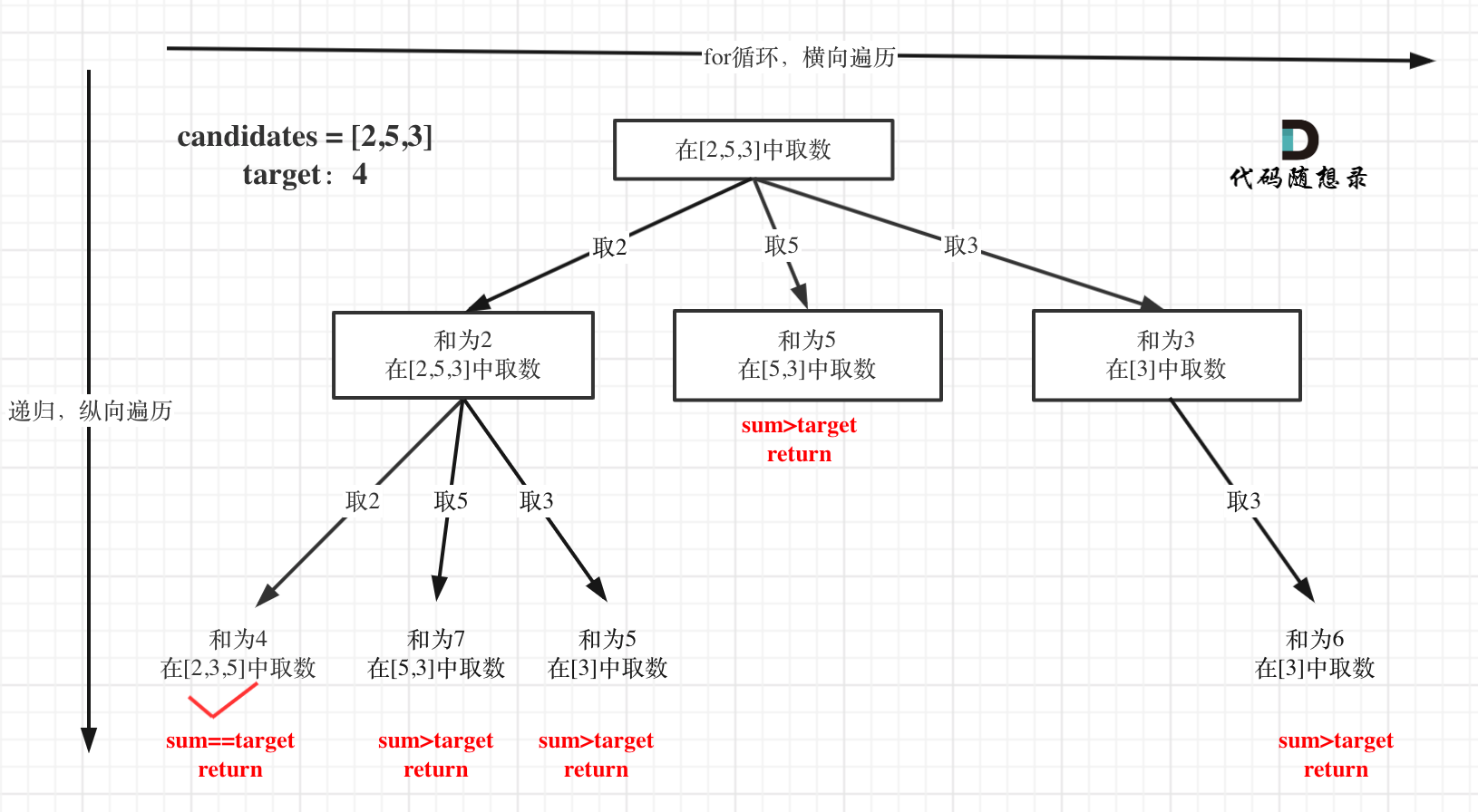
从叶子节点可以清晰看到,终止只有两种情况,sum大于target和sum等于target。
@@ -160,7 +158,7 @@ public:
在这个树形结构中:
-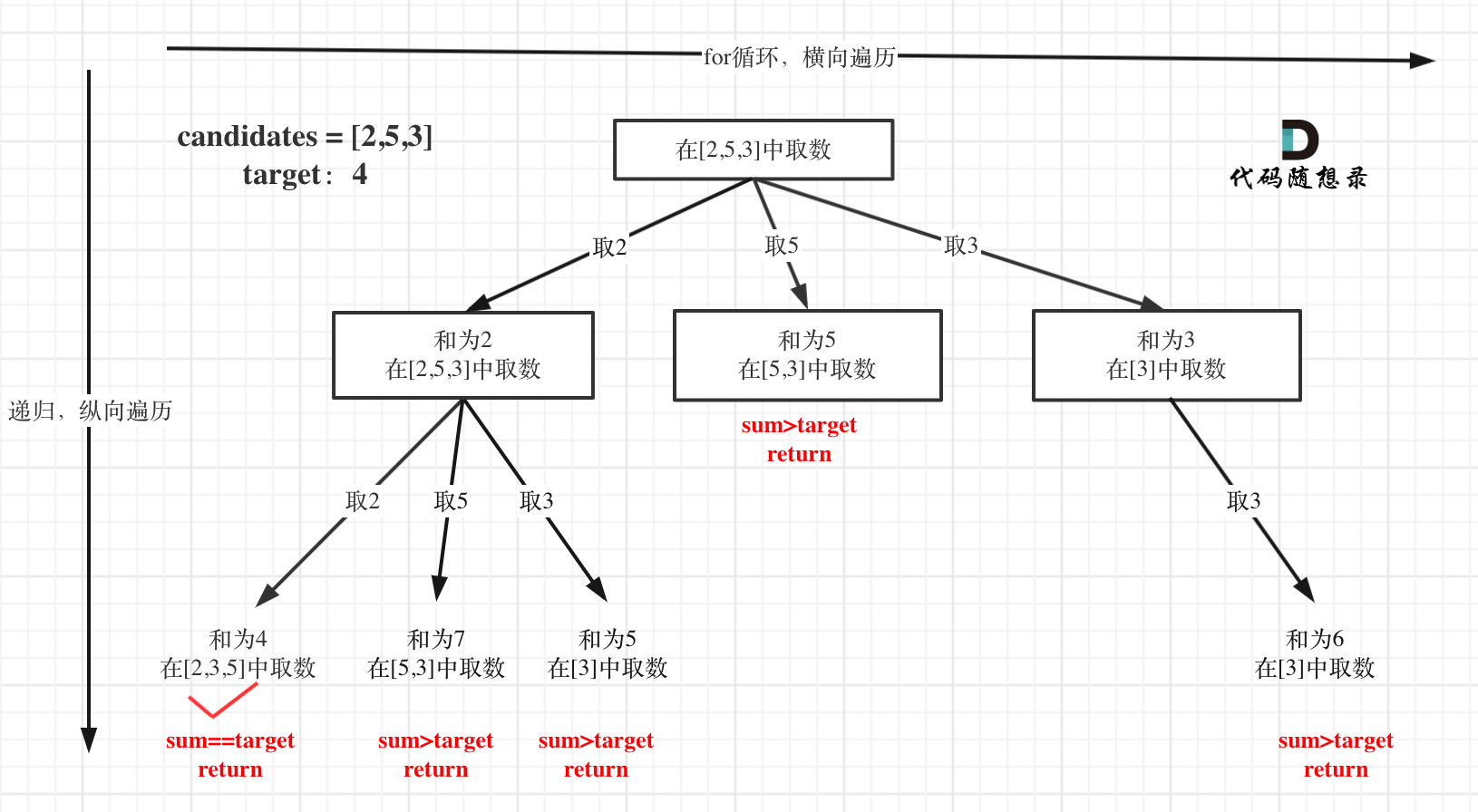
+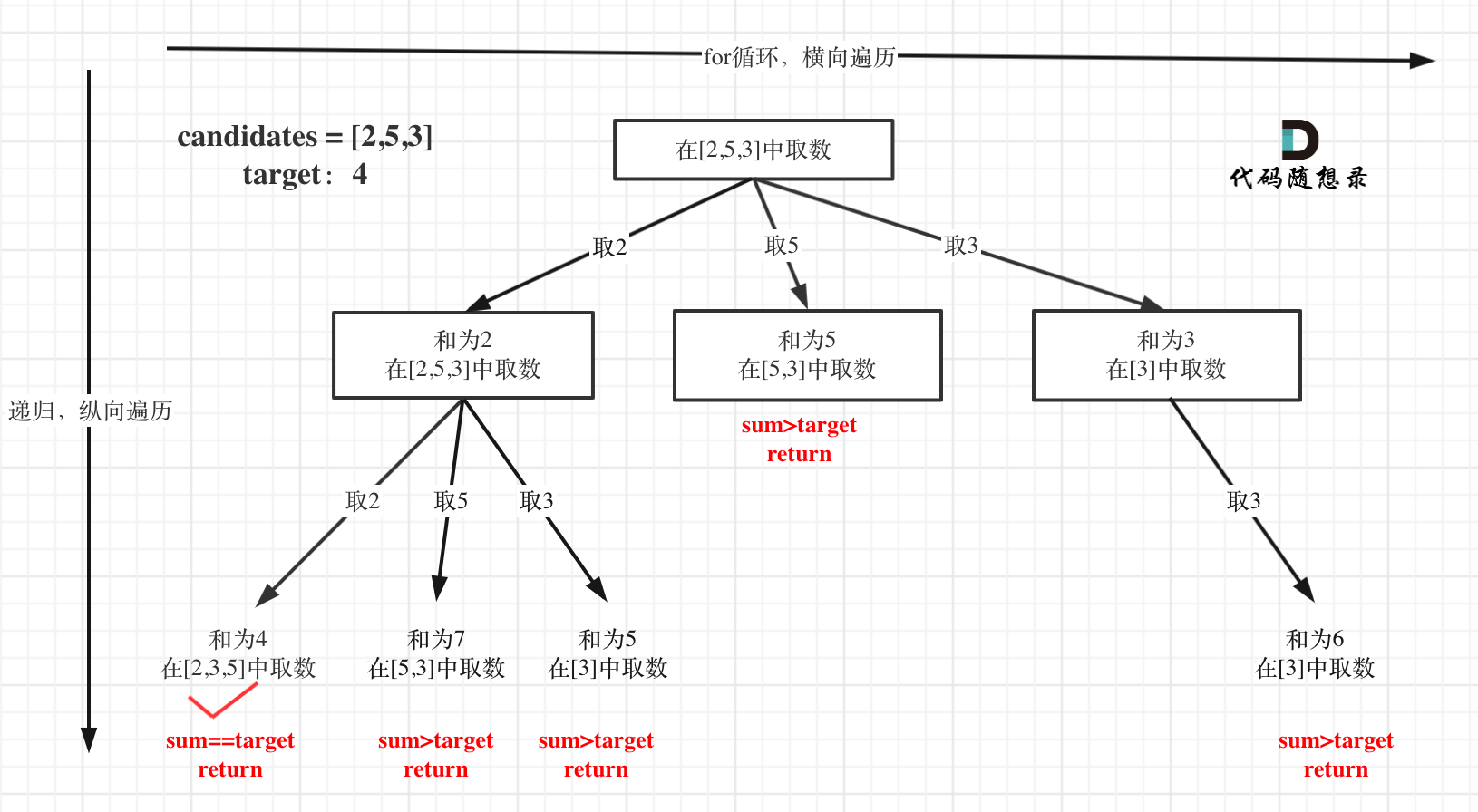
以及上面的版本一的代码大家可以看到,对于sum已经大于target的情况,其实是依然进入了下一层递归,只是下一层递归结束判断的时候,会判断sum > target的话就返回。
@@ -173,7 +171,7 @@ public:
如图:
-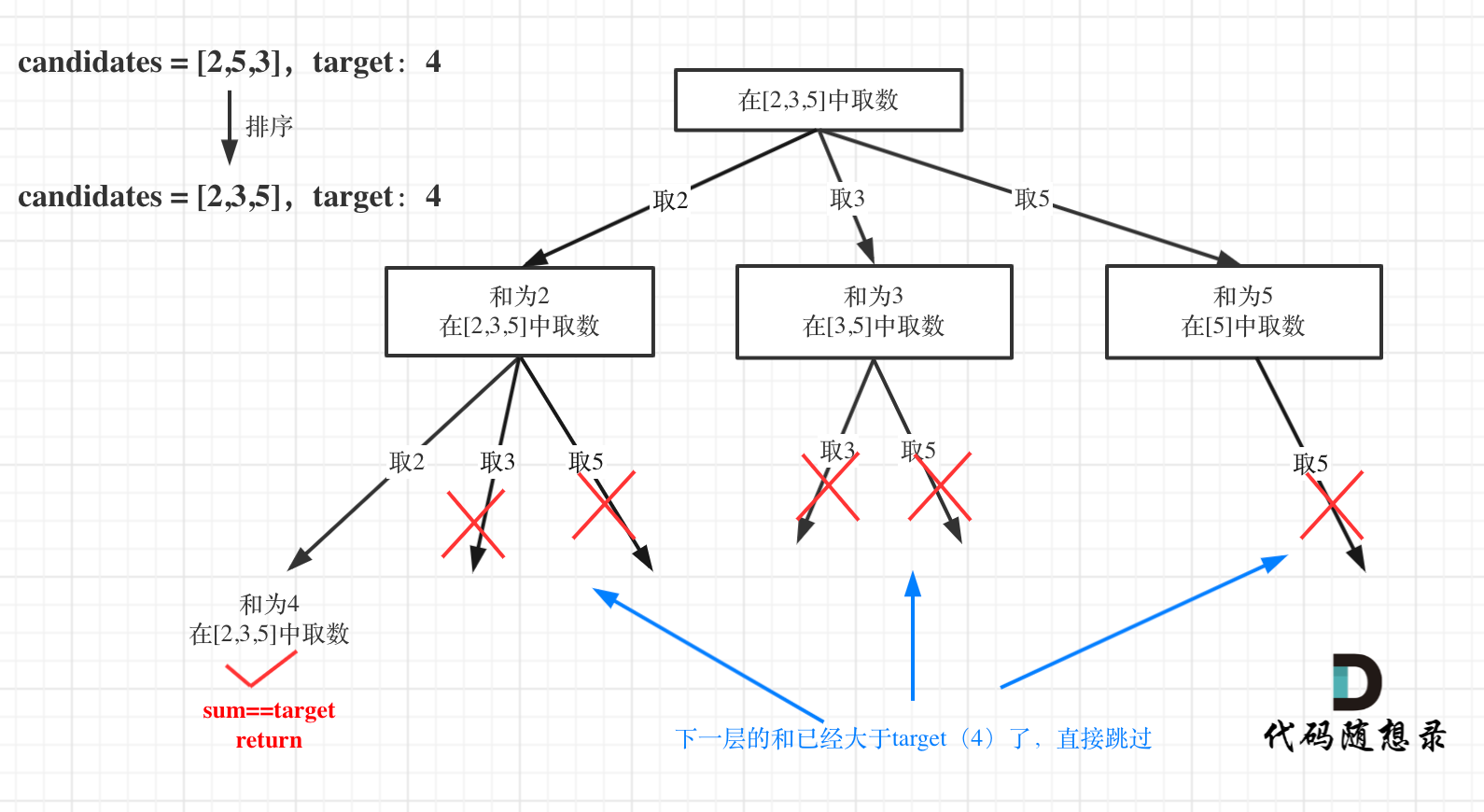
+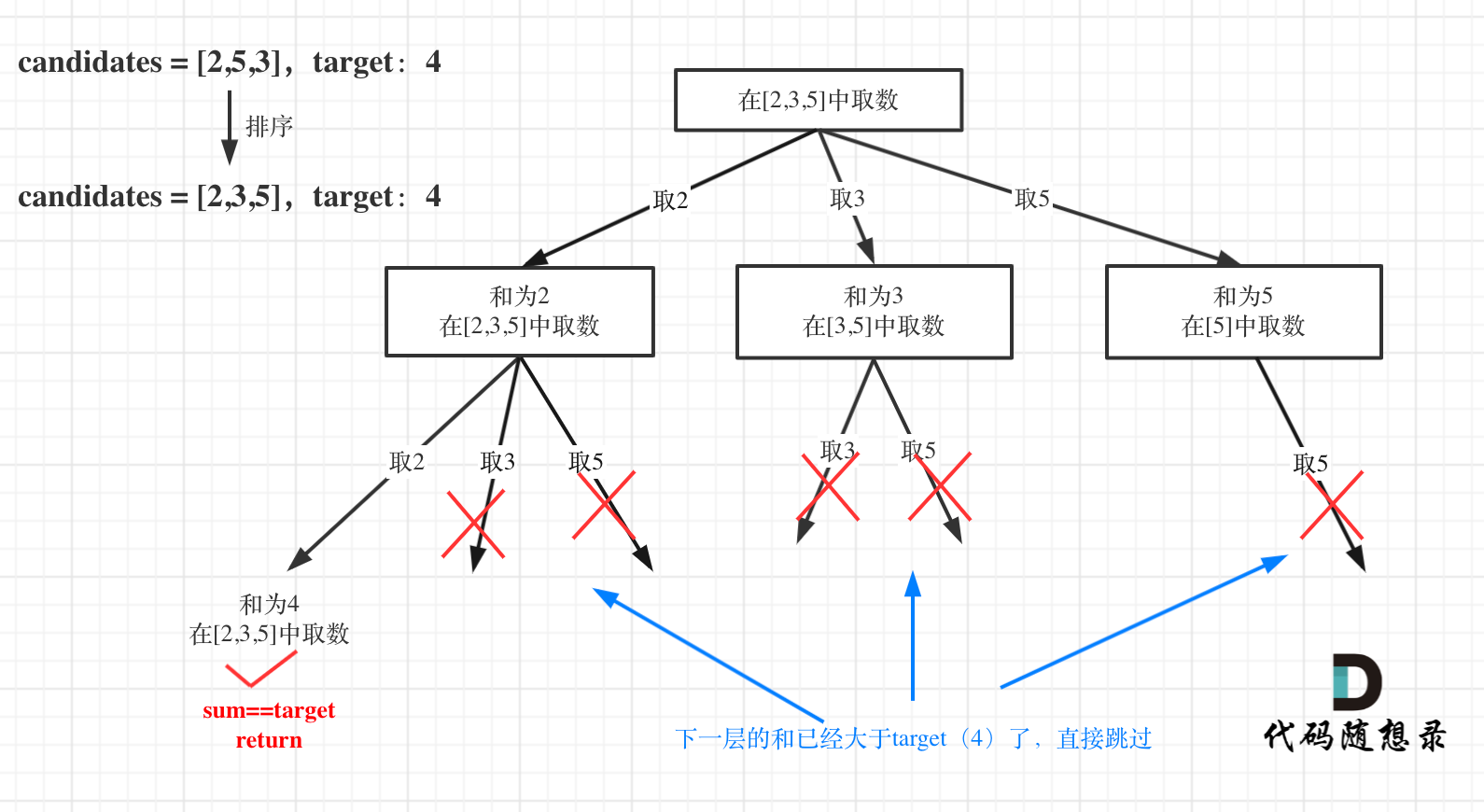
for循环剪枝代码如下:
@@ -311,7 +309,7 @@ class Solution:
for i in range(startIndex, len(candidates)):
if total + candidates[i] > target:
- continue
+ break
total += candidates[i]
path.append(candidates[i])
self.backtracking(candidates, target, total, i, path, result)
@@ -660,8 +658,4 @@ public class Solution
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0040.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214II.md" "b/problems/0040.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 994b04b82f..0d3972662f
--- "a/problems/0040.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0040.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214II.md"
@@ -1,12 +1,8 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0040.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214II.md" "b/problems/0040.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 994b04b82f..0d3972662f
--- "a/problems/0040.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0040.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214II.md"
@@ -1,12 +1,8 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-> 这篇可以说是全网把组合问题如何去重,讲的最清晰的了!
-
# 40.组合总和II
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/combination-sum-ii/)
@@ -80,7 +76,7 @@ candidates 中的每个数字在每个组合中只能使用一次。
选择过程树形结构如图所示:
-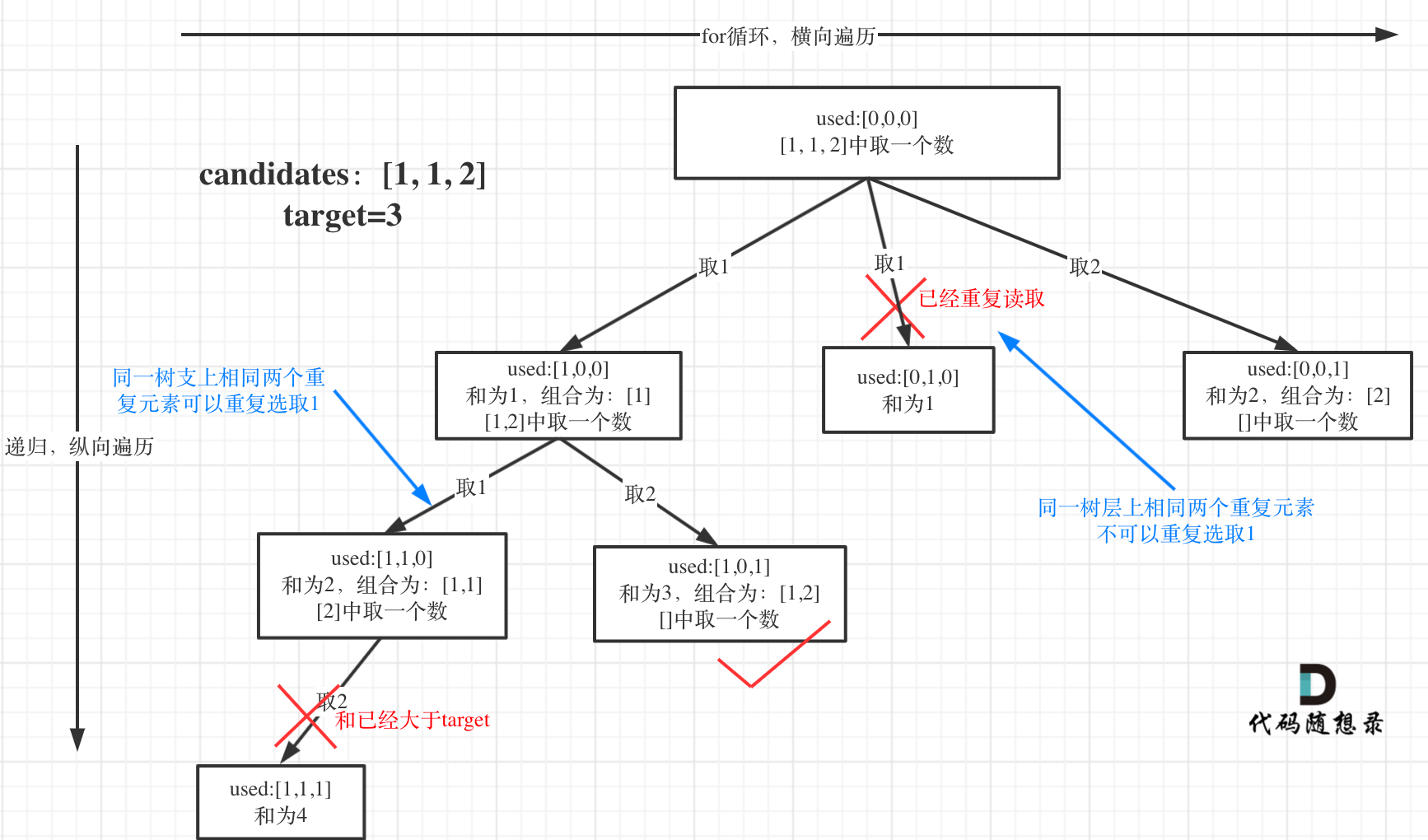
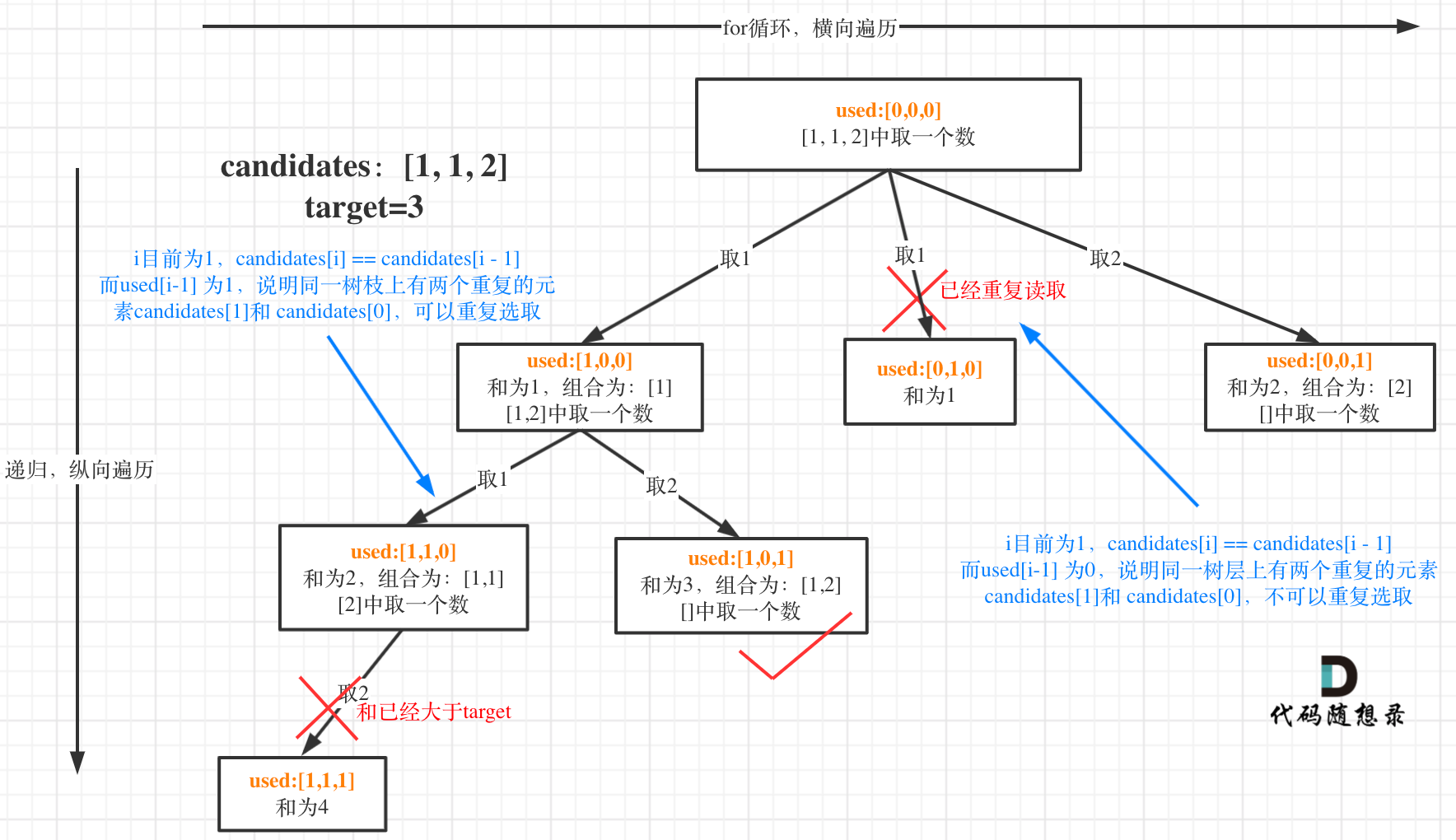
+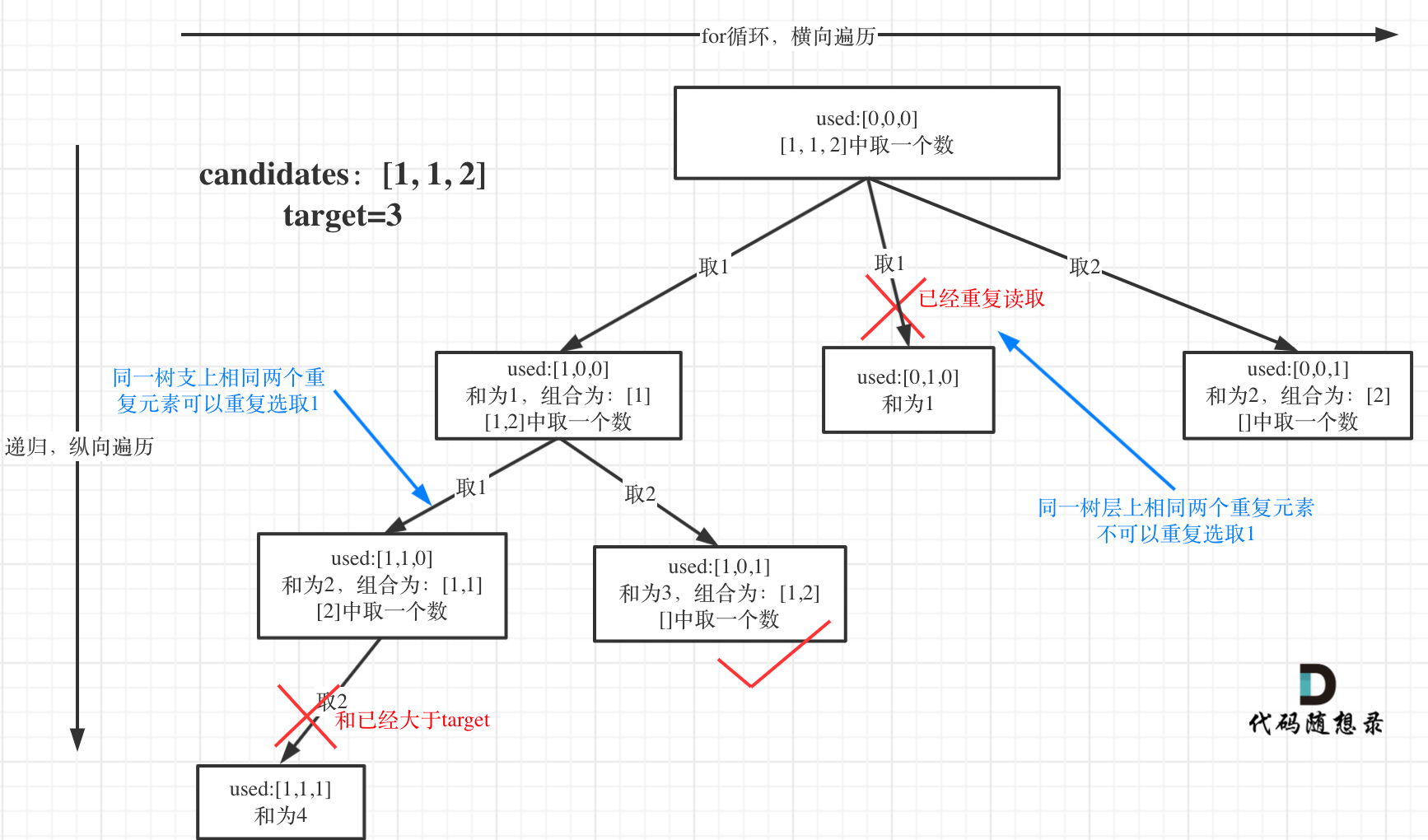
可以看到图中,每个节点相对于 [39.组合总和](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/FLg8G6EjVcxBjwCbzpACPw)我多加了used数组,这个used数组下面会重点介绍。
@@ -130,7 +126,7 @@ if (sum == target) {
这块比较抽象,如图:
-
+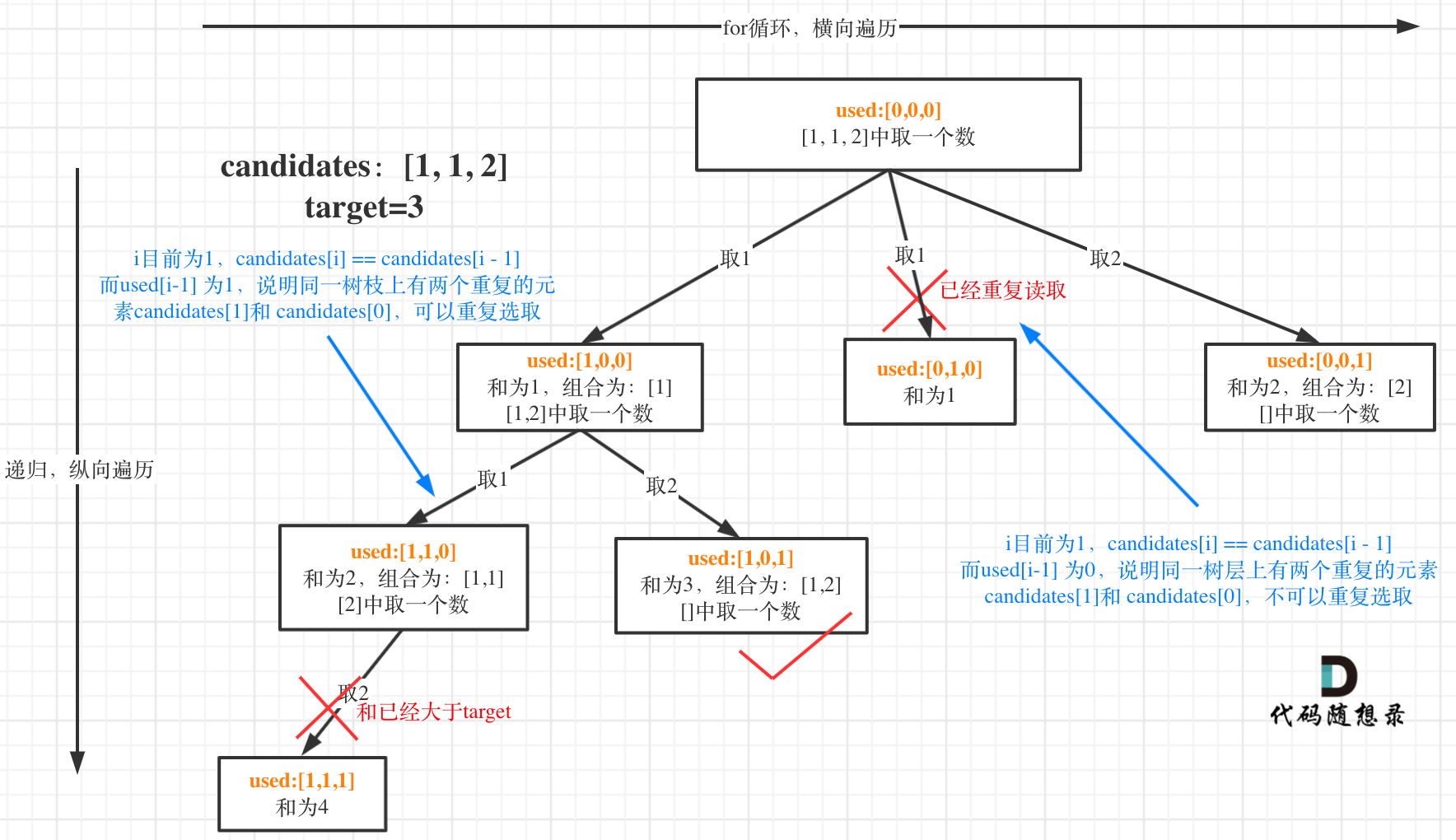
我在图中将used的变化用橘黄色标注上,可以看出在candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1]相同的情况下:
@@ -141,7 +137,7 @@ if (sum == target) {
而 used[i - 1] == true,说明是进入下一层递归,去下一个数,所以是树枝上,如图所示:
-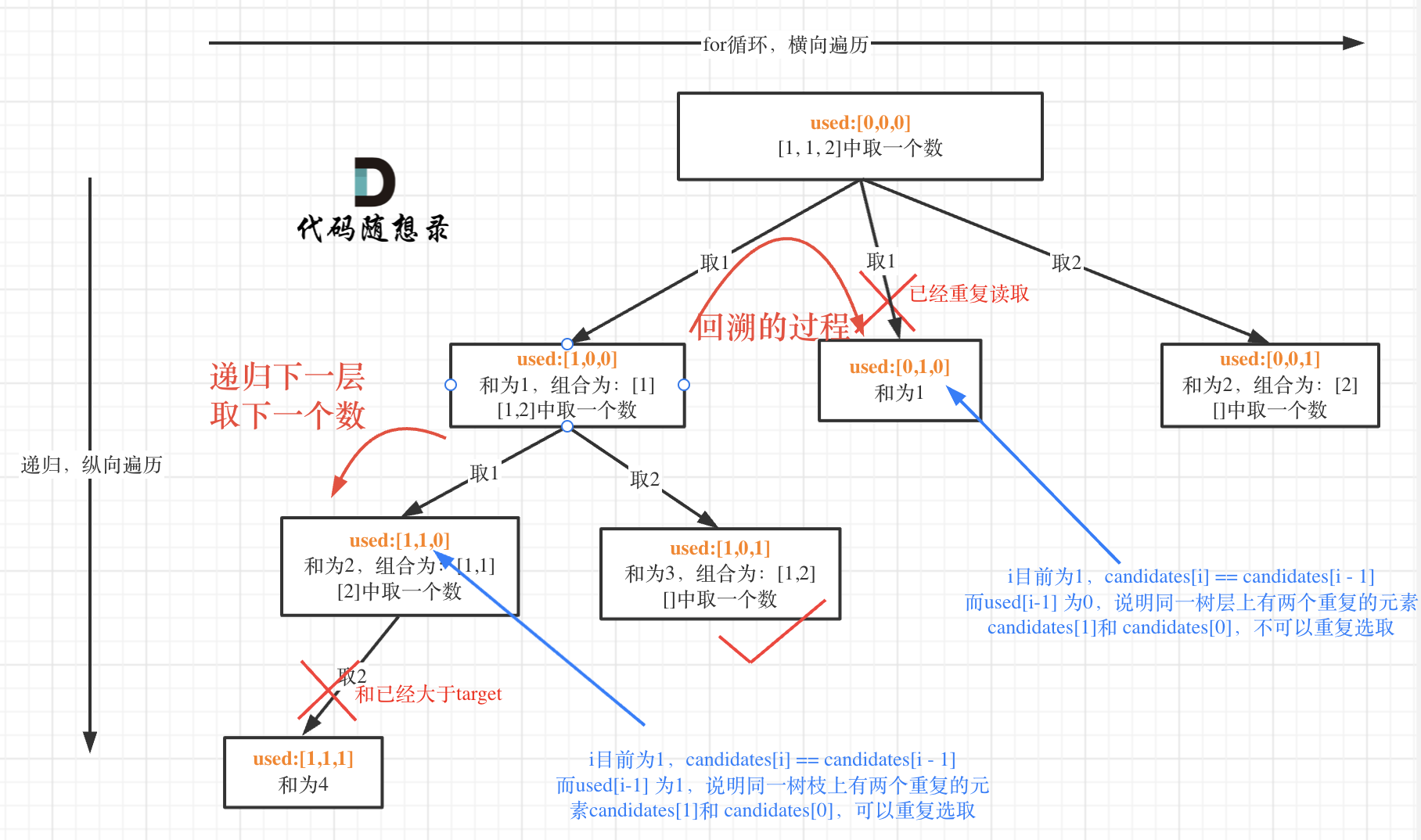
+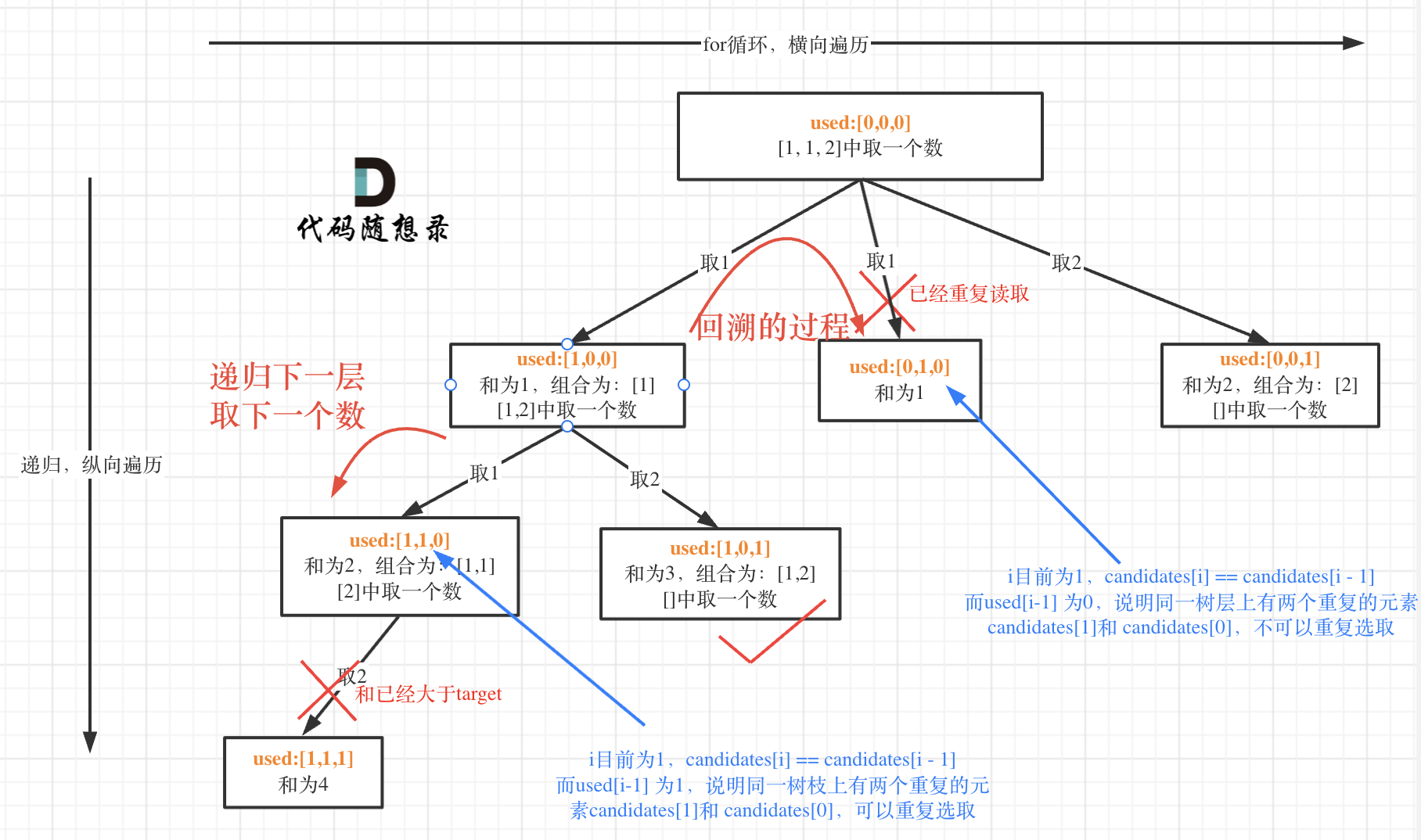
**这块去重的逻辑很抽象,网上搜的题解基本没有能讲清楚的,如果大家之前思考过这个问题或者刷过这道题目,看到这里一定会感觉通透了很多!**
@@ -806,8 +802,4 @@ public class Solution
}
}
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0042.\346\216\245\351\233\250\346\260\264.md" "b/problems/0042.\346\216\245\351\233\250\346\260\264.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 73d787b13c..c208637b2f
--- "a/problems/0042.\346\216\245\351\233\250\346\260\264.md"
+++ "b/problems/0042.\346\216\245\351\233\250\346\260\264.md"
@@ -1,13 +1,10 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0042.\346\216\245\351\233\250\346\260\264.md" "b/problems/0042.\346\216\245\351\233\250\346\260\264.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 73d787b13c..c208637b2f
--- "a/problems/0042.\346\216\245\351\233\250\346\260\264.md"
+++ "b/problems/0042.\346\216\245\351\233\250\346\260\264.md"
@@ -1,13 +1,10 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
-> 这个图就是大厂面试经典题目,接雨水! 最常青藤的一道题,面试官百出不厌!
# 42. 接雨水
@@ -50,10 +47,10 @@
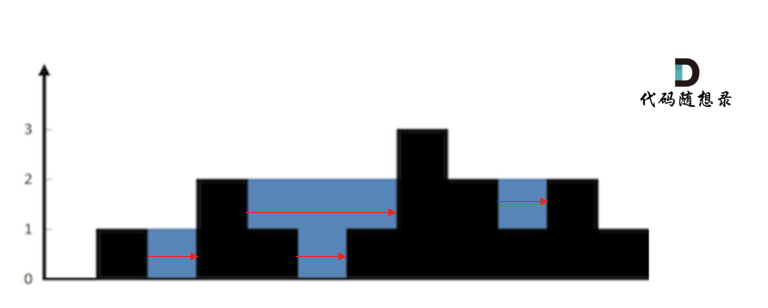
首先要明确,要按照行来计算,还是按照列来计算。
按照行来计算如图:
-
+
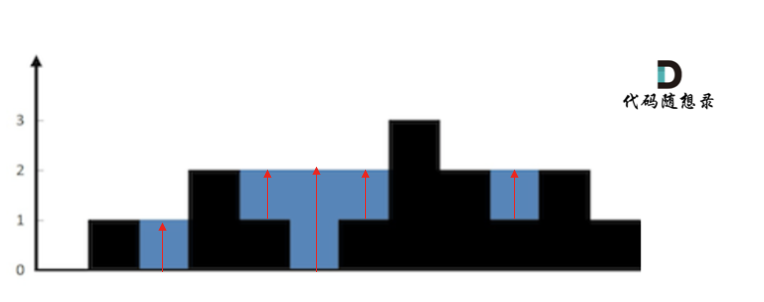
按照列来计算如图:
-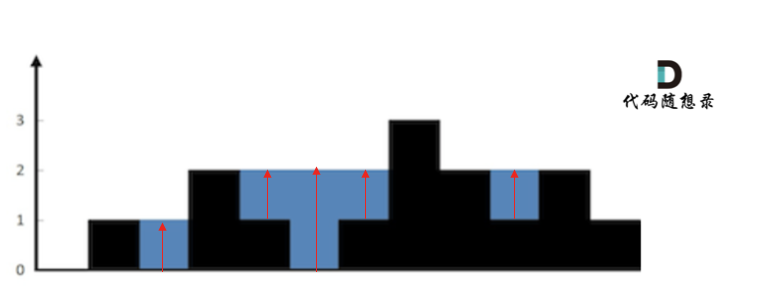
+
一些同学在实现的时候,很容易一会按照行来计算一会按照列来计算,这样就会越写越乱。
@@ -65,7 +62,7 @@
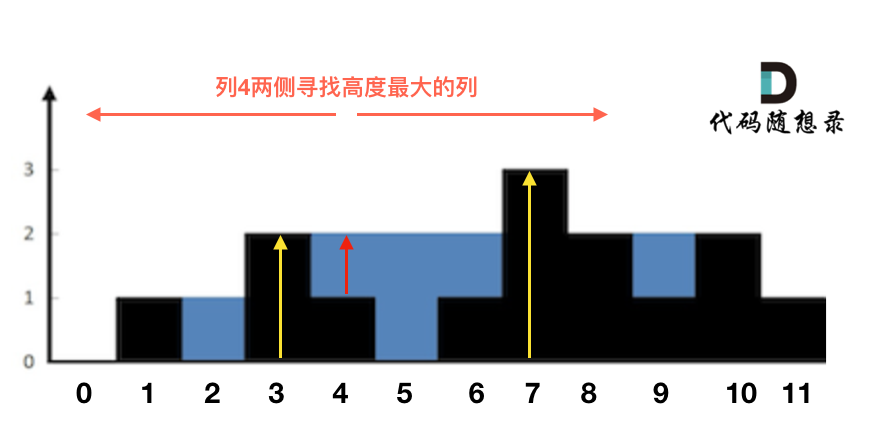
这句话可以有点绕,来举一个理解,例如求列4的雨水高度,如图:
-
+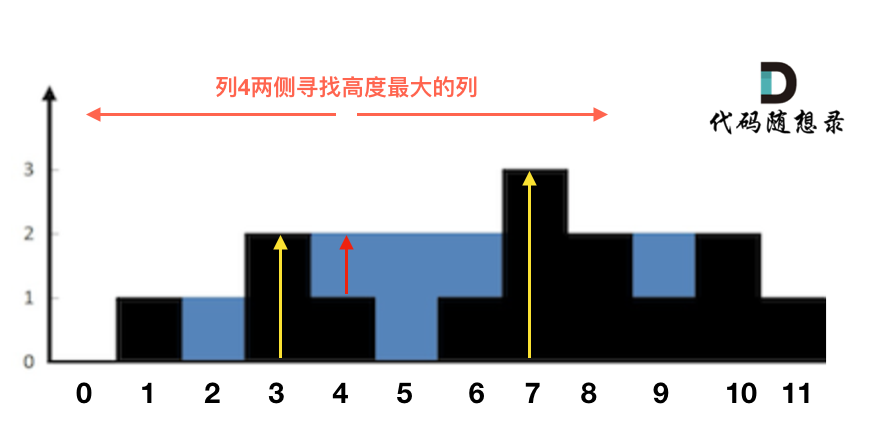
列4 左侧最高的柱子是列3,高度为2(以下用lHeight表示)。
@@ -204,7 +201,7 @@ public:
1. 首先单调栈是按照行方向来计算雨水,如图:
-
+
知道这一点,后面的就可以理解了。
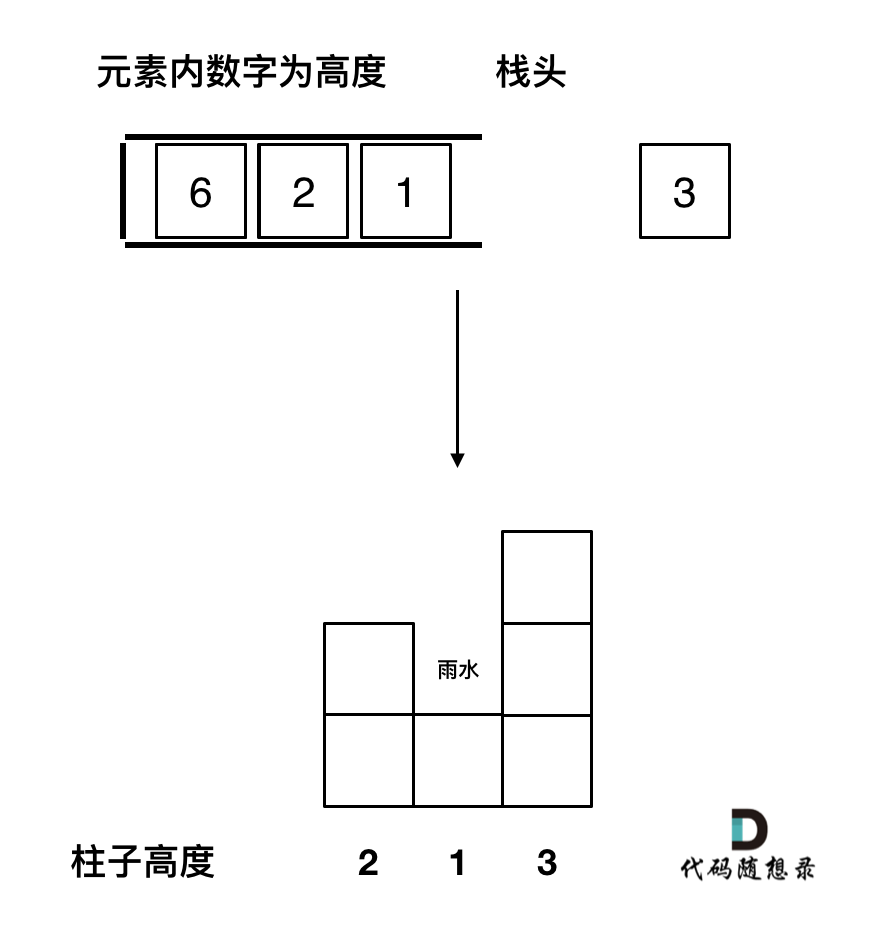
@@ -218,7 +215,7 @@ public:
如图:
-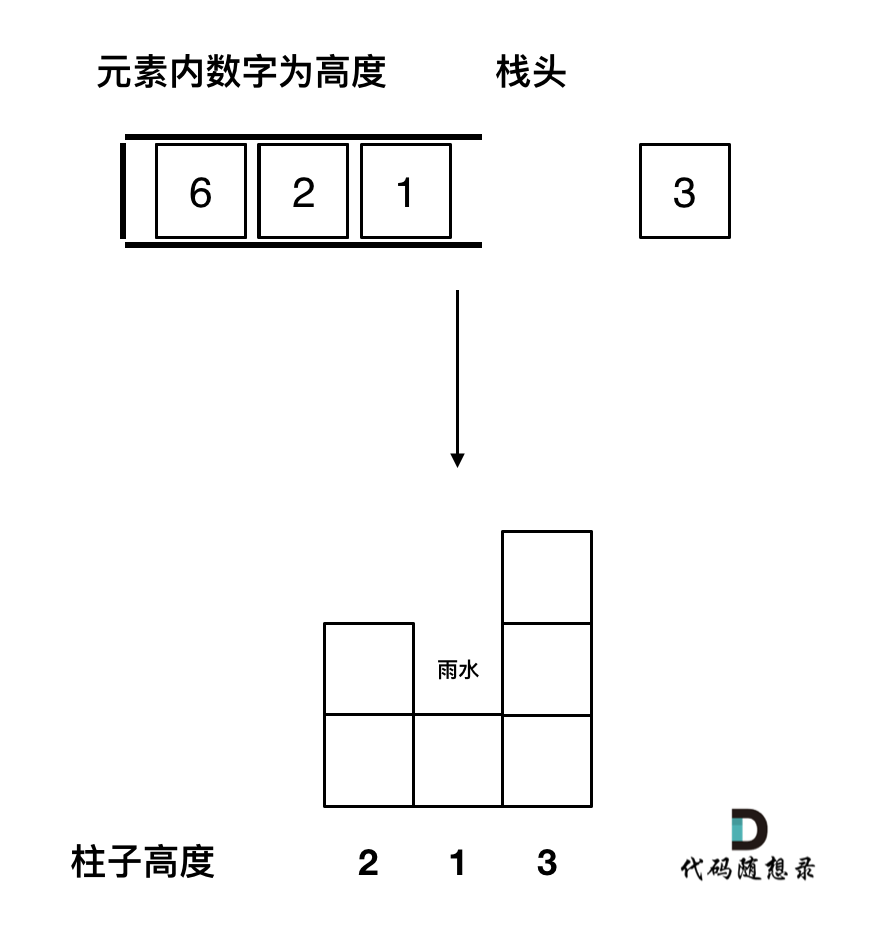
+
关于单调栈的顺序给大家一个总结: [739. 每日温度](https://programmercarl.com/0739.每日温度.html) 中求一个元素右边第一个更大元素,单调栈就是递增的,[84.柱状图中最大的矩形](https://programmercarl.com/0084.柱状图中最大的矩形.html)求一个元素右边第一个更小元素,单调栈就是递减的。
@@ -232,7 +229,7 @@ public:
如图所示:
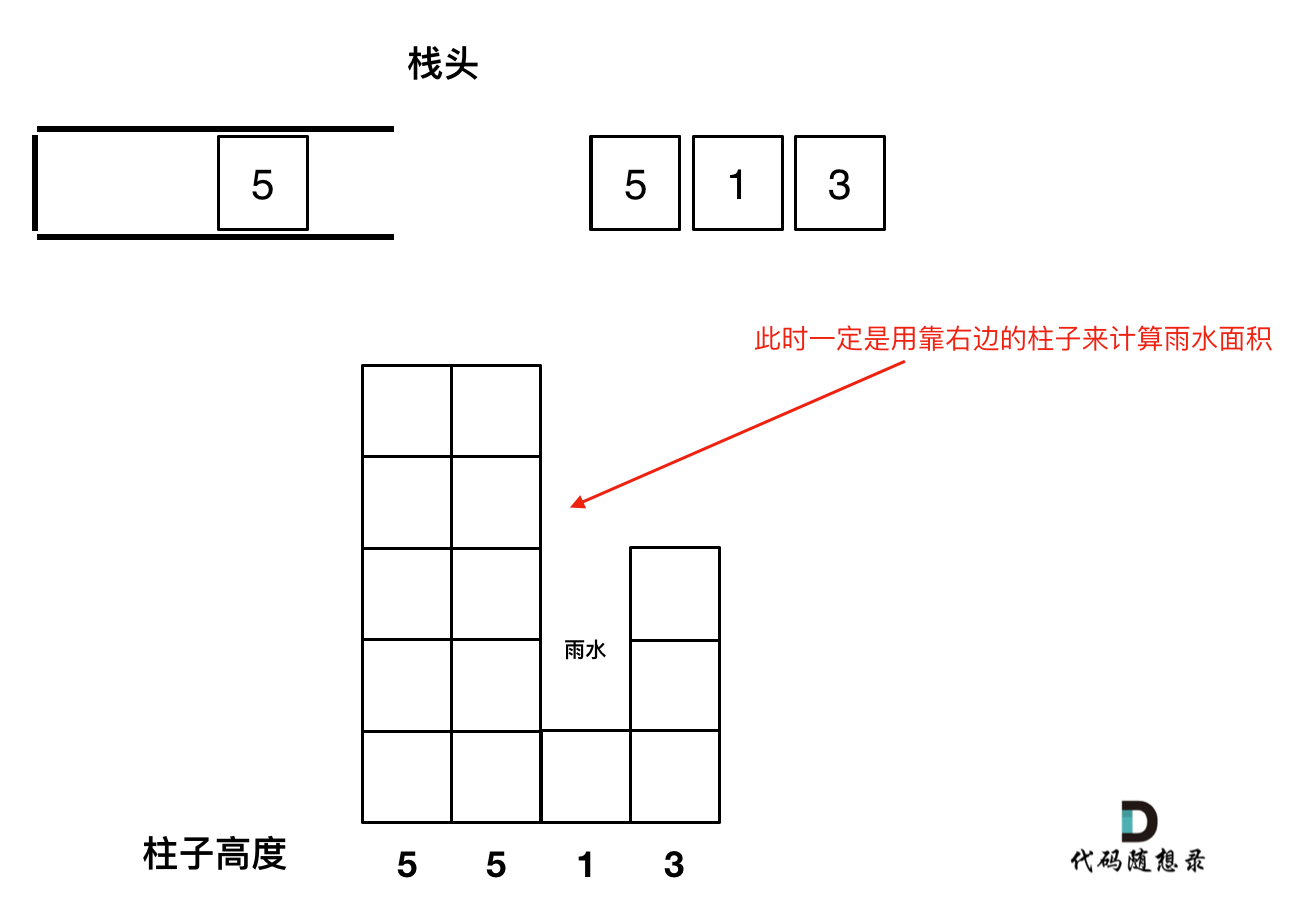
-
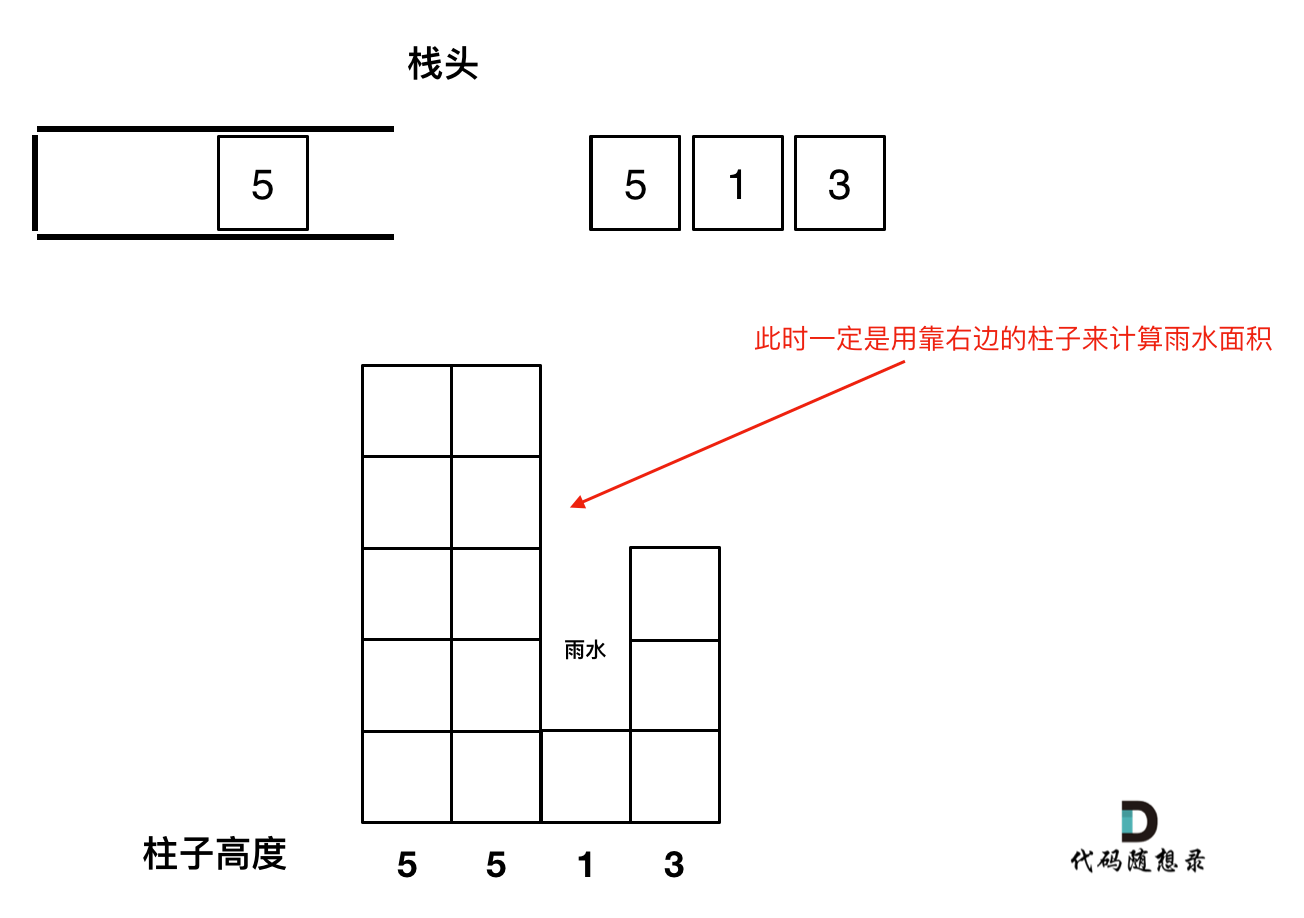
+
4. 栈里要保存什么数值
@@ -287,7 +284,7 @@ if (height[i] == height[st.top()]) { // 例如 5 5 1 7 这种情况
如果当前遍历的元素(柱子)高度大于栈顶元素的高度,此时就出现凹槽了,如图所示:
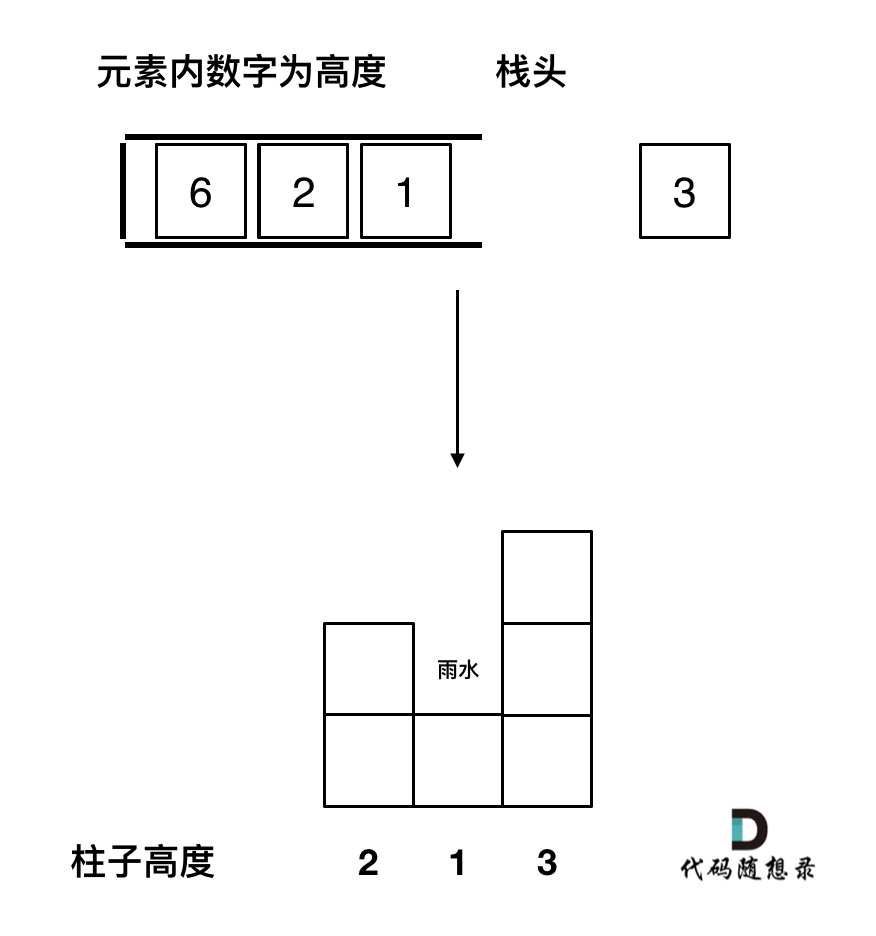
-
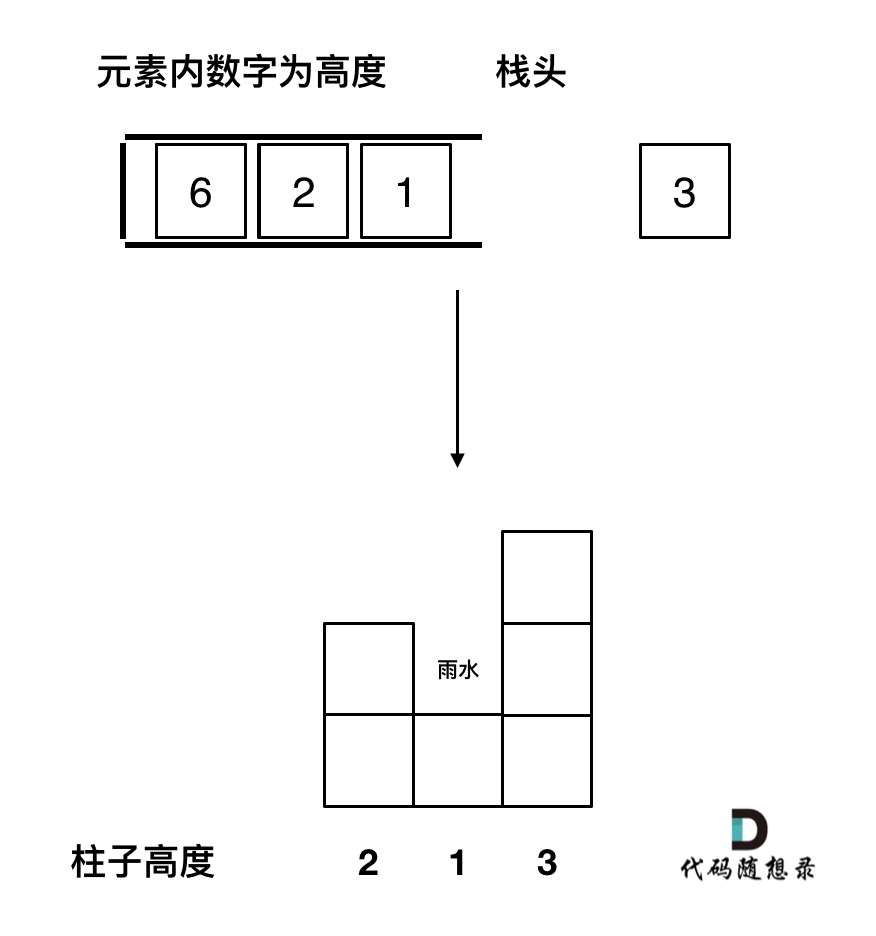
+
取栈顶元素,将栈顶元素弹出,这个就是凹槽的底部,也就是中间位置,下标记为mid,对应的高度为height[mid](就是图中的高度1)。
@@ -440,6 +437,33 @@ class Solution {
}
```
+双指针优化
+```java
+class Solution {
+ public int trap(int[] height) {
+ if (height.length <= 2) {
+ return 0;
+ }
+ // 从两边向中间寻找最值
+ int maxLeft = height[0], maxRight = height[height.length - 1];
+ int l = 1, r = height.length - 2;
+ int res = 0;
+ while (l <= r) {
+ // 不确定上一轮是左边移动还是右边移动,所以两边都需更新最值
+ maxLeft = Math.max(maxLeft, height[l]);
+ maxRight = Math.max(maxRight, height[r]);
+ // 最值较小的一边所能装的水量已定,所以移动较小的一边。
+ if (maxLeft < maxRight) {
+ res += maxLeft - height[l ++];
+ } else {
+ res += maxRight - height[r --];
+ }
+ }
+ return res;
+ }
+}
+```
+
单调栈法
```java
@@ -1068,7 +1092,3 @@ impl Solution {
}
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0045.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217II.md" "b/problems/0045.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index d290f55e80..c20cdc65e6
--- "a/problems/0045.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0045.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217II.md"
@@ -1,10 +1,8 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0045.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217II.md" "b/problems/0045.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index d290f55e80..c20cdc65e6
--- "a/problems/0045.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0045.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217II.md"
@@ -1,10 +1,8 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-> 相对于[贪心算法:跳跃游戏](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/606_N9j8ACKCODoCbV1lSA)难了不少,做好心里准备!
+> 相对于[贪心算法:跳跃游戏](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/606_N9j8ACKCODoCbV1lSA)难了不少,做好心理准备!
# 45.跳跃游戏 II
@@ -49,7 +47,7 @@
如图:
-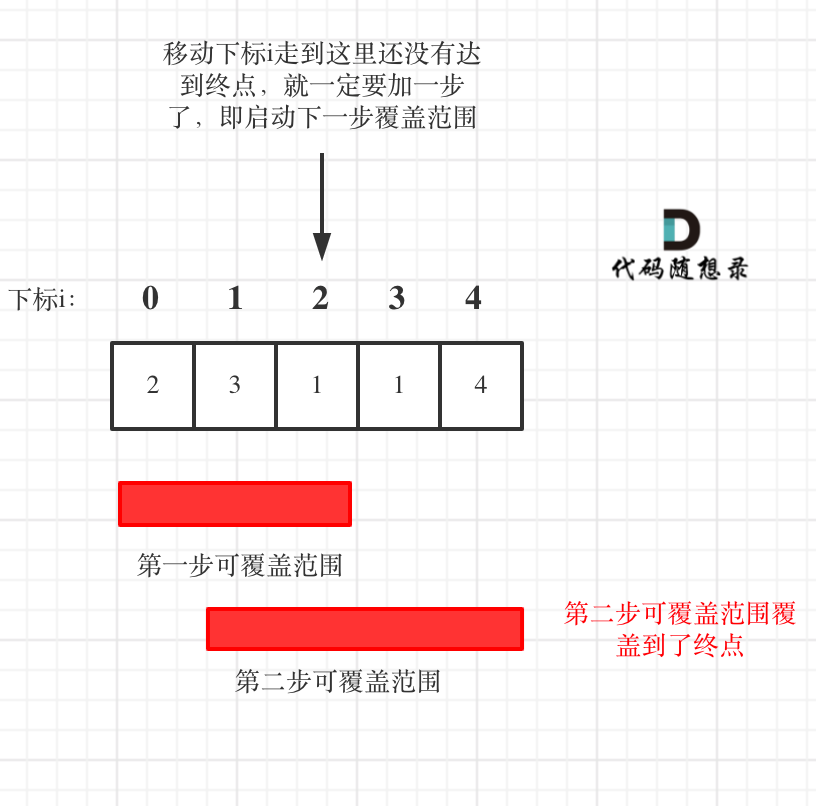
+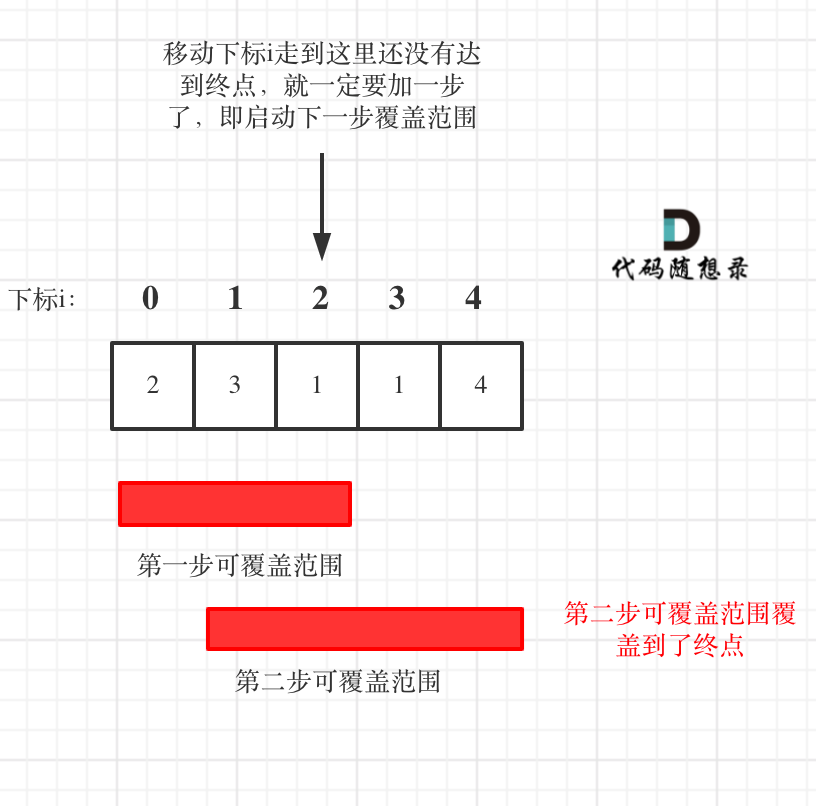
**图中覆盖范围的意义在于,只要红色的区域,最多两步一定可以到!(不用管具体怎么跳,反正一定可以跳到)**
@@ -101,11 +99,11 @@ public:
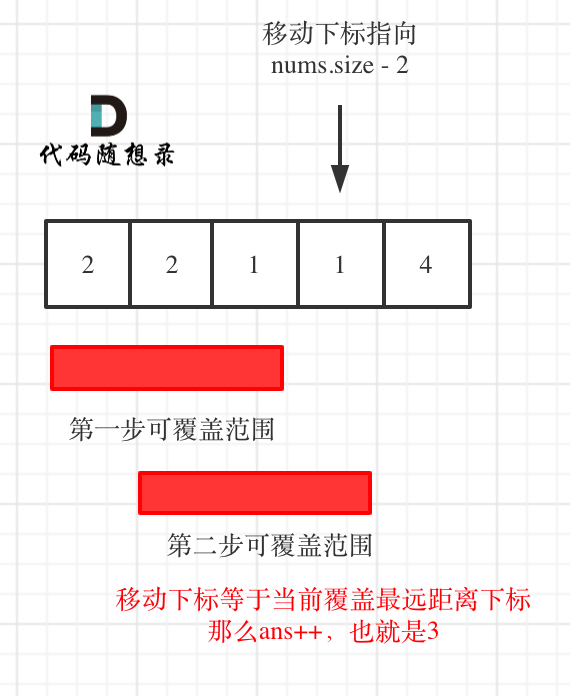
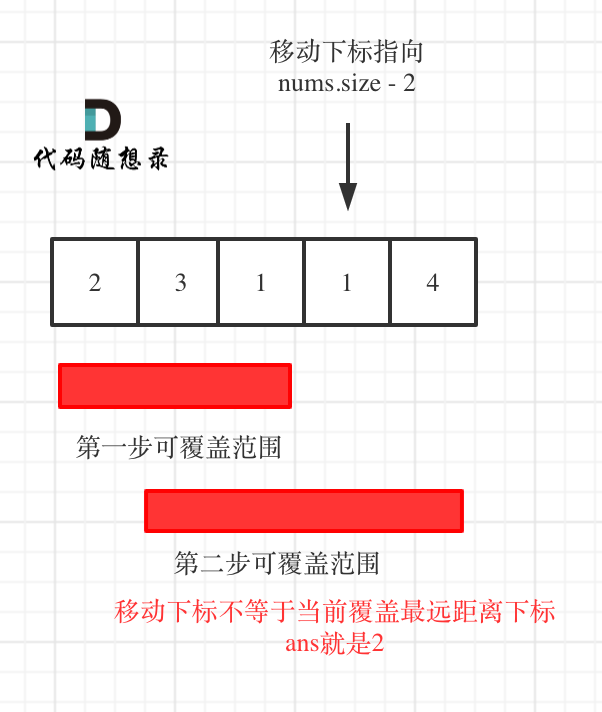
因为当移动下标指向 nums.size - 2 时:
- 如果移动下标等于当前覆盖最大距离下标, 需要再走一步(即 ans++),因为最后一步一定是可以到的终点。(题目假设总是可以到达数组的最后一个位置),如图:
- 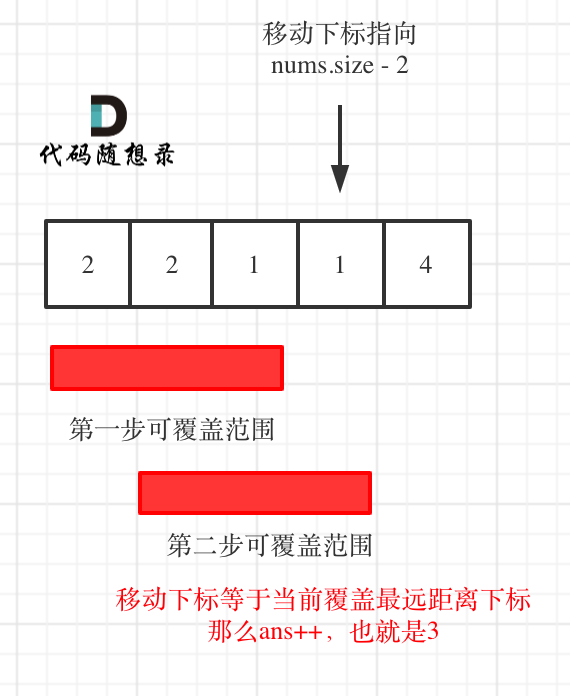
+ 
- 如果移动下标不等于当前覆盖最大距离下标,说明当前覆盖最远距离就可以直接达到终点了,不需要再走一步。如图:
-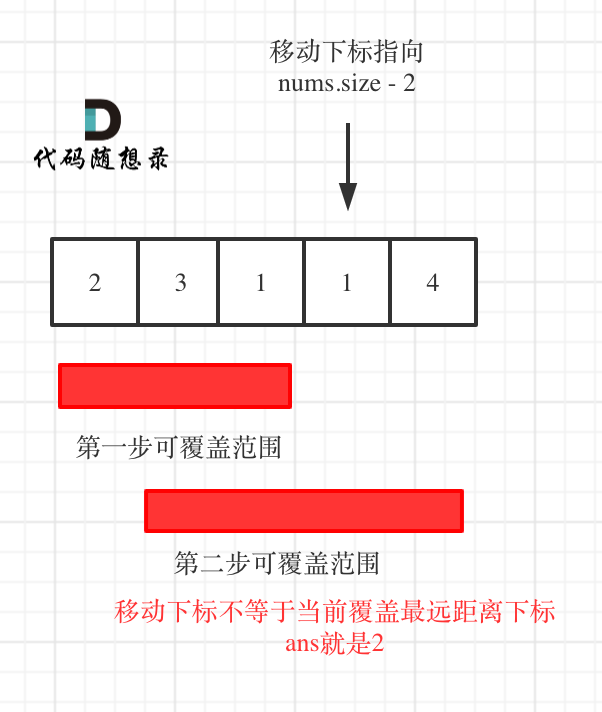
+
代码如下:
@@ -374,7 +372,7 @@ func max(a, b int) int {
}
```
-### Javascript
+### JavaScript
```Javascript
var jump = function(nums) {
@@ -492,7 +490,34 @@ impl Solution {
}
}
```
+### C
+
+```c
+#define max(a, b) ((a) > (b) ? (a) : (b))
+
+int jump(int* nums, int numsSize) {
+ if(numsSize == 1){
+ return 0;
+ }
+ int count = 0;
+ // 记录当前能走的最远距离
+ int curDistance = 0;
+ // 记录下一步能走的最远距离
+ int nextDistance = 0;
+ for(int i = 0; i < numsSize; i++){
+ nextDistance = max(i + nums[i], nextDistance);
+ // 下标到了当前的最大距离
+ if(i == nextDistance){
+ count++;
+ curDistance = nextDistance;
+ }
+ }
+ return count;
+}
+```
+
### C#
+
```csharp
// 版本二
public class Solution
@@ -514,7 +539,4 @@ public class Solution
}
```
-
-
-  -
+
diff --git "a/problems/0046.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227.md" "b/problems/0046.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 15e6ae162a..356f51b5a8
--- "a/problems/0046.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227.md"
+++ "b/problems/0046.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+
diff --git "a/problems/0046.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227.md" "b/problems/0046.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 15e6ae162a..356f51b5a8
--- "a/problems/0046.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227.md"
+++ "b/problems/0046.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 46.全排列
@@ -42,7 +40,8 @@
我以[1,2,3]为例,抽象成树形结构如下:
-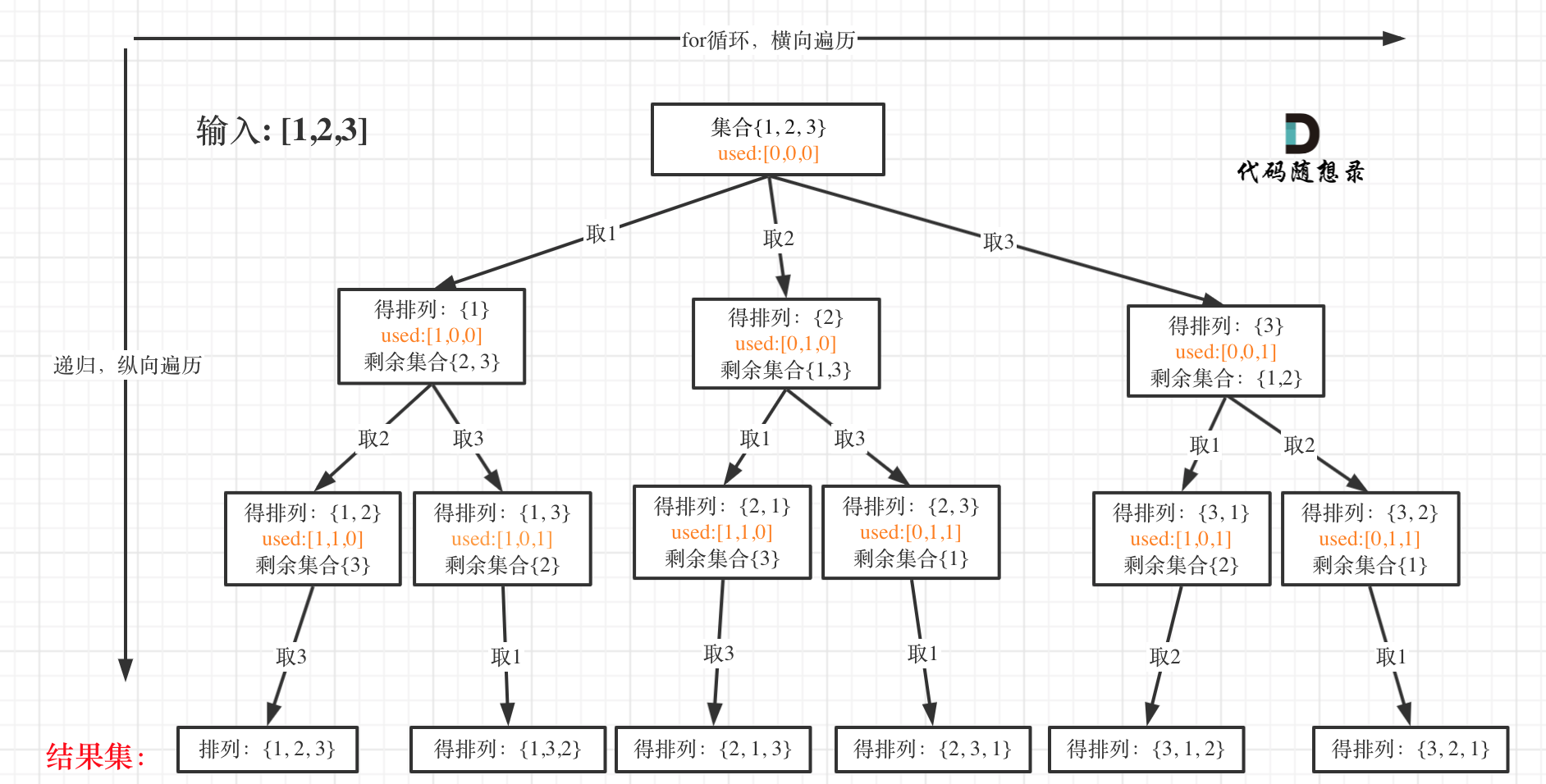
+
+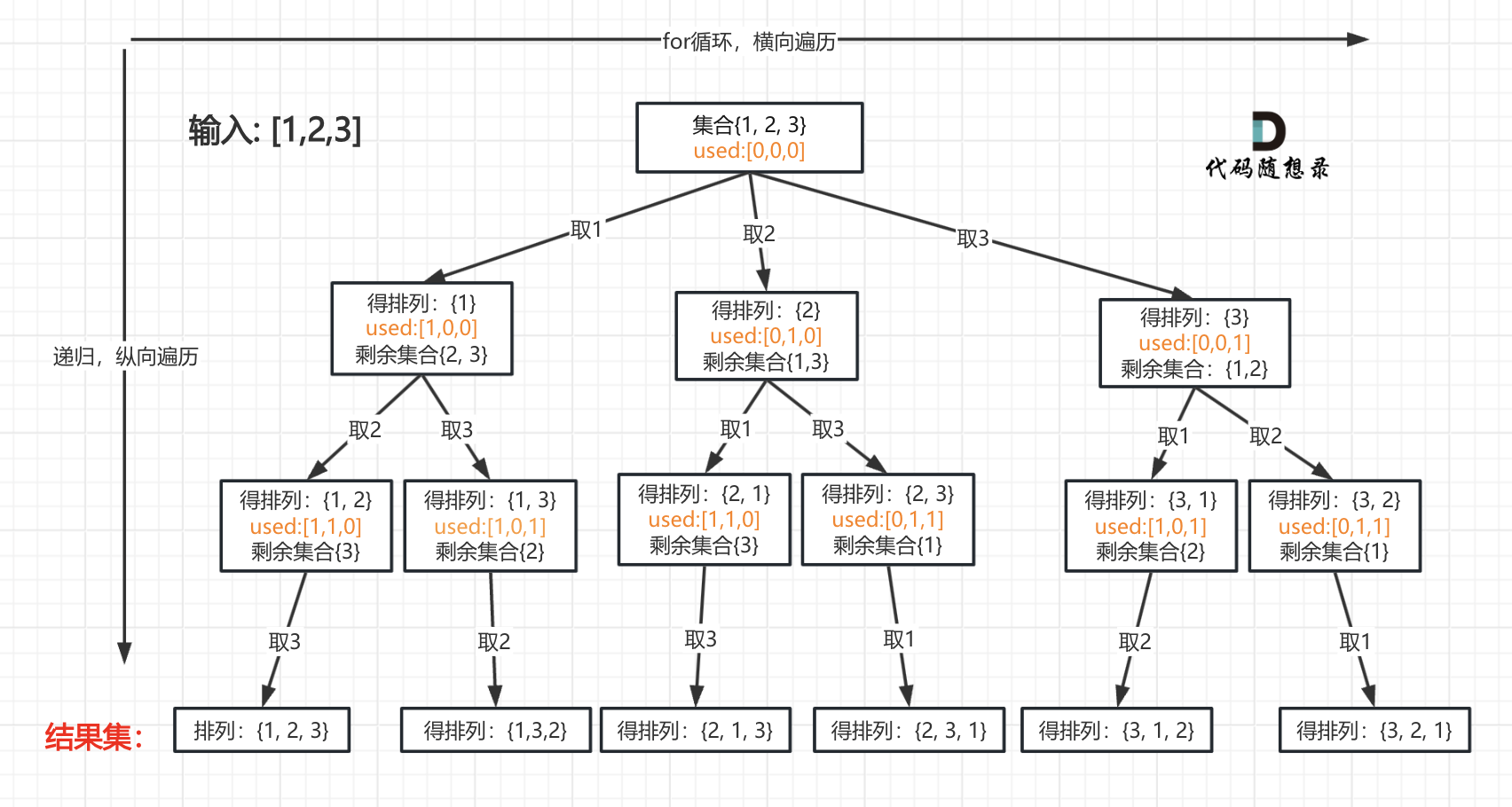
### 回溯三部曲
@@ -54,7 +53,7 @@
但排列问题需要一个used数组,标记已经选择的元素,如图橘黄色部分所示:
-
+
代码如下:
@@ -66,7 +65,7 @@ void backtracking (vector& nums, vector& used)
* 递归终止条件
-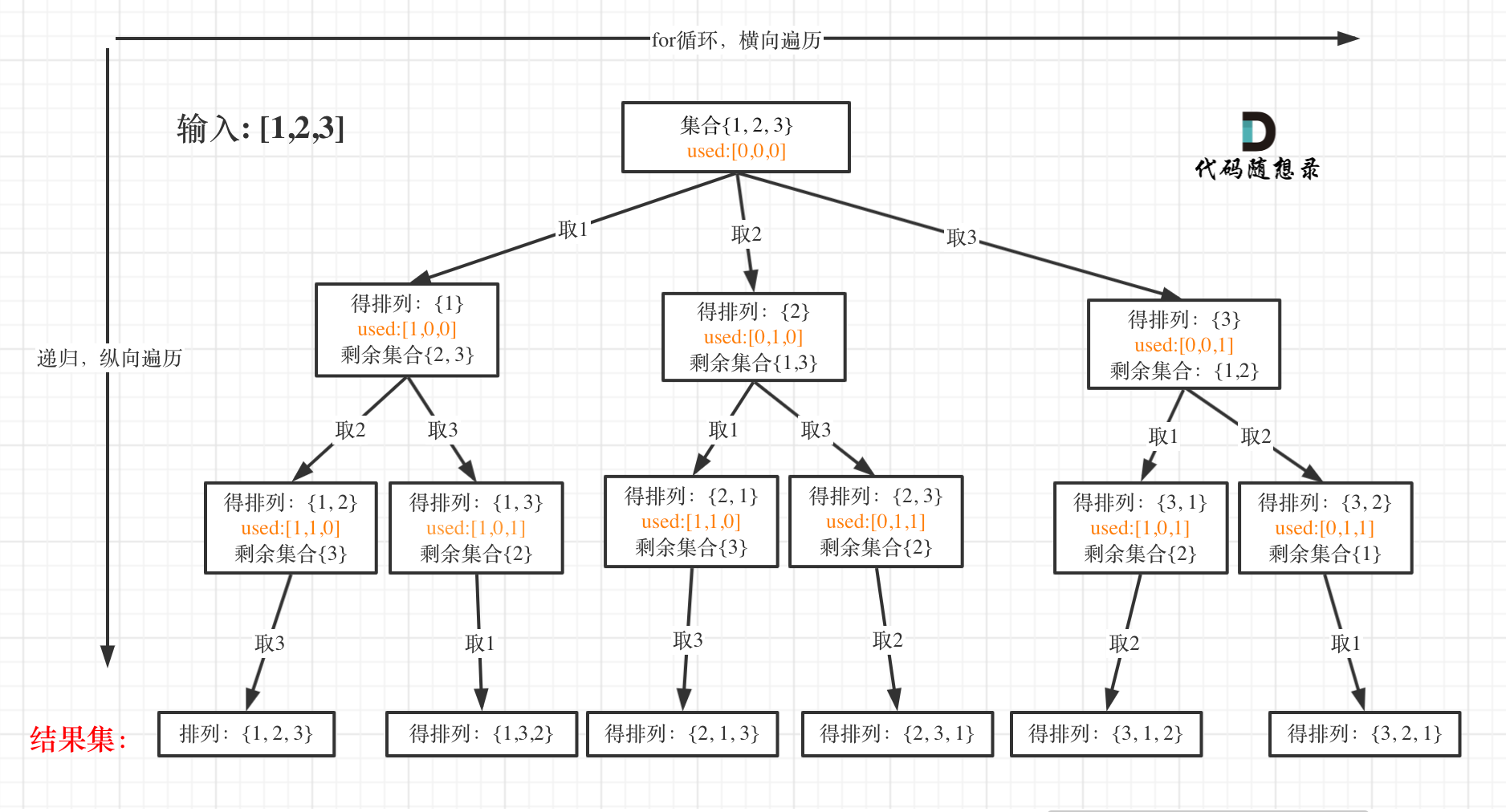
+
可以看出叶子节点,就是收割结果的地方。
@@ -200,6 +199,7 @@ class Solution {
public void backtrack(int[] nums, LinkedList path) {
if (path.size() == nums.length) {
result.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
+ return;
}
for (int i =0; i < nums.length; i++) {
// 如果path中已有,则跳过
@@ -270,7 +270,7 @@ func dfs(nums []int, cur int) {
}
```
-### Javascript
+### JavaScript
```js
@@ -518,8 +518,5 @@ public class Solution
}
```
-
-
-  -
+
diff --git "a/problems/0047.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227II.md" "b/problems/0047.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 7f2c363889..5330997a66
--- "a/problems/0047.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0047.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227II.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-
-
+
diff --git "a/problems/0047.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227II.md" "b/problems/0047.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 7f2c363889..5330997a66
--- "a/problems/0047.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0047.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227II.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
@@ -50,7 +48,7 @@
我以示例中的 [1,1,2]为例 (为了方便举例,已经排序)抽象为一棵树,去重过程如图:
-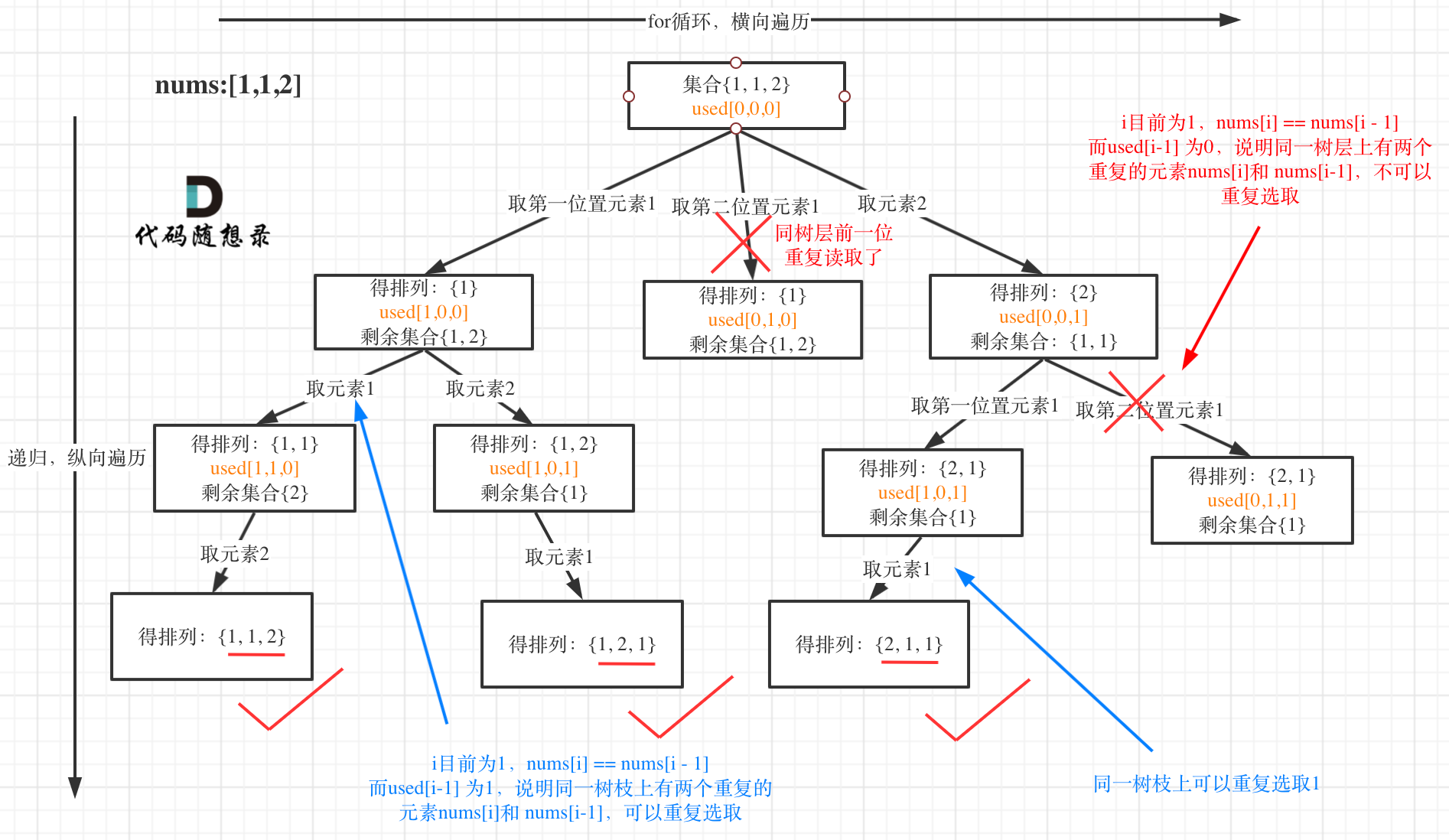
+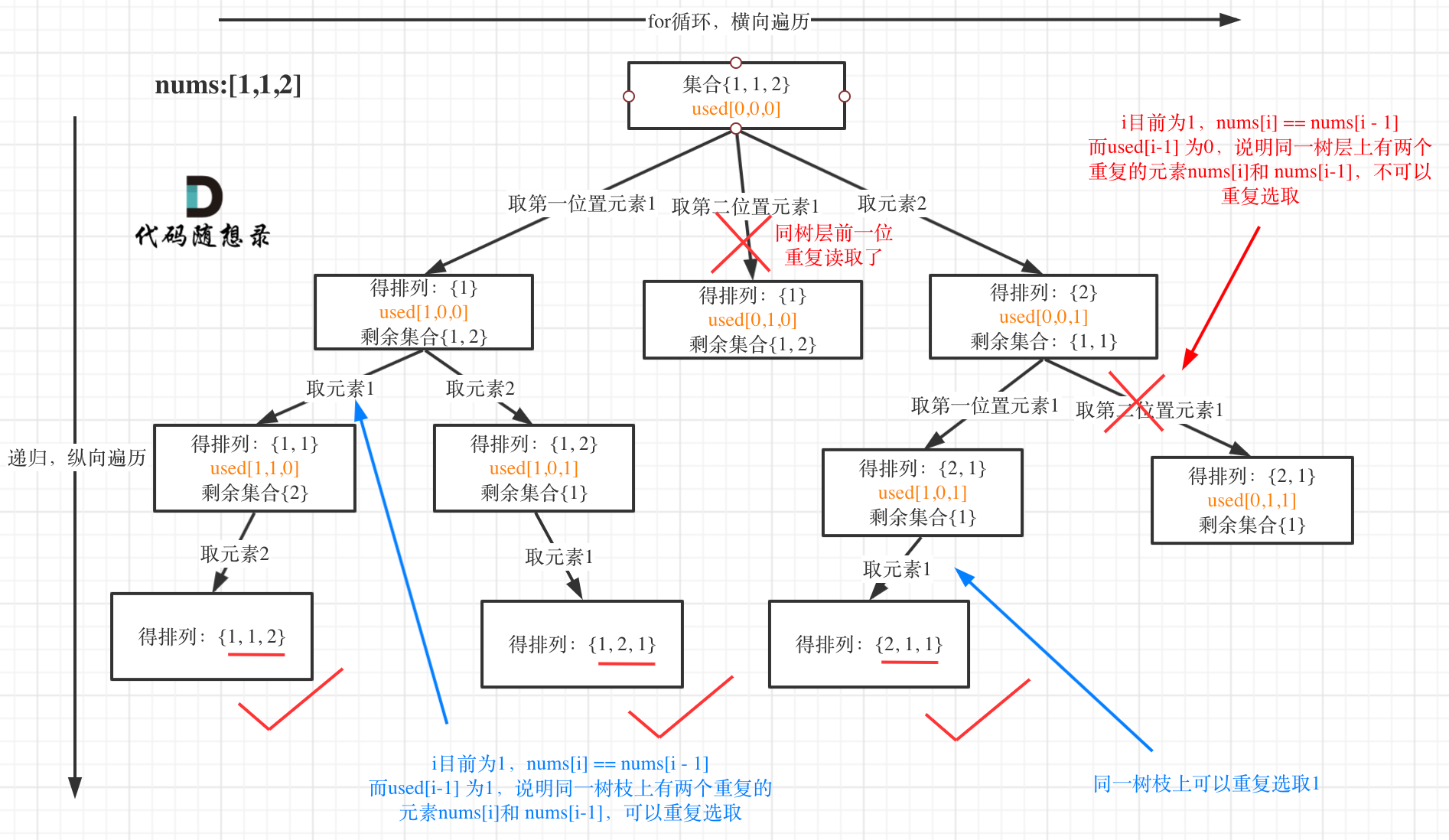
图中我们对同一树层,前一位(也就是nums[i-1])如果使用过,那么就进行去重。
@@ -132,11 +130,11 @@ if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1] && used[i - 1] == true) {
树层上去重(used[i - 1] == false),的树形结构如下:
-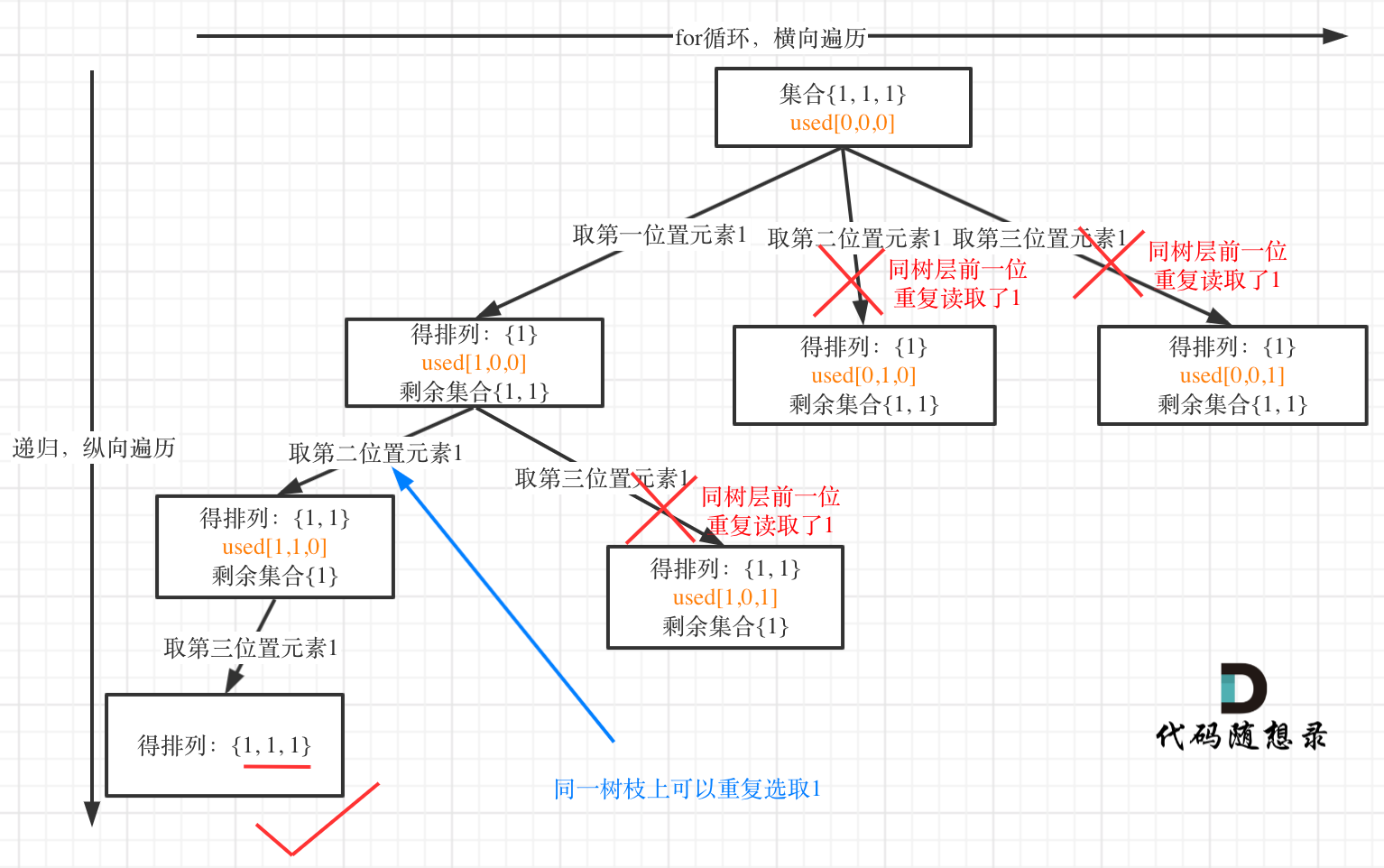
+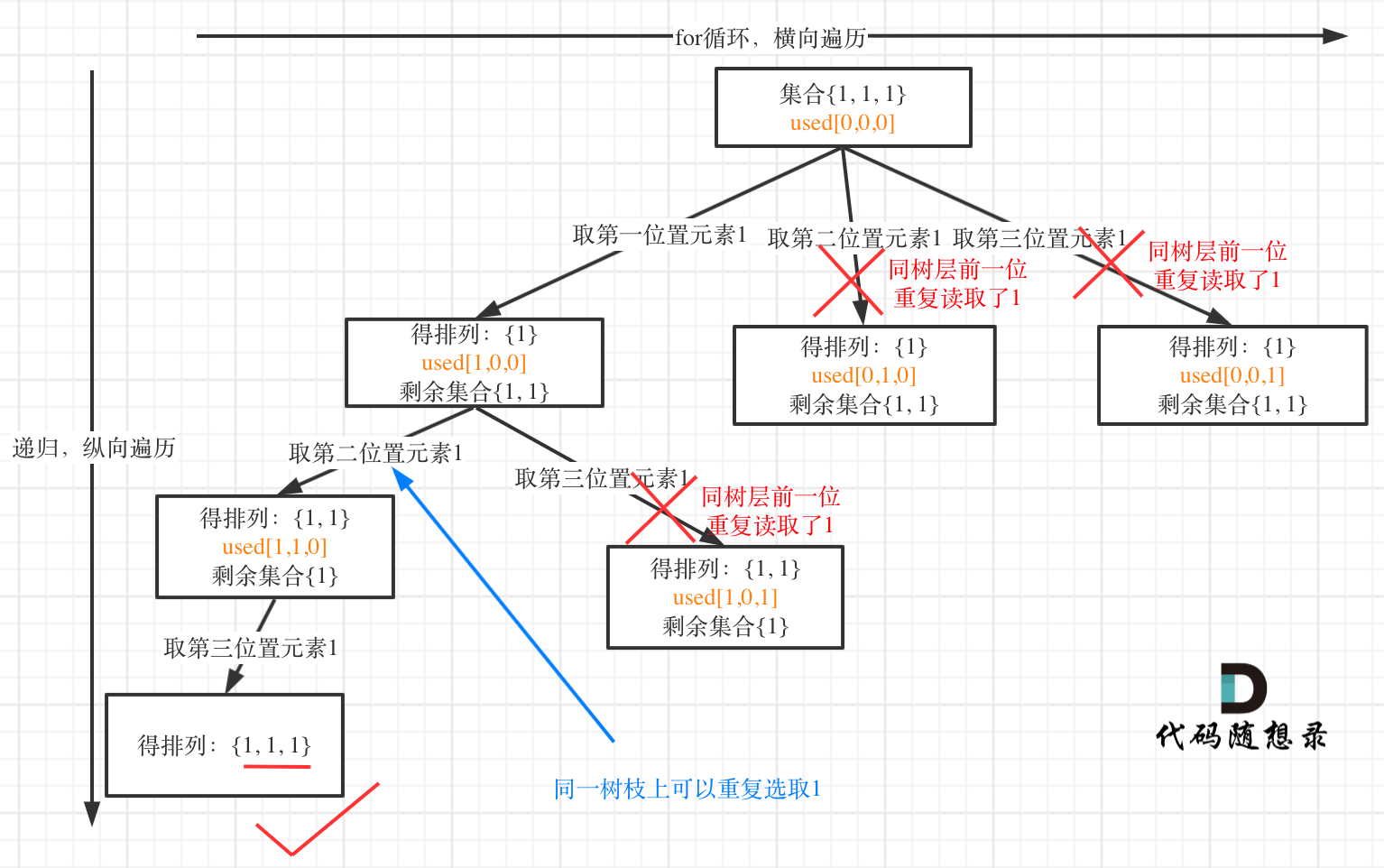
树枝上去重(used[i - 1] == true)的树型结构如下:
-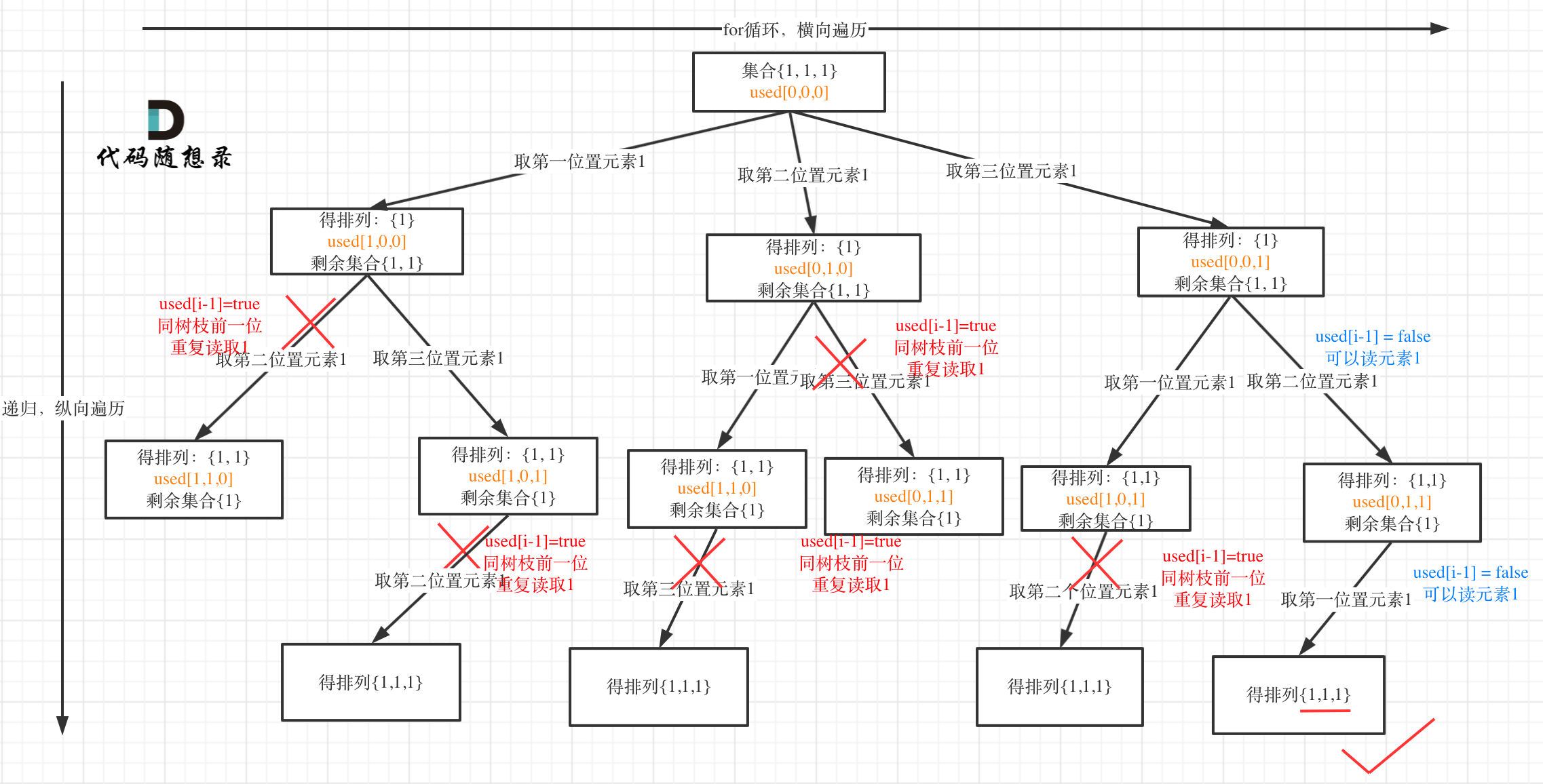
+
大家应该很清晰的看到,树层上对前一位去重非常彻底,效率很高,树枝上对前一位去重虽然最后可以得到答案,但是做了很多无用搜索。
@@ -283,7 +281,7 @@ func dfs(nums []int, cur int) {
}
```
-### Javascript
+### JavaScript
```javascript
var permuteUnique = function (nums) {
@@ -554,8 +552,4 @@ public class Solution
}
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0051.N\347\232\207\345\220\216.md" "b/problems/0051.N\347\232\207\345\220\216.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 1e1085401d..d06d7798e8
--- "a/problems/0051.N\347\232\207\345\220\216.md"
+++ "b/problems/0051.N\347\232\207\345\220\216.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0051.N\347\232\207\345\220\216.md" "b/problems/0051.N\347\232\207\345\220\216.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 1e1085401d..d06d7798e8
--- "a/problems/0051.N\347\232\207\345\220\216.md"
+++ "b/problems/0051.N\347\232\207\345\220\216.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 51. N皇后
@@ -17,7 +15,7 @@ n 皇后问题 研究的是如何将 n 个皇后放置在 n×n 的棋盘上,
示例 1:
-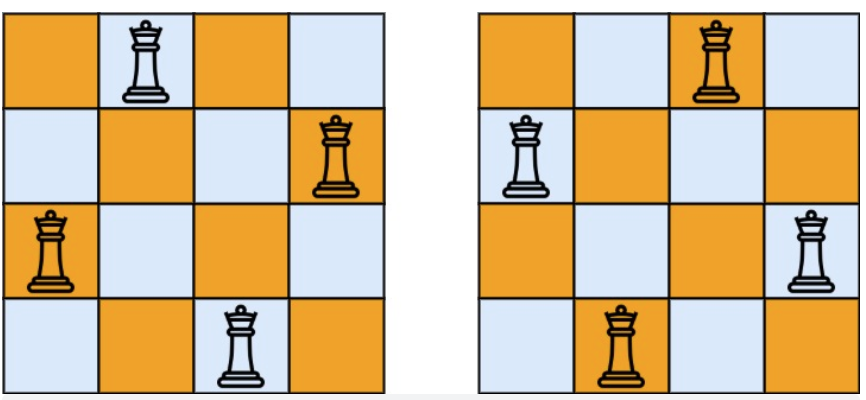
+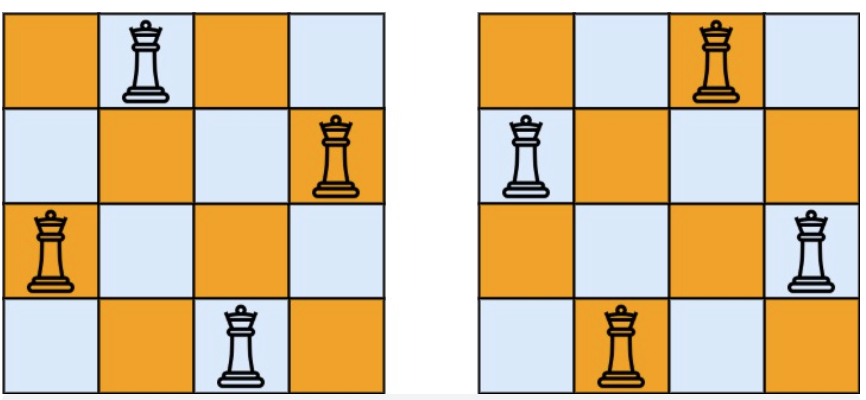
* 输入:n = 4
* 输出:[[".Q..","...Q","Q...","..Q."],["..Q.","Q...","...Q",".Q.."]]
@@ -47,7 +45,7 @@ n 皇后问题 研究的是如何将 n 个皇后放置在 n×n 的棋盘上,
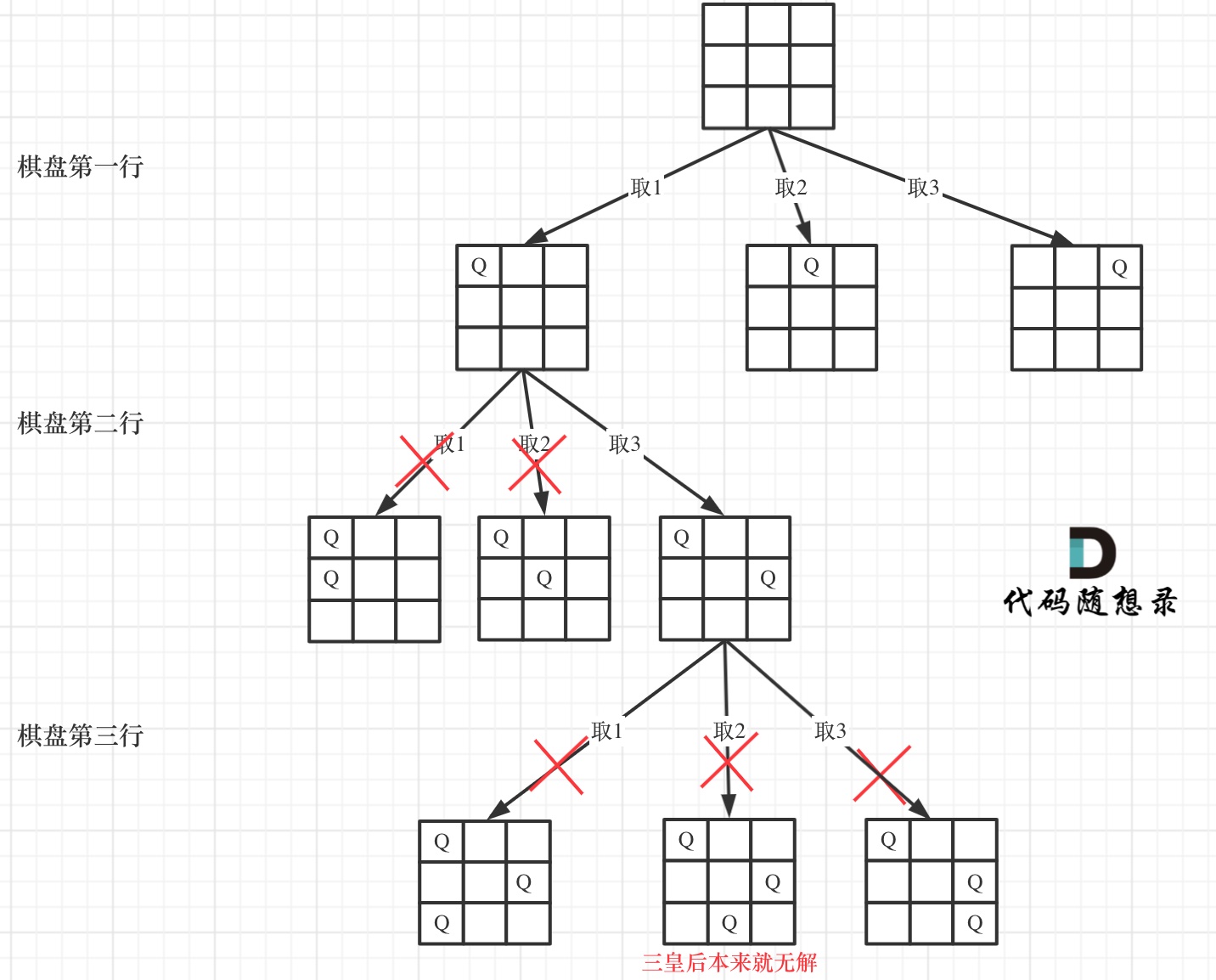
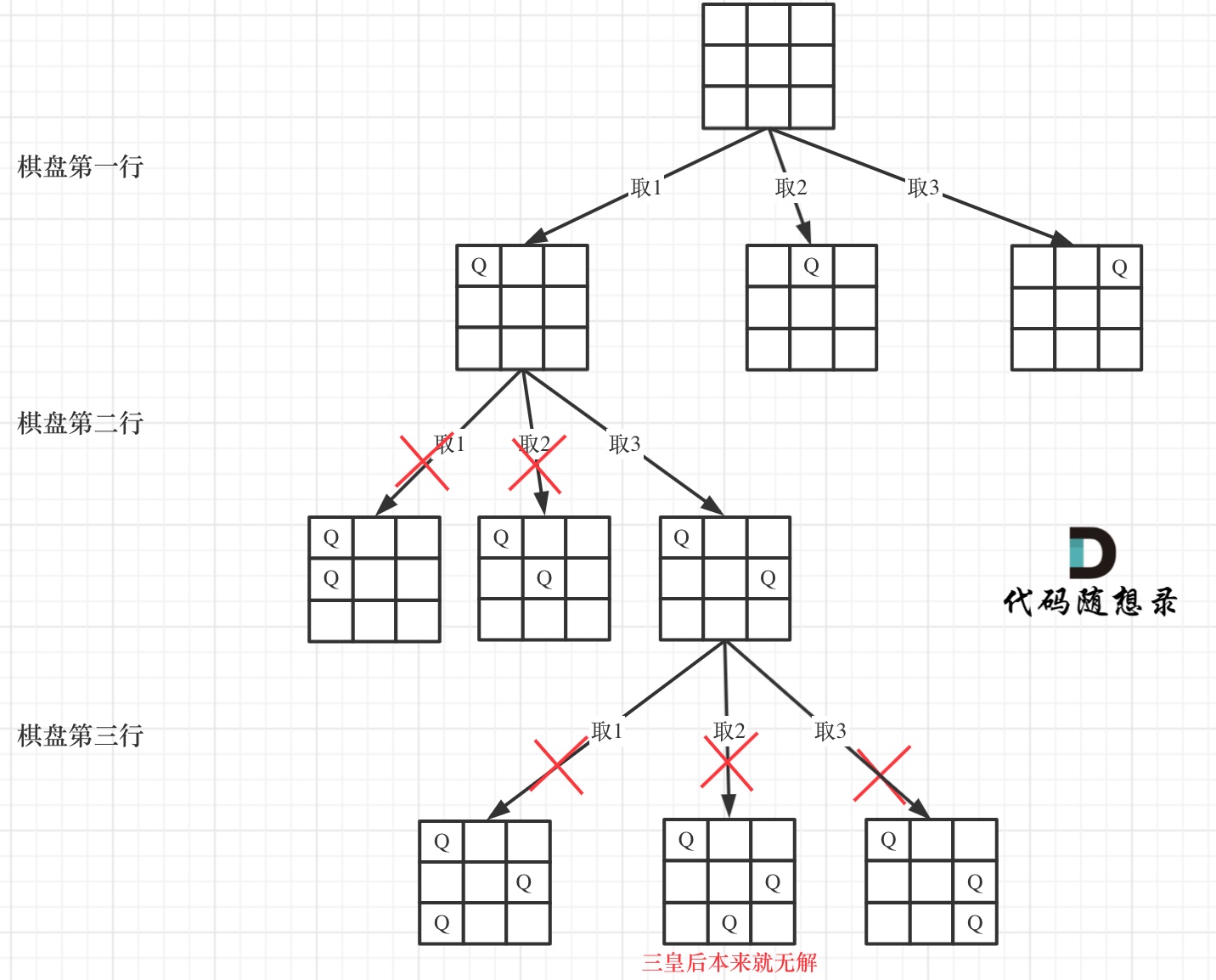
下面我用一个 3 * 3 的棋盘,将搜索过程抽象为一棵树,如图:
-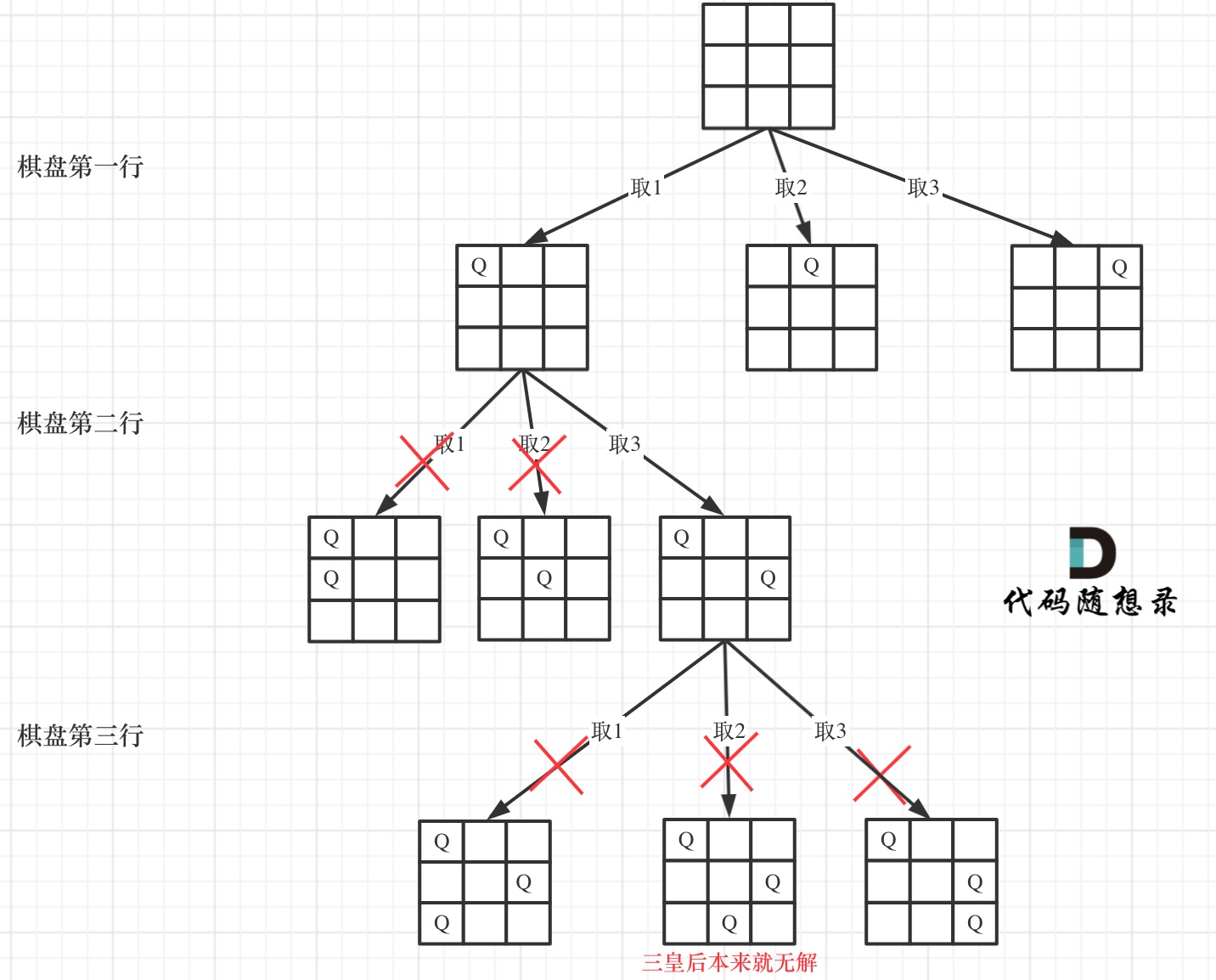
+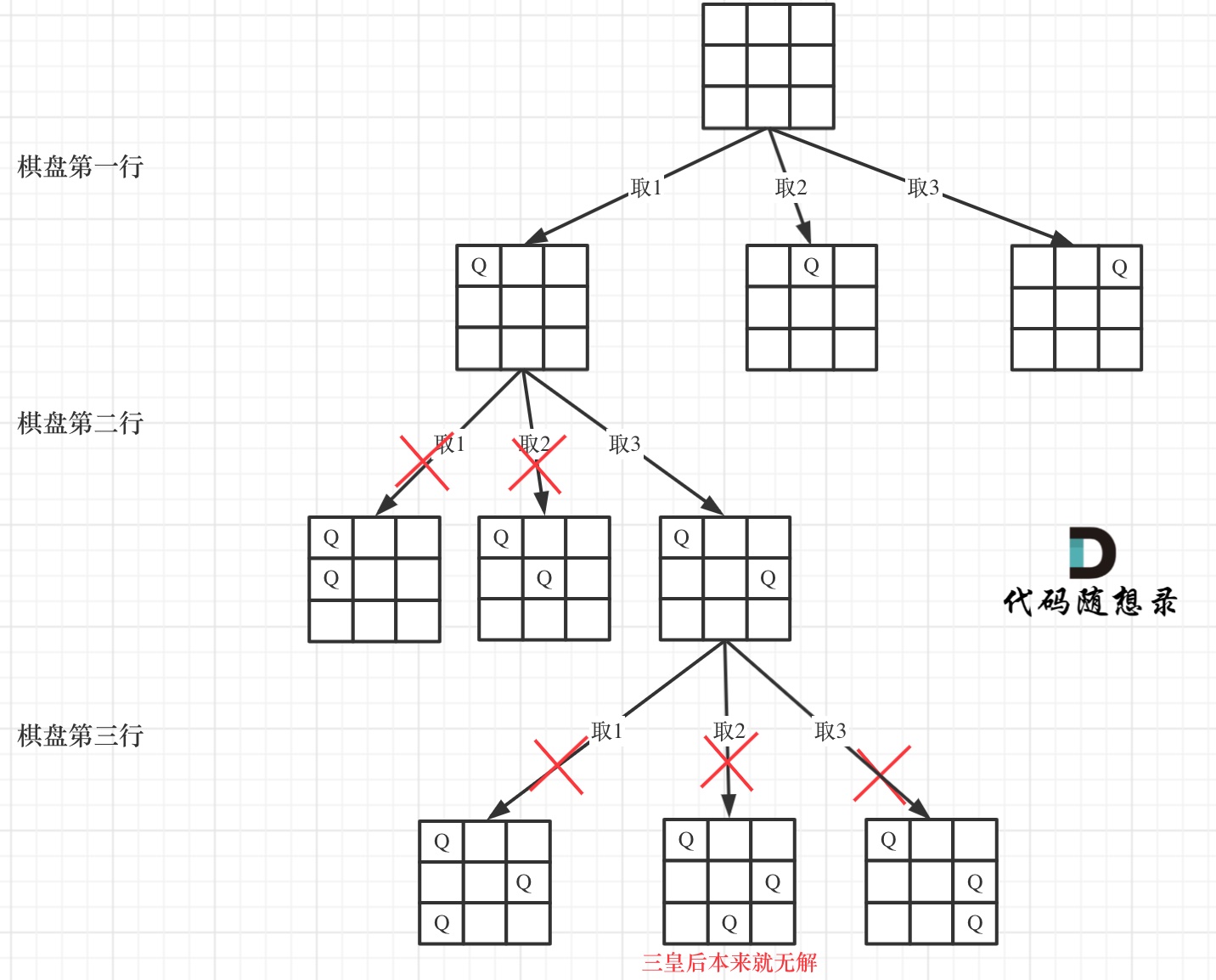
从图中,可以看出,二维矩阵中矩阵的高就是这棵树的高度,矩阵的宽就是树形结构中每一个节点的宽度。
@@ -87,7 +85,7 @@ void backtracking(int n, int row, vector& chessboard) {
* 递归终止条件
在如下树形结构中:
-
+
可以看出,当递归到棋盘最底层(也就是叶子节点)的时候,就可以收集结果并返回了。
@@ -451,7 +449,7 @@ func isValid(n, row, col int, chessboard [][]string) bool {
```
-### Javascript
+### JavaScript
```Javascript
/**
* @param {number} n
@@ -920,8 +918,4 @@ public class Solution
}
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0052.N\347\232\207\345\220\216II.md" "b/problems/0052.N\347\232\207\345\220\216II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 29c2b58818..6c6650ad00
--- "a/problems/0052.N\347\232\207\345\220\216II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0052.N\347\232\207\345\220\216II.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0052.N\347\232\207\345\220\216II.md" "b/problems/0052.N\347\232\207\345\220\216II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 29c2b58818..6c6650ad00
--- "a/problems/0052.N\347\232\207\345\220\216II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0052.N\347\232\207\345\220\216II.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
@@ -15,7 +13,7 @@ n 皇后问题研究的是如何将 n 个皇后放置在 n×n 的棋盘上,并
上图为 8 皇后问题的一种解法。
-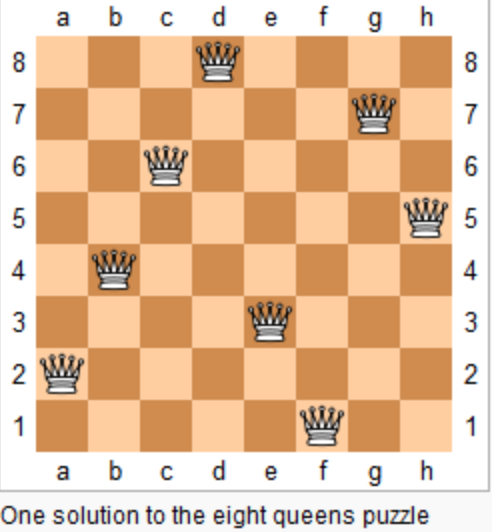
+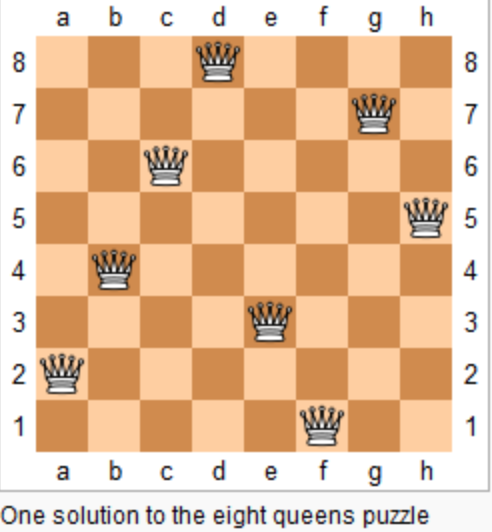
给定一个整数 n,返回 n 皇后不同的解决方案的数量。
@@ -306,8 +304,4 @@ class Solution {
}
}
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214.md" "b/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 74ff2ca40d..84bb5f6663
--- "a/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214.md"
+++ "b/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214.md" "b/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 74ff2ca40d..84bb5f6663
--- "a/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214.md"
+++ "b/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 53. 最大子序和
@@ -78,7 +76,7 @@ if (count > result) result = count;
如动画所示:
-
+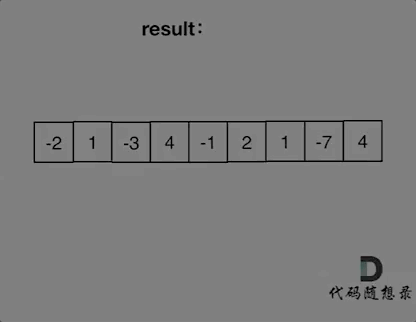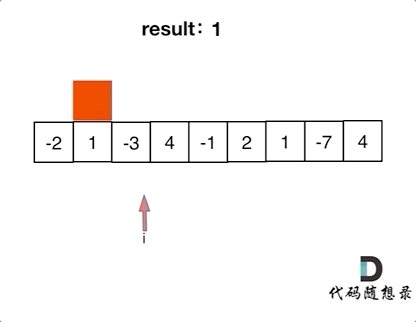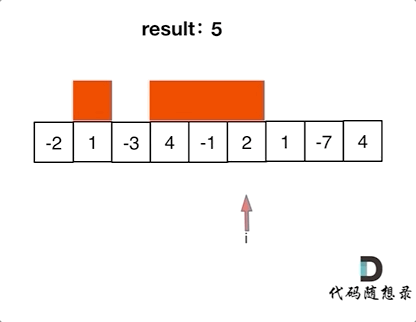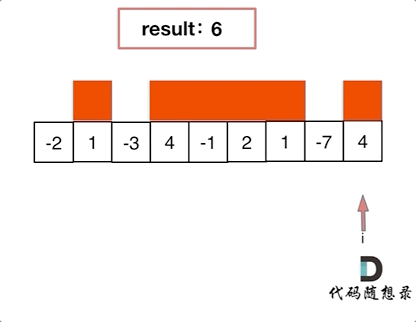
红色的起始位置就是贪心每次取 count 为正数的时候,开始一个区间的统计。
@@ -214,6 +212,7 @@ class Solution:
return result
```
+贪心法
```python
class Solution:
def maxSubArray(self, nums):
@@ -226,9 +225,55 @@ class Solution:
if count <= 0: # 相当于重置最大子序起始位置,因为遇到负数一定是拉低总和
count = 0
return result
+```
+动态规划
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def maxSubArray(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
+ dp = [0] * len(nums)
+ dp[0] = nums[0]
+ res = nums[0]
+ for i in range(1, len(nums)):
+ dp[i] = max(dp[i-1] + nums[i], nums[i])
+ res = max(res, dp[i])
+ return res
+```
+
+动态规划
+
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def maxSubArray(self, nums):
+ if not nums:
+ return 0
+ dp = [0] * len(nums) # dp[i]表示包括i之前的最大连续子序列和
+ dp[0] = nums[0]
+ result = dp[0]
+ for i in range(1, len(nums)):
+ dp[i] = max(dp[i-1]+nums[i], nums[i]) # 状态转移公式
+ if dp[i] > result:
+ result = dp[i] # result 保存dp[i]的最大值
+ return result
+```
+
+动态规划优化
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def maxSubArray(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
+ max_sum = float("-inf") # 初始化结果为负无穷大,方便比较取最大值
+ current_sum = 0 # 初始化当前连续和
+
+ for num in nums:
+ # 更新当前连续和
+ # 如果原本的连续和加上当前数字之后没有当前数字大,说明原本的连续和是负数,那么就直接从当前数字开始重新计算连续和
+ current_sum = max(current_sum+num, num)
+ max_sum = max(max_sum, current_sum) # 更新结果
+
+ return max_sum
```
+
### Go
贪心法
```go
@@ -279,7 +324,7 @@ pub fn max_sub_array(nums: Vec) -> i32 {
}
```
-### Javascript:
+### JavaScript:
```Javascript
var maxSubArray = function(nums) {
@@ -445,7 +490,3 @@ public class Solution
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md" "b/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 70ad7a8482..ba44a36104
--- "a/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md"
+++ "b/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md" "b/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 70ad7a8482..ba44a36104
--- "a/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md"
+++ "b/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 53. 最大子序和
@@ -56,7 +54,7 @@ dp[0]应该是多少呢?
5. 举例推导dp数组
以示例一为例,输入:nums = [-2,1,-3,4,-1,2,1,-5,4],对应的dp状态如下:
-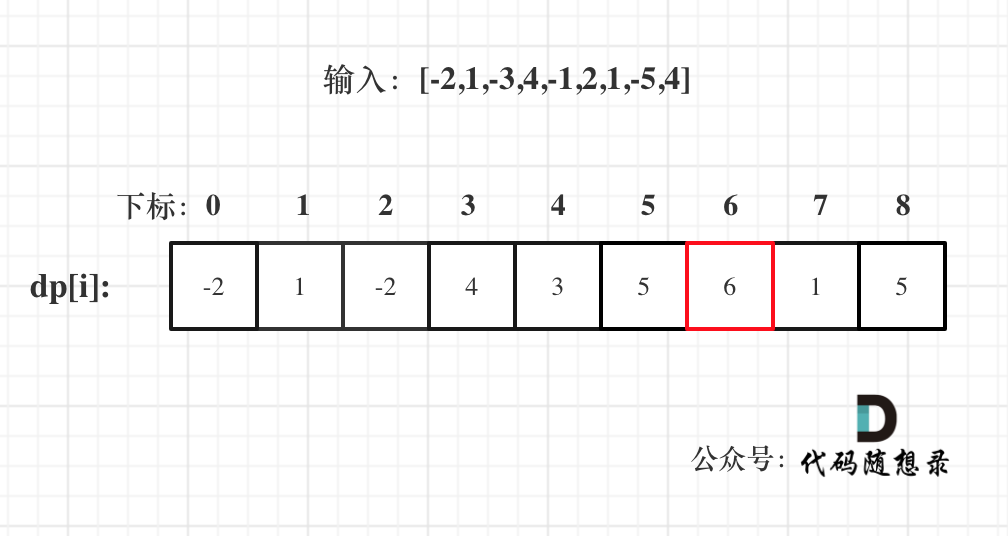
+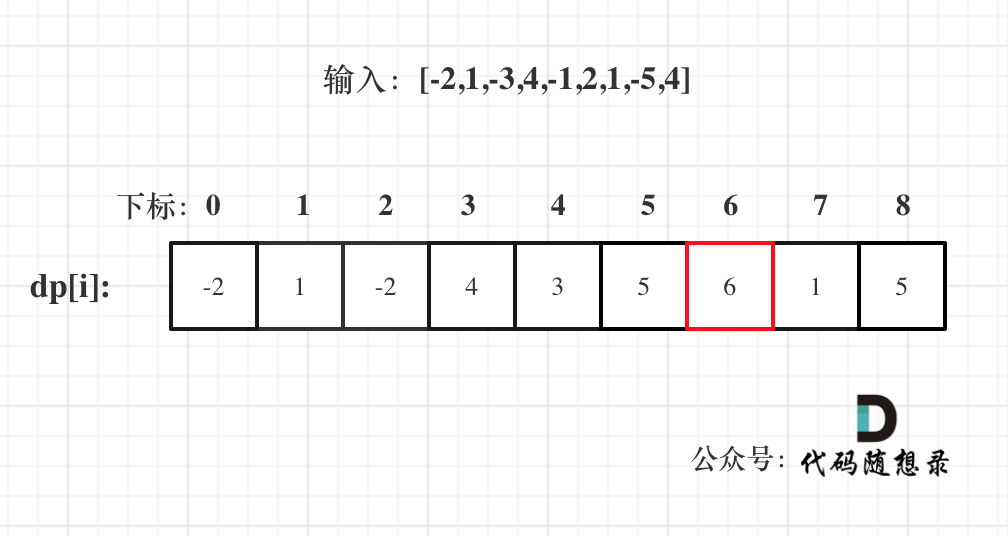
**注意最后的结果可不是dp[nums.size() - 1]!** ,而是dp[6]。
@@ -243,8 +241,4 @@ function maxSubArray(nums: number[]): number {
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0054.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265.md" "b/problems/0054.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 85e6a9364b..8b700c1fe8
--- "a/problems/0054.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265.md"
+++ "b/problems/0054.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0054.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265.md" "b/problems/0054.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 85e6a9364b..8b700c1fe8
--- "a/problems/0054.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265.md"
+++ "b/problems/0054.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
@@ -38,7 +36,7 @@
由外向内一圈一圈这么画下去,如下所示:
-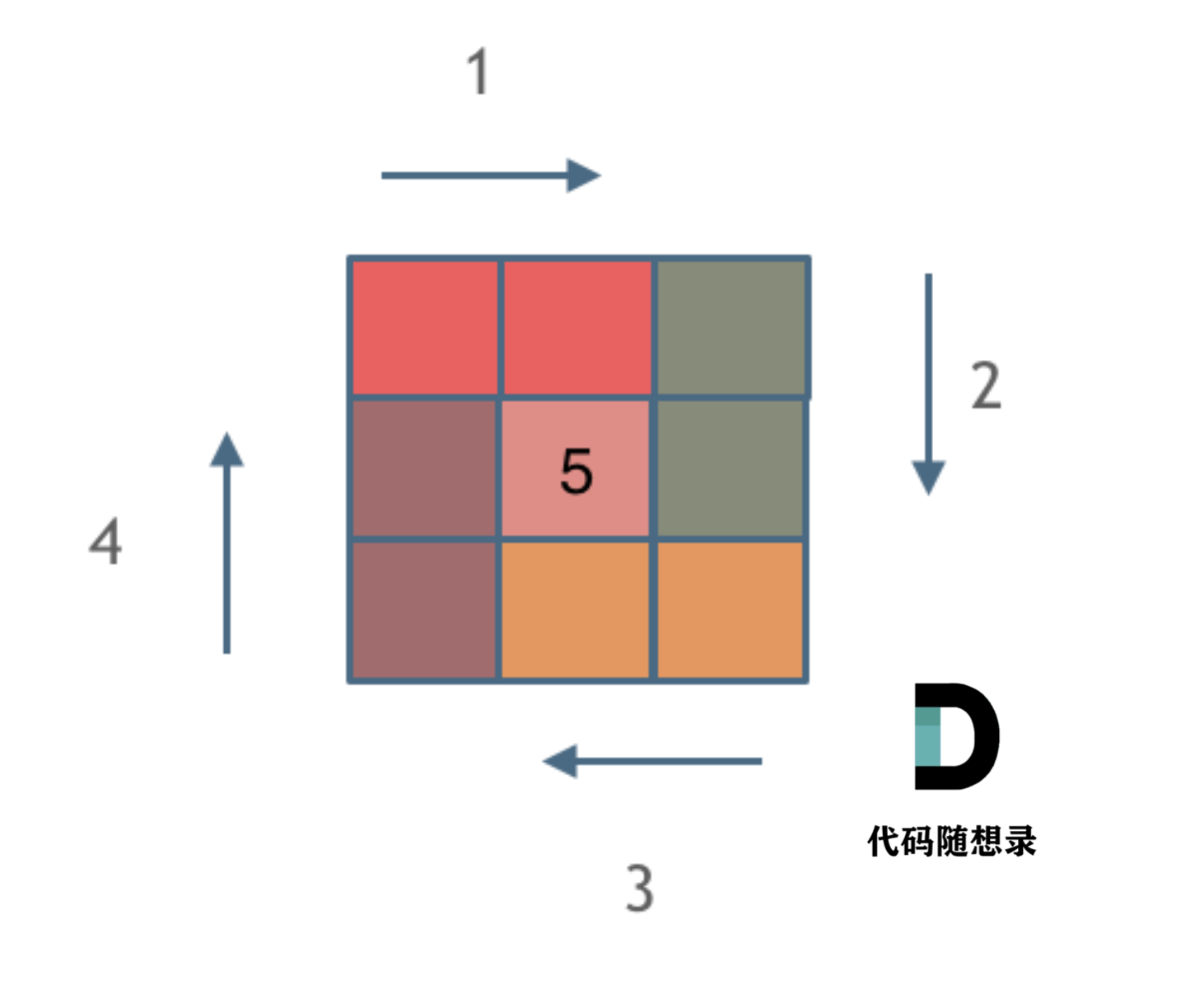
+
这里每一种颜色,代表一条边,我们遍历的长度,可以看出每一个拐角处的处理规则,拐角处让给新的一条边来继续画。
@@ -200,7 +198,67 @@ class Solution {
}
```
-### Javascript
+```java
+class Solution {
+ public List spiralOrder(int[][] matrix) {
+ List res = new ArrayList<>(); // 存放结果
+ if (matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0)
+ return res;
+ int rows = matrix.length, columns = matrix[0].length;
+ int startx = 0, starty = 0; // 定义每循环一个圈的起始位置
+ int loop = 0; // 循环次数
+ int offset = 1; // 每一圈循环,需要控制每一条边遍历的长度
+ while (loop < Math.min(rows, columns) / 2) {
+ int i = startx;
+ int j = starty;
+ // 模拟填充上行从左到右(左闭右开)
+ for (; j < columns - offset; j++) {
+ res.add(matrix[i][j]);
+ }
+ // 模拟填充右列从上到下(左闭右开)
+ for (; i < rows - offset; i++) {
+ res.add(matrix[i][j]);
+ }
+ // 模拟填充下行从右到左(左闭右开)
+ for (; j > starty; j--) {
+ res.add(matrix[i][j]);
+ }
+ // 模拟填充左列从下到上(左闭右开)
+ for (; i > startx; i--) {
+ res.add(matrix[i][j]);
+ }
+
+ // 起始位置加1 循环次数加1 并控制每条边遍历的长度
+ startx++;
+ starty++;
+ offset++;
+ loop++;
+ }
+
+ // 如果列或行中的最小值为奇数 则一定有未遍历的部分
+ // 可以自行画图理解
+ if (Math.min(rows, columns) % 2 == 1) {
+ // 当行大于列时 未遍历的部分是列
+ // (startx, starty)即下一个要遍历位置 从该位置出发 遍历完未遍历的列
+ // 遍历次数为rows - columns + 1
+ if (rows > columns) {
+ for (int i = 0; i < rows - columns + 1; i++) {
+ res.add(matrix[startx++][starty]);
+ }
+ } else {
+ // 此处与上面同理 遍历完未遍历的行
+ for (int i = 0; i < columns - rows + 1; i++) {
+ res.add(matrix[startx][starty++]);
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+ return res;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+### JavaScript
```
/**
* @param {number[][]} matrix
@@ -348,8 +406,80 @@ class Solution(object):
return print_list
```
+### Go
+
+```go
+func spiralOrder(matrix [][]int) []int {
+ rows := len(matrix)
+ if rows == 0 {
+ return []int{}
+ }
+ columns := len(matrix[0])
+ if columns == 0 {
+ return []int{}
+ }
+ res := make([]int, rows * columns)
+ startx, starty := 0, 0 // 定义每循环一个圈的起始位置
+ loop := min(rows, columns) / 2
+ mid := min(rows, columns) / 2
+ count := 0 // 用来给矩阵中每一个空格赋值
+ offset := 1 // 每一圈循环,需要控制每一条边遍历的长度
+ for loop > 0 {
+ i, j := startx, starty
+
+ // 模拟填充上行从左到右(左闭右开)
+ for ; j < starty + columns - offset; j++ {
+ res[count] = matrix[startx][j]
+ count++
+ }
+ // 模拟填充右列从上到下(左闭右开)
+ for ; i < startx + rows - offset; i++ {
+ res[count] = matrix[i][j]
+ count++
+ }
+ // 模拟填充下行从右到左(左闭右开)
+ for ; j > starty; j-- {
+ res[count] = matrix[i][j]
+ count++
+ }
+ // 模拟填充左列从下到上(左闭右开)
+ for ; i > startx; i-- {
+ res[count] = matrix[i][starty]
+ count++
+ }
+
+ // 第二圈开始的时候,起始位置要各自加1, 例如:第一圈起始位置是(0, 0),第二圈起始位置是(1, 1)
+ startx++
+ starty++
+
+ // offset 控制每一圈里每一条边遍历的长度
+ offset += 2
+ loop--
+ }
+
+ // 如果min(rows, columns)为奇数的话,需要单独给矩阵最中间的位置赋值
+ if min(rows, columns) % 2 == 1 {
+ if rows > columns {
+ for i := mid; i < mid + rows - columns + 1; i++ {
+ res[count] = matrix[i][mid]
+ count++
+ }
+ } else {
+ for i := mid; i < mid + columns - rows + 1; i++ {
+ res[count] = matrix[mid][i]
+ count++
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return res
+}
+
+func min(x, y int) int {
+ if x < y {
+ return x
+ }
+ return y
+}
+```
+
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0055.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217.md" "b/problems/0055.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 086fd64f5e..513fc2e340
--- "a/problems/0055.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217.md"
+++ "b/problems/0055.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0055.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217.md" "b/problems/0055.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 086fd64f5e..513fc2e340
--- "a/problems/0055.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217.md"
+++ "b/problems/0055.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 55. 跳跃游戏
@@ -50,7 +48,7 @@
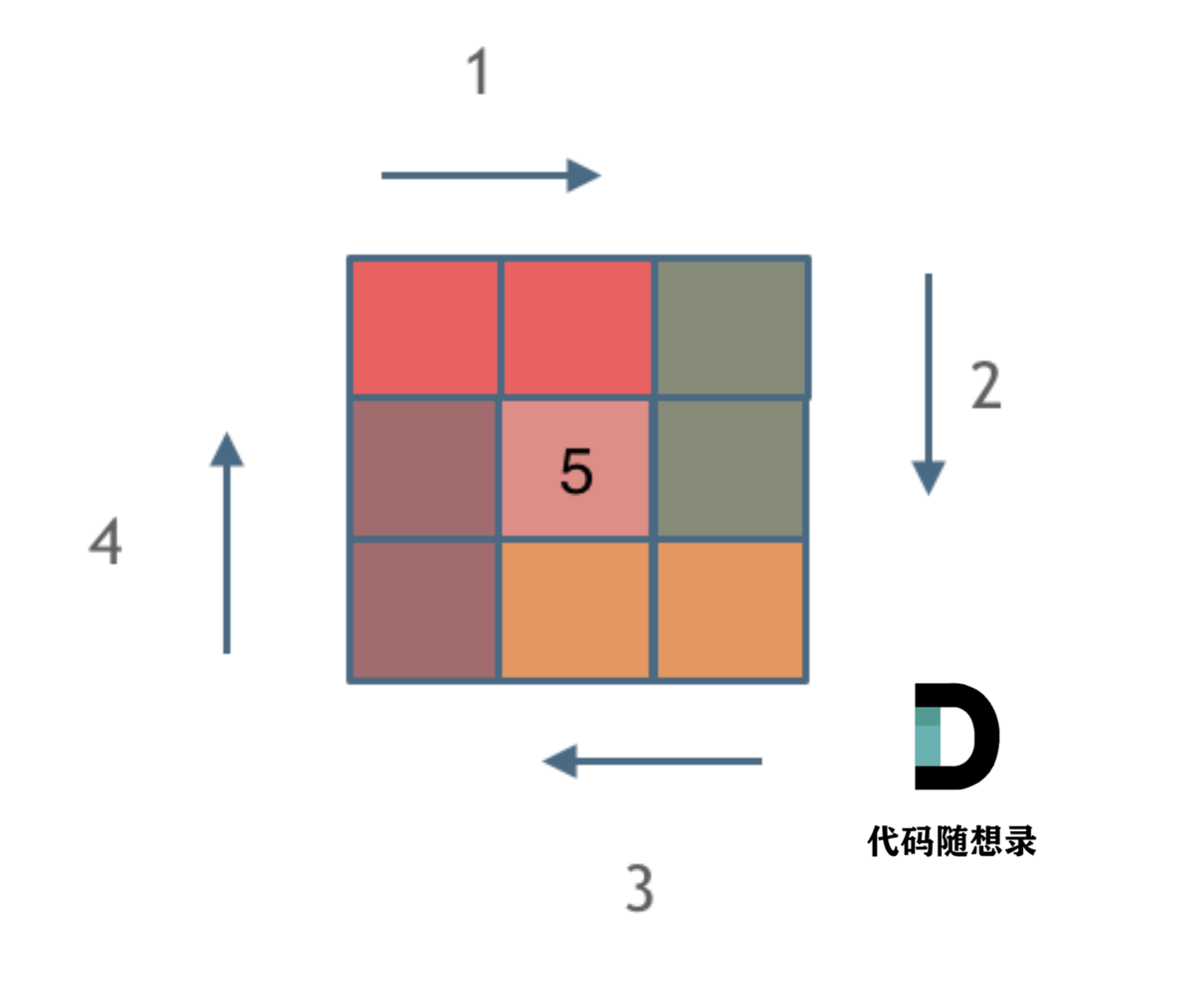
如图:
-
+
i 每次移动只能在 cover 的范围内移动,每移动一个元素,cover 得到该元素数值(新的覆盖范围)的补充,让 i 继续移动下去。
@@ -143,6 +141,23 @@ class Solution:
return False
```
+```python
+## 基于当前最远可到达位置判断
+class Solution:
+ def canJump(self, nums: List[int]) -> bool:
+ far = nums[0]
+ for i in range(len(nums)):
+ # 要考虑两个情况
+ # 1. i <= far - 表示 当前位置i 可以到达
+ # 2. i > far - 表示 当前位置i 无法到达
+ if i > far:
+ return False
+ far = max(far, nums[i]+i)
+ # 如果循环正常结束,表示最后一个位置也可以到达,否则会在中途直接退出
+ # 关键点在于,要想明白其实列表中的每个位置都是需要验证能否到达的
+ return True
+```
+
### Go
```go
@@ -166,7 +181,7 @@ func max(a, b int ) int {
}
```
-### Javascript
+### JavaScript
```Javascript
var canJump = function(nums) {
@@ -276,7 +291,3 @@ public class Solution
}
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0056.\345\220\210\345\271\266\345\214\272\351\227\264.md" "b/problems/0056.\345\220\210\345\271\266\345\214\272\351\227\264.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 122e783a27..24a97f6c5a
--- "a/problems/0056.\345\220\210\345\271\266\345\214\272\351\227\264.md"
+++ "b/problems/0056.\345\220\210\345\271\266\345\214\272\351\227\264.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0056.\345\220\210\345\271\266\345\214\272\351\227\264.md" "b/problems/0056.\345\220\210\345\271\266\345\214\272\351\227\264.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 122e783a27..24a97f6c5a
--- "a/problems/0056.\345\220\210\345\271\266\345\214\272\351\227\264.md"
+++ "b/problems/0056.\345\220\210\345\271\266\345\214\272\351\227\264.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 56. 合并区间
@@ -40,7 +38,7 @@
这么说有点抽象,看图:(**注意图中区间都是按照左边界排序之后了**)
-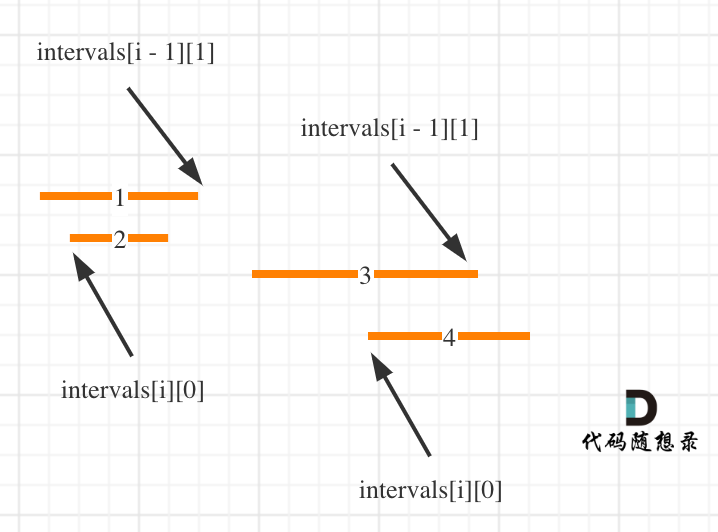
+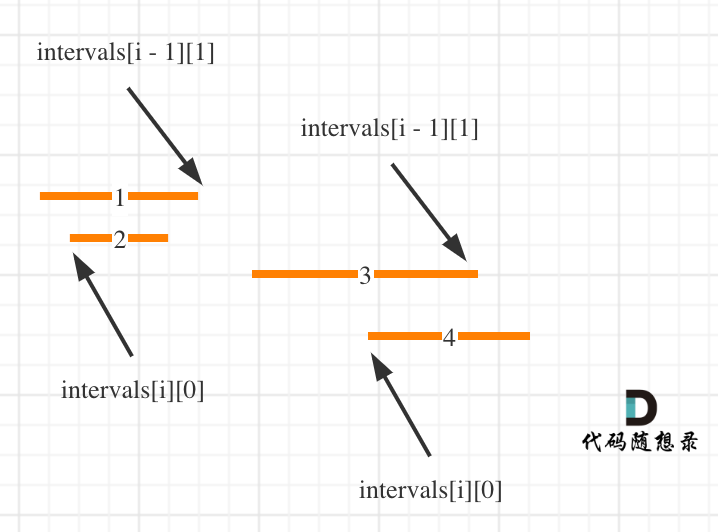
知道如何判断重复之后,剩下的就是合并了,如何去模拟合并区间呢?
@@ -215,7 +213,7 @@ func max56(a, b int) int {
```
-### Javascript
+### JavaScript
```javascript
var merge = function (intervals) {
intervals.sort((a, b) => a[0] - b[0]);
@@ -336,7 +334,49 @@ impl Solution {
}
}
```
+### C
+
+```c
+#define max(a, b) ((a) > (b) ? (a) : (b))
+
+// 根据左边界进行排序
+int cmp(const void * var1, const void * var2){
+ int *v1 = *(int **) var1;
+ int *v2 = *(int **) var2;
+ return v1[0] - v2[0];
+}
+
+int** merge(int** intervals, int intervalsSize, int* intervalsColSize, int* returnSize, int** returnColumnSizes) {
+ int ** result = malloc(sizeof (int *) * intervalsSize);
+ * returnColumnSizes = malloc(sizeof (int ) * intervalsSize);
+ for(int i = 0; i < intervalsSize; i++){
+ result[i] = malloc(sizeof (int ) * 2);
+ }
+ qsort(intervals, intervalsSize, sizeof (int *), cmp);
+ int count = 0;
+ for(int i = 0; i < intervalsSize; i++){
+ // 记录区间的左右边界
+ int L = intervals[i][0], R = intervals[i][1];
+ // 如果count为0或者前一区间的右区间小于此时的左边,加入结果中
+ if (count == 0 || result[count - 1][1] < L) {
+ returnColumnSizes[0][count] = 2;
+ result[count][0] = L;
+ result[count][1] = R;
+ count++;
+ }
+ else{ // 更新右边界的值
+ result[count - 1][1] = max(R, result[count - 1][1]);
+ }
+ }
+ *returnSize = count;
+ return result;
+}
+```
+
+
+
### C#
+
```csharp
public class Solution
{
@@ -363,8 +403,3 @@ public class Solution
}
```
-
-
-  -
-
diff --git "a/problems/0059.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265II.md" "b/problems/0059.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 7f73bc488d..927df1c6c1
--- "a/problems/0059.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0059.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265II.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0059.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265II.md" "b/problems/0059.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 7f73bc488d..927df1c6c1
--- "a/problems/0059.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0059.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265II.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
@@ -56,7 +54,7 @@
那么我按照左闭右开的原则,来画一圈,大家看一下:
-
+
这里每一种颜色,代表一条边,我们遍历的长度,可以看出每一个拐角处的处理规则,拐角处让给新的一条边来继续画。
@@ -715,26 +713,65 @@ object Solution {
### C#:
```csharp
-public class Solution {
- public int[][] GenerateMatrix(int n) {
- int[][] answer = new int[n][];
- for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
- answer[i] = new int[n];
- int start = 0;
- int end = n - 1;
- int tmp = 1;
- while(tmp < n * n)
+public int[][] GenerateMatrix(int n)
+{
+ // 参考Carl的代码随想录里面C++的思路
+ // https://www.programmercarl.com/0059.%E8%9E%BA%E6%97%8B%E7%9F%A9%E9%98%B5II.html#%E6%80%9D%E8%B7%AF
+ int startX = 0, startY = 0; // 定义每循环一个圈的起始位置
+ int loop = n / 2; // 每个圈循环几次,例如n为奇数3,那么loop = 1 只是循环一圈,矩阵中间的值需要单独处理
+ int count = 1; // 用来给矩阵每个空格赋值
+ int mid = n / 2; // 矩阵中间的位置,例如:n为3, 中间的位置就是(1,1),n为5,中间位置为(2, 2)
+ int offset = 1;// 需要控制每一条边遍历的长度,每次循环右边界收缩一位
+
+ // 构建result二维数组
+ int[][] result = new int[n][];
+ for (int k = 0; k < n; k++)
+ {
+ result[k] = new int[n];
+ }
+
+ int i = 0, j = 0; // [i,j]
+ while (loop > 0)
+ {
+ i = startX;
+ j = startY;
+ // 四个For循环模拟转一圈
+ // 第一排,从左往右遍历,不取最右侧的值(左闭右开)
+ for (; j < n - offset; j++)
+ {
+ result[i][j] = count++;
+ }
+ // 右侧的第一列,从上往下遍历,不取最下面的值(左闭右开)
+ for (; i < n - offset; i++)
+ {
+ result[i][j] = count++;
+ }
+
+ // 最下面的第一行,从右往左遍历,不取最左侧的值(左闭右开)
+ for (; j > startY; j--)
+ {
+ result[i][j] = count++;
+ }
+
+ // 左侧第一列,从下往上遍历,不取最左侧的值(左闭右开)
+ for (; i > startX; i--)
{
- for(int i = start; i < end; i++) answer[start][i] = tmp++;
- for(int i = start; i < end; i++) answer[i][end] = tmp++;
- for(int i = end; i > start; i--) answer[end][i] = tmp++;
- for(int i = end; i > start; i--) answer[i][start] = tmp++;
- start++;
- end--;
- }
- if(n % 2 == 1) answer[n / 2][n / 2] = tmp;
- return answer;
+ result[i][j] = count++;
+ }
+ // 第二圈开始的时候,起始位置要各自加1, 例如:第一圈起始位置是(0, 0),第二圈起始位置是(1, 1)
+ startX++;
+ startY++;
+
+ // offset 控制每一圈里每一条边遍历的长度
+ offset++;
+ loop--;
+ }
+ if (n % 2 == 1)
+ {
+ // n 为奇数
+ result[mid][mid] = count;
}
+ return result;
}
```
@@ -790,7 +827,3 @@ def generate_matrix(n)
end
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0062.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204.md" "b/problems/0062.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 207a66ee80..ac60767dce
--- "a/problems/0062.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204.md"
+++ "b/problems/0062.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0062.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204.md" "b/problems/0062.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 207a66ee80..ac60767dce
--- "a/problems/0062.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204.md"
+++ "b/problems/0062.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
# 62.不同路径
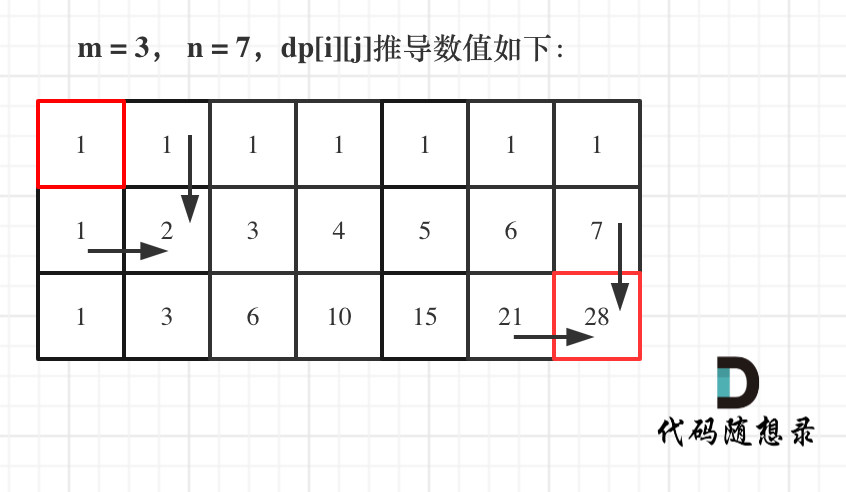
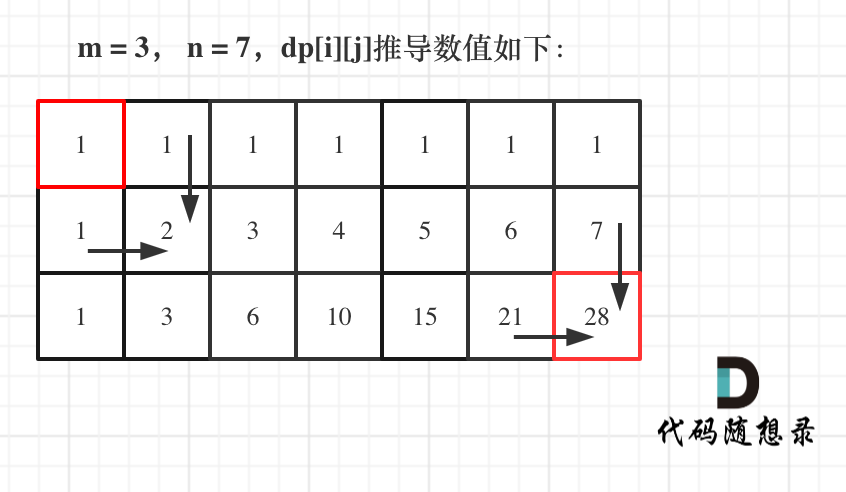
@@ -18,7 +16,7 @@
示例 1:
-
+
* 输入:m = 3, n = 7
* 输出:28
@@ -64,7 +62,7 @@
如图举例:
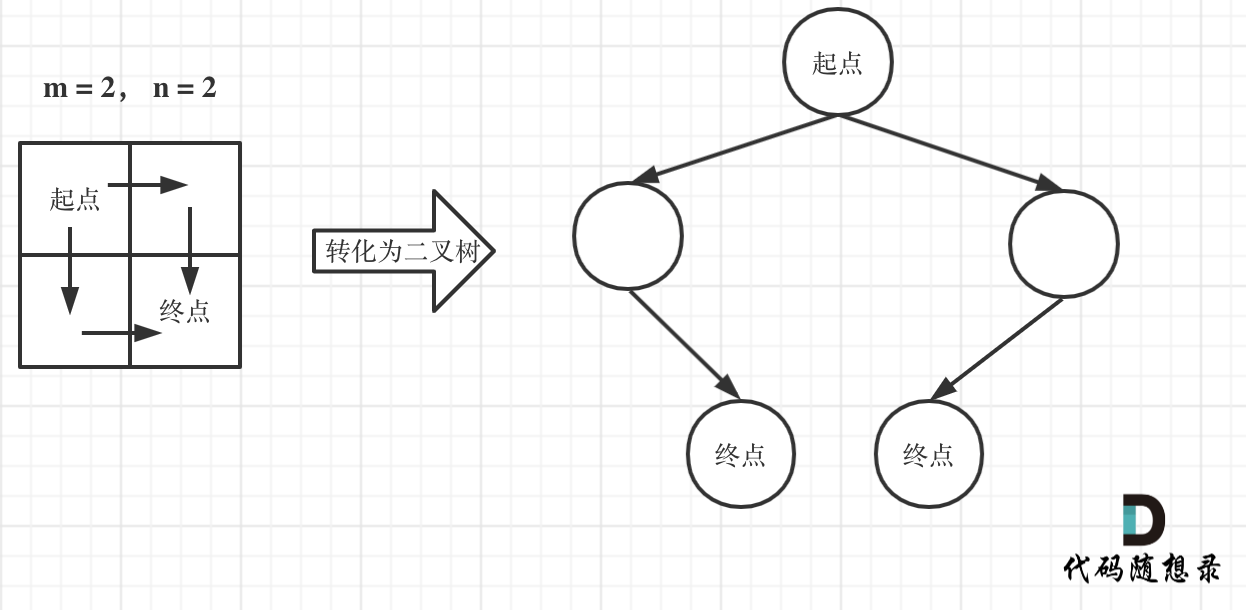
-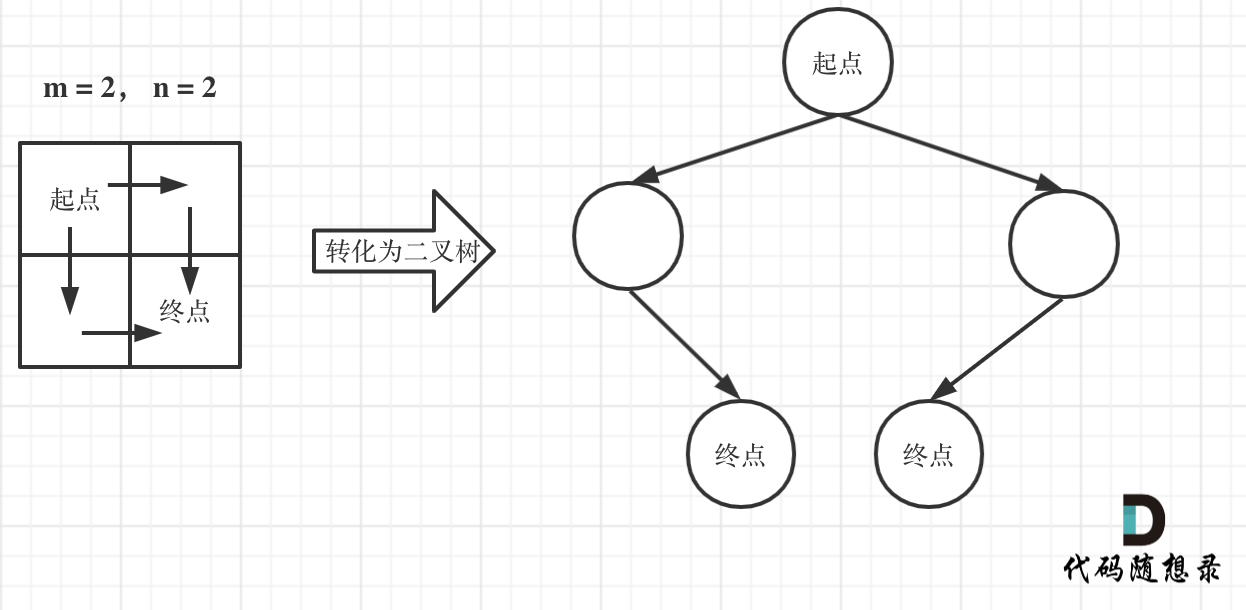
+
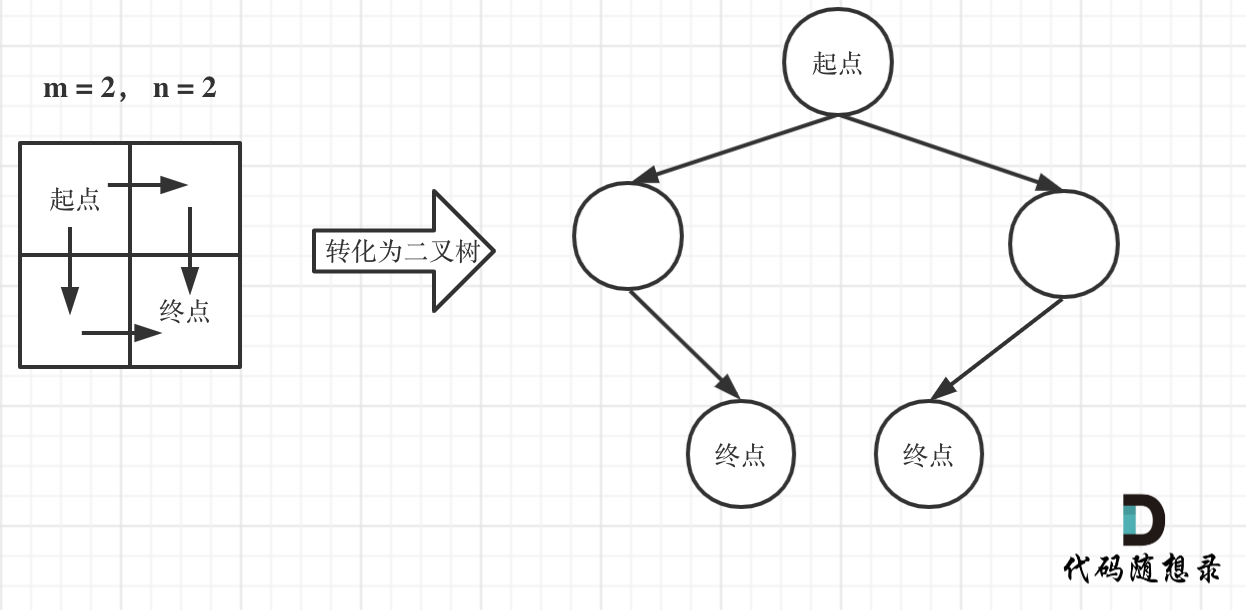
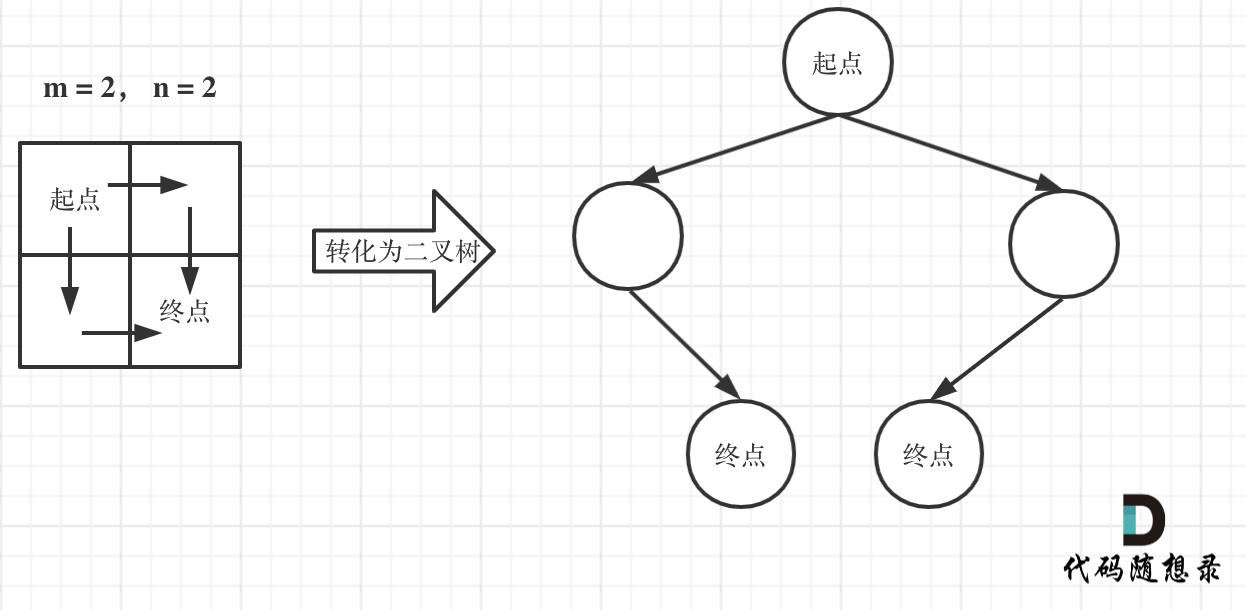
此时问题就可以转化为求二叉树叶子节点的个数,代码如下:
@@ -133,7 +131,7 @@ for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) dp[0][j] = 1;
如图所示:
-
+
以上动规五部曲分析完毕,C++代码如下:
@@ -182,7 +180,7 @@ public:
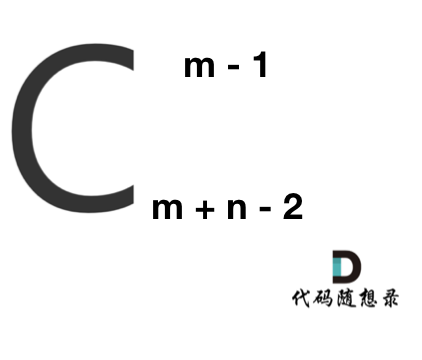
在这个图中,可以看出一共m,n的话,无论怎么走,走到终点都需要 m + n - 2 步。
-
+
在这m + n - 2 步中,一定有 m - 1 步是要向下走的,不用管什么时候向下走。
@@ -192,7 +190,7 @@ public:
那么答案,如图所示:
-
+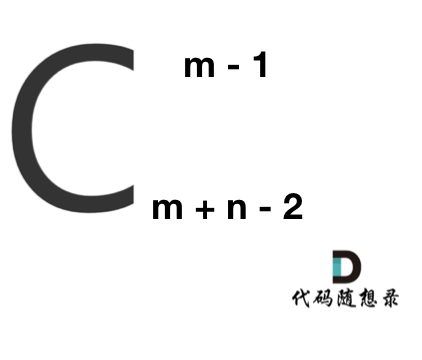
**求组合的时候,要防止两个int相乘溢出!** 所以不能把算式的分子都算出来,分母都算出来再做除法。
@@ -285,6 +283,24 @@ public:
}
```
+状态压缩
+```java
+class Solution {
+ public int uniquePaths(int m, int n) {
+ // 在二维dp数组中,当前值的计算只依赖正上方和正左方,因此可以压缩成一维数组。
+ int[] dp = new int[n];
+ // 初始化,第一行只能从正左方跳过来,所以只有一条路径。
+ Arrays.fill(dp, 1);
+ for (int i = 1; i < m; i ++) {
+ // 第一列也只有一条路,不用迭代,所以从第二列开始
+ for (int j = 1; j < n; j ++) {
+ dp[j] += dp[j - 1]; // dp[j] = dp[j] (正上方)+ dp[j - 1] (正左方)
+ }
+ }
+ return dp[n - 1];
+ }
+}
+```
### Python
递归
@@ -353,6 +369,7 @@ class Solution:
```
### Go
+动态规划
```Go
func uniquePaths(m int, n int) int {
dp := make([][]int, m)
@@ -372,7 +389,27 @@ func uniquePaths(m int, n int) int {
}
```
-### Javascript
+数论方法
+```Go
+func uniquePaths(m int, n int) int {
+ numerator := 1
+ denominator := m - 1
+ count := m - 1
+ t := m + n - 2
+ for count > 0 {
+ numerator *= t
+ t--
+ for denominator != 0 && numerator % denominator == 0 {
+ numerator /= denominator
+ denominator--
+ }
+ count--
+ }
+ return numerator
+}
+```
+
+### JavaScript
```Javascript
var uniquePaths = function(m, n) {
@@ -576,8 +613,4 @@ public class Solution
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0063.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204II.md" "b/problems/0063.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 8c208ea865..f39afe8455
--- "a/problems/0063.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0063.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204II.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0063.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204II.md" "b/problems/0063.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 8c208ea865..f39afe8455
--- "a/problems/0063.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0063.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204II.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
# 63. 不同路径 II
@@ -16,13 +14,13 @@
现在考虑网格中有障碍物。那么从左上角到右下角将会有多少条不同的路径?
-
+
网格中的障碍物和空位置分别用 1 和 0 来表示。
示例 1:
-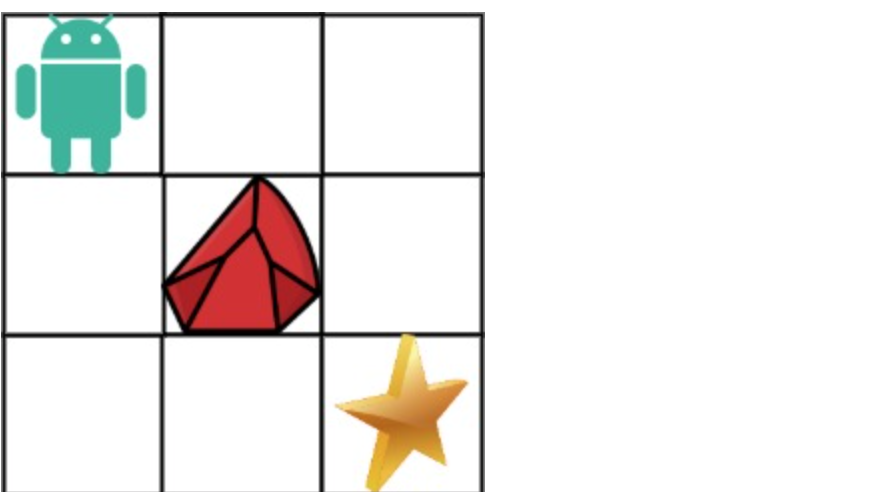
+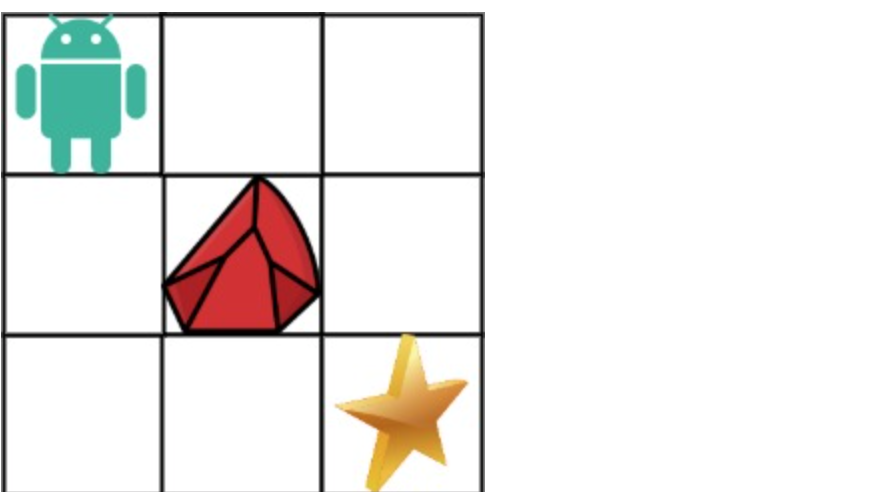
* 输入:obstacleGrid = [[0,0,0],[0,1,0],[0,0,0]]
* 输出:2
@@ -34,7 +32,7 @@
示例 2:
-
+
* 输入:obstacleGrid = [[0,1],[0,0]]
* 输出:1
@@ -95,7 +93,7 @@ for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) dp[0][j] = 1;
如图:
-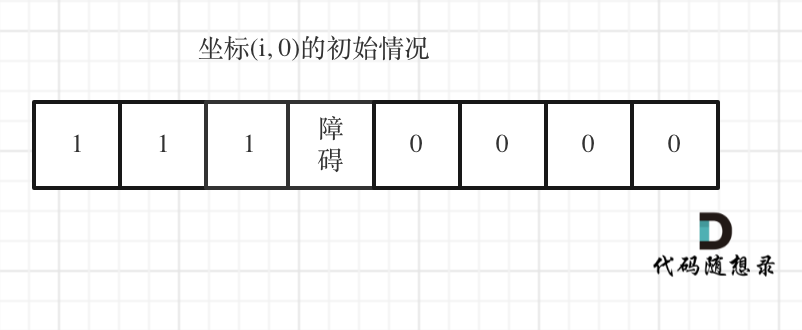
+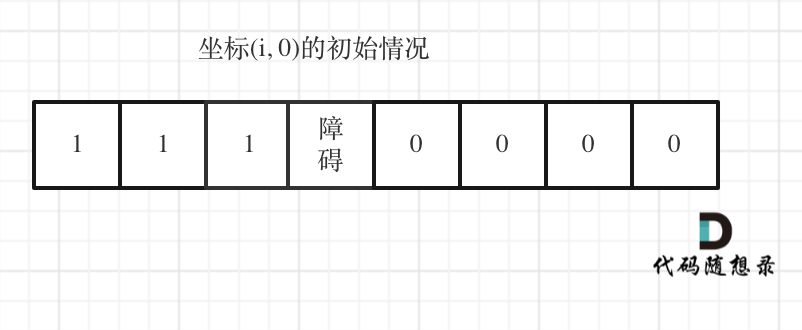
下标(0, j)的初始化情况同理。
@@ -129,11 +127,11 @@ for (int i = 1; i < m; i++) {
拿示例1来举例如题:
-
+
对应的dp table 如图:
-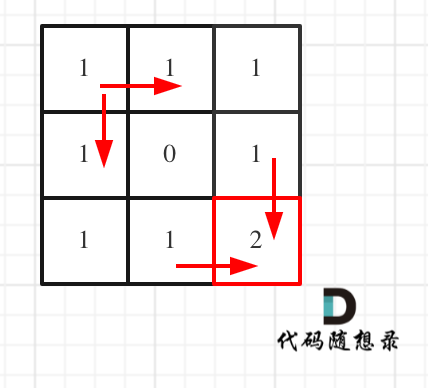
+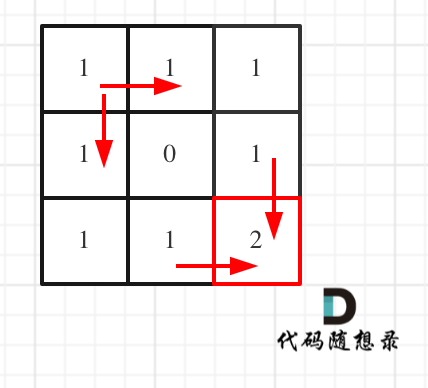
如果这个图看不懂,建议再理解一下递归公式,然后照着文章中说的遍历顺序,自己推导一下!
@@ -145,7 +143,7 @@ public:
int uniquePathsWithObstacles(vector>& obstacleGrid) {
int m = obstacleGrid.size();
int n = obstacleGrid[0].size();
- if (obstacleGrid[m - 1][n - 1] == 1 || obstacleGrid[0][0] == 1) //如果在起点或终点出现了障碍,直接返回0
+ if (obstacleGrid[m - 1][n - 1] == 1 || obstacleGrid[0][0] == 1) //如果在起点或终点出现了障碍,直接返回0
return 0;
vector> dp(m, vector(n, 0));
for (int i = 0; i < m && obstacleGrid[i][0] == 0; i++) dp[i][0] = 1;
@@ -465,7 +463,7 @@ func uniquePathsWithObstacles(obstacleGrid [][]int) int {
}
```
-### Javascript
+### JavaScript
```Javascript
var uniquePathsWithObstacles = function(obstacleGrid) {
@@ -550,6 +548,27 @@ function uniquePathsWithObstacles(obstacleGrid: number[][]): number {
};
```
+// 版本二: dp改為使用一維陣列,從終點開始遍歷
+```typescript
+function uniquePathsWithObstacles(obstacleGrid: number[][]): number {
+ const m = obstacleGrid.length;
+ const n = obstacleGrid[0].length;
+
+ const dp: number[] = new Array(n).fill(0);
+ dp[n - 1] = 1;
+
+ // 由下而上,右而左進行遍歷
+ for (let i = m - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
+ for (let j = n - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
+ if (obstacleGrid[i][j] === 1) dp[j] = 0;
+ else dp[j] = dp[j] + (dp[j + 1] || 0);
+ }
+ }
+
+ return dp[0];
+};
+```
+
### Rust
```Rust
@@ -759,8 +778,4 @@ public class Solution
}
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257.md" "b/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 67bbdd7b81..316fbd4f39
--- "a/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257.md"
+++ "b/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257.md" "b/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 67bbdd7b81..316fbd4f39
--- "a/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257.md"
+++ "b/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 70. 爬楼梯
@@ -103,7 +101,7 @@ dp[i]: 爬到第i层楼梯,有dp[i]种方法
举例当n为5的时候,dp table(dp数组)应该是这样的
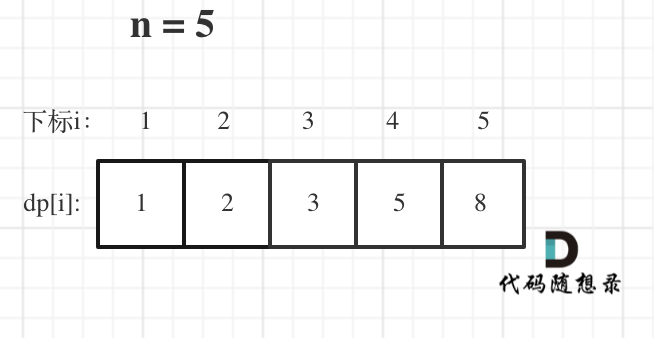
-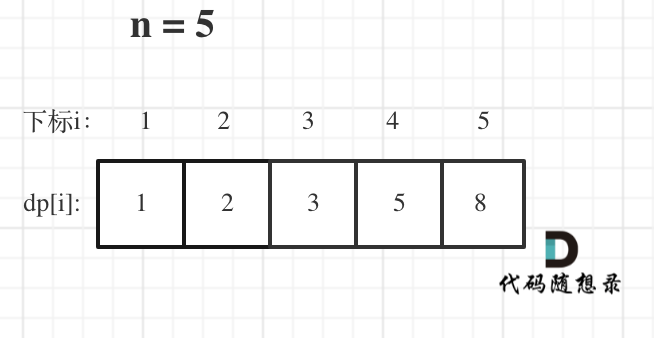
+
如果代码出问题了,就把dp table 打印出来,看看究竟是不是和自己推导的一样。
@@ -130,8 +128,8 @@ public:
};
```
-* 时间复杂度:$O(n)$
-* 空间复杂度:$O(n)$
+* 时间复杂度:O(n)
+* 空间复杂度:O(n)
当然依然也可以,优化一下空间复杂度,代码如下:
@@ -154,8 +152,8 @@ public:
};
```
-* 时间复杂度:$O(n)$
-* 空间复杂度:$O(1)$
+* 时间复杂度:O(n)
+* 空间复杂度:O(1)
后面将讲解的很多动规的题目其实都是当前状态依赖前两个,或者前三个状态,都可以做空间上的优化,**但我个人认为面试中能写出版本一就够了哈,清晰明了,如果面试官要求进一步优化空间的话,我们再去优化**。
@@ -327,7 +325,7 @@ func climbStairs(n int) int {
return dp[n]
}
```
-### Javascript
+### JavaScript
```Javascript
var climbStairs = function(n) {
// dp[i] 为第 i 阶楼梯有多少种方法爬到楼顶
@@ -519,8 +517,5 @@ impl Solution {
}
```
-
-
-  -
+
diff --git "a/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257\345\256\214\345\205\250\350\203\214\345\214\205\347\211\210\346\234\254.md" "b/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257\345\256\214\345\205\250\350\203\214\345\214\205\347\211\210\346\234\254.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 4fa294cfe2..a5435ddd71
--- "a/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257\345\256\214\345\205\250\350\203\214\345\214\205\347\211\210\346\234\254.md"
+++ "b/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257\345\256\214\345\205\250\350\203\214\345\214\205\347\211\210\346\234\254.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+
diff --git "a/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257\345\256\214\345\205\250\350\203\214\345\214\205\347\211\210\346\234\254.md" "b/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257\345\256\214\345\205\250\350\203\214\345\214\205\347\211\210\346\234\254.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 4fa294cfe2..a5435ddd71
--- "a/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257\345\256\214\345\205\250\350\203\214\345\214\205\347\211\210\346\234\254.md"
+++ "b/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257\345\256\214\345\205\250\350\203\214\345\214\205\347\211\210\346\234\254.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 70. 爬楼梯(进阶版)
@@ -165,11 +163,35 @@ class climbStairs{
```
### Python3:
+```python3
+def climbing_stairs(n,m):
+ dp = [0]*(n+1) # 背包总容量
+ dp[0] = 1
+ # 排列题,注意循环顺序,背包在外物品在内
+ for j in range(1,n+1):
+ for i in range(1,m+1):
+ if j>=i:
+ dp[j] += dp[j-i] # 这里i就是重量而非index
+ return dp[n]
+if __name__ == '__main__':
+ n,m = list(map(int,input().split(' ')))
+ print(climbing_stairs(n,m))
+```
### Go:
```go
+package main
+
+import (
+ "bufio"
+ "fmt"
+ "os"
+ "strconv"
+ "strings"
+)
+
func climbStairs(n int, m int) int {
dp := make([]int, n+1)
dp[0] = 1
@@ -197,15 +219,34 @@ func main() {
```
### JavaScript:
-
+```javaScript
+var climbStairs = function (n) {
+ let dp = new Array(n + 1).fill(0);
+ dp[0] = 1;
+ // 排列题,注意循环顺序,背包在外物品在内
+ for (let j = 1; j <= n; j++) {//遍历背包
+ for (let i = 1; i <= 2; i++) {//遍历物品
+ if (j - i >= 0) dp[j] = dp[j] + dp[j - i];
+ }
+ }
+ return dp[n];
+}
+```
### TypeScript:
-
+```typescript
+var climbStairs = function (n: number): number {
+ let dp: number[] = new Array(n + 1).fill(0);
+ dp[0] = 1;
+ for (let j = 1; j <= n; j++) {//遍历背包
+ for (let i = 1; i <= 2; i++) {//遍历物品
+ if (j - i >= 0) dp[j] = dp[j] + dp[j - i];
+ }
+ }
+ return dp[n];
+}
+```
### Rust:
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0072.\347\274\226\350\276\221\350\267\235\347\246\273.md" "b/problems/0072.\347\274\226\350\276\221\350\267\235\347\246\273.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 777b851cca..c4bcbb4338
--- "a/problems/0072.\347\274\226\350\276\221\350\267\235\347\246\273.md"
+++ "b/problems/0072.\347\274\226\350\276\221\350\267\235\347\246\273.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0072.\347\274\226\350\276\221\350\267\235\347\246\273.md" "b/problems/0072.\347\274\226\350\276\221\350\267\235\347\246\273.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 777b851cca..c4bcbb4338
--- "a/problems/0072.\347\274\226\350\276\221\350\267\235\347\246\273.md"
+++ "b/problems/0072.\347\274\226\350\276\221\350\267\235\347\246\273.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 72. 编辑距离
@@ -172,7 +170,7 @@ for (int j = 0; j <= word2.size(); j++) dp[0][j] = j;
可以看出dp[i][j]是依赖左方,上方和左上方元素的,如图:
-
+
所以在dp矩阵中一定是从左到右从上到下去遍历。
@@ -196,7 +194,7 @@ for (int i = 1; i <= word1.size(); i++) {
以示例1为例,输入:`word1 = "horse", word2 = "ros"`为例,dp矩阵状态图如下:
-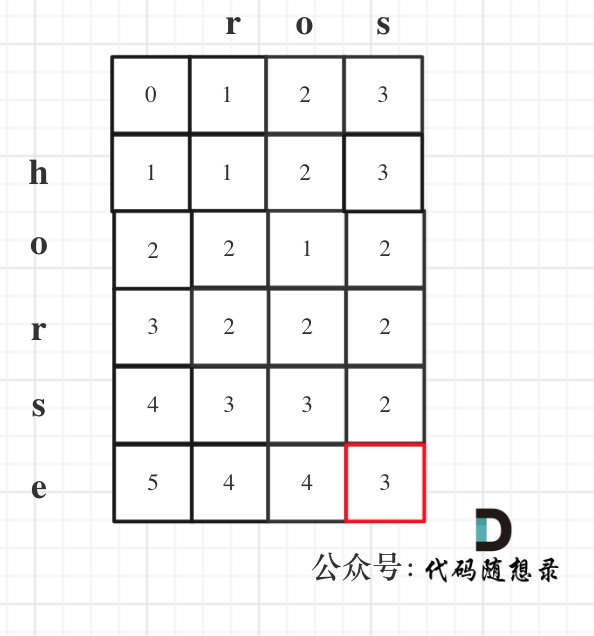
+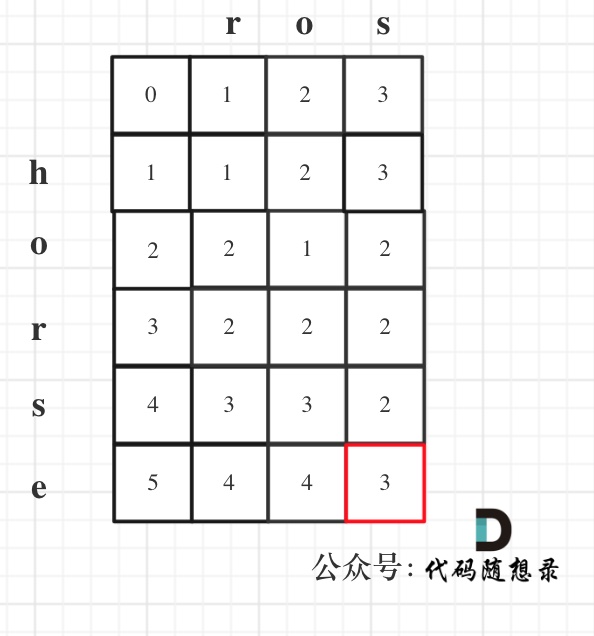
以上动规五部分析完毕,C++代码如下:
@@ -313,7 +311,7 @@ func Min(args ...int) int {
}
```
-### Javascript:
+### JavaScript:
```javascript
const minDistance = (word1, word2) => {
@@ -462,7 +460,3 @@ impl Solution {
}
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0077.\347\273\204\345\220\210.md" "b/problems/0077.\347\273\204\345\220\210.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 103fb627f5..4c9e97fd47
--- "a/problems/0077.\347\273\204\345\220\210.md"
+++ "b/problems/0077.\347\273\204\345\220\210.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0077.\347\273\204\345\220\210.md" "b/problems/0077.\347\273\204\345\220\210.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 103fb627f5..4c9e97fd47
--- "a/problems/0077.\347\273\204\345\220\210.md"
+++ "b/problems/0077.\347\273\204\345\220\210.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
# 第77题. 组合
@@ -84,7 +82,7 @@ for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
那么我把组合问题抽象为如下树形结构:
-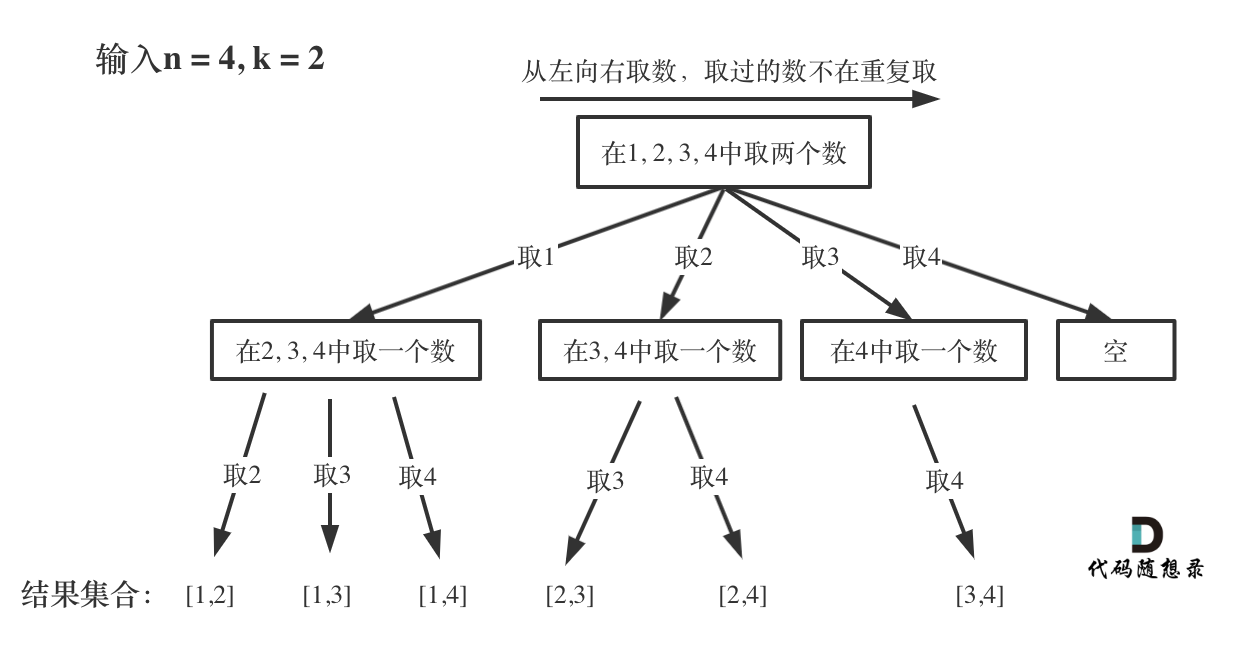
+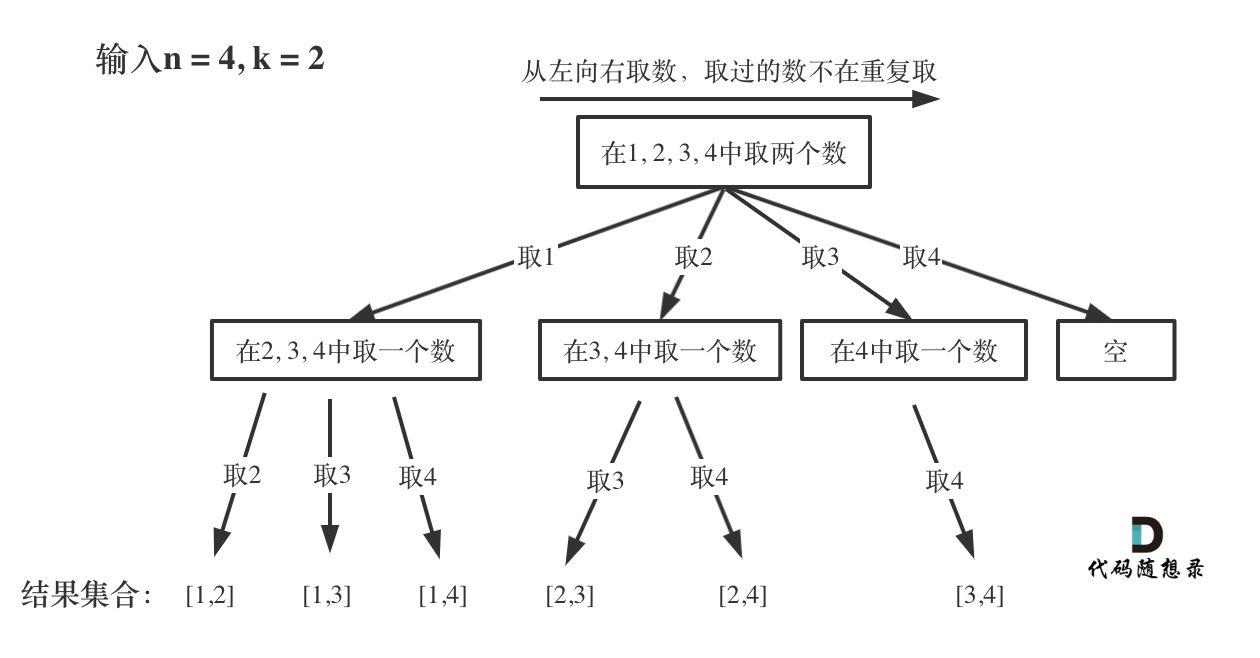
可以看出这棵树,一开始集合是 1,2,3,4, 从左向右取数,取过的数,不再重复取。
@@ -128,7 +126,7 @@ vector path; // 用来存放符合条件结果
从下图中红线部分可以看出,在集合[1,2,3,4]取1之后,下一层递归,就要在[2,3,4]中取数了,那么下一层递归如何知道从[2,3,4]中取数呢,靠的就是startIndex。
-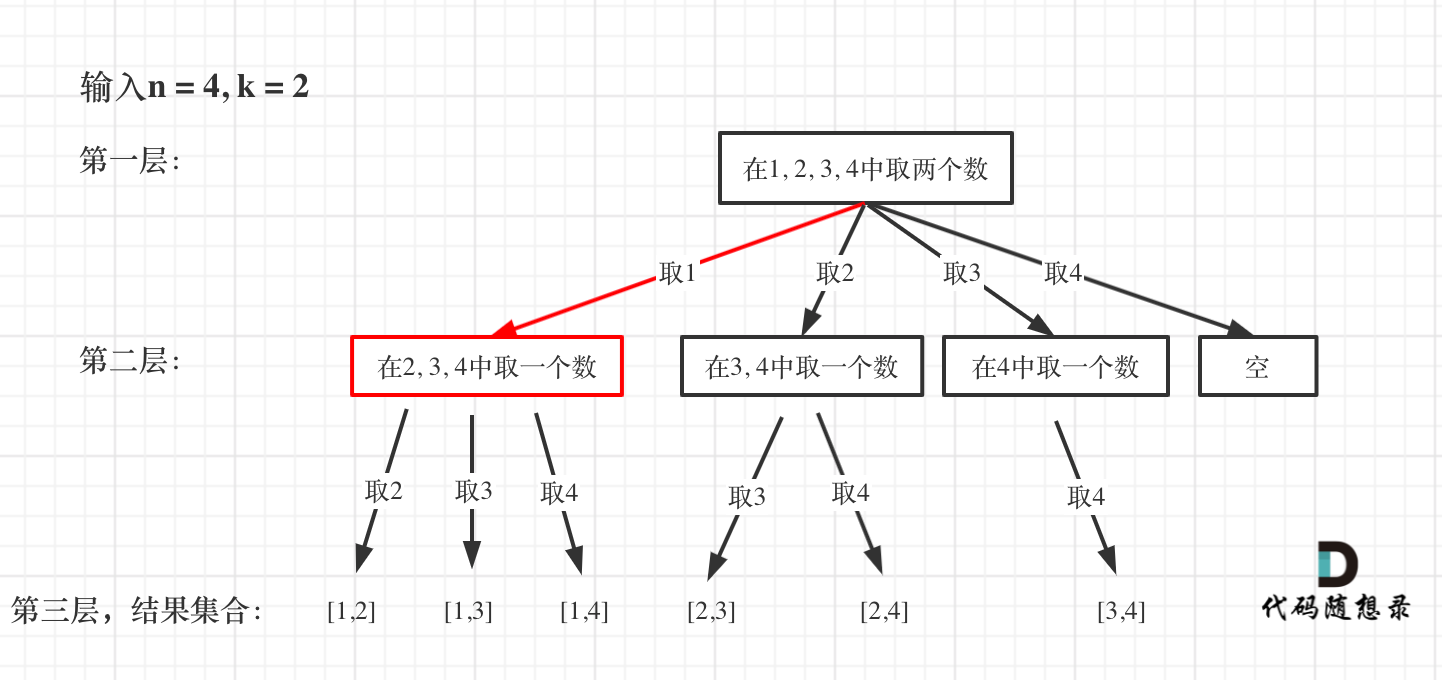
+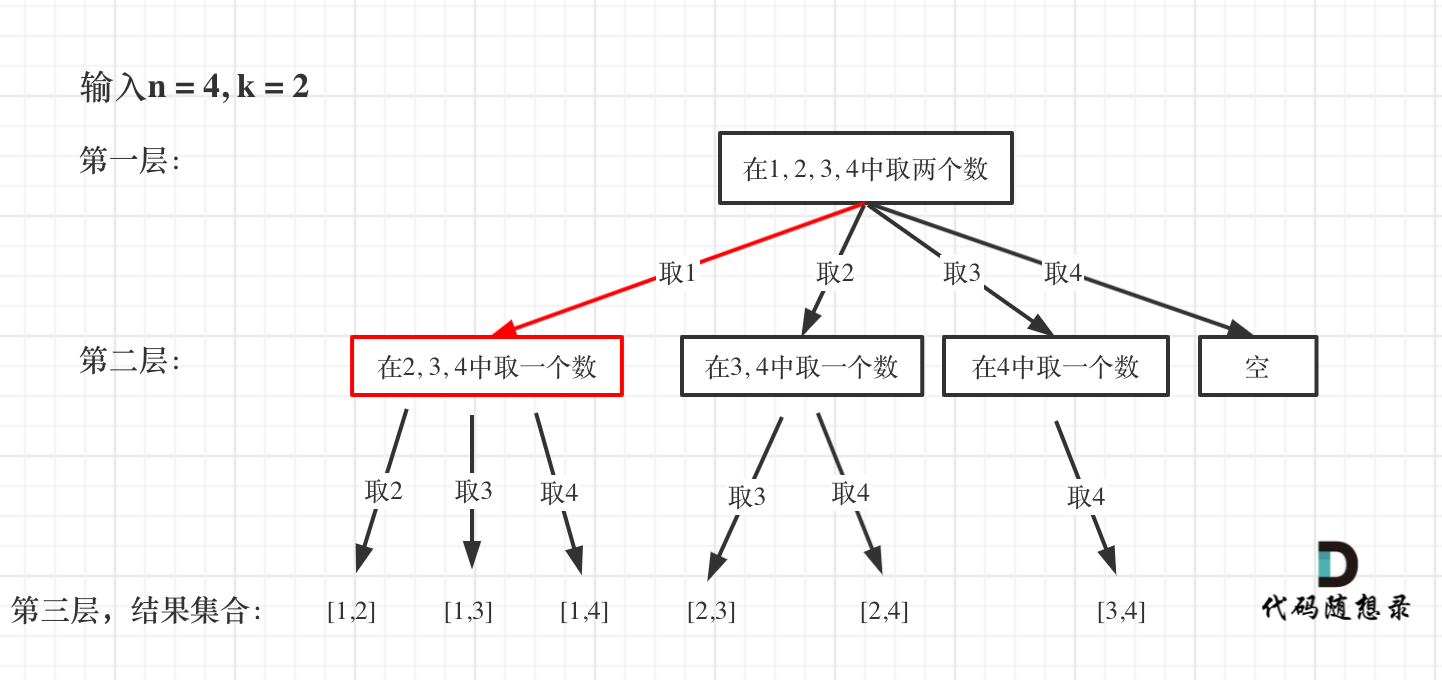
所以需要startIndex来记录下一层递归,搜索的起始位置。
@@ -148,7 +146,7 @@ path这个数组的大小如果达到k,说明我们找到了一个子集大小
如图红色部分:
-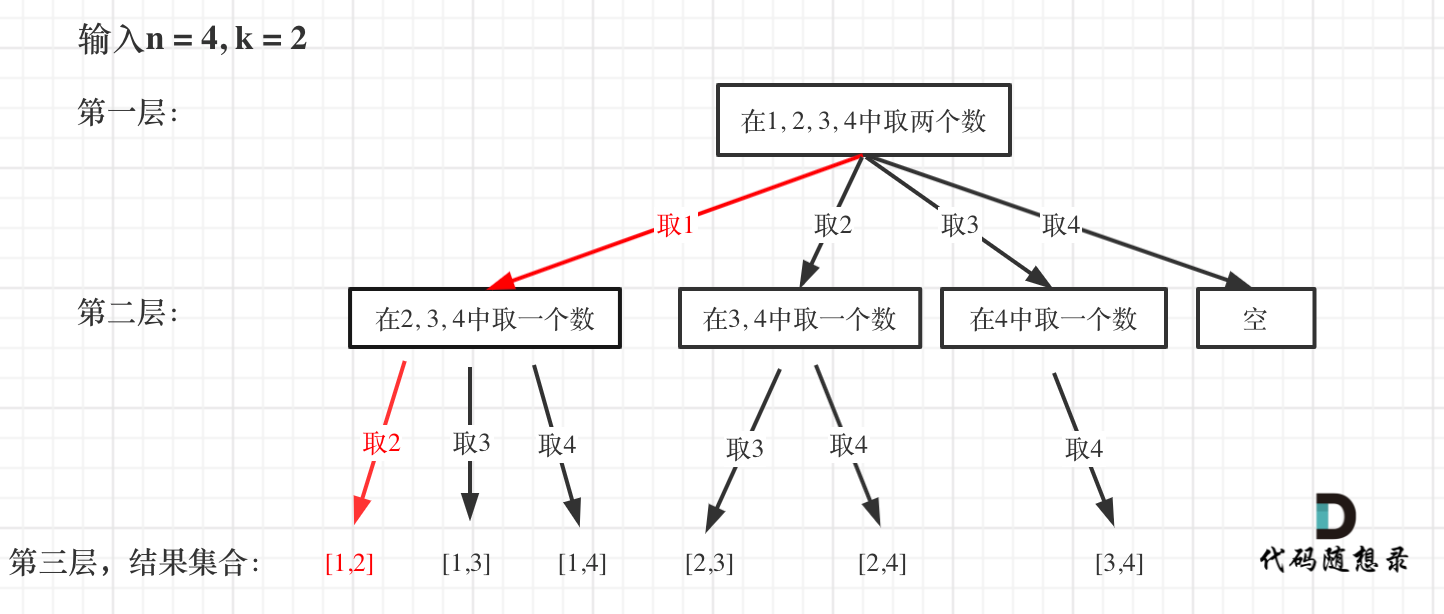
+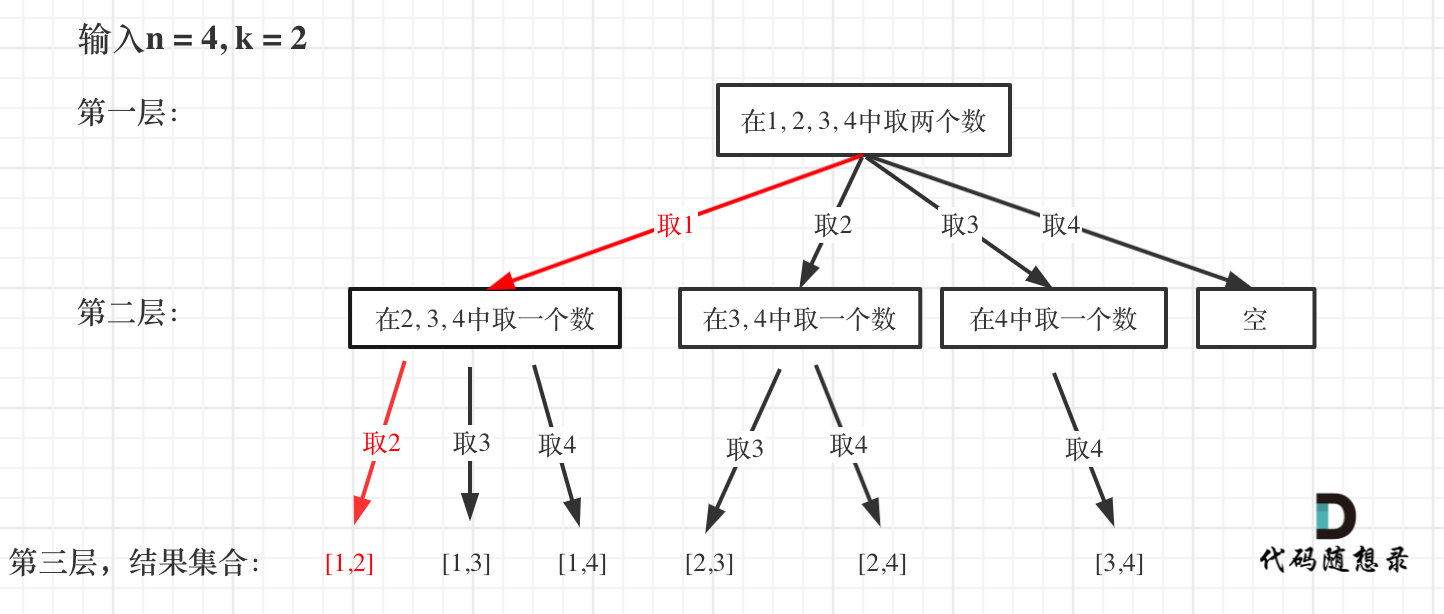
此时用result二维数组,把path保存起来,并终止本层递归。
@@ -165,7 +163,7 @@ if (path.size() == k) {
回溯法的搜索过程就是一个树型结构的遍历过程,在如下图中,可以看出for循环用来横向遍历,递归的过程是纵向遍历。
-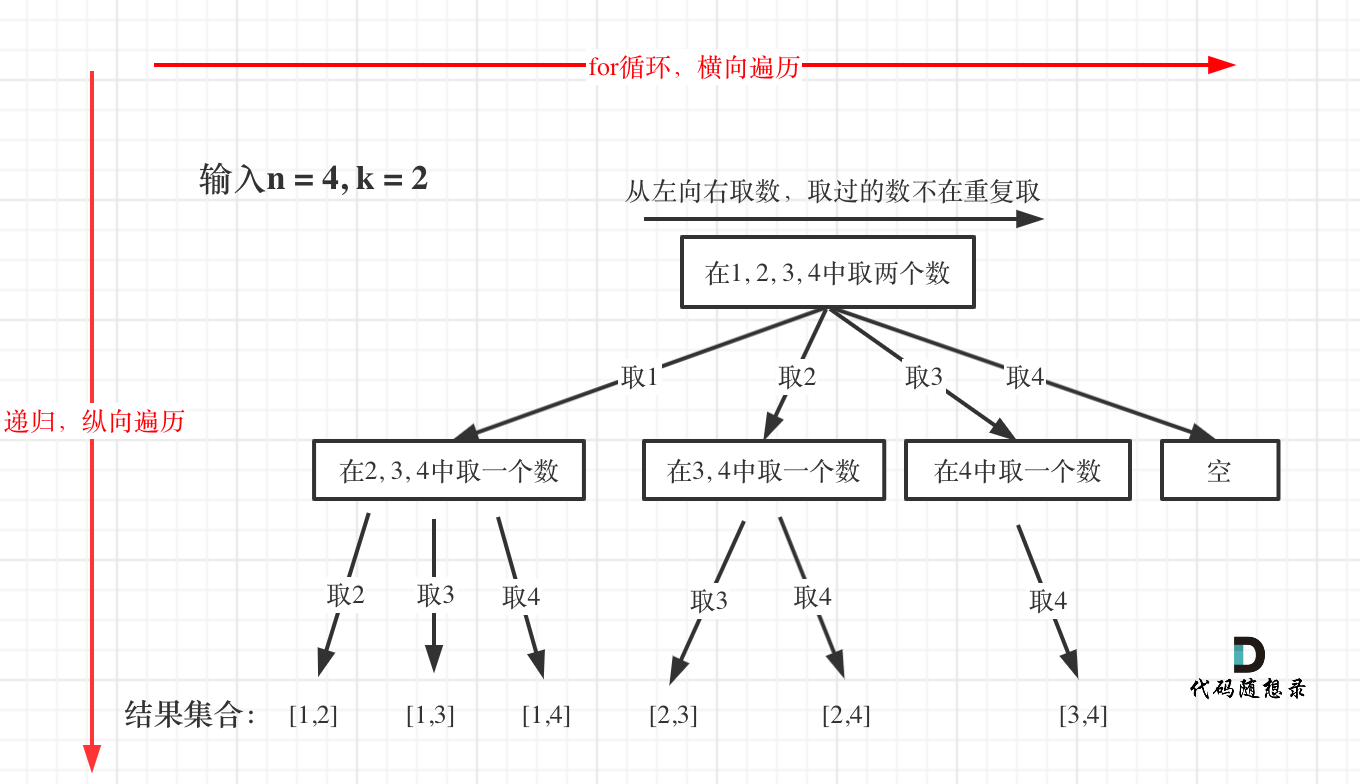
+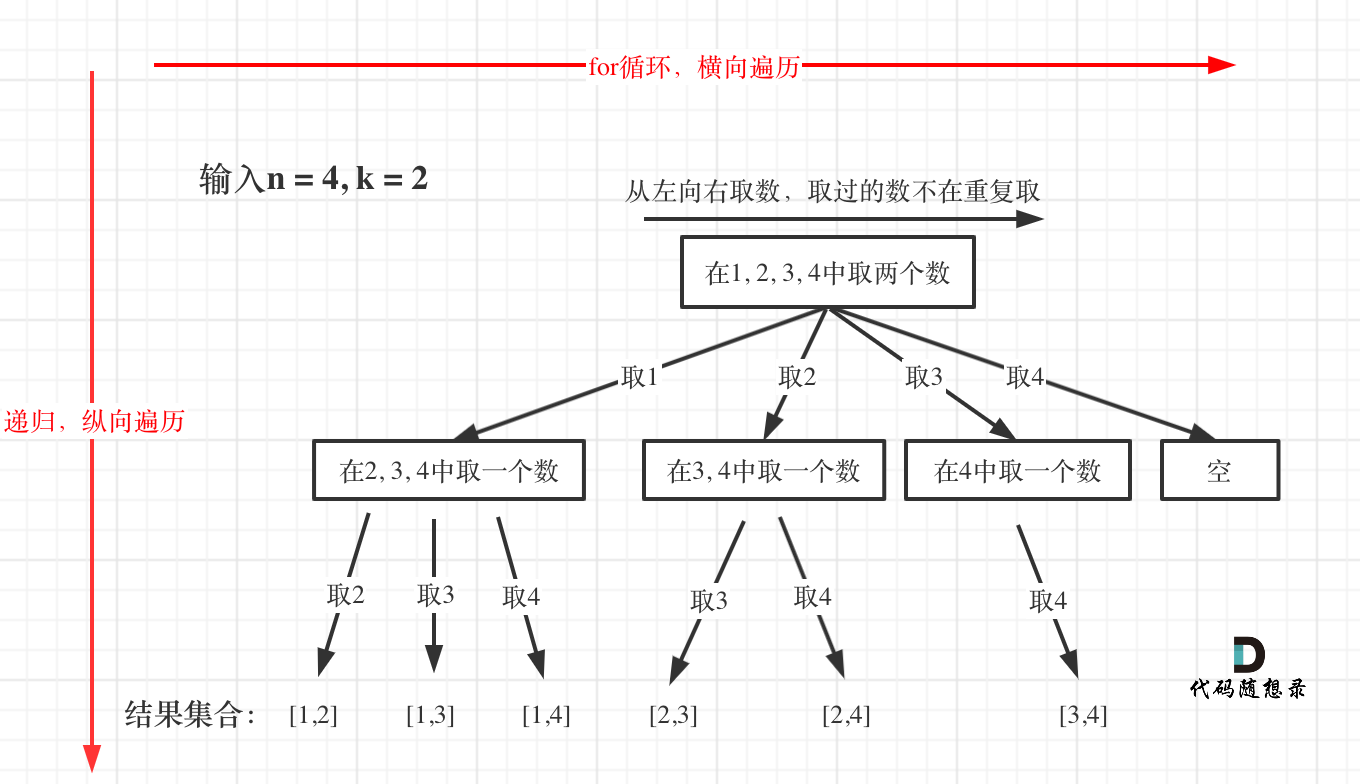
如此我们才遍历完图中的这棵树。
@@ -269,7 +267,7 @@ for (int i = startIndex; i <= n; i++) {
这么说有点抽象,如图所示:
-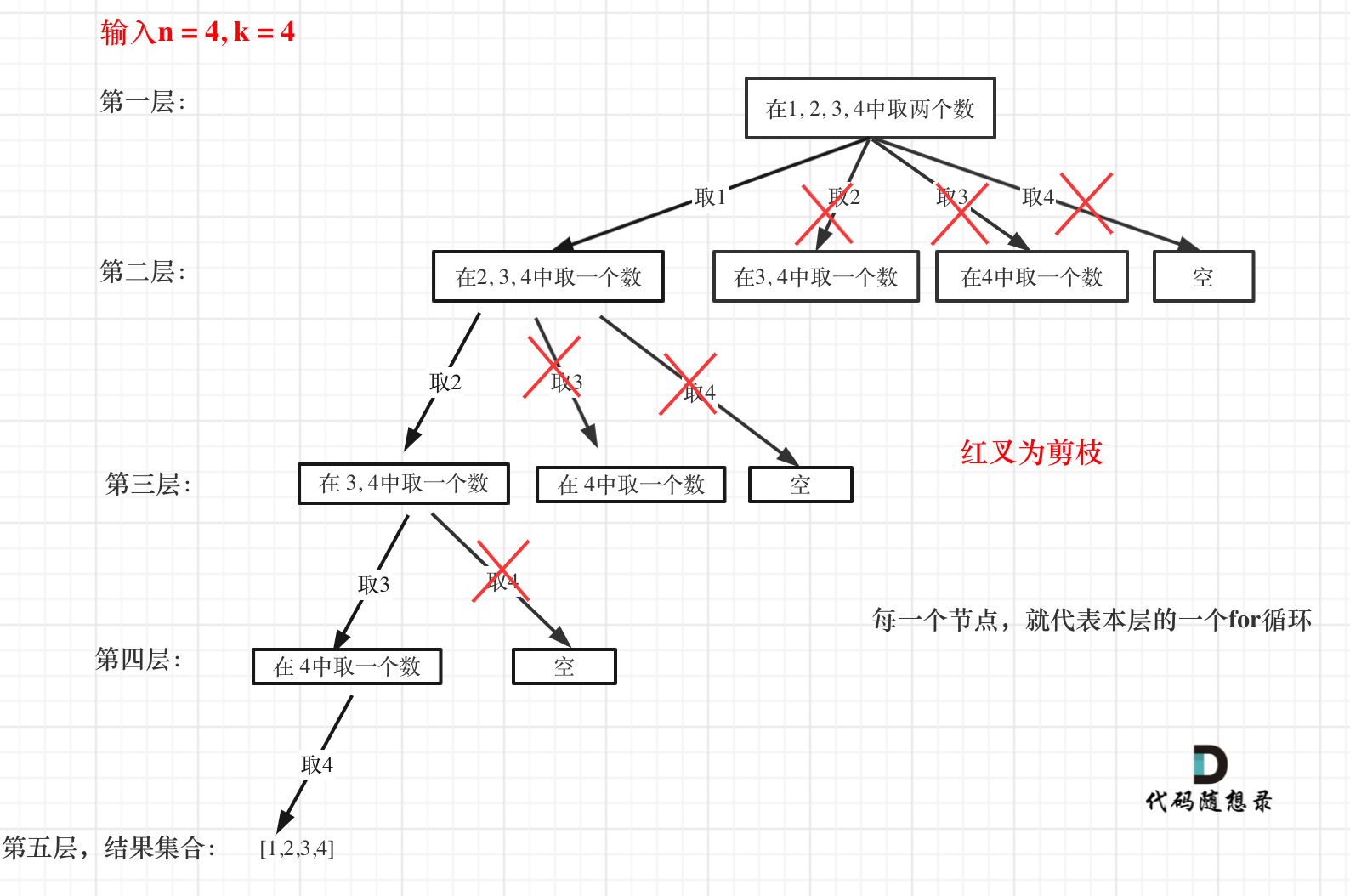
+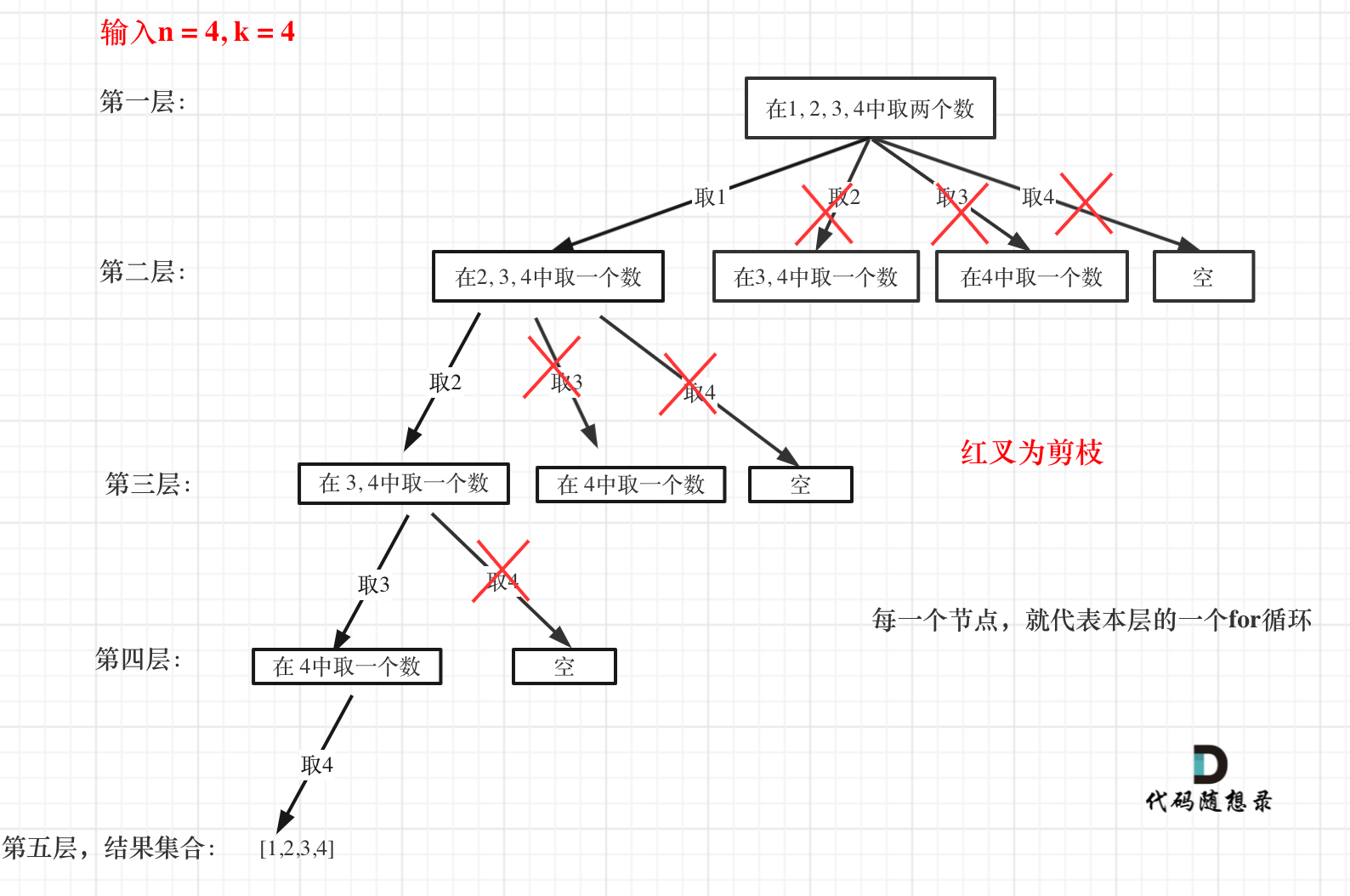
图中每一个节点(图中为矩形),就代表本层的一个for循环,那么每一层的for循环从第二个数开始遍历的话,都没有意义,都是无效遍历。
@@ -468,29 +466,59 @@ func dfs(n int, k int, start int) {
}
```
-### Javascript
+### JavaScript
+未剪枝:
+
+```js
+var combine = function (n, k) {
+ // 回溯法
+ let result = [],
+ path = [];
+ let backtracking = (_n, _k, startIndex) => {
+ // 终止条件
+ if (path.length === _k) {
+ result.push(path.slice());
+ return;
+ }
+ // 循环本层集合元素
+ for (let i = startIndex; i <= _n; i++) {
+ path.push(i);
+ // 递归
+ backtracking(_n, _k, i + 1);
+ // 回溯操作
+ path.pop();
+ }
+ };
+ backtracking(n, k, 1);
+ return result;
+};
+```
剪枝:
```javascript
-let result = []
-let path = []
-var combine = function(n, k) {
- result = []
- combineHelper(n, k, 1)
- return result
+var combine = function (n, k) {
+ // 回溯法
+ let result = [],
+ path = [];
+ let backtracking = (_n, _k, startIndex) => {
+ // 终止条件
+ if (path.length === _k) {
+ result.push(path.slice());
+ return;
+ }
+ // 循环本层集合元素
+ for (let i = startIndex; i <= _n - (_k - path.length) + 1; i++) {
+ path.push(i);
+ // 递归
+ backtracking(_n, _k, i + 1);
+ // 回溯操作
+ path.pop();
+ }
+ };
+ backtracking(n, k, 1);
+ return result;
};
-const combineHelper = (n, k, startIndex) => {
- if (path.length === k) {
- result.push([...path])
- return
- }
- for (let i = startIndex; i <= n - (k - path.length) + 1; ++i) {
- path.push(i)
- combineHelper(n, k, i + 1)
- path.pop()
- }
-}
```
### TypeScript
@@ -845,8 +873,4 @@ public class Solution
}
}
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0077.\347\273\204\345\220\210\344\274\230\345\214\226.md" "b/problems/0077.\347\273\204\345\220\210\344\274\230\345\214\226.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 9577d65f3c..8ddc4058cc
--- "a/problems/0077.\347\273\204\345\220\210\344\274\230\345\214\226.md"
+++ "b/problems/0077.\347\273\204\345\220\210\344\274\230\345\214\226.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0077.\347\273\204\345\220\210\344\274\230\345\214\226.md" "b/problems/0077.\347\273\204\345\220\210\344\274\230\345\214\226.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 9577d65f3c..8ddc4058cc
--- "a/problems/0077.\347\273\204\345\220\210\344\274\230\345\214\226.md"
+++ "b/problems/0077.\347\273\204\345\220\210\344\274\230\345\214\226.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
@@ -69,7 +67,7 @@ for (int i = startIndex; i <= n; i++) {
这么说有点抽象,如图所示:
-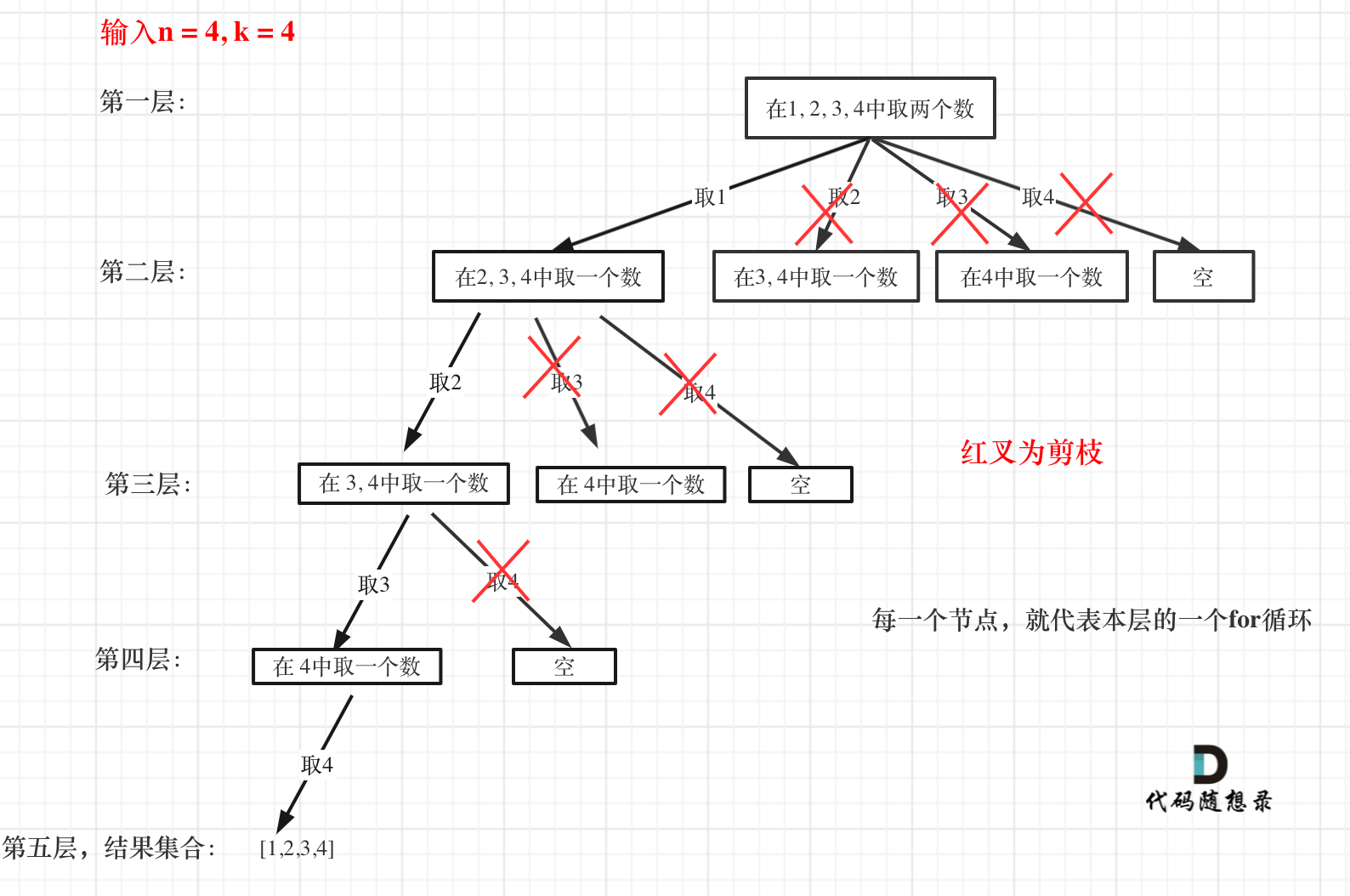
+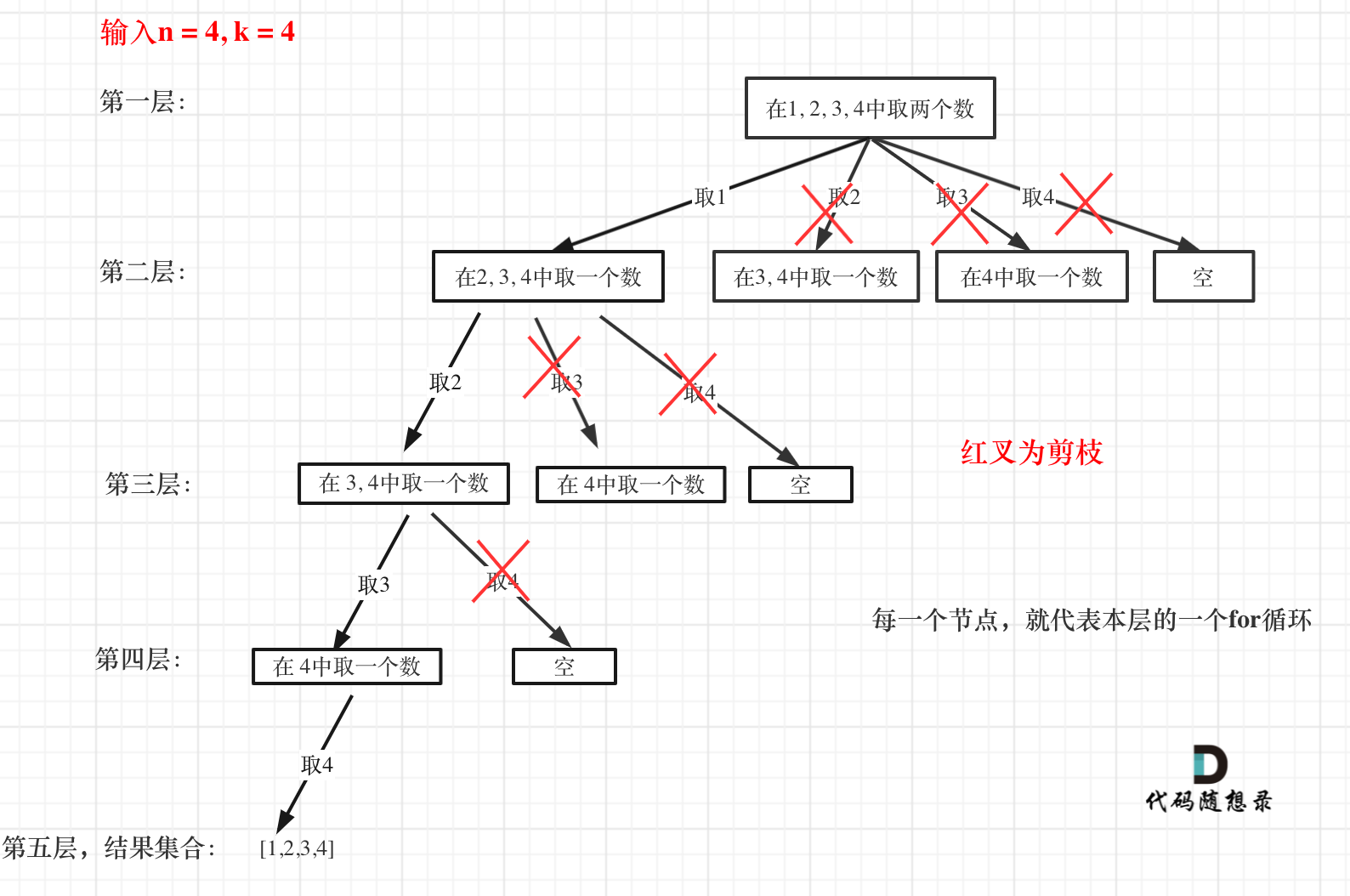
图中每一个节点(图中为矩形),就代表本层的一个for循环,那么每一层的for循环从第二个数开始遍历的话,都没有意义,都是无效遍历。
@@ -411,8 +409,4 @@ object Solution {
}
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0078.\345\255\220\351\233\206.md" "b/problems/0078.\345\255\220\351\233\206.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 06547e3df5..844b8dc2ca
--- "a/problems/0078.\345\255\220\351\233\206.md"
+++ "b/problems/0078.\345\255\220\351\233\206.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0078.\345\255\220\351\233\206.md" "b/problems/0078.\345\255\220\351\233\206.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 06547e3df5..844b8dc2ca
--- "a/problems/0078.\345\255\220\351\233\206.md"
+++ "b/problems/0078.\345\255\220\351\233\206.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 78.子集
@@ -48,7 +46,7 @@
以示例中nums = [1,2,3]为例把求子集抽象为树型结构,如下:
-
+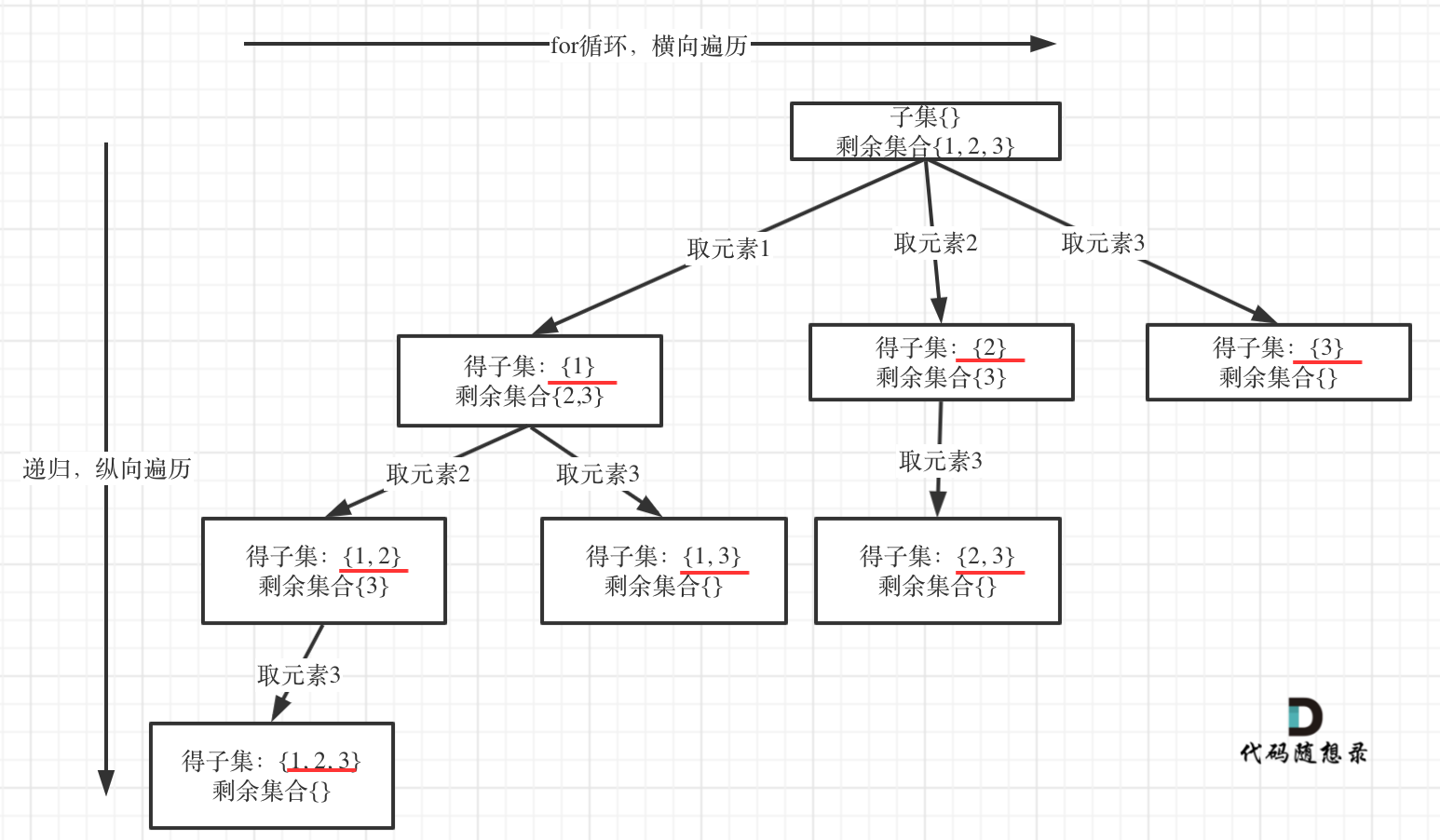
从图中红线部分,可以看出**遍历这个树的时候,把所有节点都记录下来,就是要求的子集集合**。
@@ -72,7 +70,7 @@ void backtracking(vector& nums, int startIndex) {
从图中可以看出:
-
+
剩余集合为空的时候,就是叶子节点。
@@ -246,7 +244,7 @@ func dfs(nums []int, start int) {
}
```
-### Javascript
+### JavaScript
```Javascript
var subsets = function(nums) {
@@ -287,6 +285,7 @@ function subsets(nums: number[]): number[][] {
### Rust
+思路一:使用本题的标准解法,递归回溯。
```Rust
impl Solution {
fn backtracking(result: &mut Vec>, path: &mut Vec, nums: &Vec, start_index: usize) {
@@ -308,6 +307,30 @@ impl Solution {
}
}
```
+思路二:使用二进制枚举,n个元素的子集问题一共是$2^n$种情况。如果我们使用一个二进制数字,每一位根据0和1来决定是选取该元素与否,那么一共也是$2^n$的情况,正好可以一一对应,所以我们可以不使用递归,直接利用循环枚举完成子集问题。
+这种方法的优点在于效率高,不需要递归调用,并且代码容易编写。缺点则是过滤某些非法情况时会比递归方法难写一点,不过在子集问题中不存在这个问题。
+```Rust
+impl Solution {
+ pub fn subsets(nums: Vec) -> Vec> {
+ let n = nums.len();
+ // 预分配2^n空间
+ let mut result = Vec::with_capacity(1 << n);
+ // 二进制枚举,2^n种情况
+ for i in 0..(1 << n) {
+ let mut subset = Vec::new();
+ for j in 0..n {
+ // 枚举该二进制数字的每一位
+ // 如果该位是1,对应位置上的元素加入子集,否则跳过
+ if i & (1 << j) != 0 {
+ subset.push(nums[j]);
+ }
+ }
+ result.push(subset);
+ }
+ result
+ }
+}
+```
### C
@@ -466,8 +489,4 @@ public class Solution {
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0084.\346\237\261\347\212\266\345\233\276\344\270\255\346\234\200\345\244\247\347\232\204\347\237\251\345\275\242.md" "b/problems/0084.\346\237\261\347\212\266\345\233\276\344\270\255\346\234\200\345\244\247\347\232\204\347\237\251\345\275\242.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index b836705ab5..99fb1678e6
--- "a/problems/0084.\346\237\261\347\212\266\345\233\276\344\270\255\346\234\200\345\244\247\347\232\204\347\237\251\345\275\242.md"
+++ "b/problems/0084.\346\237\261\347\212\266\345\233\276\344\270\255\346\234\200\345\244\247\347\232\204\347\237\251\345\275\242.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0084.\346\237\261\347\212\266\345\233\276\344\270\255\346\234\200\345\244\247\347\232\204\347\237\251\345\275\242.md" "b/problems/0084.\346\237\261\347\212\266\345\233\276\344\270\255\346\234\200\345\244\247\347\232\204\347\237\251\345\275\242.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index b836705ab5..99fb1678e6
--- "a/problems/0084.\346\237\261\347\212\266\345\233\276\344\270\255\346\234\200\345\244\247\347\232\204\347\237\251\345\275\242.md"
+++ "b/problems/0084.\346\237\261\347\212\266\345\233\276\344\270\255\346\234\200\345\244\247\347\232\204\347\237\251\345\275\242.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 84.柱状图中最大的矩形
@@ -13,9 +11,9 @@
求在该柱状图中,能够勾勒出来的矩形的最大面积。
-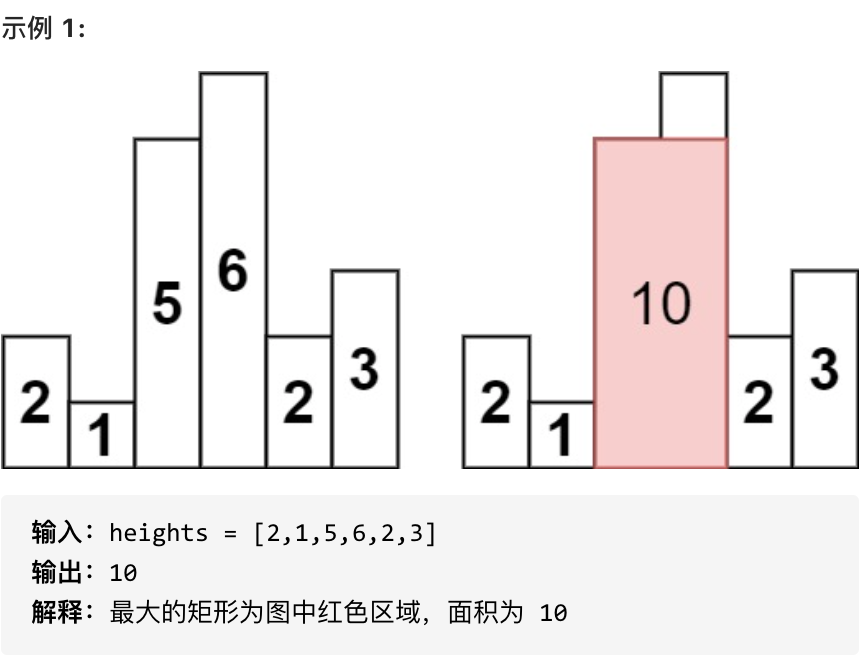
+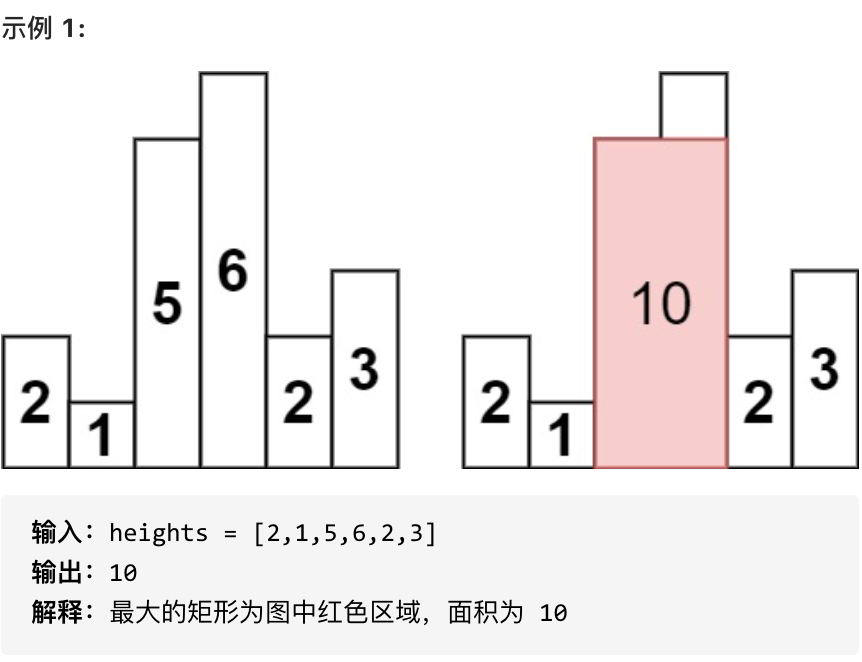
-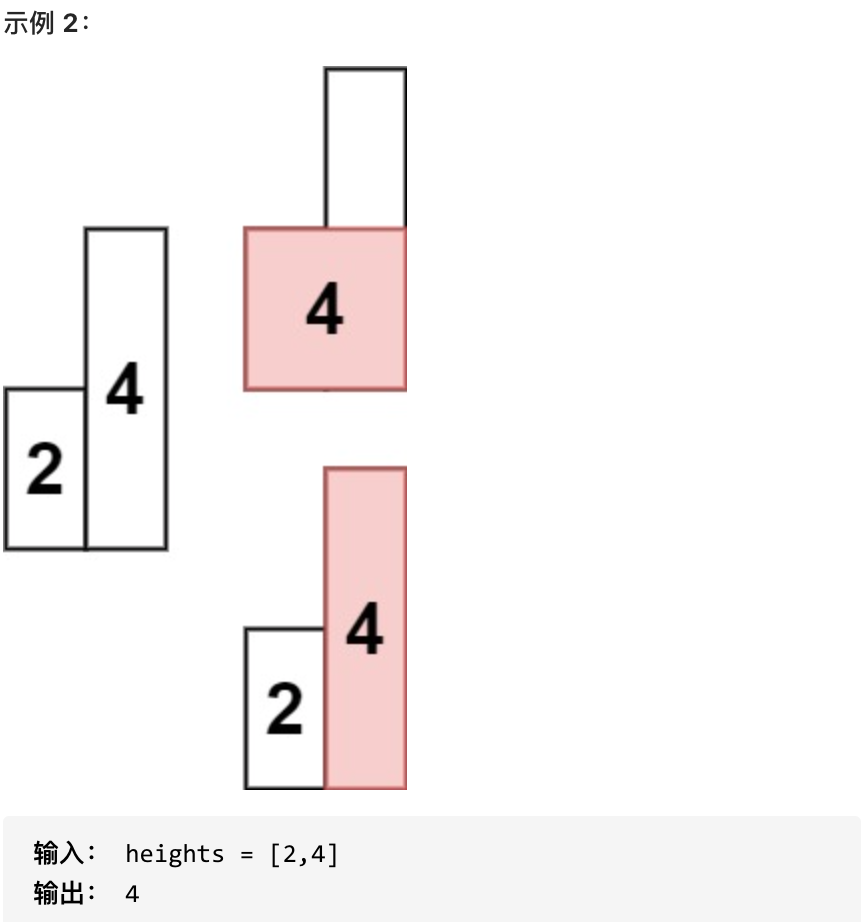
+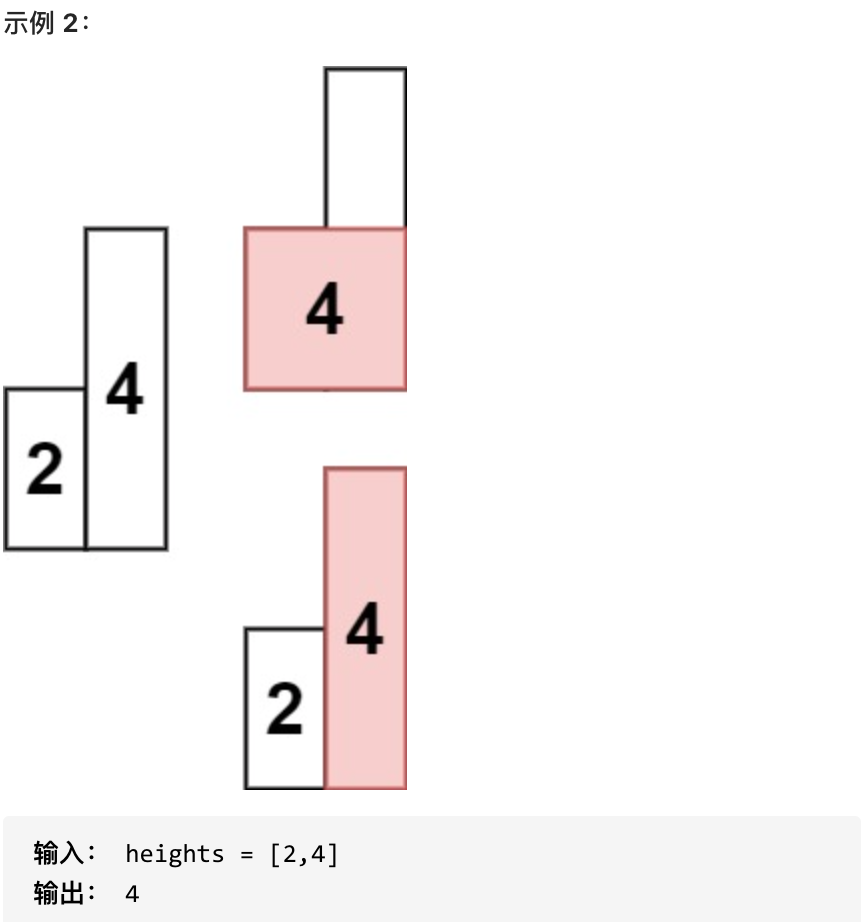
* 1 <= heights.length <=10^5
* 0 <= heights[i] <= 10^4
@@ -116,7 +114,7 @@ public:
我来举一个例子,如图:
-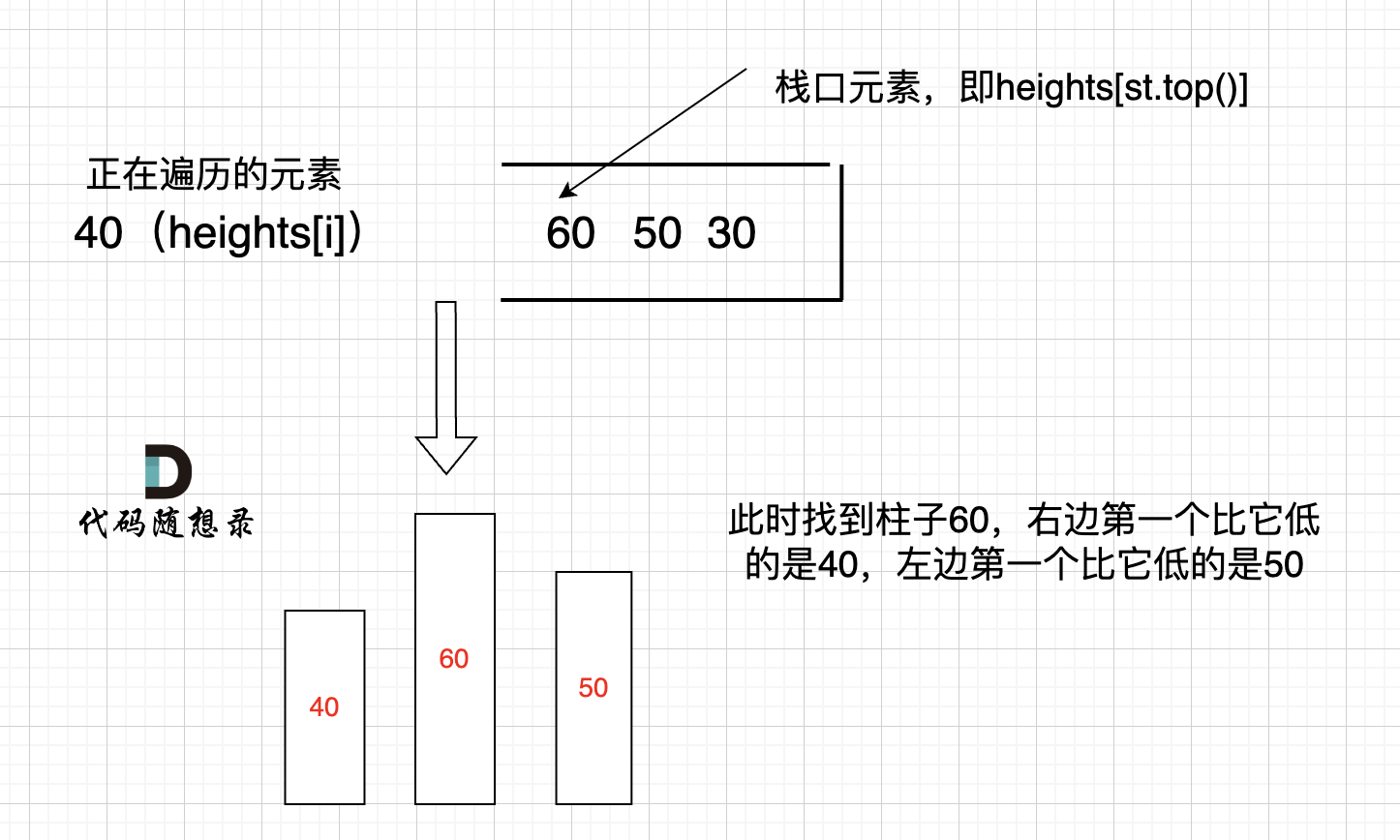
+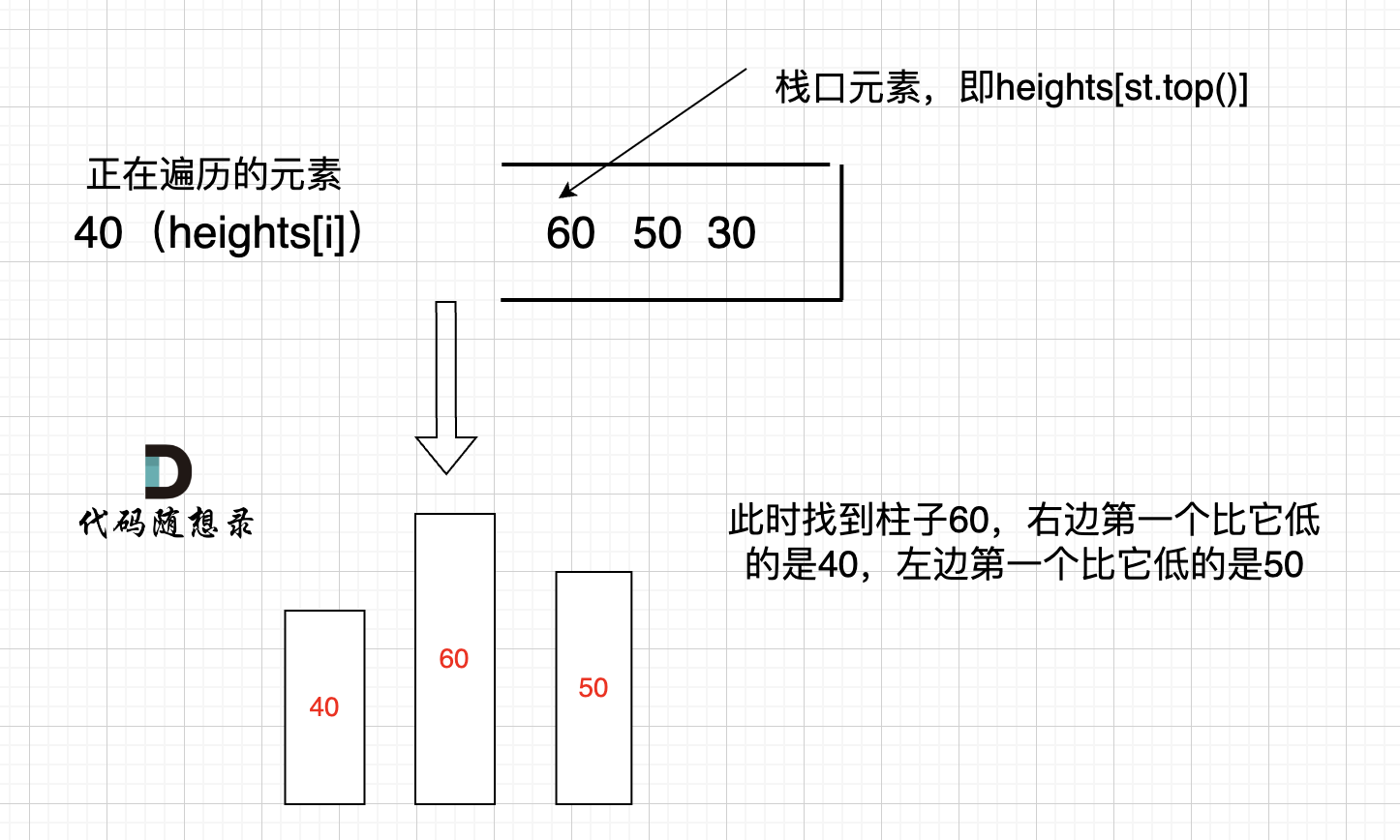
只有栈里从大到小的顺序,才能保证栈顶元素找到左右两边第一个小于栈顶元素的柱子。
@@ -181,22 +179,22 @@ public:
如果数组本身就是升序的,例如[2,4,6,8],那么入栈之后 都是单调递减,一直都没有走 情况三 计算结果的哪一步,所以最后输出的就是0了。 如图:
-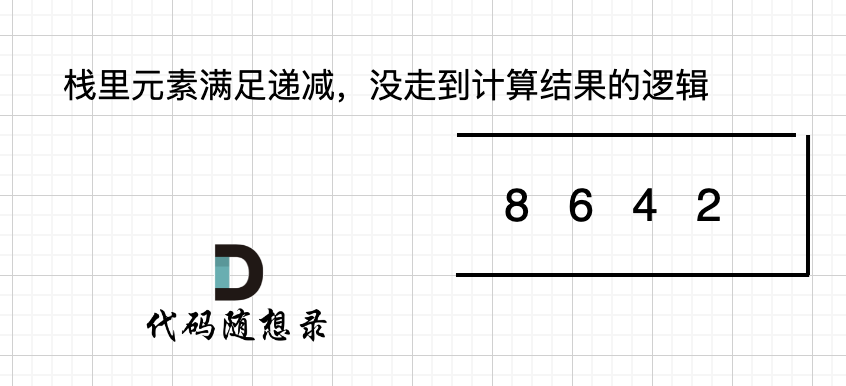
+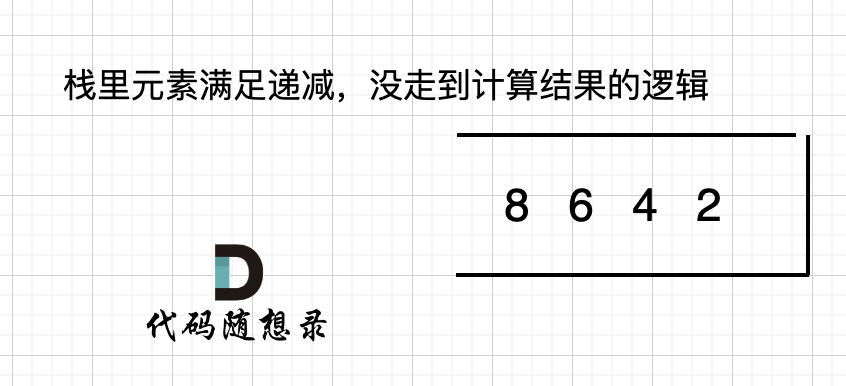
那么结尾加一个0,就会让栈里的所有元素,走到情况三的逻辑。
开头为什么要加元素0?
-如果数组本身是降序的,例如 [8,6,4,2],在 8 入栈后,6 开始与8 进行比较,此时我们得到 mid(8),rigt(6),但是得不到 left。
+如果数组本身是降序的,例如 [8,6,4,2],在 8 入栈后,6 开始与8 进行比较,此时我们得到 mid(8),right(6),但是得不到 left。
(mid、left,right 都是对应版本一里的逻辑)
因为 将 8 弹出之后,栈里没有元素了,那么为了避免空栈取值,直接跳过了计算结果的逻辑。
-之后又将6 加入栈(此时8已经弹出了),然后 就是 4 与 栈口元素 8 进行比较,周而复始,那么计算的最后结果resutl就是0。 如图所示:
+之后又将6 加入栈(此时8已经弹出了),然后 就是 4 与 栈口元素 6 进行比较,周而复始,那么计算的最后结果result就是0。 如图所示:
-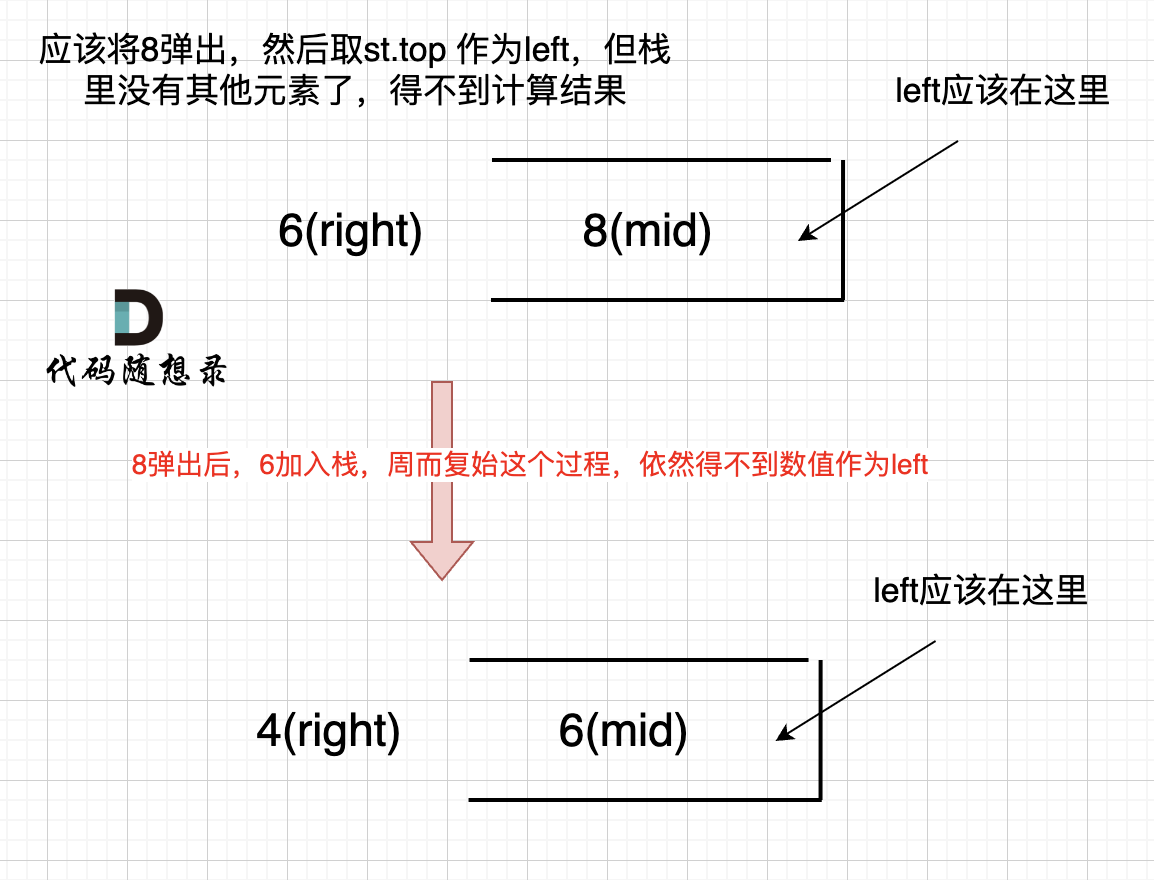
+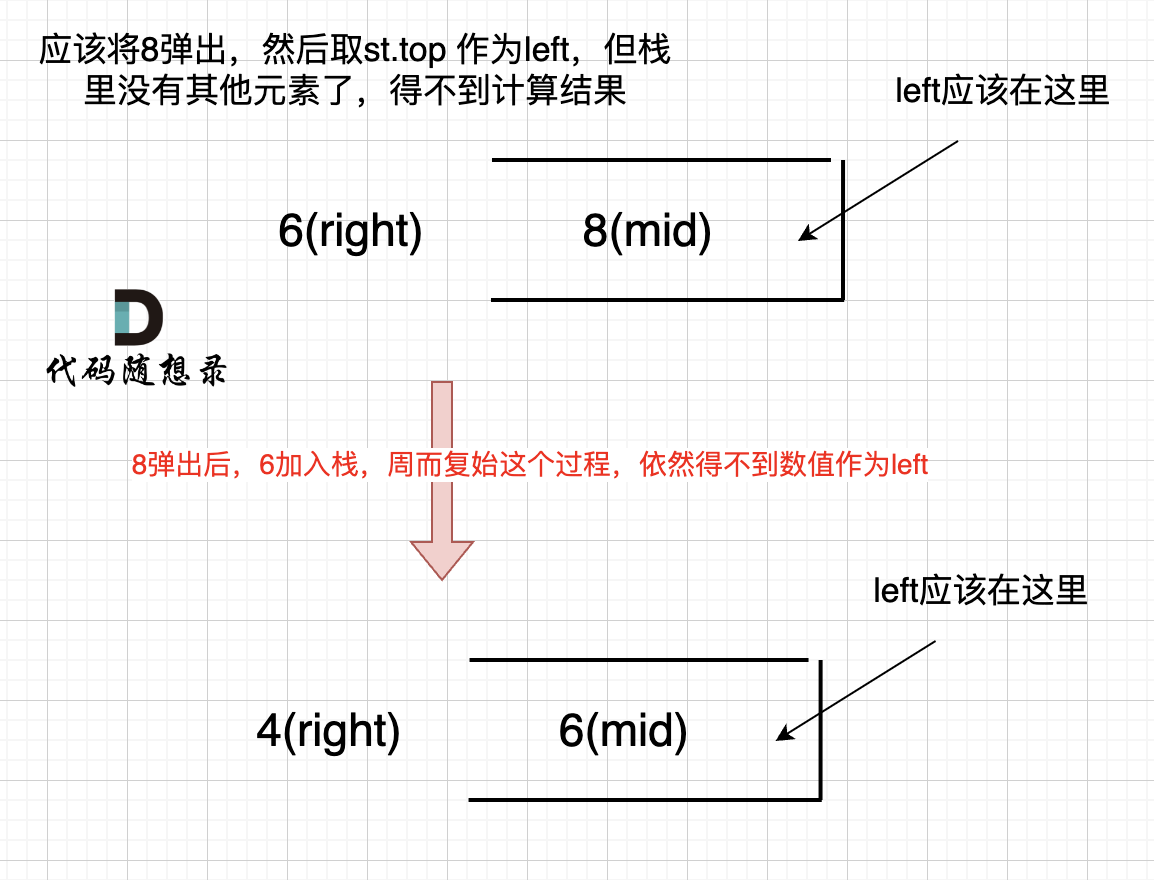
所以我们需要在 height数组前后各加一个元素0。
@@ -474,7 +472,128 @@ class Solution:
### Go:
-> 单调栈
+暴力解法
+
+```go
+func largestRectangleArea(heights []int) int {
+ sum := 0
+ for i := 0; i < len(heights); i++ {
+ left, right := i, i
+ for left >= 0 {
+ if heights[left] < heights[i] {
+ break
+ }
+ left--
+ }
+ for right < len(heights) {
+ if heights[right] < heights[i] {
+ break
+ }
+ right++
+ }
+ w := right - left - 1
+ h := heights[i]
+ sum = max(sum, w * h)
+ }
+ return sum
+}
+
+func max(x, y int) int {
+ if x > y {
+ return x
+ }
+ return y
+}
+```
+
+双指针解法
+
+```go
+func largestRectangleArea(heights []int) int {
+ size := len(heights)
+ minLeftIndex := make([]int, size)
+ minRightIndex := make([]int, size)
+
+ // 记录每个柱子 左边第一个小于该柱子的下标
+ minLeftIndex[0] = -1 // 注意这里初始化,防止下面while死循环
+ for i := 1; i < size; i++ {
+ t := i - 1
+ // 这里不是用if,而是不断向左寻找的过程
+ for t >= 0 && heights[t] >= heights[i] {
+ t = minLeftIndex[t]
+ }
+ minLeftIndex[i] = t
+ }
+ // 记录每个柱子 右边第一个小于该柱子的下标
+ minRightIndex[size - 1] = size; // 注意这里初始化,防止下面while死循环
+ for i := size - 2; i >= 0; i-- {
+ t := i + 1
+ // 这里不是用if,而是不断向右寻找的过程
+ for t < size && heights[t] >= heights[i] {
+ t = minRightIndex[t]
+ }
+ minRightIndex[i] = t
+ }
+ // 求和
+ result := 0
+ for i := 0; i < size; i++ {
+ sum := heights[i] * (minRightIndex[i] - minLeftIndex[i] - 1)
+ result = max(sum, result)
+ }
+ return result
+}
+
+func max(x, y int) int {
+ if x > y {
+ return x
+ }
+ return y
+}
+```
+
+单调栈
+
+```go
+func largestRectangleArea(heights []int) int {
+ result := 0
+ heights = append([]int{0}, heights...) // 数组头部加入元素0
+ heights = append(heights, 0) // 数组尾部加入元素0
+ st := []int{0}
+
+ // 第一个元素已经入栈,从下标1开始
+ for i := 1; i < len(heights); i++ {
+ if heights[i] > heights[st[len(st)-1]] {
+ st = append(st, i)
+ } else if heights[i] == heights[st[len(st)-1]] {
+ st = st[:len(st)-1]
+ st = append(st, i)
+ } else {
+ for len(st) > 0 && heights[i] < heights[st[len(st)-1]] {
+ mid := st[len(st)-1]
+ st = st[:len(st)-1]
+ if len(st) > 0 {
+ left := st[len(st)-1]
+ right := i
+ w := right - left - 1
+ h := heights[mid]
+ result = max(result, w * h)
+ }
+ }
+ st = append(st, i)
+ }
+ }
+ return result
+}
+
+func max(x, y int) int {
+ if x > y {
+ return x
+ }
+ return y
+}
+```
+
+单调栈精简
```go
func largestRectangleArea(heights []int) int {
@@ -741,8 +860,4 @@ impl Solution {
}
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0090.\345\255\220\351\233\206II.md" "b/problems/0090.\345\255\220\351\233\206II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 6d618978a8..2e8945c90f
--- "a/problems/0090.\345\255\220\351\233\206II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0090.\345\255\220\351\233\206II.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0090.\345\255\220\351\233\206II.md" "b/problems/0090.\345\255\220\351\233\206II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 6d618978a8..2e8945c90f
--- "a/problems/0090.\345\255\220\351\233\206II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0090.\345\255\220\351\233\206II.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 90.子集II
@@ -41,7 +39,7 @@
用示例中的[1, 2, 2] 来举例,如图所示: (**注意去重需要先对集合排序**)
-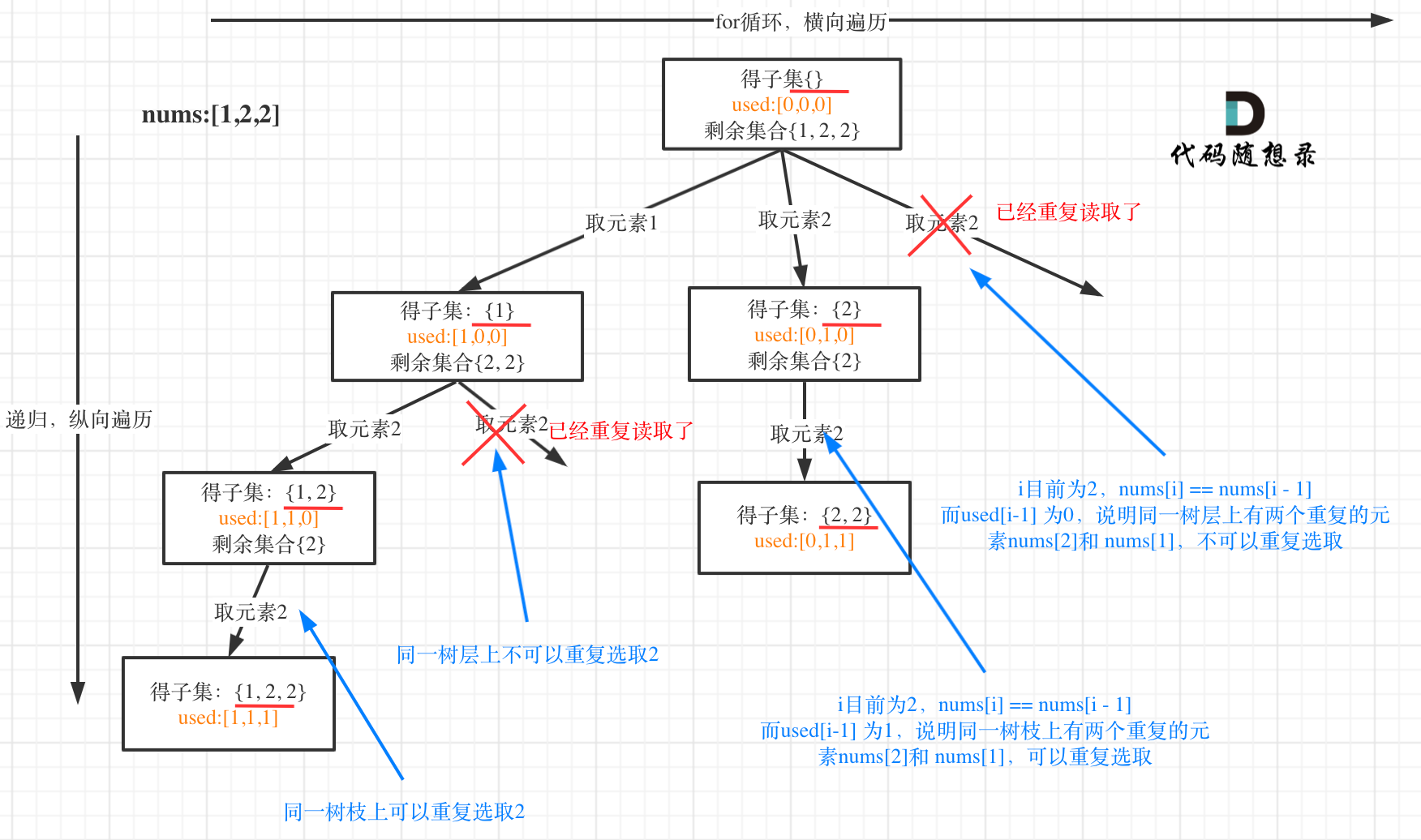
+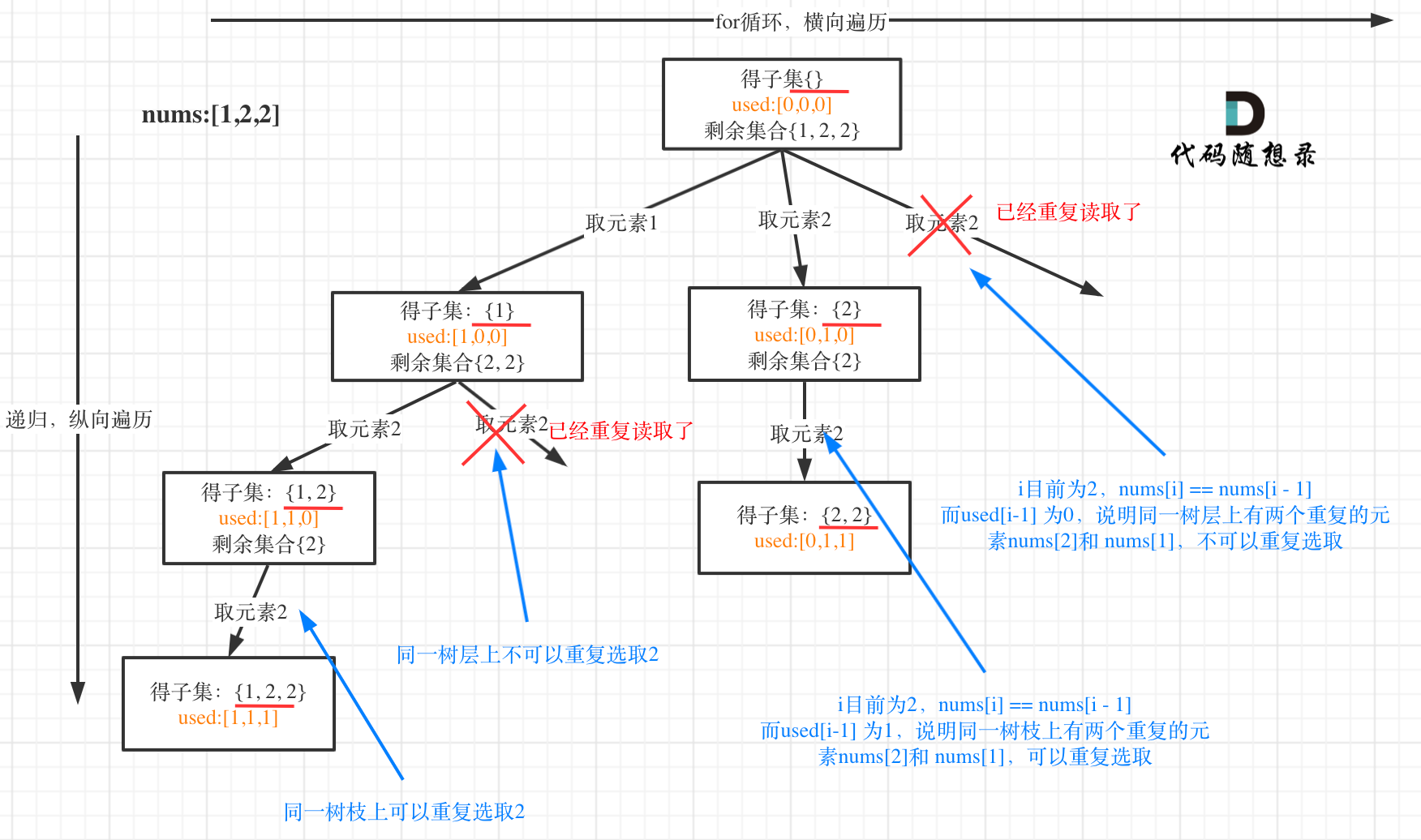
从图中可以看出,同一树层上重复取2 就要过滤掉,同一树枝上就可以重复取2,因为同一树枝上元素的集合才是唯一子集!
@@ -310,6 +308,43 @@ class Solution:
```
### Go
+使用used数组
+```Go
+var (
+ result [][]int
+ path []int
+)
+
+func subsetsWithDup(nums []int) [][]int {
+ result = make([][]int, 0)
+ path = make([]int, 0)
+ used := make([]bool, len(nums))
+ sort.Ints(nums) // 去重需要排序
+ backtracing(nums, 0, used)
+ return result
+}
+
+func backtracing(nums []int, startIndex int, used []bool) {
+ tmp := make([]int, len(path))
+ copy(tmp, path)
+ result = append(result, tmp)
+ for i := startIndex; i < len(nums); i++ {
+ // used[i - 1] == true,说明同一树枝candidates[i - 1]使用过
+ // used[i - 1] == false,说明同一树层candidates[i - 1]使用过
+ // 而我们要对同一树层使用过的元素进行跳过
+ if i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i-1] && used[i-1] == false {
+ continue
+ }
+ path = append(path, nums[i])
+ used[i] = true
+ backtracing(nums, i + 1, used)
+ path = path[:len(path)-1]
+ used[i] = false
+ }
+}
+```
+
+不使用used数组
```Go
var (
path []int
@@ -339,7 +374,7 @@ func dfs(nums []int, start int) {
```
-### Javascript
+### JavaScript
```Javascript
@@ -659,8 +694,4 @@ public class Solution
}
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0093.\345\244\215\345\216\237IP\345\234\260\345\235\200.md" "b/problems/0093.\345\244\215\345\216\237IP\345\234\260\345\235\200.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index c662957a10..6fa732d0c1
--- "a/problems/0093.\345\244\215\345\216\237IP\345\234\260\345\235\200.md"
+++ "b/problems/0093.\345\244\215\345\216\237IP\345\234\260\345\235\200.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0093.\345\244\215\345\216\237IP\345\234\260\345\235\200.md" "b/problems/0093.\345\244\215\345\216\237IP\345\234\260\345\235\200.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index c662957a10..6fa732d0c1
--- "a/problems/0093.\345\244\215\345\216\237IP\345\234\260\345\235\200.md"
+++ "b/problems/0093.\345\244\215\345\216\237IP\345\234\260\345\235\200.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
@@ -56,7 +54,7 @@
切割问题可以抽象为树型结构,如图:
-
+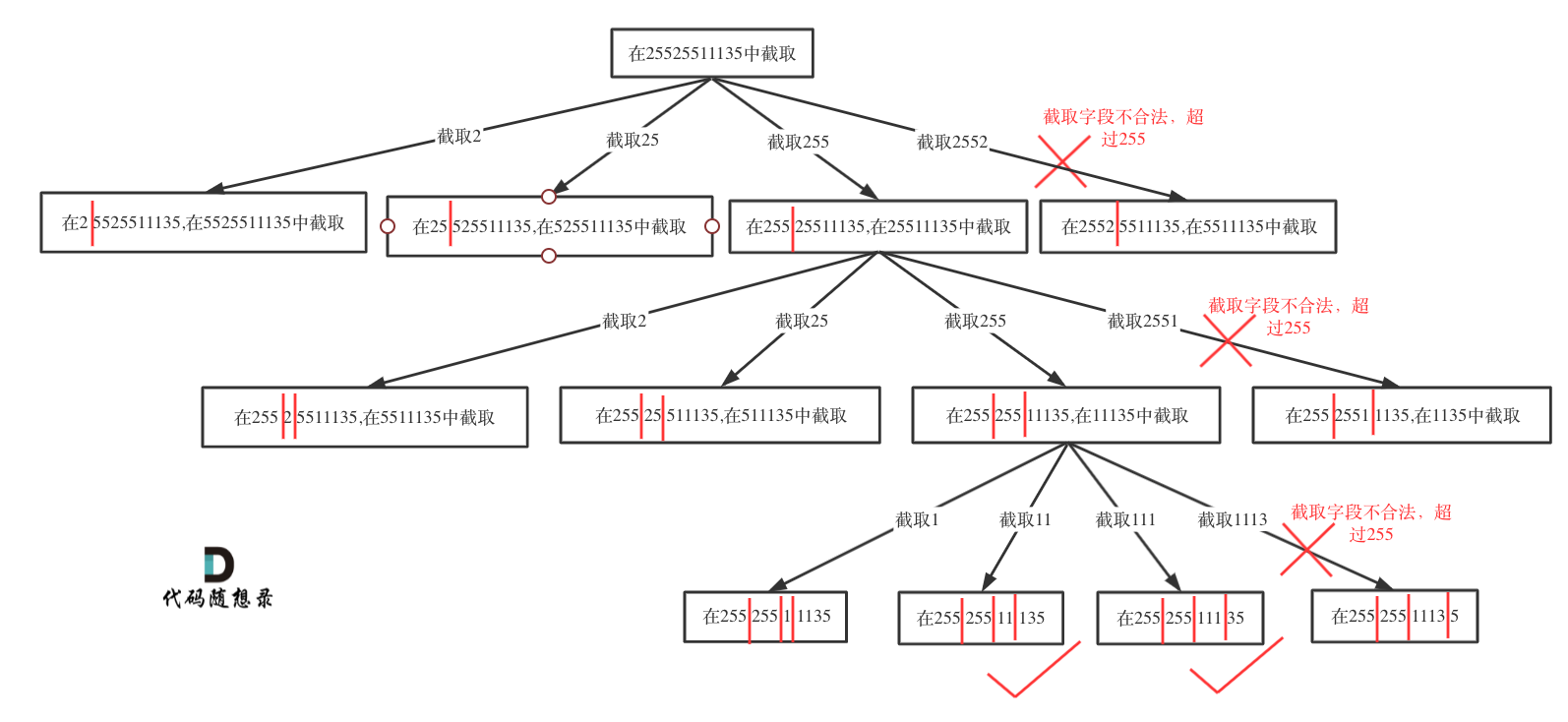
### 回溯三部曲
@@ -108,7 +106,7 @@ if (pointNum == 3) { // 逗点数量为3时,分隔结束
如果不合法就结束本层循环,如图中剪掉的分支:
-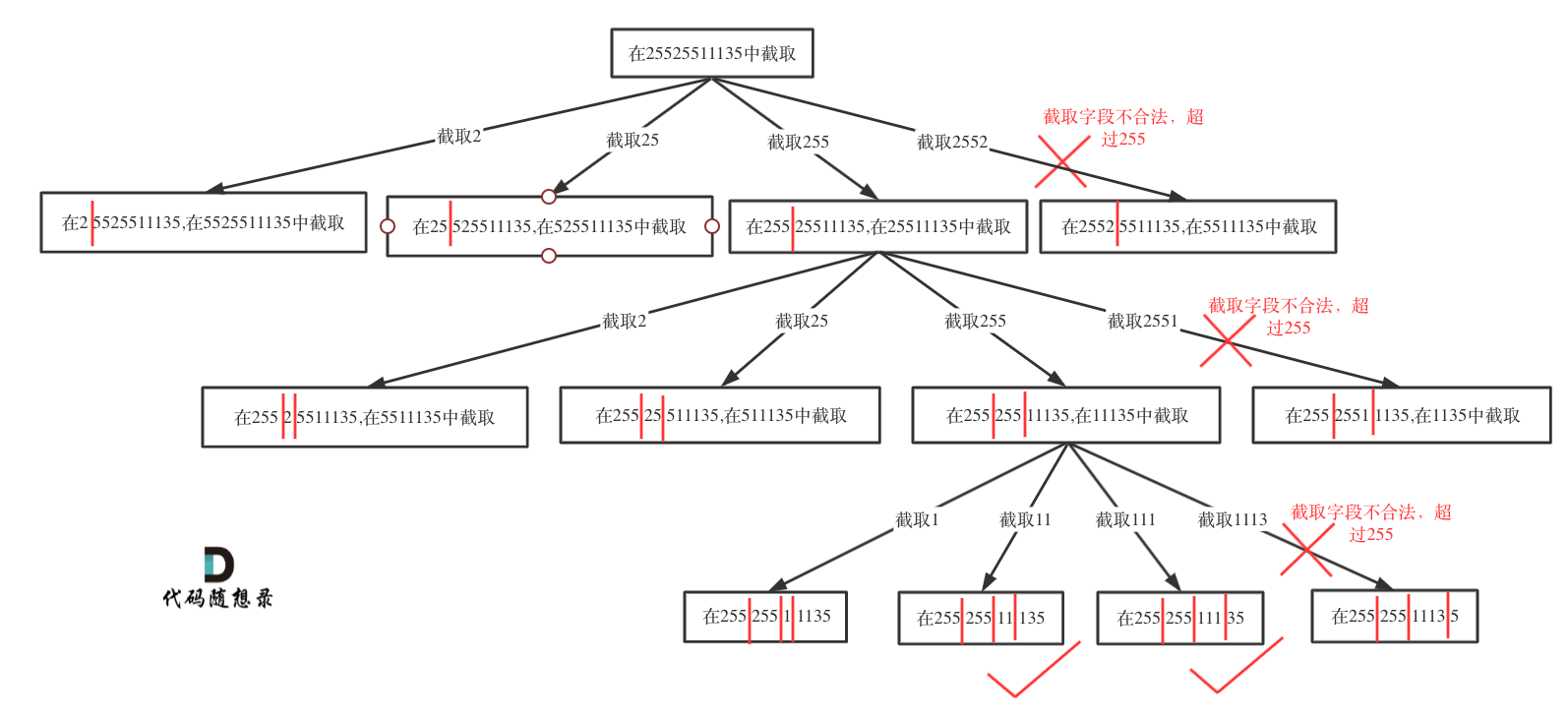
+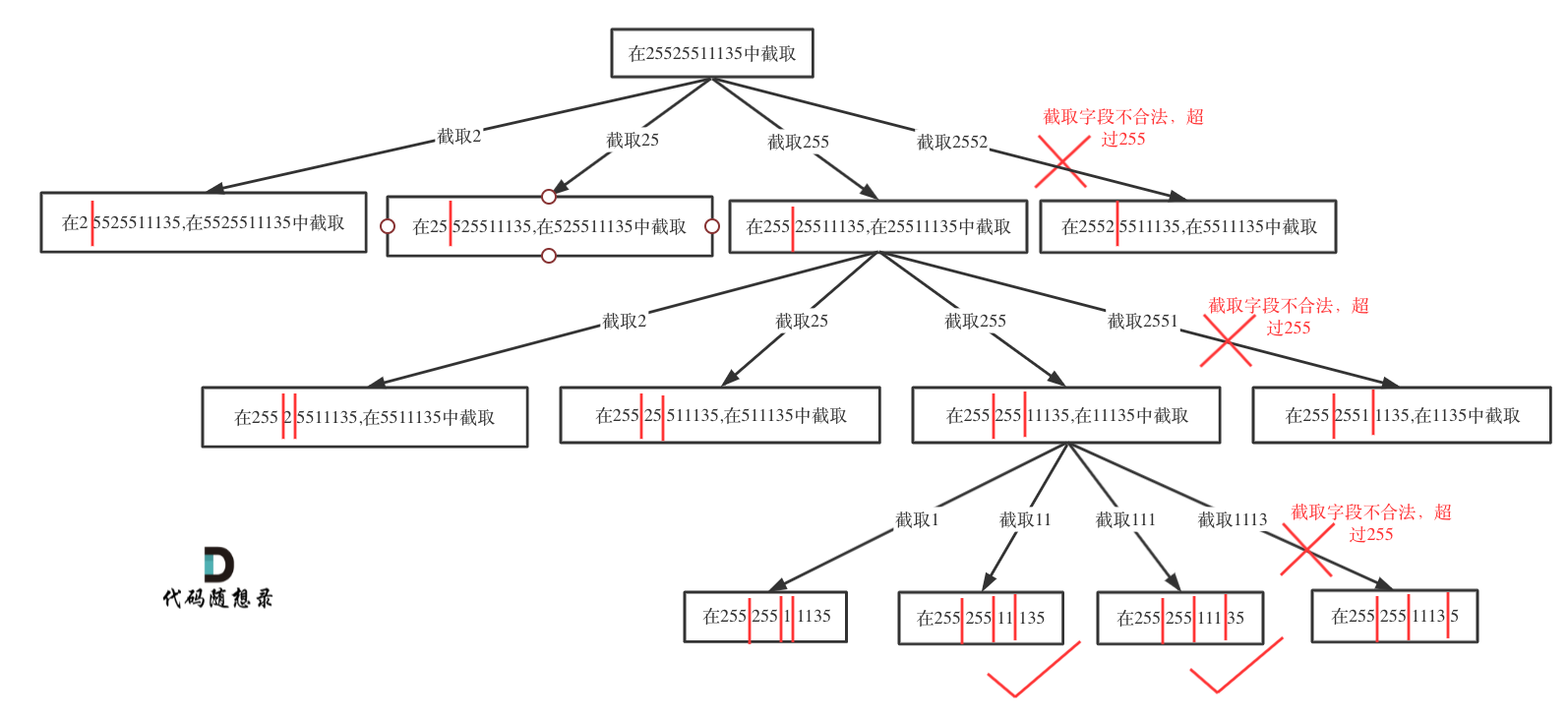
然后就是递归和回溯的过程:
@@ -143,7 +141,7 @@ for (int i = startIndex; i < s.size(); i++) {
代码如下:
```CPP
-// 判断字符串s在左闭又闭区间[start, end]所组成的数字是否合法
+// 判断字符串s在左闭右闭区间[start, end]所组成的数字是否合法
bool isValid(const string& s, int start, int end) {
if (start > end) {
return false;
@@ -208,7 +206,7 @@ private:
} else break; // 不合法,直接结束本层循环
}
}
- // 判断字符串s在左闭又闭区间[start, end]所组成的数字是否合法
+ // 判断字符串s在左闭右闭区间[start, end]所组成的数字是否合法
bool isValid(const string& s, int start, int end) {
if (start > end) {
return false;
@@ -376,9 +374,8 @@ class Solution {
// 剪枝:ip段的长度最大是3,并且ip段处于[0,255]
for (int i = start; i < s.length() && i - start < 3 && Integer.parseInt(s.substring(start, i + 1)) >= 0
&& Integer.parseInt(s.substring(start, i + 1)) <= 255; i++) {
- // 如果ip段的长度大于1,并且第一位为0的话,continue
if (i + 1 - start > 1 && s.charAt(start) - '0' == 0) {
- continue;
+ break;
}
stringBuilder.append(s.substring(start, i + 1));
// 当stringBuilder里的网段数量小于3时,才会加点;如果等于3,说明已经有3段了,最后一段不需要再加点
@@ -467,9 +464,37 @@ class Solution:
num = int(s[start:end+1])
return 0 <= num <= 255
+回溯(版本三)
-
-
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def restoreIpAddresses(self, s: str) -> List[str]:
+ result = []
+ self.backtracking(s, 0, [], result)
+ return result
+
+ def backtracking(self, s, startIndex, path, result):
+ if startIndex == len(s):
+ result.append('.'.join(path[:]))
+ return
+
+ for i in range(startIndex, min(startIndex+3, len(s))):
+ # 如果 i 往后遍历了,并且当前地址的第一个元素是 0 ,就直接退出
+ if i > startIndex and s[startIndex] == '0':
+ break
+ # 比如 s 长度为 5,当前遍历到 i = 3 这个元素
+ # 因为还没有执行任何操作,所以此时剩下的元素数量就是 5 - 3 = 2 ,即包括当前的 i 本身
+ # path 里面是当前包含的子串,所以有几个元素就表示储存了几个地址
+ # 所以 (4 - len(path)) * 3 表示当前路径至多能存放的元素个数
+ # 4 - len(path) 表示至少要存放的元素个数
+ if (4 - len(path)) * 3 < len(s) - i or 4 - len(path) > len(s) - i:
+ break
+ if i - startIndex == 2:
+ if not int(s[startIndex:i+1]) <= 255:
+ break
+ path.append(s[startIndex:i+1])
+ self.backtracking(s, i+1, path, result)
+ path.pop()
```
### Go
@@ -848,8 +873,4 @@ public class Solution
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0096.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0096.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 15b99083e0..e5bc2b6b65
--- "a/problems/0096.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0096.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0096.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0096.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 15b99083e0..e5bc2b6b65
--- "a/problems/0096.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0096.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
# 96.不同的二叉搜索树
@@ -14,7 +12,7 @@
示例:
-
+
## 算法公开课
@@ -29,11 +27,11 @@
了解了二叉搜索树之后,我们应该先举几个例子,画画图,看看有没有什么规律,如图:
-
+
n为1的时候有一棵树,n为2有两棵树,这个是很直观的。
-
+
来看看n为3的时候,有哪几种情况。
@@ -67,7 +65,7 @@ dp[3],就是 元素1为头结点搜索树的数量 + 元素2为头结点搜索
如图所示:
-
+
此时我们已经找到递推关系了,那么可以用动规五部曲再系统分析一遍。
@@ -120,7 +118,7 @@ for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
n为5时候的dp数组状态如图:
-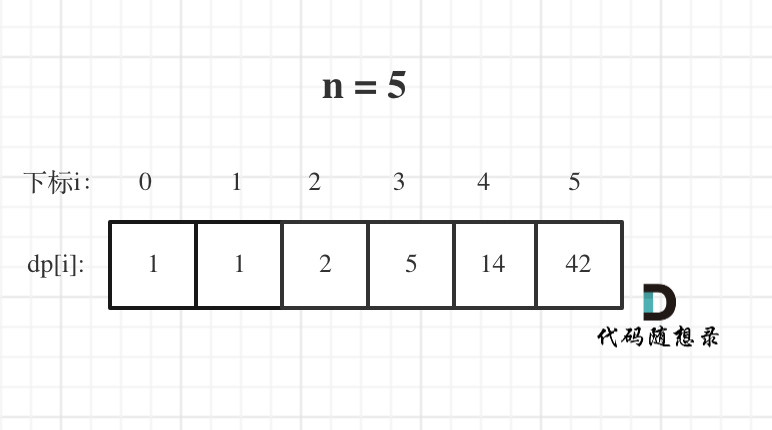
+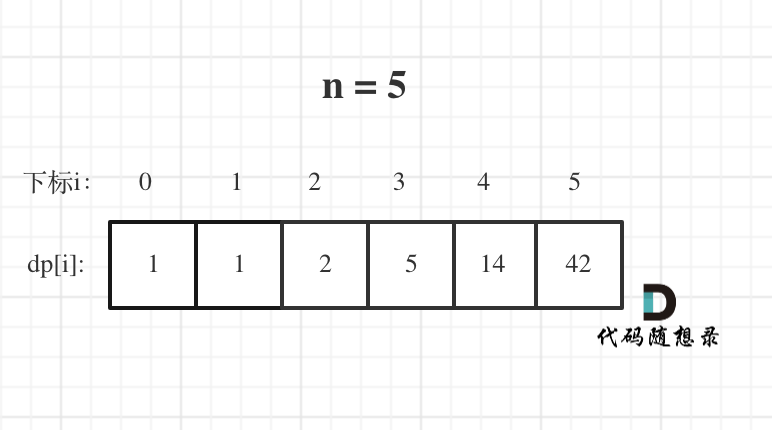
当然如果自己画图举例的话,基本举例到n为3就可以了,n为4的时候,画图已经比较麻烦了。
@@ -221,7 +219,7 @@ func numTrees(n int)int{
}
```
-### Javascript
+### JavaScript
```Javascript
const numTrees =(n) => {
@@ -348,7 +346,3 @@ public class Solution
}
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0098.\351\252\214\350\257\201\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0098.\351\252\214\350\257\201\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 88e1628243..990d3c8413
--- "a/problems/0098.\351\252\214\350\257\201\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0098.\351\252\214\350\257\201\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0098.\351\252\214\350\257\201\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0098.\351\252\214\350\257\201\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 88e1628243..990d3c8413
--- "a/problems/0098.\351\252\214\350\257\201\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0098.\351\252\214\350\257\201\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 98.验证二叉搜索树
@@ -18,11 +16,11 @@
* 节点的右子树只包含大于当前节点的数。
* 所有左子树和右子树自身必须也是二叉搜索树。
-
+
## 算法公开课
-**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[你对二叉搜索树了解的还不够! | LeetCode:98.验证二叉搜索树](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV18P411n7Q4),相信结合视频在看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
+**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[你对二叉搜索树了解的还不够! | LeetCode:98.验证二叉搜索树](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV18P411n7Q4),相信结合视频再看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
## 思路
@@ -104,7 +102,7 @@ if (root->val > root->left->val && root->val < root->right->val) {
例如: [10,5,15,null,null,6,20] 这个case:
-
+
节点10大于左节点5,小于右节点15,但右子树里出现了一个6 这就不符合了!
@@ -806,8 +804,4 @@ public bool IsValidBST(TreeNode root)
}
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0100.\347\233\270\345\220\214\347\232\204\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0100.\347\233\270\345\220\214\347\232\204\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 56a6c8840f..df1b55a462
--- "a/problems/0100.\347\233\270\345\220\214\347\232\204\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0100.\347\233\270\345\220\214\347\232\204\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0100.\347\233\270\345\220\214\347\232\204\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0100.\347\233\270\345\220\214\347\232\204\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 56a6c8840f..df1b55a462
--- "a/problems/0100.\347\233\270\345\220\214\347\232\204\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0100.\347\233\270\345\220\214\347\232\204\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
@@ -14,9 +12,9 @@
如果两个树在结构上相同,并且节点具有相同的值,则认为它们是相同的。
-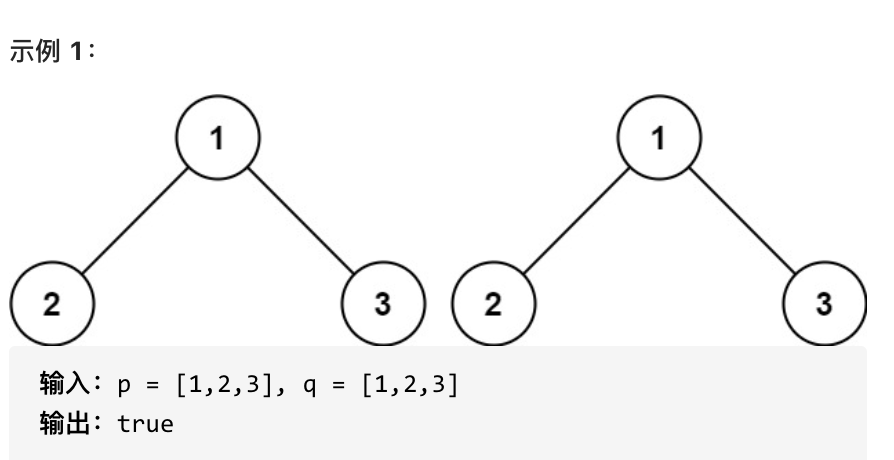
+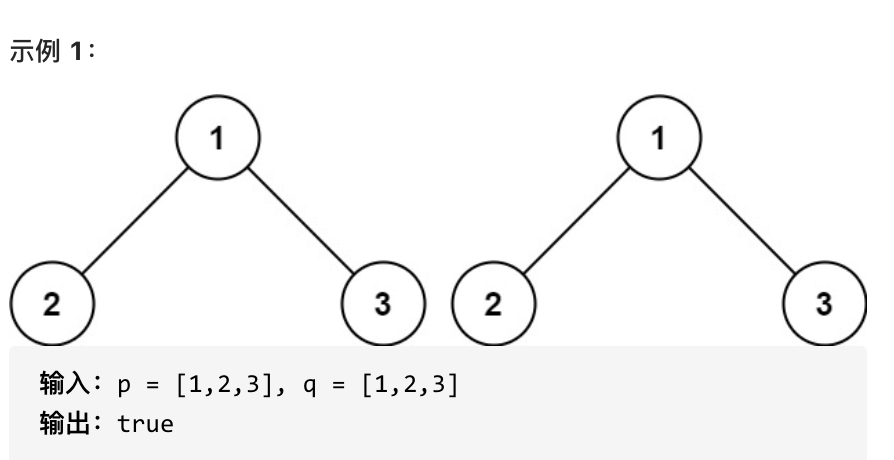
-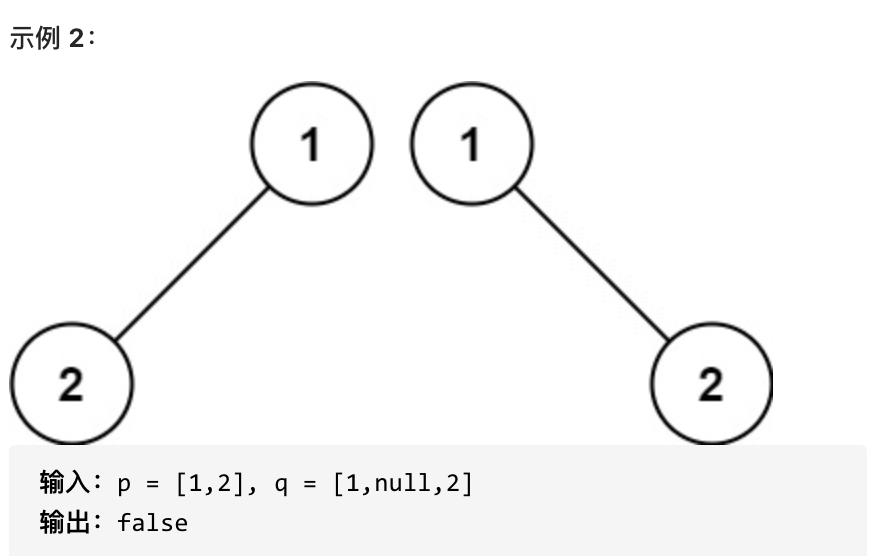
+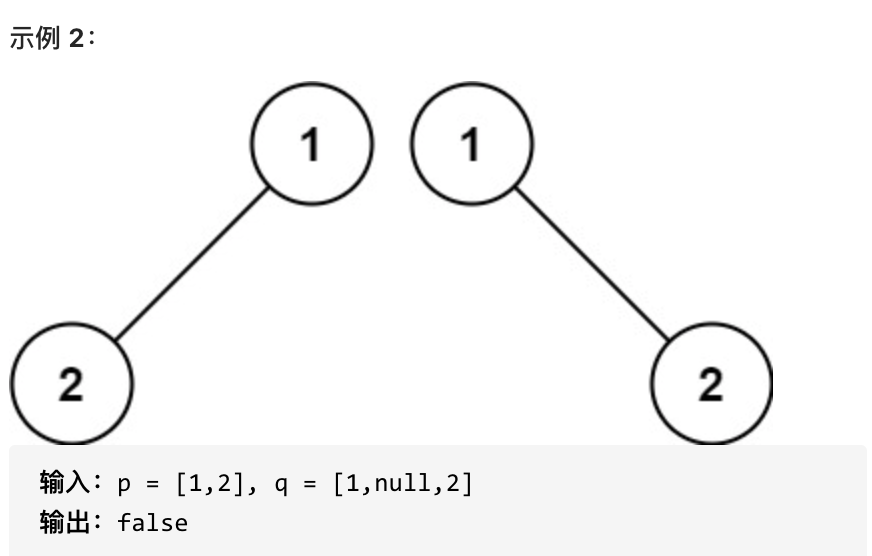
## 思路
@@ -339,8 +337,4 @@ function isSameTree(p: TreeNode | null, q: TreeNode | null): boolean {
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0101.\345\257\271\347\247\260\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0101.\345\257\271\347\247\260\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 8442f0ab9e..24e9e2684e
--- "a/problems/0101.\345\257\271\347\247\260\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0101.\345\257\271\347\247\260\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0101.\345\257\271\347\247\260\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0101.\345\257\271\347\247\260\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 8442f0ab9e..24e9e2684e
--- "a/problems/0101.\345\257\271\347\247\260\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0101.\345\257\271\347\247\260\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 101. 对称二叉树
@@ -11,7 +9,7 @@
给定一个二叉树,检查它是否是镜像对称的。
-
+
## 算法公开课
@@ -27,7 +25,7 @@
比较的是两个子树的里侧和外侧的元素是否相等。如图所示:
-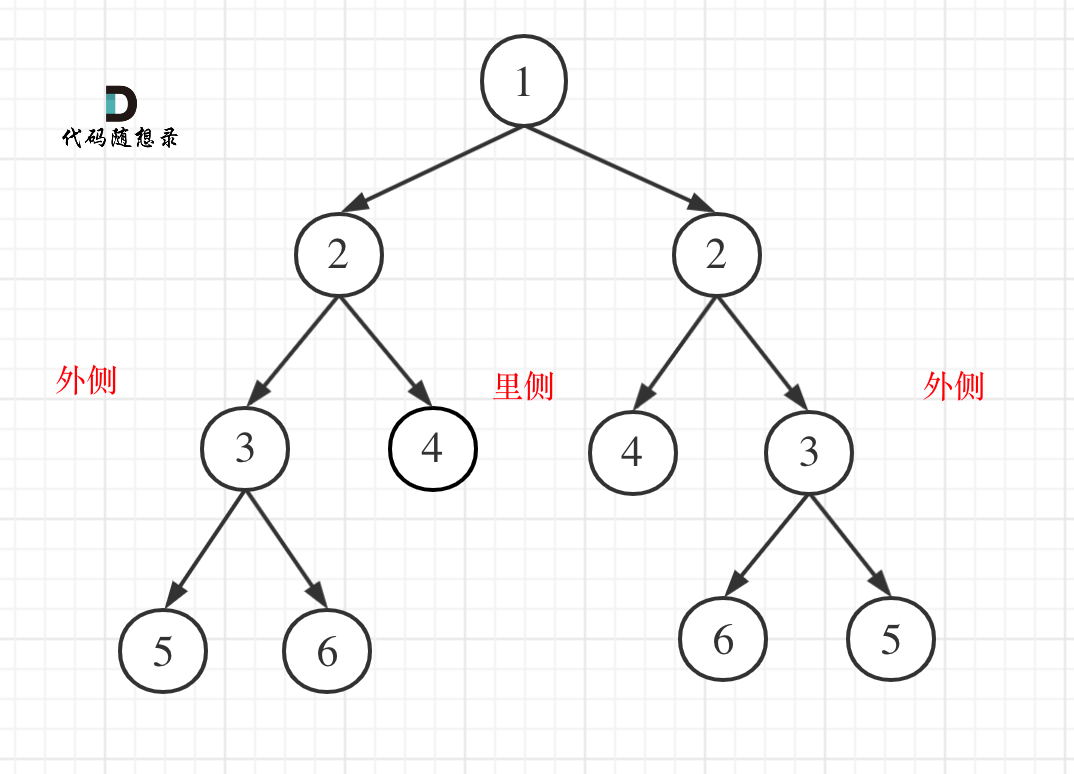
+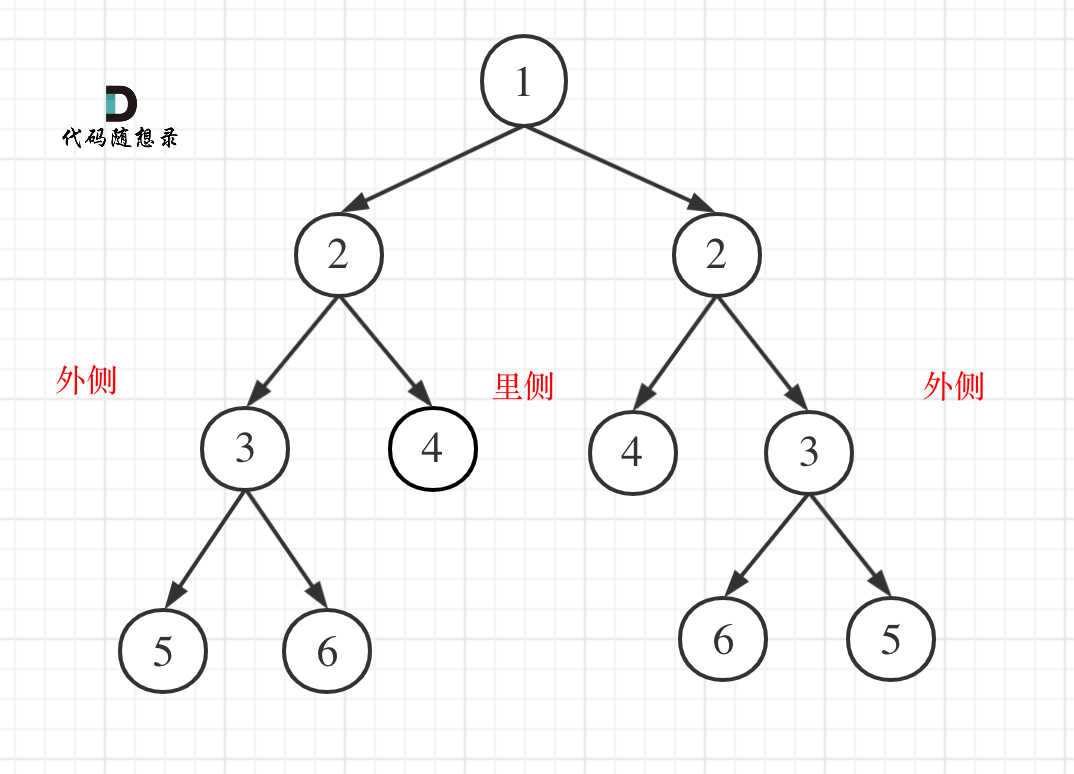
那么遍历的顺序应该是什么样的呢?
@@ -171,7 +169,7 @@ public:
通过队列来判断根节点的左子树和右子树的内侧和外侧是否相等,如动画所示:
-
+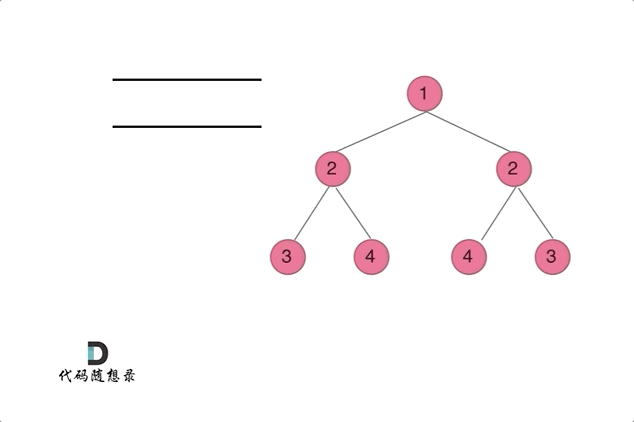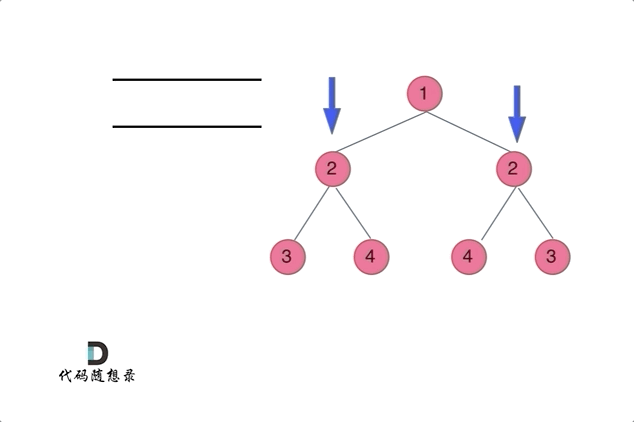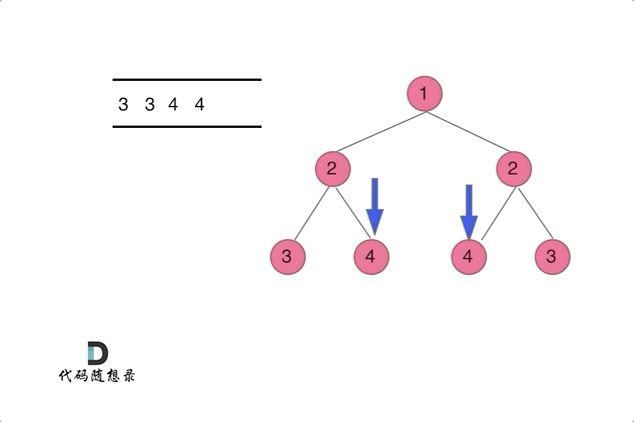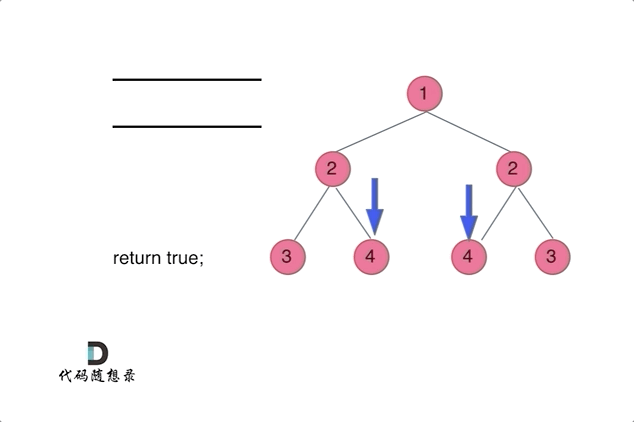
@@ -224,8 +222,8 @@ public:
st.push(root->left);
st.push(root->right);
while (!st.empty()) {
- TreeNode* leftNode = st.top(); st.pop();
TreeNode* rightNode = st.top(); st.pop();
+ TreeNode* leftNode = st.top(); st.pop();
if (!leftNode && !rightNode) {
continue;
}
@@ -945,8 +943,5 @@ public bool IsSymmetric(TreeNode root)
}
```
-
-
-  -
+
diff --git "a/problems/0102.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\345\261\202\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206.md" "b/problems/0102.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\345\261\202\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 4411b5609f..819153be97
--- "a/problems/0102.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\345\261\202\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206.md"
+++ "b/problems/0102.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\345\261\202\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-
-
+
diff --git "a/problems/0102.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\345\261\202\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206.md" "b/problems/0102.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\345\261\202\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 4411b5609f..819153be97
--- "a/problems/0102.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\345\261\202\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206.md"
+++ "b/problems/0102.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\345\261\202\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
# 二叉树层序遍历登场!
@@ -28,7 +26,7 @@
-
+
@@ -39,7 +37,7 @@
给你一个二叉树,请你返回其按 层序遍历 得到的节点值。 (即逐层地,从左到右访问所有节点)。
-
+
### 思路
@@ -59,7 +57,7 @@
使用队列实现二叉树广度优先遍历,动画如下:
-
+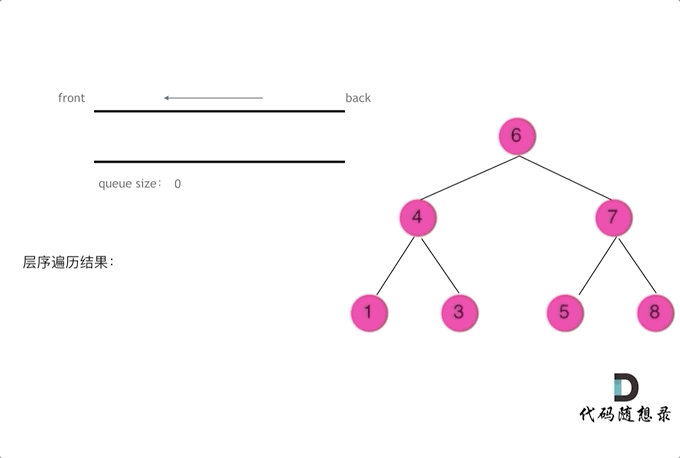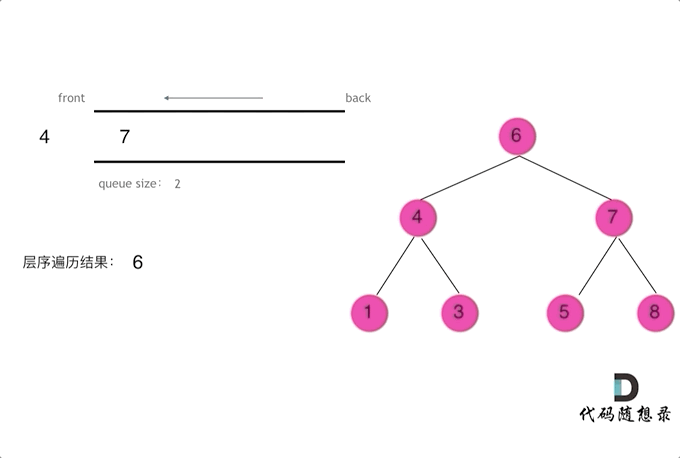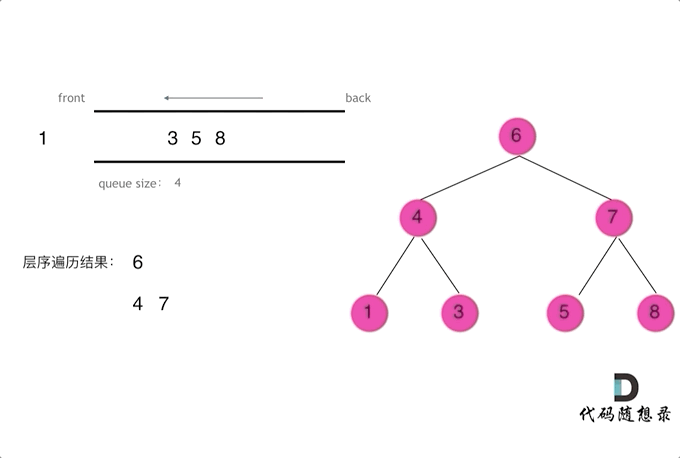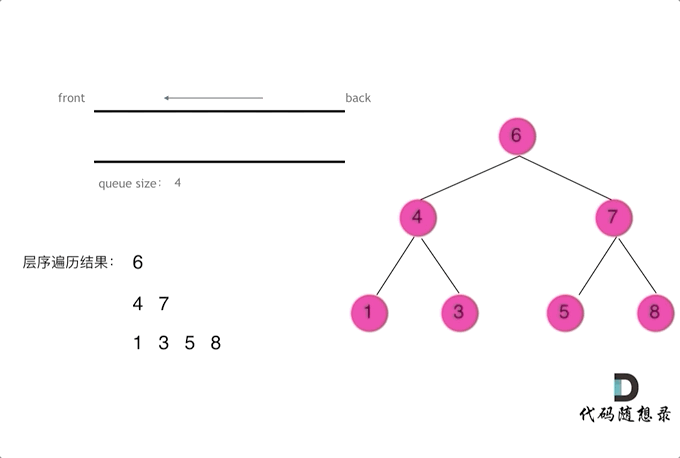
这样就实现了层序从左到右遍历二叉树。
@@ -129,7 +127,7 @@ class Solution {
return resList;
}
- //DFS--递归方式
+ //BFS--递归方式
public void checkFun01(TreeNode node, Integer deep) {
if (node == null) return;
deep++;
@@ -201,7 +199,7 @@ class Solution:
return result
```
```python
-# 递归法
+#递归法
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
@@ -210,18 +208,24 @@ class Solution:
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def levelOrder(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[List[int]]:
+ if not root:
+ return []
+
levels = []
- self.helper(root, 0, levels)
+
+ def traverse(node, level):
+ if not node:
+ return
+
+ if len(levels) == level:
+ levels.append([])
+
+ levels[level].append(node.val)
+ traverse(node.left, level + 1)
+ traverse(node.right, level + 1)
+
+ traverse(root, 0)
return levels
-
- def helper(self, node, level, levels):
- if not node:
- return
- if len(levels) == level:
- levels.append([])
- levels[level].append(node.val)
- self.helper(node.left, level + 1, levels)
- self.helper(node.right, level + 1, levels)
```
@@ -259,7 +263,7 @@ func levelOrder(root *TreeNode) [][]int {
```go
/**
-102. 二叉树的层序遍历
+102. 二叉树的层序遍历 使用container包
*/
func levelOrder(root *TreeNode) [][]int {
res := [][]int{}
@@ -290,6 +294,35 @@ func levelOrder(root *TreeNode) [][]int {
return res
}
+/**
+ 102. 二叉树的层序遍历 使用切片
+*/
+func levelOrder(root *TreeNode) [][]int {
+ res := make([][]int, 0)
+ if root == nil {
+ return res
+ }
+ queue := make([]*TreeNode, 0)
+ queue = append(queue, root)
+ for len(queue) > 0 {
+ size := len(queue)
+ level := make([]int, 0)
+ for i := 0; i < size; i++ {
+ node := queue[0]
+ queue = queue[1:]
+ level = append(level, node.Val)
+ if node.Left != nil {
+ queue = append(queue, node.Left)
+ }
+ if node.Right != nil {
+ queue = append(queue, node.Right)
+ }
+ }
+ res = append(res, level)
+ }
+ return res
+}
+
/**
102. 二叉树的层序遍历:使用切片模拟队列,易理解
*/
@@ -321,7 +354,7 @@ func levelOrder(root *TreeNode) (res [][]int) {
}
```
-#### Javascript:
+#### JavaScript:
```javascript
var levelOrder = function(root) {
@@ -499,7 +532,7 @@ public IList> LevelOrder(TreeNode root)
给定一个二叉树,返回其节点值自底向上的层次遍历。 (即按从叶子节点所在层到根节点所在的层,逐层从左向右遍历)
-
+
### 思路
@@ -689,30 +722,67 @@ func levelOrderBottom(root *TreeNode) [][]int {
}
```
-#### Javascript:
-
-```javascript
-var levelOrderBottom = function(root) {
- let res = [], queue = [];
- queue.push(root);
- while(queue.length && root!==null) {
- // 存放当前层级节点数组
- let curLevel = [];
- // 计算当前层级节点数量
- let length = queue.length;
- while(length--) {
- let node = queue.shift();
- // 把当前层节点存入curLevel数组
- curLevel.push(node.val);
- // 把下一层级的左右节点存入queue队列
- node.left && queue.push(node.left);
- node.right && queue.push(node.right);
+```GO
+// 使用切片作为队列
+func levelOrderBottom(root *TreeNode) [][]int {
+ res := make([][]int, 0)
+ if root == nil {
+ return res
+ }
+ queue := make([]*TreeNode, 0)
+ queue = append(queue, root)
+ for len(queue) > 0 {
+ size := len(queue)
+ level := make([]int, 0)
+ for i := 0; i < size; i++ {
+ node := queue[0]
+ queue = queue[1:]
+ level = append(level, node.Val)
+ if node.Left != nil {
+ queue = append(queue, node.Left)
+ }
+ if node.Right != nil {
+ queue = append(queue, node.Right)
+ }
}
- // 从数组前头插入值,避免最后反转数组,减少运算时间
- res.unshift(curLevel);
+ res = append(res, level)
}
- return res;
+ l, r := 0, len(res)-1
+ for l < r {
+ res[l], res[r] = res[r], res[l]
+ l++
+ r--
+ }
+ return res
+}
+```
+
+#### JavaScript:
+
+```javascript
+var levelOrderBottom = function (root) {
+ let res = [],
+ queue = [];
+ queue.push(root);
+ while (queue.length && root !== null) {
+ // 存放当前层级节点数组
+ let curLevel = [];
+ // 计算当前层级节点数量
+ let length = queue.length;
+ while (length--) {
+ let node = queue.shift();
+ // 把当前层节点存入curLevel数组
+ curLevel.push(node.val);
+ // 把下一层级的左右节点存入queue队列
+ node.left && queue.push(node.left);
+ node.right && queue.push(node.right);
+ }
+ // 从数组前头插入值,避免最后反转数组,减少运算时间
+ res.unshift(curLevel);
+ }
+ return res;
};
+
```
#### TypeScript:
@@ -856,7 +926,7 @@ public IList> LevelOrderBottom(TreeNode root)
给定一棵二叉树,想象自己站在它的右侧,按照从顶部到底部的顺序,返回从右侧所能看到的节点值。
-
+
### 思路
@@ -1000,7 +1070,36 @@ func rightSideView(root *TreeNode) []int {
}
```
-#### Javascript:
+```GO
+// 使用切片作为队列
+func rightSideView(root *TreeNode) []int {
+ res := make([]int, 0)
+ if root == nil {
+ return res
+ }
+ queue := make([]*TreeNode, 0)
+ queue = append(queue, root)
+ for len(queue) > 0 {
+ size := len(queue)
+ for i := 0; i < size; i++ {
+ node := queue[0]
+ queue = queue[1:]
+ if node.Left != nil {
+ queue = append(queue, node.Left)
+ }
+ if node.Right != nil {
+ queue = append(queue, node.Right)
+ }
+ if i == size-1 {
+ res = append(res, node.Val)
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return res
+}
+```
+
+#### JavaScript:
```javascript
var rightSideView = function(root) {
@@ -1130,17 +1229,58 @@ impl Solution {
}
```
+#### C#:
+
+```C# 199.二叉树的右视图
+public class Solution
+{
+ public IList RightSideView(TreeNode root)
+ {
+ var result = new List();
+ Queue queue = new();
+
+ if (root != null)
+ {
+ queue.Enqueue(root);
+ }
+ while (queue.Count > 0)
+ {
+ int count = queue.Count;
+ int lastValue = count - 1;
+ for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
+ {
+ var currentNode = queue.Dequeue();
+ if (i == lastValue)
+ {
+ result.Add(currentNode.val);
+ }
+
+ // lastValue == i == count -1 : left 先于 right 进入Queue
+ if (currentNode.left != null) queue.Enqueue(currentNode.left);
+ if (currentNode.right != null) queue.Enqueue(currentNode.right);
+
+ //// lastValue == i == 0: right 先于 left 进入Queue
+ // if(currentNode.right !=null ) queue.Enqueue(currentNode.right);
+ // if(currentNode.left !=null ) queue.Enqueue(currentNode.left);
+ }
+ }
+
+ return result;
+ }
+}
+```
+
## 637.二叉树的层平均值
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/average-of-levels-in-binary-tree/)
给定一个非空二叉树, 返回一个由每层节点平均值组成的数组。
-
+
### 思路
-本题就是层序遍历的时候把一层求个总和在取一个均值。
+本题就是层序遍历的时候把一层求个总和再取一个均值。
C++代码:
@@ -1291,30 +1431,59 @@ func averageOfLevels(root *TreeNode) []float64 {
}
```
-#### Javascript:
-
-```javascript
-var averageOfLevels = function(root) {
- //层级平均值
- let res = [], queue = [];
- queue.push(root);
-
- while(queue.length && root!==null) {
- //每一层节点个数
- let length = queue.length;
- //sum记录每一层的和
- let sum = 0;
- for(let i=0; i < length; i++) {
- let node = queue.shift();
- sum += node.val;
- node.left && queue.push(node.left);
- node.right && queue.push(node.right);
+```GO
+// 使用切片作为队列
+func averageOfLevels(root *TreeNode) []float64 {
+ res := make([]float64, 0)
+ if root == nil {
+ return res
+ }
+ queue := make([]*TreeNode, 0)
+ queue = append(queue, root)
+ for len(queue) > 0 {
+ size := len(queue)
+ sum := 0
+ for i := 0; i < size; i++ {
+ node := queue[0]
+ queue = queue[1:]
+ sum += node.Val
+ if node.Left != nil {
+ queue = append(queue, node.Left)
+ }
+ if node.Right != nil {
+ queue = append(queue, node.Right)
+ }
}
- //每一层的平均值存入数组res
- res.push(sum/length);
+ res = append(res, float64(sum)/float64(size))
}
+ return res
+}
+```
- return res;
+#### JavaScript:
+
+```javascript
+var averageOfLevels = function(root) {
+ let res = [],
+ queue = [];
+ queue.push(root);
+ while (queue.length) {
+ // 每一层节点个数;
+ let lengthLevel = queue.length,
+ len = queue.length,
+ // sum记录每一层的和;
+ sum = 0;
+ while (lengthLevel--) {
+ const node = queue.shift();
+ sum += node.val;
+ // 队列存放下一层节点
+ node.left && queue.push(node.left);
+ node.right && queue.push(node.right);
+ }
+ // 求平均值
+ res.push(sum / len);
+ }
+ return res;
};
```
@@ -1428,6 +1597,35 @@ impl Solution {
}
```
+#### C#:
+
+```C# 二叉树的层平均值
+public class Solution {
+ public IList AverageOfLevels(TreeNode root) {
+ var result= new List();
+ Queue queue = new();
+ if(root !=null) queue.Enqueue(root);
+
+ while (queue.Count > 0)
+ {
+ int count = queue.Count;
+ double value=0;
+ for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
+ {
+ var curentNode=queue.Dequeue();
+ value += curentNode.val;
+ if (curentNode.left!=null) queue.Enqueue(curentNode.left);
+ if (curentNode.right!=null) queue.Enqueue(curentNode.right);
+ }
+ result.Add(value/count);
+ }
+
+ return result;
+ }
+}
+
+```
+
## 429.N叉树的层序遍历
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/n-ary-tree-level-order-traversal/)
@@ -1436,7 +1634,7 @@ impl Solution {
例如,给定一个 3叉树 :
-
+
返回其层序遍历:
@@ -1623,6 +1821,32 @@ func levelOrder(root *Node) [][]int {
}
```
+```GO
+// 使用切片作为队列
+func levelOrder(root *Node) [][]int {
+ res := make([][]int, 0)
+ if root == nil {
+ return res
+ }
+ queue := make([]*Node, 0)
+ queue = append(queue, root)
+ for len(queue) > 0 {
+ size := len(queue)
+ level := make([]int, 0)
+ for i := 0; i < size; i++ {
+ node := queue[0]
+ queue = queue[1:]
+ level = append(level, node.Val)
+ if len(node.Children) > 0 {
+ queue = append(queue, node.Children...)
+ }
+ }
+ res = append(res, level)
+ }
+ return res
+}
+```
+
#### JavaScript:
```JavaScript
@@ -1782,7 +2006,7 @@ impl Solution {
您需要在二叉树的每一行中找到最大的值。
-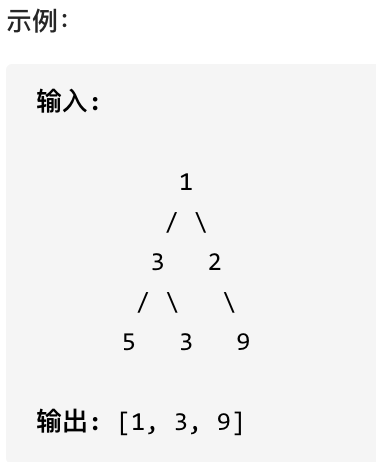
+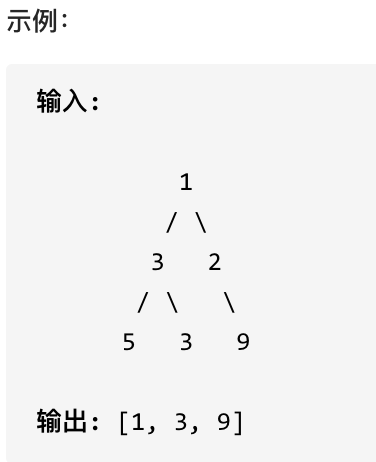
### 思路
@@ -1922,29 +2146,62 @@ func max(x, y int) int {
}
```
-#### Javascript:
-
-```javascript
-var largestValues = function(root) {
- //使用层序遍历
- let res = [], queue = [];
- queue.push(root);
-
- while(root !== null && queue.length) {
- //设置max初始值就是队列的第一个元素
- let max = queue[0].val;
- let length = queue.length;
- while(length--) {
- let node = queue.shift();
- max = max > node.val ? max : node.val;
- node.left && queue.push(node.left);
- node.right && queue.push(node.right);
+```GO
+// 使用切片作为队列
+func largestValues(root *TreeNode) []int {
+ res := make([]int, 0)
+ if root == nil {
+ return res
+ }
+ queue := make([]*TreeNode, 0)
+ queue = append(queue, root)
+ for len(queue) > 0 {
+ size := len(queue)
+ maxValue := math.MinInt64
+ for i := 0; i < size; i++ {
+ node := queue[0]
+ queue = queue[1:]
+ if node.Val > maxValue {
+ maxValue = node.Val
+ }
+ if node.Left != nil {
+ queue = append(queue, node.Left)
+ }
+ if node.Right != nil {
+ queue = append(queue, node.Right)
+ }
}
- //把每一层的最大值放到res数组
- res.push(max);
+ res = append(res, maxValue)
}
+ return res
+}
+```
+
+#### JavaScript:
+```javascript
+var largestValues = function (root) {
+ let res = [],
+ queue = [];
+ queue.push(root);
+ if (root === null) {
return res;
+ }
+ while (queue.length) {
+ let lengthLevel = queue.length,
+ // 初始值设为负无穷大
+ max = -Infinity;
+ while (lengthLevel--) {
+ const node = queue.shift();
+ // 在当前层中找到最大值
+ max = Math.max(max, node.val);
+ // 找到下一层的节点
+ node.left && queue.push(node.left);
+ node.right && queue.push(node.right);
+ }
+ res.push(max);
+ }
+ return res;
};
```
@@ -2080,7 +2337,7 @@ struct Node {
初始状态下,所有 next 指针都被设置为 NULL。
-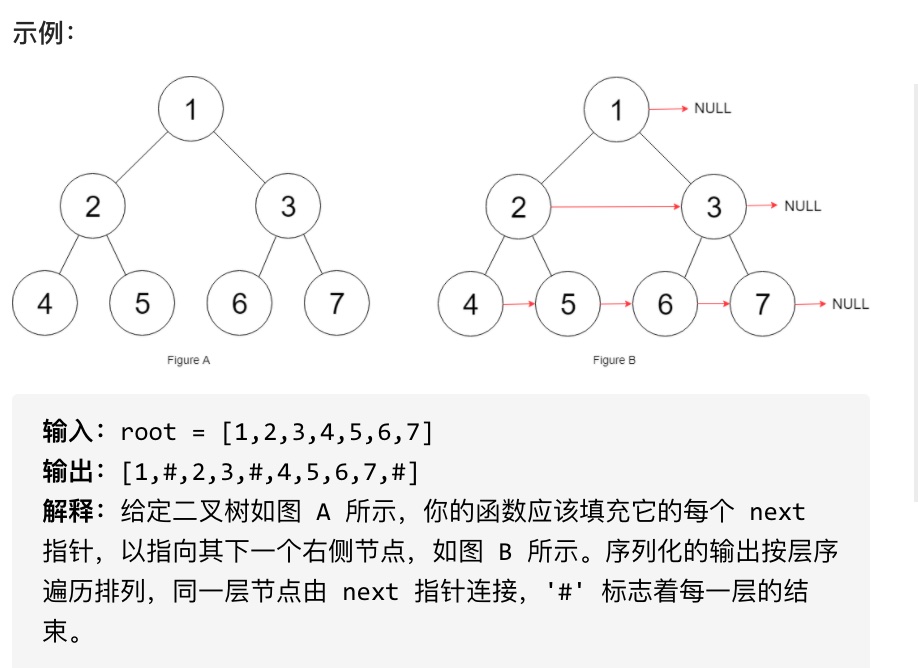
+
### 思路
@@ -2233,6 +2490,34 @@ func connect(root *Node) *Node {
```
+```GO
+// 使用切片作为队列
+func connect(root *Node) *Node {
+ if root == nil {
+ return root
+ }
+ queue := make([]*Node, 0)
+ queue = append(queue, root)
+ for len(queue) > 0 {
+ size := len(queue)
+ for i := 0; i < size; i++ {
+ node := queue[i]
+ if i != size - 1 {
+ queue[i].Next = queue[i+1]
+ }
+ if node.Left != nil {
+ queue = append(queue, node.Left)
+ }
+ if node.Right != nil {
+ queue = append(queue, node.Right)
+ }
+ }
+ queue = queue[size:]
+ }
+ return root
+}
+```
+
#### JavaScript:
```javascript
@@ -2521,6 +2806,34 @@ func connect(root *Node) *Node {
}
```
+```GO
+// 使用切片作为队列
+func connect(root *Node) *Node {
+ if root == nil {
+ return root
+ }
+ queue := make([]*Node, 0)
+ queue = append(queue, root)
+ for len(queue) > 0 {
+ size := len(queue)
+ for i := 0; i < size; i++ {
+ node := queue[i]
+ if i != size - 1 {
+ queue[i].Next = queue[i+1]
+ }
+ if node.Left != nil {
+ queue = append(queue, node.Left)
+ }
+ if node.Right != nil {
+ queue = append(queue, node.Right)
+ }
+ }
+ queue = queue[size:]
+ }
+ return root
+}
+```
+
#### JavaScript:
```javascript
@@ -2658,7 +2971,7 @@ object Solution {
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
-
+
返回它的最大深度 3 。
@@ -2668,7 +2981,7 @@ object Solution {
在二叉树中,一层一层的来遍历二叉树,记录一下遍历的层数就是二叉树的深度,如图所示:
-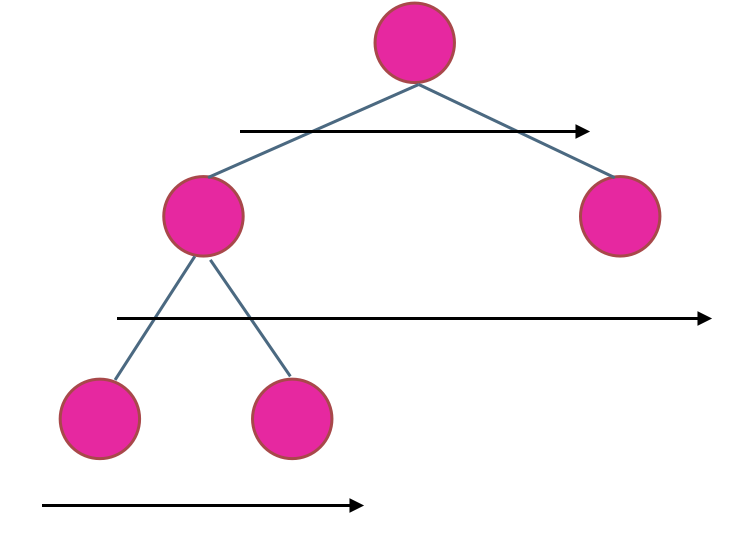
+
所以这道题的迭代法就是一道模板题,可以使用二叉树层序遍历的模板来解决的。
@@ -2790,6 +3103,33 @@ func maxDepth(root *TreeNode) int {
}
```
+```go
+// 使用切片作为队列
+func maxDepth(root *TreeNode) int {
+ if root == nil {
+ return 0
+ }
+ depth := 0
+ queue := make([]*TreeNode, 0)
+ queue = append(queue, root)
+ for len(queue) > 0 {
+ size := len(queue)
+ for i := 0; i < size; i++ {
+ node := queue[0]
+ queue = queue[1:]
+ if node.Left != nil {
+ queue = append(queue, node.Left)
+ }
+ if node.Right != nil {
+ queue = append(queue, node.Right)
+ }
+ }
+ depth++
+ }
+ return depth
+}
+```
+
#### JavaScript:
```javascript
@@ -2805,21 +3145,23 @@ func maxDepth(root *TreeNode) int {
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number}
*/
-var maxDepth = function(root) {
- // 最大的深度就是二叉树的层数
- if (root === null) return 0;
- let queue = [root];
- let height = 0;
- while (queue.length) {
- let n = queue.length;
- height++;
- for (let i=0; i 0 {
+ size := len(queue)
+ depth++
+ for i := 0; i < size; i++ {
+ node := queue[0]
+ queue = queue[1:]
+ if node.Left != nil {
+ queue = append(queue, node.Left)
+ }
+ if node.Right != nil {
+ queue = append(queue, node.Right)
+ }
+ if node.Left == nil && node.Right == nil {
+ return depth
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return depth
}
```
@@ -3226,8 +3598,4 @@ impl Solution {
**致敬叶师傅!**
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0104.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\244\247\346\267\261\345\272\246.md" "b/problems/0104.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\244\247\346\267\261\345\272\246.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 1f55f197e5..52d6d0e5fd
--- "a/problems/0104.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\244\247\346\267\261\345\272\246.md"
+++ "b/problems/0104.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\244\247\346\267\261\345\272\246.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0104.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\244\247\346\267\261\345\272\246.md" "b/problems/0104.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\244\247\346\267\261\345\272\246.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 1f55f197e5..52d6d0e5fd
--- "a/problems/0104.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\244\247\346\267\261\345\272\246.md"
+++ "b/problems/0104.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\244\247\346\267\261\345\272\246.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
@@ -20,7 +18,7 @@
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
-
+
返回它的最大深度 3 。
@@ -77,7 +75,7 @@ return depth;
所以整体c++代码如下:
```CPP
-class solution {
+class Solution {
public:
int getdepth(TreeNode* node) {
if (node == NULL) return 0;
@@ -94,7 +92,7 @@ public:
代码精简之后c++代码如下:
```CPP
-class solution {
+class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
@@ -110,7 +108,7 @@ public:
本题当然也可以使用前序,代码如下:(**充分表现出求深度回溯的过程**)
```CPP
-class solution {
+class Solution {
public:
int result;
void getdepth(TreeNode* node, int depth) {
@@ -144,7 +142,7 @@ public:
注意以上代码是为了把细节体现出来,简化一下代码如下:
```CPP
-class solution {
+class Solution {
public:
int result;
void getdepth(TreeNode* node, int depth) {
@@ -174,7 +172,7 @@ public:
在二叉树中,一层一层的来遍历二叉树,记录一下遍历的层数就是二叉树的深度,如图所示:
-
+
所以这道题的迭代法就是一道模板题,可以使用二叉树层序遍历的模板来解决的。
@@ -183,7 +181,7 @@ public:
c++代码如下:
```CPP
-class solution {
+class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) return 0;
@@ -219,7 +217,7 @@ public:
例如,给定一个 3叉树 :
-
+
我们应返回其最大深度,3。
@@ -232,7 +230,7 @@ public:
c++代码:
```CPP
-class solution {
+class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(Node* root) {
if (root == 0) return 0;
@@ -249,7 +247,7 @@ public:
依然是层序遍历,代码如下:
```CPP
-class solution {
+class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(Node* root) {
queue que;
@@ -278,7 +276,7 @@ public:
104.二叉树的最大深度
```java
-class solution {
+class Solution {
/**
* 递归法
*/
@@ -319,7 +317,7 @@ class Solution {
```
```java
-class solution {
+class Solution {
/**
* 迭代法,使用层序遍历
*/
@@ -369,7 +367,7 @@ class Solution {
```
```java
-class solution {
+class Solution {
/**
* 迭代法,使用层序遍历
*/
@@ -402,7 +400,7 @@ class solution {
递归法:
```python
-class solution:
+class Solution:
def maxdepth(self, root: treenode) -> int:
return self.getdepth(root)
@@ -417,7 +415,7 @@ class solution:
递归法:精简代码
```python
-class solution:
+class Solution:
def maxdepth(self, root: treenode) -> int:
if not root:
return 0
@@ -604,7 +602,7 @@ func maxDepth(root *Node) int {
}
```
-### Javascript :
+### JavaScript :
104.二叉树的最大深度
@@ -829,7 +827,42 @@ int maxDepth(struct TreeNode* root){
return depth;
}
```
-
+二叉树最大深度迭代——后序遍历实现
+```c
+int maxDepth(struct TreeNode *root)
+{
+ if(root == NULL)
+ return 0;
+ struct TreeNode *stack[10000] = {};
+ int top = -1;
+ struct TreeNode *p = root, *r = NULL; // r指向上一个被访问的结点
+ int depth = 0, maxDepth = -1;
+ while(p != NULL || top >= 0)
+ {
+ if(p != NULL)
+ {
+ stack[++top] = p;
+ depth++;
+ p = p->left;
+ }
+ else
+ {
+ p = stack[top];
+ if(p->right != NULL && p->right != r) // 右子树未被访问
+ p = p->right;
+ else
+ {
+ if(depth >= maxDepth) maxDepth = depth;
+ p = stack[top--];
+ depth--;
+ r = p;
+ p = NULL;
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return maxDepth;
+}
+```
### Swift:
104.二叉树的最大深度
@@ -1159,8 +1192,4 @@ public int MaxDepth(TreeNode root)
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0106.\344\273\216\344\270\255\345\272\217\344\270\216\345\220\216\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206\345\272\217\345\210\227\346\236\204\351\200\240\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0106.\344\273\216\344\270\255\345\272\217\344\270\216\345\220\216\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206\345\272\217\345\210\227\346\236\204\351\200\240\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 0e0ab1d74f..5253325835
--- "a/problems/0106.\344\273\216\344\270\255\345\272\217\344\270\216\345\220\216\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206\345\272\217\345\210\227\346\236\204\351\200\240\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0106.\344\273\216\344\270\255\345\272\217\344\270\216\345\220\216\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206\345\272\217\345\210\227\346\236\204\351\200\240\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0106.\344\273\216\344\270\255\345\272\217\344\270\216\345\220\216\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206\345\272\217\345\210\227\346\236\204\351\200\240\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0106.\344\273\216\344\270\255\345\272\217\344\270\216\345\220\216\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206\345\272\217\345\210\227\346\236\204\351\200\240\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 0e0ab1d74f..5253325835
--- "a/problems/0106.\344\273\216\344\270\255\345\272\217\344\270\216\345\220\216\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206\345\272\217\345\210\227\346\236\204\351\200\240\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0106.\344\273\216\344\270\255\345\272\217\344\270\216\345\220\216\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206\345\272\217\345\210\227\346\236\204\351\200\240\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
@@ -27,7 +25,7 @@
* 后序遍历 postorder = [9,15,7,20,3]
返回如下的二叉树:
-
+
## 算法公开课
@@ -42,7 +40,7 @@
流程如图:
-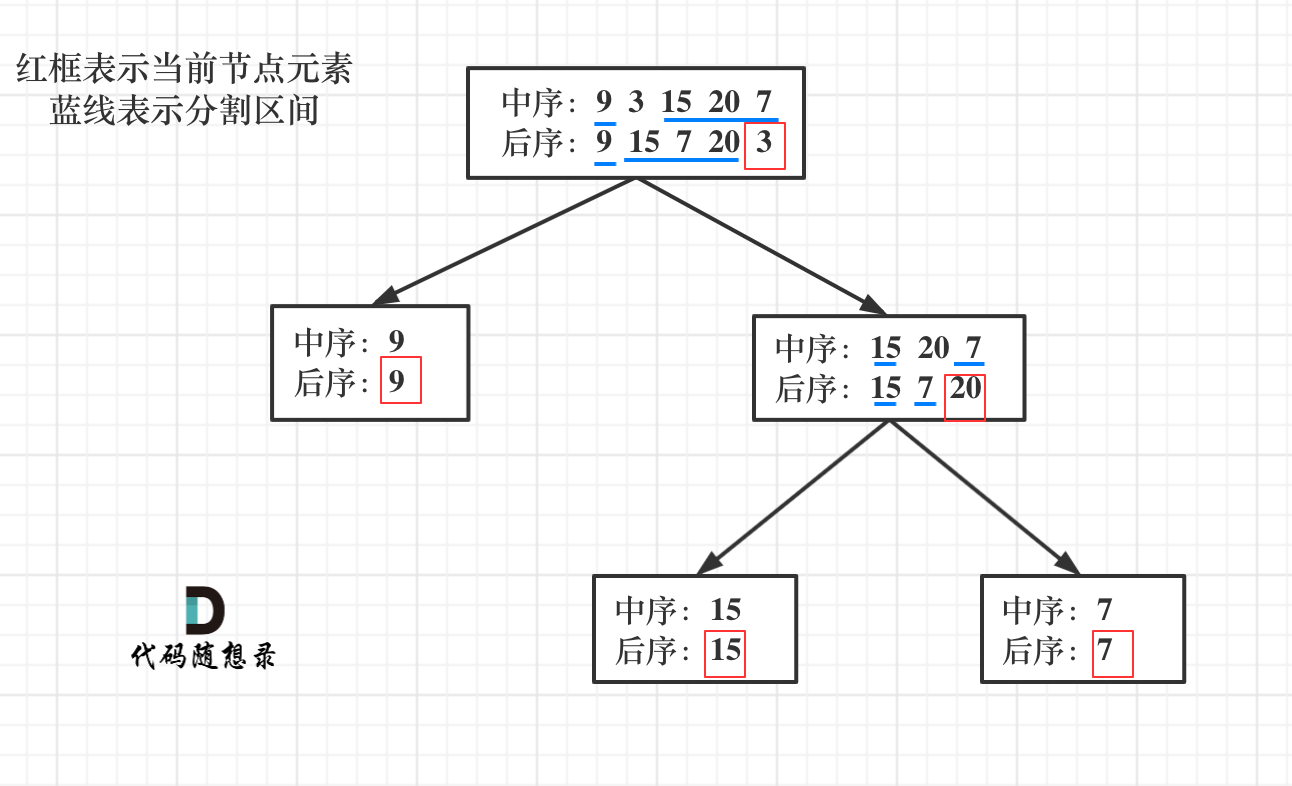
+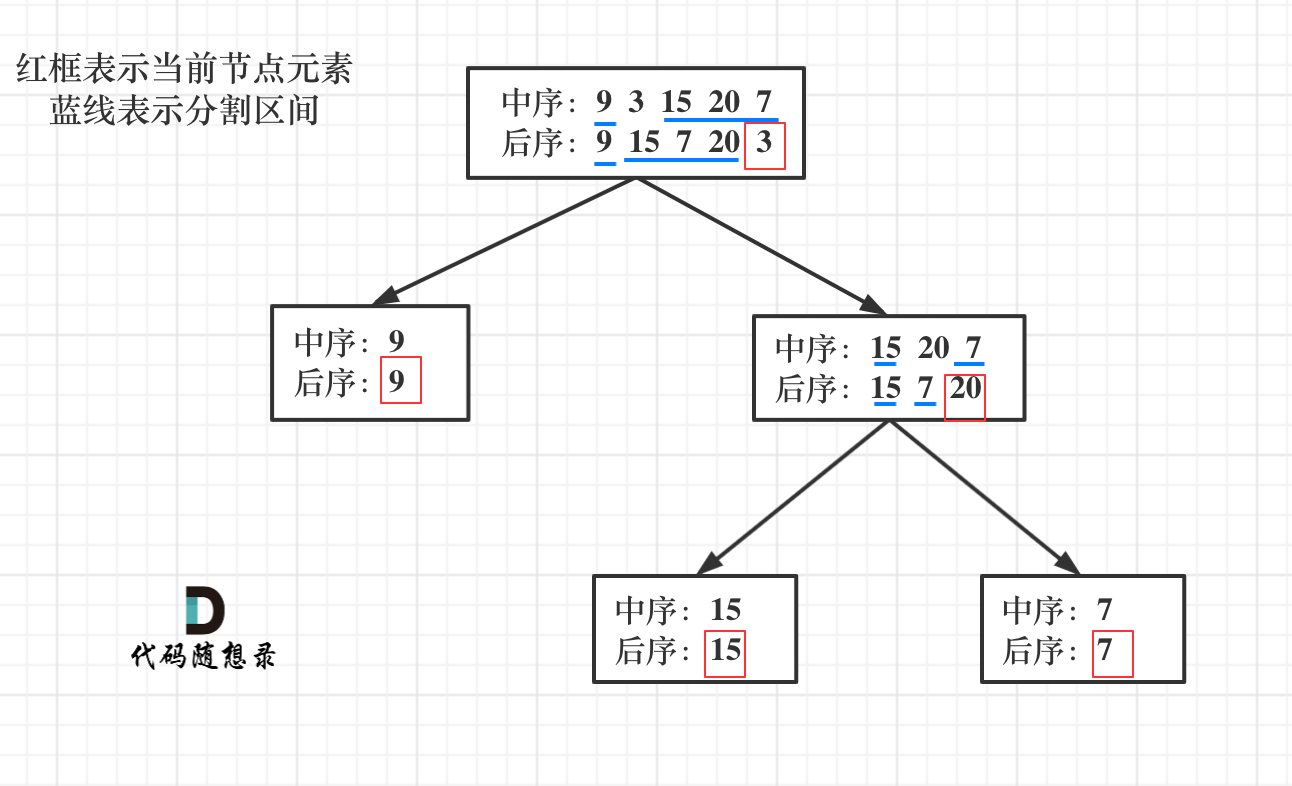
那么代码应该怎么写呢?
@@ -413,7 +411,7 @@ public:
中序遍历 inorder = [9,3,15,20,7]
返回如下的二叉树:
-
+
### 思路
@@ -556,7 +554,7 @@ public:
举一个例子:
-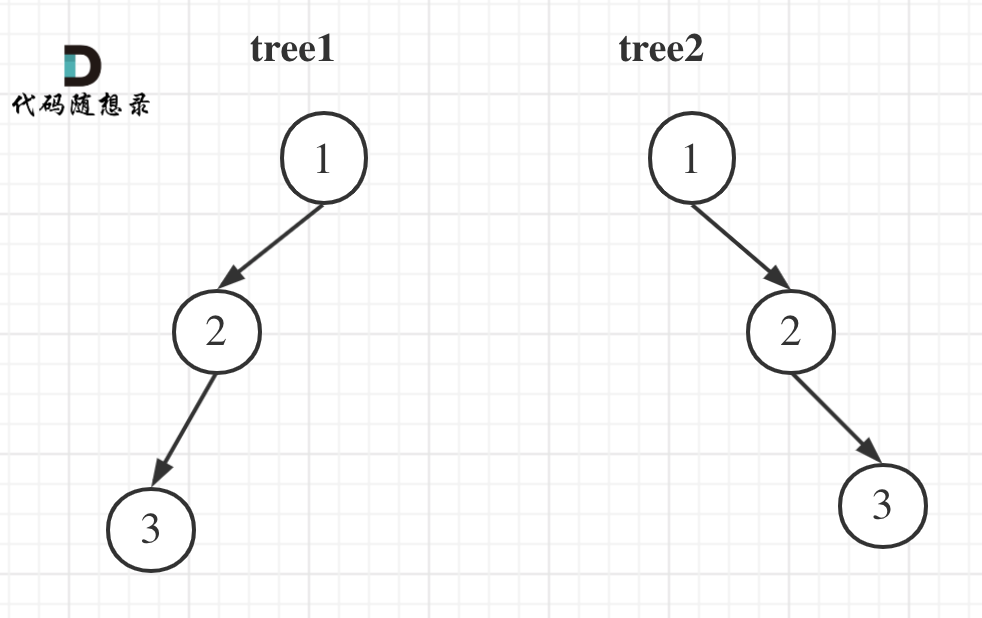
+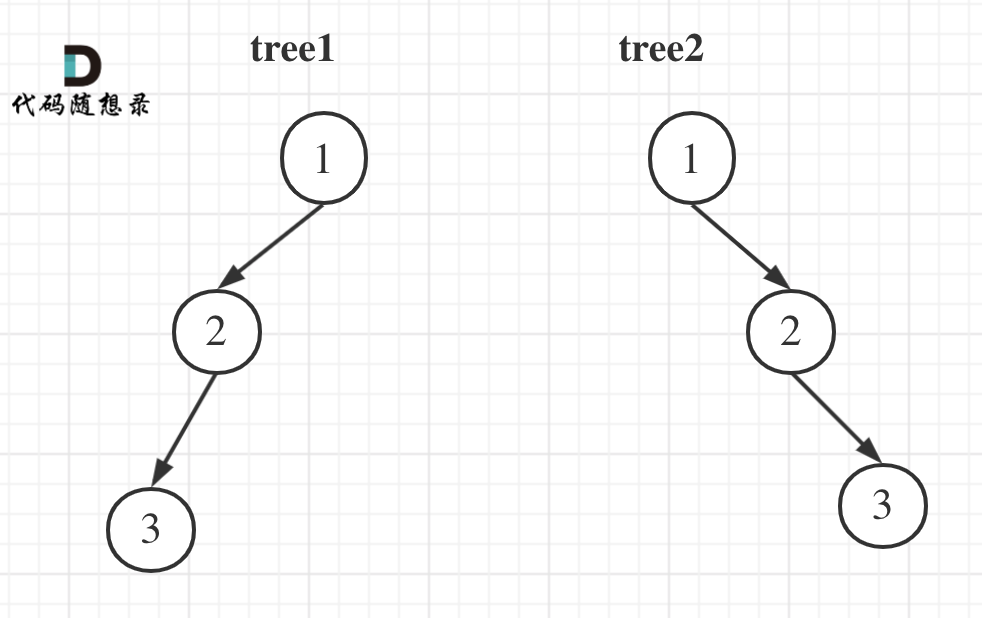
tree1 的前序遍历是[1 2 3], 后序遍历是[3 2 1]。
@@ -794,6 +792,60 @@ func rebuild(inorder []int, postorder []int, rootIdx int, l, r int) *TreeNode {
}
```
+```go
+/**
+ * Definition for a binary tree node.
+ * type TreeNode struct {
+ * Val int
+ * Left *TreeNode
+ * Right *TreeNode
+ * }
+ */
+func buildTree(inorder []int, postorder []int) *TreeNode {
+ if len(postorder) == 0 {
+ return nil
+ }
+
+ // 后序遍历数组最后一个元素,就是当前的中间节点
+ rootValue := postorder[len(postorder)-1]
+ root := &TreeNode{Val:rootValue}
+
+ // 叶子结点
+ if len(postorder) == 1 {
+ return root
+ }
+
+ // 找到中序遍历的切割点
+ var delimiterIndex int
+ for delimiterIndex = 0; delimiterIndex < len(inorder); delimiterIndex++ {
+ if inorder[delimiterIndex] == rootValue {
+ break;
+ }
+ }
+
+ // 切割中序数组
+ // 左闭右开区间:[0, delimiterIndex)
+ leftInorder := inorder[:delimiterIndex]
+ // [delimiterIndex + 1, end)
+ rightInorder := inorder[delimiterIndex+1:]
+
+ // postorder 舍弃末尾元素
+ postorder = postorder[:len(postorder)-1]
+
+ // 切割后序数组
+ // 依然左闭右开,注意这里使用了左中序数组大小作为切割点
+ // [0, len(leftInorder))
+ leftPostorder := postorder[:len(leftInorder)]
+ // [len(leftInorder), end)
+ rightPostorder := postorder[len(leftInorder):]
+
+ root.Left = buildTree(leftInorder, leftPostorder)
+ root.Right = buildTree(rightInorder, rightPostorder)
+
+ return root
+}
+```
+
105 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
```go
@@ -829,6 +881,60 @@ func build(pre []int, in []int, root int, l, r int) *TreeNode {
}
```
+```go
+/**
+ * Definition for a binary tree node.
+ * type TreeNode struct {
+ * Val int
+ * Left *TreeNode
+ * Right *TreeNode
+ * }
+ */
+func buildTree(preorder []int, inorder []int) *TreeNode {
+ if len(preorder) == 0 {
+ return nil
+ }
+
+ // 前序遍历数组第一个元素,就是当前的中间节点
+ rootValue := preorder[0]
+ root := &TreeNode{Val:rootValue}
+
+ // 叶子结点
+ if len(preorder) == 1 {
+ return root
+ }
+
+ // 找到中序遍历的切割点
+ var delimiterIndex int
+ for delimiterIndex = 0; delimiterIndex < len(inorder); delimiterIndex++ {
+ if inorder[delimiterIndex] == rootValue {
+ break
+ }
+ }
+
+ // 切割中序数组
+ // 左闭右开区间:[0, delimiterIndex)
+ leftInorder := inorder[:delimiterIndex]
+ // [delimiterIndex + 1, end)
+ rightInorder := inorder[delimiterIndex+1:]
+
+ // preorder 舍弃首位元素
+ preorder = preorder[1:]
+
+ // 切割前序数组
+ // 依然左闭右开,注意这里使用了左中序数组大小作为切割点
+ // [0, len(leftInorder))
+ leftPreorder := preorder[:len(leftInorder)]
+ // [len(leftInorder), end)
+ rightPreorder := preorder[len(leftInorder):]
+
+ root.Left = buildTree(leftPreorder, leftInorder)
+ root.Right = buildTree(rightPreorder, rightInorder)
+
+ return root
+}
+```
+
### JavaScript
@@ -1242,8 +1348,4 @@ public TreeNode BuildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder)
}
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0108.\345\260\206\346\234\211\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\350\275\254\346\215\242\344\270\272\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0108.\345\260\206\346\234\211\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\350\275\254\346\215\242\344\270\272\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 9fa684cfdf..2df1c2615b
--- "a/problems/0108.\345\260\206\346\234\211\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\350\275\254\346\215\242\344\270\272\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0108.\345\260\206\346\234\211\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\350\275\254\346\215\242\344\270\272\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0108.\345\260\206\346\234\211\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\350\275\254\346\215\242\344\270\272\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0108.\345\260\206\346\234\211\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\350\275\254\346\215\242\344\270\272\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 9fa684cfdf..2df1c2615b
--- "a/problems/0108.\345\260\206\346\234\211\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\350\275\254\346\215\242\344\270\272\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0108.\345\260\206\346\234\211\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\350\275\254\346\215\242\344\270\272\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
> 构造二叉搜索树,一不小心就平衡了
@@ -18,7 +16,7 @@
示例:
-
+
## 算法公开课
@@ -42,7 +40,7 @@
例如 有序数组[-10,-3,0,5,9] 就可以构造成这样的二叉搜索树,如图。
-
+
上图中,是符合二叉搜索树的特性吧,如果要这么做的话,是不是本题意义就不大了,所以才强调是平衡二叉搜索树。
@@ -65,7 +63,7 @@
如下两棵树,都是这个数组的平衡二叉搜索树:
-
+
如果要分割的数组长度为偶数的时候,中间元素为两个,是取左边元素 就是树1,取右边元素就是树2。
@@ -334,6 +332,18 @@ class Solution:
return root
```
+递归 精简(自身调用)
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def sortedArrayToBST(self, nums: List[int]) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
+ if not nums:
+ return
+ mid = len(nums) // 2
+ root = TreeNode(nums[mid])
+ root.left = self.sortedArrayToBST(nums[:mid])
+ root.right = self.sortedArrayToBST(nums[mid + 1 :])
+ return root
+```
迭代法
```python
@@ -549,8 +559,4 @@ public TreeNode Traversal(int[] nums, int left, int right)
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0110.\345\271\263\350\241\241\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0110.\345\271\263\350\241\241\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 40fdcd143d..d5b100ae80
--- "a/problems/0110.\345\271\263\350\241\241\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0110.\345\271\263\350\241\241\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0110.\345\271\263\350\241\241\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0110.\345\271\263\350\241\241\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 40fdcd143d..d5b100ae80
--- "a/problems/0110.\345\271\263\350\241\241\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0110.\345\271\263\350\241\241\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
@@ -21,7 +19,7 @@
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
-
+
返回 true 。
@@ -29,7 +27,7 @@
给定二叉树 [1,2,2,3,3,null,null,4,4]
-
+
返回 false 。
@@ -48,7 +46,7 @@
但leetcode中强调的深度和高度很明显是按照节点来计算的,如图:
-
+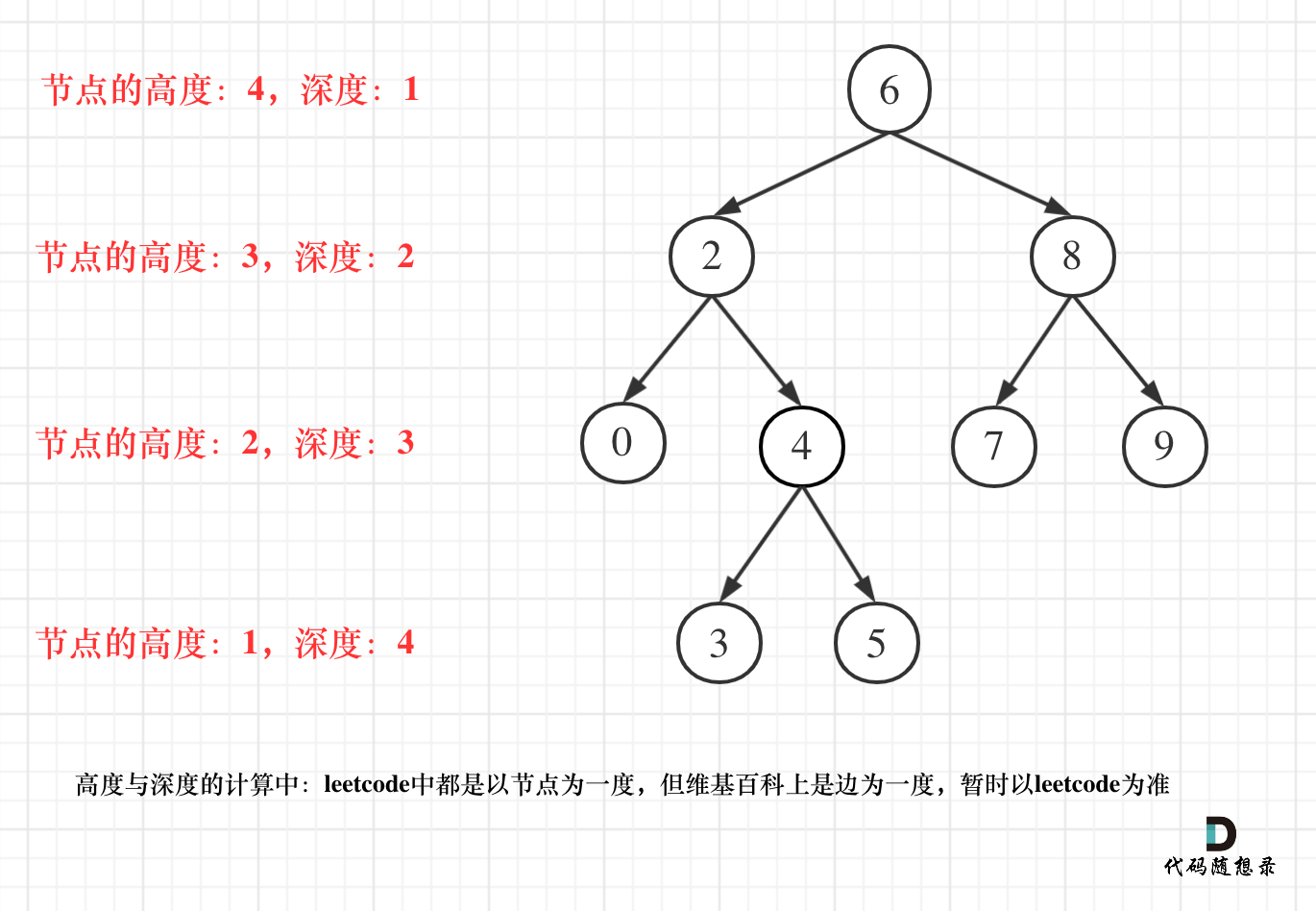
关于根节点的深度究竟是1 还是 0,不同的地方有不一样的标准,leetcode的题目中都是以节点为一度,即根节点深度是1。但维基百科上定义用边为一度,即根节点的深度是0,我们暂时以leetcode为准(毕竟要在这上面刷题)。
@@ -609,10 +607,13 @@ class Solution:
while stack:
node = stack.pop()
if node:
- stack.append(node)
+ stack.append(node) # 中
stack.append(None)
- if node.left: stack.append(node.left)
- if node.right: stack.append(node.right)
+ # 采用数组进行迭代,先将右节点加入,保证左节点能够先出栈
+ if node.right: # 右
+ stack.append(node.right)
+ if node.left: # 左
+ stack.append(node.left)
else:
real_node = stack.pop()
left, right = height_map.get(real_node.left, 0), height_map.get(real_node.right, 0)
@@ -623,6 +624,8 @@ class Solution:
```
### Go:
+递归法
+
```Go
func isBalanced(root *TreeNode) bool {
h := getHeight(root)
@@ -653,6 +656,64 @@ func max(a, b int) int {
}
```
+迭代法
+
+```Go
+func isBalanced(root *TreeNode) bool {
+ st := make([]*TreeNode, 0)
+ if root == nil {
+ return true
+ }
+ st = append(st, root)
+ for len(st) > 0 {
+ node := st[len(st)-1]
+ st = st[:len(st)-1]
+ if math.Abs(float64(getDepth(node.Left)) - float64(getDepth(node.Right))) > 1 {
+ return false
+ }
+ if node.Right != nil {
+ st = append(st, node.Right)
+ }
+ if node.Left != nil {
+ st = append(st, node.Left)
+ }
+ }
+ return true
+}
+
+func getDepth(cur *TreeNode) int {
+ st := make([]*TreeNode, 0)
+ if cur != nil {
+ st = append(st, cur)
+ }
+ depth := 0
+ result := 0
+ for len(st) > 0 {
+ node := st[len(st)-1]
+ if node != nil {
+ st = st[:len(st)-1]
+ st = append(st, node, nil)
+ depth++
+ if node.Right != nil {
+ st = append(st, node.Right)
+ }
+ if node.Left != nil {
+ st = append(st, node.Left)
+ }
+ } else {
+ st = st[:len(st)-1]
+ node = st[len(st)-1]
+ st = st[:len(st)-1]
+ depth--
+ }
+ if result < depth {
+ result = depth
+ }
+ }
+ return result
+}
+```
+
### JavaScript:
递归法:
@@ -934,8 +995,4 @@ public int GetHeight(TreeNode root)
}
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0111.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\260\217\346\267\261\345\272\246.md" "b/problems/0111.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\260\217\346\267\261\345\272\246.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 6d1632d593..e1ee42657c
--- "a/problems/0111.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\260\217\346\267\261\345\272\246.md"
+++ "b/problems/0111.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\260\217\346\267\261\345\272\246.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0111.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\260\217\346\267\261\345\272\246.md" "b/problems/0111.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\260\217\346\267\261\345\272\246.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 6d1632d593..e1ee42657c
--- "a/problems/0111.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\260\217\346\267\261\345\272\246.md"
+++ "b/problems/0111.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\260\217\346\267\261\345\272\246.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
> 和求最大深度一个套路?
@@ -22,7 +20,7 @@
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
-
+
返回它的最小深度 2.
@@ -40,7 +38,7 @@
本题依然是前序遍历和后序遍历都可以,前序求的是深度,后序求的是高度。
* 二叉树节点的深度:指从根节点到该节点的最长简单路径边的条数或者节点数(取决于深度从0开始还是从1开始)
-* 二叉树节点的高度:指从该节点到叶子节点的最长简单路径边的条数后者节点数(取决于高度从0开始还是从1开始)
+* 二叉树节点的高度:指从该节点到叶子节点的最长简单路径边的条数或者节点数(取决于高度从0开始还是从1开始)
那么使用后序遍历,其实求的是根节点到叶子节点的最小距离,就是求高度的过程,不过这个最小距离 也同样是最小深度。
@@ -48,7 +46,7 @@
本题还有一个误区,在处理节点的过程中,最大深度很容易理解,最小深度就不那么好理解,如图:
-
+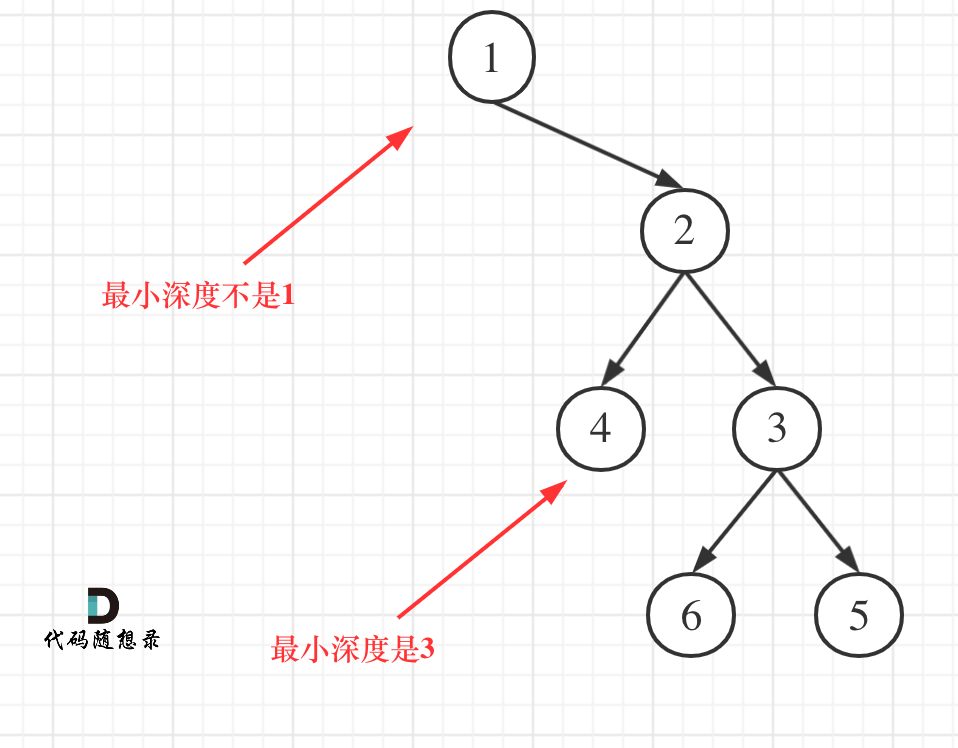
这就重新审题了,题目中说的是:**最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。**注意是**叶子节点**。
@@ -64,7 +62,7 @@
代码如下:
-```
+```CPP
int getDepth(TreeNode* node)
```
@@ -74,14 +72,14 @@ int getDepth(TreeNode* node)
代码如下:
-```
+```CPP
if (node == NULL) return 0;
```
3. 确定单层递归的逻辑
这块和求最大深度可就不一样了,一些同学可能会写如下代码:
-```
+```CPP
int leftDepth = getDepth(node->left);
int rightDepth = getDepth(node->right);
int result = 1 + min(leftDepth, rightDepth);
@@ -90,7 +88,7 @@ return result;
这个代码就犯了此图中的误区:
-
+
如果这么求的话,没有左孩子的分支会算为最短深度。
@@ -752,7 +750,3 @@ public int MinDepth(TreeNode root)
}
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0112.\350\267\257\345\276\204\346\200\273\345\222\214.md" "b/problems/0112.\350\267\257\345\276\204\346\200\273\345\222\214.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index d45be3bd82..73795bcfc9
--- "a/problems/0112.\350\267\257\345\276\204\346\200\273\345\222\214.md"
+++ "b/problems/0112.\350\267\257\345\276\204\346\200\273\345\222\214.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0112.\350\267\257\345\276\204\346\200\273\345\222\214.md" "b/problems/0112.\350\267\257\345\276\204\346\200\273\345\222\214.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index d45be3bd82..73795bcfc9
--- "a/problems/0112.\350\267\257\345\276\204\346\200\273\345\222\214.md"
+++ "b/problems/0112.\350\267\257\345\276\204\346\200\273\345\222\214.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
# 112. 路径总和
@@ -17,7 +15,7 @@
示例:
给定如下二叉树,以及目标和 sum = 22,
-
+
返回 true, 因为存在目标和为 22 的根节点到叶子节点的路径 5->4->11->2。
@@ -55,7 +53,7 @@
如图所示:
-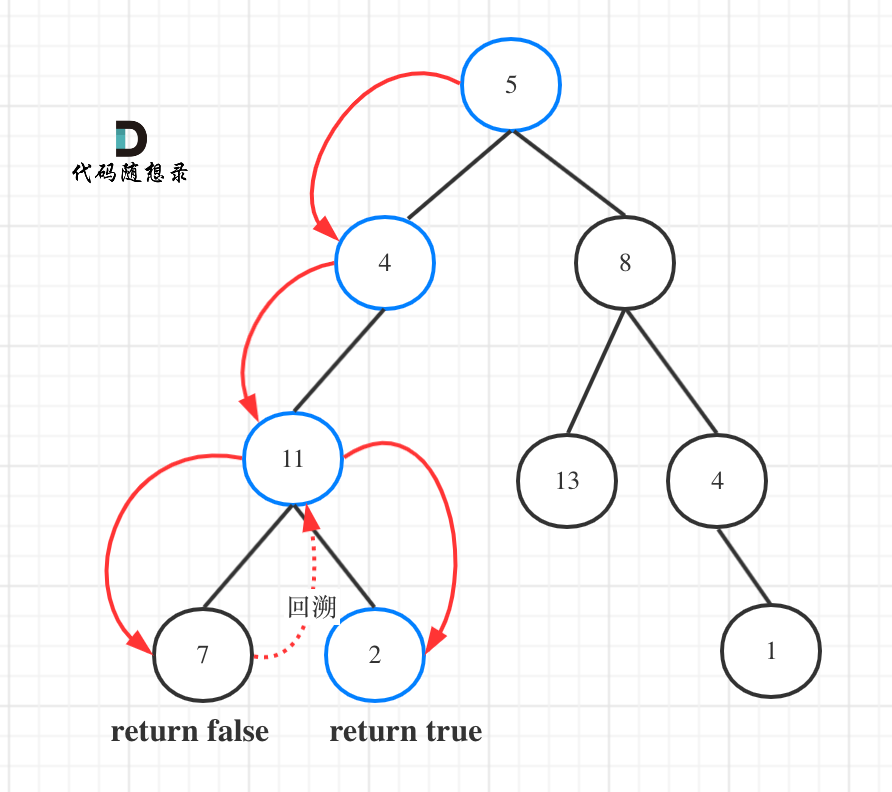
+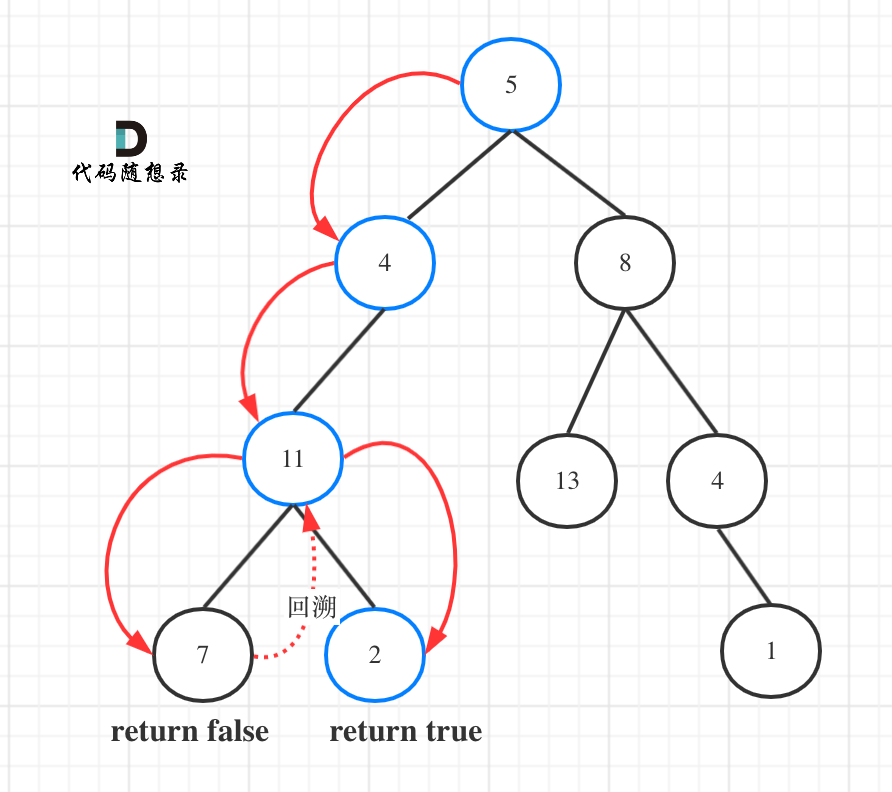
图中可以看出,遍历的路线,并不要遍历整棵树,所以递归函数需要返回值,可以用bool类型表示。
@@ -232,7 +230,7 @@ public:
给定如下二叉树,以及目标和 sum = 22,
-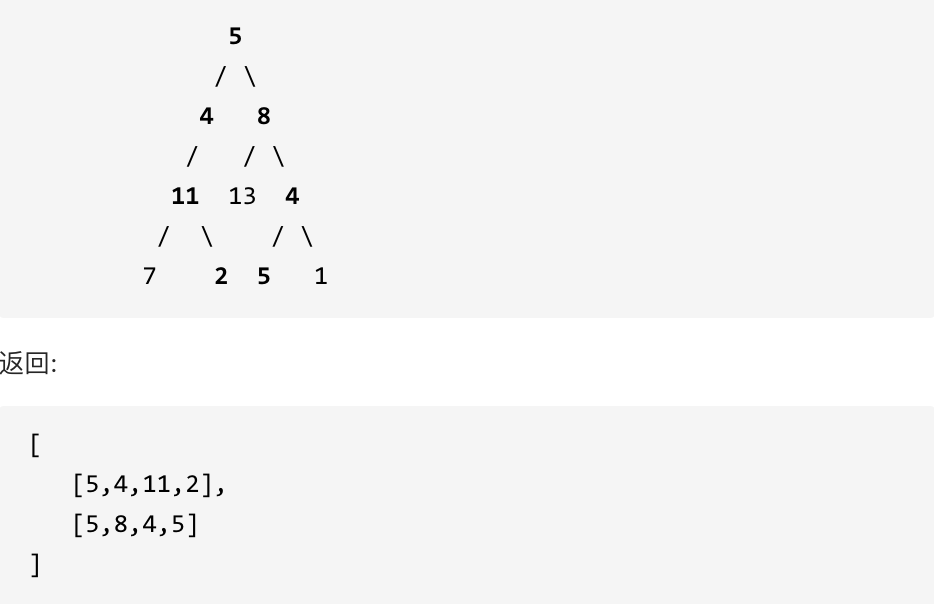
+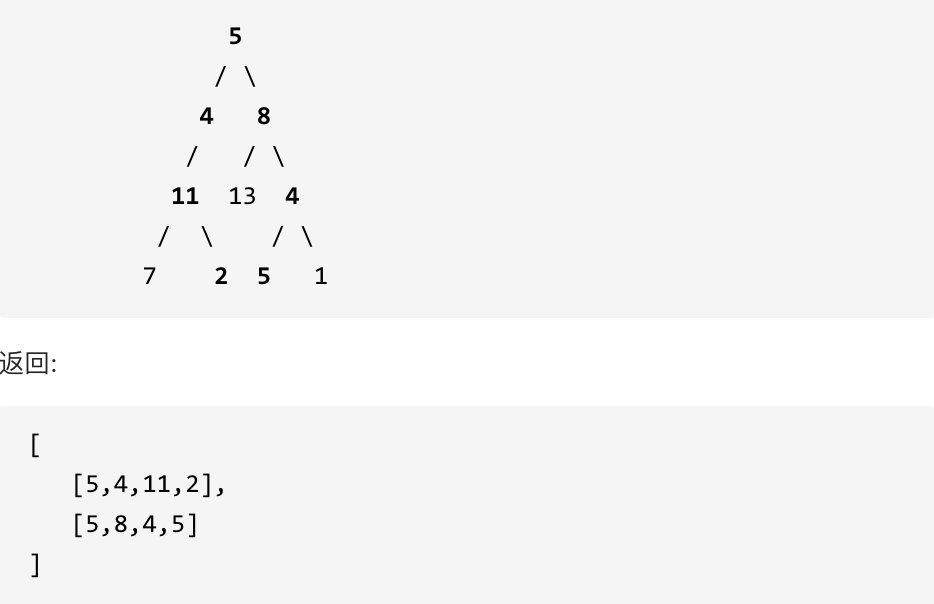
### 思路
@@ -241,7 +239,7 @@ public:
如图:
-
+
为了尽可能的把细节体现出来,我写出如下代码(**这份代码并不简洁,但是逻辑非常清晰**)
@@ -309,25 +307,25 @@ public:
0112.路径总和
```java
-class solution {
- public boolean haspathsum(treenode root, int targetsum) {
+class Solution {
+ public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
if (root == null) {
return false;
}
- targetsum -= root.val;
+ targetSum -= root.val;
// 叶子结点
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
- return targetsum == 0;
+ return targetSum == 0;
}
if (root.left != null) {
- boolean left = haspathsum(root.left, targetsum);
- if (left) { // 已经找到
+ boolean left = hasPathSum(root.left, targetSum);
+ if (left) { // 已经找到,提前返回
return true;
}
}
if (root.right != null) {
- boolean right = haspathsum(root.right, targetsum);
- if (right) { // 已经找到
+ boolean right = hasPathSum(root.right, targetSum);
+ if (right) { // 已经找到,提前返回
return true;
}
}
@@ -336,16 +334,16 @@ class solution {
}
// lc112 简洁方法
-class solution {
- public boolean haspathsum(treenode root, int targetsum) {
+class Solution {
+ public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
if (root == null) return false; // 为空退出
// 叶子节点判断是否符合
- if (root.left == null && root.right == null) return root.val == targetsum;
+ if (root.left == null && root.right == null) return root.val == targetSum;
// 求两侧分支的路径和
- return haspathsum(root.left, targetsum - root.val) || haspathsum(root.right, targetsum - root.val);
+ return hasPathSum(root.left, targetSum - root.val) || hasPathSum(root.right, targetSum - root.val);
}
}
```
@@ -353,22 +351,22 @@ class solution {
迭代
```java
-class solution {
- public boolean haspathsum(treenode root, int targetsum) {
+class Solution {
+ public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
if(root == null) return false;
- stack stack1 = new stack<>();
- stack stack2 = new stack<>();
+ Stack stack1 = new Stack<>();
+ Stack stack2 = new Stack<>();
stack1.push(root);
stack2.push(root.val);
- while(!stack1.isempty()) {
+ while(!stack1.isEmpty()) {
int size = stack1.size();
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
- treenode node = stack1.pop();
+ TreeNode node = stack1.pop();
int sum = stack2.pop();
// 如果该节点是叶子节点了,同时该节点的路径数值等于sum,那么就返回true
- if(node.left == null && node.right == null && sum == targetsum) {
+ if(node.left == null && node.right == null && sum == targetSum) {
return true;
}
// 右节点,压进去一个节点的时候,将该节点的路径数值也记录下来
@@ -387,8 +385,9 @@ class solution {
}
}
```
-```Java 統一迭代法
- public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
+```Java
+class Solution {
+ public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
Stack treeNodeStack = new Stack<>();
Stack sumStack = new Stack<>();
@@ -422,38 +421,39 @@ class solution {
}
return false;
}
+}
```
0113.路径总和-ii
```java
-class solution {
- public List> pathsum(TreeNode root, int targetsum) {
+class Solution {
+ public List> pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
List> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) return res; // 非空判断
List path = new LinkedList<>();
- preorderdfs(root, targetsum, res, path);
+ preOrderDfs(root, targetSum, res, path);
return res;
}
- public void preorderdfs(TreeNode root, int targetsum, List> res, List path) {
+ public void preOrderDfs(TreeNode root, int targetSum, List> res, List path) {
path.add(root.val);
// 遇到了叶子节点
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
// 找到了和为 targetsum 的路径
- if (targetsum - root.val == 0) {
+ if (targetSum - root.val == 0) {
res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
}
return; // 如果和不为 targetsum,返回
}
if (root.left != null) {
- preorderdfs(root.left, targetsum - root.val, res, path);
+ preOrderDfs(root.left, targetSum - root.val, res, path);
path.remove(path.size() - 1); // 回溯
}
if (root.right != null) {
- preorderdfs(root.right, targetsum - root.val, res, path);
+ preOrderDfs(root.right, targetSum - root.val, res, path);
path.remove(path.size() - 1); // 回溯
}
}
@@ -564,10 +564,10 @@ class Solution:
return False
- def hasPathSum(self, root: TreeNode, sum: int) -> bool:
+ def hasPathSum(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], targetSum: int) -> bool:
if root is None:
return False
- return self.traversal(root, sum - root.val)
+ return self.traversal(root, targetSum - root.val)
```
(版本二) 递归 + 精简
@@ -579,12 +579,12 @@ class Solution:
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
- def hasPathSum(self, root: TreeNode, sum: int) -> bool:
+ def hasPathSum(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], targetSum: int) -> bool:
if not root:
return False
- if not root.left and not root.right and sum == root.val:
+ if not root.left and not root.right and targetSum == root.val:
return True
- return self.hasPathSum(root.left, sum - root.val) or self.hasPathSum(root.right, sum - root.val)
+ return self.hasPathSum(root.left, targetSum - root.val) or self.hasPathSum(root.right, targetSum - root.val)
```
(版本三) 迭代
@@ -596,7 +596,7 @@ class Solution:
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
- def hasPathSum(self, root: TreeNode, sum: int) -> bool:
+ def hasPathSum(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], targetSum: int) -> bool:
if not root:
return False
# 此时栈里要放的是pair<节点指针,路径数值>
@@ -659,13 +659,13 @@ class Solution:
return
- def pathSum(self, root: TreeNode, sum: int) -> List[List[int]]:
+ def pathSum(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], targetSum: int) -> List[List[int]]:
self.result.clear()
self.path.clear()
if not root:
return self.result
self.path.append(root.val) # 把根节点放进路径
- self.traversal(root, sum - root.val)
+ self.traversal(root, targetSum - root.val)
return self.result
```
@@ -678,7 +678,7 @@ class Solution:
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
- def pathSum(self, root: TreeNode, targetSum: int) -> List[List[int]]:
+ def pathSum(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], targetSum: int) -> List[List[int]]:
result = []
self.traversal(root, targetSum, [], result)
@@ -703,7 +703,7 @@ class Solution:
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
- def pathSum(self, root: TreeNode, targetSum: int) -> List[List[int]]:
+ def pathSum(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], targetSum: int) -> List[List[int]]:
if not root:
return []
stack = [(root, [root.val])]
@@ -727,6 +727,48 @@ class Solution:
```go
//递归法
+/**
+ * Definition for a binary tree node.
+ * type TreeNode struct {
+ * Val int
+ * Left *TreeNode
+ * Right *TreeNode
+ * }
+ */
+func hasPathSum(root *TreeNode, targetSum int) bool {
+ if root == nil {
+ return false
+ }
+ return traversal(root, targetSum - root.Val)
+}
+
+func traversal(cur *TreeNode, count int) bool {
+ if cur.Left == nil && cur.Right == nil && count == 0 {
+ return true
+ }
+ if cur.Left == nil && cur.Right == nil {
+ return false
+ }
+ if cur.Left != nil {
+ count -= cur.Left.Val
+ if traversal(cur.Left, count) {
+ return true
+ }
+ count += cur.Left.Val
+ }
+ if cur.Right != nil {
+ count -= cur.Right.Val
+ if traversal(cur.Right, count) {
+ return true
+ }
+ count += cur.Right.Val
+ }
+ return false
+}
+```
+
+```go
+//递归法精简
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
@@ -788,7 +830,7 @@ func traverse(node *TreeNode, result *[][]int, currPath *[]int, targetSum int) {
}
```
-### Javascript
+### JavaScript
0112.路径总和
@@ -1579,8 +1621,5 @@ public class Solution {
// @lc code=end
```
-
-
-  -
+
diff --git "a/problems/0115.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md" "b/problems/0115.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 96ab2583f1..499bf100e2
--- "a/problems/0115.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
+++ "b/problems/0115.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+
diff --git "a/problems/0115.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md" "b/problems/0115.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 96ab2583f1..499bf100e2
--- "a/problems/0115.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
+++ "b/problems/0115.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 115.不同的子序列
@@ -14,7 +12,7 @@
题目数据保证答案符合 32 位带符号整数范围。
-
+
提示:
@@ -72,7 +70,7 @@ dp[i][j]:以i-1为结尾的s子序列中出现以j-1为结尾的t的个数为d
从递推公式dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + dp[i - 1][j]; 和 dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j]; 中可以看出dp[i][j] 是从上方和左上方推导而来,如图:,那么 dp[i][0] 和dp[0][j]是一定要初始化的。
-
+
每次当初始化的时候,都要回顾一下dp[i][j]的定义,不要凭感觉初始化。
@@ -103,7 +101,7 @@ for (int j = 1; j <= t.size(); j++) dp[0][j] = 0; // 其实这行代码可以和
从递推公式dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + dp[i - 1][j]; 和 dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j]; 中可以看出dp[i][j]都是根据左上方和正上方推出来的。
-
+
所以遍历的时候一定是从上到下,从左到右,这样保证dp[i][j]可以根据之前计算出来的数值进行计算。
@@ -125,7 +123,7 @@ for (int i = 1; i <= s.size(); i++) {
以s:"baegg",t:"bag"为例,推导dp数组状态如下:
-
+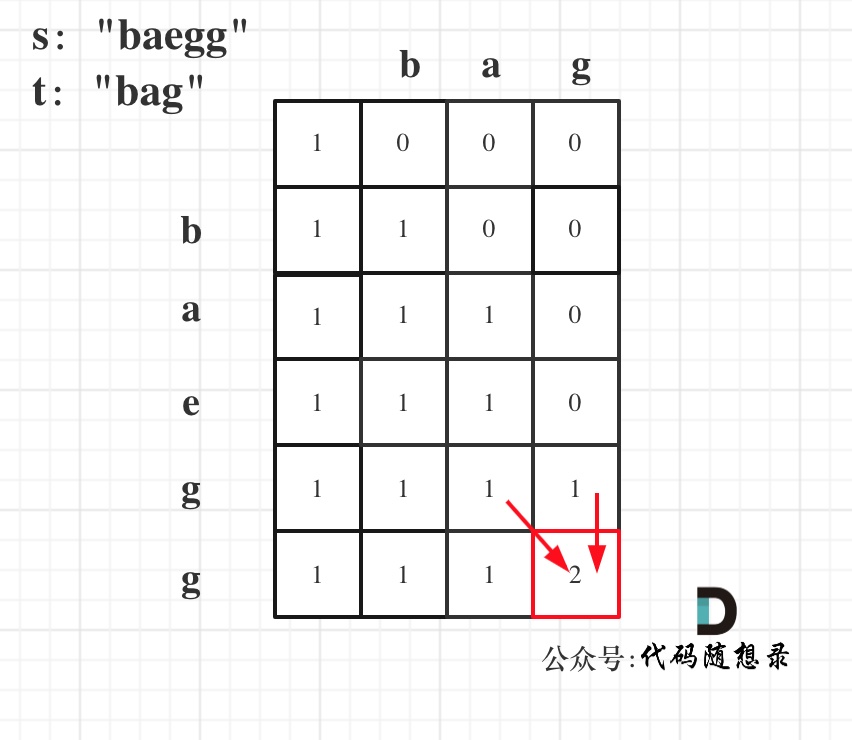
如果写出来的代码怎么改都通过不了,不妨把dp数组打印出来,看一看,是不是这样的。
@@ -265,7 +263,7 @@ func numDistinct(s string, t string) int {
}
```
-### Javascript:
+### JavaScript:
```javascript
const numDistinct = (s, t) => {
@@ -375,8 +373,4 @@ impl Solution {
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0116.\345\241\253\345\205\205\346\257\217\344\270\252\350\212\202\347\202\271\347\232\204\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\217\263\344\276\247\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\214\207\351\222\210.md" "b/problems/0116.\345\241\253\345\205\205\346\257\217\344\270\252\350\212\202\347\202\271\347\232\204\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\217\263\344\276\247\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\214\207\351\222\210.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 60ea9210a2..88d3abc93e
--- "a/problems/0116.\345\241\253\345\205\205\346\257\217\344\270\252\350\212\202\347\202\271\347\232\204\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\217\263\344\276\247\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\214\207\351\222\210.md"
+++ "b/problems/0116.\345\241\253\345\205\205\346\257\217\344\270\252\350\212\202\347\202\271\347\232\204\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\217\263\344\276\247\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\214\207\351\222\210.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0116.\345\241\253\345\205\205\346\257\217\344\270\252\350\212\202\347\202\271\347\232\204\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\217\263\344\276\247\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\214\207\351\222\210.md" "b/problems/0116.\345\241\253\345\205\205\346\257\217\344\270\252\350\212\202\347\202\271\347\232\204\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\217\263\344\276\247\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\214\207\351\222\210.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 60ea9210a2..88d3abc93e
--- "a/problems/0116.\345\241\253\345\205\205\346\257\217\344\270\252\350\212\202\347\202\271\347\232\204\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\217\263\344\276\247\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\214\207\351\222\210.md"
+++ "b/problems/0116.\345\241\253\345\205\205\346\257\217\344\270\252\350\212\202\347\202\271\347\232\204\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\217\263\344\276\247\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\214\207\351\222\210.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 116. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
@@ -28,7 +26,7 @@ struct Node {
* 你只能使用常量级额外空间。
* 使用递归解题也符合要求,本题中递归程序占用的栈空间不算做额外的空间复杂度。
-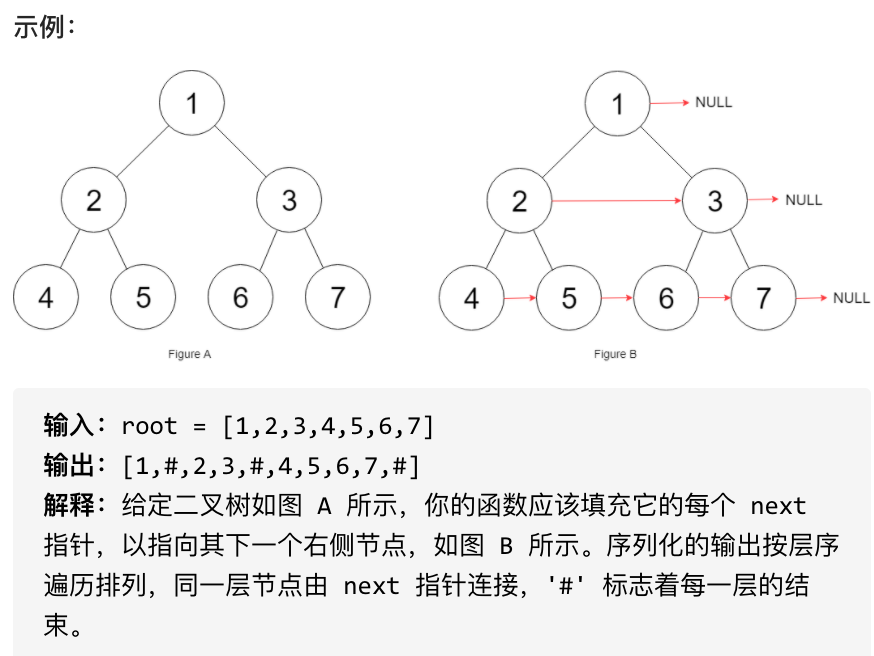
+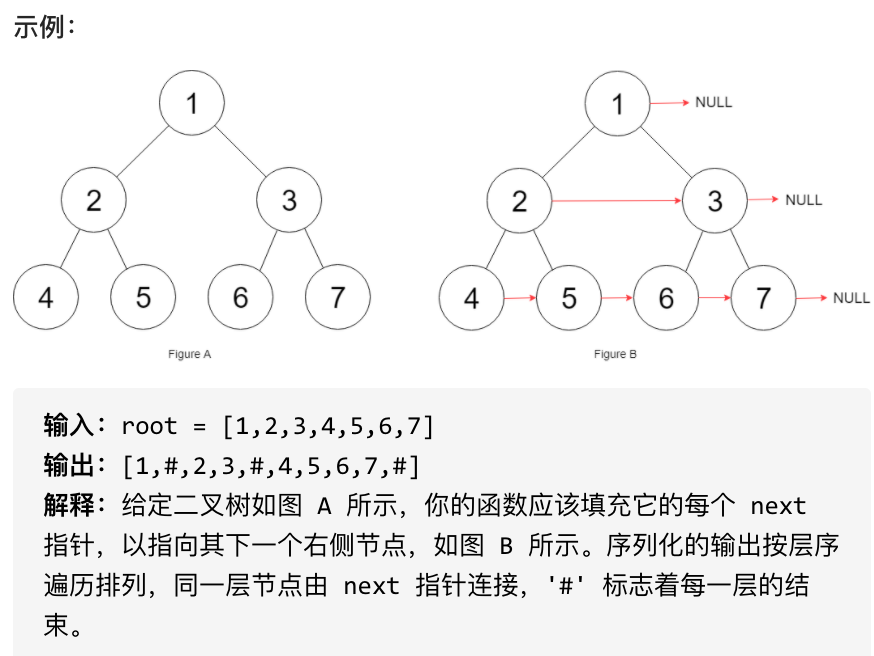
## 思路
@@ -44,7 +42,7 @@ struct Node {
如图,假如当前操作的节点是cur:
- +
+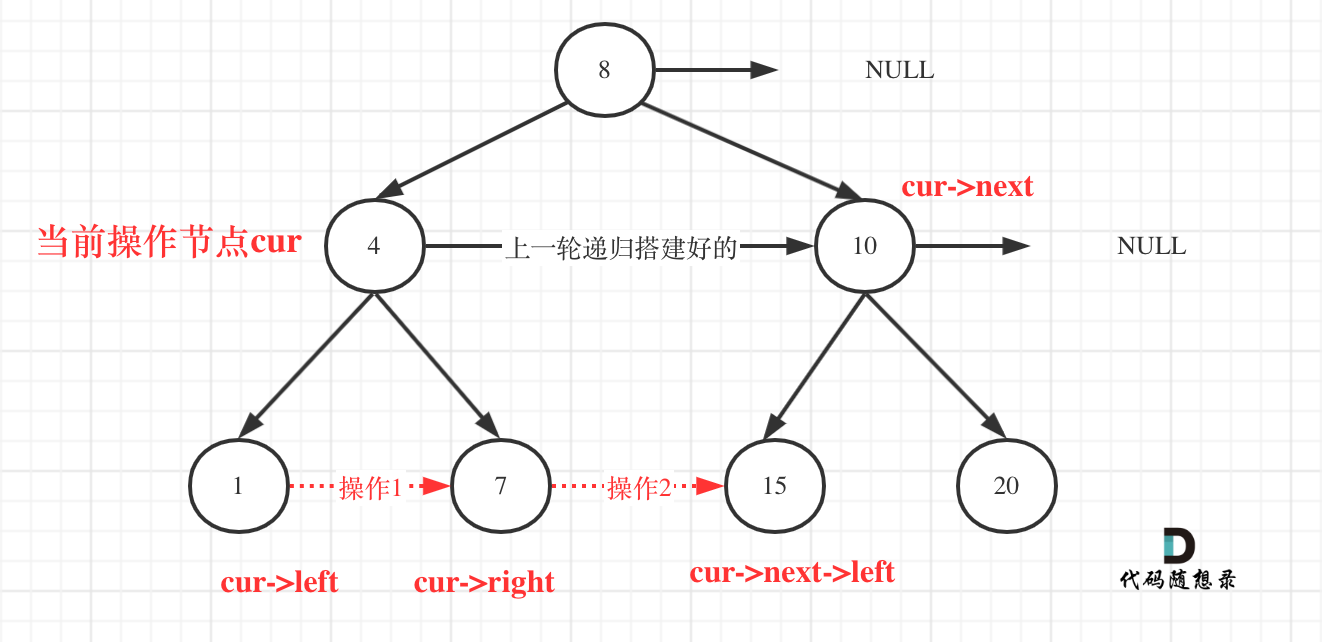 最关键的点是可以通过上一层递归 搭出来的线,进行本次搭线。
@@ -169,6 +167,56 @@ class Solution {
}
```
+```Java
+// 迭代法
+class Solution {
+ public Node connect(Node root) {
+ if (root == null) {
+ return root;
+ }
+
+ Queue queue = new LinkedList<>();
+
+ queue.add(root);
+
+ while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
+ int size = queue.size();
+
+ // 每层的第一个节点
+ Node cur = queue.poll();
+ if (cur.left != null) {
+ queue.add(cur.left);
+ }
+ if (cur.right != null) {
+ queue.add(cur.right);
+ }
+
+ // 因为已经移除了每层的第一个节点,所以将 0 改为 1
+ while (size-- > 1) {
+ Node next = queue.poll();
+
+ if (next.left != null) {
+ queue.add(next.left);
+ }
+ if (next.right != null) {
+ queue.add(next.right);
+ }
+
+ // 当前节点指向同层的下一个节点
+ cur.next = next;
+ // 更新当前节点
+ cur = next;
+ }
+
+ // 每层的最后一个节点不指向 null 在力扣也能过
+ cur.next = null;
+ }
+
+ return root;
+ }
+}
+```
+
### Python
```python
@@ -438,8 +486,5 @@ public class Solution
```
-
最关键的点是可以通过上一层递归 搭出来的线,进行本次搭线。
@@ -169,6 +167,56 @@ class Solution {
}
```
+```Java
+// 迭代法
+class Solution {
+ public Node connect(Node root) {
+ if (root == null) {
+ return root;
+ }
+
+ Queue queue = new LinkedList<>();
+
+ queue.add(root);
+
+ while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
+ int size = queue.size();
+
+ // 每层的第一个节点
+ Node cur = queue.poll();
+ if (cur.left != null) {
+ queue.add(cur.left);
+ }
+ if (cur.right != null) {
+ queue.add(cur.right);
+ }
+
+ // 因为已经移除了每层的第一个节点,所以将 0 改为 1
+ while (size-- > 1) {
+ Node next = queue.poll();
+
+ if (next.left != null) {
+ queue.add(next.left);
+ }
+ if (next.right != null) {
+ queue.add(next.right);
+ }
+
+ // 当前节点指向同层的下一个节点
+ cur.next = next;
+ // 更新当前节点
+ cur = next;
+ }
+
+ // 每层的最后一个节点不指向 null 在力扣也能过
+ cur.next = null;
+ }
+
+ return root;
+ }
+}
+```
+
### Python
```python
@@ -438,8 +486,5 @@ public class Solution
```
-
-
-  -
+
diff --git "a/problems/0121.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272.md" "b/problems/0121.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index cbdf40e85c..d12cbf2fe2
--- "a/problems/0121.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272.md"
+++ "b/problems/0121.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+
diff --git "a/problems/0121.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272.md" "b/problems/0121.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index cbdf40e85c..d12cbf2fe2
--- "a/problems/0121.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272.md"
+++ "b/problems/0121.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 121. 买卖股票的最佳时机
@@ -131,7 +129,7 @@ dp[0][1]表示第0天不持有股票,不持有股票那么现金就是0,所
以示例1,输入:[7,1,5,3,6,4]为例,dp数组状态如下:
-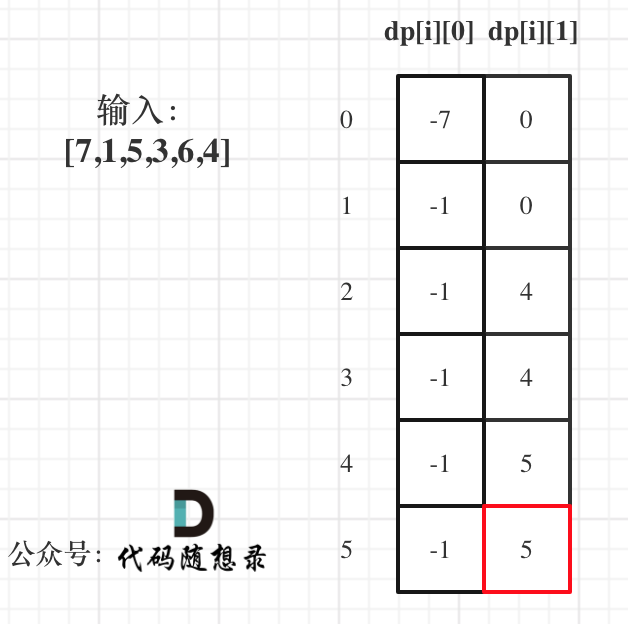
+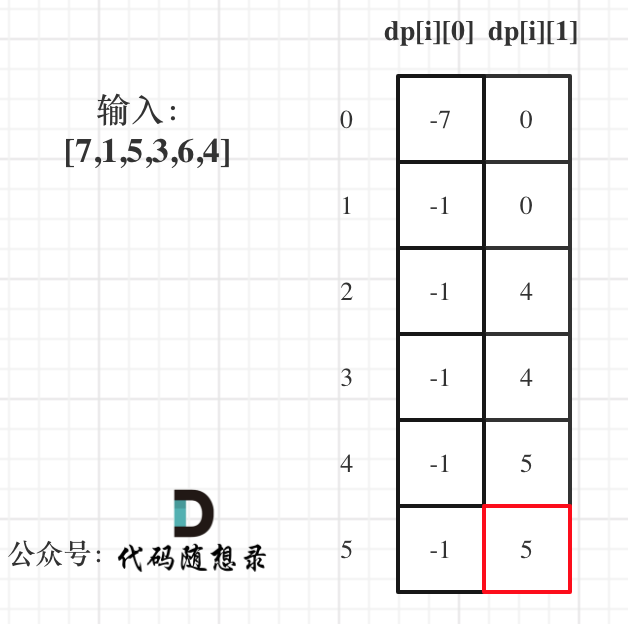
dp[5][1]就是最终结果。
@@ -287,9 +285,6 @@ class Solution {
return dp[1];
}
}
-```
-```Java
-
```
### Python:
@@ -311,7 +306,7 @@ class Solution:
class Solution:
def maxProfit(self, prices: List[int]) -> int:
length = len(prices)
- if len == 0:
+ if length == 0:
return 0
dp = [[0] * 2 for _ in range(length)]
dp[0][0] = -prices[0]
@@ -469,7 +464,7 @@ function maxProfit(prices: number[]): number {
};
```
-> 动态规划
+> 动态规划:版本一
```typescript
function maxProfit(prices: number[]): number {
@@ -490,6 +485,26 @@ function maxProfit(prices: number[]): number {
};
```
+> 动态规划:版本二
+
+```typescript
+// dp[i][0] 表示第i天持有股票所得最多现金
+// dp[i][1] 表示第i天不持有股票所得最多现金
+function maxProfit(prices: number[]): number {
+ const dp:number[][] = Array(2).fill(0).map(item => Array(2));
+ dp[0][0] = -prices[0];
+ dp[0][1] = 0;
+
+ for (let i = 1; i < prices.length; i++) {
+ dp[i % 2][0] = Math.max(dp[(i - 1) % 2][0], -prices[i]);
+ dp[i % 2][1] = Math.max(dp[(i - 1) % 2][1], dp[(i - 1) % 2][0] + prices[i]);
+ }
+
+ // 返回不持有股票的最大现金
+ return dp[(prices.length-1) % 2][1];
+};
+```
+
### C#:
> 贪心法
@@ -531,6 +546,52 @@ public class Solution
}
```
+### C:
+
+> 贪心
+
+```c
+#define max(a, b) ((a) > (b) ? (a) : (b))
+#define min(a, b) ((a) > (b) ? (b) : (a))
+
+int maxProfit(int* prices, int pricesSize) {
+ int low = INT_MIN;
+ int result = 0;
+ for(int i = 0; i < pricesSize; i++){
+ low = min(low, prices[i]);
+ result = max(result, prices[i] - low);
+ }
+ return result;
+}
+```
+
+> 动态规划
+
+```c
+#define max(a, b) ((a) > (b) ? (a) : (b))
+
+int maxProfit(int* prices, int pricesSize){
+ if(pricesSize == 0){
+ return 0;
+ }
+ // dp初始化
+ int ** dp = malloc(sizeof (int *) * pricesSize);
+ for(int i = 0; i < pricesSize; i++){
+ dp[i] = malloc(sizeof (int ) * 2);
+ }
+ // 下标0表示持有股票的情况下的最大现金,下标1表示不持有股票的情况下获得的最大现金
+ dp[0][0] = -prices[0];
+ dp[0][1] = 0;
+ for(int i = 1; i < pricesSize; i++){
+ dp[i][0] = max(dp[i - 1][0], - prices[i]);
+ dp[i][1] = max(dp[i - 1][1], dp[i - 1][0] + prices[i]);
+ }
+ return dp[pricesSize - 1][1];
+}
+```
+
+
+
### Rust:
> 贪心
@@ -564,8 +625,3 @@ impl Solution {
```
-
-
-  -
-
diff --git "a/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II.md" "b/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 69706e369a..0da4241931
--- "a/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II.md" "b/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 69706e369a..0da4241931
--- "a/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 122.买卖股票的最佳时机 II
@@ -68,7 +66,7 @@
如图:
-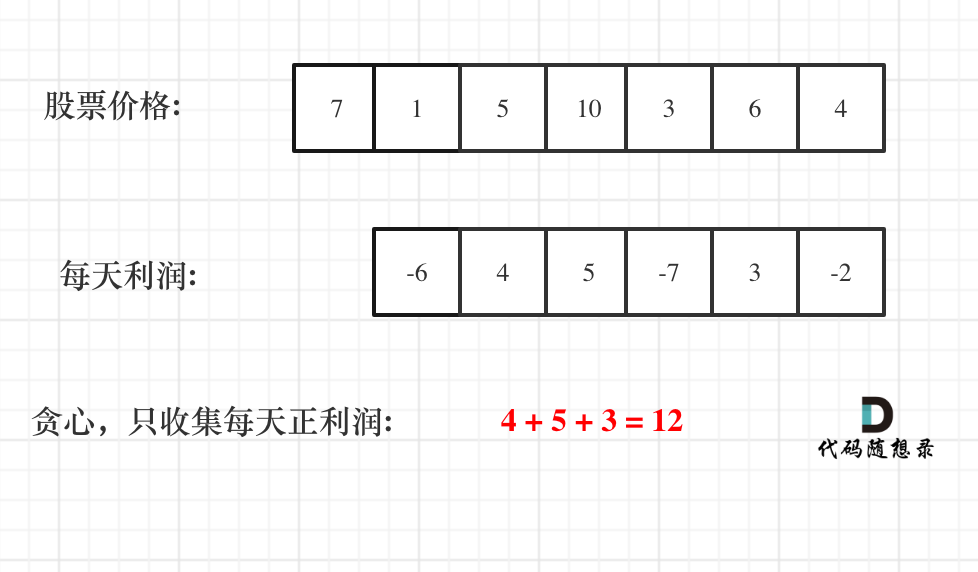
+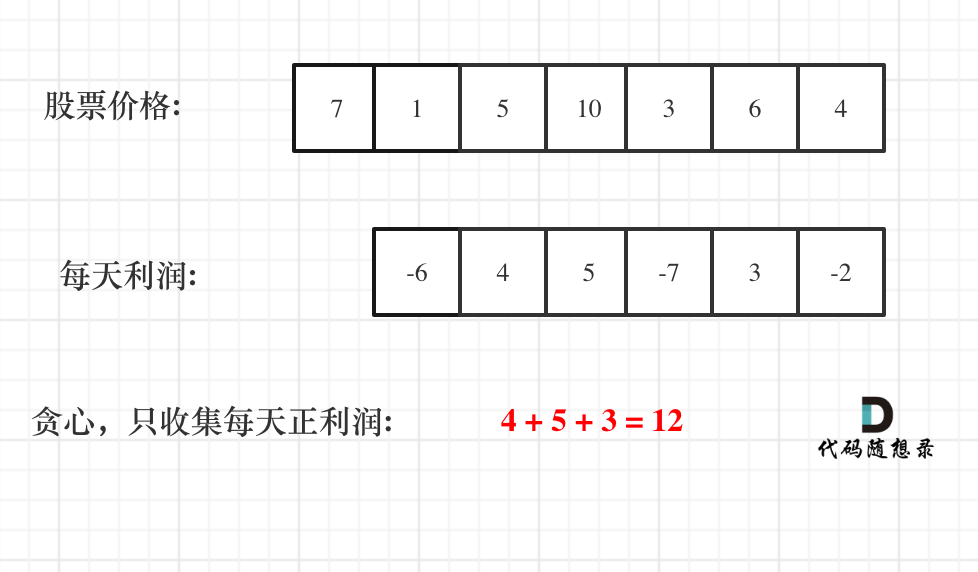
一些同学陷入:第一天怎么就没有利润呢,第一天到底算不算的困惑中。
@@ -249,7 +247,7 @@ func max(a, b int) int {
}
```
-### Javascript:
+### JavaScript:
贪心
@@ -422,8 +420,4 @@ public class Solution
}
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md" "b/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 6e08b57c1d..d8cb308b7e
--- "a/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md"
+++ "b/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md" "b/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 6e08b57c1d..d8cb308b7e
--- "a/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md"
+++ "b/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 122.买卖股票的最佳时机II
@@ -251,6 +249,27 @@ func max(a, b int) int {
}
```
+```go
+// 动态规划 版本二 滚动数组
+func maxProfit(prices []int) int {
+ dp := [2][2]int{} // 注意这里只开辟了一个2 * 2大小的二维数组
+ dp[0][0] = -prices[0]
+ dp[0][1] = 0
+ for i := 1; i < len(prices); i++ {
+ dp[i%2][0] = max(dp[(i-1)%2][0], dp[(i - 1) % 2][1] - prices[i])
+ dp[i%2][1] = max(dp[(i-1)%2][1], dp[(i-1)%2][0] + prices[i])
+ }
+ return dp[(len(prices)-1)%2][1]
+}
+
+func max(x, y int) int {
+ if x > y {
+ return x
+ }
+ return y
+}
+```
+
### JavaScript:
```javascript
@@ -365,6 +384,49 @@ public class Solution
}
```
+### C:
+
+> 动态规划
+
+```c
+#define max(a, b) ((a) > (b) ? (a) : (b))
+
+int maxProfit(int* prices, int pricesSize){
+ int **dp = malloc(sizeof (int *) * pricesSize);
+ for (int i = 0; i < pricesSize; ++i) {
+ dp[i] = malloc(sizeof (int ) * 2);
+ }
+ // 0表示持有该股票所得最大,1表示不持有所得最大
+ dp[0][0] = -prices[0];
+ dp[0][1] = 0;
+ for (int i = 1; i < pricesSize; ++i) {
+ dp[i][0] = max(dp[i - 1][0], dp[i - 1][1] - prices[i]);
+ dp[i][1] = max(dp[i - 1][1], dp[i - 1][0] + prices[i]);
+ }
+ return dp[pricesSize - 1][1];
+}
+```
+
+> 贪心
+
+```c
+int maxProfit(int* prices, int pricesSize) {
+ if(pricesSize == 0){
+ return 0;
+ }
+ int result = 0;
+ for(int i = 1; i < pricesSize; i++){
+ // 如果今天股票价格大于昨天,代表有利润
+ if(prices[i] > prices[i - 1]){
+ result += prices[i] - prices[i - 1];
+ }
+ }
+ return result;
+}
+```
+
+
+
### Rust:
> 贪心
@@ -412,7 +474,4 @@ impl Solution {
}
```
-
-
-  -
+
diff --git "a/problems/0123.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272III.md" "b/problems/0123.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272III.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 72dd90426c..063477cb5a
--- "a/problems/0123.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272III.md"
+++ "b/problems/0123.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272III.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+
diff --git "a/problems/0123.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272III.md" "b/problems/0123.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272III.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 72dd90426c..063477cb5a
--- "a/problems/0123.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272III.md"
+++ "b/problems/0123.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272III.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 123.买卖股票的最佳时机III
@@ -122,7 +120,7 @@ dp[i][4] = max(dp[i - 1][4], dp[i - 1][3] + prices[i]);
以输入[1,2,3,4,5]为例
-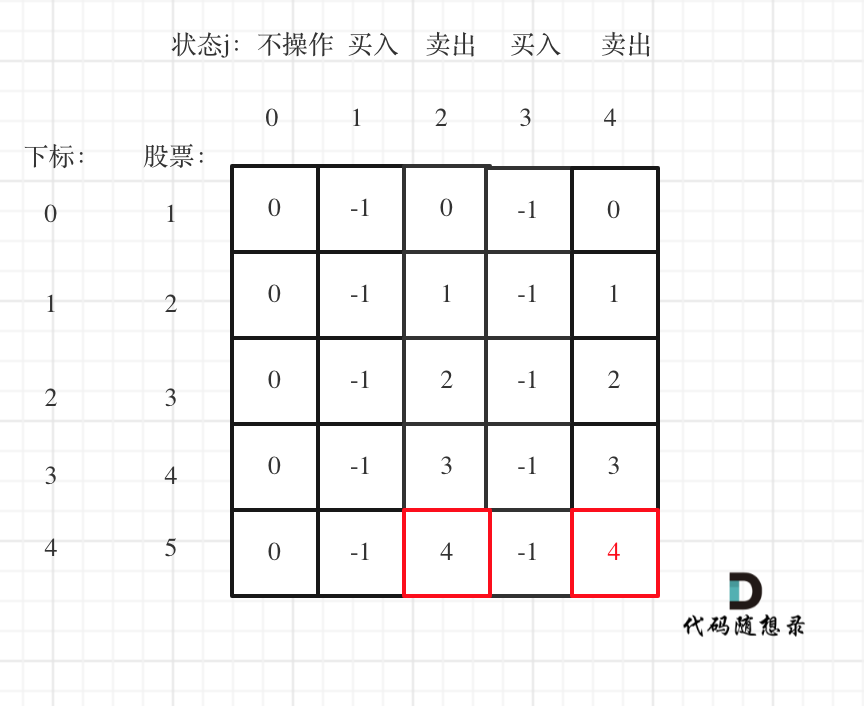
+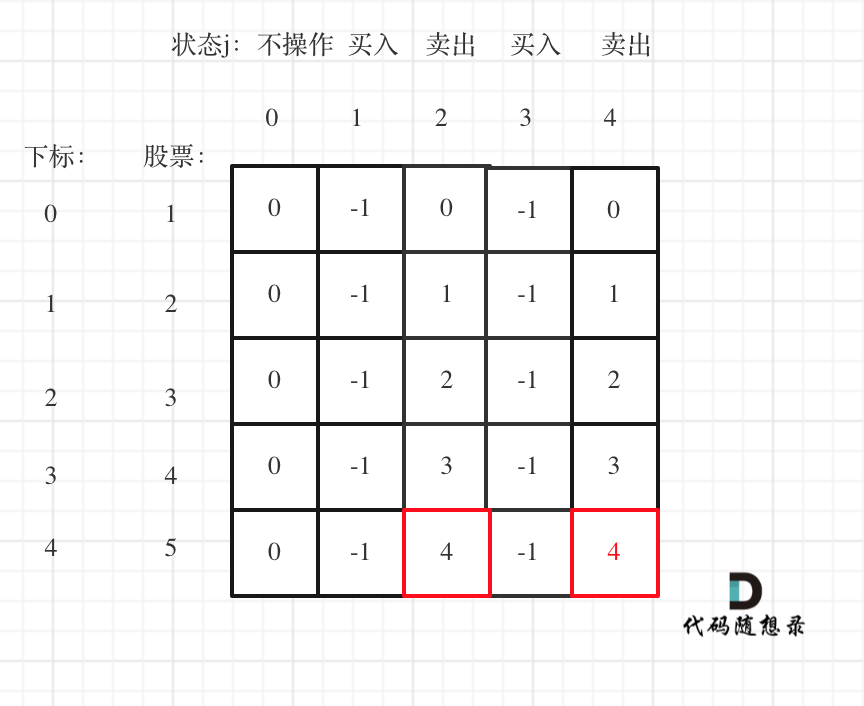
大家可以看到红色框为最后两次卖出的状态。
@@ -316,6 +314,8 @@ class Solution:
### Go:
+> 版本一
+
```go
func maxProfit(prices []int) int {
dp := make([][]int, len(prices))
@@ -344,6 +344,80 @@ func max(a, b int) int {
}
```
+> 版本二
+
+```go
+func maxProfit(prices []int) int {
+ if len(prices) == 0 {
+ return 0
+ }
+ dp := make([]int, 5)
+ dp[1] = -prices[0]
+ dp[3] = -prices[0]
+ for i := 1; i < len(prices); i++ {
+ dp[1] = max(dp[1], dp[0] - prices[i])
+ dp[2] = max(dp[2], dp[1] + prices[i])
+ dp[3] = max(dp[3], dp[2] - prices[i])
+ dp[4] = max(dp[4], dp[3] + prices[i])
+ }
+ return dp[4]
+}
+
+func max(x, y int) int {
+ if x > y {
+ return x
+ }
+ return y
+}
+```
+
+> 版本三
+
+```go
+func maxProfit(prices []int) int {
+ if len(prices) == 0 {
+ return 0
+ }
+ dp := make([][5]int, len(prices))
+ dp[0][1] = -prices[0]
+ dp[0][3] = -prices[0]
+ for i := 1; i < len(prices); i++ {
+ dp[i][1] = max(dp[i-1][1], 0 - prices[i])
+ dp[i][2] = max(dp[i-1][2], dp[i-1][1] + prices[i])
+ dp[i][3] = max(dp[i-1][3], dp[i-1][2] - prices[i])
+ dp[i][4] = max(dp[i-1][4], dp[i-1][3] + prices[i])
+ }
+ return dp[len(prices)-1][4]
+}
+
+func max(x, y int) int {
+ if x > y {
+ return x
+ }
+ return y
+}
+```
+
+> 版本四:一维 dp 易懂版本
+
+```go
+func maxProfit(prices []int) int {
+ dp := make([]int, 4)
+ dp[0] = -prices[0]
+ dp[2] = -prices[0]
+
+ for _, price := range prices[1:] {
+ dc := slices.Clone(dp) // 这句话是关键,把前一天的 dp 状态保存下来,防止被覆盖掉,后面只用它,不用 dp,逻辑简单易懂
+ dp[0] = max(dc[0], -price)
+ dp[1] = max(dc[1], dc[0] + price)
+ dp[2] = max(dc[2], dc[1] - price)
+ dp[3] = max(dc[3], dc[2] + price)
+ }
+
+ return dp[3]
+}
+```
+
### JavaScript:
> 版本一:
@@ -413,6 +487,34 @@ function maxProfit(prices: number[]): number {
};
```
+### C:
+
+```c
+#define max(a, b) ((a) > (b) ? (a) : (b))
+#define min(a, b) ((a) > (b) ? (b) : (a))
+
+int maxProfit(int* prices, int pricesSize) {
+ int buy1 = prices[0], buy2 = prices[0];
+ int profit1 = 0, profit2 = 0;
+ for (int i = 0; i < pricesSize; ++i) {
+ // 寻找最低点买入
+ buy1 = min(buy1, prices[i]);
+ // 找到第一次交易的最大盈利,并不断维护这一最大值
+ profit1 = max(profit1, prices[i] - buy1);
+
+ // 寻找第二次交易的最低投资点,并且考虑前一次交易的成本
+ // 当前价格 - 第一次操作的盈利=新的投入成本(
+ // 为了让盈利最大,要寻找最小的成本)
+ buy2 = min(buy2, prices[i] - profit1);
+ // 第二次卖出后的盈利:当前价格减去成本,不断维护这一最大的总利润
+ profit2 = max(profit2, prices[i] - buy2);
+ }
+ return profit2;
+}
+```
+
+
+
### Rust:
> 版本一
@@ -461,8 +563,3 @@ impl Solution {
```
-
-
-  -
-
diff --git "a/problems/0127.\345\215\225\350\257\215\346\216\245\351\276\231.md" "b/problems/0127.\345\215\225\350\257\215\346\216\245\351\276\231.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 6f8933101e..0204606056
--- "a/problems/0127.\345\215\225\350\257\215\346\216\245\351\276\231.md"
+++ "b/problems/0127.\345\215\225\350\257\215\346\216\245\351\276\231.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0127.\345\215\225\350\257\215\346\216\245\351\276\231.md" "b/problems/0127.\345\215\225\350\257\215\346\216\245\351\276\231.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 6f8933101e..0204606056
--- "a/problems/0127.\345\215\225\350\257\215\346\216\245\351\276\231.md"
+++ "b/problems/0127.\345\215\225\350\257\215\346\216\245\351\276\231.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 127. 单词接龙
@@ -33,7 +31,7 @@
以示例1为例,从这个图中可以看出 hit 到 cog的路线,不止一条,有三条,一条是最短的长度为5,两条长度为6。
-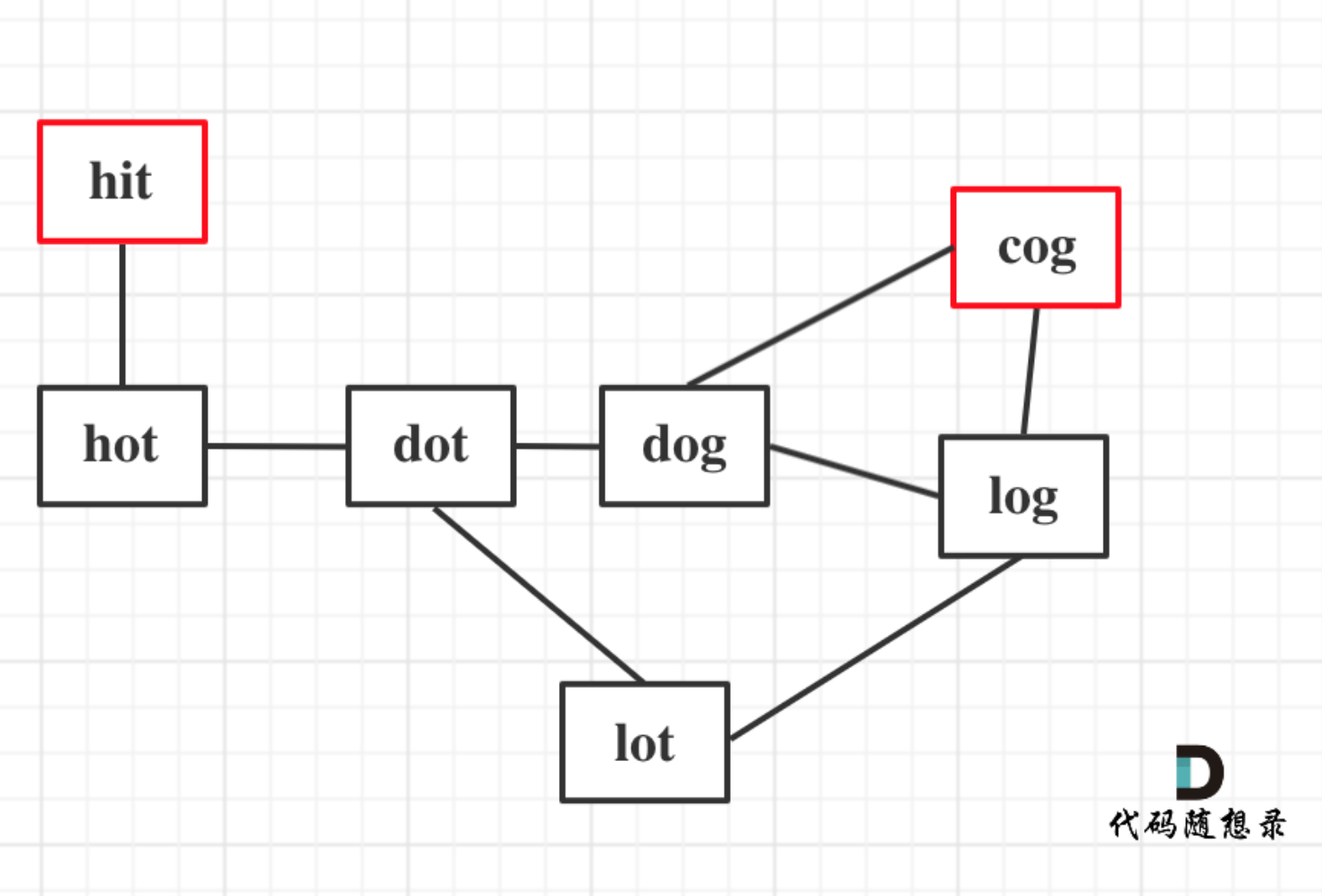
+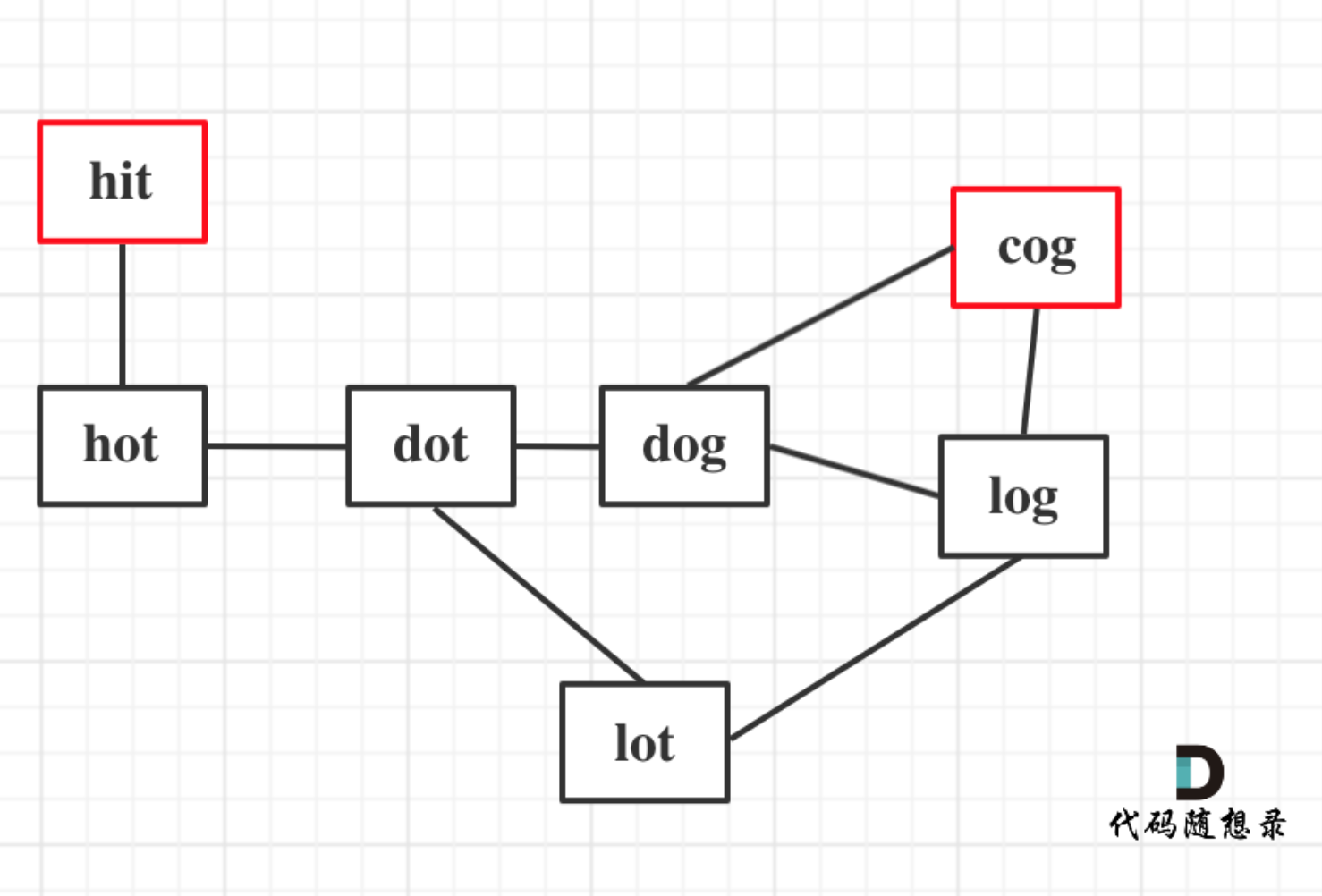
本题只需要求出最短路径的长度就可以了,不用找出路径。
@@ -360,7 +358,3 @@ function diffonechar(word1: string, word2: string): boolean {
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0129.\346\261\202\346\240\271\345\210\260\345\217\266\345\255\220\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\225\260\345\255\227\344\271\213\345\222\214.md" "b/problems/0129.\346\261\202\346\240\271\345\210\260\345\217\266\345\255\220\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\225\260\345\255\227\344\271\213\345\222\214.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index ebb36071cf..1568a49469
--- "a/problems/0129.\346\261\202\346\240\271\345\210\260\345\217\266\345\255\220\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\225\260\345\255\227\344\271\213\345\222\214.md"
+++ "b/problems/0129.\346\261\202\346\240\271\345\210\260\345\217\266\345\255\220\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\225\260\345\255\227\344\271\213\345\222\214.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0129.\346\261\202\346\240\271\345\210\260\345\217\266\345\255\220\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\225\260\345\255\227\344\271\213\345\222\214.md" "b/problems/0129.\346\261\202\346\240\271\345\210\260\345\217\266\345\255\220\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\225\260\345\255\227\344\271\213\345\222\214.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index ebb36071cf..1568a49469
--- "a/problems/0129.\346\261\202\346\240\271\345\210\260\345\217\266\345\255\220\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\225\260\345\255\227\344\271\213\345\222\214.md"
+++ "b/problems/0129.\346\261\202\346\240\271\345\210\260\345\217\266\345\255\220\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\225\260\345\255\227\344\271\213\345\222\214.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
@@ -83,7 +81,7 @@ int vectorToInt(const vector& vec) {
如图:
- +
+ 代码如下:
@@ -382,8 +380,4 @@ int sumNumbers(struct TreeNode* root){
}
```
-
代码如下:
@@ -382,8 +380,4 @@ int sumNumbers(struct TreeNode* root){
}
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0130.\350\242\253\345\233\264\347\273\225\347\232\204\345\214\272\345\237\237.md" "b/problems/0130.\350\242\253\345\233\264\347\273\225\347\232\204\345\214\272\345\237\237.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 1ddaaa7f83..10d6585c4c
--- "a/problems/0130.\350\242\253\345\233\264\347\273\225\347\232\204\345\214\272\345\237\237.md"
+++ "b/problems/0130.\350\242\253\345\233\264\347\273\225\347\232\204\345\214\272\345\237\237.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0130.\350\242\253\345\233\264\347\273\225\347\232\204\345\214\272\345\237\237.md" "b/problems/0130.\350\242\253\345\233\264\347\273\225\347\232\204\345\214\272\345\237\237.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 1ddaaa7f83..10d6585c4c
--- "a/problems/0130.\350\242\253\345\233\264\347\273\225\347\232\204\345\214\272\345\237\237.md"
+++ "b/problems/0130.\350\242\253\345\233\264\347\273\225\347\232\204\345\214\272\345\237\237.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 130. 被围绕的区域
@@ -10,7 +8,7 @@
给你一个 m x n 的矩阵 board ,由若干字符 'X' 和 'O' ,找到所有被 'X' 围绕的区域,并将这些区域里所有的 'O' 用 'X' 填充。
-
+
* 输入:board = [["X","X","X","X"],["X","O","O","X"],["X","X","O","X"],["X","O","X","X"]]
* 输出:[["X","X","X","X"],["X","X","X","X"],["X","X","X","X"],["X","O","X","X"]]
@@ -30,11 +28,11 @@
步骤一:深搜或者广搜将地图周边的'O'全部改成'A',如图所示:
-
+
步骤二:在遍历地图,将'O'全部改成'X'(地图中间的'O'改成了'X'),将'A'改回'O'(保留的地图周边的'O'),如图所示:
-
+
整体C++代码如下,以下使用dfs实现,其实遍历方式dfs,bfs都是可以的。
@@ -792,8 +790,4 @@ impl Solution {
}
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0131.\345\210\206\345\211\262\345\233\236\346\226\207\344\270\262.md" "b/problems/0131.\345\210\206\345\211\262\345\233\236\346\226\207\344\270\262.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index ca342d4bc6..c76f1ce2f1
--- "a/problems/0131.\345\210\206\345\211\262\345\233\236\346\226\207\344\270\262.md"
+++ "b/problems/0131.\345\210\206\345\211\262\345\233\236\346\226\207\344\270\262.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0131.\345\210\206\345\211\262\345\233\236\346\226\207\344\270\262.md" "b/problems/0131.\345\210\206\345\211\262\345\233\236\346\226\207\344\270\262.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index ca342d4bc6..c76f1ce2f1
--- "a/problems/0131.\345\210\206\345\211\262\345\233\236\346\226\207\344\270\262.md"
+++ "b/problems/0131.\345\210\206\345\211\262\345\233\236\346\226\207\344\270\262.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
> 切割问题其实是一种组合问题!
@@ -52,7 +50,7 @@
所以切割问题,也可以抽象为一棵树形结构,如图:
-
+
递归用来纵向遍历,for循环用来横向遍历,切割线(就是图中的红线)切割到字符串的结尾位置,说明找到了一个切割方法。
@@ -78,7 +76,7 @@ void backtracking (const string& s, int startIndex) {
* 递归函数终止条件
-
+
从树形结构的图中可以看出:切割线切到了字符串最后面,说明找到了一种切割方法,此时就是本层递归的终止条件。
@@ -310,39 +308,35 @@ public:
### Java
```Java
class Solution {
- List> lists = new ArrayList<>();
- Deque deque = new LinkedList<>();
-
+ //保持前几题一贯的格式, initialization
+ List> res = new ArrayList<>();
+ List cur = new ArrayList<>();
public List> partition(String s) {
- backTracking(s, 0);
- return lists;
+ backtracking(s, 0, new StringBuilder());
+ return res;
}
-
- private void backTracking(String s, int startIndex) {
- //如果起始位置大于s的大小,说明找到了一组分割方案
- if (startIndex >= s.length()) {
- lists.add(new ArrayList(deque));
+ private void backtracking(String s, int start, StringBuilder sb){
+ //因为是起始位置一个一个加的,所以结束时start一定等于s.length,因为进入backtracking时一定末尾也是回文,所以cur是满足条件的
+ if (start == s.length()){
+ //注意创建一个新的copy
+ res.add(new ArrayList<>(cur));
return;
}
- for (int i = startIndex; i < s.length(); i++) {
- //如果是回文子串,则记录
- if (isPalindrome(s, startIndex, i)) {
- String str = s.substring(startIndex, i + 1);
- deque.addLast(str);
- } else {
- continue;
+ //像前两题一样从前往后搜索,如果发现回文,进入backtracking,起始位置后移一位,循环结束照例移除cur的末位
+ for (int i = start; i < s.length(); i++){
+ sb.append(s.charAt(i));
+ if (check(sb)){
+ cur.add(sb.toString());
+ backtracking(s, i + 1, new StringBuilder());
+ cur.remove(cur.size() -1 );
}
- //起始位置后移,保证不重复
- backTracking(s, i + 1);
- deque.removeLast();
}
}
- //判断是否是回文串
- private boolean isPalindrome(String s, int startIndex, int end) {
- for (int i = startIndex, j = end; i < j; i++, j--) {
- if (s.charAt(i) != s.charAt(j)) {
- return false;
- }
+
+ //helper method, 检查是否是回文
+ private boolean check(StringBuilder sb){
+ for (int i = 0; i < sb.length()/ 2; i++){
+ if (sb.charAt(i) != sb.charAt(sb.length() - 1 - i)){return false;}
}
return true;
}
@@ -531,6 +525,7 @@ class Solution:
```
### Go
+回溯 基本版
```go
var (
path []string // 放已经回文的子串
@@ -569,6 +564,63 @@ func isPalindrome(s string) bool {
}
```
+回溯+动态规划优化回文串判断
+```go
+var (
+ result [][]string
+ path []string // 放已经回文的子串
+ isPalindrome [][]bool // 放事先计算好的是否回文子串的结果
+)
+
+func partition(s string) [][]string {
+ result = make([][]string, 0)
+ path = make([]string, 0)
+ computePalindrome(s)
+ backtracing(s, 0)
+ return result
+}
+
+func backtracing(s string, startIndex int) {
+ // 如果起始位置已经大于s的大小,说明已经找到了一组分割方案了
+ if startIndex >= len(s) {
+ tmp := make([]string, len(path))
+ copy(tmp, path)
+ result = append(result, tmp)
+ return
+ }
+ for i := startIndex; i < len(s); i++ {
+ if isPalindrome[startIndex][i] { // 是回文子串
+ // 获取[startIndex,i]在s中的子串
+ path = append(path, s[startIndex:i+1])
+ } else { // 不是回文,跳过
+ continue
+ }
+ backtracing(s, i + 1) // 寻找i+1为起始位置的子串
+ path = path[:len(path)-1] // 回溯过程,弹出本次已经添加的子串
+ }
+}
+
+func computePalindrome(s string) {
+ // isPalindrome[i][j] 代表 s[i:j](双边包括)是否是回文字串
+ isPalindrome = make([][]bool, len(s))
+ for i := 0; i < len(isPalindrome); i++ {
+ isPalindrome[i] = make([]bool, len(s))
+ }
+ for i := len(s)-1; i >= 0; i-- {
+ // 需要倒序计算, 保证在i行时, i+1行已经计算好了
+ for j := i; j < len(s); j++ {
+ if j == i {
+ isPalindrome[i][j] = true
+ } else if j - i == 1 {
+ isPalindrome[i][j] = s[i] == s[j]
+ } else {
+ isPalindrome[i][j] = s[i] == s[j] && isPalindrome[i+1][j-1]
+ }
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
### JavaScript
```js
@@ -952,8 +1004,4 @@ public class Solution
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0132.\345\210\206\345\211\262\345\233\236\346\226\207\344\270\262II.md" "b/problems/0132.\345\210\206\345\211\262\345\233\236\346\226\207\344\270\262II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index eb91a1899f..8bbfa4ee10
--- "a/problems/0132.\345\210\206\345\211\262\345\233\236\346\226\207\344\270\262II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0132.\345\210\206\345\211\262\345\233\236\346\226\207\344\270\262II.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0132.\345\210\206\345\211\262\345\233\236\346\226\207\344\270\262II.md" "b/problems/0132.\345\210\206\345\211\262\345\233\236\346\226\207\344\270\262II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index eb91a1899f..8bbfa4ee10
--- "a/problems/0132.\345\210\206\345\211\262\345\233\236\346\226\207\344\270\262II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0132.\345\210\206\345\211\262\345\233\236\346\226\207\344\270\262II.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
@@ -163,7 +161,7 @@ for (int i = s.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
以输入:"aabc" 为例:
-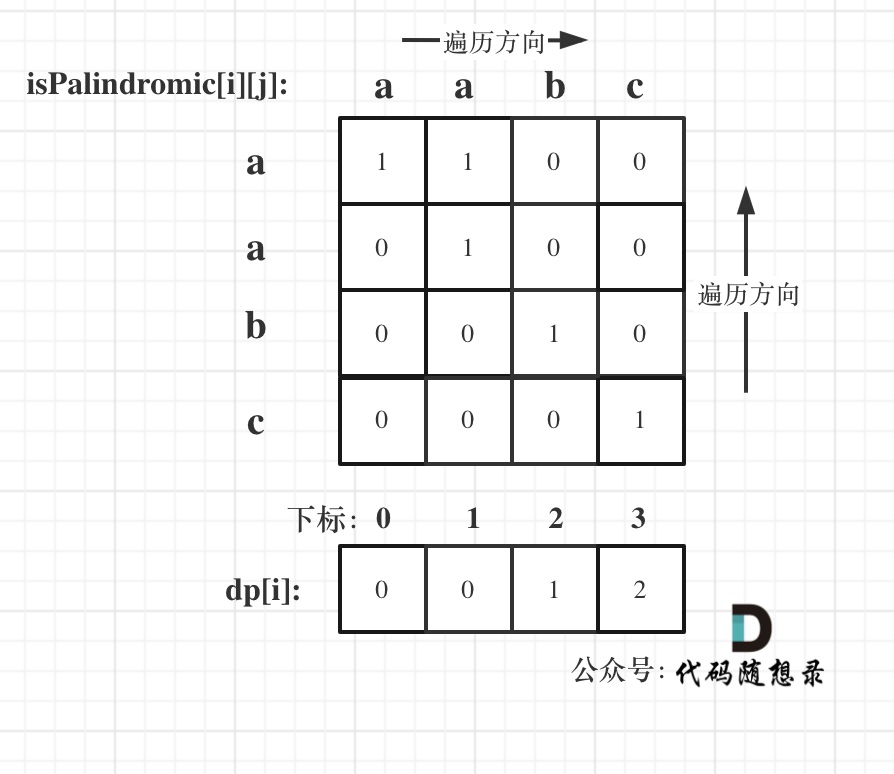
+
以上分析完毕,代码如下:
@@ -372,8 +370,4 @@ var minCut = function(s) {
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0134.\345\212\240\346\262\271\347\253\231.md" "b/problems/0134.\345\212\240\346\262\271\347\253\231.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index c093023d5f..5c8b0c3cc8
--- "a/problems/0134.\345\212\240\346\262\271\347\253\231.md"
+++ "b/problems/0134.\345\212\240\346\262\271\347\253\231.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0134.\345\212\240\346\262\271\347\253\231.md" "b/problems/0134.\345\212\240\346\262\271\347\253\231.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index c093023d5f..5c8b0c3cc8
--- "a/problems/0134.\345\212\240\346\262\271\347\253\231.md"
+++ "b/problems/0134.\345\212\240\346\262\271\347\253\231.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 134. 加油站
@@ -146,7 +144,7 @@ i从0开始累加rest[i],和记为curSum,一旦curSum小于零,说明[0, i
如图:
-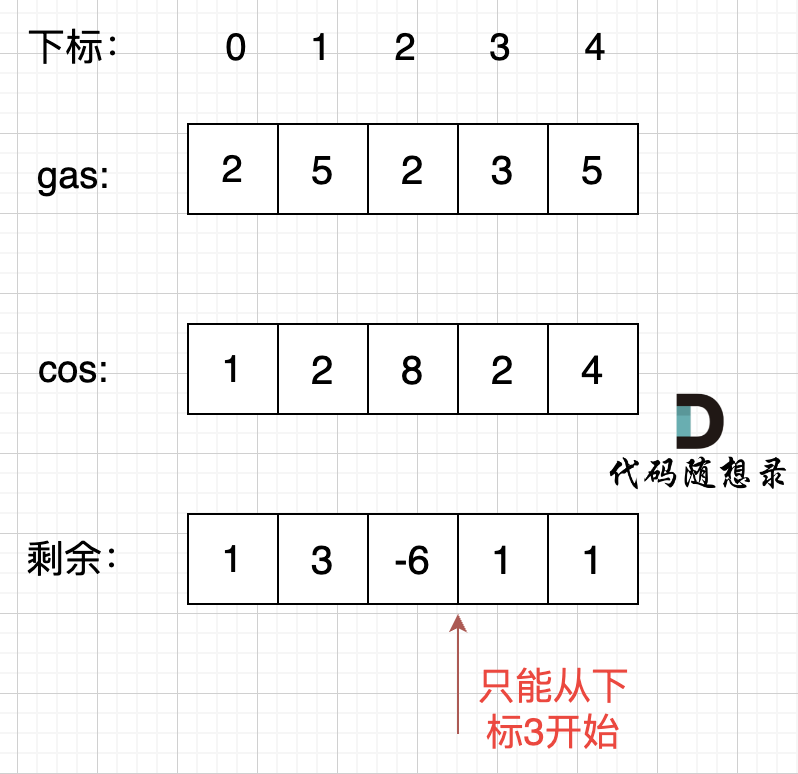
+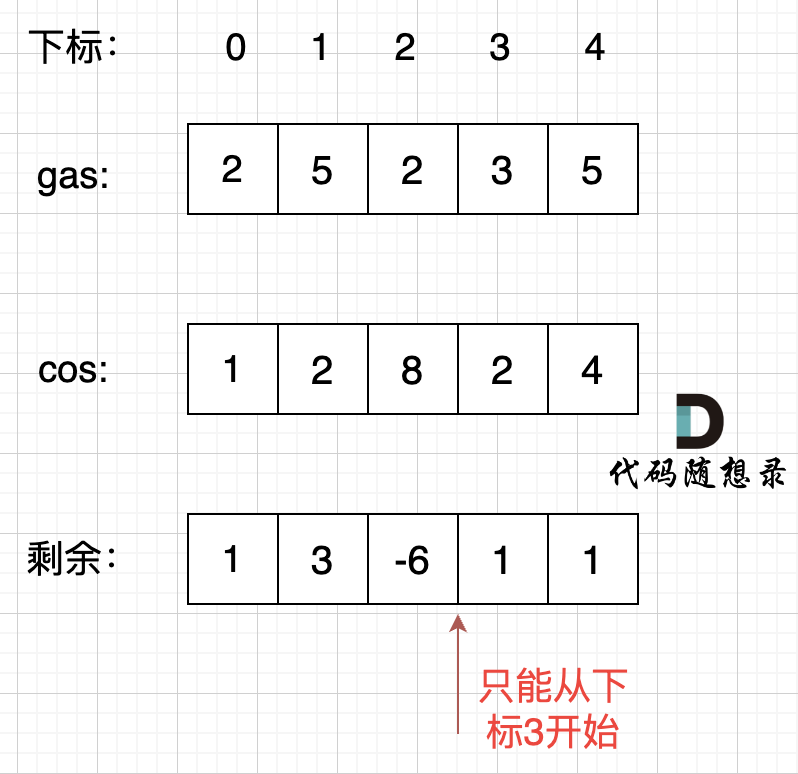
那么为什么一旦[0,i] 区间和为负数,起始位置就可以是i+1呢,i+1后面就不会出现更大的负数?
@@ -154,11 +152,11 @@ i从0开始累加rest[i],和记为curSum,一旦curSum小于零,说明[0, i
那有没有可能 [0,i] 区间 选某一个作为起点,累加到 i这里 curSum是不会小于零呢? 如图:
-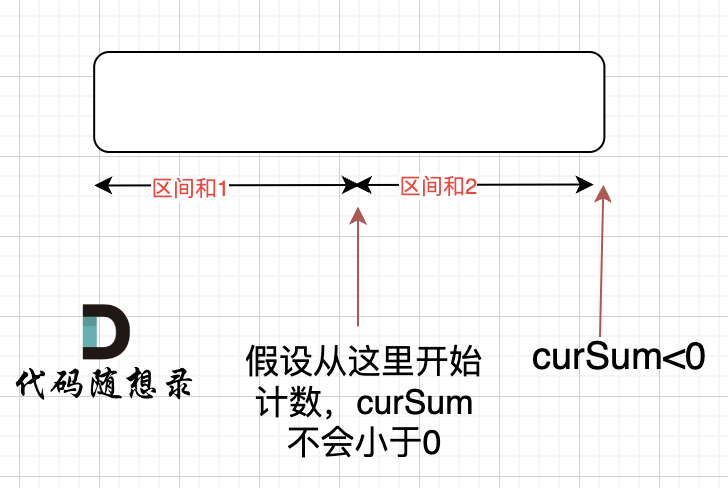
+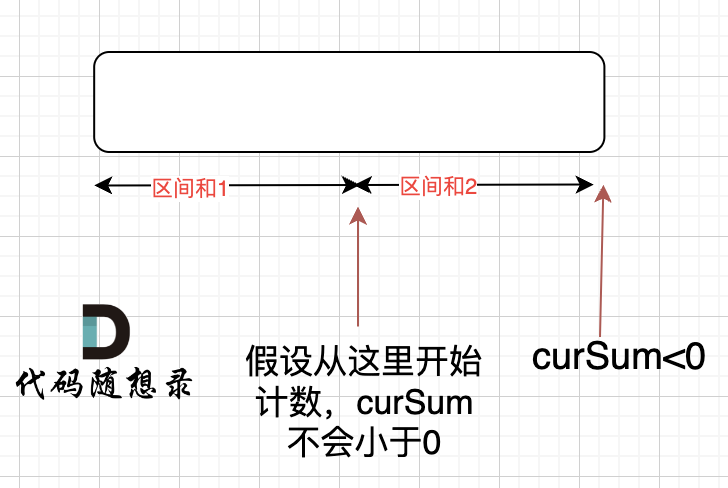
如果 curSum<0 说明 区间和1 + 区间和2 < 0, 那么 假设从上图中的位置开始计数curSum不会小于0的话,就是 区间和2>0。
-区间和1 + 区间和2 < 0 同时 区间和2>0,只能说明区间和1 < 0, 那么就会从假设的箭头初就开始从新选择其实位置了。
+区间和1 + 区间和2 < 0 同时 区间和2>0,只能说明区间和1 < 0, 那么就会从假设的箭头初就开始从新选择起始位置了。
**那么局部最优:当前累加rest[i]的和curSum一旦小于0,起始位置至少要是i+1,因为从i之前开始一定不行。全局最优:找到可以跑一圈的起始位置**。
@@ -249,6 +247,29 @@ class Solution {
}
}
```
+```
+// 解法3
+class Solution {
+ public int canCompleteCircuit(int[] gas, int[] cost) {
+ int tank = 0; // 当前油量
+ int totalGas = 0; // 总加油量
+ int totalCost = 0; // 总油耗
+ int start = 0; // 起点
+ for (int i = 0; i < gas.length; i++) {
+ totalGas += gas[i];
+ totalCost += cost[i];
+
+ tank += gas[i] - cost[i];
+ if (tank < 0) { // tank 变为负数 意味着 从0到i之间出发都不能顺利环路一周,因为在此i点必会没油
+ tank = 0; // reset tank,类似于题目53.最大子树和reset sum
+ start = i + 1; // 起点变为i点往后一位
+ }
+ }
+ if (totalCost > totalGas) return -1;
+ return start;
+ }
+}
+```
### Python
暴力法
@@ -322,6 +343,37 @@ class Solution:
```
### Go
+
+贪心算法(方法一)
+```go
+func canCompleteCircuit(gas []int, cost []int) int {
+ curSum := 0
+ min := math.MaxInt64
+ for i := 0; i < len(gas); i++ {
+ rest := gas[i] - cost[i]
+ curSum += rest
+ if curSum < min {
+ min = curSum
+ }
+ }
+ if curSum < 0 {
+ return -1
+ }
+ if min >= 0 {
+ return 0
+ }
+ for i := len(gas) - 1; i > 0; i-- {
+ rest := gas[i] - cost[i]
+ min += rest
+ if min >= 0 {
+ return i
+ }
+ }
+ return -1
+}
+```
+
+贪心算法(方法二)
```go
func canCompleteCircuit(gas []int, cost []int) int {
curSum := 0
@@ -342,7 +394,7 @@ func canCompleteCircuit(gas []int, cost []int) int {
}
```
-### Javascript
+### JavaScript
暴力:
```js
var canCompleteCircuit = function(gas, cost) {
@@ -654,8 +706,4 @@ public class Solution
}
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0135.\345\210\206\345\217\221\347\263\226\346\236\234.md" "b/problems/0135.\345\210\206\345\217\221\347\263\226\346\236\234.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 210f4995dc..9701f0f0c1
--- "a/problems/0135.\345\210\206\345\217\221\347\263\226\346\236\234.md"
+++ "b/problems/0135.\345\210\206\345\217\221\347\263\226\346\236\234.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0135.\345\210\206\345\217\221\347\263\226\346\236\234.md" "b/problems/0135.\345\210\206\345\217\221\347\263\226\346\236\234.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 210f4995dc..9701f0f0c1
--- "a/problems/0135.\345\210\206\345\217\221\347\263\226\346\236\234.md"
+++ "b/problems/0135.\345\210\206\345\217\221\347\263\226\346\236\234.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 135. 分发糖果
@@ -58,7 +56,7 @@ for (int i = 1; i < ratings.size(); i++) {
如图:
-
+
再确定左孩子大于右孩子的情况(从后向前遍历)
@@ -68,7 +66,7 @@ for (int i = 1; i < ratings.size(); i++) {
如果从前向后遍历,rating[5]与rating[4]的比较 就不能用上 rating[5]与rating[6]的比较结果了 。如图:
-
+
**所以确定左孩子大于右孩子的情况一定要从后向前遍历!**
@@ -84,7 +82,7 @@ for (int i = 1; i < ratings.size(); i++) {
如图:
-
+
所以该过程代码如下:
@@ -177,21 +175,20 @@ class Solution {
```python
class Solution:
def candy(self, ratings: List[int]) -> int:
- candyVec = [1] * len(ratings)
+ n = len(ratings)
+ candies = [1] * n
- # 从前向后遍历,处理右侧比左侧评分高的情况
- for i in range(1, len(ratings)):
+ # Forward pass: handle cases where right rating is higher than left
+ for i in range(1, n):
if ratings[i] > ratings[i - 1]:
- candyVec[i] = candyVec[i - 1] + 1
+ candies[i] = candies[i - 1] + 1
- # 从后向前遍历,处理左侧比右侧评分高的情况
- for i in range(len(ratings) - 2, -1, -1):
+ # Backward pass: handle cases where left rating is higher than right
+ for i in range(n - 2, -1, -1):
if ratings[i] > ratings[i + 1]:
- candyVec[i] = max(candyVec[i], candyVec[i + 1] + 1)
+ candies[i] = max(candies[i], candies[i + 1] + 1)
- # 统计结果
- result = sum(candyVec)
- return result
+ return sum(candies)
```
@@ -234,7 +231,7 @@ func findMax(num1 int, num2 int) int {
}
```
-### Javascript
+### JavaScript
```Javascript
var candy = function(ratings) {
let candys = new Array(ratings.length).fill(1)
@@ -401,8 +398,4 @@ public class Solution
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0139.\345\215\225\350\257\215\346\213\206\345\210\206.md" "b/problems/0139.\345\215\225\350\257\215\346\213\206\345\210\206.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index d93288ae5a..2015cb90c1
--- "a/problems/0139.\345\215\225\350\257\215\346\213\206\345\210\206.md"
+++ "b/problems/0139.\345\215\225\350\257\215\346\213\206\345\210\206.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0139.\345\215\225\350\257\215\346\213\206\345\210\206.md" "b/problems/0139.\345\215\225\350\257\215\346\213\206\345\210\206.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index d93288ae5a..2015cb90c1
--- "a/problems/0139.\345\215\225\350\257\215\346\213\206\345\210\206.md"
+++ "b/problems/0139.\345\215\225\350\257\215\346\213\206\345\210\206.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
@@ -182,7 +180,7 @@ dp[0]表示如果字符串为空的话,说明出现在字典里。
以输入: s = "leetcode", wordDict = ["leet", "code"]为例,dp状态如图:
-
+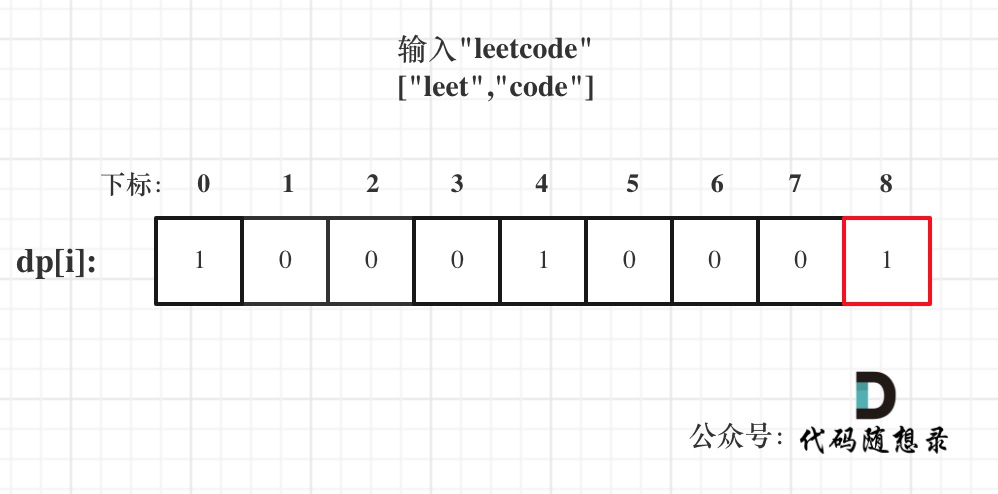
dp[s.size()]就是最终结果。
@@ -243,7 +241,7 @@ public:
使用用例:s = "applepenapple", wordDict = ["apple", "pen"],对应的dp数组状态如下:
-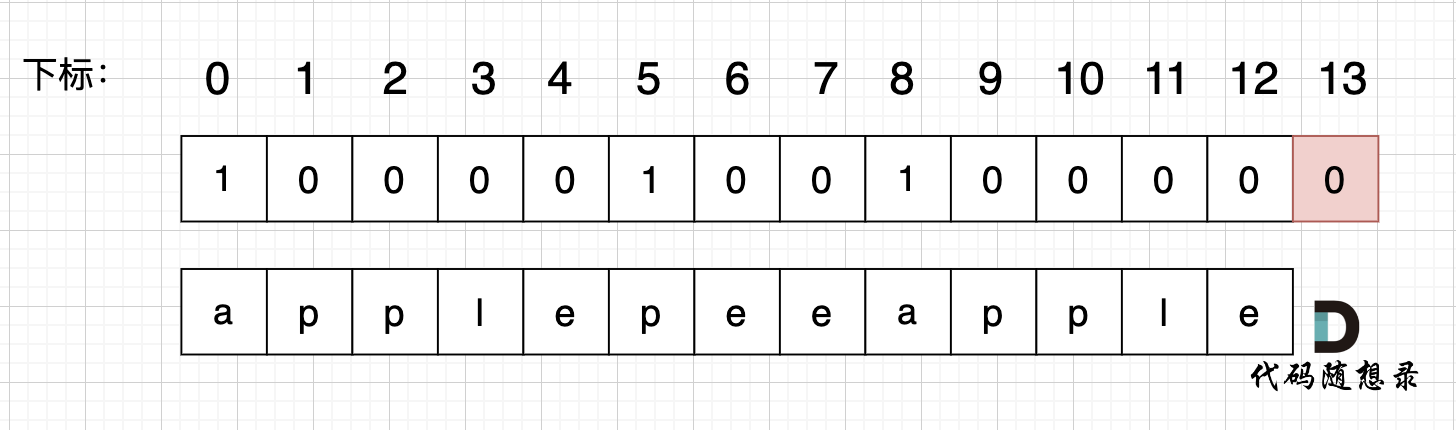
+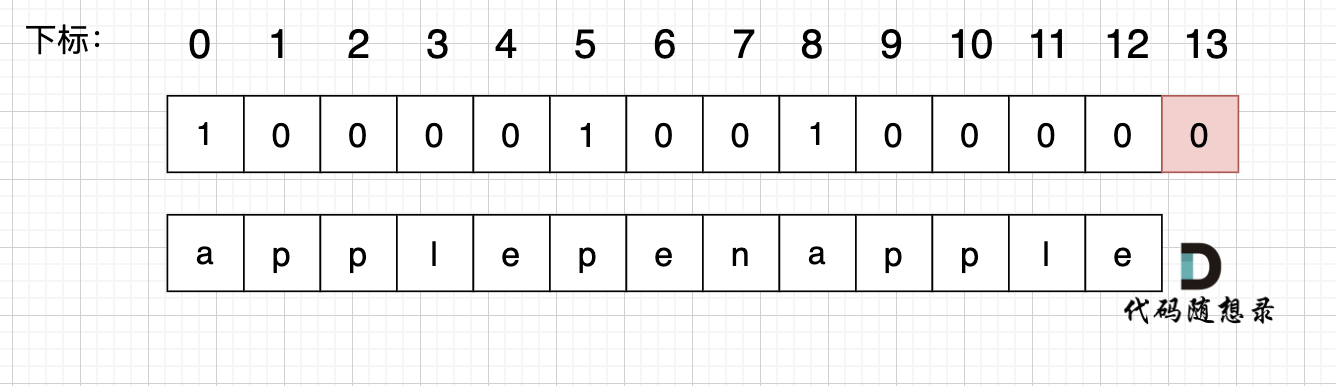
最后dp[s.size()] = 0 即 dp[13] = 0 ,而不是1,因为先用 "apple" 去遍历的时候,dp[8]并没有被赋值为1 (还没用"pen"),所以 dp[13]也不能变成1。
@@ -394,7 +392,28 @@ class Solution:
dp[j] = dp[j] or (dp[j - len(word)] and word == s[j - len(word):j])
return dp[len(s)]
```
+DP(剪枝)
+```python
+class Solution(object):
+ def wordBreak(self, s, wordDict):
+
+ # 先对单词按长度排序
+ wordDict.sort(key=lambda x: len(x))
+ n = len(s)
+ dp = [False] * (n + 1)
+ dp[0] = True
+ # 遍历背包
+ for i in range(1, n + 1):
+ # 遍历单词
+ for word in wordDict:
+ # 简单的 “剪枝”
+ if len(word) > i:
+ break
+ dp[i] = dp[i] or (dp[i - len(word)] and s[i - len(word): i] == word)
+ return dp[-1]
+
+```
### Go:
@@ -498,6 +517,33 @@ function wordBreak(s: string, wordDict: string[]): boolean {
};
```
+### C
+
+```c
+bool wordBreak(char* s, char** wordDict, int wordDictSize) {
+ int len = strlen(s);
+ // 初始化
+ bool dp[len + 1];
+ memset(dp, false, sizeof (dp));
+ dp[0] = true;
+ for (int i = 1; i < len + 1; ++i) {
+ for(int j = 0; j < wordDictSize; j++){
+ int wordLen = strlen(wordDict[j]);
+ // 分割点是由i和字典单词长度决定
+ int k = i - wordLen;
+ if(k < 0){
+ continue;
+ }
+ // 这里注意要限制长度,故用strncmp
+ dp[i] = (dp[k] && !strncmp(s + k, wordDict[j], wordLen)) || dp[i];
+ }
+ }
+ return dp[len];
+}
+```
+
+
+
### Rust:
```rust
@@ -517,8 +563,3 @@ impl Solution {
}
```
-
-
-  -
-
diff --git "a/problems/0141.\347\216\257\345\275\242\351\223\276\350\241\250.md" "b/problems/0141.\347\216\257\345\275\242\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index b1f42ba979..d3583ba866
--- "a/problems/0141.\347\216\257\345\275\242\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
+++ "b/problems/0141.\347\216\257\345\275\242\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0141.\347\216\257\345\275\242\351\223\276\350\241\250.md" "b/problems/0141.\347\216\257\345\275\242\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index b1f42ba979..d3583ba866
--- "a/problems/0141.\347\216\257\345\275\242\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
+++ "b/problems/0141.\347\216\257\345\275\242\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 141. 环形链表
@@ -15,7 +13,7 @@
如果链表中存在环,则返回 true 。 否则,返回 false 。
-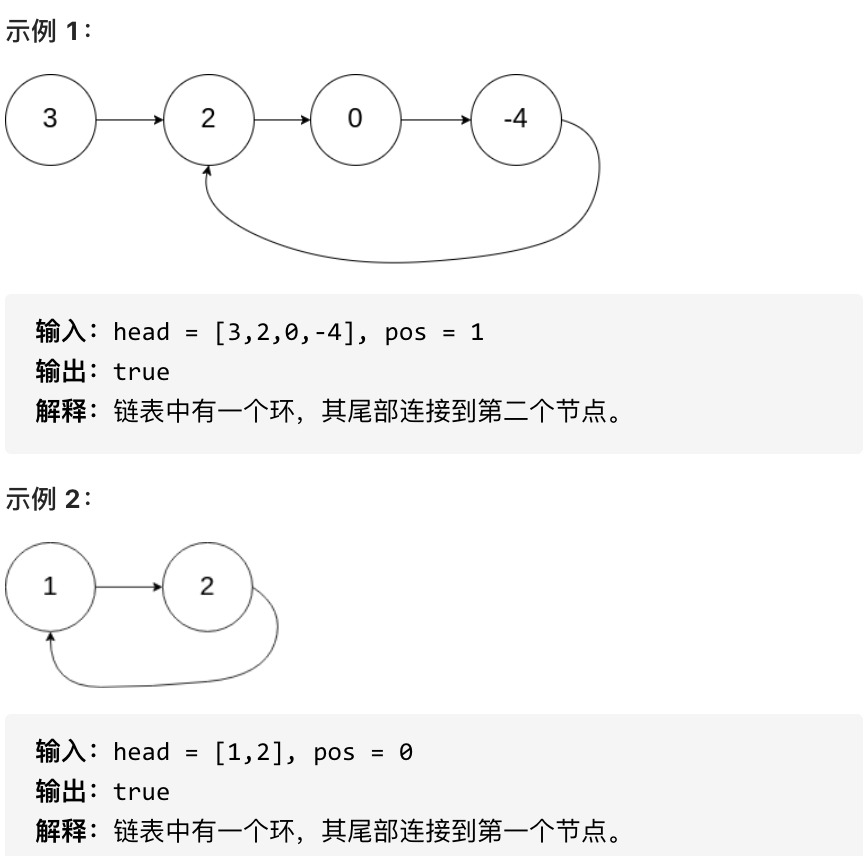
+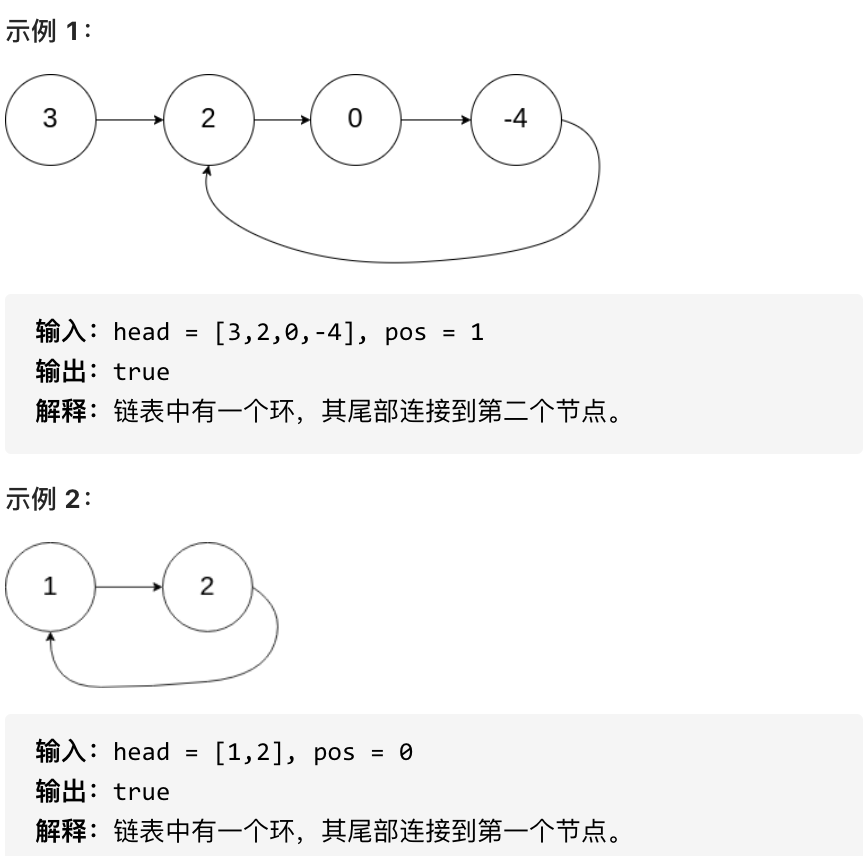
## 思路
@@ -31,7 +29,7 @@
会发现最终都是这种情况, 如下图:
- +
+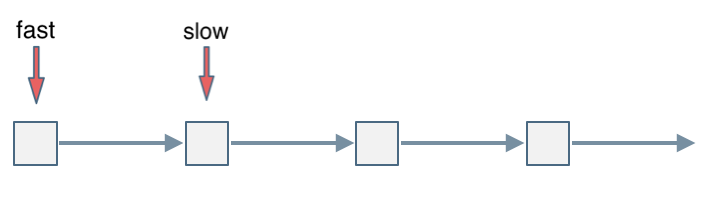 fast和slow各自再走一步, fast和slow就相遇了
@@ -40,7 +38,7 @@ fast和slow各自再走一步, fast和slow就相遇了
动画如下:
-
+
C++代码如下
@@ -159,8 +157,4 @@ function hasCycle(head: ListNode | null): boolean {
-
fast和slow各自再走一步, fast和slow就相遇了
@@ -40,7 +38,7 @@ fast和slow各自再走一步, fast和slow就相遇了
动画如下:
-
+
C++代码如下
@@ -159,8 +157,4 @@ function hasCycle(head: ListNode | null): boolean {
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0142.\347\216\257\345\275\242\351\223\276\350\241\250II.md" "b/problems/0142.\347\216\257\345\275\242\351\223\276\350\241\250II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index a643fd7091..4fd81ef0f5
--- "a/problems/0142.\347\216\257\345\275\242\351\223\276\350\241\250II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0142.\347\216\257\345\275\242\351\223\276\350\241\250II.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0142.\347\216\257\345\275\242\351\223\276\350\241\250II.md" "b/problems/0142.\347\216\257\345\275\242\351\223\276\350\241\250II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index a643fd7091..4fd81ef0f5
--- "a/problems/0142.\347\216\257\345\275\242\351\223\276\350\241\250II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0142.\347\216\257\345\275\242\351\223\276\350\241\250II.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
@@ -22,11 +20,11 @@
**说明**:不允许修改给定的链表。
-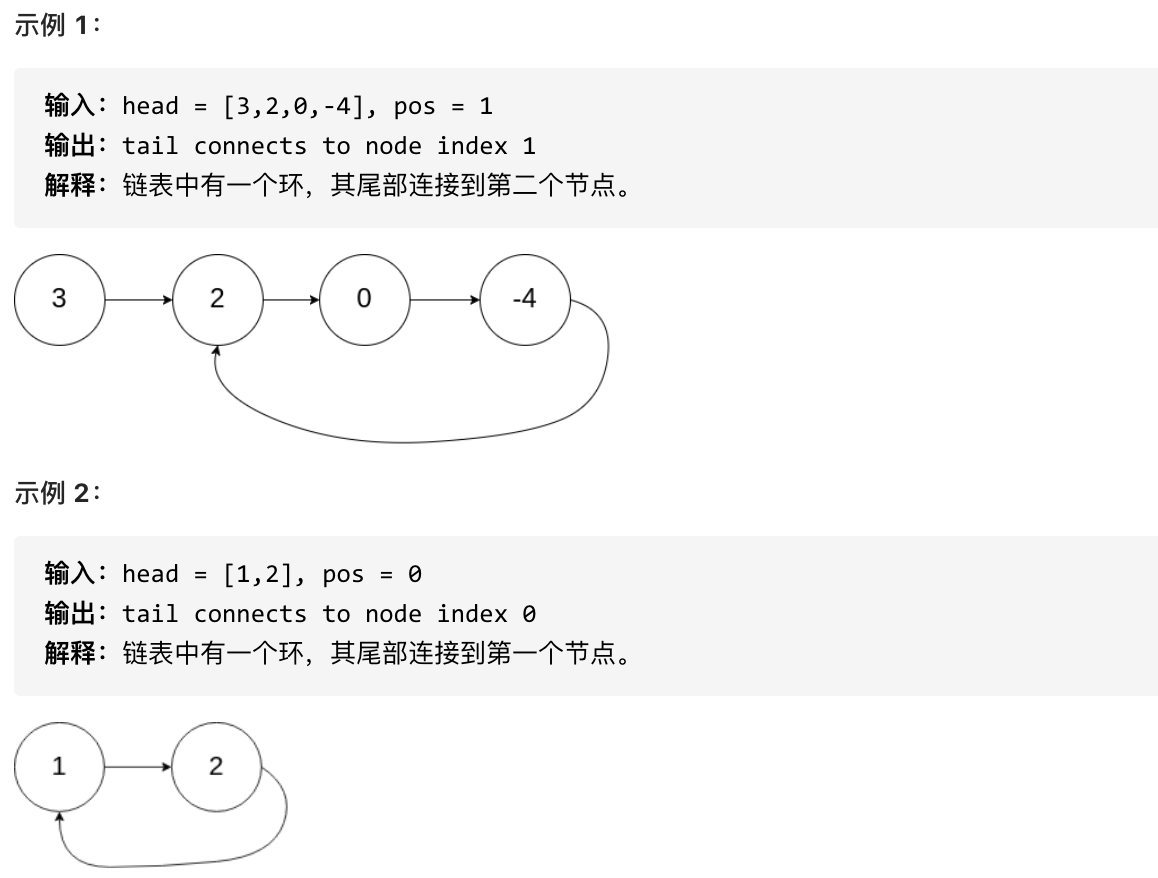
+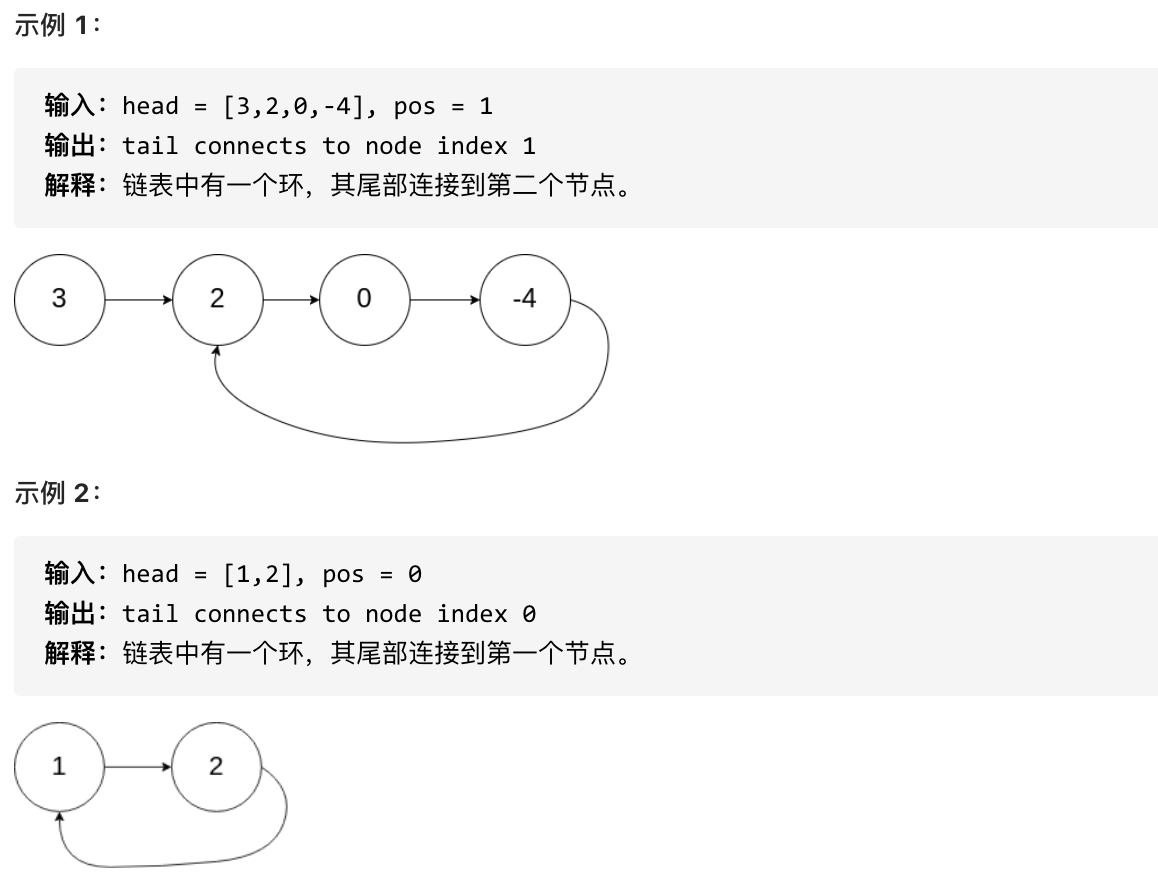
## 算法公开课
-**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[把环形链表讲清楚!| LeetCode:142.环形链表II](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1if4y1d7ob),相信结合视频在看本篇题解,更有助于大家对链表的理解。**
+**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[把环形链表讲清楚!| LeetCode:142.环形链表II](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1if4y1d7ob),相信结合视频再看本篇题解,更有助于大家对链表的理解。**
## 思路
@@ -52,7 +50,7 @@
会发现最终都是这种情况, 如下图:
-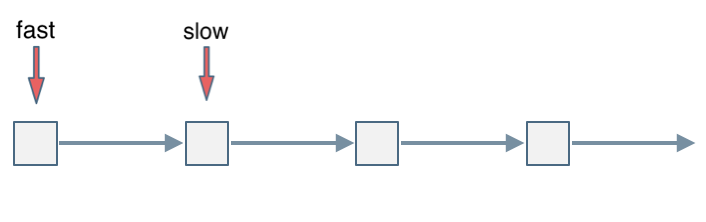
+
fast和slow各自再走一步, fast和slow就相遇了
@@ -61,7 +59,7 @@ fast和slow各自再走一步, fast和slow就相遇了
动画如下:
-
+
### 如果有环,如何找到这个环的入口
@@ -72,7 +70,7 @@ fast和slow各自再走一步, fast和slow就相遇了
环形入口节点到 fast指针与slow指针相遇节点 节点数为y。
从相遇节点 再到环形入口节点节点数为 z。 如图所示:
-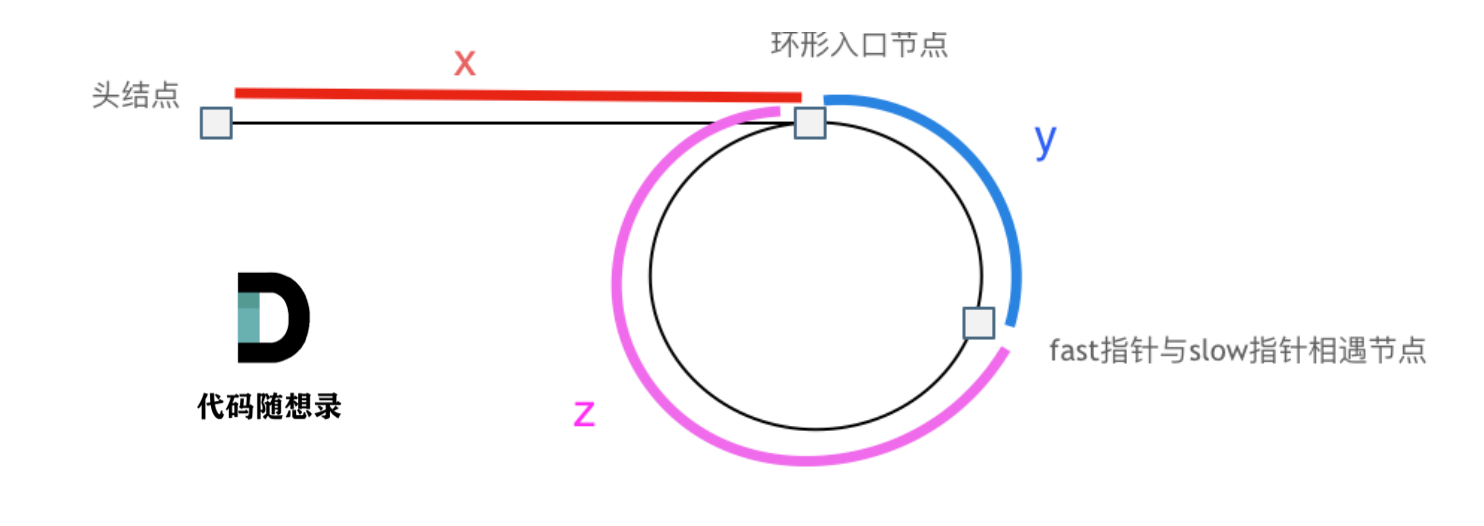
+
那么相遇时:
slow指针走过的节点数为: `x + y`,
@@ -105,7 +103,7 @@ fast指针走过的节点数:` x + y + n (y + z)`,n为fast指针在环内走
动画如下:
-
+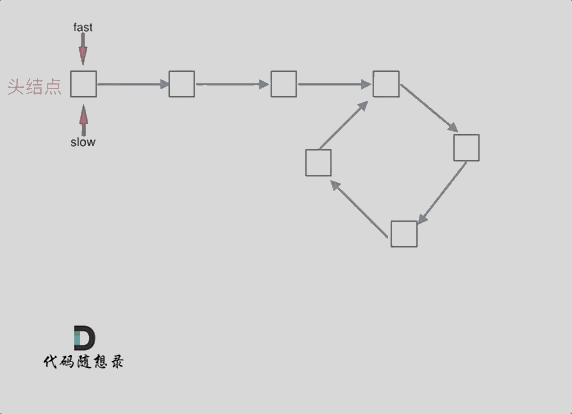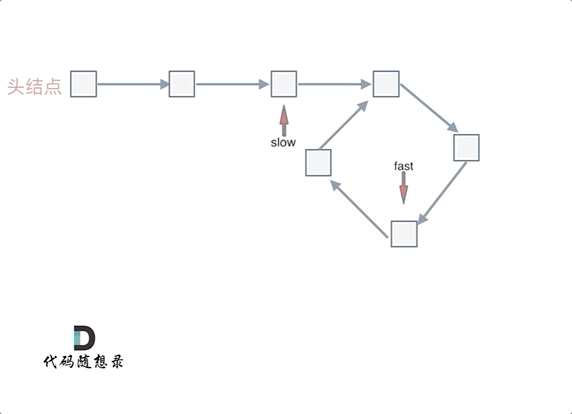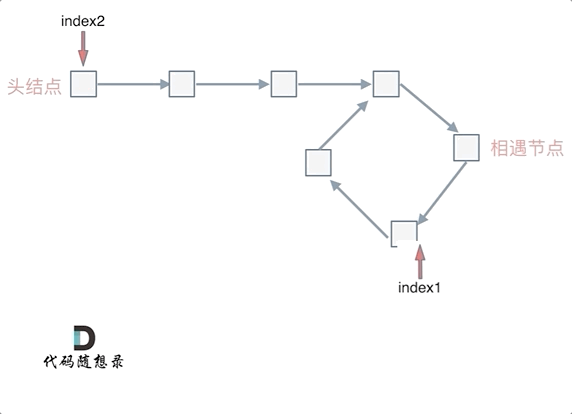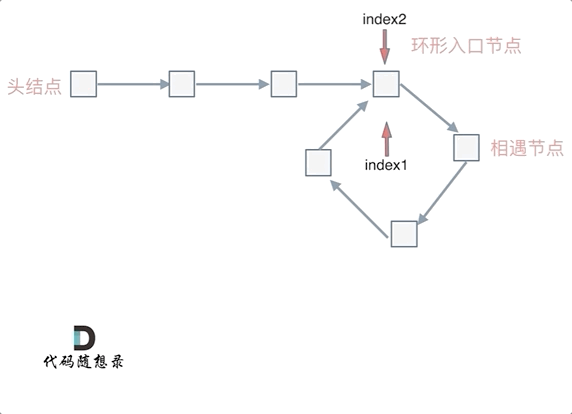
那么 n如果大于1是什么情况呢,就是fast指针在环形转n圈之后才遇到 slow指针。
@@ -156,20 +154,20 @@ public:
即文章[链表:环找到了,那入口呢?](https://programmercarl.com/0142.环形链表II.html)中如下的地方:
-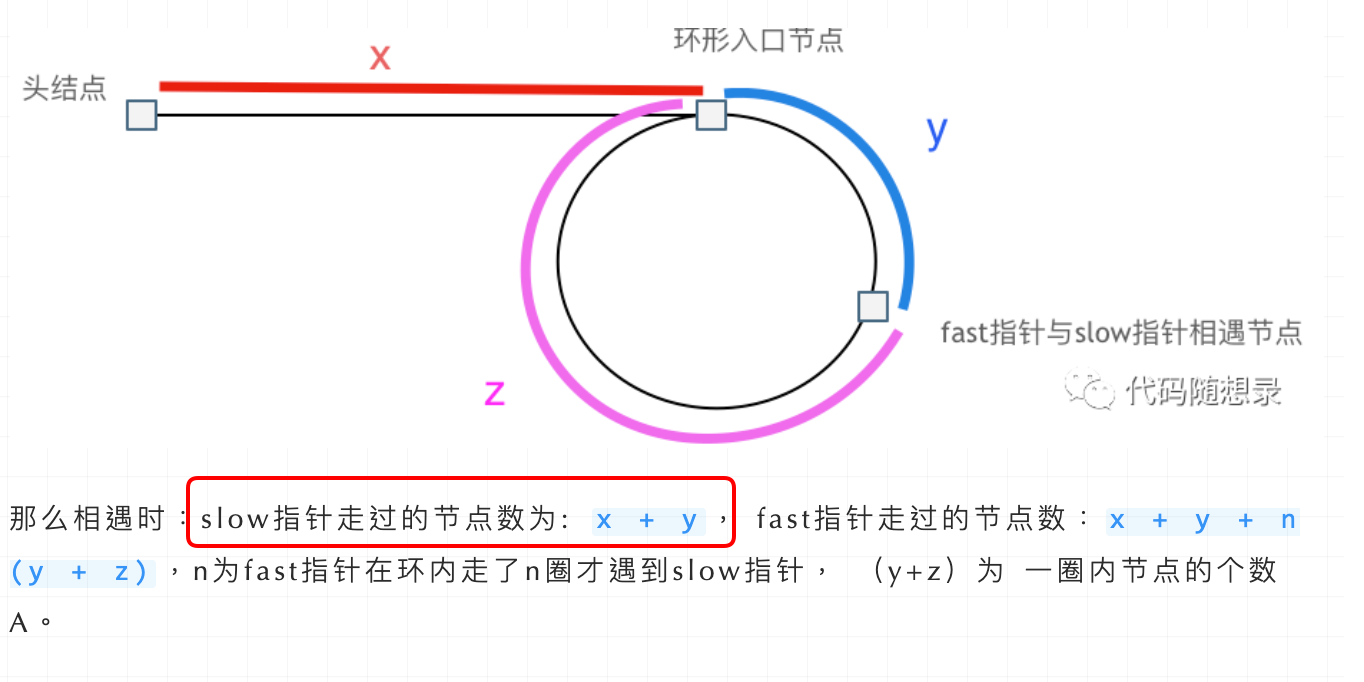
+
首先slow进环的时候,fast一定是先进环来了。
如果slow进环入口,fast也在环入口,那么把这个环展开成直线,就是如下图的样子:
-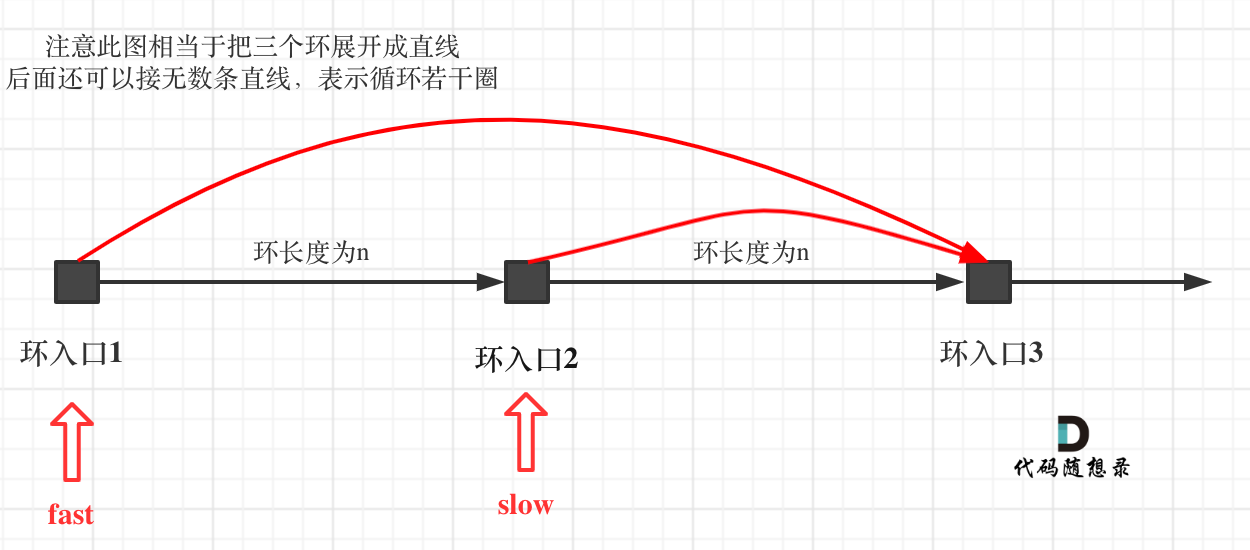
+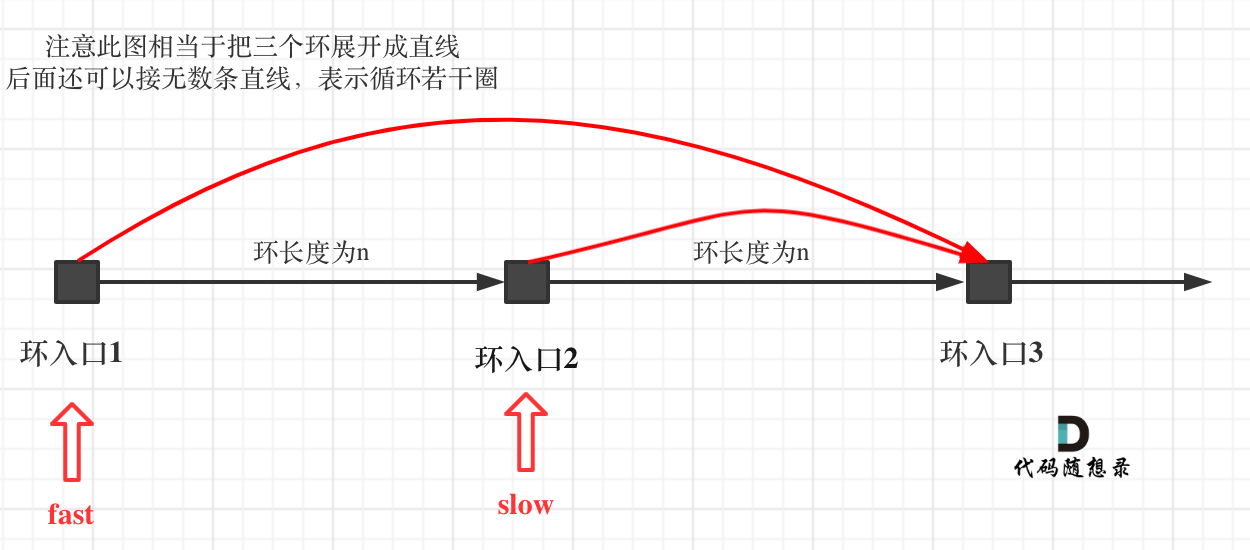
可以看出如果slow 和 fast同时在环入口开始走,一定会在环入口3相遇,slow走了一圈,fast走了两圈。
重点来了,slow进环的时候,fast一定是在环的任意一个位置,如图:
-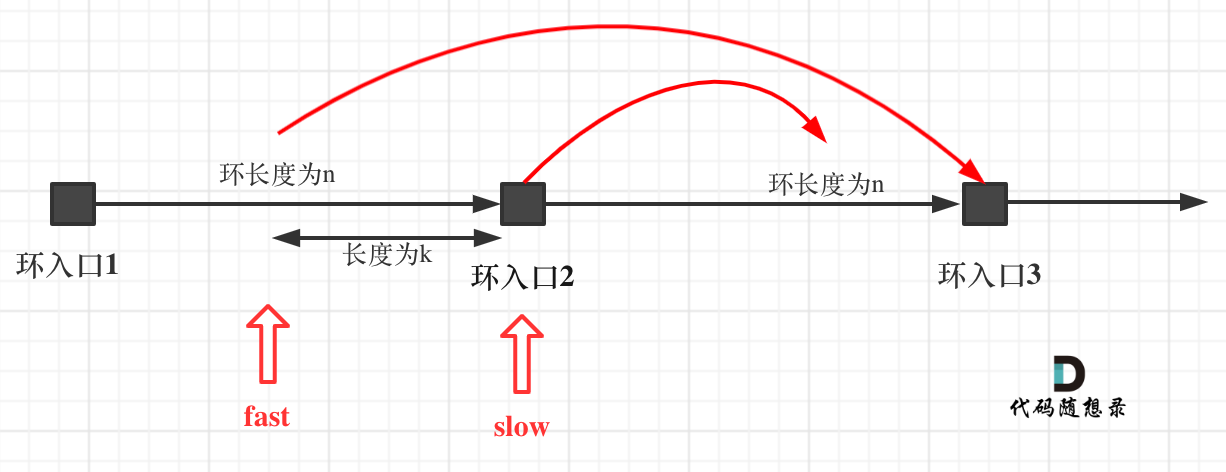
+
那么fast指针走到环入口3的时候,已经走了k + n 个节点,slow相应的应该走了(k + n) / 2 个节点。
@@ -465,7 +463,3 @@ public class Solution
}
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0143.\351\207\215\346\216\222\351\223\276\350\241\250.md" "b/problems/0143.\351\207\215\346\216\222\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 0b3be9a0f1..e7056913ee
--- "a/problems/0143.\351\207\215\346\216\222\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
+++ "b/problems/0143.\351\207\215\346\216\222\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
@@ -1,14 +1,12 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0143.\351\207\215\346\216\222\351\223\276\350\241\250.md" "b/problems/0143.\351\207\215\346\216\222\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 0b3be9a0f1..e7056913ee
--- "a/problems/0143.\351\207\215\346\216\222\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
+++ "b/problems/0143.\351\207\215\346\216\222\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
@@ -1,14 +1,12 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 143.重排链表
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/reorder-list/submissions/)
-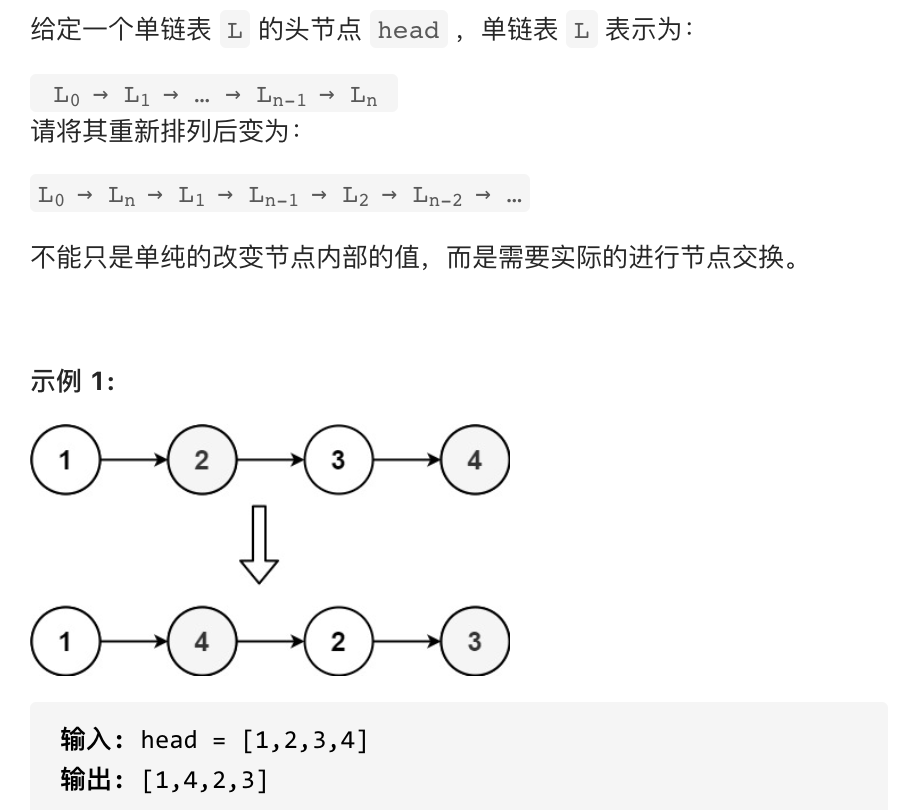
+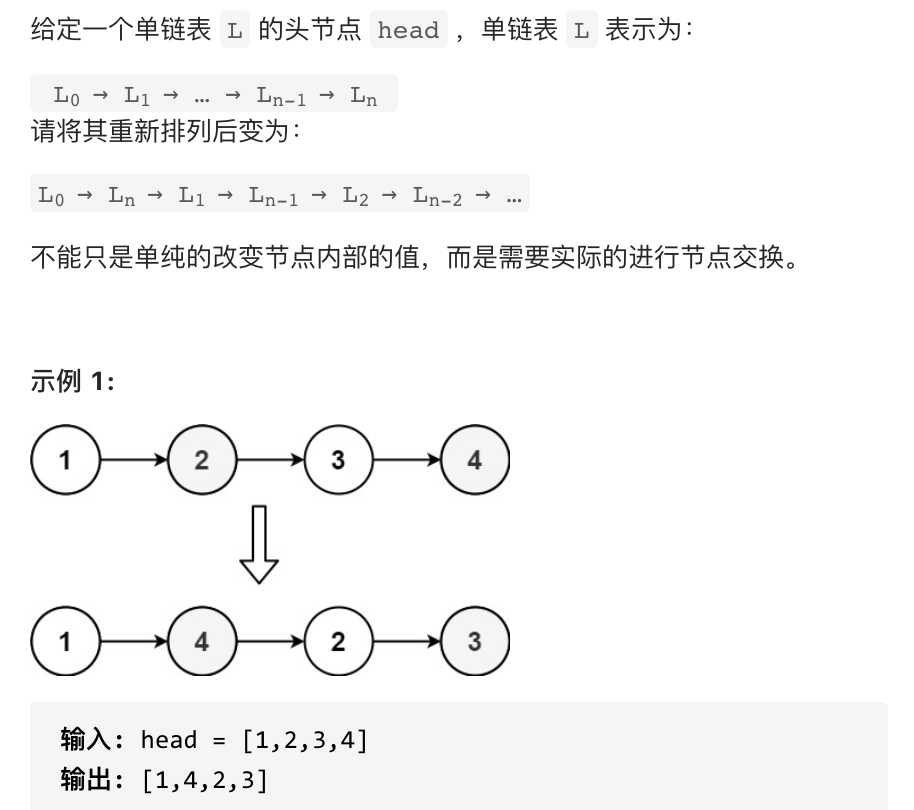
## 思路
@@ -38,7 +36,7 @@ public:
cur = head;
int i = 1;
int j = vec.size() - 1; // i j为之前前后的双指针
- int count = 0; // 计数,偶数去后面,奇数取前面
+ int count = 0; // 计数,偶数取后面,奇数取前面
while (i <= j) {
if (count % 2 == 0) {
cur->next = vec[j];
@@ -73,7 +71,7 @@ public:
}
cur = head;
- int count = 0; // 计数,偶数去后面,奇数取前面
+ int count = 0; // 计数,偶数取后面,奇数取前面
ListNode* node;
while(que.size()) {
if (count % 2 == 0) {
@@ -98,7 +96,7 @@ public:
如图:
- +
+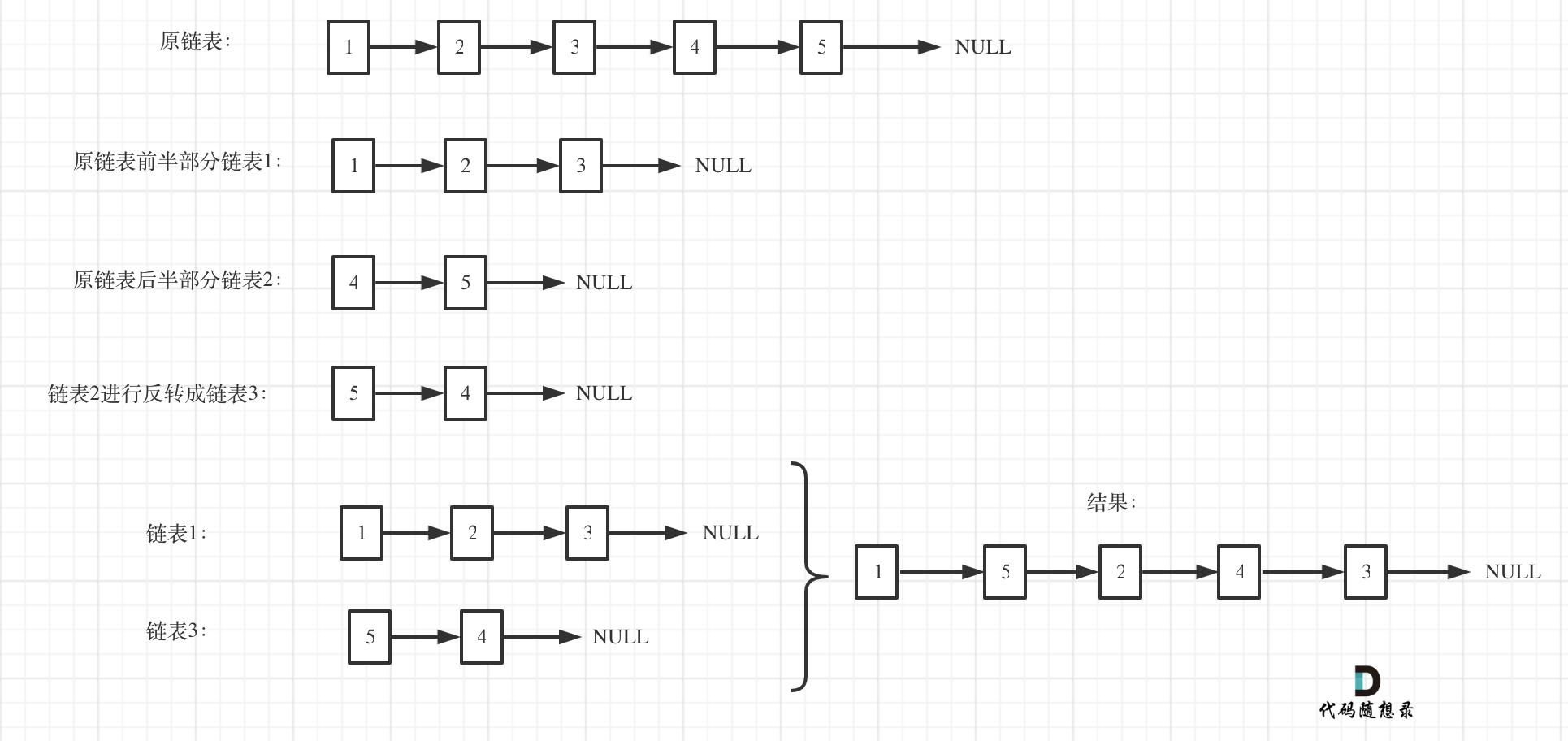 这种方法,比较难,平均切割链表,看上去很简单,真正代码写的时候有很多细节,同时两个链表最后拼装整一个新的链表也有一些细节需要注意!
@@ -338,8 +336,85 @@ class Solution:
return pre
```
### Go
+
+```go
+// 方法一 数组模拟
+/**
+ * Definition for singly-linked list.
+ * type ListNode struct {
+ * Val int
+ * Next *ListNode
+ * }
+ */
+func reorderList(head *ListNode) {
+ vec := make([]*ListNode, 0)
+ cur := head
+ if cur == nil {
+ return
+ }
+ for cur != nil {
+ vec = append(vec, cur)
+ cur = cur.Next
+ }
+ cur = head
+ i := 1
+ j := len(vec) - 1 // i j为前后的双指针
+ count := 0 // 计数,偶数取后面,奇数取前面
+ for i <= j {
+ if count % 2 == 0 {
+ cur.Next = vec[j]
+ j--
+ } else {
+ cur.Next = vec[i]
+ i++
+ }
+ cur = cur.Next
+ count++
+ }
+ cur.Next = nil // 注意结尾
+}
+```
+
+```go
+// 方法二 双向队列模拟
+/**
+ * Definition for singly-linked list.
+ * type ListNode struct {
+ * Val int
+ * Next *ListNode
+ * }
+ */
+func reorderList(head *ListNode) {
+ que := make([]*ListNode, 0)
+ cur := head
+ if cur == nil {
+ return
+ }
+
+ for cur.Next != nil {
+ que = append(que, cur.Next)
+ cur = cur.Next
+ }
+
+ cur = head
+ count := 0 // 计数,偶数取后面,奇数取前面
+ for len(que) > 0 {
+ if count % 2 == 0 {
+ cur.Next = que[len(que)-1]
+ que = que[:len(que)-1]
+ } else {
+ cur.Next = que[0]
+ que = que[1:]
+ }
+ count++
+ cur = cur.Next
+ }
+ cur.Next = nil // 注意结尾
+}
+```
+
```go
-# 方法三 分割链表
+// 方法三 分割链表
func reorderList(head *ListNode) {
var slow=head
var fast=head
@@ -612,7 +687,3 @@ void reorderList(struct ListNode* head){
```
-
这种方法,比较难,平均切割链表,看上去很简单,真正代码写的时候有很多细节,同时两个链表最后拼装整一个新的链表也有一些细节需要注意!
@@ -338,8 +336,85 @@ class Solution:
return pre
```
### Go
+
+```go
+// 方法一 数组模拟
+/**
+ * Definition for singly-linked list.
+ * type ListNode struct {
+ * Val int
+ * Next *ListNode
+ * }
+ */
+func reorderList(head *ListNode) {
+ vec := make([]*ListNode, 0)
+ cur := head
+ if cur == nil {
+ return
+ }
+ for cur != nil {
+ vec = append(vec, cur)
+ cur = cur.Next
+ }
+ cur = head
+ i := 1
+ j := len(vec) - 1 // i j为前后的双指针
+ count := 0 // 计数,偶数取后面,奇数取前面
+ for i <= j {
+ if count % 2 == 0 {
+ cur.Next = vec[j]
+ j--
+ } else {
+ cur.Next = vec[i]
+ i++
+ }
+ cur = cur.Next
+ count++
+ }
+ cur.Next = nil // 注意结尾
+}
+```
+
+```go
+// 方法二 双向队列模拟
+/**
+ * Definition for singly-linked list.
+ * type ListNode struct {
+ * Val int
+ * Next *ListNode
+ * }
+ */
+func reorderList(head *ListNode) {
+ que := make([]*ListNode, 0)
+ cur := head
+ if cur == nil {
+ return
+ }
+
+ for cur.Next != nil {
+ que = append(que, cur.Next)
+ cur = cur.Next
+ }
+
+ cur = head
+ count := 0 // 计数,偶数取后面,奇数取前面
+ for len(que) > 0 {
+ if count % 2 == 0 {
+ cur.Next = que[len(que)-1]
+ que = que[:len(que)-1]
+ } else {
+ cur.Next = que[0]
+ que = que[1:]
+ }
+ count++
+ cur = cur.Next
+ }
+ cur.Next = nil // 注意结尾
+}
+```
+
```go
-# 方法三 分割链表
+// 方法三 分割链表
func reorderList(head *ListNode) {
var slow=head
var fast=head
@@ -612,7 +687,3 @@ void reorderList(struct ListNode* head){
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0150.\351\200\206\346\263\242\345\205\260\350\241\250\350\276\276\345\274\217\346\261\202\345\200\274.md" "b/problems/0150.\351\200\206\346\263\242\345\205\260\350\241\250\350\276\276\345\274\217\346\261\202\345\200\274.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 663a68ea5c..de56c51ff7
--- "a/problems/0150.\351\200\206\346\263\242\345\205\260\350\241\250\350\276\276\345\274\217\346\261\202\345\200\274.md"
+++ "b/problems/0150.\351\200\206\346\263\242\345\205\260\350\241\250\350\276\276\345\274\217\346\261\202\345\200\274.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0150.\351\200\206\346\263\242\345\205\260\350\241\250\350\276\276\345\274\217\346\261\202\345\200\274.md" "b/problems/0150.\351\200\206\346\263\242\345\205\260\350\241\250\350\276\276\345\274\217\346\261\202\345\200\274.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 663a68ea5c..de56c51ff7
--- "a/problems/0150.\351\200\206\346\263\242\345\205\260\350\241\250\350\276\276\345\274\217\346\261\202\345\200\274.md"
+++ "b/problems/0150.\351\200\206\346\263\242\345\205\260\350\241\250\350\276\276\345\274\217\346\261\202\345\200\274.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
> 这不仅仅是一道好题,也展现出计算机的思考方式
@@ -80,9 +78,9 @@
在进一步看,本题中每一个子表达式要得出一个结果,然后拿这个结果再进行运算,那么**这岂不就是一个相邻字符串消除的过程,和[1047.删除字符串中的所有相邻重复项](https://programmercarl.com/1047.删除字符串中的所有相邻重复项.html)中的对对碰游戏是不是就非常像了。**
如动画所示:
-
+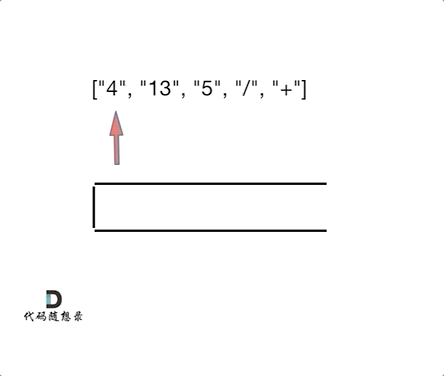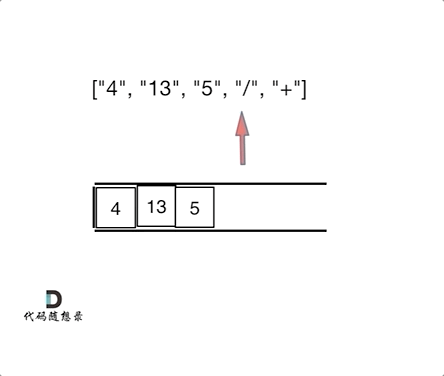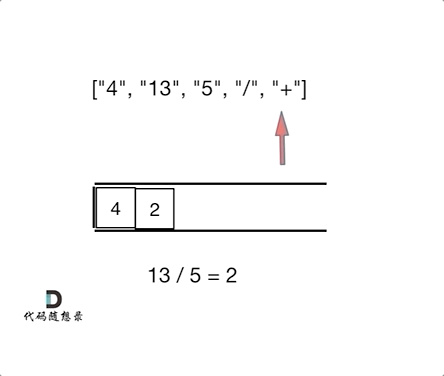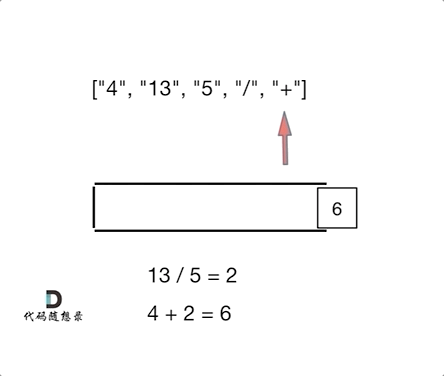
-相信看完动画大家应该知道,这和[1047. 删除字符串中的所有相邻重复项](https://programmercarl.com/1047.删除字符串中的所有相邻重复项.html)是差不错的,只不过本题不要相邻元素做消除了,而是做运算!
+相信看完动画大家应该知道,这和[1047. 删除字符串中的所有相邻重复项](https://programmercarl.com/1047.删除字符串中的所有相邻重复项.html)是差不多的,只不过本题不要相邻元素做消除了,而是做运算!
C++代码如下:
@@ -108,7 +106,7 @@ public:
}
}
- int result = st.top();
+ long long result = st.top();
st.pop(); // 把栈里最后一个元素弹出(其实不弹出也没事)
return result;
}
@@ -169,8 +167,12 @@ class Solution {
```python
from operator import add, sub, mul
-class Solution:
- op_map = {'+': add, '-': sub, '*': mul, '/': lambda x, y: int(x / y)}
+def div(x, y):
+ # 使用整数除法的向零取整方式
+ return int(x / y) if x * y > 0 else -(abs(x) // abs(y))
+
+class Solution(object):
+ op_map = {'+': add, '-': sub, '*': mul, '/': div}
def evalRPN(self, tokens: List[str]) -> int:
stack = []
@@ -184,21 +186,21 @@ class Solution:
return stack.pop()
```
-另一种可行,但因为使用eval相对较慢的方法:
+另一种可行,但因为使用eval()相对较慢的方法:
```python
-class Solution:
+class Solution(object):
def evalRPN(self, tokens: List[str]) -> int:
stack = []
- for item in tokens:
- if item not in {"+", "-", "*", "/"}:
- stack.append(item)
+ for token in tokens:
+ # 判断是否为数字,因为isdigit()不识别负数,故需要排除第一位的符号
+ if token.isdigit() or (len(token)>1 and token[1].isdigit()):
+ stack.append(token)
else:
- first_num, second_num = stack.pop(), stack.pop()
- stack.append(
- int(eval(f'{second_num} {item} {first_num}')) # 第一个出来的在运算符后面
- )
- return int(stack.pop()) # 如果一开始只有一个数,那么会是字符串形式的
-
+ op2 = stack.pop()
+ op1 = stack.pop()
+ # 由题意"The division always truncates toward zero",所以使用int()可以天然取整
+ stack.append(str(int(eval(op1 + token + op2))))
+ return int(stack.pop())
```
### Go:
@@ -485,7 +487,64 @@ impl Solution {
}
```
-
-
-  -
+### C:
+
+```c
+int str_to_int(char *str) {
+ // string转integer
+ int num = 0, tens = 1;
+ for (int i = strlen(str) - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
+ if (str[i] == '-') {
+ num *= -1;
+ break;
+ }
+ num += (str[i] - '0') * tens;
+ tens *= 10;
+ }
+ return num;
+}
+
+int evalRPN(char** tokens, int tokensSize) {
+
+ int *stack = (int *)malloc(tokensSize * sizeof(int));
+ assert(stack);
+ int stackTop = 0;
+
+ for (int i = 0; i < tokensSize; i++) {
+ char symbol = (tokens[i])[0];
+ if (symbol < '0' && (tokens[i])[1] == '\0') {
+
+ // pop两个数字
+ int num1 = stack[--stackTop];
+ int num2 = stack[--stackTop];
+
+ // 计算结果
+ int result;
+ if (symbol == '+') {
+ result = num1 + num2;
+ } else if (symbol == '-') {
+ result = num2 - num1;
+ } else if (symbol == '/') {
+ result = num2 / num1;
+ } else {
+ result = num1 * num2;
+ }
+
+ // push回stack
+ stack[stackTop++] = result;
+
+ } else {
+
+ // push数字进stack
+ int num = str_to_int(tokens[i]);
+ stack[stackTop++] = num;
+
+ }
+ }
+
+ int result = stack[0];
+ free(stack);
+ return result;
+}
+```
+
diff --git "a/problems/0151.\347\277\273\350\275\254\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262\351\207\214\347\232\204\345\215\225\350\257\215.md" "b/problems/0151.\347\277\273\350\275\254\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262\351\207\214\347\232\204\345\215\225\350\257\215.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 520f17a7ec..b5246a7dbb
--- "a/problems/0151.\347\277\273\350\275\254\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262\351\207\214\347\232\204\345\215\225\350\257\215.md"
+++ "b/problems/0151.\347\277\273\350\275\254\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262\351\207\214\347\232\204\345\215\225\350\257\215.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+### C:
+
+```c
+int str_to_int(char *str) {
+ // string转integer
+ int num = 0, tens = 1;
+ for (int i = strlen(str) - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
+ if (str[i] == '-') {
+ num *= -1;
+ break;
+ }
+ num += (str[i] - '0') * tens;
+ tens *= 10;
+ }
+ return num;
+}
+
+int evalRPN(char** tokens, int tokensSize) {
+
+ int *stack = (int *)malloc(tokensSize * sizeof(int));
+ assert(stack);
+ int stackTop = 0;
+
+ for (int i = 0; i < tokensSize; i++) {
+ char symbol = (tokens[i])[0];
+ if (symbol < '0' && (tokens[i])[1] == '\0') {
+
+ // pop两个数字
+ int num1 = stack[--stackTop];
+ int num2 = stack[--stackTop];
+
+ // 计算结果
+ int result;
+ if (symbol == '+') {
+ result = num1 + num2;
+ } else if (symbol == '-') {
+ result = num2 - num1;
+ } else if (symbol == '/') {
+ result = num2 / num1;
+ } else {
+ result = num1 * num2;
+ }
+
+ // push回stack
+ stack[stackTop++] = result;
+
+ } else {
+
+ // push数字进stack
+ int num = str_to_int(tokens[i]);
+ stack[stackTop++] = num;
+
+ }
+ }
+
+ int result = stack[0];
+ free(stack);
+ return result;
+}
+```
+
diff --git "a/problems/0151.\347\277\273\350\275\254\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262\351\207\214\347\232\204\345\215\225\350\257\215.md" "b/problems/0151.\347\277\273\350\275\254\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262\351\207\214\347\232\204\345\215\225\350\257\215.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 520f17a7ec..b5246a7dbb
--- "a/problems/0151.\347\277\273\350\275\254\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262\351\207\214\347\232\204\345\215\225\350\257\215.md"
+++ "b/problems/0151.\347\277\273\350\275\254\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262\351\207\214\347\232\204\345\215\225\350\257\215.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
@@ -440,11 +438,10 @@ class Solution {
```Python
class Solution:
def reverseWords(self, s: str) -> str:
- # 删除前后空白
- s = s.strip()
# 反转整个字符串
s = s[::-1]
# 将字符串拆分为单词,并反转每个单词
+ # split()函数能够自动忽略多余的空白字符
s = ' '.join(word[::-1] for word in s.split())
return s
@@ -467,6 +464,75 @@ class Solution:
# 将列表转换成字符串
return " ".join(words)
```
+(版本三) 拆分字符串 + 反转列表
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def reverseWords(self, s):
+ words = s.split() #type(words) --- list
+ words = words[::-1] # 反转单词
+ return ' '.join(words) #列表转换成字符串
+```
+(版本四) 将字符串转换为列表后,使用双指针去除空格
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def single_reverse(self, s, start: int, end: int):
+ while start < end:
+ s[start], s[end] = s[end], s[start]
+ start += 1
+ end -= 1
+
+ def reverseWords(self, s: str) -> str:
+ result = ""
+ fast = 0
+ # 1. 首先将原字符串反转并且除掉空格, 并且加入到新的字符串当中
+ # 由于Python字符串的不可变性,因此只能转换为列表进行处理
+ s = list(s)
+ s.reverse()
+ while fast < len(s):
+ if s[fast] != " ":
+ if len(result) != 0:
+ result += " "
+ while s[fast] != " " and fast < len(s):
+ result += s[fast]
+ fast += 1
+ else:
+ fast += 1
+ # 2.其次将每个单词进行翻转操作
+ slow = 0
+ fast = 0
+ result = list(result)
+ while fast <= len(result):
+ if fast == len(result) or result[fast] == " ":
+ self.single_reverse(result, slow, fast - 1)
+ slow = fast + 1
+ fast += 1
+ else:
+ fast += 1
+
+ return "".join(result)
+```
+
+(版本五) 遇到空格就说明前面的是一个单词,把它加入到一个数组中。
+
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def reverseWords(self, s: str) -> str:
+ words = []
+ word = ''
+ s += ' ' # 帮助处理最后一个字词
+
+ for char in s:
+ if char == ' ': # 遇到空格就说明前面的可能是一个单词
+ if word != '': # 确认是单词,把它加入到一个数组中
+ words.append(word)
+ word = '' # 清空当前单词
+ continue
+
+ word += char # 收集单词的字母
+
+ words.reverse()
+ return ' '.join(words)
+```
### Go:
@@ -571,7 +637,46 @@ func reverse(b []byte) {
}
}
```
-
+```go
+//双指针解法。指针逆序遍历,将遍历后得到的单词(间隔为空格,用以区分)顺序放置在额外空间
+//时间复杂度O(n),空间复杂度O(n)
+func reverseWords(s string) string {
+ strBytes := []byte(s)
+ n := len(strBytes)
+ // 记录有效字符范围的起始和结束位置
+ start, end := 0, n-1
+ // 去除开头空格
+ for start < n && strBytes[start] == 32 {
+ start++
+ }
+ // 处理全是空格或空字符串情况
+ if start == n {
+ return ""
+ }
+ // 去除结尾空格
+ for end >= 0 && strBytes[end] == 32 {
+ end--
+ }
+ // 结果切片,预分配容量
+ res := make([]byte, 0, end-start+1)//这里挺重要的,本人之前没有预分配容量,每次循环都添加单词,导致内存超限(也可能就是我之前的思路有问题)
+ // 从后往前遍历有效字符范围
+ for i := end; i >= start; {
+ // 找单词起始位置,直接通过循环条件判断定位
+ for ; i >= start && strBytes[i] == 32; i-- {
+ }
+ j := i
+ for ; j >= start && strBytes[j]!= 32; j-- {
+ }
+ res = append(res, strBytes[j+1:i+1]...)
+ // 只在不是最后一个单词时添加空格
+ if j > start {
+ res = append(res, 32)
+ }
+ i = j
+ }
+ return string(res)
+}
+```
### JavaScript:
@@ -979,7 +1084,4 @@ public string ReverseWords(string s) {
}
```
-
-
-  -
+
diff --git "a/problems/0160.\347\233\270\344\272\244\351\223\276\350\241\250.md" "b/problems/0160.\347\233\270\344\272\244\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index bf62ab30b5..cdc58912fe
--- "a/problems/0160.\347\233\270\344\272\244\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
+++ "b/problems/0160.\347\233\270\344\272\244\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
@@ -1,11 +1,5 @@
-
-
+
diff --git "a/problems/0160.\347\233\270\344\272\244\351\223\276\350\241\250.md" "b/problems/0160.\347\233\270\344\272\244\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index bf62ab30b5..cdc58912fe
--- "a/problems/0160.\347\233\270\344\272\244\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
+++ "b/problems/0160.\347\233\270\344\272\244\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
@@ -1,11 +1,5 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
同:[链表:链表相交](https://programmercarl.com/面试题02.07.链表相交.html)
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0188.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272IV.md" "b/problems/0188.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272IV.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index e4c5c48400..350533d8c8
--- "a/problems/0188.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272IV.md"
+++ "b/problems/0188.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272IV.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0188.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272IV.md" "b/problems/0188.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272IV.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index e4c5c48400..350533d8c8
--- "a/problems/0188.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272IV.md"
+++ "b/problems/0188.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272IV.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 188.买卖股票的最佳时机IV
@@ -134,7 +132,7 @@ for (int j = 1; j < 2 * k; j += 2) {
以输入[1,2,3,4,5],k=2为例。
-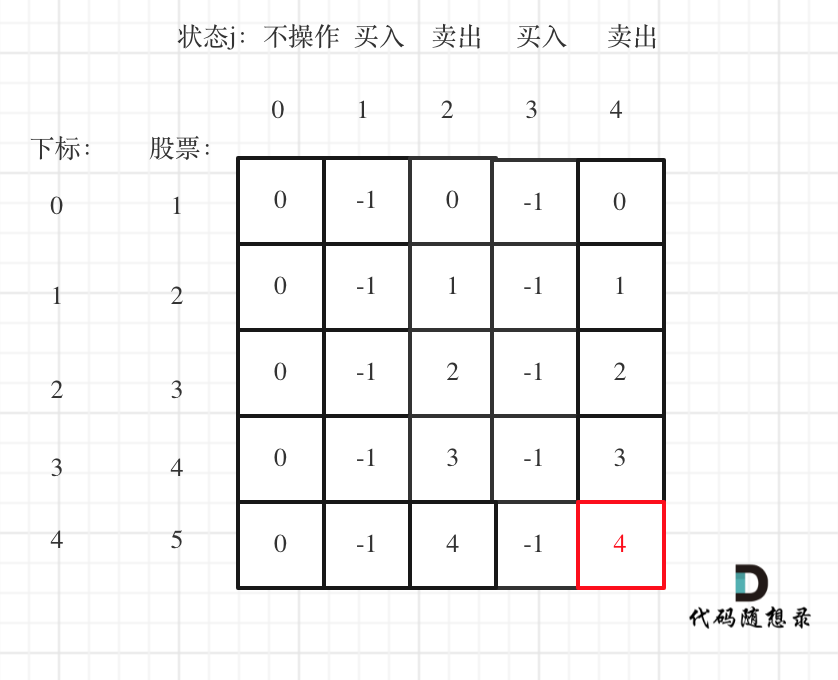
+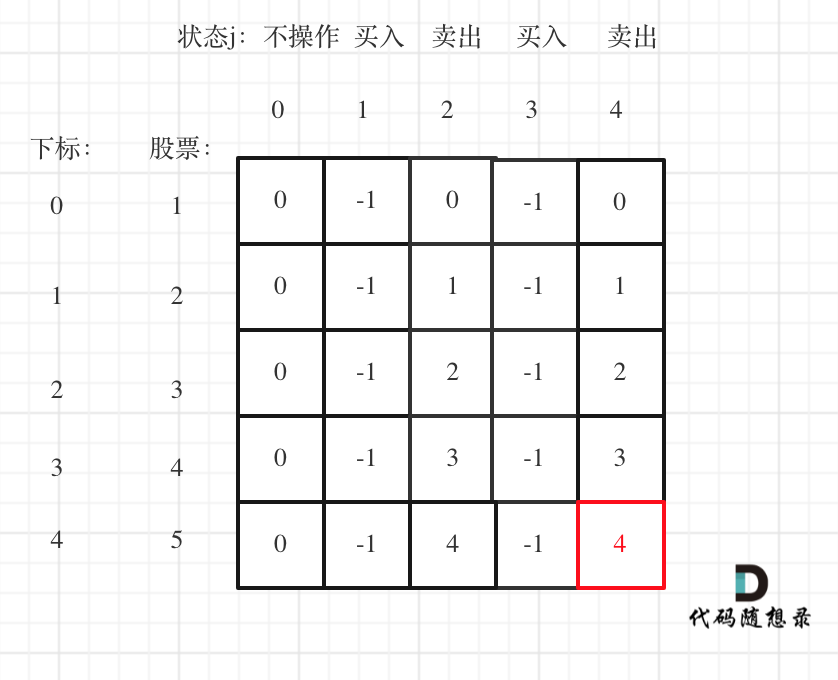
最后一次卖出,一定是利润最大的,dp[prices.size() - 1][2 * k]即红色部分就是最后求解。
@@ -297,8 +295,7 @@ class Solution {
### Python:
-版本一
-
+> 版本一
```python
class Solution:
def maxProfit(self, k: int, prices: List[int]) -> int:
@@ -313,7 +310,8 @@ class Solution:
dp[i][j+2] = max(dp[i-1][j+2], dp[i-1][j+1] + prices[i])
return dp[-1][2*k]
```
-版本二
+
+> 版本二
```python
class Solution:
def maxProfit(self, k: int, prices: List[int]) -> int:
@@ -329,9 +327,31 @@ class Solution:
dp[j] = max(dp[j],dp[j-1]+prices[i])
return dp[2*k]
```
+
+> 版本三: 一维 dp 数组(易理解版本)
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def maxProfit(self, k: int, prices: List[int]) -> int:
+ dp = [0] * k * 2
+ for i in range(k):
+ dp[i * 2] = -prices[0]
+
+ for price in prices[1:]:
+ dc = dp.copy() # 这句话是关键,把前一天的 dp 状态保存下来,防止被覆盖掉,后面只用它,不用 dp,逻辑简单易懂
+
+ for i in range(2 * k):
+ if i % 2 == 1:
+ dp[i] = max(dc[i], dc[i - 1] + price)
+ else:
+ pre = 0 if i == 0 else dc[i - 1]
+ dp[i] = max(dc[i], pre - price)
+
+ return dp[-1]
+```
+
### Go:
-版本一:
+> 版本一:
```go
// 买卖股票的最佳时机IV 动态规划
@@ -368,7 +388,7 @@ func max(a, b int) int {
}
```
-版本二: 三维 dp数组
+> 版本二: 三维 dp数组
```go
func maxProfit(k int, prices []int) int {
length := len(prices)
@@ -404,6 +424,71 @@ func max188(a, b int) int {
}
```
+版本三:空间优化版本
+
+```go
+func maxProfit(k int, prices []int) int {
+ n := len(prices)
+ // k次交易,2 * k种状态
+ // 状态从1开始计算,避免判断
+ // 奇数时持有(保持或买入)
+ // 偶数时不持有(保持或卖出)
+ dp := make([][]int, 2)
+ dp[0] = make([]int, k * 2 + 1)
+ dp[1] = make([]int, k * 2 + 1)
+
+ // 奇数状态时持有,i += 2
+ for i := 1; i <= k * 2; i += 2 {
+ dp[0][i] = -prices[0]
+ }
+
+ for i := 1; i < len(prices); i++ {
+ for j := 1; j <= k * 2; j++ {
+ if j % 2 == 1 {
+ dp[i % 2][j] = max(dp[(i - 1) % 2][j], dp[(i - 1) % 2][j - 1] - prices[i])
+ } else {
+ dp[i % 2][j] = max(dp[(i - 1) % 2][j], dp[(i - 1) % 2][j - 1] + prices[i])
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+ return dp[(n - 1) % 2][k * 2]
+}
+
+func max(a, b int) int {
+ if a > b {
+ return a
+ }
+ return b
+}
+```
+
+> 版本四:一维 dp 数组(易理解版本)
+
+```go
+func maxProfit(k int, prices []int) int {
+ dp := make([]int, 2 * k)
+ for i := range k {
+ dp[i * 2] = -prices[0]
+ }
+
+ for j := 1; j < len(prices); j++ {
+ dc := slices.Clone(dp) // 这句话是关键,把前一天的 dp 状态保存下来,防止被覆盖掉,后面只用它,不用 dp,逻辑简单易懂
+
+ for i := range k * 2 {
+ if i % 2 == 1 {
+ dp[i] = max(dc[i], dc[i - 1] + prices[j])
+ } else {
+ pre := 0; if i >= 1 { pre = dc[i - 1] }
+ dp[i] = max(dc[i], pre - prices[j])
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+ return dp[2 * k - 1]
+}
+```
+
### JavaScript:
```javascript
@@ -474,6 +559,34 @@ function maxProfit(k: number, prices: number[]): number {
};
```
+### C:
+
+```c
+#define max(a, b) ((a) > (b) ? (a) : (b))
+
+int maxProfit(int k, int* prices, int pricesSize) {
+ if(pricesSize == 0){
+ return 0;
+ }
+
+ int dp[pricesSize][2 * k + 1];
+ memset(dp, 0, sizeof(int) * pricesSize * (2 * k + 1));
+ for (int j = 1; j < 2 * k; j += 2) {
+ dp[0][j] = -prices[0];
+ }
+
+ for (int i = 1;i < pricesSize; i++) {//枚举股票
+ for (int j = 0; j < 2 * k - 1; j += 2) { //更新每一次买入卖出
+ dp[i][j + 1] = max(dp[i - 1][j + 1], dp[i - 1][j] - prices[i]);
+ dp[i][j + 2] = max(dp[i - 1][j + 2], dp[i - 1][j + 1] + prices[i]);
+ }
+ }
+ return dp[pricesSize - 1][2 * k];
+}
+```
+
+
+
### Rust:
```rust
@@ -525,7 +638,5 @@ impl Solution {
```
-
-
-  -
+
+
diff --git "a/problems/0189.\346\227\213\350\275\254\346\225\260\347\273\204.md" "b/problems/0189.\346\227\213\350\275\254\346\225\260\347\273\204.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index d60612e92b..976cbed4d1
--- "a/problems/0189.\346\227\213\350\275\254\346\225\260\347\273\204.md"
+++ "b/problems/0189.\346\227\213\350\275\254\346\225\260\347\273\204.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+
+
diff --git "a/problems/0189.\346\227\213\350\275\254\346\225\260\347\273\204.md" "b/problems/0189.\346\227\213\350\275\254\346\225\260\347\273\204.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index d60612e92b..976cbed4d1
--- "a/problems/0189.\346\227\213\350\275\254\346\225\260\347\273\204.md"
+++ "b/problems/0189.\346\227\213\350\275\254\346\225\260\347\273\204.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 189. 旋转数组
@@ -199,10 +197,16 @@ function reverseByRange(nums: number[], left: number, right: number): void {
}
```
+### Rust
+```rust
+impl Solution {
+ pub fn rotate(nums: &mut Vec, k: i32) {
+ let k = k as usize % nums.len();
+ nums.reverse();
+ nums[..k].reverse();
+ nums[k..].reverse();
+ }
+}
+```
-
-
-  -
-
diff --git "a/problems/0198.\346\211\223\345\256\266\345\212\253\350\210\215.md" "b/problems/0198.\346\211\223\345\256\266\345\212\253\350\210\215.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index a7bc4c998e..7c0aab8ec0
--- "a/problems/0198.\346\211\223\345\256\266\345\212\253\350\210\215.md"
+++ "b/problems/0198.\346\211\223\345\256\266\345\212\253\350\210\215.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0198.\346\211\223\345\256\266\345\212\253\350\210\215.md" "b/problems/0198.\346\211\223\345\256\266\345\212\253\350\210\215.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index a7bc4c998e..7c0aab8ec0
--- "a/problems/0198.\346\211\223\345\256\266\345\212\253\350\210\215.md"
+++ "b/problems/0198.\346\211\223\345\256\266\345\212\253\350\210\215.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 198.打家劫舍
@@ -89,7 +87,7 @@ for (int i = 2; i < nums.size(); i++) {
以示例二,输入[2,7,9,3,1]为例。
-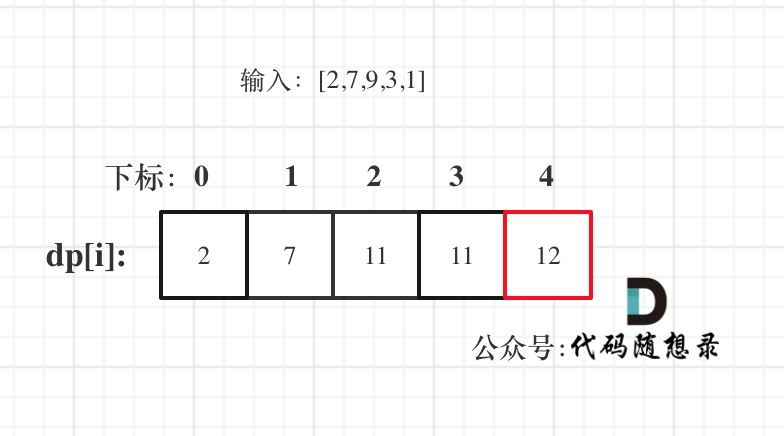
+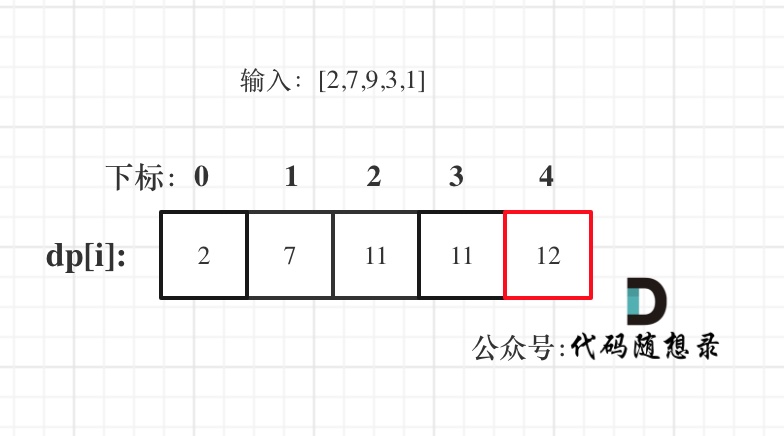
红框dp[nums.size() - 1]为结果。
@@ -315,6 +313,31 @@ function rob(nums: number[]): number {
};
```
+### C
+
+```c
+#define max(a, b) ((a) > (b) ? (a) : (b))
+
+int rob(int* nums, int numsSize) {
+ if(numsSize == 0){
+ return 0;
+ }
+ if(numsSize == 1){
+ return nums[0];
+ }
+ // dp初始化
+ int dp[numsSize];
+ dp[0] = nums[0];
+ dp[1] = max(nums[0], nums[1]);
+ for(int i = 2; i < numsSize; i++){
+ dp[i] = max(dp[i - 1], dp[i - 2] + nums[i]);
+ }
+ return dp[numsSize - 1];
+}
+```
+
+
+
### Rust:
```rust
@@ -335,7 +358,4 @@ impl Solution {
```
-
-
-  -
+
diff --git "a/problems/0200.\345\262\233\345\261\277\346\225\260\351\207\217.\345\271\277\346\220\234\347\211\210.md" "b/problems/0200.\345\262\233\345\261\277\346\225\260\351\207\217.\345\271\277\346\220\234\347\211\210.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 85471f73b5..7ae44b5222
--- "a/problems/0200.\345\262\233\345\261\277\346\225\260\351\207\217.\345\271\277\346\220\234\347\211\210.md"
+++ "b/problems/0200.\345\262\233\345\261\277\346\225\260\351\207\217.\345\271\277\346\220\234\347\211\210.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+
diff --git "a/problems/0200.\345\262\233\345\261\277\346\225\260\351\207\217.\345\271\277\346\220\234\347\211\210.md" "b/problems/0200.\345\262\233\345\261\277\346\225\260\351\207\217.\345\271\277\346\220\234\347\211\210.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 85471f73b5..7ae44b5222
--- "a/problems/0200.\345\262\233\345\261\277\346\225\260\351\207\217.\345\271\277\346\220\234\347\211\210.md"
+++ "b/problems/0200.\345\262\233\345\261\277\346\225\260\351\207\217.\345\271\277\346\220\234\347\211\210.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 200. 岛屿数量
@@ -15,7 +13,7 @@
此外,你可以假设该网格的四条边均被水包围。
-
+
提示:
@@ -30,7 +28,7 @@
也就是说斜角度链接是不算了, 例如示例二,是三个岛屿,如图:
-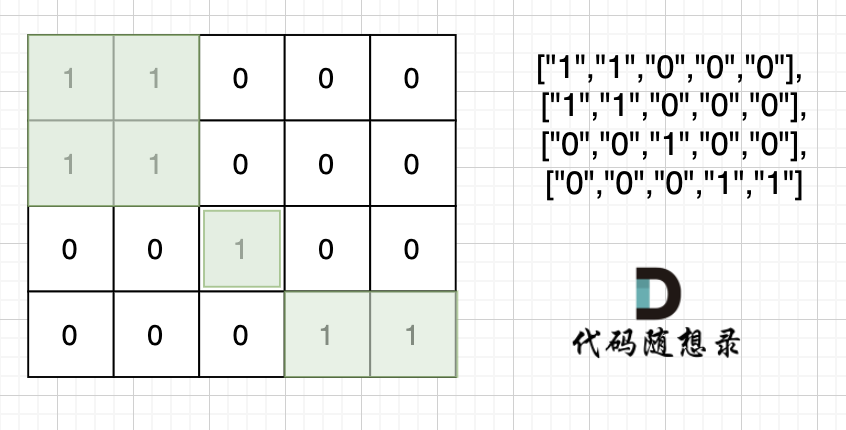
+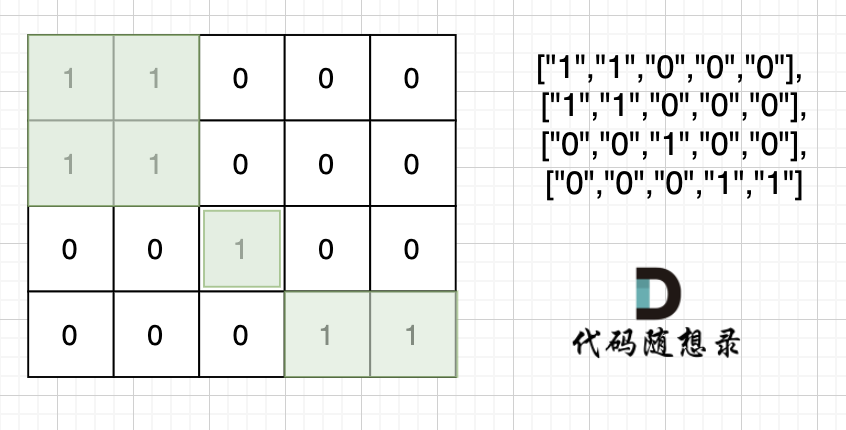
这道题题目是 DFS,BFS,并查集,基础题目。
@@ -50,7 +48,7 @@
如果从队列拿出节点,再去标记这个节点走过,就会发生下图所示的结果,会导致很多节点重复加入队列。
-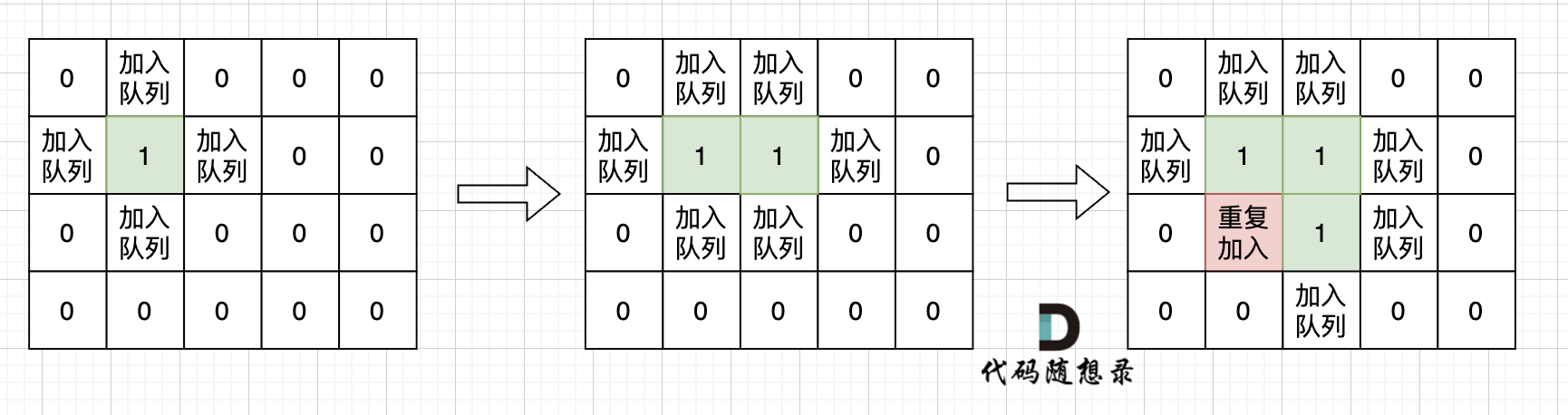
+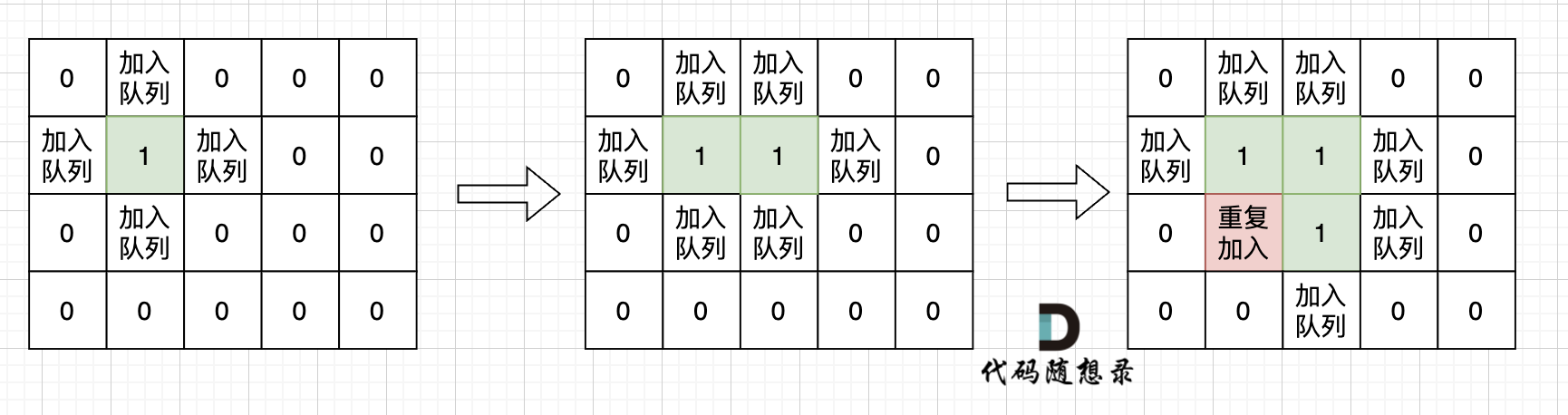
超时写法 (从队列中取出节点再标记)
@@ -408,9 +406,5 @@ impl Solution {
}
}
```
-
-
-  -
```
diff --git "a/problems/0200.\345\262\233\345\261\277\346\225\260\351\207\217.\346\267\261\346\220\234\347\211\210.md" "b/problems/0200.\345\262\233\345\261\277\346\225\260\351\207\217.\346\267\261\346\220\234\347\211\210.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 18442943ad..128007bb62
--- "a/problems/0200.\345\262\233\345\261\277\346\225\260\351\207\217.\346\267\261\346\220\234\347\211\210.md"
+++ "b/problems/0200.\345\262\233\345\261\277\346\225\260\351\207\217.\346\267\261\346\220\234\347\211\210.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
```
diff --git "a/problems/0200.\345\262\233\345\261\277\346\225\260\351\207\217.\346\267\261\346\220\234\347\211\210.md" "b/problems/0200.\345\262\233\345\261\277\346\225\260\351\207\217.\346\267\261\346\220\234\347\211\210.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 18442943ad..128007bb62
--- "a/problems/0200.\345\262\233\345\261\277\346\225\260\351\207\217.\346\267\261\346\220\234\347\211\210.md"
+++ "b/problems/0200.\345\262\233\345\261\277\346\225\260\351\207\217.\346\267\261\346\220\234\347\211\210.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 200. 岛屿数量
@@ -14,7 +12,7 @@
此外,你可以假设该网格的四条边均被水包围。
-
+
提示:
@@ -29,7 +27,7 @@
也就是说斜角度链接是不算了, 例如示例二,是三个岛屿,如图:
-
+
这道题题目是 DFS,BFS,并查集,基础题目。
@@ -37,7 +35,7 @@
在遇到标记过的陆地节点和海洋节点的时候直接跳过。 这样计数器就是最终岛屿的数量。
-那么如果把节点陆地所能遍历到的陆地都标记上呢,就可以使用 DFS,BFS或者并查集。
+那么如何把节点陆地所能遍历到的陆地都标记上呢,就可以使用 DFS,BFS或者并查集。
### 深度优先搜索
@@ -463,7 +461,3 @@ impl Solution {
}
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0202.\345\277\253\344\271\220\346\225\260.md" "b/problems/0202.\345\277\253\344\271\220\346\225\260.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 719672a281..fdcadee97c
--- "a/problems/0202.\345\277\253\344\271\220\346\225\260.md"
+++ "b/problems/0202.\345\277\253\344\271\220\346\225\260.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0202.\345\277\253\344\271\220\346\225\260.md" "b/problems/0202.\345\277\253\344\271\220\346\225\260.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 719672a281..fdcadee97c
--- "a/problems/0202.\345\277\253\344\271\220\346\225\260.md"
+++ "b/problems/0202.\345\277\253\344\271\220\346\225\260.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
@@ -533,8 +531,28 @@ public class Solution {
}
}
```
-
-
-  -
+
+### Ruby:
+
+```ruby
+# @param {Integer} n
+# @return {Boolean}
+def is_happy(n)
+ @occurred_nums = Set.new
+
+ while true
+ n = next_value(n)
+
+ return true if n == 1
+
+ return false if @occurred_nums.include?(n)
+
+ @occurred_nums << n
+ end
+end
+
+def next_value(n)
+ n.to_s.chars.sum { |char| char.to_i ** 2 }
+end
+```
diff --git "a/problems/0203.\347\247\273\351\231\244\351\223\276\350\241\250\345\205\203\347\264\240.md" "b/problems/0203.\347\247\273\351\231\244\351\223\276\350\241\250\345\205\203\347\264\240.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index d6d7e6c2ef..ffe04a5b07
--- "a/problems/0203.\347\247\273\351\231\244\351\223\276\350\241\250\345\205\203\347\264\240.md"
+++ "b/problems/0203.\347\247\273\351\231\244\351\223\276\350\241\250\345\205\203\347\264\240.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-
-
+
+### Ruby:
+
+```ruby
+# @param {Integer} n
+# @return {Boolean}
+def is_happy(n)
+ @occurred_nums = Set.new
+
+ while true
+ n = next_value(n)
+
+ return true if n == 1
+
+ return false if @occurred_nums.include?(n)
+
+ @occurred_nums << n
+ end
+end
+
+def next_value(n)
+ n.to_s.chars.sum { |char| char.to_i ** 2 }
+end
+```
diff --git "a/problems/0203.\347\247\273\351\231\244\351\223\276\350\241\250\345\205\203\347\264\240.md" "b/problems/0203.\347\247\273\351\231\244\351\223\276\350\241\250\345\205\203\347\264\240.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index d6d7e6c2ef..ffe04a5b07
--- "a/problems/0203.\347\247\273\351\231\244\351\223\276\350\241\250\345\205\203\347\264\240.md"
+++ "b/problems/0203.\347\247\273\351\231\244\351\223\276\350\241\250\345\205\203\347\264\240.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
@@ -36,11 +34,11 @@
这里以链表 1 4 2 4 来举例,移除元素4。
-
+
如果使用C,C++编程语言的话,不要忘了还要从内存中删除这两个移除的节点, 清理节点内存之后如图:
-
+
**当然如果使用java ,python的话就不用手动管理内存了。**
@@ -58,16 +56,16 @@
来看第一种操作:直接使用原来的链表来进行移除。
-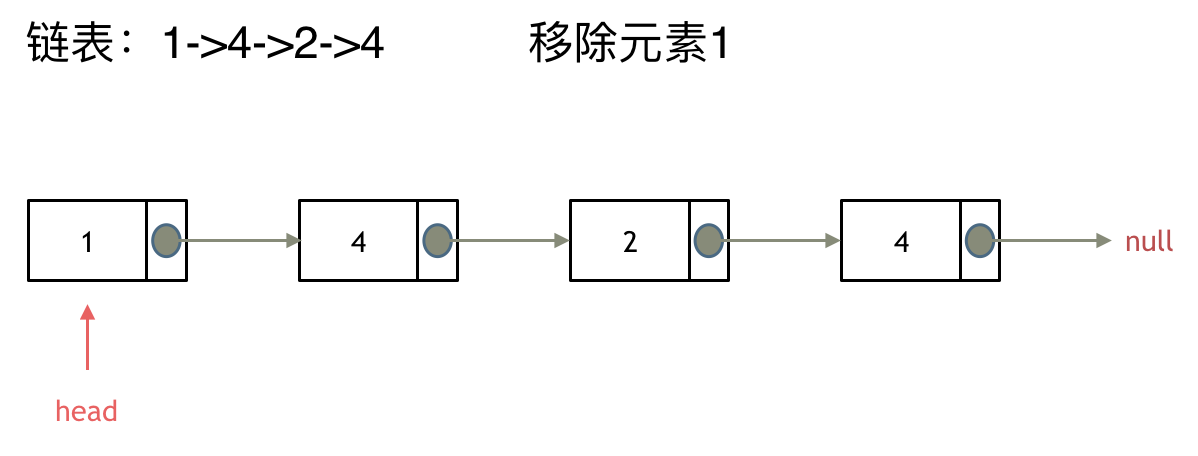
+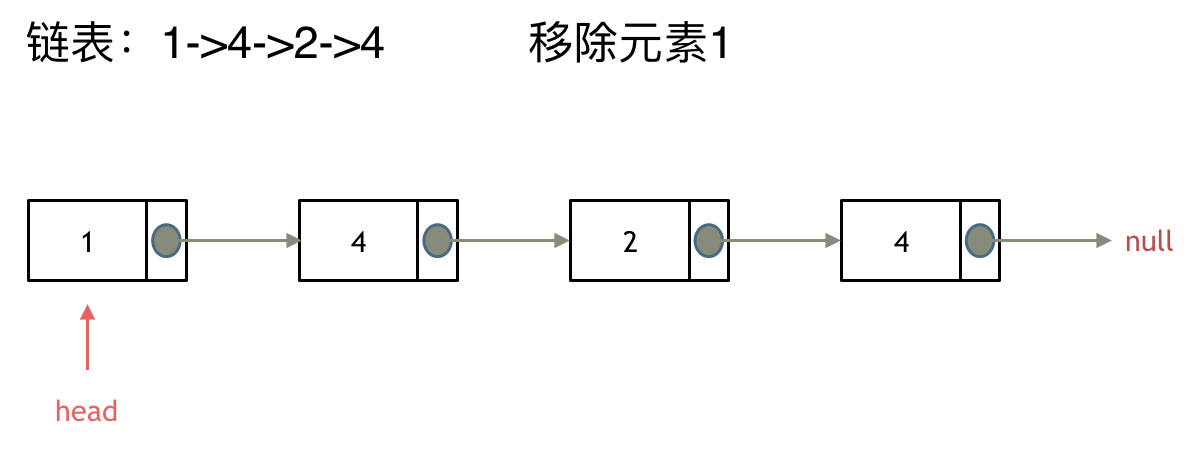
移除头结点和移除其他节点的操作是不一样的,因为链表的其他节点都是通过前一个节点来移除当前节点,而头结点没有前一个节点。
所以头结点如何移除呢,其实只要将头结点向后移动一位就可以,这样就从链表中移除了一个头结点。
-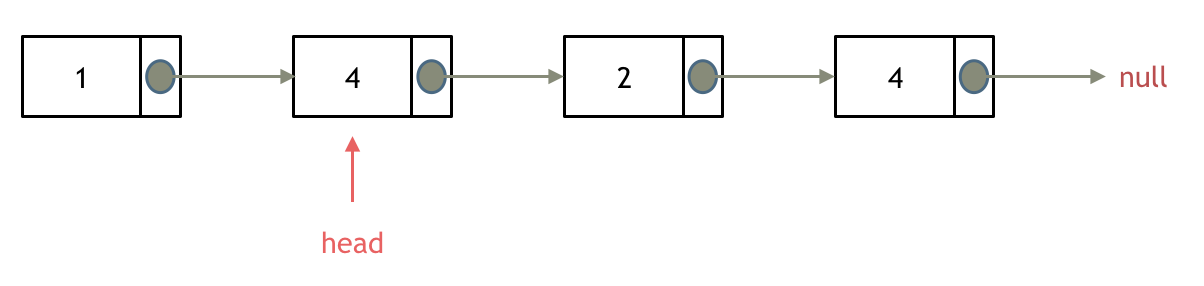
+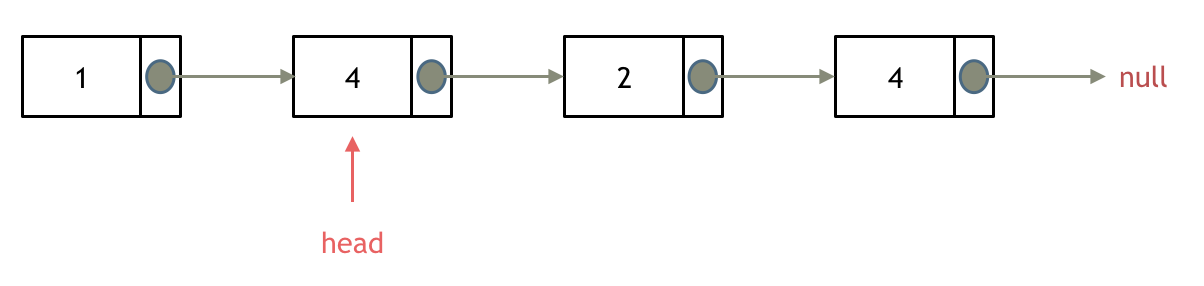
依然别忘将原头结点从内存中删掉。
-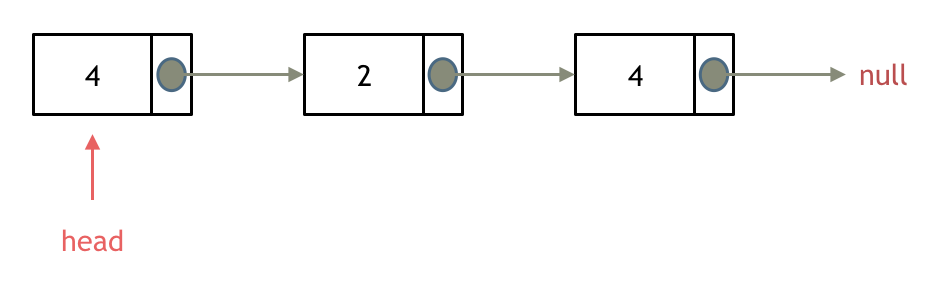
+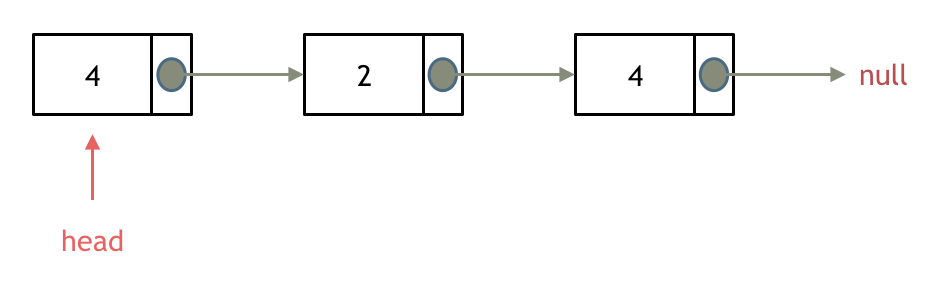
这样移除了一个头结点,是不是发现,在单链表中移除头结点 和 移除其他节点的操作方式是不一样,其实在写代码的时候也会发现,需要单独写一段逻辑来处理移除头结点的情况。
@@ -78,7 +76,7 @@
来看看如何设置一个虚拟头。依然还是在这个链表中,移除元素1。
-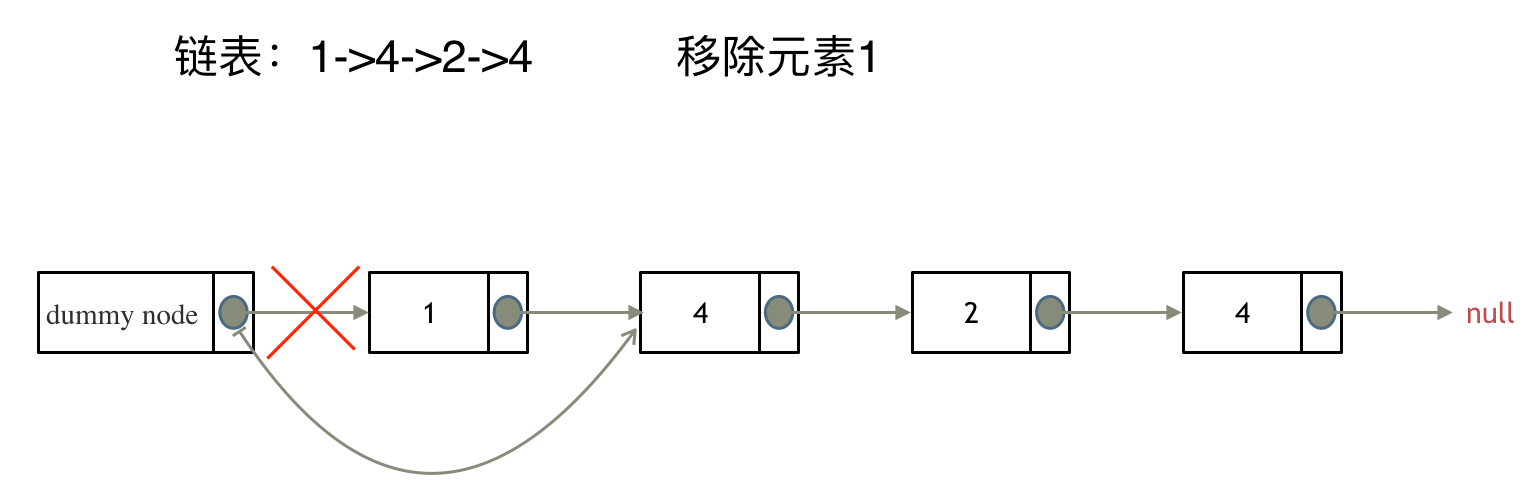
+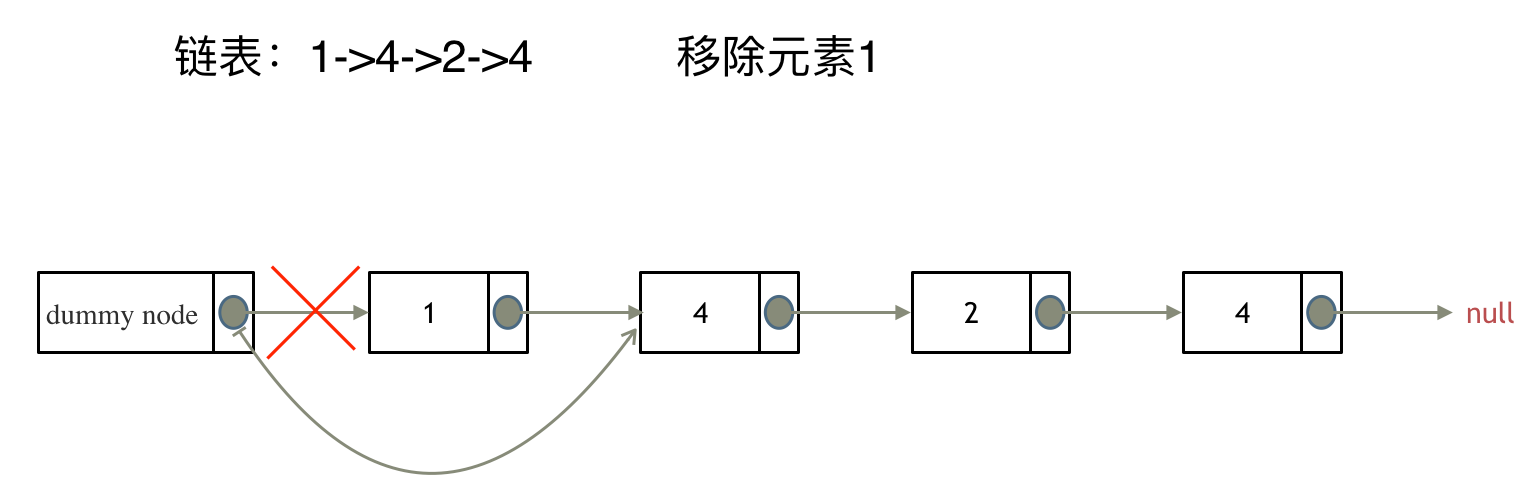
这里来给链表添加一个虚拟头结点为新的头结点,此时要移除这个旧头结点元素1。
@@ -149,7 +147,35 @@ public:
* 时间复杂度: O(n)
* 空间复杂度: O(1)
+**也可以通过递归的思路解决本题:**
+基础情况:对于空链表,不需要移除元素。
+
+递归情况:首先检查头节点的值是否为 val,如果是则移除头节点,答案即为在头节点的后续节点上递归的结果;如果头节点的值不为 val,则答案为头节点与在头节点的后续节点上递归得到的新链表拼接的结果。
+
+```CPP
+class Solution {
+public:
+ ListNode* removeElements(ListNode* head, int val) {
+ // 基础情况:空链表
+ if (head == nullptr) {
+ return nullptr;
+ }
+
+ // 递归处理
+ if (head->val == val) {
+ ListNode* newHead = removeElements(head->next, val);
+ delete head;
+ return newHead;
+ } else {
+ head->next = removeElements(head->next, val);
+ return head;
+ }
+ }
+};
+```
+* 时间复杂度:O(n)
+* 空间复杂度:O(n)
## 其他语言版本
@@ -224,9 +250,10 @@ struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val){
### Java:
+用原来的链表操作:
```java
/**
- * 添加虚节点方式
+ * 方法1
* 时间复杂度 O(n)
* 空间复杂度 O(1)
* @param head
@@ -234,25 +261,22 @@ struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val){
* @return
*/
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
- if (head == null) {
- return head;
+ while(head!=null && head.val==val) {
+ head = head.next;
}
- // 因为删除可能涉及到头节点,所以设置dummy节点,统一操作
- ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1, head);
- ListNode pre = dummy;
- ListNode cur = head;
- while (cur != null) {
- if (cur.val == val) {
- pre.next = cur.next;
+ ListNode curr = head;
+ while(curr!=null && curr.next !=null) {
+ if(curr.next.val == val){
+ curr.next = curr.next.next;
} else {
- pre = cur;
+ curr = curr.next;
}
- cur = cur.next;
}
- return dummy.next;
+ return head;
}
+
/**
- * 不添加虚拟节点方式
+ * 方法1
* 时间复杂度 O(n)
* 空间复杂度 O(1)
* @param head
@@ -280,8 +304,13 @@ public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
}
return head;
}
+
+```
+
+设置一个虚拟头结点:
+
+```java
/**
- * 不添加虚拟节点and pre Node方式
* 时间复杂度 O(n)
* 空间复杂度 O(1)
* @param head
@@ -289,17 +318,51 @@ public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
* @return
*/
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
- while(head!=null && head.val==val){
- head = head.next;
+ // 设置一个虚拟的头结点
+ ListNode dummy = new ListNode();
+ dummy.next = head;
+
+ ListNode cur = dummy;
+ while (cur.next != null) {
+ if (cur.next.val == val) {
+ cur.next = cur.next.next;
+ } else {
+ cur = cur.next;
+ }
}
- ListNode curr = head;
- while(curr!=null){
- while(curr.next!=null && curr.next.val == val){
- curr.next = curr.next.next;
+ return dummy.next;
+}
+
+```
+
+递归
+
+```java
+/**
+ * 时间复杂度 O(n)
+ * 空间复杂度 O(n)
+ * @param head
+ * @param val
+ * @return
+ */
+class Solution {
+ public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
+ if (head == null) {
+ return head;
}
- curr = curr.next;
+
+ // 假设 removeElements() 返回后面完整的已经去掉val节点的子链表
+ // 在当前递归层用当前节点接住后面的子链表
+ // 随后判断当前层的node是否需要被删除,如果是,就返回
+ // 也可以先判断是否需要删除当前node,但是这样条件语句会比较不好想
+ head.next = removeElements(head.next, val);
+ if (head.val == val) {
+ return head.next;
+ }
+ return head;
+
+ // 实际上就是还原一个从尾部开始重新构建链表的过程
}
- return head;
}
```
@@ -497,27 +560,67 @@ func removeElements(_ head: ListNode?, _ val: Int) -> ListNode? {
```php
/**
- * Definition for singly-linked list.
- * type ListNode struct {
- * Val int
- * Next *ListNode
+ * Definition for a singly-linked list.
+ * class ListNode {
+ * public $val = 0;
+ * public $next = null;
+ * function __construct($val = 0, $next = null) {
+ * $this->val = $val;
+ * $this->next = $next;
+ * }
* }
*/
- // 虚拟头+双指针
-func removeElements(head *ListNode, val int) *ListNode {
- dummyHead := &ListNode{}
- dummyHead.Next = head
- pred := dummyHead
- cur := head
- for cur != nil {
- if cur.Val == val {
- pred.Next = cur.Next
- } else {
- pred = cur
+
+//版本一(在原链表上直接删除):
+class Solution {
+
+ /**
+ * @param ListNode $head
+ * @param Integer $val
+ * @return ListNode
+ */
+ function removeElements($head, $val)
+ {
+ if ($head == null) {
+ return null;
}
- cur = cur.Next
+
+ $now = $head;
+ while ($now->next != null) {
+ if ($now->next->val == $val) {
+ $now->next = $now->next->next;
+ } else {
+ $now = $now->next;
+ }
+ }
+ if ($head->val == $val) {
+ return $head->next;
+ }
+ return $head;
+ }
+}
+
+//版本二(虚拟头结点方式):
+class Solution {
+
+ /**
+ * @param ListNode $head
+ * @param Integer $val
+ * @return ListNode
+ */
+ function removeElements($head, $val)
+ {
+ $dummyHead = new ListNode(0, $head);
+ $now = $dummyHead;
+ while ($now->next != null){
+ if ($now->next->val == $val) {
+ $now->next = $now->next->next;
+ } else {
+ $now = $now->next;
+ }
+ }
+ return $dummyHead->next;
}
- return dummyHead.Next
}
```
@@ -545,7 +648,7 @@ impl Solution {
let mut dummyHead = Box::new(ListNode::new(0));
dummyHead.next = head;
let mut cur = dummyHead.as_mut();
- // 使用take()替换std::men::replace(&mut node.next, None)达到相同的效果,并且更普遍易读
+ // 使用take()替换std::mem::replace(&mut node.next, None)达到相同的效果,并且更普遍易读
while let Some(nxt) = cur.next.take() {
if nxt.val == val {
cur.next = nxt.next;
@@ -663,9 +766,43 @@ public class Solution
}
}
```
+### Ruby#
+
+```ruby
+# 定义链表节点
+class ListNode
+ attr_accessor :val, :next
+ def initialize(val = 0, _next = nil)
+ @val = val
+ @next = _next
+ end
+end
+
+# 删除链表中值为 val 的节点
+def remove_elements(head, val)
+ # 创建一个虚拟头节点,这样可以简化删除头节点的处理
+ # 虚拟头节点的值为 0,指向当前链表的头节点
+ dummy = ListNode.new(0)
+ dummy.next = head
+
+ # 初始化当前节点为虚拟头节点
+ current = dummy
+
+ # 遍历链表,直到当前节点的下一个节点为空
+ while current.next
+ # 如果当前节点的下一个节点的值等于 val
+ if current.next.val == val
+ # 跳过该节点,即将当前节点的 next 指向下一个节点的 next
+ current.next = current.next.next
+ else
+ # 否则继续遍历,当前节点向前移动
+ current = current.next
+ end
+ end
+
+ # 返回删除 val 后的新链表的头节点,虚拟头节点的 next 就是新的头节点
+ dummy.next
+end
-
-
-  -
+```
diff --git "a/problems/0205.\345\220\214\346\236\204\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md" "b/problems/0205.\345\220\214\346\236\204\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index e07ab746d9..ba255e0685
--- "a/problems/0205.\345\220\214\346\236\204\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md"
+++ "b/problems/0205.\345\220\214\346\236\204\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+```
diff --git "a/problems/0205.\345\220\214\346\236\204\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md" "b/problems/0205.\345\220\214\346\236\204\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index e07ab746d9..ba255e0685
--- "a/problems/0205.\345\220\214\346\236\204\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md"
+++ "b/problems/0205.\345\220\214\346\236\204\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 205. 同构字符串
@@ -179,8 +177,4 @@ function isIsomorphic(s: string, t: string): boolean {
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0206.\347\277\273\350\275\254\351\223\276\350\241\250.md" "b/problems/0206.\347\277\273\350\275\254\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 5a57939af2..e49037dd2b
--- "a/problems/0206.\347\277\273\350\275\254\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
+++ "b/problems/0206.\347\277\273\350\275\254\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0206.\347\277\273\350\275\254\351\223\276\350\241\250.md" "b/problems/0206.\347\277\273\350\275\254\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 5a57939af2..e49037dd2b
--- "a/problems/0206.\347\277\273\350\275\254\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
+++ "b/problems/0206.\347\277\273\350\275\254\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
> 反转链表的写法很简单,一些同学甚至可以背下来但过一阵就忘了该咋写,主要是因为没有理解真正的反转过程。
@@ -29,7 +27,7 @@
其实只需要改变链表的next指针的指向,直接将链表反转 ,而不用重新定义一个新的链表,如图所示:
-
+
之前链表的头节点是元素1, 反转之后头结点就是元素5 ,这里并没有添加或者删除节点,仅仅是改变next指针的方向。
@@ -37,7 +35,7 @@
我们拿有示例中的链表来举例,如动画所示:(纠正:动画应该是先移动pre,在移动cur)
-
+
首先定义一个cur指针,指向头结点,再定义一个pre指针,初始化为null。
@@ -739,7 +737,3 @@ public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
> 采用这种方法需要注意一点。就是当整个出栈循环结束以后,cur正好指向原来链表的第一个结点,而此时结点1中的next指向的是结点2,因此最后还需要`cur.next = null`
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0207.\350\257\276\347\250\213\350\241\250.md" "b/problems/0207.\350\257\276\347\250\213\350\241\250.md"
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..f992c72b89
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/problems/0207.\350\257\276\347\250\213\350\241\250.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,59 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
+
+拓扑排序指的是一种 解决问题的大体思路, 而具体算法,可能是 广搜 可能是深搜。
+
+大家可能发现 各式各样的解法,纠结哪个是拓扑排序?
+
+只要能在把 有向无环图 进行线性排序 的算法 都可以叫做 拓扑排序。
+
+引用与任务调度,课程安排等等。
+
+
+「拓扑排序」是专门应用于有向图的算法;
+
+把一个 有向无环图 转成 线性的排序 就叫 拓扑排序。
+
+拓扑排序(Kahn 算法,其实就是广度优先遍历的思路)
+
+这道题的做法同样适用于第 210 题。
+
+
+```CPP
+class Solution {
+public:
+ bool canFinish(int numCourses, vector>& prerequisites) {
+ vector inDegree(numCourses, 0);
+ unordered_map> umap;
+ for (int i = 0; i < prerequisites.size(); i++) {
+
+ // prerequisites[i][0] 是 课程入度,prerequisites[i][1] 是课程出度
+ // 即: 上课prerequisites[i][0] 之前,必须先上课prerequisites[i][1]
+ // prerequisites[i][1] -> prerequisites[i][0]
+ inDegree[prerequisites[i][0]]++;//当前课程入度值+1
+ umap[prerequisites[i][1]].push_back(prerequisites[i][0]); // 添加 prerequisites[i][1] 指向的课程
+ }
+ queue que;
+ for (int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++) {
+ if (inDegree[i] == 0) que.push(i); // 所有入度为0,即为 开头课程 加入队列
+ }
+ int count = 0;
+ while (que.size()) {
+ int cur = que.front(); //当前选的课
+ que.pop();
+ count++; // 选课数+1
+ vector courses = umap[cur]; //获取这门课指向的课程,也就是这么课的后续课
+ if (courses.size()) { // 有后续课
+ for (int i = 0; i < courses.size(); i++) {
+ inDegree[courses[i]]--; // 它的后续课的入度-1
+ if (inDegree[courses[i]] == 0) que.push(courses[i]); // 如果入度为0,加入队列
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ if (count == numCourses) return true;
+ return false;
+
+ }
+};
+```
diff --git "a/problems/0209.\351\225\277\345\272\246\346\234\200\345\260\217\347\232\204\345\255\220\346\225\260\347\273\204.md" "b/problems/0209.\351\225\277\345\272\246\346\234\200\345\260\217\347\232\204\345\255\220\346\225\260\347\273\204.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 5934d5e364..c8440c4a67
--- "a/problems/0209.\351\225\277\345\272\246\346\234\200\345\260\217\347\232\204\345\255\220\346\225\260\347\273\204.md"
+++ "b/problems/0209.\351\225\277\345\272\246\346\234\200\345\260\217\347\232\204\345\255\220\346\225\260\347\273\204.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0207.\350\257\276\347\250\213\350\241\250.md" "b/problems/0207.\350\257\276\347\250\213\350\241\250.md"
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..f992c72b89
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/problems/0207.\350\257\276\347\250\213\350\241\250.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,59 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
+
+拓扑排序指的是一种 解决问题的大体思路, 而具体算法,可能是 广搜 可能是深搜。
+
+大家可能发现 各式各样的解法,纠结哪个是拓扑排序?
+
+只要能在把 有向无环图 进行线性排序 的算法 都可以叫做 拓扑排序。
+
+引用与任务调度,课程安排等等。
+
+
+「拓扑排序」是专门应用于有向图的算法;
+
+把一个 有向无环图 转成 线性的排序 就叫 拓扑排序。
+
+拓扑排序(Kahn 算法,其实就是广度优先遍历的思路)
+
+这道题的做法同样适用于第 210 题。
+
+
+```CPP
+class Solution {
+public:
+ bool canFinish(int numCourses, vector>& prerequisites) {
+ vector inDegree(numCourses, 0);
+ unordered_map> umap;
+ for (int i = 0; i < prerequisites.size(); i++) {
+
+ // prerequisites[i][0] 是 课程入度,prerequisites[i][1] 是课程出度
+ // 即: 上课prerequisites[i][0] 之前,必须先上课prerequisites[i][1]
+ // prerequisites[i][1] -> prerequisites[i][0]
+ inDegree[prerequisites[i][0]]++;//当前课程入度值+1
+ umap[prerequisites[i][1]].push_back(prerequisites[i][0]); // 添加 prerequisites[i][1] 指向的课程
+ }
+ queue que;
+ for (int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++) {
+ if (inDegree[i] == 0) que.push(i); // 所有入度为0,即为 开头课程 加入队列
+ }
+ int count = 0;
+ while (que.size()) {
+ int cur = que.front(); //当前选的课
+ que.pop();
+ count++; // 选课数+1
+ vector courses = umap[cur]; //获取这门课指向的课程,也就是这么课的后续课
+ if (courses.size()) { // 有后续课
+ for (int i = 0; i < courses.size(); i++) {
+ inDegree[courses[i]]--; // 它的后续课的入度-1
+ if (inDegree[courses[i]] == 0) que.push(courses[i]); // 如果入度为0,加入队列
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ if (count == numCourses) return true;
+ return false;
+
+ }
+};
+```
diff --git "a/problems/0209.\351\225\277\345\272\246\346\234\200\345\260\217\347\232\204\345\255\220\346\225\260\347\273\204.md" "b/problems/0209.\351\225\277\345\272\246\346\234\200\345\260\217\347\232\204\345\255\220\346\225\260\347\273\204.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 5934d5e364..c8440c4a67
--- "a/problems/0209.\351\225\277\345\272\246\346\234\200\345\260\217\347\232\204\345\255\220\346\225\260\347\273\204.md"
+++ "b/problems/0209.\351\225\277\345\272\246\346\234\200\345\260\217\347\232\204\345\255\220\346\225\260\347\273\204.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 209.长度最小的子数组
@@ -68,7 +66,7 @@ public:
接下来就开始介绍数组操作中另一个重要的方法:**滑动窗口**。
-所谓滑动窗口,**就是不断的调节子序列的起始位置和终止位置,从而得出我们要想的结果**。
+所谓滑动窗口,**就是不断的调节子序列的起始位置和终止位置,从而得出我们想要的结果**。
在暴力解法中,是一个for循环滑动窗口的起始位置,一个for循环为滑动窗口的终止位置,用两个for循环 完成了一个不断搜索区间的过程。
@@ -86,7 +84,7 @@ public:
这里还是以题目中的示例来举例,s=7, 数组是 2,3,1,2,4,3,来看一下查找的过程:
-
+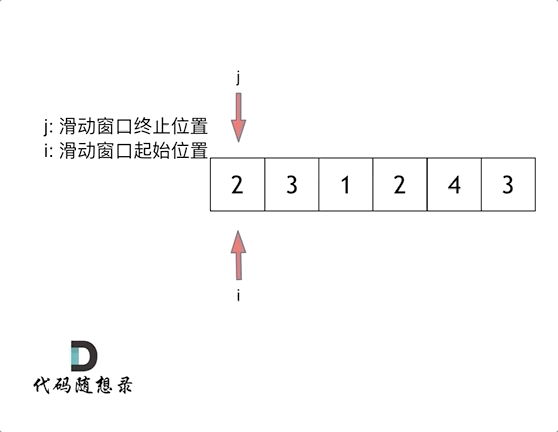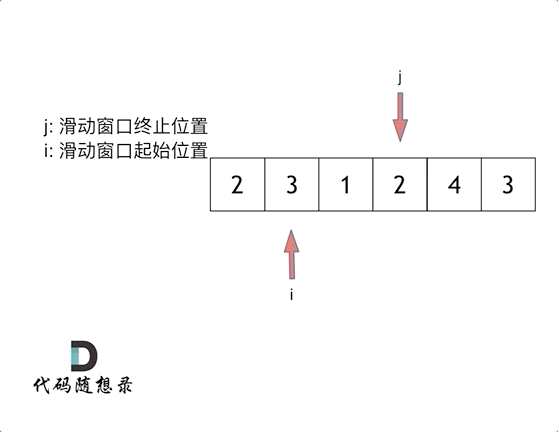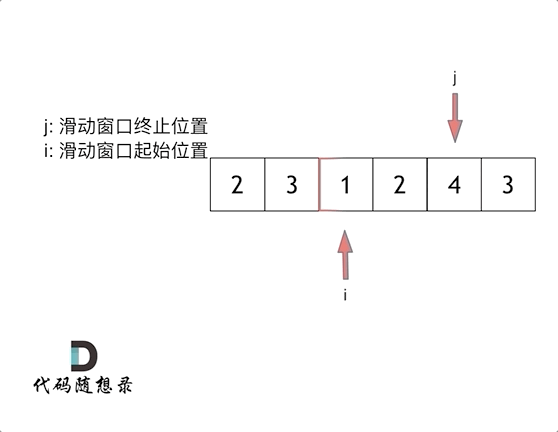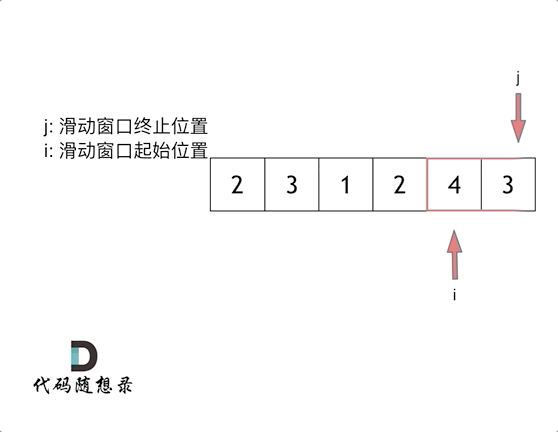
最后找到 4,3 是最短距离。
@@ -106,7 +104,7 @@ public:
解题的关键在于 窗口的起始位置如何移动,如图所示:
-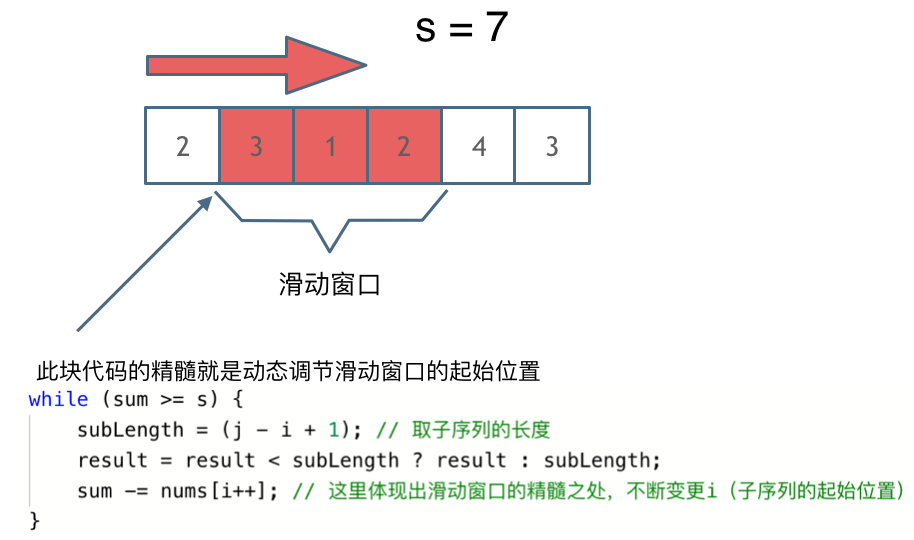
+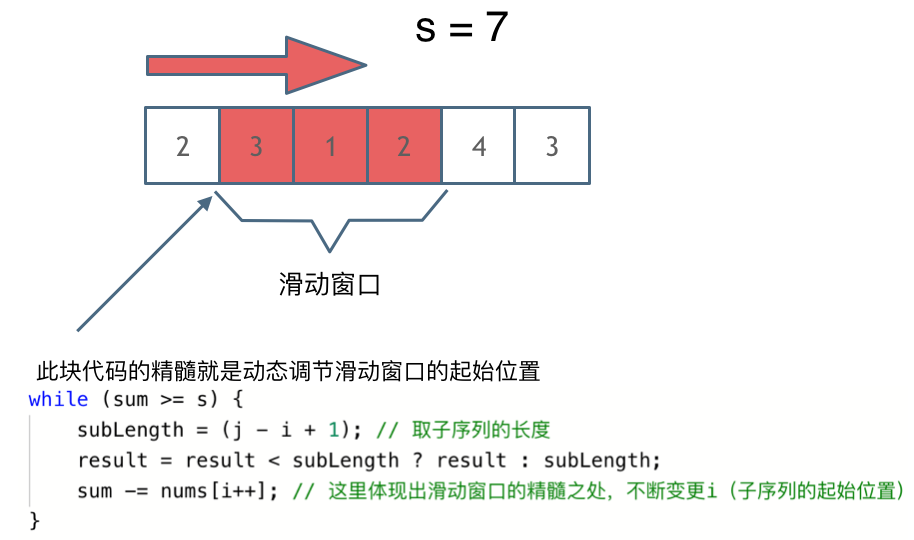
可以发现**滑动窗口的精妙之处在于根据当前子序列和大小的情况,不断调节子序列的起始位置。从而将O(n^2)暴力解法降为O(n)。**
@@ -266,26 +264,25 @@ var minSubArrayLen = function(target, nums) {
};
```
-### Typescript:
+### TypeScript:
```typescript
function minSubArrayLen(target: number, nums: number[]): number {
- let left: number = 0, right: number = 0;
- let res: number = nums.length + 1;
- let sum: number = 0;
- while (right < nums.length) {
- sum += nums[right];
- if (sum >= target) {
- // 不断移动左指针,直到不能再缩小为止
- while (sum - nums[left] >= target) {
- sum -= nums[left++];
- }
- res = Math.min(res, right - left + 1);
- }
- right++;
+ let left: number = 0,
+ res: number = Infinity,
+ subLen: number = 0,
+ sum: number = 0;
+ for (let right: number = 0; right < nums.length; right++) {
+ sum += nums[right];
+ while (sum >= target) {
+ subLen = right - left + 1;
+ res = Math.min(res, subLen);
+ sum -= nums[left];
+ left++;
}
- return res === nums.length + 1 ? 0 : res;
-};
+ }
+ return res === Infinity ? 0 : res;
+}
```
### Swift:
@@ -559,7 +556,3 @@ public class Solution {
}
}
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0210.\350\257\276\347\250\213\350\241\250II.md" "b/problems/0210.\350\257\276\347\250\213\350\241\250II.md"
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..b0d9fe8a9e
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/problems/0210.\350\257\276\347\250\213\350\241\250II.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
+
+```CPP
+class Solution {
+public:
+ vector findOrder(int numCourses, vector>& prerequisites) {
+ vector inDegree(numCourses, 0);
+ vector result;
+ unordered_map> umap;
+ for (int i = 0; i < prerequisites.size(); i++) {
+
+ // prerequisites[i][0] 是 课程入度,prerequisites[i][1] 是课程出度
+ // 即: 上课prerequisites[i][0] 之前,必须先上课prerequisites[i][1]
+ // prerequisites[i][1] -> prerequisites[i][0]
+ inDegree[prerequisites[i][0]]++;//当前课程入度值+1
+ umap[prerequisites[i][1]].push_back(prerequisites[i][0]); // 添加 prerequisites[i][1] 指向的课程
+ }
+ queue que;
+ for (int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++) {
+ if (inDegree[i] == 0) que.push(i); // 所有入度为0,即为 开头课程 加入队列
+ }
+ int count = 0;
+ while (que.size()) {
+ int cur = que.front(); //当前选的课
+ que.pop();
+ count++; // 选课数+1
+ result.push_back(cur);
+ vector courses = umap[cur]; //获取这门课指向的课程,也就是这么课的后续课
+ if (courses.size()) { // 有后续课
+ for (int i = 0; i < courses.size(); i++) {
+ inDegree[courses[i]]--; // 它的后续课的入度-1
+ if (inDegree[courses[i]] == 0) que.push(courses[i]); // 如果入度为0,加入队列
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ if (count == numCourses) return result;
+ else return vector();
+ }
+};
+```
diff --git "a/problems/0213.\346\211\223\345\256\266\345\212\253\350\210\215II.md" "b/problems/0213.\346\211\223\345\256\266\345\212\253\350\210\215II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 385c58675e..6f2fdd0610
--- "a/problems/0213.\346\211\223\345\256\266\345\212\253\350\210\215II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0213.\346\211\223\345\256\266\345\212\253\350\210\215II.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0210.\350\257\276\347\250\213\350\241\250II.md" "b/problems/0210.\350\257\276\347\250\213\350\241\250II.md"
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..b0d9fe8a9e
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/problems/0210.\350\257\276\347\250\213\350\241\250II.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
+
+```CPP
+class Solution {
+public:
+ vector findOrder(int numCourses, vector>& prerequisites) {
+ vector inDegree(numCourses, 0);
+ vector result;
+ unordered_map> umap;
+ for (int i = 0; i < prerequisites.size(); i++) {
+
+ // prerequisites[i][0] 是 课程入度,prerequisites[i][1] 是课程出度
+ // 即: 上课prerequisites[i][0] 之前,必须先上课prerequisites[i][1]
+ // prerequisites[i][1] -> prerequisites[i][0]
+ inDegree[prerequisites[i][0]]++;//当前课程入度值+1
+ umap[prerequisites[i][1]].push_back(prerequisites[i][0]); // 添加 prerequisites[i][1] 指向的课程
+ }
+ queue que;
+ for (int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++) {
+ if (inDegree[i] == 0) que.push(i); // 所有入度为0,即为 开头课程 加入队列
+ }
+ int count = 0;
+ while (que.size()) {
+ int cur = que.front(); //当前选的课
+ que.pop();
+ count++; // 选课数+1
+ result.push_back(cur);
+ vector courses = umap[cur]; //获取这门课指向的课程,也就是这么课的后续课
+ if (courses.size()) { // 有后续课
+ for (int i = 0; i < courses.size(); i++) {
+ inDegree[courses[i]]--; // 它的后续课的入度-1
+ if (inDegree[courses[i]] == 0) que.push(courses[i]); // 如果入度为0,加入队列
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ if (count == numCourses) return result;
+ else return vector();
+ }
+};
+```
diff --git "a/problems/0213.\346\211\223\345\256\266\345\212\253\350\210\215II.md" "b/problems/0213.\346\211\223\345\256\266\345\212\253\350\210\215II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 385c58675e..6f2fdd0610
--- "a/problems/0213.\346\211\223\345\256\266\345\212\253\350\210\215II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0213.\346\211\223\345\256\266\345\212\253\350\210\215II.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 213.打家劫舍II
@@ -44,15 +42,15 @@
* 情况一:考虑不包含首尾元素
-
+
* 情况二:考虑包含首元素,不包含尾元素
-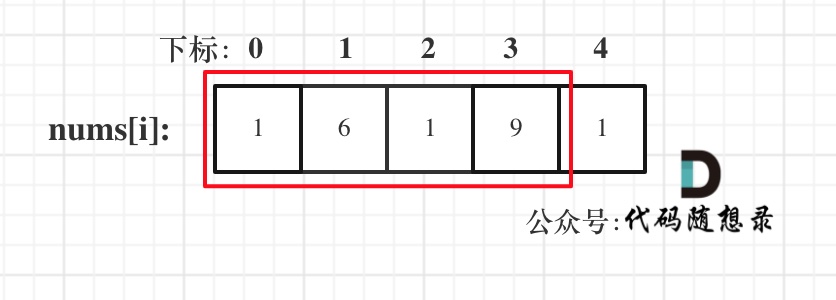
+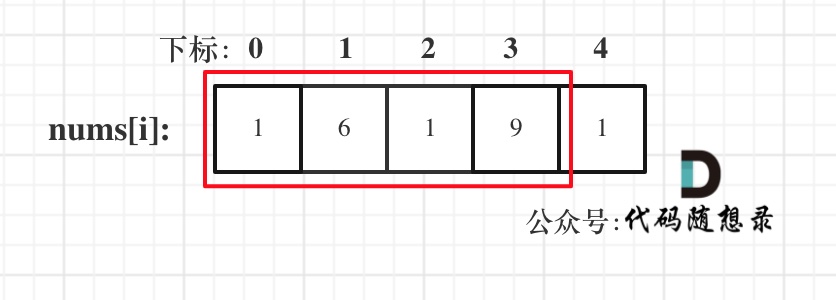
* 情况三:考虑包含尾元素,不包含首元素
-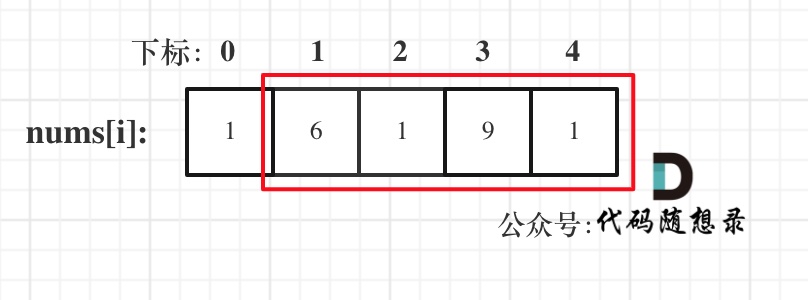
+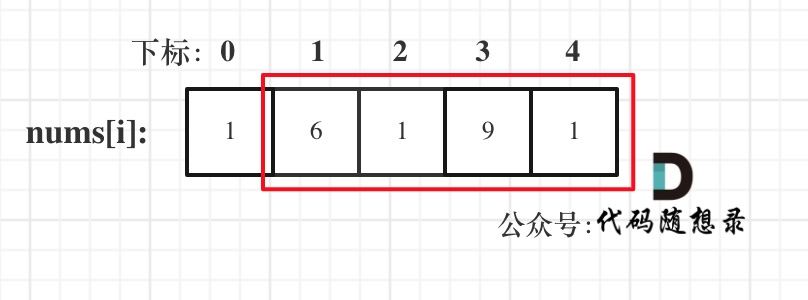
**注意我这里用的是"考虑"**,例如情况三,虽然是考虑包含尾元素,但不一定要选尾部元素! 对于情况三,取nums[1] 和 nums[3]就是最大的。
@@ -308,6 +306,34 @@ function robRange(nums: number[], start: number, end: number): number {
}
```
+### C
+
+```c
+#define max(a, b) ((a) > (b) ? (a) : (b))
+
+// 198.打家劫舍的逻辑
+int robRange(int* nums, int start, int end, int numsSize) {
+ if (end == start) return nums[start];
+ int dp[numsSize];
+ dp[start] = nums[start];
+ dp[start + 1] = max(nums[start], nums[start + 1]);
+ for (int i = start + 2; i <= end; i++) {
+ dp[i] = max(dp[i - 2] + nums[i], dp[i - 1]);
+ }
+ return dp[end];
+}
+
+int rob(int* nums, int numsSize) {
+ if (numsSize == 0) return 0;
+ if (numsSize == 1) return nums[0];
+ int result1 = robRange(nums, 0, numsSize - 2, numsSize); // 情况二
+ int result2 = robRange(nums, 1, numsSize - 1, numsSize); // 情况三
+ return max(result1, result2);
+}
+```
+
+
+
### Rust:
```rust
@@ -339,8 +365,3 @@ impl Solution {
```
-
-
-  -
-
diff --git "a/problems/0216.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214III.md" "b/problems/0216.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214III.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index ac28f9fcfa..5ef5b5e67c
--- "a/problems/0216.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214III.md"
+++ "b/problems/0216.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214III.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0216.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214III.md" "b/problems/0216.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214III.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index ac28f9fcfa..5ef5b5e67c
--- "a/problems/0216.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214III.md"
+++ "b/problems/0216.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214III.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
@@ -47,7 +45,7 @@
选取过程如图:
-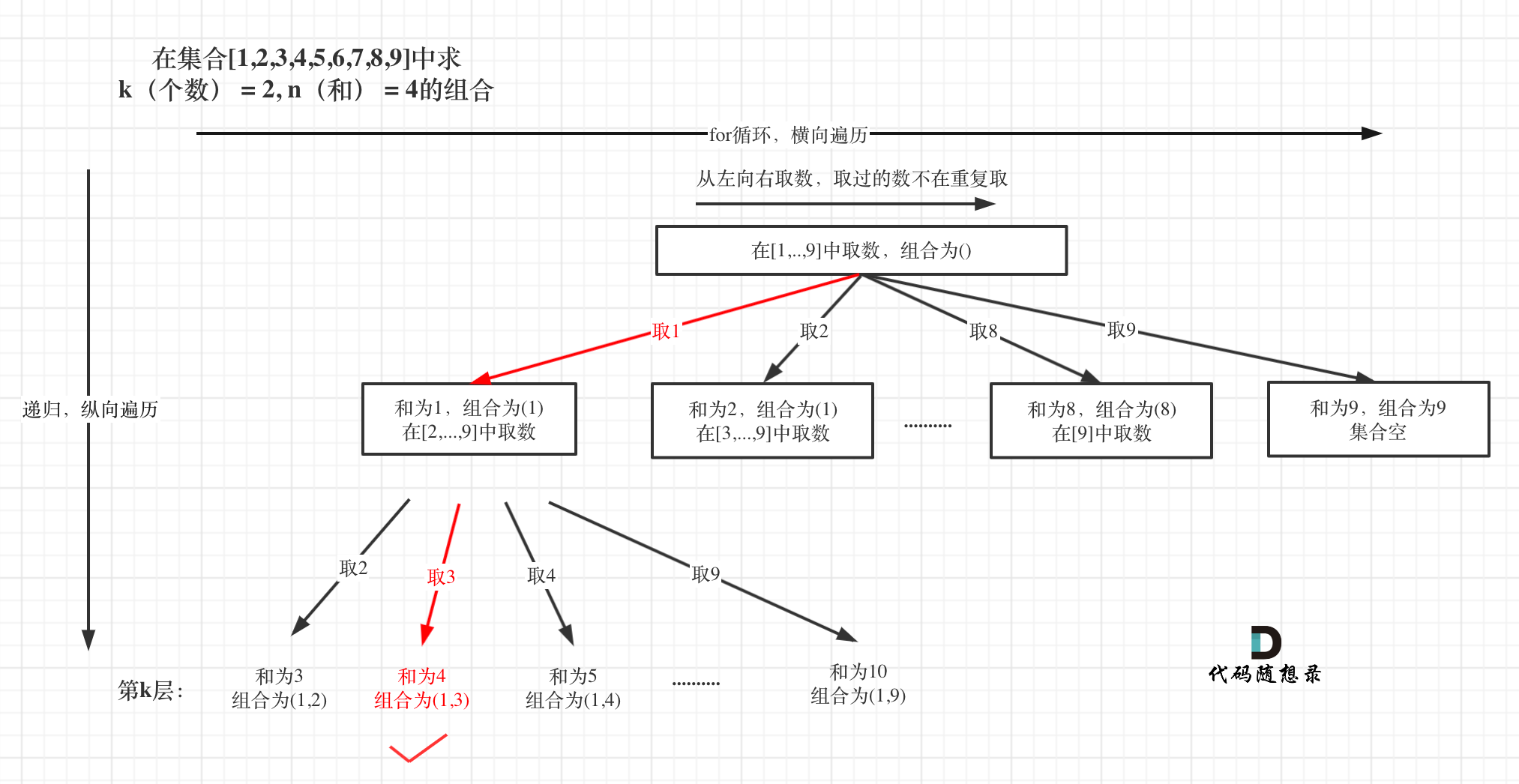
+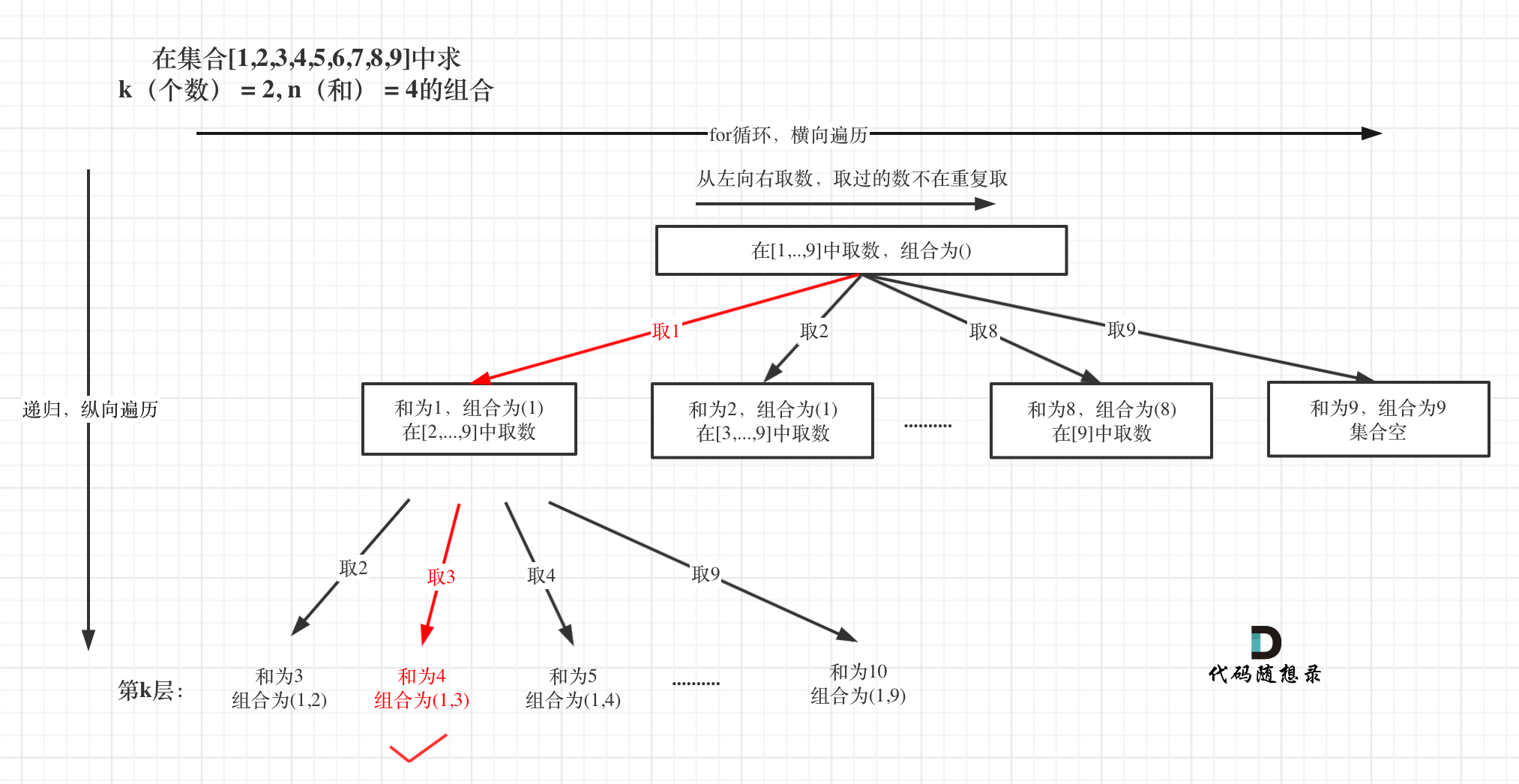
图中,可以看出,只有最后取到集合(1,3)和为4 符合条件。
@@ -110,7 +108,7 @@ if (path.size() == k) {
本题和[77. 组合](https://programmercarl.com/0077.组合.html)区别之一就是集合固定的就是9个数[1,...,9],所以for循环固定i<=9
如图:
-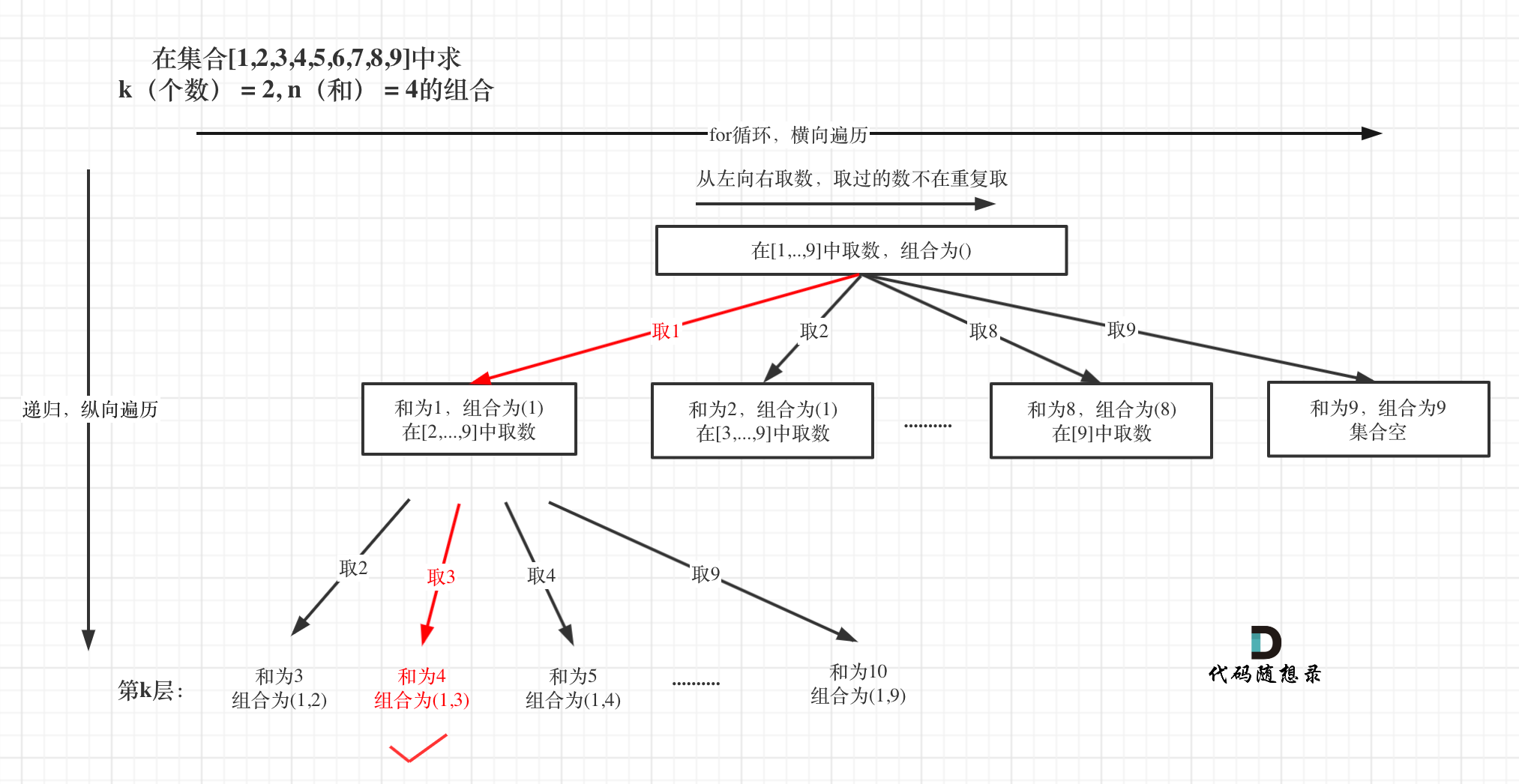
+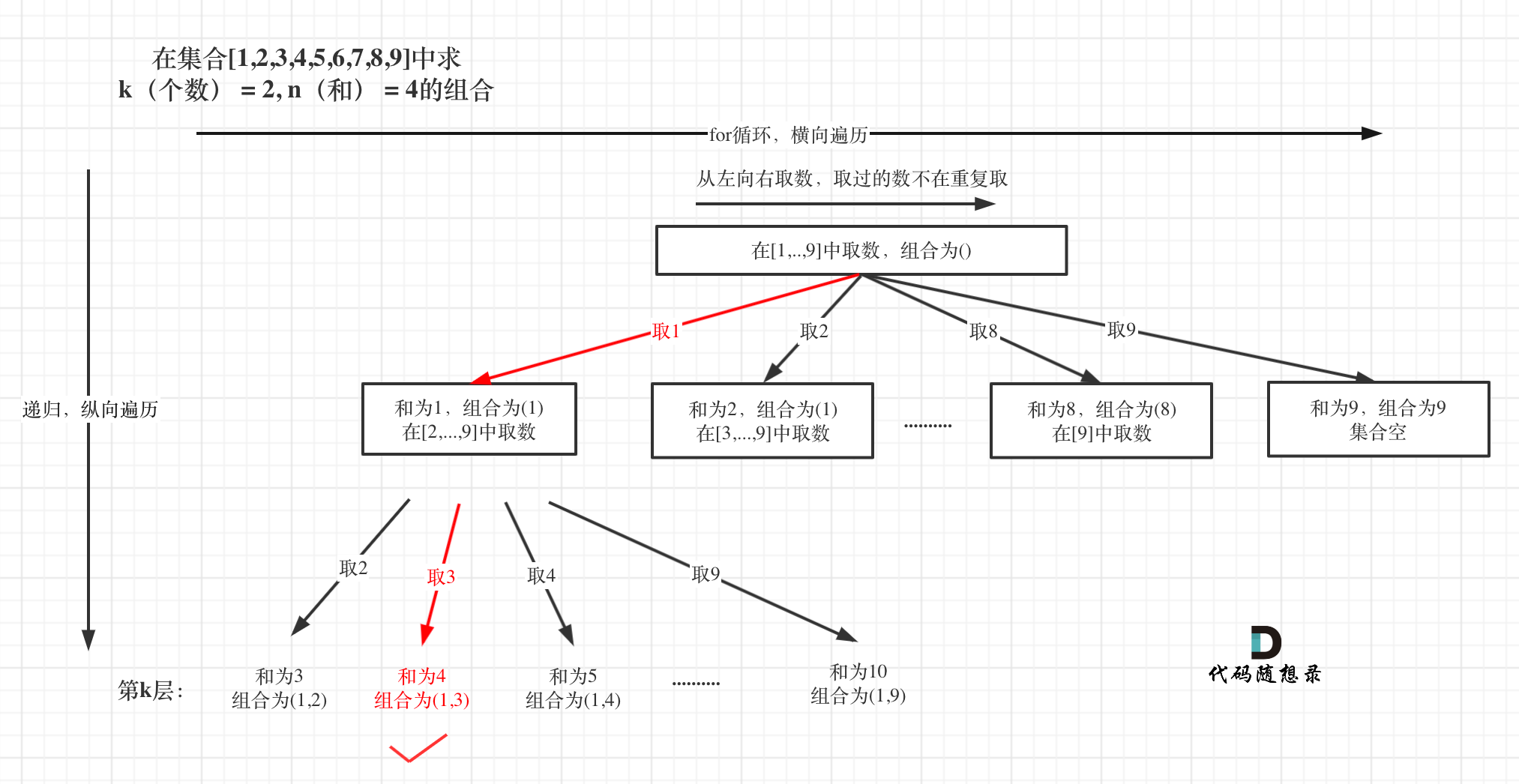
处理过程就是 path收集每次选取的元素,相当于树型结构里的边,sum来统计path里元素的总和。
@@ -168,7 +166,7 @@ public:
这道题目,剪枝操作其实是很容易想到了,想必大家看上面的树形图的时候已经想到了。
如图:
-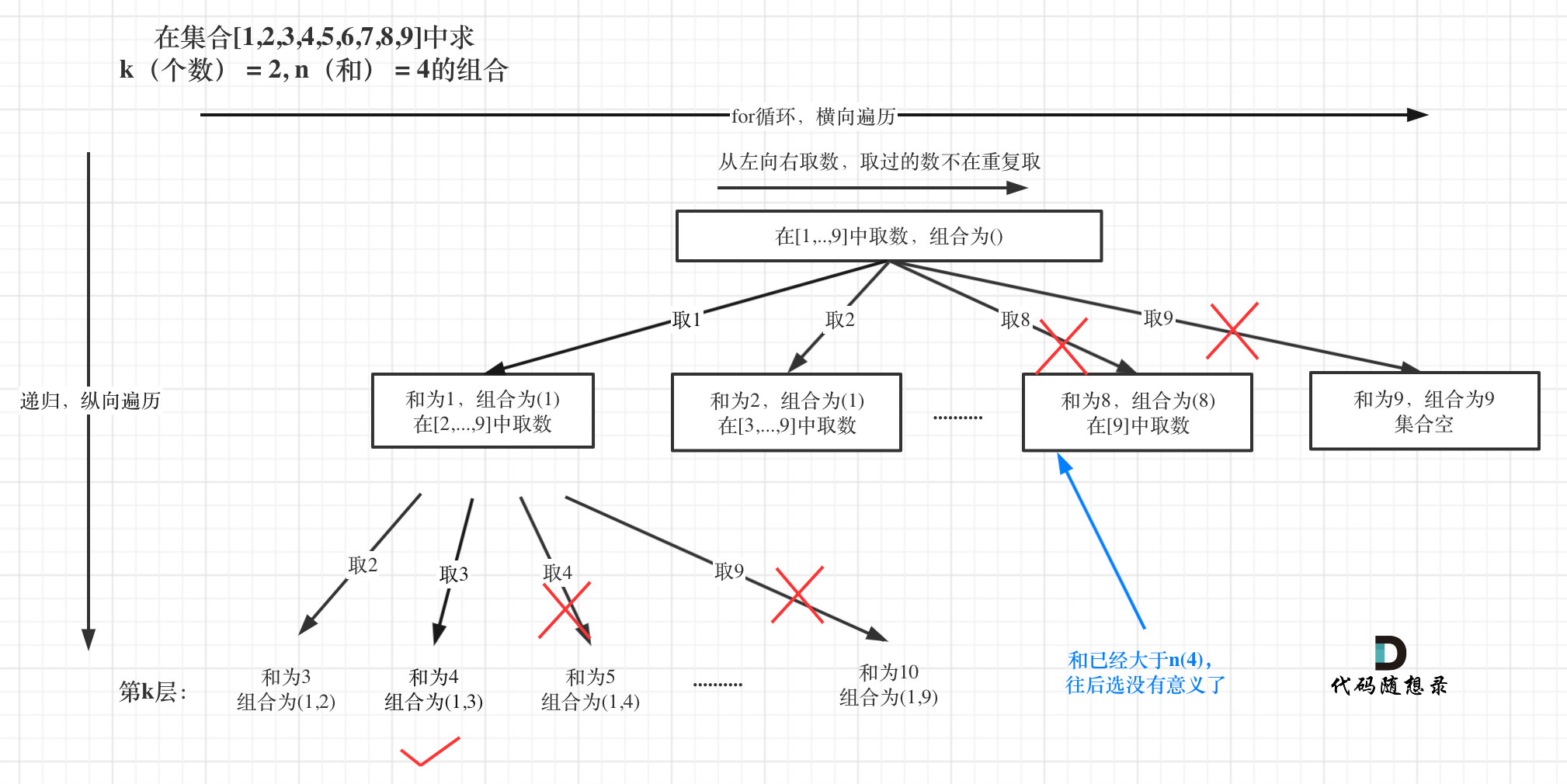
+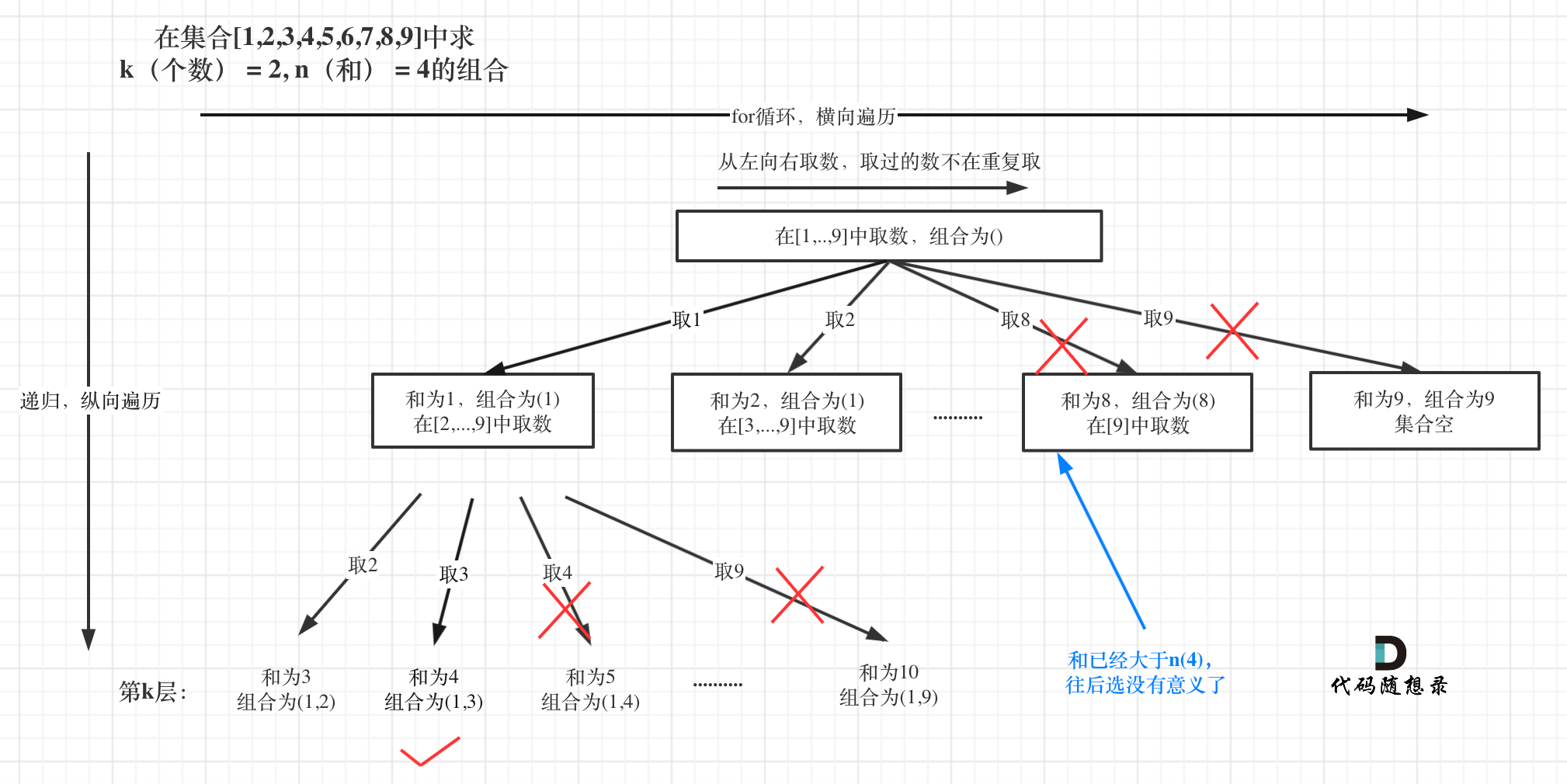
已选元素总和如果已经大于n(图中数值为4)了,那么往后遍历就没有意义了,直接剪掉。
@@ -367,7 +365,7 @@ class Solution:
def backtracking(self, targetSum, k, currentSum, startIndex, path, result):
if currentSum > targetSum: # 剪枝操作
- return # 如果path的长度等于k但currentSum不等于targetSum,则直接返回
+ return # 如果currentSum已经超过targetSum,则直接返回
if len(path) == k:
if currentSum == targetSum:
result.append(path[:])
@@ -417,6 +415,7 @@ func dfs(k, n int, start int, sum int) {
```
### JavaScript
+- 未剪枝:
```js
/**
@@ -424,32 +423,74 @@ func dfs(k, n int, start int, sum int) {
* @param {number} n
* @return {number[][]}
*/
-var combinationSum3 = function(k, n) {
- let res = [];
- let path = [];
- let sum = 0;
- const dfs = (path,index) => {
- // 剪枝操作
- if (sum > n){
- return
- }
- if (path.length == k) {
- if(sum == n){
- res.push([...path]);
- return
- }
- }
- for (let i = index; i <= 9 - (k-path.length) + 1;i++) {
- path.push(i);
- sum = sum + i;
- index += 1;
- dfs(path,index);
- sum -= i
- path.pop()
- }
+var combinationSum3 = function (k, n) {
+ // 回溯法
+ let result = [],
+ path = [];
+ const backtracking = (_k, targetSum, sum, startIndex) => {
+ // 终止条件
+ if (path.length === _k) {
+ if (sum === targetSum) {
+ result.push(path.slice());
+ }
+ // 如果总和不相等,就直接返回
+ return;
}
- dfs(path,1);
- return res
+
+ // 循环当前节点,因为只使用数字1到9,所以最大是9
+ for (let i = startIndex; i <= 9; i++) {
+ path.push(i);
+ sum += i;
+ // 回调函数
+ backtracking(_k, targetSum, sum, i + 1);
+ // 回溯
+ sum -= i;
+ path.pop();
+ }
+ };
+ backtracking(k, n, 0, 1);
+ return result;
+};
+```
+
+- 剪枝:
+
+```js
+/**
+ * @param {number} k
+ * @param {number} n
+ * @return {number[][]}
+ */
+var combinationSum3 = function (k, n) {
+ // 回溯法
+ let result = [],
+ path = [];
+ const backtracking = (_k, targetSum, sum, startIndex) => {
+ if (sum > targetSum) {
+ return;
+ }
+ // 终止条件
+ if (path.length === _k) {
+ if (sum === targetSum) {
+ result.push(path.slice());
+ }
+ // 如果总和不相等,就直接返回
+ return;
+ }
+
+ // 循环当前节点,因为只使用数字1到9,所以最大是9
+ for (let i = startIndex; i <= 9 - (_k - path.length) + 1; i++) {
+ path.push(i);
+ sum += i;
+ // 回调函数
+ backtracking(_k, targetSum, sum, i + 1);
+ // 回溯
+ sum -= i;
+ path.pop();
+ }
+ };
+ backtracking(k, n, 0, 1);
+ return result;
};
```
@@ -696,7 +737,3 @@ public class Solution
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0222.\345\256\214\345\205\250\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\350\212\202\347\202\271\344\270\252\346\225\260.md" "b/problems/0222.\345\256\214\345\205\250\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\350\212\202\347\202\271\344\270\252\346\225\260.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index d93d2a3381..eaf4eab2c9
--- "a/problems/0222.\345\256\214\345\205\250\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\350\212\202\347\202\271\344\270\252\346\225\260.md"
+++ "b/problems/0222.\345\256\214\345\205\250\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\350\212\202\347\202\271\344\270\252\346\225\260.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0222.\345\256\214\345\205\250\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\350\212\202\347\202\271\344\270\252\346\225\260.md" "b/problems/0222.\345\256\214\345\205\250\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\350\212\202\347\202\271\344\270\252\346\225\260.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index d93d2a3381..eaf4eab2c9
--- "a/problems/0222.\345\256\214\345\205\250\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\350\212\202\347\202\271\344\270\252\346\225\260.md"
+++ "b/problems/0222.\345\256\214\345\205\250\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\350\212\202\347\202\271\344\270\252\346\225\260.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 222.完全二叉树的节点个数
@@ -54,7 +52,7 @@
1. 确定递归函数的参数和返回值:参数就是传入树的根节点,返回就返回以该节点为根节点二叉树的节点数量,所以返回值为int类型。
代码如下:
-```
+```CPP
int getNodesNum(TreeNode* cur) {
```
@@ -62,7 +60,7 @@ int getNodesNum(TreeNode* cur) {
代码如下:
-```
+```CPP
if (cur == NULL) return 0;
```
@@ -70,7 +68,7 @@ if (cur == NULL) return 0;
代码如下:
-```
+```CPP
int leftNum = getNodesNum(cur->left); // 左
int rightNum = getNodesNum(cur->right); // 右
int treeNum = leftNum + rightNum + 1; // 中
@@ -155,7 +153,7 @@ public:
我来举一个典型的例子如题:
-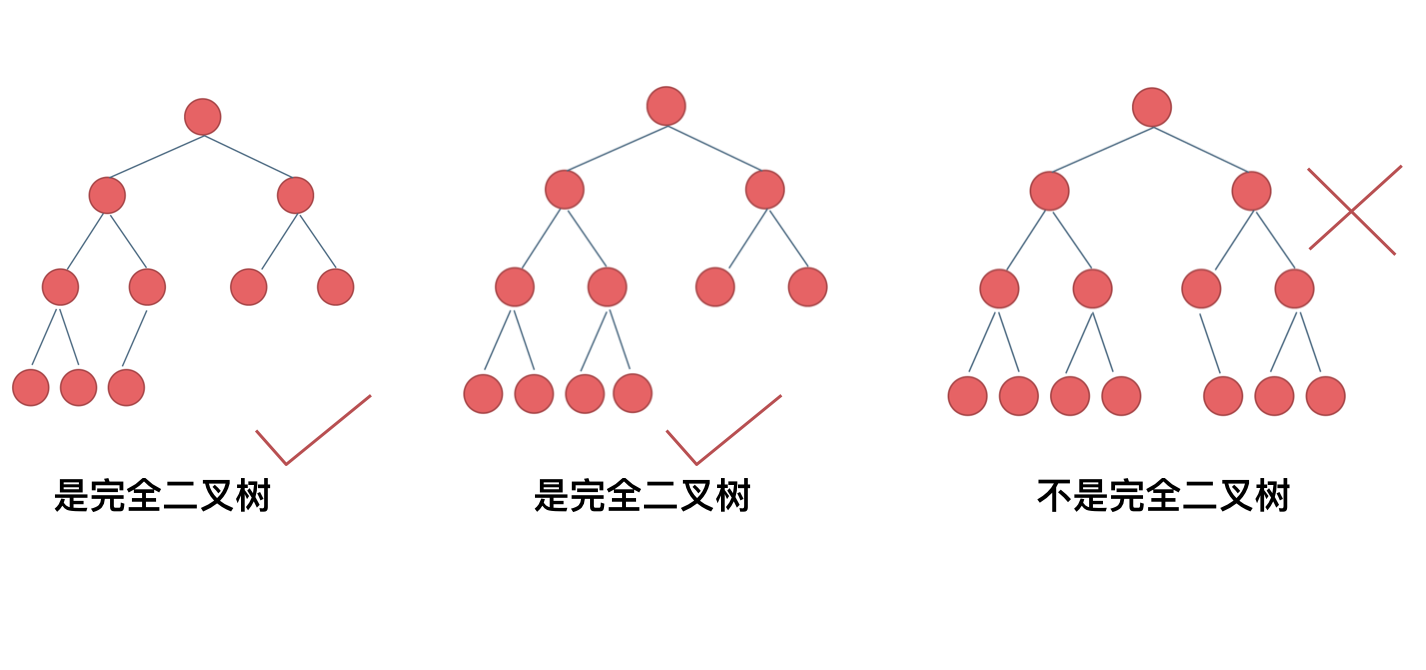 +
+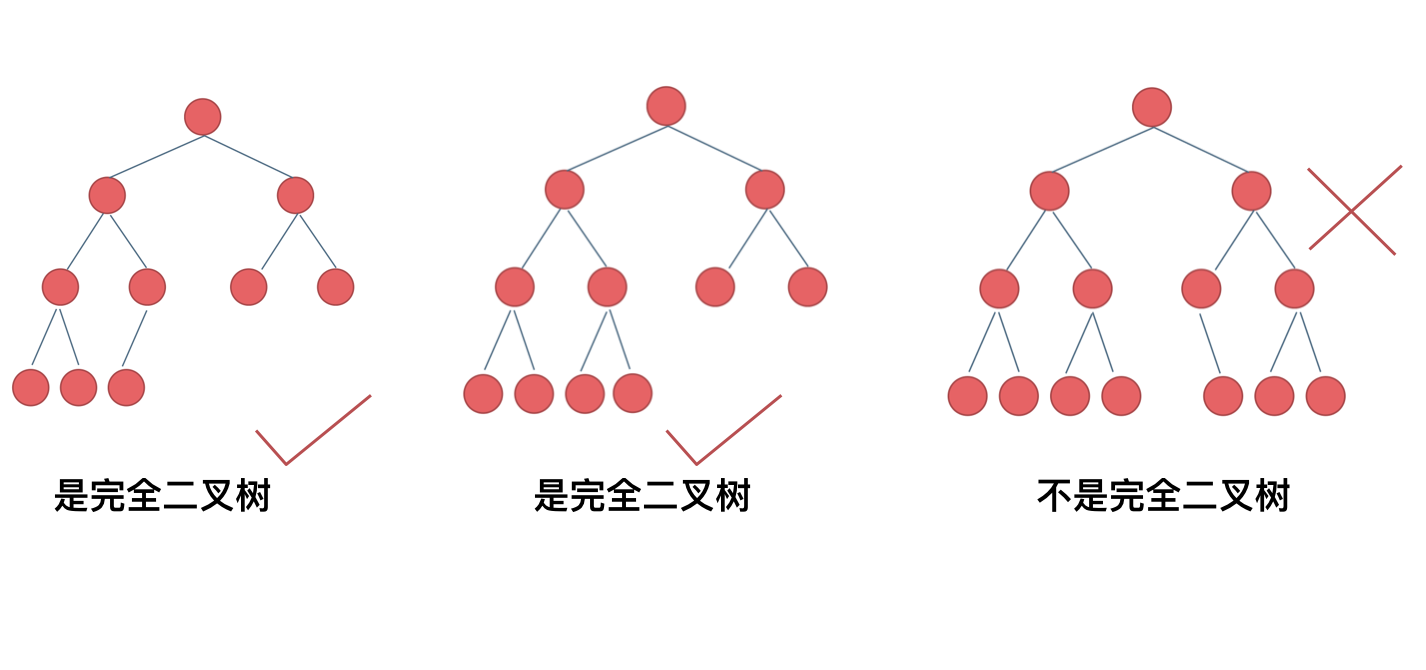 完全二叉树只有两种情况,情况一:就是满二叉树,情况二:最后一层叶子节点没有满。
@@ -164,10 +162,10 @@ public:
对于情况二,分别递归左孩子,和右孩子,递归到某一深度一定会有左孩子或者右孩子为满二叉树,然后依然可以按照情况1来计算。
完全二叉树(一)如图:
-
+
完全二叉树(二)如图:
-
+
可以看出如果整个树不是满二叉树,就递归其左右孩子,直到遇到满二叉树为止,用公式计算这个子树(满二叉树)的节点数量。
@@ -175,15 +173,15 @@ public:
在完全二叉树中,如果递归向左遍历的深度等于递归向右遍历的深度,那说明就是满二叉树。如图:
-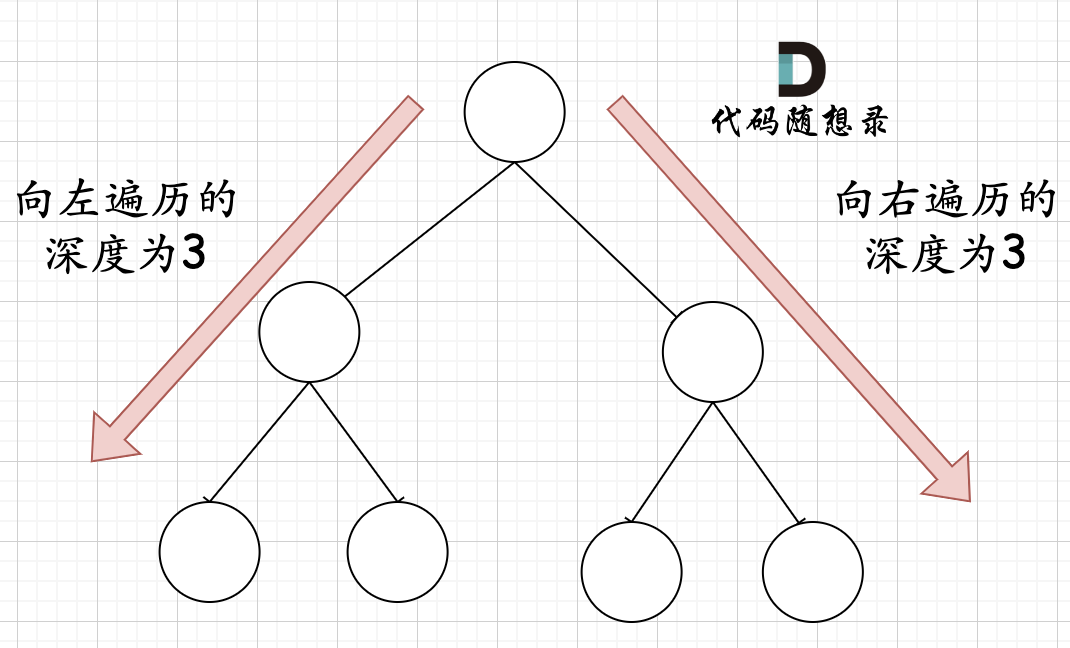
+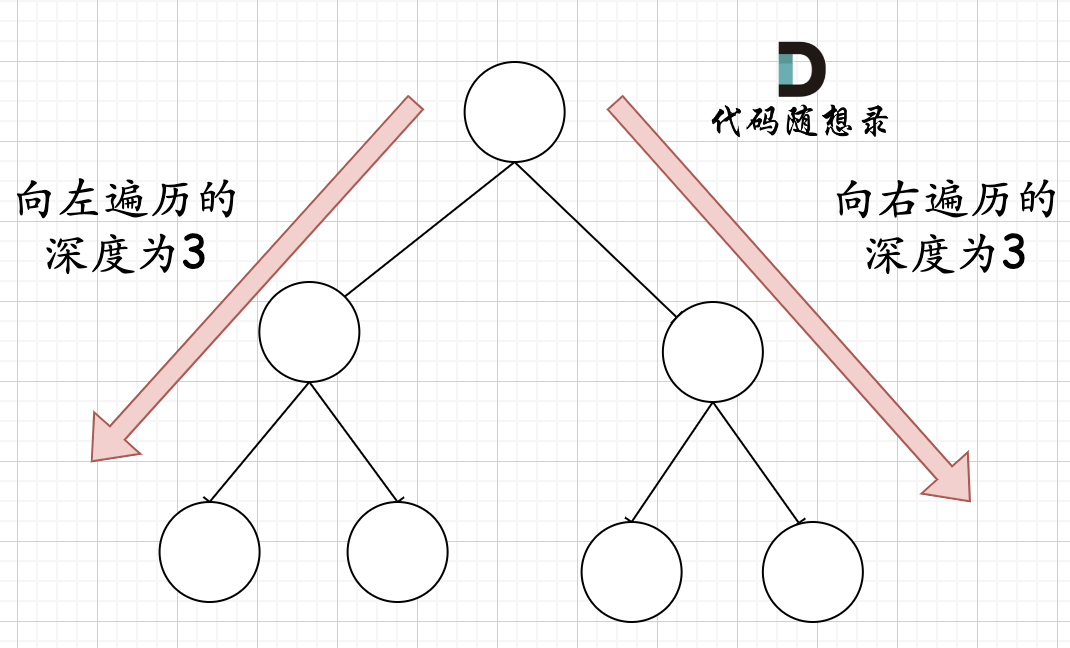
在完全二叉树中,如果递归向左遍历的深度不等于递归向右遍历的深度,则说明不是满二叉树,如图:
-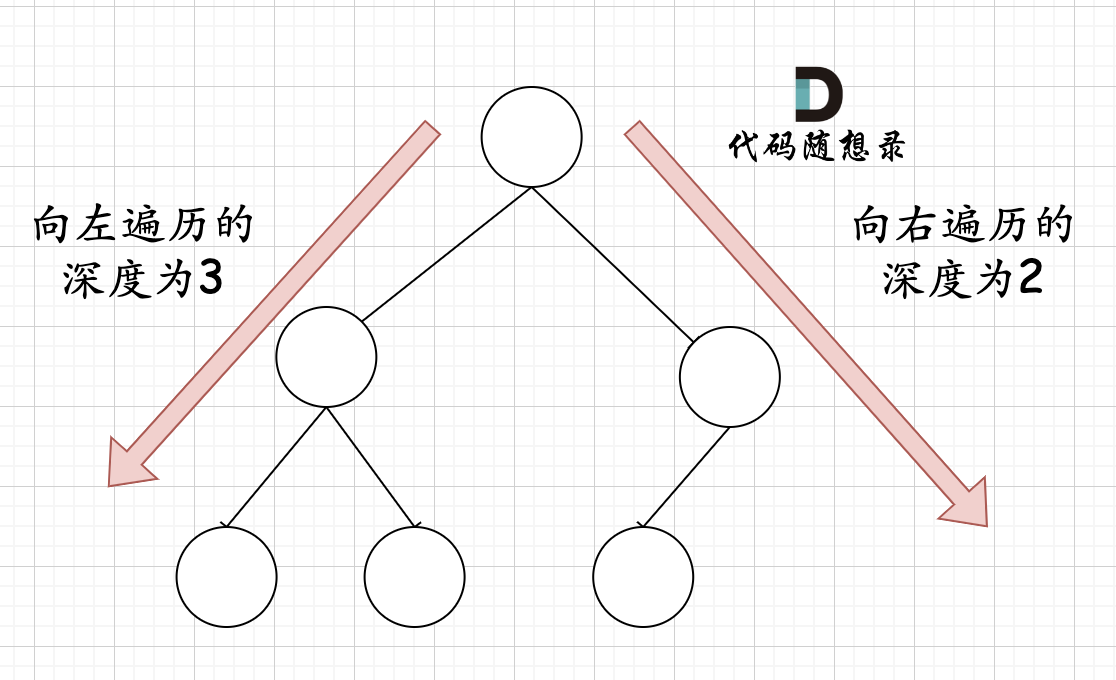
+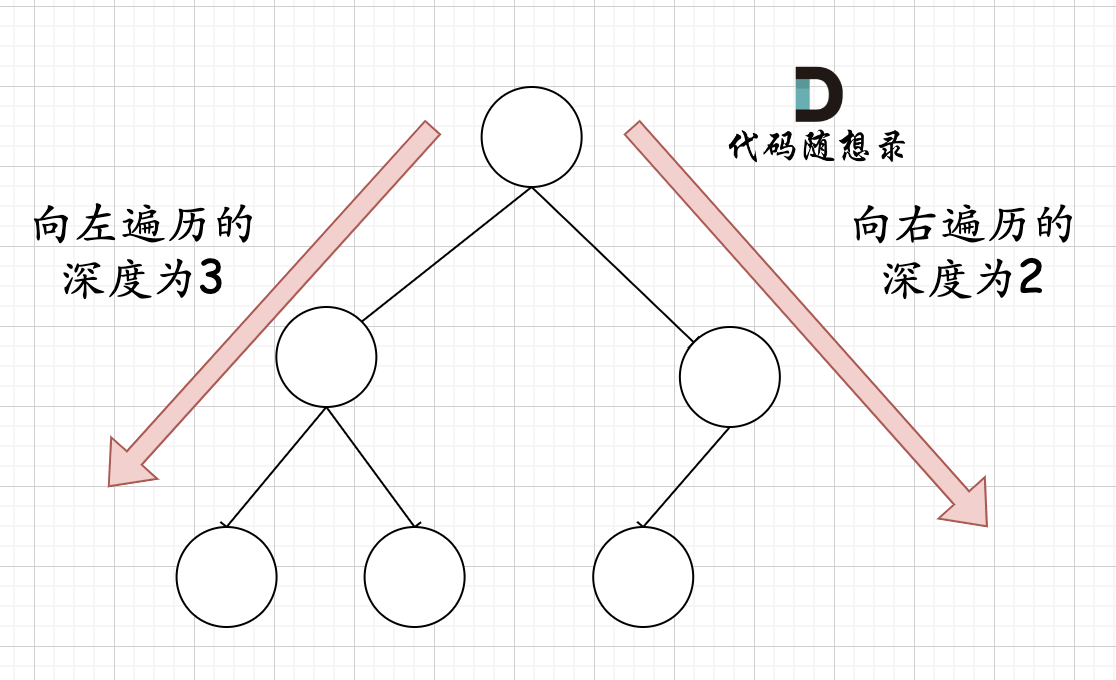
那有录友说了,这种情况,递归向左遍历的深度等于递归向右遍历的深度,但也不是满二叉树,如题:
-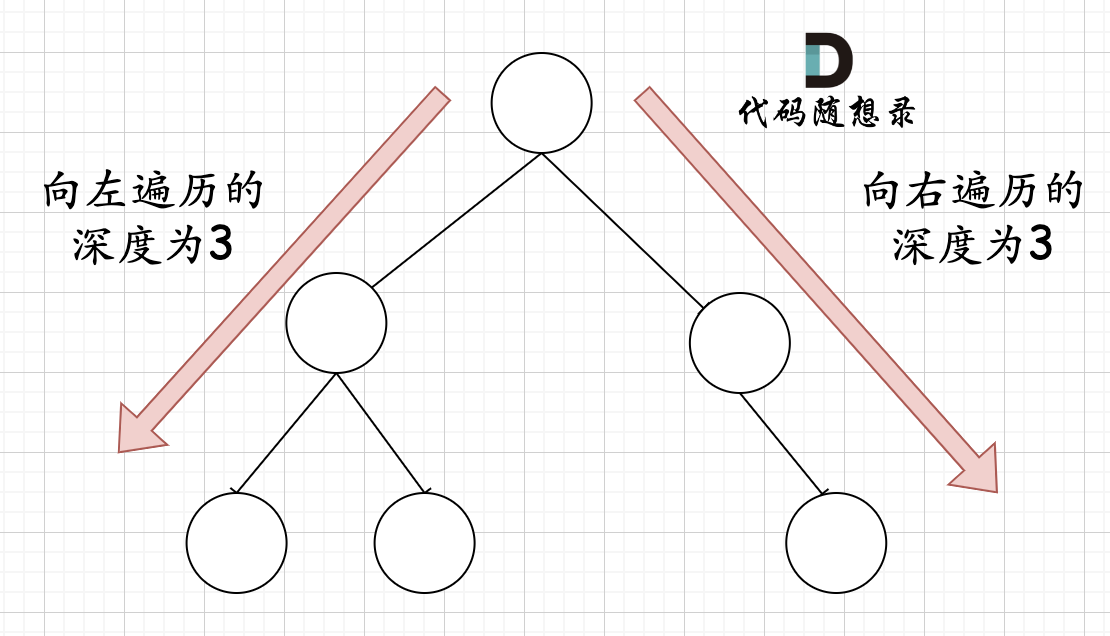
+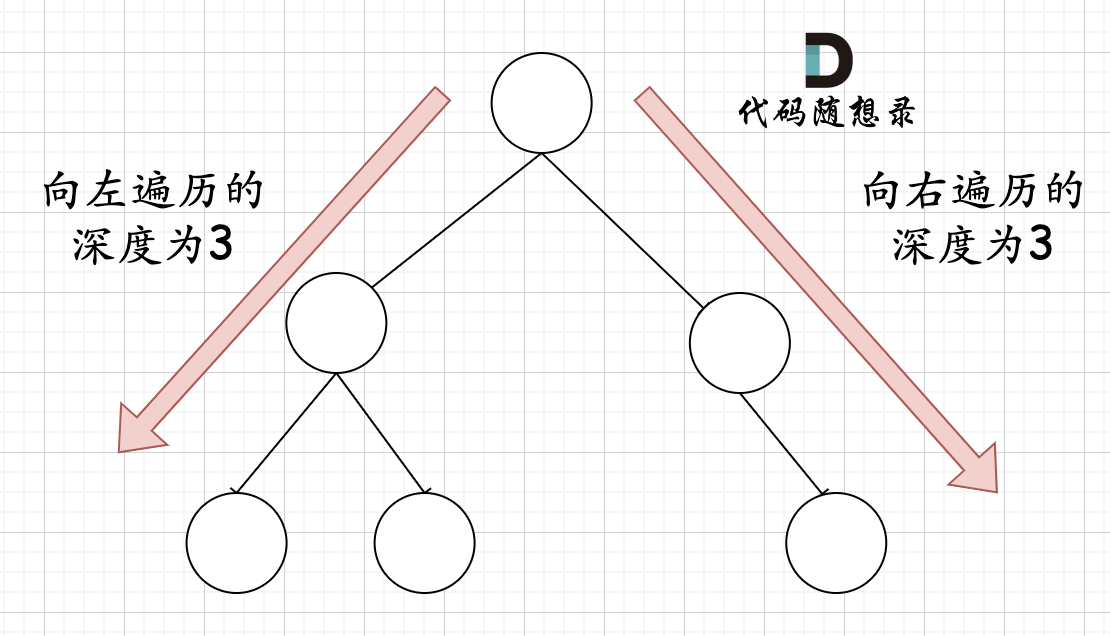
如果这么想,大家就是对 完全二叉树理解有误区了,**以上这棵二叉树,它根本就不是一个完全二叉树**!
@@ -893,8 +891,4 @@ public int CountNodes(TreeNode root)
}
```
-
完全二叉树只有两种情况,情况一:就是满二叉树,情况二:最后一层叶子节点没有满。
@@ -164,10 +162,10 @@ public:
对于情况二,分别递归左孩子,和右孩子,递归到某一深度一定会有左孩子或者右孩子为满二叉树,然后依然可以按照情况1来计算。
完全二叉树(一)如图:
-
+
完全二叉树(二)如图:
-
+
可以看出如果整个树不是满二叉树,就递归其左右孩子,直到遇到满二叉树为止,用公式计算这个子树(满二叉树)的节点数量。
@@ -175,15 +173,15 @@ public:
在完全二叉树中,如果递归向左遍历的深度等于递归向右遍历的深度,那说明就是满二叉树。如图:
-
+
在完全二叉树中,如果递归向左遍历的深度不等于递归向右遍历的深度,则说明不是满二叉树,如图:
-
+
那有录友说了,这种情况,递归向左遍历的深度等于递归向右遍历的深度,但也不是满二叉树,如题:
-
+
如果这么想,大家就是对 完全二叉树理解有误区了,**以上这棵二叉树,它根本就不是一个完全二叉树**!
@@ -893,8 +891,4 @@ public int CountNodes(TreeNode root)
}
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0225.\347\224\250\351\230\237\345\210\227\345\256\236\347\216\260\346\240\210.md" "b/problems/0225.\347\224\250\351\230\237\345\210\227\345\256\236\347\216\260\346\240\210.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 6900e66869..72dfd2aacf
--- "a/problems/0225.\347\224\250\351\230\237\345\210\227\345\256\236\347\216\260\346\240\210.md"
+++ "b/problems/0225.\347\224\250\351\230\237\345\210\227\345\256\236\347\216\260\346\240\210.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0225.\347\224\250\351\230\237\345\210\227\345\256\236\347\216\260\346\240\210.md" "b/problems/0225.\347\224\250\351\230\237\345\210\227\345\256\236\347\216\260\346\240\210.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 6900e66869..72dfd2aacf
--- "a/problems/0225.\347\224\250\351\230\237\345\210\227\345\256\236\347\216\260\346\240\210.md"
+++ "b/problems/0225.\347\224\250\351\230\237\345\210\227\345\256\236\347\216\260\346\240\210.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
@@ -62,7 +60,7 @@ queue.pop();
queue.empty();
```
-
+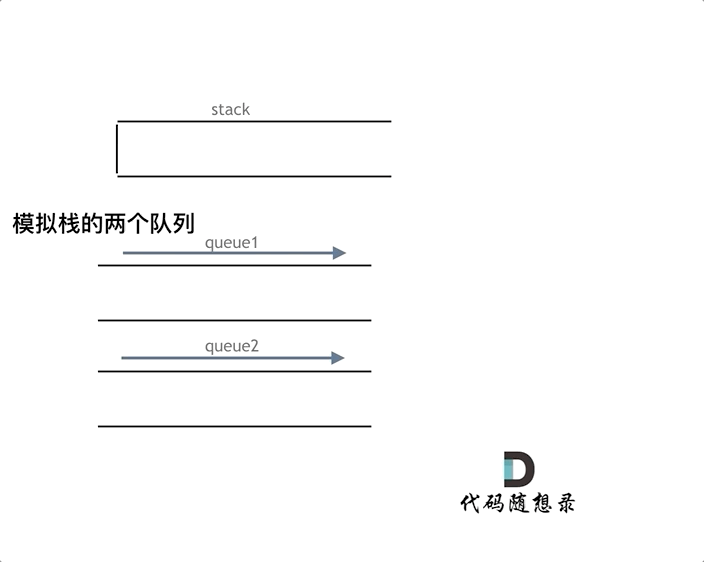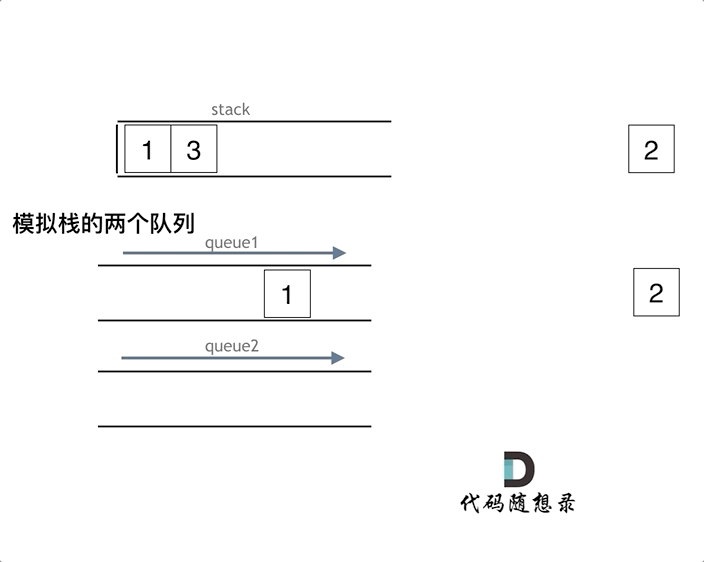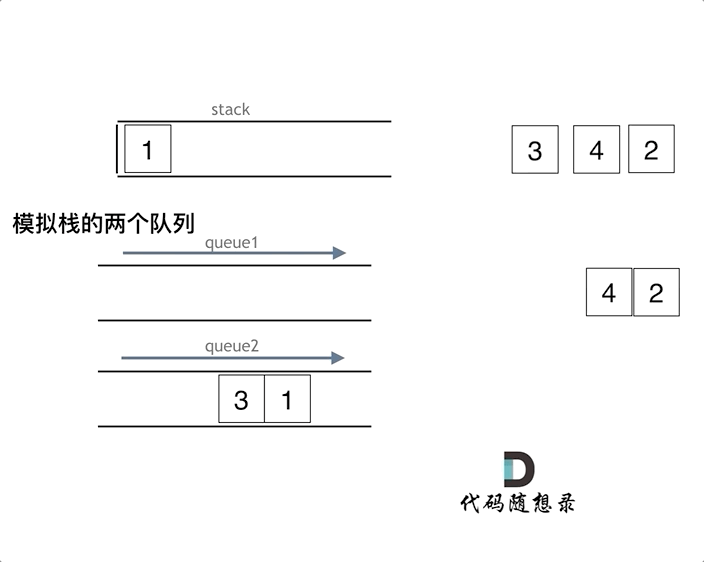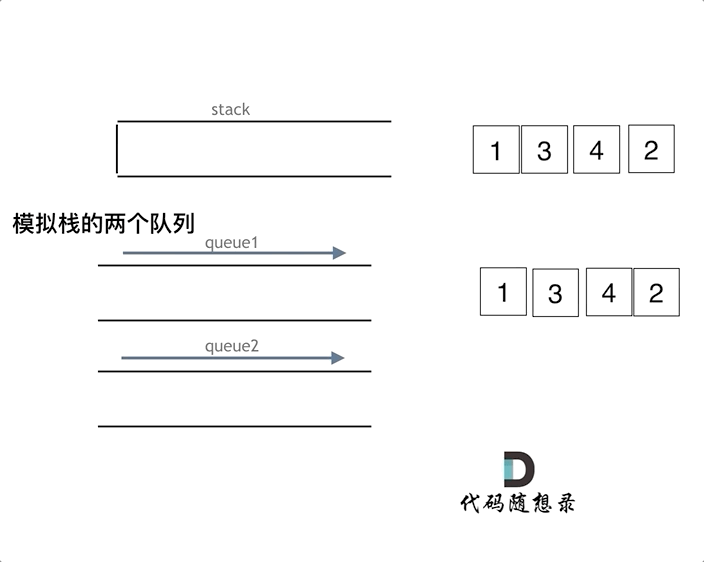
详细如代码注释所示:
@@ -72,6 +70,7 @@ class MyStack {
public:
queue que1;
queue que2; // 辅助队列,用来备份
+
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
MyStack() {
@@ -100,9 +99,28 @@ public:
return result;
}
- /** Get the top element. */
- int top() {
- return que1.back();
+ /** Get the top element.
+ ** Can not use back() direactly.
+ */
+ int top(){
+ int size = que1.size();
+ size--;
+ while (size--){
+ // 将que1 导入que2,但要留下最后一个元素
+ que2.push(que1.front());
+ que1.pop();
+ }
+
+ int result = que1.front(); // 留下的最后一个元素就是要回返的值
+ que2.push(que1.front()); // 获取值后将最后一个元素也加入que2中,保持原本的结构不变
+ que1.pop();
+
+ que1 = que2; // 再将que2赋值给que1
+ while (!que2.empty()){
+ // 清空que2
+ que2.pop();
+ }
+ return result;
}
/** Returns whether the stack is empty. */
@@ -111,7 +129,7 @@ public:
}
};
```
-* 时间复杂度: pop为O(n),其他为O(1)
+* 时间复杂度: pop为O(n),top为O(n),其他为O(1)
* 空间复杂度: O(n)
## 优化
@@ -126,15 +144,15 @@ C++优化代码
class MyStack {
public:
queue que;
- /** Initialize your data structure here. */
+
MyStack() {
}
- /** Push element x onto stack. */
+
void push(int x) {
que.push(x);
}
- /** Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. */
+
int pop() {
int size = que.size();
size--;
@@ -147,18 +165,26 @@ public:
return result;
}
- /** Get the top element. */
- int top() {
- return que.back();
+ int top(){
+ int size = que.size();
+ size--;
+ while (size--){
+ // 将队列头部的元素(除了最后一个元素外) 重新添加到队列尾部
+ que.push(que.front());
+ que.pop();
+ }
+ int result = que.front(); // 此时获得的元素就是栈顶的元素了
+ que.push(que.front()); // 将获取完的元素也重新添加到队列尾部,保证数据结构没有变化
+ que.pop();
+ return result;
}
- /** Returns whether the stack is empty. */
bool empty() {
return que.empty();
}
};
```
-* 时间复杂度: pop为O(n),其他为O(1)
+* 时间复杂度: pop为O(n),top为O(n),其他为O(1)
* 空间复杂度: O(n)
@@ -1249,8 +1275,93 @@ impl MyStack {
}
```
-
-
-  -
+### C:
+
+> C:单队列
+
+```c
+typedef struct Node {
+ int val;
+ struct Node *next;
+} Node_t;
+
+// 用单向链表实现queue
+typedef struct {
+ Node_t *head;
+ Node_t *foot;
+ int size;
+} MyStack;
+
+MyStack* myStackCreate() {
+ MyStack *obj = (MyStack *)malloc(sizeof(MyStack));
+ assert(obj);
+ obj->head = NULL;
+ obj->foot = NULL;
+ obj->size = 0;
+ return obj;
+}
+
+void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x) {
+
+ Node_t *temp = (Node_t *)malloc(sizeof(Node_t));
+ assert(temp);
+ temp->val = x;
+ temp->next = NULL;
+
+ // 添加至queue末尾
+ if (obj->foot) {
+ obj->foot->next = temp;
+ } else {
+ obj->head = temp;
+ }
+ obj->foot = temp;
+ obj->size++;
+}
+
+int myStackPop(MyStack* obj) {
+
+ // 获取末尾元素
+ int target = obj->foot->val;
+
+ if (obj->head == obj->foot) {
+ free(obj->foot);
+ obj->head = NULL;
+ obj->foot = NULL;
+ } else {
+
+ Node_t *prev = obj->head;
+ // 移动至queue尾部节点前一个节点
+ while (prev->next != obj->foot) {
+ prev = prev->next;
+ }
+
+ free(obj->foot);
+ obj->foot = prev;
+ obj->foot->next = NULL;
+ }
+
+ obj->size--;
+ return target;
+}
+
+int myStackTop(MyStack* obj) {
+ return obj->foot->val;
+}
+
+bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj) {
+ return obj->size == 0;
+}
+
+void myStackFree(MyStack* obj) {
+ Node_t *curr = obj->head;
+ while (curr != NULL) {
+ Node_t *temp = curr->next;
+ free(curr);
+ curr = temp;
+ }
+ free(obj);
+}
+
+```
+
diff --git "a/problems/0226.\347\277\273\350\275\254\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0226.\347\277\273\350\275\254\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 8691953a3e..67a1a59338
--- "a/problems/0226.\347\277\273\350\275\254\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0226.\347\277\273\350\275\254\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+### C:
+
+> C:单队列
+
+```c
+typedef struct Node {
+ int val;
+ struct Node *next;
+} Node_t;
+
+// 用单向链表实现queue
+typedef struct {
+ Node_t *head;
+ Node_t *foot;
+ int size;
+} MyStack;
+
+MyStack* myStackCreate() {
+ MyStack *obj = (MyStack *)malloc(sizeof(MyStack));
+ assert(obj);
+ obj->head = NULL;
+ obj->foot = NULL;
+ obj->size = 0;
+ return obj;
+}
+
+void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x) {
+
+ Node_t *temp = (Node_t *)malloc(sizeof(Node_t));
+ assert(temp);
+ temp->val = x;
+ temp->next = NULL;
+
+ // 添加至queue末尾
+ if (obj->foot) {
+ obj->foot->next = temp;
+ } else {
+ obj->head = temp;
+ }
+ obj->foot = temp;
+ obj->size++;
+}
+
+int myStackPop(MyStack* obj) {
+
+ // 获取末尾元素
+ int target = obj->foot->val;
+
+ if (obj->head == obj->foot) {
+ free(obj->foot);
+ obj->head = NULL;
+ obj->foot = NULL;
+ } else {
+
+ Node_t *prev = obj->head;
+ // 移动至queue尾部节点前一个节点
+ while (prev->next != obj->foot) {
+ prev = prev->next;
+ }
+
+ free(obj->foot);
+ obj->foot = prev;
+ obj->foot->next = NULL;
+ }
+
+ obj->size--;
+ return target;
+}
+
+int myStackTop(MyStack* obj) {
+ return obj->foot->val;
+}
+
+bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj) {
+ return obj->size == 0;
+}
+
+void myStackFree(MyStack* obj) {
+ Node_t *curr = obj->head;
+ while (curr != NULL) {
+ Node_t *temp = curr->next;
+ free(curr);
+ curr = temp;
+ }
+ free(obj);
+}
+
+```
+
diff --git "a/problems/0226.\347\277\273\350\275\254\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0226.\347\277\273\350\275\254\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 8691953a3e..67a1a59338
--- "a/problems/0226.\347\277\273\350\275\254\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0226.\347\277\273\350\275\254\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 226.翻转二叉树
@@ -12,9 +10,9 @@
翻转一棵二叉树。
-
+
-这道题目背后有一个让程序员心酸的故事,听说 Homebrew的作者Max Howell,就是因为没在白板上写出翻转二叉树,最后被Google拒绝了。(真假不做判断,权当一个乐子哈)
+这道题目背后有一个让程序员心酸的故事,听说 Homebrew的作者Max Howell,就是因为没在白板上写出翻转二叉树,最后被Google拒绝了。(真假不做判断,全当一个乐子哈)
## 算法公开课
@@ -37,7 +35,7 @@
如果要从整个树来看,翻转还真的挺复杂,整个树以中间分割线进行翻转,如图:
-
+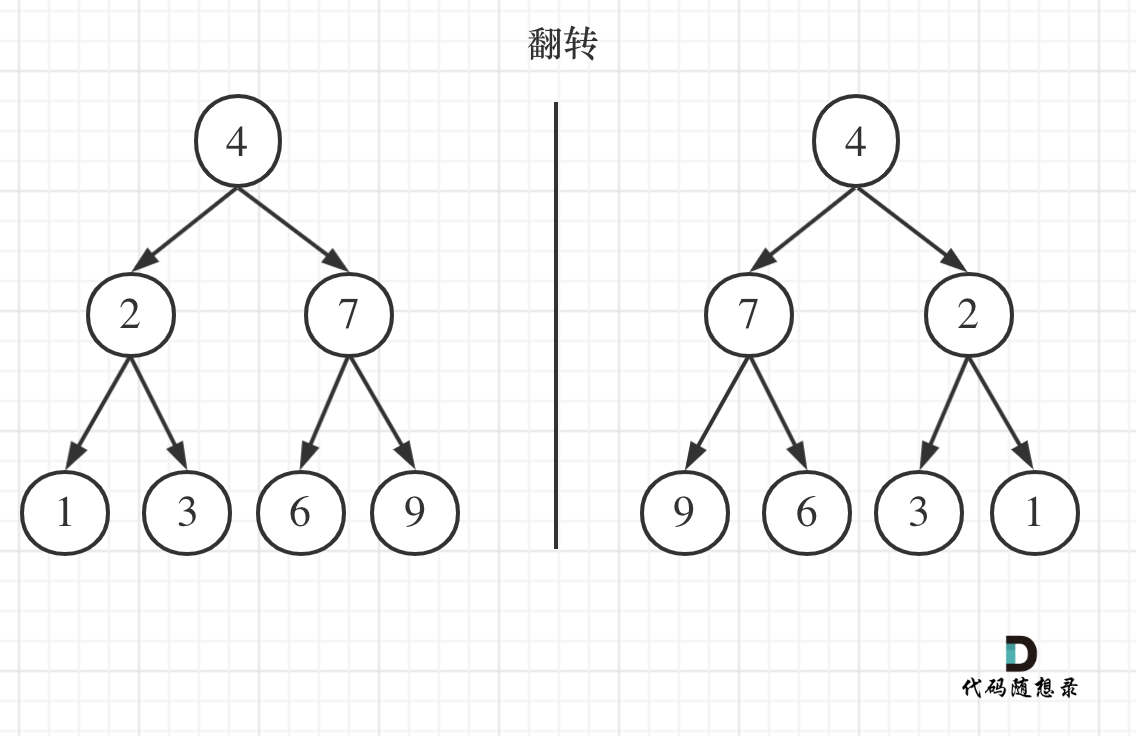
可以发现想要翻转它,其实就把每一个节点的左右孩子交换一下就可以了。
@@ -57,7 +55,7 @@
我们下文以前序遍历为例,通过动画来看一下翻转的过程:
-
+
我们来看一下递归三部曲:
@@ -81,7 +79,7 @@ if (root == NULL) return root;
3. 确定单层递归的逻辑
-因为是先前序遍历,所以先进行交换左右孩子节点,然后反转左子树,反转右子树。
+因为是前序遍历,所以先进行交换左右孩子节点,然后反转左子树,反转右子树。
```cpp
swap(root->left, root->right);
@@ -348,14 +346,13 @@ class Solution:
while stack:
node = stack.pop()
node.left, node.right = node.right, node.left
+ if node.right:
+ stack.append(node.right)
if node.left:
stack.append(node.left)
- if node.right:
- stack.append(node.right)
return root
```
-
递归法:中序遍历:
```python
# Definition for a binary tree node.
@@ -374,7 +371,7 @@ class Solution:
return root
```
-迭代法:中序遍历:
+迭代法,伪中序遍历(结果是对的,看起来像是中序遍历,实际上它是前序遍历,只不过把中间节点处理逻辑放到了中间。还是要用'统一写法'才是真正的中序遍历):
```python
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
@@ -386,18 +383,17 @@ class Solution:
def invertTree(self, root: TreeNode) -> TreeNode:
if not root:
return None
- stack = [root]
+ stack = [root]
while stack:
- node = stack.pop()
- if node.left:
- stack.append(node.left)
- node.left, node.right = node.right, node.left
- if node.left:
- stack.append(node.left)
+ node = stack.pop()
+ if node.right:
+ stack.append(node.right)
+ node.left, node.right = node.right, node.left # 放到中间,依然是前序遍历
+ if node.right:
+ stack.append(node.right)
return root
```
-
递归法:后序遍历:
```python
# Definition for a binary tree node.
@@ -416,7 +412,7 @@ class Solution:
return root
```
-迭代法:后序遍历:
+迭代法,伪后序遍历(结果是对的,看起来像是后序遍历,实际上它是前序遍历,只不过把中间节点处理逻辑放到了最后。还是要用'统一写法'才是真正的后序遍历):
```python
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
@@ -427,23 +423,19 @@ class Solution:
class Solution:
def invertTree(self, root: TreeNode) -> TreeNode:
if not root:
- return None
- stack = [root]
+ return None
+ stack = [root]
while stack:
- node = stack.pop()
+ node = stack.pop()
+ if node.right:
+ stack.append(node.right)
if node.left:
stack.append(node.left)
- if node.right:
- stack.append(node.right)
node.left, node.right = node.right, node.left
return root
```
-
-
-
-
迭代法:广度优先遍历(层序遍历):
```python
# Definition for a binary tree node.
@@ -459,11 +451,10 @@ class Solution:
queue = collections.deque([root])
while queue:
- for i in range(len(queue)):
- node = queue.popleft()
- node.left, node.right = node.right, node.left
- if node.left: queue.append(node.left)
- if node.right: queue.append(node.right)
+ node = queue.popleft()
+ node.left, node.right = node.right, node.left
+ if node.left: queue.append(node.left)
+ if node.right: queue.append(node.right)
return root
```
@@ -1028,8 +1019,4 @@ public TreeNode InvertTree(TreeNode root) {
}
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0232.\347\224\250\346\240\210\345\256\236\347\216\260\351\230\237\345\210\227.md" "b/problems/0232.\347\224\250\346\240\210\345\256\236\347\216\260\351\230\237\345\210\227.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 41933ca4ba..56698e023f
--- "a/problems/0232.\347\224\250\346\240\210\345\256\236\347\216\260\351\230\237\345\210\227.md"
+++ "b/problems/0232.\347\224\250\346\240\210\345\256\236\347\216\260\351\230\237\345\210\227.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0232.\347\224\250\346\240\210\345\256\236\347\216\260\351\230\237\345\210\227.md" "b/problems/0232.\347\224\250\346\240\210\345\256\236\347\216\260\351\230\237\345\210\227.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 41933ca4ba..56698e023f
--- "a/problems/0232.\347\224\250\346\240\210\345\256\236\347\216\260\351\230\237\345\210\227.md"
+++ "b/problems/0232.\347\224\250\346\240\210\345\256\236\347\216\260\351\230\237\345\210\227.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
> 工作上一定没人这么搞,但是考察对栈、队列理解程度的好题
@@ -44,7 +42,7 @@ queue.empty(); // 返回 false
这是一道模拟题,不涉及到具体算法,考察的就是对栈和队列的掌握程度。
-使用栈来模式队列的行为,如果仅仅用一个栈,是一定不行的,所以需要两个栈**一个输入栈,一个输出栈**,这里要注意输入栈和输出栈的关系。
+使用栈来模拟队列的行为,如果仅仅用一个栈,是一定不行的,所以需要两个栈**一个输入栈,一个输出栈**,这里要注意输入栈和输出栈的关系。
下面动画模拟以下队列的执行过程:
@@ -59,7 +57,7 @@ queue.pop();**注意此时的输出栈的操作**
queue.pop();
queue.empty();
-
+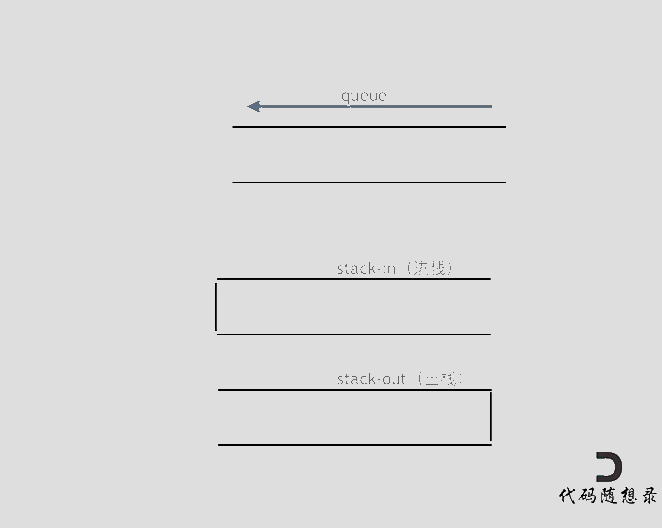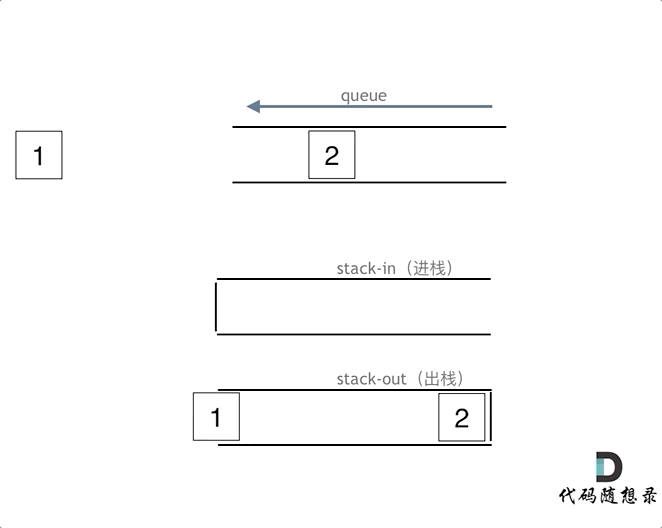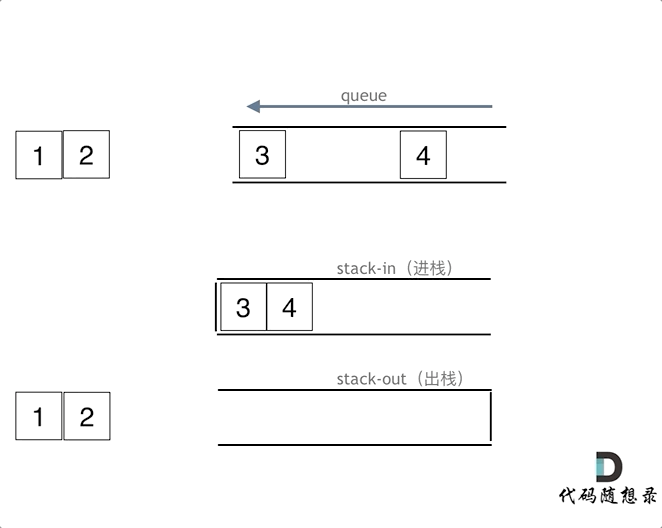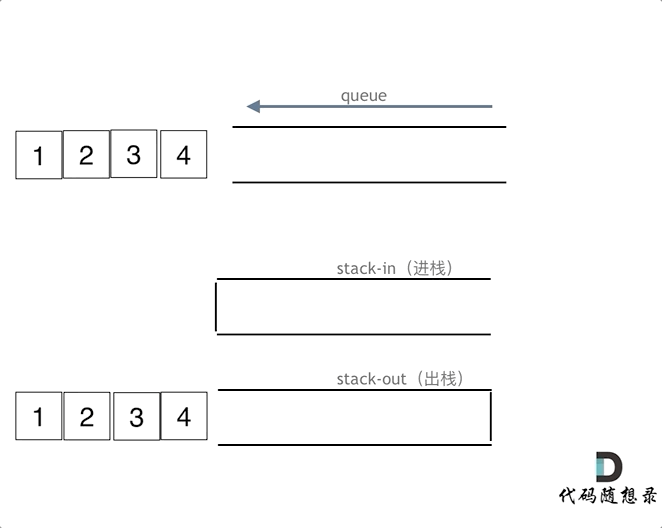
在push数据的时候,只要数据放进输入栈就好,**但在pop的时候,操作就复杂一些,输出栈如果为空,就把进栈数据全部导入进来(注意是全部导入)**,再从出栈弹出数据,如果输出栈不为空,则直接从出栈弹出数据就可以了。
@@ -113,7 +111,7 @@ public:
```
-* 时间复杂度: push和empty为O(1), pop和peek为O(n)
+* 时间复杂度: 都为O(1)。pop和peek看起来像O(n),实际上一个循环n会被使用n次,最后还是O(1)。
* 空间复杂度: O(n)
@@ -691,7 +689,3 @@ impl MyQueue {
}
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0234.\345\233\236\346\226\207\351\223\276\350\241\250.md" "b/problems/0234.\345\233\236\346\226\207\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index fef942fc49..6248861d94
--- "a/problems/0234.\345\233\236\346\226\207\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
+++ "b/problems/0234.\345\233\236\346\226\207\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0234.\345\233\236\346\226\207\351\223\276\350\241\250.md" "b/problems/0234.\345\233\236\346\226\207\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index fef942fc49..6248861d94
--- "a/problems/0234.\345\233\236\346\226\207\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
+++ "b/problems/0234.\345\233\236\346\226\207\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 234.回文链表
@@ -89,7 +87,7 @@ public:
如图所示:
- +
+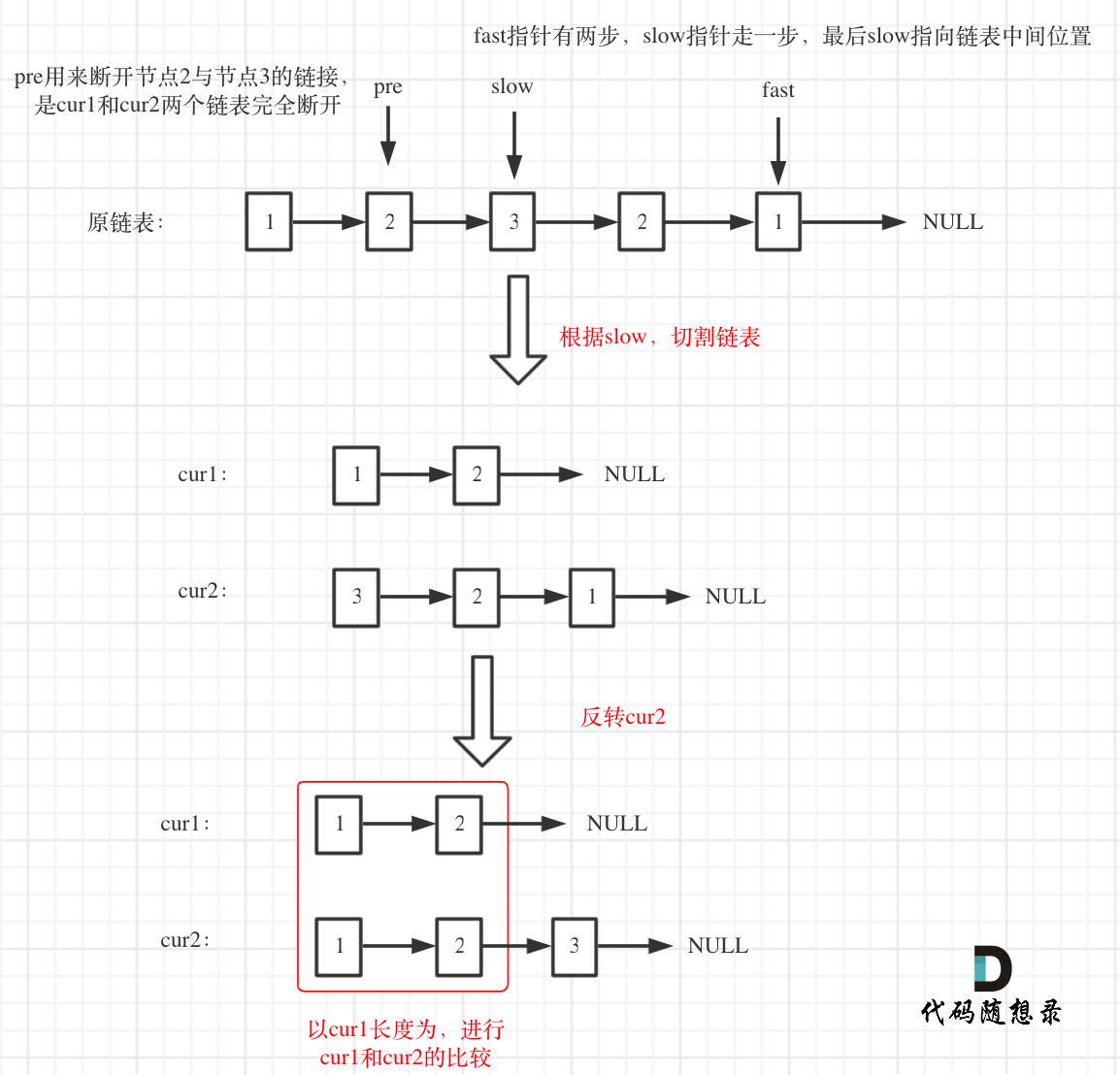 代码如下:
@@ -428,8 +426,4 @@ function reverseList(head: ListNode | null): ListNode | null {
-
代码如下:
@@ -428,8 +426,4 @@ function reverseList(head: ListNode | null): ListNode | null {
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0235.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\350\277\221\345\205\254\345\205\261\347\245\226\345\205\210.md" "b/problems/0235.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\350\277\221\345\205\254\345\205\261\347\245\226\345\205\210.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 2a11f9f4b7..a1fe78d169
--- "a/problems/0235.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\350\277\221\345\205\254\345\205\261\347\245\226\345\205\210.md"
+++ "b/problems/0235.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\350\277\221\345\205\254\345\205\261\347\245\226\345\205\210.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0235.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\350\277\221\345\205\254\345\205\261\347\245\226\345\205\210.md" "b/problems/0235.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\350\277\221\345\205\254\345\205\261\347\245\226\345\205\210.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 2a11f9f4b7..a1fe78d169
--- "a/problems/0235.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\350\277\221\345\205\254\345\205\261\347\245\226\345\205\210.md"
+++ "b/problems/0235.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\350\277\221\345\205\254\345\205\261\347\245\226\345\205\210.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 235. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
@@ -16,7 +14,7 @@
例如,给定如下二叉搜索树: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5]
-
+
示例 1:
@@ -38,7 +36,7 @@
## 算法公开课
-**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[二叉搜索树找祖先就有点不一样了!| 235. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Zt4y1F7ww?share_source=copy_web),相信结合视频在看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
+**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[二叉搜索树找祖先就有点不一样了!| 235. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Zt4y1F7ww?share_source=copy_web),相信结合视频再看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
## 思路
@@ -54,7 +52,7 @@
如图,我们从根节点搜索,第一次遇到 cur节点是数值在[q, p]区间中,即 节点5,此时可以说明 q 和 p 一定分别存在于 节点 5的左子树,和右子树中。
-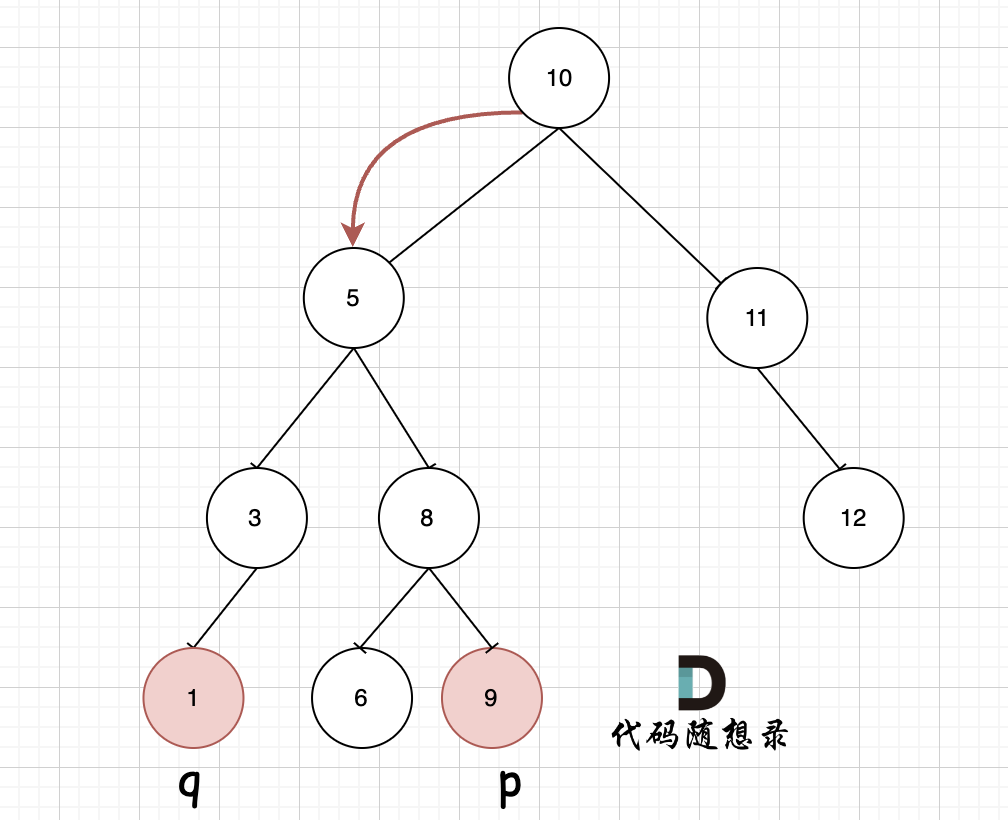
+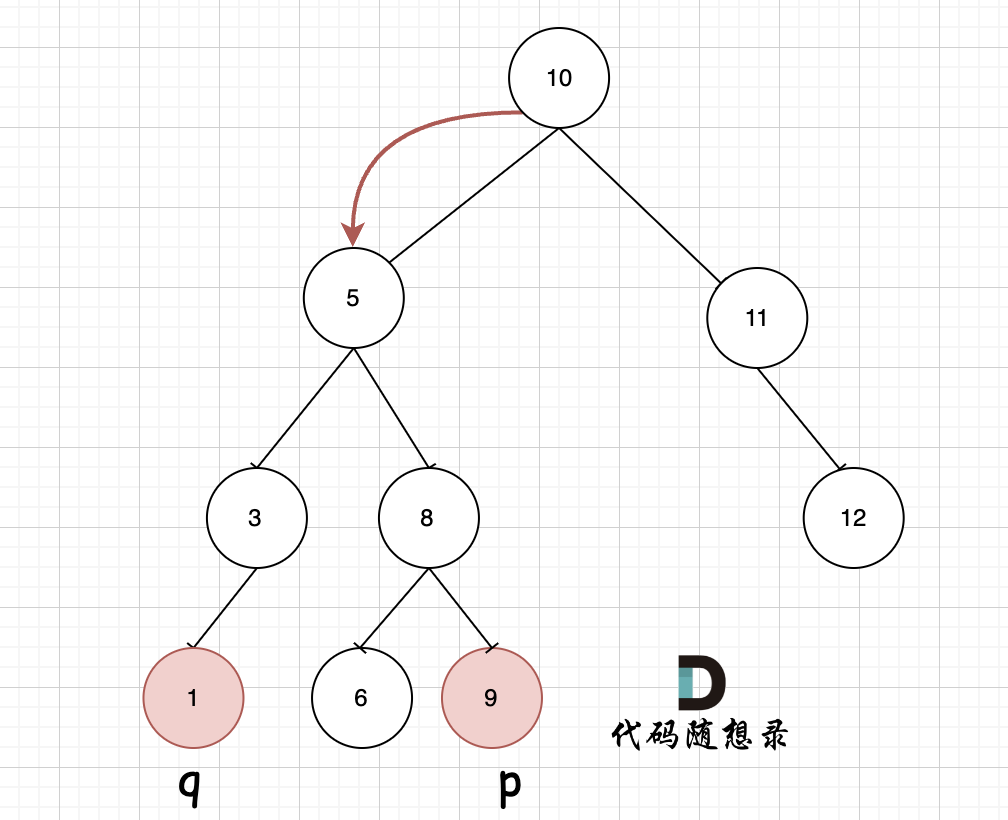
此时节点5是不是最近公共祖先? 如果 从节点5继续向左遍历,那么将错过成为p的祖先, 如果从节点5继续向右遍历则错过成为q的祖先。
@@ -66,7 +64,7 @@
如图所示:p为节点6,q为节点9
-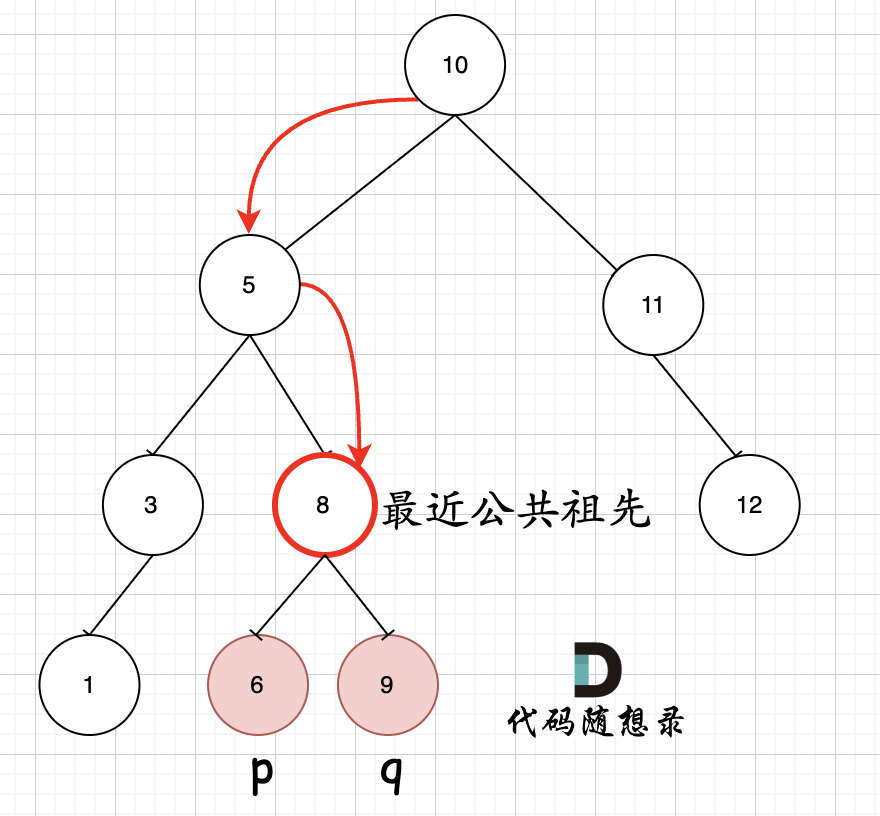
+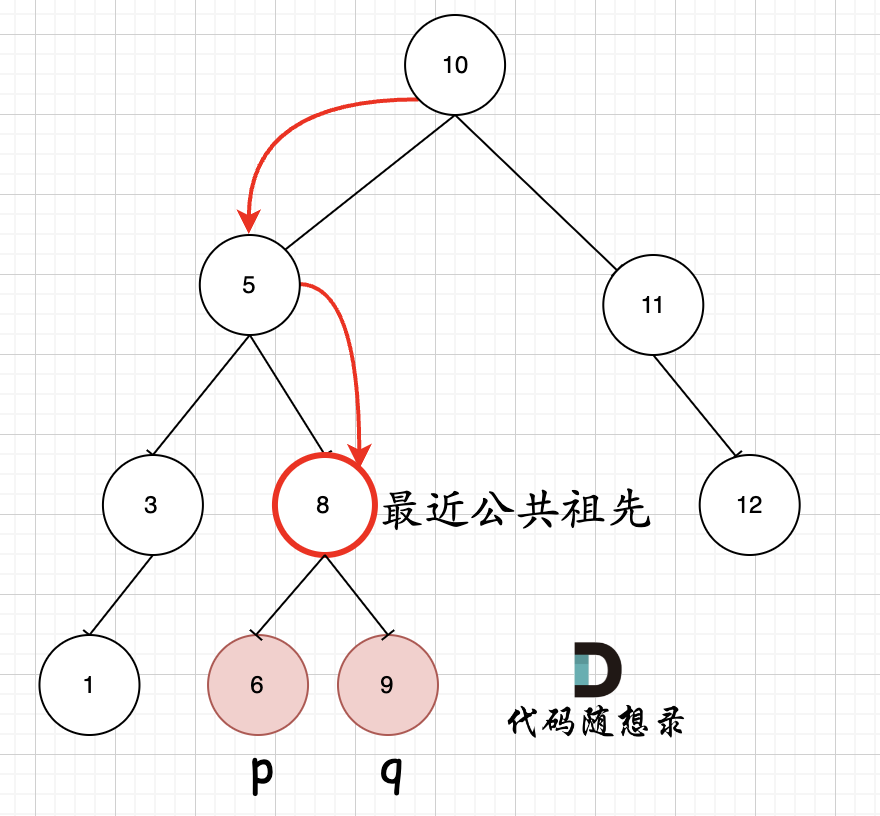
可以看出直接按照指定的方向,就可以找到节点8,为最近公共祖先,而且不需要遍历整棵树,找到结果直接返回!
@@ -99,7 +97,7 @@ if (cur == NULL) return cur;
* 确定单层递归的逻辑
-在遍历二叉搜索树的时候就是寻找区间[p->val, q->val](注意这里是左闭又闭)
+在遍历二叉搜索树的时候就是寻找区间[p->val, q->val](注意这里是左闭右闭)
那么如果 cur->val 大于 p->val,同时 cur->val 大于q->val,那么就应该向左遍历(说明目标区间在左子树上)。
@@ -547,8 +545,4 @@ public TreeNode LowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q)
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0236.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\350\277\221\345\205\254\345\205\261\347\245\226\345\205\210.md" "b/problems/0236.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\350\277\221\345\205\254\345\205\261\347\245\226\345\205\210.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 049f70c7ae..5044e3ba00
--- "a/problems/0236.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\350\277\221\345\205\254\345\205\261\347\245\226\345\205\210.md"
+++ "b/problems/0236.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\350\277\221\345\205\254\345\205\261\347\245\226\345\205\210.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0236.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\350\277\221\345\205\254\345\205\261\347\245\226\345\205\210.md" "b/problems/0236.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\350\277\221\345\205\254\345\205\261\347\245\226\345\205\210.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 049f70c7ae..5044e3ba00
--- "a/problems/0236.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\350\277\221\345\205\254\345\205\261\347\245\226\345\205\210.md"
+++ "b/problems/0236.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\350\277\221\345\205\254\345\205\261\347\245\226\345\205\210.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
> 本来是打算将二叉树和二叉搜索树的公共祖先问题一起讲,后来发现篇幅过长了,只能先说一说二叉树的公共祖先问题。
@@ -18,7 +16,7 @@
例如,给定如下二叉树: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4]
-
+
示例 1:
输入: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 1
@@ -36,7 +34,7 @@
## 算法公开课
-**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[自底向上查找,有点难度! | LeetCode:236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1jd4y1B7E2),相信结合视频在看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
+**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[自底向上查找,有点难度! | LeetCode:236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1jd4y1B7E2),相信结合视频再看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
## 思路
@@ -45,7 +43,7 @@
那么二叉树如何可以自底向上查找呢?
-回溯啊,二叉树回溯的过程就是从低到上。
+回溯啊,二叉树回溯的过程就是从底到上。
后序遍历(左右中)就是天然的回溯过程,可以根据左右子树的返回值,来处理中节点的逻辑。
@@ -53,7 +51,7 @@
**首先最容易想到的一个情况:如果找到一个节点,发现左子树出现结点p,右子树出现节点q,或者 左子树出现结点q,右子树出现节点p,那么该节点就是节点p和q的最近公共祖先。** 即情况一:
-
+
判断逻辑是 如果递归遍历遇到q,就将q返回,遇到p 就将p返回,那么如果 左右子树的返回值都不为空,说明此时的中节点,一定是q 和p 的最近祖先。
@@ -63,7 +61,7 @@
**但是很多人容易忽略一个情况,就是节点本身p(q),它拥有一个子孙节点q(p)。** 情况二:
-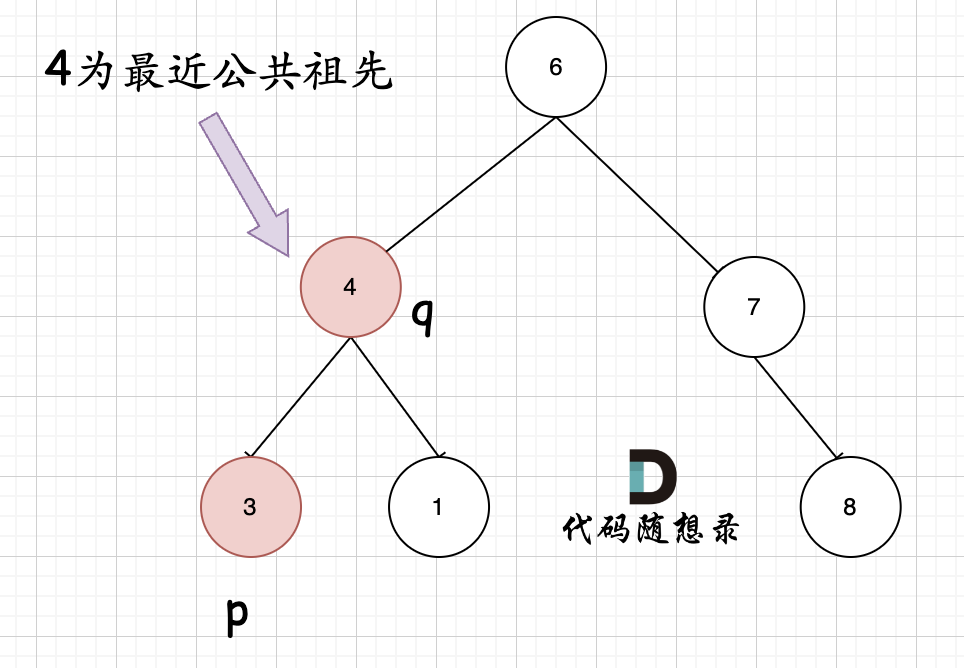
+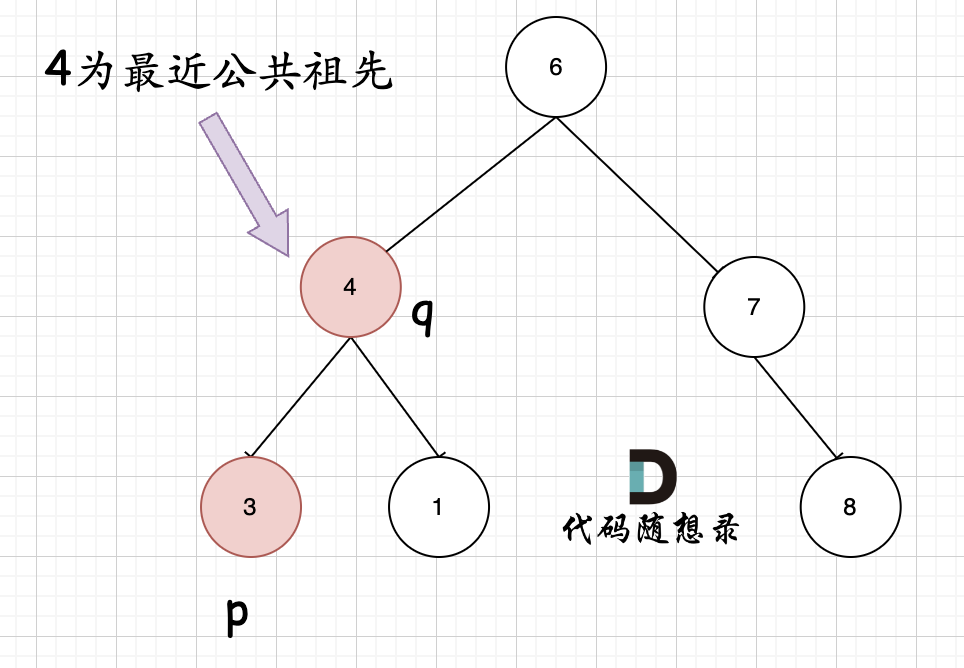
其实情况一 和 情况二 代码实现过程都是一样的,也可以说,实现情况一的逻辑,顺便包含了情况二。
@@ -131,7 +129,7 @@ left与right的逻辑处理; // 中
如图:
-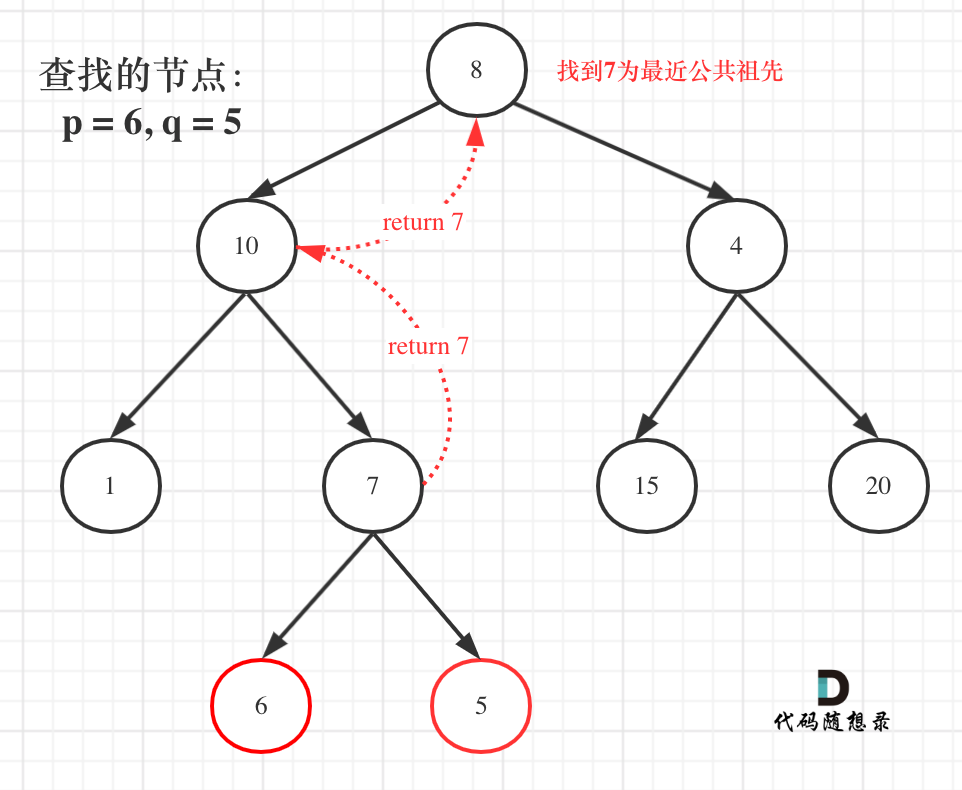
+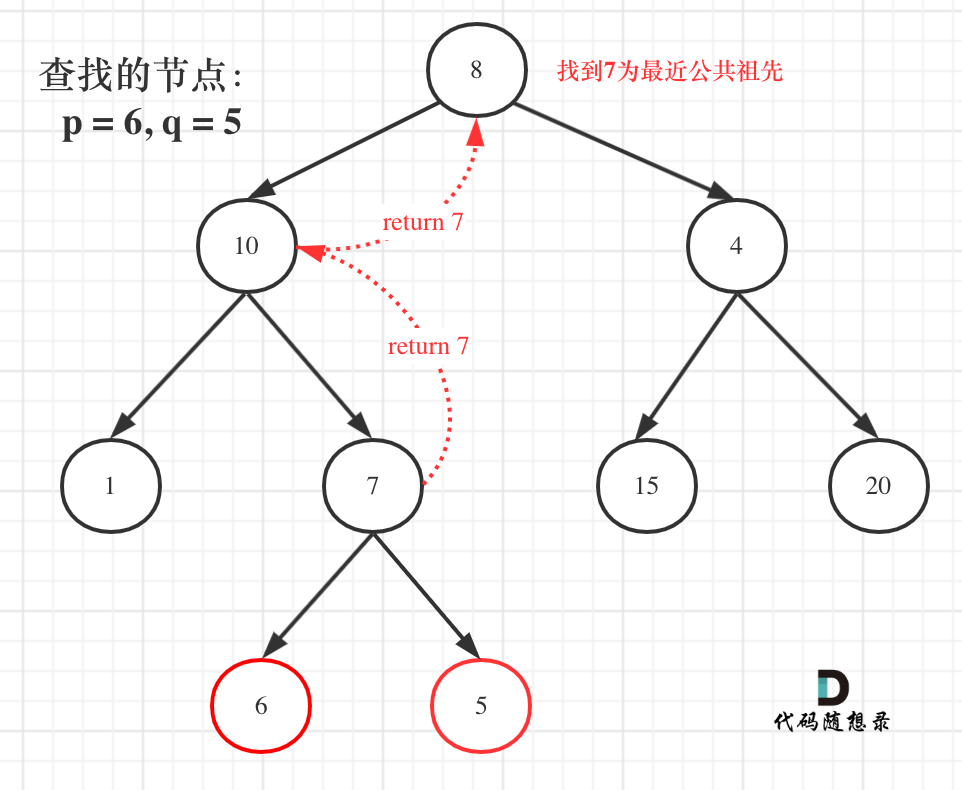
就像图中一样直接返回7。
@@ -164,7 +162,7 @@ TreeNode* right = lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p, q);
如图:
-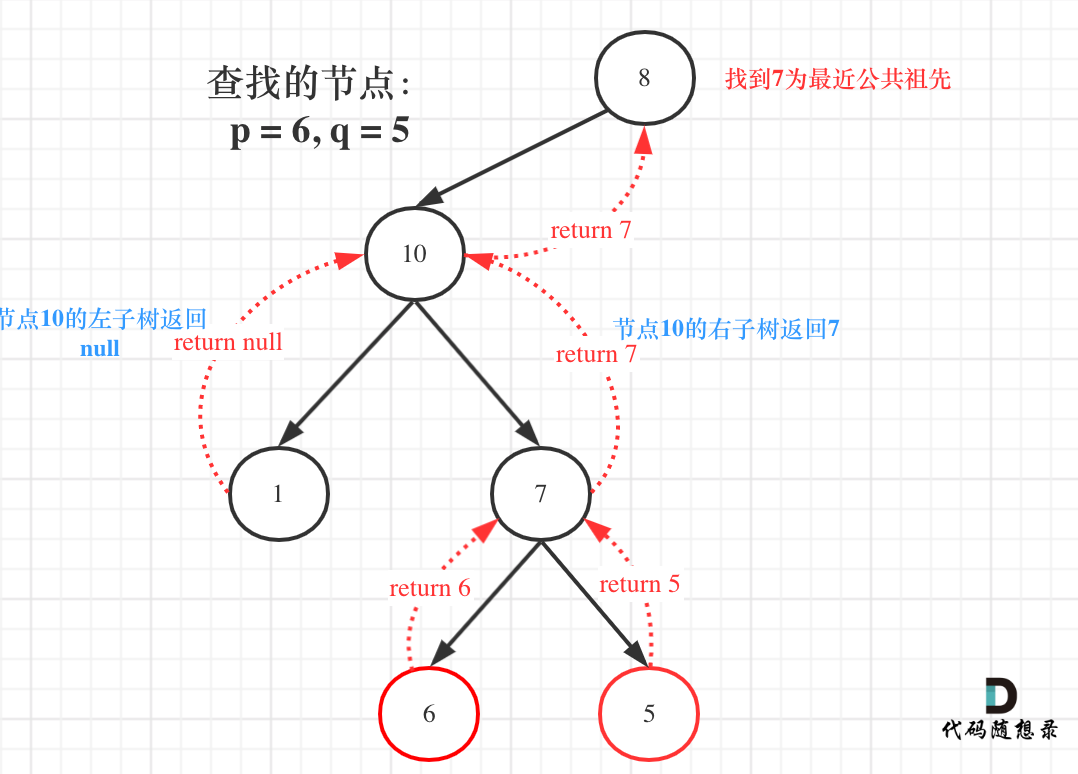
+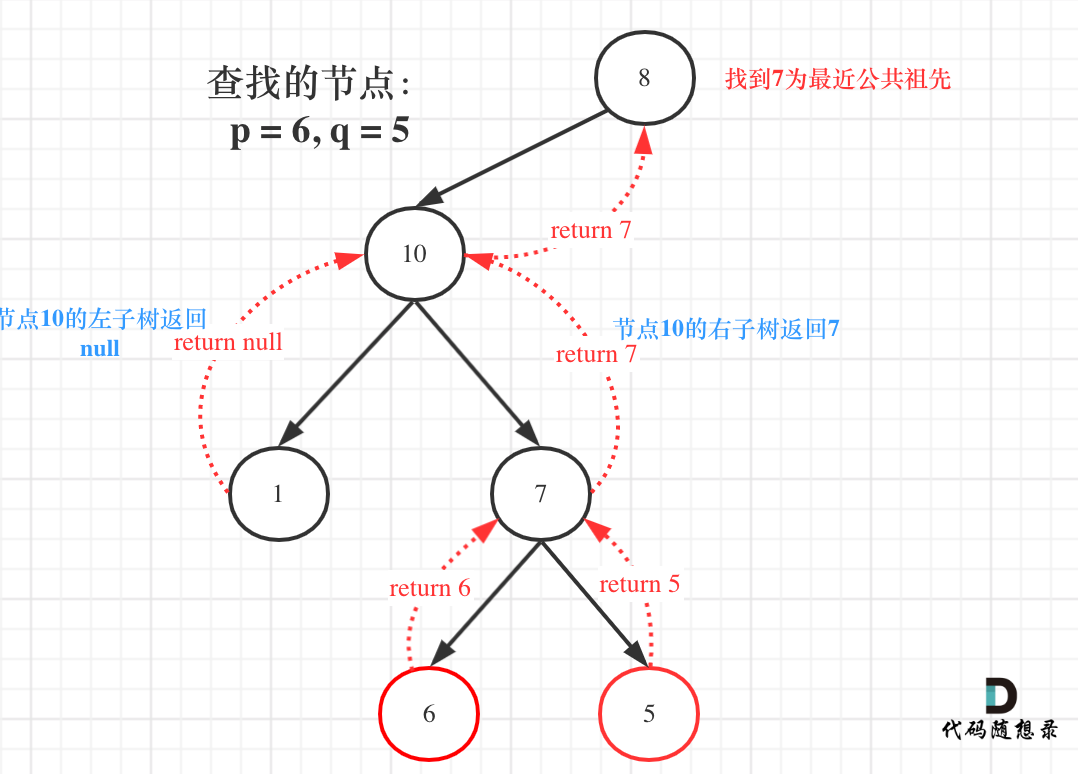
图中节点10的左子树返回null,右子树返回目标值7,那么此时节点10的处理逻辑就是把右子树的返回值(最近公共祖先7)返回上去!
@@ -185,7 +183,7 @@ else { // (left == NULL && right == NULL)
那么寻找最小公共祖先,完整流程图如下:
-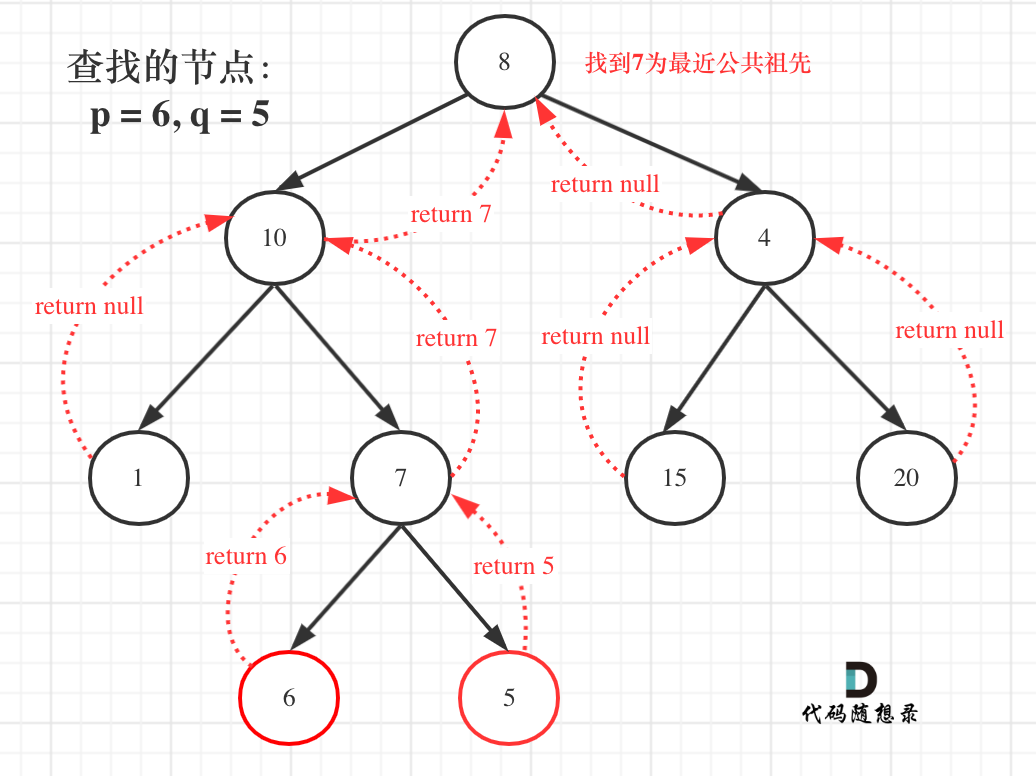
+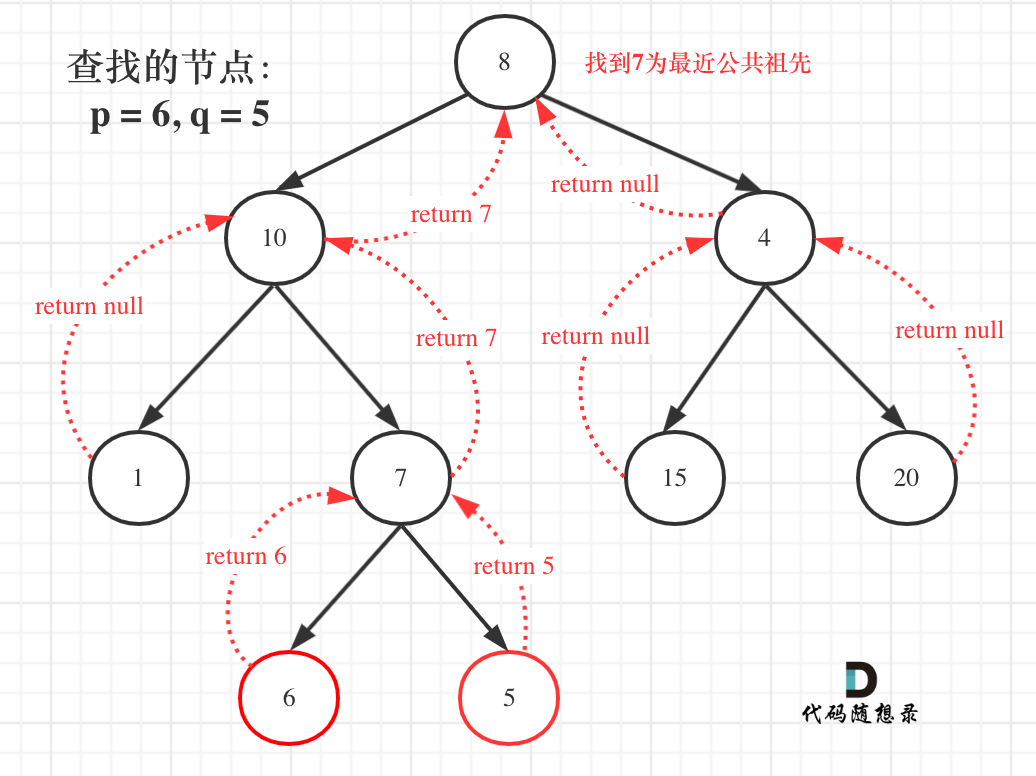
**从图中,大家可以看到,我们是如何回溯遍历整棵二叉树,将结果返回给头结点的!**
@@ -247,7 +245,7 @@ public:
### Java
-
+递归
```Java
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
@@ -271,6 +269,47 @@ class Solution {
}
}
+```
+迭代
+```Java
+class Solution {
+ public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
+ int max = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
+ Stack st = new Stack<>();
+ TreeNode cur = root, pre = null;
+ while (cur != null || !st.isEmpty()) {
+ while (cur != null) {
+ st.push(cur);
+ cur = cur.left;
+ }
+ cur = st.pop();
+ if (cur.right == null || cur.right == pre) {
+ // p/q是 中/左 或者 中/右 , 返回中
+ if (cur == p || cur == q) {
+ if ((cur.left != null && cur.left.val == max) || (cur.right != null && cur.right.val == max)) {
+ return cur;
+ }
+ cur.val = max;
+ }
+ // p/q是 左/右 , 返回中
+ if (cur.left != null && cur.left.val == max && cur.right != null && cur.right.val == max) {
+ return cur;
+ }
+ // MAX_VALUE 往上传递
+ if ((cur.left != null && cur.left.val == max) || (cur.right != null && cur.right.val == max)) {
+ cur.val = max;
+ }
+ pre = cur;
+ cur = null;
+ } else {
+ st.push(cur);
+ cur = cur.right;
+ }
+ }
+ return null;
+ }
+}
+
```
### Python
@@ -413,7 +452,11 @@ impl Solution {
p: Option>>,
q: Option>>,
) -> Option>> {
- if root == p || root == q || root.is_none() {
+ if root.is_none() {
+ return root;
+ }
+ if Rc::ptr_eq(root.as_ref().unwrap(), p.as_ref().unwrap())
+ || Rc::ptr_eq(root.as_ref().unwrap(), q.as_ref().unwrap()) {
return root;
}
let left = Self::lowest_common_ancestor(
@@ -445,8 +488,4 @@ public TreeNode LowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q)
}
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0239.\346\273\221\345\212\250\347\252\227\345\217\243\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\200\274.md" "b/problems/0239.\346\273\221\345\212\250\347\252\227\345\217\243\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\200\274.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 19ac12619e..5ea810104d
--- "a/problems/0239.\346\273\221\345\212\250\347\252\227\345\217\243\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\200\274.md"
+++ "b/problems/0239.\346\273\221\345\212\250\347\252\227\345\217\243\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\200\274.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0239.\346\273\221\345\212\250\347\252\227\345\217\243\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\200\274.md" "b/problems/0239.\346\273\221\345\212\250\347\252\227\345\217\243\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\200\274.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 19ac12619e..5ea810104d
--- "a/problems/0239.\346\273\221\345\212\250\347\252\227\345\217\243\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\200\274.md"
+++ "b/problems/0239.\346\273\221\345\212\250\347\252\227\345\217\243\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\200\274.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
@@ -20,7 +18,7 @@
你能在线性时间复杂度内解决此题吗?
- +
+ 提示:
@@ -84,7 +82,7 @@ public:
动画如下:
-
+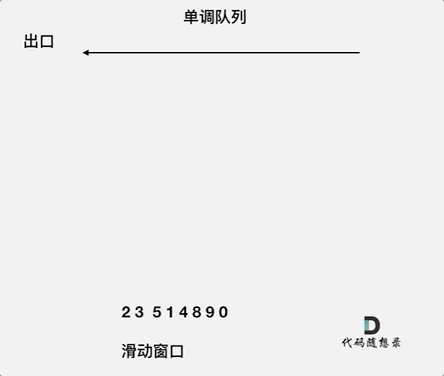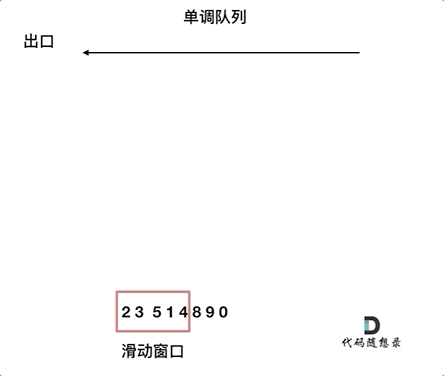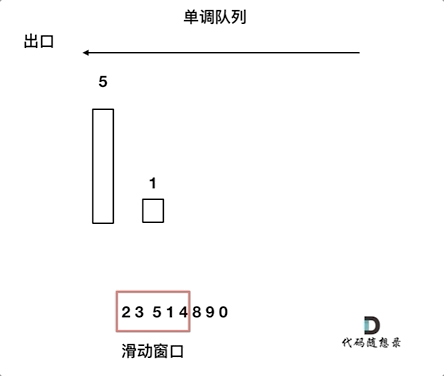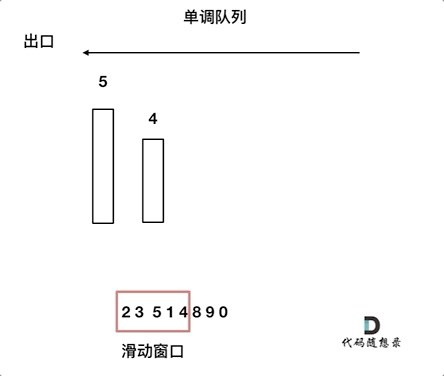
对于窗口里的元素{2, 3, 5, 1 ,4},单调队列里只维护{5, 4} 就够了,保持单调队列里单调递减,此时队列出口元素就是窗口里最大元素。
@@ -100,7 +98,7 @@ public:
为了更直观的感受到单调队列的工作过程,以题目示例为例,输入: nums = [1,3,-1,-3,5,3,6,7], 和 k = 3,动画如下:
-
+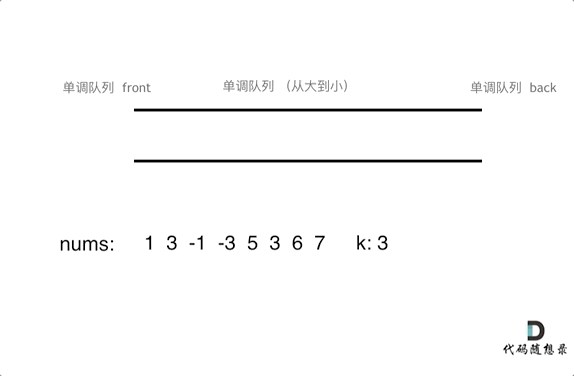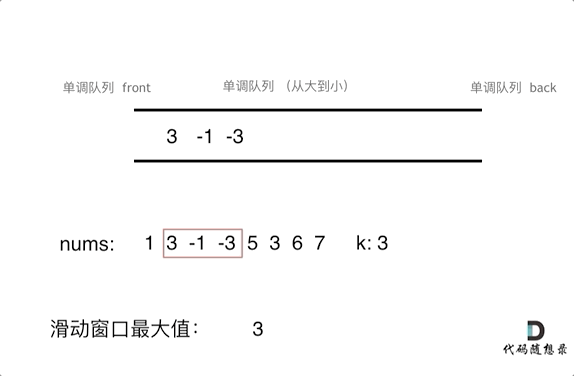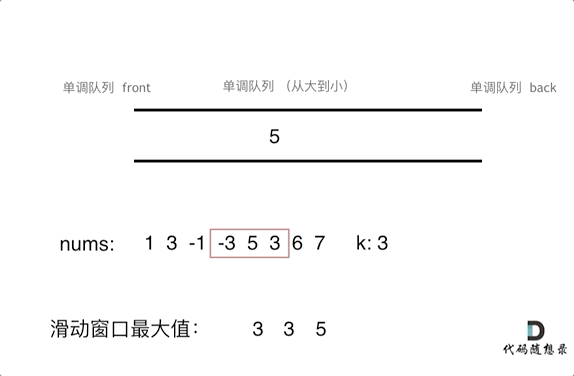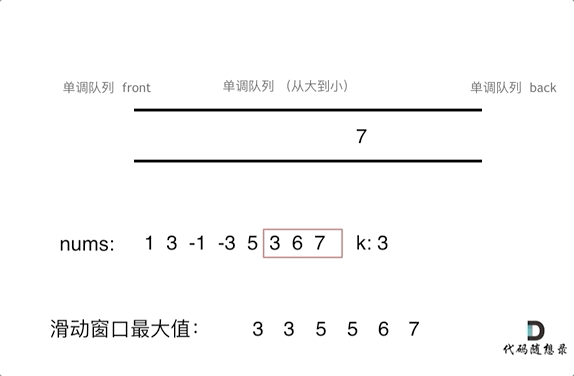
那么我们用什么数据结构来实现这个单调队列呢?
@@ -267,7 +265,7 @@ class Solution {
//利用双端队列手动实现单调队列
/**
* 用一个单调队列来存储对应的下标,每当窗口滑动的时候,直接取队列的头部指针对应的值放入结果集即可
- * 单调队列类似 (tail -->) 3 --> 2 --> 1 --> 0 (--> head) (右边为头结点,元素存的是下标)
+ * 单调递减队列类似 (head -->) 3 --> 2 --> 1 --> 0 (--> tail) (左边为头结点,元素存的是下标)
*/
class Solution {
public int[] maxSlidingWindow(int[] nums, int k) {
@@ -281,7 +279,7 @@ class Solution {
while(!deque.isEmpty() && deque.peek() < i - k + 1){
deque.poll();
}
- // 2.既然是单调,就要保证每次放进去的数字要比末尾的都大,否则也弹出
+ // 2.维护单调递减队列:新元素若大于队尾元素,则弹出队尾元素,直到满足单调性
while(!deque.isEmpty() && nums[deque.peekLast()] < nums[i]) {
deque.pollLast();
}
@@ -299,7 +297,7 @@ class Solution {
```
### Python:
-
+#### 解法一:使用自定义的单调队列类
```python
from collections import deque
@@ -339,6 +337,35 @@ class Solution:
return result
```
+
+#### 解法二:直接用单调队列
+```python
+from collections import deque
+class Solution:
+ def maxSlidingWindow(self, nums: List[int], k: int) -> List[int]:
+ max_list = [] # 结果集合
+ kept_nums = deque() # 单调队列
+
+ for i in range(len(nums)):
+ update_kept_nums(kept_nums, nums[i]) # 右侧新元素加入
+
+ if i >= k and nums[i - k] == kept_nums[0]: # 左侧旧元素如果等于单调队列头元素,需要移除头元素
+ kept_nums.popleft()
+
+ if i >= k - 1:
+ max_list.append(kept_nums[0])
+
+ return max_list
+
+def update_kept_nums(kept_nums, num): # num 是新加入的元素
+ # 所有小于新元素的队列尾部元素,在新元素出现后,都是没有价值的,都需要被移除
+ while kept_nums and num > kept_nums[-1]:
+ kept_nums.pop()
+
+ kept_nums.append(num)
+
+```
+
### Go:
```go
@@ -401,7 +428,7 @@ func maxSlidingWindow(nums []int, k int) []int {
}
```
-### Javascript:
+### JavaScript:
```javascript
/**
@@ -861,7 +888,36 @@ public:
};
```
-
提示:
@@ -84,7 +82,7 @@ public:
动画如下:
-
+
对于窗口里的元素{2, 3, 5, 1 ,4},单调队列里只维护{5, 4} 就够了,保持单调队列里单调递减,此时队列出口元素就是窗口里最大元素。
@@ -100,7 +98,7 @@ public:
为了更直观的感受到单调队列的工作过程,以题目示例为例,输入: nums = [1,3,-1,-3,5,3,6,7], 和 k = 3,动画如下:
-
+
那么我们用什么数据结构来实现这个单调队列呢?
@@ -267,7 +265,7 @@ class Solution {
//利用双端队列手动实现单调队列
/**
* 用一个单调队列来存储对应的下标,每当窗口滑动的时候,直接取队列的头部指针对应的值放入结果集即可
- * 单调队列类似 (tail -->) 3 --> 2 --> 1 --> 0 (--> head) (右边为头结点,元素存的是下标)
+ * 单调递减队列类似 (head -->) 3 --> 2 --> 1 --> 0 (--> tail) (左边为头结点,元素存的是下标)
*/
class Solution {
public int[] maxSlidingWindow(int[] nums, int k) {
@@ -281,7 +279,7 @@ class Solution {
while(!deque.isEmpty() && deque.peek() < i - k + 1){
deque.poll();
}
- // 2.既然是单调,就要保证每次放进去的数字要比末尾的都大,否则也弹出
+ // 2.维护单调递减队列:新元素若大于队尾元素,则弹出队尾元素,直到满足单调性
while(!deque.isEmpty() && nums[deque.peekLast()] < nums[i]) {
deque.pollLast();
}
@@ -299,7 +297,7 @@ class Solution {
```
### Python:
-
+#### 解法一:使用自定义的单调队列类
```python
from collections import deque
@@ -339,6 +337,35 @@ class Solution:
return result
```
+
+#### 解法二:直接用单调队列
+```python
+from collections import deque
+class Solution:
+ def maxSlidingWindow(self, nums: List[int], k: int) -> List[int]:
+ max_list = [] # 结果集合
+ kept_nums = deque() # 单调队列
+
+ for i in range(len(nums)):
+ update_kept_nums(kept_nums, nums[i]) # 右侧新元素加入
+
+ if i >= k and nums[i - k] == kept_nums[0]: # 左侧旧元素如果等于单调队列头元素,需要移除头元素
+ kept_nums.popleft()
+
+ if i >= k - 1:
+ max_list.append(kept_nums[0])
+
+ return max_list
+
+def update_kept_nums(kept_nums, num): # num 是新加入的元素
+ # 所有小于新元素的队列尾部元素,在新元素出现后,都是没有价值的,都需要被移除
+ while kept_nums and num > kept_nums[-1]:
+ kept_nums.pop()
+
+ kept_nums.append(num)
+
+```
+
### Go:
```go
@@ -401,7 +428,7 @@ func maxSlidingWindow(nums []int, k int) []int {
}
```
-### Javascript:
+### JavaScript:
```javascript
/**
@@ -861,7 +888,36 @@ public:
};
```
-
-
-  -
+### C
+
+```c
+int* maxSlidingWindow(int* nums, int numsSize, int k, int* returnSize) {
+ *returnSize = numsSize - k + 1;
+ int *res = (int*)malloc((*returnSize) * sizeof(int));
+ assert(res);
+ int *deque = (int*)malloc(numsSize * sizeof(int));
+ assert(deque);
+ int front = 0, rear = 0, idx = 0;
+
+ for (int i = 0 ; i < numsSize ; i++) {
+ while (front < rear && deque[front] <= i - k) {
+ front++;
+ }
+
+ while (front < rear && nums[deque[rear - 1]] <= nums[i]) {
+ rear--;
+ }
+
+ deque[rear++] = i;
+
+ if (i >= k - 1) {
+ res[idx++] = nums[deque[front]];
+ }
+ }
+
+ return res;
+}
+
+```
+
+
diff --git "a/problems/0242.\346\234\211\346\225\210\347\232\204\345\255\227\346\257\215\345\274\202\344\275\215\350\257\215.md" "b/problems/0242.\346\234\211\346\225\210\347\232\204\345\255\227\346\257\215\345\274\202\344\275\215\350\257\215.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 6eed90a73a..0a37ea26cc
--- "a/problems/0242.\346\234\211\346\225\210\347\232\204\345\255\227\346\257\215\345\274\202\344\275\215\350\257\215.md"
+++ "b/problems/0242.\346\234\211\346\225\210\347\232\204\345\255\227\346\257\215\345\274\202\344\275\215\350\257\215.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+### C
+
+```c
+int* maxSlidingWindow(int* nums, int numsSize, int k, int* returnSize) {
+ *returnSize = numsSize - k + 1;
+ int *res = (int*)malloc((*returnSize) * sizeof(int));
+ assert(res);
+ int *deque = (int*)malloc(numsSize * sizeof(int));
+ assert(deque);
+ int front = 0, rear = 0, idx = 0;
+
+ for (int i = 0 ; i < numsSize ; i++) {
+ while (front < rear && deque[front] <= i - k) {
+ front++;
+ }
+
+ while (front < rear && nums[deque[rear - 1]] <= nums[i]) {
+ rear--;
+ }
+
+ deque[rear++] = i;
+
+ if (i >= k - 1) {
+ res[idx++] = nums[deque[front]];
+ }
+ }
+
+ return res;
+}
+
+```
+
+
diff --git "a/problems/0242.\346\234\211\346\225\210\347\232\204\345\255\227\346\257\215\345\274\202\344\275\215\350\257\215.md" "b/problems/0242.\346\234\211\346\225\210\347\232\204\345\255\227\346\257\215\345\274\202\344\275\215\350\257\215.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 6eed90a73a..0a37ea26cc
--- "a/problems/0242.\346\234\211\346\225\210\347\232\204\345\255\227\346\257\215\345\274\202\344\275\215\350\257\215.md"
+++ "b/problems/0242.\346\234\211\346\225\210\347\232\204\345\255\227\346\257\215\345\274\202\344\275\215\350\257\215.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
> 数组就是简单的哈希表,但是数组的大小可不是无限开辟的
@@ -44,7 +42,7 @@
操作动画如下:
-
+
定义一个数组叫做record用来上记录字符串s里字符出现的次数。
@@ -383,6 +381,31 @@ object Solution {
}
```
+### C
+
+```c
+bool isAnagram(char* s, char* t) {
+ int len1 = strlen(s), len2 = strlen(t);
+ if (len1 != len2) {
+ return false;
+ }
+
+ int map1[26] = {0}, map2[26] = {0};
+ for (int i = 0; i < len1; i++) {
+ map1[s[i] - 'a'] += 1;
+ map2[t[i] - 'a'] += 1;
+ }
+
+ for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
+ if (map1[i] != map2[i]) {
+ return false;
+ }
+ }
+
+ return true;
+}
+```
+
## 相关题目
* [383.赎金信](https://programmercarl.com/0383.%E8%B5%8E%E9%87%91%E4%BF%A1.html)
@@ -390,8 +413,4 @@ object Solution {
* [438.找到字符串中所有字母异位词](https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-all-anagrams-in-a-string/)
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0257.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\211\200\346\234\211\350\267\257\345\276\204.md" "b/problems/0257.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\211\200\346\234\211\350\267\257\345\276\204.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 4c6c92c5b4..4a66c816bc
--- "a/problems/0257.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\211\200\346\234\211\350\267\257\345\276\204.md"
+++ "b/problems/0257.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\211\200\346\234\211\350\267\257\345\276\204.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0257.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\211\200\346\234\211\350\267\257\345\276\204.md" "b/problems/0257.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\211\200\346\234\211\350\267\257\345\276\204.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 4c6c92c5b4..4a66c816bc
--- "a/problems/0257.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\211\200\346\234\211\350\267\257\345\276\204.md"
+++ "b/problems/0257.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\211\200\346\234\211\350\267\257\345\276\204.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
> 以为只用了递归,其实还用了回溯
@@ -16,7 +14,7 @@
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例:
-
+
## 算法公开课
@@ -30,7 +28,7 @@
前序遍历以及回溯的过程如图:
-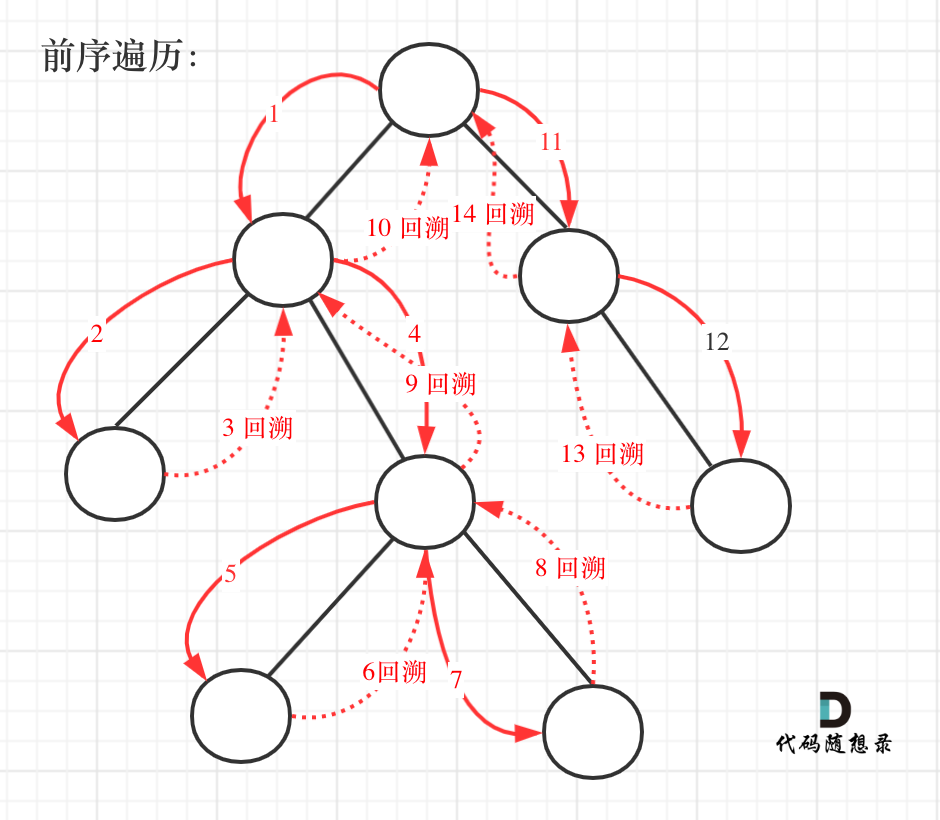
+
我们先使用递归的方式,来做前序遍历。**要知道递归和回溯就是一家的,本题也需要回溯。**
@@ -40,7 +38,7 @@
要传入根节点,记录每一条路径的path,和存放结果集的result,这里递归不需要返回值,代码如下:
-```
+```CPP
void traversal(TreeNode* cur, vector& path, vector& result)
```
@@ -48,7 +46,7 @@ void traversal(TreeNode* cur, vector& path, vector& result)
在写递归的时候都习惯了这么写:
-```
+```CPP
if (cur == NULL) {
终止处理逻辑
}
@@ -59,7 +57,7 @@ if (cur == NULL) {
**那么什么时候算是找到了叶子节点?** 是当 cur不为空,其左右孩子都为空的时候,就找到叶子节点。
所以本题的终止条件是:
-```
+```CPP
if (cur->left == NULL && cur->right == NULL) {
终止处理逻辑
}
@@ -69,15 +67,15 @@ if (cur->left == NULL && cur->right == NULL) {
再来看一下终止处理的逻辑。
-这里使用vector 结构path来记录路径,所以要把vector 结构的path转为string格式,再把这个string 放进 result里。
+这里使用`vector` 结构path来记录路径,所以要把`vector` 结构的path转为string格式,再把这个string 放进 result里。
-**那么为什么使用了vector 结构来记录路径呢?** 因为在下面处理单层递归逻辑的时候,要做回溯,使用vector方便来做回溯。
+**那么为什么使用了`vector` 结构来记录路径呢?** 因为在下面处理单层递归逻辑的时候,要做回溯,使用vector方便来做回溯。
可能有的同学问了,我看有些人的代码也没有回溯啊。
**其实是有回溯的,只不过隐藏在函数调用时的参数赋值里**,下文我还会提到。
-这里我们先使用vector结构的path容器来记录路径,那么终止处理逻辑如下:
+这里我们先使用`vector`结构的path容器来记录路径,那么终止处理逻辑如下:
```CPP
if (cur->left == NULL && cur->right == NULL) { // 遇到叶子节点
@@ -102,7 +100,7 @@ if (cur->left == NULL && cur->right == NULL) { // 遇到叶子节点
所以递归前要加上判断语句,下面要递归的节点是否为空,如下
-```
+```CPP
if (cur->left) {
traversal(cur->left, path, result);
}
@@ -317,7 +315,7 @@ public:
其实关键还在于 参数,使用的是 `string path`,这里并没有加上引用`&` ,即本层递归中,path + 该节点数值,但该层递归结束,上一层path的数值并不会受到任何影响。 如图所示:
-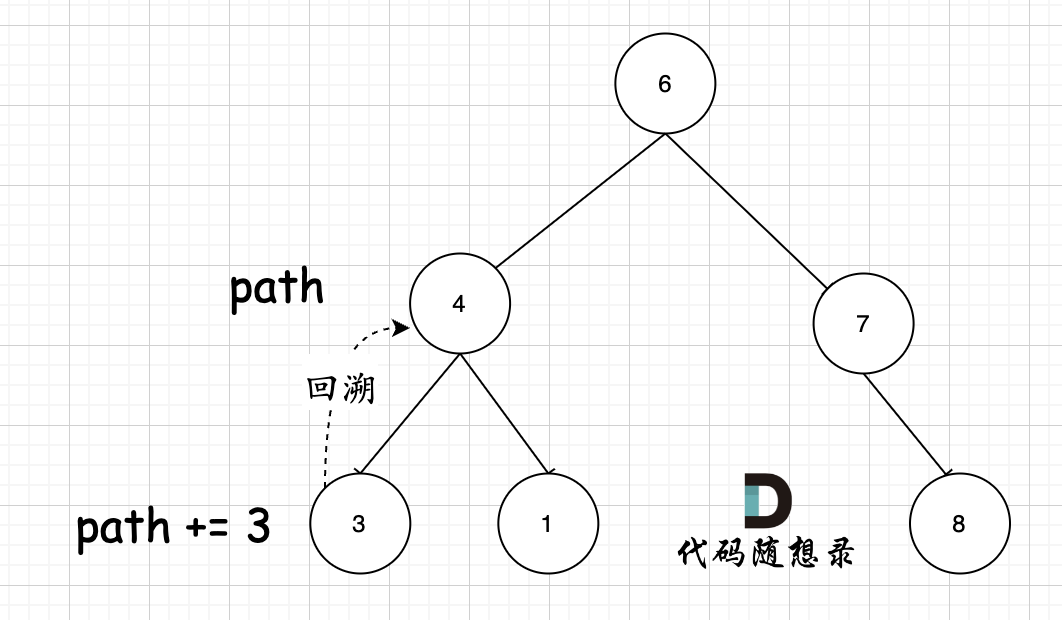
+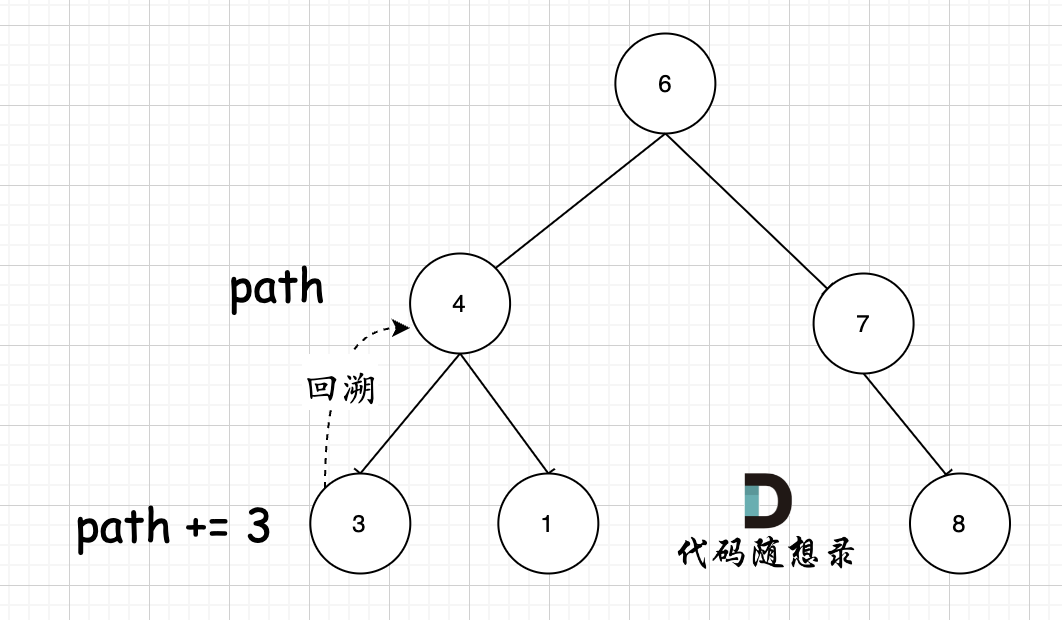
节点4 的path,在遍历到节点3,path+3,遍历节点3的递归结束之后,返回节点4(回溯的过程),path并不会把3加上。
@@ -938,7 +936,3 @@ public void Traversal(TreeNode node, List path, List res)
}
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0279.\345\256\214\345\205\250\345\271\263\346\226\271\346\225\260.md" "b/problems/0279.\345\256\214\345\205\250\345\271\263\346\226\271\346\225\260.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index a0e62d4800..7c5d7c9c9f
--- "a/problems/0279.\345\256\214\345\205\250\345\271\263\346\226\271\346\225\260.md"
+++ "b/problems/0279.\345\256\214\345\205\250\345\271\263\346\226\271\346\225\260.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0279.\345\256\214\345\205\250\345\271\263\346\226\271\346\225\260.md" "b/problems/0279.\345\256\214\345\205\250\345\271\263\346\226\271\346\225\260.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index a0e62d4800..7c5d7c9c9f
--- "a/problems/0279.\345\256\214\345\205\250\345\271\263\346\226\271\346\225\260.md"
+++ "b/problems/0279.\345\256\214\345\205\250\345\271\263\346\226\271\346\225\260.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 279.完全平方数
@@ -95,7 +93,7 @@ for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) { // 遍历背包
已输入n为5例,dp状态图如下:
-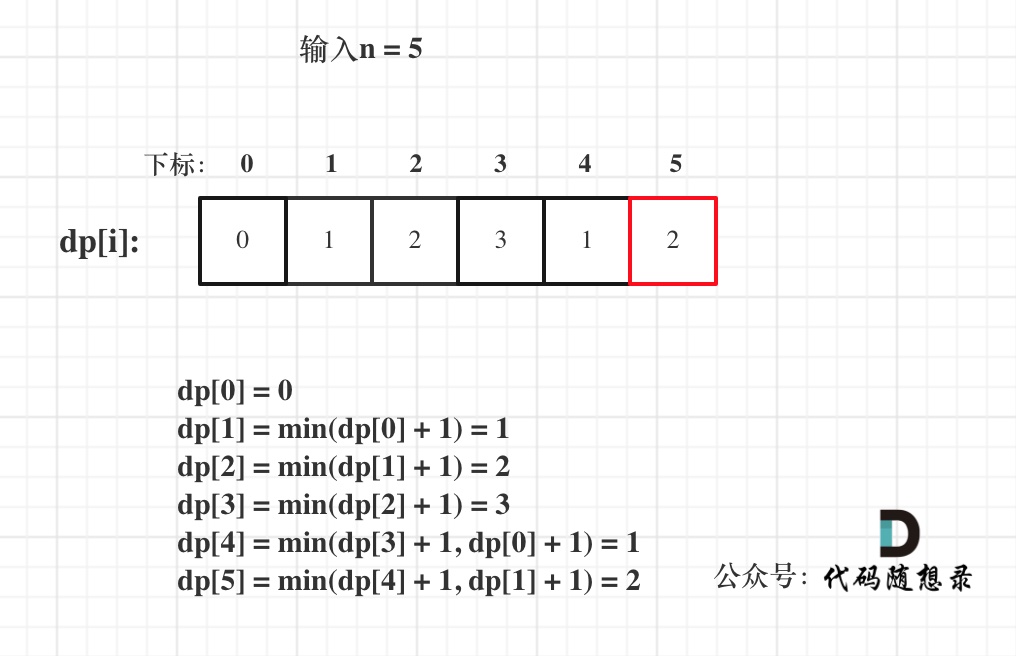
+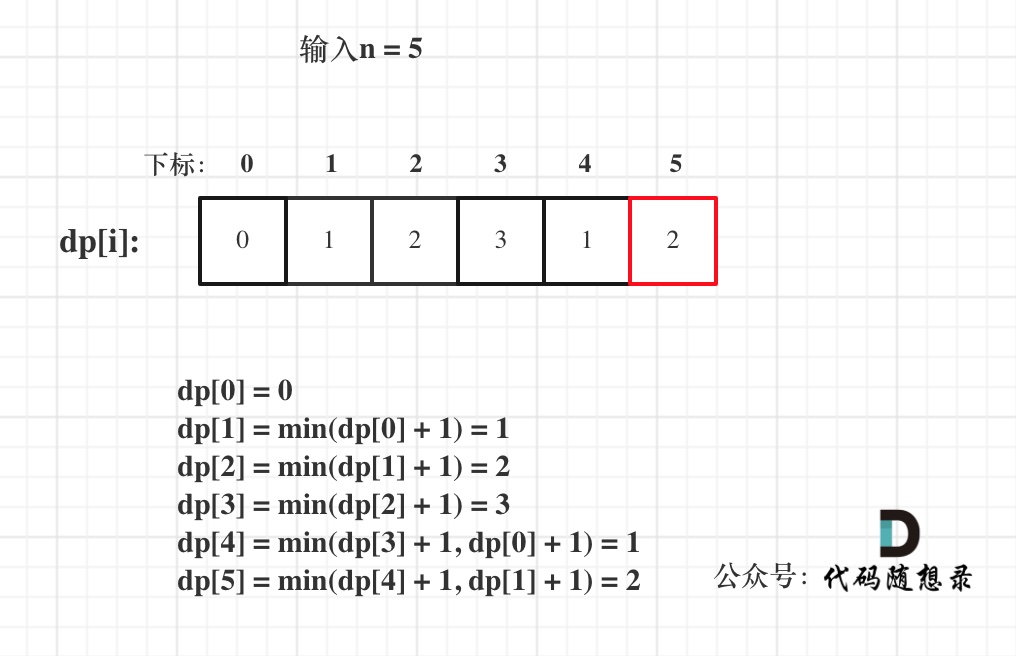
dp[0] = 0
dp[1] = min(dp[0] + 1) = 1
@@ -219,7 +217,7 @@ class Solution {
### Python:
-先遍历物品, 再遍历背包
+先遍历背包, 再遍历物品
```python
class Solution:
def numSquares(self, n: int) -> int:
@@ -234,7 +232,7 @@ class Solution:
return dp[n]
```
-先遍历背包, 再遍历物品
+先遍历物品, 再遍历背包
```python
class Solution:
def numSquares(self, n: int) -> int:
@@ -271,7 +269,27 @@ class Solution:
# 返回结果
return dp[n]
+```
+```python
+class Solution(object):
+ def numSquares(self, n):
+ # 先把可以选的数准备好,更好理解
+ nums, num = [], 1
+ while num ** 2 <= n:
+ nums.append(num ** 2)
+ num += 1
+ # dp数组初始化
+ dp = [float('inf')] * (n + 1)
+ dp[0] = 0
+ # 遍历准备好的完全平方数
+ for i in range(len(nums)):
+ # 遍历背包容量
+ for j in range(nums[i], n+1):
+ dp[j] = min(dp[j], dp[j-nums[i]]+1)
+ # 返回结果
+ return dp[-1]
+
```
### Go:
@@ -326,7 +344,7 @@ func min(a, b int) int {
}
```
-### Javascript:
+### JavaScript:
```Javascript
// 先遍历物品,再遍历背包
@@ -389,6 +407,30 @@ function numSquares(n: number): number {
};
```
+### C
+
+```c
+#define min(a, b) ((a) > (b) ? (b) : (a))
+
+int numSquares(int n) {
+ int* dp = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * (n + 1));
+ for (int j = 0; j < n + 1; j++) {
+ dp[j] = INT_MAX;
+ }
+ dp[0] = 0;
+ // 遍历背包
+ for (int i = 0; i <= n; ++i) {
+ // 遍历物品
+ for (int j = 1; j * j <= i; ++j) {
+ dp[i] = min(dp[i - j * j] + 1, dp[i]);
+ }
+ }
+ return dp[n];
+}
+```
+
+
+
### Rust:
```rust
@@ -435,8 +477,3 @@ impl Solution {
```
-
-
-  -
-
diff --git "a/problems/0283.\347\247\273\345\212\250\351\233\266.md" "b/problems/0283.\347\247\273\345\212\250\351\233\266.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index fc708844bd..e25525684e
--- "a/problems/0283.\347\247\273\345\212\250\351\233\266.md"
+++ "b/problems/0283.\347\247\273\345\212\250\351\233\266.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0283.\347\247\273\345\212\250\351\233\266.md" "b/problems/0283.\347\247\273\345\212\250\351\233\266.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index fc708844bd..e25525684e
--- "a/problems/0283.\347\247\273\345\212\250\351\233\266.md"
+++ "b/problems/0283.\347\247\273\345\212\250\351\233\266.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 283. 移动零:动态规划:一样的套路,再求一次完全平方数
@@ -34,7 +32,7 @@
如动画所示:
-
+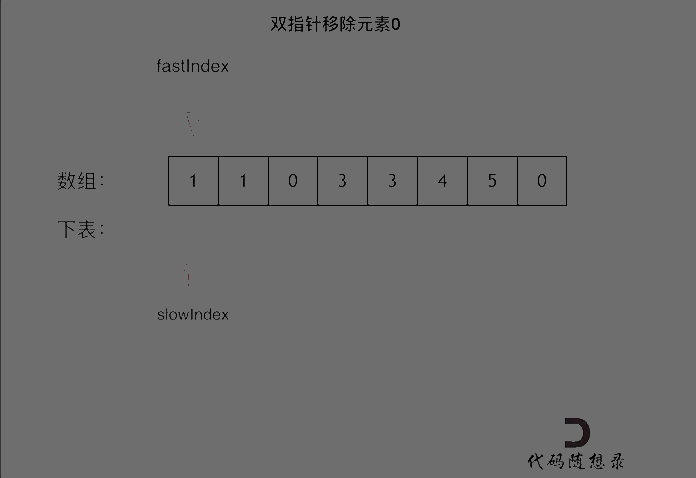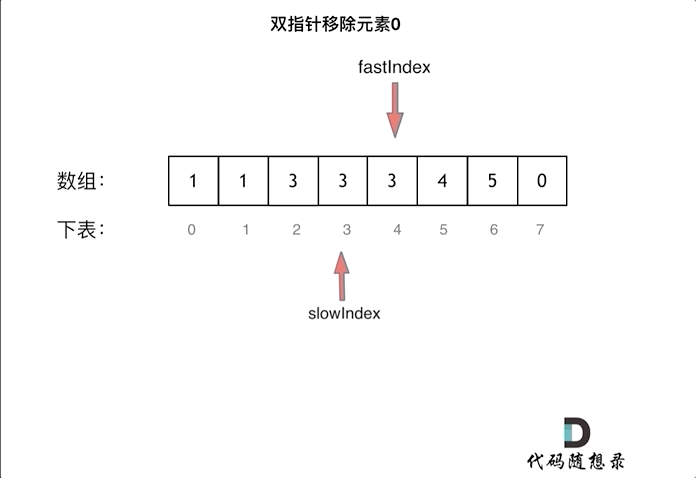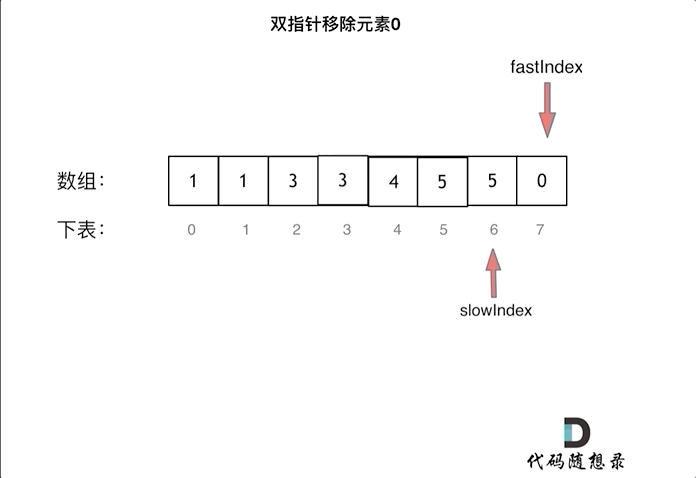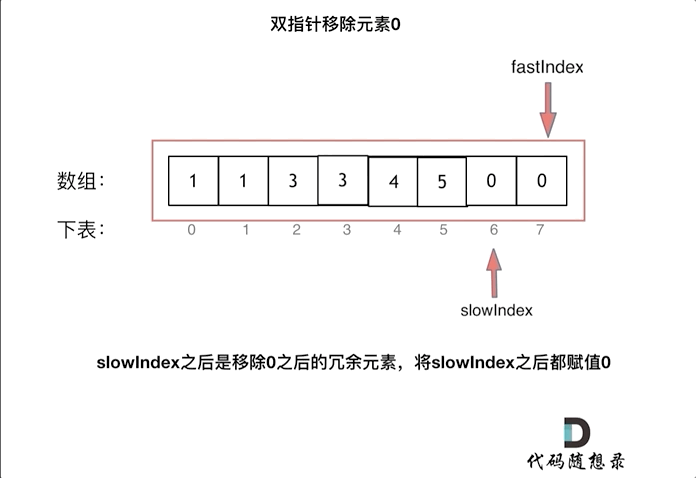
C++代码如下:
@@ -169,11 +167,20 @@ void moveZeroes(int* nums, int numsSize){
}
```
+### Rust
+```rust
+impl Solution {
+ pub fn move_zeroes(nums: &mut Vec) {
+ let mut slow = 0;
+ for fast in 0..nums.len() {
+ if nums[fast] != 0 {
+ nums.swap(slow, fast);
+ slow += 1;
+ }
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
-
-
-  -
-
diff --git "a/problems/0300.\346\234\200\351\225\277\344\270\212\345\215\207\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md" "b/problems/0300.\346\234\200\351\225\277\344\270\212\345\215\207\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 64f75291f5..06adfd950d
--- "a/problems/0300.\346\234\200\351\225\277\344\270\212\345\215\207\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
+++ "b/problems/0300.\346\234\200\351\225\277\344\270\212\345\215\207\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0300.\346\234\200\351\225\277\344\270\212\345\215\207\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md" "b/problems/0300.\346\234\200\351\225\277\344\270\212\345\215\207\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 64f75291f5..06adfd950d
--- "a/problems/0300.\346\234\200\351\225\277\344\270\212\345\215\207\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
+++ "b/problems/0300.\346\234\200\351\225\277\344\270\212\345\215\207\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 300.最长递增子序列
@@ -41,7 +39,7 @@
首先通过本题大家要明确什么是子序列,“子序列是由数组派生而来的序列,删除(或不删除)数组中的元素而不改变其余元素的顺序”。
本题也是代码随想录中子序列问题的第一题,如果没接触过这种题目的话,本题还是很难的,甚至想暴力去搜索也不知道怎么搜。
-子序列问题是动态规划解决的经典问题,当前下标i的递增子序列长度,其实和i之前的下表j的子序列长度有关系,那又是什么样的关系呢。
+子序列问题是动态规划解决的经典问题,当前下标i的递增子序列长度,其实和i之前的下标j的子序列长度有关系,那又是什么样的关系呢。
接下来,我们依然用动规五部曲来详细分析一波:
@@ -87,7 +85,7 @@ for (int i = 1; i < nums.size(); i++) {
输入:[0,1,0,3,2],dp数组的变化如下:
-
+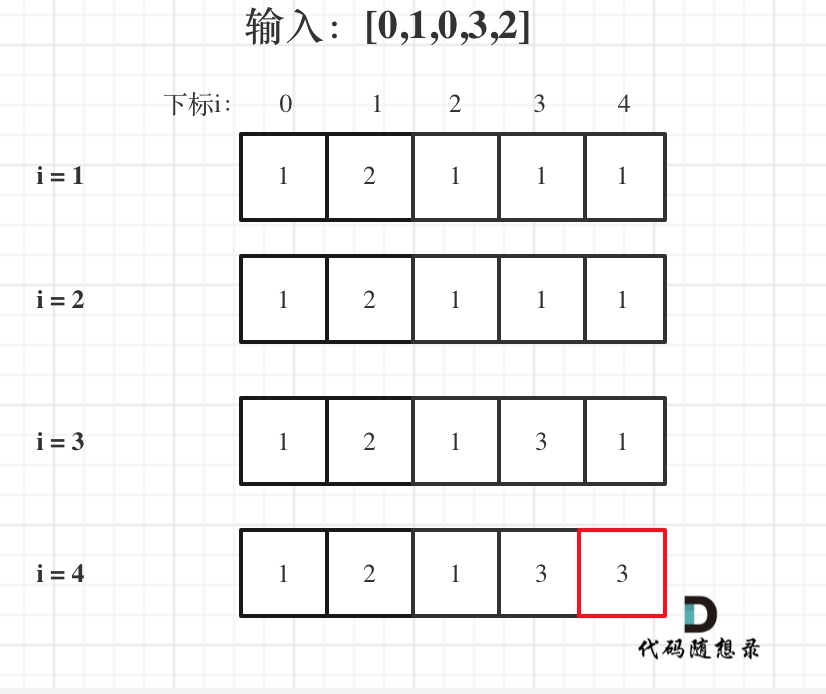
如果代码写出来,但一直AC不了,那么就把dp数组打印出来,看看对不对!
@@ -129,6 +127,7 @@ public:
```Java
class Solution {
public int lengthOfLIS(int[] nums) {
+ if (nums.length <= 1) return nums.length;
int[] dp = new int[nums.length];
int res = 1;
Arrays.fill(dp, 1);
@@ -137,8 +136,8 @@ class Solution {
if (nums[i] > nums[j]) {
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i], dp[j] + 1);
}
- res = Math.max(res, dp[i]);
}
+ res = Math.max(res, dp[i]);
}
return res;
}
@@ -247,7 +246,7 @@ func lengthOfLIS(nums []int ) int {
}
```
-### Javascript:
+### JavaScript:
```javascript
const lengthOfLIS = (nums) => {
@@ -288,6 +287,36 @@ function lengthOfLIS(nums: number[]): number {
};
```
+### C:
+
+```c
+#define max(a, b) ((a) > (b) ? (a) : (b))
+
+int lengthOfLIS(int* nums, int numsSize) {
+ if(numsSize <= 1){
+ return numsSize;
+ }
+ int dp[numsSize];
+ for(int i = 0; i < numsSize; i++){
+ dp[i]=1;
+ }
+ int result = 1;
+ for (int i = 1; i < numsSize; ++i) {
+ for (int j = 0; j < i; ++j) {
+ if(nums[i] > nums[j]){
+ dp[i] = max(dp[i], dp[j] + 1);
+ }
+ if(dp[i] > result){
+ result = dp[i];
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return result;
+}
+```
+
+
+
### Rust:
```rust
@@ -306,9 +335,27 @@ pub fn length_of_lis(nums: Vec) -> i32 {
}
```
+### Cangjie:
+
+```cangjie
+func lengthOfLIS(nums: Array): Int64 {
+ let n = nums.size
+ if (n <= 1) {
+ return n
+ }
+
+ let dp = Array(n, item: 1)
+ var res = 0
+ for (i in 1..n) {
+ for (j in 0..i) {
+ if (nums[i] > nums[j]) {
+ dp[i] = max(dp[i], dp[j] + 1)
+ }
+ }
+ res = max(dp[i], res)
+ }
+ return res
+}
+```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0309.\346\234\200\344\275\263\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\346\227\266\346\234\272\345\220\253\345\206\267\345\206\273\346\234\237.md" "b/problems/0309.\346\234\200\344\275\263\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\346\227\266\346\234\272\345\220\253\345\206\267\345\206\273\346\234\237.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 0eb66fb543..d396e521b3
--- "a/problems/0309.\346\234\200\344\275\263\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\346\227\266\346\234\272\345\220\253\345\206\267\345\206\273\346\234\237.md"
+++ "b/problems/0309.\346\234\200\344\275\263\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\346\227\266\346\234\272\345\220\253\345\206\267\345\206\273\346\234\237.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0309.\346\234\200\344\275\263\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\346\227\266\346\234\272\345\220\253\345\206\267\345\206\273\346\234\237.md" "b/problems/0309.\346\234\200\344\275\263\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\346\227\266\346\234\272\345\220\253\345\206\267\345\206\273\346\234\237.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 0eb66fb543..d396e521b3
--- "a/problems/0309.\346\234\200\344\275\263\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\346\227\266\346\234\272\345\220\253\345\206\267\345\206\273\346\234\237.md"
+++ "b/problems/0309.\346\234\200\344\275\263\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\346\227\266\346\234\272\345\220\253\345\206\267\345\206\273\346\234\237.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 309.最佳买卖股票时机含冷冻期
@@ -49,7 +47,7 @@ dp[i][j],第i天状态为j,所剩的最多现金为dp[i][j]。
* 状态三:今天卖出股票
* 状态四:今天为冷冻期状态,但冷冻期状态不可持续,只有一天!
-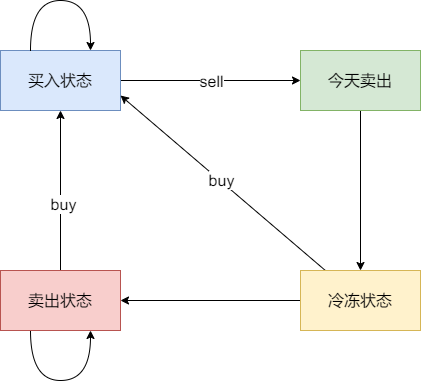
+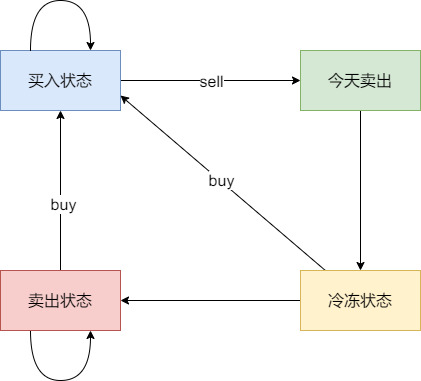
j的状态为:
@@ -138,7 +136,7 @@ dp[i][3] = dp[i - 1][2];
以 [1,2,3,0,2] 为例,dp数组如下:
-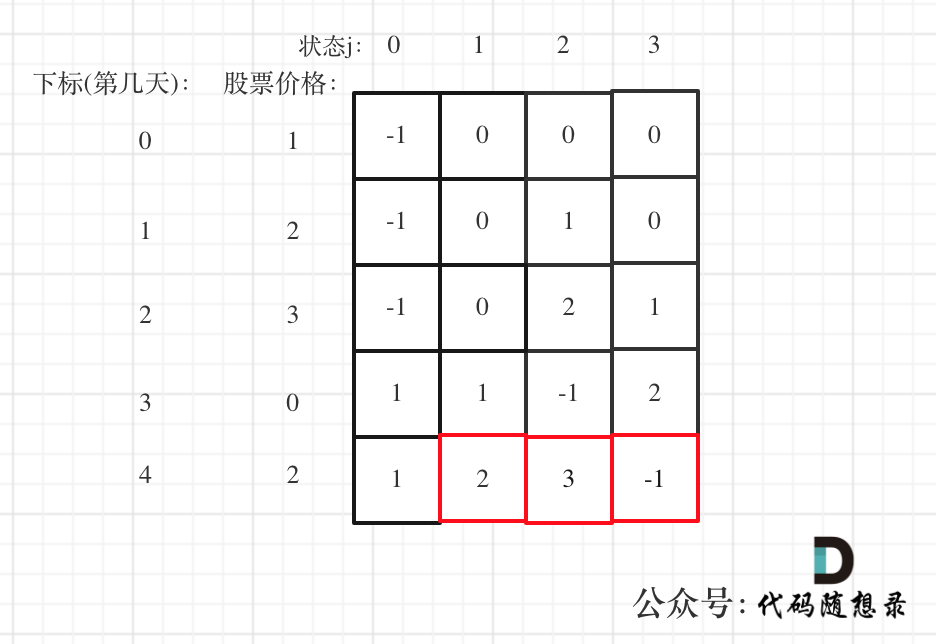
+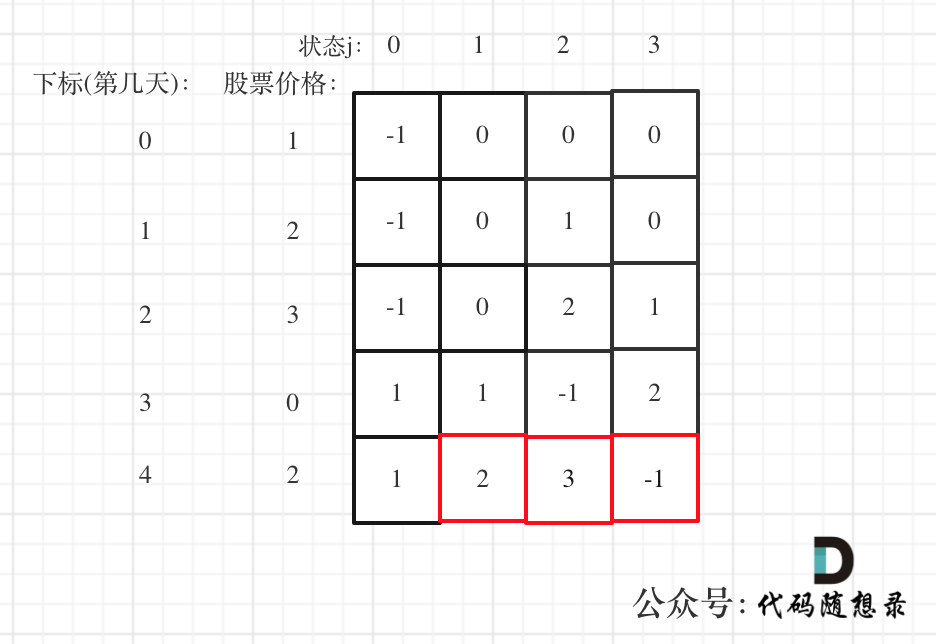
最后结果是取 状态二,状态三,和状态四的最大值,不少同学会把状态四忘了,状态四是冷冻期,最后一天如果是冷冻期也可能是最大值。
@@ -274,7 +272,7 @@ class Solution {
```
### Python:
-版本一
+> 版本一
```python
from typing import List
@@ -294,7 +292,8 @@ class Solution:
return max(dp[n-1][3], dp[n-1][1], dp[n-1][2]) # 返回最后一天不持有股票的最大利润
```
-版本二
+
+> 版本二
```python
class Solution:
def maxProfit(self, prices: List[int]) -> int:
@@ -320,6 +319,36 @@ class Solution:
return max(dp[-1][1], dp[-1][2])
```
+
+> 版本三
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def maxProfit(self, prices: List[int]) -> int:
+ # 0: holding stocks
+ # (1) keep holding stocks: dp[i][0] = dp[i - 1][0]
+ # (2) buy stocks: dp[i][0] = dp[i - 1][1] - price, or dp[i - 1][3] - price
+ # 1: keep no stocks: dp[i][1] = dp[i - 1][1]
+ # 2: sell stocks: dp[i][2] = dp[i - 1][0] + price
+ # 3: cooldown day: dp[i][3] = dp[i - 1][2]
+ dp = [-prices[0], 0, 0, 0]
+
+ for price in prices[1:]:
+ dc = dp.copy() # 这句话是关键,把前一天的 dp 状态保存下来,防止被覆盖掉,后面只用它,不用 dp,逻辑简单易懂
+ dp[0] = max(
+ dc[0],
+ dc[1] - price,
+ dc[3] - price
+ )
+ dp[1] = max(
+ dc[1],
+ dc[3]
+ )
+ dp[2] = dc[0] + price
+ dp[3] = dc[2]
+
+ return max(dp)
+```
+
### Go:
```go
@@ -357,7 +386,63 @@ func max(a, b int) int {
}
```
-### Javascript:
+```go
+// 一维优化版本
+// 时间复杂度O(n), 空间复杂度O(1)
+func maxProfit(prices []int) int {
+
+ // 0: 持有,一直持有和买入
+ // 1: 不持有,一直不持有(不包含前一天卖出,因为这样的一天是冷静期,状态有区别)
+ // 2:不持有,今天卖出
+ // 3:冷静期,前一天卖出(一直不持有)
+ dp0, dp1, dp2, dp3 := -prices[0], 0, 0, 0
+
+ n := len(prices)
+
+ for i := 1; i < n; i++ {
+ t0 := max(dp0, max(dp1, dp3)-prices[i])
+ t1 := max(dp1, dp3)
+ t2 := dp0 + prices[i]
+ t3 := dp2
+
+ // 更新
+ dp0, dp1, dp2, dp3 = t0, t1, t2, t3
+ }
+
+ return max(dp1, max(dp2, dp3))
+}
+
+func max(a, b int) int {
+ if a > b {
+ return a
+ }
+ return b
+}
+```
+
+
+
+### JavaScript:
+
+> 不同的状态定义 感觉更容易理解些
+```javascript
+function maxProfit(prices) {
+ // 第i天状态 持股 卖出 非冷冻期(不持股) 处于冷冻期
+ const dp = new Array(prices.length).fill(0).map(() => [0, 0, 0, 0]);
+ dp[0][0] = -prices[0];
+ for (let i = 1; i < prices.length; i++) {
+ // 持股
+ dp[i][0] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][0], dp[i - 1][2] - prices[i]);
+ // 卖出
+ dp[i][1] = dp[i - 1][0] + prices[i];
+ // 非冷冻期(不持股)
+ dp[i][2] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][2], dp[i - 1][1]);
+ // 冷冻期(上一天卖出)
+ dp[i][3] = dp[i - 1][1];
+ }
+ return Math.max(...dp.pop());
+};
+```
```javascript
const maxProfit = (prices) => {
@@ -457,6 +542,40 @@ function maxProfit(prices: number[]): number {
};
```
+### C:
+
+```c
+#define max(a, b) ((a) > (b) ? (a) : (b))
+
+/**
+ * 状态一:持有股票状态(今天买入股票,
+ * 或者是之前就买入了股票然后没有操作,一直持有)
+ * 不持有股票状态,这里就有两种卖出股票状态
+ * 状态二:保持卖出股票的状态(两天前就卖出了股票,度过一天冷冻期。
+ * 或者是前一天就是卖出股票状态,一直没操作)
+ * 状态三:今天卖出股票
+ * 状态四:今天为冷冻期状态,但冷冻期状态不可持续,只有一天!
+
+ */
+int maxProfit(int* prices, int pricesSize) {
+ if(pricesSize == 0){
+ return 0;
+ }
+ int dp[pricesSize][4];
+ memset(dp, 0, sizeof (int ) * pricesSize * 4);
+ dp[0][0] = -prices[0];
+ for (int i = 1; i < pricesSize; ++i) {
+ dp[i][0] = max(dp[i - 1][0], max(dp[i - 1][1] - prices[i], dp[i - 1][3] - prices[i]));
+ dp[i][1] = max(dp[i - 1][1], dp[i - 1][3]);
+ dp[i][2] = dp[i - 1][0] + prices[i];
+ dp[i][3] = dp[i - 1][2];
+ }
+ return max(dp[pricesSize - 1][1], max(dp[pricesSize - 1][2], dp[pricesSize - 1][3]));
+}
+```
+
+
+
### Rust:
```rust
@@ -482,8 +601,4 @@ impl Solution {
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0322.\351\233\266\351\222\261\345\205\221\346\215\242.md" "b/problems/0322.\351\233\266\351\222\261\345\205\221\346\215\242.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index eae4ab3ac0..f3a0a07dd9
--- "a/problems/0322.\351\233\266\351\222\261\345\205\221\346\215\242.md"
+++ "b/problems/0322.\351\233\266\351\222\261\345\205\221\346\215\242.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0322.\351\233\266\351\222\261\345\205\221\346\215\242.md" "b/problems/0322.\351\233\266\351\222\261\345\205\221\346\215\242.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index eae4ab3ac0..f3a0a07dd9
--- "a/problems/0322.\351\233\266\351\222\261\345\205\221\346\215\242.md"
+++ "b/problems/0322.\351\233\266\351\222\261\345\205\221\346\215\242.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 322. 零钱兑换
@@ -106,7 +104,7 @@ dp[0] = 0;
以输入:coins = [1, 2, 5], amount = 5为例
-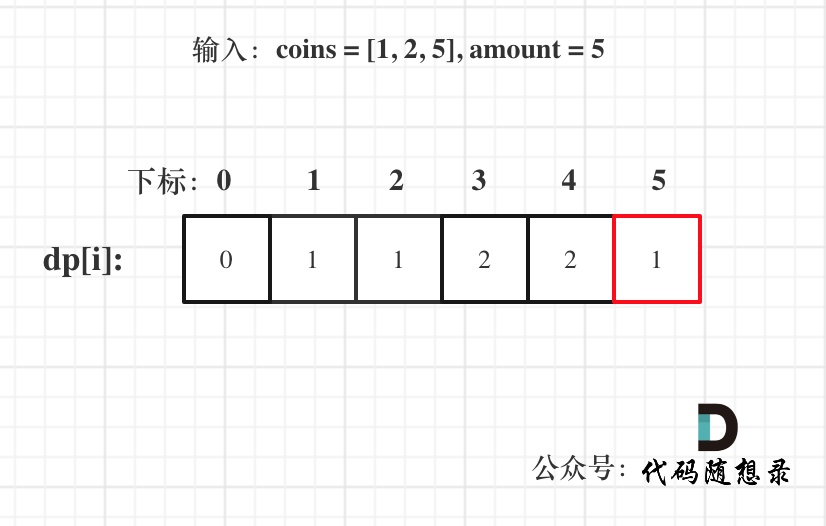
+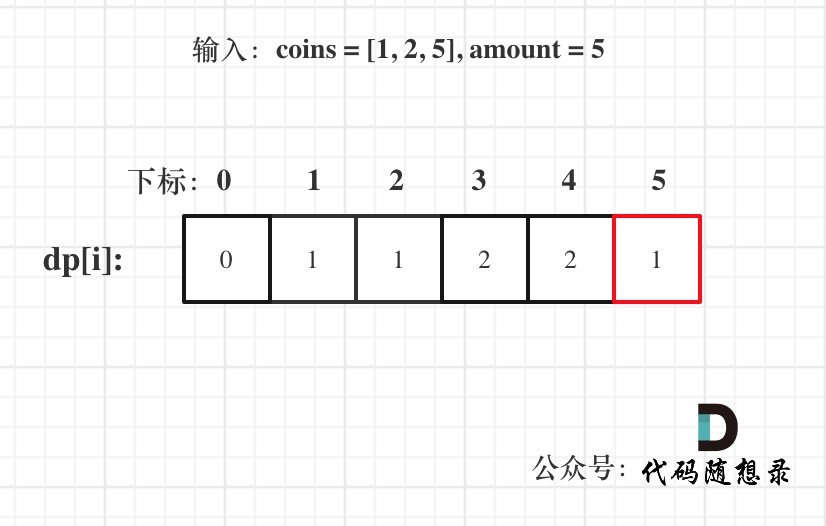
dp[amount]为最终结果。
@@ -352,6 +350,35 @@ func min(a, b int) int {
```
+## C
+
+```c
+#define min(a, b) ((a) > (b) ? (b) : (a))
+
+int coinChange(int* coins, int coinsSize, int amount) {
+ int* dp = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * (amount + 1));
+ for (int j = 0; j < amount + 1; j++) {
+ dp[j] = INT_MAX;
+ }
+ dp[0] = 0;
+ // 遍历背包
+ for(int i = 0; i <= amount; i++){
+ // 遍历物品
+ for(int j = 0; j < coinsSize; j++){
+ if(i - coins[j] >= 0 && dp[i - coins[j]] != INT_MAX){
+ dp[i] = min(dp[i], dp[i - coins[j]] + 1);
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ if(dp[amount] == INT_MAX){
+ return -1;
+ }
+ return dp[amount];
+}
+```
+
+
+
### Rust:
```rust
@@ -398,7 +425,7 @@ impl Solution {
}
```
-### Javascript:
+### JavaScript:
```javascript
// 遍历物品
@@ -470,8 +497,3 @@ function coinChange(coins: number[], amount: number): number {
```
-
-
-  -
-
diff --git "a/problems/0332.\351\207\215\346\226\260\345\256\211\346\216\222\350\241\214\347\250\213.md" "b/problems/0332.\351\207\215\346\226\260\345\256\211\346\216\222\350\241\214\347\250\213.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 036cfc51b5..1168277a8d
--- "a/problems/0332.\351\207\215\346\226\260\345\256\211\346\216\222\350\241\214\347\250\213.md"
+++ "b/problems/0332.\351\207\215\346\226\260\345\256\211\346\216\222\350\241\214\347\250\213.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0332.\351\207\215\346\226\260\345\256\211\346\216\222\350\241\214\347\250\213.md" "b/problems/0332.\351\207\215\346\226\260\345\256\211\346\216\222\350\241\214\347\250\213.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 036cfc51b5..1168277a8d
--- "a/problems/0332.\351\207\215\346\226\260\345\256\211\346\216\222\350\241\214\347\250\213.md"
+++ "b/problems/0332.\351\207\215\346\226\260\345\256\211\346\216\222\350\241\214\347\250\213.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
> 这也可以用回溯法? 其实深搜和回溯也是相辅相成的,毕竟都用递归。
@@ -59,7 +57,7 @@
对于死循环,我来举一个有重复机场的例子:
-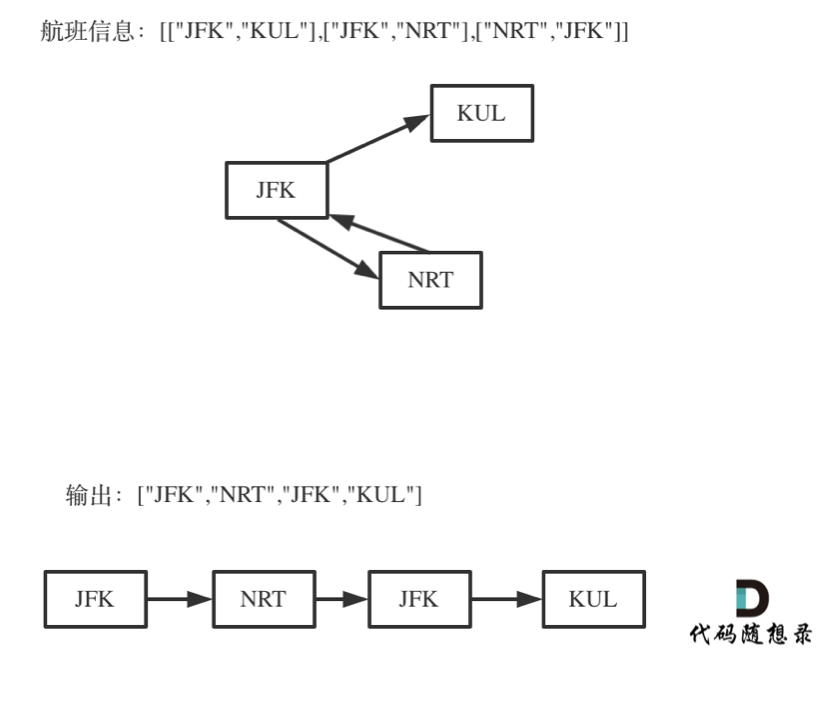
+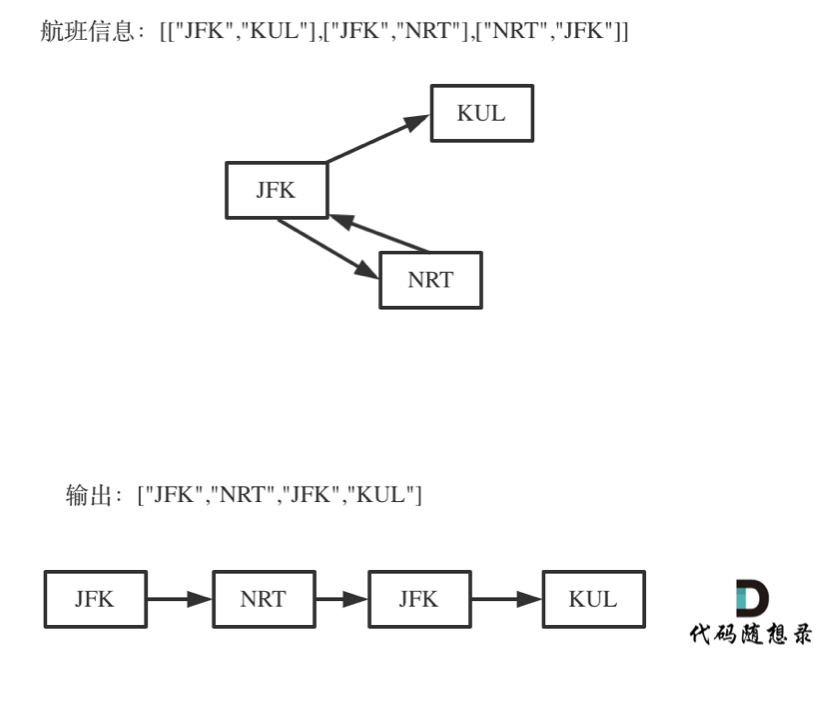
为什么要举这个例子呢,就是告诉大家,出发机场和到达机场也会重复的,**如果在解题的过程中没有对集合元素处理好,就会死循环。**
@@ -113,7 +111,7 @@ void backtracking(参数) {
本题以输入:[["JFK", "KUL"], ["JFK", "NRT"], ["NRT", "JFK"]为例,抽象为树形结构如下:
-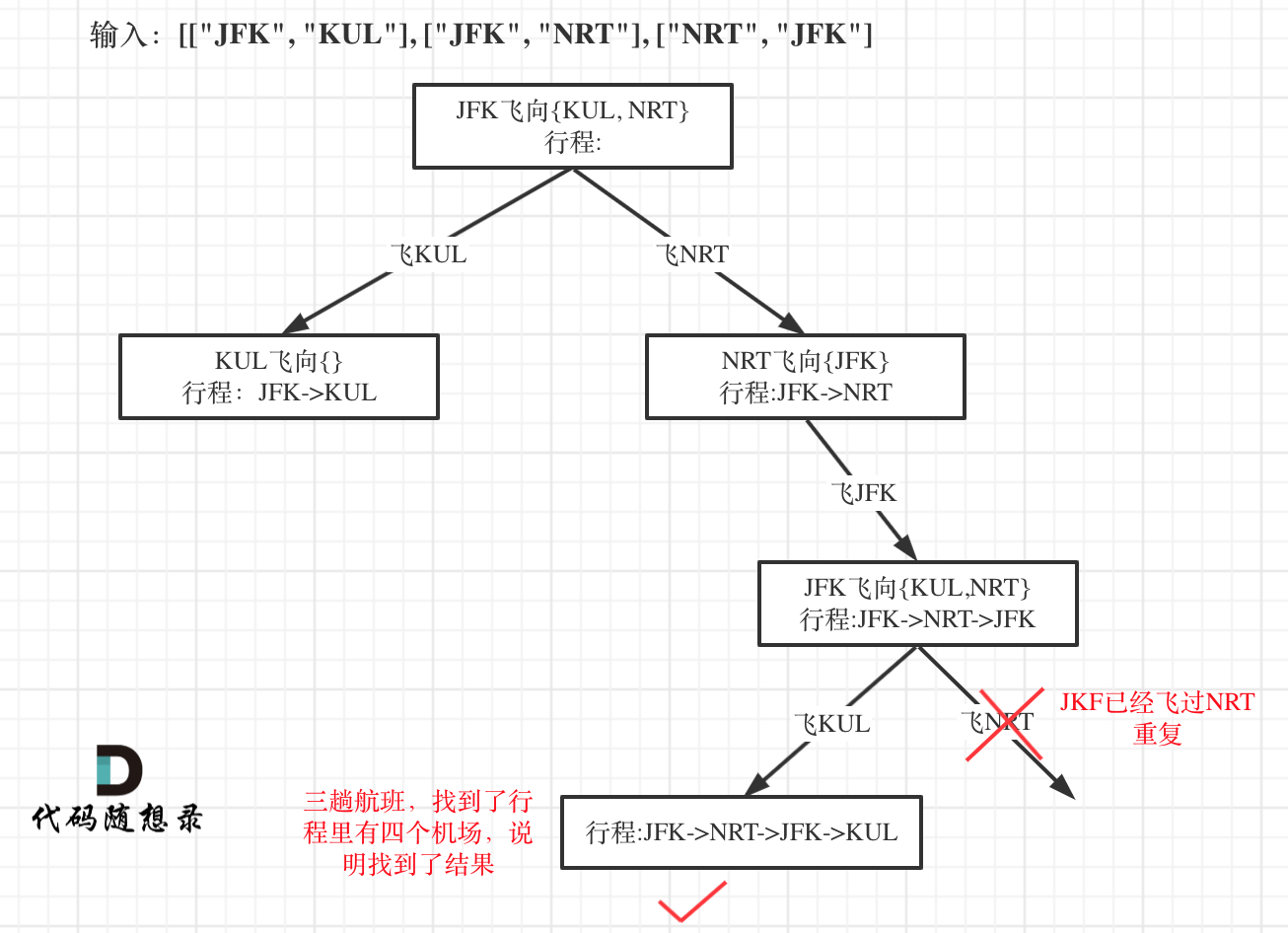
+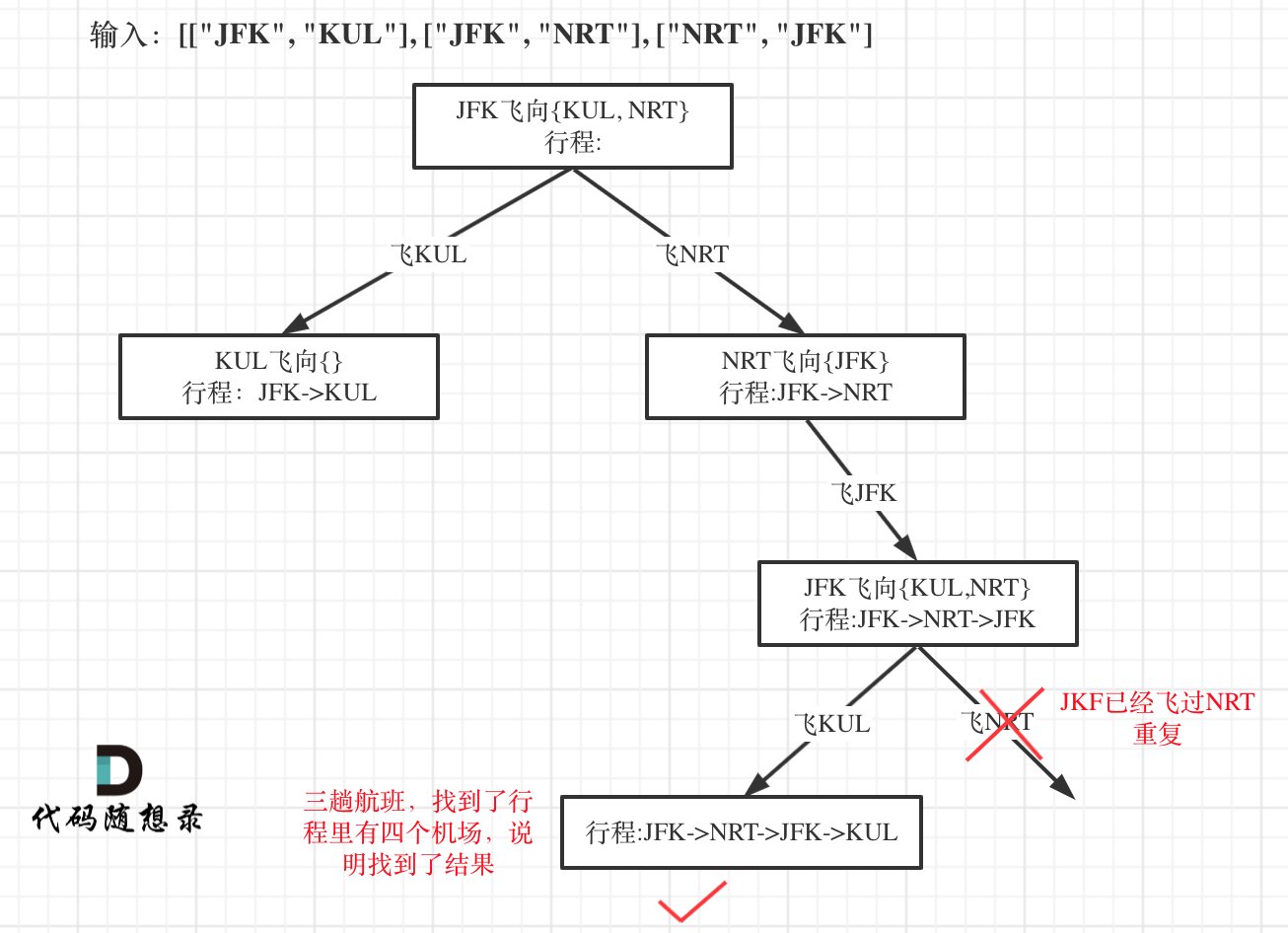
开始回溯三部曲讲解:
@@ -139,7 +137,7 @@ bool backtracking(int ticketNum, vector& result) {
因为我们只需要找到一个行程,就是在树形结构中唯一的一条通向叶子节点的路线,如图:
-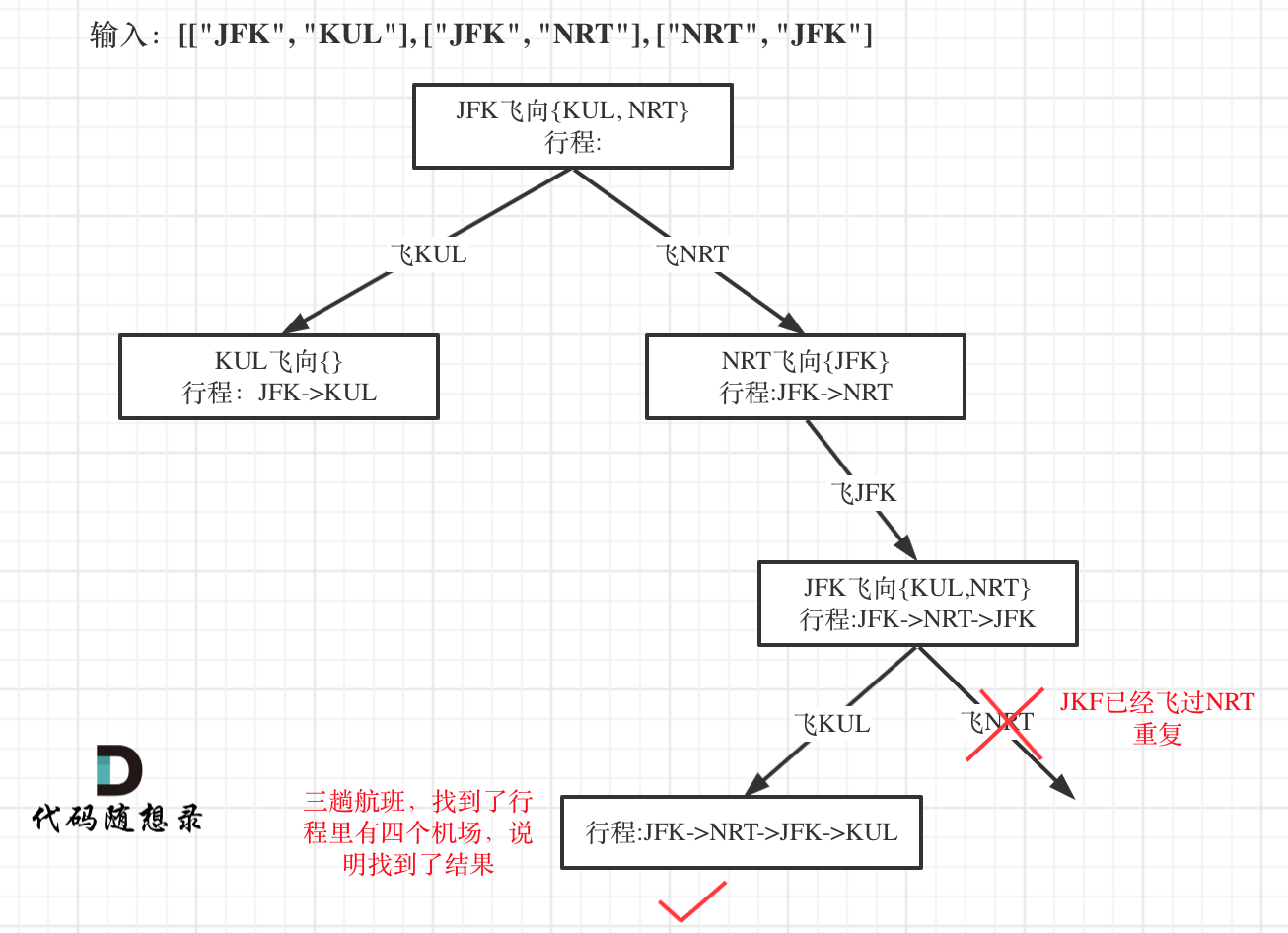
+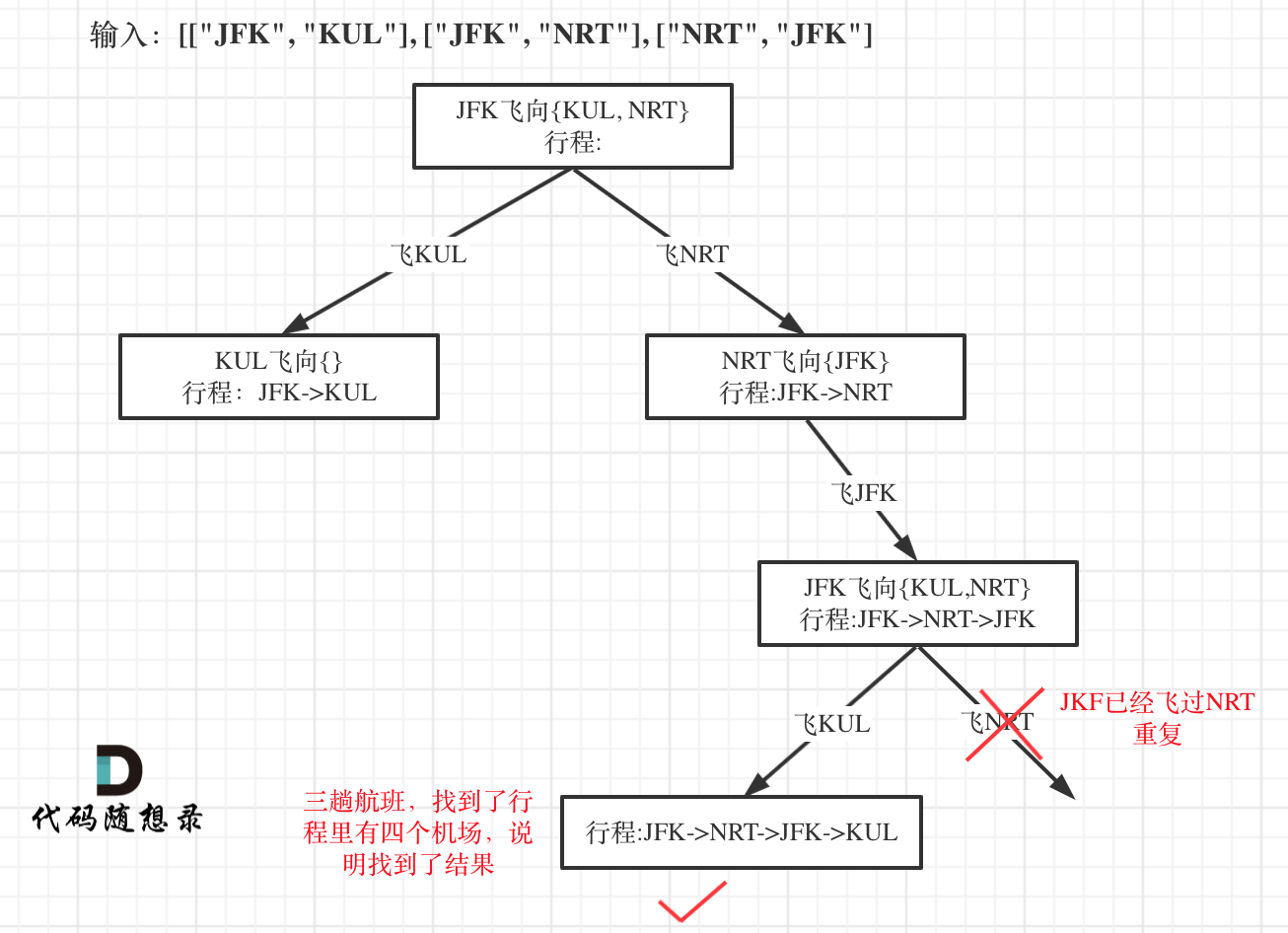
所以找到了这个叶子节点了直接返回,这个递归函数的返回值问题我们在讲解二叉树的系列的时候,在这篇[二叉树:递归函数究竟什么时候需要返回值,什么时候不要返回值?](https://programmercarl.com/0112.路径总和.html)详细介绍过。
@@ -172,7 +170,7 @@ if (result.size() == ticketNum + 1) {
回溯的过程中,如何遍历一个机场所对应的所有机场呢?
-这里刚刚说过,在选择映射函数的时候,不能选择`unordered_map> targets`, 因为一旦有元素增删multiset的迭代器就会失效,当然可能有牛逼的容器删除元素迭代器不会失效,这里就不在讨论了。
+这里刚刚说过,在选择映射函数的时候,不能选择`unordered_map> targets`, 因为一旦有元素增删multiset的迭代器就会失效,当然可能有牛逼的容器删除元素迭代器不会失效,这里就不再讨论了。
**可以说本题既要找到一个对数据进行排序的容器,而且还要容易增删元素,迭代器还不能失效**。
@@ -253,9 +251,6 @@ for (pair& target : targets[result[result.size() - 1]])
如果最终代码,发现照着回溯法模板画的话好像也能画出来,但难就难如何知道可以使用回溯,以及如果套进去,所以我再写了这么长的一篇来详细讲解。
-就酱,很多录友表示和「代码随想录」相见恨晚,那么帮Carl宣传一波吧,让更多同学知道这里!
-
-
## 其他语言版本
@@ -379,6 +374,8 @@ class Solution {
String targetLocation;
//遍历从当前位置出发的机票
for (int i = 0; i < targetLocations.size(); i++) {
+ //去重,否则在最后一个测试用例中遇到循环时会无限递归
+ if(i > 0 && targetLocations.get(i).equals(targetLocations.get(i - 1))) continue;
targetLocation = targetLocations.get(i);
//删除终点列表中当前的终点
targetLocations.remove(i);
@@ -418,35 +415,7 @@ class Solution {
}
```
-### Python
-回溯 使用used数组
-
-```python
-class Solution:
- def findItinerary(self, tickets: List[List[str]]) -> List[str]:
- tickets.sort() # 先排序,这样一旦找到第一个可行路径,一定是字母排序最小的
- used = [0] * len(tickets)
- path = ['JFK']
- results = []
- self.backtracking(tickets, used, path, 'JFK', results)
- return results[0]
-
- def backtracking(self, tickets, used, path, cur, results):
- if len(path) == len(tickets) + 1: # 终止条件:路径长度等于机票数量+1
- results.append(path[:]) # 将当前路径添加到结果列表
- return True
-
- for i, ticket in enumerate(tickets): # 遍历机票列表
- if ticket[0] == cur and used[i] == 0: # 找到起始机场为cur且未使用过的机票
- used[i] = 1 # 标记该机票为已使用
- path.append(ticket[1]) # 将到达机场添加到路径中
- state = self.backtracking(tickets, used, path, ticket[1], results) # 递归搜索
- path.pop() # 回溯,移除最后添加的到达机场
- used[i] = 0 # 标记该机票为未使用
- if state:
- return True # 只要找到一个可行路径就返回,不继续搜索
-
-```
+### Python
回溯 使用字典
```python
class Solution:
@@ -564,7 +533,7 @@ func findItinerary(tickets [][]string) []string {
}
```
-### Javascript
+### JavaScript
```Javascript
@@ -969,8 +938,4 @@ impl Solution {
}
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0337.\346\211\223\345\256\266\345\212\253\350\210\215III.md" "b/problems/0337.\346\211\223\345\256\266\345\212\253\350\210\215III.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index f616ec7417..44af86bb4c
--- "a/problems/0337.\346\211\223\345\256\266\345\212\253\350\210\215III.md"
+++ "b/problems/0337.\346\211\223\345\256\266\345\212\253\350\210\215III.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0337.\346\211\223\345\256\266\345\212\253\350\210\215III.md" "b/problems/0337.\346\211\223\345\256\266\345\212\253\350\210\215III.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index f616ec7417..44af86bb4c
--- "a/problems/0337.\346\211\223\345\256\266\345\212\253\350\210\215III.md"
+++ "b/problems/0337.\346\211\223\345\256\266\345\212\253\350\210\215III.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 337.打家劫舍 III
@@ -14,7 +12,7 @@
计算在不触动警报的情况下,小偷一晚能够盗取的最高金额。
-
+
## 算法公开课
@@ -179,7 +177,7 @@ return {val2, val1};
以示例1为例,dp数组状态如下:(**注意用后序遍历的方式推导**)
-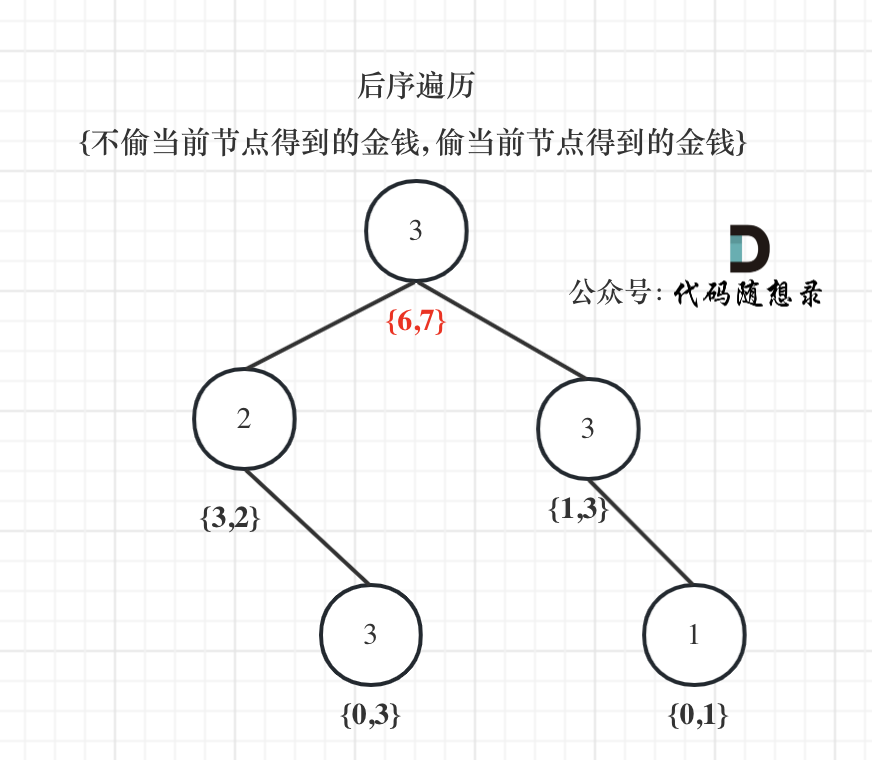
+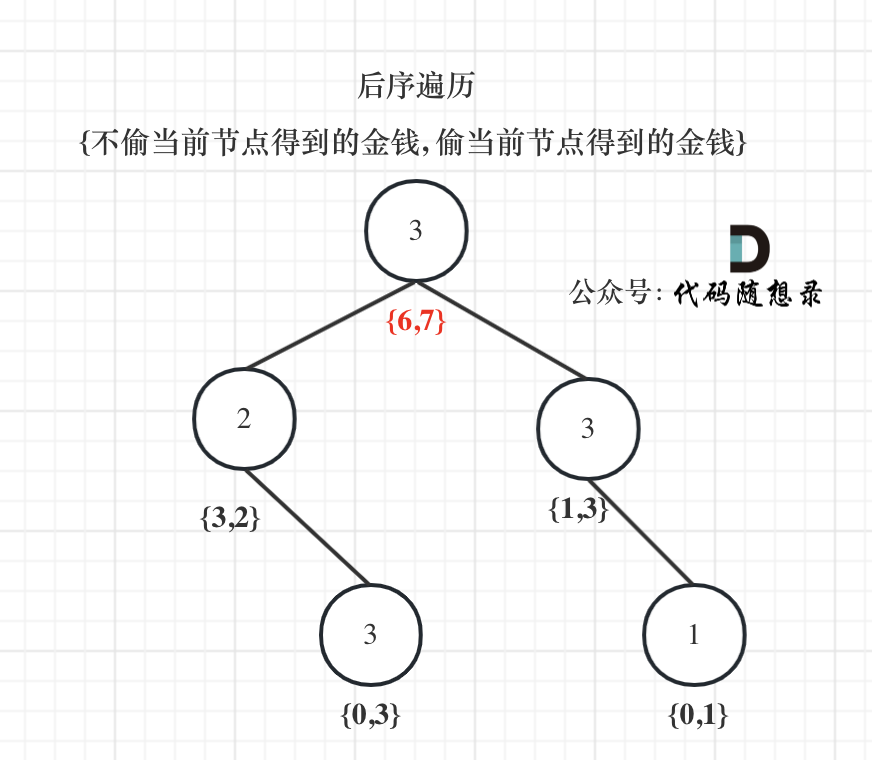
**最后头结点就是 取下标0 和 下标1的最大值就是偷得的最大金钱**。
@@ -388,19 +386,96 @@ class Solution:
### Go
-动态规划
+暴力递归
```go
+/**
+ * Definition for a binary tree node.
+ * type TreeNode struct {
+ * Val int
+ * Left *TreeNode
+ * Right *TreeNode
+ * }
+ */
func rob(root *TreeNode) int {
- res := robTree(root)
- return max(res[0], res[1])
+ if root == nil {
+ return 0
+ }
+ if root.Left == nil && root.Right == nil {
+ return root.Val
+ }
+ // 偷父节点
+ val1 := root.Val
+ if root.Left != nil {
+ val1 += rob(root.Left.Left) + rob(root.Left.Right) // 跳过root->left,相当于不考虑左孩子了
+ }
+ if root.Right != nil {
+ val1 += rob(root.Right.Left) + rob(root.Right.Right) // 跳过root->right,相当于不考虑右孩子了
+ }
+ // 不偷父节点
+ val2 := rob(root.Left) + rob(root.Right) // 考虑root的左右孩子
+ return max(val1, val2)
}
-func max(a, b int) int {
- if a > b {
- return a
- }
- return b
+func max(x, y int) int {
+ if x > y {
+ return x
+ }
+ return y
+}
+```
+
+记忆化递推
+
+```go
+/**
+ * Definition for a binary tree node.
+ * type TreeNode struct {
+ * Val int
+ * Left *TreeNode
+ * Right *TreeNode
+ * }
+ */
+var umap = make(map[*TreeNode]int)
+
+func rob(root *TreeNode) int {
+ if root == nil {
+ return 0
+ }
+ if root.Left == nil && root.Right == nil {
+ return root.Val
+ }
+ if val, ok := umap[root]; ok {
+ return val // 如果umap里已经有记录则直接返回
+ }
+ // 偷父节点
+ val1 := root.Val
+ if root.Left != nil {
+ val1 += rob(root.Left.Left) + rob(root.Left.Right) // 跳过root->left,相当于不考虑左孩子了
+ }
+ if root.Right != nil {
+ val1 += rob(root.Right.Left) + rob(root.Right.Right) // 跳过root->right,相当于不考虑右孩子了
+ }
+ // 不偷父节点
+ val2 := rob(root.Left) + rob(root.Right) // 考虑root的左右孩子
+ umap[root] = max(val1, val2) // umap记录一下结果
+ return max(val1, val2)
+}
+
+func max(x, y int) int {
+ if x > y {
+ return x
+ }
+ return y
+}
+```
+
+动态规划
+
+```go
+func rob(root *TreeNode) int {
+ res := robTree(root)
+ return slices.Max(res)
}
func robTree(cur *TreeNode) []int {
@@ -414,7 +489,7 @@ func robTree(cur *TreeNode) []int {
// 考虑去偷当前的屋子
robCur := cur.Val + left[0] + right[0]
// 考虑不去偷当前的屋子
- notRobCur := max(left[0], left[1]) + max(right[0], right[1])
+ notRobCur := slices.Max(left) + slices.Max(right)
// 注意顺序:0:不偷,1:去偷
return []int{notRobCur, robCur}
@@ -490,6 +565,33 @@ function robNode(node: TreeNode | null): MaxValueArr {
}
```
+### C
+
+```c
+int *robTree(struct TreeNode *node) {
+ int* amounts = (int*) malloc(sizeof(int) * 2);
+ memset(amounts, 0, sizeof(int) * 2);
+ if(node == NULL){
+ return amounts;
+ }
+ int * left = robTree(node->left);
+ int * right = robTree(node->right);
+ // 偷当前节点
+ amounts[1] = node->val + left[0] + right[0];
+ // 不偷当前节点
+ amounts[0] = max(left[0], left[1]) + max(right[0], right[1]);
+ return amounts;
+}
+
+int rob(struct TreeNode* root) {
+ int * dp = robTree(root);
+ // 0代表不偷当前节点可以获得的最大值,1表示偷当前节点可以获取的最大值
+ return max(dp[0], dp[1]);
+}
+```
+
+
+
### Rust
动态规划:
@@ -519,8 +621,3 @@ impl Solution {
```
-
-
-  -
-
diff --git "a/problems/0343.\346\225\264\346\225\260\346\213\206\345\210\206.md" "b/problems/0343.\346\225\264\346\225\260\346\213\206\345\210\206.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index bbbd5c6379..c9467e361f
--- "a/problems/0343.\346\225\264\346\225\260\346\213\206\345\210\206.md"
+++ "b/problems/0343.\346\225\264\346\225\260\346\213\206\345\210\206.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0343.\346\225\264\346\225\260\346\213\206\345\210\206.md" "b/problems/0343.\346\225\264\346\225\260\346\213\206\345\210\206.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index bbbd5c6379..c9467e361f
--- "a/problems/0343.\346\225\264\346\225\260\346\213\206\345\210\206.md"
+++ "b/problems/0343.\346\225\264\346\225\260\346\213\206\345\210\206.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 343. 整数拆分
@@ -129,7 +127,7 @@ for (int i = 3; i <= n ; i++) {
举例当n为10 的时候,dp数组里的数值,如下:
-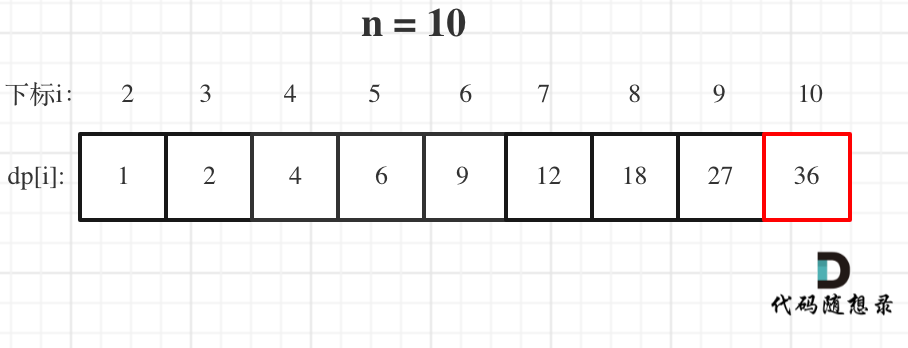
+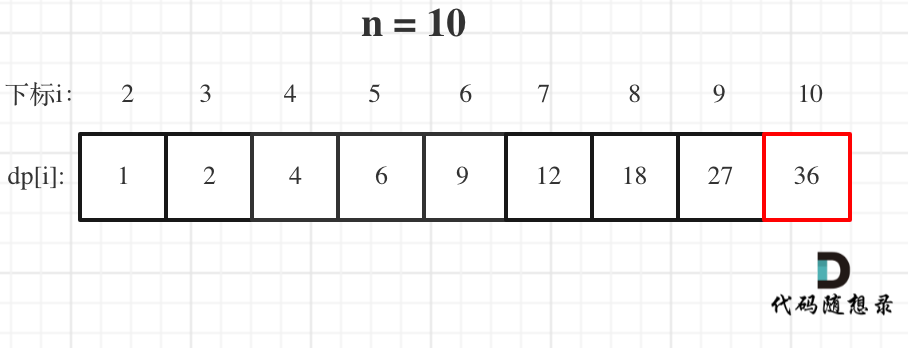
以上动规五部曲分析完毕,C++代码如下:
@@ -243,6 +241,29 @@ class Solution {
}
}
```
+贪心
+```Java
+class Solution {
+ public int integerBreak(int n) {
+ // with 贪心
+ // 通过数学原理拆出更多的3乘积越大,则
+ /**
+ @Param: an int, the integer we need to break.
+ @Return: an int, the maximum integer after breaking
+ @Method: Using math principle to solve this problem
+ @Time complexity: O(1)
+ **/
+ if(n == 2) return 1;
+ if(n == 3) return 2;
+ int result = 1;
+ while(n > 4) {
+ n-=3;
+ result *=3;
+ }
+ return result*n;
+ }
+}
+```
### Python
动态规划(版本一)
@@ -296,7 +317,7 @@ class Solution:
def integerBreak(self, n):
if n == 2: # 当n等于2时,只有一种拆分方式:1+1=2,乘积为1
return 1
- if n == 3: # 当n等于3时,只有一种拆分方式:1+1+1=3,乘积为1
+ if n == 3: # 当n等于3时,只有一种拆分方式:2+1=3,乘积为2
return 2
if n == 4: # 当n等于4时,有两种拆分方式:2+2=4和1+1+1+1=4,乘积都为4
return 4
@@ -309,6 +330,8 @@ class Solution:
```
### Go
+
+动态规划
```go
func integerBreak(n int) int {
/**
@@ -338,7 +361,29 @@ func max(a, b int) int{
}
```
-### Javascript
+贪心
+```go
+func integerBreak(n int) int {
+ if n == 2 {
+ return 1
+ }
+ if n == 3 {
+ return 2
+ }
+ if n == 4 {
+ return 4
+ }
+ result := 1
+ for n > 4 {
+ result *= 3
+ n -= 3
+ }
+ result *= n
+ return result
+}
+```
+
+### JavaScript
```Javascript
var integerBreak = function(n) {
let dp = new Array(n + 1).fill(0)
@@ -516,8 +561,4 @@ public class Solution
}
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0344.\345\217\215\350\275\254\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md" "b/problems/0344.\345\217\215\350\275\254\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 44184c53bc..cadb31c97b
--- "a/problems/0344.\345\217\215\350\275\254\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md"
+++ "b/problems/0344.\345\217\215\350\275\254\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0344.\345\217\215\350\275\254\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md" "b/problems/0344.\345\217\215\350\275\254\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 44184c53bc..cadb31c97b
--- "a/problems/0344.\345\217\215\350\275\254\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md"
+++ "b/problems/0344.\345\217\215\350\275\254\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
@@ -71,7 +69,7 @@
以字符串`hello`为例,过程如下:
-
+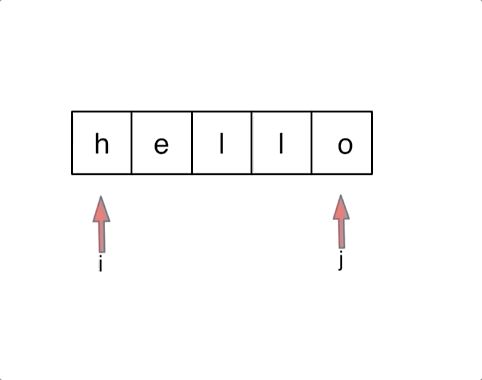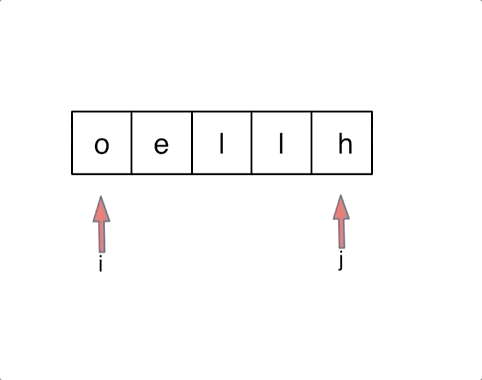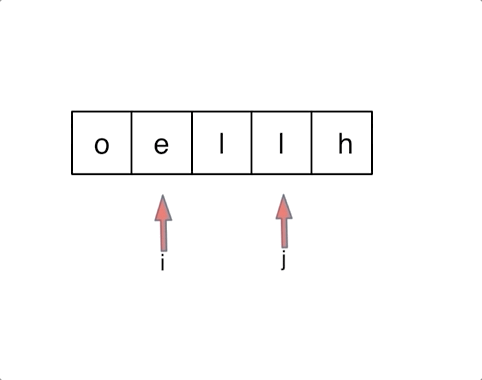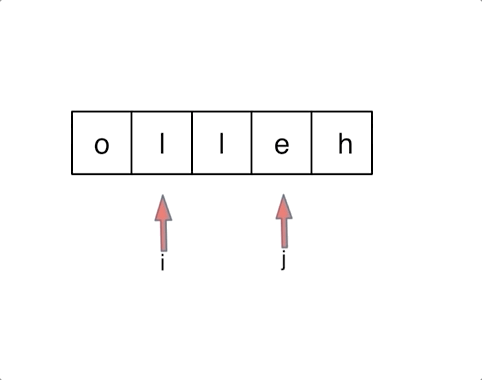
不难写出如下C++代码:
@@ -429,7 +427,3 @@ object Solution {
}
}
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0347.\345\211\215K\344\270\252\351\253\230\351\242\221\345\205\203\347\264\240.md" "b/problems/0347.\345\211\215K\344\270\252\351\253\230\351\242\221\345\205\203\347\264\240.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 93d605f5fe..fa7d6155a5
--- "a/problems/0347.\345\211\215K\344\270\252\351\253\230\351\242\221\345\205\203\347\264\240.md"
+++ "b/problems/0347.\345\211\215K\344\270\252\351\253\230\351\242\221\345\205\203\347\264\240.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0347.\345\211\215K\344\270\252\351\253\230\351\242\221\345\205\203\347\264\240.md" "b/problems/0347.\345\211\215K\344\270\252\351\253\230\351\242\221\345\205\203\347\264\240.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 93d605f5fe..fa7d6155a5
--- "a/problems/0347.\345\211\215K\344\270\252\351\253\230\351\242\221\345\205\203\347\264\240.md"
+++ "b/problems/0347.\345\211\215K\344\270\252\351\253\230\351\242\221\345\205\203\347\264\240.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
> 前K个大数问题,老生常谈,不得不谈
@@ -72,7 +70,7 @@
寻找前k个最大元素流程如图所示:(图中的频率只有三个,所以正好构成一个大小为3的小顶堆,如果频率更多一些,则用这个小顶堆进行扫描)
-
+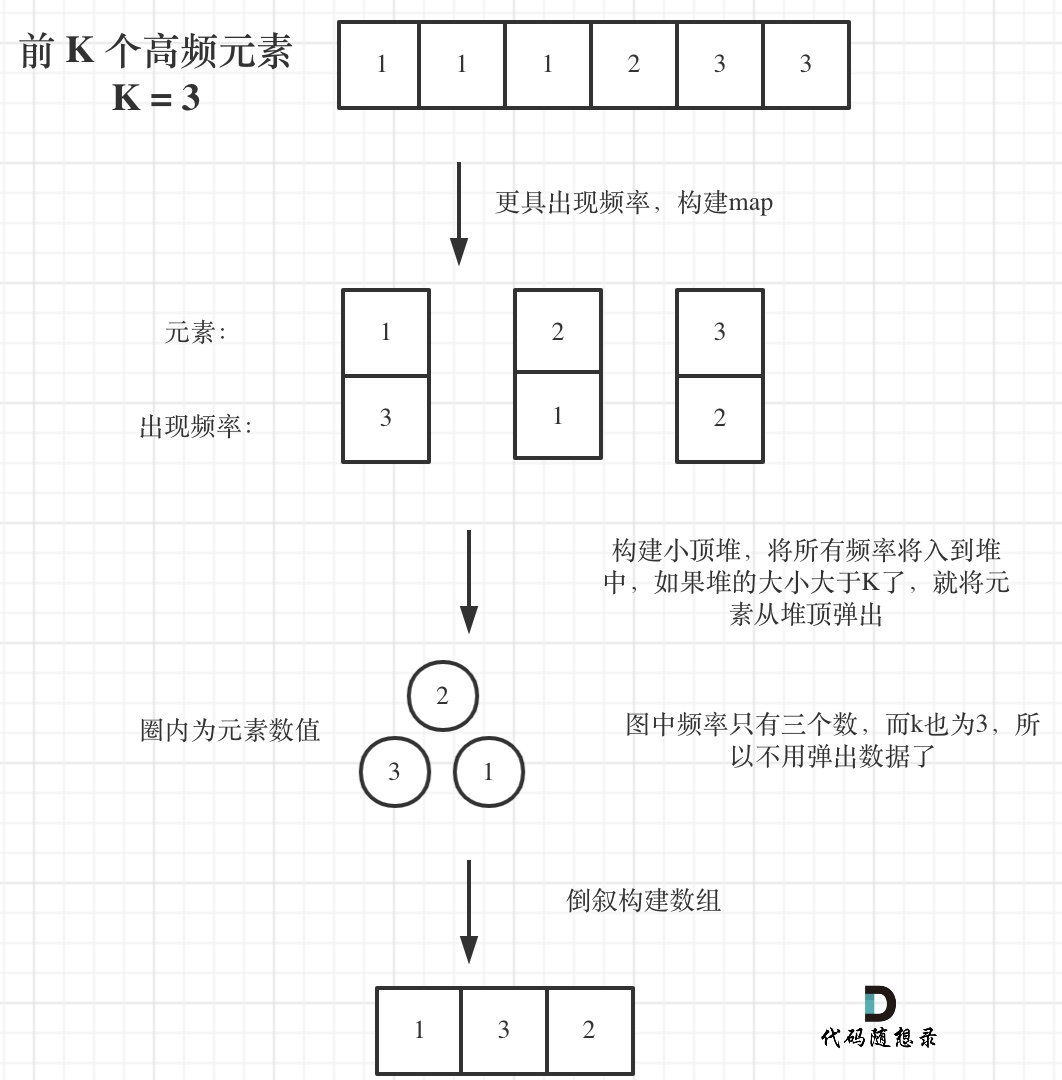
我们来看一下C++代码:
@@ -218,7 +216,7 @@ class Solution {
```
### Python:
-
+解法一:
```python
#时间复杂度:O(nlogk)
#空间复杂度:O(n)
@@ -246,6 +244,31 @@ class Solution:
result[i] = heapq.heappop(pri_que)[1]
return result
```
+解法二:
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def topKFrequent(self, nums: List[int], k: int) -> List[int]:
+ # 使用字典统计数字出现次数
+ time_dict = defaultdict(int)
+ for num in nums:
+ time_dict[num] += 1
+ # 更改字典,key为出现次数,value为相应的数字的集合
+ index_dict = defaultdict(list)
+ for key in time_dict:
+ index_dict[time_dict[key]].append(key)
+ # 排序
+ key = list(index_dict.keys())
+ key.sort()
+ result = []
+ cnt = 0
+ # 获取前k项
+ while key and cnt != k:
+ result += index_dict[key[-1]]
+ cnt += len(index_dict[key[-1]])
+ key.pop()
+
+ return result[0: k]
+```
### Go:
@@ -380,6 +403,11 @@ class Heap {
// 获取堆顶元素并移除
pop() {
+ // 边界情况,只有一个元素或没有元素应直接弹出
+ if (this.size() <= 1) {
+ return this.queue.pop()
+ }
+
// 堆顶元素
const out = this.queue[0];
@@ -391,7 +419,7 @@ class Heap {
let left = 1; // left 是左子节点下标 left + 1 则是右子节点下标
let searchChild = this.compare(left, left + 1) > 0 ? left + 1 : left;
- while (searchChild !== undefined && this.compare(index, searchChild) > 0) { // 注意compare参数顺序
+ while (this.compare(index, searchChild) > 0) { // 注意compare参数顺序
[this.queue[index], this.queue[searchChild]] = [this.queue[searchChild], this.queue[index]];
// 更新下标
@@ -578,8 +606,5 @@ impl Solution {
}
```
-
-
-  -
+
diff --git "a/problems/0349.\344\270\244\344\270\252\346\225\260\347\273\204\347\232\204\344\272\244\351\233\206.md" "b/problems/0349.\344\270\244\344\270\252\346\225\260\347\273\204\347\232\204\344\272\244\351\233\206.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 9902fff880..77e895da61
--- "a/problems/0349.\344\270\244\344\270\252\346\225\260\347\273\204\347\232\204\344\272\244\351\233\206.md"
+++ "b/problems/0349.\344\270\244\344\270\252\346\225\260\347\273\204\347\232\204\344\272\244\351\233\206.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+
diff --git "a/problems/0349.\344\270\244\344\270\252\346\225\260\347\273\204\347\232\204\344\272\244\351\233\206.md" "b/problems/0349.\344\270\244\344\270\252\346\225\260\347\273\204\347\232\204\344\272\244\351\233\206.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 9902fff880..77e895da61
--- "a/problems/0349.\344\270\244\344\270\252\346\225\260\347\273\204\347\232\204\344\272\244\351\233\206.md"
+++ "b/problems/0349.\344\270\244\344\270\252\346\225\260\347\273\204\347\232\204\344\272\244\351\233\206.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
@@ -16,7 +14,7 @@
题意:给定两个数组,编写一个函数来计算它们的交集。
-
+
**说明:**
输出结果中的每个元素一定是唯一的。
@@ -53,7 +51,7 @@ std::set和std::multiset底层实现都是红黑树,std::unordered_set的底
思路如图所示:
-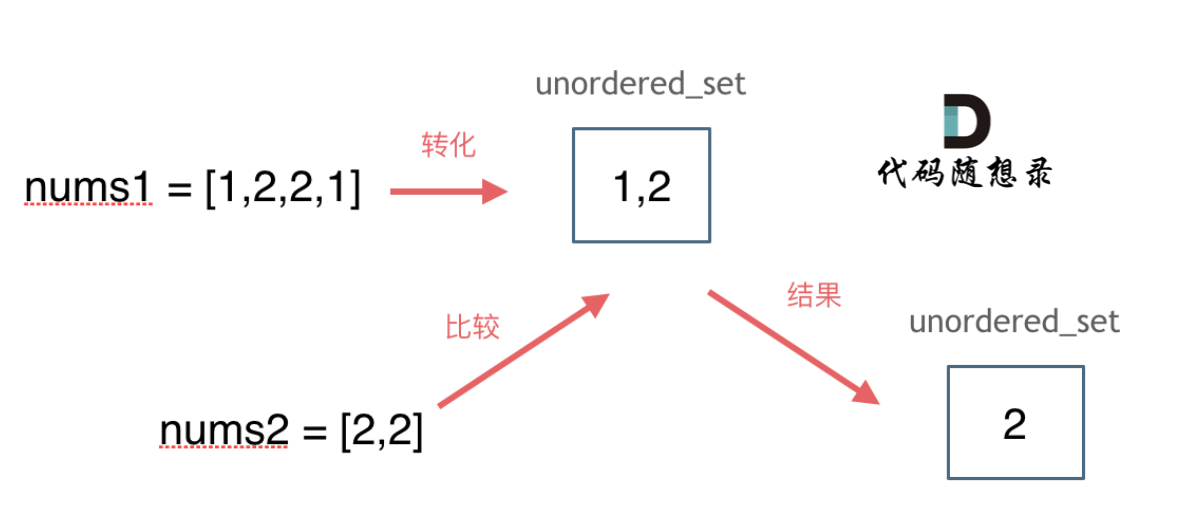
+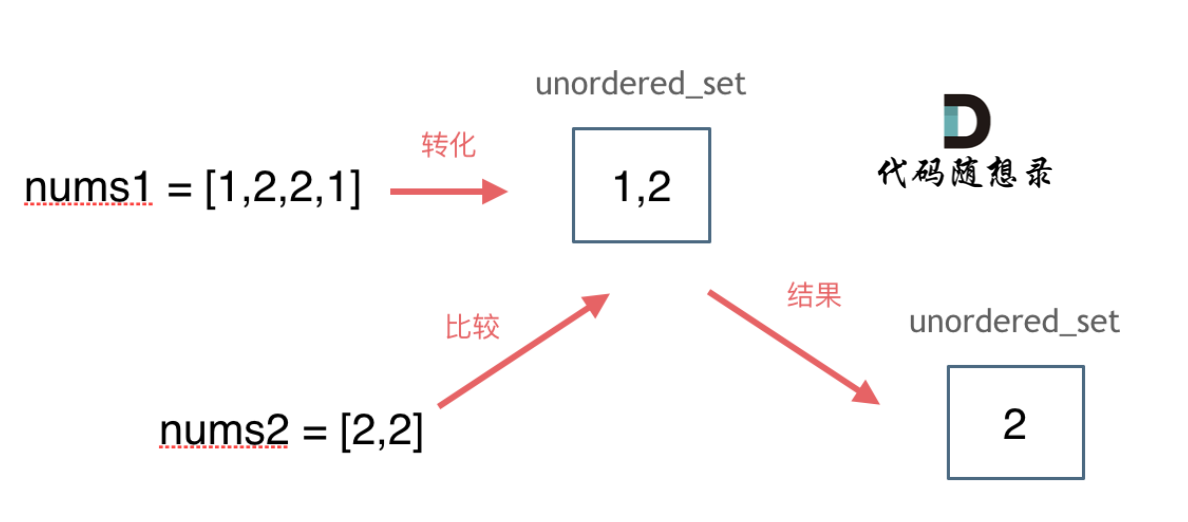
C++代码如下:
@@ -123,6 +121,9 @@ public:
### Java:
版本一:使用HashSet
```Java
+// 时间复杂度O(n+m+k) 空间复杂度O(n+k)
+// 其中n是数组nums1的长度,m是数组nums2的长度,k是交集元素的个数
+
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
@@ -145,8 +146,15 @@ class Solution {
}
//方法1:将结果集合转为数组
-
- return resSet.stream().mapToInt(x -> x).toArray();
+ return res.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).toArray();
+ /**
+ * 将 Set 转换为 int[] 数组:
+ * 1. stream() : Collection 接口的方法,将集合转换为 Stream
+ * 2. mapToInt(Integer::intValue) :
+ * - 中间操作,将 Stream 转换为 IntStream
+ * - 使用方法引用 Integer::intValue,将 Integer 对象拆箱为 int 基本类型
+ * 3. toArray() : 终端操作,将 IntStream 转换为 int[] 数组。
+ */
//方法2:另外申请一个数组存放setRes中的元素,最后返回数组
int[] arr = new int[resSet.size()];
@@ -511,7 +519,7 @@ object Solution {
```
-###Ruby
+### Ruby:
```ruby
def intersection(nums1, nums2)
hash = {}
@@ -534,7 +542,4 @@ end
* [350.两个数组的交集 II](https://leetcode.cn/problems/intersection-of-two-arrays-ii/)
-
-
-  -
+
diff --git "a/problems/0376.\346\221\206\345\212\250\345\272\217\345\210\227.md" "b/problems/0376.\346\221\206\345\212\250\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 5c2241c805..1be9cb4178
--- "a/problems/0376.\346\221\206\345\212\250\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
+++ "b/problems/0376.\346\221\206\345\212\250\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+
diff --git "a/problems/0376.\346\221\206\345\212\250\345\272\217\345\210\227.md" "b/problems/0376.\346\221\206\345\212\250\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 5c2241c805..1be9cb4178
--- "a/problems/0376.\346\221\206\345\212\250\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
+++ "b/problems/0376.\346\221\206\345\212\250\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 376. 摆动序列
@@ -48,7 +46,7 @@
用示例二来举例,如图所示:
-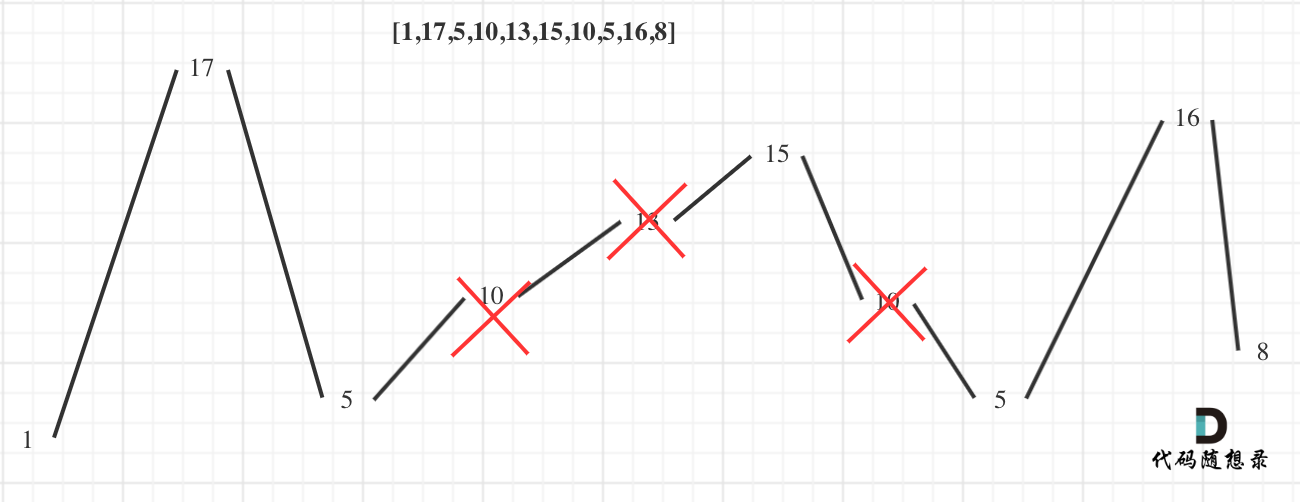
+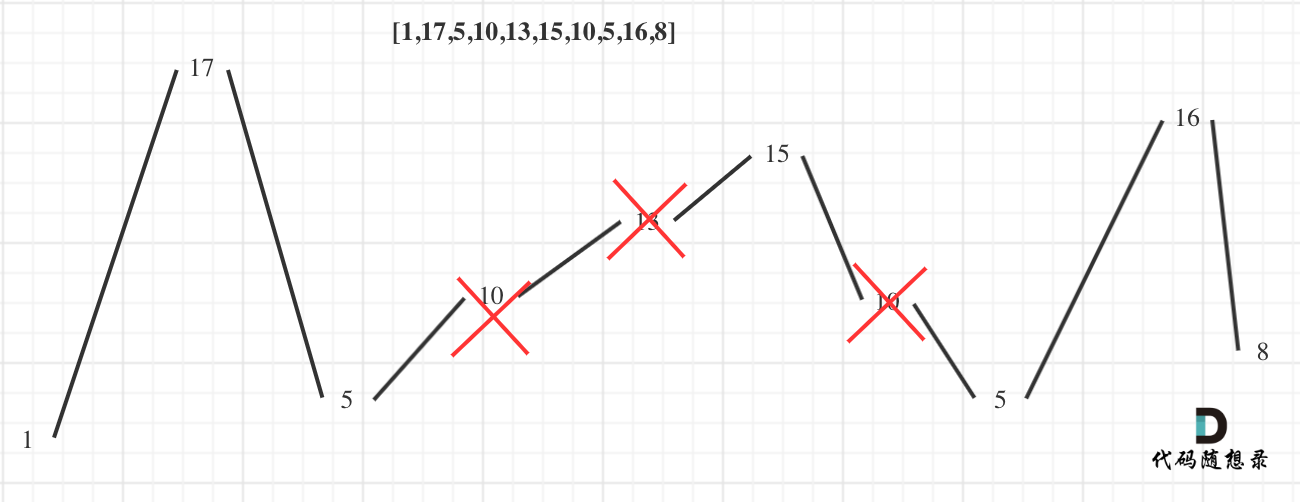
**局部最优:删除单调坡度上的节点(不包括单调坡度两端的节点),那么这个坡度就可以有两个局部峰值**。
@@ -72,15 +70,15 @@
#### 情况一:上下坡中有平坡
-例如 [1,2,2,2,1]这样的数组,如图:
+例如 [1,2,2,2,2,1]这样的数组,如图:
-
+
它的摇摆序列长度是多少呢? **其实是长度是 3**,也就是我们在删除的时候 要不删除左面的三个 2,要不就删除右边的三个 2。
如图,可以统一规则,删除左边的三个 2:
-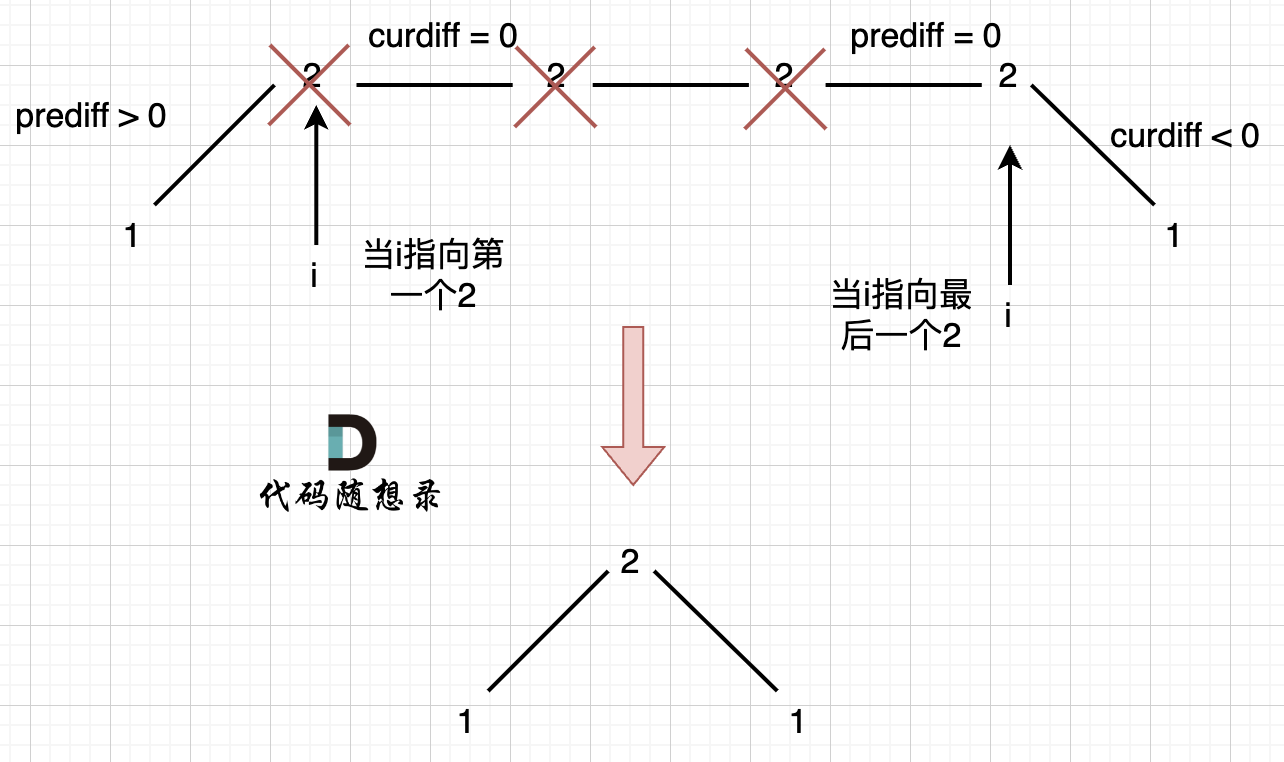
+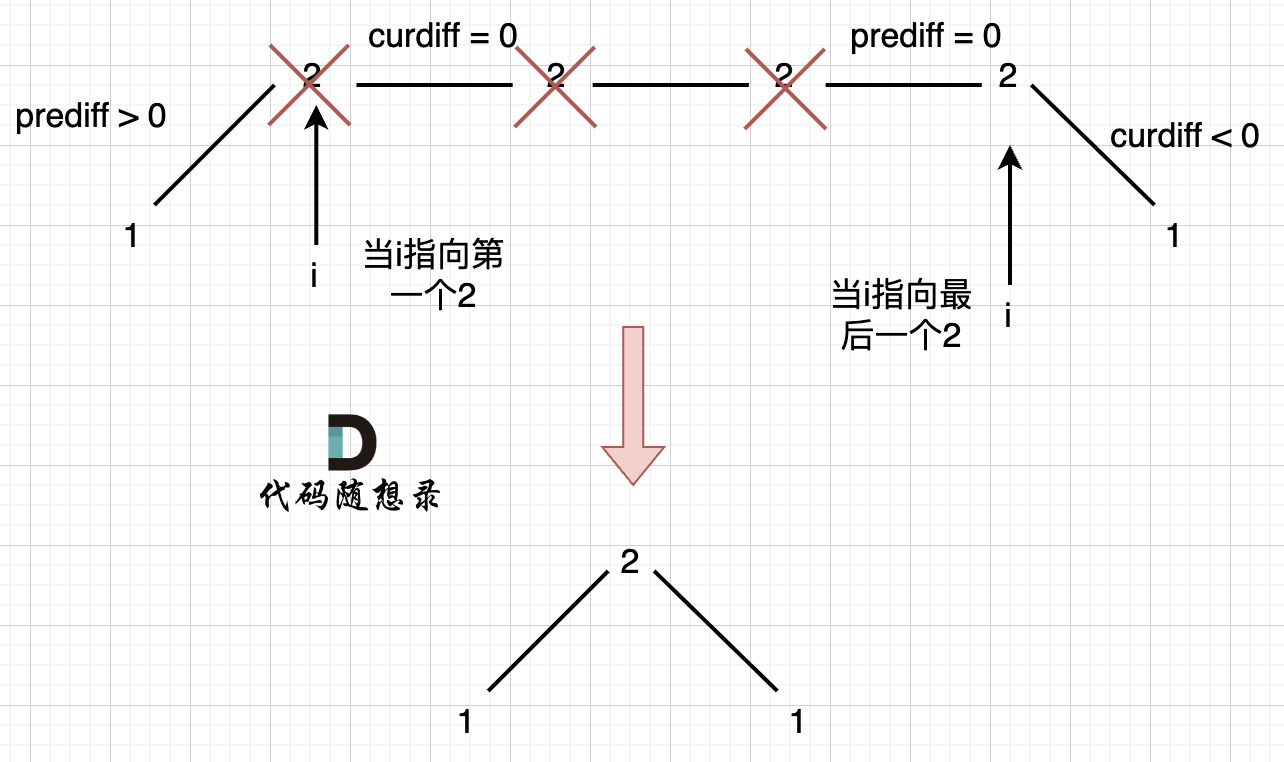
在图中,当 i 指向第一个 2 的时候,`prediff > 0 && curdiff = 0` ,当 i 指向最后一个 2 的时候 `prediff = 0 && curdiff < 0`。
@@ -108,7 +106,7 @@
那么为了规则统一,针对序列[2,5],可以假设为[2,2,5],这样它就有坡度了即 preDiff = 0,如图:
-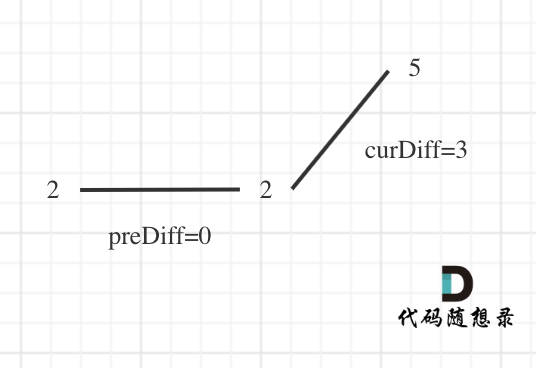
+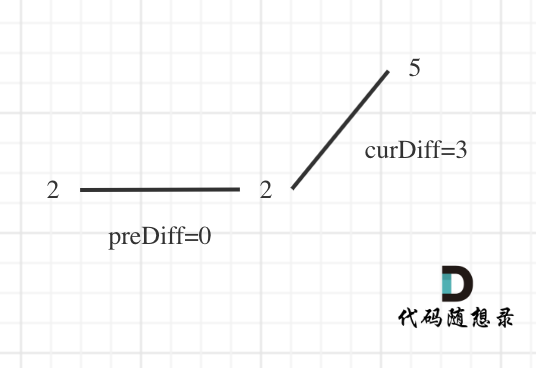
针对以上情形,result 初始为 1(默认最右面有一个峰值),此时 curDiff > 0 && preDiff <= 0,那么 result++(计算了左面的峰值),最后得到的 result 就是 2(峰值个数为 2 即摆动序列长度为 2)
@@ -147,7 +145,7 @@ public:
在版本一中,我们忽略了一种情况,即 如果在一个单调坡度上有平坡,例如[1,2,2,2,3,4],如图:
-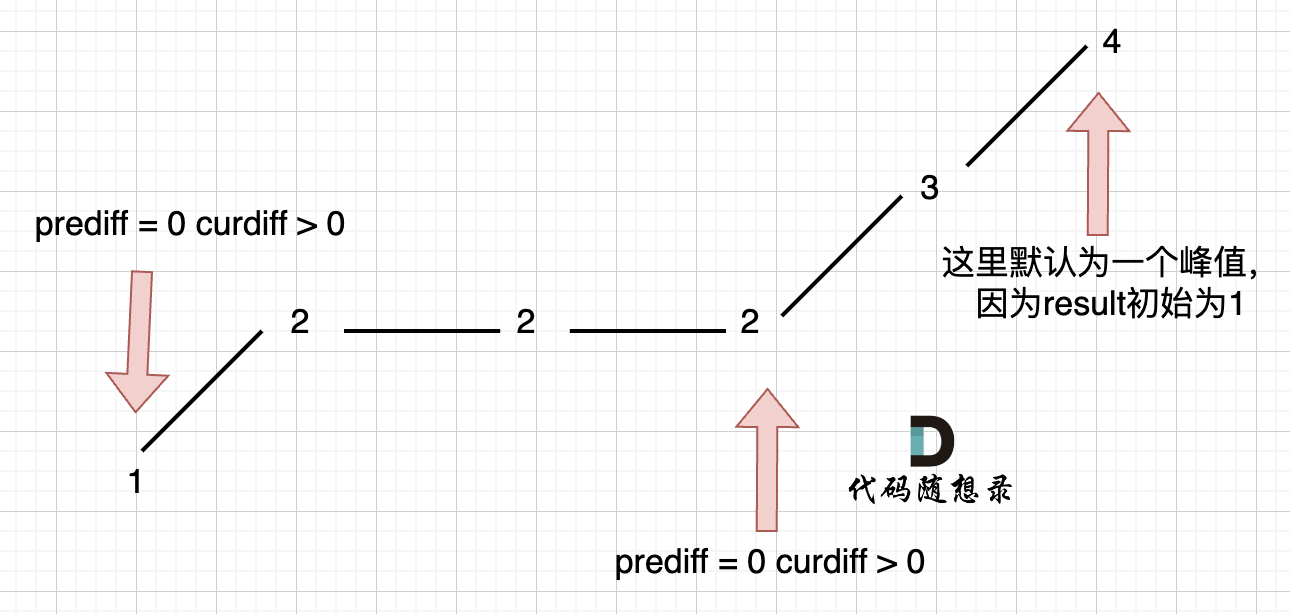
+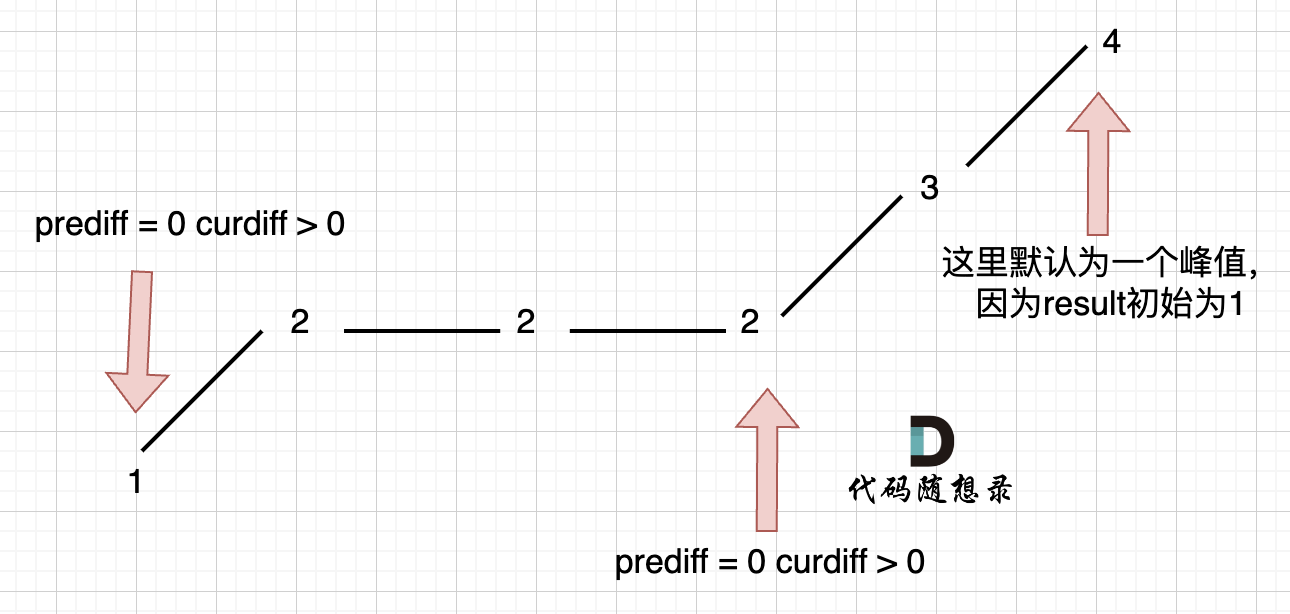
图中,我们可以看出,版本一的代码在三个地方记录峰值,但其实结果因为是 2,因为 单调中的平坡 不能算峰值(即摆动)。
@@ -186,7 +184,7 @@ public:
**本题异常情况的本质,就是要考虑平坡**, 平坡分两种,一个是 上下中间有平坡,一个是单调有平坡,如图:
-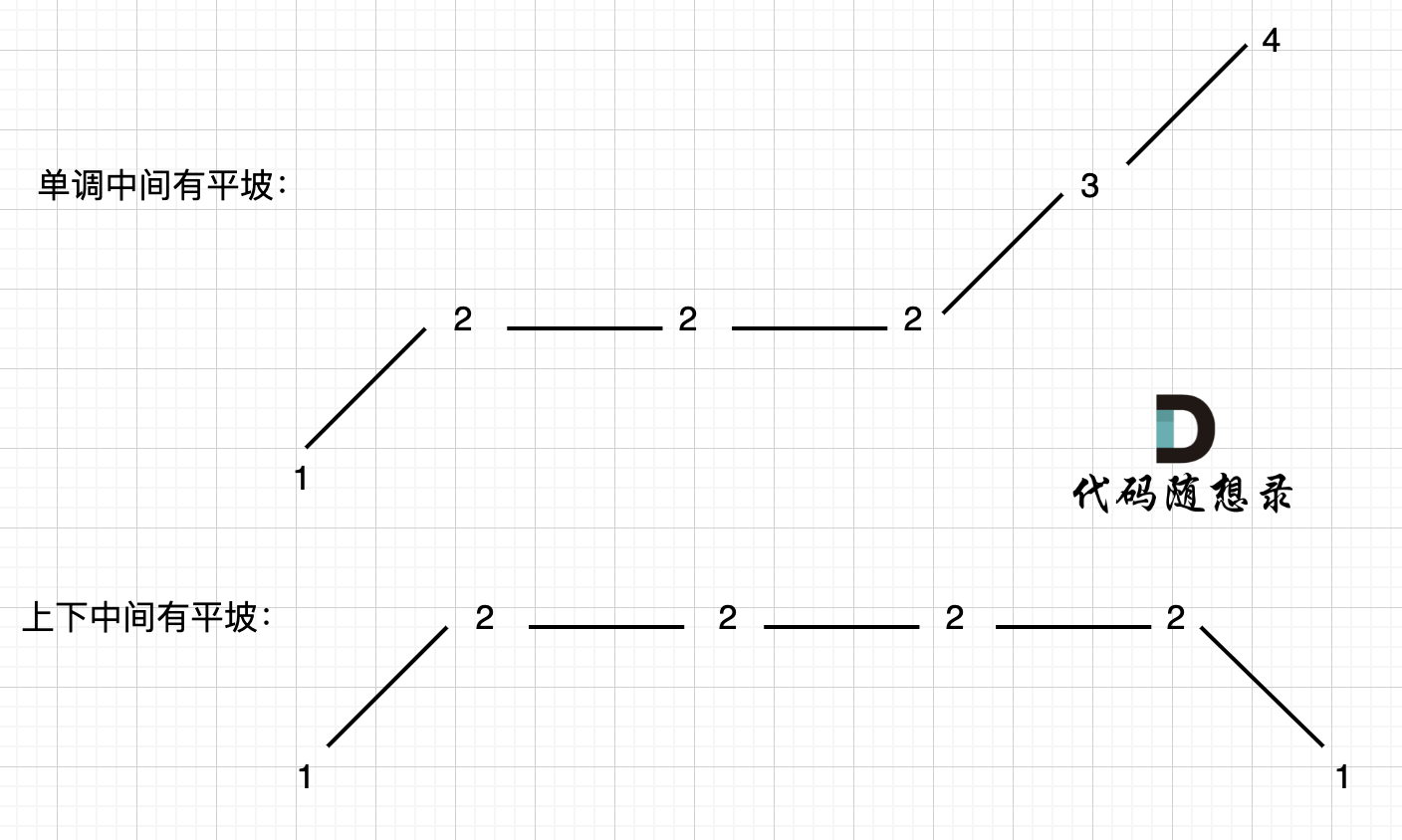
+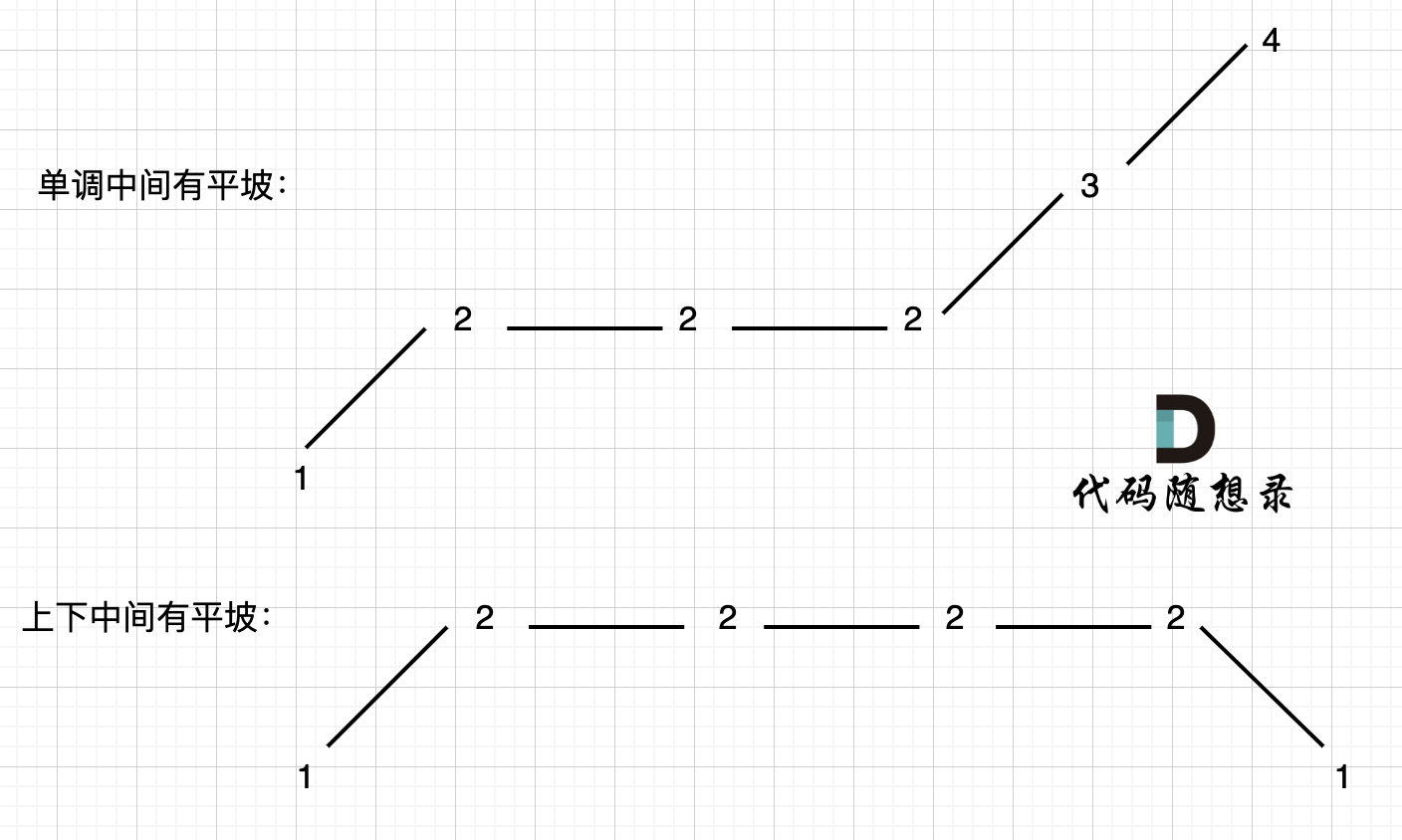
### 思路 2(动态规划)
@@ -466,7 +464,7 @@ func max(a, b int) int {
}
```
-### Javascript
+### JavaScript
**贪心**
@@ -714,7 +712,3 @@ public class Solution
}
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0377.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214\342\205\243.md" "b/problems/0377.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214\342\205\243.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index a840ec9bcc..ab92f24aef
--- "a/problems/0377.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214\342\205\243.md"
+++ "b/problems/0377.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214\342\205\243.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0377.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214\342\205\243.md" "b/problems/0377.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214\342\205\243.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index a840ec9bcc..ab92f24aef
--- "a/problems/0377.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214\342\205\243.md"
+++ "b/problems/0377.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214\342\205\243.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 377. 组合总和 Ⅳ
@@ -105,7 +103,7 @@ dp[i](考虑nums[j])可以由 dp[i - nums[j]](不考虑nums[j]) 推导
我们再来用示例中的例子推导一下:
-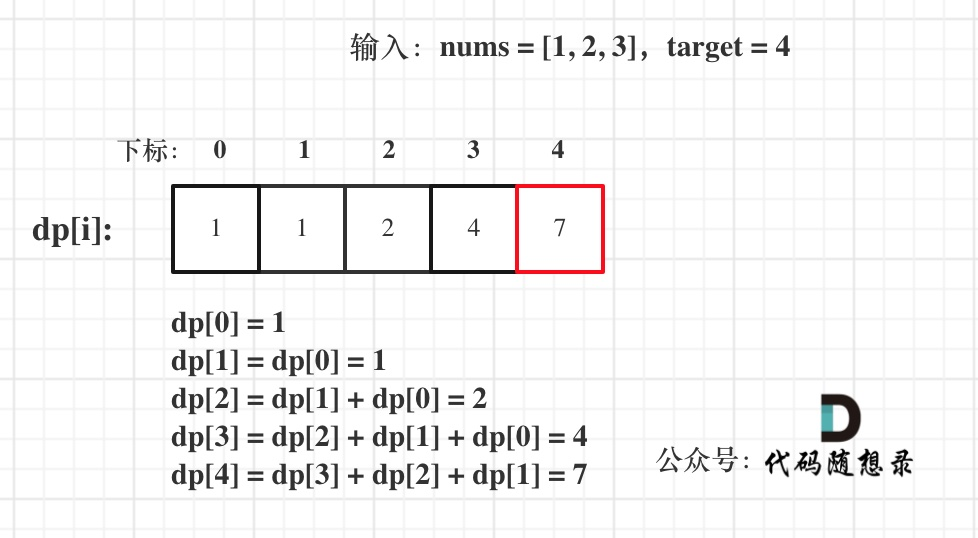
+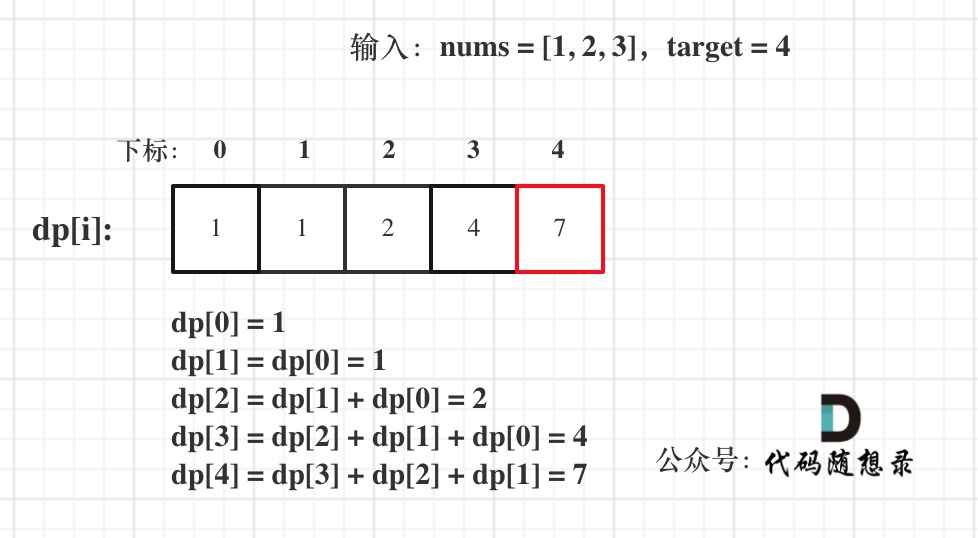
如果代码运行处的结果不是想要的结果,就把dp[i]都打出来,看看和我们推导的一不一样。
@@ -254,7 +252,7 @@ func combinationSum4(nums []int, target int) int {
}
```
-### Javascript:
+### JavaScript:
```javascript
const combinationSum4 = (nums, target) => {
@@ -312,7 +310,28 @@ impl Solution {
}
}
```
+### C
+
+```c
+int combinationSum4(int* nums, int numsSize, int target) {
+ int dp[target + 1];
+ memset(dp, 0, sizeof (dp ));
+ dp[0] = 1;
+ for(int i = 0; i <= target; i++){
+ for(int j = 0; j < numsSize; j++){
+ if(i - nums[j] >= 0 && dp[i] < INT_MAX - dp[i - nums[j]]){
+ dp[i] += dp[i - nums[j]];
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return dp[target];
+}
+```
+
+
+
### C#
+
```csharp
public class Solution
{
@@ -336,8 +355,3 @@ public class Solution
```
-
-
-  -
-
diff --git "a/problems/0383.\350\265\216\351\207\221\344\277\241.md" "b/problems/0383.\350\265\216\351\207\221\344\277\241.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index ff5aafed62..8a2f52ae42
--- "a/problems/0383.\350\265\216\351\207\221\344\277\241.md"
+++ "b/problems/0383.\350\265\216\351\207\221\344\277\241.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0383.\350\265\216\351\207\221\344\277\241.md" "b/problems/0383.\350\265\216\351\207\221\344\277\241.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index ff5aafed62..8a2f52ae42
--- "a/problems/0383.\350\265\216\351\207\221\344\277\241.md"
+++ "b/problems/0383.\350\265\216\351\207\221\344\277\241.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
@@ -104,7 +102,7 @@ public:
};
```
-* 时间复杂度: O(n)
+* 时间复杂度: O(m+n),其中m表示ransomNote的长度,n表示magazine的长度
* 空间复杂度: O(1)
@@ -133,7 +131,7 @@ class Solution {
record[c - 'a'] -= 1;
}
- // 如果数组中存在负数,说明ransomNote字符串总存在magazine中没有的字符
+ // 如果数组中存在负数,说明ransomNote字符串中存在magazine中没有的字符
for(int i : record){
if(i < 0){
return false;
@@ -176,7 +174,7 @@ class Solution:
for x in ransomNote:
value = hashmap.get(x)
- if not value or not value:
+ if not value:
return False
else:
hashmap[x] -= 1
@@ -465,8 +463,5 @@ bool canConstruct(char* ransomNote, char* magazine) {
}
```
-
-
-  -
+
diff --git "a/problems/0392.\345\210\244\346\226\255\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md" "b/problems/0392.\345\210\244\346\226\255\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index ebd567cbb7..bf2d959682
--- "a/problems/0392.\345\210\244\346\226\255\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
+++ "b/problems/0392.\345\210\244\346\226\255\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+
diff --git "a/problems/0392.\345\210\244\346\226\255\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md" "b/problems/0392.\345\210\244\346\226\255\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index ebd567cbb7..bf2d959682
--- "a/problems/0392.\345\210\244\346\226\255\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
+++ "b/problems/0392.\345\210\244\346\226\255\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 392.判断子序列
@@ -82,7 +80,7 @@ if (s[i - 1] != t[j - 1]),此时相当于t要删除元素,t如果把当前
因为这样的定义在dp二维矩阵中可以留出初始化的区间,如图:
-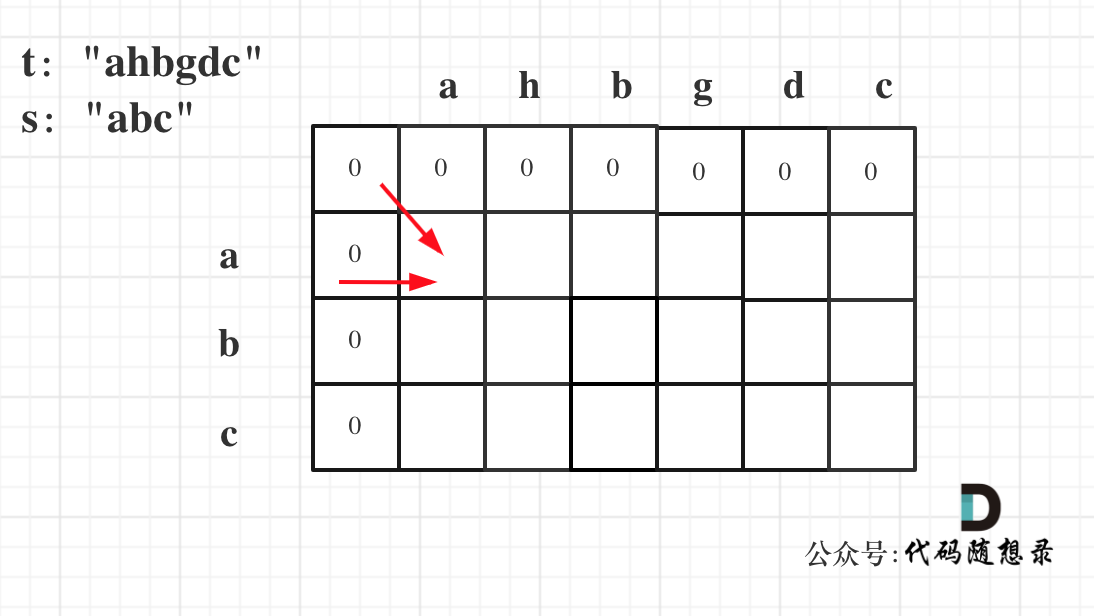
+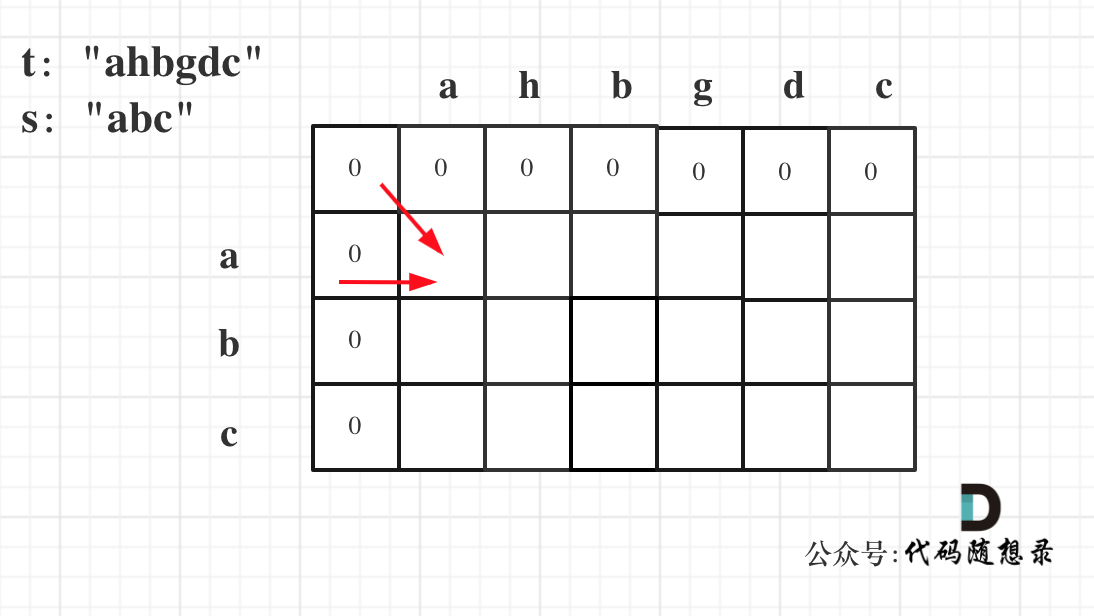
如果要是定义的dp[i][j]是以下标i为结尾的字符串s和以下标j为结尾的字符串t,初始化就比较麻烦了。
@@ -100,14 +98,14 @@ vector> dp(s.size() + 1, vector(t.size() + 1, 0));
如图所示:
-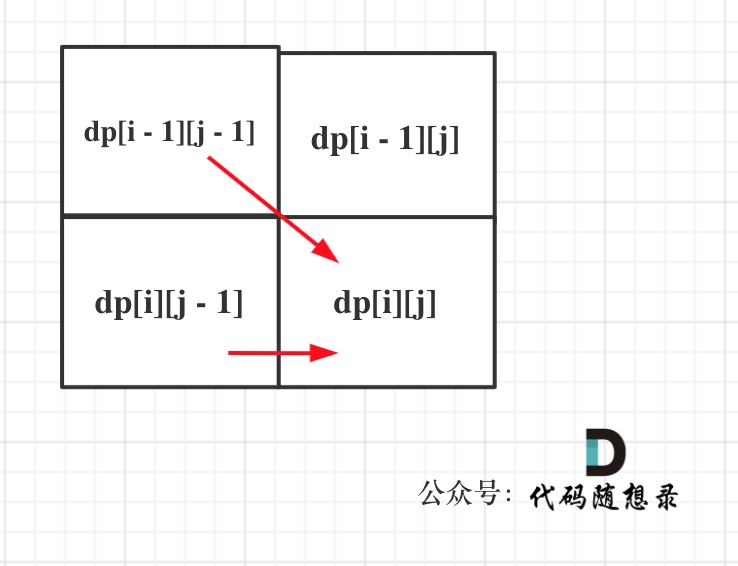
+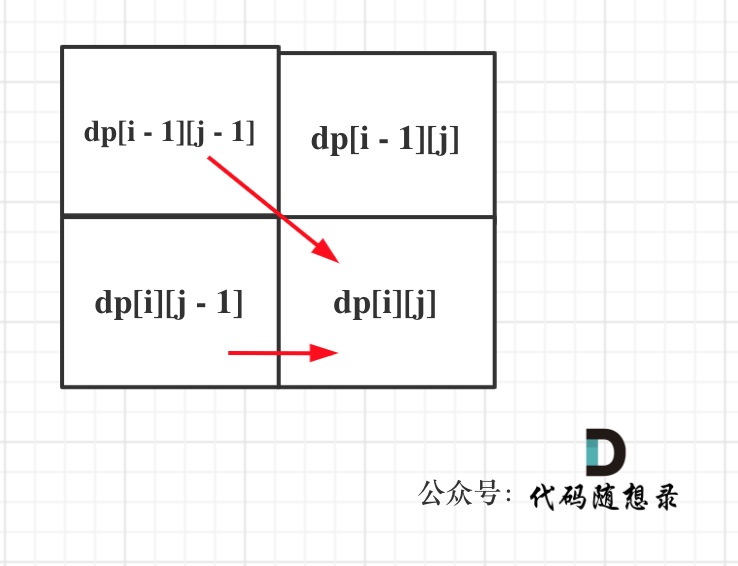
5. 举例推导dp数组
以示例一为例,输入:s = "abc", t = "ahbgdc",dp状态转移图如下:
-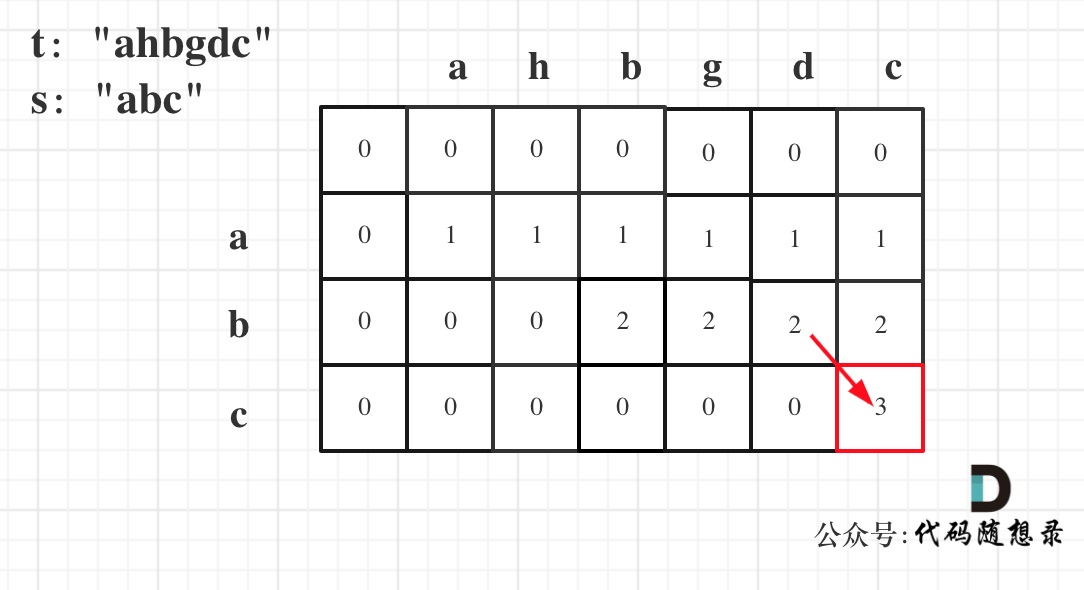
+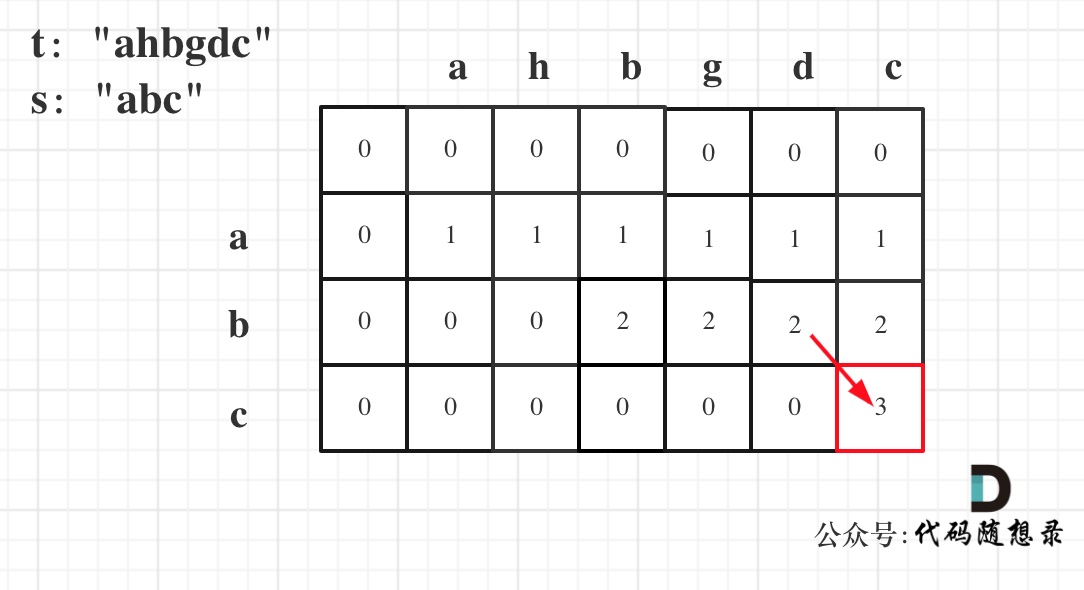
dp[i][j]表示以下标i-1为结尾的字符串s和以下标j-1为结尾的字符串t 相同子序列的长度,所以如果dp[s.size()][t.size()] 与 字符串s的长度相同说明:s与t的最长相同子序列就是s,那么s 就是 t 的子序列。
@@ -173,6 +171,63 @@ class Solution {
}
}
```
+> 修改遍历顺序后,可以利用滚动数组,对dp数组进行压缩
+```java
+class Solution {
+ public boolean isSubsequence(String s, String t) {
+ // 修改遍历顺序,外圈遍历t,内圈遍历s。使得dp的推算只依赖正上方和左上方,方便压缩。
+ int[][] dp = new int[t.length() + 1][s.length() + 1];
+ for (int i = 1; i < dp.length; i++) { // 遍历t字符串
+ for (int j = 1; j < dp[i].length; j++) { // 遍历s字符串
+ if (t.charAt(i - 1) == s.charAt(j - 1)) {
+ dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
+ } else {
+ dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j];
+ }
+ }
+ System.out.println(Arrays.toString(dp[i]));
+ }
+ return dp[t.length()][s.length()] == s.length();
+ }
+}
+```
+> 状态压缩
+```java
+class Solution {
+ public boolean isSubsequence(String s, String t) {
+ int[] dp = new int[s.length() + 1];
+ for (int i = 0; i < t.length(); i ++) {
+ // 需要使用上一轮的dp[j - 1],所以使用倒序遍历
+ for (int j = dp.length - 1; j > 0; j --) {
+ // i遍历的是t字符串,j遍历的是dp数组,dp数组的长度比s的大1,因此需要减1。
+ if (t.charAt(i) == s.charAt(j - 1)) {
+ dp[j] = dp[j - 1] + 1;
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return dp[s.length()] == s.length();
+ }
+}
+```
+> 将dp定义为boolean类型,dp[i]直接表示s.substring(0, i)是否为t的子序列
+
+```java
+class Solution {
+ public boolean isSubsequence(String s, String t) {
+ boolean[] dp = new boolean[s.length() + 1];
+ // 表示 “” 是t的子序列
+ dp[0] = true;
+ for (int i = 0; i < t.length(); i ++) {
+ for (int j = dp.length - 1; j > 0; j --) {
+ if (t.charAt(i) == s.charAt(j - 1)) {
+ dp[j] = dp[j - 1];
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return dp[dp.length - 1];
+ }
+}
+```
### Python:
@@ -347,8 +402,4 @@ impl Solution {
}
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0404.\345\267\246\345\217\266\345\255\220\344\271\213\345\222\214.md" "b/problems/0404.\345\267\246\345\217\266\345\255\220\344\271\213\345\222\214.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 3d0f5a8abf..10b159b181
--- "a/problems/0404.\345\267\246\345\217\266\345\255\220\344\271\213\345\222\214.md"
+++ "b/problems/0404.\345\267\246\345\217\266\345\255\220\344\271\213\345\222\214.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0404.\345\267\246\345\217\266\345\255\220\344\271\213\345\222\214.md" "b/problems/0404.\345\267\246\345\217\266\345\255\220\344\271\213\345\222\214.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 3d0f5a8abf..10b159b181
--- "a/problems/0404.\345\267\246\345\217\266\345\255\220\344\271\213\345\222\214.md"
+++ "b/problems/0404.\345\267\246\345\217\266\345\255\220\344\271\213\345\222\214.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 404.左叶子之和
@@ -14,7 +12,7 @@
示例:
-
+
## 算法公开课
@@ -28,12 +26,12 @@
大家思考一下如下图中二叉树,左叶子之和究竟是多少?
-
+
**其实是0,因为这棵树根本没有左叶子!**
但看这个图的左叶子之和是多少?
-
+
相信通过这两个图,大家对最左叶子的定义有明确理解了。
@@ -337,6 +335,21 @@ func sumOfLeftLeaves(root *TreeNode) int {
}
```
+**递归精简版**
+
+```go
+func sumOfLeftLeaves(root *TreeNode) int {
+ if root == nil {
+ return 0
+ }
+ leftValue := 0
+ if root.Left != nil && root.Left.Left == nil && root.Left.Right == nil {
+ leftValue = root.Left.Val
+ }
+ return leftValue + sumOfLeftLeaves(root.Left) + sumOfLeftLeaves(root.Right)
+}
+```
+
**迭代法(前序遍历)**
```go
@@ -669,8 +682,4 @@ public int SumOfLeftLeaves(TreeNode root)
}
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0406.\346\240\271\346\215\256\350\272\253\351\253\230\351\207\215\345\273\272\351\230\237\345\210\227.md" "b/problems/0406.\346\240\271\346\215\256\350\272\253\351\253\230\351\207\215\345\273\272\351\230\237\345\210\227.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index b0b02c1454..ce9d3bfb4e
--- "a/problems/0406.\346\240\271\346\215\256\350\272\253\351\253\230\351\207\215\345\273\272\351\230\237\345\210\227.md"
+++ "b/problems/0406.\346\240\271\346\215\256\350\272\253\351\253\230\351\207\215\345\273\272\351\230\237\345\210\227.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0406.\346\240\271\346\215\256\350\272\253\351\253\230\351\207\215\345\273\272\351\230\237\345\210\227.md" "b/problems/0406.\346\240\271\346\215\256\350\272\253\351\253\230\351\207\215\345\273\272\351\230\237\345\210\227.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index b0b02c1454..ce9d3bfb4e
--- "a/problems/0406.\346\240\271\346\215\256\350\272\253\351\253\230\351\207\215\345\273\272\351\230\237\345\210\227.md"
+++ "b/problems/0406.\346\240\271\346\215\256\350\272\253\351\253\230\351\207\215\345\273\272\351\230\237\345\210\227.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 406.根据身高重建队列
@@ -63,7 +61,7 @@
以图中{5,2} 为例:
-
+
按照身高排序之后,优先按身高高的people的k来插入,后序插入节点也不会影响前面已经插入的节点,最终按照k的规则完成了队列。
@@ -87,7 +85,7 @@
回归本题,整个插入过程如下:
排序完的people:
-[[7,0], [7,1], [6,1], [5,0], [5,2],[4,4]]
+[[7,0], [7,1], [6,1], [5,0], [5,2], [4,4]]
插入的过程:
* 插入[7,0]:[[7,0]]
@@ -270,7 +268,7 @@ func reconstructQueue(people [][]int) [][]int {
}
```
-### Javascript
+### JavaScript
```Javascript
var reconstructQueue = function(people) {
@@ -421,8 +419,4 @@ public class Solution
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0416.\345\210\206\345\211\262\347\255\211\345\222\214\345\255\220\351\233\206.md" "b/problems/0416.\345\210\206\345\211\262\347\255\211\345\222\214\345\255\220\351\233\206.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 71e01ae392..75bc5d0e10
--- "a/problems/0416.\345\210\206\345\211\262\347\255\211\345\222\214\345\255\220\351\233\206.md"
+++ "b/problems/0416.\345\210\206\345\211\262\347\255\211\345\222\214\345\255\220\351\233\206.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0416.\345\210\206\345\211\262\347\255\211\345\222\214\345\255\220\351\233\206.md" "b/problems/0416.\345\210\206\345\211\262\347\255\211\345\222\214\345\255\220\351\233\206.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 71e01ae392..75bc5d0e10
--- "a/problems/0416.\345\210\206\345\211\262\347\255\211\345\222\214\345\255\220\351\233\206.md"
+++ "b/problems/0416.\345\210\206\345\211\262\347\255\211\345\222\214\345\255\220\351\233\206.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 416. 分割等和子集
@@ -47,16 +45,22 @@
那么只要找到集合里能够出现 sum / 2 的子集总和,就算是可以分割成两个相同元素和子集了。
-本题是可以用回溯暴力搜索出所有答案的,但最后超时了,也不想再优化了,放弃回溯,直接上01背包吧。
+本题是可以用回溯暴力搜索出所有答案的,但最后超时了,也不想再优化了,放弃回溯。
+
+是否有其他解法可以解决此题。
+
+本题的本质是,能否把容量为 sum / 2的背包装满。
+
+**这是 背包算法可以解决的经典类型题目**。
如果对01背包不够了解,建议仔细看完如下两篇:
* [动态规划:关于01背包问题,你该了解这些!](https://programmercarl.com/背包理论基础01背包-1.html)
* [动态规划:关于01背包问题,你该了解这些!(滚动数组)](https://programmercarl.com/背包理论基础01背包-2.html)
-### 01背包问题
+## 01背包问题
-背包问题,大家都知道,有N件物品和一个最多能背重量为W 的背包。第i件物品的重量是weight[i],得到的价值是value[i] 。每件物品只能用一次,求解将哪些物品装入背包里物品价值总和最大。
+01背包问题,大家都知道,有N件物品和一个最多能背重量为W 的背包。第i件物品的重量是weight[i],得到的价值是value[i] 。每件物品只能用一次,求解将哪些物品装入背包里物品价值总和最大。
**背包问题有多种背包方式,常见的有:01背包、完全背包、多重背包、分组背包和混合背包等等。**
@@ -64,32 +68,33 @@
**即一个商品如果可以重复多次放入是完全背包,而只能放入一次是01背包,写法还是不一样的。**
-**要明确本题中我们要使用的是01背包,因为元素我们只能用一次。**
+**元素我们只能用一次,如果使用背包,那么也是01背包**
回归主题:首先,本题要求集合里能否出现总和为 sum / 2 的子集。
-那么来一一对应一下本题,看看背包问题如何来解决。
+既有一个 只能装重量为 sum / 2 的背包,商品为数字,这些数字能不能把 这个背包装满。
-**只有确定了如下四点,才能把01背包问题套到本题上来。**
+那每一件商品是数字的话,对应的重量 和 价值是多少呢?
-* 背包的体积为sum / 2
-* 背包要放入的商品(集合里的元素)重量为 元素的数值,价值也为元素的数值
-* 背包如果正好装满,说明找到了总和为 sum / 2 的子集。
-* 背包中每一个元素是不可重复放入。
+一个数字只有一个维度,即 重量等于价值。
-以上分析完,我们就可以套用01背包,来解决这个问题了。
+当数字 可以装满 承载重量为 sum / 2 的背包的背包时,这个背包的价值也是 sum / 2。
-动规五部曲分析如下:
+那么这道题就是 装满 承载重量为 sum / 2 的背包,价值最大是多少?
-1. 确定dp数组以及下标的含义
+如果最大价值是 sum / 2,说明正好被商品装满了。
-01背包中,dp[j] 表示: 容量为j的背包,所背的物品价值最大可以为dp[j]。
+因为商品是数字,重量和对应的价值是相同的。
+
+以上分析完,我们就可以直接用01背包 来解决这个问题了。
+
+动规五部曲分析如下:
-本题中每一个元素的数值既是重量,也是价值。
+### 1. 确定dp数组以及下标的含义
-**套到本题,dp[j]表示 背包总容量(所能装的总重量)是j,放进物品后,背的最大重量为dp[j]**。
+01背包中,dp[j] 表示: 容量(所能装的重量)为j的背包,所背的物品价值最大可以为dp[j]。
-那么如果背包容量为target, dp[target]就是装满 背包之后的重量,所以 当 dp[target] == target 的时候,背包就装满了。
+如果背包所载重量为target, dp[target]就是装满 背包之后的总价值,因为 本题中每一个元素的数值既是重量,也是价值,所以,当 dp[target] == target 的时候,背包就装满了。
有录友可能想,那还有装不满的时候?
@@ -97,7 +102,7 @@
而dp[6] 就可以等于6了,放进1 和 5,那么dp[6] == 6,说明背包装满了。
-2. 确定递推公式
+### 2. 确定递推公式
01背包的递推公式为:dp[j] = max(dp[j], dp[j - weight[i]] + value[i]);
@@ -106,7 +111,7 @@
所以递推公式:dp[j] = max(dp[j], dp[j - nums[i]] + nums[i]);
-3. dp数组如何初始化
+### 3. dp数组如何初始化
在01背包,一维dp如何初始化,已经讲过,
@@ -126,7 +131,7 @@
vector dp(10001, 0);
```
-4. 确定遍历顺序
+### 4. 确定遍历顺序
在[动态规划:关于01背包问题,你该了解这些!(滚动数组)](https://programmercarl.com/背包理论基础01背包-2.html)中就已经说明:如果使用一维dp数组,物品遍历的for循环放在外层,遍历背包的for循环放在内层,且内层for循环倒序遍历!
@@ -141,7 +146,7 @@ for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
}
```
-5. 举例推导dp数组
+### 5. 举例推导dp数组
dp[j]的数值一定是小于等于j的。
@@ -150,7 +155,7 @@ dp[j]的数值一定是小于等于j的。
用例1,输入[1,5,11,5] 为例,如图:
-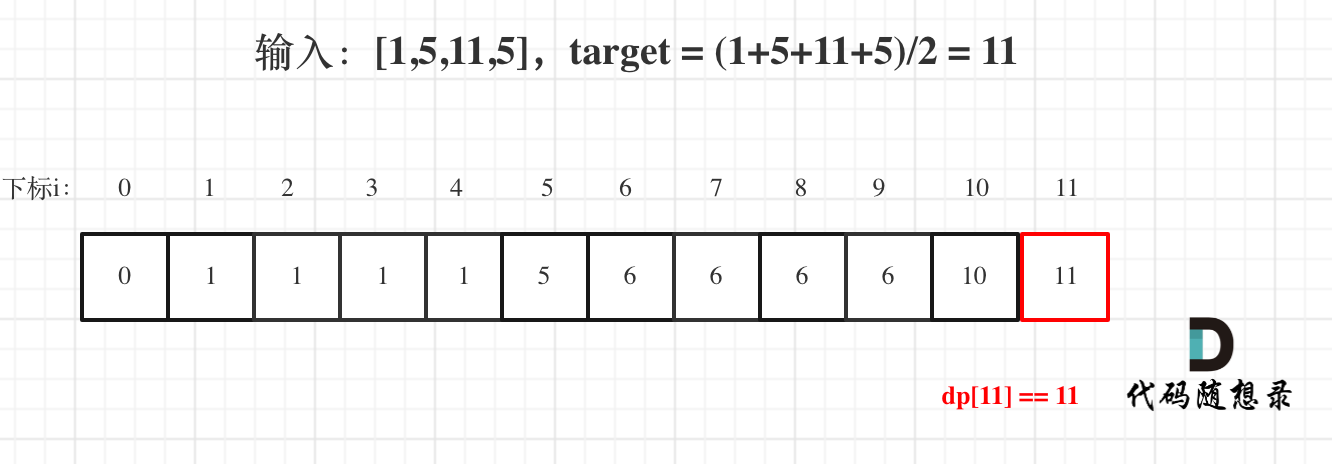
+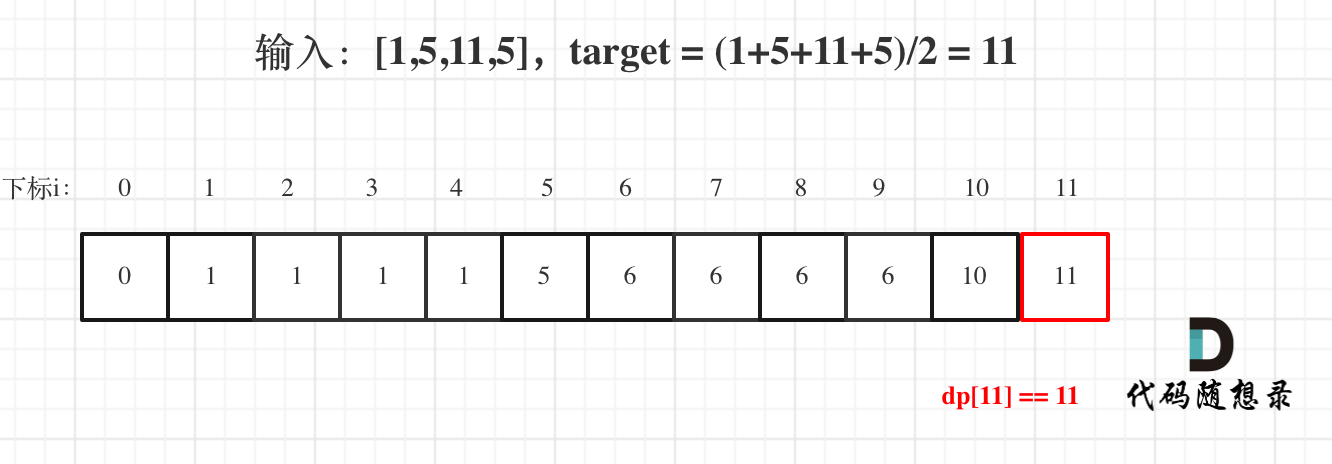
最后dp[11] == 11,说明可以将这个数组分割成两个子集,使得两个子集的元素和相等。
@@ -192,12 +197,11 @@ public:
## 总结
-这道题目就是一道01背包应用类的题目,需要我们拆解题目,然后套入01背包的场景。
+这道题目就是一道01背包经典应用类的题目,需要我们拆解题目,然后才能发现可以使用01背包。
01背包相对于本题,主要要理解,题目中物品是nums[i],重量是nums[i],价值也是nums[i],背包体积是sum/2。
-看代码的话,就可以发现,基本就是按照01背包的写法来的。
-
+做完本题后,需要大家清晰:背包问题,不仅可以求 背包能被的最大价值,还可以求这个背包是否可以装满。
## 其他语言版本
@@ -453,6 +457,7 @@ class Solution:
```
### Go:
+一维dp
```go
// 分割等和子集 动态规划
// 时间复杂度O(n^2) 空间复杂度O(n)
@@ -480,6 +485,44 @@ func canPartition(nums []int) bool {
}
```
+二维dp
+```go
+func canPartition(nums []int) bool {
+ sum := 0
+ for _, val := range nums {
+ sum += val
+ }
+ if sum % 2 == 1 {
+ return false
+ }
+ target := sum / 2
+ dp := make([][]int, len(nums))
+ for i := range dp {
+ dp[i] = make([]int, target + 1)
+ }
+ for j := nums[0]; j <= target; j++ {
+ dp[0][j] = nums[0]
+ }
+ for i := 1; i < len(nums); i++ {
+ for j := 0; j <= target; j++ {
+ if j < nums[i] {
+ dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j]
+ } else {
+ dp[i][j] = max(dp[i-1][j], dp[i-1][j-nums[i]] + nums[i])
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return dp[len(nums)-1][target] == target
+}
+
+func max(x, y int) int {
+ if x > y {
+ return x
+ }
+ return y
+}
+```
+
### JavaScript:
```js
@@ -755,8 +798,4 @@ public class Solution
}
}
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0417.\345\244\252\345\271\263\346\264\213\345\244\247\350\245\277\346\264\213\346\260\264\346\265\201\351\227\256\351\242\230.md" "b/problems/0417.\345\244\252\345\271\263\346\264\213\345\244\247\350\245\277\346\264\213\346\260\264\346\265\201\351\227\256\351\242\230.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 8fe0f1b426..c9494313a1
--- "a/problems/0417.\345\244\252\345\271\263\346\264\213\345\244\247\350\245\277\346\264\213\346\260\264\346\265\201\351\227\256\351\242\230.md"
+++ "b/problems/0417.\345\244\252\345\271\263\346\264\213\345\244\247\350\245\277\346\264\213\346\260\264\346\265\201\351\227\256\351\242\230.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0417.\345\244\252\345\271\263\346\264\213\345\244\247\350\245\277\346\264\213\346\260\264\346\265\201\351\227\256\351\242\230.md" "b/problems/0417.\345\244\252\345\271\263\346\264\213\345\244\247\350\245\277\346\264\213\346\260\264\346\265\201\351\227\256\351\242\230.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 8fe0f1b426..c9494313a1
--- "a/problems/0417.\345\244\252\345\271\263\346\264\213\345\244\247\350\245\277\346\264\213\346\260\264\346\265\201\351\227\256\351\242\230.md"
+++ "b/problems/0417.\345\244\252\345\271\263\346\264\213\345\244\247\350\245\277\346\264\213\346\260\264\346\265\201\351\227\256\351\242\230.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
@@ -20,7 +18,7 @@
示例 1:
-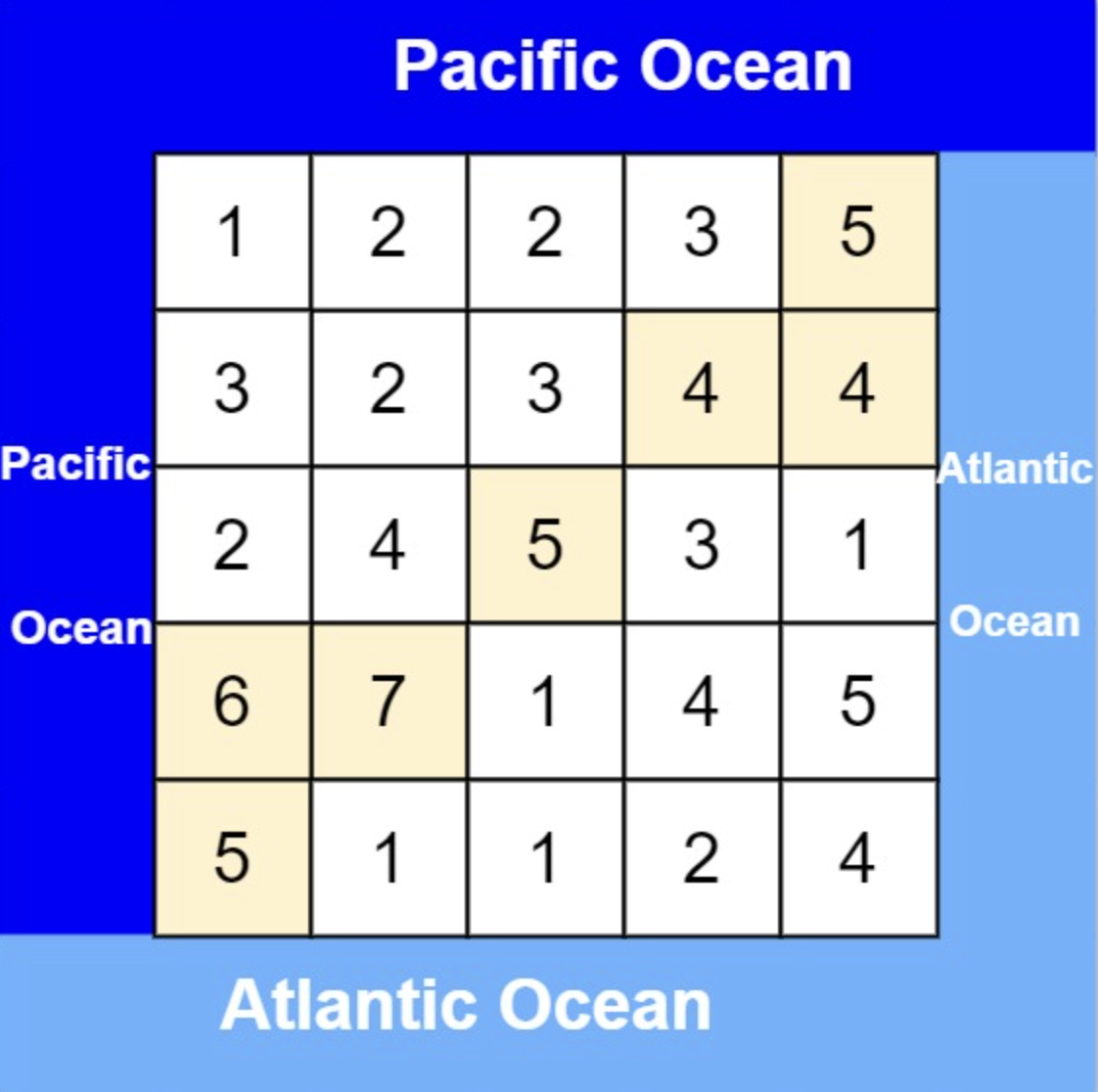
+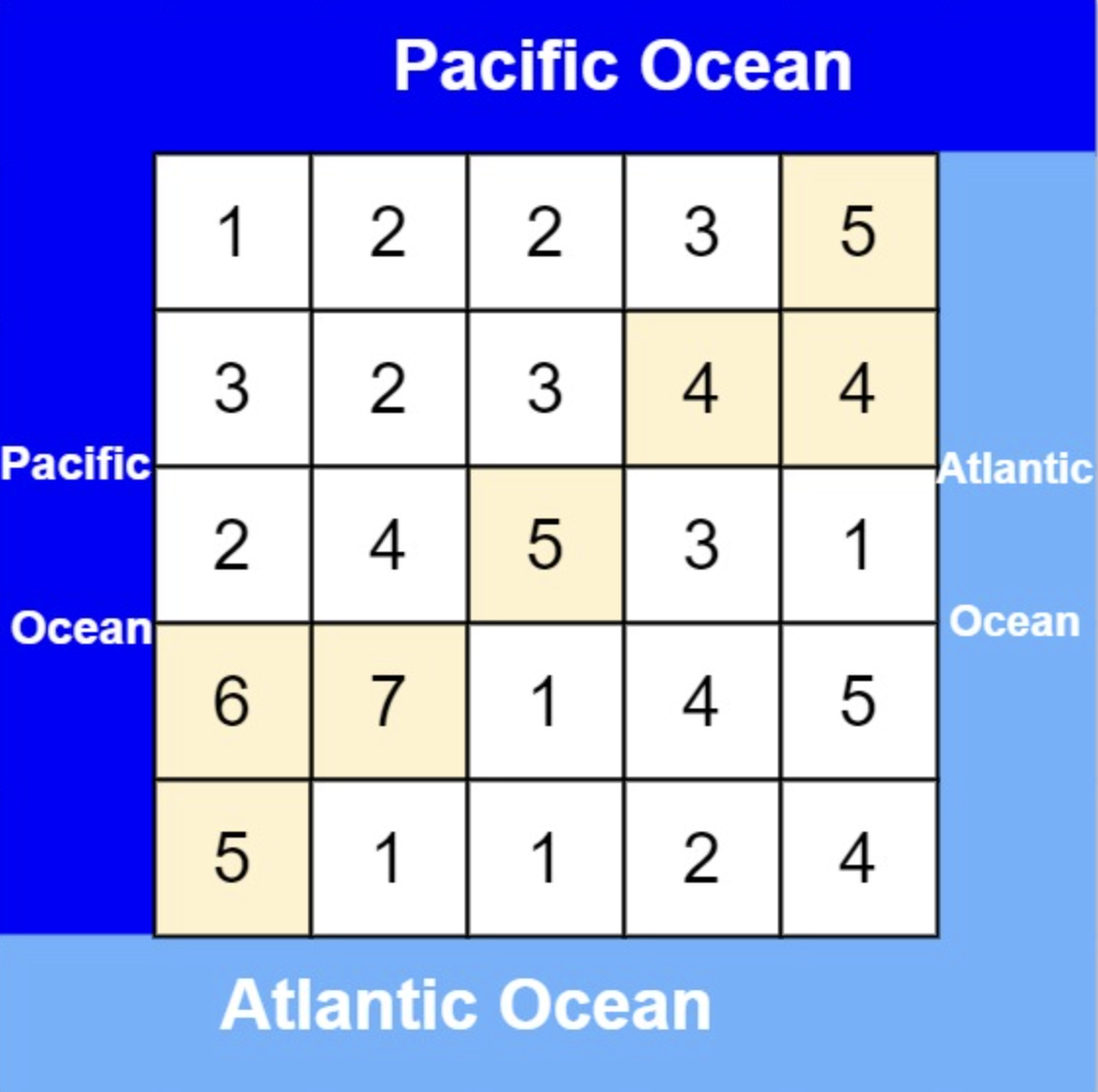
* 输入: heights = [[1,2,2,3,5],[3,2,3,4,4],[2,4,5,3,1],[6,7,1,4,5],[5,1,1,2,4]]
* 输出: [[0,4],[1,3],[1,4],[2,2],[3,0],[3,1],[4,0]]
@@ -132,11 +130,11 @@ public:
从太平洋边上节点出发,如图:
-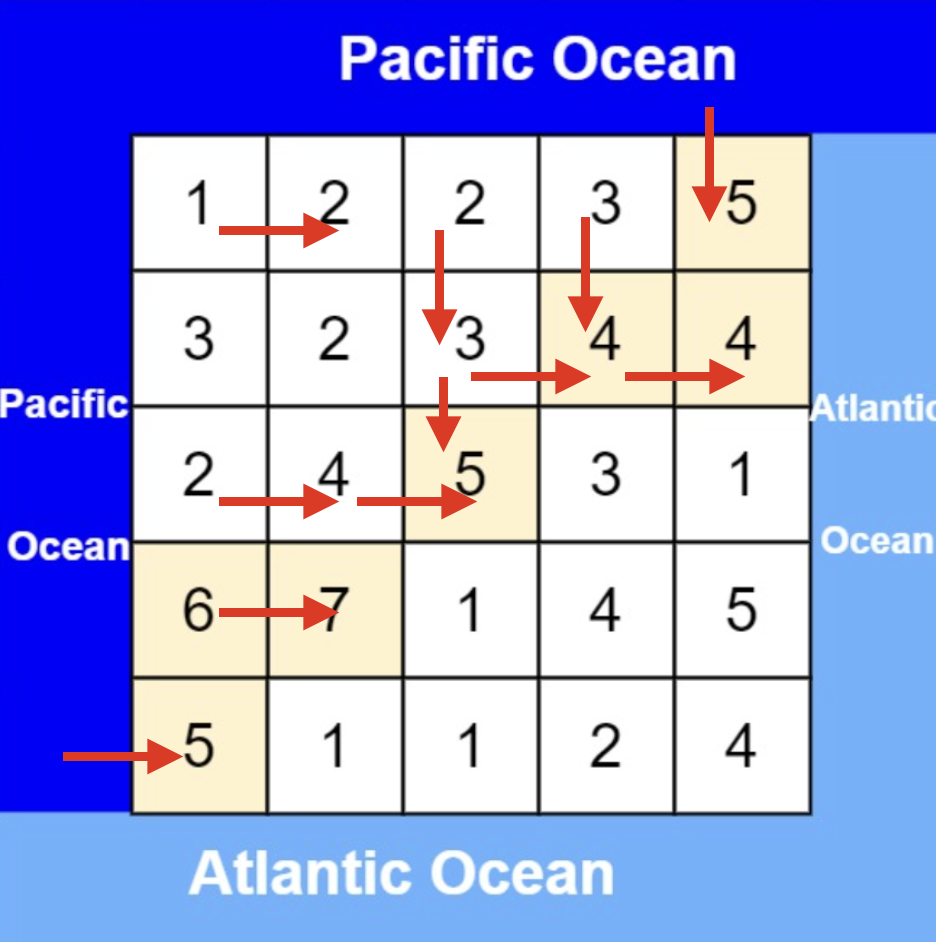
+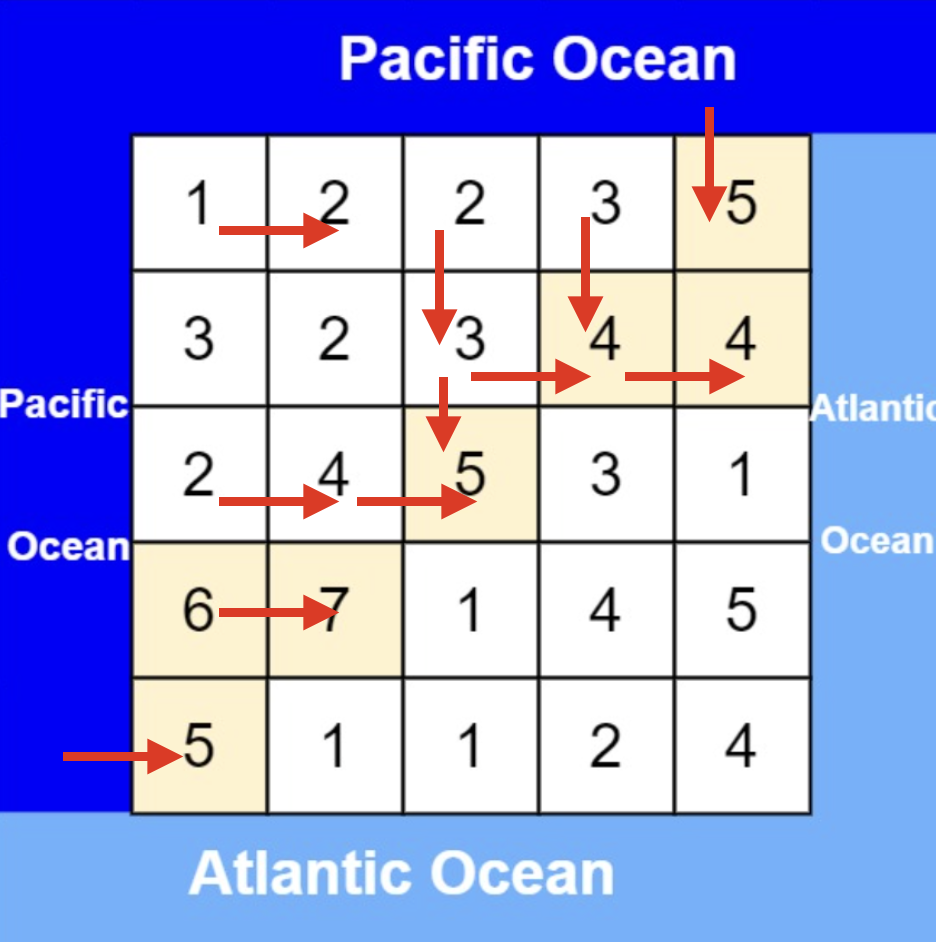
从大西洋边上节点出发,如图:
-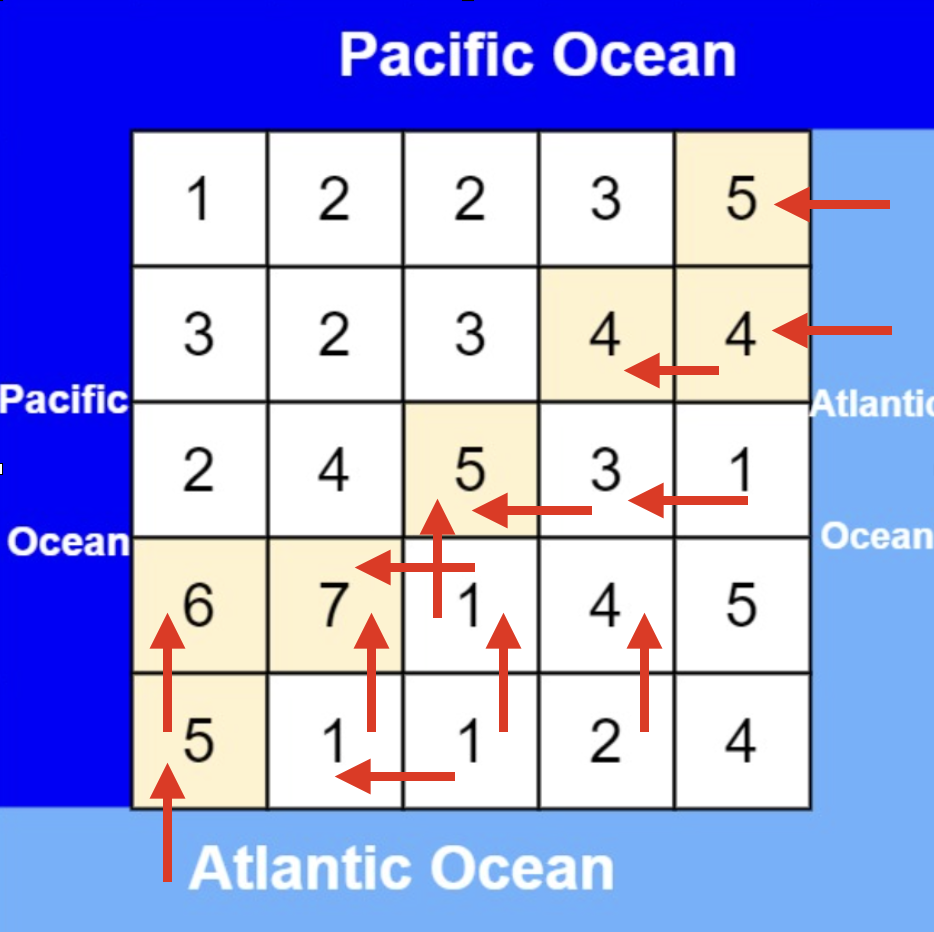
+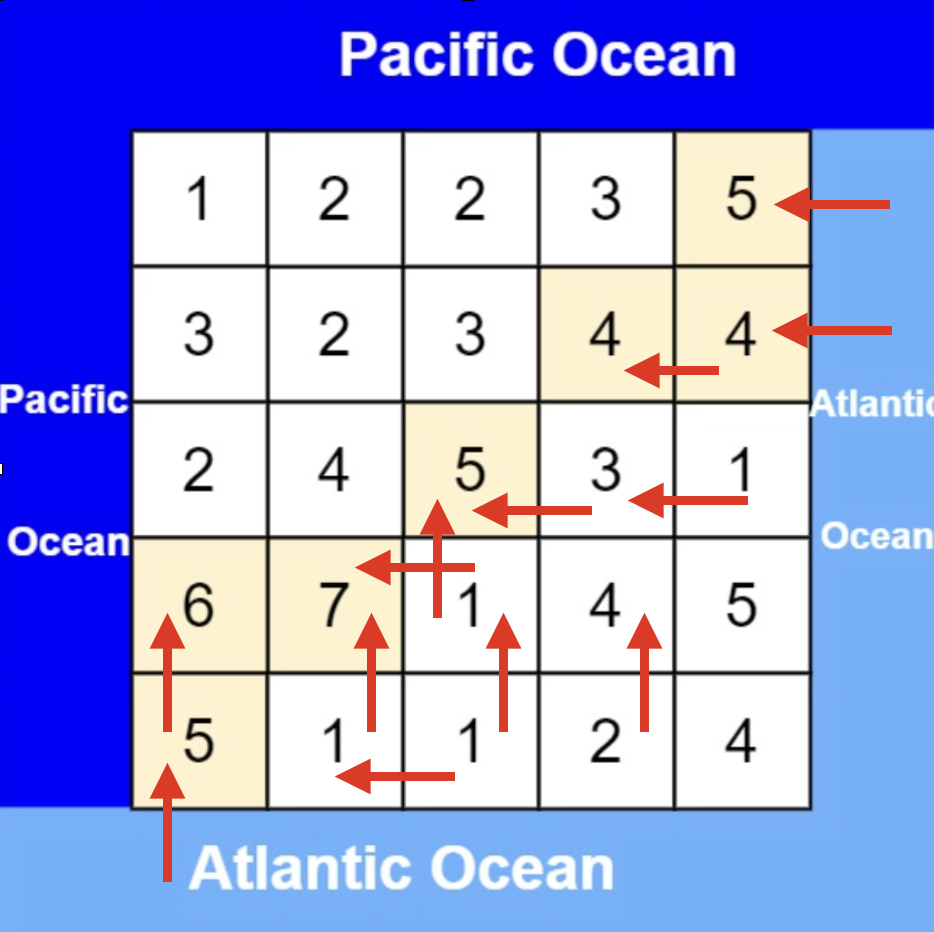
按照这样的逻辑,就可以写出如下遍历代码:(详细注释)
@@ -177,14 +175,14 @@ public:
// 记录从大西洋出发,可以遍历的节点
vector> atlantic = vector>(n, vector(m, false));
-
- // 从最上最下行的节点出发,向高处遍历
+
+ // 从最左最右列的节点出发,向高处遍历
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
dfs (heights, pacific, i, 0); // 遍历最左列,接触太平洋
dfs (heights, atlantic, i, m - 1); // 遍历最右列,接触大西
}
- // 从最左最右列的节点出发,向高处遍历
+ // 从最上最下行的节点出发,向高处遍历
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
dfs (heights, pacific, 0, j); // 遍历最上行,接触太平洋
dfs (heights, atlantic, n - 1, j); // 遍历最下行,接触大西洋
@@ -297,6 +295,73 @@ class Solution {
}
```
+```Java
+class Solution {
+
+ // 和Carl题解更加符合的Java DFS
+ private int[][] directions = {{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, 1}, {0, -1}};
+
+ /**
+ * @param heights 题目给定的二维数组
+ * @param m 当前位置的行号
+ * @param n 当前位置的列号
+ * @param visited 记录这个位置可以到哪条河
+ */
+
+ public void dfs(int[][] heights, boolean[][] visited, int m, int n){
+ if(visited[m][n]) return;
+ visited[m][n] = true;
+
+ for(int[] dir: directions){
+ int nextm = m + dir[0];
+ int nextn = n + dir[1];
+ //出了2D array的边界,continue
+ if(nextm < 0||nextm == heights.length||nextn <0||nextn== heights[0].length) continue;
+ //下一个位置比当下位置还要低,跳过,继续找下一个更高的位置
+ if(heights[m][n] > heights[nextm][nextn]) continue;
+ dfs(heights, visited, nextm, nextn);
+ }
+ }
+
+
+ public List> pacificAtlantic(int[][] heights) {
+ int m = heights.length;
+ int n = heights[0].length;
+
+ // 记录从太平洋边出发,可以遍历的节点
+ boolean[][] pacific = new boolean[m][n];
+ // 记录从大西洋出发,可以遍历的节点
+ boolean[][] atlantic = new boolean[m][n];
+
+ // 从最左最右列的节点出发,向高处遍历
+ for(int i = 0; i> result = new ArrayList<>();
+ for(int a = 0; a pair = new ArrayList<>();
+ pair.add(a);
+ pair.add(b);
+ result.add(pair);
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return result;
+ }
+}
+```
+
广度优先遍历:
```Java
@@ -770,7 +835,3 @@ impl Solution {
}
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0435.\346\227\240\351\207\215\345\217\240\345\214\272\351\227\264.md" "b/problems/0435.\346\227\240\351\207\215\345\217\240\345\214\272\351\227\264.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index cf9996ddef..4231a8ee90
--- "a/problems/0435.\346\227\240\351\207\215\345\217\240\345\214\272\351\227\264.md"
+++ "b/problems/0435.\346\227\240\351\207\215\345\217\240\345\214\272\351\227\264.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0435.\346\227\240\351\207\215\345\217\240\345\214\272\351\227\264.md" "b/problems/0435.\346\227\240\351\207\215\345\217\240\345\214\272\351\227\264.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index cf9996ddef..4231a8ee90
--- "a/problems/0435.\346\227\240\351\207\215\345\217\240\345\214\272\351\227\264.md"
+++ "b/problems/0435.\346\227\240\351\207\215\345\217\240\345\214\272\351\227\264.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 435. 无重叠区间
@@ -46,7 +44,7 @@
这里记录非交叉区间的个数还是有技巧的,如图:
-
+
区间,1,2,3,4,5,6都按照右边界排好序。
@@ -311,7 +309,7 @@ func min(a, b int) int {
}
```
-### Javascript
+### JavaScript
- 按右边界排序
```Javascript
var eraseOverlapIntervals = function(intervals) {
@@ -441,7 +439,37 @@ impl Solution {
}
}
```
+### C
+
+```c
+// 按照区间右边界排序
+int cmp(const void * var1, const void * var2){
+ return (*(int **) var1)[1] - (*(int **) var2)[1];
+}
+
+int eraseOverlapIntervals(int** intervals, int intervalsSize, int* intervalsColSize) {
+ if(intervalsSize == 0){
+ return 0;
+ }
+ qsort(intervals, intervalsSize, sizeof (int *), cmp);
+ // 记录非重叠的区间数量
+ int count = 1;
+ // 记录区间分割点
+ int end = intervals[0][1];
+ for(int i = 1; i < intervalsSize; i++){
+ if(end <= intervals[i][0]){
+ end = intervals[i][1];
+ count++;
+ }
+ }
+ return intervalsSize - count;
+}
+```
+
+
+
### C#
+
```csharp
public class Solution
{
@@ -464,7 +492,4 @@ public class Solution
```
-
-
-  -
+
diff --git "a/problems/0450.\345\210\240\351\231\244\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\350\212\202\347\202\271.md" "b/problems/0450.\345\210\240\351\231\244\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\350\212\202\347\202\271.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 8922a14e14..44575b8aff
--- "a/problems/0450.\345\210\240\351\231\244\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\350\212\202\347\202\271.md"
+++ "b/problems/0450.\345\210\240\351\231\244\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\350\212\202\347\202\271.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+
diff --git "a/problems/0450.\345\210\240\351\231\244\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\350\212\202\347\202\271.md" "b/problems/0450.\345\210\240\351\231\244\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\350\212\202\347\202\271.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 8922a14e14..44575b8aff
--- "a/problems/0450.\345\210\240\351\231\244\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\350\212\202\347\202\271.md"
+++ "b/problems/0450.\345\210\240\351\231\244\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\350\212\202\347\202\271.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
> 二叉搜索树删除节点就涉及到结构调整了
@@ -22,11 +20,11 @@
示例:
-
+
## 算法公开课
-**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[调整二叉树的结构最难!| LeetCode:450.删除二叉搜索树中的节点](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1tP41177us?share_source=copy_web),相信结合视频在看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
+**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[调整二叉树的结构最难!| LeetCode:450.删除二叉搜索树中的节点](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1tP41177us?share_source=copy_web),相信结合视频再看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
## 思路
@@ -42,7 +40,7 @@
代码如下:
-```
+```cpp
TreeNode* deleteNode(TreeNode* root, int key)
```
@@ -50,7 +48,7 @@ TreeNode* deleteNode(TreeNode* root, int key)
遇到空返回,其实这也说明没找到删除的节点,遍历到空节点直接返回了
-```
+```cpp
if (root == nullptr) return root;
```
@@ -69,7 +67,7 @@ if (root == nullptr) return root;
第五种情况有点难以理解,看下面动画:
-
+
动画中的二叉搜索树中,删除元素7, 那么删除节点(元素7)的左孩子就是5,删除节点(元素7)的右子树的最左面节点是元素8。
@@ -106,7 +104,7 @@ if (root->val == key) {
这里相当于把新的节点返回给上一层,上一层就要用 root->left 或者 root->right接住,代码如下:
-```
+```cpp
if (root->val > key) root->left = deleteNode(root->left, key);
if (root->val < key) root->right = deleteNode(root->right, key);
return root;
@@ -801,8 +799,38 @@ impl Solution {
}
```
-
-
-  -
+### Ruby
+> 递归法:
+```ruby
+# @param {TreeNode} root
+# @param {Integer} key
+# @return {TreeNode}
+def delete_node(root, key)
+ return nil if root.nil?
+
+ right = root.right
+ left = root.left
+
+ if root.val == key
+ return right if left.nil?
+ return left if right.nil?
+
+ node = right
+ while node.left
+ node = node.left
+ end
+ node.left = left
+
+ return right
+ end
+
+ if root.val > key
+ root.left = delete_node(left, key)
+ else
+ root.right = delete_node(right, key)
+ end
+
+ return root
+end
+```
diff --git "a/problems/0452.\347\224\250\346\234\200\345\260\221\346\225\260\351\207\217\347\232\204\347\256\255\345\274\225\347\210\206\346\260\224\347\220\203.md" "b/problems/0452.\347\224\250\346\234\200\345\260\221\346\225\260\351\207\217\347\232\204\347\256\255\345\274\225\347\210\206\346\260\224\347\220\203.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index cd57f83b26..76de3f93a2
--- "a/problems/0452.\347\224\250\346\234\200\345\260\221\346\225\260\351\207\217\347\232\204\347\256\255\345\274\225\347\210\206\346\260\224\347\220\203.md"
+++ "b/problems/0452.\347\224\250\346\234\200\345\260\221\346\225\260\351\207\217\347\232\204\347\256\255\345\274\225\347\210\206\346\260\224\347\220\203.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+### Ruby
+> 递归法:
+```ruby
+# @param {TreeNode} root
+# @param {Integer} key
+# @return {TreeNode}
+def delete_node(root, key)
+ return nil if root.nil?
+
+ right = root.right
+ left = root.left
+
+ if root.val == key
+ return right if left.nil?
+ return left if right.nil?
+
+ node = right
+ while node.left
+ node = node.left
+ end
+ node.left = left
+
+ return right
+ end
+
+ if root.val > key
+ root.left = delete_node(left, key)
+ else
+ root.right = delete_node(right, key)
+ end
+
+ return root
+end
+```
diff --git "a/problems/0452.\347\224\250\346\234\200\345\260\221\346\225\260\351\207\217\347\232\204\347\256\255\345\274\225\347\210\206\346\260\224\347\220\203.md" "b/problems/0452.\347\224\250\346\234\200\345\260\221\346\225\260\351\207\217\347\232\204\347\256\255\345\274\225\347\210\206\346\260\224\347\220\203.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index cd57f83b26..76de3f93a2
--- "a/problems/0452.\347\224\250\346\234\200\345\260\221\346\225\260\351\207\217\347\232\204\347\256\255\345\274\225\347\210\206\346\260\224\347\220\203.md"
+++ "b/problems/0452.\347\224\250\346\234\200\345\260\221\346\225\260\351\207\217\347\232\204\347\256\255\345\274\225\347\210\206\346\260\224\347\220\203.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 452. 用最少数量的箭引爆气球
@@ -78,7 +76,7 @@
以题目示例: [[10,16],[2,8],[1,6],[7,12]]为例,如图:(方便起见,已经排序)
-
+
可以看出首先第一组重叠气球,一定是需要一个箭,气球3,的左边界大于了 第一组重叠气球的最小右边界,所以再需要一支箭来射气球3了。
@@ -110,7 +108,7 @@ public:
```
* 时间复杂度:O(nlog n),因为有一个快排
-* 空间复杂度:O(1),有一个快排,最差情况(倒序)时,需要n次递归调用。因此确实需要O(n)的栈空间
+* 空间复杂度:O(n),有一个快排,最差情况(倒序)时,需要n次递归调用。因此确实需要O(n)的栈空间
可以看出代码并不复杂。
@@ -180,19 +178,25 @@ class Solution:
```python
class Solution: # 不改变原数组
def findMinArrowShots(self, points: List[List[int]]) -> int:
+ if len(points) == 0:
+ return 0
+
points.sort(key = lambda x: x[0])
- sl,sr = points[0][0],points[0][1]
+
+ # points已经按照第一个坐标正序排列,因此只需要设置一个变量,记录右侧坐标(阈值)
+ # 考虑一个气球范围包含两个不相交气球的情况:气球1: [1, 10], 气球2: [2, 5], 气球3: [6, 10]
+ curr_min_right = points[0][1]
count = 1
+
for i in points:
- if i[0]>sr:
- count+=1
- sl,sr = i[0],i[1]
+ if i[0] > curr_min_right:
+ # 当气球左侧大于这个阈值,那么一定就需要在发射一只箭,并且将阈值更新为当前气球的右侧
+ count += 1
+ curr_min_right = i[1]
else:
- sl = max(sl,i[0])
- sr = min(sr,i[1])
+ # 否则的话,我们只需要求阈值和当前气球的右侧的较小值来更新阈值
+ curr_min_right = min(curr_min_right, i[1])
return count
-
-
```
### Go
```go
@@ -220,7 +224,7 @@ func min(a, b int) int {
}
```
-### Javascript
+### JavaScript
```Javascript
var findMinArrowShots = function(points) {
points.sort((a, b) => {
@@ -351,7 +355,3 @@ public class Solution
}
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0454.\345\233\233\346\225\260\347\233\270\345\212\240II.md" "b/problems/0454.\345\233\233\346\225\260\347\233\270\345\212\240II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index a0bf84da83..a26071a1fa
--- "a/problems/0454.\345\233\233\346\225\260\347\233\270\345\212\240II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0454.\345\233\233\346\225\260\347\233\270\345\212\240II.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0454.\345\233\233\346\225\260\347\233\270\345\212\240II.md" "b/problems/0454.\345\233\233\346\225\260\347\233\270\345\212\240II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index a0bf84da83..a26071a1fa
--- "a/problems/0454.\345\233\233\346\225\260\347\233\270\345\212\240II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0454.\345\233\233\346\225\260\347\233\270\345\212\240II.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
> 需要哈希的地方都能找到map的身影
@@ -54,7 +52,7 @@
1. 首先定义 一个unordered_map,key放a和b两数之和,value 放a和b两数之和出现的次数。
2. 遍历大A和大B数组,统计两个数组元素之和,和出现的次数,放到map中。
3. 定义int变量count,用来统计 a+b+c+d = 0 出现的次数。
-4. 在遍历大C和大D数组,找到如果 0-(c+d) 在map中出现过的话,就用count把map中key对应的value也就是出现次数统计出来。
+4. 再遍历大C和大D数组,找到如果 0-(c+d) 在map中出现过的话,就用count把map中key对应的value也就是出现次数统计出来。
5. 最后返回统计值 count 就可以了
C++代码:
@@ -71,7 +69,7 @@ public:
}
}
int count = 0; // 统计a+b+c+d = 0 出现的次数
- // 在遍历大C和大D数组,找到如果 0-(c+d) 在map中出现过的话,就把map中key对应的value也就是出现次数统计出来。
+ // 再遍历大C和大D数组,找到如果 0-(c+d) 在map中出现过的话,就把map中key对应的value也就是出现次数统计出来。
for (int c : C) {
for (int d : D) {
if (umap.find(0 - (c + d)) != umap.end()) {
@@ -185,22 +183,28 @@ class Solution:
### Go:
```go
-func fourSumCount(nums1 []int, nums2 []int, nums3 []int, nums4 []int) int {
- m := make(map[int]int) //key:a+b的数值,value:a+b数值出现的次数
- count := 0
- // 遍历nums1和nums2数组,统计两个数组元素之和,和出现的次数,放到map中
+func fourSumCount(nums1 []int, nums2 []int, nums3 []int, nums4 []int) int {
+ m := make(map[int]int)
+ count := 0
+
+ // 构建nums1和nums2的和的map
for _, v1 := range nums1 {
- for _, v2 := range nums2 {
- m[v1+v2]++
- }
- }
- // 遍历nums3和nums4数组,找到如果 0-(c+d) 在map中出现过的话,就把map中key对应的value也就是出现次数统计出来
- for _, v3 := range nums3 {
- for _, v4 := range nums4 {
- count += m[-v3-v4]
- }
- }
- return count
+ for _, v2 := range nums2 {
+ m[v1+v2]++
+ }
+ }
+
+ // 遍历nums3和nums4,检查-c-d是否在map中
+ for _, v3 := range nums3 {
+ for _, v4 := range nums4 {
+ sum := -v3 - v4
+ if countVal, ok := m[sum]; ok {
+ count += countVal
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+ return count
}
```
@@ -481,8 +485,42 @@ int fourSumCount(int* nums1, int nums1Size, int* nums2, int nums2Size, int* nums
return count;
}
```
-
-
-  -
+
+### Ruby:
+
+```ruby
+# @param {Integer[]} nums1
+# @param {Integer[]} nums2
+# @param {Integer[]} nums3
+# @param {Integer[]} nums4
+# @return {Integer}
+# 新思路:和版主的思路基本相同,只是对后面两个数组的二重循环,用一个方法调用外加一重循环替代,简化了一点。
+# 简单的说,就是把四数和变成了两个两数和的统计(结果放到两个 hash 中),然后再来一次两数和为0.
+# 把四个数分成两组两个数,然后分别计算每组可能的和情况,分别存入 hash 中,key 是 和,value 是 数量;
+# 最后,得到的两个 hash 只需要遍历一次,符合和为零的 value 相乘并加总。
+def four_sum_count(nums1, nums2, nums3, nums4)
+ num_to_count_1 = two_sum_mapping(nums1, nums2)
+ num_to_count_2 = two_sum_mapping(nums3, nums4)
+
+ count_sum = 0
+
+ num_to_count_1.each do |num, count|
+ count_sum += num_to_count_2[-num] * count # 反查另一个 hash,看有没有匹配的,没有的话,hash 默认值为 0,不影响加总;有匹配的,乘积就是可能的情况
+ end
+
+ count_sum
+end
+
+def two_sum_mapping(nums1, nums2)
+ num_to_count = Hash.new(0)
+
+ nums1.each do |num1|
+ nums2.each do |nums2|
+ num_to_count[num1 + nums2] += 1 # 统计和为 num1 + nums2 的有几个
+ end
+ end
+
+ num_to_count
+end
+```
diff --git "a/problems/0455.\345\210\206\345\217\221\351\245\274\345\271\262.md" "b/problems/0455.\345\210\206\345\217\221\351\245\274\345\271\262.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 6ae206dba2..2c38ab9ec1
--- "a/problems/0455.\345\210\206\345\217\221\351\245\274\345\271\262.md"
+++ "b/problems/0455.\345\210\206\345\217\221\351\245\274\345\271\262.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+
+### Ruby:
+
+```ruby
+# @param {Integer[]} nums1
+# @param {Integer[]} nums2
+# @param {Integer[]} nums3
+# @param {Integer[]} nums4
+# @return {Integer}
+# 新思路:和版主的思路基本相同,只是对后面两个数组的二重循环,用一个方法调用外加一重循环替代,简化了一点。
+# 简单的说,就是把四数和变成了两个两数和的统计(结果放到两个 hash 中),然后再来一次两数和为0.
+# 把四个数分成两组两个数,然后分别计算每组可能的和情况,分别存入 hash 中,key 是 和,value 是 数量;
+# 最后,得到的两个 hash 只需要遍历一次,符合和为零的 value 相乘并加总。
+def four_sum_count(nums1, nums2, nums3, nums4)
+ num_to_count_1 = two_sum_mapping(nums1, nums2)
+ num_to_count_2 = two_sum_mapping(nums3, nums4)
+
+ count_sum = 0
+
+ num_to_count_1.each do |num, count|
+ count_sum += num_to_count_2[-num] * count # 反查另一个 hash,看有没有匹配的,没有的话,hash 默认值为 0,不影响加总;有匹配的,乘积就是可能的情况
+ end
+
+ count_sum
+end
+
+def two_sum_mapping(nums1, nums2)
+ num_to_count = Hash.new(0)
+
+ nums1.each do |num1|
+ nums2.each do |nums2|
+ num_to_count[num1 + nums2] += 1 # 统计和为 num1 + nums2 的有几个
+ end
+ end
+
+ num_to_count
+end
+```
diff --git "a/problems/0455.\345\210\206\345\217\221\351\245\274\345\271\262.md" "b/problems/0455.\345\210\206\345\217\221\351\245\274\345\271\262.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 6ae206dba2..2c38ab9ec1
--- "a/problems/0455.\345\210\206\345\217\221\351\245\274\345\271\262.md"
+++ "b/problems/0455.\345\210\206\345\217\221\351\245\274\345\271\262.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 455.分发饼干
@@ -48,7 +46,7 @@
如图:
-
+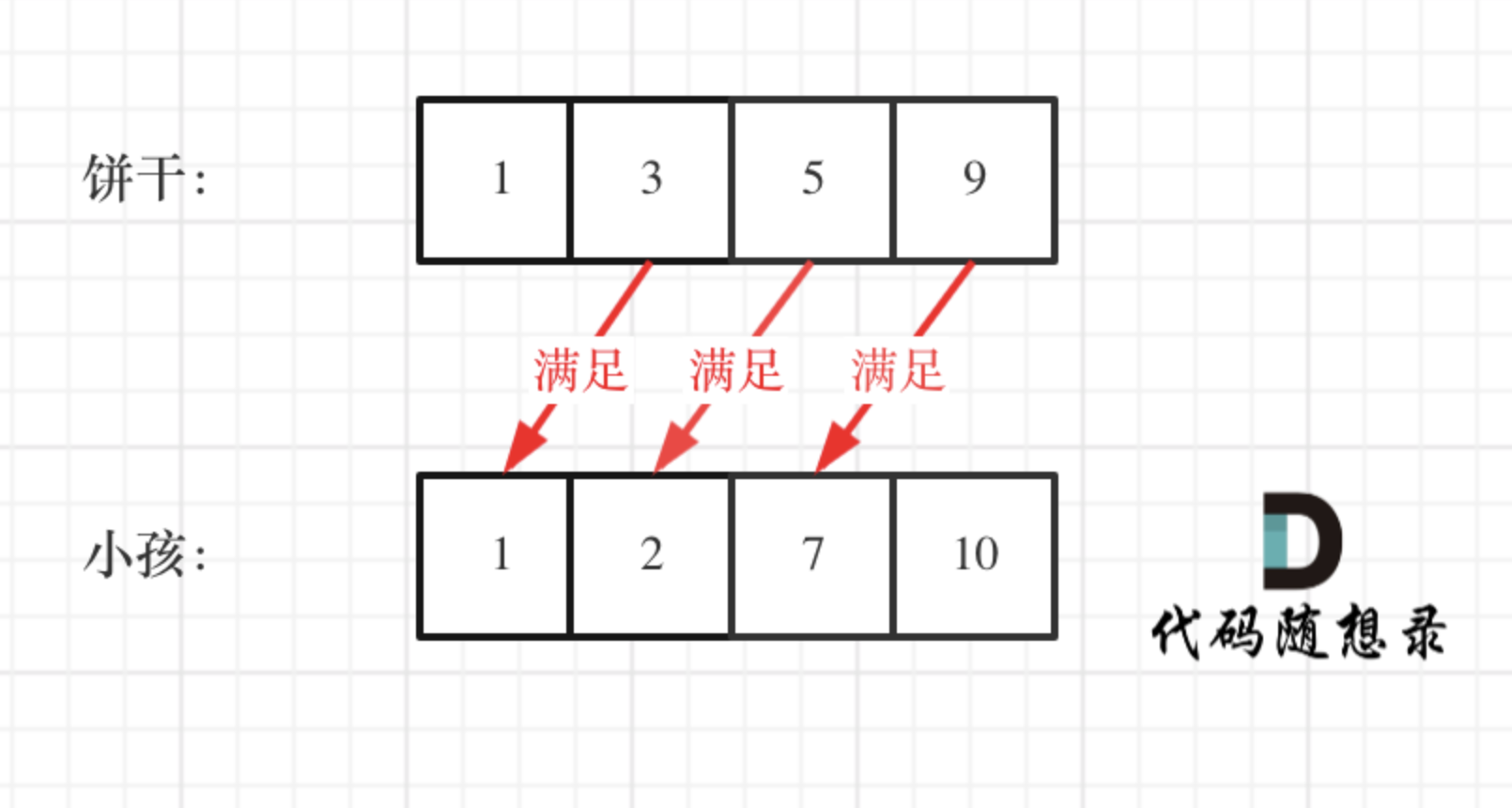
这个例子可以看出饼干 9 只有喂给胃口为 7 的小孩,这样才是整体最优解,并想不出反例,那么就可以撸代码了。
@@ -91,7 +89,7 @@ public:
如果 for 控制的是饼干, if 控制胃口,就是出现如下情况 :
-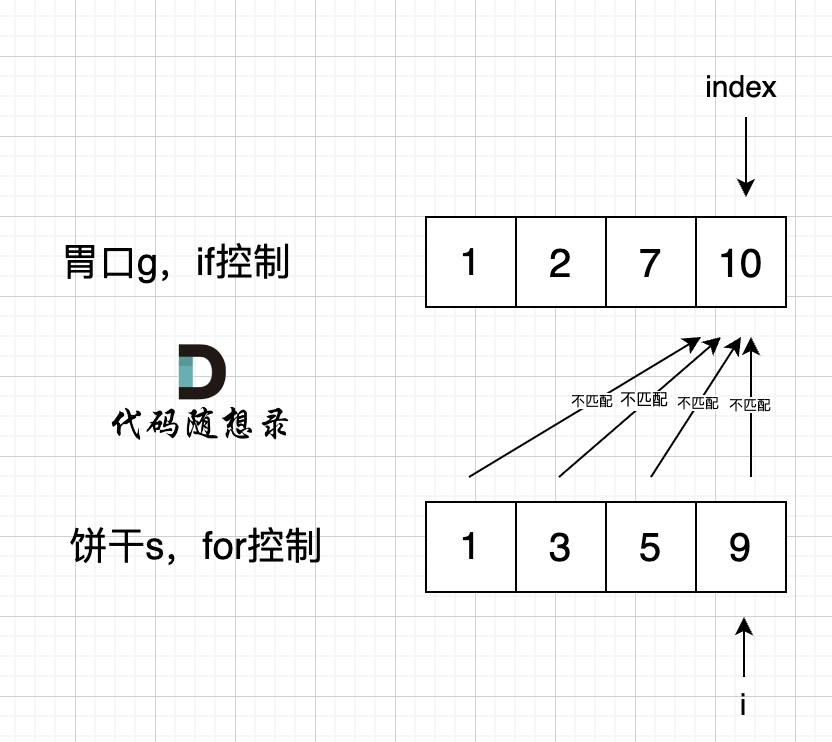
+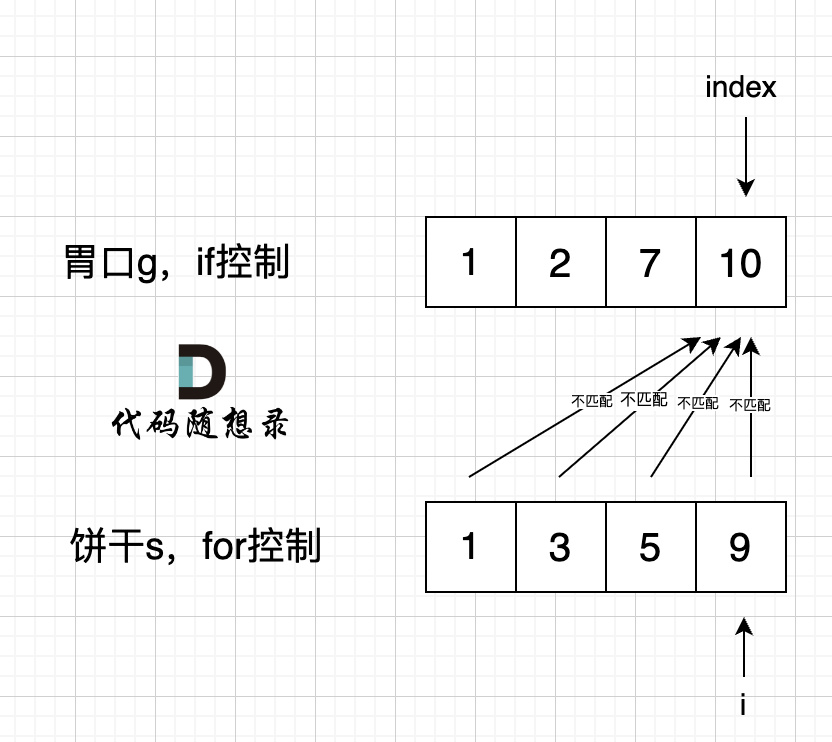
if 里的 index 指向 胃口 10, for 里的 i 指向饼干 9,因为 饼干 9 满足不了 胃口 10,所以 i 持续向前移动,而 index 走不到` s[index] >= g[i]` 的逻辑,所以 index 不会移动,那么当 i 持续向前移动,最后所有的饼干都匹配不上。
@@ -206,23 +204,56 @@ class Solution:
```
+栈 大饼干优先
+```python
+from collecion import deque
+class Solution:
+ def findContentChildren(self, g: List[int], s: List[int]) -> int:
+ #思路,饼干和孩子按从大到小排序,依次从栈中取出,若满足条件result += 1 否则将饼干栈顶元素重新返回
+ result = 0
+ queue_g = deque(sorted(g, reverse = True))
+ queue_s = deque(sorted(s, reverse = True))
+ while queue_g and queue_s:
+ child = queue_g.popleft()
+ cookies = queue_s.popleft()
+ if child <= cookies:
+ result += 1
+ else:
+ queue_s.appendleft(cookies)
+ return result
+```
+
### Go
-```golang
-//排序后,局部最优
+版本一 大饼干优先
+```Go
func findContentChildren(g []int, s []int) int {
- sort.Ints(g)
- sort.Ints(s)
-
- // 从小到大
- child := 0
- for sIdx := 0; child < len(g) && sIdx < len(s); sIdx++ {
- if s[sIdx] >= g[child] {//如果饼干的大小大于或等于孩子的为空则给与,否则不给予,继续寻找选一个饼干是否符合
- child++
+ sort.Ints(g)
+ sort.Ints(s)
+ index := len(s) - 1
+ result := 0
+ for i := len(g) - 1; i >= 0; i-- {
+ if index >= 0 && s[index] >= g[i] {
+ result++
+ index--
+ }
}
- }
+ return result
+}
+```
- return child
+版本二 小饼干优先
+```Go
+func findContentChildren(g []int, s []int) int {
+ sort.Ints(g)
+ sort.Ints(s)
+ index := 0
+ for i := 0; i < len(s); i++ {
+ if index < len(g) && g[index] <= s[i] {
+ index++
+ }
+ }
+ return index
}
```
@@ -245,7 +276,7 @@ pub fn find_content_children(mut children: Vec, mut cookies: Vec) -> i
}
```
-### Javascript
+### JavaScript
```js
var findContentChildren = function (g, s) {
@@ -401,7 +432,3 @@ public class Solution
}
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0459.\351\207\215\345\244\215\347\232\204\345\255\220\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md" "b/problems/0459.\351\207\215\345\244\215\347\232\204\345\255\220\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 311e3a695e..d164277731
--- "a/problems/0459.\351\207\215\345\244\215\347\232\204\345\255\220\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md"
+++ "b/problems/0459.\351\207\215\345\244\215\347\232\204\345\255\220\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0459.\351\207\215\345\244\215\347\232\204\345\255\220\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md" "b/problems/0459.\351\207\215\345\244\215\347\232\204\345\255\220\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 311e3a695e..d164277731
--- "a/problems/0459.\351\207\215\345\244\215\347\232\204\345\255\220\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md"
+++ "b/problems/0459.\351\207\215\345\244\215\347\232\204\345\255\220\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
> KMP算法还能干这个
@@ -48,18 +46,74 @@
当一个字符串s:abcabc,内部由重复的子串组成,那么这个字符串的结构一定是这样的:
-
+
也就是由前后相同的子串组成。
那么既然前面有相同的子串,后面有相同的子串,用 s + s,这样组成的字符串中,后面的子串做前串,前面的子串做后串,就一定还能组成一个s,如图:
-
+
-所以判断字符串s是否由重复子串组成,只要两个s拼接在一起,里面还出现一个s的话,就说明是由重复子串组成。
当然,我们在判断 s + s 拼接的字符串里是否出现一个s的的时候,**要刨除 s + s 的首字符和尾字符**,这样避免在s+s中搜索出原来的s,我们要搜索的是中间拼接出来的s。
+
+以上证明的充分性,接下来证明必要性:
+
+如果有一个字符串s,在 s + s 拼接后, 不算首尾字符,如果能凑成s字符串,说明s 一定是重复子串组成。
+
+如图,字符串s,图中数字为数组下标,在 s + s 拼接后, 不算首尾字符,中间凑成s字符串。 (图中数字为数组下标)
+
+
+
+图中,因为中间拼接成了s,根据红色框 可以知道 s[4] = s[0], s[5] = s[1], s[0] = s[2], s[1] = s[3] s[2] = s[4] ,s[3] = s[5]
+
+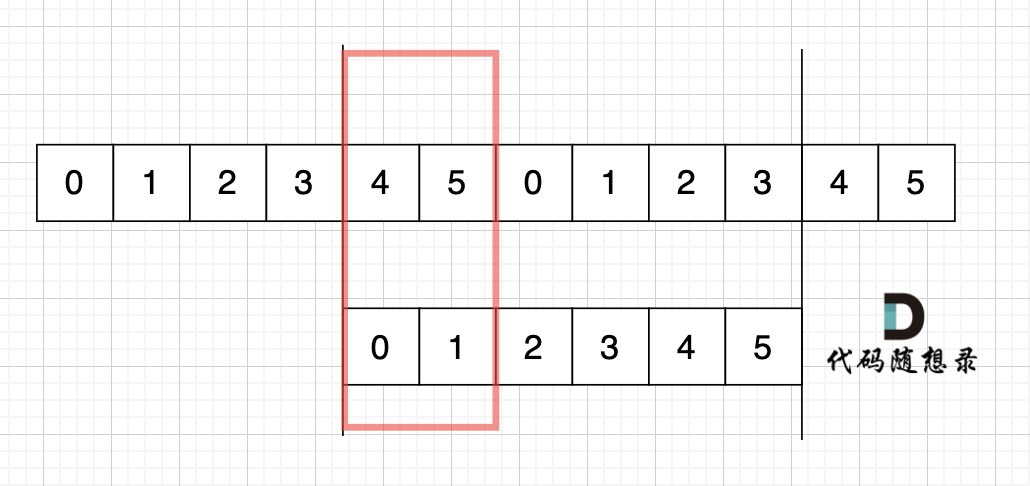
+
+以上相等关系我们串联一下:
+
+s[4] = s[0] = s[2]
+
+s[5] = s[1] = s[3]
+
+
+即:s[4],s[5] = s[0],s[1] = s[2],s[3]
+
+**说明这个字符串,是由 两个字符 s[0] 和 s[1] 重复组成的**!
+
+这里可以有录友想,凭什么就是这样组成的s呢,我换一个方式组成s 行不行,如图:
+
+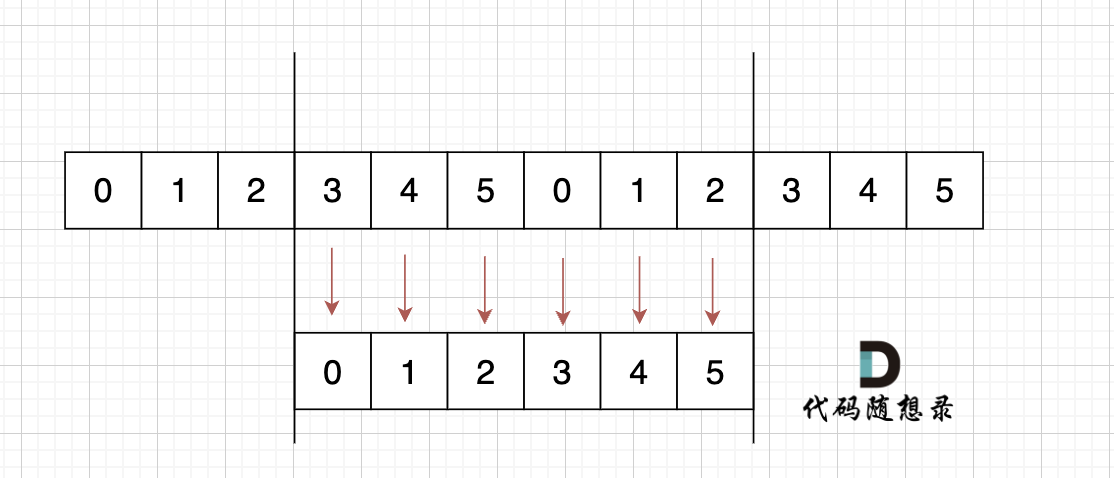
+
+s[3] = s[0],s[4] = s[1] ,s[5] = s[2],s[0] = s[3],s[1] = s[4],s[2] = s[5]
+
+以上相等关系串联:
+
+s[3] = s[0]
+
+s[1] = s[4]
+
+s[2] = s[5]
+
+s[0] s[1] s[2] = s[3] s[4] s[5]
+
+和以上推导过程一样,最后可以推导出,这个字符串是由 s[0] ,s[1] ,s[2] 重复组成。
+
+如果是这样的呢,如图:
+
+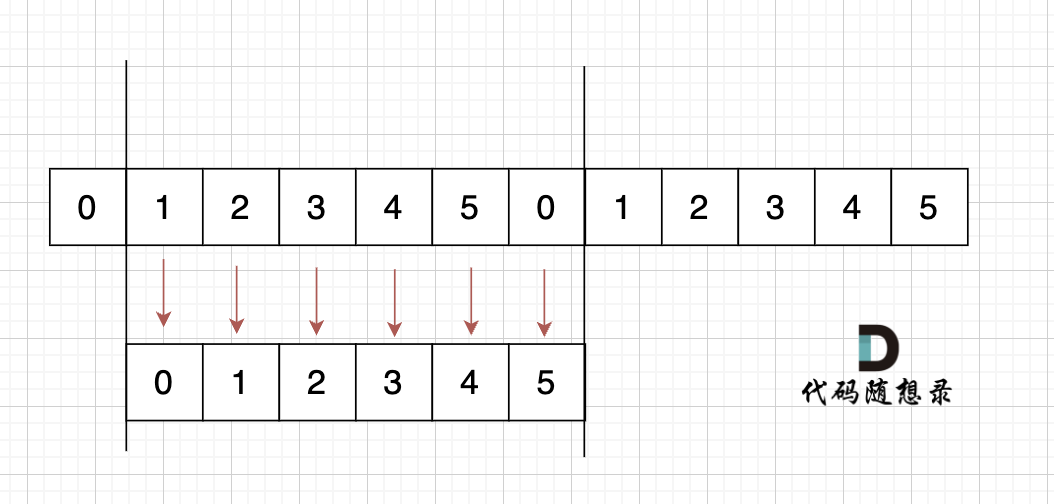
+
+s[1] = s[0],s[2] = s[1] ,s[3] = s[2],s[4] = s[3],s[5] = s[4],s[0] = s[5]
+
+以上相等关系串联
+
+s[0] = s[1] = s[2] = s[3] = s[4] = s[5]
+
+最后可以推导出,这个字符串是由 s[0] 重复组成。
+
+以上 充分和必要性都证明了,所以判断字符串s是否由重复子串组成,只要两个s拼接在一起,里面还出现一个s的话,就说明是由重复子串组成。
+
+
代码如下:
```CPP
@@ -76,13 +130,14 @@ public:
* 时间复杂度: O(n)
* 空间复杂度: O(1)
-不过这种解法还有一个问题,就是 我们最终还是要判断 一个字符串(s + s)是否出现过 s 的过程,大家可能直接用contains,find 之类的库函数。 却忽略了实现这些函数的时间复杂度(暴力解法是m * n,一般库函数实现为 O(m + n))。
+不过这种解法还有一个问题,就是 我们最终还是要判断 一个字符串(s + s)是否出现过 s 的过程,大家可能直接用contains,find 之类的库函数, 却忽略了实现这些函数的时间复杂度(暴力解法是m * n,一般库函数实现为 O(m + n))。
如果我们做过 [28.实现strStr](https://programmercarl.com/0028.实现strStr.html) 题目的话,其实就知道,**实现一个 高效的算法来判断 一个字符串中是否出现另一个字符串是很复杂的**,这里就涉及到了KMP算法。
### KMP
#### 为什么会使用KMP
+
以下使用KMP方式讲解,强烈建议大家先把以下两个视频看了,理解KMP算法,再来看下面讲解,否则会很懵。
* [视频讲解版:帮你把KMP算法学个通透!(理论篇)](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1PD4y1o7nd/)
@@ -91,7 +146,9 @@ public:
在一个串中查找是否出现过另一个串,这是KMP的看家本领。那么寻找重复子串怎么也涉及到KMP算法了呢?
-KMP算法中next数组为什么遇到字符不匹配的时候可以找到上一个匹配过的位置继续匹配,靠的是有计算好的前缀表。 前缀表里,统计了各个位置为终点字符串的最长相同前后缀的长度。
+KMP算法中next数组为什么遇到字符不匹配的时候可以找到上一个匹配过的位置继续匹配,靠的是有计算好的前缀表。
+
+前缀表里,统计了各个位置为终点字符串的最长相同前后缀的长度。
那么 最长相同前后缀和重复子串的关系又有什么关系呢。
@@ -100,16 +157,61 @@ KMP算法中next数组为什么遇到字符不匹配的时候可以找到上一
* 前缀是指不包含最后一个字符的所有以第一个字符开头的连续子串;
* 后缀是指不包含第一个字符的所有以最后一个字符结尾的连续子串
-在由重复子串组成的字符串中,最长相等前后缀不包含的子串就是最小重复子串,这里拿字符串s:abababab 来举例,ab就是最小重复单位,如图所示:
+#### 充分性证明
+
+如果一个字符串s是由重复子串组成,那么 最长相等前后缀不包含的子串一定是字符串s的最小重复子串。
+
+如果s 是由最小重复子串p组成,即 s = n * p
+
+那么相同前后缀可以是这样:
+
+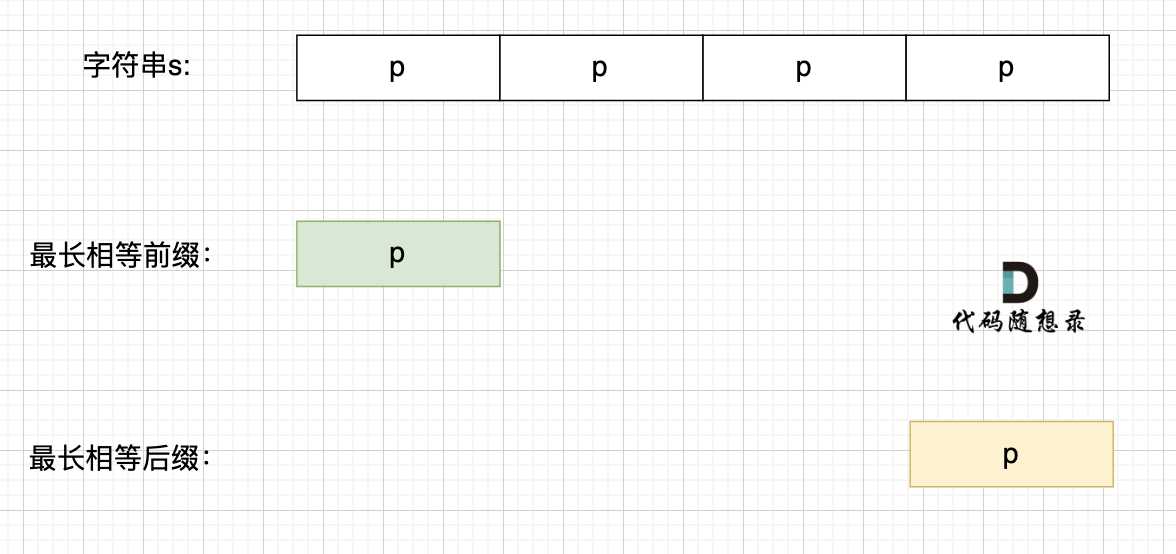
+
+也可以是这样:
+
+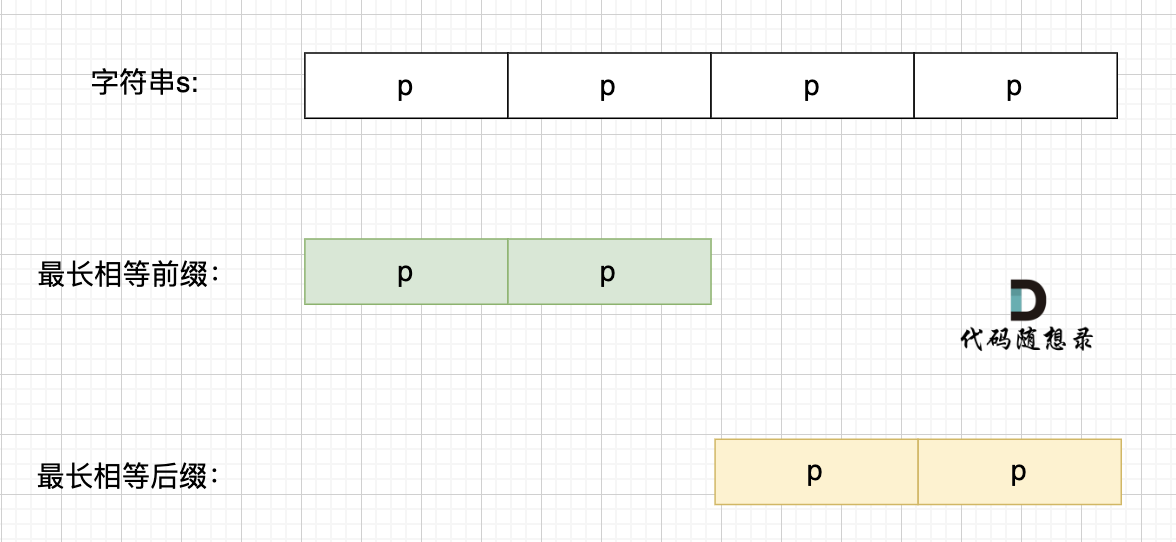
+
+最长的相等前后缀,也就是这样:
+
+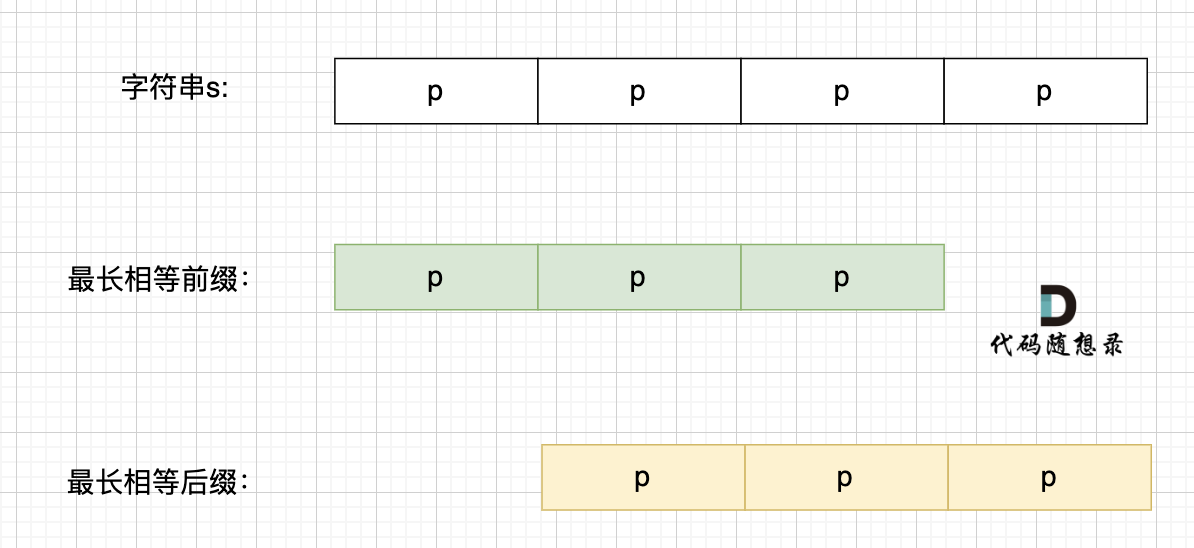
-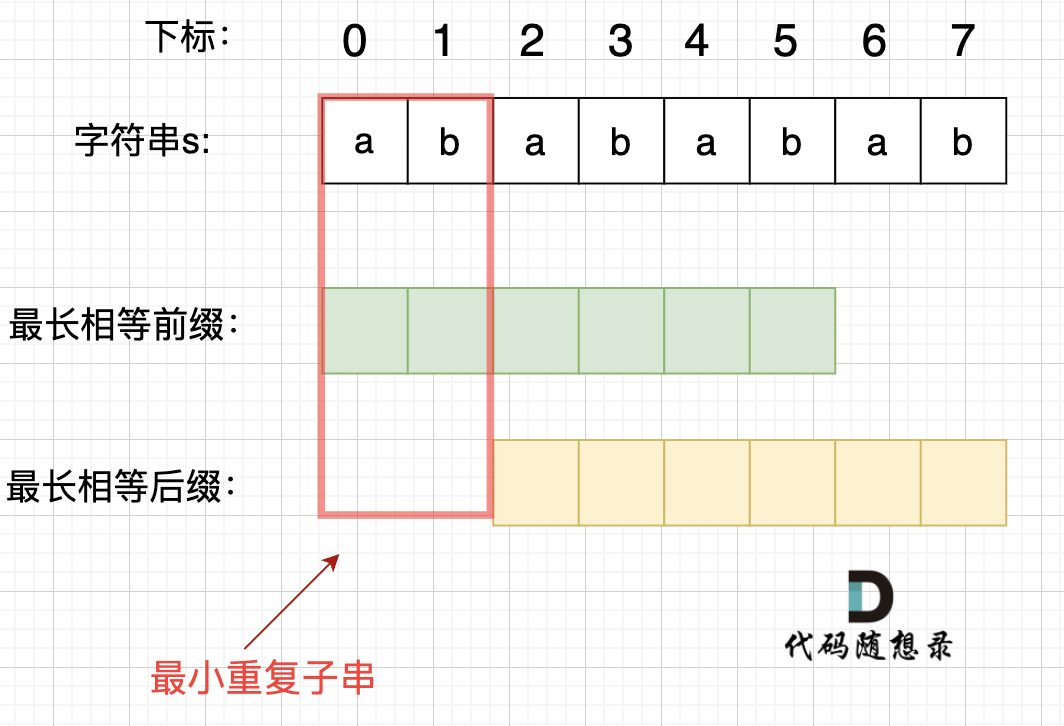
+这里有录友就想:如果字符串s 是由最小重复子串p组成,最长相等前后缀就不能更长一些? 例如这样:
+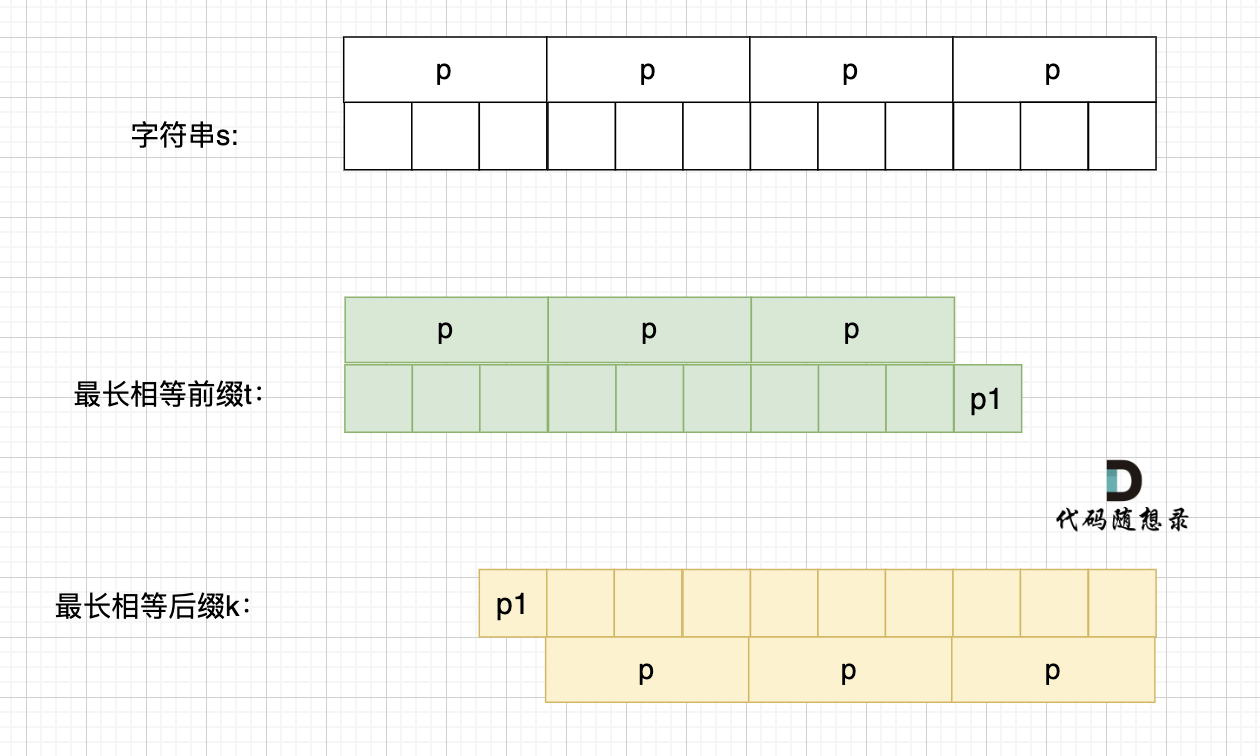
-#### 如何找到最小重复子串
+如果这样的话,因为前后缀要相同,所以 p2 = p1,p3 = p2,如图:
-这里有同学就问了,为啥一定是开头的ab呢。 其实最关键还是要理解 最长相等前后缀,如图:
+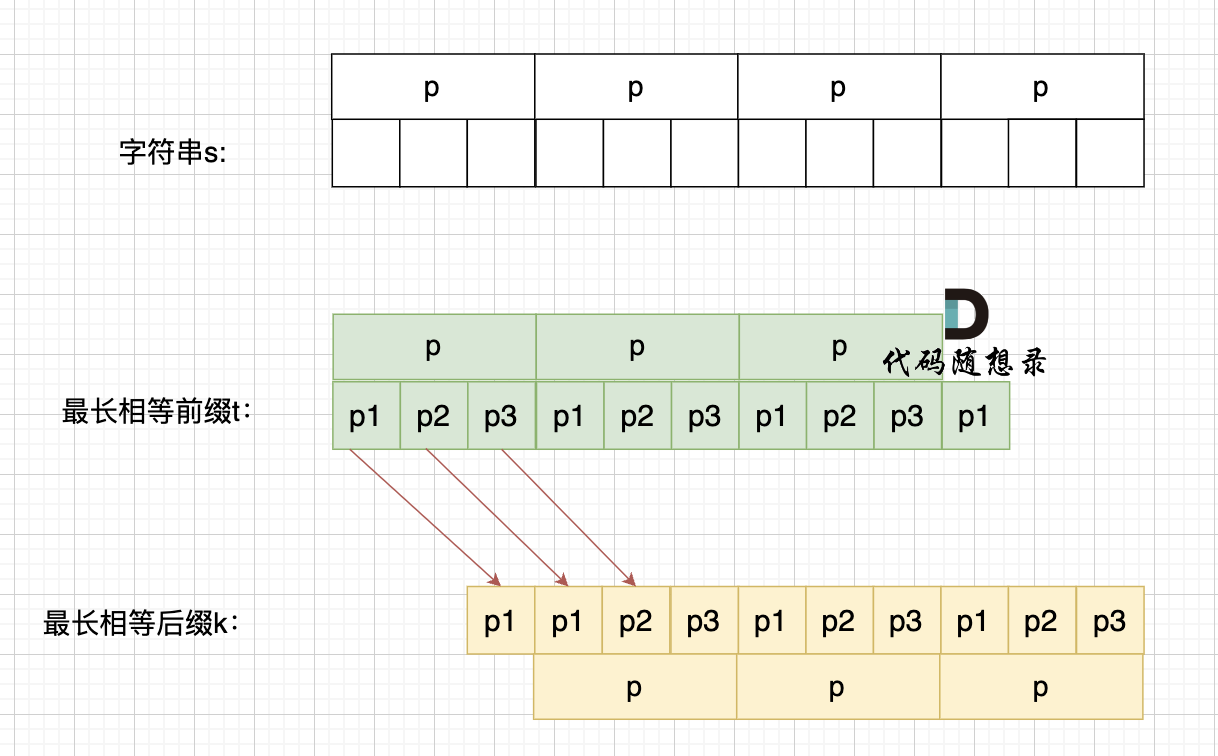
-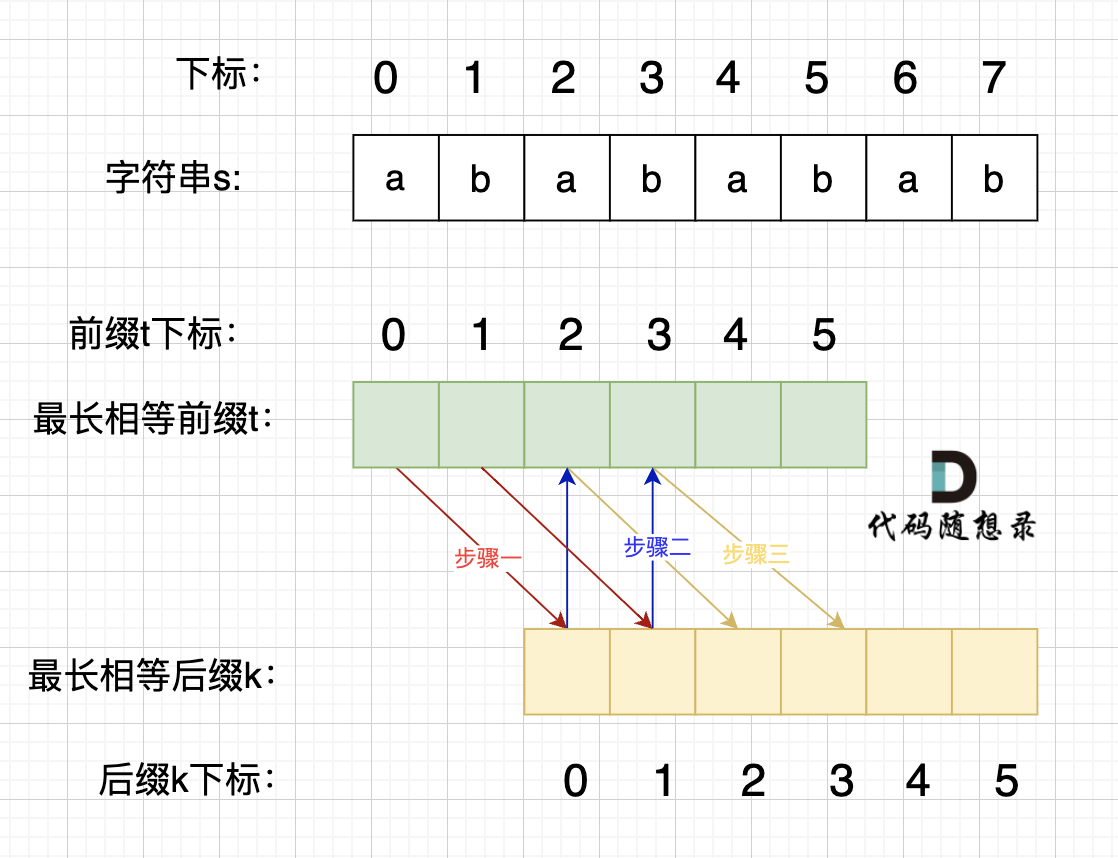
+p2 = p1,p3 = p2 即: p1 = p2 = p3
+
+说明 p = p1 * 3。
+
+这样p 就不是最小重复子串了,不符合我们定义的条件。
+
+所以,**如果这个字符串s是由重复子串组成,那么最长相等前后缀不包含的子串是字符串s的最小重复子串**。
+
+#### 必要性证明
+
+以上是充分性证明,以下是必要性证明:
+
+**如果 最长相等前后缀不包含的子串是字符串s的最小重复子串, 那么字符串s一定由重复子串组成吗**?
+
+最长相等前后缀不包含的子串已经是字符串s的最小重复子串,那么字符串s一定由重复子串组成,这个不需要证明了。
+
+关键是要证明:最长相等前后缀不包含的子串什么时候才是字符串s的最小重复子串呢。
+
+情况一, 最长相等前后缀不包含的子串的长度 比 字符串s的一半的长度还大,那一定不是字符串s的重复子串,如图:
+
+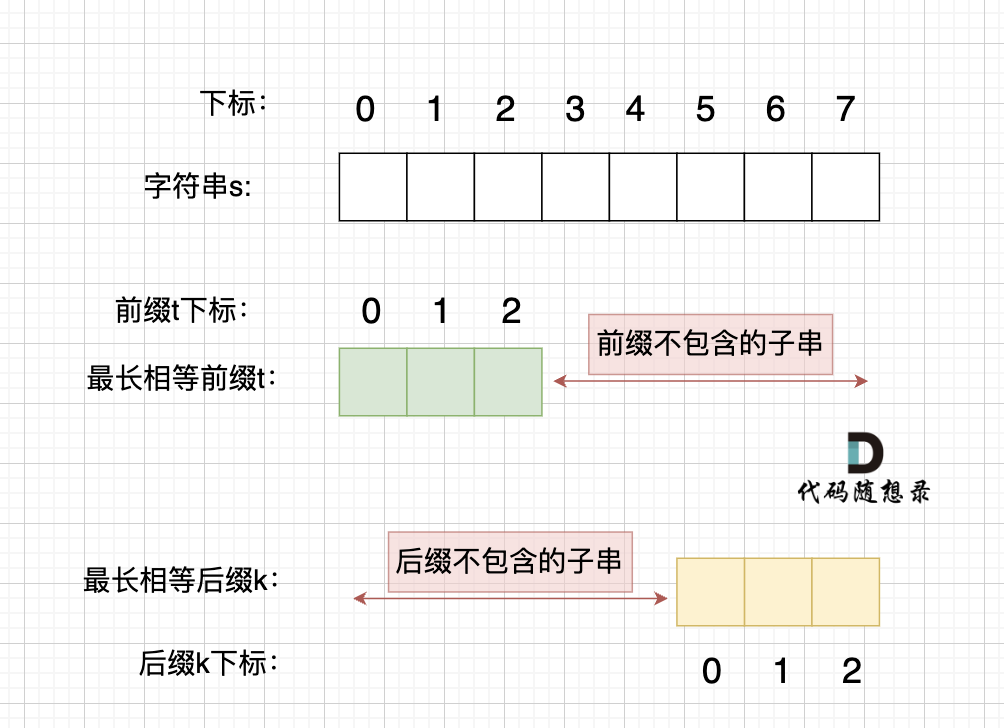
+
+图中:前后缀不包含的子串的长度 大于 字符串s的长度的 二分之一
+
+--------------
+
+情况二,最长相等前后缀不包含的子串的长度 可以被 字符串s的长度整除,如图:
+
+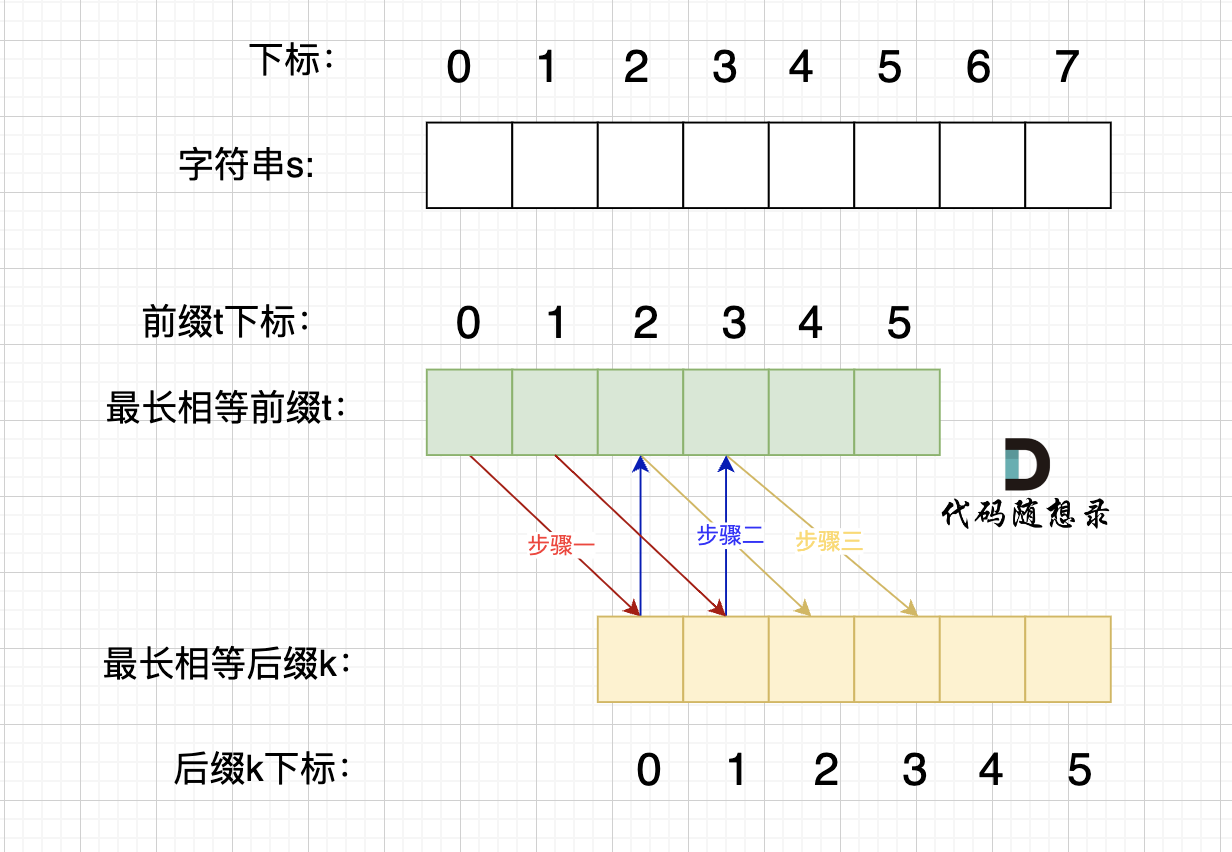
步骤一:因为 这是相等的前缀和后缀,t[0] 与 k[0]相同, t[1] 与 k[1]相同,所以 s[0] 一定和 s[2]相同,s[1] 一定和 s[3]相同,即:,s[0]s[1]与s[2]s[3]相同 。
@@ -121,39 +223,94 @@ KMP算法中next数组为什么遇到字符不匹配的时候可以找到上一
所以字符串s,s[0]s[1]与s[2]s[3]相同, s[2]s[3] 与 s[4]s[5]相同,s[4]s[5] 与 s[6]s[7] 相同。
-正是因为 最长相等前后缀的规则,当一个字符串由重复子串组成的,最长相等前后缀不包含的子串就是最小重复子串。
+可以推出,在由重复子串组成的字符串中,最长相等前后缀不包含的子串就是最小重复子串。
+
+即 s[0]s[1] 是最小重复子串
+
+
+以上推导中,录友可能想,你怎么知道 s[0] 和 s[1] 就不相同呢? s[0] 为什么就不能是最小重复子串。
+
+如果 s[0] 和 s[1] 也相同,同时 s[0]s[1]与s[2]s[3]相同,s[2]s[3] 与 s[4]s[5]相同,s[4]s[5] 与 s[6]s[7] 相同,那么这个字符串就是有一个字符构成的字符串。
+
+那么它的最长相同前后缀,就不是上图中的前后缀,而是这样的的前后缀:
+
+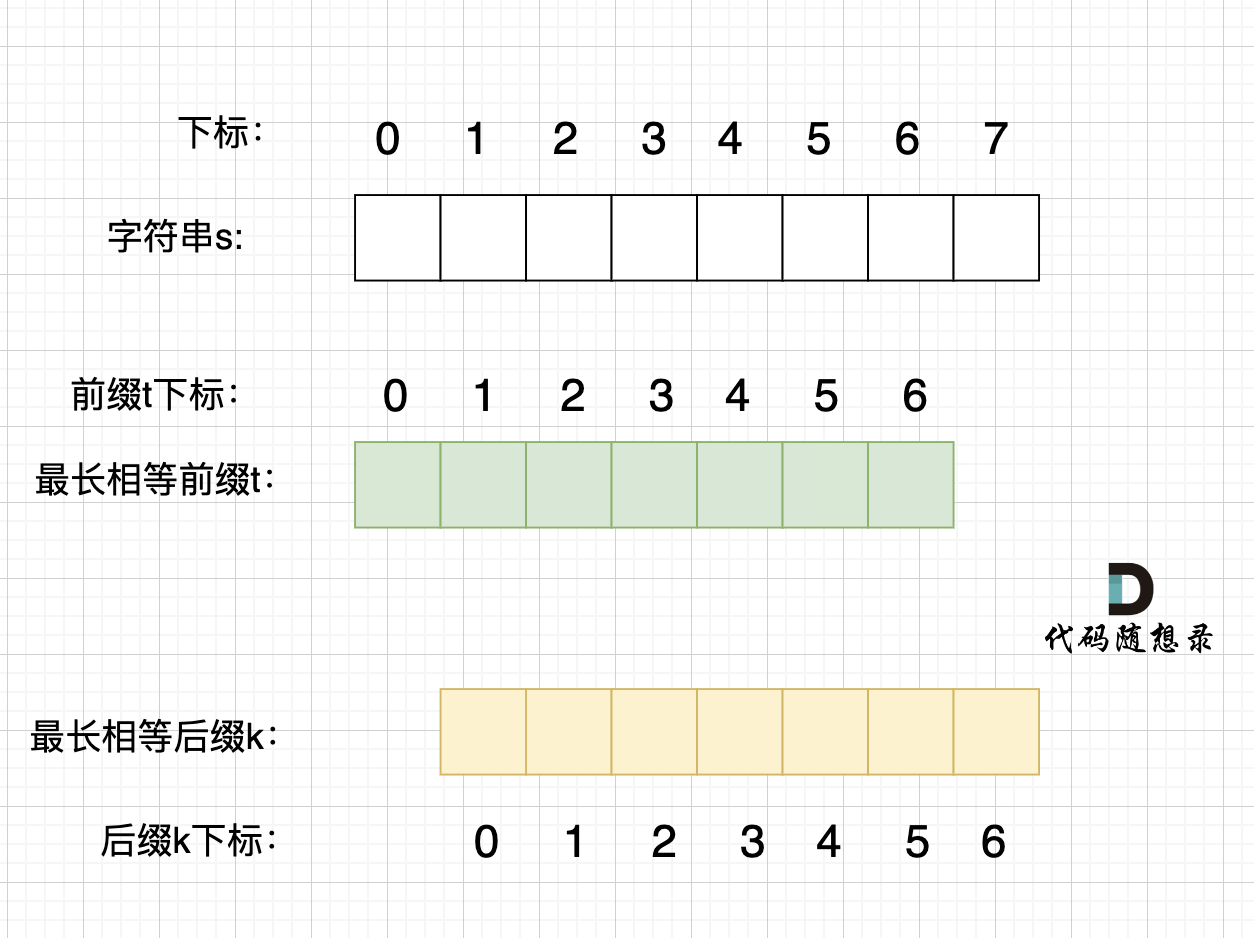
+
+录友可能再问,由一个字符组成的字符串,最长相等前后缀凭什么就是这样的。
+
+有这种疑惑的录友,就是还不知道 最长相等前后缀 是怎么算的。
+
+可以看这里:[KMP讲解](https://programmercarl.com/0028.%E5%AE%9E%E7%8E%B0strStr.html),再去回顾一下。
+
+或者说,自己举个例子,`aaaaaa`,这个字符串,他的最长相等前后缀是什么?
+
+同上以上推导,最长相等前后缀不包含的子串的长度只要被 字符串s的长度整除,最长相等前后缀不包含的子串一定是最小重复子串。
+
+----------------
+
+**情况三,最长相等前后缀不包含的子串的长度 不被 字符串s的长度整除得情况**,如图:
+
+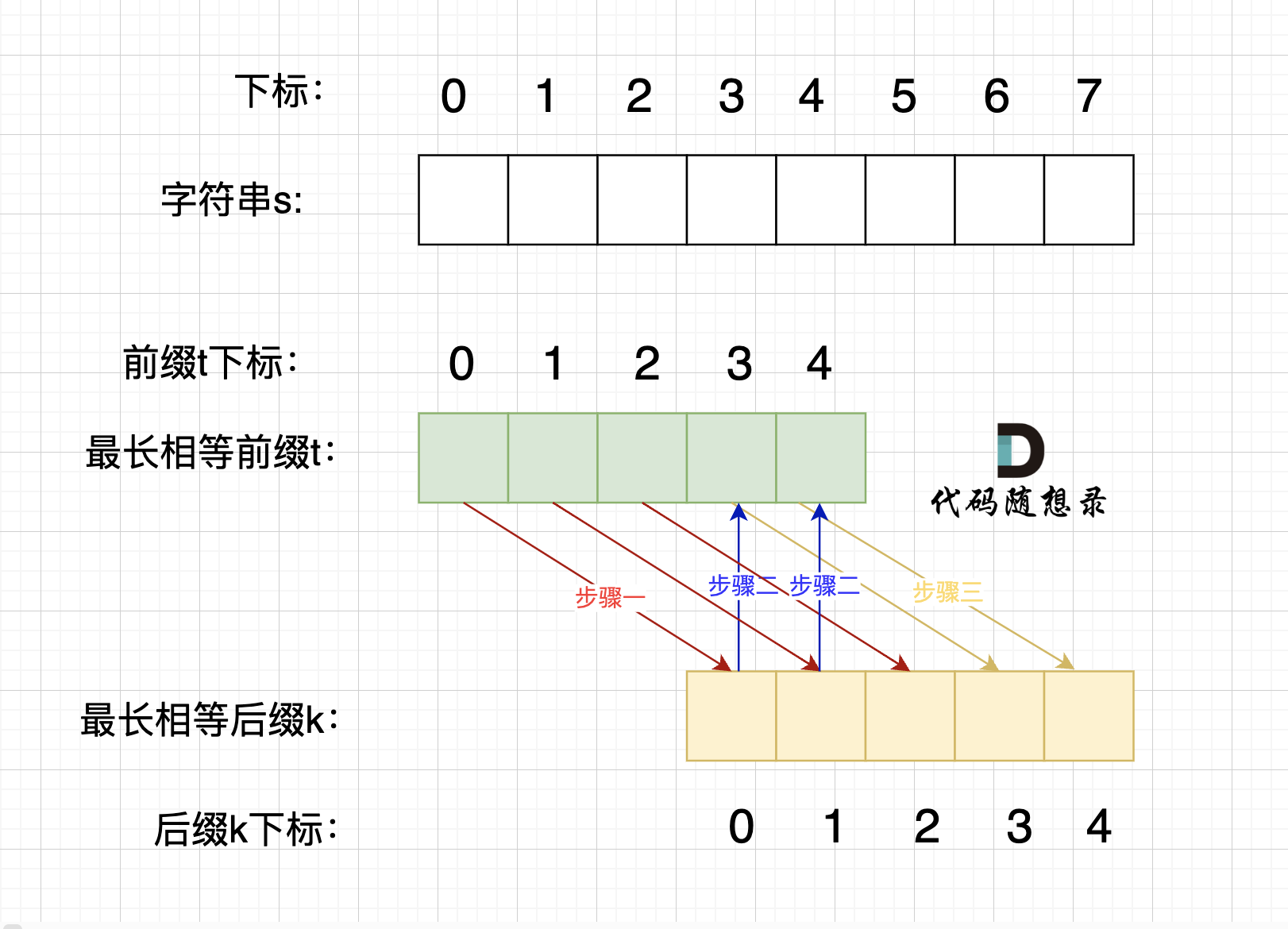
+
+
+步骤一:因为 这是相等的前缀和后缀,t[0] 与 k[0]相同, t[1] 与 k[1]相同,t[2] 与 k[2]相同。
+
+所以 s[0] 与 s[3]相同,s[1] 与 s[4]相同,s[2] 与s[5],即:,s[0]s[1]与s[2]s[3]相同 。
+
+步骤二: 因为在同一个字符串位置,所以 t[3] 与 k[0]相同,t[4] 与 k[1]相同。
+
+
+步骤三: 因为 这是相等的前缀和后缀,t[3] 与 k[3]相同 ,t[4]与k[5] 相同,所以,s[3]一定和s[6]相同,s[4]一定和s[7]相同,即:s[3]s[4] 与 s[6]s[7]相同。
+
+
+以上推导,可以得出 s[0],s[1],s[2] 与 s[3],s[4],s[5] 相同,s[3]s[4] 与 s[6]s[7]相同。
+
+那么 最长相等前后缀不包含的子串的长度 不被 字符串s的长度整除 ,最长相等前后缀不包含的子串就不是s的重复子串
+
+-----------
+
+充分条件:如果字符串s是由重复子串组成,那么 最长相等前后缀不包含的子串 一定是 s的最小重复子串。
-#### 简单推理
+必要条件:如果字符串s的最长相等前后缀不包含的子串 是 s最小重复子串,那么 s是由重复子串组成。
-这里再给出一个数学推导,就容易理解很多。
+在必要条件,这个是 显而易见的,都已经假设 最长相等前后缀不包含的子串 是 s的最小重复子串了,那s必然是重复子串。
-假设字符串s使用多个重复子串构成(这个子串是最小重复单位),重复出现的子字符串长度是x,所以s是由n * x组成。
+**关键是需要证明, 字符串s的最长相等前后缀不包含的子串 什么时候才是 s最小重复子串**。
-因为字符串s的最长相同前后缀的长度一定是不包含s本身,所以 最长相同前后缀长度必然是m * x,而且 n - m = 1,(这里如果不懂,看上面的推理)
+同上我们证明了,当 最长相等前后缀不包含的子串的长度 可以被 字符串s的长度整除,那么不包含的子串 就是s的最小重复子串。
-所以如果 nx % (n - m)x = 0,就可以判定有重复出现的子字符串。
-next 数组记录的就是最长相同前后缀 [字符串:KMP算法精讲](https://programmercarl.com/0028.实现strStr.html) 这里介绍了什么是前缀,什么是后缀,什么又是最长相同前后缀), 如果 next[len - 1] != -1,则说明字符串有最长相同的前后缀(就是字符串里的前缀子串和后缀子串相同的最长长度)。
+-------------
-最长相等前后缀的长度为:next[len - 1] + 1。(这里的next数组是以统一减一的方式计算的,因此需要+1,两种计算next数组的具体区别看这里:[字符串:KMP算法精讲](https://programmercarl.com/0028.实现strStr.html))
+
+### 代码分析
+
+next 数组记录的就是最长相同前后缀( [字符串:KMP算法精讲](https://programmercarl.com/0028.实现strStr.html)), 如果 `next[len - 1] != -1`,则说明字符串有最长相同的前后缀(就是字符串里的前缀子串和后缀子串相同的最长长度)。
+
+最长相等前后缀的长度为:`next[len - 1] + 1`。(这里的next数组是以统一减一的方式计算的,因此需要+1,两种计算next数组的具体区别看这里:[字符串:KMP算法精讲](https://programmercarl.com/0028.实现strStr.html))
数组长度为:len。
-如果len % (len - (next[len - 1] + 1)) == 0 ,则说明数组的长度正好可以被 (数组长度-最长相等前后缀的长度) 整除 ,说明该字符串有重复的子字符串。
+`len - (next[len - 1] + 1)` 是最长相等前后缀不包含的子串的长度。
-**数组长度减去最长相同前后缀的长度相当于是第一个周期的长度,也就是一个周期的长度,如果这个周期可以被整除,就说明整个数组就是这个周期的循环。**
+如果`len % (len - (next[len - 1] + 1)) == 0` ,则说明数组的长度正好可以被 最长相等前后缀不包含的子串的长度 整除 ,说明该字符串有重复的子字符串。
+### 打印数组
**强烈建议大家把next数组打印出来,看看next数组里的规律,有助于理解KMP算法**
如图:
-
+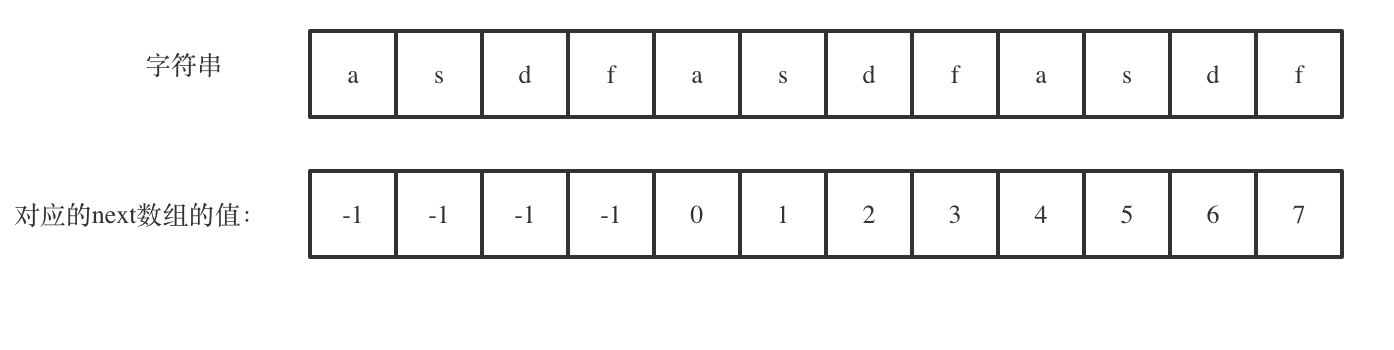
+
+`next[len - 1] = 7`,`next[len - 1] + 1 = 8`,8就是此时字符串asdfasdfasdf的最长相同前后缀的长度。
+
+`(len - (next[len - 1] + 1))` 也就是: 12(字符串的长度) - 8(最长公共前后缀的长度) = 4, 为最长相同前后缀不包含的子串长度
-next[len - 1] = 7,next[len - 1] + 1 = 8,8就是此时字符串asdfasdfasdf的最长相同前后缀的长度。
-(len - (next[len - 1] + 1)) 也就是: 12(字符串的长度) - 8(最长公共前后缀的长度) = 4, 4正好可以被 12(字符串的长度) 整除,所以说明有重复的子字符串(asdf)。
+4可以被 12(字符串的长度) 整除,所以说明有重复的子字符串(asdf)。
+### 代码实现
C++代码如下:(这里使用了前缀表统一减一的实现方式)
@@ -231,6 +388,8 @@ public:
### Java:
+(版本一) 前缀表 减一
+
```java
class Solution {
public boolean repeatedSubstringPattern(String s) {
@@ -261,6 +420,45 @@ class Solution {
}
```
+(版本二) 前缀表 不减一
+
+```java
+/*
+ * 充分条件:如果字符串s是由重复子串组成的,那么它的最长相等前后缀不包含的子串一定是s的最小重复子串。
+ * 必要条件:如果字符串s的最长相等前后缀不包含的子串是s的最小重复子串,那么s必然是由重复子串组成的。
+ * 推得:当字符串s的长度可以被其最长相等前后缀不包含的子串的长度整除时,不包含的子串就是s的最小重复子串。
+ *
+ * 时间复杂度:O(n)
+ * 空间复杂度:O(n)
+ */
+class Solution {
+ public boolean repeatedSubstringPattern(String s) {
+ // if (s.equals("")) return false;
+ // 边界判断(可以去掉,因为题目给定范围是1 <= s.length <= 10^4)
+ int n = s.length();
+
+ // Step 1.构建KMP算法的前缀表
+ int[] next = new int[n]; // 前缀表的值表示 以该位置结尾的字符串的最长相等前后缀的长度
+ int j = 0;
+ next[0] = 0;
+ for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
+ while (j > 0 && s.charAt(i) != s.charAt(j)) // 只要前缀后缀还不一致,就根据前缀表回退j直到起点为止
+ j = next[j - 1];
+ if (s.charAt(i) == s.charAt(j))
+ j++;
+ next[i] = j;
+ }
+
+ // Step 2.判断重复子字符串
+ if (next[n - 1] > 0 && n % (n - next[n - 1]) == 0) { // 当字符串s的长度可以被其最长相等前后缀不包含的子串的长度整除时
+ return true; // 不包含的子串就是s的最小重复子串
+ } else {
+ return false;
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
### Python:
(版本一) 前缀表 减一
@@ -403,6 +601,18 @@ func repeatedSubstringPattern(s string) bool {
}
```
+移动匹配
+
+```go
+func repeatedSubstringPattern(s string) bool {
+ if len(s) == 0 {
+ return false
+ }
+ t := s + s
+ return strings.Contains(t[1:len(t)-1], s)
+}
+```
+
### JavaScript:
> 前缀表统一减一
@@ -477,6 +687,29 @@ var repeatedSubstringPattern = function (s) {
};
```
+> 正则匹配
+```javascript
+/**
+ * @param {string} s
+ * @return {boolean}
+ */
+var repeatedSubstringPattern = function(s) {
+ let reg = /^(\w+)\1+$/
+ return reg.test(s)
+};
+```
+> 移动匹配
+```javascript
+/**
+ * @param {string} s
+ * @return {boolean}
+ */
+var repeatedSubstringPattern = function (s) {
+ let ss = s + s;
+ return ss.substring(1, ss.length - 1).includes(s);
+};
+```
+
### TypeScript:
> 前缀表统一减一
@@ -682,8 +915,10 @@ impl Solution {
}
```
### C#
+
+> 前缀表不减一
+
```csharp
-// 前缀表不减一
public bool RepeatedSubstringPattern(string s)
{
if (s.Length == 0)
@@ -708,8 +943,57 @@ public int[] GetNext(string s)
}
```
+> 移动匹配
+```csharp
+public bool RepeatedSubstringPattern(string s) {
+ string ss = (s + s).Substring(1, (s + s).Length - 2);
+ return ss.Contains(s);
+}
+```
+### C
+
+```c
+// 前缀表不减一
+int *build_next(char* s, int len) {
+
+ int *next = (int *)malloc(len * sizeof(int));
+ assert(next);
+
+ // 初始化前缀表
+ next[0] = 0;
+
+ // 构建前缀表表
+ int i = 1, j = 0;
+ while (i < len) {
+ if (s[i] == s[j]) {
+ j++;
+ next[i] = j;
+ i++;
+ } else if (j > 0) {
+ j = next[j - 1];
+ } else {
+ next[i] = 0;
+ i++;
+ }
+ }
+ return next;
+}
+
+bool repeatedSubstringPattern(char* s) {
+
+ int len = strlen(s);
+ int *next = build_next(s, len);
+ bool result = false;
+
+ // 检查最小重复片段能否被长度整除
+ if (next[len - 1]) {
+ result = len % (len - next[len - 1]) == 0;
+ }
+
+ free(next);
+ return result;
+}
+
+```
+
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0463.\345\262\233\345\261\277\347\232\204\345\221\250\351\225\277.md" "b/problems/0463.\345\262\233\345\261\277\347\232\204\345\221\250\351\225\277.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 2e954e30ad..ba60bc4564
--- "a/problems/0463.\345\262\233\345\261\277\347\232\204\345\221\250\351\225\277.md"
+++ "b/problems/0463.\345\262\233\345\261\277\347\232\204\345\221\250\351\225\277.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0463.\345\262\233\345\261\277\347\232\204\345\221\250\351\225\277.md" "b/problems/0463.\345\262\233\345\261\277\347\232\204\345\221\250\351\225\277.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 2e954e30ad..ba60bc4564
--- "a/problems/0463.\345\262\233\345\261\277\347\232\204\345\221\250\351\225\277.md"
+++ "b/problems/0463.\345\262\233\345\261\277\347\232\204\345\221\250\351\225\277.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
@@ -17,7 +15,7 @@
岛屿中没有“湖”(“湖” 指水域在岛屿内部且不和岛屿周围的水相连)。格子是边长为 1 的正方形。网格为长方形,且宽度和高度均不超过 100 。计算这个岛屿的周长。
-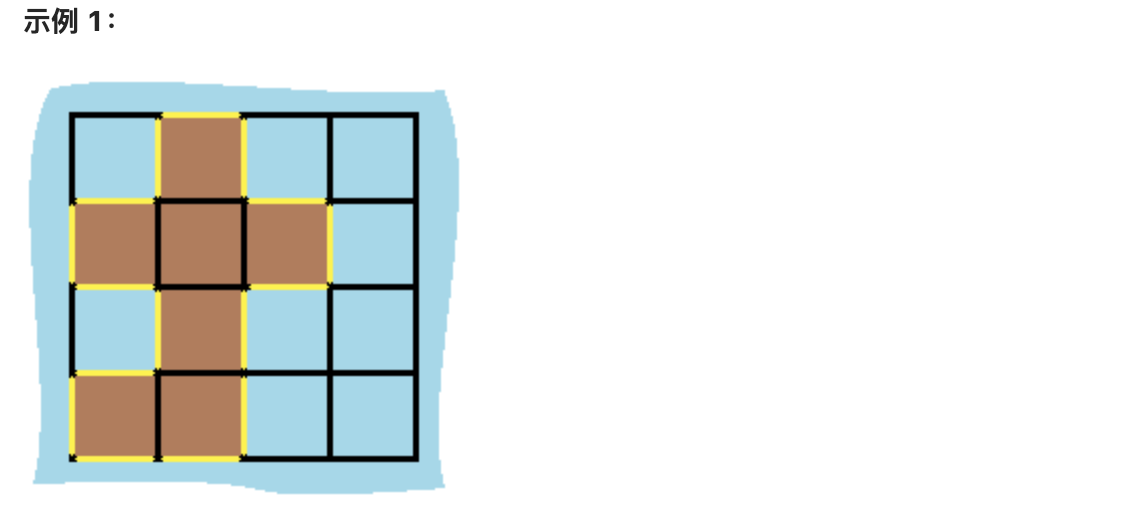
+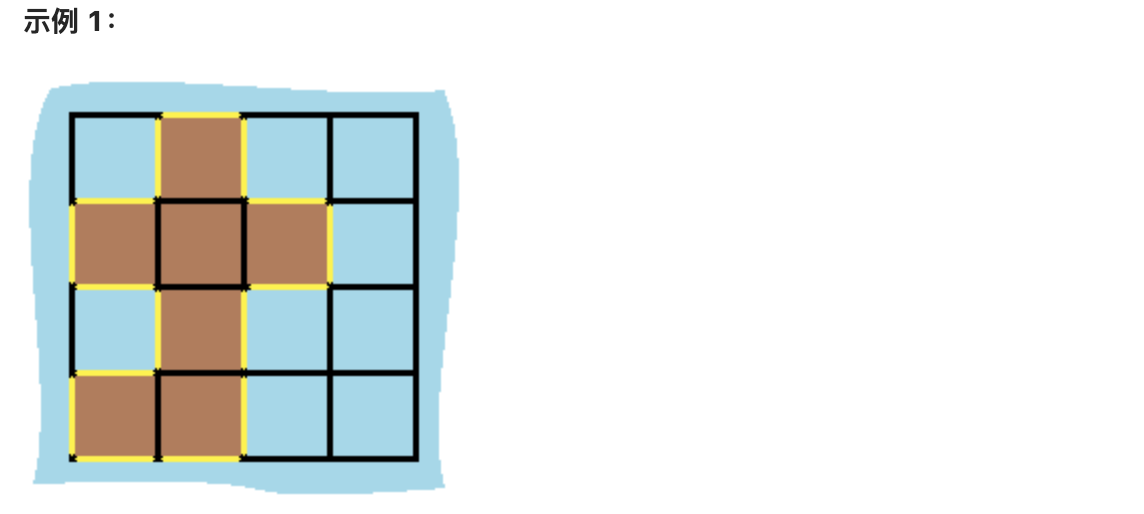
* 输入:grid = [[0,1,0,0],[1,1,1,0],[0,1,0,0],[1,1,0,0]]
* 输出:16
@@ -51,7 +49,7 @@
如图:
- +
+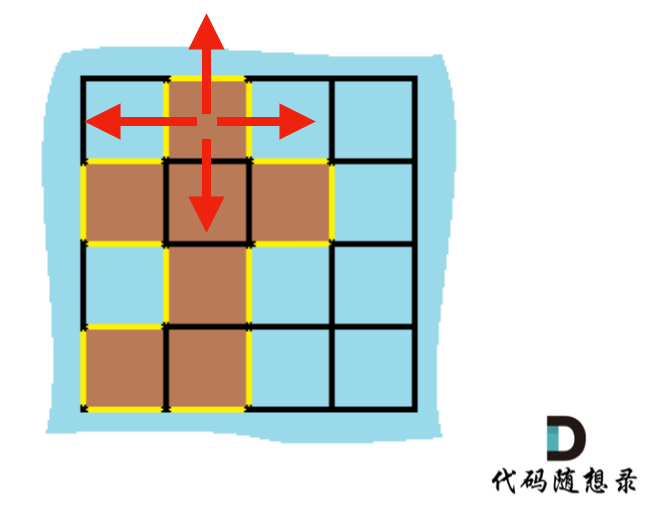 C++代码如下:(详细注释)
@@ -91,7 +89,7 @@ result = 岛屿数量 * 4 - cover * 2;
如图:
-
C++代码如下:(详细注释)
@@ -91,7 +89,7 @@ result = 岛屿数量 * 4 - cover * 2;
如图:
- +
+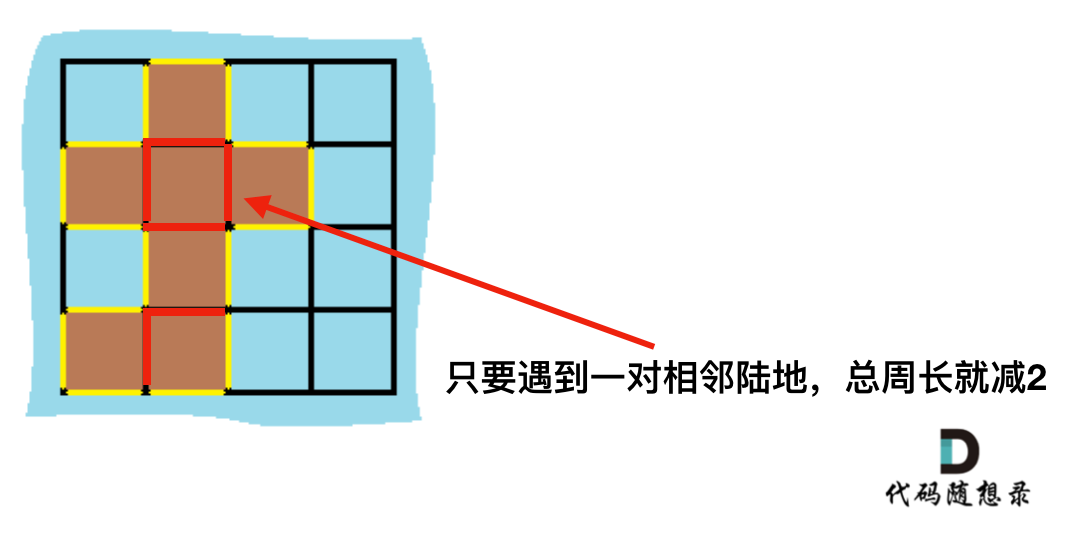 C++代码如下:(详细注释)
@@ -432,8 +430,4 @@ function islandPerimeter(grid: number[][]): number {
}
```
-
C++代码如下:(详细注释)
@@ -432,8 +430,4 @@ function islandPerimeter(grid: number[][]): number {
}
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0474.\344\270\200\345\222\214\351\233\266.md" "b/problems/0474.\344\270\200\345\222\214\351\233\266.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 904d941e9d..750917de3e
--- "a/problems/0474.\344\270\200\345\222\214\351\233\266.md"
+++ "b/problems/0474.\344\270\200\345\222\214\351\233\266.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0474.\344\270\200\345\222\214\351\233\266.md" "b/problems/0474.\344\270\200\345\222\214\351\233\266.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 904d941e9d..750917de3e
--- "a/problems/0474.\344\270\200\345\222\214\351\233\266.md"
+++ "b/problems/0474.\344\270\200\345\222\214\351\233\266.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 474.一和零
@@ -53,7 +51,7 @@
其实本题并不是多重背包,再来看一下这个图,捋清几种背包的关系
-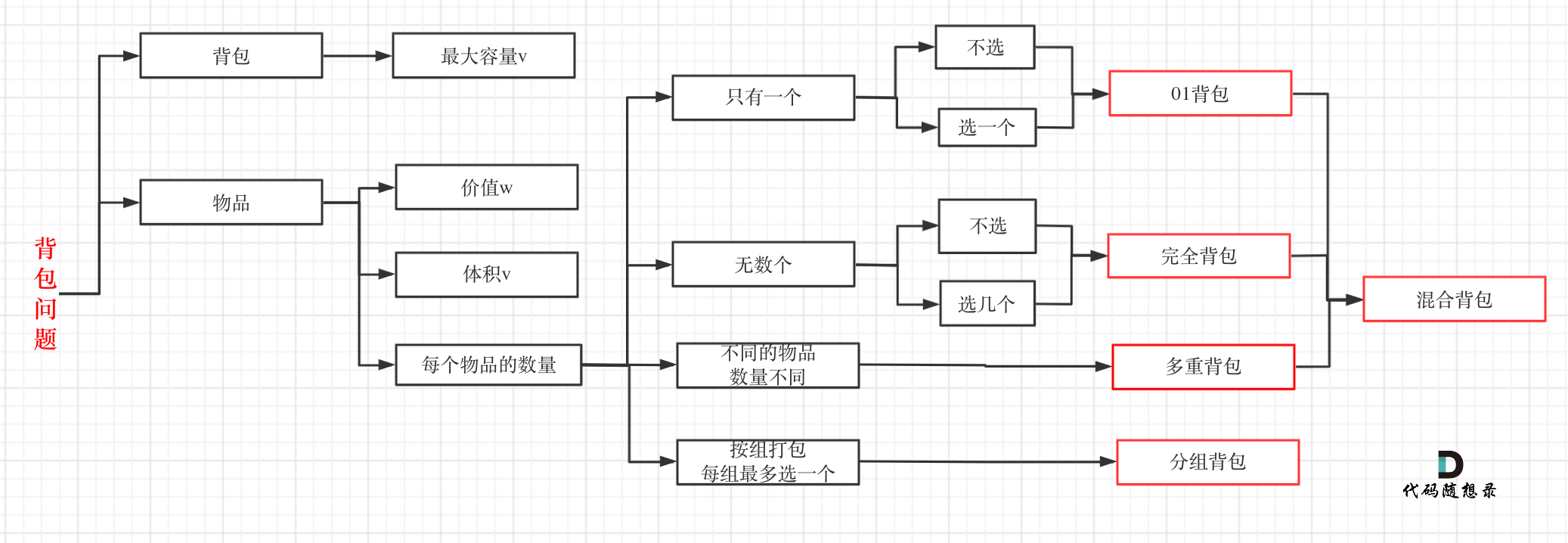
+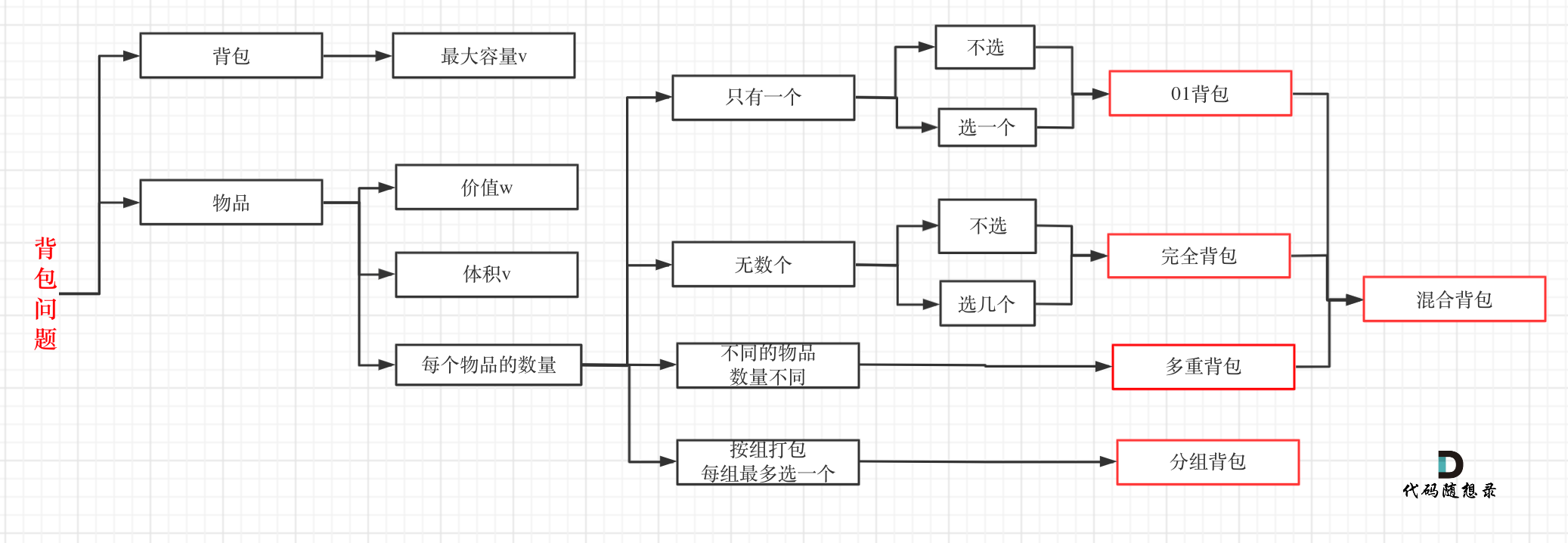
多重背包是每个物品,数量不同的情况。
@@ -129,7 +127,7 @@ for (string str : strs) { // 遍历物品
最后dp数组的状态如下所示:
-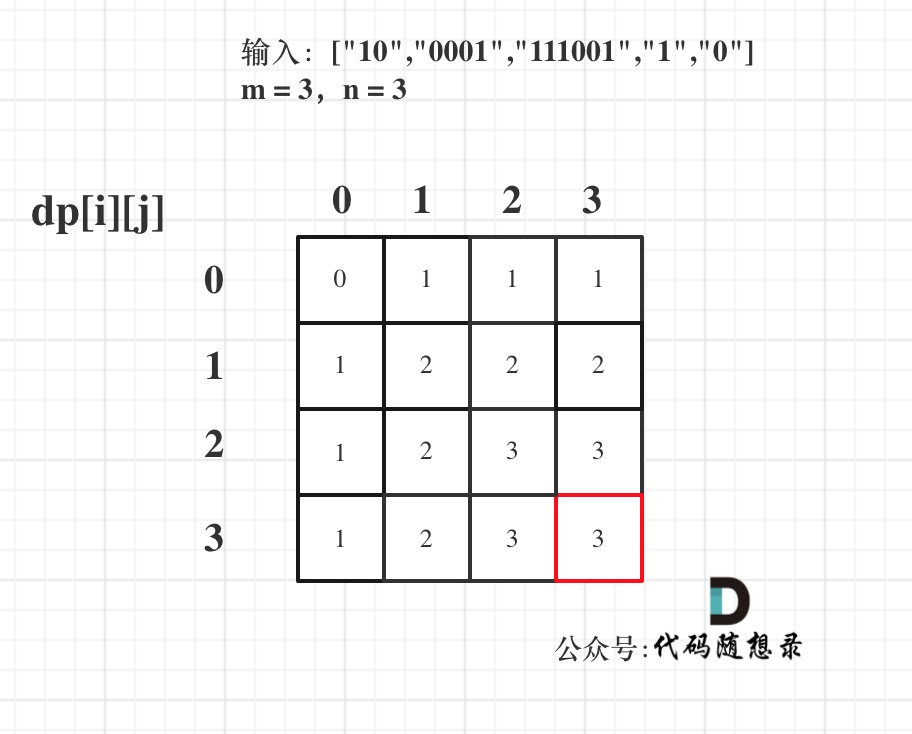
+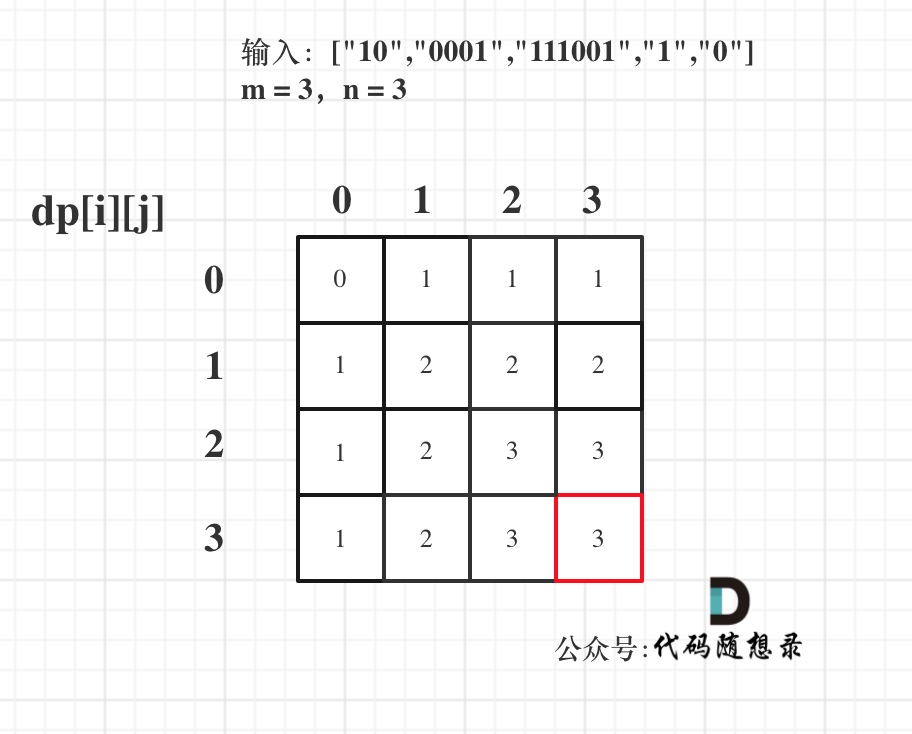
以上动规五部曲分析完毕,C++代码如下:
@@ -159,7 +157,89 @@ public:
* 时间复杂度: O(kmn),k 为strs的长度
* 空间复杂度: O(mn)
+C++:
+使用三维数组的版本
+```CPP
+class Solution {
+public:
+ int findMaxForm(vector& strs, int m, int n) {
+ int num_of_str = strs.size();
+
+ vector>> dp(num_of_str, vector>(m + 1,vector(n + 1, 0)));
+
+ /* dp[i][j][k] represents, if choosing items among strs[0] to strs[i] to form a subset,
+ what is the maximum size of this subset such that there are no more than m 0's and n 1's in this subset.
+ Each entry of dp[i][j][k] is initialized with 0
+
+ transition formula:
+ using x[i] to indicates the number of 0's in strs[i]
+ using y[i] to indicates the number of 1's in strs[i]
+
+ dp[i][j][k] = max(dp[i-1][j][k], dp[i-1][j - x[i]][k - y[i]] + 1)
+
+ */
+
+
+ // num_of_zeros records the number of 0's for each str
+ // num_of_ones records the number of 1's for each str
+ // find the number of 0's and the number of 1's for each str in strs
+ vector num_of_zeros;
+ vector num_of_ones;
+ for (auto& str : strs){
+ int count_of_zero = 0;
+ int count_of_one = 0;
+ for (char &c : str){
+ if(c == '0') count_of_zero ++;
+ else count_of_one ++;
+ }
+ num_of_zeros.push_back(count_of_zero);
+ num_of_ones.push_back(count_of_one);
+
+ }
+
+
+ // num_of_zeros[0] indicates the number of 0's for str[0]
+ // num_of_ones[0] indiates the number of 1's for str[1]
+
+ // initialize the 1st plane of dp[i][j][k], i.e., dp[0][j][k]
+ // if num_of_zeros[0] > m or num_of_ones[0] > n, no need to further initialize dp[0][j][k],
+ // because they have been intialized to 0 previously
+ if(num_of_zeros[0] <= m && num_of_ones[0] <= n){
+ // for j < num_of_zeros[0] or k < num_of_ones[0], dp[0][j][k] = 0
+ for(int j = num_of_zeros[0]; j <= m; j++){
+ for(int k = num_of_ones[0]; k <= n; k++){
+ dp[0][j][k] = 1;
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+ /* if j - num_of_zeros[i] >= 0 and k - num_of_ones[i] >= 0:
+ dp[i][j][k] = max(dp[i-1][j][k], dp[i-1][j - num_of_zeros[i]][k - num_of_ones[i]] + 1)
+ else:
+ dp[i][j][k] = dp[i-1][j][k]
+ */
+
+ for (int i = 1; i < num_of_str; i++){
+ int count_of_zeros = num_of_zeros[i];
+ int count_of_ones = num_of_ones[i];
+ for (int j = 0; j <= m; j++){
+ for (int k = 0; k <= n; k++){
+ if( j < count_of_zeros || k < count_of_ones){
+ dp[i][j][k] = dp[i-1][j][k];
+ }else{
+ dp[i][j][k] = max(dp[i-1][j][k], dp[i-1][j - count_of_zeros][k - count_of_ones] + 1);
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+ }
+
+ return dp[num_of_str-1][m][n];
+
+ }
+};
+```
## 总结
@@ -179,8 +259,70 @@ public:
## 其他语言版本
-
### Java
+
+三维DP数组实现
+
+```java
+class Solution {
+ public int findMaxForm(String[] strs, int m, int n) {
+ /// 数组有三个维度
+ // 第一个维度:取前面的几个字符串
+ // 第二个维度:0的数量限制(背包维度 1 容量)
+ // 第三个维度:1的数量限制(背包维度 2 容量)
+ int[][][] dpArr = new int[strs.length][m + 1][n + 1];
+
+ /// 初始化dpArr数组
+ // 计算第一个字符串的零数量和1数量
+ int zeroNum = 0;
+ int oneNum = 0;
+ for (char c : strs[0].toCharArray()) {
+ if (c == '0') {
+ zeroNum++;
+ } else {
+ oneNum++;
+ }
+ }
+ // 当0数量、1数量都容得下第一个字符串时,将DP数组的相应位置初始化为1,因为当前的子集数量为1
+ for (int j = zeroNum; j <= m; j++) {
+ for (int k = oneNum; k <= n; k++) {
+ dpArr[0][j][k] = 1;
+ }
+ }
+ /// 依次填充加入第i个字符串之后的DP数组
+ for (int i = 1; i < strs.length; i++) {
+ zeroNum = 0;
+ oneNum = 0;
+ for (char c : strs[i].toCharArray()) {
+ if (c == '0') {
+ zeroNum++;
+ } else {
+ oneNum++;
+ }
+ }
+ for (int j = 0; j <= m; j++) {
+ for (int k = 0; k <= n; k++) {
+ if (j >= zeroNum && k >= oneNum) {
+ // --if-- 当0数量维度和1数量维度的容量都大于等于当前字符串的0数量和1数量时,才考虑是否将当前字符串放入背包
+ // 不放入第i个字符串,子集数量仍为 dpArr[i - 1][j][k]
+ // 放入第i个字符串,需要在0维度腾出 zeroNum 个容量,1维度腾出 oneNum 个容量,然后放入当前字符串,即 dpArr[i - 1][j - zeroNum][k - oneNum] + 1)
+ dpArr[i][j][k] = Math.max(dpArr[i - 1][j][k], dpArr[i - 1][j - zeroNum][k - oneNum] + 1);
+ } else {
+ // --if-- 无法放入第i个字符串,子集数量仍为 dpArr[i - 1][j][k]
+ dpArr[i][j][k] = dpArr[i - 1][j][k];
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return dpArr[dpArr.length - 1][m][n];
+ }
+}
+```
+
+
+
+二维DP数组实现
+
```Java
class Solution {
public int findMaxForm(String[] strs, int m, int n) {
@@ -280,7 +422,7 @@ func max(a,b int) int {
}
```
-### Javascript
+### JavaScript
```javascript
const findMaxForm = (strs, m, n) => {
const dp = Array.from(Array(m+1), () => Array(n+1).fill(0));
@@ -533,7 +675,41 @@ impl Solution {
}
}
```
+### C
+
+```c
+#define max(a, b) ((a) > (b) ? (a) : (b))
+
+int findMaxForm(char** strs, int strsSize, int m, int n) {
+ int dp[m + 1][n + 1];
+ memset(dp, 0, sizeof (int ) * (m + 1) * (n + 1));
+ for(int i = 0; i < strsSize; i++){
+ // 统计0和1的数量
+ int count0 = 0;
+ int count1 = 0;
+ char *str = strs[i];
+ while (*str != '\0'){
+ if(*str == '0'){
+ count0++;
+ } else{
+ count1++;
+ }
+ str++;
+ }
+ for(int j = m; j >= count0; j--){
+ for(int k = n; k >= count1; k--){
+ dp[j][k] = max(dp[j][k], dp[j - count0][k - count1] + 1);
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return dp[m][n];
+}
+```
+
+
+
### C#
+
```csharp
public class Solution
{
@@ -561,8 +737,5 @@ public class Solution
}
```
-
-
-  -
+
diff --git "a/problems/0491.\351\200\222\345\242\236\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md" "b/problems/0491.\351\200\222\345\242\236\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 1aa69a3669..5d37737169
--- "a/problems/0491.\351\200\222\345\242\236\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
+++ "b/problems/0491.\351\200\222\345\242\236\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+
diff --git "a/problems/0491.\351\200\222\345\242\236\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md" "b/problems/0491.\351\200\222\345\242\236\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 1aa69a3669..5d37737169
--- "a/problems/0491.\351\200\222\345\242\236\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
+++ "b/problems/0491.\351\200\222\345\242\236\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
> 和子集问题有点像,但又处处是陷阱
@@ -47,7 +45,7 @@
为了有鲜明的对比,我用[4, 7, 6, 7]这个数组来举例,抽象为树形结构如图:
-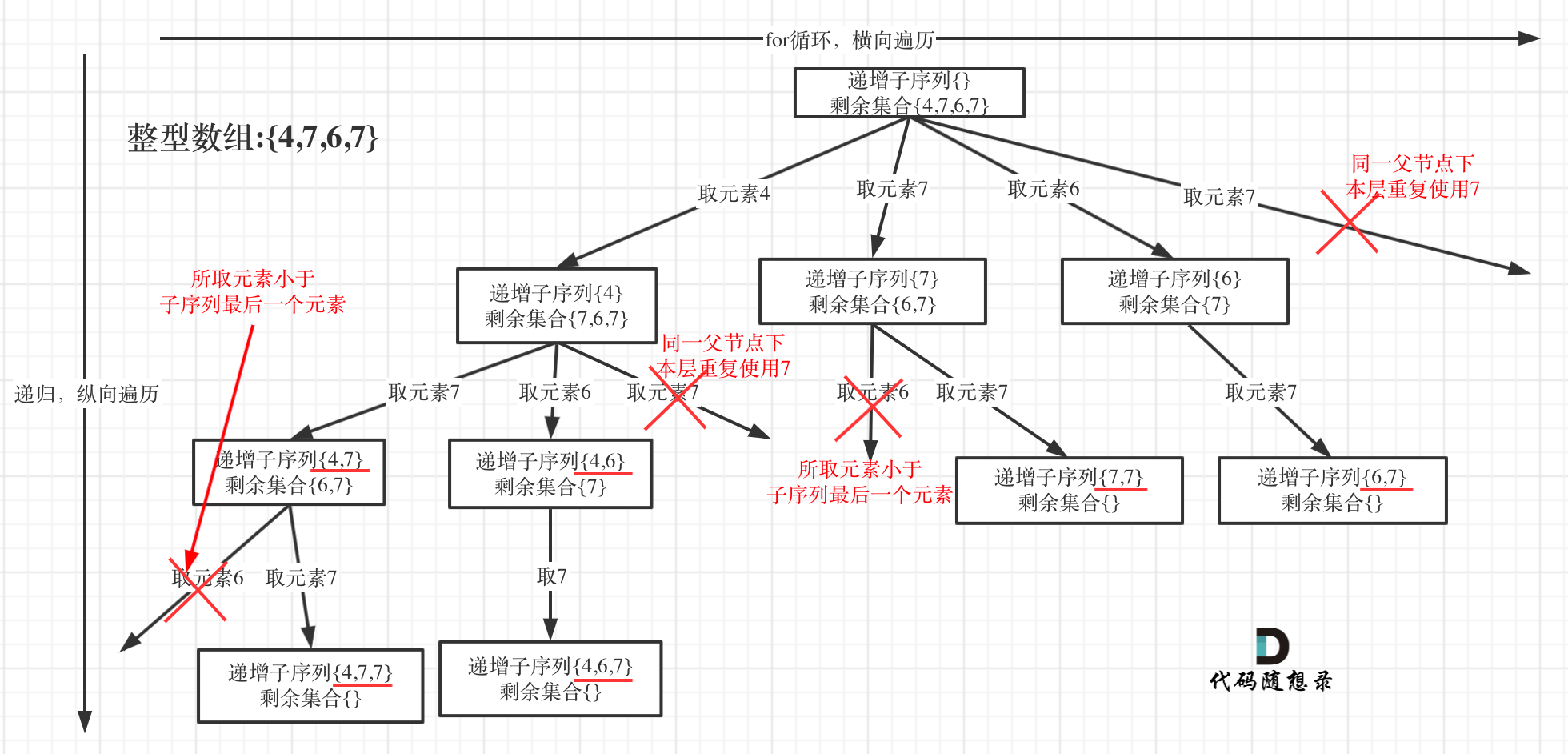
+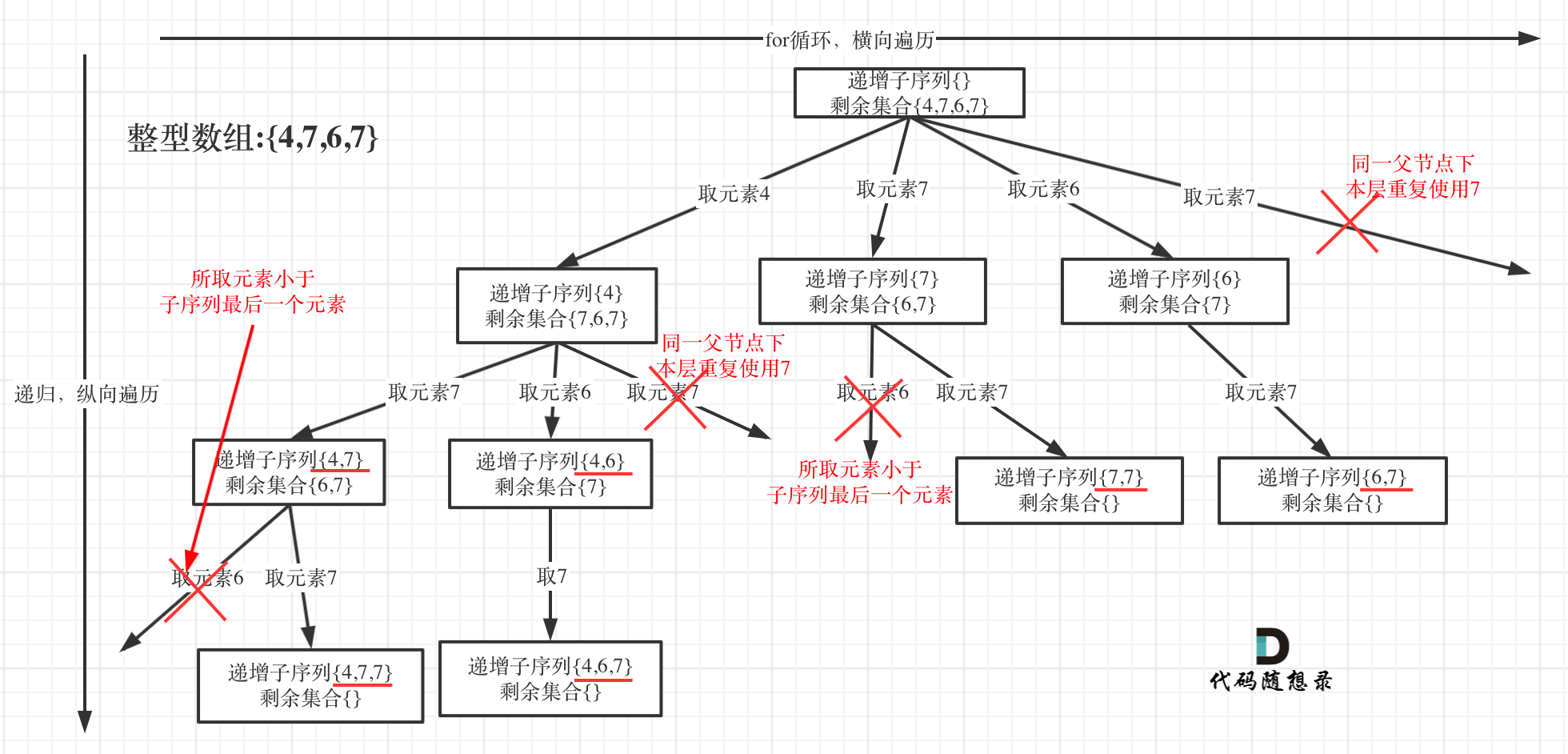
@@ -81,7 +79,7 @@ if (path.size() > 1) {
* 单层搜索逻辑
-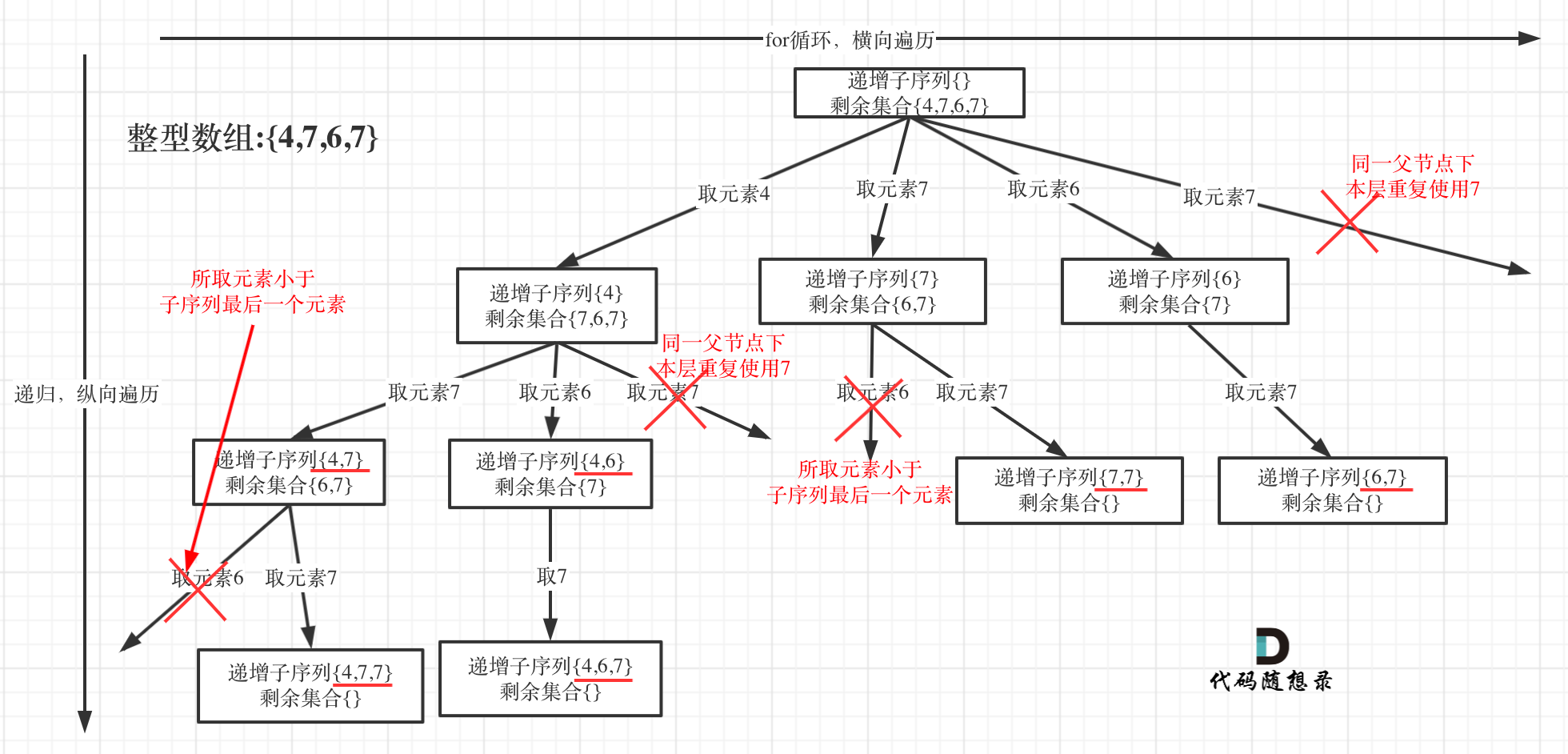
+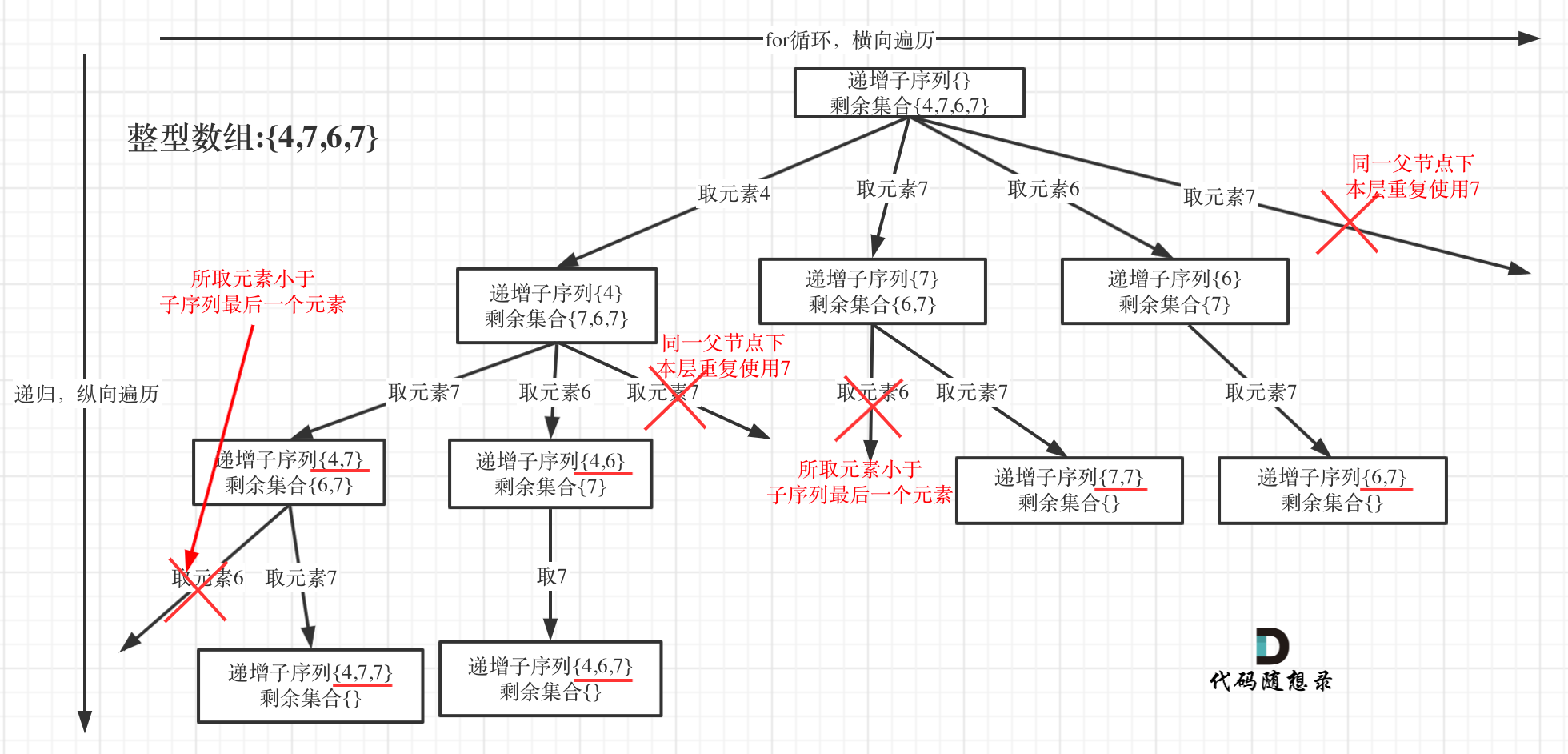
在图中可以看出,**同一父节点下的同层上使用过的元素就不能再使用了**
那么单层搜索代码如下:
@@ -206,7 +204,6 @@ public:
### Java
```Java
-//using set, aligned with the unimproved method
class Solution {
List> result = new ArrayList<>();
List path = new ArrayList<>();
@@ -376,7 +373,7 @@ func dfs(nums []int, start int) {
}
```
-### Javascript
+### JavaScript
```Javascript
@@ -641,7 +638,3 @@ public class Solution {
}
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0494.\347\233\256\346\240\207\345\222\214.md" "b/problems/0494.\347\233\256\346\240\207\345\222\214.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index e7a05d45c3..b161bc57a8
--- "a/problems/0494.\347\233\256\346\240\207\345\222\214.md"
+++ "b/problems/0494.\347\233\256\346\240\207\345\222\214.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0494.\347\233\256\346\240\207\345\222\214.md" "b/problems/0494.\347\233\256\346\240\207\345\222\214.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index e7a05d45c3..b161bc57a8
--- "a/problems/0494.\347\233\256\346\240\207\345\222\214.md"
+++ "b/problems/0494.\347\233\256\346\240\207\345\222\214.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
@@ -49,7 +47,7 @@
* [动态规划:关于01背包问题,你该了解这些!](https://programmercarl.com/背包理论基础01背包-1.html)
* [动态规划:关于01背包问题,你该了解这些!(滚动数组)](https://programmercarl.com/背包理论基础01背包-2.html)
-如果跟着「代码随想录」一起学过[回溯算法系列](https://programmercarl.com/回溯总结.html)的录友,看到这道题,应该有一种直觉,就是感觉好像回溯法可以爆搜出来。
+如果跟着「代码随想录」一起学过[回溯算法系列](https://programmercarl.com/回溯总结.html)的录友,看到这道题,应该有一种直觉,就是感觉好像回溯法可以暴搜出来。
事实确实如此,下面我也会给出相应的代码,只不过会超时。
@@ -61,7 +59,7 @@
left + right = sum,而sum是固定的。right = sum - left
-公式来了, left - (sum - left) = target 推导出 left = (target + sum)/2 。
+left - (sum - left) = target 推导出 left = (target + sum)/2 。
target是固定的,sum是固定的,left就可以求出来。
@@ -101,7 +99,7 @@ public:
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) sum += nums[i];
if (S > sum) return 0; // 此时没有方案
- if ((S + sum) % 2) return 0; // 此时没有方案,两个int相加的时候要各位小心数值溢出的问题
+ if ((S + sum) % 2) return 0; // 此时没有方案,两个int相加的时候要格外小心数值溢出的问题
int bagSize = (S + sum) / 2; // 转变为组合总和问题,bagsize就是要求的和
// 以下为回溯法代码
@@ -118,9 +116,7 @@ public:
也可以使用记忆化回溯,但这里我就不在回溯上下功夫了,直接看动规吧
-### 动态规划
-
-如何转化为01背包问题呢。
+### 动态规划 (二维dp数组)
假设加法的总和为x,那么减法对应的总和就是sum - x。
@@ -128,110 +124,342 @@ public:
x = (target + sum) / 2
-**此时问题就转化为,装满容量为x的背包,有几种方法**。
+**此时问题就转化为,用nums装满容量为x的背包,有几种方法**。
这里的x,就是bagSize,也就是我们后面要求的背包容量。
-大家看到(target + sum) / 2 应该担心计算的过程中向下取整有没有影响。
+大家看到`(target + sum) / 2` 应该担心计算的过程中向下取整有没有影响。
-这么担心就对了,例如sum 是5,S是2的话其实就是无解的,所以:
+这么担心就对了,例如sum是5,target是2 的话其实就是无解的,所以:
```CPP
(C++代码中,输入的S 就是题目描述的 target)
-if ((S + sum) % 2 == 1) return 0; // 此时没有方案
+if ((target + sum) % 2 == 1) return 0; // 此时没有方案
```
-同时如果 S的绝对值已经大于sum,那么也是没有方案的。
+同时如果target 的绝对值已经大于sum,那么也是没有方案的。
+
```CPP
-(C++代码中,输入的S 就是题目描述的 target)
-if (abs(S) > sum) return 0; // 此时没有方案
+if (abs(target) > sum) return 0; // 此时没有方案
```
-再回归到01背包问题,为什么是01背包呢?
-
因为每个物品(题目中的1)只用一次!
这次和之前遇到的背包问题不一样了,之前都是求容量为j的背包,最多能装多少。
本题则是装满有几种方法。其实这就是一个组合问题了。
-1. 确定dp数组以及下标的含义
+#### 1. 确定dp数组以及下标的含义
-dp[j] 表示:填满j(包括j)这么大容积的包,有dp[j]种方法
+先用 二维 dp数组求解本题,dp[i][j]:使用 下标为[0, i]的nums[i]能够凑满j(包括j)这么大容量的包,有dp[i][j]种方法。
-其实也可以使用二维dp数组来求解本题,dp[i][j]:使用 下标为[0, i]的nums[i]能够凑满j(包括j)这么大容量的包,有dp[i][j]种方法。
+01背包为什么这么定义dp数组,我在[0-1背包理论基础](https://www.programmercarl.com/%E8%83%8C%E5%8C%85%E7%90%86%E8%AE%BA%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%8001%E8%83%8C%E5%8C%85-1.html)中 确定dp数组的含义里讲解过。
-下面我都是统一使用一维数组进行讲解, 二维降为一维(滚动数组),其实就是上一层拷贝下来,这个我在[动态规划:关于01背包问题,你该了解这些!(滚动数组)](https://programmercarl.com/背包理论基础01背包-2.html)也有介绍。
+#### 2. 确定递推公式
-2. 确定递推公式
+我们先手动推导一下,这个二维数组里面的数值。
-有哪些来源可以推出dp[j]呢?
+------------
-只要搞到nums[i],凑成dp[j]就有dp[j - nums[i]] 种方法。
+先只考虑物品0,如图:
-例如:dp[j],j 为5,
+
-* 已经有一个1(nums[i]) 的话,有 dp[4]种方法 凑成 容量为5的背包。
-* 已经有一个2(nums[i]) 的话,有 dp[3]种方法 凑成 容量为5的背包。
-* 已经有一个3(nums[i]) 的话,有 dp[2]中方法 凑成 容量为5的背包
-* 已经有一个4(nums[i]) 的话,有 dp[1]中方法 凑成 容量为5的背包
-* 已经有一个5 (nums[i])的话,有 dp[0]中方法 凑成 容量为5的背包
+(这里的所有物品,都是题目中的数字1)。
-那么凑整dp[5]有多少方法呢,也就是把 所有的 dp[j - nums[i]] 累加起来。
+装满背包容量为0 的方法个数是1,即 放0件物品。
-所以求组合类问题的公式,都是类似这种:
+装满背包容量为1 的方法个数是1,即 放物品0。
+
+装满背包容量为2 的方法个数是0,目前没有办法能装满容量为2的背包。
+
+--------------
+
+接下来 考虑 物品0 和 物品1,如图:
+
+
+
+装满背包容量为0 的方法个数是1,即 放0件物品。
+
+装满背包容量为1 的方法个数是2,即 放物品0 或者 放物品1。
+
+装满背包容量为2 的方法个数是1,即 放物品0 和 放物品1。
+
+其他容量都不能装满,所以方法是0。
+
+-----------------
+
+接下来 考虑 物品0 、物品1 和 物品2 ,如图:
+
+
+
+装满背包容量为0 的方法个数是1,即 放0件物品。
+
+装满背包容量为1 的方法个数是3,即 放物品0 或者 放物品1 或者 放物品2。
+
+装满背包容量为2 的方法个数是3,即 放物品0 和 放物品1、放物品0 和 物品2、放物品1 和 物品2。
+
+装满背包容量为3的方法个数是1,即 放物品0 和 物品1 和 物品2。
+
+---------------
+通过以上举例,我们来看 dp[2][2] 可以有哪些方向推出来。
+
+如图红色部分:
+
+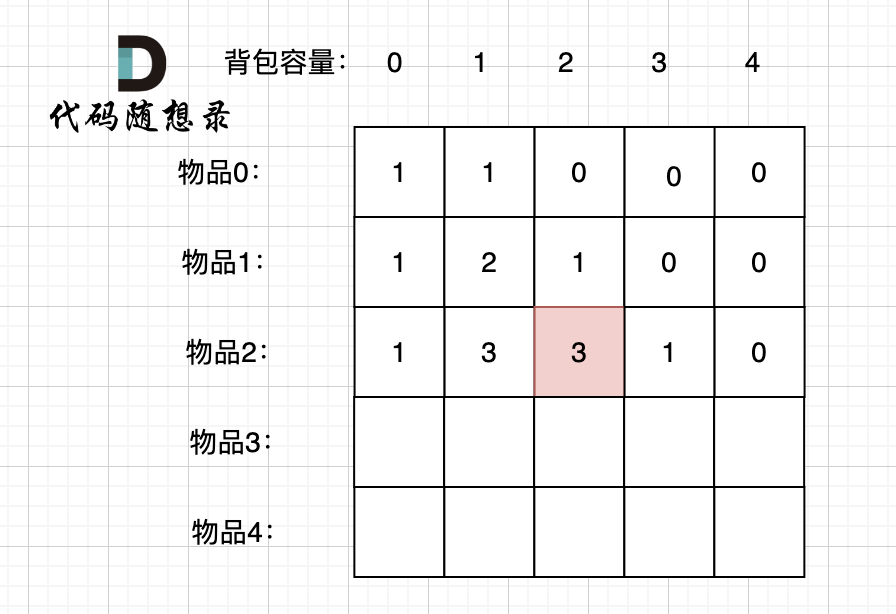
+
+dp[2][2] = 3,即 放物品0 和 放物品1、放物品0 和 物品 2、放物品1 和 物品2, 如图所示,三种方法:
+
+
+
+**容量为2 的背包,如果不放 物品2 有几种方法呢**?
+
+有 dp[1][2] 种方法,即 背包容量为2,只考虑物品0 和 物品1 ,有 dp[1][2] 种方法,如图:
+
+
+
+**容量为2 的背包, 如果放 物品2 有几种方法呢**?
+
+首先 要在背包里 先把物品2的容量空出来, 装满 刨除物品2容量 的背包 有几种方法呢?
+
+刨除物品2容量后的背包容量为 1。
+
+此时装满背包容量为1 有 dp[1][1] 种方法,即: 不放物品2,背包容量为1,只考虑物品 0 和 物品 1,有 dp[1][1] 种方法。
+
+如图:
+
+
+
+有录友可能疑惑,这里计算的是放满 容量为2的背包 有几种方法,那物品2去哪了?
+
+在上面图中,你把物品2补上就好,同样是两种方法。
+
+dp[2][2] = 容量为2的背包不放物品2有几种方法 + 容量为2的背包放物品2有几种方法
+
+所以 dp[2][2] = dp[1][2] + dp[1][1] ,如图:
+
+
+
+以上过程,抽象化如下:
+
+* **不放物品i**:即背包容量为j,里面不放物品i,装满有dp[i - 1][j]中方法。
+
+* **放物品i**: 即:先空出物品i的容量,背包容量为(j - 物品i容量),放满背包有 dp[i - 1][j - 物品i容量] 种方法。
+
+本题中,物品i的容量是nums[i],价值也是nums[i]。
+
+递推公式:dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j] + dp[i - 1][j - nums[i]];
+
+考到这个递推公式,我们应该注意到,`j - nums[i]` 作为数组下标,如果 `j - nums[i]` 小于零呢?
+
+说明背包容量装不下 物品i,所以此时装满背包的方法值 等于 不放物品i的装满背包的方法,即:dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j];
+
+所以递推公式:
+
+```CPP
+if (nums[i] > j) dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j];
+else dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j] + dp[i - 1][j - nums[i]];
```
-dp[j] += dp[j - nums[i]]
+
+#### 3. dp数组如何初始化
+
+先明确递推的方向,如图,求解 dp[2][2] 是由 上方和左上方推出。
+
+
+
+那么二维数组的最上行 和 最左列一定要初始化,这是递推公式推导的基础,如图红色部分:
+
+
+
+关于dp[0][0]的值,在上面的递推公式讲解中已经讲过,装满背包容量为0 的方法数量是1,即 放0件物品。
+
+那么最上行dp[0][j] 如何初始化呢?
+
+dp[0][j]:只放物品0, 把容量为j的背包填满有几种方法。
+
+只有背包容量为 物品0 的容量的时候,方法为1,正好装满。
+
+其他情况下,要不是装不满,要不是装不下。
+
+所以初始化:dp[0][nums[0]] = 1 ,其他均为0 。
+
+表格最左列也要初始化,dp[i][0] : 背包容量为0, 放物品0 到 物品i,装满有几种方法。
+
+都是有一种方法,就是放0件物品。
+
+即 dp[i][0] = 1
+
+但这里有例外,就是如果 物品数值就是0呢?
+
+如果有两个物品,物品0为0, 物品1为0,装满背包容量为0的方法有几种。
+
+* 放0件物品
+* 放物品0
+* 放物品1
+* 放物品0 和 物品1
+
+此时是有4种方法。
+
+其实就是算数组里有t个0,然后按照组合数量求,即 2^t 。
+
+初始化如下:
+
+```CPP
+int numZero = 0;
+for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
+ if (nums[i] == 0) numZero++;
+ dp[i][0] = (int) pow(2.0, numZero);
+}
```
-**这个公式在后面在讲解背包解决排列组合问题的时候还会用到!**
+#### 4. 确定遍历顺序
-3. dp数组如何初始化
+在明确递推方向时,我们知道 当前值 是由上方和左上方推出。
-从递推公式可以看出,在初始化的时候dp[0] 一定要初始化为1,因为dp[0]是在公式中一切递推结果的起源,如果dp[0]是0的话,递推结果将都是0。
+那么我们的遍历顺序一定是 从上到下,从左到右。
-这里有录友可能认为从dp数组定义来说 dp[0] 应该是0,也有录友认为dp[0]应该是1。
+因为只有这样,我们才能基于之前的数值做推导。
-其实不要硬去解释它的含义,咱就把 dp[0]的情况带入本题看看应该等于多少。
+例如下图,如果上方没数值,左上方没数值,就无法推出 dp[2][2]。
-如果数组[0] ,target = 0,那么 bagSize = (target + sum) / 2 = 0。 dp[0]也应该是1, 也就是说给数组里的元素 0 前面无论放加法还是减法,都是 1 种方法。
+
-所以本题我们应该初始化 dp[0] 为 1。
+那么是先 从上到下 ,再从左到右遍历,例如这样:
-可能有同学想了,那 如果是 数组[0,0,0,0,0] target = 0 呢。
+```CPP
+for (int i = 1; i < nums.size(); i++) { // 行,遍历物品
+ for (int j = 0; j <= bagSize; j++) { // 列,遍历背包
+ }
+}
+```
-其实 此时最终的dp[0] = 32,也就是这五个零 子集的所有组合情况,但此dp[0]非彼dp[0],dp[0]能算出32,其基础是因为dp[0] = 1 累加起来的。
+还是先 从左到右,再从上到下呢,例如这样:
-dp[j]其他下标对应的数值也应该初始化为0,从递推公式也可以看出,dp[j]要保证是0的初始值,才能正确的由dp[j - nums[i]]推导出来。
+```CPP
+for (int j = 0; j <= bagSize; j++) { // 列,遍历背包
+ for (int i = 1; i < nums.size(); i++) { // 行,遍历物品
+ }
+}
+```
+
+**其实以上两种遍历都可以**! (但仅针对二维DP数组是这样的)
+
+这一点我在 [01背包理论基础](https://www.programmercarl.com/%E8%83%8C%E5%8C%85%E7%90%86%E8%AE%BA%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%8001%E8%83%8C%E5%8C%85-1.html)中的 遍历顺序部分讲过。
+
+这里我再画图讲一下,以求dp[2][2]为例,当先从上到下,再从左到右遍历,矩阵是这样:
+
+
+当先从左到右,再从上到下遍历,矩阵是这样:
-4. 确定遍历顺序
+
-在[动态规划:关于01背包问题,你该了解这些!(滚动数组)](https://programmercarl.com/背包理论基础01背包-2.html)中,我们讲过对于01背包问题一维dp的遍历,nums放在外循环,target在内循环,且内循环倒序。
+这里大家可以看出,无论是以上哪种遍历,都不影响 dp[2][2]的求值,用来 推导 dp[2][2] 的数值都在。
-5. 举例推导dp数组
+#### 5. 举例推导dp数组
-输入:nums: [1, 1, 1, 1, 1], S: 3
+输入:nums: [1, 1, 1, 1, 1], target: 3
-bagSize = (S + sum) / 2 = (3 + 5) / 2 = 4
+bagSize = (target + sum) / 2 = (3 + 5) / 2 = 4
dp数组状态变化如下:
-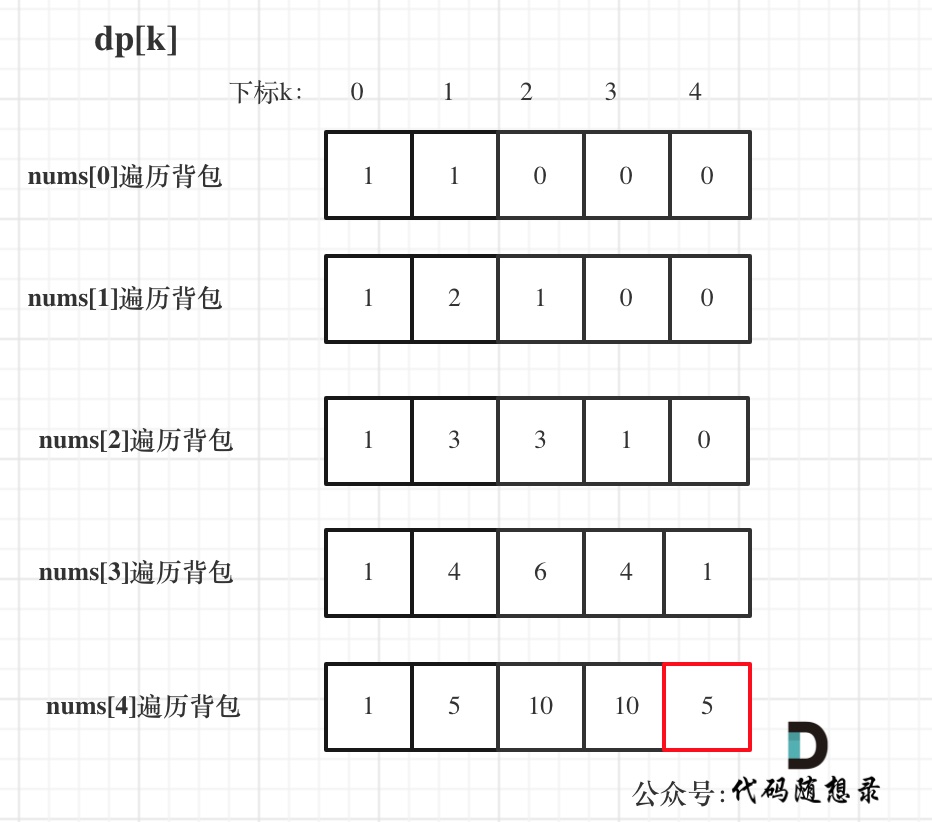
+
-C++代码如下:
+这么大的矩阵,我们是可以自己手动模拟出来的。
+
+在模拟的过程中,既可以帮我们寻找规律,也可以帮我们验证 递推公式加遍历顺序是不是按照我们想象的结果推进的。
+
+
+最后二维dp数组的C++代码如下:
+
+```CPP
+class Solution {
+public:
+ int findTargetSumWays(vector& nums, int target) {
+ int sum = 0;
+ for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) sum += nums[i];
+ if (abs(target) > sum) return 0; // 此时没有方案
+ if ((target + sum) % 2 == 1) return 0; // 此时没有方案
+ int bagSize = (target + sum) / 2;
+
+ vector> dp(nums.size(), vector(bagSize + 1, 0));
+
+ // 初始化最上行
+ if (nums[0] <= bagSize) dp[0][nums[0]] = 1;
+
+ // 初始化最左列,最左列其他数值在递推公式中就完成了赋值
+ dp[0][0] = 1;
+
+ int numZero = 0;
+ for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
+ if (nums[i] == 0) numZero++;
+ dp[i][0] = (int) pow(2.0, numZero);
+ }
+
+ // 以下遍历顺序行列可以颠倒
+ for (int i = 1; i < nums.size(); i++) { // 行,遍历物品
+ for (int j = 0; j <= bagSize; j++) { // 列,遍历背包
+ if (nums[i] > j) dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j];
+ else dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j] + dp[i - 1][j - nums[i]];
+ }
+ }
+ return dp[nums.size() - 1][bagSize];
+ }
+};
+```
+
+### 动态规划 (一维dp数组)
+
+将二维dp数组压缩成一维dp数组,我们在 [01背包理论基础(滚动数组)](https://programmercarl.com/背包理论基础01背包-2.html) 讲过滚动数组,原理是一样的,即重复利用每一行的数值。
+
+既然是重复利用每一行,就是将二维数组压缩成一行。
+
+dp[i][j] 去掉 行的维度,即 dp[j],表示:填满j(包括j)这么大容积的包,有dp[j]种方法。
+
+#### 2. 确定递推公式
+
+二维DP数组递推公式: `dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j] + dp[i - 1][j - nums[i]];`
+
+去掉维度i 之后,递推公式:`dp[j] = dp[j] + dp[j - nums[i]]` ,即:`dp[j] += dp[j - nums[i]]`
+
+**这个公式在后面在讲解背包解决排列组合问题的时候还会用到!**
+
+#### 3. dp数组如何初始化
+
+在上面 二维dp数组中,我们讲解过 dp[0][0] 初始为1,这里dp[0] 同样初始为1 ,即装满背包为0的方法有一种,放0件物品。
+
+#### 4. 确定遍历顺序
+
+在[动态规划:关于01背包问题,你该了解这些!(滚动数组)](https://programmercarl.com/背包理论基础01背包-2.html)中,我们系统讲过对于01背包问题一维dp的遍历。
+
+遍历物品放在外循环,遍历背包在内循环,且内循环倒序(为了保证物品只使用一次)。
+
+#### 5. 举例推导dp数组
+
+输入:nums: [1, 1, 1, 1, 1], target: 3
+
+bagSize = (target + sum) / 2 = (3 + 5) / 2 = 4
+
+dp数组状态变化如下:
+
+
+
+大家可以和 二维dp数组的打印结果做一下对比。
+
+一维DP的C++代码如下:
```CPP
class Solution {
public:
- int findTargetSumWays(vector& nums, int S) {
+ int findTargetSumWays(vector& nums, int target) {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) sum += nums[i];
- if (abs(S) > sum) return 0; // 此时没有方案
- if ((S + sum) % 2 == 1) return 0; // 此时没有方案
- int bagSize = (S + sum) / 2;
+ if (abs(target) > sum) return 0; // 此时没有方案
+ if ((target + sum) % 2 == 1) return 0; // 此时没有方案
+ int bagSize = (target + sum) / 2;
vector dp(bagSize + 1, 0);
dp[0] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
@@ -248,26 +476,53 @@ public:
* 空间复杂度:O(m),m为背包容量
-## 总结
-此时 大家应该不禁想起,我们之前讲过的[回溯算法:39. 组合总和](https://programmercarl.com/0039.组合总和.html)是不是应该也可以用dp来做啊?
+### 拓展
-是的,如果仅仅是求个数的话,就可以用dp,但[回溯算法:39. 组合总和](https://programmercarl.com/0039.组合总和.html)要求的是把所有组合列出来,还是要使用回溯法爆搜的。
+关于一维dp数组的递推公式解释,也可以从以下维度来理解。 (**但还是从二维DP数组到一维DP数组这样更容易理解一些**)
-本题还是有点难度,大家也可以记住,在求装满背包有几种方法的情况下,递推公式一般为:
+2. 确定递推公式
-```CPP
-dp[j] += dp[j - nums[i]];
+有哪些来源可以推出dp[j]呢?
+
+只要搞到nums[i],凑成dp[j]就有dp[j - nums[i]] 种方法。
+
+例如:dp[j],j 为5,
+
+* 已经有一个1(nums[i]) 的话,有 dp[4]种方法 凑成 容量为5的背包。
+* 已经有一个2(nums[i]) 的话,有 dp[3]种方法 凑成 容量为5的背包。
+* 已经有一个3(nums[i]) 的话,有 dp[2]种方法 凑成 容量为5的背包
+* 已经有一个4(nums[i]) 的话,有 dp[1]种方法 凑成 容量为5的背包
+* 已经有一个5 (nums[i])的话,有 dp[0]种方法 凑成 容量为5的背包
+
+那么凑整dp[5]有多少方法呢,也就是把 所有的 dp[j - nums[i]] 累加起来。
+
+所以求组合类问题的公式,都是类似这种:
+
+```
+dp[j] += dp[j - nums[i]]
```
-后面我们在讲解完全背包的时候,还会用到这个递推公式!
+## 总结
+此时 大家应该不禁想起,我们之前讲过的[回溯算法:39. 组合总和](https://programmercarl.com/0039.组合总和.html)是不是应该也可以用dp来做啊?
+是可以求的,如果仅仅是求个数的话,就可以用dp,但[回溯算法:39. 组合总和](https://programmercarl.com/0039.组合总和.html)要求的是把所有组合列出来,还是要使用回溯法暴搜的。
+本题还是有点难度,理解上从二维DP数组更容易理解,做题上直接用一维DP更简洁一些。
-## 其他语言版本
+大家可以选择哪种方式自己更容易理解。
+
+在后面得题目中,在求装满背包有几种方法的情况下,递推公式一般为:
+
+```CPP
+dp[j] += dp[j - nums[i]];
+```
+
+我们在讲解完全背包的时候,还会用到这个递推公式!
+## 其他语言版本
### Java
```java
@@ -359,13 +614,6 @@ class Solution {
}
}
- // 打印dp数组
- // for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
- // for(int j = 0; j <= left; j++) {
- // System.out.print(dp[i][j] + " ");
- // }
- // System.out.println("");
- // }
return dp[nums.length - 1][left];
@@ -420,18 +668,26 @@ class Solution:
# 创建二维动态规划数组,行表示选取的元素数量,列表示累加和
dp = [[0] * (target_sum + 1) for _ in range(len(nums) + 1)]
+ dp = [[0] * (target_sum + 1) for _ in range(len(nums))]
# 初始化状态
dp[0][0] = 1
+ if nums[0] <= target_sum:
+ dp[0][nums[0]] = 1
+ numZero = 0
+ for i in range(len(nums)):
+ if nums[i] == 0:
+ numZero += 1
+ dp[i][0] = int(math.pow(2, numZero))
# 动态规划过程
- for i in range(1, len(nums) + 1):
+ for i in range(1, len(nums)):
for j in range(target_sum + 1):
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j] # 不选取当前元素
if j >= nums[i - 1]:
- dp[i][j] += dp[i - 1][j - nums[i - 1]] # 选取当前元素
+ dp[i][j] += dp[i - 1][j - nums[i]] # 选取当前元素
- return dp[len(nums)][target_sum] # 返回达到目标和的方案数
+ return dp[len(nums)-1][target_sum] # 返回达到目标和的方案数
```
@@ -455,6 +711,82 @@ class Solution:
```
### Go
+回溯法思路
+```go
+func findTargetSumWays(nums []int, target int) int {
+ var result int
+ var backtracking func(nums []int, target int, index int, currentSum int)
+
+ backtracking = func(nums []int, target int, index int, currentSum int) {
+ if index == len(nums) {
+ if currentSum == target {
+ result++
+ }
+ return
+ }
+
+ // 选择加上当前数字
+ backtracking(nums, target, index+1, currentSum+nums[index])
+
+ // 选择减去当前数字
+ backtracking(nums, target, index+1, currentSum-nums[index])
+ }
+
+ backtracking(nums, target, 0, 0)
+ return result
+}
+```
+二维dp
+```go
+func findTargetSumWays(nums []int, target int) int {
+ sum := 0
+ for _, v := range nums {
+ sum += v
+ }
+ if math.Abs(float64(target)) > float64(sum) {
+ return 0 // 此时没有方案
+ }
+ if (target + sum) % 2 == 1 {
+ return 0 // 此时没有方案
+ }
+ bagSize := (target + sum) / 2
+
+ dp := make([][]int, len(nums))
+ for i := range dp {
+ dp[i] = make([]int, bagSize + 1)
+ }
+
+ // 初始化最上行
+ if nums[0] <= bagSize {
+ dp[0][nums[0]] = 1
+ }
+
+ // 初始化最左列,最左列其他数值在递推公式中就完成了赋值
+ dp[0][0] = 1
+
+ var numZero float64
+ for i := range nums {
+ if nums[i] == 0 {
+ numZero++
+ }
+ dp[i][0] = int(math.Pow(2, numZero))
+ }
+
+ // 以下遍历顺序行列可以颠倒
+ for i := 1; i < len(nums); i++ { // 行,遍历物品
+ for j := 0; j <= bagSize; j++ { // 列,遍历背包
+ if nums[i] > j {
+ dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j]
+ } else {
+ dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j] + dp[i-1][j-nums[i]]
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return dp[len(nums)-1][bagSize]
+}
+```
+
+一维dp
```go
func findTargetSumWays(nums []int, target int) int {
sum := 0
@@ -489,32 +821,71 @@ func abs(x int) int {
}
```
-### Javascript
+### JavaScript
```javascript
+/**
+ * 题目来源: {@link https://leetcode.cn/problems/target-sum/}
+ *
+ * 题解来源: {@link https://programmercarl.com/0494.%E7%9B%AE%E6%A0%87%E5%92%8C.html#%E7%AE%97%E6%B3%95%E5%85%AC%E5%BC%80%E8%AF%BE}
+ *
+ * 时间复杂度: O(n * C), C 为数组元素总和与目标值之和的一半
+ *
+ * 空间复杂度: O(C)
+ *
+ * @param { number[] } nums
+ * @param { number } target
+ * @return { number }
+ */
const findTargetSumWays = (nums, target) => {
-
- const sum = nums.reduce((a, b) => a+b);
+ // 原题目可转化为:
+ //
+ // 将所有元素划分为 2 个集合,
+ // 一个集合中包含所有要添加 "+" 号的元素, 一个集合中包含所有要添加 "-" 号的元素
+ //
+ // 设两个集合的元素和分别为 positive 和 negative, 所有元素总和为 sum, 那么有如下等式:
+ // positive + negative = sum (1)
+ // positive - negative = target (2)
+ // (1) 与 (2) 联立可得: positive = (sum + target) / 2,
+ // 所以如果能从原数组中取出若干个元素形成 1 个元素总和为 (sum + target) / 2 的集合,
+ // 就算得到了 1 种满足题意的组合方法
+ //
+ // 因此, 所求变为: 有多少种取法, 可使得容量为 (sum + target) / 2 的背包被装满?
+
+ const sum = nums.reduce((a, b) => a + b);
- if(Math.abs(target) > sum) {
+ if (Math.abs(target) > sum) {
return 0;
}
- if((target + sum) % 2) {
+ if ((target + sum) % 2) {
return 0;
}
- const halfSum = (target + sum) / 2;
-
- let dp = new Array(halfSum+1).fill(0);
+ const bagWeight = (target + sum) / 2;
+
+ // 1. dp 数组的含义
+ // dp[j]: 装满容量为 j 的背包, 有 dp[j] 种方法
+ let dp = new Array(bagWeight + 1).fill(0);
+
+ // 2. 递推公式
+ // dp[j] = Σ(dp[j - nums[j]]), (j ∈ [0, j] 且 j >= nums[j])
+ // 因为 dp[j - nums[j]] 表示: 装满容量为 j - nums[j] 背包有 dp[j - nums[j]] 种方法
+ // 而容量为 j - nums[j] 的背包只需要再将 nums[j] 放入背包就能使得背包容量达到 j
+ // 因此, 让背包容量达到 j 有 Σ(dp[j - nums[j]]) 种方法
+
+ // 3. dp 数组如何初始化
+ // dp[0] = 1, dp[1 ~ bagWeight] = 0
dp[0] = 1;
-
- for(let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
- for(let j = halfSum; j >= nums[i]; j--) {
+
+ // 4. 遍历顺序
+ // 先物品后背包, 物品从前往后遍历, 背包容量从后往前遍历
+ for (let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
+ for (let j = bagWeight; j >= nums[i]; j--) {
dp[j] += dp[j - nums[i]];
}
}
- return dp[halfSum];
+ return dp[bagWeight];
};
```
@@ -585,7 +956,44 @@ impl Solution {
}
}
```
+### C
+
+```c
+int getSum(int * nums, int numsSize){
+ int sum = 0;
+ for(int i = 0; i < numsSize; i++){
+ sum += nums[i];
+ }
+ return sum;
+}
+
+int findTargetSumWays(int* nums, int numsSize, int target) {
+ int sum = getSum(nums, numsSize);
+ int diff = sum - target;
+ // 两种情况不满足
+ if(diff < 0 || diff % 2 != 0){
+ return 0;
+ }
+ int bagSize = diff / 2;
+ int dp[numsSize + 1][bagSize + 1];
+ dp[0][0] = 1;
+ for(int i = 1; i <= numsSize; i++){
+ int num = nums[i - 1];
+ for(int j = 0; j <= bagSize; j++){
+ dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j];
+ if(j >= num){
+ dp[i][j] += dp[i - 1][j - num];
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return dp[numsSize][bagSize];
+}
+```
+
+
+
### C#
+
```csharp
public class Solution
{
@@ -613,8 +1021,5 @@ public class Solution
}
```
-
-
-  -
+
diff --git "a/problems/0496.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\233\264\345\244\247\345\205\203\347\264\240I.md" "b/problems/0496.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\233\264\345\244\247\345\205\203\347\264\240I.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index d97a3e8482..628149b75d
--- "a/problems/0496.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\233\264\345\244\247\345\205\203\347\264\240I.md"
+++ "b/problems/0496.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\233\264\345\244\247\345\205\203\347\264\240I.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+
diff --git "a/problems/0496.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\233\264\345\244\247\345\205\203\347\264\240I.md" "b/problems/0496.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\233\264\345\244\247\345\205\203\347\264\240I.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index d97a3e8482..628149b75d
--- "a/problems/0496.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\233\264\345\244\247\345\205\203\347\264\240I.md"
+++ "b/problems/0496.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\233\264\345\244\247\345\205\203\347\264\240I.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 496.下一个更大元素 I
@@ -195,6 +193,62 @@ public:
建议大家把情况一二三想清楚了,先写出版本一的代码,然后在其基础上在做精简!
## 其他语言版本
+
+### C
+
+``` C
+/* 先用单调栈的方法计算出结果,再根据nums1中的元素去查找对应的结果 */
+/**
+ * Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free().
+ */
+int* nextGreaterElement(int* nums1, int nums1Size, int* nums2, int nums2Size, int* returnSize) {
+
+ /* stcak */
+ int top = -1;
+ int stack_len = nums2Size;
+ int stack[stack_len];
+ //memset(stack, 0x00, sizeof(stack));
+
+ /* nums2 result */
+ int* result_nums2 = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * nums2Size);
+ //memset(result_nums2, 0x00, sizeof(int) * nums2Size);
+
+ /* result */
+ int* result = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * nums1Size);
+ //memset(result, 0x00, sizeof(int) * nums1Size);
+ *returnSize = nums1Size;
+
+ /* init */
+ stack[++top] = 0; /* stack loaded with array subscripts */
+
+ for (int i = 0; i < nums2Size; i++) {
+ result_nums2[i] = -1;
+ }
+
+ /* get the result_nums2 */
+ for (int i = 1; i < nums2Size; i++) {
+ if (nums2[i] <= nums2[stack[top]]) {
+ stack[++top] = i; /* push */
+ } else {
+ while ((top >= 0) && (nums2[i] > nums2[stack[top]])) {
+ result_nums2[stack[top]] = nums2[i];
+ top--; /* pop */
+ }
+ stack[++top] = i;
+ }
+ }
+
+ /* get the result */
+ for (int i = 0; i < nums1Size; i++) {
+ for (int j = 0; j < nums2Size; j++) {
+ if (nums1[i] == nums2[j]) {
+ result[i] = result_nums2[j];
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return result;
+}
+```
### Java
```java
@@ -450,8 +504,4 @@ impl Solution {
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0501.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\344\274\227\346\225\260.md" "b/problems/0501.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\344\274\227\346\225\260.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 20627d1ad6..457fd61d24
--- "a/problems/0501.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\344\274\227\346\225\260.md"
+++ "b/problems/0501.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\344\274\227\346\225\260.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0501.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\344\274\227\346\225\260.md" "b/problems/0501.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\344\274\227\346\225\260.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 20627d1ad6..457fd61d24
--- "a/problems/0501.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\344\274\227\346\225\260.md"
+++ "b/problems/0501.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\344\274\227\346\225\260.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
> 二叉树上应该怎么求,二叉搜索树上又应该怎么求?
@@ -25,7 +23,7 @@
给定 BST [1,null,2,2],
-
+
返回[2].
@@ -35,7 +33,7 @@
## 算法公开课
-**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[不仅双指针,还有代码技巧可以惊艳到你! | LeetCode:501.二叉搜索树中的众数](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1fD4y117gp),相信结合视频在看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
+**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[不仅双指针,还有代码技巧可以惊艳到你! | LeetCode:501.二叉搜索树中的众数](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1fD4y117gp),相信结合视频再看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
## 思路
@@ -146,7 +144,7 @@ public:
如图:
-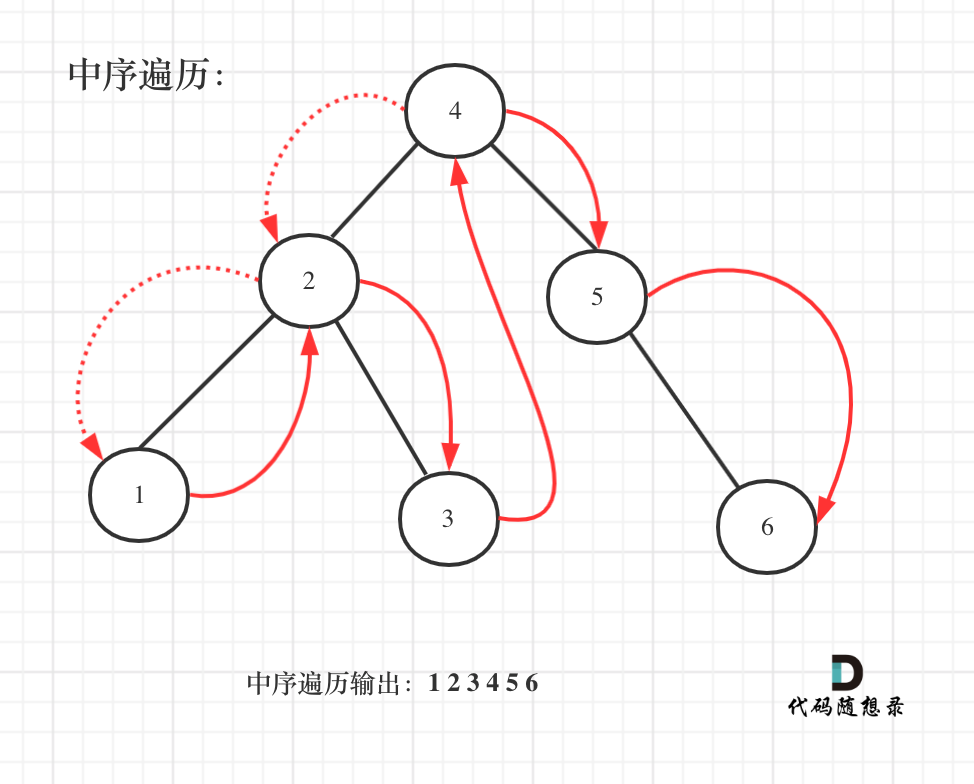
+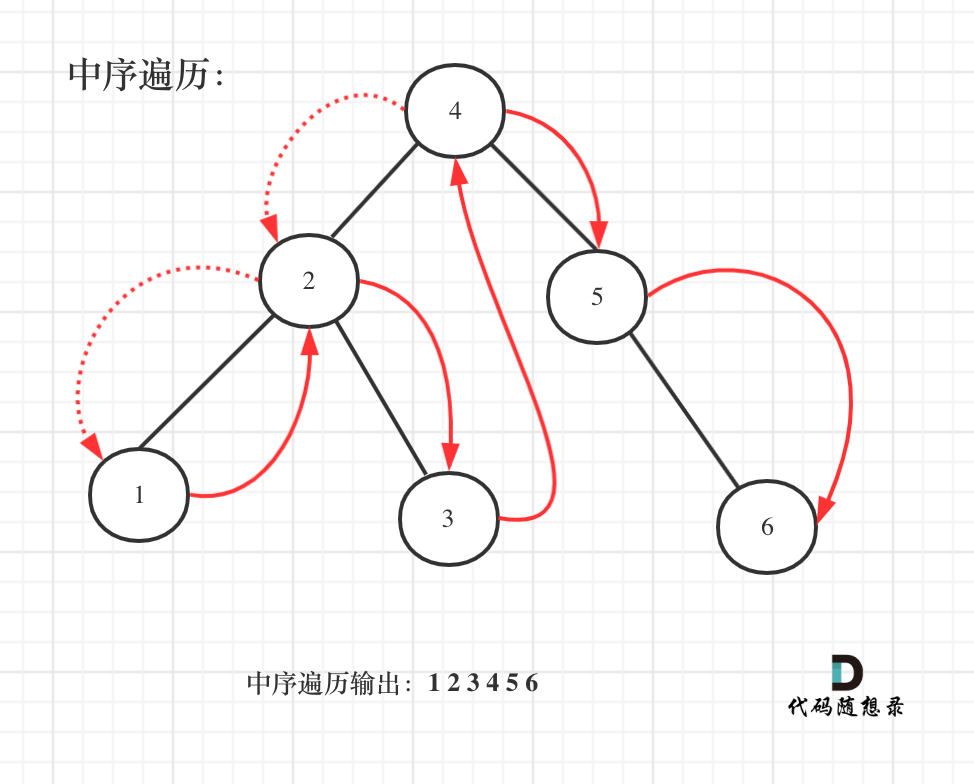
中序遍历代码如下:
@@ -1051,8 +1049,4 @@ public class Solution
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0503.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\233\264\345\244\247\345\205\203\347\264\240II.md" "b/problems/0503.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\233\264\345\244\247\345\205\203\347\264\240II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 6df83fb208..93924483f3
--- "a/problems/0503.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\233\264\345\244\247\345\205\203\347\264\240II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0503.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\233\264\345\244\247\345\205\203\347\264\240II.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0503.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\233\264\345\244\247\345\205\203\347\264\240II.md" "b/problems/0503.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\233\264\345\244\247\345\205\203\347\264\240II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 6df83fb208..93924483f3
--- "a/problems/0503.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\233\264\345\244\247\345\205\203\347\264\240II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0503.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\233\264\345\244\247\345\205\203\347\264\240II.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 503.下一个更大元素II
@@ -168,6 +166,7 @@ class Solution {
```
### Python:
+> 版本一:
```python
class Solution:
@@ -181,9 +180,71 @@ class Solution:
stack.append(i%len(nums))
return dp
```
+
+> 版本二:针对版本一的优化
+
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def nextGreaterElements(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[int]:
+ res = [-1] * len(nums)
+ stack = []
+ #第一次遍历nums
+ for i, num in enumerate(nums):
+ while stack and num > nums[stack[-1]]:
+ res[stack[-1]] = num
+ stack.pop()
+ stack.append(i)
+ #此时stack仍有剩余,有部分数‘无下一个更大元素’待修正
+ #第二次遍历nums
+ for num in nums:
+ #一旦stack为空,就表明所有数都有下一个更大元素,可以返回结果
+ if not stack:
+ return res
+ while stack and num > nums[stack[-1]]:
+ res[stack[-1]] = num
+ stack.pop()
+ #不要将已经有下一个更大元素的数加入栈,这样会重复赋值,只需对第一次遍历剩余的数再尝试寻找下一个更大元素即可
+ #最后仍有部分最大数无法有下一个更大元素,返回结果
+ return res
+```
+
### Go:
```go
+// 版本一
+func nextGreaterElements(nums []int) []int {
+ // 拼接一个新的nums
+ numsNew := make([]int, len(nums) * 2)
+ copy(numsNew, nums)
+ copy(numsNew[len(nums):], nums)
+ // 用新的nums大小来初始化result
+ result := make([]int, len(numsNew))
+ for i := range result {
+ result[i] = -1
+ }
+
+ // 开始单调栈
+ st := []int{0}
+ for i := 1; i < len(numsNew); i++ {
+ if numsNew[i] < numsNew[st[len(st)-1]] {
+ st = append(st, i)
+ } else if numsNew[i] == numsNew[st[len(st)-1]] {
+ st = append(st, i)
+ } else {
+ for len(st) > 0 && numsNew[i] > numsNew[st[len(st)-1]] {
+ result[st[len(st)-1]] = numsNew[i]
+ st = st[:len(st)-1]
+ }
+ st = append(st, i)
+ }
+ }
+ result = result[:len(result)/2]
+ return result
+}
+```
+
+```go
+// 版本二
func nextGreaterElements(nums []int) []int {
length := len(nums)
result := make([]int,length)
@@ -203,7 +264,6 @@ func nextGreaterElements(nums []int) []int {
return result
}
```
-
### JavaScript:
```JS
@@ -295,8 +355,4 @@ impl Solution {
}
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0509.\346\226\220\346\263\242\351\202\243\345\245\221\346\225\260.md" "b/problems/0509.\346\226\220\346\263\242\351\202\243\345\245\221\346\225\260.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 71c022bd34..b2e56a613c
--- "a/problems/0509.\346\226\220\346\263\242\351\202\243\345\245\221\346\225\260.md"
+++ "b/problems/0509.\346\226\220\346\263\242\351\202\243\345\245\221\346\225\260.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0509.\346\226\220\346\263\242\351\202\243\345\245\221\346\225\260.md" "b/problems/0509.\346\226\220\346\263\242\351\202\243\345\245\221\346\225\260.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 71c022bd34..b2e56a613c
--- "a/problems/0509.\346\226\220\346\263\242\351\202\243\345\245\221\346\225\260.md"
+++ "b/problems/0509.\346\226\220\346\263\242\351\202\243\345\245\221\346\225\260.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 509. 斐波那契数
@@ -151,7 +149,7 @@ public:
* 时间复杂度:O(2^n)
* 空间复杂度:O(n),算上了编程语言中实现递归的系统栈所占空间
-这个递归的时间复杂度大家画一下树形图就知道了,如果不清晰的同学,可以看这篇:[通过一道面试题目,讲一讲递归算法的时间复杂度!](https://programmercarl.com/前序/通过一道面试题目,讲一讲递归算法的时间复杂度!.html)
+这个递归的时间复杂度大家画一下树形图就知道了,如果不清晰的同学,可以看这篇:[通过一道面试题目,讲一讲递归算法的时间复杂度!](./前序/递归算法的时间复杂度.md)
## 总结
@@ -292,7 +290,7 @@ func fib(n int) int {
return c
}
```
-### Javascript
+### JavaScript
解法一
```Javascript
var fib = function(n) {
@@ -475,8 +473,4 @@ public class Solution
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0513.\346\211\276\346\240\221\345\267\246\344\270\213\350\247\222\347\232\204\345\200\274.md" "b/problems/0513.\346\211\276\346\240\221\345\267\246\344\270\213\350\247\222\347\232\204\345\200\274.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index d897bba13a..03f076a2c9
--- "a/problems/0513.\346\211\276\346\240\221\345\267\246\344\270\213\350\247\222\347\232\204\345\200\274.md"
+++ "b/problems/0513.\346\211\276\346\240\221\345\267\246\344\270\213\350\247\222\347\232\204\345\200\274.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0513.\346\211\276\346\240\221\345\267\246\344\270\213\350\247\222\347\232\204\345\200\274.md" "b/problems/0513.\346\211\276\346\240\221\345\267\246\344\270\213\350\247\222\347\232\204\345\200\274.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index d897bba13a..03f076a2c9
--- "a/problems/0513.\346\211\276\346\240\221\345\267\246\344\270\213\350\247\222\347\232\204\345\200\274.md"
+++ "b/problems/0513.\346\211\276\346\240\221\345\267\246\344\270\213\350\247\222\347\232\204\345\200\274.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 513.找树左下角的值
@@ -14,11 +12,11 @@
示例 1:
-
+
示例 2:
-
+
## 算法公开课
@@ -55,7 +53,7 @@
参数必须有要遍历的树的根节点,还有就是一个int型的变量用来记录最长深度。 这里就不需要返回值了,所以递归函数的返回类型为void。
-本题还需要类里的两个全局变量,maxLen用来记录最大深度,result记录最大深度最左节点的数值。
+本题还需要类里的两个全局变量,maxDepth用来记录最大深度,result记录最大深度最左节点的数值。
代码如下:
@@ -764,7 +762,3 @@ public class Solution
// @lc code=end
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0516.\346\234\200\351\225\277\345\233\236\346\226\207\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md" "b/problems/0516.\346\234\200\351\225\277\345\233\236\346\226\207\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 44bdec1f19..882c36bb05
--- "a/problems/0516.\346\234\200\351\225\277\345\233\236\346\226\207\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
+++ "b/problems/0516.\346\234\200\351\225\277\345\233\236\346\226\207\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0516.\346\234\200\351\225\277\345\233\236\346\226\207\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md" "b/problems/0516.\346\234\200\351\225\277\345\233\236\346\226\207\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 44bdec1f19..882c36bb05
--- "a/problems/0516.\346\234\200\351\225\277\345\233\236\346\226\207\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
+++ "b/problems/0516.\346\234\200\351\225\277\345\233\236\346\226\207\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
# 516.最长回文子序列
@@ -58,7 +56,7 @@
如果s[i]与s[j]相同,那么dp[i][j] = dp[i + 1][j - 1] + 2;
如图:
-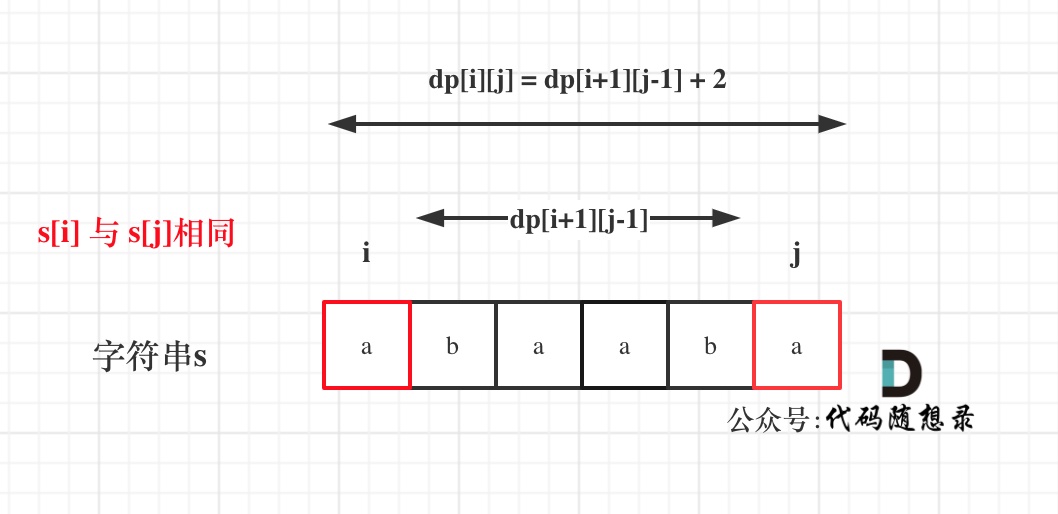
+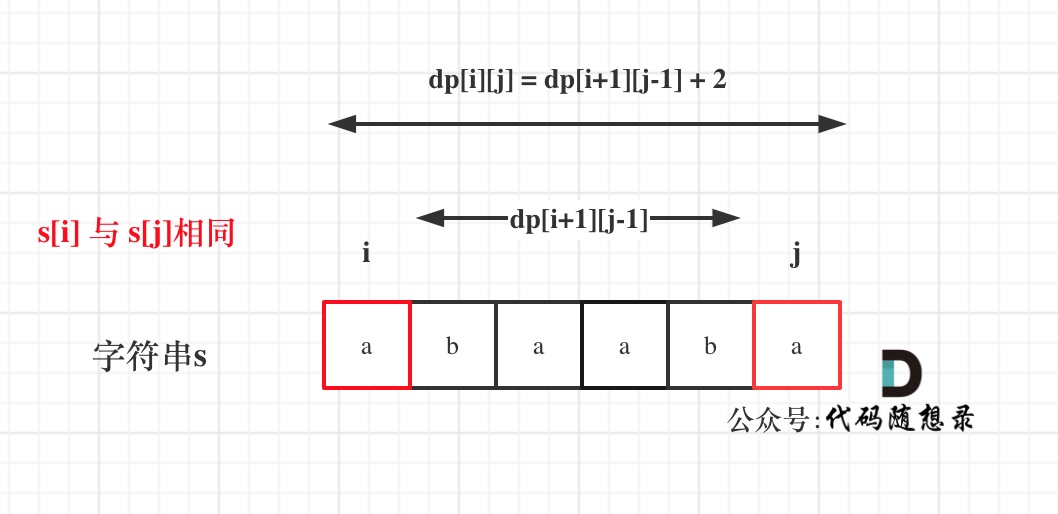
(如果这里看不懂,回忆一下dp[i][j]的定义)
@@ -70,7 +68,7 @@
那么dp[i][j]一定是取最大的,即:dp[i][j] = max(dp[i + 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]);
-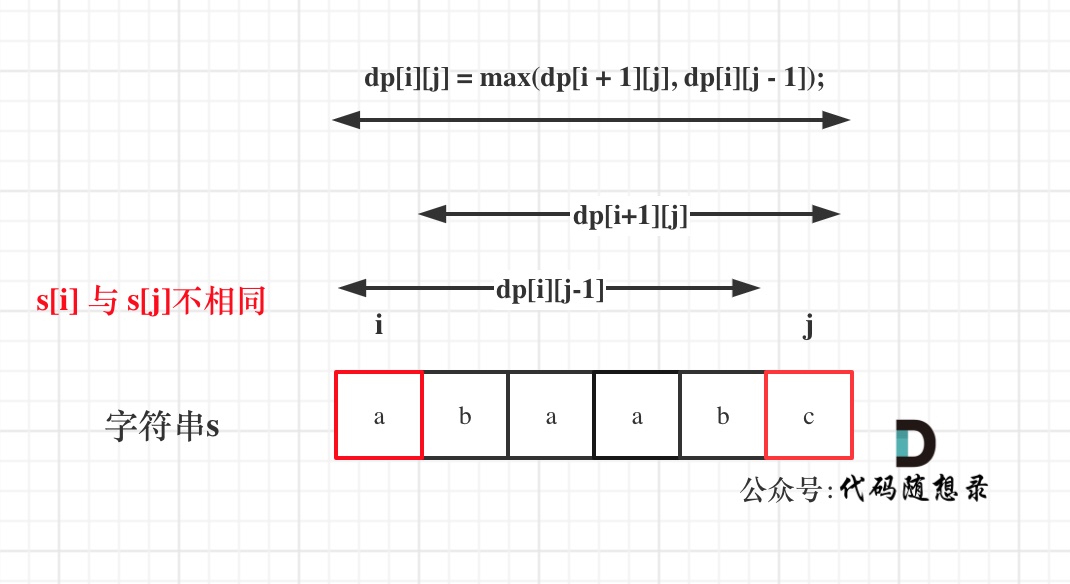
+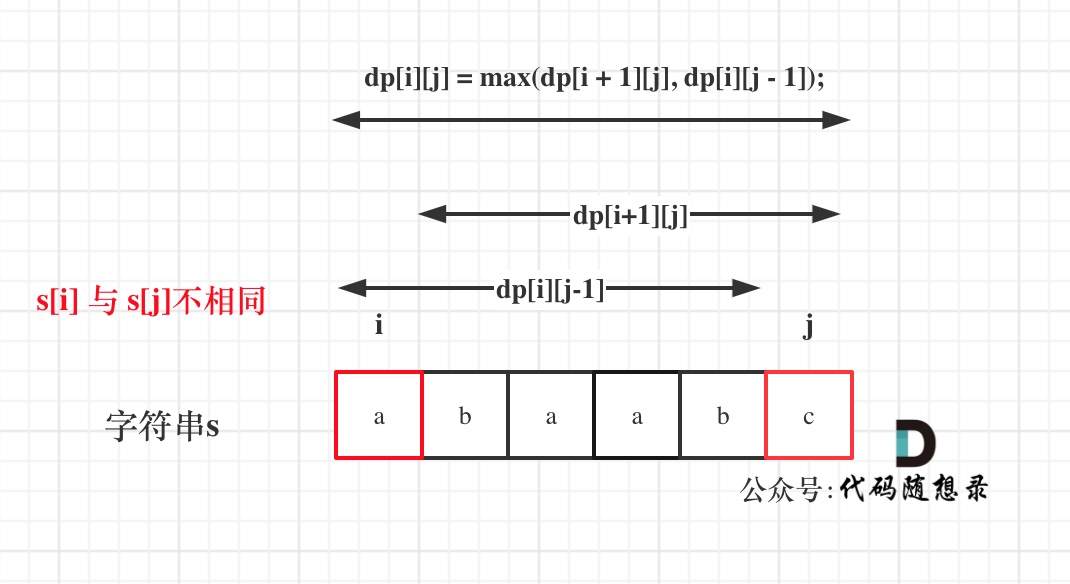
代码如下:
@@ -99,7 +97,7 @@ for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) dp[i][i] = 1;
从递归公式中,可以看出,dp[i][j] 依赖于 dp[i + 1][j - 1] ,dp[i + 1][j] 和 dp[i][j - 1],如图:
-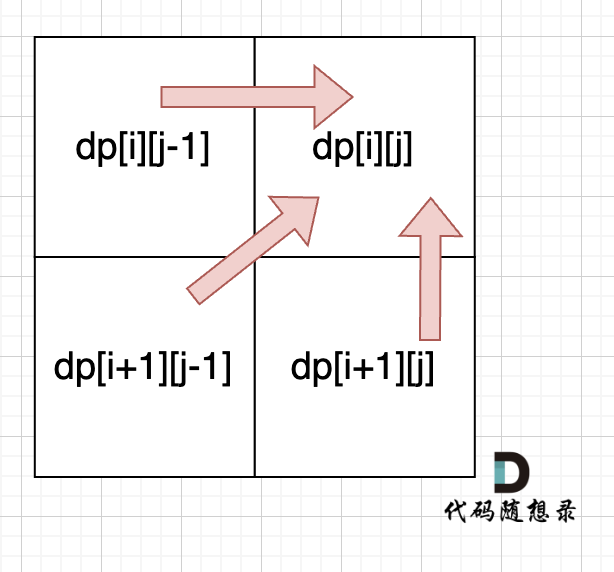
+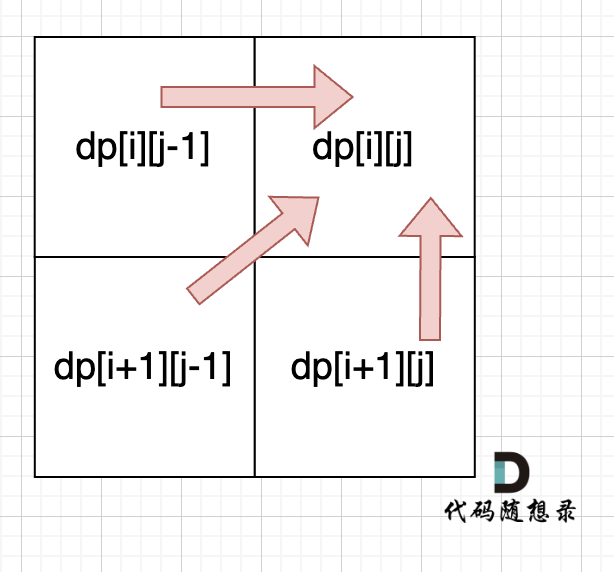
**所以遍历i的时候一定要从下到上遍历,这样才能保证下一行的数据是经过计算的**。
@@ -123,7 +121,7 @@ for (int i = s.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
输入s:"cbbd" 为例,dp数组状态如图:
-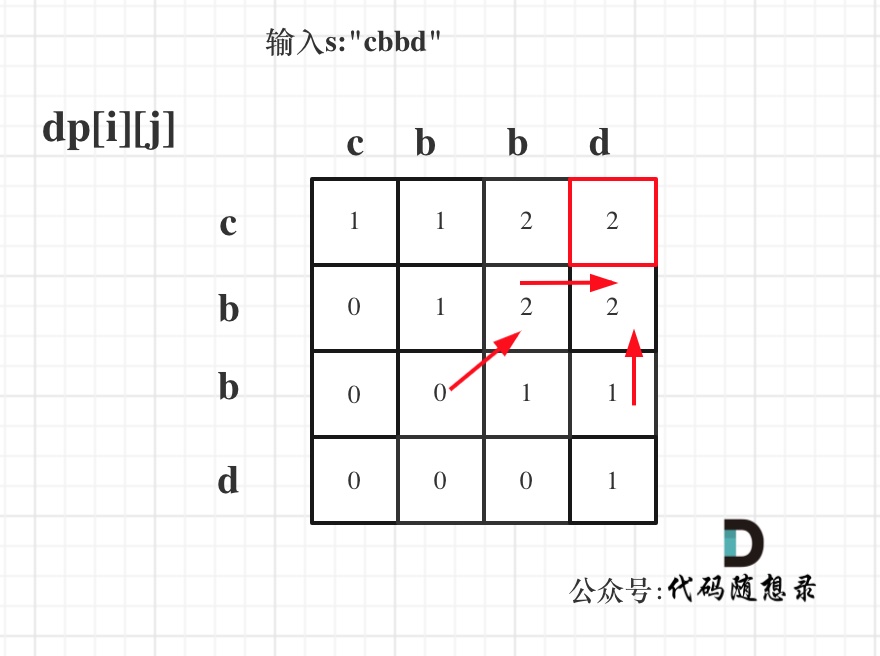
+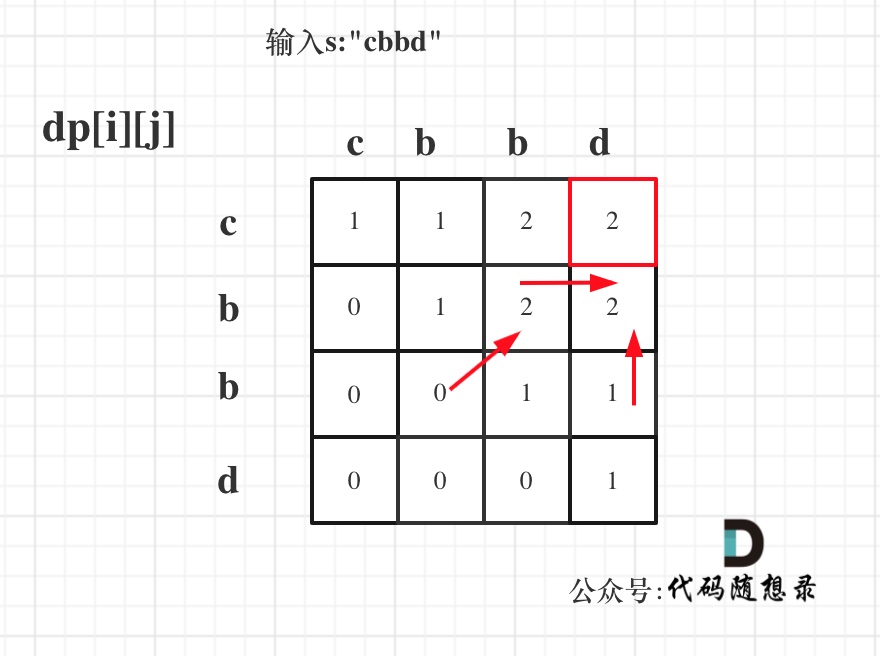
红色框即:dp[0][s.size() - 1]; 为最终结果。
@@ -224,7 +222,7 @@ func longestPalindromeSubseq(s string) int {
}
```
-### Javascript:
+### JavaScript:
```javascript
const longestPalindromeSubseq = (s) => {
@@ -298,8 +296,4 @@ impl Solution {
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0518.\351\233\266\351\222\261\345\205\221\346\215\242II.md" "b/problems/0518.\351\233\266\351\222\261\345\205\221\346\215\242II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index da1c475565..7e4bbb9a81
--- "a/problems/0518.\351\233\266\351\222\261\345\205\221\346\215\242II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0518.\351\233\266\351\222\261\345\205\221\346\215\242II.md"
@@ -1,10 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0518.\351\233\266\351\222\261\345\205\221\346\215\242II.md" "b/problems/0518.\351\233\266\351\222\261\345\205\221\346\215\242II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index da1c475565..7e4bbb9a81
--- "a/problems/0518.\351\233\266\351\222\261\345\205\221\346\215\242II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0518.\351\233\266\351\222\261\345\205\221\346\215\242II.md"
@@ -1,10 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
-
-
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 518.零钱兑换II
@@ -45,15 +41,19 @@
**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[装满背包有多少种方法?组合与排列有讲究!| LeetCode:518.零钱兑换II](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1KM411k75j/),相信结合视频再看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
+## 二维dp讲解
+如果大家认真做完:[分割等和子集](https://www.programmercarl.com/0416.%E5%88%86%E5%89%B2%E7%AD%89%E5%92%8C%E5%AD%90%E9%9B%86.html) , [最后一块石头的重量II](https://www.programmercarl.com/1049.%E6%9C%80%E5%90%8E%E4%B8%80%E5%9D%97%E7%9F%B3%E5%A4%B4%E7%9A%84%E9%87%8D%E9%87%8FII.html) 和 [目标和](https://www.programmercarl.com/0494.%E7%9B%AE%E6%A0%87%E5%92%8C.html)
+应该会知道类似这种题目:给出一个总数,一些物品,问能否凑成这个总数。
-## 思路
+这是典型的背包问题!
-这是一道典型的背包问题,一看到钱币数量不限,就知道这是一个完全背包。
+本题求的是装满这个背包的物品组合数是多少。
+因为每一种面额的硬币有无限个,所以这是完全背包。
-对完全背包还不了解的同学,可以看这篇:[动态规划:关于完全背包,你该了解这些!](https://programmercarl.com/背包问题理论基础完全背包.html)
+对完全背包还不了解的同学,可以看这篇:[完全背包理论基础](https://programmercarl.com/背包问题理论基础完全背包.html)
但本题和纯完全背包不一样,**纯完全背包是凑成背包最大价值是多少,而本题是要求凑成总金额的物品组合个数!**
@@ -69,44 +69,182 @@
如果问的是排列数,那么上面就是两种排列了。
-**组合不强调元素之间的顺序,排列强调元素之间的顺序**。 其实这一点我们在讲解回溯算法专题的时候就讲过了哈。
+**组合不强调元素之间的顺序,排列强调元素之间的顺序**。 其实这一点我们在讲解回溯算法专题的时候就讲过。
那我为什么要介绍这些呢,因为这和下文讲解遍历顺序息息相关!
-回归本题,动规五步曲来分析如下:
+本题其实与我们讲过 [494. 目标和](https://programmercarl.com/0494.目标和.html) 十分类似。
-1. 确定dp数组以及下标的含义
+[494. 目标和](https://programmercarl.com/0494.目标和.html) 求的是装满背包有多少种方法,而本题是求装满背包有多少种组合。
-dp[j]:凑成总金额j的货币组合数为dp[j]
+这有啥区别?
-2. 确定递推公式
+**求装满背包有几种方法其实就是求组合数**。 不过 [494. 目标和](https://programmercarl.com/0494.目标和.html) 是 01背包,即每一类物品只有一个。
-dp[j] 就是所有的dp[j - coins[i]](考虑coins[i]的情况)相加。
+以下动规五部曲:
-所以递推公式:dp[j] += dp[j - coins[i]];
+### 1、确定dp数组以及下标的含义
-**这个递推公式大家应该不陌生了,我在讲解01背包题目的时候在这篇[494. 目标和](https://programmercarl.com/0494.目标和.html)中就讲解了,求装满背包有几种方法,公式都是:dp[j] += dp[j - nums[i]];**
+定义二维dp数值 dp[i][j]:使用 下标为[0, i]的coins[i]能够凑满j(包括j)这么大容量的包,有dp[i][j]种组合方法。
-3. dp数组如何初始化
+很多录友也会疑惑,凭什么上来就定义 dp数组,思考过程是什么样的, 这个思考过程我在 [01背包理论基础(二维数组)](https://programmercarl.com/背包理论基础01背包-1.html) 中的 “确定dp数组以及下标的含义” 有详细讲解。
-首先dp[0]一定要为1,dp[0] = 1是 递归公式的基础。如果dp[0] = 0 的话,后面所有推导出来的值都是0了。
+(**强烈建议按照代码随想录的顺序学习,否则可能看不懂我的讲解**)
-那么 dp[0] = 1 有没有含义,其实既可以说 凑成总金额0的货币组合数为1,也可以说 凑成总金额0的货币组合数为0,好像都没有毛病。
-但题目描述中,也没明确说 amount = 0 的情况,结果应该是多少。
+### 2、确定递推公式
-这里我认为题目描述还是要说明一下,因为后台测试数据是默认,amount = 0 的情况,组合数为1的。
+> **注意**: 这里的公式推导,与之前讲解过的 [494. 目标和](https://programmercarl.com/0494.目标和.html) 、[完全背包理论基础](https://programmercarl.com/背包问题理论基础完全背包.html) 有极大重复,所以我不在重复讲解原理,而是只讲解区别。
-下标非0的dp[j]初始化为0,这样累计加dp[j - coins[i]]的时候才不会影响真正的dp[j]
+我们再回顾一下,[01背包理论基础](https://programmercarl.com/背包理论基础01背包-1.html),中二维DP数组的递推公式为:
-dp[0]=1还说明了一种情况:如果正好选了coins[i]后,也就是j-coins[i] == 0的情况表示这个硬币刚好能选,此时dp[0]为1表示只选coins[i]存在这样的一种选法。
+`dp[i][j] = max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i - 1][j - weight[i]] + value[i])`
-4. 确定遍历顺序
+在 [完全背包理论基础](https://programmercarl.com/背包问题理论基础完全背包.html) 详细讲解了完全背包二维DP数组的递推公式为:
-本题中我们是外层for循环遍历物品(钱币),内层for遍历背包(金钱总额),还是外层for遍历背包(金钱总额),内层for循环遍历物品(钱币)呢?
+`dp[i][j] = max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - weight[i]] + value[i])`
+
+
+看去完全背包 和 01背包的差别在哪里?
+
+在于01背包是 `dp[i - 1][j - weight[i]] + value[i]` ,完全背包是 `dp[i][j - weight[i]] + value[i])`
+
+主要原因就是 完全背包单类物品有无限个。
+
+具体原因我在 [完全背包理论基础(二维)](https://programmercarl.com/背包问题理论基础完全背包.html) 的 「确定递推公式」有详细讲解,如果大家忘了,再回顾一下。
+
+我上面有说过,本题和 [494. 目标和](https://programmercarl.com/0494.目标和.html) 是一样的,唯一区别就是 [494. 目标和](https://programmercarl.com/0494.目标和.html) 是 01背包,本题是完全背包。
+
+
+在[494. 目标和](https://programmercarl.com/0494.目标和.html)中详解讲解了装满背包有几种方法,二维DP数组的递推公式:
+`dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j] + dp[i - 1][j - nums[i]]`
+
+所以本题递推公式:`dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j] + dp[i][j - nums[i]]` ,区别依然是 ` dp[i - 1][j - nums[i]]` 和 `dp[i][j - nums[i]]`
+
+这个 ‘所以’ 我省略了很多推导的内容,因为这些内容在 [494. 目标和](https://programmercarl.com/0494.目标和.html) 和 [完全背包理论基础](https://programmercarl.com/背包问题理论基础完全背包.html) 都详细讲过。
+
+这里不再重复讲解。
+
+大家主要疑惑点
+
+1、 `dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j] + dp[i][j - nums[i]]` 这个递归公式框架怎么来的,在 [494. 目标和](https://programmercarl.com/0494.目标和.html) 有详细讲解。
+
+2、为什么是 ` dp[i][j - nums[i]]` 而不是 ` dp[i - 1][j - nums[i]]` ,在[完全背包理论基础(二维)](https://programmercarl.com/背包问题理论基础完全背包.html) 有详细讲解
+
+
+### 3. dp数组如何初始化
+
+那么二维数组的最上行 和 最左列一定要初始化,这是递推公式推导的基础,如图红色部分:
+
+
+
+
+这里首先要关注的就是 dp[0][0] 应该是多少?
+
+背包空间为0,装满「物品0」 的组合数有多少呢?
+
+应该是 0 个, 但如果 「物品0」 的 数值就是0呢? 岂不是可以有无限个0 组合 和为0!
+
+题目描述中说了`1 <= coins.length <= 300` ,所以不用考虑 物品数值为0的情况。
+
+那么最上行dp[0][j] 如何初始化呢?
+
+dp[0][j]的含义:用「物品0」(即coins[0]) 装满 背包容量为j的背包,有几种组合方法。 (如果看不懂dp数组的含义,建议先学习[494. 目标和](https://programmercarl.com/0494.目标和.html))
+
+如果 j 可以整除 物品0,那么装满背包就有1种组合方法。
+
+初始化代码:
+```CPP
+for (int j = 0; j <= bagSize; j++) {
+ if (j % coins[0] == 0) dp[0][j] = 1;
+}
+```
+
+最左列如何初始化呢?
+
+dp[i][0] 的含义:用物品i(即coins[i]) 装满容量为0的背包 有几种组合方法。
+
+都有一种方法,即不装。
+
+所以 dp[i][0] 都初始化为1
+
+### 4. 确定遍历顺序
+
+二维DP数组的完全背包的两个for循环先后顺序是无所谓的。
-我在[动态规划:关于完全背包,你该了解这些!](https://programmercarl.com/背包问题理论基础完全背包.html)中讲解了完全背包的两个for循环的先后顺序都是可以的。
+先遍历背包,还是先遍历物品都是可以的。
+
+原理和 [01背包理论基础(二维数组)](https://programmercarl.com/背包理论基础01背包-1.html) 中的 「遍历顺序」是一样的,都是因为 两个for循环的先后顺序不影响 递推公式 所需要的数值。
+
+具体分析过程看 [01背包理论基础(二维数组)](https://programmercarl.com/背包理论基础01背包-1.html) 中的 「遍历顺序」
+
+### 5. 打印DP数组
+
+以amount为5,coins为:[2,3,5] 为例:
+
+dp数组应该是这样的:
+
+```
+1 0 1 0 1 0
+1 0 1 1 1 1
+1 0 1 1 1 2
+```
+
+### 代码实现:
+
+```CPP
+class Solution {
+public:
+ int change(int amount, vector& coins) {
+ int bagSize = amount;
+
+ vector> dp(coins.size(), vector(bagSize + 1, 0));
+
+ // 初始化最上行
+ for (int j = 0; j <= bagSize; j++) {
+ if (j % coins[0] == 0) dp[0][j] = 1;
+ }
+ // 初始化最左列
+ for (int i = 0; i < coins.size(); i++) {
+ dp[i][0] = 1;
+ }
+ // 以下遍历顺序行列可以颠倒
+ for (int i = 1; i < coins.size(); i++) { // 行,遍历物品
+ for (int j = 0; j <= bagSize; j++) { // 列,遍历背包
+ if (coins[i] > j) dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j];
+ else dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j] + dp[i][j - coins[i]];
+ }
+ }
+ return dp[coins.size() - 1][bagSize];
+ }
+};
+```
+
+## 一维dp讲解
+
+### 1、确定dp数组以及下标的含义
+
+dp[j]:凑成总金额j的货币组合数为dp[j]
+
+### 2、确定递推公式
+
+本题 二维dp 递推公式: `dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j] + dp[i][j - coins[i]]`
+
+压缩成一维:`dp[j] += dp[j - coins[i]]`
+
+这个递推公式大家应该不陌生了,我在讲解01背包题目的时候在这篇[494. 目标和](https://programmercarl.com/0494.目标和.html)中就讲解了,求装满背包有几种方法,公式都是:`dp[j] += dp[j - nums[i]]`
+
+### 3. dp数组如何初始化
+
+装满背包容量为0 的方法是1,即不放任何物品,`dp[0] = 1`
+
+### 4. 确定遍历顺序
+
+
+本题中我们是外层for循环遍历物品(钱币),内层for遍历背包(金钱总额),还是外层for遍历背包(金钱总额),内层for循环遍历物品(钱币)呢?
+
+我在[完全背包(一维DP)](./背包问题完全背包一维.md)中讲解了完全背包的两个for循环的先后顺序都是可以的。
**但本题就不行了!**
@@ -116,7 +254,7 @@ dp[0]=1还说明了一种情况:如果正好选了coins[i]后,也就是j-coi
所以纯完全背包是能凑成总和就行,不用管怎么凑的。
-本题是求凑出来的方案个数,且每个方案个数是为组合数。
+本题是求凑出来的方案个数,且每个方案个数是组合数。
那么本题,两个for循环的先后顺序可就有说法了。
@@ -154,11 +292,11 @@ for (int j = 0; j <= amount; j++) { // 遍历背包容量
可能这里很多同学还不是很理解,**建议动手把这两种方案的dp数组数值变化打印出来,对比看一看!(实践出真知)**
-5. 举例推导dp数组
+### 5. 举例推导dp数组
输入: amount = 5, coins = [1, 2, 5] ,dp状态图如下:
-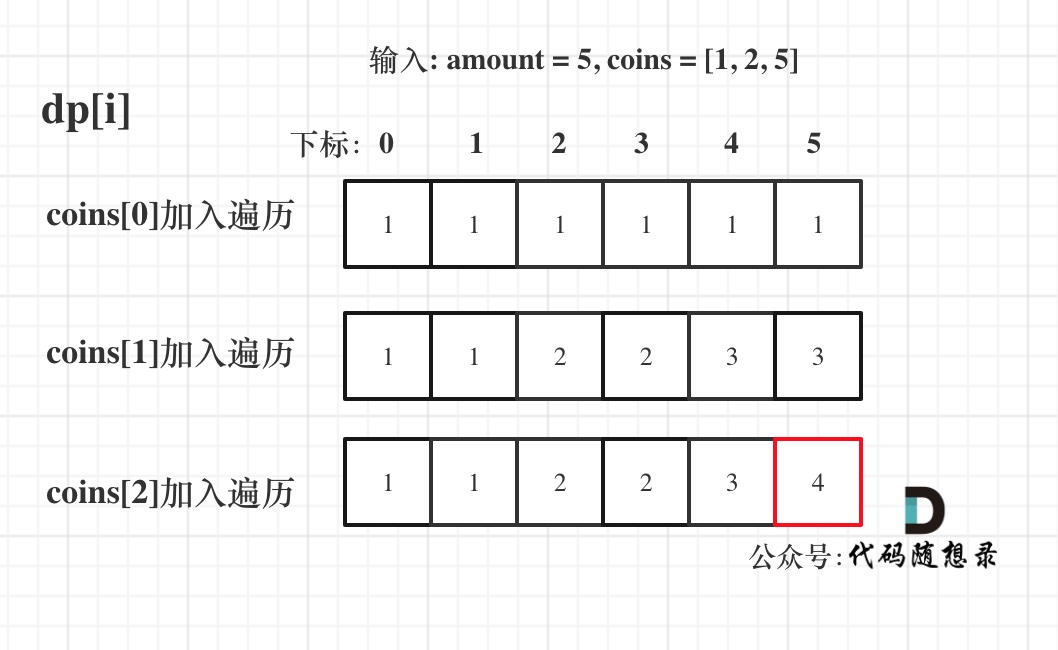
+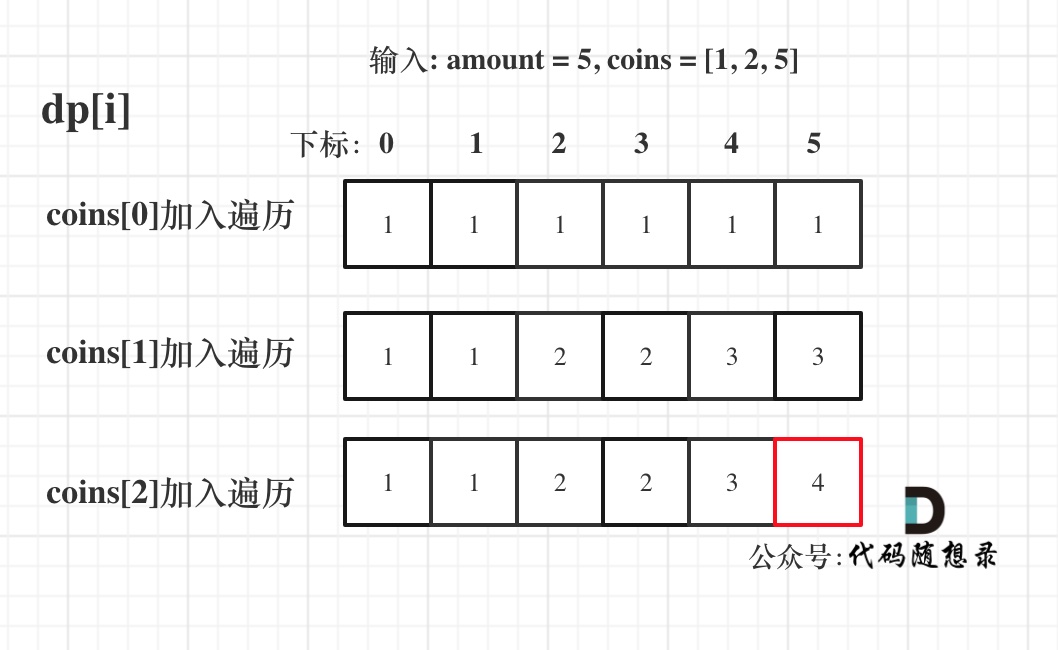
最后红色框dp[amount]为最终结果。
@@ -168,27 +306,57 @@ for (int j = 0; j <= amount; j++) { // 遍历背包容量
class Solution {
public:
int change(int amount, vector& coins) {
- vector dp(amount + 1, 0);
- dp[0] = 1;
+ vector dp(amount + 1, 0); // 防止相加数据超int
+ dp[0] = 1; // 只有一种方式达到0
for (int i = 0; i < coins.size(); i++) { // 遍历物品
for (int j = coins[i]; j <= amount; j++) { // 遍历背包
dp[j] += dp[j - coins[i]];
}
}
- return dp[amount];
+ return dp[amount]; // 返回组合数
}
};
```
+C++测试用例有两个数相加超过int的数据,所以需要在if里加上dp[i] < INT_MAX - dp[i - num]。
+
* 时间复杂度: O(mn),其中 m 是amount,n 是 coins 的长度
* 空间复杂度: O(m)
+为了防止相加的数据 超int 也可以这么写:
+
+```CPP
+class Solution {
+public:
+ int change(int amount, vector& coins) {
+ vector dp(amount + 1, 0);
+ dp[0] = 1; // 只有一种方式达到0
+ for (int i = 0; i < coins.size(); i++) { // 遍历物品
+ for (int j = coins[i]; j <= amount; j++) { // 遍历背包
+ if (dp[j] < INT_MAX - dp[j - coins[i]]) { //防止相加数据超int
+ dp[j] += dp[j - coins[i]];
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return dp[amount]; // 返回组合数
+ }
+};
+```
-是不是发现代码如此精简
## 总结
-本题的递推公式,其实我们在[494. 目标和](https://programmercarl.com/0494.目标和.html)中就已经讲过了,**而难点在于遍历顺序!**
+本题我们从 二维 分析到 一维。
+
+大家在刚开始学习的时候,从二维开始学习 容易理解。
+
+之后,推荐大家直接掌握一维的写法,熟练后更容易写出来。
+
+本题中,二维dp主要是就要 想清楚和我们之前讲解的 [01背包理论基础](https://programmercarl.com/背包理论基础01背包-1.html)、[494. 目标和](https://programmercarl.com/0494.目标和.html)、 [完全背包理论基础](https://programmercarl.com/背包问题理论基础完全背包.html) 联系与区别。
+
+这也是代码随想录安排刷题顺序的精髓所在。
+
+本题的一维dp中,难点在于理解便利顺序。
在求装满背包有几种方案的时候,认清遍历顺序是非常关键的。
@@ -196,8 +364,7 @@ public:
**如果求排列数就是外层for遍历背包,内层for循环遍历物品**。
-可能说到排列数录友们已经有点懵了,后面Carl还会安排求排列数的题目,到时候在对比一下,大家就会发现神奇所在!
-
+可能说到排列数录友们已经有点懵了,后面我还会安排求排列数的题目,到时候在对比一下,大家就会发现神奇所在!
## 其他语言版本
@@ -268,6 +435,7 @@ class Solution:
### Go:
+一维dp
```go
func change(amount int, coins []int) int {
// 定义dp数组
@@ -286,6 +454,29 @@ func change(amount int, coins []int) int {
return dp[amount]
}
```
+二维dp
+```go
+func change(amount int, coins []int) int {
+ dp := make([][]int, len(coins))
+ for i := range dp {
+ dp[i] = make([]int, amount + 1)
+ dp[i][0] = 1
+ }
+ for j := coins[0]; j <= amount; j++ {
+ dp[0][j] += dp[0][j-coins[0]]
+ }
+ for i := 1; i < len(coins); i++ {
+ for j := 1; j <= amount; j++ {
+ if j < coins[i] {
+ dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j]
+ } else {
+ dp[i][j] = dp[i][j-coins[i]] + dp[i-1][j]
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return dp[len(coins)-1][amount]
+}
+```
### Rust:
@@ -305,7 +496,7 @@ impl Solution {
}
```
-### Javascript:
+### JavaScript:
```javascript
const change = (amount, coins) => {
@@ -353,7 +544,28 @@ object Solution {
}
}
```
+### C
+
+```c
+int change(int amount, int* coins, int coinsSize) {
+ int dp[amount + 1];
+ memset(dp, 0, sizeof (dp));
+ dp[0] = 1;
+ // 遍历物品
+ for(int i = 0; i < coinsSize; i++){
+ // 遍历背包
+ for(int j = coins[i]; j <= amount; j++){
+ dp[j] += dp[j - coins[i]];
+ }
+ }
+ return dp[amount];
+}
+```
+
+
+
### C#
+
```csharp
public class Solution
{
@@ -374,7 +586,4 @@ public class Solution
}
```
-
-
-  -
+
diff --git "a/problems/0530.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\260\217\347\273\235\345\257\271\345\267\256.md" "b/problems/0530.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\260\217\347\273\235\345\257\271\345\267\256.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 82b3f5d4e9..a8eca862ef
--- "a/problems/0530.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\260\217\347\273\235\345\257\271\345\267\256.md"
+++ "b/problems/0530.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\260\217\347\273\235\345\257\271\345\267\256.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+
diff --git "a/problems/0530.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\260\217\347\273\235\345\257\271\345\267\256.md" "b/problems/0530.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\260\217\347\273\235\345\257\271\345\267\256.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 82b3f5d4e9..a8eca862ef
--- "a/problems/0530.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\260\217\347\273\235\345\257\271\345\267\256.md"
+++ "b/problems/0530.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\260\217\347\273\235\345\257\271\345\267\256.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
> 利用二叉搜索树的特性搞起!
@@ -15,13 +13,13 @@
示例:
-
+
提示:树中至少有 2 个节点。
## 算法公开课
-**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[二叉搜索树中,需要掌握如何双指针遍历!| LeetCode:530.二叉搜索树的最小绝对差](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1DD4y11779),相信结合视频在看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
+**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[二叉搜索树中,需要掌握如何双指针遍历!| LeetCode:530.二叉搜索树的最小绝对差](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1DD4y11779),相信结合视频再看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
## 思路
@@ -72,7 +70,7 @@ public:
如图:
-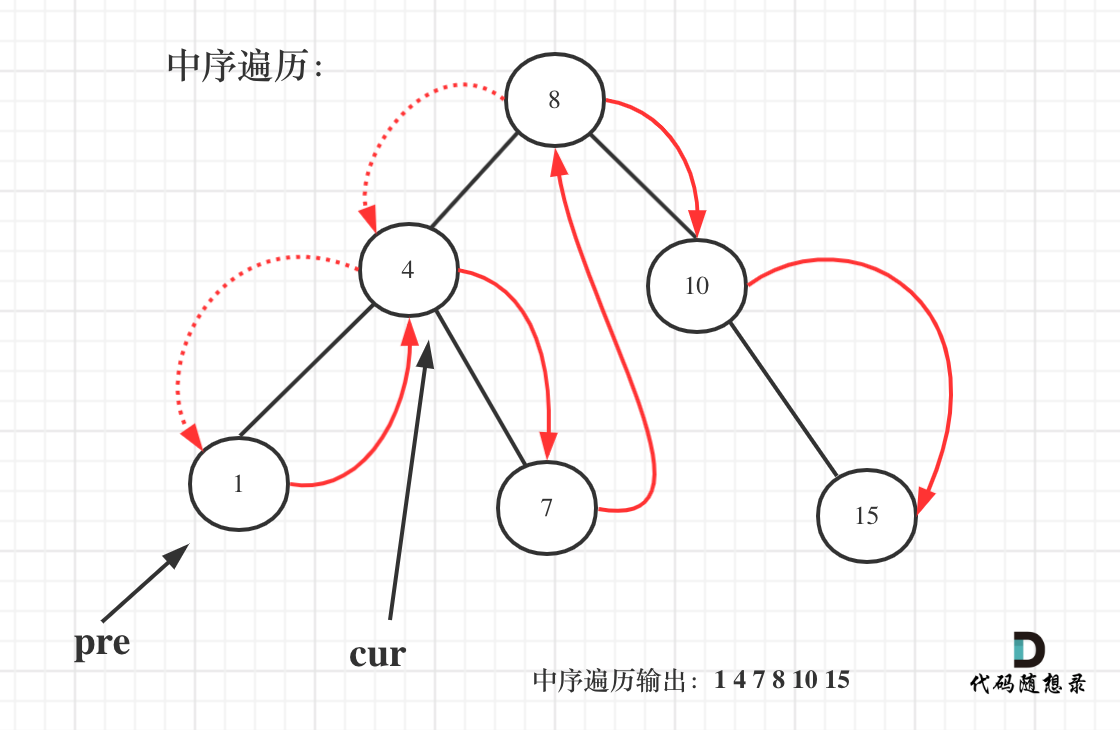
+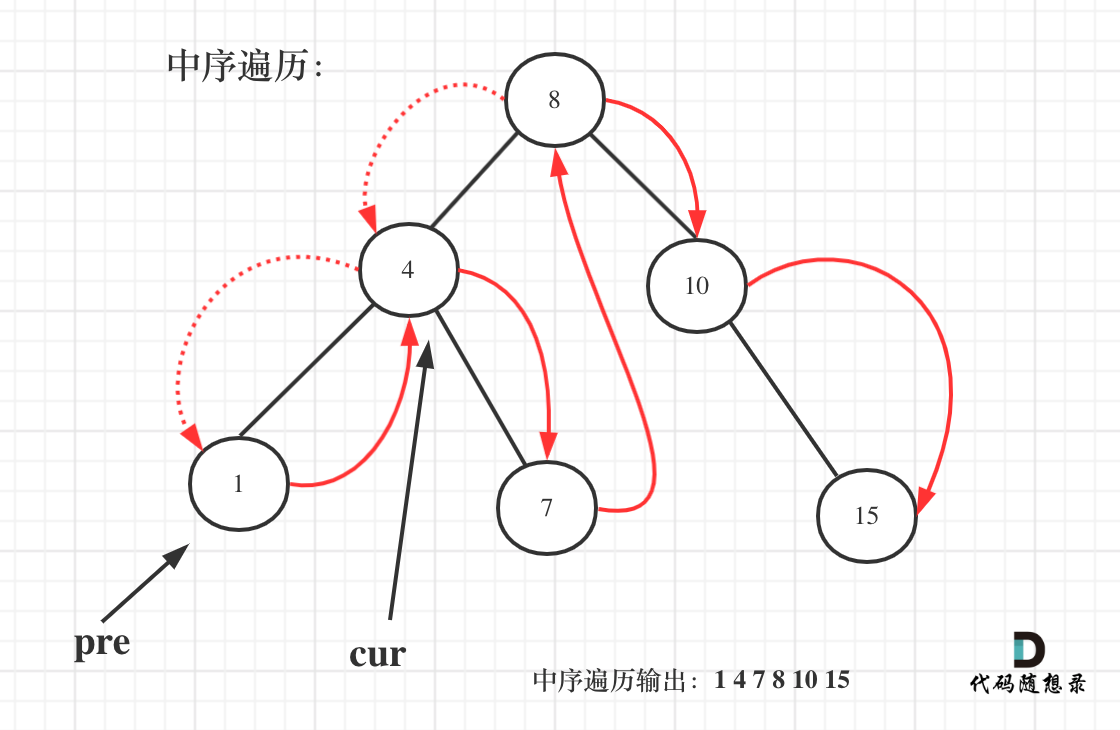
一些同学不知道在递归中如何记录前一个节点的指针,其实实现起来是很简单的,大家只要看过一次,写过一次,就掌握了。
@@ -153,23 +151,27 @@ public:
递归
```java
class Solution {
- TreeNode pre;// 记录上一个遍历的结点
+ TreeNode pre; // 记录上一个遍历的结点
int result = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
+
public int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode root) {
- if(root==null)return 0;
- traversal(root);
- return result;
+ if (root == null)
+ return 0;
+ traversal(root);
+ return result;
}
- public void traversal(TreeNode root){
- if(root==null)return;
- //左
+
+ public void traversal(TreeNode root) {
+ if (root == null)
+ return;
+ // 左
traversal(root.left);
- //中
- if(pre!=null){
- result = Math.min(result,root.val-pre.val);
+ // 中
+ if (pre != null) {
+ result = Math.min(result, root.val - pre.val);
}
pre = root;
- //右
+ // 右
traversal(root.right);
}
}
@@ -182,22 +184,27 @@ class Solution {
TreeNode pre = null;
int result = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
- if(root != null)
+ if (root != null)
stack.add(root);
- while(!stack.isEmpty()){
+
+ // 中序遍历(左中右),由于栈先入后出,反序(右中左)
+ while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode curr = stack.peek();
- if(curr != null){
+ if (curr != null) {
stack.pop();
- if(curr.right != null)
+ // 右
+ if (curr.right != null)
stack.add(curr.right);
+ // 中(先用null标记)
stack.add(curr);
stack.add(null);
- if(curr.left != null)
+ // 左
+ if (curr.left != null)
stack.add(curr.left);
- }else{
+ } else { // 中(遇到null再处理)
stack.pop();
TreeNode temp = stack.pop();
- if(pre != null)
+ if (pre != null)
result = Math.min(result, temp.val - pre.val);
pre = temp;
}
@@ -669,8 +676,5 @@ public class Solution
}
```
-
-
-  -
+
diff --git "a/problems/0538.\346\212\212\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\350\275\254\346\215\242\344\270\272\347\264\257\345\212\240\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0538.\346\212\212\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\350\275\254\346\215\242\344\270\272\347\264\257\345\212\240\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 7fcb5efd32..c4bfeae4b8
--- "a/problems/0538.\346\212\212\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\350\275\254\346\215\242\344\270\272\347\264\257\345\212\240\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0538.\346\212\212\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\350\275\254\346\215\242\344\270\272\347\264\257\345\212\240\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+
diff --git "a/problems/0538.\346\212\212\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\350\275\254\346\215\242\344\270\272\347\264\257\345\212\240\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0538.\346\212\212\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\350\275\254\346\215\242\344\270\272\347\264\257\345\212\240\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 7fcb5efd32..c4bfeae4b8
--- "a/problems/0538.\346\212\212\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\350\275\254\346\215\242\344\270\272\347\264\257\345\212\240\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0538.\346\212\212\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\350\275\254\346\215\242\344\270\272\347\264\257\345\212\240\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 538.把二叉搜索树转换为累加树
@@ -20,7 +18,7 @@
示例 1:
-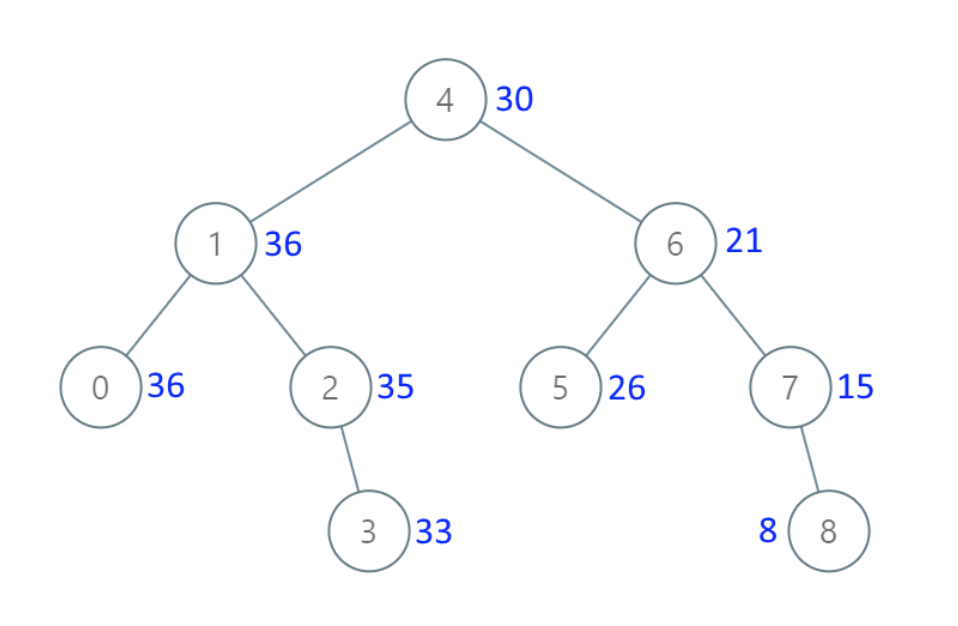
+
* 输入:[4,1,6,0,2,5,7,null,null,null,3,null,null,null,8]
* 输出:[30,36,21,36,35,26,15,null,null,null,33,null,null,null,8]
@@ -69,7 +67,7 @@
遍历顺序如图所示:
-
+
本题依然需要一个pre指针记录当前遍历节点cur的前一个节点,这样才方便做累加。
@@ -548,8 +546,4 @@ public class Solution
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0541.\345\217\215\350\275\254\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262II.md" "b/problems/0541.\345\217\215\350\275\254\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 80e662f9dd..d5ad95c112
--- "a/problems/0541.\345\217\215\350\275\254\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0541.\345\217\215\350\275\254\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262II.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0541.\345\217\215\350\275\254\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262II.md" "b/problems/0541.\345\217\215\350\275\254\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 80e662f9dd..d5ad95c112
--- "a/problems/0541.\345\217\215\350\275\254\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0541.\345\217\215\350\275\254\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262II.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
@@ -37,10 +35,10 @@
因为要找的也就是每2 * k 区间的起点,这样写,程序会高效很多。
-**所以当需要固定规律一段一段去处理字符串的时候,要想想在在for循环的表达式上做做文章。**
+**所以当需要固定规律一段一段去处理字符串的时候,要想想在for循环的表达式上做做文章。**
性能如下:
- +
+ 那么这里具体反转的逻辑我们要不要使用库函数呢,其实用不用都可以,使用reverse来实现反转也没毛病,毕竟不是解题关键部分。
@@ -282,7 +280,7 @@ class Solution:
return ''.join(res)
```
-### Python3 (v2):
+#### Python3 (v2):
```python
class Solution:
@@ -297,6 +295,21 @@ class Solution:
return s
```
+#### Python3 (v3):
+
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def reverseStr(self, s: str, k: int) -> str:
+ i = 0
+ chars = list(s)
+
+ while i < len(chars):
+ chars[i:i + k] = chars[i:i + k][::-1] # 反转后,更改原值为反转后值
+ i += k * 2
+
+ return ''.join(chars)
+```
+
### Go:
```go
@@ -501,7 +514,4 @@ impl Solution {
}
```
-
那么这里具体反转的逻辑我们要不要使用库函数呢,其实用不用都可以,使用reverse来实现反转也没毛病,毕竟不是解题关键部分。
@@ -282,7 +280,7 @@ class Solution:
return ''.join(res)
```
-### Python3 (v2):
+#### Python3 (v2):
```python
class Solution:
@@ -297,6 +295,21 @@ class Solution:
return s
```
+#### Python3 (v3):
+
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def reverseStr(self, s: str, k: int) -> str:
+ i = 0
+ chars = list(s)
+
+ while i < len(chars):
+ chars[i:i + k] = chars[i:i + k][::-1] # 反转后,更改原值为反转后值
+ i += k * 2
+
+ return ''.join(chars)
+```
+
### Go:
```go
@@ -501,7 +514,4 @@ impl Solution {
}
```
-
-
-  -
+
diff --git "a/problems/0583.\344\270\244\344\270\252\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262\347\232\204\345\210\240\351\231\244\346\223\215\344\275\234.md" "b/problems/0583.\344\270\244\344\270\252\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262\347\232\204\345\210\240\351\231\244\346\223\215\344\275\234.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 7dbb8ef542..8208d9a1eb
--- "a/problems/0583.\344\270\244\344\270\252\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262\347\232\204\345\210\240\351\231\244\346\223\215\344\275\234.md"
+++ "b/problems/0583.\344\270\244\344\270\252\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262\347\232\204\345\210\240\351\231\244\346\223\215\344\275\234.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+
diff --git "a/problems/0583.\344\270\244\344\270\252\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262\347\232\204\345\210\240\351\231\244\346\223\215\344\275\234.md" "b/problems/0583.\344\270\244\344\270\252\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262\347\232\204\345\210\240\351\231\244\346\223\215\344\275\234.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 7dbb8ef542..8208d9a1eb
--- "a/problems/0583.\344\270\244\344\270\252\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262\347\232\204\345\210\240\351\231\244\346\223\215\344\275\234.md"
+++ "b/problems/0583.\344\270\244\344\270\252\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262\347\232\204\345\210\240\351\231\244\346\223\215\344\275\234.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 583. 两个字符串的删除操作
@@ -33,7 +31,7 @@
dp[i][j]:以i-1为结尾的字符串word1,和以j-1位结尾的字符串word2,想要达到相等,所需要删除元素的最少次数。
-这里dp数组的定义有点点绕,大家要撸清思路。
+这里dp数组的定义有点点绕,大家要理清思路。
2. 确定递推公式
@@ -83,7 +81,7 @@ for (int j = 0; j <= word2.size(); j++) dp[0][j] = j;
以word1:"sea",word2:"eat"为例,推导dp数组状态图如下:
-
+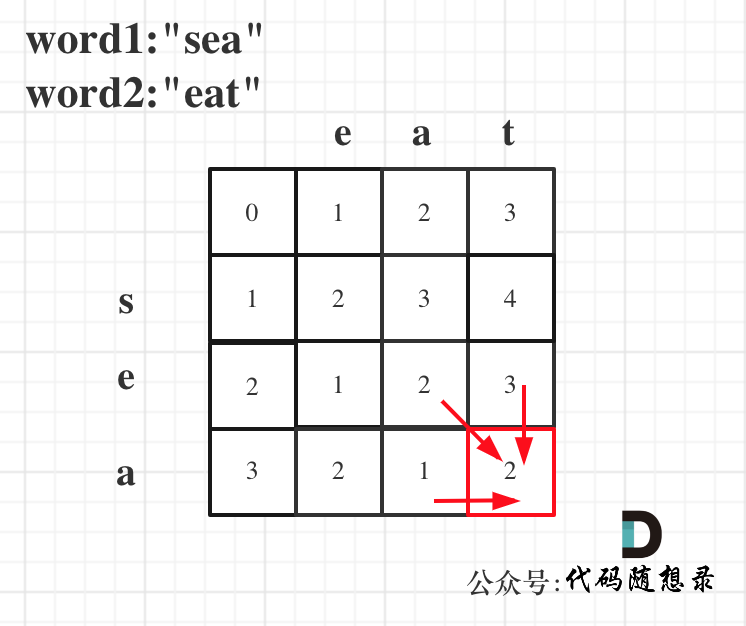
以上分析完毕,代码如下:
@@ -234,8 +232,29 @@ class Solution:
return dp[-1][-1]
```
+> 版本 2
+
+```python
+class Solution(object):
+ def minDistance(self, word1, word2):
+ m, n = len(word1), len(word2)
+
+ # dp 求解两字符串最长公共子序列
+ dp = [[0] * (n+1) for _ in range(m+1)]
+ for i in range(1, m+1):
+ for j in range(1, n+1):
+ if word1[i-1] == word2[j-1]:
+ dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + 1
+ else:
+ dp[i][j] = max(dp[i-1][j], dp[i][j-1])
+
+ # 删去最长公共子序列以外元素
+ return m + n - 2 * dp[-1][-1]
+```
### Go:
+动态规划一
+
```go
func minDistance(word1 string, word2 string) int {
dp := make([][]int, len(word1)+1)
@@ -268,7 +287,39 @@ func min(a, b int) int {
return b
}
```
-### Javascript:
+
+
+动态规划二
+
+```go
+func minDistance(word1 string, word2 string) int {
+ dp := make([][]int, len(word1) + 1)
+ for i := range dp {
+ dp[i] = make([]int, len(word2) + 1)
+ }
+ for i := 1; i <= len(word1); i++ {
+ for j := 1; j <= len(word2); j++ {
+ if word1[i-1] == word2[j-1] {
+ dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + 1
+ } else {
+ dp[i][j] = max(dp[i-1][j], dp[i][j-1])
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return len(word1) + len(word2) - dp[len(word1)][len(word2)] * 2
+}
+
+func max(x, y int) int {
+ if x > y {
+ return x
+ }
+ return y
+}
+```
+
+
+### JavaScript:
+
```javascript
// 方法一
@@ -417,7 +468,3 @@ impl Solution {
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0617.\345\220\210\345\271\266\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0617.\345\220\210\345\271\266\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 3478a2af5d..3ca5feb9da
--- "a/problems/0617.\345\220\210\345\271\266\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0617.\345\220\210\345\271\266\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0617.\345\220\210\345\271\266\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0617.\345\220\210\345\271\266\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 3478a2af5d..3ca5feb9da
--- "a/problems/0617.\345\220\210\345\271\266\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0617.\345\220\210\345\271\266\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 617.合并二叉树
@@ -15,7 +13,7 @@
示例 1:
-
+
注意: 合并必须从两个树的根节点开始。
@@ -40,7 +38,7 @@
动画如下:
-
+
那么我们来按照递归三部曲来解决:
@@ -803,8 +801,4 @@ public TreeNode MergeTrees(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2)
}
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0647.\345\233\236\346\226\207\345\255\220\344\270\262.md" "b/problems/0647.\345\233\236\346\226\207\345\255\220\344\270\262.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index d94d18c5c0..fd2ae43886
--- "a/problems/0647.\345\233\236\346\226\207\345\255\220\344\270\262.md"
+++ "b/problems/0647.\345\233\236\346\226\207\345\255\220\344\270\262.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0647.\345\233\236\346\226\207\345\255\220\344\270\262.md" "b/problems/0647.\345\233\236\346\226\207\345\255\220\344\270\262.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index d94d18c5c0..fd2ae43886
--- "a/problems/0647.\345\233\236\346\226\207\345\255\220\344\270\262.md"
+++ "b/problems/0647.\345\233\236\346\226\207\345\255\220\344\270\262.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 647. 回文子串
@@ -50,12 +48,12 @@ dp[i] 和 dp[i-1] ,dp[i + 1] 看上去都没啥关系。
所以我们要看回文串的性质。 如图:
-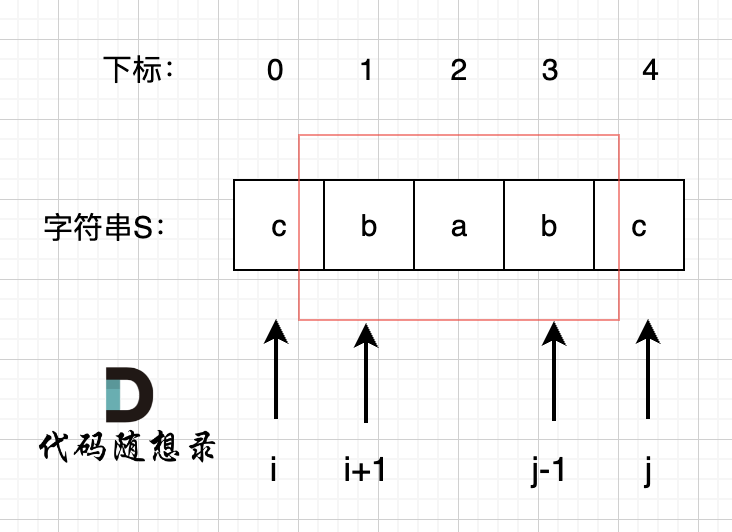
+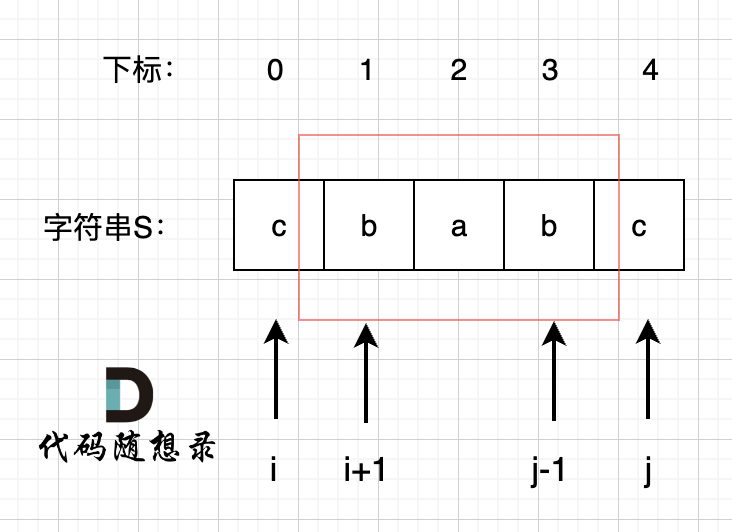
我们在判断字符串S是否是回文,那么如果我们知道 s[1],s[2],s[3] 这个子串是回文的,那么只需要比较 s[0]和s[4]这两个元素是否相同,如果相同的话,这个字符串s 就是回文串。
-那么此时我们是不是能找到一种递归关系,也就是判断一个子字符串(字符串的下表范围[i,j])是否回文,依赖于,子字符串(下表范围[i + 1, j - 1])) 是否是回文。
+那么此时我们是不是能找到一种递归关系,也就是判断一个子字符串(字符串下标范围[i,j])是否回文,依赖于,子字符串(下标范围[i + 1, j - 1])) 是否是回文。
所以为了明确这种递归关系,我们的dp数组是要定义成一位二维dp数组。
@@ -102,13 +100,13 @@ dp[i][j]可以初始化为true么? 当然不行,怎能刚开始就全都匹
4. 确定遍历顺序
-遍历顺序可有有点讲究了。
+遍历顺序可就有点讲究了。
首先从递推公式中可以看出,情况三是根据dp[i + 1][j - 1]是否为true,在对dp[i][j]进行赋值true的。
dp[i + 1][j - 1] 在 dp[i][j]的左下角,如图:
-
+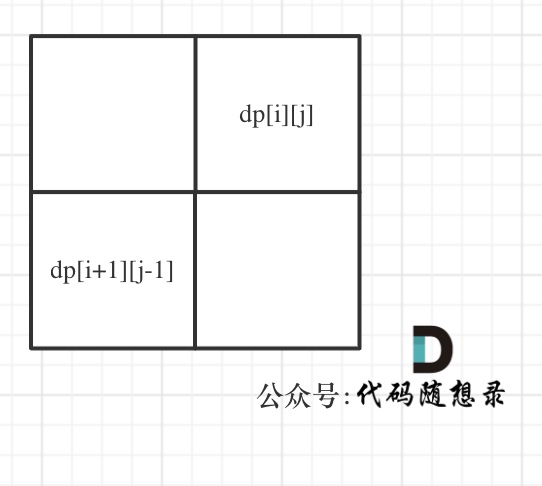
如果这矩阵是从上到下,从左到右遍历,那么会用到没有计算过的dp[i + 1][j - 1],也就是根据不确定是不是回文的区间[i+1,j-1],来判断了[i,j]是不是回文,那结果一定是不对的。
@@ -138,7 +136,7 @@ for (int i = s.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) { // 注意遍历顺序
举例,输入:"aaa",dp[i][j]状态如下:
-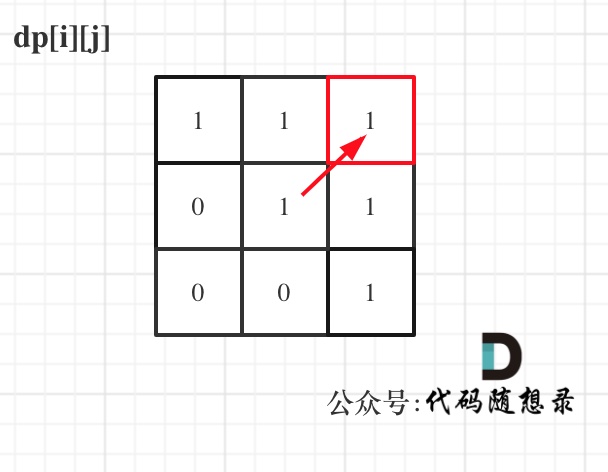
+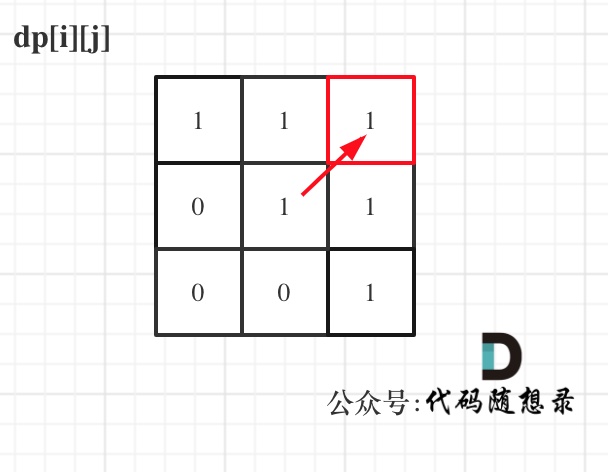
图中有6个true,所以就是有6个回文子串。
@@ -397,6 +395,7 @@ class Solution:
```
### Go:
+> 动态规划:
```Go
func countSubstrings(s string) int {
@@ -422,8 +421,49 @@ func countSubstrings(s string) int {
return res
}
```
+> 动态规划:简洁版
+```Go
+func countSubstrings(s string) int {
+ res := 0
+ dp := make([][]bool, len(s))
+ for i := 0; i < len(s); i++ {
+ dp[i] = make([]bool, len(s))
+ }
+
+ for i := len(s) - 1; i >= 0; i-- {
+ for j := i; j < len(s); j++ {
+ if s[i] == s[j] && (j-i <= 1 || dp[i+1][j-1]) {
+ res++
+ dp[i][j] = true
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return res
+}
+```
+
+> 双指针法:
+```Go
+func countSubstrings(s string) int {
+ extend := func(i, j int) int {
+ res := 0
+ for i >= 0 && j < len(s) && s[i] == s[j] {
+ i --
+ j ++
+ res ++
+ }
+ return res
+ }
+ res := 0
+ for i := 0; i < len(s); i++ {
+ res += extend(i, i) // 以i为中心
+ res += extend(i, i+1) // 以i和i+1为中心
+ }
+ return res
+}
+```
-### Javascript:
+### JavaScript:
> 动态规划
```javascript
@@ -571,7 +611,3 @@ impl Solution {
}
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0649.Dota2\345\217\202\350\256\256\351\231\242.md" "b/problems/0649.Dota2\345\217\202\350\256\256\351\231\242.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index db6b43df8e..e77070fcf8
--- "a/problems/0649.Dota2\345\217\202\350\256\256\351\231\242.md"
+++ "b/problems/0649.Dota2\345\217\202\350\256\256\351\231\242.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0649.Dota2\345\217\202\350\256\256\351\231\242.md" "b/problems/0649.Dota2\345\217\202\350\256\256\351\231\242.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index db6b43df8e..e77070fcf8
--- "a/problems/0649.Dota2\345\217\202\350\256\256\351\231\242.md"
+++ "b/problems/0649.Dota2\345\217\202\350\256\256\351\231\242.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
@@ -283,8 +281,4 @@ function predictPartyVictory(senate: string): string {
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0654.\346\234\200\345\244\247\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0654.\346\234\200\345\244\247\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index f54558a68c..49ccc9cdea
--- "a/problems/0654.\346\234\200\345\244\247\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0654.\346\234\200\345\244\247\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0654.\346\234\200\345\244\247\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0654.\346\234\200\345\244\247\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index f54558a68c..49ccc9cdea
--- "a/problems/0654.\346\234\200\345\244\247\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0654.\346\234\200\345\244\247\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 654.最大二叉树
@@ -19,7 +17,7 @@
示例 :
-
+
提示:
@@ -34,7 +32,7 @@
最大二叉树的构建过程如下:
-
+
构造树一般采用的是前序遍历,因为先构造中间节点,然后递归构造左子树和右子树。
@@ -598,8 +596,4 @@ public TreeNode ConstructMaximumBinaryTree(int[] nums)
}
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0657.\346\234\272\345\231\250\344\272\272\350\203\275\345\220\246\350\277\224\345\233\236\345\216\237\347\202\271.md" "b/problems/0657.\346\234\272\345\231\250\344\272\272\350\203\275\345\220\246\350\277\224\345\233\236\345\216\237\347\202\271.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index ef58739122..c1706df4fa
--- "a/problems/0657.\346\234\272\345\231\250\344\272\272\350\203\275\345\220\246\350\277\224\345\233\236\345\216\237\347\202\271.md"
+++ "b/problems/0657.\346\234\272\345\231\250\344\272\272\350\203\275\345\220\246\350\277\224\345\233\236\345\216\237\347\202\271.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0657.\346\234\272\345\231\250\344\272\272\350\203\275\345\220\246\350\277\224\345\233\236\345\216\237\347\202\271.md" "b/problems/0657.\346\234\272\345\231\250\344\272\272\350\203\275\345\220\246\350\277\224\345\233\236\345\216\237\347\202\271.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index ef58739122..c1706df4fa
--- "a/problems/0657.\346\234\272\345\231\250\344\272\272\350\203\275\345\220\246\350\277\224\345\233\236\345\216\237\347\202\271.md"
+++ "b/problems/0657.\346\234\272\345\231\250\344\272\272\350\203\275\345\220\246\350\277\224\345\233\236\345\216\237\347\202\271.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 657. 机器人能否返回原点
@@ -42,7 +40,7 @@
最后判断一下x,y是否回到了(0, 0)位置就可以了。
如图所示:
- +
+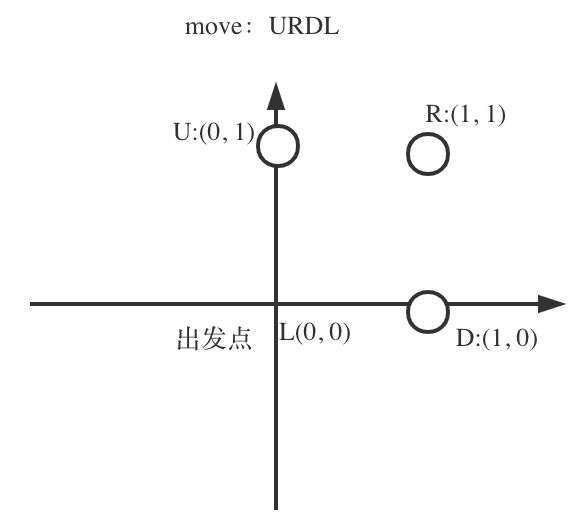 C++代码如下:
@@ -181,8 +179,4 @@ var judgeCircle = function (moves) {
```
-
C++代码如下:
@@ -181,8 +179,4 @@ var judgeCircle = function (moves) {
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0669.\344\277\256\345\211\252\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0669.\344\277\256\345\211\252\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 916013c52c..dbcc6ed63d
--- "a/problems/0669.\344\277\256\345\211\252\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0669.\344\277\256\345\211\252\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0669.\344\277\256\345\211\252\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0669.\344\277\256\345\211\252\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 916013c52c..dbcc6ed63d
--- "a/problems/0669.\344\277\256\345\211\252\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0669.\344\277\256\345\211\252\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
@@ -16,13 +14,13 @@
给定一个二叉搜索树,同时给定最小边界L 和最大边界 R。通过修剪二叉搜索树,使得所有节点的值在[L, R]中 (R>=L) 。你可能需要改变树的根节点,所以结果应当返回修剪好的二叉搜索树的新的根节点。
-
+
-
+
## 算法公开课
-**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[你修剪的方式不对,我来给你纠正一下!| LeetCode:669. 修剪二叉搜索树](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV17P41177ud?share_source=copy_web),相信结合视频在看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
+**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[你修剪的方式不对,我来给你纠正一下!| LeetCode:669. 修剪二叉搜索树](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV17P41177ud?share_source=copy_web),相信结合视频再看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
## 思路
@@ -52,7 +50,7 @@ public:
我们在重新关注一下第二个示例,如图:
-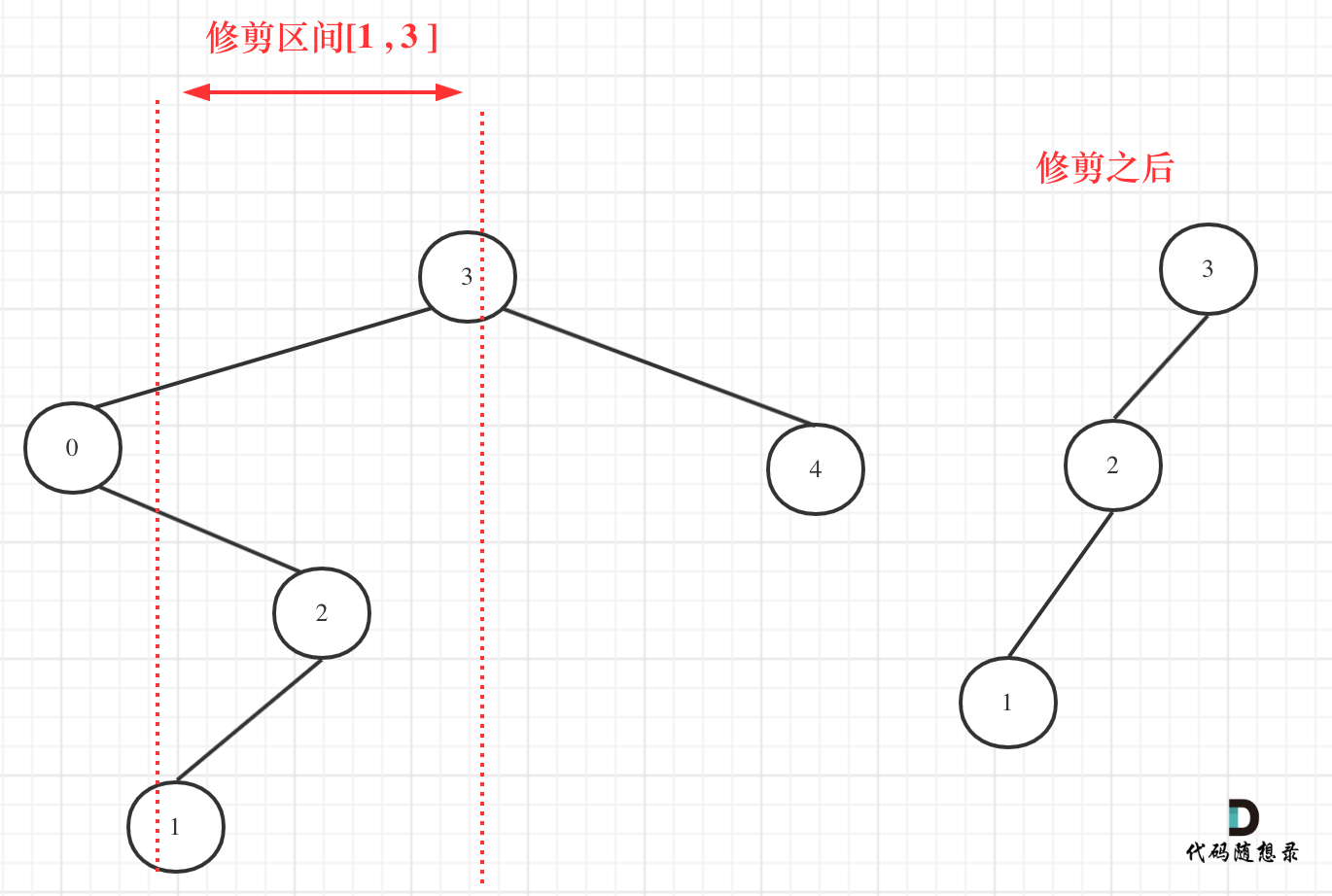
+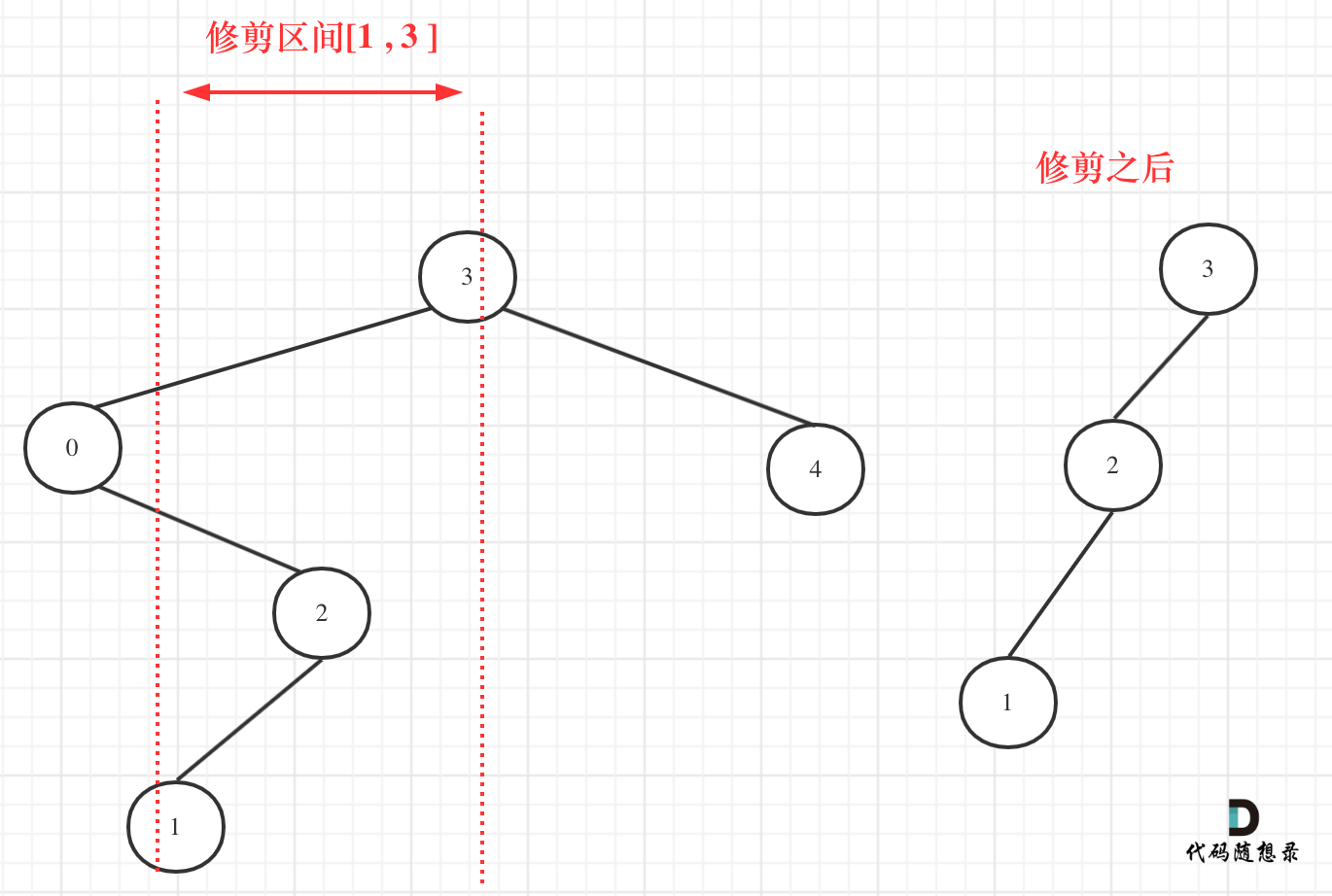
**所以以上的代码是不可行的!**
@@ -62,7 +60,7 @@ public:
在上图中我们发现节点0并不符合区间要求,那么将节点0的右孩子 节点2 直接赋给 节点3的左孩子就可以了(就是把节点0从二叉树中移除),如图:
-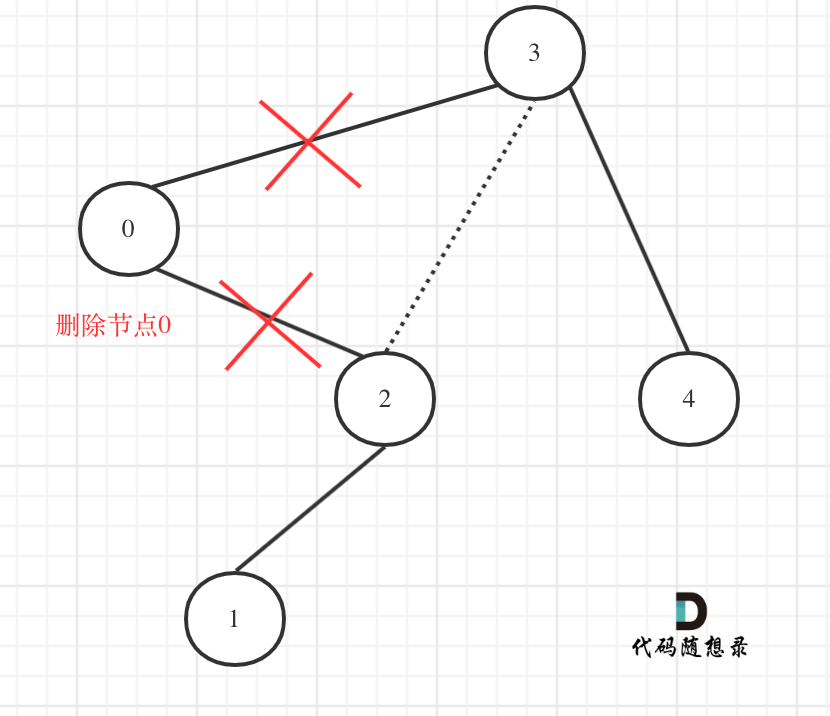
+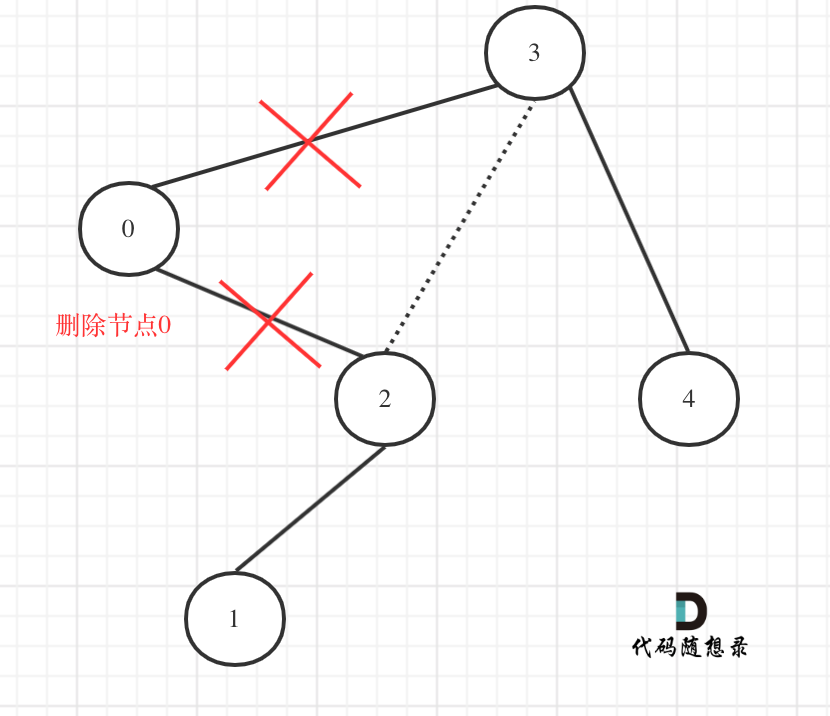
理解了最关键部分了我们再递归三部曲:
@@ -79,7 +77,7 @@ public:
代码如下:
-```
+```cpp
TreeNode* trimBST(TreeNode* root, int low, int high)
```
@@ -87,7 +85,7 @@ TreeNode* trimBST(TreeNode* root, int low, int high)
修剪的操作并不是在终止条件上进行的,所以就是遇到空节点返回就可以了。
-```
+```cpp
if (root == nullptr ) return nullptr;
```
@@ -97,7 +95,7 @@ if (root == nullptr ) return nullptr;
代码如下:
-```
+```cpp
if (root->val < low) {
TreeNode* right = trimBST(root->right, low, high); // 寻找符合区间[low, high]的节点
return right;
@@ -108,7 +106,7 @@ if (root->val < low) {
代码如下:
-```
+```cpp
if (root->val > high) {
TreeNode* left = trimBST(root->left, low, high); // 寻找符合区间[low, high]的节点
return left;
@@ -119,7 +117,7 @@ if (root->val > high) {
最后返回root节点,代码如下:
-```
+```cpp
root->left = trimBST(root->left, low, high); // root->left接入符合条件的左孩子
root->right = trimBST(root->right, low, high); // root->right接入符合条件的右孩子
return root;
@@ -129,11 +127,11 @@ return root;
在回顾一下上面的代码,针对下图中二叉树的情况:
-
+
如下代码相当于把节点0的右孩子(节点2)返回给上一层,
-```
+```cpp
if (root->val < low) {
TreeNode* right = trimBST(root->right, low, high); // 寻找符合区间[low, high]的节点
return right;
@@ -142,7 +140,7 @@ if (root->val < low) {
然后如下代码相当于用节点3的左孩子 把下一层返回的 节点0的右孩子(节点2) 接住。
-```
+``` cpp
root->left = trimBST(root->left, low, high);
```
@@ -586,8 +584,4 @@ public TreeNode TrimBST(TreeNode root, int low, int high)
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0673.\346\234\200\351\225\277\351\200\222\345\242\236\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227\347\232\204\344\270\252\346\225\260.md" "b/problems/0673.\346\234\200\351\225\277\351\200\222\345\242\236\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227\347\232\204\344\270\252\346\225\260.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 0277f24989..9e61229abb
--- "a/problems/0673.\346\234\200\351\225\277\351\200\222\345\242\236\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227\347\232\204\344\270\252\346\225\260.md"
+++ "b/problems/0673.\346\234\200\351\225\277\351\200\222\345\242\236\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227\347\232\204\344\270\252\346\225\260.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0673.\346\234\200\351\225\277\351\200\222\345\242\236\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227\347\232\204\344\270\252\346\225\260.md" "b/problems/0673.\346\234\200\351\225\277\351\200\222\345\242\236\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227\347\232\204\344\270\252\346\225\260.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 0277f24989..9e61229abb
--- "a/problems/0673.\346\234\200\351\225\277\351\200\222\345\242\236\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227\347\232\204\344\270\252\346\225\260.md"
+++ "b/problems/0673.\346\234\200\351\225\277\351\200\222\345\242\236\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227\347\232\204\344\270\252\346\225\260.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 673.最长递增子序列的个数
@@ -180,7 +178,7 @@ for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
输入:[1,3,5,4,7]
-
+
**如果代码写出来了,怎么改都通过不了,那么把dp和count打印出来看看对不对!**
@@ -360,8 +358,4 @@ var findNumberOfLIS = function(nums) {
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0674.\346\234\200\351\225\277\350\277\236\347\273\255\351\200\222\345\242\236\345\272\217\345\210\227.md" "b/problems/0674.\346\234\200\351\225\277\350\277\236\347\273\255\351\200\222\345\242\236\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 485e321c99..dae64a11ac
--- "a/problems/0674.\346\234\200\351\225\277\350\277\236\347\273\255\351\200\222\345\242\236\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
+++ "b/problems/0674.\346\234\200\351\225\277\350\277\236\347\273\255\351\200\222\345\242\236\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0674.\346\234\200\351\225\277\350\277\236\347\273\255\351\200\222\345\242\236\345\272\217\345\210\227.md" "b/problems/0674.\346\234\200\351\225\277\350\277\236\347\273\255\351\200\222\345\242\236\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 485e321c99..dae64a11ac
--- "a/problems/0674.\346\234\200\351\225\277\350\277\236\347\273\255\351\200\222\345\242\236\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
+++ "b/problems/0674.\346\234\200\351\225\277\350\277\236\347\273\255\351\200\222\345\242\236\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 674. 最长连续递增序列
@@ -87,7 +85,7 @@ for (int i = 1; i < nums.size(); i++) {
已输入nums = [1,3,5,4,7]为例,dp数组状态如下:
-
+
**注意这里要取dp[i]里的最大值,所以dp[2]才是结果!**
@@ -186,7 +184,23 @@ public:
return res;
}
```
-
+> 动态规划状态压缩
+```java
+class Solution {
+ public int findLengthOfLCIS(int[] nums) {
+ // 记录以 前一个元素结尾的最长连续递增序列的长度 和 以当前 结尾的......
+ int beforeOneMaxLen = 1, currentMaxLen = 0;
+ // res 赋最小值返回的最小值1
+ int res = 1;
+ for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i ++) {
+ currentMaxLen = nums[i] > nums[i - 1] ? beforeOneMaxLen + 1 : 1;
+ beforeOneMaxLen = currentMaxLen;
+ res = Math.max(res, currentMaxLen);
+ }
+ return res;
+ }
+}
+```
> 贪心法:
```Java
@@ -343,7 +357,7 @@ impl Solution {
```
-### Javascript:
+### JavaScript:
> 动态规划:
```javascript
@@ -425,11 +439,76 @@ function findLengthOfLCIS(nums: number[]): number {
};
```
+### C:
+
+> 动态规划:
+
+```c
+int findLengthOfLCIS(int* nums, int numsSize) {
+ if(numsSize == 0){
+ return 0;
+ }
+ int dp[numsSize];
+ for(int i = 0; i < numsSize; i++){
+ dp[i] = 1;
+ }
+ int result = 1;
+ for (int i = 1; i < numsSize; ++i) {
+ if(nums[i] > nums[i - 1]){
+ dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + 1;
+ }
+ if(dp[i] > result){
+ result = dp[i];
+ }
+ }
+ return result;
+}
+```
+
+
+
+> 贪心:
+```c
+int findLengthOfLCIS(int* nums, int numsSize) {
+ int result = 1;
+ int count = 1;
+ if(numsSize == 0){
+ return result;
+ }
+ for (int i = 1; i < numsSize; ++i) {
+ if(nums[i] > nums[i - 1]){
+ count++;
+ } else{
+ count = 1;
+ }
+ if(count > result){
+ result = count;
+ }
+ }
+ return result;
+}
+```
+
+### Cangjie
+
+```cangjie
+func findLengthOfLCIS(nums: Array): Int64 {
+ let n = nums.size
+ if (n <= 1) {
+ return n
+ }
+ let dp = Array(n, repeat: 1)
+ var res = 0
+ for (i in 1..n) {
+ if (nums[i] > nums[i - 1]) {
+ dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + 1
+ }
+ res = max(res, dp[i])
+ }
+ return res
+}
+```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0684.\345\206\227\344\275\231\350\277\236\346\216\245.md" "b/problems/0684.\345\206\227\344\275\231\350\277\236\346\216\245.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index f5e84223b1..2f939d0827
--- "a/problems/0684.\345\206\227\344\275\231\350\277\236\346\216\245.md"
+++ "b/problems/0684.\345\206\227\344\275\231\350\277\236\346\216\245.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0684.\345\206\227\344\275\231\350\277\236\346\216\245.md" "b/problems/0684.\345\206\227\344\275\231\350\277\236\346\216\245.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index f5e84223b1..2f939d0827
--- "a/problems/0684.\345\206\227\344\275\231\350\277\236\346\216\245.md"
+++ "b/problems/0684.\345\206\227\344\275\231\350\277\236\346\216\245.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 684.冗余连接
@@ -14,7 +12,7 @@
请找出一条可以删去的边,删除后可使得剩余部分是一个有着 n 个节点的树。如果有多个答案,则返回数组 edges 中最后出现的边。
-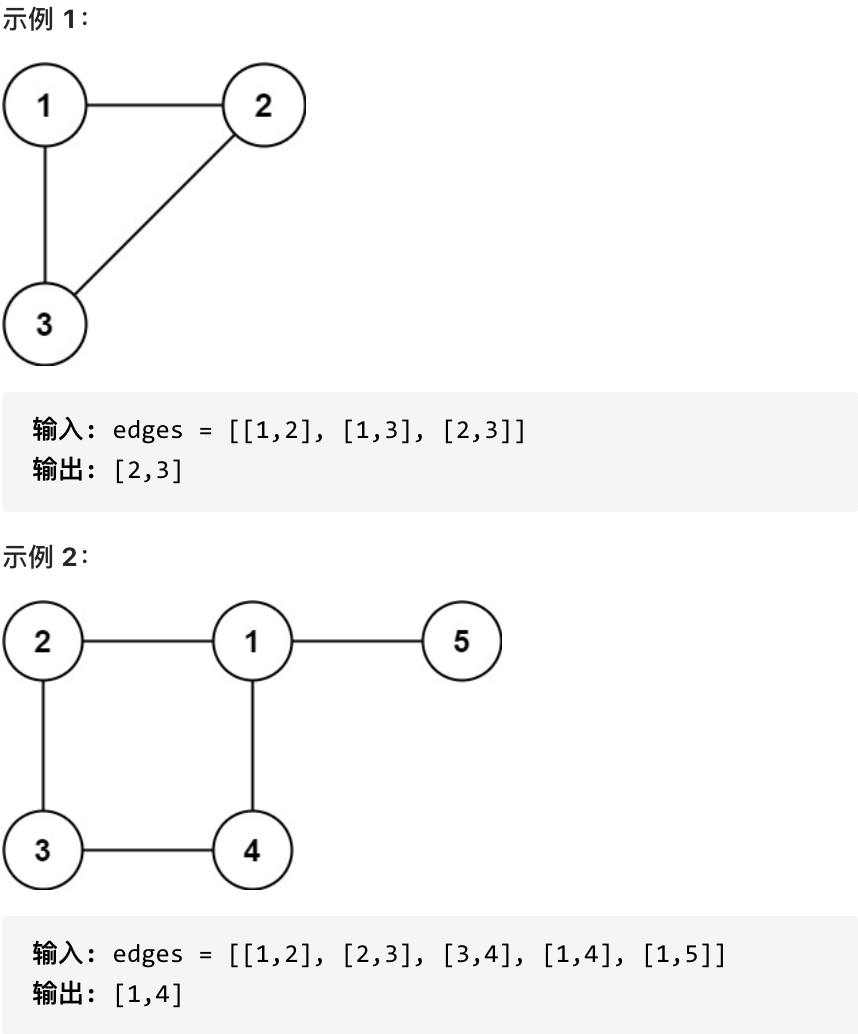
+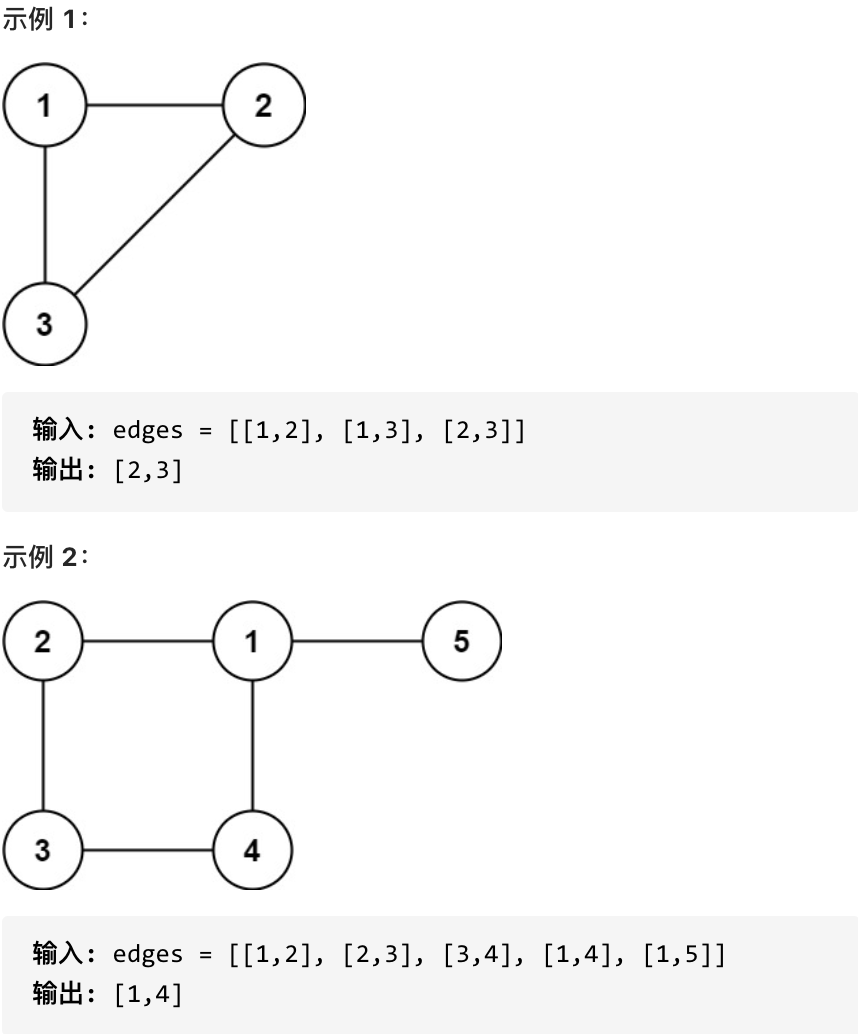
提示:
* n == edges.length
@@ -75,7 +73,7 @@ void join(int u, int v) {
2. 将两个节点接入到同一个集合,函数:join(int u, int v),将两个节点连在同一个根节点上
3. 判断两个节点是否在同一个集合,函数:isSame(int u, int v),就是判断两个节点是不是同一个根节点
-如果还不了解并查集,可以看这里:[并查集理论基础](https://programmercarl.com/图论并查集理论基础.html)
+如果还不了解并查集,可以看这里:[并查集理论基础](https://programmercarl.com/kamacoder/图论并查集理论基础.html)
我们再来看一下这道题目。
@@ -87,7 +85,7 @@ void join(int u, int v) {
如图所示:
-
+
节点A 和节点 B 不在同一个集合,那么就可以将两个 节点连在一起。
@@ -97,7 +95,7 @@ void join(int u, int v) {
如图所示:
-
+
已经判断 节点A 和 节点B 在在同一个集合(同一个根),如果将 节点A 和 节点B 连在一起就一定会出现环。
@@ -378,8 +376,4 @@ var findRedundantConnection = function(edges) {
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0685.\345\206\227\344\275\231\350\277\236\346\216\245II.md" "b/problems/0685.\345\206\227\344\275\231\350\277\236\346\216\245II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 0cad5ad581..27161d174c
--- "a/problems/0685.\345\206\227\344\275\231\350\277\236\346\216\245II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0685.\345\206\227\344\275\231\350\277\236\346\216\245II.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0685.\345\206\227\344\275\231\350\277\236\346\216\245II.md" "b/problems/0685.\345\206\227\344\275\231\350\277\236\346\216\245II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 0cad5ad581..27161d174c
--- "a/problems/0685.\345\206\227\344\275\231\350\277\236\346\216\245II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0685.\345\206\227\344\275\231\350\277\236\346\216\245II.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 685.冗余连接II
@@ -18,9 +16,9 @@
返回一条能删除的边,使得剩下的图是有 n 个节点的有根树。若有多个答案,返回最后出现在给定二维数组的答案。
-
+
-
+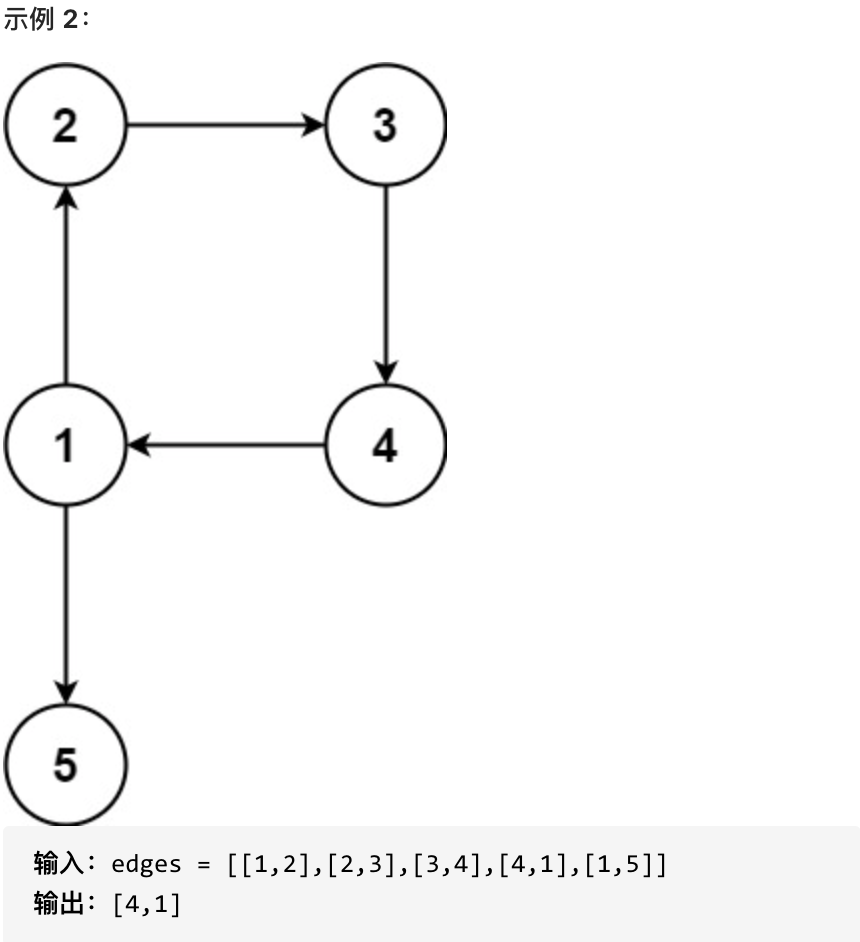
提示:
@@ -40,7 +38,7 @@
那么有如下三种情况,前两种情况是出现入度为2的点,如图:
- +
+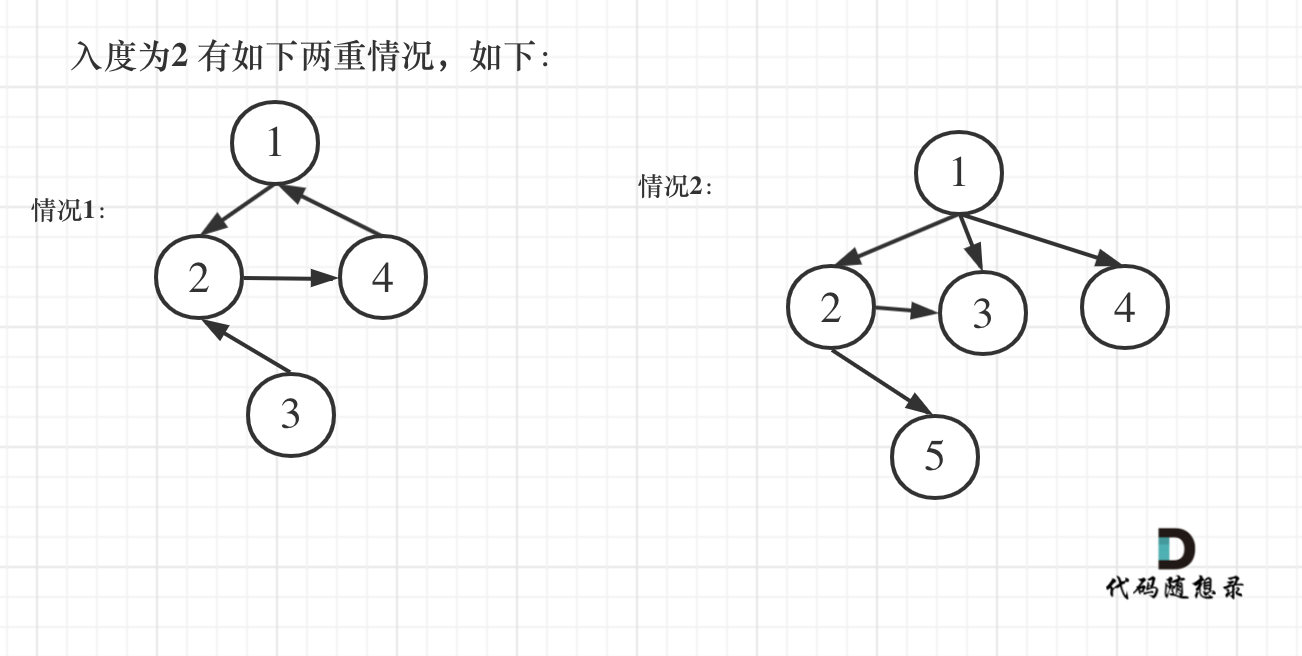 且只有一个节点入度为2,为什么不看出度呢,出度没有意义,一棵树中随便一个父节点就有多个出度。
@@ -48,7 +46,7 @@
如图:
-
且只有一个节点入度为2,为什么不看出度呢,出度没有意义,一棵树中随便一个父节点就有多个出度。
@@ -48,7 +46,7 @@
如图:
- +
+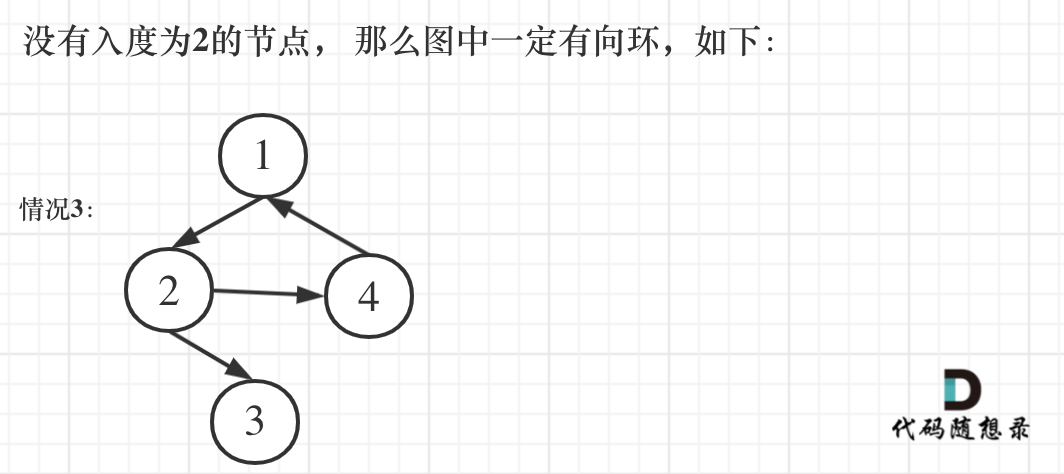 首先先计算节点的入度,这里不少录友在计算入度的时候就搞蒙了,分不清 edges[i][j] 表示的都是什么。
@@ -69,7 +67,7 @@ edges[2][0] = 2,edges[2][1] = 3,
搞清楚之后,我们如何统计入度呢?
-即 edges[i][1] 表示的节点都是 箭头指向的节点,即这个几点有一个入度! (如果想统计出度,那么就是 edges[i][0])。
+即 edges[i][1] 表示的节点都是 箭头指向的节点,即这个节点有一个入度! (如果想统计出度,那么就是 edges[i][0])。
所以,统计入度的代码如下:
@@ -108,7 +106,7 @@ if (vec.size() > 0) {
可以定义一个函数,代码如下:
-```
+```cpp
// 在有向图里找到删除的那条边,使其变成树,返回值就是要删除的边
vector getRemoveEdge(const vector>& edges)
```
@@ -619,8 +617,4 @@ var findRedundantDirectedConnection = function(edges) {
-
首先先计算节点的入度,这里不少录友在计算入度的时候就搞蒙了,分不清 edges[i][j] 表示的都是什么。
@@ -69,7 +67,7 @@ edges[2][0] = 2,edges[2][1] = 3,
搞清楚之后,我们如何统计入度呢?
-即 edges[i][1] 表示的节点都是 箭头指向的节点,即这个几点有一个入度! (如果想统计出度,那么就是 edges[i][0])。
+即 edges[i][1] 表示的节点都是 箭头指向的节点,即这个节点有一个入度! (如果想统计出度,那么就是 edges[i][0])。
所以,统计入度的代码如下:
@@ -108,7 +106,7 @@ if (vec.size() > 0) {
可以定义一个函数,代码如下:
-```
+```cpp
// 在有向图里找到删除的那条边,使其变成树,返回值就是要删除的边
vector getRemoveEdge(const vector>& edges)
```
@@ -619,8 +617,4 @@ var findRedundantDirectedConnection = function(edges) {
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0695.\345\262\233\345\261\277\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\244\247\351\235\242\347\247\257.md" "b/problems/0695.\345\262\233\345\261\277\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\244\247\351\235\242\347\247\257.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 87b1b5bbbb..a63d2b0e06
--- "a/problems/0695.\345\262\233\345\261\277\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\244\247\351\235\242\347\247\257.md"
+++ "b/problems/0695.\345\262\233\345\261\277\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\244\247\351\235\242\347\247\257.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0695.\345\262\233\345\261\277\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\244\247\351\235\242\347\247\257.md" "b/problems/0695.\345\262\233\345\261\277\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\244\247\351\235\242\347\247\257.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 87b1b5bbbb..a63d2b0e06
--- "a/problems/0695.\345\262\233\345\261\277\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\244\247\351\235\242\347\247\257.md"
+++ "b/problems/0695.\345\262\233\345\261\277\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\244\247\351\235\242\347\247\257.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 695. 岛屿的最大面积
@@ -16,7 +14,7 @@
计算并返回 grid 中最大的岛屿面积。如果没有岛屿,则返回面积为 0 。
-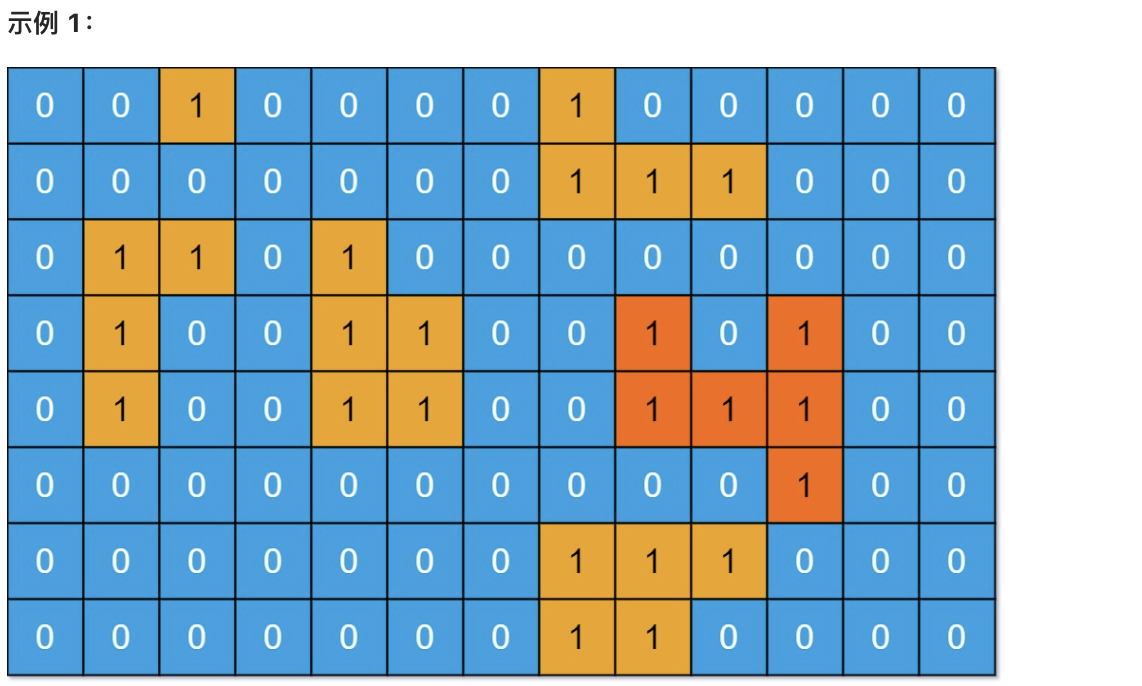
+
* 输入:grid = [[0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,0,0,0],[0,1,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0],[0,1,0,0,1,1,0,0,1,0,1,0,0],[0,1,0,0,1,1,0,0,1,1,1,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,0,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,0,0,0]]
* 输出:6
@@ -29,7 +27,7 @@
也就是说斜角度链接是不算了, 例如示例二,是三个岛屿,如图:
-
+
这道题目也是 dfs bfs基础类题目,就是搜索每个岛屿上“1”的数量,然后取一个最大的。
@@ -44,7 +42,7 @@
这里其实涉及到dfs的两种写法。
-写法一,dfs只处理下一个节点,即在主函数遇到岛屿就计数为1,dfs处理接下来的相邻陆地
+写法一,dfs处理当前节点的相邻节点,即在主函数遇到岛屿就计数为1,dfs处理接下来的相邻陆地
```CPP
// 版本一
@@ -87,7 +85,7 @@ public:
};
```
-写法二,dfs处理当前节点,即即在主函数遇到岛屿就计数为0,dfs处理接下来的全部陆地
+写法二,dfs处理当前节点,即在主函数遇到岛屿就计数为0,dfs处理接下来的全部陆地
dfs
```CPP
@@ -708,8 +706,4 @@ impl Solution {
}
}
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0700.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\346\220\234\347\264\242.md" "b/problems/0700.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\346\220\234\347\264\242.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 9efb1e0519..40777a67a2
--- "a/problems/0700.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\346\220\234\347\264\242.md"
+++ "b/problems/0700.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\346\220\234\347\264\242.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0700.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\346\220\234\347\264\242.md" "b/problems/0700.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\346\220\234\347\264\242.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 9efb1e0519..40777a67a2
--- "a/problems/0700.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\346\220\234\347\264\242.md"
+++ "b/problems/0700.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\346\220\234\347\264\242.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 700.二叉搜索树中的搜索
@@ -14,7 +12,7 @@
例如,
-
+
在上述示例中,如果要找的值是 5,但因为没有节点值为 5,我们应该返回 NULL。
@@ -126,7 +124,7 @@ public:
中间节点如果大于3就向左走,如果小于3就向右走,如图:
-
+
所以迭代法代码如下:
@@ -262,6 +260,26 @@ class Solution:
return None
```
+(方法三) 栈-遍历
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def searchBST(self, root: TreeNode, val: int) -> TreeNode:
+ stack = [root]
+ while stack:
+ node = stack.pop()
+ # 根据TreeNode的定义
+ # node携带有三类信息 node.left/node.right/node.val
+ # 找到val直接返回node 即是找到了该节点为根的子树
+ # 此处node.left/node.right/val的前后顺序可打乱
+ if node.val == val:
+ return node
+ if node.right:
+ stack.append(node.right)
+ if node.left:
+ stack.append(node.left)
+ return None
+```
+
### Go
@@ -487,8 +505,4 @@ public TreeNode SearchBST(TreeNode root, int val)
}
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0701.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\346\217\222\345\205\245\346\223\215\344\275\234.md" "b/problems/0701.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\346\217\222\345\205\245\346\223\215\344\275\234.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 98e60d5f5f..fec287449c
--- "a/problems/0701.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\346\217\222\345\205\245\346\223\215\344\275\234.md"
+++ "b/problems/0701.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\346\217\222\345\205\245\346\223\215\344\275\234.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0701.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\346\217\222\345\205\245\346\223\215\344\275\234.md" "b/problems/0701.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\346\217\222\345\205\245\346\223\215\344\275\234.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 98e60d5f5f..fec287449c
--- "a/problems/0701.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\346\217\222\345\205\245\346\223\215\344\275\234.md"
+++ "b/problems/0701.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\346\217\222\345\205\245\346\223\215\344\275\234.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 701.二叉搜索树中的插入操作
@@ -14,7 +12,7 @@
注意,可能存在多种有效的插入方式,只要树在插入后仍保持为二叉搜索树即可。 你可以返回任意有效的结果。
-
+
提示:
@@ -35,7 +33,7 @@
如下演示视频中可以看出:只要按照二叉搜索树的规则去遍历,遇到空节点就插入节点就可以了。
-
+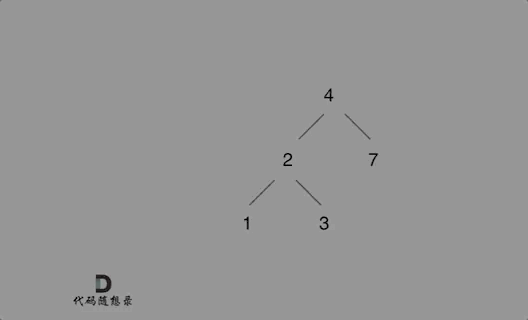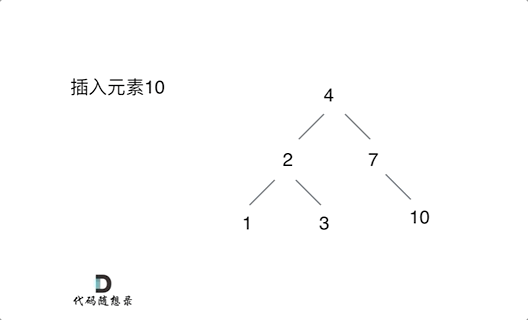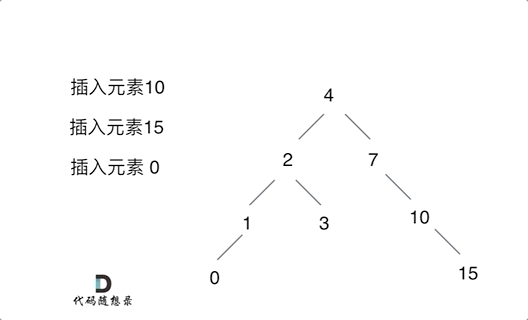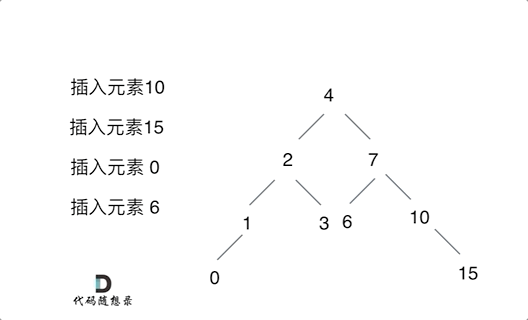
例如插入元素10 ,需要找到末尾节点插入便可,一样的道理来插入元素15,插入元素0,插入元素6,**需要调整二叉树的结构么? 并不需要。**。
@@ -59,7 +57,7 @@
代码如下:
-```
+```cpp
TreeNode* insertIntoBST(TreeNode* root, int val)
```
@@ -69,7 +67,7 @@ TreeNode* insertIntoBST(TreeNode* root, int val)
代码如下:
-```
+```cpp
if (root == NULL) {
TreeNode* node = new TreeNode(val);
return node;
@@ -88,7 +86,7 @@ if (root == NULL) {
代码如下:
-```
+```cpp
if (root->val > val) root->left = insertIntoBST(root->left, val);
if (root->val < val) root->right = insertIntoBST(root->right, val);
return root;
@@ -120,7 +118,7 @@ public:
那么递归函数定义如下:
-```
+```cpp
TreeNode* parent; // 记录遍历节点的父节点
void traversal(TreeNode* cur, int val)
```
@@ -283,32 +281,10 @@ class Solution:
return TreeNode(val)
self.traversal(root, val)
return root
-
```
递归法(版本二)
```python
-class Solution:
- def insertIntoBST(self, root, val):
- if root is None:
- return TreeNode(val)
- parent = None
- cur = root
- while cur:
- parent = cur
- if val < cur.val:
- cur = cur.left
- else:
- cur = cur.right
- if val < parent.val:
- parent.left = TreeNode(val)
- else:
- parent.right = TreeNode(val)
- return root
-```
-
-递归法(版本三)
-```python
class Solution:
def insertIntoBST(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], val: int) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
if root is None or root.val == val:
@@ -326,7 +302,7 @@ class Solution:
return root
```
-递归法(版本四)
+递归法(版本三)
```python
class Solution:
def insertIntoBST(self, root, val):
@@ -340,10 +316,9 @@ class Solution:
root.right = self.insertIntoBST(root.right, val)
return root
-
```
-迭代法
+迭代法(版本一)
```python
class Solution:
def insertIntoBST(self, root, val):
@@ -366,10 +341,53 @@ class Solution:
else:
parent.right = node # 将新节点连接到父节点的右子树
+ return root
+```
+
+迭代法(版本二)
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def insertIntoBST(self, root, val):
+ if root is None:
+ return TreeNode(val)
+ parent = None
+ cur = root
+ while cur:
+ parent = cur
+ if val < cur.val:
+ cur = cur.left
+ else:
+ cur = cur.right
+ if val < parent.val:
+ parent.left = TreeNode(val)
+ else:
+ parent.right = TreeNode(val)
return root
+```
+
+迭代法(精简)
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def insertIntoBST(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], val: int) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
+ if not root: # 如果根节点为空,创建新节点作为根节点并返回
+ return TreeNode(val)
+ cur = root
+ while cur:
+ if val < cur.val:
+ if not cur.left: # 如果此时父节点的左子树为空
+ cur.left = TreeNode(val) # 将新节点连接到父节点的左子树
+ return root
+ else:
+ cur = cur.left
+ elif val > cur.val:
+ if not cur.right: # 如果此时父节点的左子树为空
+ cur.right = TreeNode(val) # 将新节点连接到父节点的右子树
+ return root
+ else:
+ cur = cur.right
-
```
+
-----
### Go
@@ -704,7 +722,3 @@ public TreeNode InsertIntoBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0704.\344\272\214\345\210\206\346\237\245\346\211\276.md" "b/problems/0704.\344\272\214\345\210\206\346\237\245\346\211\276.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 31e89ae344..e529629492
--- "a/problems/0704.\344\272\214\345\210\206\346\237\245\346\211\276.md"
+++ "b/problems/0704.\344\272\214\345\210\206\346\237\245\346\211\276.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0704.\344\272\214\345\210\206\346\237\245\346\211\276.md" "b/problems/0704.\344\272\214\345\210\206\346\237\245\346\211\276.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 31e89ae344..e529629492
--- "a/problems/0704.\344\272\214\345\210\206\346\237\245\346\211\276.md"
+++ "b/problems/0704.\344\272\214\345\210\206\346\237\245\346\211\276.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们受益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 704. 二分查找
@@ -61,7 +59,7 @@
例如在数组:1,2,3,4,7,9,10中查找元素2,如图所示:
-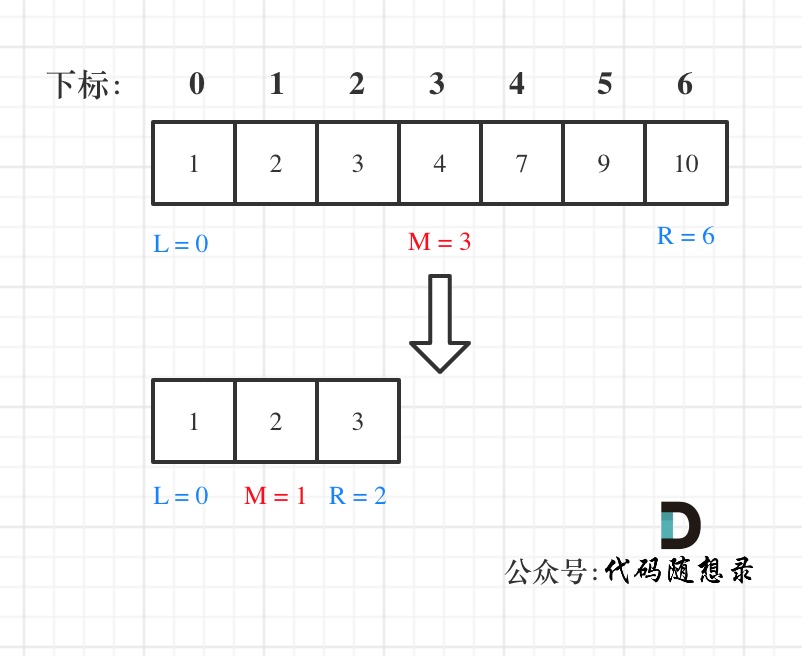
+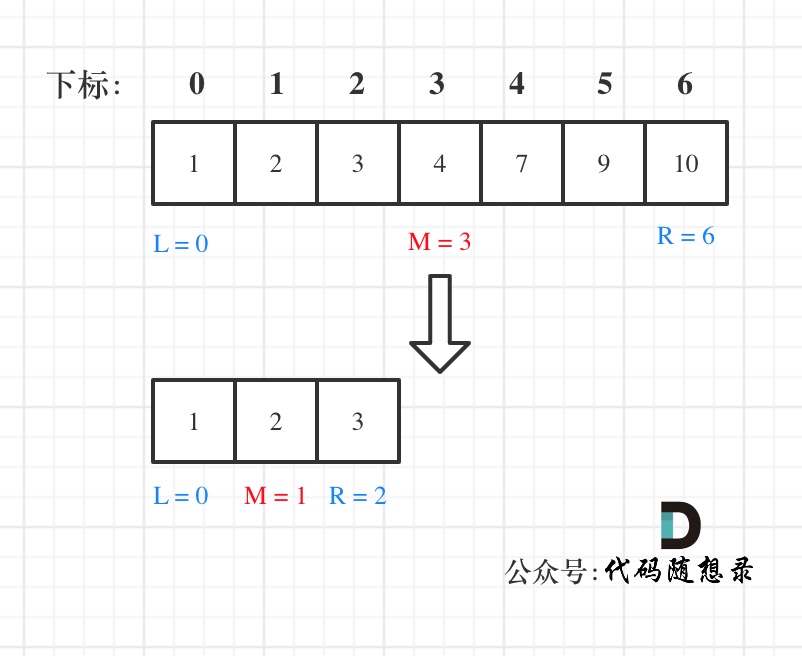
代码如下:(详细注释)
@@ -104,7 +102,7 @@ public:
在数组:1,2,3,4,7,9,10中查找元素2,如图所示:(**注意和方法一的区别**)
-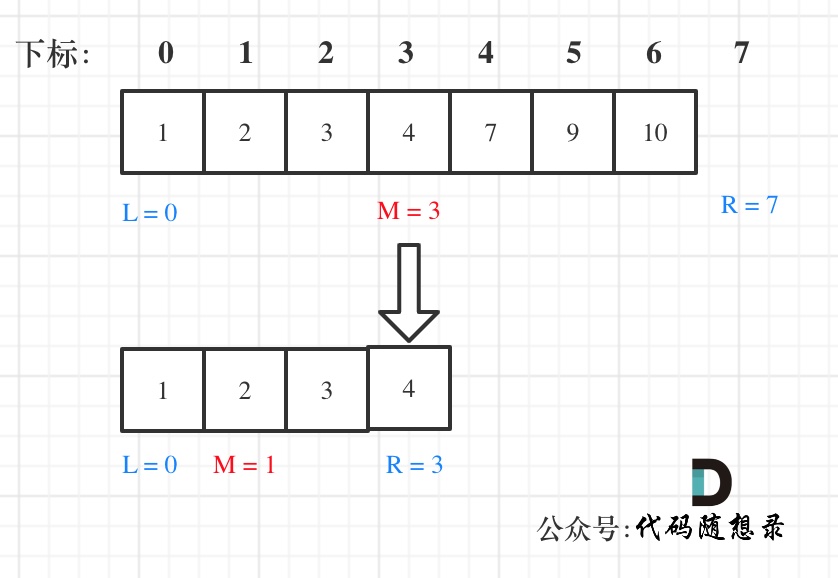
+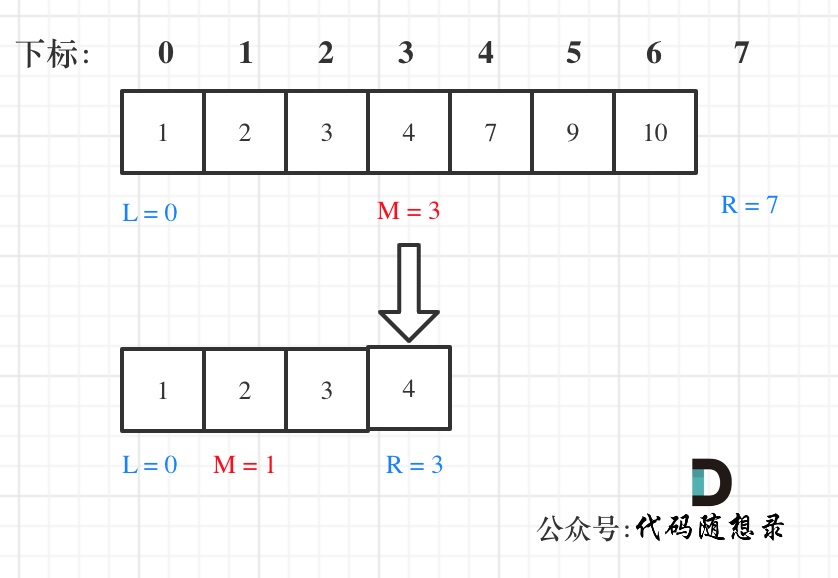
代码如下:(详细注释)
@@ -174,13 +172,17 @@ class Solution {
int left = 0, right = nums.length - 1;
while (left <= right) {
int mid = left + ((right - left) >> 1);
- if (nums[mid] == target)
+ if (nums[mid] == target) {
return mid;
- else if (nums[mid] < target)
+ }
+ else if (nums[mid] < target) {
left = mid + 1;
- else if (nums[mid] > target)
+ }
+ else { // nums[mid] > target
right = mid - 1;
+ }
}
+ // 未找到目标值
return -1;
}
}
@@ -194,13 +196,17 @@ class Solution {
int left = 0, right = nums.length;
while (left < right) {
int mid = left + ((right - left) >> 1);
- if (nums[mid] == target)
+ if (nums[mid] == target) {
return mid;
- else if (nums[mid] < target)
+ }
+ else if (nums[mid] < target) {
left = mid + 1;
- else if (nums[mid] > target)
+ }
+ else { // nums[mid] > target
right = mid;
+ }
}
+ // 未找到目标值
return -1;
}
}
@@ -501,19 +507,19 @@ func search(nums: [Int], target: Int) -> Int {
### **Rust:**
-(版本一)左闭右开区间
+(版本一)左闭右闭区间
```rust
use std::cmp::Ordering;
impl Solution {
pub fn search(nums: Vec, target: i32) -> i32 {
- let (mut left, mut right) = (0, nums.len());
- while left < right {
+ let (mut left, mut right) = (0_i32, nums.len() as i32 - 1);
+ while left <= right {
let mid = (right + left) / 2;
- match nums[mid].cmp(&target) {
+ match nums[mid as usize].cmp(&target) {
Ordering::Less => left = mid + 1,
- Ordering::Greater => right = mid,
- Ordering::Equal => return mid as i32,
+ Ordering::Greater => right = mid - 1,
+ Ordering::Equal => return mid,
}
}
-1
@@ -521,19 +527,19 @@ impl Solution {
}
```
-//(版本二)左闭右闭区间
+//(版本二)左闭右开区间
```rust
use std::cmp::Ordering;
impl Solution {
pub fn search(nums: Vec, target: i32) -> i32 {
- let (mut left, mut right) = (0, nums.len());
- while left <= right {
+ let (mut left, mut right) = (0_i32, nums.len() as i32);
+ while left < right {
let mid = (right + left) / 2;
- match nums[mid].cmp(&target) {
+ match nums[mid as usize].cmp(&target) {
Ordering::Less => left = mid + 1,
- Ordering::Greater => right = mid - 1,
- Ordering::Equal => return mid as i32,
+ Ordering::Greater => right = mid,
+ Ordering::Equal => return mid,
}
}
-1
@@ -828,8 +834,4 @@ class Solution {
}
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0707.\350\256\276\350\256\241\351\223\276\350\241\250.md" "b/problems/0707.\350\256\276\350\256\241\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index fecdbc3cad..72e35f430f
--- "a/problems/0707.\350\256\276\350\256\241\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
+++ "b/problems/0707.\350\256\276\350\256\241\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0707.\350\256\276\350\256\241\351\223\276\350\241\250.md" "b/problems/0707.\350\256\276\350\256\241\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index fecdbc3cad..72e35f430f
--- "a/problems/0707.\350\256\276\350\256\241\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
+++ "b/problems/0707.\350\256\276\350\256\241\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
> 听说这道题目把链表常见的五个操作都覆盖了?
@@ -22,7 +20,7 @@
* deleteAtIndex(index):如果索引 index 有效,则删除链表中的第 index 个节点。
-
+
## 算法公开课
@@ -37,10 +35,10 @@
如果对链表的虚拟头结点不清楚,可以看这篇文章:[链表:听说用虚拟头节点会方便很多?](https://programmercarl.com/0203.移除链表元素.html)
删除链表节点:
-
+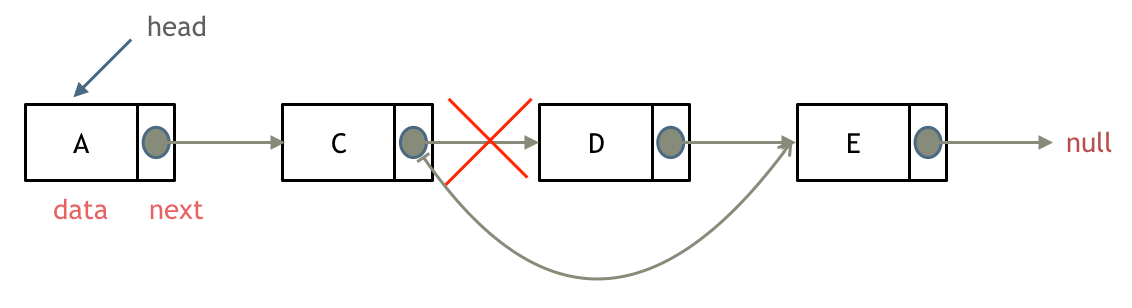
添加链表节点:
-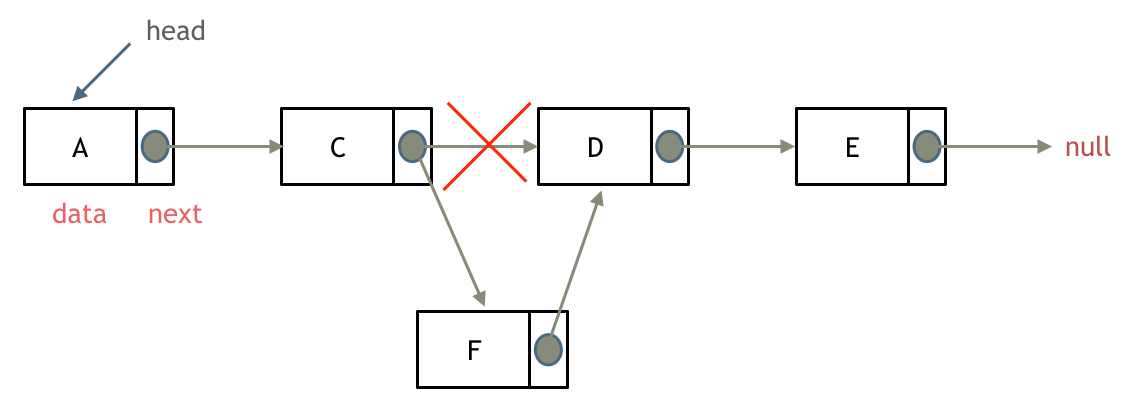
+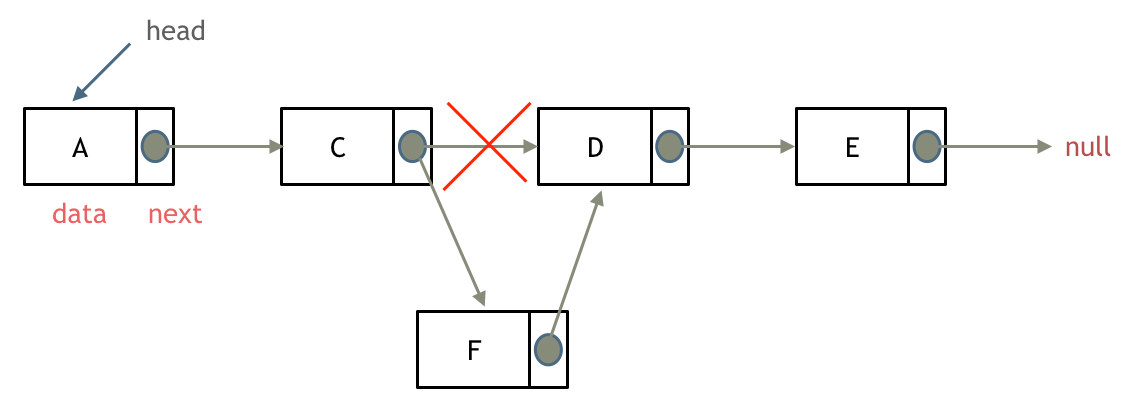
这道题目设计链表的五个接口:
* 获取链表第index个节点的数值
@@ -165,112 +163,240 @@ private:
## 其他语言版本
+### C++双链表法:
+
+```CPP
+//采用循环虚拟结点的双链表实现
+class MyLinkedList {
+public:
+ // 定义双向链表节点结构体
+ struct DList {
+ int elem; // 节点存储的元素
+ DList *next; // 指向下一个节点的指针
+ DList *prev; // 指向上一个节点的指针
+ // 构造函数,创建一个值为elem的新节点
+ DList(int elem) : elem(elem), next(nullptr), prev(nullptr) {};
+ };
+
+ // 构造函数,初始化链表
+ MyLinkedList() {
+ sentinelNode = new DList(0); // 创建哨兵节点,不存储有效数据
+ sentinelNode->next = sentinelNode; // 哨兵节点的下一个节点指向自身,形成循环
+ sentinelNode->prev = sentinelNode; // 哨兵节点的上一个节点指向自身,形成循环
+ size = 0; // 初始化链表大小为0
+ }
+
+ // 获取链表中第index个节点的值
+ int get(int index) {
+ if (index > (size - 1) || index < 0) { // 检查索引是否超出范围
+ return -1; // 如果超出范围,返回-1
+ }
+ int num;
+ int mid = size >> 1; // 计算链表中部位置
+ DList *curNode = sentinelNode; // 从哨兵节点开始
+ if (index < mid) { // 如果索引小于中部位置,从前往后遍历
+ for (int i = 0; i < index + 1; i++) {
+ curNode = curNode->next; // 移动到目标节点
+ }
+ } else { // 如果索引大于等于中部位置,从后往前遍历
+ for (int i = 0; i < size - index; i++) {
+ curNode = curNode->prev; // 移动到目标节点
+ }
+ }
+ num = curNode->elem; // 获取目标节点的值
+ return num; // 返回节点的值
+ }
+
+ // 在链表头部添加节点
+ void addAtHead(int val) {
+ DList *newNode = new DList(val); // 创建新节点
+ DList *next = sentinelNode->next; // 获取当前头节点的下一个节点
+ newNode->prev = sentinelNode; // 新节点的上一个节点指向哨兵节点
+ newNode->next = next; // 新节点的下一个节点指向原来的头节点
+ size++; // 链表大小加1
+ sentinelNode->next = newNode; // 哨兵节点的下一个节点指向新节点
+ next->prev = newNode; // 原来的头节点的上一个节点指向新节点
+ }
+
+ // 在链表尾部添加节点
+ void addAtTail(int val) {
+ DList *newNode = new DList(val); // 创建新节点
+ DList *prev = sentinelNode->prev; // 获取当前尾节点的上一个节点
+ newNode->next = sentinelNode; // 新节点的下一个节点指向哨兵节点
+ newNode->prev = prev; // 新节点的上一个节点指向原来的尾节点
+ size++; // 链表大小加1
+ sentinelNode->prev = newNode; // 哨兵节点的上一个节点指向新节点
+ prev->next = newNode; // 原来的尾节点的下一个节点指向新节点
+ }
+
+ // 在链表中的第index个节点之前添加值为val的节点
+ void addAtIndex(int index, int val) {
+ if (index > size) { // 检查索引是否超出范围
+ return; // 如果超出范围,直接返回
+ }
+ if (index <= 0) { // 如果索引为0或负数,在头部添加节点
+ addAtHead(val);
+ return;
+ }
+ int num;
+ int mid = size >> 1; // 计算链表中部位置
+ DList *curNode = sentinelNode; // 从哨兵节点开始
+ if (index < mid) { // 如果索引小于中部位置,从前往后遍历
+ for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
+ curNode = curNode->next; // 移动到目标位置的前一个节点
+ }
+ DList *temp = curNode->next; // 获取目标位置的节点
+ DList *newNode = new DList(val); // 创建新节点
+ curNode->next = newNode; // 在目标位置前添加新节点
+ temp->prev = newNode; // 目标位置的节点的前一个节点指向新节点
+ newNode->next = temp; // 新节点的下一个节点指向目标位置的结点
+ newNode->prev = curNode; // 新节点的上一个节点指向当前节点
+ } else { // 如果索引大于等于中部位置,从后往前遍历
+ for (int i = 0; i < size - index; i++) {
+ curNode = curNode->prev; // 移动到目标位置的后一个节点
+ }
+ DList *temp = curNode->prev; // 获取目标位置的节点
+ DList *newNode = new DList(val); // 创建新节点
+ curNode->prev = newNode; // 在目标位置后添加新节点
+ temp->next = newNode; // 目标位置的节点的下一个节点指向新节点
+ newNode->prev = temp; // 新节点的上一个节点指向目标位置的节点
+ newNode->next = curNode; // 新节点的下一个节点指向当前节点
+ }
+ size++; // 链表大小加1
+ }
+
+ // 删除链表中的第index个节点
+ void deleteAtIndex(int index) {
+ if (index > (size - 1) || index < 0) { // 检查索引是否超出范围
+ return; // 如果超出范围,直接返回
+ }
+ int num;
+ int mid = size >> 1; // 计算链表中部位置
+ DList *curNode = sentinelNode; // 从哨兵节点开始
+ if (index < mid) { // 如果索引小于中部位置,从前往后遍历
+ for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
+ curNode = curNode->next; // 移动到目标位置的前一个节点
+ }
+ DList *next = curNode->next->next; // 获取目标位置的下一个节点
+ curNode->next = next; // 删除目标位置的节点
+ next->prev = curNode; // 目标位置的下一个节点的前一个节点指向当前节点
+ } else { // 如果索引大于等于中部位置,从后往前遍历
+ for (int i = 0; i < size - index - 1; i++) {
+ curNode = curNode->prev; // 移动到目标位置的后一个节点
+ }
+ DList *prev = curNode->prev->prev; // 获取目标位置的下一个节点
+ curNode->prev = prev; // 删除目标位置的节点
+ prev->next = curNode; // 目标位置的下一个节点的下一个节点指向当前节点
+ }
+ size--; // 链表大小减1
+ }
+
+private:
+ int size; // 链表的大小
+ DList *sentinelNode; // 哨兵节点的指针
+};
+```
+
### C:
```C
-typedef struct MyLinkedList {
- int val;
- struct MyLinkedList* next;
-}MyLinkedList;
+typedef struct Node {
+ int val;
+ struct Node* next;
+} Node;
+
+
+typedef struct {
+ int size;
+ Node* data;
+} MyLinkedList;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
MyLinkedList* myLinkedListCreate() {
- //这个题必须用虚拟头指针,参数都是一级指针,头节点确定后没法改指向了!!!
- MyLinkedList* head = (MyLinkedList *)malloc(sizeof (MyLinkedList));
- head->next = NULL;
- return head;
+ MyLinkedList* obj = (MyLinkedList*)malloc(sizeof(MyLinkedList));
+ Node* head = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
+ head->next = (void*)0;
+ obj->data = head;
+ obj->size = 0;
+ return obj;
}
/** Get the value of the index-th node in the linked list. If the index is invalid, return -1. */
int myLinkedListGet(MyLinkedList* obj, int index) {
- MyLinkedList *cur = obj->next;
- for (int i = 0; cur != NULL; i++){
- if (i == index){
- return cur->val;
- }
- else{
- cur = cur->next;
- }
+ if (index < 0 || index >= obj->size) return -1;
+
+ Node* cur = obj->data;
+ while (index-- >= 0) {
+ cur = cur->next;
}
- return -1;
+
+ return cur->val;
}
/** Add a node of value val before the first element of the linked list. After the insertion, the new node will be the first node of the linked list. */
void myLinkedListAddAtHead(MyLinkedList* obj, int val) {
- MyLinkedList *nhead = (MyLinkedList *)malloc(sizeof (MyLinkedList));
- nhead->val = val;
- nhead->next = obj->next;
- obj->next = nhead;
+ Node* node = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
+ node->val = val;
+ node->next = obj->data->next;
+ obj->data->next = node;
+ obj->size++;
}
/** Append a node of value val to the last element of the linked list. */
void myLinkedListAddAtTail(MyLinkedList* obj, int val) {
- MyLinkedList *cur = obj;
- while(cur->next != NULL){
+ Node* cur = obj->data;
+ while (cur->next != ((void*)0)) {
cur = cur->next;
}
- MyLinkedList *ntail = (MyLinkedList *)malloc(sizeof (MyLinkedList));
- ntail->val = val;
- ntail->next = NULL;
- cur->next = ntail;
+
+ Node* tail = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
+ tail->val = val;
+ tail->next = (void*)0;
+ cur->next = tail;
+ obj->size++;
}
/** Add a node of value val before the index-th node in the linked list. If index equals to the length of linked list, the node will be appended to the end of linked list. If index is greater than the length, the node will not be inserted. */
void myLinkedListAddAtIndex(MyLinkedList* obj, int index, int val) {
- if (index == 0){
- myLinkedListAddAtHead(obj, val);
- return;
- }
- MyLinkedList *cur = obj->next;
- for (int i = 1 ;cur != NULL; i++){
- if (i == index){
- MyLinkedList* newnode = (MyLinkedList *)malloc(sizeof (MyLinkedList));
- newnode->val = val;
- newnode->next = cur->next;
- cur->next = newnode;
- return;
- }
- else{
- cur = cur->next;
- }
+ if (index > obj->size) return;
+
+ Node* cur = obj->data;
+ while (index-- > 0) {
+ cur = cur->next;
}
+
+ Node* node = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
+ node->val = val;
+ node->next = cur->next;
+ cur->next = node;
+ obj->size++;
}
/** Delete the index-th node in the linked list, if the index is valid. */
void myLinkedListDeleteAtIndex(MyLinkedList* obj, int index) {
- if (index == 0){
- MyLinkedList *tmp = obj->next;
- if (tmp != NULL){
- obj->next = tmp->next;
- free(tmp);
- }
- return;
- }
- MyLinkedList *cur = obj->next;
- for (int i = 1 ;cur != NULL && cur->next != NULL; i++){
- if (i == index){
- MyLinkedList *tmp = cur->next;
- if (tmp != NULL) {
- cur->next = tmp->next;
- free(tmp);
- }
- return;
- }
- else{
- cur = cur->next;
- }
+ if (index < 0 || index >= obj->size) return;
+
+ Node* cur = obj->data;
+ while (index-- > 0) {
+ cur = cur->next;
}
-
+
+ Node* temp = cur->next;
+ cur->next = temp->next;
+ free(temp);
+ obj->size--;
}
void myLinkedListFree(MyLinkedList* obj) {
- while(obj != NULL){
- MyLinkedList *tmp = obj;
- obj = obj->next;
- free(tmp);
- }
+ Node* tmp = obj->data;
+ while (tmp != NULL) {
+ Node* n = tmp;
+ tmp = tmp->next;
+ free(n);
+ }
+ free(obj);
}
/**
@@ -294,106 +420,115 @@ void myLinkedListFree(MyLinkedList* obj) {
```Java
//单链表
-class ListNode {
- int val;
- ListNode next;
- ListNode(){}
- ListNode(int val) {
- this.val=val;
- }
-}
class MyLinkedList {
+
+ class ListNode {
+ int val;
+ ListNode next;
+ ListNode(int val) {
+ this.val=val;
+ }
+ }
//size存储链表元素的个数
- int size;
- //虚拟头结点
- ListNode head;
+ private int size;
+ //注意这里记录的是虚拟头结点
+ private ListNode head;
//初始化链表
public MyLinkedList() {
- size = 0;
- head = new ListNode(0);
+ this.size = 0;
+ this.head = new ListNode(0);
}
- //获取第index个节点的数值,注意index是从0开始的,第0个节点就是头结点
+ //获取第index个节点的数值,注意index是从0开始的,第0个节点就是虚拟头结点
public int get(int index) {
//如果index非法,返回-1
if (index < 0 || index >= size) {
return -1;
}
- ListNode currentNode = head;
- //包含一个虚拟头节点,所以查找第 index+1 个节点
+ ListNode cur = head;
+ //第0个节点是虚拟头节点,所以查找第 index+1 个节点
for (int i = 0; i <= index; i++) {
- currentNode = currentNode.next;
+ cur = cur.next;
}
- return currentNode.val;
+ return cur.val;
}
- //在链表最前面插入一个节点,等价于在第0个元素前添加
public void addAtHead(int val) {
- addAtIndex(0, val);
+ ListNode newNode = new ListNode(val);
+ newNode.next = head.next;
+ head.next = newNode;
+ size++;
+
+ // 在链表最前面插入一个节点,等价于在第0个元素前添加
+ // addAtIndex(0, val);
}
- //在链表的最后插入一个节点,等价于在(末尾+1)个元素前添加
+
public void addAtTail(int val) {
- addAtIndex(size, val);
+ ListNode newNode = new ListNode(val);
+ ListNode cur = head;
+ while (cur.next != null) {
+ cur = cur.next;
+ }
+ cur.next = newNode;
+ size++;
+
+ // 在链表的最后插入一个节点,等价于在(末尾+1)个元素前添加
+ // addAtIndex(size, val);
}
// 在第 index 个节点之前插入一个新节点,例如index为0,那么新插入的节点为链表的新头节点。
// 如果 index 等于链表的长度,则说明是新插入的节点为链表的尾结点
// 如果 index 大于链表的长度,则返回空
public void addAtIndex(int index, int val) {
- if (index > size) {
+ if (index < 0 || index > size) {
return;
}
- if (index < 0) {
- index = 0;
- }
- size++;
+
//找到要插入节点的前驱
- ListNode pred = head;
+ ListNode pre = head;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
- pred = pred.next;
+ pre = pre.next;
}
- ListNode toAdd = new ListNode(val);
- toAdd.next = pred.next;
- pred.next = toAdd;
+ ListNode newNode = new ListNode(val);
+ newNode.next = pre.next;
+ pre.next = newNode;
+ size++;
}
- //删除第index个节点
public void deleteAtIndex(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= size) {
return;
}
- size--;
- if (index == 0) {
- head = head.next;
- return;
- }
- ListNode pred = head;
+
+ //因为有虚拟头节点,所以不用对index=0的情况进行特殊处理
+ ListNode pre = head;
for (int i = 0; i < index ; i++) {
- pred = pred.next;
+ pre = pre.next;
}
- pred.next = pred.next.next;
+ pre.next = pre.next.next;
+ size--;
}
}
+```
+```Java
//双链表
-class ListNode{
- int val;
- ListNode next,prev;
- ListNode() {};
- ListNode(int val){
- this.val = val;
- }
-}
-
-
class MyLinkedList {
+ class ListNode{
+ int val;
+ ListNode next, prev;
+ ListNode(int val){
+ this.val = val;
+ }
+ }
+
//记录链表中元素的数量
- int size;
+ private int size;
//记录链表的虚拟头结点和尾结点
- ListNode head,tail;
+ private ListNode head, tail;
public MyLinkedList() {
//初始化操作
@@ -401,25 +536,25 @@ class MyLinkedList {
this.head = new ListNode(0);
this.tail = new ListNode(0);
//这一步非常关键,否则在加入头结点的操作中会出现null.next的错误!!!
- head.next=tail;
- tail.prev=head;
+ this.head.next = tail;
+ this.tail.prev = head;
}
public int get(int index) {
//判断index是否有效
- if(index<0 || index>=size){
+ if(index < 0 || index >= size){
return -1;
}
- ListNode cur = this.head;
+ ListNode cur = head;
//判断是哪一边遍历时间更短
if(index >= size / 2){
//tail开始
cur = tail;
- for(int i=0; i< size-index; i++){
+ for(int i = 0; i < size - index; i++){
cur = cur.prev;
}
}else{
- for(int i=0; i<= index; i++){
+ for(int i = 0; i <= index; i++){
cur = cur.next;
}
}
@@ -428,27 +563,23 @@ class MyLinkedList {
public void addAtHead(int val) {
//等价于在第0个元素前添加
- addAtIndex(0,val);
+ addAtIndex(0, val);
}
public void addAtTail(int val) {
//等价于在最后一个元素(null)前添加
- addAtIndex(size,val);
+ addAtIndex(size, val);
}
public void addAtIndex(int index, int val) {
- //index大于链表长度
- if(index>size){
+ //判断index是否有效
+ if(index < 0 || index > size){
return;
}
- //index小于0
- if(index<0){
- index = 0;
- }
- size++;
+
//找到前驱
- ListNode pre = this.head;
- for(int i=0; i=size){
+ //判断index是否有效
+ if(index < 0 || index >= size){
return;
}
+
//删除操作
- size--;
- ListNode pre = this.head;
- for(int i=0; i this.size) {
+ return -1
+ }
+
+ let cur = this.head
+ for (let i = 0; i <= index; i++) {
+ cur = cur.next
+ }
+
+ return cur.val
+};
+
+/**
+ * 在链表头部添加一个新节点
+ *
+ * @param {number} val
+ * @return {void}
+ *
+ * 时间复杂度: O(1)
+ * 空间复杂度: O(1)
+ */
+MyLinkedList.prototype.addAtHead = function (val) {
+ /**
+ head <-> [newNode] <-> originNode
+ */
+ this.size++
+ const originNode = this.head.next
+ // 创建新节点,并建立连接
+ const newNode = new Node(val, this.head, originNode)
+
+ // 取消原前后结点的连接
+ this.head.next = newNode
+ originNode.prev = newNode
+};
+
+/**
+ * 在链表尾部添加一个新节点
+ *
+ * @param {number} val
+ * @return {void}
+ *
+ * 时间复杂度: O(1)
+ * 空间复杂度: O(1)
+ */
+MyLinkedList.prototype.addAtTail = function (val) {
+ /**
+ originNode <-> [newNode] <-> tail
+ */
+ this.size++
+ const originNode = this.tail.prev
+
+ // 创建新节点,并建立连接
+ const newNode = new Node(val, originNode, this.tail)
+
+ // 取消原前后结点的连接
+ this.tail.prev = newNode
+ originNode.next = newNode
+};
+
+/**
+ * 在指定索引位置前添加一个新节点
+ *
+ * @param {number} index
+ * @param {number} val
+ * @return {void}
+ *
+ * 时间复杂度: O(n)
+ * 空间复杂度: O(1)
+ */
+MyLinkedList.prototype.addAtIndex = function (index, val) {
+ // 当索引超出范围时,直接返回
+ if (index > this.size) {
+ return
+ }
+ this.size++
+
+ let cur = this.head
+ for (let i = 0; i < index; i++) {
+ cur = cur.next
+ }
+
+ const new_next = cur.next
+
+ // 创建新节点,并建立连接
+ const node = new Node(val, cur, new_next)
+
+ // 取消原前后结点的连接
+ cur.next = node
+ new_next.prev = node
+};
+
+/**
+ * 删除指定索引位置的节点
+ *
+ * @param {number} index
+ * @return {void}
+ *
+ * 时间复杂度: O(n)
+ * 空间复杂度: O(1)
+ */
+MyLinkedList.prototype.deleteAtIndex = function (index) {
+ // 当索引超出范围时,直接返回
+ if (index >= this.size) {
+ return
+ }
+
+ this.size--
+ let cur = this.head
+ for (let i = 0; i < index; i++) {
+ cur = cur.next
+ }
+
+ const new_next = cur.next.next
+ // 取消原前后结点的连接
+ new_next.prev = cur
+ cur.next = new_next
+};
+```
+
### TypeScript:
```TypeScript
@@ -1556,7 +1843,4 @@ public class MyLinkedList
}
```
-
-
-  -
+
diff --git "a/problems/0714.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272\345\220\253\346\211\213\347\273\255\350\264\271.md" "b/problems/0714.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272\345\220\253\346\211\213\347\273\255\350\264\271.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index db39864908..fb095d7518
--- "a/problems/0714.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272\345\220\253\346\211\213\347\273\255\350\264\271.md"
+++ "b/problems/0714.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272\345\220\253\346\211\213\347\273\255\350\264\271.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+
diff --git "a/problems/0714.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272\345\220\253\346\211\213\347\273\255\350\264\271.md" "b/problems/0714.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272\345\220\253\346\211\213\347\273\255\350\264\271.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index db39864908..fb095d7518
--- "a/problems/0714.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272\345\220\253\346\211\213\347\273\255\350\264\271.md"
+++ "b/problems/0714.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272\345\220\253\346\211\213\347\273\255\350\264\271.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 714. 买卖股票的最佳时机含手续费
@@ -43,7 +41,7 @@
在[贪心算法:122.买卖股票的最佳时机II](https://programmercarl.com/0122.买卖股票的最佳时机II.html)中使用贪心策略不用关心具体什么时候买卖,只要收集每天的正利润,最后稳稳的就是最大利润了。
-而本题有了手续费,就要关系什么时候买卖了,因为计算所获得利润,需要考虑买卖利润可能不足以手续费的情况。
+而本题有了手续费,就要关心什么时候买卖了,因为计算所获得利润,需要考虑买卖利润可能不足以扣减手续费的情况。
如果使用贪心策略,就是最低值买,最高值(如果算上手续费还盈利)就卖。
@@ -122,7 +120,7 @@ public:
* 时间复杂度:O(n)
* 空间复杂度:O(n)
-当然可以对空间经行优化,因为当前状态只是依赖前一个状态。
+当然可以对空间进行优化,因为当前状态只是依赖前一个状态。
C++ 代码如下:
@@ -243,7 +241,7 @@ func maxProfit(prices []int, fee int) int {
return res
}
```
-### Javascript
+### JavaScript
```Javascript
// 贪心思路
var maxProfit = function(prices, fee) {
@@ -360,8 +358,4 @@ object Solution {
}
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0714.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272\345\220\253\346\211\213\347\273\255\350\264\271\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md" "b/problems/0714.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272\345\220\253\346\211\213\347\273\255\350\264\271\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 7e8e3d7c61..ebed4a0b30
--- "a/problems/0714.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272\345\220\253\346\211\213\347\273\255\350\264\271\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md"
+++ "b/problems/0714.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272\345\220\253\346\211\213\347\273\255\350\264\271\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0714.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272\345\220\253\346\211\213\347\273\255\350\264\271\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md" "b/problems/0714.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272\345\220\253\346\211\213\347\273\255\350\264\271\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 7e8e3d7c61..ebed4a0b30
--- "a/problems/0714.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272\345\220\253\346\211\213\347\273\255\350\264\271\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md"
+++ "b/problems/0714.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272\345\220\253\346\211\213\347\273\255\350\264\271\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 714.买卖股票的最佳时机含手续费
@@ -46,7 +44,7 @@
* 时间复杂度:O(n)
* 空间复杂度:O(1)
-本题使用贪心算法并不好理解,也很容易出错,那么我们再来看看是使用动规的方法如何解题。
+本题使用贪心算法并不好理解,也很容易出错,那么我们再来看看使用动规的方法如何解题。
相对于[动态规划:122.买卖股票的最佳时机II](https://programmercarl.com/0122.买卖股票的最佳时机II(动态规划).html),本题只需要在计算卖出操作的时候减去手续费就可以了,代码几乎是一样的。
@@ -54,7 +52,7 @@
这里重申一下dp数组的含义:
-dp[i][0] 表示第i天持有股票所省最多现金。
+dp[i][0] 表示第i天持有股票所得最多现金。
dp[i][1] 表示第i天不持有股票所得最多现金
@@ -188,6 +186,20 @@ class Solution:
return max(dp[-1][0], dp[-1][1])
```
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def maxProfit(self, prices: List[int], fee: int) -> int:
+ # 持有股票手上的最大現金
+ hold = -prices[0] - fee
+ # 不持有股票手上的最大現金
+ not_hold = 0
+ for price in prices[1:]:
+ new_hold = max(hold, not_hold - price - fee)
+ new_not_hold = max(not_hold, hold + price)
+ hold, not_hold = new_hold, new_not_hold
+ return not_hold
+```
+
### Go:
```go
@@ -212,7 +224,7 @@ func max(a, b int) int {
}
```
-### Javascript:
+### JavaScript:
```javascript
const maxProfit = (prices,fee) => {
@@ -247,7 +259,29 @@ function maxProfit(prices: number[], fee: number): number {
};
```
+### C:
+
+```c
+#define max(a, b) ((a) > (b) ? (a) : (b))
+
+// dp[i][0] 表示第i天持有股票所省最多现金。
+// dp[i][1] 表示第i天不持有股票所得最多现金
+int maxProfit(int* prices, int pricesSize, int fee) {
+ int dp[pricesSize][2];
+ dp[0][0] = -prices[0];
+ dp[0][1] = 0;
+ for (int i = 1; i < pricesSize; ++i) {
+ dp[i][0] = max(dp[i - 1][0], dp[i - 1][1] - prices[i]);
+ dp[i][1] = max(dp[i - 1][1], dp[i - 1][0] + prices[i] - fee);
+ }
+ return dp[pricesSize - 1][1];
+}
+```
+
+
+
### Rust:
+
**贪心**
```Rust
@@ -300,7 +334,4 @@ impl Solution {
}
```
-
-
-  -
+
diff --git "a/problems/0718.\346\234\200\351\225\277\351\207\215\345\244\215\345\255\220\346\225\260\347\273\204.md" "b/problems/0718.\346\234\200\351\225\277\351\207\215\345\244\215\345\255\220\346\225\260\347\273\204.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 272cf2b2a4..12384a57a7
--- "a/problems/0718.\346\234\200\351\225\277\351\207\215\345\244\215\345\255\220\346\225\260\347\273\204.md"
+++ "b/problems/0718.\346\234\200\351\225\277\351\207\215\345\244\215\345\255\220\346\225\260\347\273\204.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+
diff --git "a/problems/0718.\346\234\200\351\225\277\351\207\215\345\244\215\345\255\220\346\225\260\347\273\204.md" "b/problems/0718.\346\234\200\351\225\277\351\207\215\345\244\215\345\255\220\346\225\260\347\273\204.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 272cf2b2a4..12384a57a7
--- "a/problems/0718.\346\234\200\351\225\277\351\207\215\345\244\215\345\255\220\346\225\260\347\273\204.md"
+++ "b/problems/0718.\346\234\200\351\225\277\351\207\215\345\244\215\345\255\220\346\225\260\347\273\204.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 718. 最长重复子数组
@@ -97,7 +95,7 @@ for (int i = 1; i <= nums1.size(); i++) {
拿示例1中,A: [1,2,3,2,1],B: [3,2,1,4,7]为例,画一个dp数组的状态变化,如下:
-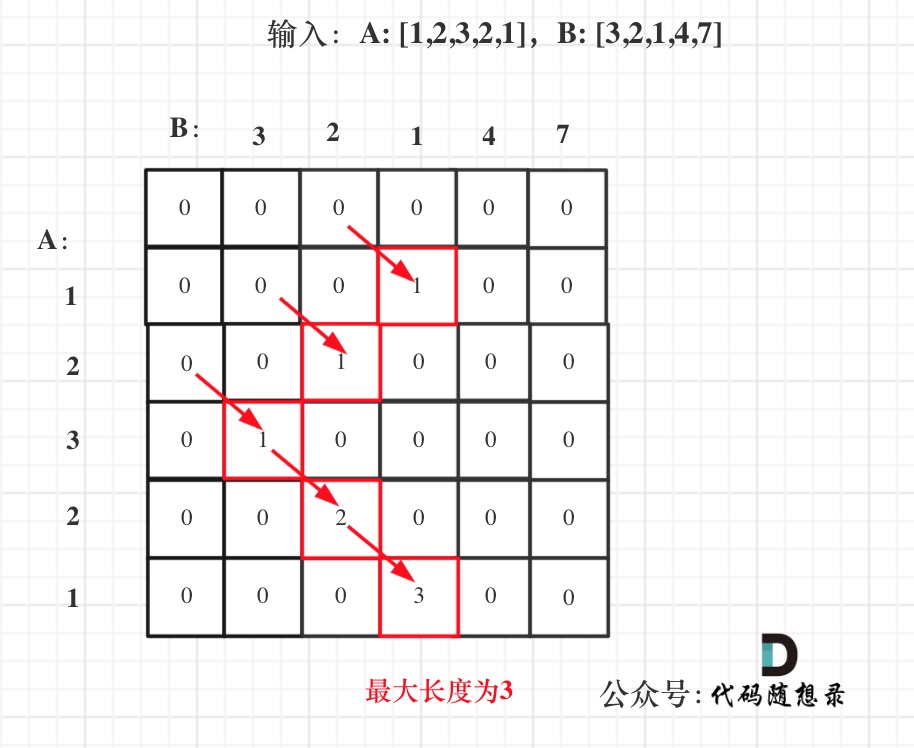
+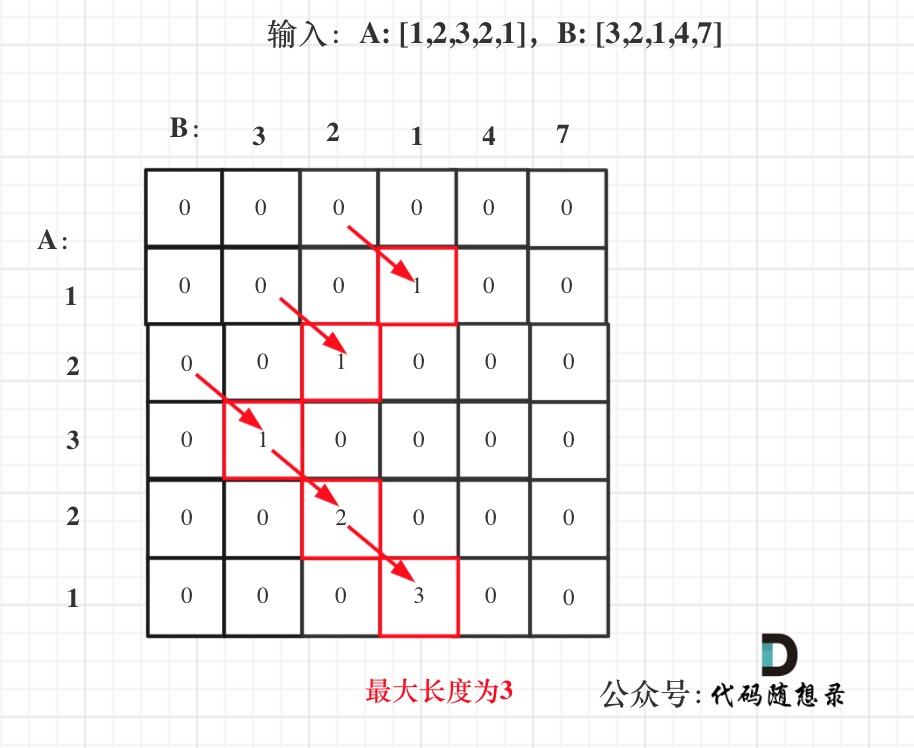
以上五部曲分析完毕,C++代码如下:
@@ -129,7 +127,7 @@ public:
在如下图中:
-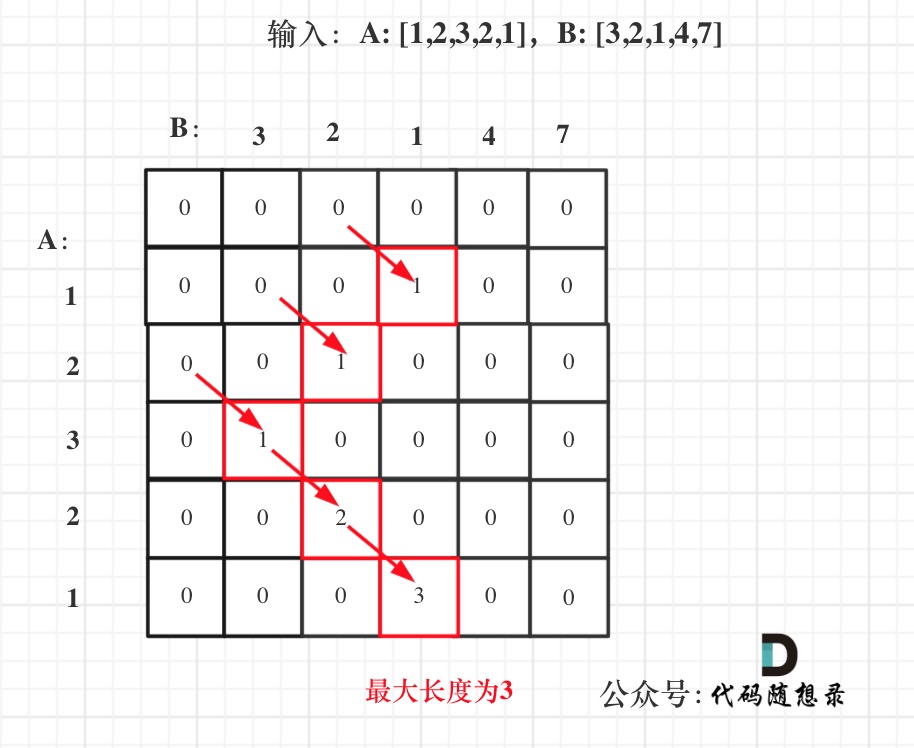
+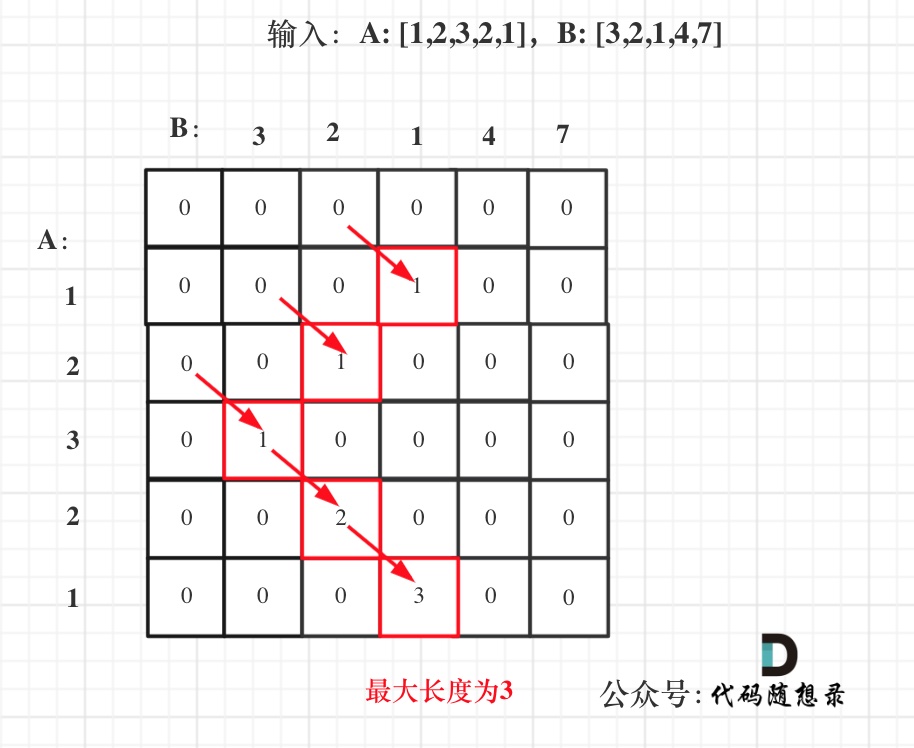
我们可以看出dp[i][j]都是由dp[i - 1][j - 1]推出。那么压缩为一维数组,也就是dp[j]都是由dp[j - 1]推出。
@@ -560,10 +558,45 @@ impl Solution {
}
```
+### C:
+```c
+int findLength(int* nums1, int nums1Size, int* nums2, int nums2Size) {
+ int dp[nums1Size + 1][nums2Size + 1];
+ memset(dp, 0, sizeof(dp));
+ int result = 0;
+ for (int i = 1; i <= nums1Size; ++i) {
+ for (int j = 1; j <= nums2Size; ++j) {
+ if(nums1[i - 1] == nums2[j - 1]){
+ dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
+ }
+ if(dp[i][j] > result){
+ result = dp[i][j];
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return result;
+}
+```
+
+### Cangjie
+
+```cangjie
+func findLength(nums1: Array, nums2: Array): Int64 {
+ let n = nums1.size
+ let m = nums2.size
+ let dp = Array(n + 1, {_ => Array(m + 1, item: 0)})
+ var res = 0
+ for (i in 1..=n) {
+ for (j in 1..=m) {
+ if (nums1[i - 1] == nums2[j - 1]) {
+ dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1
+ }
+ res = max(res, dp[i][j])
+ }
+ }
+ return res
+}
+```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0724.\345\257\273\346\211\276\346\225\260\347\273\204\347\232\204\344\270\255\345\277\203\347\264\242\345\274\225.md" "b/problems/0724.\345\257\273\346\211\276\346\225\260\347\273\204\347\232\204\344\270\255\345\277\203\347\264\242\345\274\225.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 9ed8535e0d..bccca4f2d4
--- "a/problems/0724.\345\257\273\346\211\276\346\225\260\347\273\204\347\232\204\344\270\255\345\277\203\347\264\242\345\274\225.md"
+++ "b/problems/0724.\345\257\273\346\211\276\346\225\260\347\273\204\347\232\204\344\270\255\345\277\203\347\264\242\345\274\225.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0724.\345\257\273\346\211\276\346\225\260\347\273\204\347\232\204\344\270\255\345\277\203\347\264\242\345\274\225.md" "b/problems/0724.\345\257\273\346\211\276\346\225\260\347\273\204\347\232\204\344\270\255\345\277\203\347\264\242\345\274\225.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 9ed8535e0d..bccca4f2d4
--- "a/problems/0724.\345\257\273\346\211\276\346\225\260\347\273\204\347\232\204\344\270\255\345\277\203\347\264\242\345\274\225.md"
+++ "b/problems/0724.\345\257\273\346\211\276\346\225\260\347\273\204\347\232\204\344\270\255\345\277\203\347\264\242\345\274\225.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 724.寻找数组的中心下标
@@ -159,7 +157,3 @@ function pivotIndex(nums: number[]): number {
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0738.\345\215\225\350\260\203\351\200\222\345\242\236\347\232\204\346\225\260\345\255\227.md" "b/problems/0738.\345\215\225\350\260\203\351\200\222\345\242\236\347\232\204\346\225\260\345\255\227.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 400dc90daa..17182778ae
--- "a/problems/0738.\345\215\225\350\260\203\351\200\222\345\242\236\347\232\204\346\225\260\345\255\227.md"
+++ "b/problems/0738.\345\215\225\350\260\203\351\200\222\345\242\236\347\232\204\346\225\260\345\255\227.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0738.\345\215\225\350\260\203\351\200\222\345\242\236\347\232\204\346\225\260\345\255\227.md" "b/problems/0738.\345\215\225\350\260\203\351\200\222\345\242\236\347\232\204\346\225\260\345\255\227.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 400dc90daa..17182778ae
--- "a/problems/0738.\345\215\225\350\260\203\351\200\222\345\242\236\347\232\204\346\225\260\345\255\227.md"
+++ "b/problems/0738.\345\215\225\350\260\203\351\200\222\345\242\236\347\232\204\346\225\260\345\255\227.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 738.单调递增的数字
@@ -190,9 +188,9 @@ class Solution:
贪心(版本一)
```python
class Solution:
- def monotoneIncreasingDigits(self, N: int) -> int:
+ def monotoneIncreasingDigits(self, n: int) -> int:
# 将整数转换为字符串
- strNum = str(N)
+ strNum = str(n)
# flag用来标记赋值9从哪里开始
# 设置为字符串长度,为了防止第二个for循环在flag没有被赋值的情况下执行
flag = len(strNum)
@@ -216,9 +214,9 @@ class Solution:
贪心(版本二)
```python
class Solution:
- def monotoneIncreasingDigits(self, N: int) -> int:
+ def monotoneIncreasingDigits(self, n: int) -> int:
# 将整数转换为字符串
- strNum = list(str(N))
+ strNum = list(str(n))
# 从右往左遍历字符串
for i in range(len(strNum) - 1, 0, -1):
@@ -238,9 +236,9 @@ class Solution:
```python
class Solution:
- def monotoneIncreasingDigits(self, N: int) -> int:
+ def monotoneIncreasingDigits(self, n: int) -> int:
# 将整数转换为字符串
- strNum = list(str(N))
+ strNum = list(str(n))
# 从右往左遍历字符串
for i in range(len(strNum) - 1, 0, -1):
@@ -258,8 +256,8 @@ class Solution:
```python
class Solution:
- def monotoneIncreasingDigits(self, N: int) -> int:
- strNum = str(N)
+ def monotoneIncreasingDigits(self, n: int) -> int:
+ strNum = str(n)
for i in range(len(strNum) - 1, 0, -1):
# 如果当前字符比前一个字符小,说明需要修改前一个字符
if strNum[i - 1] > strNum[i]:
@@ -272,27 +270,25 @@ class Solution:
```
### Go
```go
-func monotoneIncreasingDigits(N int) int {
- s := strconv.Itoa(N)//将数字转为字符串,方便使用下标
- ss := []byte(s)//将字符串转为byte数组,方便更改。
- n := len(ss)
- if n <= 1 {
- return N
- }
- for i := n-1; i > 0; i-- {
- if ss[i-1] > ss[i] { //前一个大于后一位,前一位减1,后面的全部置为9
- ss[i-1] -= 1
- for j := i; j < n; j++ { //后面的全部置为9
- ss[j] = '9'
- }
- }
- }
- res, _ := strconv.Atoi(string(ss))
- return res
+func monotoneIncreasingDigits(n int) int {
+ s := strconv.Itoa(n)
+ // 从左到右遍历字符串,找到第一个不满足单调递增的位置
+ for i := len(s) - 2; i >= 0; i-- {
+ if s[i] > s[i+1] {
+ // 将该位置的数字减1
+ s = s[:i] + string(s[i]-1) + s[i+1:]
+ // 将该位置之后的所有数字置为9
+ for j := i + 1; j < len(s); j++ {
+ s = s[:j] + "9" + s[j+1:]
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ result, _ := strconv.Atoi(s)
+ return result
}
```
-### Javascript
+### JavaScript
```Javascript
var monotoneIncreasingDigits = function(n) {
n = n.toString()
@@ -392,7 +388,33 @@ impl Solution {
}
}
```
+### C
+
+```c
+int monotoneIncreasingDigits(int n) {
+ char str[11];
+ // 将数字转换为字符串
+ sprintf(str, "%d", n);
+ int len = strlen(str);
+ int flag = strlen(str);
+ for(int i = len - 1; i > 0; i--){
+ if(str[i] < str[i - 1]){
+ str[i - 1]--;
+ flag = i;
+ }
+ }
+ for(int i = flag; i < len; i++){
+ str[i] = '9';
+ }
+ // 字符串转数字
+ return atoi(str);
+}
+```
+
+
+
### C#
+
```csharp
public class Solution
{
@@ -417,8 +439,4 @@ public class Solution
}
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0739.\346\257\217\346\227\245\346\270\251\345\272\246.md" "b/problems/0739.\346\257\217\346\227\245\346\270\251\345\272\246.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index fdb11c63e3..2ad7e6b79b
--- "a/problems/0739.\346\257\217\346\227\245\346\270\251\345\272\246.md"
+++ "b/problems/0739.\346\257\217\346\227\245\346\270\251\345\272\246.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0739.\346\257\217\346\227\245\346\270\251\345\272\246.md" "b/problems/0739.\346\257\217\346\227\245\346\270\251\345\272\246.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index fdb11c63e3..2ad7e6b79b
--- "a/problems/0739.\346\257\217\346\227\245\346\270\251\345\272\246.md"
+++ "b/problems/0739.\346\257\217\346\227\245\346\270\251\345\272\246.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
@@ -71,7 +69,7 @@
首先先将第一个遍历元素加入单调栈
-
+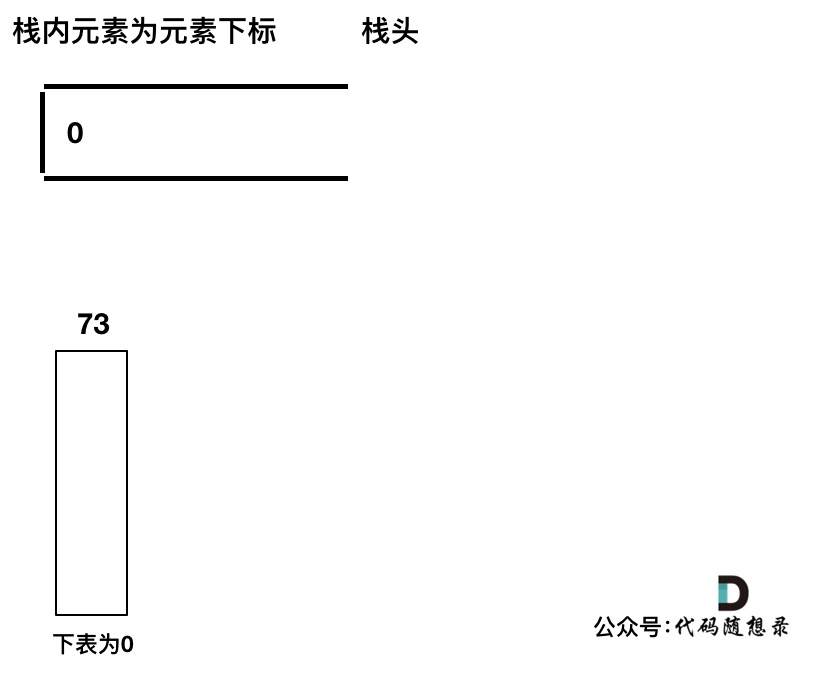
---------
@@ -79,65 +77,65 @@
我们要保持一个递增单调栈(从栈头到栈底),所以将T[0]弹出,T[1]加入,此时result数组可以记录了,result[0] = 1,即T[0]右面第一个比T[0]大的元素是T[1]。
-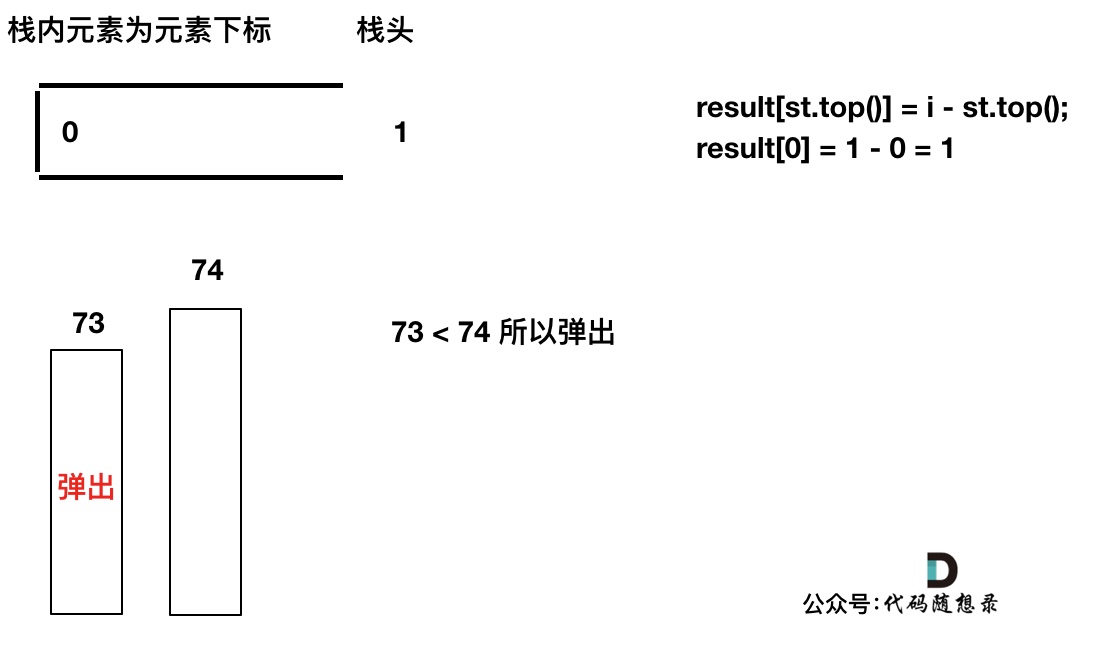
+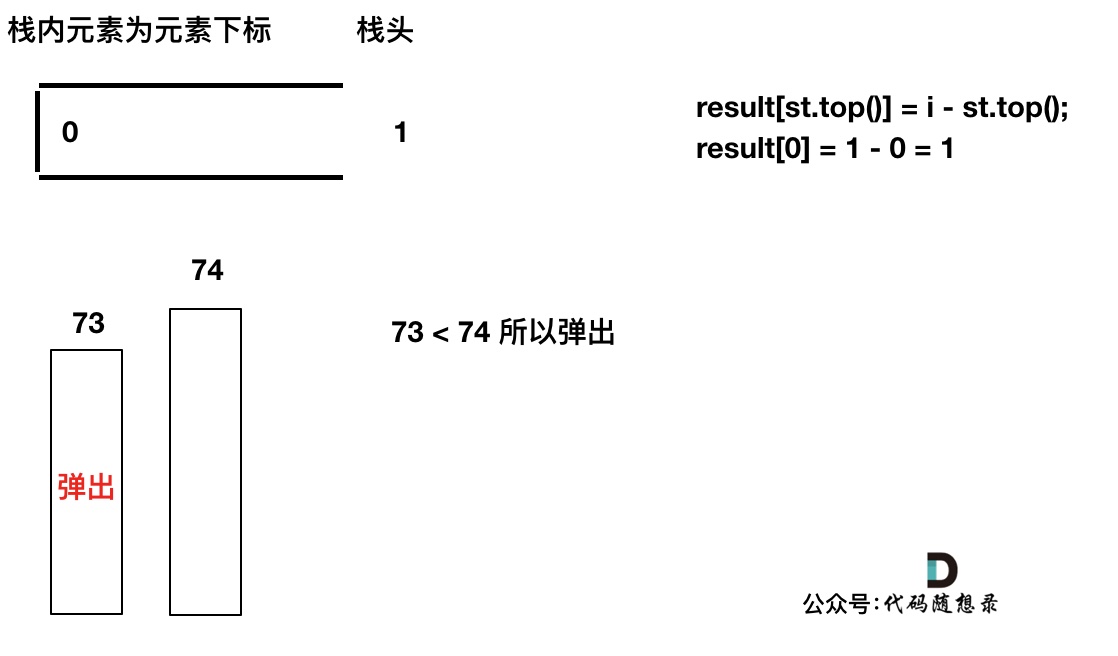
-----------
加入T[2],同理,T[1]弹出
-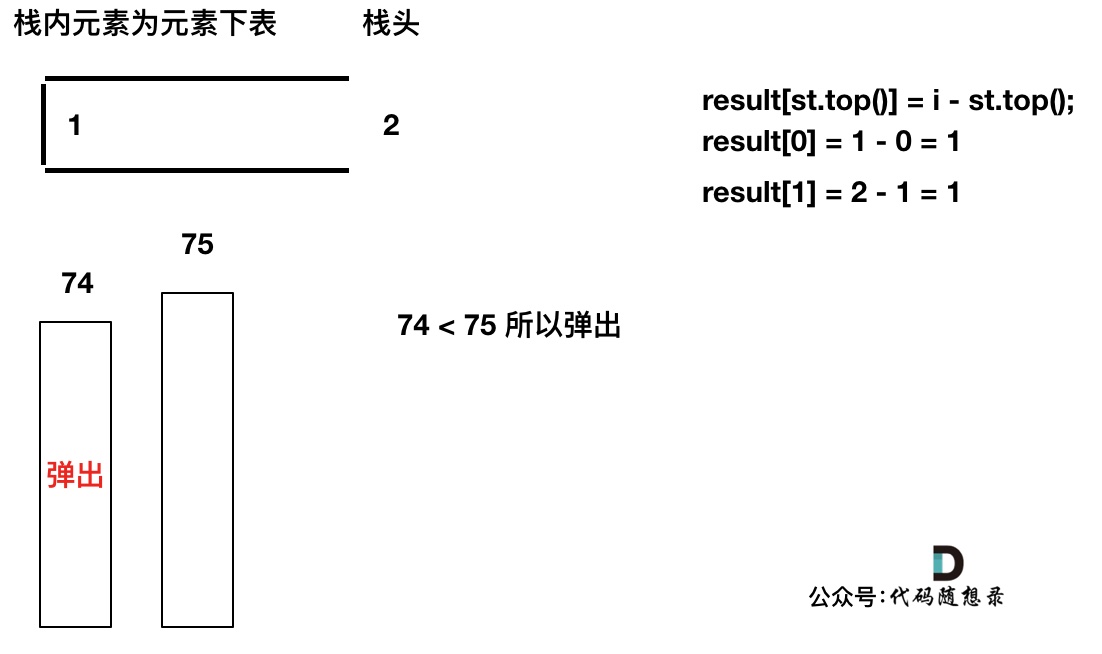
+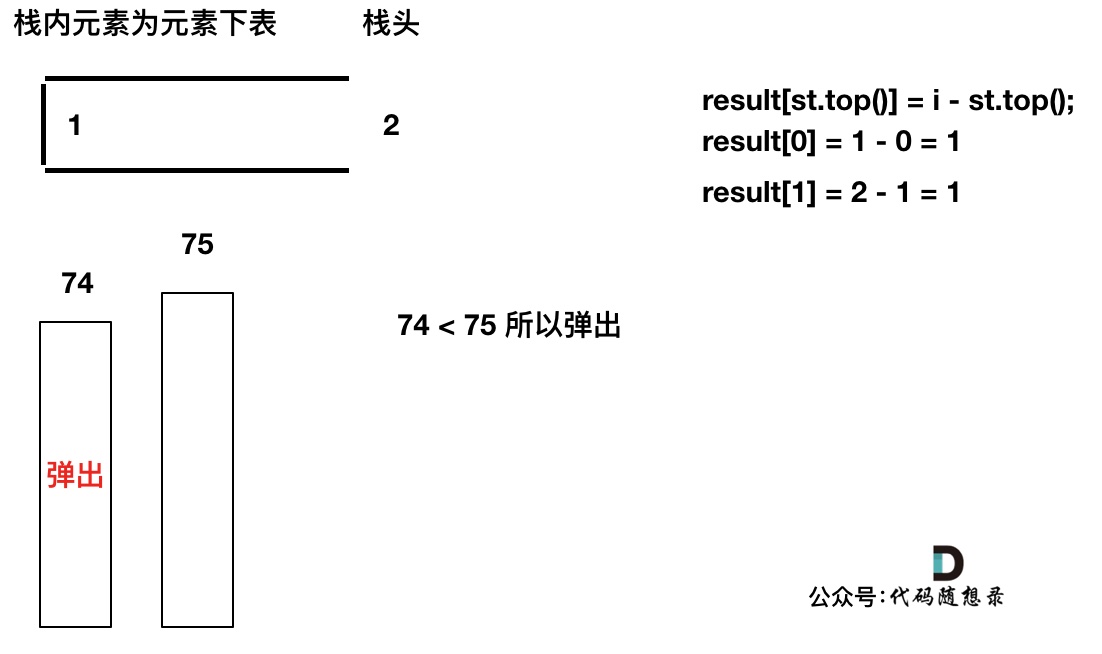
-------
加入T[3],T[3] < T[2] (当前遍历的元素T[i]小于栈顶元素T[st.top()]的情况),加T[3]加入单调栈。
-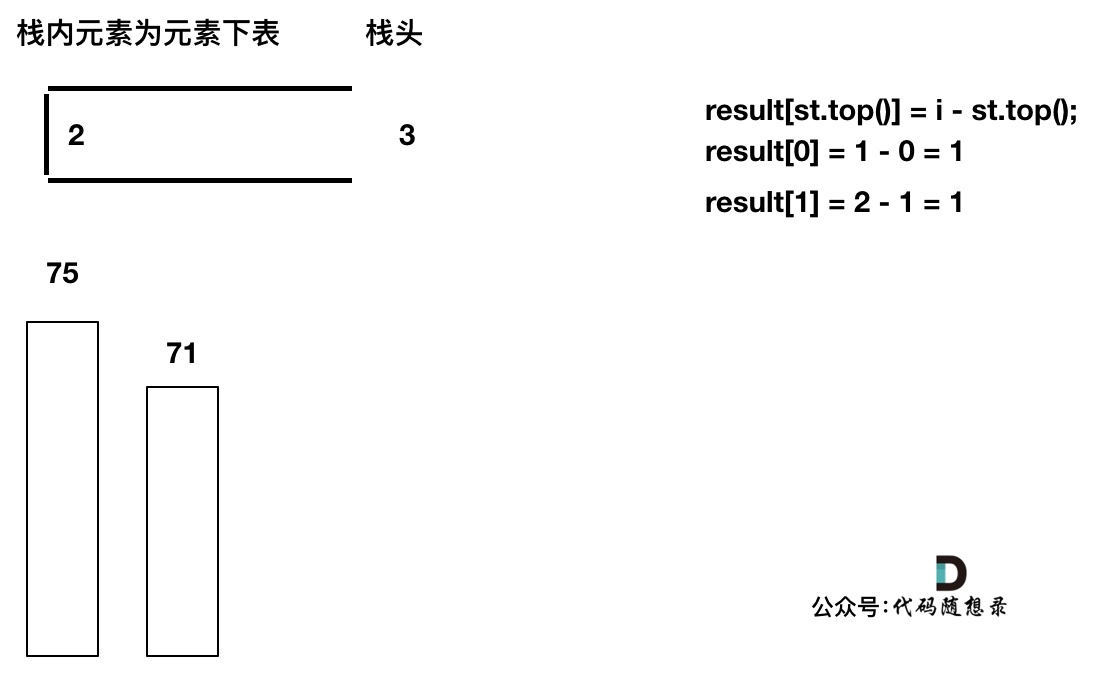
+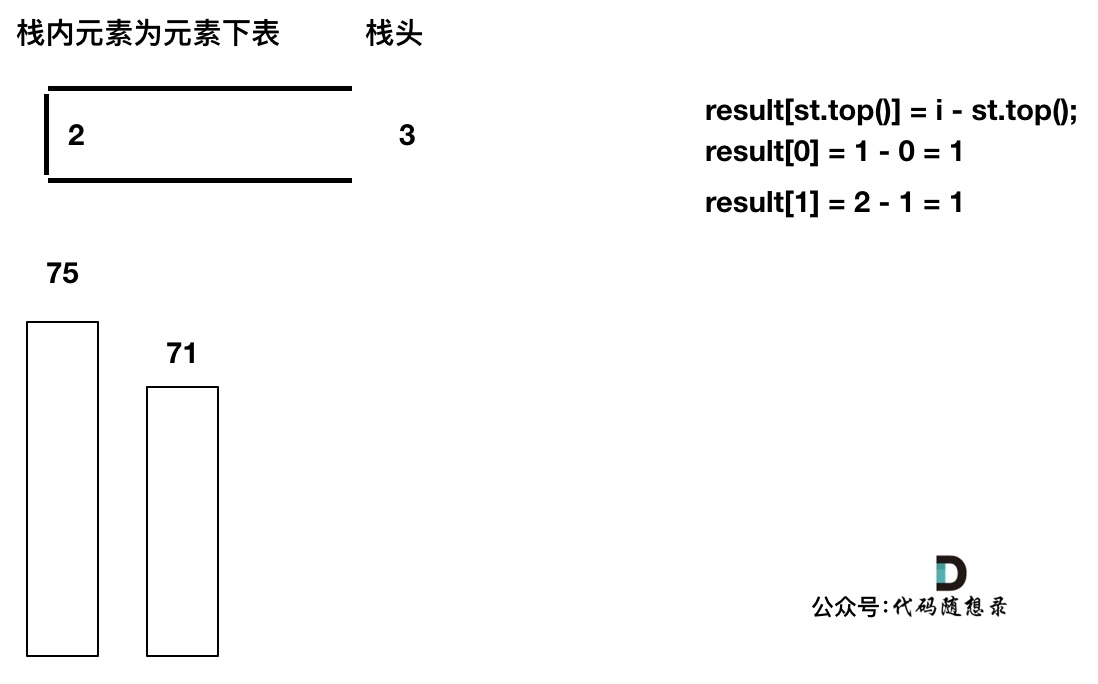
---------
加入T[4],T[4] == T[3] (当前遍历的元素T[i]等于栈顶元素T[st.top()]的情况),此时依然要加入栈,不用计算距离,因为我们要求的是右面第一个大于本元素的位置,而不是大于等于!
-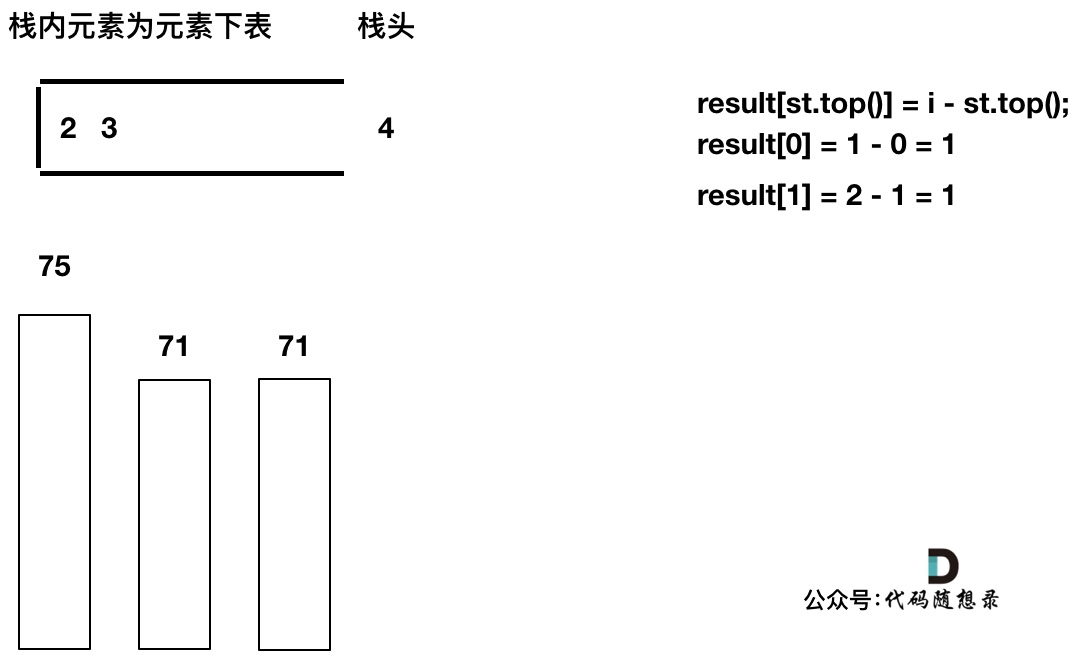
+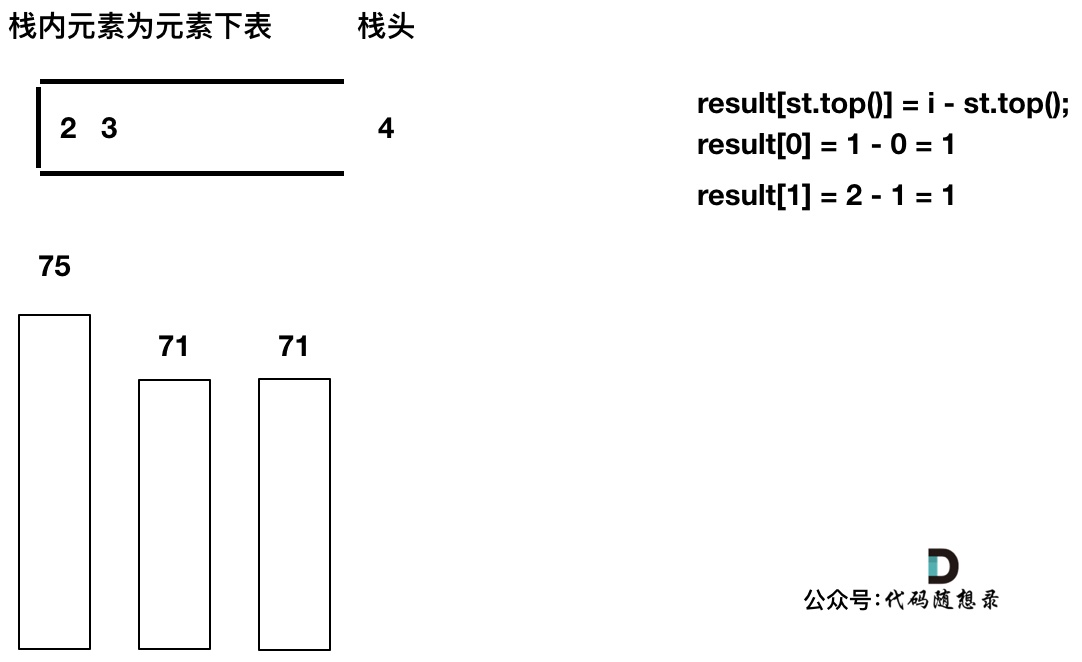
---------
加入T[5],T[5] > T[4] (当前遍历的元素T[i]大于栈顶元素T[st.top()]的情况),将T[4]弹出,同时计算距离,更新result
-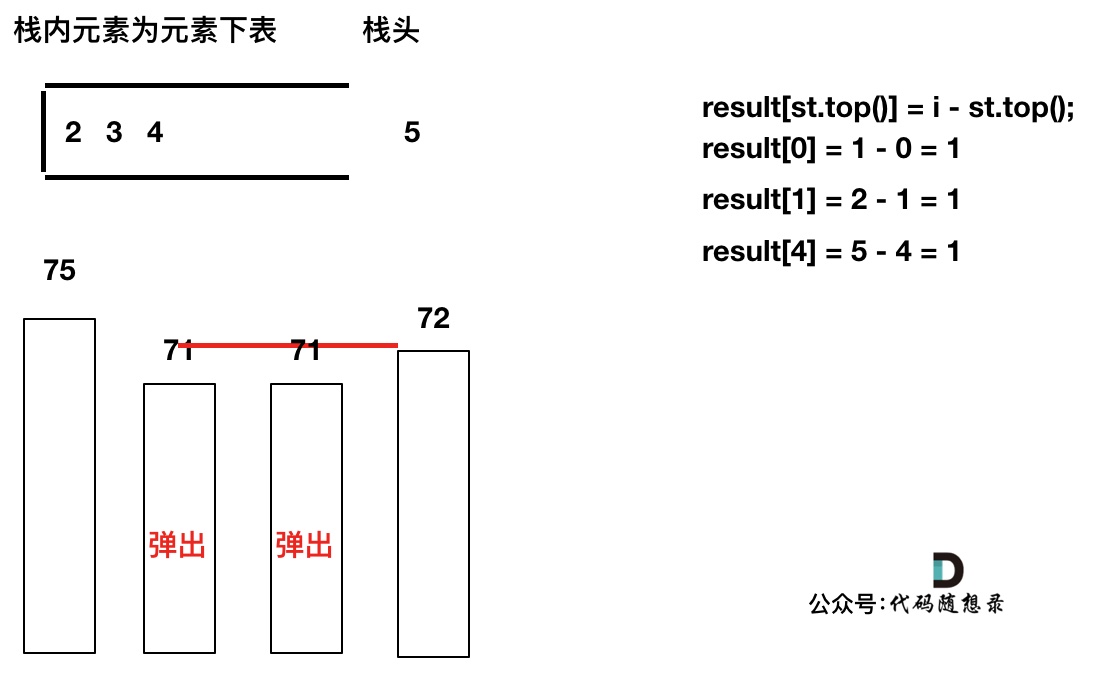
+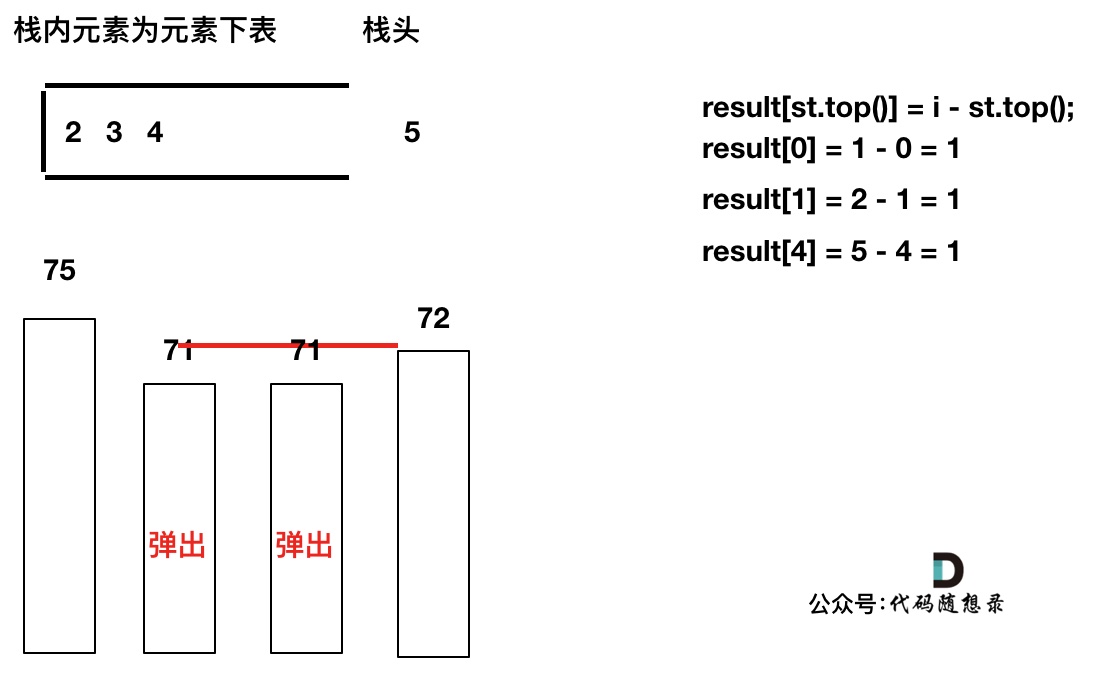
----------
T[4]弹出之后, T[5] > T[3] (当前遍历的元素T[i]大于栈顶元素T[st.top()]的情况),将T[3]继续弹出,同时计算距离,更新result
-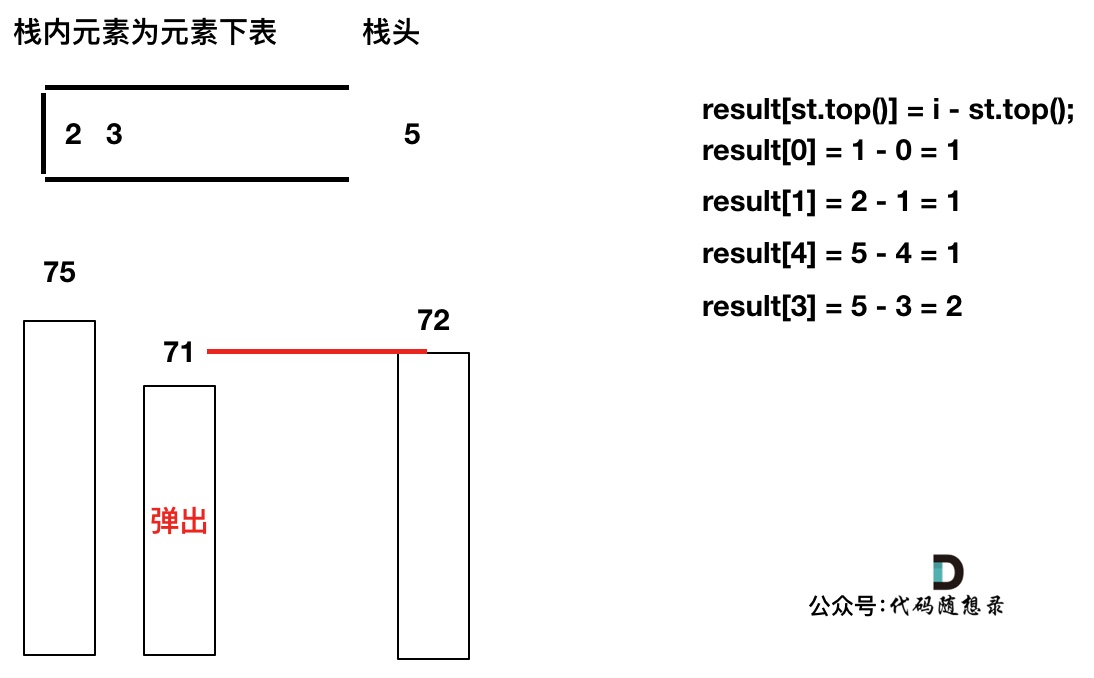
+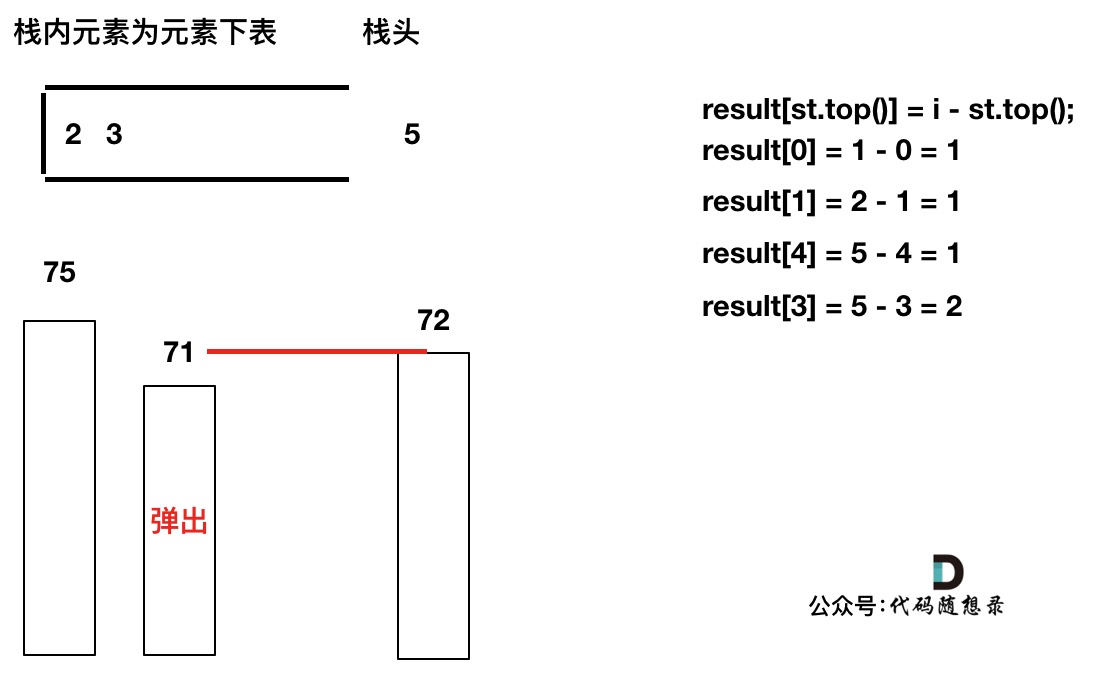
-------
直到发现T[5]小于T[st.top()],终止弹出,将T[5]加入单调栈
-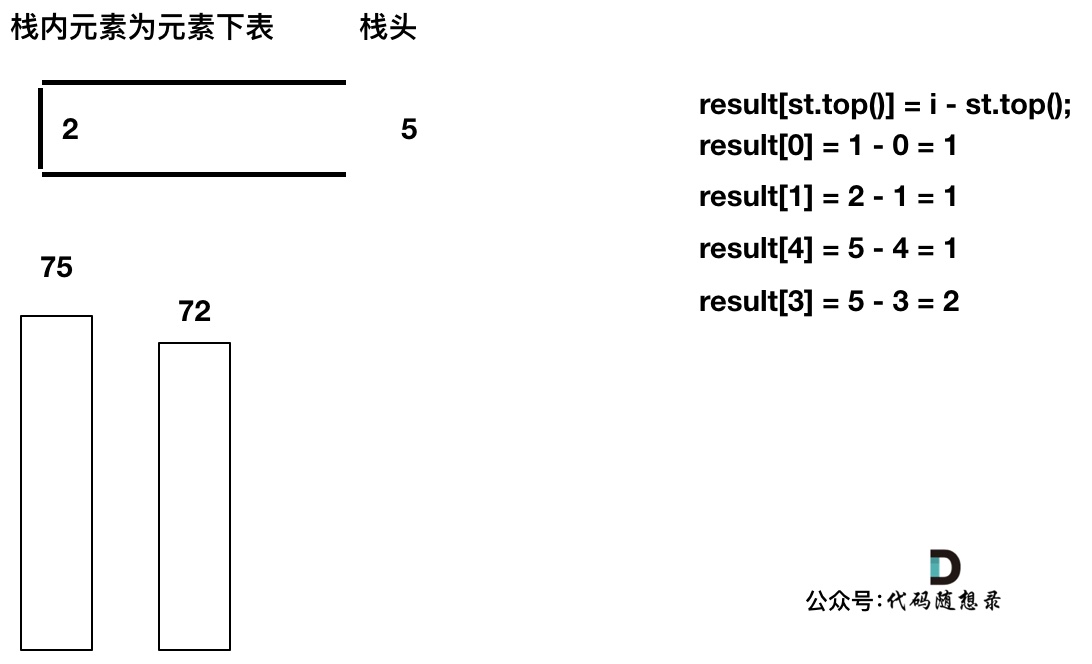
+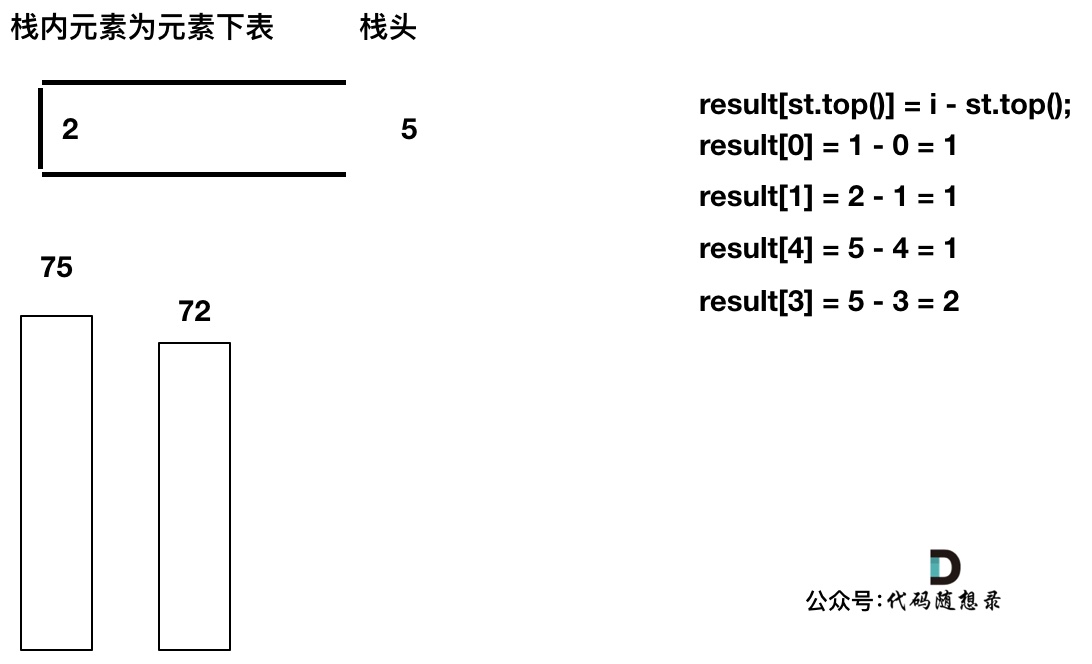
-------
加入T[6],同理,需要将栈里的T[5],T[2]弹出
-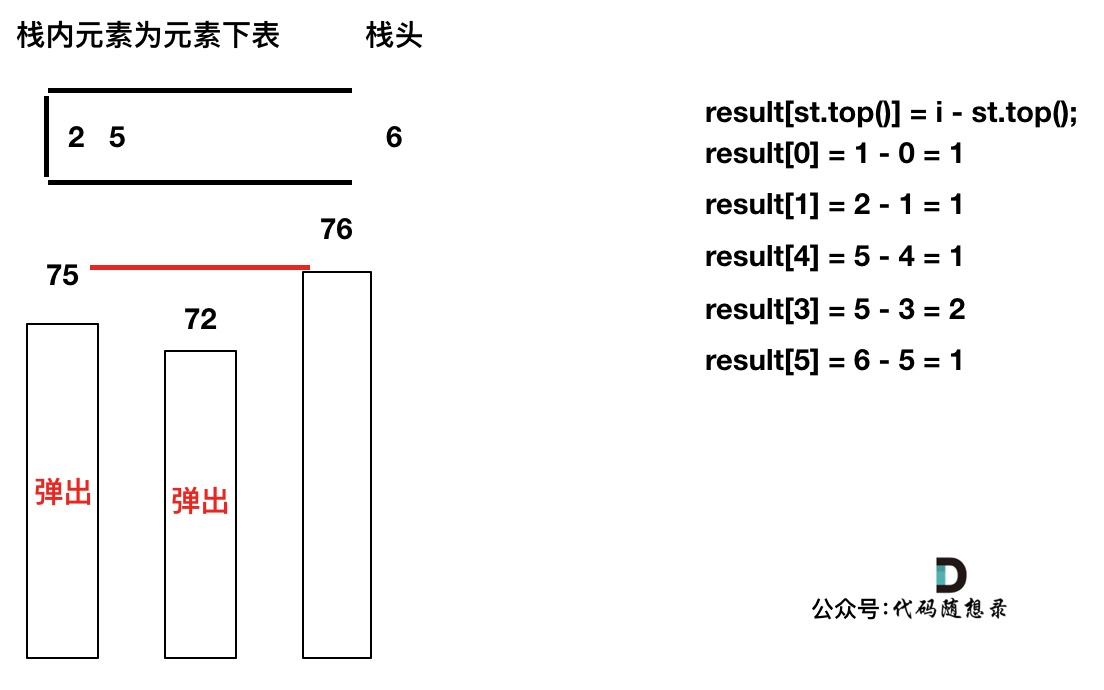
+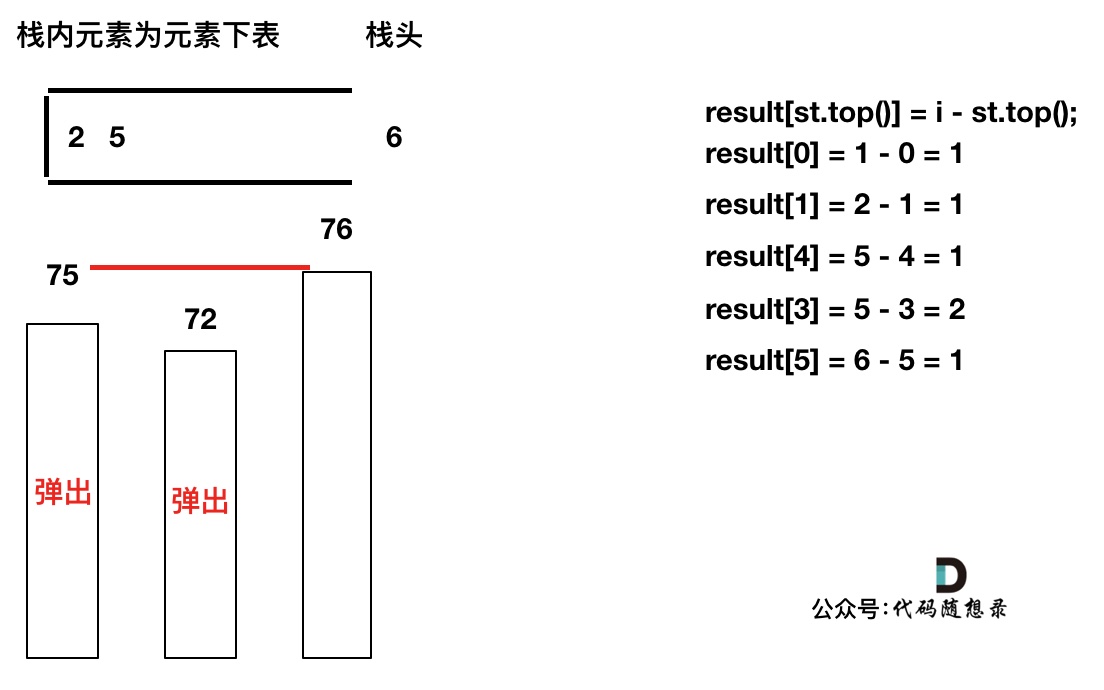
-------
同理,继续弹出
-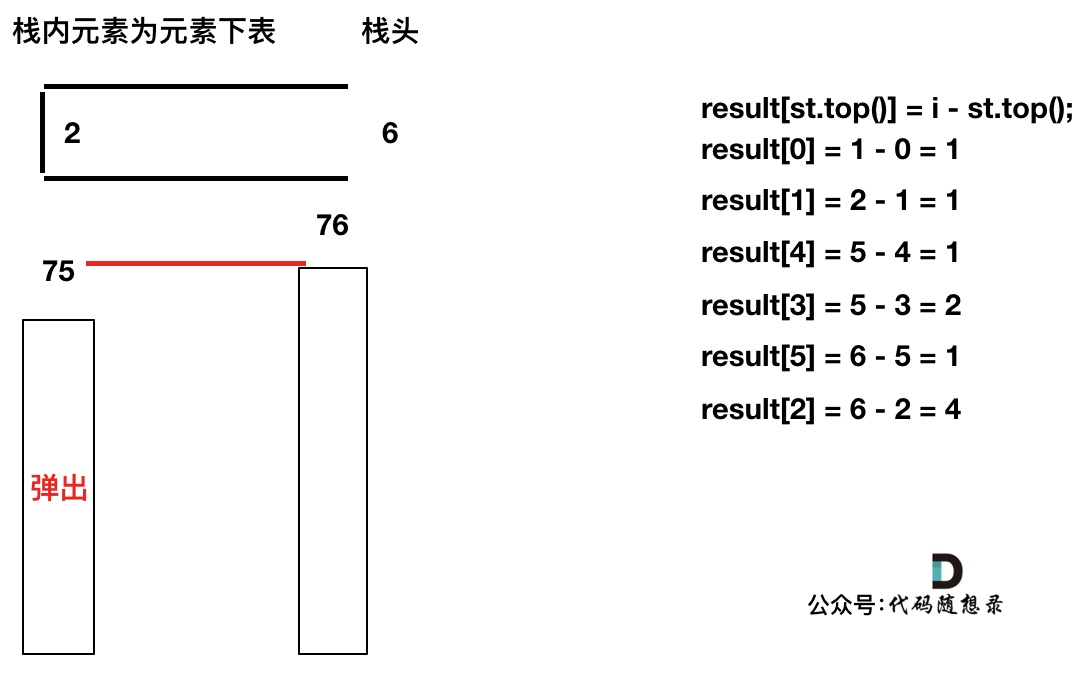
+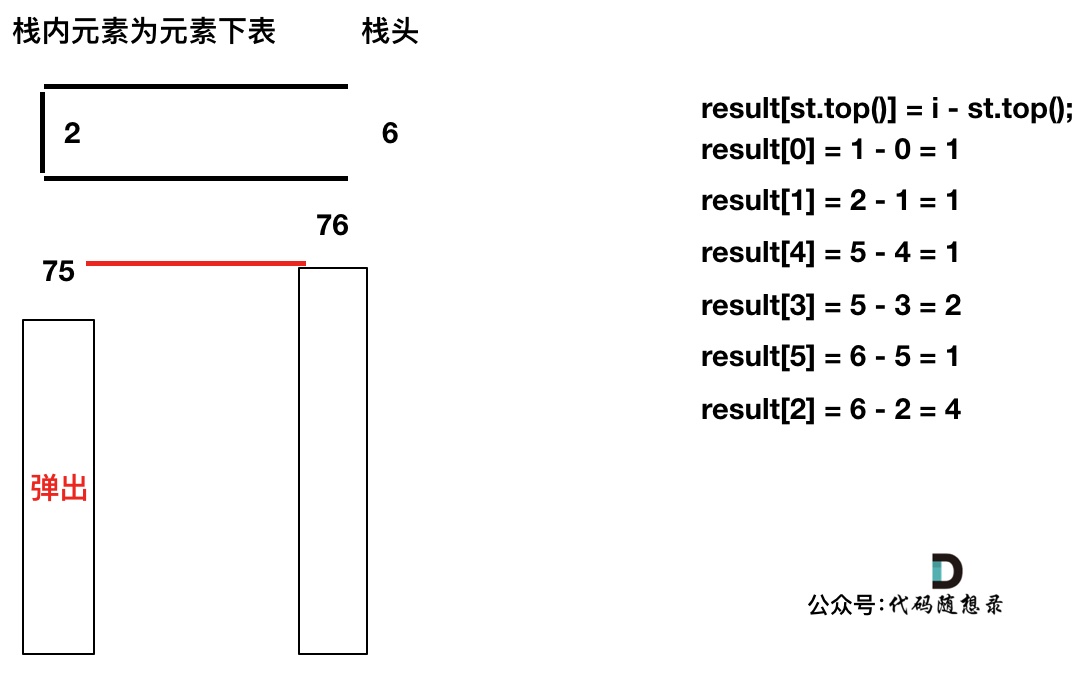
------
此时栈里只剩下了T[6]
-
+
------------
加入T[7], T[7] < T[6] 直接入栈,这就是最后的情况,result数组也更新完了。
-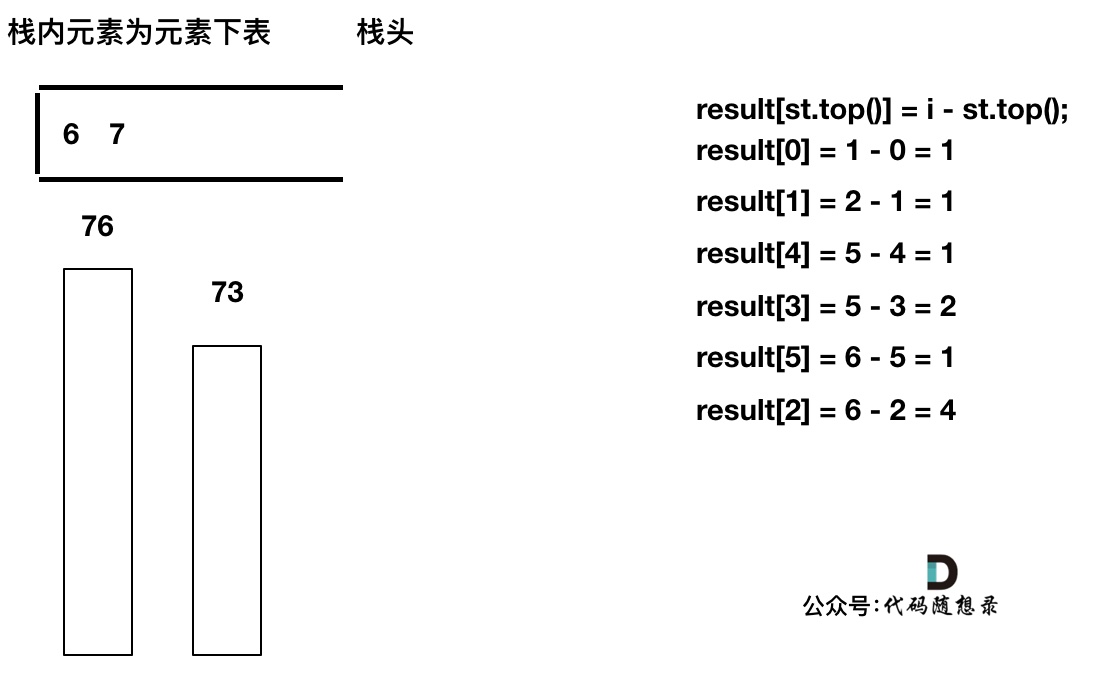
+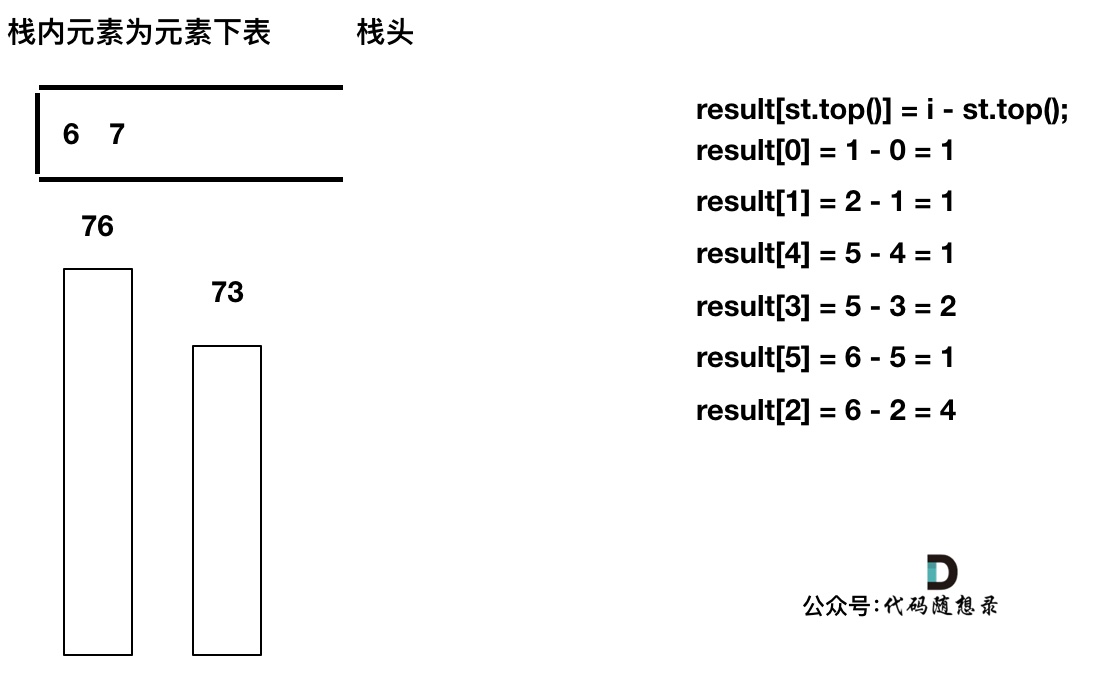
此时有同学可能就疑惑了,那result[6] , result[7]怎么没更新啊,元素也一直在栈里。
@@ -215,6 +213,38 @@ public:
## 其他语言版本
+### C:
+
+```C
+/**
+ * Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free().
+ */
+int* dailyTemperatures(int* temperatures, int temperaturesSize, int* returnSize) {
+ int len = temperaturesSize;
+ *returnSize = len;
+
+ int *result = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * len);
+ memset(result, 0x00, sizeof(int) * len);
+
+ int stack[len];
+ memset(stack, 0x00, sizeof(stack));
+ int top = 0;
+
+ for (int i = 1; i < len; i++) {
+ if (temperatures[i] <= temperatures[stack[top]]) { /* push */
+ stack[++top] = i;
+ } else {
+ while (top >= 0 && temperatures[i] > temperatures[stack[top]]) { /* stack not empty */
+ result[stack[top]] = i - stack[top];
+ top--; /* pop */
+ }
+ stack[++top] = i; /* push */
+ }
+ }
+ return result;
+}
+```
+
### Java:
```java
@@ -482,8 +512,4 @@ impl Solution {
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0743.\347\275\221\347\273\234\345\273\266\350\277\237\346\227\266\351\227\264.md" "b/problems/0743.\347\275\221\347\273\234\345\273\266\350\277\237\346\227\266\351\227\264.md"
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..40b699c18f
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/problems/0743.\347\275\221\347\273\234\345\273\266\350\277\237\346\227\266\351\227\264.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,1230 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
+
+# 743.网络延迟时间
+
+https://leetcode.cn/problems/network-delay-time/description/
+
+
+有 n 个网络节点,标记为 1 到 n。
+
+给你一个列表 times,表示信号经过 有向 边的传递时间。 times[i] = (ui, vi, wi),其中 ui 是源节点,vi 是目标节点, wi 是一个信号从源节点传递到目标节点的时间。
+
+现在,从某个节点 K 发出一个信号。需要多久才能使所有节点都收到信号?如果不能使所有节点收到信号,返回 -1 。
+
+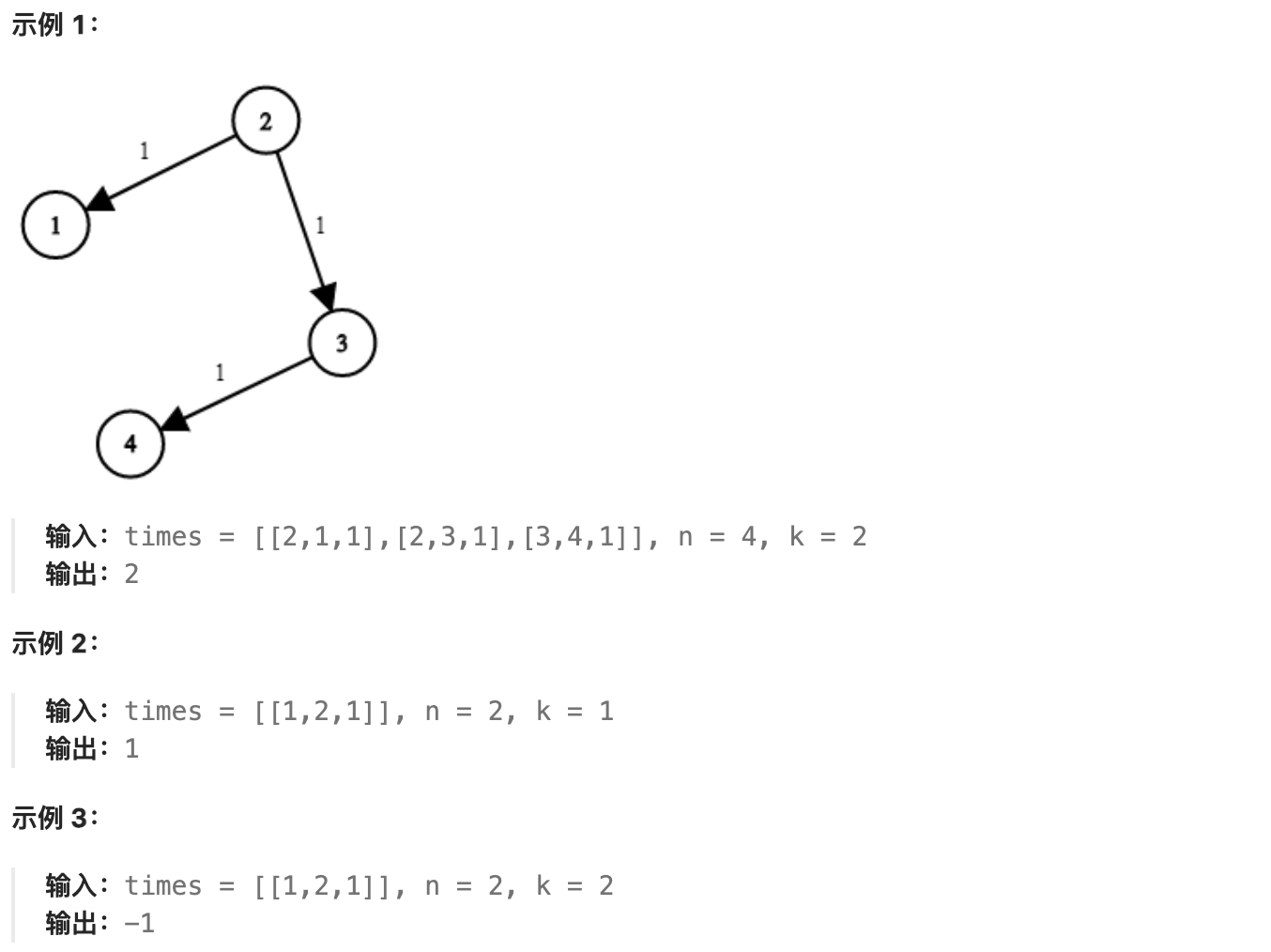
+
+提示:
+
+* 1 <= k <= n <= 100
+* 1 <= times.length <= 6000
+* times[i].length == 3
+* 1 <= ui, vi <= n
+* ui != vi
+* 0 <= wi <= 100
+* 所有 (ui, vi) 对都 互不相同(即,不含重复边)
+
+# dijkstra 精讲
+
+本题就是求最短路,最短路是图论中的经典问题即:给出一个有向图,一个起点,一个终点,问起点到终点的最短路径。
+
+接下来,我们来详细讲解最短路算法中的 dijkstra 算法。
+
+dijkstra算法:在有权图(权值非负数)中求从起点到其他节点的最短路径算法。
+
+需要注意两点:
+
+* dijkstra 算法可以同时求 起点到所有节点的最短路径
+* 权值不能为负数
+
+(这两点后面我们会讲到)
+
+如本题示例中的图:
+
+
+
+起点(节点1)到终点(节点7) 的最短路径是 图中 标记绿线的部分。
+
+最短路径的权值为12。
+
+其实 dijkstra 算法 和 我们之前讲解的prim算法思路非常接近,如果大家认真学过[prim算法](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/yX936hHC6Z10K36Vm1Wl9w),那么理解 Dijkstra 算法会相对容易很多。(这也是我要先讲prim再讲dijkstra的原因)
+
+dijkstra 算法 同样是贪心的思路,不断寻找距离 源点最近的没有访问过的节点。
+
+这里我也给出 **dijkstra三部曲**:
+
+1. 第一步,选源点到哪个节点近且该节点未被访问过
+2. 第二步,该最近节点被标记访问过
+3. 第三步,更新非访问节点到源点的距离(即更新minDist数组)
+
+大家此时已经会发现,这和prim算法 怎么这么像呢。
+
+我在[prim算法](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/yX936hHC6Z10K36Vm1Wl9w)讲解中也给出了三部曲。 prim 和 dijkstra 确实很像,思路也是类似的,这一点我在后面还会详细来讲。
+
+在dijkstra算法中,同样有一个数组很重要,起名为:minDist。
+
+**minDist数组 用来记录 每一个节点距离源点的最小距离**。
+
+理解这一点很重要,也是理解 dijkstra 算法的核心所在。
+
+大家现在看着可能有点懵,不知道什么意思。
+
+没关系,先让大家有一个印象,对理解后面讲解有帮助。
+
+我们先来画图看一下 dijkstra 的工作过程,以本题示例为例: (以下为朴素版dijkstra的思路)
+
+(**示例中节点编号是从1开始,所以为了让大家看的不晕,minDist数组下标我也从 1 开始计数,下标0 就不使用了,这样 下标和节点标号就可以对应上了,避免大家搞混**)
+
+## 朴素版dijkstra
+
+### 模拟过程
+
+-----------
+
+0、初始化
+
+minDist数组数值初始化为int最大值。
+
+这里在强点一下 **minDist数组的含义:记录所有节点到源点的最短路径**,那么初始化的时候就应该初始为最大值,这样才能在后续出现最短路径的时候及时更新。
+
+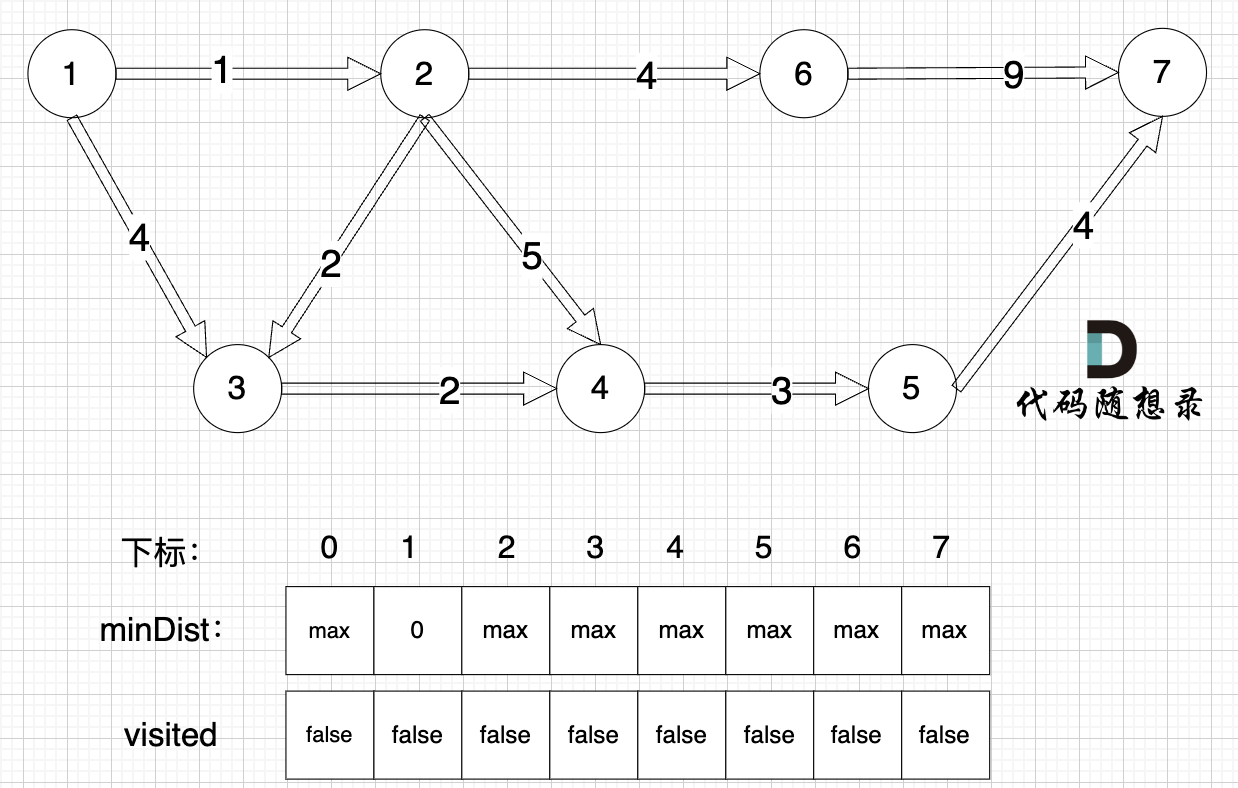
+
+(图中,max 表示默认值,节点0 不做处理,统一从下标1 开始计算,这样下标和节点数值统一, 方便大家理解,避免搞混)
+
+源点(节点1) 到自己的距离为0,所以 minDist[1] = 0
+
+此时所有节点都没有被访问过,所以 visited数组都为0
+
+---------------
+
+以下为dijkstra 三部曲
+
+1、选源点到哪个节点近且该节点未被访问过
+
+源点距离源点最近,距离为0,且未被访问。
+
+2、该最近节点被标记访问过
+
+标记源点访问过
+
+3、更新非访问节点到源点的距离(即更新minDist数组) ,如图:
+
+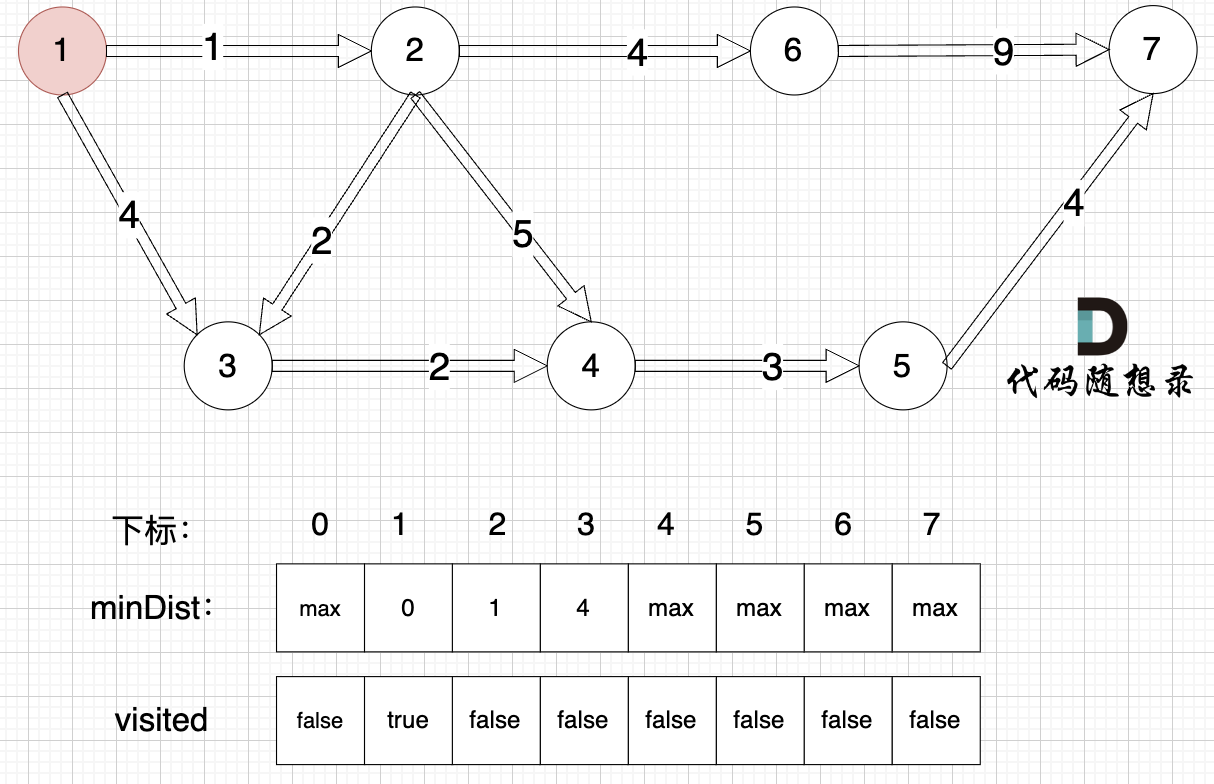
+
+
+更新 minDist数组,即:源点(节点1) 到 节点2 和 节点3的距离。
+
+* 源点到节点2的最短距离为1,小于原minDist[2]的数值max,更新minDist[2] = 1
+* 源点到节点3的最短距离为4,小于原minDist[3]的数值max,更新minDist[4] = 4
+
+可能有录友问:为啥和 minDist[2] 比较?
+
+再强调一下 minDist[2] 的含义,它表示源点到节点2的最短距离,那么目前我们得到了 源点到节点2的最短距离为1,小于默认值max,所以更新。 minDist[3]的更新同理
+
+
+-------------
+
+1、选源点到哪个节点近且该节点未被访问过
+
+未访问过的节点中,源点到节点2距离最近,选节点2
+
+2、该最近节点被标记访问过
+
+节点2被标记访问过
+
+3、更新非访问节点到源点的距离(即更新minDist数组) ,如图:
+
+
+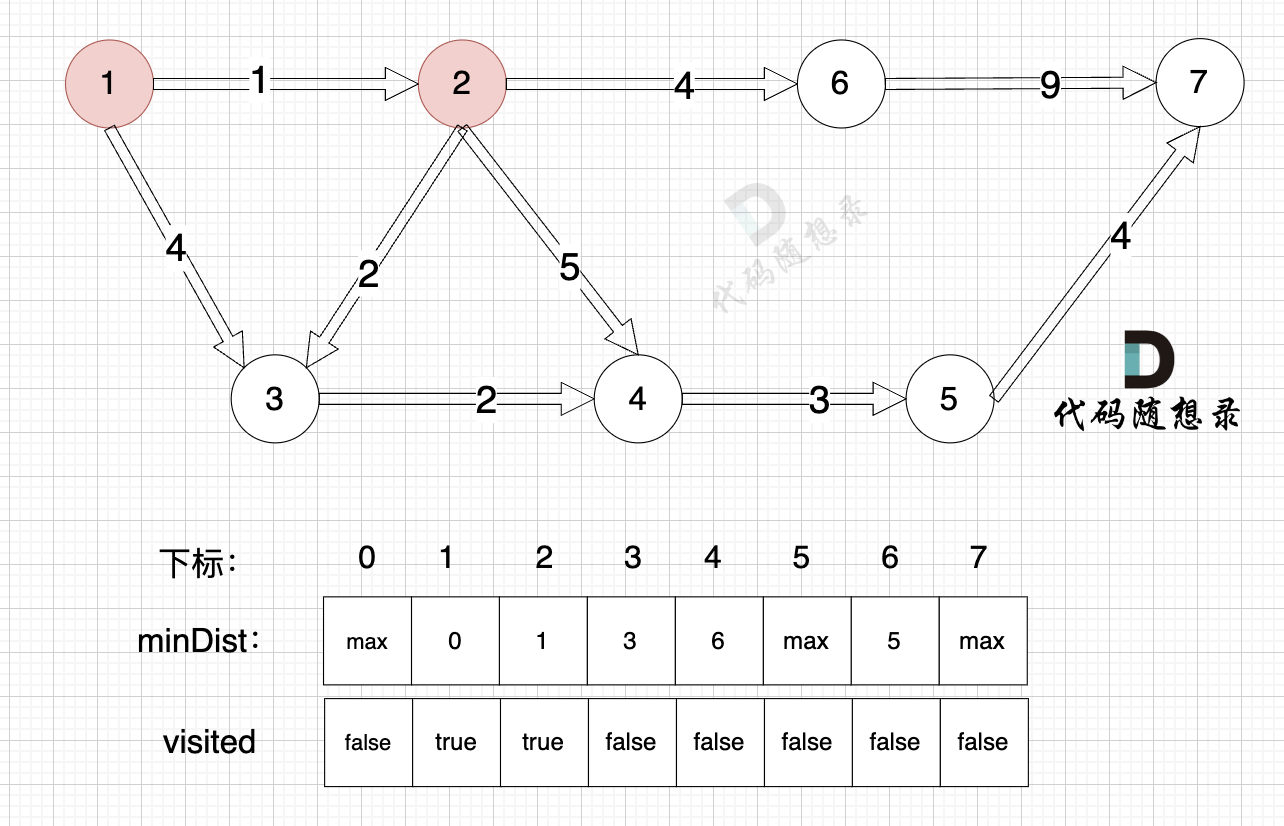
+
+更新 minDist数组,即:源点(节点1) 到 节点6 、 节点3 和 节点4的距离。
+
+**为什么更新这些节点呢? 怎么不更新其他节点呢**?
+
+因为 源点(节点1)通过 已经计算过的节点(节点2) 可以链接到的节点 有 节点3,节点4和节点6.
+
+
+更新 minDist数组:
+
+* 源点到节点6的最短距离为5,小于原minDist[6]的数值max,更新minDist[6] = 5
+* 源点到节点3的最短距离为3,小于原minDist[3]的数值4,更新minDist[3] = 3
+* 源点到节点4的最短距离为6,小于原minDist[4]的数值max,更新minDist[4] = 6
+
+
+
+-------------------
+
+1、选源点到哪个节点近且该节点未被访问过
+
+未访问过的节点中,源点距离哪些节点最近,怎么算的?
+
+其实就是看 minDist数组里的数值,minDist 记录了 源点到所有节点的最近距离,结合visited数组筛选出未访问的节点就好。
+
+从 上面的图,或者 从minDist数组中,我们都能看出 未访问过的节点中,源点(节点1)到节点3距离最近。
+
+
+2、该最近节点被标记访问过
+
+节点3被标记访问过
+
+3、更新非访问节点到源点的距离(即更新minDist数组) ,如图:
+
+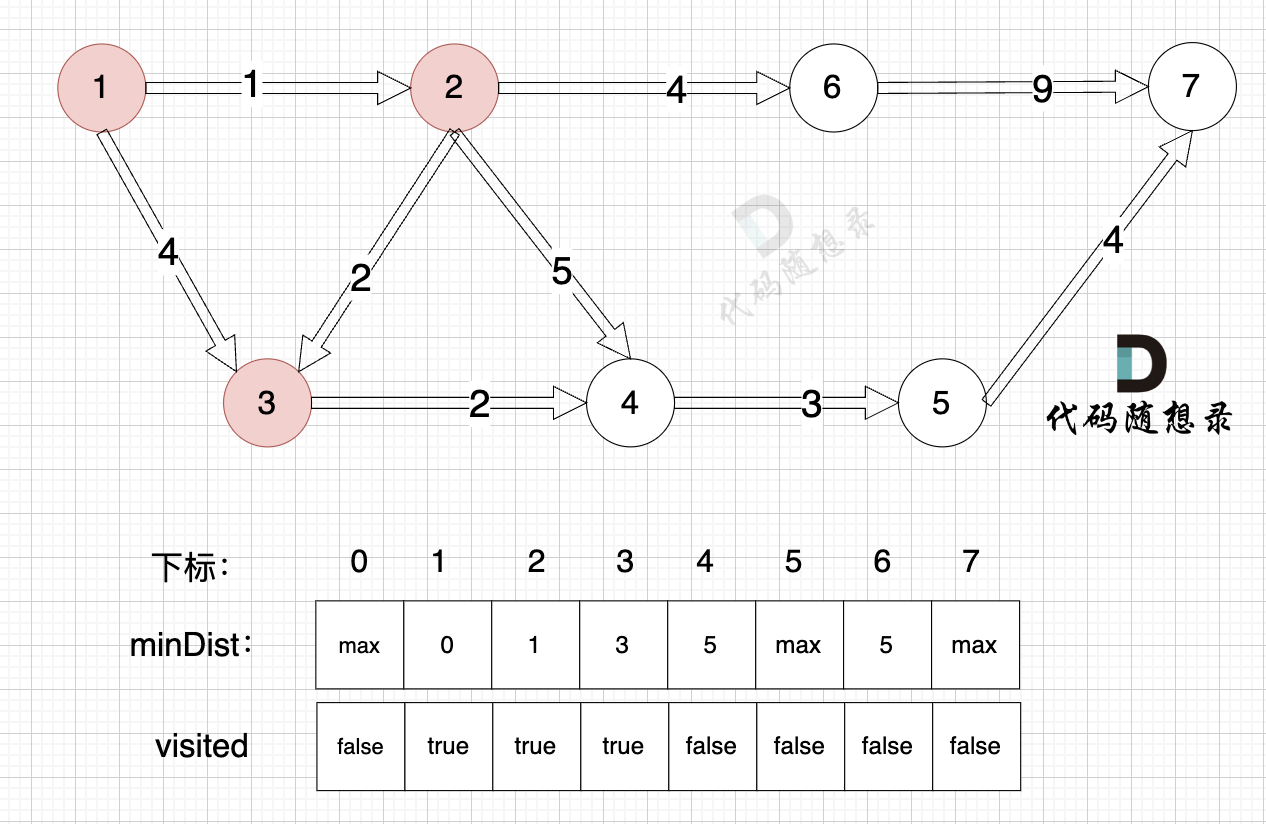
+
+由于节点3的加入,那么源点可以有新的路径链接到节点4 所以更新minDist数组:
+
+更新 minDist数组:
+
+* 源点到节点4的最短距离为5,小于原minDist[4]的数值6,更新minDist[4] = 5
+
+------------------
+
+1、选源点到哪个节点近且该节点未被访问过
+
+距离源点最近且没有被访问过的节点,有节点4 和 节点6,距离源点距离都是 5 (minDist[4] = 5,minDist[6] = 5) ,选哪个节点都可以。
+
+2、该最近节点被标记访问过
+
+节点4被标记访问过
+
+3、更新非访问节点到源点的距离(即更新minDist数组) ,如图:
+
+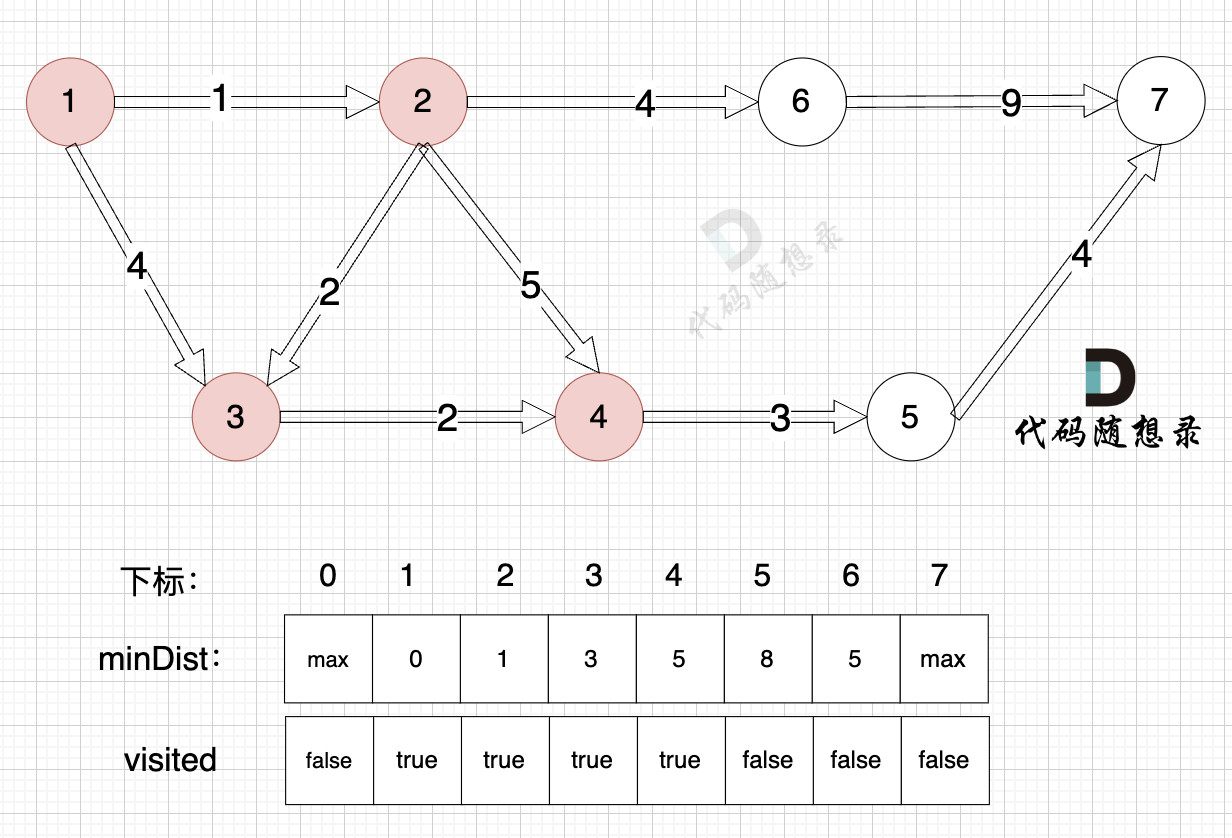
+
+由于节点4的加入,那么源点可以链接到节点5 所以更新minDist数组:
+
+* 源点到节点5的最短距离为8,小于原minDist[5]的数值max,更新minDist[5] = 8
+
+--------------
+
+1、选源点到哪个节点近且该节点未被访问过
+
+距离源点最近且没有被访问过的节点,是节点6,距离源点距离是 5 (minDist[6] = 5)
+
+
+2、该最近节点被标记访问过
+
+节点6 被标记访问过
+
+
+3、更新非访问节点到源点的距离(即更新minDist数组) ,如图:
+
+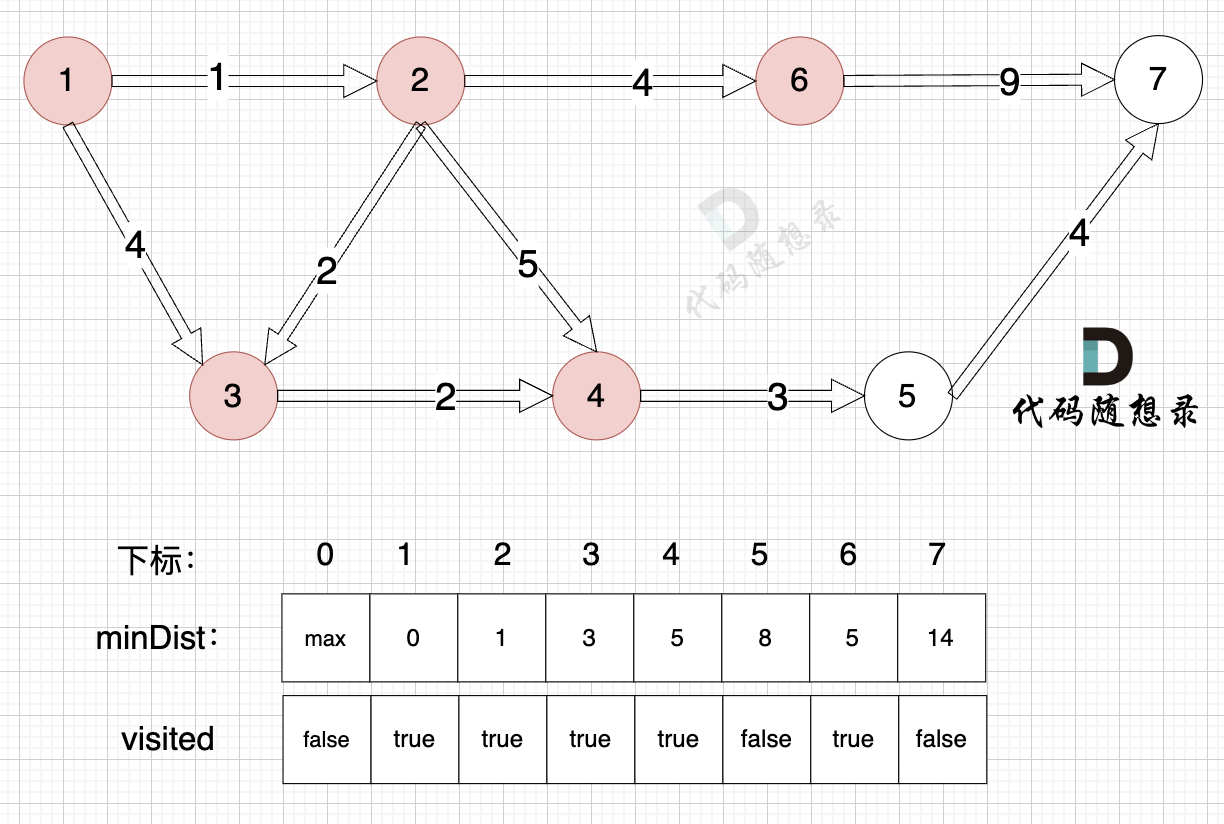
+
+由于节点6的加入,那么源点可以链接到节点7 所以 更新minDist数组:
+
+* 源点到节点7的最短距离为14,小于原minDist[7]的数值max,更新minDist[7] = 14
+
+
+
+-------------------
+
+1、选源点到哪个节点近且该节点未被访问过
+
+距离源点最近且没有被访问过的节点,是节点5,距离源点距离是 8 (minDist[5] = 8)
+
+2、该最近节点被标记访问过
+
+节点5 被标记访问过
+
+3、更新非访问节点到源点的距离(即更新minDist数组) ,如图:
+
+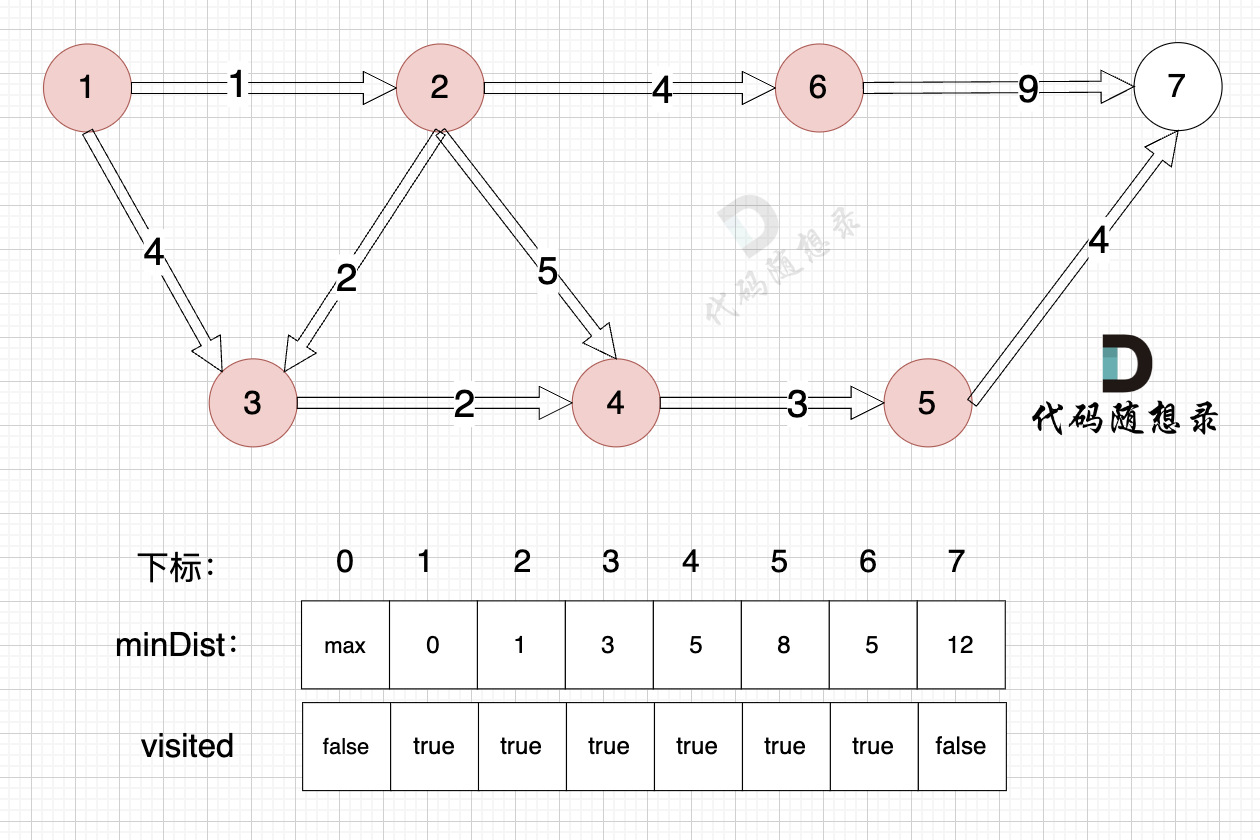
+
+由于节点5的加入,那么源点有新的路径可以链接到节点7 所以 更新minDist数组:
+
+* 源点到节点7的最短距离为12,小于原minDist[7]的数值14,更新minDist[7] = 12
+
+-----------------
+
+1、选源点到哪个节点近且该节点未被访问过
+
+距离源点最近且没有被访问过的节点,是节点7(终点),距离源点距离是 12 (minDist[7] = 12)
+
+2、该最近节点被标记访问过
+
+节点7 被标记访问过
+
+3、更新非访问节点到源点的距离(即更新minDist数组) ,如图:
+
+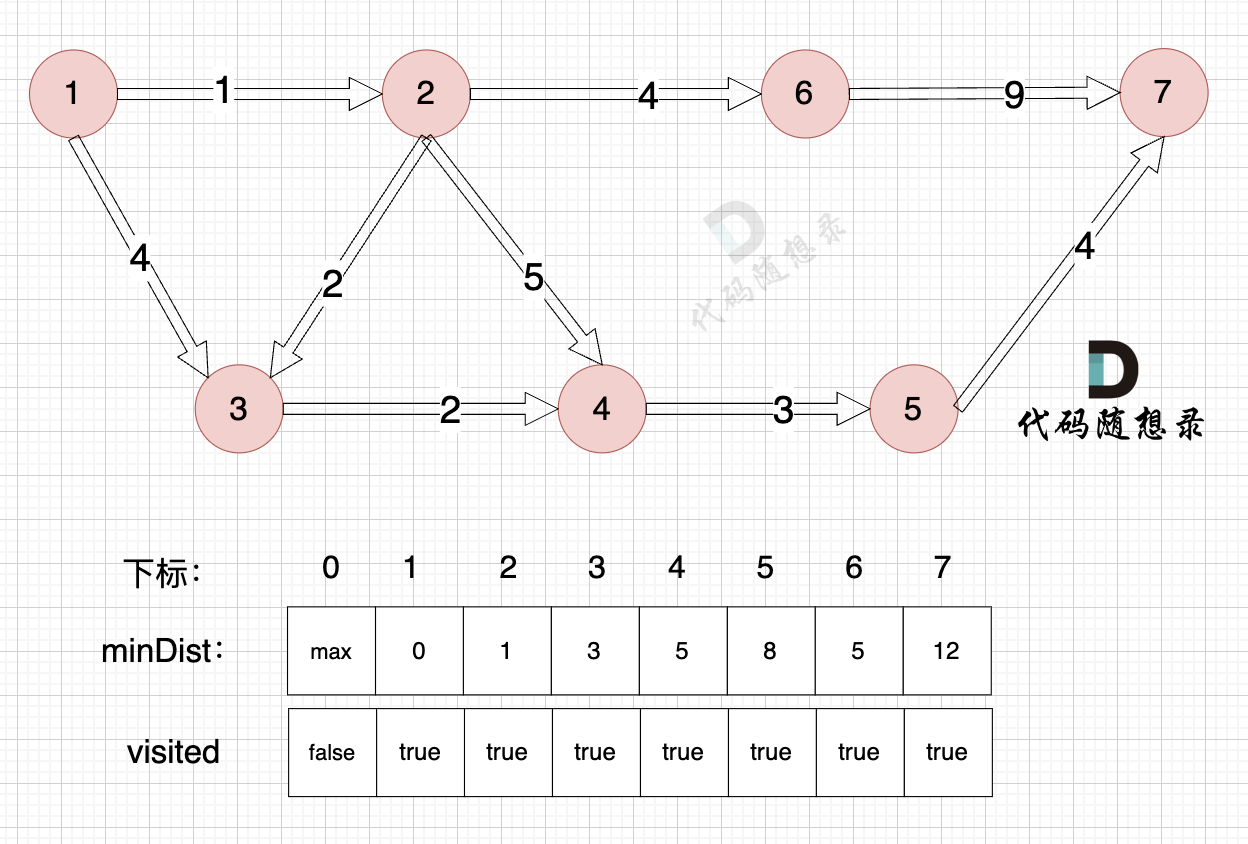
+
+节点7加入,但节点7到节点7的距离为0,所以 不用更新minDist数组
+
+--------------------
+
+最后我们要求起点(节点1) 到终点 (节点7)的距离。
+
+再来回顾一下minDist数组的含义:记录 每一个节点距离源点的最小距离。
+
+那么起到(节点1)到终点(节点7)的最短距离就是 minDist[7] ,按上面举例讲解来说,minDist[7] = 12,节点1 到节点7的最短路径为 12。
+
+路径如图:
+
+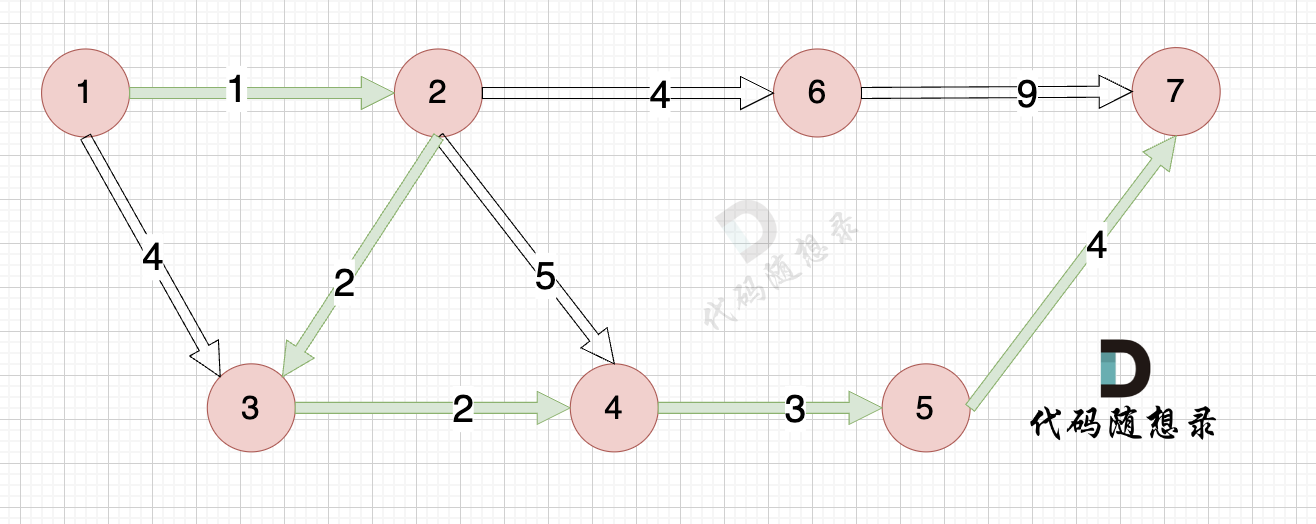
+
+在上面的讲解中,每一步 我都是按照 dijkstra 三部曲来讲解的,理解了这三部曲,代码也就好懂的。
+
+### 代码实现
+
+本题代码如下,里面的 三部曲 我都做了注释,大家按照我上面的讲解 来看如下代码:
+
+```CPP
+class Solution {
+public:
+ int networkDelayTime(vector>& times, int n, int k) {
+
+ // 注意题目中给的二维数组并不是领接矩阵
+ // 需要邻接矩阵来存图
+ // 因为本题处理方式是节点标号从1开始,所以数组的大小都是 n+1
+ vector> grid(n + 1, vector(n + 1, INT_MAX));
+ for(int i = 0; i < times.size(); i++){
+ int p1 = times[i][0];
+ int p2 = times[i][1];
+ grid[p1][p2] = times[i][2];
+ }
+
+ // 存储从源点到每个节点的最短距离
+ std::vector minDist(n + 1, INT_MAX);
+
+ // 记录顶点是否被访问过
+ std::vector visited(n + 1, false);
+
+ minDist[k] = 0; // 起始点到自身的距离为0
+ for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
+
+ int minVal = INT_MAX;
+ int cur = 1;
+
+ // 遍历每个节点,选择未被访问的节点集合中哪个节点到源点的距离最小
+ for (int v = 1; v <= n; ++v) {
+ if (!visited[v] && minDist[v] <= minVal) {
+ minVal = minDist[v];
+ cur = v;
+ }
+ }
+
+ visited[cur] = true; // 标记该顶点已被访问
+
+ for (int v = 1; v <= n; v++) {
+ if (!visited[v] && grid[cur][v] != INT_MAX && minDist[cur] + grid[cur][v] < minDist[v]) {
+ minDist[v] = minDist[cur] + grid[cur][v];
+ }
+ }
+
+
+ }
+ // 源点到最远的节点的时间,也就是寻找 源点到所有节点最短路径的最大值
+ int result = 0;
+ for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
+ if (minDist[i] == INT_MAX) return -1;// 没有路径
+ result = max(minDist[i], result);
+ }
+ return result;
+
+ }
+};
+```
+
+* 时间复杂度:O(n^2)
+* 空间复杂度:O(n^2)
+
+### debug方法
+
+写这种题目难免会有各种各样的问题,我们如何发现自己的代码是否有问题呢?
+
+最好的方式就是打日志,本题的话,就是将 minDist 数组打印出来,就可以很明显发现 哪里出问题了。
+
+每次选择节点后,minDist数组的变化是否符合预期 ,是否和我上面讲的逻辑是对应的。
+
+例如本题,如果想debug的话,打印日志可以这样写:
+
+
+```CPP
+class Solution {
+public:
+ int networkDelayTime(vector>& times, int n, int k) {
+
+ // 注意题目中给的二维数组并不是领接矩阵
+ // 需要邻接矩阵来存图
+ // 因为本题处理方式是节点标号从1开始,所以数组的大小都是 n+1
+ vector> grid(n + 1, vector(n + 1, INT_MAX));
+ for(int i = 0; i < times.size(); i++){
+ int p1 = times[i][0];
+ int p2 = times[i][1];
+ grid[p1][p2] = times[i][2];
+ }
+
+ // 存储从源点到每个节点的最短距离
+ std::vector minDist(n + 1, INT_MAX);
+
+ // 记录顶点是否被访问过
+ std::vector visited(n + 1, false);
+
+ minDist[k] = 0; // 起始点到自身的距离为0
+ for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
+
+ int minVal = INT_MAX;
+ int cur = 1;
+
+ // 遍历每个节点,选择未被访问的节点集合中哪个节点到源点的距离最小
+ for (int v = 1; v <= n; ++v) {
+ if (!visited[v] && minDist[v] <= minVal) {
+ minVal = minDist[v];
+ cur = v;
+ }
+ }
+
+ visited[cur] = true; // 标记该顶点已被访问
+
+ for (int v = 1; v <= n; v++) {
+ if (!visited[v] && grid[cur][v] != INT_MAX && minDist[cur] + grid[cur][v] < minDist[v]) {
+ minDist[v] = minDist[cur] + grid[cur][v];
+ }
+ }
+ // 打印日志:
+ cout << "select:" << cur << endl;
+ for (int v = 1; v <= n; v++) cout << v << ":" << minDist[v] << " ";
+ cout << endl << endl;;
+
+
+
+ }
+ // 源点到最远的节点的时间,也就是寻找 源点到所有节点最短路径的最大值
+ int result = 0;
+ for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
+ if (minDist[i] == INT_MAX) return -1;// 没有路径
+ result = max(minDist[i], result);
+ }
+ return result;
+
+ }
+};
+
+
+```
+
+打印后的结果:
+
+```
+select:2
+1:1 2:0 3:1 4:2147483647
+
+select:3
+1:1 2:0 3:1 4:2
+
+select:1
+1:1 2:0 3:1 4:2
+
+select:4
+1:1 2:0 3:1 4:2
+```
+
+打印日志可以和上面我讲解的过程进行对比,每一步的结果是完全对应的。
+
+所以如果大家如果代码有问题,打日志来debug是最好的方法
+
+### 出现负数
+
+如果图中边的权值为负数,dijkstra 还合适吗?
+
+看一下这个图: (有负权值)
+
+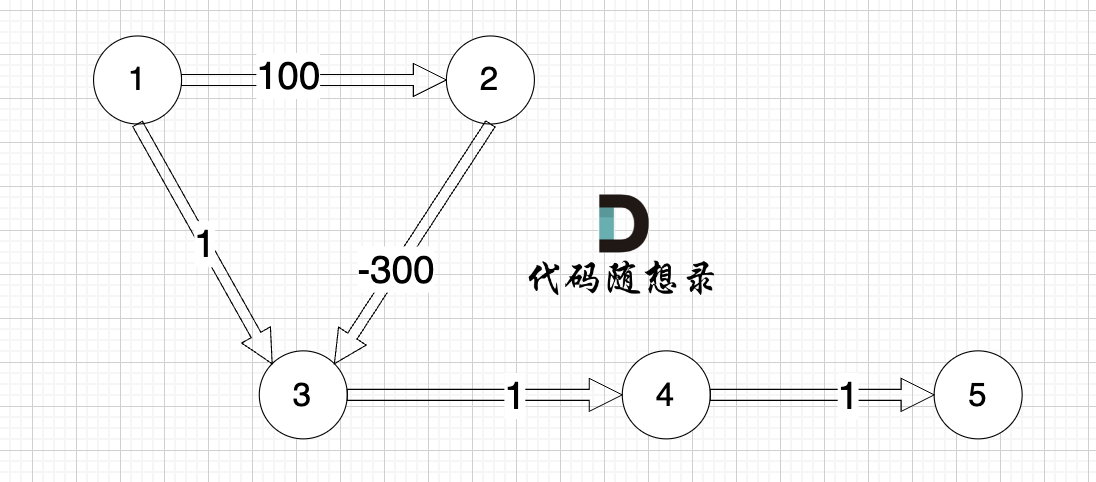
+
+节点1 到 节点5 的最短路径 应该是 节点1 -> 节点2 -> 节点3 -> 节点4 -> 节点5
+
+那我们来看dijkstra 求解的路径是什么样的,继续dijkstra 三部曲来模拟 :(dijkstra模拟过程上面已经详细讲过,以下只模拟重要过程,例如如何初始化就省略讲解了)
+
+-----------
+
+初始化:
+
+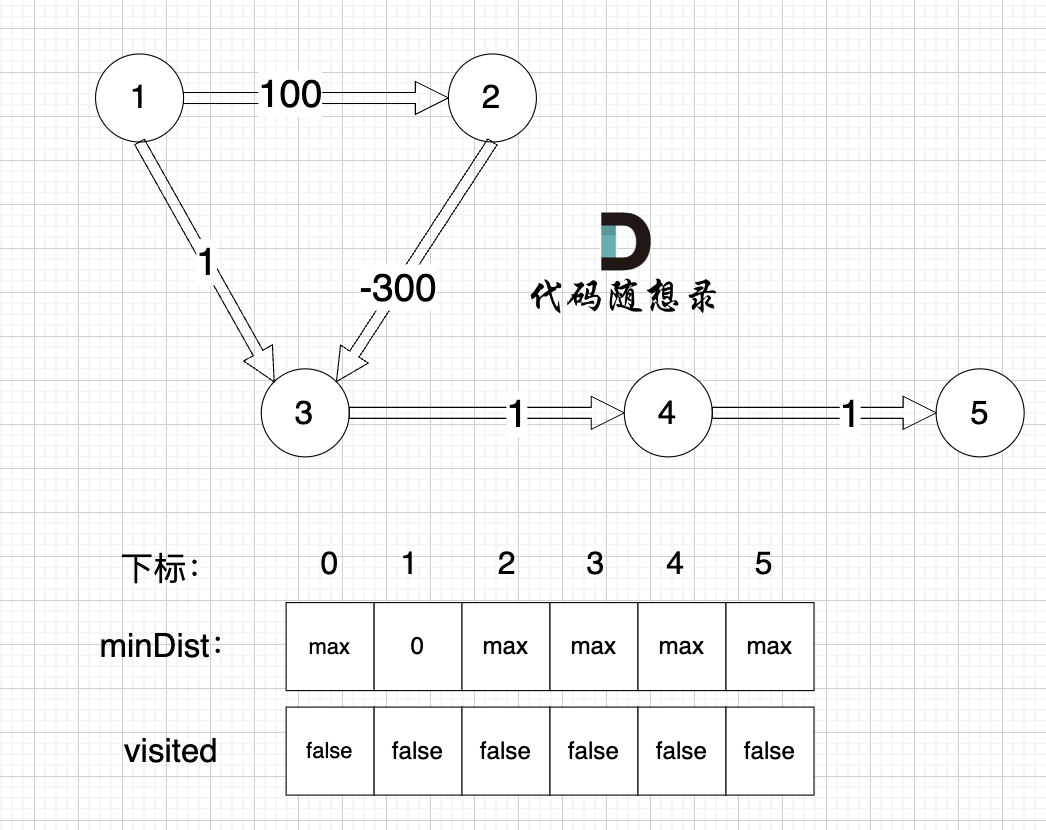
+
+---------------
+
+1、选源点到哪个节点近且该节点未被访问过
+
+源点距离源点最近,距离为0,且未被访问。
+
+2、该最近节点被标记访问过
+
+标记源点访问过
+
+3、更新非访问节点到源点的距离(即更新minDist数组) ,如图:
+
+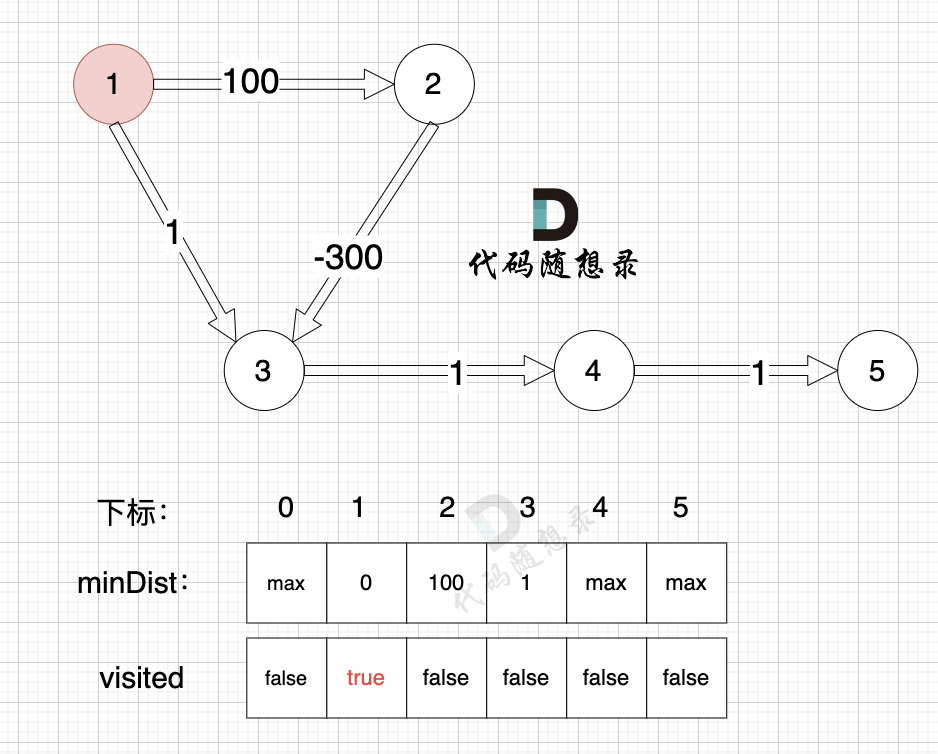
+
+更新 minDist数组,即:源点(节点1) 到 节点2 和 节点3的距离。
+
+* 源点到节点2的最短距离为100,小于原minDist[2]的数值max,更新minDist[2] = 100
+* 源点到节点3的最短距离为1,小于原minDist[3]的数值max,更新minDist[4] = 1
+
+-------------------
+
+1、选源点到哪个节点近且该节点未被访问过
+
+源点距离节点3最近,距离为1,且未被访问。
+
+2、该最近节点被标记访问过
+
+标记节点3访问过
+
+3、更新非访问节点到源点的距离(即更新minDist数组) ,如图:
+
+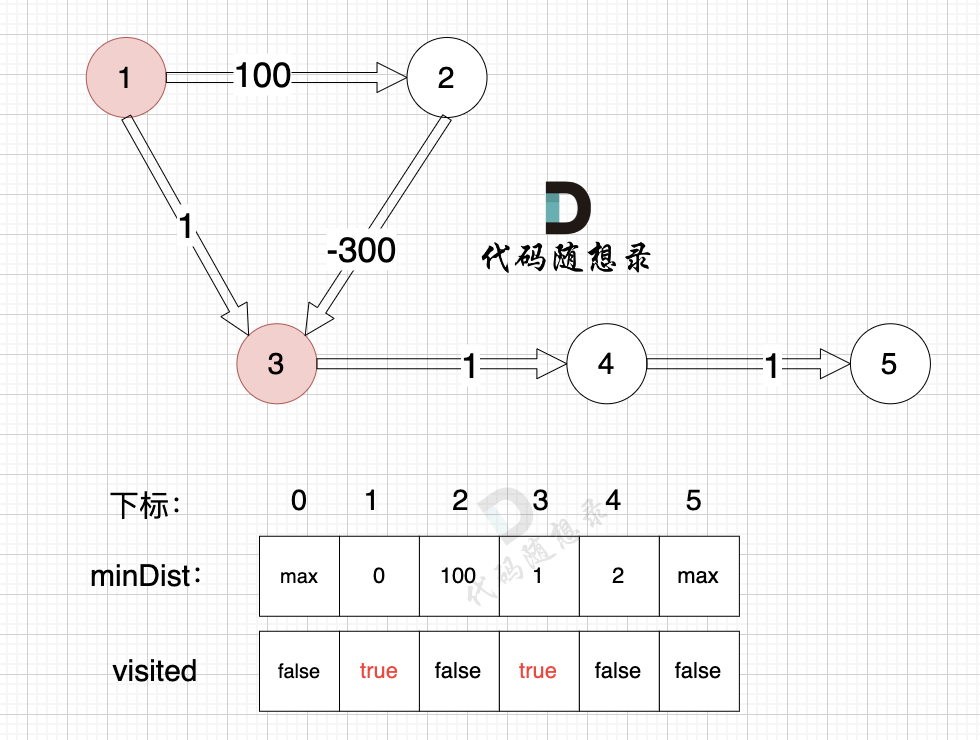
+
+由于节点3的加入,那么源点可以有新的路径链接到节点4 所以更新minDist数组:
+
+* 源点到节点4的最短距离为2,小于原minDist[4]的数值max,更新minDist[4] = 2
+
+--------------
+
+1、选源点到哪个节点近且该节点未被访问过
+
+源点距离节点4最近,距离为2,且未被访问。
+
+2、该最近节点被标记访问过
+
+标记节点4访问过
+
+3、更新非访问节点到源点的距离(即更新minDist数组) ,如图:
+
+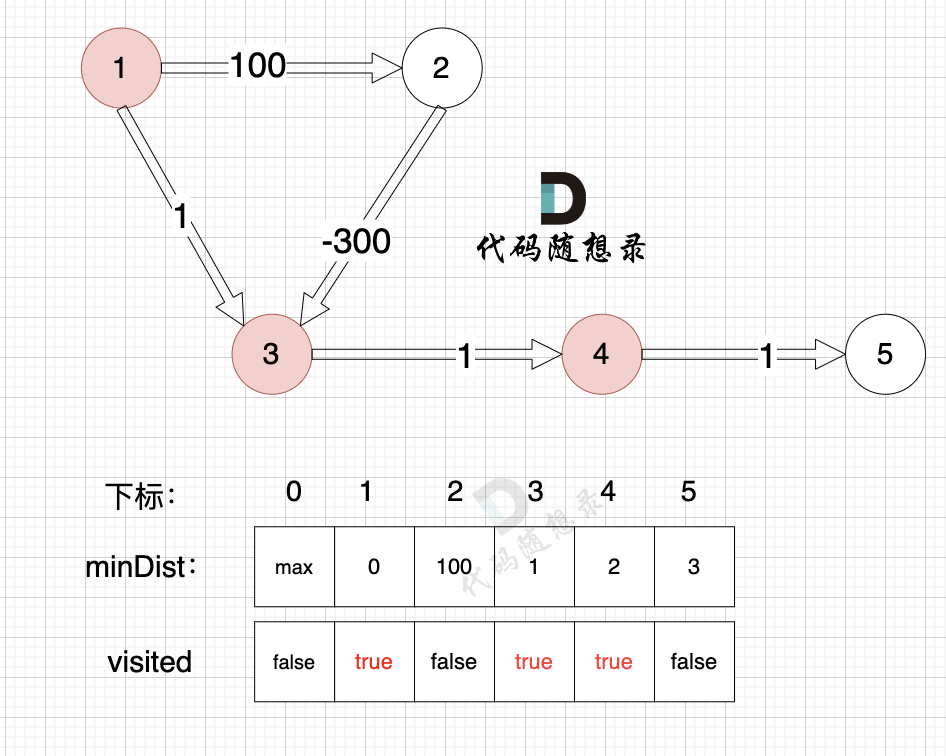
+
+由于节点4的加入,那么源点可以有新的路径链接到节点5 所以更新minDist数组:
+
+* 源点到节点5的最短距离为3,小于原minDist[5]的数值max,更新minDist[5] = 5
+
+------------
+
+1、选源点到哪个节点近且该节点未被访问过
+
+源点距离节点5最近,距离为3,且未被访问。
+
+2、该最近节点被标记访问过
+
+标记节点5访问过
+
+3、更新非访问节点到源点的距离(即更新minDist数组) ,如图:
+
+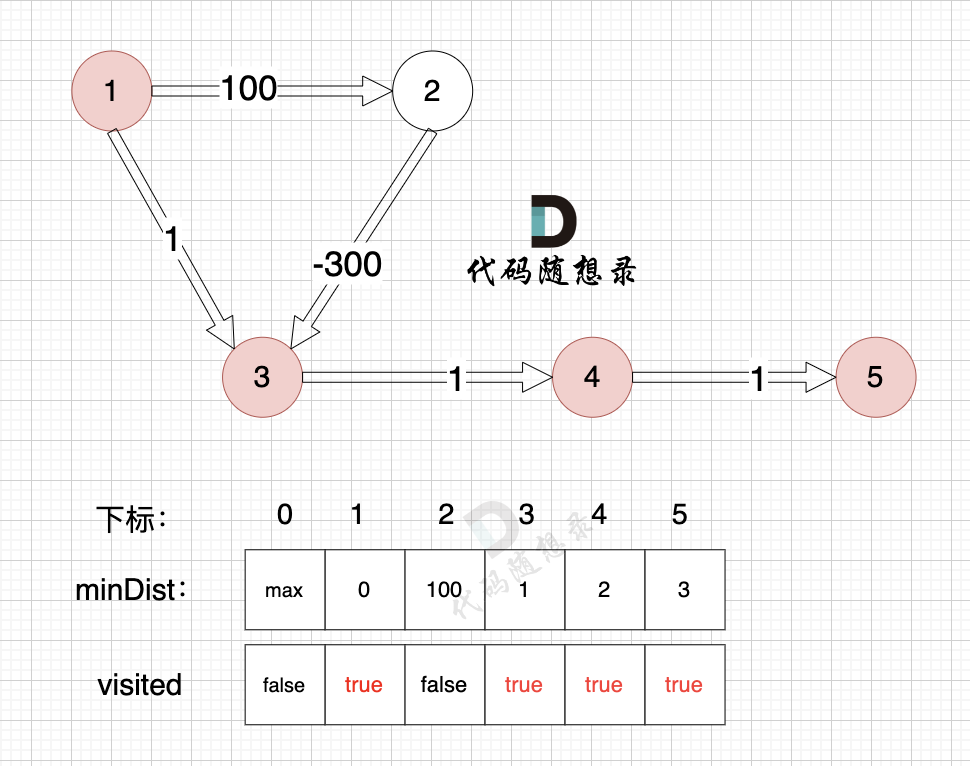
+
+节点5的加入,而节点5 没有链接其他节点, 所以不用更新minDist数组,仅标记节点5被访问过了
+
+------------
+
+1、选源点到哪个节点近且该节点未被访问过
+
+源点距离节点2最近,距离为100,且未被访问。
+
+2、该最近节点被标记访问过
+
+标记节点2访问过
+
+3、更新非访问节点到源点的距离(即更新minDist数组) ,如图:
+
+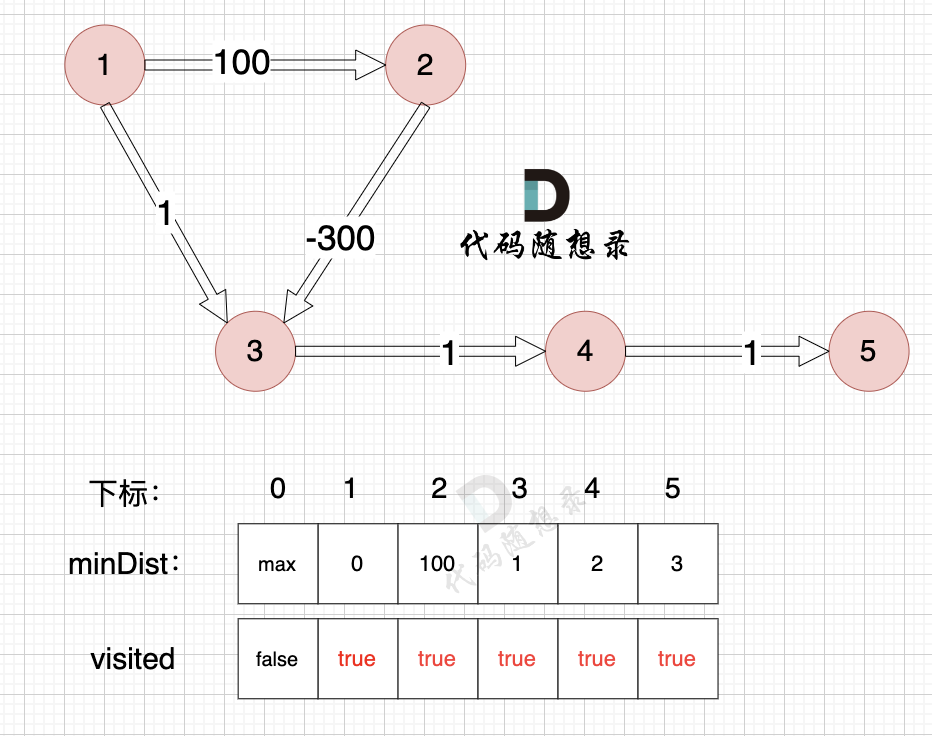
+
+--------------
+
+至此dijkstra的模拟过程就结束了,根据最后的minDist数组,我们求 节点1 到 节点5 的最短路径的权值总和为 3,路径: 节点1 -> 节点3 -> 节点4 -> 节点5
+
+通过以上的过程模拟,我们可以发现 之所以 没有走有负权值的最短路径 是因为 在 访问 节点 2 的时候,节点 3 已经访问过了,就不会再更新了。
+
+那有录友可能会想: 我可以改代码逻辑啊,访问过的节点,也让它继续访问不就好了?
+
+那么访问过的节点还能继续访问会不会有死循环的出现呢?控制逻辑不让其死循环?那特殊情况自己能都想清楚吗?(可以试试,实践出真知)
+
+对于负权值的出现,大家可以针对某一个场景 不断去修改 dijkstra 的代码,**但最终会发现只是 拆了东墙补西墙**,对dijkstra的补充逻辑只能满足某特定场景最短路求解。
+
+对于求解带有负权值的最短路问题,可以使用 Floyd 算法 ,我在后序会详细讲解。
+
+## dijkstra与prim算法的区别
+
+> 这里再次提示,需要先看我的 [prim算法精讲](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/yX936hHC6Z10K36Vm1Wl9w) ,否则可能不知道我下面讲的是什么。
+
+大家可以发现 dijkstra的代码看上去 怎么和 prim算法这么像呢。
+
+其实代码大体不差,唯一区别在 三部曲中的 第三步: 更新minDist数组
+
+因为**prim是求 非访问节点到最小生成树的最小距离,而 dijkstra是求 非访问节点到源点的最小距离**。
+
+prim 更新 minDist数组的写法:
+
+
+```CPP
+for (int j = 1; j <= v; j++) {
+ if (!isInTree[j] && grid[cur][j] < minDist[j]) {
+ minDist[j] = grid[cur][j];
+ }
+}
+```
+
+因为 minDist表示 节点到最小生成树的最小距离,所以 新节点cur的加入,只需要 使用 grid[cur][j] ,grid[cur][j] 就表示 cur 加入生成树后,生成树到 节点j 的距离。
+
+dijkstra 更新 minDist数组的写法:
+
+```CPP
+for (int v = 1; v <= n; v++) {
+ if (!visited[v] && grid[cur][v] != INT_MAX && minDist[cur] + grid[cur][v] < minDist[v]) {
+ minDist[v] = minDist[cur] + grid[cur][v];
+ }
+}
+```
+
+因为 minDist表示 节点到源点的最小距离,所以 新节点 cur 的加入,需要使用 源点到cur的距离 (minDist[cur]) + cur 到 节点 v 的距离 (grid[cur][v]),才是 源点到节点v的距离。
+
+此时大家可能不禁要想 prim算法 可以有负权值吗?
+
+当然可以!
+
+录友们可以自己思考思考一下,这是为什么?
+
+这里我提示一下:prim算法只需要将节点以最小权值和链接在一起,不涉及到单一路径。
+
+
+
+## 总结
+
+本篇,我们深入讲解的dijkstra算法,详细模拟其工作的流程。
+
+这里我给出了 **dijkstra 三部曲 来 帮助大家理解 该算法**,不至于 每次写 dijkstra 都是黑盒操作,没有框架没有章法。
+
+在给出的代码中,我也按照三部曲的逻辑来给大家注释,只要理解这三部曲,即使 过段时间 对 dijkstra 算法有些遗忘,依然可以写出一个框架出来,然后再去调试细节。
+
+对于图论算法,一般代码都比较长,很难写出代码直接可以提交通过,都需要一个debug的过程,所以 **学习如何debug 非常重要**!
+
+这也是我为什么 在本文中 单独用来讲解 debug方法。
+
+本题求的是最短路径和是多少,**同时我们也要掌握 如何把最短路径打印出来**。
+
+我还写了大篇幅来讲解 负权值的情况, 只有画图带大家一步一步去 看 出现负权值 dijkstra的求解过程,才能帮助大家理解,问题出在哪里。
+
+如果我直接讲:是**因为访问过的节点 不能再访问,导致错过真正的最短路**,我相信大家都不知道我在说啥。
+
+最后我还讲解了 dijkstra 和 prim 算法的 相同 与 不同之处, 我在图论的讲解安排中 先讲 prim算法 再讲 dijkstra 是有目的的, **理解这两个算法的相同与不同之处 有助于大家学习的更深入**。
+
+而不是 学了 dijkstra 就只看 dijkstra, 算法之间 都是有联系的,多去思考 算法之间的相互联系,会帮助大家思考的更深入,掌握的更彻底。
+
+本篇写了这么长,我也只讲解了 朴素版dijkstra,**关于 堆优化dijkstra,我会在下一篇再来给大家详细讲解**。
+
+
+
+## 堆优化版本dijkstra
+
+> 本篇我们来讲解 堆优化版dijkstra,看本篇之前,一定要先看 我讲解的 朴素版dijkstra,否则本篇会有部分内容看不懂。
+
+在上一篇中,我们讲解了朴素版的dijkstra,该解法的时间复杂度为 O(n^2),可以看出时间复杂度 只和 n (节点数量)有关系。
+
+如果n很大的话,我们可以换一个角度来优先性能。
+
+在 讲解 最小生成树的时候,我们 讲了两个算法,[prim算法](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/yX936hHC6Z10K36Vm1Wl9w)(从点的角度来求最小生成树)、[Kruskal算法](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/rUVaBjCES_4eSjngceT5bw)(从边的角度来求最小生成树)
+
+这么在n 很大的时候,也有另一个思考维度,即:从边的数量出发。
+
+当 n 很大,边 的数量 也很多的时候(稠密图),那么 上述解法没问题。
+
+但 n 很大,边 的数量 很小的时候(稀疏图),是不是可以换成从边的角度来求最短路呢?
+
+毕竟边的数量少。
+
+有的录友可能会想,n (节点数量)很大,边不就多吗? 怎么会边的数量少呢?
+
+别忘了,谁也没有规定 节点之间一定要有边连接着,例如有一万个节点,只有一条边,这也是一张图。
+
+了解背景之后,再来看 解法思路。
+
+### 图的存储
+
+首先是 图的存储。
+
+关于图的存储 主流有两种方式: 邻接矩阵和邻接表
+
+#### 邻接矩阵
+
+邻接矩阵 使用 二维数组来表示图结构。 邻接矩阵是从节点的角度来表示图,有多少节点就申请多大的二维数组。
+
+例如: grid[2][5] = 6,表示 节点 2 链接 节点5 为有向图,节点2 指向 节点5,边的权值为6 (套在题意里,可能是距离为6 或者 消耗为6 等等)
+
+如果想表示无向图,即:grid[2][5] = 6,grid[5][2] = 6,表示节点2 与 节点5 相互连通,权值为6。
+
+
+如图:
+
+
+
+在一个 n (节点数)为8 的图中,就需要申请 8 * 8 这么大的空间,有一条双向边,即:grid[2][5] = 6,grid[5][2] = 6
+
+这种表达方式(邻接矩阵) 在 边少,节点多的情况下,会导致申请过大的二维数组,造成空间浪费。
+
+而且在寻找节点链接情况的时候,需要遍历整个矩阵,即 n * n 的时间复杂度,同样造成时间浪费。
+
+邻接矩阵的优点:
+
+* 表达方式简单,易于理解
+* 检查任意两个顶点间是否存在边的操作非常快
+* 适合稠密图,在边数接近顶点数平方的图中,邻接矩阵是一种空间效率较高的表示方法。
+
+缺点:
+
+* 遇到稀疏图,会导致申请过大的二维数组造成空间浪费 且遍历 边 的时候需要遍历整个n * n矩阵,造成时间浪费
+
+#### 邻接表
+
+邻接表 使用 数组 + 链表的方式来表示。 邻接表是从边的数量来表示图,有多少边 才会申请对应大小的链表。
+
+邻接表的构造如图:
+
+
+
+这里表达的图是:
+
+* 节点1 指向 节点3 和 节点5
+* 节点2 指向 节点4、节点3、节点5
+* 节点3 指向 节点4,节点4指向节点1。
+
+有多少边 邻接表才会申请多少个对应的链表节点。
+
+从图中可以直观看出 使用 数组 + 链表 来表达 边的链接情况 。
+
+邻接表的优点:
+
+* 对于稀疏图的存储,只需要存储边,空间利用率高
+* 遍历节点链接情况相对容易
+
+缺点:
+
+* 检查任意两个节点间是否存在边,效率相对低,需要 O(V)时间,V表示某节点链接其他节点的数量。
+* 实现相对复杂,不易理解
+
+#### 本题图的存储
+
+接下来我们继续按照稀疏图的角度来分析本题。
+
+在第一个版本的实现思路中,我们提到了三部曲:
+
+1. 第一步,选源点到哪个节点近且该节点未被访问过
+2. 第二步,该最近节点被标记访问过
+3. 第三步,更新非访问节点到源点的距离(即更新minDist数组)
+
+在第一个版本的代码中,这三部曲是套在一个 for 循环里,为什么?
+
+因为我们是从节点的角度来解决问题。
+
+三部曲中第一步(选源点到哪个节点近且该节点未被访问过),这个操作本身需要for循环遍历 minDist 来寻找最近的节点。
+
+同时我们需要 遍历所有 未访问过的节点,所以 我们从 节点角度出发,代码会有两层for循环,代码是这样的: (注意代码中的注释,标记两层for循环的用处)
+
+```CPP
+
+for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { // 遍历所有节点,第一层for循环
+
+ int minVal = INT_MAX;
+ int cur = 1;
+
+ // 1、选距离源点最近且未访问过的节点 , 第二层for循环
+ for (int v = 1; v <= n; ++v) {
+ if (!visited[v] && minDist[v] < minVal) {
+ minVal = minDist[v];
+ cur = v;
+ }
+ }
+
+ visited[cur] = true; // 2、标记该节点已被访问
+
+ // 3、第三步,更新非访问节点到源点的距离(即更新minDist数组)
+ for (int v = 1; v <= n; v++) {
+ if (!visited[v] && grid[cur][v] != INT_MAX && minDist[cur] + grid[cur][v] < minDist[v]) {
+ minDist[v] = minDist[cur] + grid[cur][v];
+ }
+ }
+
+}
+```
+
+那么当从 边 的角度出发, 在处理 三部曲里的第一步(选源点到哪个节点近且该节点未被访问过)的时候 ,我们可以不用去遍历所有节点了。
+
+而且 直接把 边(带权值)加入到 小顶堆(利用堆来自动排序),那么每次我们从 堆顶里 取出 边 自然就是 距离源点最近的节点所在的边。
+
+这样我们就不需要两层for循环来寻找最近的节点了。
+
+了解了大体思路,我们再来看代码实现。
+
+首先是 如何使用 邻接表来表述图结构,这是摆在很多录友面前的第一个难题。
+
+邻接表用 数组+链表 来表示,代码如下:(C++中 vector 为数组,list 为链表, 定义了 n+1 这么大的数组空间)
+
+```CPP
+vector> grid(n + 1);
+```
+
+不少录友,不知道 如何定义的数据结构,怎么表示邻接表的,我来给大家画一个图:
+
+
+
+图中邻接表表示:
+
+* 节点1 指向 节点3 和 节点5
+* 节点2 指向 节点4、节点3、节点5
+* 节点3 指向 节点4
+* 节点4 指向 节点1
+
+大家发现图中的边没有权值,而本题中 我们的边是有权值的,权值怎么表示?在哪里表示?
+
+所以 在`vector> grid(n + 1);` 中 就不能使用int了,而是需要一个键值对 来存两个数字,一个数表示节点,一个数表示 指向该节点的这条边的权值。
+
+那么 代码可以改成这样: (pair 为键值对,可以存放两个int)
+
+```CPP
+vector>> grid(n + 1);
+```
+
+举例来给大家展示 该代码表达的数据 如下:
+
+
+
+* 节点1 指向 节点3 权值为 1
+* 节点1 指向 节点5 权值为 2
+* 节点2 指向 节点4 权值为 7
+* 节点2 指向 节点3 权值为 6
+* 节点2 指向 节点5 权值为 3
+* 节点3 指向 节点4 权值为 3
+* 节点5 指向 节点1 权值为 10
+
+这样 我们就把图中权值表示出来了。
+
+但是在代码中 使用 `pair` 很容易让我们搞混了,第一个int 表示什么,第二个int表示什么,导致代码可读性很差,或者说别人看你的代码看不懂。
+
+那么 可以 定一个类 来取代 `pair`
+
+类(或者说是结构体)定义如下:
+
+```CPP
+struct Edge {
+ int to; // 邻接顶点
+ int val; // 边的权重
+
+ Edge(int t, int w): to(t), val(w) {} // 构造函数
+};
+```
+
+这个类里有两个成员变量,有对应的命名,这样不容易搞混 两个int的含义。
+
+所以 本题中邻接表的定义如下:
+
+```CPP
+struct Edge {
+ int to; // 链接的节点
+ int val; // 边的权重
+
+ Edge(int t, int w): to(t), val(w) {} // 构造函数
+};
+
+vector> grid(n + 1); // 邻接表
+
+```
+
+(我们在下面的讲解中会直接使用这个邻接表的代码表示方式)
+
+### 堆优化细节
+
+其实思路依然是 dijkstra 三部曲:
+
+1. 第一步,选源点到哪个节点近且该节点未被访问过
+2. 第二步,该最近节点被标记访问过
+3. 第三步,更新非访问节点到源点的距离(即更新minDist数组)
+
+只不过之前是 通过遍历节点来遍历边,通过两层for循环来寻找距离源点最近节点。 这次我们直接遍历边,且通过堆来对边进行排序,达到直接选择距离源点最近节点。
+
+先来看一下针对这三部曲,如果用 堆来优化。
+
+那么三部曲中的第一步(选源点到哪个节点近且该节点未被访问过),我们如何选?
+
+我们要选择距离源点近的节点(即:该边的权值最小),所以 我们需要一个 小顶堆 来帮我们对边的权值排序,每次从小顶堆堆顶 取边就是权值最小的边。
+
+C++定义小顶堆,可以用优先级队列实现,代码如下:
+
+```CPP
+// 小顶堆
+class mycomparison {
+public:
+ bool operator()(const pair& lhs, const pair& rhs) {
+ return lhs.second > rhs.second;
+ }
+};
+// 优先队列中存放 pair<节点编号,源点到该节点的权值>
+priority_queue, vector>, mycomparison> pq;
+```
+
+(`pair`中 第二个int 为什么要存 源点到该节点的权值,因为 这个小顶堆需要按照权值来排序)
+
+
+有了小顶堆自动对边的权值排序,那我们只需要直接从 堆里取堆顶元素(小顶堆中,最小的权值在上面),就可以取到离源点最近的节点了 (未访问过的节点,不会加到堆里进行排序)
+
+所以三部曲中的第一步,我们不用 for循环去遍历,直接取堆顶元素:
+
+```CPP
+// pair<节点编号,源点到该节点的权值>
+pair cur = pq.top(); pq.pop();
+
+```
+
+第二步(该最近节点被标记访问过) 这个就是将 节点做访问标记,和 朴素dijkstra 一样 ,代码如下:
+
+```CPP
+// 2. 第二步,该最近节点被标记访问过
+visited[cur.first] = true;
+
+```
+
+(`cur.first` 是指取 `pair` 里的第一个int,即节点编号 )
+
+第三步(更新非访问节点到源点的距离),这里的思路 也是 和朴素dijkstra一样的。
+
+但很多录友对这里是最懵的,主要是因为两点:
+
+* 没有理解透彻 dijkstra 的思路
+* 没有理解 邻接表的表达方式
+
+我们来回顾一下 朴素dijkstra 在这一步的代码和思路(如果没看过我讲解的朴素版dijkstra,这里会看不懂)
+
+```CPP
+
+// 3、第三步,更新非访问节点到源点的距离(即更新minDist数组)
+for (int v = 1; v <= n; v++) {
+ if (!visited[v] && grid[cur][v] != INT_MAX && minDist[cur] + grid[cur][v] < minDist[v]) {
+ minDist[v] = minDist[cur] + grid[cur][v];
+ }
+}
+```
+
+其中 for循环是用来做什么的? 是为了 找到 节点cur 链接指向了哪些节点,因为使用邻接矩阵的表达方式 所以把所有节点遍历一遍。
+
+而在邻接表中,我们可以以相对高效的方式知道一个节点链接指向哪些节点。
+
+再回顾一下邻接表的构造(数组 + 链表):
+
+
+
+假如 加入的cur 是节点 2, 那么 grid[2] 表示的就是图中第二行链表。 (grid数组的构造我们在 上面 「图的存储」中讲过)
+
+所以在邻接表中,我们要获取 节点cur 链接指向哪些节点,就是遍历 grid[cur节点编号] 这个链表。
+
+这个遍历方式,C++代码如下:
+
+```CPP
+for (Edge edge : grid[cur.first])
+```
+
+(如果不知道 Edge 是什么,看上面「图的存储」中邻接表的讲解)
+
+`cur.first` 就是cur节点编号, 参考上面pair的定义: pair<节点编号,源点到该节点的权值>
+
+接下来就是更新 非访问节点到源点的距离,代码实现和 朴素dijkstra 是一样的,代码如下:
+
+```CPP
+// 3. 第三步,更新非访问节点到源点的距离(即更新minDist数组)
+for (Edge edge : grid[cur.first]) { // 遍历 cur指向的节点,cur指向的节点为 edge
+ // cur指向的节点edge.to,这条边的权值为 edge.val
+ if (!visited[edge.to] && minDist[cur.first] + edge.val < minDist[edge.to]) { // 更新minDist
+ minDist[edge.to] = minDist[cur.first] + edge.val;
+ pq.push(pair(edge.to, minDist[edge.to]));
+ }
+}
+```
+
+但为什么思路一样,有的录友能写出朴素dijkstra,但堆优化这里的逻辑就是写不出来呢?
+
+**主要就是因为对邻接表的表达方式不熟悉**!
+
+以上代码中,cur 链接指向的节点编号 为 edge.to, 这条边的权值为 edge.val ,如果对这里模糊的就再回顾一下 Edge的定义:
+
+```CPP
+struct Edge {
+ int to; // 邻接顶点
+ int val; // 边的权重
+
+ Edge(int t, int w): to(t), val(w) {} // 构造函数
+};
+```
+
+确定该节点没有被访问过,`!visited[edge.to]` , 目前 源点到cur.first的最短距离(minDist) + cur.first 到 edge.to 的距离 (edge.val) 是否 小于 minDist已经记录的 源点到 edge.to 的距离 (minDist[edge.to])
+
+如果是的话,就开始更新操作。
+
+即:
+
+```CPP
+if (!visited[edge.to] && minDist[cur.first] + edge.val < minDist[edge.to]) { // 更新minDist
+ minDist[edge.to] = minDist[cur.first] + edge.val;
+ pq.push(pair(edge.to, minDist[edge.to])); // 由于cur节点的加入,而新链接的边,加入到优先级队里中
+}
+
+```
+
+同时,由于cur节点的加入,源点又有可以新链接到的边,将这些边加入到优先级队里中。
+
+
+以上代码思路 和 朴素版dijkstra 是一样一样的,主要区别是两点:
+
+* 邻接表的表示方式不同
+* 使用优先级队列(小顶堆)来对新链接的边排序
+
+### 代码实现
+
+堆优化dijkstra完整代码如下:
+
+```CPP
+class Solution {
+public:
+ // 小顶堆
+ class mycomparison {
+ public:
+ bool operator()(const pair& lhs, const pair& rhs) {
+ return lhs.second > rhs.second;
+ }
+ };
+ // 定义一个结构体来表示带权重的边
+ struct Edge {
+ int to; // 邻接顶点
+ int val; // 边的权重
+
+ Edge(int t, int w): to(t), val(w) {} // 构造函数
+ };
+ int networkDelayTime(vector>& times, int n, int k) {
+
+
+ std::vector> grid(n + 1);
+ for(int i = 0; i < times.size(); i++){
+ int p1 = times[i][0];
+ int p2 = times[i][1];
+ // p1 指向 p2,权值为 times[i][2]
+ grid[p1].push_back(Edge(p2, times[i][2]));
+ }
+
+ // 存储从源点到每个节点的最短距离
+ std::vector minDist(n + 1, INT_MAX);
+
+ // 记录顶点是否被访问过
+ std::vector visited(n + 1, false);
+
+ // 优先队列中存放 pair<节点,源点到该节点的距离>
+ priority_queue, vector>, mycomparison> pq;
+
+ pq.push(pair(k, 0));
+ minDist[k] = 0; // 这个不要忘了
+
+ while (!pq.empty()) {
+ // <节点, 源点到该节点的距离>
+ // 1. 第一步,选源点到哪个节点近且该节点未被访问过 (通过优先级队列来实现)
+ pair cur = pq.top(); pq.pop();
+
+ if (visited[cur.first]) continue;
+
+ // 2. 第二步,该最近节点被标记访问过
+ visited[cur.first] = true;
+
+
+ // 3. 第三步,更新非访问节点到源点的距离(即更新minDist数组)
+ for (Edge edge : grid[cur.first]) { // 遍历 cur指向的节点,cur指向的节点为 edge
+ // cur指向的节点edge.to,这条边的权值为 edge.val
+ if (!visited[edge.to] && minDist[cur.first] + edge.val < minDist[edge.to]) { // 更新minDist
+ minDist[edge.to] = minDist[cur.first] + edge.val;
+ pq.push(pair(edge.to, minDist[edge.to]));
+ }
+ }
+
+ }
+
+ // 源点到最远的节点的时间,也就是寻找 源点到所有节点最短路径的最大值
+ int result = 0;
+ for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
+ if (minDist[i] == INT_MAX) return -1;// 没有路径
+ result = max(minDist[i], result);
+ }
+ return result;
+
+ }
+};
+
+```
+
+* 时间复杂度:O(ElogE) E 为边的数量
+* 空间复杂度:O(N + E) N 为节点的数量
+
+堆优化的时间复杂度 只和边的数量有关 和节点数无关,在 优先级队列中 放的也是边。
+
+以上代码中,`while (!pq.empty())` 里套了 `for (Edge edge : grid[cur.first])`
+
+`for` 里 遍历的是 当前节点 cur 所连接边。
+
+那 当前节点cur 所连接的边 也是不固定的, 这就让大家分不清,这时间复杂度究竟是多少?
+
+其实 `for (Edge edge : grid[cur.first])` 里最终的数据走向 是 给队列里添加边。
+
+那么跳出局部代码,整个队列 一定是 所有边添加了一次,同时也弹出了一次。
+
+所以边添加一次时间复杂度是 O(E), `while (!pq.empty())` 里每次都要弹出一个边来进行操作,在优先级队列(小顶堆)中 弹出一个元素的时间复杂度是 O(logE) ,这是堆排序的时间复杂度。
+
+(当然小顶堆里 是 添加元素的时候 排序,还是 取数元素的时候排序,这个无所谓,时间复杂度都是O(E),总是是一定要排序的,而小顶堆里也不会滞留元素,有多少元素添加 一定就有多少元素弹出)
+
+所以 该算法整体时间复杂度为 O(ElogE)
+
+网上的不少分析 会把 n (节点的数量)算进来,这个分析是有问题的,举一个极端例子,在n 为 10000,且是有一条边的 图里,以上代码,大家感觉执行了多少次?
+
+`while (!pq.empty())` 中的 pq 存的是边,其实只执行了一次。
+
+所以该算法时间复杂度 和 节点没有关系。
+
+至于空间复杂度,邻接表是 数组 + 链表 数组的空间 是 N ,有E条边 就申请对应多少个链表节点,所以是 复杂度是 N + E
+
+## 拓展
+
+当然也有录友可能想 堆优化dijkstra 中 我为什么一定要用邻接表呢,我就用邻接矩阵 行不行 ?
+
+也行的。
+
+但 正是因为稀疏图,所以我们使用堆优化的思路, 如果我们还用 邻接矩阵 去表达这个图的话,就是 一个高效的算法 使用了低效的数据结构,那么 整体算法效率 依然是低的。
+
+如果还不清楚为什么要使用 邻接表,可以再看看上面 我在 「图的存储」标题下的讲解。
+
+这里我也给出 邻接矩阵版本的堆优化dijkstra代码:
+
+```CPP
+class Solution {
+public:
+ // 小顶堆(按照中的v 来从小到大排序)
+ class mycomparison {
+ public:
+ bool operator()(const pair& lhs, const pair& rhs) {
+ return lhs.second > rhs.second;
+ }
+ };
+ int networkDelayTime(vector>& times, int n, int k) {
+
+ // 注意题目中给的二维数组并不是邻接矩阵
+ // 需要邻接矩阵来存图
+ // 因为本题处理方式是节点标号从1开始,所以数组的大小都是 n+1
+ vector> grid(n + 1, vector(n + 1, INT_MAX));
+ for(int i = 0; i < times.size(); i++){
+ int p1 = times[i][0];
+ int p2 = times[i][1];
+ grid[p1][p2] = times[i][2];
+ }
+
+ // 存储从源点到每个节点的最短距离
+ std::vector minDist(n + 1, INT_MAX);
+
+ // 记录顶点是否被访问过
+ std::vector visited(n + 1, false);
+
+ // 优先队列中存放 [节点,源点到该节点的距离]
+ priority_queue, vector>, mycomparison> pq;
+
+ pq.push(pair(k, 0));
+ minDist[k] = 0; // 这个不要忘了
+
+ while (!pq.empty()) {
+ // <节点, 源点到该节点的距离>
+ // 1、选距离源点最近且未访问过的节点
+ pair cur = pq.top(); pq.pop();
+
+ if (visited[cur.first]) continue;
+
+ // 2、标记该节点已被访问
+ visited[cur.first] = true;
+
+ // 3、第三步,更新非访问节点到源点的距离(即更新minDist数组)
+ // 遍历 cur 可以链接的节点,更新 minDist[j]
+ for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
+ if (!visited[j] && grid[cur.first][j] != INT_MAX && (minDist[cur.first] + grid[cur.first][j] < minDist[j])) {
+ minDist[j] = minDist[cur.first] + grid[cur.first][j];
+ pq.push(pair(j, minDist[j]));
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+ // 源点到最远的节点的时间,也就是寻找 源点到所有节点最短路径的最大值
+ int result = 0;
+ for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
+ if (minDist[i] == INT_MAX) return -1;// 没有路径
+ result = max(minDist[i], result);
+ }
+
+
+ return result;
+
+ }
+};
+
+```
+
+* 时间复杂度:O(E * (N + logE)) E为边的数量,N为节点数量
+* 空间复杂度:O(log(N^2))
+
+`while (!pq.empty())` 时间复杂度为 E ,while 里面 每次取元素 时间复杂度 为 logE,和 一个for循环 时间复杂度 为 N 。
+
+所以整体是 E * (N + logE)
+
+
+## 总结
+
+在学习一种优化思路的时候,首先就要知道为什么要优化,遇到了什么问题。
+
+正如我在开篇就给大家交代清楚 堆优化方式的背景。
+
+堆优化的整体思路和 朴素版是大体一样的,区别是 堆优化从边的角度触发,且利用堆来排序。
+
+很多录友别说写堆优化 就是看 堆优化的代码也看的很懵。
+
+主要是因为两点:
+
+* 不熟悉邻接表的表达方式
+* 对dijkstra的实现思路还是不熟
+
+这是我为什么 本篇花了大力气来讲解 图的存储,就是为了让大家彻底理解邻接表以及邻接表的代码写法。
+
+至于 dijkstra的实现思路 ,朴素版 和 堆优化版本 都是 按照 dijkstra 三部曲来的。
+
+理解了三部曲,dijkstra 的思路就是清晰的。
+
+针对邻接表版本代码 我做了详细的 时间复杂度分析,也让录友们清楚,相对于 朴素版,时间都优化到哪了。
+
+最后 我也给出了 邻接矩阵的版本代码,分析了这一版本的必要性以及时间复杂度。
+
+至此通过 两篇dijkstra的文章,终于把 dijkstra 讲完了,如果大家对我讲解里所涉及的内容都吃透的话,详细对 dijkstra 算法也就理解到位了。
+
+这里在给出本题的Bellman_ford解法,关于 Bellman_ford ,后面我会专门来讲解的,Bellman_ford 有其独特的应用场景
+
+```CPP
+class Solution {
+public:
+
+ int networkDelayTime(vector>& times, int n, int k) {
+ vector minDist(n + 1 , INT_MAX/2);
+ minDist[k] = 0;
+ //vector minDist_copy(n); // 用来记录每一次遍历的结果
+ for (int i = 1; i <= n + 1; i++) {
+ //minDist_copy = minDist; // 获取上一次计算的结果
+ for (auto &f : times) {
+ int from = f[0];
+ int to = f[1];
+ int price = f[2];
+ if (minDist[to] > minDist[from] + price) minDist[to] = minDist[from] + price;
+ }
+
+ }
+ int result = 0;
+ for (int i = 1;i <= n; i++) {
+ if (minDist[i] == INT_MAX/2) return -1;// 没有路径
+ result = max(minDist[i], result);
+ }
+ return result;
+
+ }
+};
+```
+
diff --git "a/problems/0746.\344\275\277\347\224\250\346\234\200\345\260\217\350\212\261\350\264\271\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257.md" "b/problems/0746.\344\275\277\347\224\250\346\234\200\345\260\217\350\212\261\350\264\271\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index d13ff19f5a..952d4d2ab7
--- "a/problems/0746.\344\275\277\347\224\250\346\234\200\345\260\217\350\212\261\350\264\271\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257.md"
+++ "b/problems/0746.\344\275\277\347\224\250\346\234\200\345\260\217\350\212\261\350\264\271\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0743.\347\275\221\347\273\234\345\273\266\350\277\237\346\227\266\351\227\264.md" "b/problems/0743.\347\275\221\347\273\234\345\273\266\350\277\237\346\227\266\351\227\264.md"
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..40b699c18f
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/problems/0743.\347\275\221\347\273\234\345\273\266\350\277\237\346\227\266\351\227\264.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,1230 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
+
+# 743.网络延迟时间
+
+https://leetcode.cn/problems/network-delay-time/description/
+
+
+有 n 个网络节点,标记为 1 到 n。
+
+给你一个列表 times,表示信号经过 有向 边的传递时间。 times[i] = (ui, vi, wi),其中 ui 是源节点,vi 是目标节点, wi 是一个信号从源节点传递到目标节点的时间。
+
+现在,从某个节点 K 发出一个信号。需要多久才能使所有节点都收到信号?如果不能使所有节点收到信号,返回 -1 。
+
+
+
+提示:
+
+* 1 <= k <= n <= 100
+* 1 <= times.length <= 6000
+* times[i].length == 3
+* 1 <= ui, vi <= n
+* ui != vi
+* 0 <= wi <= 100
+* 所有 (ui, vi) 对都 互不相同(即,不含重复边)
+
+# dijkstra 精讲
+
+本题就是求最短路,最短路是图论中的经典问题即:给出一个有向图,一个起点,一个终点,问起点到终点的最短路径。
+
+接下来,我们来详细讲解最短路算法中的 dijkstra 算法。
+
+dijkstra算法:在有权图(权值非负数)中求从起点到其他节点的最短路径算法。
+
+需要注意两点:
+
+* dijkstra 算法可以同时求 起点到所有节点的最短路径
+* 权值不能为负数
+
+(这两点后面我们会讲到)
+
+如本题示例中的图:
+
+
+
+起点(节点1)到终点(节点7) 的最短路径是 图中 标记绿线的部分。
+
+最短路径的权值为12。
+
+其实 dijkstra 算法 和 我们之前讲解的prim算法思路非常接近,如果大家认真学过[prim算法](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/yX936hHC6Z10K36Vm1Wl9w),那么理解 Dijkstra 算法会相对容易很多。(这也是我要先讲prim再讲dijkstra的原因)
+
+dijkstra 算法 同样是贪心的思路,不断寻找距离 源点最近的没有访问过的节点。
+
+这里我也给出 **dijkstra三部曲**:
+
+1. 第一步,选源点到哪个节点近且该节点未被访问过
+2. 第二步,该最近节点被标记访问过
+3. 第三步,更新非访问节点到源点的距离(即更新minDist数组)
+
+大家此时已经会发现,这和prim算法 怎么这么像呢。
+
+我在[prim算法](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/yX936hHC6Z10K36Vm1Wl9w)讲解中也给出了三部曲。 prim 和 dijkstra 确实很像,思路也是类似的,这一点我在后面还会详细来讲。
+
+在dijkstra算法中,同样有一个数组很重要,起名为:minDist。
+
+**minDist数组 用来记录 每一个节点距离源点的最小距离**。
+
+理解这一点很重要,也是理解 dijkstra 算法的核心所在。
+
+大家现在看着可能有点懵,不知道什么意思。
+
+没关系,先让大家有一个印象,对理解后面讲解有帮助。
+
+我们先来画图看一下 dijkstra 的工作过程,以本题示例为例: (以下为朴素版dijkstra的思路)
+
+(**示例中节点编号是从1开始,所以为了让大家看的不晕,minDist数组下标我也从 1 开始计数,下标0 就不使用了,这样 下标和节点标号就可以对应上了,避免大家搞混**)
+
+## 朴素版dijkstra
+
+### 模拟过程
+
+-----------
+
+0、初始化
+
+minDist数组数值初始化为int最大值。
+
+这里在强点一下 **minDist数组的含义:记录所有节点到源点的最短路径**,那么初始化的时候就应该初始为最大值,这样才能在后续出现最短路径的时候及时更新。
+
+
+
+(图中,max 表示默认值,节点0 不做处理,统一从下标1 开始计算,这样下标和节点数值统一, 方便大家理解,避免搞混)
+
+源点(节点1) 到自己的距离为0,所以 minDist[1] = 0
+
+此时所有节点都没有被访问过,所以 visited数组都为0
+
+---------------
+
+以下为dijkstra 三部曲
+
+1、选源点到哪个节点近且该节点未被访问过
+
+源点距离源点最近,距离为0,且未被访问。
+
+2、该最近节点被标记访问过
+
+标记源点访问过
+
+3、更新非访问节点到源点的距离(即更新minDist数组) ,如图:
+
+
+
+
+更新 minDist数组,即:源点(节点1) 到 节点2 和 节点3的距离。
+
+* 源点到节点2的最短距离为1,小于原minDist[2]的数值max,更新minDist[2] = 1
+* 源点到节点3的最短距离为4,小于原minDist[3]的数值max,更新minDist[4] = 4
+
+可能有录友问:为啥和 minDist[2] 比较?
+
+再强调一下 minDist[2] 的含义,它表示源点到节点2的最短距离,那么目前我们得到了 源点到节点2的最短距离为1,小于默认值max,所以更新。 minDist[3]的更新同理
+
+
+-------------
+
+1、选源点到哪个节点近且该节点未被访问过
+
+未访问过的节点中,源点到节点2距离最近,选节点2
+
+2、该最近节点被标记访问过
+
+节点2被标记访问过
+
+3、更新非访问节点到源点的距离(即更新minDist数组) ,如图:
+
+
+
+
+更新 minDist数组,即:源点(节点1) 到 节点6 、 节点3 和 节点4的距离。
+
+**为什么更新这些节点呢? 怎么不更新其他节点呢**?
+
+因为 源点(节点1)通过 已经计算过的节点(节点2) 可以链接到的节点 有 节点3,节点4和节点6.
+
+
+更新 minDist数组:
+
+* 源点到节点6的最短距离为5,小于原minDist[6]的数值max,更新minDist[6] = 5
+* 源点到节点3的最短距离为3,小于原minDist[3]的数值4,更新minDist[3] = 3
+* 源点到节点4的最短距离为6,小于原minDist[4]的数值max,更新minDist[4] = 6
+
+
+
+-------------------
+
+1、选源点到哪个节点近且该节点未被访问过
+
+未访问过的节点中,源点距离哪些节点最近,怎么算的?
+
+其实就是看 minDist数组里的数值,minDist 记录了 源点到所有节点的最近距离,结合visited数组筛选出未访问的节点就好。
+
+从 上面的图,或者 从minDist数组中,我们都能看出 未访问过的节点中,源点(节点1)到节点3距离最近。
+
+
+2、该最近节点被标记访问过
+
+节点3被标记访问过
+
+3、更新非访问节点到源点的距离(即更新minDist数组) ,如图:
+
+
+
+由于节点3的加入,那么源点可以有新的路径链接到节点4 所以更新minDist数组:
+
+更新 minDist数组:
+
+* 源点到节点4的最短距离为5,小于原minDist[4]的数值6,更新minDist[4] = 5
+
+------------------
+
+1、选源点到哪个节点近且该节点未被访问过
+
+距离源点最近且没有被访问过的节点,有节点4 和 节点6,距离源点距离都是 5 (minDist[4] = 5,minDist[6] = 5) ,选哪个节点都可以。
+
+2、该最近节点被标记访问过
+
+节点4被标记访问过
+
+3、更新非访问节点到源点的距离(即更新minDist数组) ,如图:
+
+
+
+由于节点4的加入,那么源点可以链接到节点5 所以更新minDist数组:
+
+* 源点到节点5的最短距离为8,小于原minDist[5]的数值max,更新minDist[5] = 8
+
+--------------
+
+1、选源点到哪个节点近且该节点未被访问过
+
+距离源点最近且没有被访问过的节点,是节点6,距离源点距离是 5 (minDist[6] = 5)
+
+
+2、该最近节点被标记访问过
+
+节点6 被标记访问过
+
+
+3、更新非访问节点到源点的距离(即更新minDist数组) ,如图:
+
+
+
+由于节点6的加入,那么源点可以链接到节点7 所以 更新minDist数组:
+
+* 源点到节点7的最短距离为14,小于原minDist[7]的数值max,更新minDist[7] = 14
+
+
+
+-------------------
+
+1、选源点到哪个节点近且该节点未被访问过
+
+距离源点最近且没有被访问过的节点,是节点5,距离源点距离是 8 (minDist[5] = 8)
+
+2、该最近节点被标记访问过
+
+节点5 被标记访问过
+
+3、更新非访问节点到源点的距离(即更新minDist数组) ,如图:
+
+
+
+由于节点5的加入,那么源点有新的路径可以链接到节点7 所以 更新minDist数组:
+
+* 源点到节点7的最短距离为12,小于原minDist[7]的数值14,更新minDist[7] = 12
+
+-----------------
+
+1、选源点到哪个节点近且该节点未被访问过
+
+距离源点最近且没有被访问过的节点,是节点7(终点),距离源点距离是 12 (minDist[7] = 12)
+
+2、该最近节点被标记访问过
+
+节点7 被标记访问过
+
+3、更新非访问节点到源点的距离(即更新minDist数组) ,如图:
+
+
+
+节点7加入,但节点7到节点7的距离为0,所以 不用更新minDist数组
+
+--------------------
+
+最后我们要求起点(节点1) 到终点 (节点7)的距离。
+
+再来回顾一下minDist数组的含义:记录 每一个节点距离源点的最小距离。
+
+那么起到(节点1)到终点(节点7)的最短距离就是 minDist[7] ,按上面举例讲解来说,minDist[7] = 12,节点1 到节点7的最短路径为 12。
+
+路径如图:
+
+
+
+在上面的讲解中,每一步 我都是按照 dijkstra 三部曲来讲解的,理解了这三部曲,代码也就好懂的。
+
+### 代码实现
+
+本题代码如下,里面的 三部曲 我都做了注释,大家按照我上面的讲解 来看如下代码:
+
+```CPP
+class Solution {
+public:
+ int networkDelayTime(vector>& times, int n, int k) {
+
+ // 注意题目中给的二维数组并不是领接矩阵
+ // 需要邻接矩阵来存图
+ // 因为本题处理方式是节点标号从1开始,所以数组的大小都是 n+1
+ vector> grid(n + 1, vector(n + 1, INT_MAX));
+ for(int i = 0; i < times.size(); i++){
+ int p1 = times[i][0];
+ int p2 = times[i][1];
+ grid[p1][p2] = times[i][2];
+ }
+
+ // 存储从源点到每个节点的最短距离
+ std::vector minDist(n + 1, INT_MAX);
+
+ // 记录顶点是否被访问过
+ std::vector visited(n + 1, false);
+
+ minDist[k] = 0; // 起始点到自身的距离为0
+ for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
+
+ int minVal = INT_MAX;
+ int cur = 1;
+
+ // 遍历每个节点,选择未被访问的节点集合中哪个节点到源点的距离最小
+ for (int v = 1; v <= n; ++v) {
+ if (!visited[v] && minDist[v] <= minVal) {
+ minVal = minDist[v];
+ cur = v;
+ }
+ }
+
+ visited[cur] = true; // 标记该顶点已被访问
+
+ for (int v = 1; v <= n; v++) {
+ if (!visited[v] && grid[cur][v] != INT_MAX && minDist[cur] + grid[cur][v] < minDist[v]) {
+ minDist[v] = minDist[cur] + grid[cur][v];
+ }
+ }
+
+
+ }
+ // 源点到最远的节点的时间,也就是寻找 源点到所有节点最短路径的最大值
+ int result = 0;
+ for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
+ if (minDist[i] == INT_MAX) return -1;// 没有路径
+ result = max(minDist[i], result);
+ }
+ return result;
+
+ }
+};
+```
+
+* 时间复杂度:O(n^2)
+* 空间复杂度:O(n^2)
+
+### debug方法
+
+写这种题目难免会有各种各样的问题,我们如何发现自己的代码是否有问题呢?
+
+最好的方式就是打日志,本题的话,就是将 minDist 数组打印出来,就可以很明显发现 哪里出问题了。
+
+每次选择节点后,minDist数组的变化是否符合预期 ,是否和我上面讲的逻辑是对应的。
+
+例如本题,如果想debug的话,打印日志可以这样写:
+
+
+```CPP
+class Solution {
+public:
+ int networkDelayTime(vector>& times, int n, int k) {
+
+ // 注意题目中给的二维数组并不是领接矩阵
+ // 需要邻接矩阵来存图
+ // 因为本题处理方式是节点标号从1开始,所以数组的大小都是 n+1
+ vector> grid(n + 1, vector(n + 1, INT_MAX));
+ for(int i = 0; i < times.size(); i++){
+ int p1 = times[i][0];
+ int p2 = times[i][1];
+ grid[p1][p2] = times[i][2];
+ }
+
+ // 存储从源点到每个节点的最短距离
+ std::vector minDist(n + 1, INT_MAX);
+
+ // 记录顶点是否被访问过
+ std::vector visited(n + 1, false);
+
+ minDist[k] = 0; // 起始点到自身的距离为0
+ for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
+
+ int minVal = INT_MAX;
+ int cur = 1;
+
+ // 遍历每个节点,选择未被访问的节点集合中哪个节点到源点的距离最小
+ for (int v = 1; v <= n; ++v) {
+ if (!visited[v] && minDist[v] <= minVal) {
+ minVal = minDist[v];
+ cur = v;
+ }
+ }
+
+ visited[cur] = true; // 标记该顶点已被访问
+
+ for (int v = 1; v <= n; v++) {
+ if (!visited[v] && grid[cur][v] != INT_MAX && minDist[cur] + grid[cur][v] < minDist[v]) {
+ minDist[v] = minDist[cur] + grid[cur][v];
+ }
+ }
+ // 打印日志:
+ cout << "select:" << cur << endl;
+ for (int v = 1; v <= n; v++) cout << v << ":" << minDist[v] << " ";
+ cout << endl << endl;;
+
+
+
+ }
+ // 源点到最远的节点的时间,也就是寻找 源点到所有节点最短路径的最大值
+ int result = 0;
+ for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
+ if (minDist[i] == INT_MAX) return -1;// 没有路径
+ result = max(minDist[i], result);
+ }
+ return result;
+
+ }
+};
+
+
+```
+
+打印后的结果:
+
+```
+select:2
+1:1 2:0 3:1 4:2147483647
+
+select:3
+1:1 2:0 3:1 4:2
+
+select:1
+1:1 2:0 3:1 4:2
+
+select:4
+1:1 2:0 3:1 4:2
+```
+
+打印日志可以和上面我讲解的过程进行对比,每一步的结果是完全对应的。
+
+所以如果大家如果代码有问题,打日志来debug是最好的方法
+
+### 出现负数
+
+如果图中边的权值为负数,dijkstra 还合适吗?
+
+看一下这个图: (有负权值)
+
+
+
+节点1 到 节点5 的最短路径 应该是 节点1 -> 节点2 -> 节点3 -> 节点4 -> 节点5
+
+那我们来看dijkstra 求解的路径是什么样的,继续dijkstra 三部曲来模拟 :(dijkstra模拟过程上面已经详细讲过,以下只模拟重要过程,例如如何初始化就省略讲解了)
+
+-----------
+
+初始化:
+
+
+
+---------------
+
+1、选源点到哪个节点近且该节点未被访问过
+
+源点距离源点最近,距离为0,且未被访问。
+
+2、该最近节点被标记访问过
+
+标记源点访问过
+
+3、更新非访问节点到源点的距离(即更新minDist数组) ,如图:
+
+
+
+更新 minDist数组,即:源点(节点1) 到 节点2 和 节点3的距离。
+
+* 源点到节点2的最短距离为100,小于原minDist[2]的数值max,更新minDist[2] = 100
+* 源点到节点3的最短距离为1,小于原minDist[3]的数值max,更新minDist[4] = 1
+
+-------------------
+
+1、选源点到哪个节点近且该节点未被访问过
+
+源点距离节点3最近,距离为1,且未被访问。
+
+2、该最近节点被标记访问过
+
+标记节点3访问过
+
+3、更新非访问节点到源点的距离(即更新minDist数组) ,如图:
+
+
+
+由于节点3的加入,那么源点可以有新的路径链接到节点4 所以更新minDist数组:
+
+* 源点到节点4的最短距离为2,小于原minDist[4]的数值max,更新minDist[4] = 2
+
+--------------
+
+1、选源点到哪个节点近且该节点未被访问过
+
+源点距离节点4最近,距离为2,且未被访问。
+
+2、该最近节点被标记访问过
+
+标记节点4访问过
+
+3、更新非访问节点到源点的距离(即更新minDist数组) ,如图:
+
+
+
+由于节点4的加入,那么源点可以有新的路径链接到节点5 所以更新minDist数组:
+
+* 源点到节点5的最短距离为3,小于原minDist[5]的数值max,更新minDist[5] = 5
+
+------------
+
+1、选源点到哪个节点近且该节点未被访问过
+
+源点距离节点5最近,距离为3,且未被访问。
+
+2、该最近节点被标记访问过
+
+标记节点5访问过
+
+3、更新非访问节点到源点的距离(即更新minDist数组) ,如图:
+
+
+
+节点5的加入,而节点5 没有链接其他节点, 所以不用更新minDist数组,仅标记节点5被访问过了
+
+------------
+
+1、选源点到哪个节点近且该节点未被访问过
+
+源点距离节点2最近,距离为100,且未被访问。
+
+2、该最近节点被标记访问过
+
+标记节点2访问过
+
+3、更新非访问节点到源点的距离(即更新minDist数组) ,如图:
+
+
+
+--------------
+
+至此dijkstra的模拟过程就结束了,根据最后的minDist数组,我们求 节点1 到 节点5 的最短路径的权值总和为 3,路径: 节点1 -> 节点3 -> 节点4 -> 节点5
+
+通过以上的过程模拟,我们可以发现 之所以 没有走有负权值的最短路径 是因为 在 访问 节点 2 的时候,节点 3 已经访问过了,就不会再更新了。
+
+那有录友可能会想: 我可以改代码逻辑啊,访问过的节点,也让它继续访问不就好了?
+
+那么访问过的节点还能继续访问会不会有死循环的出现呢?控制逻辑不让其死循环?那特殊情况自己能都想清楚吗?(可以试试,实践出真知)
+
+对于负权值的出现,大家可以针对某一个场景 不断去修改 dijkstra 的代码,**但最终会发现只是 拆了东墙补西墙**,对dijkstra的补充逻辑只能满足某特定场景最短路求解。
+
+对于求解带有负权值的最短路问题,可以使用 Floyd 算法 ,我在后序会详细讲解。
+
+## dijkstra与prim算法的区别
+
+> 这里再次提示,需要先看我的 [prim算法精讲](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/yX936hHC6Z10K36Vm1Wl9w) ,否则可能不知道我下面讲的是什么。
+
+大家可以发现 dijkstra的代码看上去 怎么和 prim算法这么像呢。
+
+其实代码大体不差,唯一区别在 三部曲中的 第三步: 更新minDist数组
+
+因为**prim是求 非访问节点到最小生成树的最小距离,而 dijkstra是求 非访问节点到源点的最小距离**。
+
+prim 更新 minDist数组的写法:
+
+
+```CPP
+for (int j = 1; j <= v; j++) {
+ if (!isInTree[j] && grid[cur][j] < minDist[j]) {
+ minDist[j] = grid[cur][j];
+ }
+}
+```
+
+因为 minDist表示 节点到最小生成树的最小距离,所以 新节点cur的加入,只需要 使用 grid[cur][j] ,grid[cur][j] 就表示 cur 加入生成树后,生成树到 节点j 的距离。
+
+dijkstra 更新 minDist数组的写法:
+
+```CPP
+for (int v = 1; v <= n; v++) {
+ if (!visited[v] && grid[cur][v] != INT_MAX && minDist[cur] + grid[cur][v] < minDist[v]) {
+ minDist[v] = minDist[cur] + grid[cur][v];
+ }
+}
+```
+
+因为 minDist表示 节点到源点的最小距离,所以 新节点 cur 的加入,需要使用 源点到cur的距离 (minDist[cur]) + cur 到 节点 v 的距离 (grid[cur][v]),才是 源点到节点v的距离。
+
+此时大家可能不禁要想 prim算法 可以有负权值吗?
+
+当然可以!
+
+录友们可以自己思考思考一下,这是为什么?
+
+这里我提示一下:prim算法只需要将节点以最小权值和链接在一起,不涉及到单一路径。
+
+
+
+## 总结
+
+本篇,我们深入讲解的dijkstra算法,详细模拟其工作的流程。
+
+这里我给出了 **dijkstra 三部曲 来 帮助大家理解 该算法**,不至于 每次写 dijkstra 都是黑盒操作,没有框架没有章法。
+
+在给出的代码中,我也按照三部曲的逻辑来给大家注释,只要理解这三部曲,即使 过段时间 对 dijkstra 算法有些遗忘,依然可以写出一个框架出来,然后再去调试细节。
+
+对于图论算法,一般代码都比较长,很难写出代码直接可以提交通过,都需要一个debug的过程,所以 **学习如何debug 非常重要**!
+
+这也是我为什么 在本文中 单独用来讲解 debug方法。
+
+本题求的是最短路径和是多少,**同时我们也要掌握 如何把最短路径打印出来**。
+
+我还写了大篇幅来讲解 负权值的情况, 只有画图带大家一步一步去 看 出现负权值 dijkstra的求解过程,才能帮助大家理解,问题出在哪里。
+
+如果我直接讲:是**因为访问过的节点 不能再访问,导致错过真正的最短路**,我相信大家都不知道我在说啥。
+
+最后我还讲解了 dijkstra 和 prim 算法的 相同 与 不同之处, 我在图论的讲解安排中 先讲 prim算法 再讲 dijkstra 是有目的的, **理解这两个算法的相同与不同之处 有助于大家学习的更深入**。
+
+而不是 学了 dijkstra 就只看 dijkstra, 算法之间 都是有联系的,多去思考 算法之间的相互联系,会帮助大家思考的更深入,掌握的更彻底。
+
+本篇写了这么长,我也只讲解了 朴素版dijkstra,**关于 堆优化dijkstra,我会在下一篇再来给大家详细讲解**。
+
+
+
+## 堆优化版本dijkstra
+
+> 本篇我们来讲解 堆优化版dijkstra,看本篇之前,一定要先看 我讲解的 朴素版dijkstra,否则本篇会有部分内容看不懂。
+
+在上一篇中,我们讲解了朴素版的dijkstra,该解法的时间复杂度为 O(n^2),可以看出时间复杂度 只和 n (节点数量)有关系。
+
+如果n很大的话,我们可以换一个角度来优先性能。
+
+在 讲解 最小生成树的时候,我们 讲了两个算法,[prim算法](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/yX936hHC6Z10K36Vm1Wl9w)(从点的角度来求最小生成树)、[Kruskal算法](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/rUVaBjCES_4eSjngceT5bw)(从边的角度来求最小生成树)
+
+这么在n 很大的时候,也有另一个思考维度,即:从边的数量出发。
+
+当 n 很大,边 的数量 也很多的时候(稠密图),那么 上述解法没问题。
+
+但 n 很大,边 的数量 很小的时候(稀疏图),是不是可以换成从边的角度来求最短路呢?
+
+毕竟边的数量少。
+
+有的录友可能会想,n (节点数量)很大,边不就多吗? 怎么会边的数量少呢?
+
+别忘了,谁也没有规定 节点之间一定要有边连接着,例如有一万个节点,只有一条边,这也是一张图。
+
+了解背景之后,再来看 解法思路。
+
+### 图的存储
+
+首先是 图的存储。
+
+关于图的存储 主流有两种方式: 邻接矩阵和邻接表
+
+#### 邻接矩阵
+
+邻接矩阵 使用 二维数组来表示图结构。 邻接矩阵是从节点的角度来表示图,有多少节点就申请多大的二维数组。
+
+例如: grid[2][5] = 6,表示 节点 2 链接 节点5 为有向图,节点2 指向 节点5,边的权值为6 (套在题意里,可能是距离为6 或者 消耗为6 等等)
+
+如果想表示无向图,即:grid[2][5] = 6,grid[5][2] = 6,表示节点2 与 节点5 相互连通,权值为6。
+
+
+如图:
+
+
+
+在一个 n (节点数)为8 的图中,就需要申请 8 * 8 这么大的空间,有一条双向边,即:grid[2][5] = 6,grid[5][2] = 6
+
+这种表达方式(邻接矩阵) 在 边少,节点多的情况下,会导致申请过大的二维数组,造成空间浪费。
+
+而且在寻找节点链接情况的时候,需要遍历整个矩阵,即 n * n 的时间复杂度,同样造成时间浪费。
+
+邻接矩阵的优点:
+
+* 表达方式简单,易于理解
+* 检查任意两个顶点间是否存在边的操作非常快
+* 适合稠密图,在边数接近顶点数平方的图中,邻接矩阵是一种空间效率较高的表示方法。
+
+缺点:
+
+* 遇到稀疏图,会导致申请过大的二维数组造成空间浪费 且遍历 边 的时候需要遍历整个n * n矩阵,造成时间浪费
+
+#### 邻接表
+
+邻接表 使用 数组 + 链表的方式来表示。 邻接表是从边的数量来表示图,有多少边 才会申请对应大小的链表。
+
+邻接表的构造如图:
+
+
+
+这里表达的图是:
+
+* 节点1 指向 节点3 和 节点5
+* 节点2 指向 节点4、节点3、节点5
+* 节点3 指向 节点4,节点4指向节点1。
+
+有多少边 邻接表才会申请多少个对应的链表节点。
+
+从图中可以直观看出 使用 数组 + 链表 来表达 边的链接情况 。
+
+邻接表的优点:
+
+* 对于稀疏图的存储,只需要存储边,空间利用率高
+* 遍历节点链接情况相对容易
+
+缺点:
+
+* 检查任意两个节点间是否存在边,效率相对低,需要 O(V)时间,V表示某节点链接其他节点的数量。
+* 实现相对复杂,不易理解
+
+#### 本题图的存储
+
+接下来我们继续按照稀疏图的角度来分析本题。
+
+在第一个版本的实现思路中,我们提到了三部曲:
+
+1. 第一步,选源点到哪个节点近且该节点未被访问过
+2. 第二步,该最近节点被标记访问过
+3. 第三步,更新非访问节点到源点的距离(即更新minDist数组)
+
+在第一个版本的代码中,这三部曲是套在一个 for 循环里,为什么?
+
+因为我们是从节点的角度来解决问题。
+
+三部曲中第一步(选源点到哪个节点近且该节点未被访问过),这个操作本身需要for循环遍历 minDist 来寻找最近的节点。
+
+同时我们需要 遍历所有 未访问过的节点,所以 我们从 节点角度出发,代码会有两层for循环,代码是这样的: (注意代码中的注释,标记两层for循环的用处)
+
+```CPP
+
+for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { // 遍历所有节点,第一层for循环
+
+ int minVal = INT_MAX;
+ int cur = 1;
+
+ // 1、选距离源点最近且未访问过的节点 , 第二层for循环
+ for (int v = 1; v <= n; ++v) {
+ if (!visited[v] && minDist[v] < minVal) {
+ minVal = minDist[v];
+ cur = v;
+ }
+ }
+
+ visited[cur] = true; // 2、标记该节点已被访问
+
+ // 3、第三步,更新非访问节点到源点的距离(即更新minDist数组)
+ for (int v = 1; v <= n; v++) {
+ if (!visited[v] && grid[cur][v] != INT_MAX && minDist[cur] + grid[cur][v] < minDist[v]) {
+ minDist[v] = minDist[cur] + grid[cur][v];
+ }
+ }
+
+}
+```
+
+那么当从 边 的角度出发, 在处理 三部曲里的第一步(选源点到哪个节点近且该节点未被访问过)的时候 ,我们可以不用去遍历所有节点了。
+
+而且 直接把 边(带权值)加入到 小顶堆(利用堆来自动排序),那么每次我们从 堆顶里 取出 边 自然就是 距离源点最近的节点所在的边。
+
+这样我们就不需要两层for循环来寻找最近的节点了。
+
+了解了大体思路,我们再来看代码实现。
+
+首先是 如何使用 邻接表来表述图结构,这是摆在很多录友面前的第一个难题。
+
+邻接表用 数组+链表 来表示,代码如下:(C++中 vector 为数组,list 为链表, 定义了 n+1 这么大的数组空间)
+
+```CPP
+vector> grid(n + 1);
+```
+
+不少录友,不知道 如何定义的数据结构,怎么表示邻接表的,我来给大家画一个图:
+
+
+
+图中邻接表表示:
+
+* 节点1 指向 节点3 和 节点5
+* 节点2 指向 节点4、节点3、节点5
+* 节点3 指向 节点4
+* 节点4 指向 节点1
+
+大家发现图中的边没有权值,而本题中 我们的边是有权值的,权值怎么表示?在哪里表示?
+
+所以 在`vector> grid(n + 1);` 中 就不能使用int了,而是需要一个键值对 来存两个数字,一个数表示节点,一个数表示 指向该节点的这条边的权值。
+
+那么 代码可以改成这样: (pair 为键值对,可以存放两个int)
+
+```CPP
+vector>> grid(n + 1);
+```
+
+举例来给大家展示 该代码表达的数据 如下:
+
+
+
+* 节点1 指向 节点3 权值为 1
+* 节点1 指向 节点5 权值为 2
+* 节点2 指向 节点4 权值为 7
+* 节点2 指向 节点3 权值为 6
+* 节点2 指向 节点5 权值为 3
+* 节点3 指向 节点4 权值为 3
+* 节点5 指向 节点1 权值为 10
+
+这样 我们就把图中权值表示出来了。
+
+但是在代码中 使用 `pair` 很容易让我们搞混了,第一个int 表示什么,第二个int表示什么,导致代码可读性很差,或者说别人看你的代码看不懂。
+
+那么 可以 定一个类 来取代 `pair`
+
+类(或者说是结构体)定义如下:
+
+```CPP
+struct Edge {
+ int to; // 邻接顶点
+ int val; // 边的权重
+
+ Edge(int t, int w): to(t), val(w) {} // 构造函数
+};
+```
+
+这个类里有两个成员变量,有对应的命名,这样不容易搞混 两个int的含义。
+
+所以 本题中邻接表的定义如下:
+
+```CPP
+struct Edge {
+ int to; // 链接的节点
+ int val; // 边的权重
+
+ Edge(int t, int w): to(t), val(w) {} // 构造函数
+};
+
+vector> grid(n + 1); // 邻接表
+
+```
+
+(我们在下面的讲解中会直接使用这个邻接表的代码表示方式)
+
+### 堆优化细节
+
+其实思路依然是 dijkstra 三部曲:
+
+1. 第一步,选源点到哪个节点近且该节点未被访问过
+2. 第二步,该最近节点被标记访问过
+3. 第三步,更新非访问节点到源点的距离(即更新minDist数组)
+
+只不过之前是 通过遍历节点来遍历边,通过两层for循环来寻找距离源点最近节点。 这次我们直接遍历边,且通过堆来对边进行排序,达到直接选择距离源点最近节点。
+
+先来看一下针对这三部曲,如果用 堆来优化。
+
+那么三部曲中的第一步(选源点到哪个节点近且该节点未被访问过),我们如何选?
+
+我们要选择距离源点近的节点(即:该边的权值最小),所以 我们需要一个 小顶堆 来帮我们对边的权值排序,每次从小顶堆堆顶 取边就是权值最小的边。
+
+C++定义小顶堆,可以用优先级队列实现,代码如下:
+
+```CPP
+// 小顶堆
+class mycomparison {
+public:
+ bool operator()(const pair& lhs, const pair& rhs) {
+ return lhs.second > rhs.second;
+ }
+};
+// 优先队列中存放 pair<节点编号,源点到该节点的权值>
+priority_queue, vector>, mycomparison> pq;
+```
+
+(`pair`中 第二个int 为什么要存 源点到该节点的权值,因为 这个小顶堆需要按照权值来排序)
+
+
+有了小顶堆自动对边的权值排序,那我们只需要直接从 堆里取堆顶元素(小顶堆中,最小的权值在上面),就可以取到离源点最近的节点了 (未访问过的节点,不会加到堆里进行排序)
+
+所以三部曲中的第一步,我们不用 for循环去遍历,直接取堆顶元素:
+
+```CPP
+// pair<节点编号,源点到该节点的权值>
+pair cur = pq.top(); pq.pop();
+
+```
+
+第二步(该最近节点被标记访问过) 这个就是将 节点做访问标记,和 朴素dijkstra 一样 ,代码如下:
+
+```CPP
+// 2. 第二步,该最近节点被标记访问过
+visited[cur.first] = true;
+
+```
+
+(`cur.first` 是指取 `pair` 里的第一个int,即节点编号 )
+
+第三步(更新非访问节点到源点的距离),这里的思路 也是 和朴素dijkstra一样的。
+
+但很多录友对这里是最懵的,主要是因为两点:
+
+* 没有理解透彻 dijkstra 的思路
+* 没有理解 邻接表的表达方式
+
+我们来回顾一下 朴素dijkstra 在这一步的代码和思路(如果没看过我讲解的朴素版dijkstra,这里会看不懂)
+
+```CPP
+
+// 3、第三步,更新非访问节点到源点的距离(即更新minDist数组)
+for (int v = 1; v <= n; v++) {
+ if (!visited[v] && grid[cur][v] != INT_MAX && minDist[cur] + grid[cur][v] < minDist[v]) {
+ minDist[v] = minDist[cur] + grid[cur][v];
+ }
+}
+```
+
+其中 for循环是用来做什么的? 是为了 找到 节点cur 链接指向了哪些节点,因为使用邻接矩阵的表达方式 所以把所有节点遍历一遍。
+
+而在邻接表中,我们可以以相对高效的方式知道一个节点链接指向哪些节点。
+
+再回顾一下邻接表的构造(数组 + 链表):
+
+
+
+假如 加入的cur 是节点 2, 那么 grid[2] 表示的就是图中第二行链表。 (grid数组的构造我们在 上面 「图的存储」中讲过)
+
+所以在邻接表中,我们要获取 节点cur 链接指向哪些节点,就是遍历 grid[cur节点编号] 这个链表。
+
+这个遍历方式,C++代码如下:
+
+```CPP
+for (Edge edge : grid[cur.first])
+```
+
+(如果不知道 Edge 是什么,看上面「图的存储」中邻接表的讲解)
+
+`cur.first` 就是cur节点编号, 参考上面pair的定义: pair<节点编号,源点到该节点的权值>
+
+接下来就是更新 非访问节点到源点的距离,代码实现和 朴素dijkstra 是一样的,代码如下:
+
+```CPP
+// 3. 第三步,更新非访问节点到源点的距离(即更新minDist数组)
+for (Edge edge : grid[cur.first]) { // 遍历 cur指向的节点,cur指向的节点为 edge
+ // cur指向的节点edge.to,这条边的权值为 edge.val
+ if (!visited[edge.to] && minDist[cur.first] + edge.val < minDist[edge.to]) { // 更新minDist
+ minDist[edge.to] = minDist[cur.first] + edge.val;
+ pq.push(pair(edge.to, minDist[edge.to]));
+ }
+}
+```
+
+但为什么思路一样,有的录友能写出朴素dijkstra,但堆优化这里的逻辑就是写不出来呢?
+
+**主要就是因为对邻接表的表达方式不熟悉**!
+
+以上代码中,cur 链接指向的节点编号 为 edge.to, 这条边的权值为 edge.val ,如果对这里模糊的就再回顾一下 Edge的定义:
+
+```CPP
+struct Edge {
+ int to; // 邻接顶点
+ int val; // 边的权重
+
+ Edge(int t, int w): to(t), val(w) {} // 构造函数
+};
+```
+
+确定该节点没有被访问过,`!visited[edge.to]` , 目前 源点到cur.first的最短距离(minDist) + cur.first 到 edge.to 的距离 (edge.val) 是否 小于 minDist已经记录的 源点到 edge.to 的距离 (minDist[edge.to])
+
+如果是的话,就开始更新操作。
+
+即:
+
+```CPP
+if (!visited[edge.to] && minDist[cur.first] + edge.val < minDist[edge.to]) { // 更新minDist
+ minDist[edge.to] = minDist[cur.first] + edge.val;
+ pq.push(pair(edge.to, minDist[edge.to])); // 由于cur节点的加入,而新链接的边,加入到优先级队里中
+}
+
+```
+
+同时,由于cur节点的加入,源点又有可以新链接到的边,将这些边加入到优先级队里中。
+
+
+以上代码思路 和 朴素版dijkstra 是一样一样的,主要区别是两点:
+
+* 邻接表的表示方式不同
+* 使用优先级队列(小顶堆)来对新链接的边排序
+
+### 代码实现
+
+堆优化dijkstra完整代码如下:
+
+```CPP
+class Solution {
+public:
+ // 小顶堆
+ class mycomparison {
+ public:
+ bool operator()(const pair& lhs, const pair& rhs) {
+ return lhs.second > rhs.second;
+ }
+ };
+ // 定义一个结构体来表示带权重的边
+ struct Edge {
+ int to; // 邻接顶点
+ int val; // 边的权重
+
+ Edge(int t, int w): to(t), val(w) {} // 构造函数
+ };
+ int networkDelayTime(vector>& times, int n, int k) {
+
+
+ std::vector> grid(n + 1);
+ for(int i = 0; i < times.size(); i++){
+ int p1 = times[i][0];
+ int p2 = times[i][1];
+ // p1 指向 p2,权值为 times[i][2]
+ grid[p1].push_back(Edge(p2, times[i][2]));
+ }
+
+ // 存储从源点到每个节点的最短距离
+ std::vector minDist(n + 1, INT_MAX);
+
+ // 记录顶点是否被访问过
+ std::vector visited(n + 1, false);
+
+ // 优先队列中存放 pair<节点,源点到该节点的距离>
+ priority_queue, vector>, mycomparison> pq;
+
+ pq.push(pair(k, 0));
+ minDist[k] = 0; // 这个不要忘了
+
+ while (!pq.empty()) {
+ // <节点, 源点到该节点的距离>
+ // 1. 第一步,选源点到哪个节点近且该节点未被访问过 (通过优先级队列来实现)
+ pair cur = pq.top(); pq.pop();
+
+ if (visited[cur.first]) continue;
+
+ // 2. 第二步,该最近节点被标记访问过
+ visited[cur.first] = true;
+
+
+ // 3. 第三步,更新非访问节点到源点的距离(即更新minDist数组)
+ for (Edge edge : grid[cur.first]) { // 遍历 cur指向的节点,cur指向的节点为 edge
+ // cur指向的节点edge.to,这条边的权值为 edge.val
+ if (!visited[edge.to] && minDist[cur.first] + edge.val < minDist[edge.to]) { // 更新minDist
+ minDist[edge.to] = minDist[cur.first] + edge.val;
+ pq.push(pair(edge.to, minDist[edge.to]));
+ }
+ }
+
+ }
+
+ // 源点到最远的节点的时间,也就是寻找 源点到所有节点最短路径的最大值
+ int result = 0;
+ for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
+ if (minDist[i] == INT_MAX) return -1;// 没有路径
+ result = max(minDist[i], result);
+ }
+ return result;
+
+ }
+};
+
+```
+
+* 时间复杂度:O(ElogE) E 为边的数量
+* 空间复杂度:O(N + E) N 为节点的数量
+
+堆优化的时间复杂度 只和边的数量有关 和节点数无关,在 优先级队列中 放的也是边。
+
+以上代码中,`while (!pq.empty())` 里套了 `for (Edge edge : grid[cur.first])`
+
+`for` 里 遍历的是 当前节点 cur 所连接边。
+
+那 当前节点cur 所连接的边 也是不固定的, 这就让大家分不清,这时间复杂度究竟是多少?
+
+其实 `for (Edge edge : grid[cur.first])` 里最终的数据走向 是 给队列里添加边。
+
+那么跳出局部代码,整个队列 一定是 所有边添加了一次,同时也弹出了一次。
+
+所以边添加一次时间复杂度是 O(E), `while (!pq.empty())` 里每次都要弹出一个边来进行操作,在优先级队列(小顶堆)中 弹出一个元素的时间复杂度是 O(logE) ,这是堆排序的时间复杂度。
+
+(当然小顶堆里 是 添加元素的时候 排序,还是 取数元素的时候排序,这个无所谓,时间复杂度都是O(E),总是是一定要排序的,而小顶堆里也不会滞留元素,有多少元素添加 一定就有多少元素弹出)
+
+所以 该算法整体时间复杂度为 O(ElogE)
+
+网上的不少分析 会把 n (节点的数量)算进来,这个分析是有问题的,举一个极端例子,在n 为 10000,且是有一条边的 图里,以上代码,大家感觉执行了多少次?
+
+`while (!pq.empty())` 中的 pq 存的是边,其实只执行了一次。
+
+所以该算法时间复杂度 和 节点没有关系。
+
+至于空间复杂度,邻接表是 数组 + 链表 数组的空间 是 N ,有E条边 就申请对应多少个链表节点,所以是 复杂度是 N + E
+
+## 拓展
+
+当然也有录友可能想 堆优化dijkstra 中 我为什么一定要用邻接表呢,我就用邻接矩阵 行不行 ?
+
+也行的。
+
+但 正是因为稀疏图,所以我们使用堆优化的思路, 如果我们还用 邻接矩阵 去表达这个图的话,就是 一个高效的算法 使用了低效的数据结构,那么 整体算法效率 依然是低的。
+
+如果还不清楚为什么要使用 邻接表,可以再看看上面 我在 「图的存储」标题下的讲解。
+
+这里我也给出 邻接矩阵版本的堆优化dijkstra代码:
+
+```CPP
+class Solution {
+public:
+ // 小顶堆(按照中的v 来从小到大排序)
+ class mycomparison {
+ public:
+ bool operator()(const pair& lhs, const pair& rhs) {
+ return lhs.second > rhs.second;
+ }
+ };
+ int networkDelayTime(vector>& times, int n, int k) {
+
+ // 注意题目中给的二维数组并不是邻接矩阵
+ // 需要邻接矩阵来存图
+ // 因为本题处理方式是节点标号从1开始,所以数组的大小都是 n+1
+ vector> grid(n + 1, vector(n + 1, INT_MAX));
+ for(int i = 0; i < times.size(); i++){
+ int p1 = times[i][0];
+ int p2 = times[i][1];
+ grid[p1][p2] = times[i][2];
+ }
+
+ // 存储从源点到每个节点的最短距离
+ std::vector minDist(n + 1, INT_MAX);
+
+ // 记录顶点是否被访问过
+ std::vector visited(n + 1, false);
+
+ // 优先队列中存放 [节点,源点到该节点的距离]
+ priority_queue, vector>, mycomparison> pq;
+
+ pq.push(pair(k, 0));
+ minDist[k] = 0; // 这个不要忘了
+
+ while (!pq.empty()) {
+ // <节点, 源点到该节点的距离>
+ // 1、选距离源点最近且未访问过的节点
+ pair cur = pq.top(); pq.pop();
+
+ if (visited[cur.first]) continue;
+
+ // 2、标记该节点已被访问
+ visited[cur.first] = true;
+
+ // 3、第三步,更新非访问节点到源点的距离(即更新minDist数组)
+ // 遍历 cur 可以链接的节点,更新 minDist[j]
+ for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
+ if (!visited[j] && grid[cur.first][j] != INT_MAX && (minDist[cur.first] + grid[cur.first][j] < minDist[j])) {
+ minDist[j] = minDist[cur.first] + grid[cur.first][j];
+ pq.push(pair(j, minDist[j]));
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+ // 源点到最远的节点的时间,也就是寻找 源点到所有节点最短路径的最大值
+ int result = 0;
+ for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
+ if (minDist[i] == INT_MAX) return -1;// 没有路径
+ result = max(minDist[i], result);
+ }
+
+
+ return result;
+
+ }
+};
+
+```
+
+* 时间复杂度:O(E * (N + logE)) E为边的数量,N为节点数量
+* 空间复杂度:O(log(N^2))
+
+`while (!pq.empty())` 时间复杂度为 E ,while 里面 每次取元素 时间复杂度 为 logE,和 一个for循环 时间复杂度 为 N 。
+
+所以整体是 E * (N + logE)
+
+
+## 总结
+
+在学习一种优化思路的时候,首先就要知道为什么要优化,遇到了什么问题。
+
+正如我在开篇就给大家交代清楚 堆优化方式的背景。
+
+堆优化的整体思路和 朴素版是大体一样的,区别是 堆优化从边的角度触发,且利用堆来排序。
+
+很多录友别说写堆优化 就是看 堆优化的代码也看的很懵。
+
+主要是因为两点:
+
+* 不熟悉邻接表的表达方式
+* 对dijkstra的实现思路还是不熟
+
+这是我为什么 本篇花了大力气来讲解 图的存储,就是为了让大家彻底理解邻接表以及邻接表的代码写法。
+
+至于 dijkstra的实现思路 ,朴素版 和 堆优化版本 都是 按照 dijkstra 三部曲来的。
+
+理解了三部曲,dijkstra 的思路就是清晰的。
+
+针对邻接表版本代码 我做了详细的 时间复杂度分析,也让录友们清楚,相对于 朴素版,时间都优化到哪了。
+
+最后 我也给出了 邻接矩阵的版本代码,分析了这一版本的必要性以及时间复杂度。
+
+至此通过 两篇dijkstra的文章,终于把 dijkstra 讲完了,如果大家对我讲解里所涉及的内容都吃透的话,详细对 dijkstra 算法也就理解到位了。
+
+这里在给出本题的Bellman_ford解法,关于 Bellman_ford ,后面我会专门来讲解的,Bellman_ford 有其独特的应用场景
+
+```CPP
+class Solution {
+public:
+
+ int networkDelayTime(vector>& times, int n, int k) {
+ vector minDist(n + 1 , INT_MAX/2);
+ minDist[k] = 0;
+ //vector minDist_copy(n); // 用来记录每一次遍历的结果
+ for (int i = 1; i <= n + 1; i++) {
+ //minDist_copy = minDist; // 获取上一次计算的结果
+ for (auto &f : times) {
+ int from = f[0];
+ int to = f[1];
+ int price = f[2];
+ if (minDist[to] > minDist[from] + price) minDist[to] = minDist[from] + price;
+ }
+
+ }
+ int result = 0;
+ for (int i = 1;i <= n; i++) {
+ if (minDist[i] == INT_MAX/2) return -1;// 没有路径
+ result = max(minDist[i], result);
+ }
+ return result;
+
+ }
+};
+```
+
diff --git "a/problems/0746.\344\275\277\347\224\250\346\234\200\345\260\217\350\212\261\350\264\271\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257.md" "b/problems/0746.\344\275\277\347\224\250\346\234\200\345\260\217\350\212\261\350\264\271\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index d13ff19f5a..952d4d2ab7
--- "a/problems/0746.\344\275\277\347\224\250\346\234\200\345\260\217\350\212\261\350\264\271\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257.md"
+++ "b/problems/0746.\344\275\277\347\224\250\346\234\200\345\260\217\350\212\261\350\264\271\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
@@ -54,7 +52,7 @@
请你计算并返回达到楼梯顶部的最低花费。
-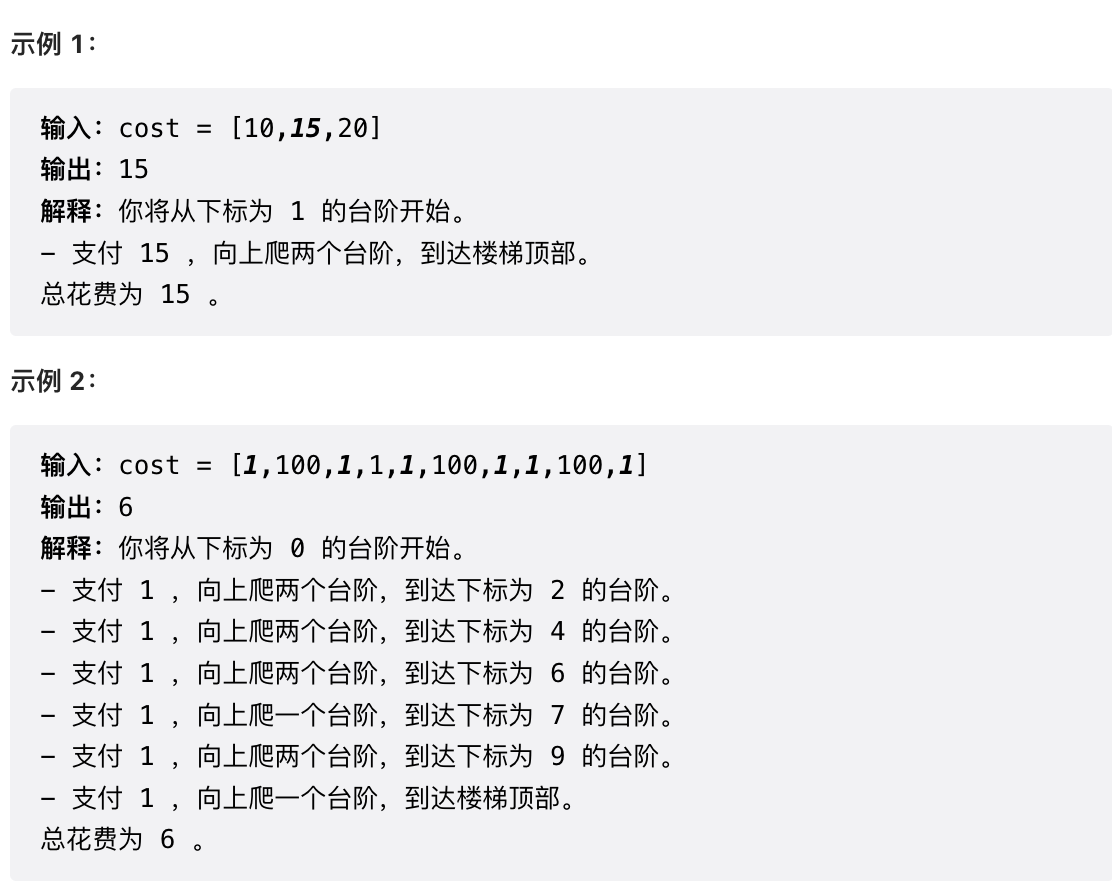
+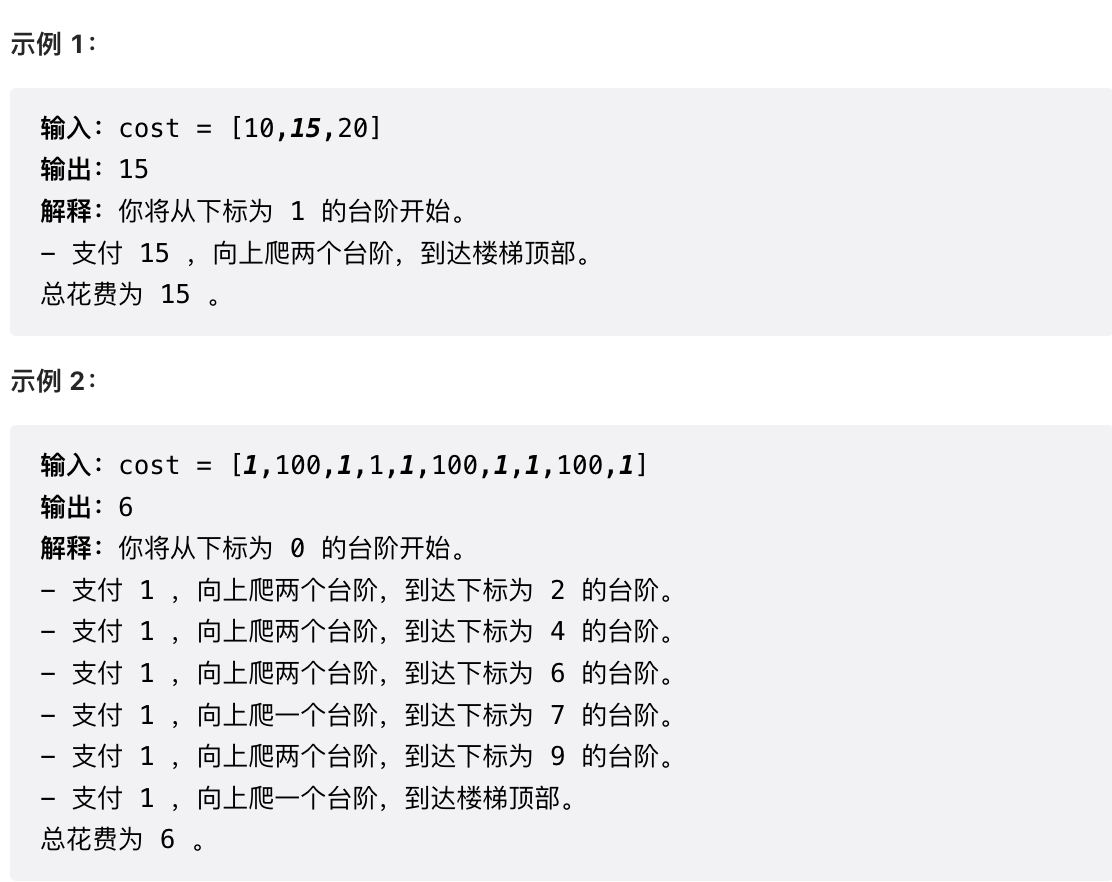
## 思路
@@ -114,7 +112,7 @@ dp[i - 2] 跳到 dp[i] 需要花费 dp[i - 2] + cost[i - 2]。
拿示例2:cost = [1, 100, 1, 1, 1, 100, 1, 1, 100, 1] ,来模拟一下dp数组的状态变化,如下:
-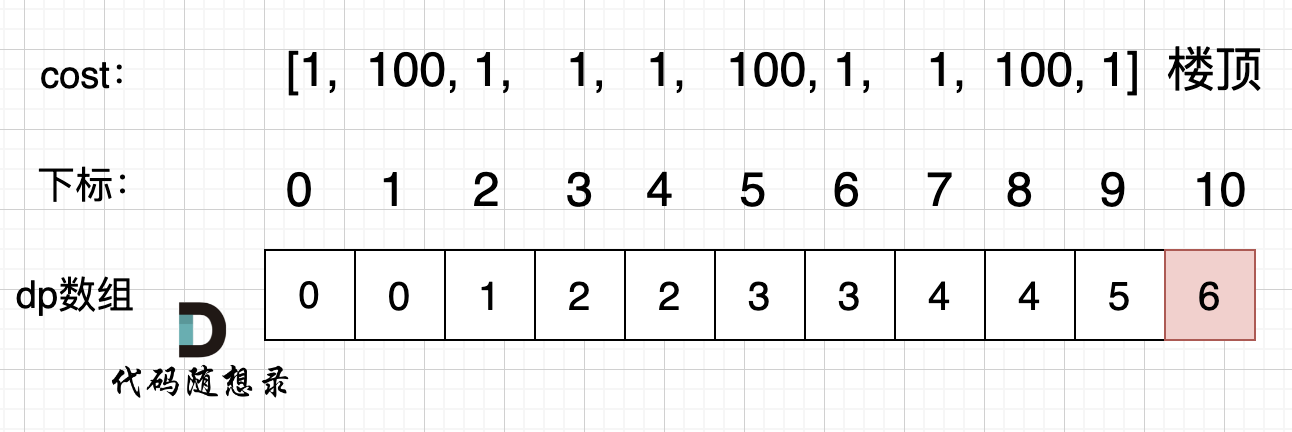
+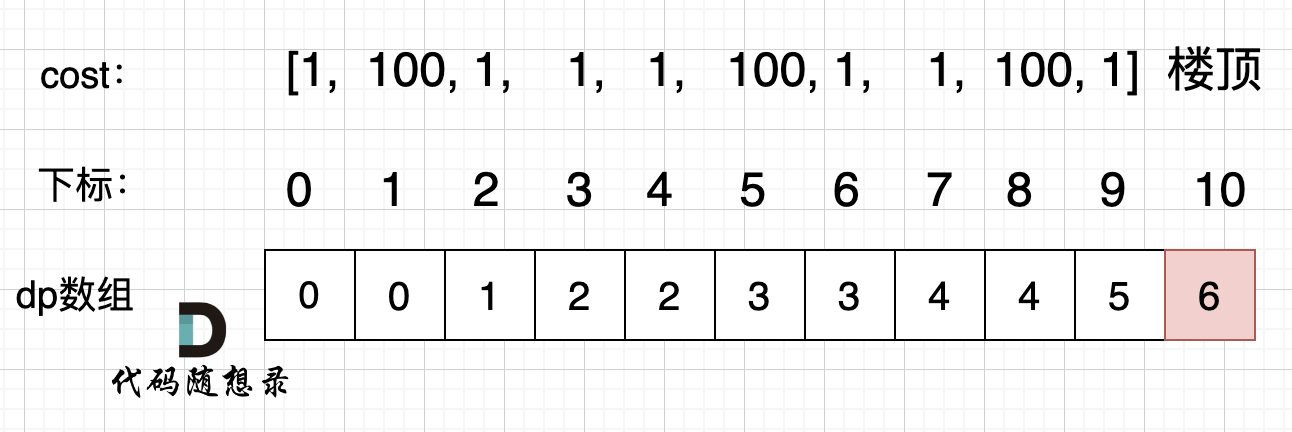
如果大家代码写出来有问题,就把dp数组打印出来,看看和如上推导的是不是一样的。
@@ -244,6 +242,24 @@ class Solution {
}
```
+```Java
+// 状态压缩,使用三个变量来代替数组
+class Solution {
+ public int minCostClimbingStairs(int[] cost) {
+ // 以下三个变量分别表示前两个台阶的最少费用、前一个的、当前的。
+ int beforeTwoCost = 0, beforeOneCost = 0, currentCost = 0;
+ // 前两个台阶不需要费用就能上到,因此从下标2开始;因为最后一个台阶需要跨越,所以需要遍历到cost.length
+ for (int i = 2; i <= cost.length; i ++) {
+ // 此处遍历的是cost[i - 1],不会越界
+ currentCost = Math.min(beforeOneCost + cost[i - 1], beforeTwoCost + cost[i - 2]);
+ beforeTwoCost = beforeOneCost;
+ beforeOneCost = currentCost;
+ }
+ return currentCost;
+ }
+}
+```
+
### Python
动态规划(版本一)
@@ -519,8 +535,4 @@ public class Solution
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0763.\345\210\222\345\210\206\345\255\227\346\257\215\345\214\272\351\227\264.md" "b/problems/0763.\345\210\222\345\210\206\345\255\227\346\257\215\345\214\272\351\227\264.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 4e9ec578bc..d17878381f
--- "a/problems/0763.\345\210\222\345\210\206\345\255\227\346\257\215\345\214\272\351\227\264.md"
+++ "b/problems/0763.\345\210\222\345\210\206\345\255\227\346\257\215\345\214\272\351\227\264.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0763.\345\210\222\345\210\206\345\255\227\346\257\215\345\214\272\351\227\264.md" "b/problems/0763.\345\210\222\345\210\206\345\255\227\346\257\215\345\214\272\351\227\264.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 4e9ec578bc..d17878381f
--- "a/problems/0763.\345\210\222\345\210\206\345\255\227\346\257\215\345\214\272\351\227\264.md"
+++ "b/problems/0763.\345\210\222\345\210\206\345\255\227\346\257\215\345\214\272\351\227\264.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 763.划分字母区间
@@ -46,7 +44,7 @@
如图:
-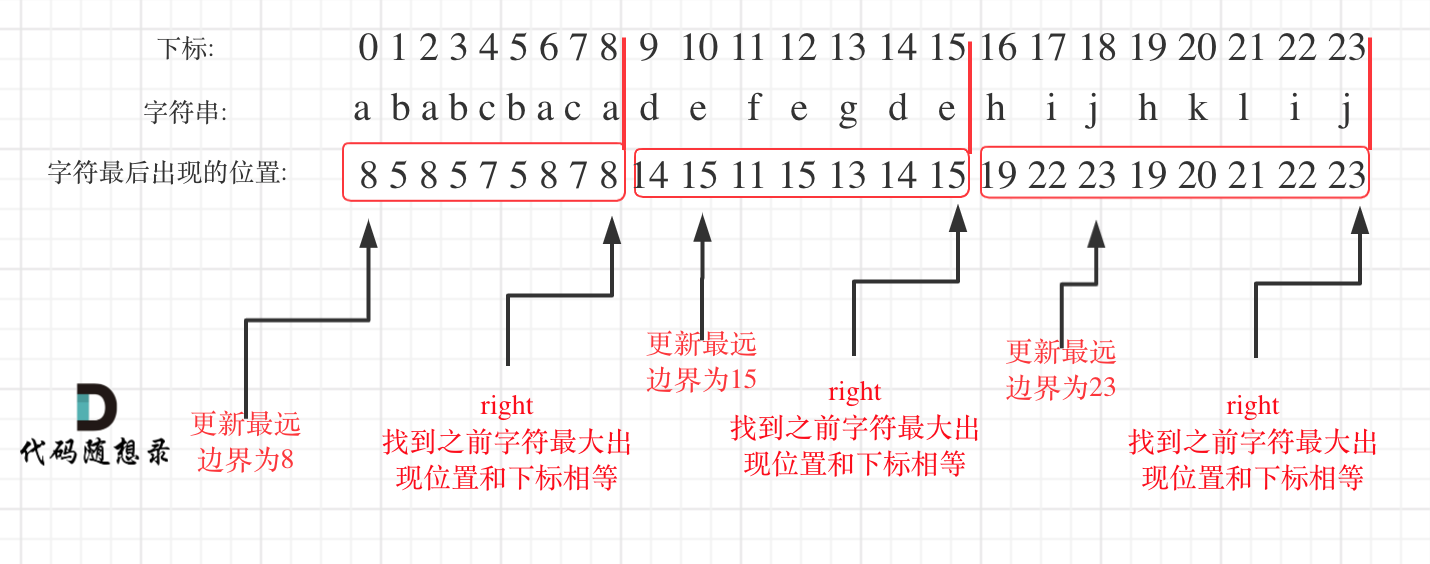
+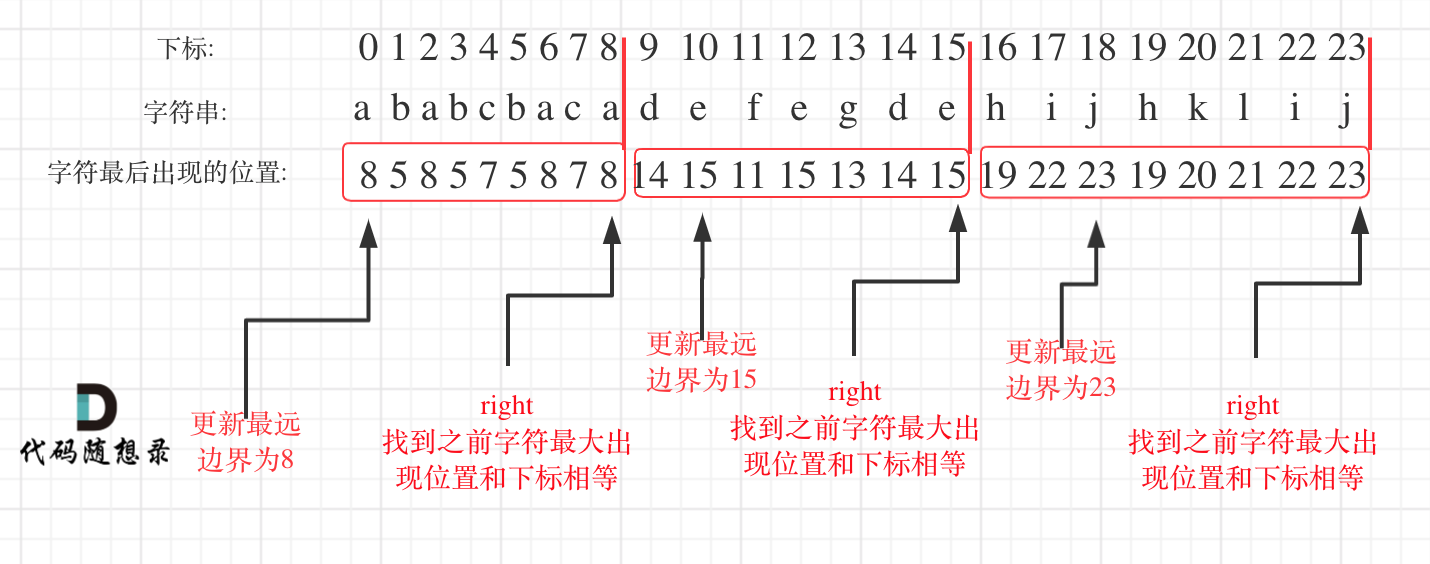
明白原理之后,代码并不复杂,如下:
@@ -312,7 +310,7 @@ func max(a, b int) int {
}
```
-### Javascript
+### JavaScript
```Javascript
var partitionLabels = function(s) {
let hash = {}
@@ -404,7 +402,38 @@ impl Solution {
}
}
```
+### C
+
+```c
+#define max(a, b) ((a) > (b) ? (a) : (b))
+
+int* partitionLabels(char* s, int* returnSize) {
+ // 记录每个字符最远出现的位置
+ int last[26] = {0};
+ int len = strlen(s);
+ for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i) {
+ last[s[i] - 'a'] = i;
+ }
+ int left = 0, right = 0;
+ int * partition = malloc(sizeof (int ) * len);
+ // 初始化值
+ *returnSize = 0;
+ for(int i = 0; i < len; i++){
+ right = max(right, last[s[i] - 'a']);
+ // 到达最远位置,加入答案,并且更新左边下标
+ if(i == right){
+ partition[(*returnSize)++] = right - left + 1;
+ left = i + 1;
+ }
+ }
+ return partition;
+}
+```
+
+
+
### C#
+
```csharp
public class Solution
{
@@ -431,8 +460,3 @@ public class Solution
}
```
-
-
-  -
-
diff --git "a/problems/0787.K\347\253\231\344\270\255\350\275\254\345\206\205\346\234\200\344\276\277\345\256\234\347\232\204\350\210\252\347\217\255.md" "b/problems/0787.K\347\253\231\344\270\255\350\275\254\345\206\205\346\234\200\344\276\277\345\256\234\347\232\204\350\210\252\347\217\255.md"
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..fb58c14816
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/problems/0787.K\347\253\231\344\270\255\350\275\254\345\206\205\346\234\200\344\276\277\345\256\234\347\232\204\350\210\252\347\217\255.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,180 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
+
+# 787. K 站中转内最便宜的航班
+
+有 n 个城市通过一些航班连接。给你一个数组 flights ,其中 flights[i] = [fromi, toi, pricei] ,表示该航班都从城市 fromi 开始,以价格 pricei 抵达 toi。
+
+现在给定所有的城市和航班,以及出发城市 src 和目的地 dst,你的任务是找到出一条最多经过 k 站中转的路线,使得从 src 到 dst 的 价格最便宜 ,并返回该价格。 如果不存在这样的路线,则输出 -1。
+
+
+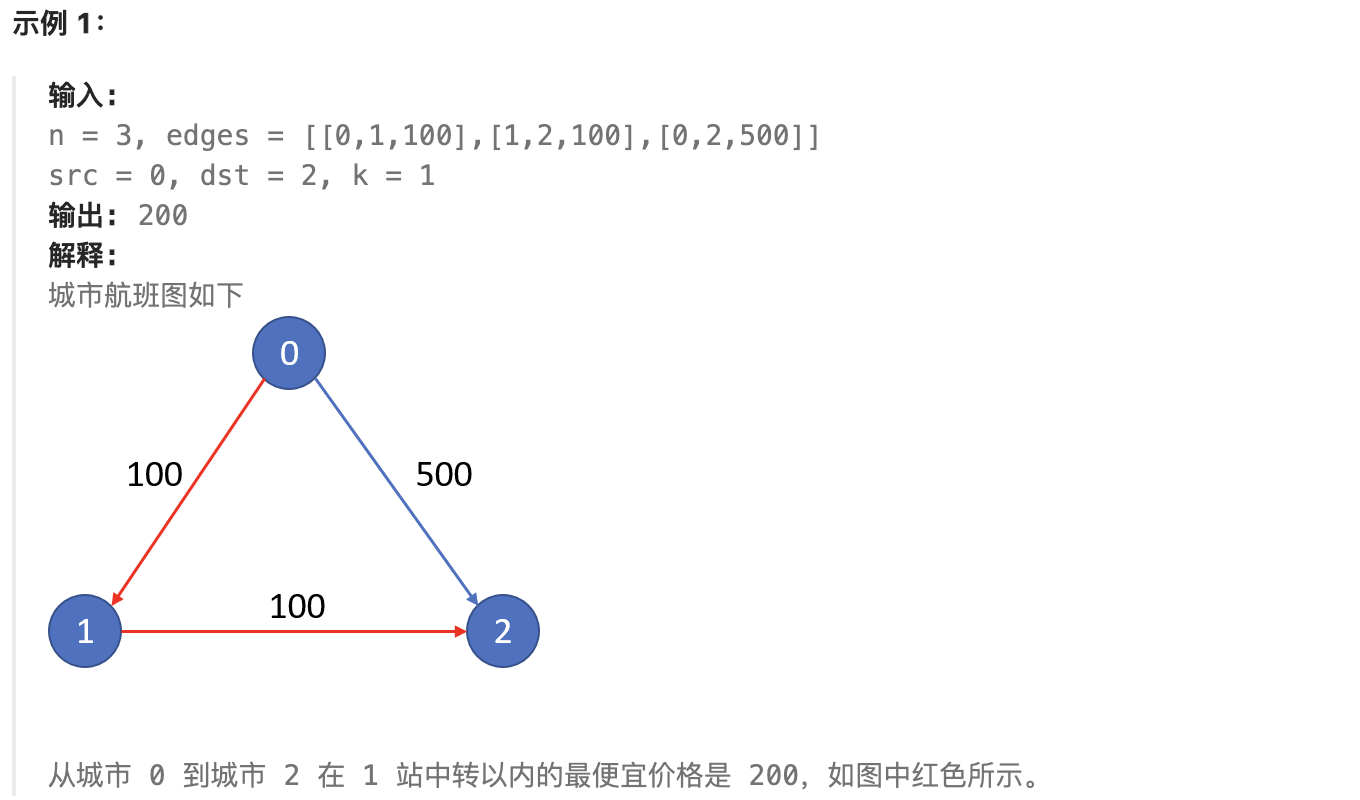
+
+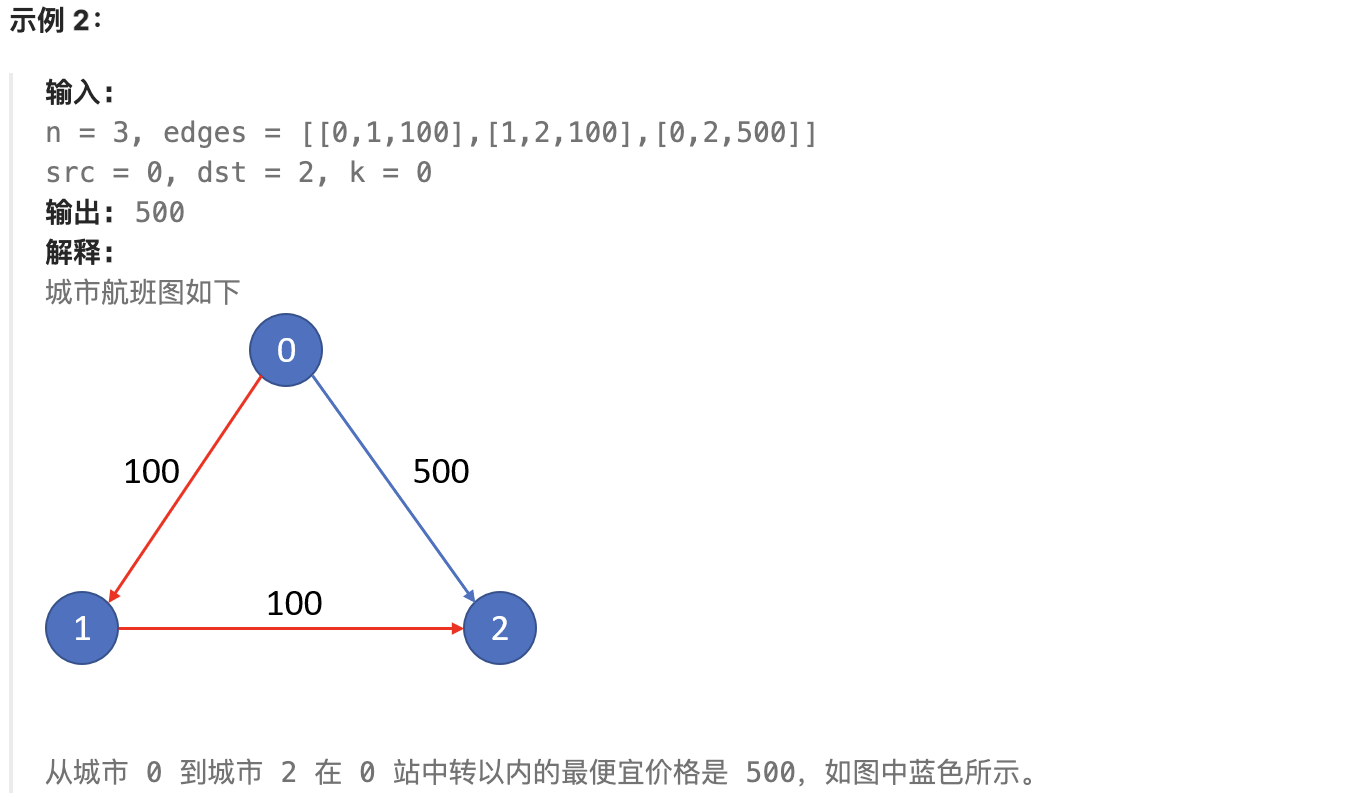
+
+
+
+
+## 思路
+
+
+
+```CPP
+class Solution {
+public:
+ int findCheapestPrice(int n, vector>& flights, int src, int dst, int k) {
+ vector minDist(n , INT_MAX/2);
+ minDist[src] = 0;
+ vector minDist_copy(n); // 用来记录每一次遍历的结果
+ for (int i = 1; i <= k + 1; i++) {
+ minDist_copy = minDist; // 获取上一次计算的结果
+ for (auto &f : flights) {
+ int from = f[0];
+ int to = f[1];
+ int price = f[2];
+ minDist[to] = min(minDist_copy[from] + price, minDist[to]);
+ // if (minDist[to] > minDist_copy[from] + price) minDist[to] = minDist_copy[from] + price;
+ }
+
+ }
+ int result = minDist[dst] == INT_MAX/2 ? -1 : minDist[dst];
+ return result;
+ }
+};
+```
+
+下面是典型的错误写法
+
+```CPP
+class Solution {
+public:
+ int findCheapestPrice(int n, vector>& flights, int src, int dst, int k) {
+ vector minDist(n , INT_MAX/2);
+ minDist[src] = 0;
+ for (int i = 1; i <= k + 1; i++) {
+ for (auto &f : flights) {
+ int from = f[0];
+ int to = f[1];
+ int price = f[2];
+ if (minDist[to] > minDist[from] + price) minDist[to] = minDist[from] + price;
+ }
+ }
+ int result = minDist[dst] == INT_MAX/2 ? -1 : minDist[dst];
+ return result;
+ }
+};
+```
+
+
+-----------
+
+SPFA
+
+
+class Solution {
+struct Edge {
+ int to; // 链接的节点
+ int val; // 边的权重
+
+ Edge(int t, int w): to(t), val(w) {} // 构造函数
+};
+
+public:
+ int findCheapestPrice(int n, vector>& flights, int src, int dst, int k) {
+ vector minDist(n , INT_MAX/2);
+ vector> grid(n + 1); // 邻接表
+ for (auto &f : flights) {
+ int from = f[0];
+ int to = f[1];
+ int price = f[2];
+ grid[from].push_back(Edge(to, price));
+
+ }
+ minDist[src] = 0;
+ vector minDist_copy(n); // 用来记录每一次遍历的结果
+ k++;
+ queue que;
+ que.push(src);
+ std::vector visited(n + 1, false); // 可加,可不加,加了效率高一些,防止重复访问
+ int que_size;
+ while (k-- && !que.empty()) {
+
+ minDist_copy = minDist; // 获取上一次计算的结果
+ que_size = que.size();
+ while (que_size--) { // 这个while循环的设计实在是妙啊
+ int node = que.front(); que.pop();
+ for (Edge edge : grid[node]) {
+ int from = node;
+ int to = edge.to;
+ int price = edge.val;
+ if (minDist[to] > minDist_copy[from] + price) {
+ minDist[to] = minDist_copy[from] + price;
+ que.push(to);
+ }
+ }
+
+ }
+ }
+ int result = minDist[dst] == INT_MAX/2 ? -1 : minDist[dst];
+ return result;
+ }
+};
+
+
+
+队列加上 visited 不能重复访问
+
+class Solution {
+struct Edge {
+ int to; // 链接的节点
+ int val; // 边的权重
+
+ Edge(int t, int w): to(t), val(w) {} // 构造函数
+};
+
+public:
+ int findCheapestPrice(int n, vector>& flights, int src, int dst, int k) {
+ vector minDist(n , INT_MAX/2);
+ vector> grid(n + 1); // 邻接表
+ for (auto &f : flights) {
+ int from = f[0];
+ int to = f[1];
+ int price = f[2];
+ grid[from].push_back(Edge(to, price));
+
+ }
+ minDist[src] = 0;
+ vector minDist_copy(n); // 用来记录每一次遍历的结果
+ k++;
+ queue que;
+ que.push(src);
+ int que_size;
+ while (k-- && !que.empty()) {
+ // 注意这个数组放的位置
+ vector visited(n + 1, false); // 可加,可不加,加了效率高一些,防止队列里重复访问,其数值已经算过了
+ minDist_copy = minDist; // 获取上一次计算的结果
+ que_size = que.size();
+ while (que_size--) {
+ int node = que.front(); que.pop();
+ for (Edge edge : grid[node]) {
+ int from = node;
+ int to = edge.to;
+ int price = edge.val;
+ if (minDist[to] > minDist_copy[from] + price) {
+ minDist[to] = minDist_copy[from] + price;
+ if(visited[to]) continue; // 不用重复放入队列,但需要重复计算,所以放在这里位置
+ visited[to] = true;
+ que.push(to);
+ }
+ }
+
+ }
+ }
+ int result = minDist[dst] == INT_MAX/2 ? -1 : minDist[dst];
+ return result;
+ }
+};
+
+
+
diff --git "a/problems/0797.\346\211\200\346\234\211\345\217\257\350\203\275\347\232\204\350\267\257\345\276\204.md" "b/problems/0797.\346\211\200\346\234\211\345\217\257\350\203\275\347\232\204\350\267\257\345\276\204.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 05b55b5b16..db4d249a15
--- "a/problems/0797.\346\211\200\346\234\211\345\217\257\350\203\275\347\232\204\350\267\257\345\276\204.md"
+++ "b/problems/0797.\346\211\200\346\234\211\345\217\257\350\203\275\347\232\204\350\267\257\345\276\204.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0787.K\347\253\231\344\270\255\350\275\254\345\206\205\346\234\200\344\276\277\345\256\234\347\232\204\350\210\252\347\217\255.md" "b/problems/0787.K\347\253\231\344\270\255\350\275\254\345\206\205\346\234\200\344\276\277\345\256\234\347\232\204\350\210\252\347\217\255.md"
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..fb58c14816
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/problems/0787.K\347\253\231\344\270\255\350\275\254\345\206\205\346\234\200\344\276\277\345\256\234\347\232\204\350\210\252\347\217\255.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,180 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
+
+# 787. K 站中转内最便宜的航班
+
+有 n 个城市通过一些航班连接。给你一个数组 flights ,其中 flights[i] = [fromi, toi, pricei] ,表示该航班都从城市 fromi 开始,以价格 pricei 抵达 toi。
+
+现在给定所有的城市和航班,以及出发城市 src 和目的地 dst,你的任务是找到出一条最多经过 k 站中转的路线,使得从 src 到 dst 的 价格最便宜 ,并返回该价格。 如果不存在这样的路线,则输出 -1。
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+## 思路
+
+
+
+```CPP
+class Solution {
+public:
+ int findCheapestPrice(int n, vector>& flights, int src, int dst, int k) {
+ vector minDist(n , INT_MAX/2);
+ minDist[src] = 0;
+ vector minDist_copy(n); // 用来记录每一次遍历的结果
+ for (int i = 1; i <= k + 1; i++) {
+ minDist_copy = minDist; // 获取上一次计算的结果
+ for (auto &f : flights) {
+ int from = f[0];
+ int to = f[1];
+ int price = f[2];
+ minDist[to] = min(minDist_copy[from] + price, minDist[to]);
+ // if (minDist[to] > minDist_copy[from] + price) minDist[to] = minDist_copy[from] + price;
+ }
+
+ }
+ int result = minDist[dst] == INT_MAX/2 ? -1 : minDist[dst];
+ return result;
+ }
+};
+```
+
+下面是典型的错误写法
+
+```CPP
+class Solution {
+public:
+ int findCheapestPrice(int n, vector>& flights, int src, int dst, int k) {
+ vector minDist(n , INT_MAX/2);
+ minDist[src] = 0;
+ for (int i = 1; i <= k + 1; i++) {
+ for (auto &f : flights) {
+ int from = f[0];
+ int to = f[1];
+ int price = f[2];
+ if (minDist[to] > minDist[from] + price) minDist[to] = minDist[from] + price;
+ }
+ }
+ int result = minDist[dst] == INT_MAX/2 ? -1 : minDist[dst];
+ return result;
+ }
+};
+```
+
+
+-----------
+
+SPFA
+
+
+class Solution {
+struct Edge {
+ int to; // 链接的节点
+ int val; // 边的权重
+
+ Edge(int t, int w): to(t), val(w) {} // 构造函数
+};
+
+public:
+ int findCheapestPrice(int n, vector>& flights, int src, int dst, int k) {
+ vector minDist(n , INT_MAX/2);
+ vector> grid(n + 1); // 邻接表
+ for (auto &f : flights) {
+ int from = f[0];
+ int to = f[1];
+ int price = f[2];
+ grid[from].push_back(Edge(to, price));
+
+ }
+ minDist[src] = 0;
+ vector minDist_copy(n); // 用来记录每一次遍历的结果
+ k++;
+ queue que;
+ que.push(src);
+ std::vector visited(n + 1, false); // 可加,可不加,加了效率高一些,防止重复访问
+ int que_size;
+ while (k-- && !que.empty()) {
+
+ minDist_copy = minDist; // 获取上一次计算的结果
+ que_size = que.size();
+ while (que_size--) { // 这个while循环的设计实在是妙啊
+ int node = que.front(); que.pop();
+ for (Edge edge : grid[node]) {
+ int from = node;
+ int to = edge.to;
+ int price = edge.val;
+ if (minDist[to] > minDist_copy[from] + price) {
+ minDist[to] = minDist_copy[from] + price;
+ que.push(to);
+ }
+ }
+
+ }
+ }
+ int result = minDist[dst] == INT_MAX/2 ? -1 : minDist[dst];
+ return result;
+ }
+};
+
+
+
+队列加上 visited 不能重复访问
+
+class Solution {
+struct Edge {
+ int to; // 链接的节点
+ int val; // 边的权重
+
+ Edge(int t, int w): to(t), val(w) {} // 构造函数
+};
+
+public:
+ int findCheapestPrice(int n, vector>& flights, int src, int dst, int k) {
+ vector minDist(n , INT_MAX/2);
+ vector> grid(n + 1); // 邻接表
+ for (auto &f : flights) {
+ int from = f[0];
+ int to = f[1];
+ int price = f[2];
+ grid[from].push_back(Edge(to, price));
+
+ }
+ minDist[src] = 0;
+ vector minDist_copy(n); // 用来记录每一次遍历的结果
+ k++;
+ queue que;
+ que.push(src);
+ int que_size;
+ while (k-- && !que.empty()) {
+ // 注意这个数组放的位置
+ vector visited(n + 1, false); // 可加,可不加,加了效率高一些,防止队列里重复访问,其数值已经算过了
+ minDist_copy = minDist; // 获取上一次计算的结果
+ que_size = que.size();
+ while (que_size--) {
+ int node = que.front(); que.pop();
+ for (Edge edge : grid[node]) {
+ int from = node;
+ int to = edge.to;
+ int price = edge.val;
+ if (minDist[to] > minDist_copy[from] + price) {
+ minDist[to] = minDist_copy[from] + price;
+ if(visited[to]) continue; // 不用重复放入队列,但需要重复计算,所以放在这里位置
+ visited[to] = true;
+ que.push(to);
+ }
+ }
+
+ }
+ }
+ int result = minDist[dst] == INT_MAX/2 ? -1 : minDist[dst];
+ return result;
+ }
+};
+
+
+
diff --git "a/problems/0797.\346\211\200\346\234\211\345\217\257\350\203\275\347\232\204\350\267\257\345\276\204.md" "b/problems/0797.\346\211\200\346\234\211\345\217\257\350\203\275\347\232\204\350\267\257\345\276\204.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 05b55b5b16..db4d249a15
--- "a/problems/0797.\346\211\200\346\234\211\345\217\257\350\203\275\347\232\204\350\267\257\345\276\204.md"
+++ "b/problems/0797.\346\211\200\346\234\211\345\217\257\350\203\275\347\232\204\350\267\257\345\276\204.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 797.所有可能的路径
@@ -13,7 +11,7 @@
graph[i] 是一个从节点 i 可以访问的所有节点的列表(即从节点 i 到节点 graph[i][j]存在一条有向边)。
-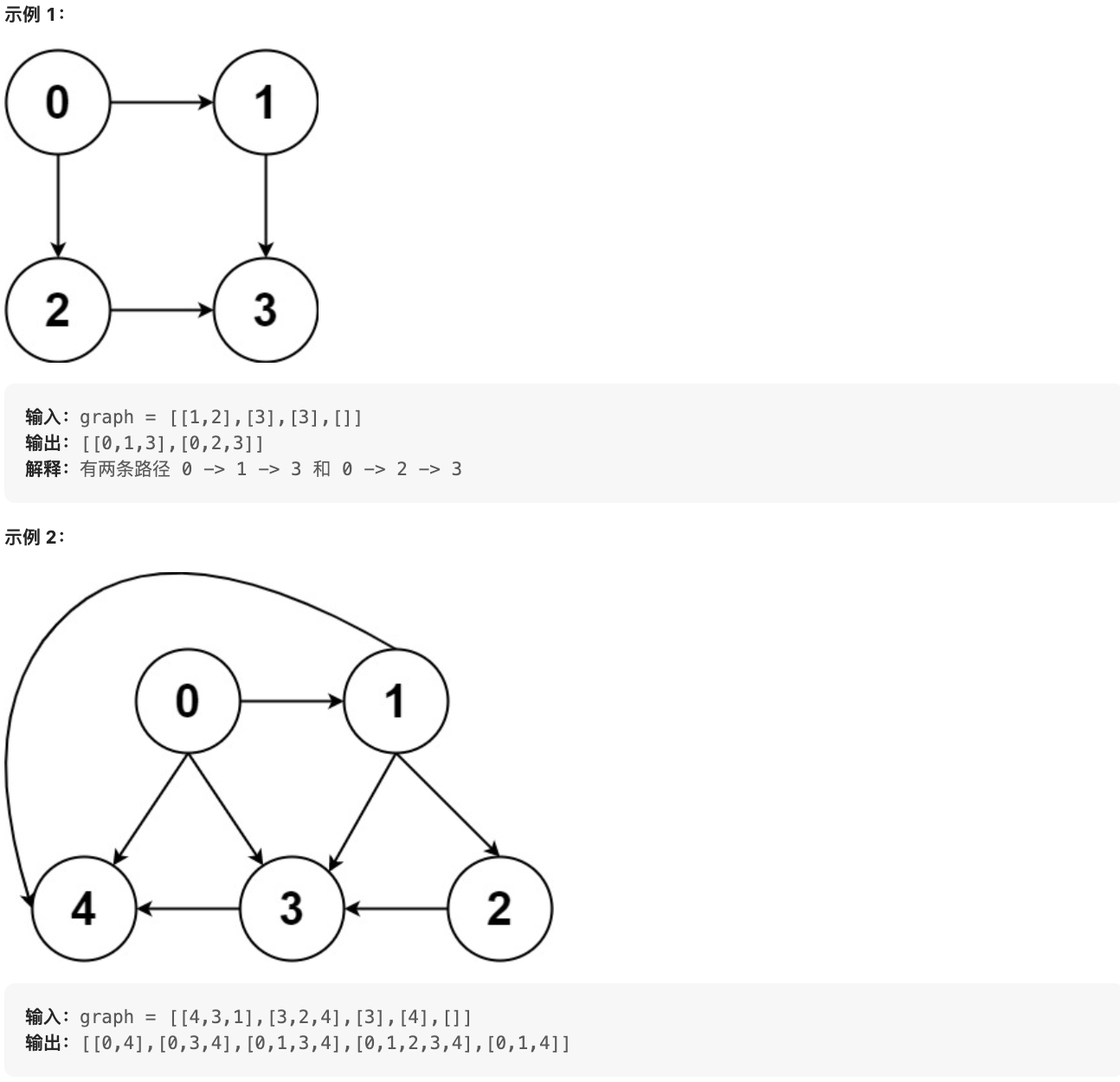
+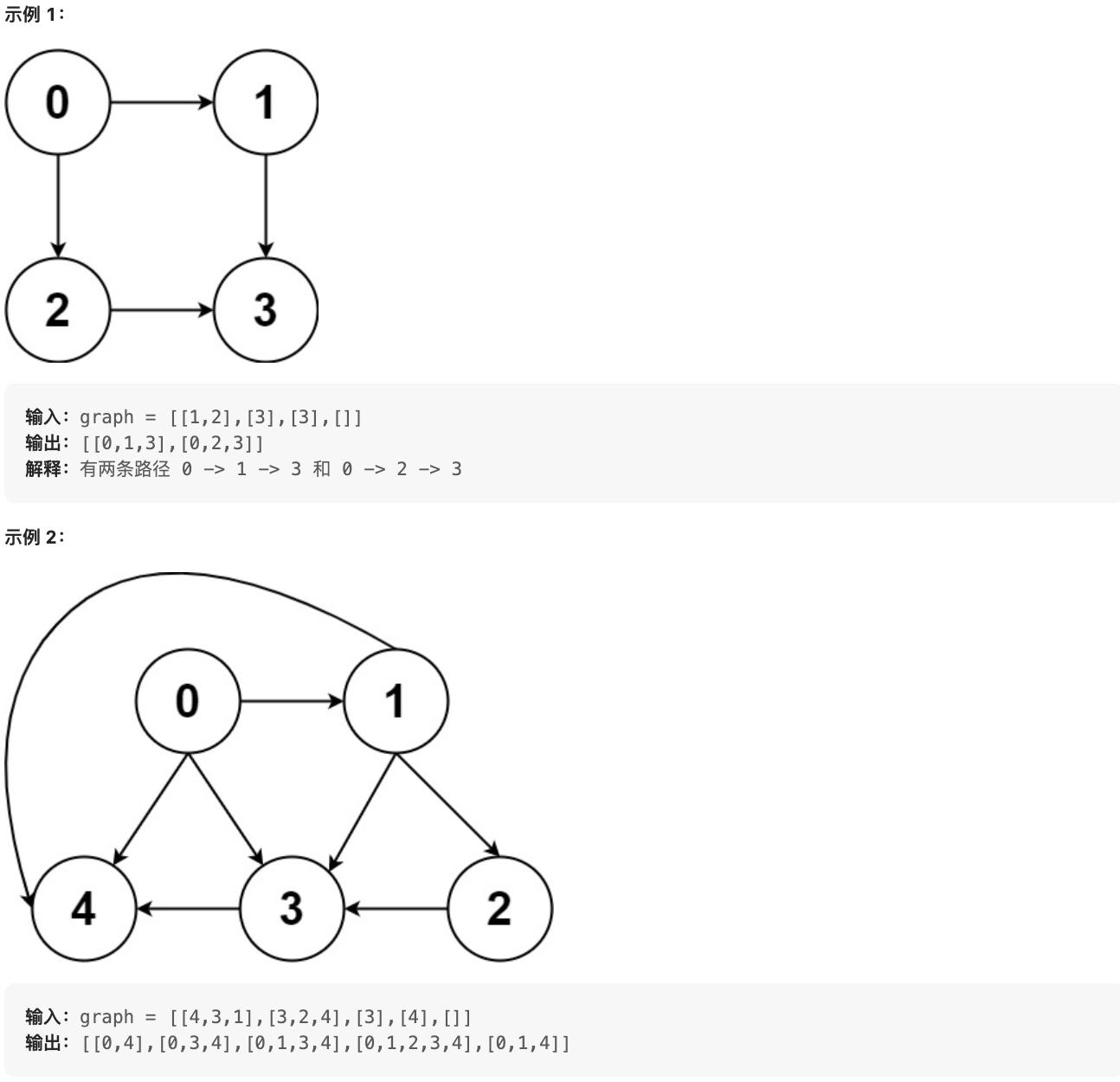
提示:
@@ -52,7 +50,7 @@ graph[i] 是一个从节点 i 可以访问的所有节点的列表(即从节
至于 单一路径,和路径集合可以放在全局变量,那么代码是这样的:
-```c++
+```CPP
vector> result; // 收集符合条件的路径
vector path; // 0节点到终点的路径
// x:目前遍历的节点
@@ -71,7 +69,7 @@ void dfs (vector>& graph, int x)
所以 但 x 等于 graph.size() - 1 的时候就找到一条有效路径。 代码如下:
-```c++
+```CPP
// 要求从节点 0 到节点 n-1 的路径并输出,所以是 graph.size() - 1
if (x == graph.size() - 1) { // 找到符合条件的一条路径
result.push_back(path); // 收集有效路径
@@ -98,19 +96,19 @@ path.push_back(graph[x][i]); // 遍历到的节点加入到路径中来
一些录友可以疑惑这里如果找到x 链接的节点的,例如如果x目前是节点0,那么目前的过程就是这样的:
-
+
二维数组中,graph[x][i] 都是x链接的节点,当前遍历的节点就是 `graph[x][i]` 。
进入下一层递归
-```C++
+```CPP
dfs(graph, graph[x][i]); // 进入下一层递归
```
最后就是回溯的过程,撤销本次添加节点的操作。 该过程整体代码:
-```C++
+```CPP
for (int i = 0; i < graph[x].size(); i++) { // 遍历节点n链接的所有节点
path.push_back(graph[x][i]); // 遍历到的节点加入到路径中来
dfs(graph, graph[x][i]); // 进入下一层递归
@@ -120,7 +118,7 @@ for (int i = 0; i < graph[x].size(); i++) { // 遍历节点n链接的所有节
本题整体代码如下:
-```c++
+```CPP
class Solution {
private:
vector> result; // 收集符合条件的路径
@@ -294,7 +292,3 @@ impl Solution {
}
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0827.\346\234\200\345\244\247\344\272\272\345\267\245\345\262\233.md" "b/problems/0827.\346\234\200\345\244\247\344\272\272\345\267\245\345\262\233.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 3f32dd7aa1..118735e943
--- "a/problems/0827.\346\234\200\345\244\247\344\272\272\345\267\245\345\262\233.md"
+++ "b/problems/0827.\346\234\200\345\244\247\344\272\272\345\267\245\345\262\233.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0827.\346\234\200\345\244\247\344\272\272\345\267\245\345\262\233.md" "b/problems/0827.\346\234\200\345\244\247\344\272\272\345\267\245\345\262\233.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 3f32dd7aa1..118735e943
--- "a/problems/0827.\346\234\200\345\244\247\344\272\272\345\267\245\345\262\233.md"
+++ "b/problems/0827.\346\234\200\345\244\247\344\272\272\345\267\245\345\262\233.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 827.最大人工岛
@@ -39,7 +37,7 @@
每改变一个0的方格,都需要重新计算一个地图的最大面积,所以 整体时间复杂度为:n^4。
-如果对深度优先搜索不了解的录友,可以看这里:[深度优先搜索精讲](https://programmercarl.com/图论深搜理论基础.html)
+如果对深度优先搜索不了解的录友,可以看这里:[深度优先搜索精讲](https://programmercarl.com/kamacoder/图论深搜理论基础.html)
## 优化思路
@@ -53,11 +51,11 @@
拿如下地图的岛屿情况来举例: (1为陆地)
-
+
第一步,则遍历题目,并将岛屿到编号和面积上的统计,过程如图所示:
-
+
本过程代码如下:
@@ -104,7 +102,7 @@ int largestIsland(vector>& grid) {
第二步过程如图所示:
-
+
也就是遍历每一个0的方格,并统计其相邻岛屿面积,最后取一个最大值。
@@ -348,6 +346,99 @@ class Solution:
```
+
+### Go
+
+```go
+func largestIsland(grid [][]int) int {
+ dir := [][]int{{0, 1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}, {0, -1}}
+ n := len(grid)
+ m := len(grid[0])
+ area := 0
+ visited := make([][]bool, n)
+ for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
+ visited[i] = make([]bool, m)
+ }
+ gridNum := make(map[int]int, 0) // 记录每一个岛屿的面积
+ mark := 2 // 记录每个岛屿的编号
+ isAllGrid := true
+ res := 0 // 标记是否整个地图都是陆地
+
+ var dfs func(grid [][]int, visited [][]bool, x, y, mark int)
+ dfs = func(grid [][]int, visited [][]bool, x, y, mark int) {
+ // 终止条件:访问过的节点 或者 遇到海水
+ if visited[x][y] || grid[x][y] == 0 {
+ return
+ }
+ visited[x][y] = true // 标记访问过
+ grid[x][y] = mark // 给陆地标记新标签
+ area++
+ for i := 0; i < 4; i++ {
+ nextX := x + dir[i][0]
+ nextY := y + dir[i][1]
+ if nextX < 0 || nextX >= len(grid) || nextY < 0 || nextY >= len(grid[0]) {
+ continue
+ }
+ dfs(grid, visited, nextX, nextY, mark)
+ }
+ }
+
+ for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
+ for j := 0; j < m; j++ {
+ if grid[i][j] == 0 {
+ isAllGrid = false
+ }
+ if !visited[i][j] && grid[i][j] == 1 {
+ area = 0
+ dfs(grid, visited, i, j, mark) // 将与其链接的陆地都标记上 true
+ gridNum[mark] = area // 记录每一个岛屿的面积
+ mark++ // 更新下一个岛屿编号
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ if isAllGrid {
+ return n * m
+ }
+ // 根据添加陆地的位置,计算周边岛屿面积之和
+ visitedGrid := make(map[int]struct{}) // 标记访问过的岛屿
+ for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
+ for j := 0; j < m; j++ {
+ count := 1 // 记录连接之后的岛屿数量
+ visitedGrid = make(map[int]struct{}) // 每次使用时,清空
+ if grid[i][j] == 0 {
+ for k := 0; k < 4; k++ {
+ // 计算相邻坐标
+ nearI := i + dir[k][0]
+ nearJ := j + dir[k][1]
+ if nearI < 0 || nearI >= len(grid) || nearJ < 0 || nearJ >= len(grid[0]) {
+ continue
+ }
+ // 添加过的岛屿不要重复添加
+ if _, ok := visitedGrid[grid[nearI][nearJ]]; ok {
+ continue
+ }
+ // 把相邻四面的岛屿数量加起来
+ count += gridNum[grid[nearI][nearJ]]
+ // 标记该岛屿已经添加过
+ visitedGrid[grid[nearI][nearJ]] = struct{}{}
+ }
+ }
+ res = max827(res, count)
+ }
+ }
+ return res
+}
+
+func max827(x, y int) int {
+ if x > y {
+ return x
+ }
+ return y
+}
+
+```
+
+
### JavaScript
```JavaScript
@@ -411,9 +502,3 @@ return res;
```
-
-
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0841.\351\222\245\345\214\231\345\222\214\346\210\277\351\227\264.md" "b/problems/0841.\351\222\245\345\214\231\345\222\214\346\210\277\351\227\264.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index b4785d1b02..ffcf2fb919
--- "a/problems/0841.\351\222\245\345\214\231\345\222\214\346\210\277\351\227\264.md"
+++ "b/problems/0841.\351\222\245\345\214\231\345\222\214\346\210\277\351\227\264.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0841.\351\222\245\345\214\231\345\222\214\346\210\277\351\227\264.md" "b/problems/0841.\351\222\245\345\214\231\345\222\214\346\210\277\351\227\264.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index b4785d1b02..ffcf2fb919
--- "a/problems/0841.\351\222\245\345\214\231\345\222\214\346\210\277\351\227\264.md"
+++ "b/problems/0841.\351\222\245\345\214\231\345\222\214\346\210\277\351\227\264.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
@@ -37,7 +35,7 @@
图中给我的两个示例: `[[1],[2],[3],[]]` `[[1,3],[3,0,1],[2],[0]]`,画成对应的图如下:
-
+
我们可以看出图1的所有节点都是链接的,而图二中,节点2 是孤立的。
@@ -50,7 +48,7 @@
图3:[[5], [], [1, 3], [5]] ,如图:
-
+
在图3中,大家可以发现,节点0只能到节点5,然后就哪也去不了了。
@@ -484,7 +482,3 @@ function canVisitAllRooms(rooms: number[][]): boolean {
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0844.\346\257\224\350\276\203\345\220\253\351\200\200\346\240\274\347\232\204\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md" "b/problems/0844.\346\257\224\350\276\203\345\220\253\351\200\200\346\240\274\347\232\204\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index c7f5220288..6d0cd68578
--- "a/problems/0844.\346\257\224\350\276\203\345\220\253\351\200\200\346\240\274\347\232\204\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md"
+++ "b/problems/0844.\346\257\224\350\276\203\345\220\253\351\200\200\346\240\274\347\232\204\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0844.\346\257\224\350\276\203\345\220\253\351\200\200\346\240\274\347\232\204\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md" "b/problems/0844.\346\257\224\350\276\203\345\220\253\351\200\200\346\240\274\347\232\204\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index c7f5220288..6d0cd68578
--- "a/problems/0844.\346\257\224\350\276\203\345\220\253\351\200\200\346\240\274\347\232\204\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md"
+++ "b/problems/0844.\346\257\224\350\276\203\345\220\253\351\200\200\346\240\274\347\232\204\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 844.比较含退格的字符串
@@ -108,7 +106,7 @@ public:
动画如下:
- +
+ 如果S[i]和S[j]不相同返回false,如果有一个指针(i或者j)先走到的字符串头部位置,也返回false。
@@ -587,8 +585,4 @@ impl Solution {
}
```
-
如果S[i]和S[j]不相同返回false,如果有一个指针(i或者j)先走到的字符串头部位置,也返回false。
@@ -587,8 +585,4 @@ impl Solution {
}
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0860.\346\237\240\346\252\254\346\260\264\346\211\276\351\233\266.md" "b/problems/0860.\346\237\240\346\252\254\346\260\264\346\211\276\351\233\266.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index db70112d8f..aeb470fe5a
--- "a/problems/0860.\346\237\240\346\252\254\346\260\264\346\211\276\351\233\266.md"
+++ "b/problems/0860.\346\237\240\346\252\254\346\260\264\346\211\276\351\233\266.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0860.\346\237\240\346\252\254\346\260\264\346\211\276\351\233\266.md" "b/problems/0860.\346\237\240\346\252\254\346\260\264\346\211\276\351\233\266.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index db70112d8f..aeb470fe5a
--- "a/problems/0860.\346\237\240\346\252\254\346\260\264\346\211\276\351\233\266.md"
+++ "b/problems/0860.\346\237\240\346\252\254\346\260\264\346\211\276\351\233\266.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 860.柠檬水找零
@@ -226,7 +224,7 @@ func lemonadeChange(bills []int) bool {
}
```
-### Javascript
+### JavaScript
```Javascript
var lemonadeChange = function(bills) {
let fiveCount = 0
@@ -439,8 +437,4 @@ public class Solution
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0922.\346\214\211\345\245\207\345\201\266\346\216\222\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204II.md" "b/problems/0922.\346\214\211\345\245\207\345\201\266\346\216\222\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 72be8fa732..484099f89f
--- "a/problems/0922.\346\214\211\345\245\207\345\201\266\346\216\222\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0922.\346\214\211\345\245\207\345\201\266\346\216\222\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204II.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0922.\346\214\211\345\245\207\345\201\266\346\216\222\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204II.md" "b/problems/0922.\346\214\211\345\245\207\345\201\266\346\216\222\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 72be8fa732..484099f89f
--- "a/problems/0922.\346\214\211\345\245\207\345\201\266\346\216\222\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0922.\346\214\211\345\245\207\345\201\266\346\216\222\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204II.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
@@ -11,9 +9,9 @@
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/sort-array-by-parity-ii/)
-给定一个非负整数数组 A, A 中一半整数是奇数,一半整数是偶数。
+给定一个非负整数数组 nums, nums 中一半整数是奇数,一半整数是偶数。
-对数组进行排序,以便当 A[i] 为奇数时,i 也是奇数;当 A[i] 为偶数时, i 也是偶数。
+对数组进行排序,以便当 nums[i] 为奇数时,i 也是奇数;当 nums[i] 为偶数时, i 也是偶数。
你可以返回任何满足上述条件的数组作为答案。
@@ -35,17 +33,17 @@
```CPP
class Solution {
public:
- vector sortArrayByParityII(vector& A) {
- vector even(A.size() / 2); // 初始化就确定数组大小,节省开销
- vector odd(A.size() / 2);
- vector result(A.size());
+ vector sortArrayByParityII(vector& nums) {
+ vector even(nums.size() / 2); // 初始化就确定数组大小,节省开销
+ vector odd(nums.size() / 2);
+ vector result(nums.size());
int evenIndex = 0;
int oddIndex = 0;
int resultIndex = 0;
- // 把A数组放进偶数数组,和奇数数组
- for (int i = 0; i < A.size(); i++) {
- if (A[i] % 2 == 0) even[evenIndex++] = A[i];
- else odd[oddIndex++] = A[i];
+ // 把nums数组放进偶数数组,和奇数数组
+ for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
+ if (nums[i] % 2 == 0) even[evenIndex++] = nums[i];
+ else odd[oddIndex++] = nums[i];
}
// 把偶数数组,奇数数组分别放进result数组中
for (int i = 0; i < evenIndex; i++) {
@@ -62,22 +60,22 @@ public:
### 方法二
-以上代码我是建了两个辅助数组,而且A数组还相当于遍历了两次,用辅助数组的好处就是思路清晰,优化一下就是不用这两个辅助树,代码如下:
+以上代码我是建了两个辅助数组,而且nums数组还相当于遍历了两次,用辅助数组的好处就是思路清晰,优化一下就是不用这两个辅助数组,代码如下:
```CPP
class Solution {
public:
- vector sortArrayByParityII(vector& A) {
- vector result(A.size());
+ vector sortArrayByParityII(vector& nums) {
+ vector result(nums.size());
int evenIndex = 0; // 偶数下标
int oddIndex = 1; // 奇数下标
- for (int i = 0; i < A.size(); i++) {
- if (A[i] % 2 == 0) {
- result[evenIndex] = A[i];
+ for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
+ if (nums[i] % 2 == 0) {
+ result[evenIndex] = nums[i];
evenIndex += 2;
}
else {
- result[oddIndex] = A[i];
+ result[oddIndex] = nums[i];
oddIndex += 2;
}
}
@@ -96,15 +94,15 @@ public:
```CPP
class Solution {
public:
- vector sortArrayByParityII(vector& A) {
+ vector sortArrayByParityII(vector& nums) {
int oddIndex = 1;
- for (int i = 0; i < A.size(); i += 2) {
- if (A[i] % 2 == 1) { // 在偶数位遇到了奇数
- while(A[oddIndex] % 2 != 0) oddIndex += 2; // 在奇数位找一个偶数
- swap(A[i], A[oddIndex]); // 替换
+ for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i += 2) {
+ if (nums[i] % 2 == 1) { // 在偶数位遇到了奇数
+ while(nums[oddIndex] % 2 != 0) oddIndex += 2; // 在奇数位找一个偶数
+ swap(nums[i], nums[oddIndex]); // 替换
}
}
- return A;
+ return nums;
}
};
```
@@ -253,6 +251,37 @@ func sortArrayByParityII(nums []int) []int {
}
return result;
}
+
+// 方法二
+func sortArrayByParityII(nums []int) []int {
+ result := make([]int, len(nums))
+ evenIndex := 0 // 偶数下标
+ oddIndex := 1 // 奇数下标
+ for _, v := range nums {
+ if v % 2 == 0 {
+ result[evenIndex] = v
+ evenIndex += 2
+ } else {
+ result[oddIndex] = v
+ oddIndex += 2
+ }
+ }
+ return result
+}
+
+// 方法三
+func sortArrayByParityII(nums []int) []int {
+ oddIndex := 1
+ for i := 0; i < len(nums); i += 2 {
+ if nums[i] % 2 == 1 { // 在偶数位遇到了奇数
+ for nums[oddIndex] % 2 != 0 {
+ oddIndex += 2 // 在奇数位找一个偶数
+ }
+ nums[i], nums[oddIndex] = nums[oddIndex], nums[i]
+ }
+ }
+ return nums
+}
```
### JavaScript
@@ -378,8 +407,4 @@ function sortArrayByParityII(nums: number[]): number[] {
};
```
-
-


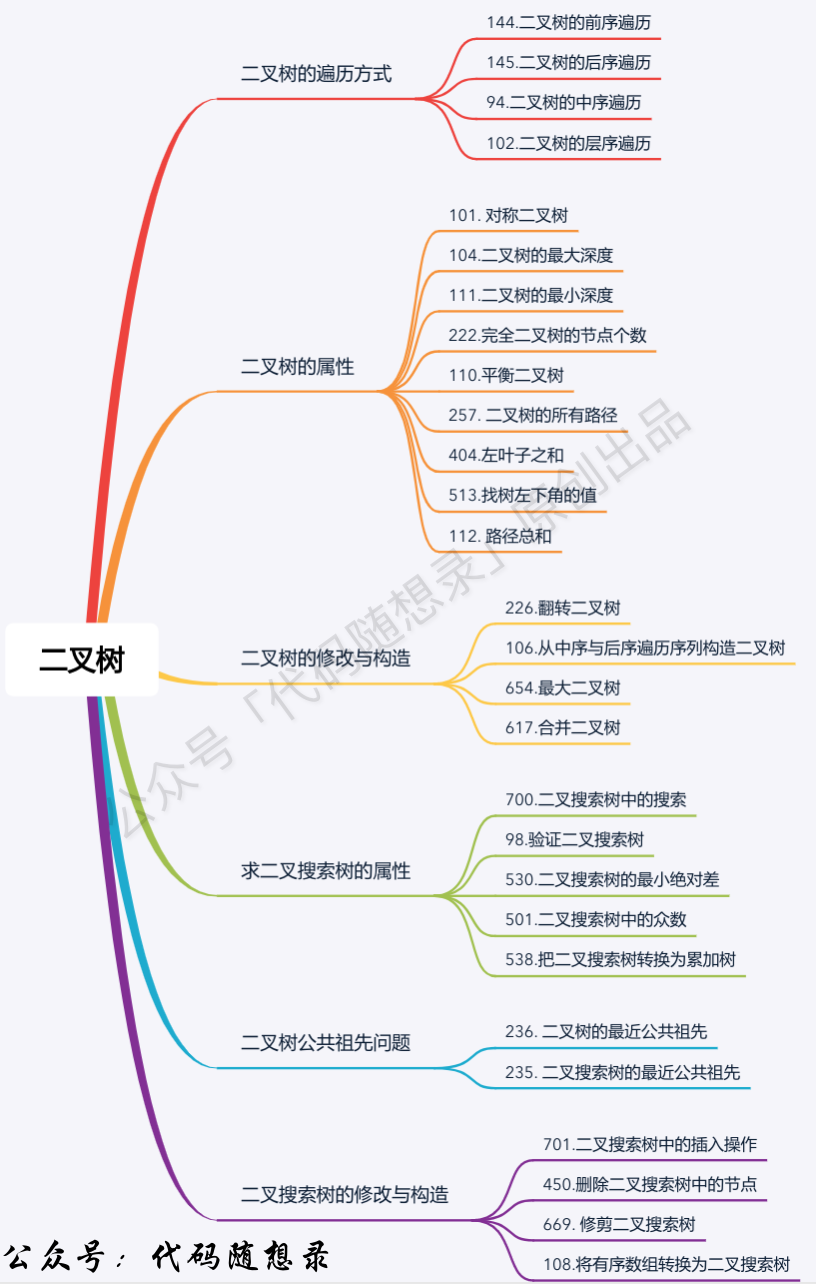 +
+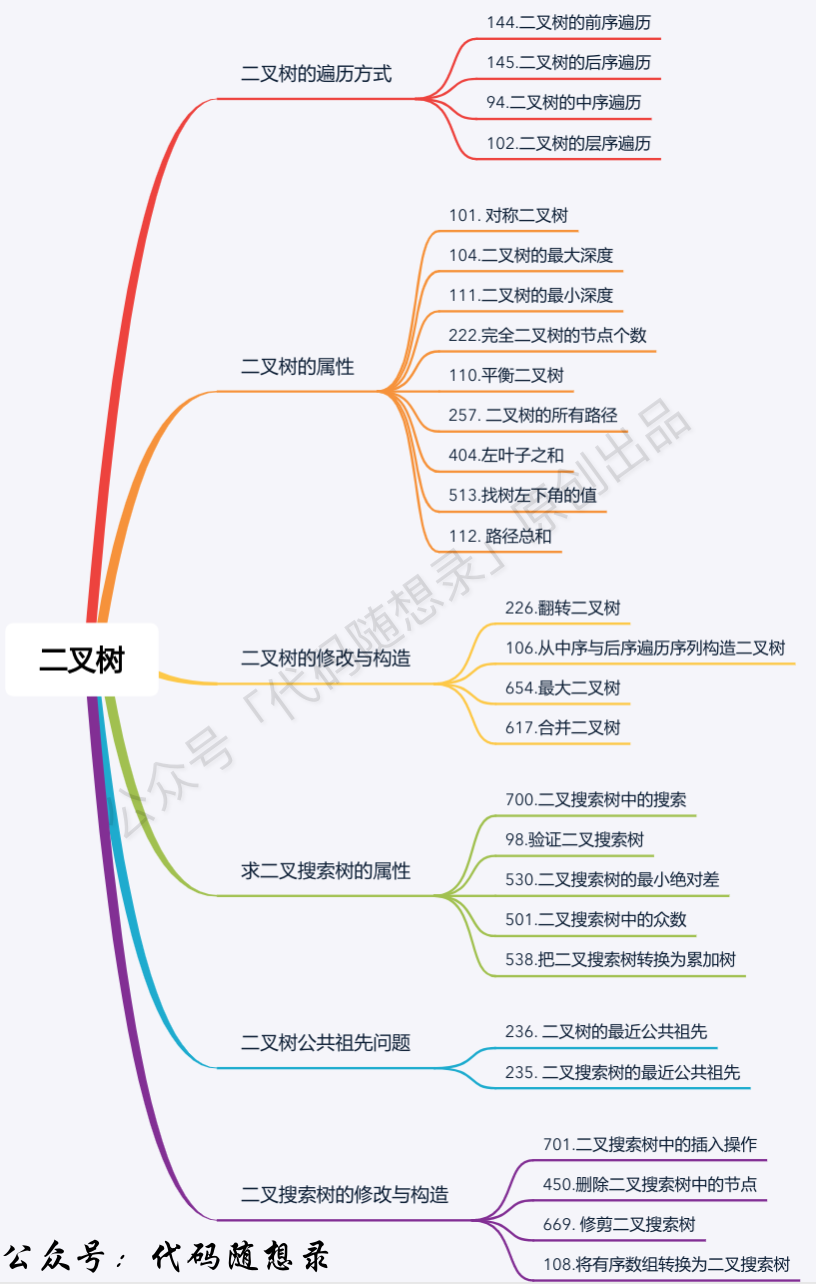 1. [关于二叉树,你该了解这些!](./problems/二叉树理论基础.md)
2. [二叉树:二叉树的递归遍历](./problems/二叉树的递归遍历.md)
@@ -207,7 +197,6 @@
12. [二叉树:110.平衡二叉树](./problems/0110.平衡二叉树.md)
13. [二叉树:257.二叉树的所有路径](./problems/0257.二叉树的所有路径.md)
14. [本周总结!(二叉树)](./problems/周总结/20201003二叉树周末总结.md)
-15. [二叉树:二叉树中递归带着回溯](./problems/二叉树中递归带着回溯.md)
16. [二叉树:404.左叶子之和](./problems/0404.左叶子之和.md)
17. [二叉树:513.找树左下角的值](./problems/0513.找树左下角的值.md)
18. [二叉树:112.路径总和](./problems/0112.路径总和.md)
@@ -233,7 +222,7 @@
题目分类大纲如下:
-
1. [关于二叉树,你该了解这些!](./problems/二叉树理论基础.md)
2. [二叉树:二叉树的递归遍历](./problems/二叉树的递归遍历.md)
@@ -207,7 +197,6 @@
12. [二叉树:110.平衡二叉树](./problems/0110.平衡二叉树.md)
13. [二叉树:257.二叉树的所有路径](./problems/0257.二叉树的所有路径.md)
14. [本周总结!(二叉树)](./problems/周总结/20201003二叉树周末总结.md)
-15. [二叉树:二叉树中递归带着回溯](./problems/二叉树中递归带着回溯.md)
16. [二叉树:404.左叶子之和](./problems/0404.左叶子之和.md)
17. [二叉树:513.找树左下角的值](./problems/0513.找树左下角的值.md)
18. [二叉树:112.路径总和](./problems/0112.路径总和.md)
@@ -233,7 +222,7 @@
题目分类大纲如下:
- +
+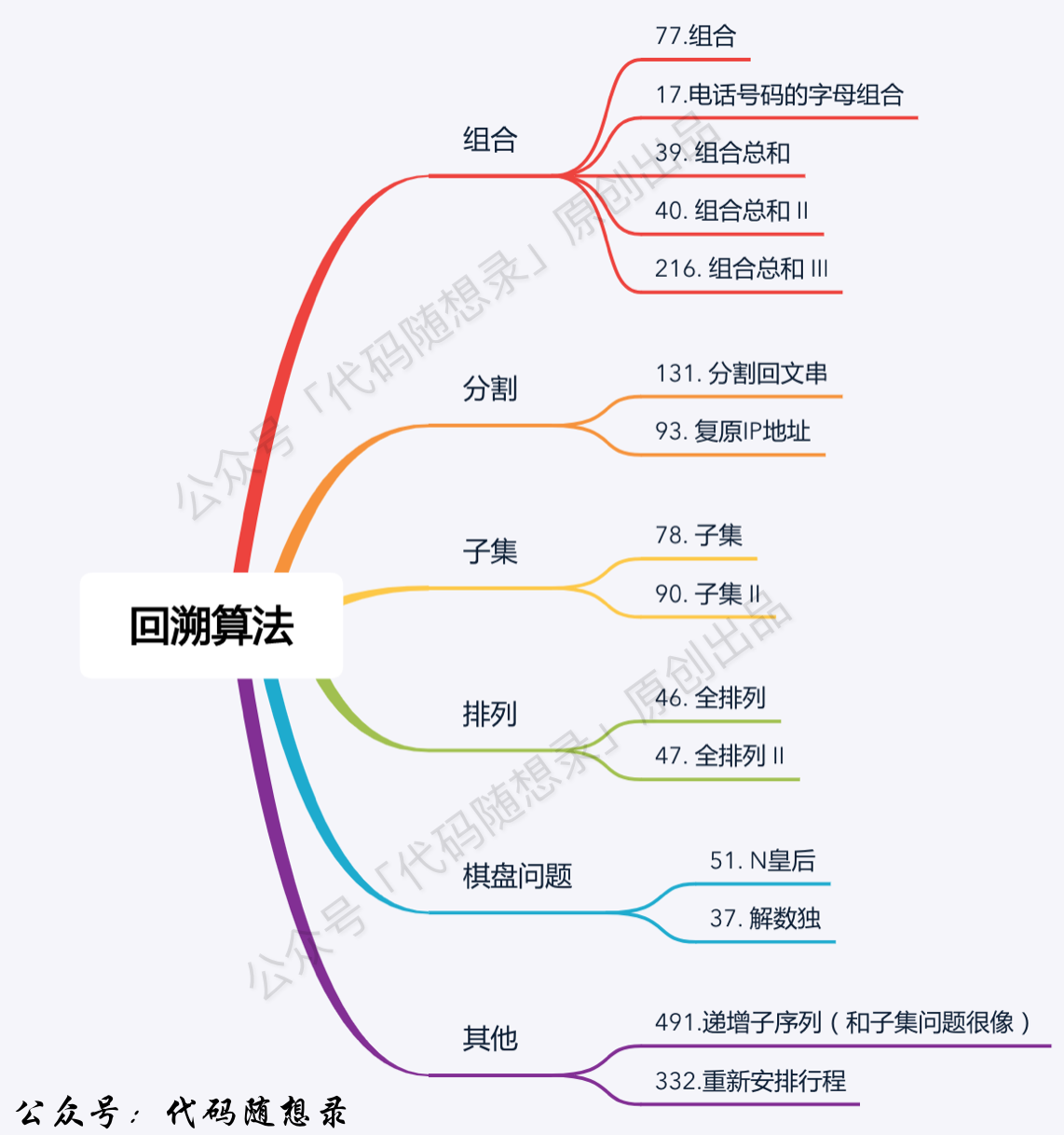 1. [关于回溯算法,你该了解这些!](./problems/回溯算法理论基础.md)
2. [回溯算法:77.组合](./problems/0077.组合.md)
@@ -263,7 +252,7 @@
题目分类大纲如下:
-
1. [关于回溯算法,你该了解这些!](./problems/回溯算法理论基础.md)
2. [回溯算法:77.组合](./problems/0077.组合.md)
@@ -263,7 +252,7 @@
题目分类大纲如下:
-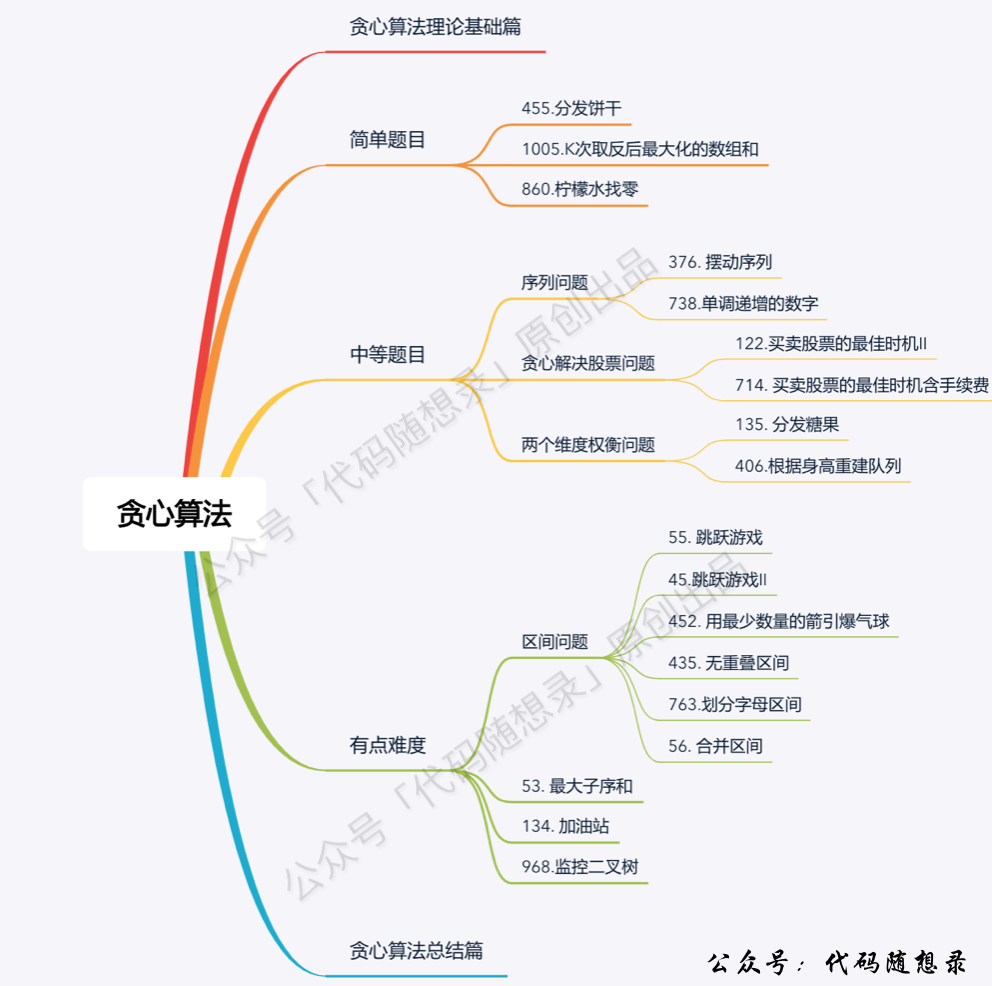 +
+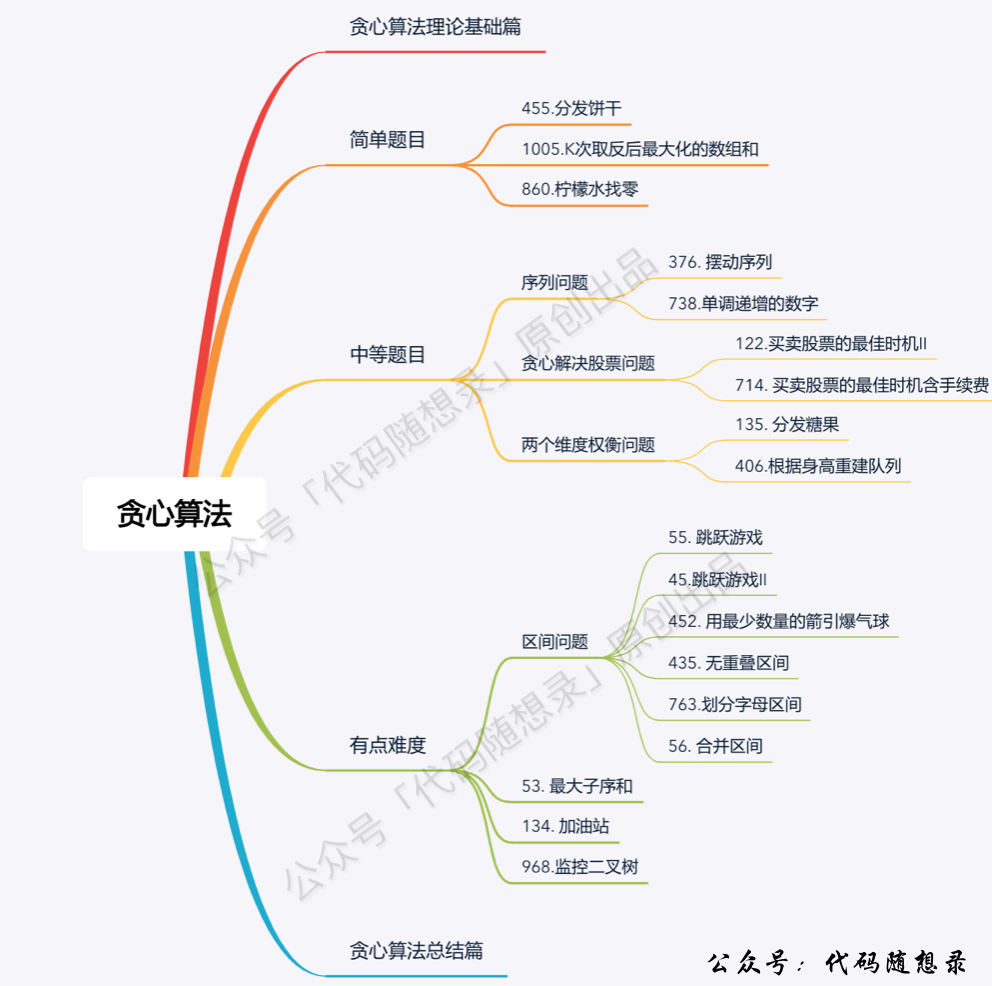 1. [关于贪心算法,你该了解这些!](./problems/贪心算法理论基础.md)
2. [贪心算法:455.分发饼干](./problems/0455.分发饼干.md)
@@ -294,7 +283,7 @@
动态规划专题已经开始啦,来不及解释了,小伙伴们上车别掉队!
-
1. [关于贪心算法,你该了解这些!](./problems/贪心算法理论基础.md)
2. [贪心算法:455.分发饼干](./problems/0455.分发饼干.md)
@@ -294,7 +283,7 @@
动态规划专题已经开始啦,来不及解释了,小伙伴们上车别掉队!
- +
+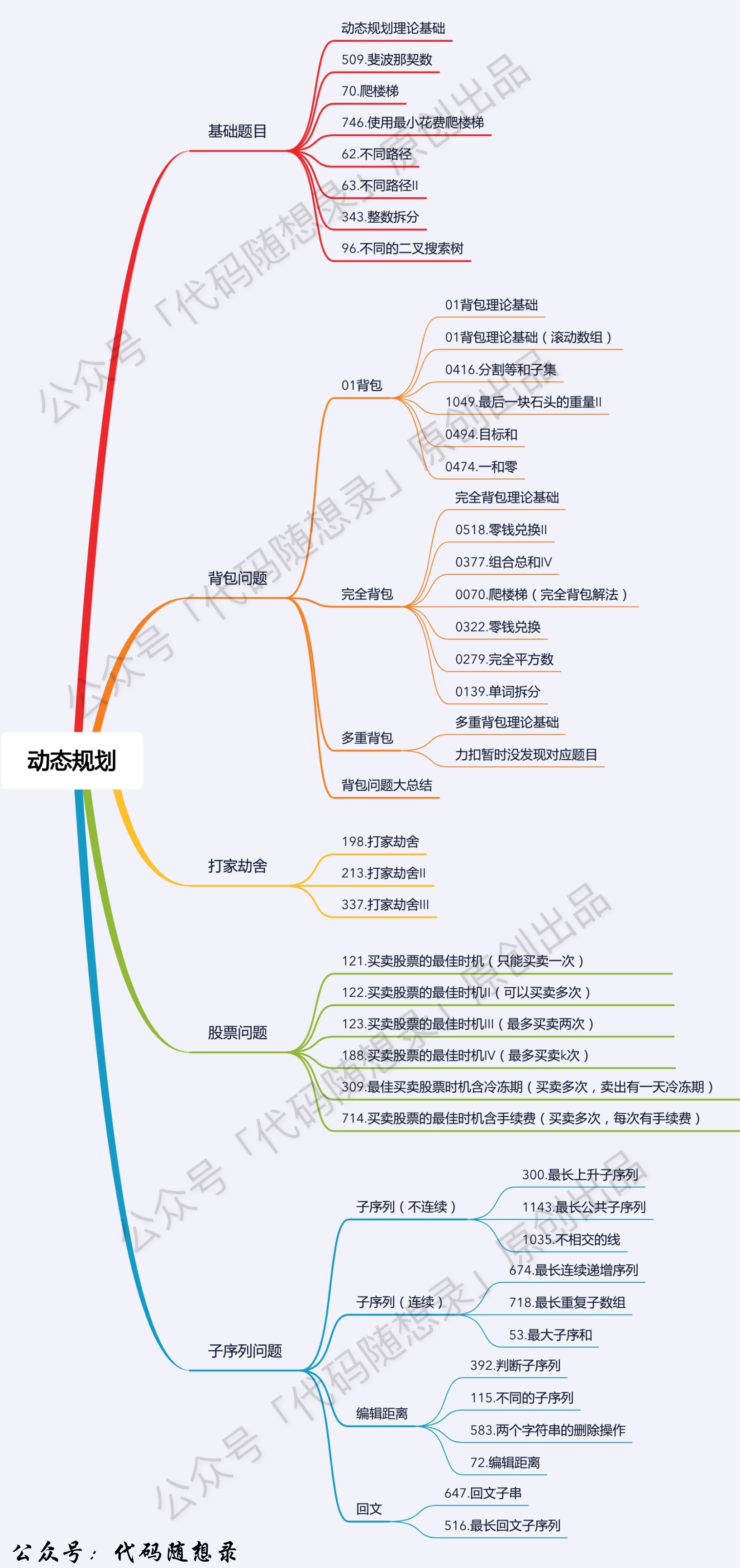 1. [关于动态规划,你该了解这些!](./problems/动态规划理论基础.md)
2. [动态规划:509.斐波那契数](./problems/0509.斐波那契数.md)
3. [动态规划:70.爬楼梯](./problems/0070.爬楼梯.md)
@@ -308,27 +297,28 @@
背包问题系列:
-
1. [关于动态规划,你该了解这些!](./problems/动态规划理论基础.md)
2. [动态规划:509.斐波那契数](./problems/0509.斐波那契数.md)
3. [动态规划:70.爬楼梯](./problems/0070.爬楼梯.md)
@@ -308,27 +297,28 @@
背包问题系列:
- +
+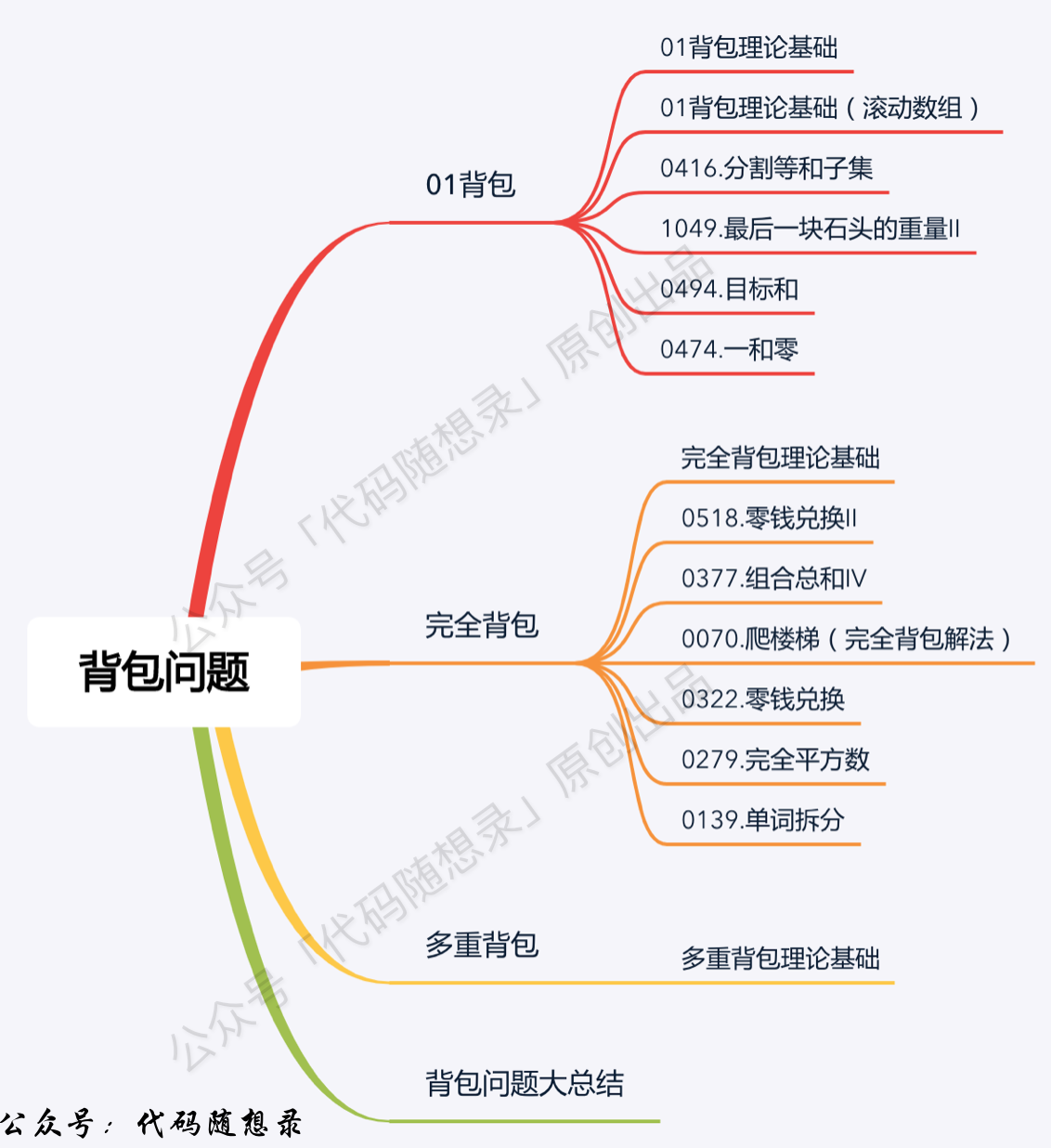 -11. [动态规划:01背包理论基础](./problems/背包理论基础01背包-1.md)
-12. [动态规划:01背包理论基础(滚动数组)](./problems/背包理论基础01背包-2.md)
+11. [动态规划:01背包理论基础(二维dp数组)](./problems/背包理论基础01背包-1.md)
+12. [动态规划:01背包理论基础(一维dp数组)](./problems/背包理论基础01背包-2.md)
13. [动态规划:416.分割等和子集](./problems/0416.分割等和子集.md)
14. [动态规划:1049.最后一块石头的重量II](./problems/1049.最后一块石头的重量II.md)
15. [本周小结!(动态规划系列三)](./problems/周总结/20210121动规周末总结.md)
16. [动态规划:494.目标和](./problems/0494.目标和.md)
17. [动态规划:474.一和零](./problems/0474.一和零.md)
-18. [动态规划:完全背包总结篇](./problems/背包问题理论基础完全背包.md)
-19. [动态规划:518.零钱兑换II](./problems/0518.零钱兑换II.md)
-20. [本周小结!(动态规划系列四)](./problems/周总结/20210128动规周末总结.md)
-21. [动态规划:377.组合总和Ⅳ](./problems/0377.组合总和Ⅳ.md)
-22. [动态规划:70.爬楼梯(完全背包版本)](./problems/0070.爬楼梯完全背包版本.md)
-23. [动态规划:322.零钱兑换](./problems/0322.零钱兑换.md)
-24. [动态规划:279.完全平方数](./problems/0279.完全平方数.md)
-25. [本周小结!(动态规划系列五)](./problems/周总结/20210204动规周末总结.md)
-26. [动态规划:139.单词拆分](./problems/0139.单词拆分.md)
-27. [动态规划:多重背包理论基础](./problems/背包问题理论基础多重背包.md)
-28. [背包问题总结篇](./problems/背包总结篇.md)
+18. [动态规划:完全背包理论基础(二维dp数组)](./problems/背包问题理论基础完全背包.md)
+19. [动态规划:完全背包理论基础(一维dp数组)](./problems/背包问题完全背包一维.md)
+20. [动态规划:518.零钱兑换II](./problems/0518.零钱兑换II.md)
+21. [本周小结!(动态规划系列四)](./problems/周总结/20210128动规周末总结.md)
+22. [动态规划:377.组合总和Ⅳ](./problems/0377.组合总和Ⅳ.md)
+23. [动态规划:70.爬楼梯(完全背包版本)](./problems/0070.爬楼梯完全背包版本.md)
+24. [动态规划:322.零钱兑换](./problems/0322.零钱兑换.md)
+25. [动态规划:279.完全平方数](./problems/0279.完全平方数.md)
+26. [本周小结!(动态规划系列五)](./problems/周总结/20210204动规周末总结.md)
+27. [动态规划:139.单词拆分](./problems/0139.单词拆分.md)
+28. [动态规划:多重背包理论基础](./problems/背包问题理论基础多重背包.md)
+29. [背包问题总结篇](./problems/背包总结篇.md)
打家劫舍系列:
@@ -338,7 +328,7 @@
股票系列:
-
-11. [动态规划:01背包理论基础](./problems/背包理论基础01背包-1.md)
-12. [动态规划:01背包理论基础(滚动数组)](./problems/背包理论基础01背包-2.md)
+11. [动态规划:01背包理论基础(二维dp数组)](./problems/背包理论基础01背包-1.md)
+12. [动态规划:01背包理论基础(一维dp数组)](./problems/背包理论基础01背包-2.md)
13. [动态规划:416.分割等和子集](./problems/0416.分割等和子集.md)
14. [动态规划:1049.最后一块石头的重量II](./problems/1049.最后一块石头的重量II.md)
15. [本周小结!(动态规划系列三)](./problems/周总结/20210121动规周末总结.md)
16. [动态规划:494.目标和](./problems/0494.目标和.md)
17. [动态规划:474.一和零](./problems/0474.一和零.md)
-18. [动态规划:完全背包总结篇](./problems/背包问题理论基础完全背包.md)
-19. [动态规划:518.零钱兑换II](./problems/0518.零钱兑换II.md)
-20. [本周小结!(动态规划系列四)](./problems/周总结/20210128动规周末总结.md)
-21. [动态规划:377.组合总和Ⅳ](./problems/0377.组合总和Ⅳ.md)
-22. [动态规划:70.爬楼梯(完全背包版本)](./problems/0070.爬楼梯完全背包版本.md)
-23. [动态规划:322.零钱兑换](./problems/0322.零钱兑换.md)
-24. [动态规划:279.完全平方数](./problems/0279.完全平方数.md)
-25. [本周小结!(动态规划系列五)](./problems/周总结/20210204动规周末总结.md)
-26. [动态规划:139.单词拆分](./problems/0139.单词拆分.md)
-27. [动态规划:多重背包理论基础](./problems/背包问题理论基础多重背包.md)
-28. [背包问题总结篇](./problems/背包总结篇.md)
+18. [动态规划:完全背包理论基础(二维dp数组)](./problems/背包问题理论基础完全背包.md)
+19. [动态规划:完全背包理论基础(一维dp数组)](./problems/背包问题完全背包一维.md)
+20. [动态规划:518.零钱兑换II](./problems/0518.零钱兑换II.md)
+21. [本周小结!(动态规划系列四)](./problems/周总结/20210128动规周末总结.md)
+22. [动态规划:377.组合总和Ⅳ](./problems/0377.组合总和Ⅳ.md)
+23. [动态规划:70.爬楼梯(完全背包版本)](./problems/0070.爬楼梯完全背包版本.md)
+24. [动态规划:322.零钱兑换](./problems/0322.零钱兑换.md)
+25. [动态规划:279.完全平方数](./problems/0279.完全平方数.md)
+26. [本周小结!(动态规划系列五)](./problems/周总结/20210204动规周末总结.md)
+27. [动态规划:139.单词拆分](./problems/0139.单词拆分.md)
+28. [动态规划:多重背包理论基础](./problems/背包问题理论基础多重背包.md)
+29. [背包问题总结篇](./problems/背包总结篇.md)
打家劫舍系列:
@@ -338,7 +328,7 @@
股票系列:
- +
+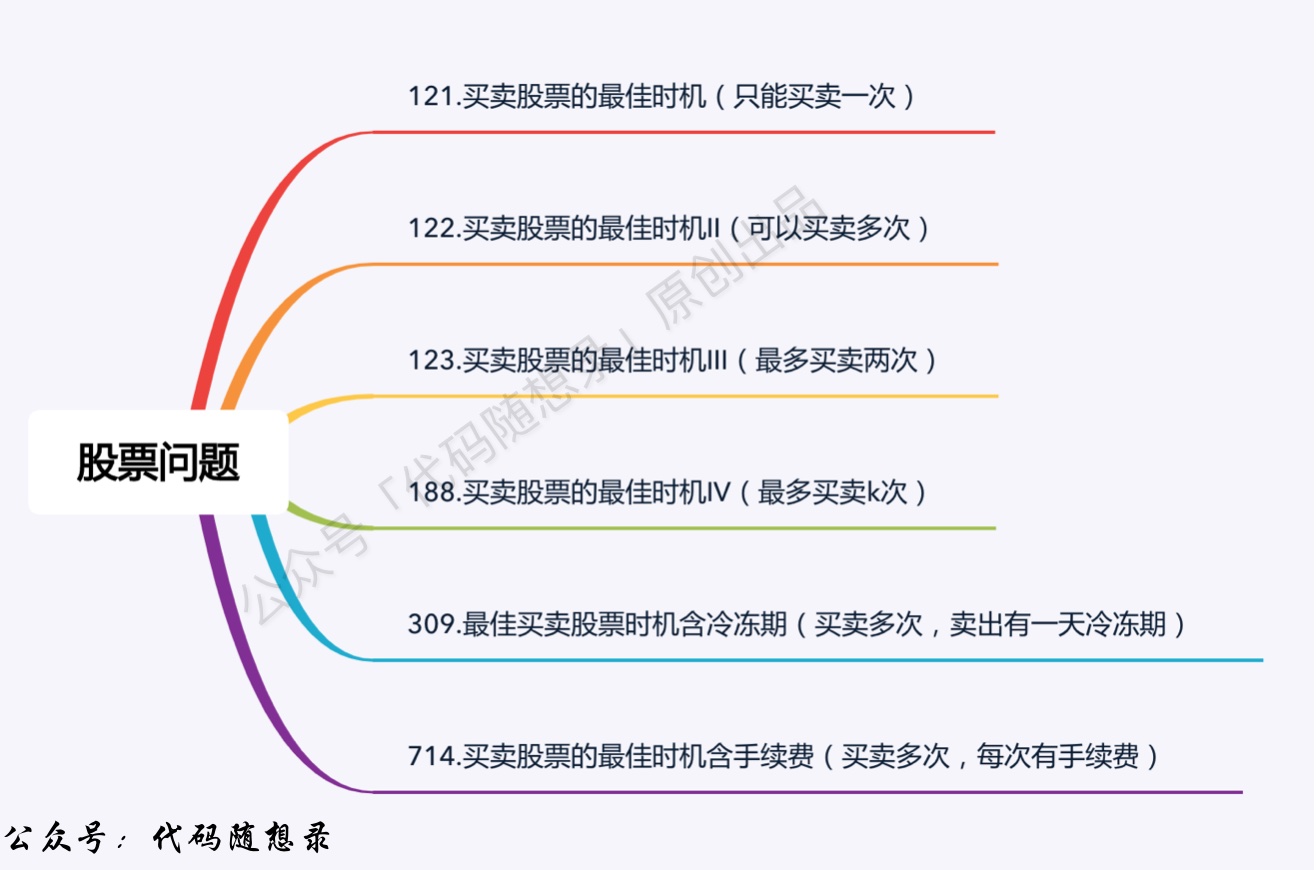 32. [动态规划:121.买卖股票的最佳时机](./problems/0121.买卖股票的最佳时机.md)
@@ -353,7 +343,7 @@
子序列系列:
-
32. [动态规划:121.买卖股票的最佳时机](./problems/0121.买卖股票的最佳时机.md)
@@ -353,7 +343,7 @@
子序列系列:
- +
+ 41. [动态规划:300.最长递增子序列](./problems/0300.最长上升子序列.md)
@@ -383,44 +373,42 @@
## 图论
-通知:开始更新图论内容,图论部分还没有其他语言版本,欢迎录友们提交PR,成为contributor
-
-### 深搜广搜
-
-* [图论:深度优先搜索理论基础](./problems/图论深搜理论基础.md)
-* [图论:797.所有可能的路径](./problems/0797.所有可能的路径.md)
-* [图论:广度优先搜索理论基础](./problems/图论广搜理论基础.md)
-* [图论:200.岛屿数量.深搜版](./problems/0200.岛屿数量.深搜版.md)
-* [图论:200.岛屿数量.广搜版](./problems/0200.岛屿数量.广搜版.md)
-* [图论:695.岛屿的最大面积](./problems/0695.岛屿的最大面积.md)
-* [图论:1020.飞地的数量](./problems/1020.飞地的数量.md)
-* [图论:130.被围绕的区域](./problems/0130.被围绕的区域.md)
-* [图论:417.太平洋大西洋水流问题](./problems/0417.太平洋大西洋水流问题.md)
-* [图论:827.最大人工岛](./problems/0827.最大人工岛.md)
-* [图论:127. 单词接龙](./problems/0127.单词接龙.md)
-* [图论:841.钥匙和房间](./problems/0841.钥匙和房间.md)
-* [图论:463. 岛屿的周长](./problems/0463.岛屿的周长.md)
-* [图论:并查集理论基础](./problems/图论并查集理论基础.md)
-* [图论:1971. 寻找图中是否存在路径](./problems/1971.寻找图中是否存在路径.md)
-* [图论:684.冗余连接](./problems/0684.冗余连接.md)
-* [图论:685.冗余连接II](./problems/0685.冗余连接II.md)
-
-(持续更新中....)
-
-
-## 十大排序
-
-## 数论
-
-## 高级数据结构经典题目
+**[图论正式发布](./problems/qita/tulunfabu.md)**
+
+1. [图论:理论基础](./problems/kamacoder/图论理论基础.md)
+2. [图论:深度优先搜索理论基础](./problems/kamacoder/图论深搜理论基础.md)
+3. [图论:所有可达路径](./problems/kamacoder/0098.所有可达路径.md)
+4. [图论:广度优先搜索理论基础](./problems/kamacoder/图论广搜理论基础.md)
+5. [图论:岛屿数量.深搜版](./problems/kamacoder/0099.岛屿的数量深搜.md)
+6. [图论:岛屿数量.广搜版](./problems/kamacoder/0099.岛屿的数量广搜.md)
+7. [图论:岛屿的最大面积](./problems/kamacoder/0100.岛屿的最大面积.md)
+8. [图论:孤岛的总面积](./problems/kamacoder/0101.孤岛的总面积.md)
+9. [图论:沉没孤岛](./problems/kamacoder/0102.沉没孤岛.md)
+10. [图论:水流问题](./problems/kamacoder/0103.水流问题.md)
+11. [图论:建造最大岛屿](./problems/kamacoder/0104.建造最大岛屿.md)
+12. [图论:岛屿的周长](./problems/kamacoder/0106.岛屿的周长.md)
+13. [图论:字符串接龙](./problems/kamacoder/0110.字符串接龙.md)
+14. [图论:有向图的完全可达性](./problems/kamacoder/0105.有向图的完全可达性.md)
+15. [图论:并查集理论基础](./problems/kamacoder/图论并查集理论基础.md)
+16. [图论:寻找存在的路径](./problems/kamacoder/0107.寻找存在的路径.md)
+17. [图论:冗余连接](./problems/kamacoder/0108.冗余连接.md)
+18. [图论:冗余连接II](./problems/kamacoder/0109.冗余连接II.md)
+19. [图论:最小生成树之prim](./problems/kamacoder/0053.寻宝-prim.md)
+20. [图论:最小生成树之kruskal](./problems/kamacoder/0053.寻宝-Kruskal.md)
+21. [图论:拓扑排序](./problems/kamacoder/0117.软件构建.md)
+22. [图论:dijkstra(朴素版)](./problems/kamacoder/0047.参会dijkstra朴素.md)
+23. [图论:dijkstra(堆优化版)](./problems/kamacoder/0047.参会dijkstra堆.md)
+24. [图论:Bellman_ford 算法](./problems/kamacoder/0094.城市间货物运输I.md)
+25. [图论:Bellman_ford 队列优化算法(又名SPFA)](./problems/kamacoder/0094.城市间货物运输I-SPFA.md)
+26. [图论:Bellman_ford之判断负权回路](./problems/kamacoder/0095.城市间货物运输II.md)
+27. [图论:Bellman_ford之单源有限最短路](./problems/kamacoder/0096.城市间货物运输III.md)
+28. [图论:Floyd 算法](./problems/kamacoder/0097.小明逛公园.md)
+29. [图论:A * 算法](./problems/kamacoder/0126.骑士的攻击astar.md)
+30. [图论:最短路算法总结篇](./problems/kamacoder/最短路问题总结篇.md)
+31. [图论:图论总结篇](./problems/kamacoder/图论总结篇.md)
-* 并查集
-* 最小生成树
-* 线段树
-* 树状数组
-* 字典树
-## 海量数据处理
+(持续更新中....)
# 补充题目
@@ -499,7 +487,7 @@
# 贡献者
-[点此这里](https://github.com/youngyangyang04/leetcode-master/graphs/contributors)查看LeetCode-Master的所有贡献者。感谢他们补充了LeetCode-Master的其他语言版本,让更多的读者收益于此项目。
+[点此这里](https://github.com/youngyangyang04/leetcode-master/graphs/contributors)查看LeetCode-Master的所有贡献者。感谢他们补充了LeetCode-Master的其他语言版本,让更多的读者受益于此项目。
# Star 趋势
@@ -507,24 +495,13 @@
# 关于作者
-大家好,我是程序员Carl,哈工大师兄,《代码随想录》作者,先后在腾讯和百度从事后端技术研发。对算法和C++后端技术有一定的见解,利用工作之余重新刷leetcode。
-
-加入「代码随想录」刷题小分队(微信群),可以扫下方二维码,加代码随想录客服微信。
-
-如果是已工作,备注:姓名-城市-岗位-组队刷题。如果学生,备注:姓名-学校-年级-组队刷题。**备注没有自我介绍不通过哦**
-
-
-
41. [动态规划:300.最长递增子序列](./problems/0300.最长上升子序列.md)
@@ -383,44 +373,42 @@
## 图论
-通知:开始更新图论内容,图论部分还没有其他语言版本,欢迎录友们提交PR,成为contributor
-
-### 深搜广搜
-
-* [图论:深度优先搜索理论基础](./problems/图论深搜理论基础.md)
-* [图论:797.所有可能的路径](./problems/0797.所有可能的路径.md)
-* [图论:广度优先搜索理论基础](./problems/图论广搜理论基础.md)
-* [图论:200.岛屿数量.深搜版](./problems/0200.岛屿数量.深搜版.md)
-* [图论:200.岛屿数量.广搜版](./problems/0200.岛屿数量.广搜版.md)
-* [图论:695.岛屿的最大面积](./problems/0695.岛屿的最大面积.md)
-* [图论:1020.飞地的数量](./problems/1020.飞地的数量.md)
-* [图论:130.被围绕的区域](./problems/0130.被围绕的区域.md)
-* [图论:417.太平洋大西洋水流问题](./problems/0417.太平洋大西洋水流问题.md)
-* [图论:827.最大人工岛](./problems/0827.最大人工岛.md)
-* [图论:127. 单词接龙](./problems/0127.单词接龙.md)
-* [图论:841.钥匙和房间](./problems/0841.钥匙和房间.md)
-* [图论:463. 岛屿的周长](./problems/0463.岛屿的周长.md)
-* [图论:并查集理论基础](./problems/图论并查集理论基础.md)
-* [图论:1971. 寻找图中是否存在路径](./problems/1971.寻找图中是否存在路径.md)
-* [图论:684.冗余连接](./problems/0684.冗余连接.md)
-* [图论:685.冗余连接II](./problems/0685.冗余连接II.md)
-
-(持续更新中....)
-
-
-## 十大排序
-
-## 数论
-
-## 高级数据结构经典题目
+**[图论正式发布](./problems/qita/tulunfabu.md)**
+
+1. [图论:理论基础](./problems/kamacoder/图论理论基础.md)
+2. [图论:深度优先搜索理论基础](./problems/kamacoder/图论深搜理论基础.md)
+3. [图论:所有可达路径](./problems/kamacoder/0098.所有可达路径.md)
+4. [图论:广度优先搜索理论基础](./problems/kamacoder/图论广搜理论基础.md)
+5. [图论:岛屿数量.深搜版](./problems/kamacoder/0099.岛屿的数量深搜.md)
+6. [图论:岛屿数量.广搜版](./problems/kamacoder/0099.岛屿的数量广搜.md)
+7. [图论:岛屿的最大面积](./problems/kamacoder/0100.岛屿的最大面积.md)
+8. [图论:孤岛的总面积](./problems/kamacoder/0101.孤岛的总面积.md)
+9. [图论:沉没孤岛](./problems/kamacoder/0102.沉没孤岛.md)
+10. [图论:水流问题](./problems/kamacoder/0103.水流问题.md)
+11. [图论:建造最大岛屿](./problems/kamacoder/0104.建造最大岛屿.md)
+12. [图论:岛屿的周长](./problems/kamacoder/0106.岛屿的周长.md)
+13. [图论:字符串接龙](./problems/kamacoder/0110.字符串接龙.md)
+14. [图论:有向图的完全可达性](./problems/kamacoder/0105.有向图的完全可达性.md)
+15. [图论:并查集理论基础](./problems/kamacoder/图论并查集理论基础.md)
+16. [图论:寻找存在的路径](./problems/kamacoder/0107.寻找存在的路径.md)
+17. [图论:冗余连接](./problems/kamacoder/0108.冗余连接.md)
+18. [图论:冗余连接II](./problems/kamacoder/0109.冗余连接II.md)
+19. [图论:最小生成树之prim](./problems/kamacoder/0053.寻宝-prim.md)
+20. [图论:最小生成树之kruskal](./problems/kamacoder/0053.寻宝-Kruskal.md)
+21. [图论:拓扑排序](./problems/kamacoder/0117.软件构建.md)
+22. [图论:dijkstra(朴素版)](./problems/kamacoder/0047.参会dijkstra朴素.md)
+23. [图论:dijkstra(堆优化版)](./problems/kamacoder/0047.参会dijkstra堆.md)
+24. [图论:Bellman_ford 算法](./problems/kamacoder/0094.城市间货物运输I.md)
+25. [图论:Bellman_ford 队列优化算法(又名SPFA)](./problems/kamacoder/0094.城市间货物运输I-SPFA.md)
+26. [图论:Bellman_ford之判断负权回路](./problems/kamacoder/0095.城市间货物运输II.md)
+27. [图论:Bellman_ford之单源有限最短路](./problems/kamacoder/0096.城市间货物运输III.md)
+28. [图论:Floyd 算法](./problems/kamacoder/0097.小明逛公园.md)
+29. [图论:A * 算法](./problems/kamacoder/0126.骑士的攻击astar.md)
+30. [图论:最短路算法总结篇](./problems/kamacoder/最短路问题总结篇.md)
+31. [图论:图论总结篇](./problems/kamacoder/图论总结篇.md)
-* 并查集
-* 最小生成树
-* 线段树
-* 树状数组
-* 字典树
-## 海量数据处理
+(持续更新中....)
# 补充题目
@@ -499,7 +487,7 @@
# 贡献者
-[点此这里](https://github.com/youngyangyang04/leetcode-master/graphs/contributors)查看LeetCode-Master的所有贡献者。感谢他们补充了LeetCode-Master的其他语言版本,让更多的读者收益于此项目。
+[点此这里](https://github.com/youngyangyang04/leetcode-master/graphs/contributors)查看LeetCode-Master的所有贡献者。感谢他们补充了LeetCode-Master的其他语言版本,让更多的读者受益于此项目。
# Star 趋势
@@ -507,24 +495,13 @@
# 关于作者
-大家好,我是程序员Carl,哈工大师兄,《代码随想录》作者,先后在腾讯和百度从事后端技术研发。对算法和C++后端技术有一定的见解,利用工作之余重新刷leetcode。
-
-加入「代码随想录」刷题小分队(微信群),可以扫下方二维码,加代码随想录客服微信。
-
-如果是已工作,备注:姓名-城市-岗位-组队刷题。如果学生,备注:姓名-学校-年级-组队刷题。**备注没有自我介绍不通过哦**
-
-
-


 -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0005.\346\234\200\351\225\277\345\233\236\346\226\207\345\255\220\344\270\262.md" "b/problems/0005.\346\234\200\351\225\277\345\233\236\346\226\207\345\255\220\344\270\262.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index b13f9ac356..05dd610a72
--- "a/problems/0005.\346\234\200\351\225\277\345\233\236\346\226\207\345\255\220\344\270\262.md"
+++ "b/problems/0005.\346\234\200\351\225\277\345\233\236\346\226\207\345\255\220\344\270\262.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0005.\346\234\200\351\225\277\345\233\236\346\226\207\345\255\220\344\270\262.md" "b/problems/0005.\346\234\200\351\225\277\345\233\236\346\226\207\345\255\220\344\270\262.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index b13f9ac356..05dd610a72
--- "a/problems/0005.\346\234\200\351\225\277\345\233\236\346\226\207\345\255\220\344\270\262.md"
+++ "b/problems/0005.\346\234\200\351\225\277\345\233\236\346\226\207\345\255\220\344\270\262.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
+
diff --git "a/problems/0015.\344\270\211\346\225\260\344\271\213\345\222\214.md" "b/problems/0015.\344\270\211\346\225\260\344\271\213\345\222\214.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index bf165788f8..e2cb3f4612
--- "a/problems/0015.\344\270\211\346\225\260\344\271\213\345\222\214.md"
+++ "b/problems/0015.\344\270\211\346\225\260\344\271\213\345\222\214.md"
@@ -1,13 +1,9 @@
-
-
+
diff --git "a/problems/0015.\344\270\211\346\225\260\344\271\213\345\222\214.md" "b/problems/0015.\344\270\211\346\225\260\344\271\213\345\222\214.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index bf165788f8..e2cb3f4612
--- "a/problems/0015.\344\270\211\346\225\260\344\271\213\345\222\214.md"
+++ "b/problems/0015.\344\270\211\346\225\260\344\271\213\345\222\214.md"
@@ -1,13 +1,9 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0017.\347\224\265\350\257\235\345\217\267\347\240\201\347\232\204\345\255\227\346\257\215\347\273\204\345\220\210.md" "b/problems/0017.\347\224\265\350\257\235\345\217\267\347\240\201\347\232\204\345\255\227\346\257\215\347\273\204\345\220\210.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index cbd99f8d93..6dcf9ee690
--- "a/problems/0017.\347\224\265\350\257\235\345\217\267\347\240\201\347\232\204\345\255\227\346\257\215\347\273\204\345\220\210.md"
+++ "b/problems/0017.\347\224\265\350\257\235\345\217\267\347\240\201\347\232\204\345\255\227\346\257\215\347\273\204\345\220\210.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0017.\347\224\265\350\257\235\345\217\267\347\240\201\347\232\204\345\255\227\346\257\215\347\273\204\345\220\210.md" "b/problems/0017.\347\224\265\350\257\235\345\217\267\347\240\201\347\232\204\345\255\227\346\257\215\347\273\204\345\220\210.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index cbd99f8d93..6dcf9ee690
--- "a/problems/0017.\347\224\265\350\257\235\345\217\267\347\240\201\347\232\204\345\255\227\346\257\215\347\273\204\345\220\210.md"
+++ "b/problems/0017.\347\224\265\350\257\235\345\217\267\347\240\201\347\232\204\345\255\227\346\257\215\347\273\204\345\220\210.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0018.\345\233\233\346\225\260\344\271\213\345\222\214.md" "b/problems/0018.\345\233\233\346\225\260\344\271\213\345\222\214.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 17715b2e6f..bf7d3bd4ee
--- "a/problems/0018.\345\233\233\346\225\260\344\271\213\345\222\214.md"
+++ "b/problems/0018.\345\233\233\346\225\260\344\271\213\345\222\214.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0018.\345\233\233\346\225\260\344\271\213\345\222\214.md" "b/problems/0018.\345\233\233\346\225\260\344\271\213\345\222\214.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 17715b2e6f..bf7d3bd4ee
--- "a/problems/0018.\345\233\233\346\225\260\344\271\213\345\222\214.md"
+++ "b/problems/0018.\345\233\233\346\225\260\344\271\213\345\222\214.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
+
diff --git "a/problems/0019.\345\210\240\351\231\244\351\223\276\350\241\250\347\232\204\345\200\222\346\225\260\347\254\254N\344\270\252\350\212\202\347\202\271.md" "b/problems/0019.\345\210\240\351\231\244\351\223\276\350\241\250\347\232\204\345\200\222\346\225\260\347\254\254N\344\270\252\350\212\202\347\202\271.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index f508b523e3..08f602c1c1
--- "a/problems/0019.\345\210\240\351\231\244\351\223\276\350\241\250\347\232\204\345\200\222\346\225\260\347\254\254N\344\270\252\350\212\202\347\202\271.md"
+++ "b/problems/0019.\345\210\240\351\231\244\351\223\276\350\241\250\347\232\204\345\200\222\346\225\260\347\254\254N\344\270\252\350\212\202\347\202\271.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+
diff --git "a/problems/0019.\345\210\240\351\231\244\351\223\276\350\241\250\347\232\204\345\200\222\346\225\260\347\254\254N\344\270\252\350\212\202\347\202\271.md" "b/problems/0019.\345\210\240\351\231\244\351\223\276\350\241\250\347\232\204\345\200\222\346\225\260\347\254\254N\344\270\252\350\212\202\347\202\271.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index f508b523e3..08f602c1c1
--- "a/problems/0019.\345\210\240\351\231\244\351\223\276\350\241\250\347\232\204\345\200\222\346\225\260\347\254\254N\344\270\252\350\212\202\347\202\271.md"
+++ "b/problems/0019.\345\210\240\351\231\244\351\223\276\350\241\250\347\232\204\345\200\222\346\225\260\347\254\254N\344\270\252\350\212\202\347\202\271.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- +
+ * fast首先走n + 1步 ,为什么是n+1呢,因为只有这样同时移动的时候slow才能指向删除节点的上一个节点(方便做删除操作),如图:
-
* fast首先走n + 1步 ,为什么是n+1呢,因为只有这样同时移动的时候slow才能指向删除节点的上一个节点(方便做删除操作),如图:
- +
+ * fast和slow同时移动,直到fast指向末尾,如题:
-
* fast和slow同时移动,直到fast指向末尾,如题:
- -
+
-
+ +//图片中有错别词:应该将“只到”改为“直到”
* 删除slow指向的下一个节点,如图:
-
+//图片中有错别词:应该将“只到”改为“直到”
* 删除slow指向的下一个节点,如图:
- +
+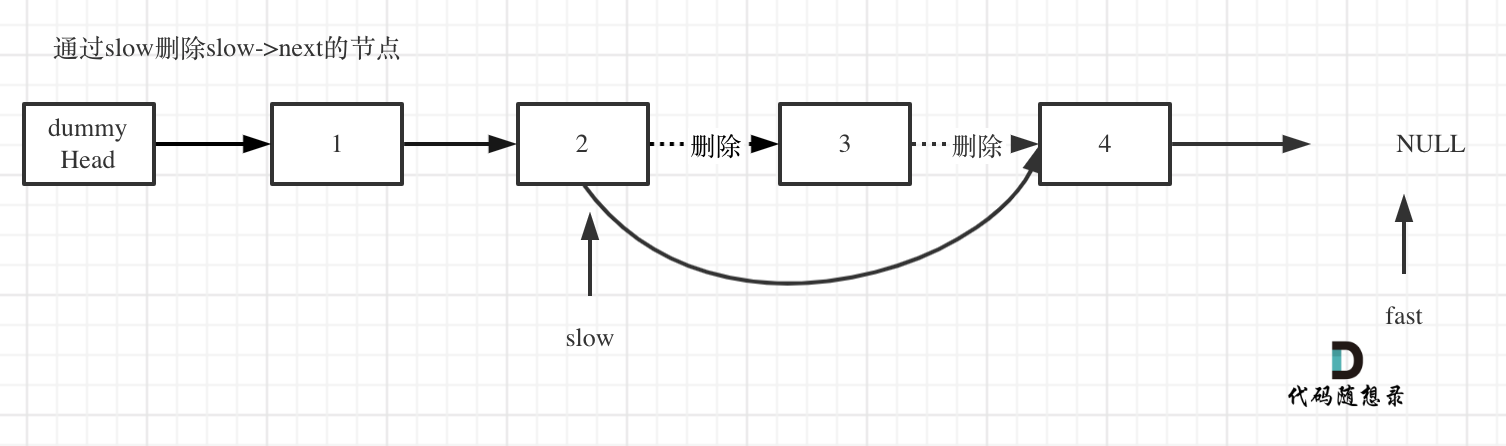 此时不难写出如下C++代码:
@@ -82,7 +82,7 @@ public:
// ListNode *tmp = slow->next; C++释放内存的逻辑
// slow->next = tmp->next;
- // delete nth;
+ // delete tmp;
return dummyHead->next;
}
@@ -98,30 +98,65 @@ public:
### Java:
```java
-public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n){
- ListNode dummyNode = new ListNode(0);
- dummyNode.next = head;
-
- ListNode fastIndex = dummyNode;
- ListNode slowIndex = dummyNode;
+class Solution {
+ public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
+ //新建一个虚拟头节点指向head
+ ListNode dummyNode = new ListNode(0);
+ dummyNode.next = head;
+ //快慢指针指向虚拟头节点
+ ListNode fastIndex = dummyNode;
+ ListNode slowIndex = dummyNode;
+
+ // 只要快慢指针相差 n 个结点即可
+ for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
+ fastIndex = fastIndex.next;
+ }
+ while (fastIndex != null) {
+ fastIndex = fastIndex.next;
+ slowIndex = slowIndex.next;
+ }
- // 只要快慢指针相差 n 个结点即可
- for (int i = 0; i < n ; i++){
- fastIndex = fastIndex.next;
+ // 此时 slowIndex 的位置就是待删除元素的前一个位置。
+ // 具体情况可自己画一个链表长度为 3 的图来模拟代码来理解
+ // 检查 slowIndex.next 是否为 null,以避免空指针异常
+ if (slowIndex.next != null) {
+ slowIndex.next = slowIndex.next.next;
+ }
+ return dummyNode.next;
}
+}
+```
- while (fastIndex != null){
- fastIndex = fastIndex.next;
- slowIndex = slowIndex.next;
- }
- //此时 slowIndex 的位置就是待删除元素的前一个位置。
- //具体情况可自己画一个链表长度为 3 的图来模拟代码来理解
- slowIndex.next = slowIndex.next.next;
- return dummyNode.next;
+```java
+class Solution {
+ public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
+ // 创建一个新的哑节点,指向原链表头
+ ListNode s = new ListNode(-1, head);
+ // 递归调用remove方法,从哑节点开始进行删除操作
+ remove(s, n);
+ // 返回新链表的头(去掉可能的哑节点)
+ return s.next;
+ }
+
+ public int remove(ListNode p, int n) {
+ // 递归结束条件:如果当前节点为空,返回0
+ if (p == null) {
+ return 0;
+ }
+ // 递归深入到下一个节点
+ int net = remove(p.next, n);
+ // 如果当前节点是倒数第n个节点,进行删除操作
+ if (net == n) {
+ p.next = p.next.next;
+ }
+ // 返回当前节点的总深度
+ return net + 1;
+ }
}
```
+
### Python:
```python
@@ -165,20 +200,17 @@ class Solution:
* }
*/
func removeNthFromEnd(head *ListNode, n int) *ListNode {
- dummyHead := &ListNode{}
- dummyHead.Next = head
- cur := head
- prev := dummyHead
- i := 1
- for cur != nil {
- cur = cur.Next
- if i > n {
- prev = prev.Next
- }
- i++
- }
- prev.Next = prev.Next.Next
- return dummyHead.Next
+ dummyNode := &ListNode{0, head}
+ fast, slow := dummyNode, dummyNode
+ for i := 0; i <= n; i++ { // 注意<=,否则快指针为空时,慢指针正好在倒数第n个上面
+ fast = fast.Next
+ }
+ for fast != nil {
+ fast = fast.Next
+ slow = slow.Next
+ }
+ slow.Next = slow.Next.Next
+ return dummyNode.Next
}
```
@@ -190,16 +222,18 @@ func removeNthFromEnd(head *ListNode, n int) *ListNode {
* @param {number} n
* @return {ListNode}
*/
-var removeNthFromEnd = function(head, n) {
- let ret = new ListNode(0, head),
- slow = fast = ret;
- while(n--) fast = fast.next;
- while (fast.next !== null) {
- fast = fast.next;
- slow = slow.next
- };
- slow.next = slow.next.next;
- return ret.next;
+var removeNthFromEnd = function (head, n) {
+ // 创建哨兵节点,简化解题逻辑
+ let dummyHead = new ListNode(0, head);
+ let fast = dummyHead;
+ let slow = dummyHead;
+ while (n--) fast = fast.next;
+ while (fast.next !== null) {
+ slow = slow.next;
+ fast = fast.next;
+ }
+ slow.next = slow.next.next;
+ return dummyHead.next;
};
```
### TypeScript:
@@ -443,7 +477,3 @@ public class Solution {
}
}
```
-
此时不难写出如下C++代码:
@@ -82,7 +82,7 @@ public:
// ListNode *tmp = slow->next; C++释放内存的逻辑
// slow->next = tmp->next;
- // delete nth;
+ // delete tmp;
return dummyHead->next;
}
@@ -98,30 +98,65 @@ public:
### Java:
```java
-public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n){
- ListNode dummyNode = new ListNode(0);
- dummyNode.next = head;
-
- ListNode fastIndex = dummyNode;
- ListNode slowIndex = dummyNode;
+class Solution {
+ public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
+ //新建一个虚拟头节点指向head
+ ListNode dummyNode = new ListNode(0);
+ dummyNode.next = head;
+ //快慢指针指向虚拟头节点
+ ListNode fastIndex = dummyNode;
+ ListNode slowIndex = dummyNode;
+
+ // 只要快慢指针相差 n 个结点即可
+ for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
+ fastIndex = fastIndex.next;
+ }
+ while (fastIndex != null) {
+ fastIndex = fastIndex.next;
+ slowIndex = slowIndex.next;
+ }
- // 只要快慢指针相差 n 个结点即可
- for (int i = 0; i < n ; i++){
- fastIndex = fastIndex.next;
+ // 此时 slowIndex 的位置就是待删除元素的前一个位置。
+ // 具体情况可自己画一个链表长度为 3 的图来模拟代码来理解
+ // 检查 slowIndex.next 是否为 null,以避免空指针异常
+ if (slowIndex.next != null) {
+ slowIndex.next = slowIndex.next.next;
+ }
+ return dummyNode.next;
}
+}
+```
- while (fastIndex != null){
- fastIndex = fastIndex.next;
- slowIndex = slowIndex.next;
- }
- //此时 slowIndex 的位置就是待删除元素的前一个位置。
- //具体情况可自己画一个链表长度为 3 的图来模拟代码来理解
- slowIndex.next = slowIndex.next.next;
- return dummyNode.next;
+```java
+class Solution {
+ public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
+ // 创建一个新的哑节点,指向原链表头
+ ListNode s = new ListNode(-1, head);
+ // 递归调用remove方法,从哑节点开始进行删除操作
+ remove(s, n);
+ // 返回新链表的头(去掉可能的哑节点)
+ return s.next;
+ }
+
+ public int remove(ListNode p, int n) {
+ // 递归结束条件:如果当前节点为空,返回0
+ if (p == null) {
+ return 0;
+ }
+ // 递归深入到下一个节点
+ int net = remove(p.next, n);
+ // 如果当前节点是倒数第n个节点,进行删除操作
+ if (net == n) {
+ p.next = p.next.next;
+ }
+ // 返回当前节点的总深度
+ return net + 1;
+ }
}
```
+
### Python:
```python
@@ -165,20 +200,17 @@ class Solution:
* }
*/
func removeNthFromEnd(head *ListNode, n int) *ListNode {
- dummyHead := &ListNode{}
- dummyHead.Next = head
- cur := head
- prev := dummyHead
- i := 1
- for cur != nil {
- cur = cur.Next
- if i > n {
- prev = prev.Next
- }
- i++
- }
- prev.Next = prev.Next.Next
- return dummyHead.Next
+ dummyNode := &ListNode{0, head}
+ fast, slow := dummyNode, dummyNode
+ for i := 0; i <= n; i++ { // 注意<=,否则快指针为空时,慢指针正好在倒数第n个上面
+ fast = fast.Next
+ }
+ for fast != nil {
+ fast = fast.Next
+ slow = slow.Next
+ }
+ slow.Next = slow.Next.Next
+ return dummyNode.Next
}
```
@@ -190,16 +222,18 @@ func removeNthFromEnd(head *ListNode, n int) *ListNode {
* @param {number} n
* @return {ListNode}
*/
-var removeNthFromEnd = function(head, n) {
- let ret = new ListNode(0, head),
- slow = fast = ret;
- while(n--) fast = fast.next;
- while (fast.next !== null) {
- fast = fast.next;
- slow = slow.next
- };
- slow.next = slow.next.next;
- return ret.next;
+var removeNthFromEnd = function (head, n) {
+ // 创建哨兵节点,简化解题逻辑
+ let dummyHead = new ListNode(0, head);
+ let fast = dummyHead;
+ let slow = dummyHead;
+ while (n--) fast = fast.next;
+ while (fast.next !== null) {
+ slow = slow.next;
+ fast = fast.next;
+ }
+ slow.next = slow.next.next;
+ return dummyHead.next;
};
```
### TypeScript:
@@ -443,7 +477,3 @@ public class Solution {
}
}
```
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0020.\346\234\211\346\225\210\347\232\204\346\213\254\345\217\267.md" "b/problems/0020.\346\234\211\346\225\210\347\232\204\346\213\254\345\217\267.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 17fbe2be2d..09cf997839
--- "a/problems/0020.\346\234\211\346\225\210\347\232\204\346\213\254\345\217\267.md"
+++ "b/problems/0020.\346\234\211\346\225\210\347\232\204\346\213\254\345\217\267.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0020.\346\234\211\346\225\210\347\232\204\346\213\254\345\217\267.md" "b/problems/0020.\346\234\211\346\225\210\347\232\204\346\213\254\345\217\267.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 17fbe2be2d..09cf997839
--- "a/problems/0020.\346\234\211\346\225\210\347\232\204\346\213\254\345\217\267.md"
+++ "b/problems/0020.\346\234\211\346\225\210\347\232\204\346\213\254\345\217\267.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
+
diff --git "a/problems/0024.\344\270\244\344\270\244\344\272\244\346\215\242\351\223\276\350\241\250\344\270\255\347\232\204\350\212\202\347\202\271.md" "b/problems/0024.\344\270\244\344\270\244\344\272\244\346\215\242\351\223\276\350\241\250\344\270\255\347\232\204\350\212\202\347\202\271.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index b2a830a746..14d2538f45
--- "a/problems/0024.\344\270\244\344\270\244\344\272\244\346\215\242\351\223\276\350\241\250\344\270\255\347\232\204\350\212\202\347\202\271.md"
+++ "b/problems/0024.\344\270\244\344\270\244\344\272\244\346\215\242\351\223\276\350\241\250\344\270\255\347\232\204\350\212\202\347\202\271.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+
diff --git "a/problems/0024.\344\270\244\344\270\244\344\272\244\346\215\242\351\223\276\350\241\250\344\270\255\347\232\204\350\212\202\347\202\271.md" "b/problems/0024.\344\270\244\344\270\244\344\272\244\346\215\242\351\223\276\350\241\250\344\270\255\347\232\204\350\212\202\347\202\271.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index b2a830a746..14d2538f45
--- "a/problems/0024.\344\270\244\344\270\244\344\272\244\346\215\242\351\223\276\350\241\250\344\270\255\347\232\204\350\212\202\347\202\271.md"
+++ "b/problems/0024.\344\270\244\344\270\244\344\272\244\346\215\242\351\223\276\350\241\250\344\270\255\347\232\204\350\212\202\347\202\271.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- +
+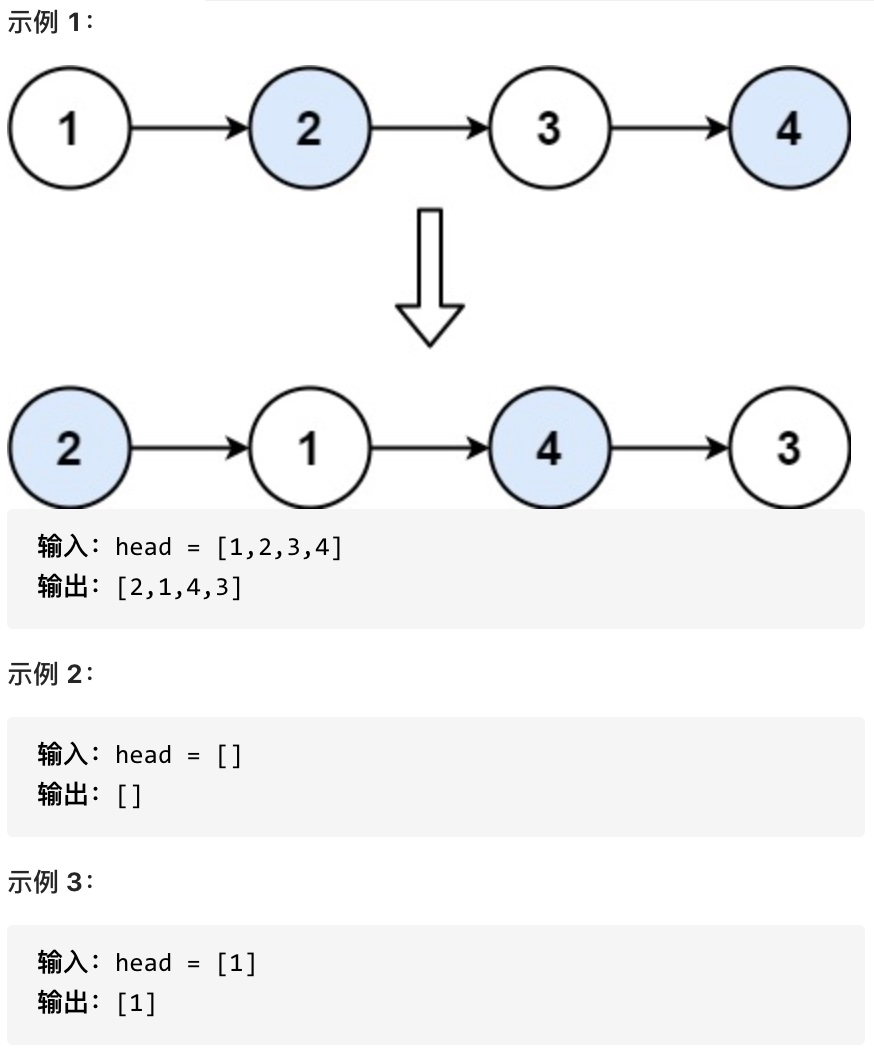 ## 算法公开课
@@ -33,16 +31,16 @@
初始时,cur指向虚拟头结点,然后进行如下三步:
-
+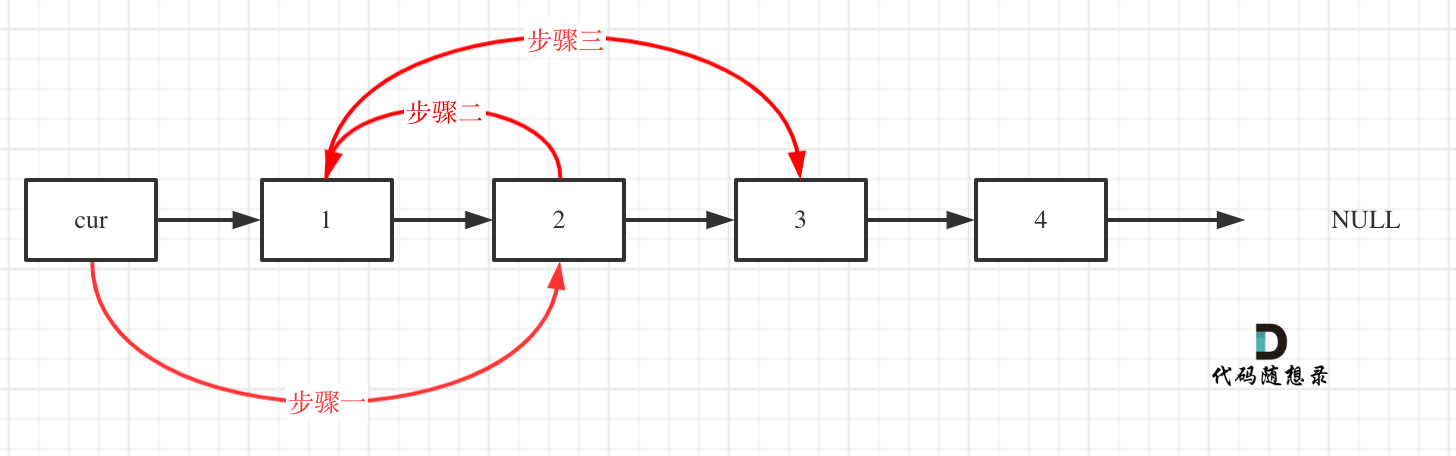
操作之后,链表如下:
-
+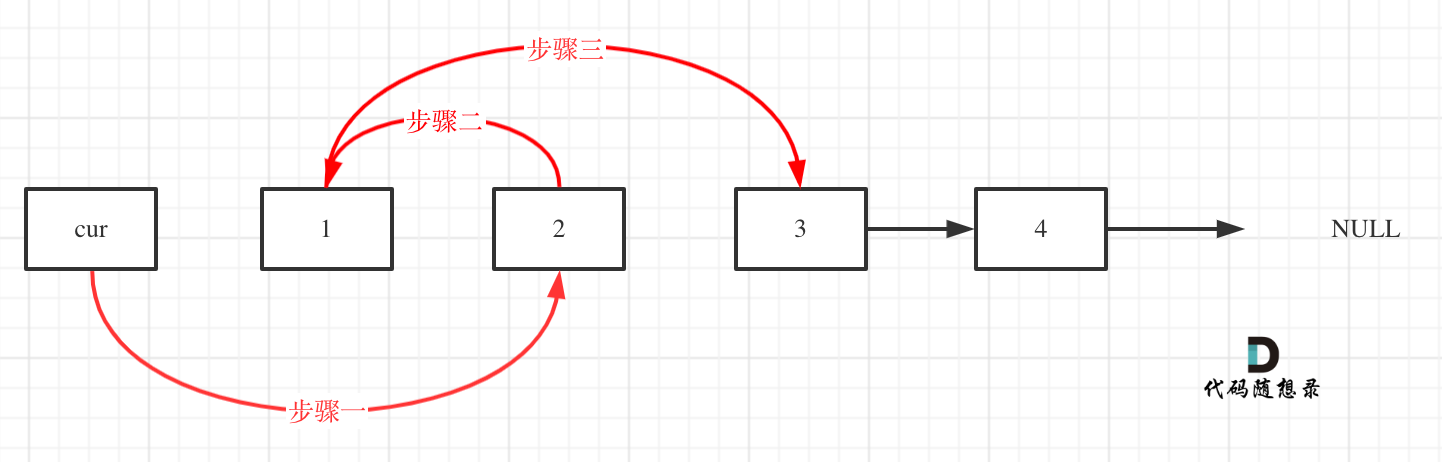
看这个可能就更直观一些了:
-
+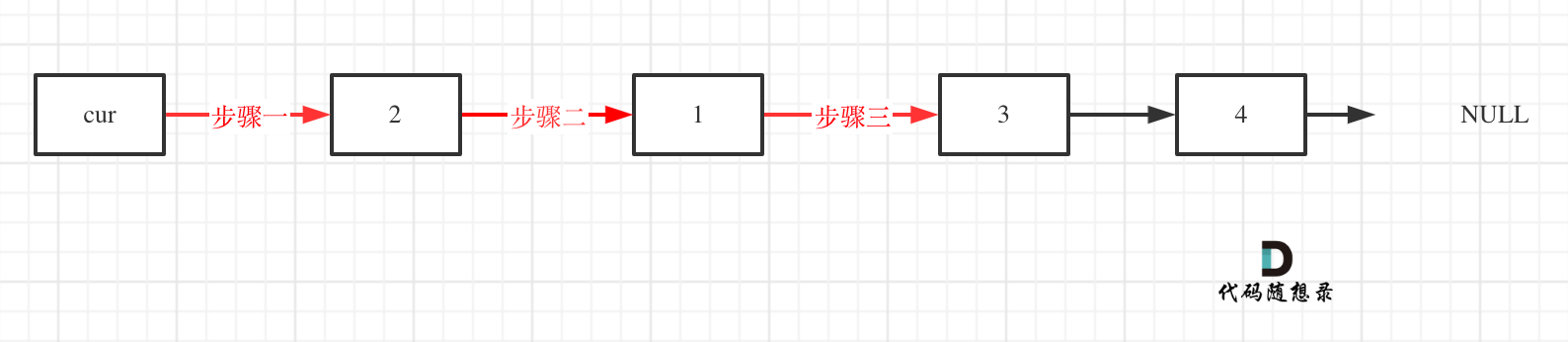
对应的C++代码实现如下: (注释中详细和如上图中的三步做对应)
@@ -81,9 +79,9 @@ public:
上面的代码我第一次提交执行用时8ms,打败6.5%的用户,差点吓到我了。
-心想应该没有更好的方法了吧,也就$O(n)$的时间复杂度,重复提交几次,这样了:
+心想应该没有更好的方法了吧,也就 $O(n)$ 的时间复杂度,重复提交几次,这样了:
-
+
力扣上的统计如果两份代码是 100ms 和 300ms的耗时,其实是需要注意的。
@@ -181,6 +179,23 @@ class Solution {
}
```
+```java
+// 将步骤 2,3 交换顺序,这样不用定义 temp 节点
+public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
+ ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0, head);
+ ListNode cur = dummy;
+ while (cur.next != null && cur.next.next != null) {
+ ListNode node1 = cur.next;// 第 1 个节点
+ ListNode node2 = cur.next.next;// 第 2 个节点
+ cur.next = node2; // 步骤 1
+ node1.next = node2.next;// 步骤 3
+ node2.next = node1;// 步骤 2
+ cur = cur.next.next;
+ }
+ return dummy.next;
+}
+```
+
### Python:
```python
@@ -269,7 +284,7 @@ func swapPairs(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
}
```
-### Javascript:
+### JavaScript:
```javascript
var swapPairs = function (head) {
@@ -285,6 +300,21 @@ var swapPairs = function (head) {
};
```
+```javascript
+// 递归版本
+var swapPairs = function (head) {
+ if (head == null || head.next == null) {
+ return head;
+ }
+
+ let after = head.next;
+ head.next = swapPairs(after.next);
+ after.next = head;
+
+ return after;
+};
+```
+
### TypeScript:
```typescript
@@ -495,7 +525,3 @@ public ListNode SwapPairs(ListNode head)
}
```
-
## 算法公开课
@@ -33,16 +31,16 @@
初始时,cur指向虚拟头结点,然后进行如下三步:
-
+
操作之后,链表如下:
-
+
看这个可能就更直观一些了:
-
+
对应的C++代码实现如下: (注释中详细和如上图中的三步做对应)
@@ -81,9 +79,9 @@ public:
上面的代码我第一次提交执行用时8ms,打败6.5%的用户,差点吓到我了。
-心想应该没有更好的方法了吧,也就$O(n)$的时间复杂度,重复提交几次,这样了:
+心想应该没有更好的方法了吧,也就 $O(n)$ 的时间复杂度,重复提交几次,这样了:
-
+
力扣上的统计如果两份代码是 100ms 和 300ms的耗时,其实是需要注意的。
@@ -181,6 +179,23 @@ class Solution {
}
```
+```java
+// 将步骤 2,3 交换顺序,这样不用定义 temp 节点
+public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
+ ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0, head);
+ ListNode cur = dummy;
+ while (cur.next != null && cur.next.next != null) {
+ ListNode node1 = cur.next;// 第 1 个节点
+ ListNode node2 = cur.next.next;// 第 2 个节点
+ cur.next = node2; // 步骤 1
+ node1.next = node2.next;// 步骤 3
+ node2.next = node1;// 步骤 2
+ cur = cur.next.next;
+ }
+ return dummy.next;
+}
+```
+
### Python:
```python
@@ -269,7 +284,7 @@ func swapPairs(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
}
```
-### Javascript:
+### JavaScript:
```javascript
var swapPairs = function (head) {
@@ -285,6 +300,21 @@ var swapPairs = function (head) {
};
```
+```javascript
+// 递归版本
+var swapPairs = function (head) {
+ if (head == null || head.next == null) {
+ return head;
+ }
+
+ let after = head.next;
+ head.next = swapPairs(after.next);
+ after.next = head;
+
+ return after;
+};
+```
+
### TypeScript:
```typescript
@@ -495,7 +525,3 @@ public ListNode SwapPairs(ListNode head)
}
```
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0027.\347\247\273\351\231\244\345\205\203\347\264\240.md" "b/problems/0027.\347\247\273\351\231\244\345\205\203\347\264\240.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index dbde3d198c..47e05eec6a
--- "a/problems/0027.\347\247\273\351\231\244\345\205\203\347\264\240.md"
+++ "b/problems/0027.\347\247\273\351\231\244\345\205\203\347\264\240.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0027.\347\247\273\351\231\244\345\205\203\347\264\240.md" "b/problems/0027.\347\247\273\351\231\244\345\205\203\347\264\240.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index dbde3d198c..47e05eec6a
--- "a/problems/0027.\347\247\273\351\231\244\345\205\203\347\264\240.md"
+++ "b/problems/0027.\347\247\273\351\231\244\345\205\203\347\264\240.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
+###Dart:
+```dart
+int removeElement(List
-
+###Dart:
+```dart
+int removeElement(List -
-
-
- +
+ 然后就找到了下标2,指向b,继续匹配:如图:
-
然后就找到了下标2,指向b,继续匹配:如图:
- +
+ 以下这句话,对于理解为什么使用前缀表可以告诉我们匹配失败之后跳到哪里重新匹配 非常重要!
@@ -169,15 +167,15 @@ next数组就是一个前缀表(prefix table)。
如图:
-
以下这句话,对于理解为什么使用前缀表可以告诉我们匹配失败之后跳到哪里重新匹配 非常重要!
@@ -169,15 +167,15 @@ next数组就是一个前缀表(prefix table)。
如图:
- +
+ 长度为前1个字符的子串`a`,最长相同前后缀的长度为0。(注意字符串的**前缀是指不包含最后一个字符的所有以第一个字符开头的连续子串**;**后缀是指不包含第一个字符的所有以最后一个字符结尾的连续子串**。)
-
长度为前1个字符的子串`a`,最长相同前后缀的长度为0。(注意字符串的**前缀是指不包含最后一个字符的所有以第一个字符开头的连续子串**;**后缀是指不包含第一个字符的所有以最后一个字符结尾的连续子串**。)
- +
+ 长度为前2个字符的子串`aa`,最长相同前后缀的长度为1。
-
长度为前2个字符的子串`aa`,最长相同前后缀的长度为1。
- +
+ 长度为前3个字符的子串`aab`,最长相同前后缀的长度为0。
@@ -187,13 +185,13 @@ next数组就是一个前缀表(prefix table)。
长度为前6个字符的子串`aabaaf`,最长相同前后缀的长度为0。
那么把求得的最长相同前后缀的长度就是对应前缀表的元素,如图:
-
长度为前3个字符的子串`aab`,最长相同前后缀的长度为0。
@@ -187,13 +185,13 @@ next数组就是一个前缀表(prefix table)。
长度为前6个字符的子串`aabaaf`,最长相同前后缀的长度为0。
那么把求得的最长相同前后缀的长度就是对应前缀表的元素,如图:
- +
+ 可以看出模式串与前缀表对应位置的数字表示的就是:**下标i之前(包括i)的字符串中,有多大长度的相同前缀后缀。**
再来看一下如何利用 前缀表找到 当字符不匹配的时候应该指针应该移动的位置。如动画所示:
-
+
找到的不匹配的位置, 那么此时我们要看它的前一个字符的前缀表的数值是多少。
@@ -227,7 +225,7 @@ next数组就可以是前缀表,但是很多实现都是把前缀表统一减
匹配过程动画如下:
-
+
### 时间复杂度分析
@@ -334,7 +332,7 @@ void getNext(int* next, const string& s){
代码构造next数组的逻辑流程动画如下:
-
+
得到了next数组之后,就要用这个来做匹配了。
@@ -564,6 +562,38 @@ public:
## 其他语言版本
### Java:
+```Java
+class Solution {
+ /**
+ 牺牲空间,换取最直白的暴力法
+ 时间复杂度 O(n * m)
+ 空间 O(n + m)
+ */
+ public int strStr(String haystack, String needle) {
+ // 获取 haystack 和 needle 的长度
+ int n = haystack.length(), m = needle.length();
+ // 将字符串转换为字符数组,方便索引操作
+ char[] s = haystack.toCharArray(), p = needle.toCharArray();
+
+ // 遍历 haystack 字符串
+ for (int i = 0; i < n - m + 1; i++) {
+ // 初始化匹配的指针
+ int a = i, b = 0;
+ // 循环检查 needle 是否在当前位置开始匹配
+ while (b < m && s[a] == p[b]) {
+ // 如果当前字符匹配,则移动指针
+ a++;
+ b++;
+ }
+ // 如果 b 等于 m,说明 needle 已经完全匹配,返回当前位置 i
+ if (b == m) return i;
+ }
+
+ // 如果遍历完毕仍未找到匹配的子串,则返回 -1
+ return -1;
+ }
+}
+```
```Java
class Solution {
@@ -1424,7 +1454,67 @@ public int[] GetNext(string needle)
}
```
-
可以看出模式串与前缀表对应位置的数字表示的就是:**下标i之前(包括i)的字符串中,有多大长度的相同前缀后缀。**
再来看一下如何利用 前缀表找到 当字符不匹配的时候应该指针应该移动的位置。如动画所示:
-
+
找到的不匹配的位置, 那么此时我们要看它的前一个字符的前缀表的数值是多少。
@@ -227,7 +225,7 @@ next数组就可以是前缀表,但是很多实现都是把前缀表统一减
匹配过程动画如下:
-
+
### 时间复杂度分析
@@ -334,7 +332,7 @@ void getNext(int* next, const string& s){
代码构造next数组的逻辑流程动画如下:
-
+
得到了next数组之后,就要用这个来做匹配了。
@@ -564,6 +562,38 @@ public:
## 其他语言版本
### Java:
+```Java
+class Solution {
+ /**
+ 牺牲空间,换取最直白的暴力法
+ 时间复杂度 O(n * m)
+ 空间 O(n + m)
+ */
+ public int strStr(String haystack, String needle) {
+ // 获取 haystack 和 needle 的长度
+ int n = haystack.length(), m = needle.length();
+ // 将字符串转换为字符数组,方便索引操作
+ char[] s = haystack.toCharArray(), p = needle.toCharArray();
+
+ // 遍历 haystack 字符串
+ for (int i = 0; i < n - m + 1; i++) {
+ // 初始化匹配的指针
+ int a = i, b = 0;
+ // 循环检查 needle 是否在当前位置开始匹配
+ while (b < m && s[a] == p[b]) {
+ // 如果当前字符匹配,则移动指针
+ a++;
+ b++;
+ }
+ // 如果 b 等于 m,说明 needle 已经完全匹配,返回当前位置 i
+ if (b == m) return i;
+ }
+
+ // 如果遍历完毕仍未找到匹配的子串,则返回 -1
+ return -1;
+ }
+}
+```
```Java
class Solution {
@@ -1424,7 +1454,67 @@ public int[] GetNext(string needle)
}
```
- -
+### C:
+
+> 前缀表统一右移和减一
+
+```c
+
+int *build_next(char* needle, int len) {
+
+ int *next = (int *)malloc(len * sizeof(int));
+ assert(next); // 确保分配成功
+
+ // 初始化next数组
+ next[0] = -1; // next[0] 设置为 -1,表示没有有效前缀匹配
+ if (len <= 1) { // 如果模式串长度小于等于 1,直接返回
+ return next;
+ }
+ next[1] = 0; // next[1] 设置为 0,表示第一个字符没有公共前后缀
+
+ // 构建next数组, i 从模式串的第三个字符开始, j 指向当前匹配的最长前缀长度
+ int i = 2, j = 0;
+ while (i < len) {
+ if (needle[i - 1] == needle[j]) {
+ j++;
+ next[i] = j;
+ i++;
+ } else if (j > 0) {
+ // 如果不匹配且 j > 0, 回退到次长匹配前缀的长度
+ j = next[j];
+ } else {
+ next[i] = 0;
+ i++;
+ }
+ }
+ return next;
+}
+
+int strStr(char* haystack, char* needle) {
+
+ int needle_len = strlen(needle);
+ int haystack_len = strlen(haystack);
+
+ int *next = build_next(needle, needle_len);
+
+ int i = 0, j = 0; // i 指向主串的当前起始位置, j 指向模式串的当前匹配位置
+ while (i <= haystack_len - needle_len) {
+ if (haystack[i + j] == needle[j]) {
+ j++;
+ if (j == needle_len) {
+ free(next);
+ next = NULL
+ return i;
+ }
+ } else {
+ i += j - next[j]; // 调整主串的起始位置
+ j = j > 0 ? next[j] : 0;
+ }
+ }
+
+ free(next);
+ next = NULL;
+ return -1;
+}
+```
+
diff --git "a/problems/0031.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\216\222\345\210\227.md" "b/problems/0031.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\216\222\345\210\227.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 3cfb673a29..4bbf20fbb8
--- "a/problems/0031.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\216\222\345\210\227.md"
+++ "b/problems/0031.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\216\222\345\210\227.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+### C:
+
+> 前缀表统一右移和减一
+
+```c
+
+int *build_next(char* needle, int len) {
+
+ int *next = (int *)malloc(len * sizeof(int));
+ assert(next); // 确保分配成功
+
+ // 初始化next数组
+ next[0] = -1; // next[0] 设置为 -1,表示没有有效前缀匹配
+ if (len <= 1) { // 如果模式串长度小于等于 1,直接返回
+ return next;
+ }
+ next[1] = 0; // next[1] 设置为 0,表示第一个字符没有公共前后缀
+
+ // 构建next数组, i 从模式串的第三个字符开始, j 指向当前匹配的最长前缀长度
+ int i = 2, j = 0;
+ while (i < len) {
+ if (needle[i - 1] == needle[j]) {
+ j++;
+ next[i] = j;
+ i++;
+ } else if (j > 0) {
+ // 如果不匹配且 j > 0, 回退到次长匹配前缀的长度
+ j = next[j];
+ } else {
+ next[i] = 0;
+ i++;
+ }
+ }
+ return next;
+}
+
+int strStr(char* haystack, char* needle) {
+
+ int needle_len = strlen(needle);
+ int haystack_len = strlen(haystack);
+
+ int *next = build_next(needle, needle_len);
+
+ int i = 0, j = 0; // i 指向主串的当前起始位置, j 指向模式串的当前匹配位置
+ while (i <= haystack_len - needle_len) {
+ if (haystack[i + j] == needle[j]) {
+ j++;
+ if (j == needle_len) {
+ free(next);
+ next = NULL
+ return i;
+ }
+ } else {
+ i += j - next[j]; // 调整主串的起始位置
+ j = j > 0 ? next[j] : 0;
+ }
+ }
+
+ free(next);
+ next = NULL;
+ return -1;
+}
+```
+
diff --git "a/problems/0031.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\216\222\345\210\227.md" "b/problems/0031.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\216\222\345\210\227.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 3cfb673a29..4bbf20fbb8
--- "a/problems/0031.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\216\222\345\210\227.md"
+++ "b/problems/0031.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\216\222\345\210\227.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- +
+ 对应的C++代码如下:
@@ -268,8 +266,4 @@ var nextPermutation = function(nums) {
```
-
对应的C++代码如下:
@@ -268,8 +266,4 @@ var nextPermutation = function(nums) {
```
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0034.\345\234\250\346\216\222\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\344\270\255\346\237\245\346\211\276\345\205\203\347\264\240\347\232\204\347\254\254\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\222\214\346\234\200\345\220\216\344\270\200\344\270\252\344\275\215\347\275\256.md" "b/problems/0034.\345\234\250\346\216\222\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\344\270\255\346\237\245\346\211\276\345\205\203\347\264\240\347\232\204\347\254\254\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\222\214\346\234\200\345\220\216\344\270\200\344\270\252\344\275\215\347\275\256.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 22936fef13..37248e4819
--- "a/problems/0034.\345\234\250\346\216\222\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\344\270\255\346\237\245\346\211\276\345\205\203\347\264\240\347\232\204\347\254\254\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\222\214\346\234\200\345\220\216\344\270\200\344\270\252\344\275\215\347\275\256.md"
+++ "b/problems/0034.\345\234\250\346\216\222\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\344\270\255\346\237\245\346\211\276\345\205\203\347\264\240\347\232\204\347\254\254\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\222\214\346\234\200\345\220\216\344\270\200\344\270\252\344\275\215\347\275\256.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0034.\345\234\250\346\216\222\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\344\270\255\346\237\245\346\211\276\345\205\203\347\264\240\347\232\204\347\254\254\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\222\214\346\234\200\345\220\216\344\270\200\344\270\252\344\275\215\347\275\256.md" "b/problems/0034.\345\234\250\346\216\222\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\344\270\255\346\237\245\346\211\276\345\205\203\347\264\240\347\232\204\347\254\254\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\222\214\346\234\200\345\220\216\344\270\200\344\270\252\344\275\215\347\275\256.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 22936fef13..37248e4819
--- "a/problems/0034.\345\234\250\346\216\222\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\344\270\255\346\237\245\346\211\276\345\205\203\347\264\240\347\232\204\347\254\254\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\222\214\346\234\200\345\220\216\344\270\200\344\270\252\344\275\215\347\275\256.md"
+++ "b/problems/0034.\345\234\250\346\216\222\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\344\270\255\346\237\245\346\211\276\345\205\203\347\264\240\347\232\204\347\254\254\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\222\214\346\234\200\345\220\216\344\270\200\344\270\252\344\275\215\347\275\256.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0035.\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\217\222\345\205\245\344\275\215\347\275\256.md" "b/problems/0035.\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\217\222\345\205\245\344\275\215\347\275\256.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 80b7e40e4a..b48910eef7
--- "a/problems/0035.\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\217\222\345\205\245\344\275\215\347\275\256.md"
+++ "b/problems/0035.\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\217\222\345\205\245\344\275\215\347\275\256.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0035.\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\217\222\345\205\245\344\275\215\347\275\256.md" "b/problems/0035.\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\217\222\345\205\245\344\275\215\347\275\256.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 80b7e40e4a..b48910eef7
--- "a/problems/0035.\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\217\222\345\205\245\344\275\215\347\275\256.md"
+++ "b/problems/0035.\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\217\222\345\205\245\344\275\215\347\275\256.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0037.\350\247\243\346\225\260\347\213\254.md" "b/problems/0037.\350\247\243\346\225\260\347\213\254.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index d96e59dfeb..204f0cc092
--- "a/problems/0037.\350\247\243\346\225\260\347\213\254.md"
+++ "b/problems/0037.\350\247\243\346\225\260\347\213\254.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0037.\350\247\243\346\225\260\347\213\254.md" "b/problems/0037.\350\247\243\346\225\260\347\213\254.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index d96e59dfeb..204f0cc092
--- "a/problems/0037.\350\247\243\346\225\260\347\213\254.md"
+++ "b/problems/0037.\350\247\243\346\225\260\347\213\254.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0039.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214.md" "b/problems/0039.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 81558cc12c..d8dac0b45b
--- "a/problems/0039.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214.md"
+++ "b/problems/0039.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0039.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214.md" "b/problems/0039.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 81558cc12c..d8dac0b45b
--- "a/problems/0039.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214.md"
+++ "b/problems/0039.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0040.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214II.md" "b/problems/0040.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 994b04b82f..0d3972662f
--- "a/problems/0040.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0040.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214II.md"
@@ -1,12 +1,8 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0040.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214II.md" "b/problems/0040.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 994b04b82f..0d3972662f
--- "a/problems/0040.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0040.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214II.md"
@@ -1,12 +1,8 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0042.\346\216\245\351\233\250\346\260\264.md" "b/problems/0042.\346\216\245\351\233\250\346\260\264.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 73d787b13c..c208637b2f
--- "a/problems/0042.\346\216\245\351\233\250\346\260\264.md"
+++ "b/problems/0042.\346\216\245\351\233\250\346\260\264.md"
@@ -1,13 +1,10 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0042.\346\216\245\351\233\250\346\260\264.md" "b/problems/0042.\346\216\245\351\233\250\346\260\264.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 73d787b13c..c208637b2f
--- "a/problems/0042.\346\216\245\351\233\250\346\260\264.md"
+++ "b/problems/0042.\346\216\245\351\233\250\346\260\264.md"
@@ -1,13 +1,10 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0045.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217II.md" "b/problems/0045.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index d290f55e80..c20cdc65e6
--- "a/problems/0045.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0045.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217II.md"
@@ -1,10 +1,8 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0045.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217II.md" "b/problems/0045.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index d290f55e80..c20cdc65e6
--- "a/problems/0045.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0045.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217II.md"
@@ -1,10 +1,8 @@
- -
-
-
- -
+
diff --git "a/problems/0046.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227.md" "b/problems/0046.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 15e6ae162a..356f51b5a8
--- "a/problems/0046.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227.md"
+++ "b/problems/0046.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+
diff --git "a/problems/0046.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227.md" "b/problems/0046.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 15e6ae162a..356f51b5a8
--- "a/problems/0046.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227.md"
+++ "b/problems/0046.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
+
diff --git "a/problems/0047.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227II.md" "b/problems/0047.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 7f2c363889..5330997a66
--- "a/problems/0047.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0047.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227II.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-
-
+
diff --git "a/problems/0047.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227II.md" "b/problems/0047.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 7f2c363889..5330997a66
--- "a/problems/0047.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0047.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227II.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0051.N\347\232\207\345\220\216.md" "b/problems/0051.N\347\232\207\345\220\216.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 1e1085401d..d06d7798e8
--- "a/problems/0051.N\347\232\207\345\220\216.md"
+++ "b/problems/0051.N\347\232\207\345\220\216.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0051.N\347\232\207\345\220\216.md" "b/problems/0051.N\347\232\207\345\220\216.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 1e1085401d..d06d7798e8
--- "a/problems/0051.N\347\232\207\345\220\216.md"
+++ "b/problems/0051.N\347\232\207\345\220\216.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0052.N\347\232\207\345\220\216II.md" "b/problems/0052.N\347\232\207\345\220\216II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 29c2b58818..6c6650ad00
--- "a/problems/0052.N\347\232\207\345\220\216II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0052.N\347\232\207\345\220\216II.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0052.N\347\232\207\345\220\216II.md" "b/problems/0052.N\347\232\207\345\220\216II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 29c2b58818..6c6650ad00
--- "a/problems/0052.N\347\232\207\345\220\216II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0052.N\347\232\207\345\220\216II.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214.md" "b/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 74ff2ca40d..84bb5f6663
--- "a/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214.md"
+++ "b/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214.md" "b/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 74ff2ca40d..84bb5f6663
--- "a/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214.md"
+++ "b/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md" "b/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 70ad7a8482..ba44a36104
--- "a/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md"
+++ "b/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md" "b/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 70ad7a8482..ba44a36104
--- "a/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md"
+++ "b/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0054.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265.md" "b/problems/0054.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 85e6a9364b..8b700c1fe8
--- "a/problems/0054.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265.md"
+++ "b/problems/0054.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0054.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265.md" "b/problems/0054.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 85e6a9364b..8b700c1fe8
--- "a/problems/0054.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265.md"
+++ "b/problems/0054.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0055.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217.md" "b/problems/0055.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 086fd64f5e..513fc2e340
--- "a/problems/0055.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217.md"
+++ "b/problems/0055.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0055.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217.md" "b/problems/0055.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 086fd64f5e..513fc2e340
--- "a/problems/0055.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217.md"
+++ "b/problems/0055.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0056.\345\220\210\345\271\266\345\214\272\351\227\264.md" "b/problems/0056.\345\220\210\345\271\266\345\214\272\351\227\264.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 122e783a27..24a97f6c5a
--- "a/problems/0056.\345\220\210\345\271\266\345\214\272\351\227\264.md"
+++ "b/problems/0056.\345\220\210\345\271\266\345\214\272\351\227\264.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0056.\345\220\210\345\271\266\345\214\272\351\227\264.md" "b/problems/0056.\345\220\210\345\271\266\345\214\272\351\227\264.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 122e783a27..24a97f6c5a
--- "a/problems/0056.\345\220\210\345\271\266\345\214\272\351\227\264.md"
+++ "b/problems/0056.\345\220\210\345\271\266\345\214\272\351\227\264.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
-
diff --git "a/problems/0059.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265II.md" "b/problems/0059.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 7f73bc488d..927df1c6c1
--- "a/problems/0059.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0059.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265II.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0059.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265II.md" "b/problems/0059.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 7f73bc488d..927df1c6c1
--- "a/problems/0059.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0059.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265II.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0062.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204.md" "b/problems/0062.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 207a66ee80..ac60767dce
--- "a/problems/0062.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204.md"
+++ "b/problems/0062.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0062.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204.md" "b/problems/0062.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 207a66ee80..ac60767dce
--- "a/problems/0062.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204.md"
+++ "b/problems/0062.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0063.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204II.md" "b/problems/0063.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 8c208ea865..f39afe8455
--- "a/problems/0063.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0063.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204II.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0063.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204II.md" "b/problems/0063.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 8c208ea865..f39afe8455
--- "a/problems/0063.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0063.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204II.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257.md" "b/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 67bbdd7b81..316fbd4f39
--- "a/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257.md"
+++ "b/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257.md" "b/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 67bbdd7b81..316fbd4f39
--- "a/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257.md"
+++ "b/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
+
diff --git "a/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257\345\256\214\345\205\250\350\203\214\345\214\205\347\211\210\346\234\254.md" "b/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257\345\256\214\345\205\250\350\203\214\345\214\205\347\211\210\346\234\254.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 4fa294cfe2..a5435ddd71
--- "a/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257\345\256\214\345\205\250\350\203\214\345\214\205\347\211\210\346\234\254.md"
+++ "b/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257\345\256\214\345\205\250\350\203\214\345\214\205\347\211\210\346\234\254.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+
diff --git "a/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257\345\256\214\345\205\250\350\203\214\345\214\205\347\211\210\346\234\254.md" "b/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257\345\256\214\345\205\250\350\203\214\345\214\205\347\211\210\346\234\254.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 4fa294cfe2..a5435ddd71
--- "a/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257\345\256\214\345\205\250\350\203\214\345\214\205\347\211\210\346\234\254.md"
+++ "b/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257\345\256\214\345\205\250\350\203\214\345\214\205\347\211\210\346\234\254.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0072.\347\274\226\350\276\221\350\267\235\347\246\273.md" "b/problems/0072.\347\274\226\350\276\221\350\267\235\347\246\273.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 777b851cca..c4bcbb4338
--- "a/problems/0072.\347\274\226\350\276\221\350\267\235\347\246\273.md"
+++ "b/problems/0072.\347\274\226\350\276\221\350\267\235\347\246\273.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0072.\347\274\226\350\276\221\350\267\235\347\246\273.md" "b/problems/0072.\347\274\226\350\276\221\350\267\235\347\246\273.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 777b851cca..c4bcbb4338
--- "a/problems/0072.\347\274\226\350\276\221\350\267\235\347\246\273.md"
+++ "b/problems/0072.\347\274\226\350\276\221\350\267\235\347\246\273.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0077.\347\273\204\345\220\210.md" "b/problems/0077.\347\273\204\345\220\210.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 103fb627f5..4c9e97fd47
--- "a/problems/0077.\347\273\204\345\220\210.md"
+++ "b/problems/0077.\347\273\204\345\220\210.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0077.\347\273\204\345\220\210.md" "b/problems/0077.\347\273\204\345\220\210.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 103fb627f5..4c9e97fd47
--- "a/problems/0077.\347\273\204\345\220\210.md"
+++ "b/problems/0077.\347\273\204\345\220\210.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0077.\347\273\204\345\220\210\344\274\230\345\214\226.md" "b/problems/0077.\347\273\204\345\220\210\344\274\230\345\214\226.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 9577d65f3c..8ddc4058cc
--- "a/problems/0077.\347\273\204\345\220\210\344\274\230\345\214\226.md"
+++ "b/problems/0077.\347\273\204\345\220\210\344\274\230\345\214\226.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0077.\347\273\204\345\220\210\344\274\230\345\214\226.md" "b/problems/0077.\347\273\204\345\220\210\344\274\230\345\214\226.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 9577d65f3c..8ddc4058cc
--- "a/problems/0077.\347\273\204\345\220\210\344\274\230\345\214\226.md"
+++ "b/problems/0077.\347\273\204\345\220\210\344\274\230\345\214\226.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0078.\345\255\220\351\233\206.md" "b/problems/0078.\345\255\220\351\233\206.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 06547e3df5..844b8dc2ca
--- "a/problems/0078.\345\255\220\351\233\206.md"
+++ "b/problems/0078.\345\255\220\351\233\206.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0078.\345\255\220\351\233\206.md" "b/problems/0078.\345\255\220\351\233\206.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 06547e3df5..844b8dc2ca
--- "a/problems/0078.\345\255\220\351\233\206.md"
+++ "b/problems/0078.\345\255\220\351\233\206.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0084.\346\237\261\347\212\266\345\233\276\344\270\255\346\234\200\345\244\247\347\232\204\347\237\251\345\275\242.md" "b/problems/0084.\346\237\261\347\212\266\345\233\276\344\270\255\346\234\200\345\244\247\347\232\204\347\237\251\345\275\242.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index b836705ab5..99fb1678e6
--- "a/problems/0084.\346\237\261\347\212\266\345\233\276\344\270\255\346\234\200\345\244\247\347\232\204\347\237\251\345\275\242.md"
+++ "b/problems/0084.\346\237\261\347\212\266\345\233\276\344\270\255\346\234\200\345\244\247\347\232\204\347\237\251\345\275\242.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0084.\346\237\261\347\212\266\345\233\276\344\270\255\346\234\200\345\244\247\347\232\204\347\237\251\345\275\242.md" "b/problems/0084.\346\237\261\347\212\266\345\233\276\344\270\255\346\234\200\345\244\247\347\232\204\347\237\251\345\275\242.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index b836705ab5..99fb1678e6
--- "a/problems/0084.\346\237\261\347\212\266\345\233\276\344\270\255\346\234\200\345\244\247\347\232\204\347\237\251\345\275\242.md"
+++ "b/problems/0084.\346\237\261\347\212\266\345\233\276\344\270\255\346\234\200\345\244\247\347\232\204\347\237\251\345\275\242.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0090.\345\255\220\351\233\206II.md" "b/problems/0090.\345\255\220\351\233\206II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 6d618978a8..2e8945c90f
--- "a/problems/0090.\345\255\220\351\233\206II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0090.\345\255\220\351\233\206II.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0090.\345\255\220\351\233\206II.md" "b/problems/0090.\345\255\220\351\233\206II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 6d618978a8..2e8945c90f
--- "a/problems/0090.\345\255\220\351\233\206II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0090.\345\255\220\351\233\206II.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0093.\345\244\215\345\216\237IP\345\234\260\345\235\200.md" "b/problems/0093.\345\244\215\345\216\237IP\345\234\260\345\235\200.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index c662957a10..6fa732d0c1
--- "a/problems/0093.\345\244\215\345\216\237IP\345\234\260\345\235\200.md"
+++ "b/problems/0093.\345\244\215\345\216\237IP\345\234\260\345\235\200.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0093.\345\244\215\345\216\237IP\345\234\260\345\235\200.md" "b/problems/0093.\345\244\215\345\216\237IP\345\234\260\345\235\200.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index c662957a10..6fa732d0c1
--- "a/problems/0093.\345\244\215\345\216\237IP\345\234\260\345\235\200.md"
+++ "b/problems/0093.\345\244\215\345\216\237IP\345\234\260\345\235\200.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0096.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0096.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 15b99083e0..e5bc2b6b65
--- "a/problems/0096.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0096.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0096.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0096.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 15b99083e0..e5bc2b6b65
--- "a/problems/0096.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0096.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0098.\351\252\214\350\257\201\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0098.\351\252\214\350\257\201\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 88e1628243..990d3c8413
--- "a/problems/0098.\351\252\214\350\257\201\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0098.\351\252\214\350\257\201\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0098.\351\252\214\350\257\201\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0098.\351\252\214\350\257\201\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 88e1628243..990d3c8413
--- "a/problems/0098.\351\252\214\350\257\201\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0098.\351\252\214\350\257\201\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0100.\347\233\270\345\220\214\347\232\204\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0100.\347\233\270\345\220\214\347\232\204\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 56a6c8840f..df1b55a462
--- "a/problems/0100.\347\233\270\345\220\214\347\232\204\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0100.\347\233\270\345\220\214\347\232\204\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0100.\347\233\270\345\220\214\347\232\204\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0100.\347\233\270\345\220\214\347\232\204\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 56a6c8840f..df1b55a462
--- "a/problems/0100.\347\233\270\345\220\214\347\232\204\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0100.\347\233\270\345\220\214\347\232\204\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0101.\345\257\271\347\247\260\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0101.\345\257\271\347\247\260\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 8442f0ab9e..24e9e2684e
--- "a/problems/0101.\345\257\271\347\247\260\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0101.\345\257\271\347\247\260\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0101.\345\257\271\347\247\260\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0101.\345\257\271\347\247\260\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 8442f0ab9e..24e9e2684e
--- "a/problems/0101.\345\257\271\347\247\260\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0101.\345\257\271\347\247\260\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
+
diff --git "a/problems/0102.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\345\261\202\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206.md" "b/problems/0102.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\345\261\202\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 4411b5609f..819153be97
--- "a/problems/0102.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\345\261\202\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206.md"
+++ "b/problems/0102.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\345\261\202\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-
-
+
diff --git "a/problems/0102.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\345\261\202\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206.md" "b/problems/0102.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\345\261\202\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 4411b5609f..819153be97
--- "a/problems/0102.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\345\261\202\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206.md"
+++ "b/problems/0102.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\345\261\202\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0104.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\244\247\346\267\261\345\272\246.md" "b/problems/0104.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\244\247\346\267\261\345\272\246.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 1f55f197e5..52d6d0e5fd
--- "a/problems/0104.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\244\247\346\267\261\345\272\246.md"
+++ "b/problems/0104.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\244\247\346\267\261\345\272\246.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0104.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\244\247\346\267\261\345\272\246.md" "b/problems/0104.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\244\247\346\267\261\345\272\246.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 1f55f197e5..52d6d0e5fd
--- "a/problems/0104.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\244\247\346\267\261\345\272\246.md"
+++ "b/problems/0104.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\244\247\346\267\261\345\272\246.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0106.\344\273\216\344\270\255\345\272\217\344\270\216\345\220\216\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206\345\272\217\345\210\227\346\236\204\351\200\240\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0106.\344\273\216\344\270\255\345\272\217\344\270\216\345\220\216\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206\345\272\217\345\210\227\346\236\204\351\200\240\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 0e0ab1d74f..5253325835
--- "a/problems/0106.\344\273\216\344\270\255\345\272\217\344\270\216\345\220\216\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206\345\272\217\345\210\227\346\236\204\351\200\240\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0106.\344\273\216\344\270\255\345\272\217\344\270\216\345\220\216\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206\345\272\217\345\210\227\346\236\204\351\200\240\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0106.\344\273\216\344\270\255\345\272\217\344\270\216\345\220\216\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206\345\272\217\345\210\227\346\236\204\351\200\240\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0106.\344\273\216\344\270\255\345\272\217\344\270\216\345\220\216\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206\345\272\217\345\210\227\346\236\204\351\200\240\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 0e0ab1d74f..5253325835
--- "a/problems/0106.\344\273\216\344\270\255\345\272\217\344\270\216\345\220\216\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206\345\272\217\345\210\227\346\236\204\351\200\240\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0106.\344\273\216\344\270\255\345\272\217\344\270\216\345\220\216\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206\345\272\217\345\210\227\346\236\204\351\200\240\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0108.\345\260\206\346\234\211\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\350\275\254\346\215\242\344\270\272\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0108.\345\260\206\346\234\211\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\350\275\254\346\215\242\344\270\272\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 9fa684cfdf..2df1c2615b
--- "a/problems/0108.\345\260\206\346\234\211\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\350\275\254\346\215\242\344\270\272\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0108.\345\260\206\346\234\211\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\350\275\254\346\215\242\344\270\272\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0108.\345\260\206\346\234\211\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\350\275\254\346\215\242\344\270\272\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0108.\345\260\206\346\234\211\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\350\275\254\346\215\242\344\270\272\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 9fa684cfdf..2df1c2615b
--- "a/problems/0108.\345\260\206\346\234\211\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\350\275\254\346\215\242\344\270\272\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0108.\345\260\206\346\234\211\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\350\275\254\346\215\242\344\270\272\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0110.\345\271\263\350\241\241\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0110.\345\271\263\350\241\241\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 40fdcd143d..d5b100ae80
--- "a/problems/0110.\345\271\263\350\241\241\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0110.\345\271\263\350\241\241\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0110.\345\271\263\350\241\241\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0110.\345\271\263\350\241\241\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 40fdcd143d..d5b100ae80
--- "a/problems/0110.\345\271\263\350\241\241\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0110.\345\271\263\350\241\241\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0111.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\260\217\346\267\261\345\272\246.md" "b/problems/0111.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\260\217\346\267\261\345\272\246.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 6d1632d593..e1ee42657c
--- "a/problems/0111.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\260\217\346\267\261\345\272\246.md"
+++ "b/problems/0111.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\260\217\346\267\261\345\272\246.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0111.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\260\217\346\267\261\345\272\246.md" "b/problems/0111.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\260\217\346\267\261\345\272\246.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 6d1632d593..e1ee42657c
--- "a/problems/0111.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\260\217\346\267\261\345\272\246.md"
+++ "b/problems/0111.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\260\217\346\267\261\345\272\246.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0112.\350\267\257\345\276\204\346\200\273\345\222\214.md" "b/problems/0112.\350\267\257\345\276\204\346\200\273\345\222\214.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index d45be3bd82..73795bcfc9
--- "a/problems/0112.\350\267\257\345\276\204\346\200\273\345\222\214.md"
+++ "b/problems/0112.\350\267\257\345\276\204\346\200\273\345\222\214.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0112.\350\267\257\345\276\204\346\200\273\345\222\214.md" "b/problems/0112.\350\267\257\345\276\204\346\200\273\345\222\214.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index d45be3bd82..73795bcfc9
--- "a/problems/0112.\350\267\257\345\276\204\346\200\273\345\222\214.md"
+++ "b/problems/0112.\350\267\257\345\276\204\346\200\273\345\222\214.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
- -
-
-
- -
+
diff --git "a/problems/0115.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md" "b/problems/0115.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 96ab2583f1..499bf100e2
--- "a/problems/0115.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
+++ "b/problems/0115.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+
diff --git "a/problems/0115.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md" "b/problems/0115.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 96ab2583f1..499bf100e2
--- "a/problems/0115.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
+++ "b/problems/0115.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0116.\345\241\253\345\205\205\346\257\217\344\270\252\350\212\202\347\202\271\347\232\204\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\217\263\344\276\247\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\214\207\351\222\210.md" "b/problems/0116.\345\241\253\345\205\205\346\257\217\344\270\252\350\212\202\347\202\271\347\232\204\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\217\263\344\276\247\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\214\207\351\222\210.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 60ea9210a2..88d3abc93e
--- "a/problems/0116.\345\241\253\345\205\205\346\257\217\344\270\252\350\212\202\347\202\271\347\232\204\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\217\263\344\276\247\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\214\207\351\222\210.md"
+++ "b/problems/0116.\345\241\253\345\205\205\346\257\217\344\270\252\350\212\202\347\202\271\347\232\204\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\217\263\344\276\247\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\214\207\351\222\210.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0116.\345\241\253\345\205\205\346\257\217\344\270\252\350\212\202\347\202\271\347\232\204\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\217\263\344\276\247\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\214\207\351\222\210.md" "b/problems/0116.\345\241\253\345\205\205\346\257\217\344\270\252\350\212\202\347\202\271\347\232\204\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\217\263\344\276\247\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\214\207\351\222\210.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 60ea9210a2..88d3abc93e
--- "a/problems/0116.\345\241\253\345\205\205\346\257\217\344\270\252\350\212\202\347\202\271\347\232\204\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\217\263\344\276\247\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\214\207\351\222\210.md"
+++ "b/problems/0116.\345\241\253\345\205\205\346\257\217\344\270\252\350\212\202\347\202\271\347\232\204\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\217\263\344\276\247\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\214\207\351\222\210.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- +
+ 最关键的点是可以通过上一层递归 搭出来的线,进行本次搭线。
@@ -169,6 +167,56 @@ class Solution {
}
```
+```Java
+// 迭代法
+class Solution {
+ public Node connect(Node root) {
+ if (root == null) {
+ return root;
+ }
+
+ Queue
最关键的点是可以通过上一层递归 搭出来的线,进行本次搭线。
@@ -169,6 +167,56 @@ class Solution {
}
```
+```Java
+// 迭代法
+class Solution {
+ public Node connect(Node root) {
+ if (root == null) {
+ return root;
+ }
+
+ Queue -
+
diff --git "a/problems/0121.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272.md" "b/problems/0121.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index cbdf40e85c..d12cbf2fe2
--- "a/problems/0121.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272.md"
+++ "b/problems/0121.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+
diff --git "a/problems/0121.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272.md" "b/problems/0121.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index cbdf40e85c..d12cbf2fe2
--- "a/problems/0121.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272.md"
+++ "b/problems/0121.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
-
diff --git "a/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II.md" "b/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 69706e369a..0da4241931
--- "a/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II.md" "b/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 69706e369a..0da4241931
--- "a/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md" "b/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 6e08b57c1d..d8cb308b7e
--- "a/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md"
+++ "b/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md" "b/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 6e08b57c1d..d8cb308b7e
--- "a/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md"
+++ "b/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
+
diff --git "a/problems/0123.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272III.md" "b/problems/0123.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272III.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 72dd90426c..063477cb5a
--- "a/problems/0123.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272III.md"
+++ "b/problems/0123.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272III.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+
diff --git "a/problems/0123.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272III.md" "b/problems/0123.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272III.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 72dd90426c..063477cb5a
--- "a/problems/0123.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272III.md"
+++ "b/problems/0123.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272III.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
-
diff --git "a/problems/0127.\345\215\225\350\257\215\346\216\245\351\276\231.md" "b/problems/0127.\345\215\225\350\257\215\346\216\245\351\276\231.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 6f8933101e..0204606056
--- "a/problems/0127.\345\215\225\350\257\215\346\216\245\351\276\231.md"
+++ "b/problems/0127.\345\215\225\350\257\215\346\216\245\351\276\231.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0127.\345\215\225\350\257\215\346\216\245\351\276\231.md" "b/problems/0127.\345\215\225\350\257\215\346\216\245\351\276\231.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 6f8933101e..0204606056
--- "a/problems/0127.\345\215\225\350\257\215\346\216\245\351\276\231.md"
+++ "b/problems/0127.\345\215\225\350\257\215\346\216\245\351\276\231.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0129.\346\261\202\346\240\271\345\210\260\345\217\266\345\255\220\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\225\260\345\255\227\344\271\213\345\222\214.md" "b/problems/0129.\346\261\202\346\240\271\345\210\260\345\217\266\345\255\220\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\225\260\345\255\227\344\271\213\345\222\214.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index ebb36071cf..1568a49469
--- "a/problems/0129.\346\261\202\346\240\271\345\210\260\345\217\266\345\255\220\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\225\260\345\255\227\344\271\213\345\222\214.md"
+++ "b/problems/0129.\346\261\202\346\240\271\345\210\260\345\217\266\345\255\220\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\225\260\345\255\227\344\271\213\345\222\214.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0129.\346\261\202\346\240\271\345\210\260\345\217\266\345\255\220\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\225\260\345\255\227\344\271\213\345\222\214.md" "b/problems/0129.\346\261\202\346\240\271\345\210\260\345\217\266\345\255\220\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\225\260\345\255\227\344\271\213\345\222\214.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index ebb36071cf..1568a49469
--- "a/problems/0129.\346\261\202\346\240\271\345\210\260\345\217\266\345\255\220\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\225\260\345\255\227\344\271\213\345\222\214.md"
+++ "b/problems/0129.\346\261\202\346\240\271\345\210\260\345\217\266\345\255\220\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\225\260\345\255\227\344\271\213\345\222\214.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- +
+ 代码如下:
@@ -382,8 +380,4 @@ int sumNumbers(struct TreeNode* root){
}
```
-
代码如下:
@@ -382,8 +380,4 @@ int sumNumbers(struct TreeNode* root){
}
```
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0130.\350\242\253\345\233\264\347\273\225\347\232\204\345\214\272\345\237\237.md" "b/problems/0130.\350\242\253\345\233\264\347\273\225\347\232\204\345\214\272\345\237\237.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 1ddaaa7f83..10d6585c4c
--- "a/problems/0130.\350\242\253\345\233\264\347\273\225\347\232\204\345\214\272\345\237\237.md"
+++ "b/problems/0130.\350\242\253\345\233\264\347\273\225\347\232\204\345\214\272\345\237\237.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0130.\350\242\253\345\233\264\347\273\225\347\232\204\345\214\272\345\237\237.md" "b/problems/0130.\350\242\253\345\233\264\347\273\225\347\232\204\345\214\272\345\237\237.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 1ddaaa7f83..10d6585c4c
--- "a/problems/0130.\350\242\253\345\233\264\347\273\225\347\232\204\345\214\272\345\237\237.md"
+++ "b/problems/0130.\350\242\253\345\233\264\347\273\225\347\232\204\345\214\272\345\237\237.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0131.\345\210\206\345\211\262\345\233\236\346\226\207\344\270\262.md" "b/problems/0131.\345\210\206\345\211\262\345\233\236\346\226\207\344\270\262.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index ca342d4bc6..c76f1ce2f1
--- "a/problems/0131.\345\210\206\345\211\262\345\233\236\346\226\207\344\270\262.md"
+++ "b/problems/0131.\345\210\206\345\211\262\345\233\236\346\226\207\344\270\262.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0131.\345\210\206\345\211\262\345\233\236\346\226\207\344\270\262.md" "b/problems/0131.\345\210\206\345\211\262\345\233\236\346\226\207\344\270\262.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index ca342d4bc6..c76f1ce2f1
--- "a/problems/0131.\345\210\206\345\211\262\345\233\236\346\226\207\344\270\262.md"
+++ "b/problems/0131.\345\210\206\345\211\262\345\233\236\346\226\207\344\270\262.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0132.\345\210\206\345\211\262\345\233\236\346\226\207\344\270\262II.md" "b/problems/0132.\345\210\206\345\211\262\345\233\236\346\226\207\344\270\262II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index eb91a1899f..8bbfa4ee10
--- "a/problems/0132.\345\210\206\345\211\262\345\233\236\346\226\207\344\270\262II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0132.\345\210\206\345\211\262\345\233\236\346\226\207\344\270\262II.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0132.\345\210\206\345\211\262\345\233\236\346\226\207\344\270\262II.md" "b/problems/0132.\345\210\206\345\211\262\345\233\236\346\226\207\344\270\262II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index eb91a1899f..8bbfa4ee10
--- "a/problems/0132.\345\210\206\345\211\262\345\233\236\346\226\207\344\270\262II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0132.\345\210\206\345\211\262\345\233\236\346\226\207\344\270\262II.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0134.\345\212\240\346\262\271\347\253\231.md" "b/problems/0134.\345\212\240\346\262\271\347\253\231.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index c093023d5f..5c8b0c3cc8
--- "a/problems/0134.\345\212\240\346\262\271\347\253\231.md"
+++ "b/problems/0134.\345\212\240\346\262\271\347\253\231.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0134.\345\212\240\346\262\271\347\253\231.md" "b/problems/0134.\345\212\240\346\262\271\347\253\231.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index c093023d5f..5c8b0c3cc8
--- "a/problems/0134.\345\212\240\346\262\271\347\253\231.md"
+++ "b/problems/0134.\345\212\240\346\262\271\347\253\231.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0135.\345\210\206\345\217\221\347\263\226\346\236\234.md" "b/problems/0135.\345\210\206\345\217\221\347\263\226\346\236\234.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 210f4995dc..9701f0f0c1
--- "a/problems/0135.\345\210\206\345\217\221\347\263\226\346\236\234.md"
+++ "b/problems/0135.\345\210\206\345\217\221\347\263\226\346\236\234.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0135.\345\210\206\345\217\221\347\263\226\346\236\234.md" "b/problems/0135.\345\210\206\345\217\221\347\263\226\346\236\234.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 210f4995dc..9701f0f0c1
--- "a/problems/0135.\345\210\206\345\217\221\347\263\226\346\236\234.md"
+++ "b/problems/0135.\345\210\206\345\217\221\347\263\226\346\236\234.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0139.\345\215\225\350\257\215\346\213\206\345\210\206.md" "b/problems/0139.\345\215\225\350\257\215\346\213\206\345\210\206.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index d93288ae5a..2015cb90c1
--- "a/problems/0139.\345\215\225\350\257\215\346\213\206\345\210\206.md"
+++ "b/problems/0139.\345\215\225\350\257\215\346\213\206\345\210\206.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0139.\345\215\225\350\257\215\346\213\206\345\210\206.md" "b/problems/0139.\345\215\225\350\257\215\346\213\206\345\210\206.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index d93288ae5a..2015cb90c1
--- "a/problems/0139.\345\215\225\350\257\215\346\213\206\345\210\206.md"
+++ "b/problems/0139.\345\215\225\350\257\215\346\213\206\345\210\206.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
-
diff --git "a/problems/0141.\347\216\257\345\275\242\351\223\276\350\241\250.md" "b/problems/0141.\347\216\257\345\275\242\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index b1f42ba979..d3583ba866
--- "a/problems/0141.\347\216\257\345\275\242\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
+++ "b/problems/0141.\347\216\257\345\275\242\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0141.\347\216\257\345\275\242\351\223\276\350\241\250.md" "b/problems/0141.\347\216\257\345\275\242\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index b1f42ba979..d3583ba866
--- "a/problems/0141.\347\216\257\345\275\242\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
+++ "b/problems/0141.\347\216\257\345\275\242\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- +
+ fast和slow各自再走一步, fast和slow就相遇了
@@ -40,7 +38,7 @@ fast和slow各自再走一步, fast和slow就相遇了
动画如下:
-
+
C++代码如下
@@ -159,8 +157,4 @@ function hasCycle(head: ListNode | null): boolean {
-
fast和slow各自再走一步, fast和slow就相遇了
@@ -40,7 +38,7 @@ fast和slow各自再走一步, fast和slow就相遇了
动画如下:
-
+
C++代码如下
@@ -159,8 +157,4 @@ function hasCycle(head: ListNode | null): boolean {
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0142.\347\216\257\345\275\242\351\223\276\350\241\250II.md" "b/problems/0142.\347\216\257\345\275\242\351\223\276\350\241\250II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index a643fd7091..4fd81ef0f5
--- "a/problems/0142.\347\216\257\345\275\242\351\223\276\350\241\250II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0142.\347\216\257\345\275\242\351\223\276\350\241\250II.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0142.\347\216\257\345\275\242\351\223\276\350\241\250II.md" "b/problems/0142.\347\216\257\345\275\242\351\223\276\350\241\250II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index a643fd7091..4fd81ef0f5
--- "a/problems/0142.\347\216\257\345\275\242\351\223\276\350\241\250II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0142.\347\216\257\345\275\242\351\223\276\350\241\250II.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0143.\351\207\215\346\216\222\351\223\276\350\241\250.md" "b/problems/0143.\351\207\215\346\216\222\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 0b3be9a0f1..e7056913ee
--- "a/problems/0143.\351\207\215\346\216\222\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
+++ "b/problems/0143.\351\207\215\346\216\222\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
@@ -1,14 +1,12 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0143.\351\207\215\346\216\222\351\223\276\350\241\250.md" "b/problems/0143.\351\207\215\346\216\222\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 0b3be9a0f1..e7056913ee
--- "a/problems/0143.\351\207\215\346\216\222\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
+++ "b/problems/0143.\351\207\215\346\216\222\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
@@ -1,14 +1,12 @@
- -
-
-
- +
+ 这种方法,比较难,平均切割链表,看上去很简单,真正代码写的时候有很多细节,同时两个链表最后拼装整一个新的链表也有一些细节需要注意!
@@ -338,8 +336,85 @@ class Solution:
return pre
```
### Go
+
+```go
+// 方法一 数组模拟
+/**
+ * Definition for singly-linked list.
+ * type ListNode struct {
+ * Val int
+ * Next *ListNode
+ * }
+ */
+func reorderList(head *ListNode) {
+ vec := make([]*ListNode, 0)
+ cur := head
+ if cur == nil {
+ return
+ }
+ for cur != nil {
+ vec = append(vec, cur)
+ cur = cur.Next
+ }
+ cur = head
+ i := 1
+ j := len(vec) - 1 // i j为前后的双指针
+ count := 0 // 计数,偶数取后面,奇数取前面
+ for i <= j {
+ if count % 2 == 0 {
+ cur.Next = vec[j]
+ j--
+ } else {
+ cur.Next = vec[i]
+ i++
+ }
+ cur = cur.Next
+ count++
+ }
+ cur.Next = nil // 注意结尾
+}
+```
+
+```go
+// 方法二 双向队列模拟
+/**
+ * Definition for singly-linked list.
+ * type ListNode struct {
+ * Val int
+ * Next *ListNode
+ * }
+ */
+func reorderList(head *ListNode) {
+ que := make([]*ListNode, 0)
+ cur := head
+ if cur == nil {
+ return
+ }
+
+ for cur.Next != nil {
+ que = append(que, cur.Next)
+ cur = cur.Next
+ }
+
+ cur = head
+ count := 0 // 计数,偶数取后面,奇数取前面
+ for len(que) > 0 {
+ if count % 2 == 0 {
+ cur.Next = que[len(que)-1]
+ que = que[:len(que)-1]
+ } else {
+ cur.Next = que[0]
+ que = que[1:]
+ }
+ count++
+ cur = cur.Next
+ }
+ cur.Next = nil // 注意结尾
+}
+```
+
```go
-# 方法三 分割链表
+// 方法三 分割链表
func reorderList(head *ListNode) {
var slow=head
var fast=head
@@ -612,7 +687,3 @@ void reorderList(struct ListNode* head){
```
-
这种方法,比较难,平均切割链表,看上去很简单,真正代码写的时候有很多细节,同时两个链表最后拼装整一个新的链表也有一些细节需要注意!
@@ -338,8 +336,85 @@ class Solution:
return pre
```
### Go
+
+```go
+// 方法一 数组模拟
+/**
+ * Definition for singly-linked list.
+ * type ListNode struct {
+ * Val int
+ * Next *ListNode
+ * }
+ */
+func reorderList(head *ListNode) {
+ vec := make([]*ListNode, 0)
+ cur := head
+ if cur == nil {
+ return
+ }
+ for cur != nil {
+ vec = append(vec, cur)
+ cur = cur.Next
+ }
+ cur = head
+ i := 1
+ j := len(vec) - 1 // i j为前后的双指针
+ count := 0 // 计数,偶数取后面,奇数取前面
+ for i <= j {
+ if count % 2 == 0 {
+ cur.Next = vec[j]
+ j--
+ } else {
+ cur.Next = vec[i]
+ i++
+ }
+ cur = cur.Next
+ count++
+ }
+ cur.Next = nil // 注意结尾
+}
+```
+
+```go
+// 方法二 双向队列模拟
+/**
+ * Definition for singly-linked list.
+ * type ListNode struct {
+ * Val int
+ * Next *ListNode
+ * }
+ */
+func reorderList(head *ListNode) {
+ que := make([]*ListNode, 0)
+ cur := head
+ if cur == nil {
+ return
+ }
+
+ for cur.Next != nil {
+ que = append(que, cur.Next)
+ cur = cur.Next
+ }
+
+ cur = head
+ count := 0 // 计数,偶数取后面,奇数取前面
+ for len(que) > 0 {
+ if count % 2 == 0 {
+ cur.Next = que[len(que)-1]
+ que = que[:len(que)-1]
+ } else {
+ cur.Next = que[0]
+ que = que[1:]
+ }
+ count++
+ cur = cur.Next
+ }
+ cur.Next = nil // 注意结尾
+}
+```
+
```go
-# 方法三 分割链表
+// 方法三 分割链表
func reorderList(head *ListNode) {
var slow=head
var fast=head
@@ -612,7 +687,3 @@ void reorderList(struct ListNode* head){
```
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0150.\351\200\206\346\263\242\345\205\260\350\241\250\350\276\276\345\274\217\346\261\202\345\200\274.md" "b/problems/0150.\351\200\206\346\263\242\345\205\260\350\241\250\350\276\276\345\274\217\346\261\202\345\200\274.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 663a68ea5c..de56c51ff7
--- "a/problems/0150.\351\200\206\346\263\242\345\205\260\350\241\250\350\276\276\345\274\217\346\261\202\345\200\274.md"
+++ "b/problems/0150.\351\200\206\346\263\242\345\205\260\350\241\250\350\276\276\345\274\217\346\261\202\345\200\274.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0150.\351\200\206\346\263\242\345\205\260\350\241\250\350\276\276\345\274\217\346\261\202\345\200\274.md" "b/problems/0150.\351\200\206\346\263\242\345\205\260\350\241\250\350\276\276\345\274\217\346\261\202\345\200\274.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 663a68ea5c..de56c51ff7
--- "a/problems/0150.\351\200\206\346\263\242\345\205\260\350\241\250\350\276\276\345\274\217\346\261\202\345\200\274.md"
+++ "b/problems/0150.\351\200\206\346\263\242\345\205\260\350\241\250\350\276\276\345\274\217\346\261\202\345\200\274.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
+### C:
+
+```c
+int str_to_int(char *str) {
+ // string转integer
+ int num = 0, tens = 1;
+ for (int i = strlen(str) - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
+ if (str[i] == '-') {
+ num *= -1;
+ break;
+ }
+ num += (str[i] - '0') * tens;
+ tens *= 10;
+ }
+ return num;
+}
+
+int evalRPN(char** tokens, int tokensSize) {
+
+ int *stack = (int *)malloc(tokensSize * sizeof(int));
+ assert(stack);
+ int stackTop = 0;
+
+ for (int i = 0; i < tokensSize; i++) {
+ char symbol = (tokens[i])[0];
+ if (symbol < '0' && (tokens[i])[1] == '\0') {
+
+ // pop两个数字
+ int num1 = stack[--stackTop];
+ int num2 = stack[--stackTop];
+
+ // 计算结果
+ int result;
+ if (symbol == '+') {
+ result = num1 + num2;
+ } else if (symbol == '-') {
+ result = num2 - num1;
+ } else if (symbol == '/') {
+ result = num2 / num1;
+ } else {
+ result = num1 * num2;
+ }
+
+ // push回stack
+ stack[stackTop++] = result;
+
+ } else {
+
+ // push数字进stack
+ int num = str_to_int(tokens[i]);
+ stack[stackTop++] = num;
+
+ }
+ }
+
+ int result = stack[0];
+ free(stack);
+ return result;
+}
+```
+
diff --git "a/problems/0151.\347\277\273\350\275\254\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262\351\207\214\347\232\204\345\215\225\350\257\215.md" "b/problems/0151.\347\277\273\350\275\254\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262\351\207\214\347\232\204\345\215\225\350\257\215.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 520f17a7ec..b5246a7dbb
--- "a/problems/0151.\347\277\273\350\275\254\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262\351\207\214\347\232\204\345\215\225\350\257\215.md"
+++ "b/problems/0151.\347\277\273\350\275\254\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262\351\207\214\347\232\204\345\215\225\350\257\215.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+### C:
+
+```c
+int str_to_int(char *str) {
+ // string转integer
+ int num = 0, tens = 1;
+ for (int i = strlen(str) - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
+ if (str[i] == '-') {
+ num *= -1;
+ break;
+ }
+ num += (str[i] - '0') * tens;
+ tens *= 10;
+ }
+ return num;
+}
+
+int evalRPN(char** tokens, int tokensSize) {
+
+ int *stack = (int *)malloc(tokensSize * sizeof(int));
+ assert(stack);
+ int stackTop = 0;
+
+ for (int i = 0; i < tokensSize; i++) {
+ char symbol = (tokens[i])[0];
+ if (symbol < '0' && (tokens[i])[1] == '\0') {
+
+ // pop两个数字
+ int num1 = stack[--stackTop];
+ int num2 = stack[--stackTop];
+
+ // 计算结果
+ int result;
+ if (symbol == '+') {
+ result = num1 + num2;
+ } else if (symbol == '-') {
+ result = num2 - num1;
+ } else if (symbol == '/') {
+ result = num2 / num1;
+ } else {
+ result = num1 * num2;
+ }
+
+ // push回stack
+ stack[stackTop++] = result;
+
+ } else {
+
+ // push数字进stack
+ int num = str_to_int(tokens[i]);
+ stack[stackTop++] = num;
+
+ }
+ }
+
+ int result = stack[0];
+ free(stack);
+ return result;
+}
+```
+
diff --git "a/problems/0151.\347\277\273\350\275\254\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262\351\207\214\347\232\204\345\215\225\350\257\215.md" "b/problems/0151.\347\277\273\350\275\254\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262\351\207\214\347\232\204\345\215\225\350\257\215.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 520f17a7ec..b5246a7dbb
--- "a/problems/0151.\347\277\273\350\275\254\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262\351\207\214\347\232\204\345\215\225\350\257\215.md"
+++ "b/problems/0151.\347\277\273\350\275\254\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262\351\207\214\347\232\204\345\215\225\350\257\215.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
+
diff --git "a/problems/0160.\347\233\270\344\272\244\351\223\276\350\241\250.md" "b/problems/0160.\347\233\270\344\272\244\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index bf62ab30b5..cdc58912fe
--- "a/problems/0160.\347\233\270\344\272\244\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
+++ "b/problems/0160.\347\233\270\344\272\244\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
@@ -1,11 +1,5 @@
-
-
+
diff --git "a/problems/0160.\347\233\270\344\272\244\351\223\276\350\241\250.md" "b/problems/0160.\347\233\270\344\272\244\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index bf62ab30b5..cdc58912fe
--- "a/problems/0160.\347\233\270\344\272\244\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
+++ "b/problems/0160.\347\233\270\344\272\244\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
@@ -1,11 +1,5 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0188.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272IV.md" "b/problems/0188.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272IV.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index e4c5c48400..350533d8c8
--- "a/problems/0188.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272IV.md"
+++ "b/problems/0188.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272IV.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0188.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272IV.md" "b/problems/0188.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272IV.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index e4c5c48400..350533d8c8
--- "a/problems/0188.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272IV.md"
+++ "b/problems/0188.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272IV.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
+
+
diff --git "a/problems/0189.\346\227\213\350\275\254\346\225\260\347\273\204.md" "b/problems/0189.\346\227\213\350\275\254\346\225\260\347\273\204.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index d60612e92b..976cbed4d1
--- "a/problems/0189.\346\227\213\350\275\254\346\225\260\347\273\204.md"
+++ "b/problems/0189.\346\227\213\350\275\254\346\225\260\347\273\204.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+
+
diff --git "a/problems/0189.\346\227\213\350\275\254\346\225\260\347\273\204.md" "b/problems/0189.\346\227\213\350\275\254\346\225\260\347\273\204.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index d60612e92b..976cbed4d1
--- "a/problems/0189.\346\227\213\350\275\254\346\225\260\347\273\204.md"
+++ "b/problems/0189.\346\227\213\350\275\254\346\225\260\347\273\204.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
-
diff --git "a/problems/0198.\346\211\223\345\256\266\345\212\253\350\210\215.md" "b/problems/0198.\346\211\223\345\256\266\345\212\253\350\210\215.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index a7bc4c998e..7c0aab8ec0
--- "a/problems/0198.\346\211\223\345\256\266\345\212\253\350\210\215.md"
+++ "b/problems/0198.\346\211\223\345\256\266\345\212\253\350\210\215.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0198.\346\211\223\345\256\266\345\212\253\350\210\215.md" "b/problems/0198.\346\211\223\345\256\266\345\212\253\350\210\215.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index a7bc4c998e..7c0aab8ec0
--- "a/problems/0198.\346\211\223\345\256\266\345\212\253\350\210\215.md"
+++ "b/problems/0198.\346\211\223\345\256\266\345\212\253\350\210\215.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
+
diff --git "a/problems/0200.\345\262\233\345\261\277\346\225\260\351\207\217.\345\271\277\346\220\234\347\211\210.md" "b/problems/0200.\345\262\233\345\261\277\346\225\260\351\207\217.\345\271\277\346\220\234\347\211\210.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 85471f73b5..7ae44b5222
--- "a/problems/0200.\345\262\233\345\261\277\346\225\260\351\207\217.\345\271\277\346\220\234\347\211\210.md"
+++ "b/problems/0200.\345\262\233\345\261\277\346\225\260\351\207\217.\345\271\277\346\220\234\347\211\210.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+
diff --git "a/problems/0200.\345\262\233\345\261\277\346\225\260\351\207\217.\345\271\277\346\220\234\347\211\210.md" "b/problems/0200.\345\262\233\345\261\277\346\225\260\351\207\217.\345\271\277\346\220\234\347\211\210.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 85471f73b5..7ae44b5222
--- "a/problems/0200.\345\262\233\345\261\277\346\225\260\351\207\217.\345\271\277\346\220\234\347\211\210.md"
+++ "b/problems/0200.\345\262\233\345\261\277\346\225\260\351\207\217.\345\271\277\346\220\234\347\211\210.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
```
diff --git "a/problems/0200.\345\262\233\345\261\277\346\225\260\351\207\217.\346\267\261\346\220\234\347\211\210.md" "b/problems/0200.\345\262\233\345\261\277\346\225\260\351\207\217.\346\267\261\346\220\234\347\211\210.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 18442943ad..128007bb62
--- "a/problems/0200.\345\262\233\345\261\277\346\225\260\351\207\217.\346\267\261\346\220\234\347\211\210.md"
+++ "b/problems/0200.\345\262\233\345\261\277\346\225\260\351\207\217.\346\267\261\346\220\234\347\211\210.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
```
diff --git "a/problems/0200.\345\262\233\345\261\277\346\225\260\351\207\217.\346\267\261\346\220\234\347\211\210.md" "b/problems/0200.\345\262\233\345\261\277\346\225\260\351\207\217.\346\267\261\346\220\234\347\211\210.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 18442943ad..128007bb62
--- "a/problems/0200.\345\262\233\345\261\277\346\225\260\351\207\217.\346\267\261\346\220\234\347\211\210.md"
+++ "b/problems/0200.\345\262\233\345\261\277\346\225\260\351\207\217.\346\267\261\346\220\234\347\211\210.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0202.\345\277\253\344\271\220\346\225\260.md" "b/problems/0202.\345\277\253\344\271\220\346\225\260.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 719672a281..fdcadee97c
--- "a/problems/0202.\345\277\253\344\271\220\346\225\260.md"
+++ "b/problems/0202.\345\277\253\344\271\220\346\225\260.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0202.\345\277\253\344\271\220\346\225\260.md" "b/problems/0202.\345\277\253\344\271\220\346\225\260.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 719672a281..fdcadee97c
--- "a/problems/0202.\345\277\253\344\271\220\346\225\260.md"
+++ "b/problems/0202.\345\277\253\344\271\220\346\225\260.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
+
+### Ruby:
+
+```ruby
+# @param {Integer} n
+# @return {Boolean}
+def is_happy(n)
+ @occurred_nums = Set.new
+
+ while true
+ n = next_value(n)
+
+ return true if n == 1
+
+ return false if @occurred_nums.include?(n)
+
+ @occurred_nums << n
+ end
+end
+
+def next_value(n)
+ n.to_s.chars.sum { |char| char.to_i ** 2 }
+end
+```
diff --git "a/problems/0203.\347\247\273\351\231\244\351\223\276\350\241\250\345\205\203\347\264\240.md" "b/problems/0203.\347\247\273\351\231\244\351\223\276\350\241\250\345\205\203\347\264\240.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index d6d7e6c2ef..ffe04a5b07
--- "a/problems/0203.\347\247\273\351\231\244\351\223\276\350\241\250\345\205\203\347\264\240.md"
+++ "b/problems/0203.\347\247\273\351\231\244\351\223\276\350\241\250\345\205\203\347\264\240.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-
-
+
+### Ruby:
+
+```ruby
+# @param {Integer} n
+# @return {Boolean}
+def is_happy(n)
+ @occurred_nums = Set.new
+
+ while true
+ n = next_value(n)
+
+ return true if n == 1
+
+ return false if @occurred_nums.include?(n)
+
+ @occurred_nums << n
+ end
+end
+
+def next_value(n)
+ n.to_s.chars.sum { |char| char.to_i ** 2 }
+end
+```
diff --git "a/problems/0203.\347\247\273\351\231\244\351\223\276\350\241\250\345\205\203\347\264\240.md" "b/problems/0203.\347\247\273\351\231\244\351\223\276\350\241\250\345\205\203\347\264\240.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index d6d7e6c2ef..ffe04a5b07
--- "a/problems/0203.\347\247\273\351\231\244\351\223\276\350\241\250\345\205\203\347\264\240.md"
+++ "b/problems/0203.\347\247\273\351\231\244\351\223\276\350\241\250\345\205\203\347\264\240.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
- -
-
-
- -
+```
diff --git "a/problems/0205.\345\220\214\346\236\204\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md" "b/problems/0205.\345\220\214\346\236\204\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index e07ab746d9..ba255e0685
--- "a/problems/0205.\345\220\214\346\236\204\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md"
+++ "b/problems/0205.\345\220\214\346\236\204\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+```
diff --git "a/problems/0205.\345\220\214\346\236\204\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md" "b/problems/0205.\345\220\214\346\236\204\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index e07ab746d9..ba255e0685
--- "a/problems/0205.\345\220\214\346\236\204\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md"
+++ "b/problems/0205.\345\220\214\346\236\204\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0206.\347\277\273\350\275\254\351\223\276\350\241\250.md" "b/problems/0206.\347\277\273\350\275\254\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 5a57939af2..e49037dd2b
--- "a/problems/0206.\347\277\273\350\275\254\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
+++ "b/problems/0206.\347\277\273\350\275\254\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0206.\347\277\273\350\275\254\351\223\276\350\241\250.md" "b/problems/0206.\347\277\273\350\275\254\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 5a57939af2..e49037dd2b
--- "a/problems/0206.\347\277\273\350\275\254\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
+++ "b/problems/0206.\347\277\273\350\275\254\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0207.\350\257\276\347\250\213\350\241\250.md" "b/problems/0207.\350\257\276\347\250\213\350\241\250.md"
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..f992c72b89
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/problems/0207.\350\257\276\347\250\213\350\241\250.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,59 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
+
+拓扑排序指的是一种 解决问题的大体思路, 而具体算法,可能是 广搜 可能是深搜。
+
+大家可能发现 各式各样的解法,纠结哪个是拓扑排序?
+
+只要能在把 有向无环图 进行线性排序 的算法 都可以叫做 拓扑排序。
+
+引用与任务调度,课程安排等等。
+
+
+「拓扑排序」是专门应用于有向图的算法;
+
+把一个 有向无环图 转成 线性的排序 就叫 拓扑排序。
+
+拓扑排序(Kahn 算法,其实就是广度优先遍历的思路)
+
+这道题的做法同样适用于第 210 题。
+
+
+```CPP
+class Solution {
+public:
+ bool canFinish(int numCourses, vector
-
diff --git "a/problems/0207.\350\257\276\347\250\213\350\241\250.md" "b/problems/0207.\350\257\276\347\250\213\350\241\250.md"
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..f992c72b89
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/problems/0207.\350\257\276\347\250\213\350\241\250.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,59 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
+
+拓扑排序指的是一种 解决问题的大体思路, 而具体算法,可能是 广搜 可能是深搜。
+
+大家可能发现 各式各样的解法,纠结哪个是拓扑排序?
+
+只要能在把 有向无环图 进行线性排序 的算法 都可以叫做 拓扑排序。
+
+引用与任务调度,课程安排等等。
+
+
+「拓扑排序」是专门应用于有向图的算法;
+
+把一个 有向无环图 转成 线性的排序 就叫 拓扑排序。
+
+拓扑排序(Kahn 算法,其实就是广度优先遍历的思路)
+
+这道题的做法同样适用于第 210 题。
+
+
+```CPP
+class Solution {
+public:
+ bool canFinish(int numCourses, vector -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0210.\350\257\276\347\250\213\350\241\250II.md" "b/problems/0210.\350\257\276\347\250\213\350\241\250II.md"
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..b0d9fe8a9e
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/problems/0210.\350\257\276\347\250\213\350\241\250II.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
+
+```CPP
+class Solution {
+public:
+ vector
-
diff --git "a/problems/0210.\350\257\276\347\250\213\350\241\250II.md" "b/problems/0210.\350\257\276\347\250\213\350\241\250II.md"
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..b0d9fe8a9e
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/problems/0210.\350\257\276\347\250\213\350\241\250II.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
+
+```CPP
+class Solution {
+public:
+ vector -
-
-
- -
-
diff --git "a/problems/0216.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214III.md" "b/problems/0216.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214III.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index ac28f9fcfa..5ef5b5e67c
--- "a/problems/0216.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214III.md"
+++ "b/problems/0216.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214III.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0216.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214III.md" "b/problems/0216.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214III.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index ac28f9fcfa..5ef5b5e67c
--- "a/problems/0216.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214III.md"
+++ "b/problems/0216.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214III.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0222.\345\256\214\345\205\250\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\350\212\202\347\202\271\344\270\252\346\225\260.md" "b/problems/0222.\345\256\214\345\205\250\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\350\212\202\347\202\271\344\270\252\346\225\260.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index d93d2a3381..eaf4eab2c9
--- "a/problems/0222.\345\256\214\345\205\250\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\350\212\202\347\202\271\344\270\252\346\225\260.md"
+++ "b/problems/0222.\345\256\214\345\205\250\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\350\212\202\347\202\271\344\270\252\346\225\260.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0222.\345\256\214\345\205\250\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\350\212\202\347\202\271\344\270\252\346\225\260.md" "b/problems/0222.\345\256\214\345\205\250\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\350\212\202\347\202\271\344\270\252\346\225\260.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index d93d2a3381..eaf4eab2c9
--- "a/problems/0222.\345\256\214\345\205\250\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\350\212\202\347\202\271\344\270\252\346\225\260.md"
+++ "b/problems/0222.\345\256\214\345\205\250\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\350\212\202\347\202\271\344\270\252\346\225\260.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- +
+ 完全二叉树只有两种情况,情况一:就是满二叉树,情况二:最后一层叶子节点没有满。
@@ -164,10 +162,10 @@ public:
对于情况二,分别递归左孩子,和右孩子,递归到某一深度一定会有左孩子或者右孩子为满二叉树,然后依然可以按照情况1来计算。
完全二叉树(一)如图:
-
+
完全二叉树(二)如图:
-
+
可以看出如果整个树不是满二叉树,就递归其左右孩子,直到遇到满二叉树为止,用公式计算这个子树(满二叉树)的节点数量。
@@ -175,15 +173,15 @@ public:
在完全二叉树中,如果递归向左遍历的深度等于递归向右遍历的深度,那说明就是满二叉树。如图:
-
+
在完全二叉树中,如果递归向左遍历的深度不等于递归向右遍历的深度,则说明不是满二叉树,如图:
-
+
那有录友说了,这种情况,递归向左遍历的深度等于递归向右遍历的深度,但也不是满二叉树,如题:
-
+
如果这么想,大家就是对 完全二叉树理解有误区了,**以上这棵二叉树,它根本就不是一个完全二叉树**!
@@ -893,8 +891,4 @@ public int CountNodes(TreeNode root)
}
```
-
完全二叉树只有两种情况,情况一:就是满二叉树,情况二:最后一层叶子节点没有满。
@@ -164,10 +162,10 @@ public:
对于情况二,分别递归左孩子,和右孩子,递归到某一深度一定会有左孩子或者右孩子为满二叉树,然后依然可以按照情况1来计算。
完全二叉树(一)如图:
-
+
完全二叉树(二)如图:
-
+
可以看出如果整个树不是满二叉树,就递归其左右孩子,直到遇到满二叉树为止,用公式计算这个子树(满二叉树)的节点数量。
@@ -175,15 +173,15 @@ public:
在完全二叉树中,如果递归向左遍历的深度等于递归向右遍历的深度,那说明就是满二叉树。如图:
-
+
在完全二叉树中,如果递归向左遍历的深度不等于递归向右遍历的深度,则说明不是满二叉树,如图:
-
+
那有录友说了,这种情况,递归向左遍历的深度等于递归向右遍历的深度,但也不是满二叉树,如题:
-
+
如果这么想,大家就是对 完全二叉树理解有误区了,**以上这棵二叉树,它根本就不是一个完全二叉树**!
@@ -893,8 +891,4 @@ public int CountNodes(TreeNode root)
}
```
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0225.\347\224\250\351\230\237\345\210\227\345\256\236\347\216\260\346\240\210.md" "b/problems/0225.\347\224\250\351\230\237\345\210\227\345\256\236\347\216\260\346\240\210.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 6900e66869..72dfd2aacf
--- "a/problems/0225.\347\224\250\351\230\237\345\210\227\345\256\236\347\216\260\346\240\210.md"
+++ "b/problems/0225.\347\224\250\351\230\237\345\210\227\345\256\236\347\216\260\346\240\210.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0225.\347\224\250\351\230\237\345\210\227\345\256\236\347\216\260\346\240\210.md" "b/problems/0225.\347\224\250\351\230\237\345\210\227\345\256\236\347\216\260\346\240\210.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 6900e66869..72dfd2aacf
--- "a/problems/0225.\347\224\250\351\230\237\345\210\227\345\256\236\347\216\260\346\240\210.md"
+++ "b/problems/0225.\347\224\250\351\230\237\345\210\227\345\256\236\347\216\260\346\240\210.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
+### C:
+
+> C:单队列
+
+```c
+typedef struct Node {
+ int val;
+ struct Node *next;
+} Node_t;
+
+// 用单向链表实现queue
+typedef struct {
+ Node_t *head;
+ Node_t *foot;
+ int size;
+} MyStack;
+
+MyStack* myStackCreate() {
+ MyStack *obj = (MyStack *)malloc(sizeof(MyStack));
+ assert(obj);
+ obj->head = NULL;
+ obj->foot = NULL;
+ obj->size = 0;
+ return obj;
+}
+
+void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x) {
+
+ Node_t *temp = (Node_t *)malloc(sizeof(Node_t));
+ assert(temp);
+ temp->val = x;
+ temp->next = NULL;
+
+ // 添加至queue末尾
+ if (obj->foot) {
+ obj->foot->next = temp;
+ } else {
+ obj->head = temp;
+ }
+ obj->foot = temp;
+ obj->size++;
+}
+
+int myStackPop(MyStack* obj) {
+
+ // 获取末尾元素
+ int target = obj->foot->val;
+
+ if (obj->head == obj->foot) {
+ free(obj->foot);
+ obj->head = NULL;
+ obj->foot = NULL;
+ } else {
+
+ Node_t *prev = obj->head;
+ // 移动至queue尾部节点前一个节点
+ while (prev->next != obj->foot) {
+ prev = prev->next;
+ }
+
+ free(obj->foot);
+ obj->foot = prev;
+ obj->foot->next = NULL;
+ }
+
+ obj->size--;
+ return target;
+}
+
+int myStackTop(MyStack* obj) {
+ return obj->foot->val;
+}
+
+bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj) {
+ return obj->size == 0;
+}
+
+void myStackFree(MyStack* obj) {
+ Node_t *curr = obj->head;
+ while (curr != NULL) {
+ Node_t *temp = curr->next;
+ free(curr);
+ curr = temp;
+ }
+ free(obj);
+}
+
+```
+
diff --git "a/problems/0226.\347\277\273\350\275\254\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0226.\347\277\273\350\275\254\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 8691953a3e..67a1a59338
--- "a/problems/0226.\347\277\273\350\275\254\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0226.\347\277\273\350\275\254\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+### C:
+
+> C:单队列
+
+```c
+typedef struct Node {
+ int val;
+ struct Node *next;
+} Node_t;
+
+// 用单向链表实现queue
+typedef struct {
+ Node_t *head;
+ Node_t *foot;
+ int size;
+} MyStack;
+
+MyStack* myStackCreate() {
+ MyStack *obj = (MyStack *)malloc(sizeof(MyStack));
+ assert(obj);
+ obj->head = NULL;
+ obj->foot = NULL;
+ obj->size = 0;
+ return obj;
+}
+
+void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x) {
+
+ Node_t *temp = (Node_t *)malloc(sizeof(Node_t));
+ assert(temp);
+ temp->val = x;
+ temp->next = NULL;
+
+ // 添加至queue末尾
+ if (obj->foot) {
+ obj->foot->next = temp;
+ } else {
+ obj->head = temp;
+ }
+ obj->foot = temp;
+ obj->size++;
+}
+
+int myStackPop(MyStack* obj) {
+
+ // 获取末尾元素
+ int target = obj->foot->val;
+
+ if (obj->head == obj->foot) {
+ free(obj->foot);
+ obj->head = NULL;
+ obj->foot = NULL;
+ } else {
+
+ Node_t *prev = obj->head;
+ // 移动至queue尾部节点前一个节点
+ while (prev->next != obj->foot) {
+ prev = prev->next;
+ }
+
+ free(obj->foot);
+ obj->foot = prev;
+ obj->foot->next = NULL;
+ }
+
+ obj->size--;
+ return target;
+}
+
+int myStackTop(MyStack* obj) {
+ return obj->foot->val;
+}
+
+bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj) {
+ return obj->size == 0;
+}
+
+void myStackFree(MyStack* obj) {
+ Node_t *curr = obj->head;
+ while (curr != NULL) {
+ Node_t *temp = curr->next;
+ free(curr);
+ curr = temp;
+ }
+ free(obj);
+}
+
+```
+
diff --git "a/problems/0226.\347\277\273\350\275\254\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0226.\347\277\273\350\275\254\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 8691953a3e..67a1a59338
--- "a/problems/0226.\347\277\273\350\275\254\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0226.\347\277\273\350\275\254\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0232.\347\224\250\346\240\210\345\256\236\347\216\260\351\230\237\345\210\227.md" "b/problems/0232.\347\224\250\346\240\210\345\256\236\347\216\260\351\230\237\345\210\227.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 41933ca4ba..56698e023f
--- "a/problems/0232.\347\224\250\346\240\210\345\256\236\347\216\260\351\230\237\345\210\227.md"
+++ "b/problems/0232.\347\224\250\346\240\210\345\256\236\347\216\260\351\230\237\345\210\227.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0232.\347\224\250\346\240\210\345\256\236\347\216\260\351\230\237\345\210\227.md" "b/problems/0232.\347\224\250\346\240\210\345\256\236\347\216\260\351\230\237\345\210\227.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 41933ca4ba..56698e023f
--- "a/problems/0232.\347\224\250\346\240\210\345\256\236\347\216\260\351\230\237\345\210\227.md"
+++ "b/problems/0232.\347\224\250\346\240\210\345\256\236\347\216\260\351\230\237\345\210\227.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0234.\345\233\236\346\226\207\351\223\276\350\241\250.md" "b/problems/0234.\345\233\236\346\226\207\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index fef942fc49..6248861d94
--- "a/problems/0234.\345\233\236\346\226\207\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
+++ "b/problems/0234.\345\233\236\346\226\207\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0234.\345\233\236\346\226\207\351\223\276\350\241\250.md" "b/problems/0234.\345\233\236\346\226\207\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index fef942fc49..6248861d94
--- "a/problems/0234.\345\233\236\346\226\207\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
+++ "b/problems/0234.\345\233\236\346\226\207\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- +
+ 代码如下:
@@ -428,8 +426,4 @@ function reverseList(head: ListNode | null): ListNode | null {
-
代码如下:
@@ -428,8 +426,4 @@ function reverseList(head: ListNode | null): ListNode | null {
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0235.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\350\277\221\345\205\254\345\205\261\347\245\226\345\205\210.md" "b/problems/0235.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\350\277\221\345\205\254\345\205\261\347\245\226\345\205\210.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 2a11f9f4b7..a1fe78d169
--- "a/problems/0235.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\350\277\221\345\205\254\345\205\261\347\245\226\345\205\210.md"
+++ "b/problems/0235.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\350\277\221\345\205\254\345\205\261\347\245\226\345\205\210.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0235.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\350\277\221\345\205\254\345\205\261\347\245\226\345\205\210.md" "b/problems/0235.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\350\277\221\345\205\254\345\205\261\347\245\226\345\205\210.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 2a11f9f4b7..a1fe78d169
--- "a/problems/0235.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\350\277\221\345\205\254\345\205\261\347\245\226\345\205\210.md"
+++ "b/problems/0235.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\350\277\221\345\205\254\345\205\261\347\245\226\345\205\210.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0236.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\350\277\221\345\205\254\345\205\261\347\245\226\345\205\210.md" "b/problems/0236.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\350\277\221\345\205\254\345\205\261\347\245\226\345\205\210.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 049f70c7ae..5044e3ba00
--- "a/problems/0236.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\350\277\221\345\205\254\345\205\261\347\245\226\345\205\210.md"
+++ "b/problems/0236.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\350\277\221\345\205\254\345\205\261\347\245\226\345\205\210.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0236.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\350\277\221\345\205\254\345\205\261\347\245\226\345\205\210.md" "b/problems/0236.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\350\277\221\345\205\254\345\205\261\347\245\226\345\205\210.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 049f70c7ae..5044e3ba00
--- "a/problems/0236.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\350\277\221\345\205\254\345\205\261\347\245\226\345\205\210.md"
+++ "b/problems/0236.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\350\277\221\345\205\254\345\205\261\347\245\226\345\205\210.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0239.\346\273\221\345\212\250\347\252\227\345\217\243\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\200\274.md" "b/problems/0239.\346\273\221\345\212\250\347\252\227\345\217\243\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\200\274.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 19ac12619e..5ea810104d
--- "a/problems/0239.\346\273\221\345\212\250\347\252\227\345\217\243\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\200\274.md"
+++ "b/problems/0239.\346\273\221\345\212\250\347\252\227\345\217\243\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\200\274.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0239.\346\273\221\345\212\250\347\252\227\345\217\243\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\200\274.md" "b/problems/0239.\346\273\221\345\212\250\347\252\227\345\217\243\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\200\274.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 19ac12619e..5ea810104d
--- "a/problems/0239.\346\273\221\345\212\250\347\252\227\345\217\243\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\200\274.md"
+++ "b/problems/0239.\346\273\221\345\212\250\347\252\227\345\217\243\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\200\274.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- +
+ 提示:
@@ -84,7 +82,7 @@ public:
动画如下:
-
+
对于窗口里的元素{2, 3, 5, 1 ,4},单调队列里只维护{5, 4} 就够了,保持单调队列里单调递减,此时队列出口元素就是窗口里最大元素。
@@ -100,7 +98,7 @@ public:
为了更直观的感受到单调队列的工作过程,以题目示例为例,输入: nums = [1,3,-1,-3,5,3,6,7], 和 k = 3,动画如下:
-
+
那么我们用什么数据结构来实现这个单调队列呢?
@@ -267,7 +265,7 @@ class Solution {
//利用双端队列手动实现单调队列
/**
* 用一个单调队列来存储对应的下标,每当窗口滑动的时候,直接取队列的头部指针对应的值放入结果集即可
- * 单调队列类似 (tail -->) 3 --> 2 --> 1 --> 0 (--> head) (右边为头结点,元素存的是下标)
+ * 单调递减队列类似 (head -->) 3 --> 2 --> 1 --> 0 (--> tail) (左边为头结点,元素存的是下标)
*/
class Solution {
public int[] maxSlidingWindow(int[] nums, int k) {
@@ -281,7 +279,7 @@ class Solution {
while(!deque.isEmpty() && deque.peek() < i - k + 1){
deque.poll();
}
- // 2.既然是单调,就要保证每次放进去的数字要比末尾的都大,否则也弹出
+ // 2.维护单调递减队列:新元素若大于队尾元素,则弹出队尾元素,直到满足单调性
while(!deque.isEmpty() && nums[deque.peekLast()] < nums[i]) {
deque.pollLast();
}
@@ -299,7 +297,7 @@ class Solution {
```
### Python:
-
+#### 解法一:使用自定义的单调队列类
```python
from collections import deque
@@ -339,6 +337,35 @@ class Solution:
return result
```
+
+#### 解法二:直接用单调队列
+```python
+from collections import deque
+class Solution:
+ def maxSlidingWindow(self, nums: List[int], k: int) -> List[int]:
+ max_list = [] # 结果集合
+ kept_nums = deque() # 单调队列
+
+ for i in range(len(nums)):
+ update_kept_nums(kept_nums, nums[i]) # 右侧新元素加入
+
+ if i >= k and nums[i - k] == kept_nums[0]: # 左侧旧元素如果等于单调队列头元素,需要移除头元素
+ kept_nums.popleft()
+
+ if i >= k - 1:
+ max_list.append(kept_nums[0])
+
+ return max_list
+
+def update_kept_nums(kept_nums, num): # num 是新加入的元素
+ # 所有小于新元素的队列尾部元素,在新元素出现后,都是没有价值的,都需要被移除
+ while kept_nums and num > kept_nums[-1]:
+ kept_nums.pop()
+
+ kept_nums.append(num)
+
+```
+
### Go:
```go
@@ -401,7 +428,7 @@ func maxSlidingWindow(nums []int, k int) []int {
}
```
-### Javascript:
+### JavaScript:
```javascript
/**
@@ -861,7 +888,36 @@ public:
};
```
-
提示:
@@ -84,7 +82,7 @@ public:
动画如下:
-
+
对于窗口里的元素{2, 3, 5, 1 ,4},单调队列里只维护{5, 4} 就够了,保持单调队列里单调递减,此时队列出口元素就是窗口里最大元素。
@@ -100,7 +98,7 @@ public:
为了更直观的感受到单调队列的工作过程,以题目示例为例,输入: nums = [1,3,-1,-3,5,3,6,7], 和 k = 3,动画如下:
-
+
那么我们用什么数据结构来实现这个单调队列呢?
@@ -267,7 +265,7 @@ class Solution {
//利用双端队列手动实现单调队列
/**
* 用一个单调队列来存储对应的下标,每当窗口滑动的时候,直接取队列的头部指针对应的值放入结果集即可
- * 单调队列类似 (tail -->) 3 --> 2 --> 1 --> 0 (--> head) (右边为头结点,元素存的是下标)
+ * 单调递减队列类似 (head -->) 3 --> 2 --> 1 --> 0 (--> tail) (左边为头结点,元素存的是下标)
*/
class Solution {
public int[] maxSlidingWindow(int[] nums, int k) {
@@ -281,7 +279,7 @@ class Solution {
while(!deque.isEmpty() && deque.peek() < i - k + 1){
deque.poll();
}
- // 2.既然是单调,就要保证每次放进去的数字要比末尾的都大,否则也弹出
+ // 2.维护单调递减队列:新元素若大于队尾元素,则弹出队尾元素,直到满足单调性
while(!deque.isEmpty() && nums[deque.peekLast()] < nums[i]) {
deque.pollLast();
}
@@ -299,7 +297,7 @@ class Solution {
```
### Python:
-
+#### 解法一:使用自定义的单调队列类
```python
from collections import deque
@@ -339,6 +337,35 @@ class Solution:
return result
```
+
+#### 解法二:直接用单调队列
+```python
+from collections import deque
+class Solution:
+ def maxSlidingWindow(self, nums: List[int], k: int) -> List[int]:
+ max_list = [] # 结果集合
+ kept_nums = deque() # 单调队列
+
+ for i in range(len(nums)):
+ update_kept_nums(kept_nums, nums[i]) # 右侧新元素加入
+
+ if i >= k and nums[i - k] == kept_nums[0]: # 左侧旧元素如果等于单调队列头元素,需要移除头元素
+ kept_nums.popleft()
+
+ if i >= k - 1:
+ max_list.append(kept_nums[0])
+
+ return max_list
+
+def update_kept_nums(kept_nums, num): # num 是新加入的元素
+ # 所有小于新元素的队列尾部元素,在新元素出现后,都是没有价值的,都需要被移除
+ while kept_nums and num > kept_nums[-1]:
+ kept_nums.pop()
+
+ kept_nums.append(num)
+
+```
+
### Go:
```go
@@ -401,7 +428,7 @@ func maxSlidingWindow(nums []int, k int) []int {
}
```
-### Javascript:
+### JavaScript:
```javascript
/**
@@ -861,7 +888,36 @@ public:
};
```
- -
+### C
+
+```c
+int* maxSlidingWindow(int* nums, int numsSize, int k, int* returnSize) {
+ *returnSize = numsSize - k + 1;
+ int *res = (int*)malloc((*returnSize) * sizeof(int));
+ assert(res);
+ int *deque = (int*)malloc(numsSize * sizeof(int));
+ assert(deque);
+ int front = 0, rear = 0, idx = 0;
+
+ for (int i = 0 ; i < numsSize ; i++) {
+ while (front < rear && deque[front] <= i - k) {
+ front++;
+ }
+
+ while (front < rear && nums[deque[rear - 1]] <= nums[i]) {
+ rear--;
+ }
+
+ deque[rear++] = i;
+
+ if (i >= k - 1) {
+ res[idx++] = nums[deque[front]];
+ }
+ }
+
+ return res;
+}
+
+```
+
+
diff --git "a/problems/0242.\346\234\211\346\225\210\347\232\204\345\255\227\346\257\215\345\274\202\344\275\215\350\257\215.md" "b/problems/0242.\346\234\211\346\225\210\347\232\204\345\255\227\346\257\215\345\274\202\344\275\215\350\257\215.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 6eed90a73a..0a37ea26cc
--- "a/problems/0242.\346\234\211\346\225\210\347\232\204\345\255\227\346\257\215\345\274\202\344\275\215\350\257\215.md"
+++ "b/problems/0242.\346\234\211\346\225\210\347\232\204\345\255\227\346\257\215\345\274\202\344\275\215\350\257\215.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+### C
+
+```c
+int* maxSlidingWindow(int* nums, int numsSize, int k, int* returnSize) {
+ *returnSize = numsSize - k + 1;
+ int *res = (int*)malloc((*returnSize) * sizeof(int));
+ assert(res);
+ int *deque = (int*)malloc(numsSize * sizeof(int));
+ assert(deque);
+ int front = 0, rear = 0, idx = 0;
+
+ for (int i = 0 ; i < numsSize ; i++) {
+ while (front < rear && deque[front] <= i - k) {
+ front++;
+ }
+
+ while (front < rear && nums[deque[rear - 1]] <= nums[i]) {
+ rear--;
+ }
+
+ deque[rear++] = i;
+
+ if (i >= k - 1) {
+ res[idx++] = nums[deque[front]];
+ }
+ }
+
+ return res;
+}
+
+```
+
+
diff --git "a/problems/0242.\346\234\211\346\225\210\347\232\204\345\255\227\346\257\215\345\274\202\344\275\215\350\257\215.md" "b/problems/0242.\346\234\211\346\225\210\347\232\204\345\255\227\346\257\215\345\274\202\344\275\215\350\257\215.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 6eed90a73a..0a37ea26cc
--- "a/problems/0242.\346\234\211\346\225\210\347\232\204\345\255\227\346\257\215\345\274\202\344\275\215\350\257\215.md"
+++ "b/problems/0242.\346\234\211\346\225\210\347\232\204\345\255\227\346\257\215\345\274\202\344\275\215\350\257\215.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0257.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\211\200\346\234\211\350\267\257\345\276\204.md" "b/problems/0257.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\211\200\346\234\211\350\267\257\345\276\204.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 4c6c92c5b4..4a66c816bc
--- "a/problems/0257.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\211\200\346\234\211\350\267\257\345\276\204.md"
+++ "b/problems/0257.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\211\200\346\234\211\350\267\257\345\276\204.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0257.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\211\200\346\234\211\350\267\257\345\276\204.md" "b/problems/0257.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\211\200\346\234\211\350\267\257\345\276\204.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 4c6c92c5b4..4a66c816bc
--- "a/problems/0257.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\211\200\346\234\211\350\267\257\345\276\204.md"
+++ "b/problems/0257.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\211\200\346\234\211\350\267\257\345\276\204.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0279.\345\256\214\345\205\250\345\271\263\346\226\271\346\225\260.md" "b/problems/0279.\345\256\214\345\205\250\345\271\263\346\226\271\346\225\260.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index a0e62d4800..7c5d7c9c9f
--- "a/problems/0279.\345\256\214\345\205\250\345\271\263\346\226\271\346\225\260.md"
+++ "b/problems/0279.\345\256\214\345\205\250\345\271\263\346\226\271\346\225\260.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0279.\345\256\214\345\205\250\345\271\263\346\226\271\346\225\260.md" "b/problems/0279.\345\256\214\345\205\250\345\271\263\346\226\271\346\225\260.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index a0e62d4800..7c5d7c9c9f
--- "a/problems/0279.\345\256\214\345\205\250\345\271\263\346\226\271\346\225\260.md"
+++ "b/problems/0279.\345\256\214\345\205\250\345\271\263\346\226\271\346\225\260.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
-
diff --git "a/problems/0283.\347\247\273\345\212\250\351\233\266.md" "b/problems/0283.\347\247\273\345\212\250\351\233\266.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index fc708844bd..e25525684e
--- "a/problems/0283.\347\247\273\345\212\250\351\233\266.md"
+++ "b/problems/0283.\347\247\273\345\212\250\351\233\266.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0283.\347\247\273\345\212\250\351\233\266.md" "b/problems/0283.\347\247\273\345\212\250\351\233\266.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index fc708844bd..e25525684e
--- "a/problems/0283.\347\247\273\345\212\250\351\233\266.md"
+++ "b/problems/0283.\347\247\273\345\212\250\351\233\266.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
-
diff --git "a/problems/0300.\346\234\200\351\225\277\344\270\212\345\215\207\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md" "b/problems/0300.\346\234\200\351\225\277\344\270\212\345\215\207\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 64f75291f5..06adfd950d
--- "a/problems/0300.\346\234\200\351\225\277\344\270\212\345\215\207\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
+++ "b/problems/0300.\346\234\200\351\225\277\344\270\212\345\215\207\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0300.\346\234\200\351\225\277\344\270\212\345\215\207\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md" "b/problems/0300.\346\234\200\351\225\277\344\270\212\345\215\207\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 64f75291f5..06adfd950d
--- "a/problems/0300.\346\234\200\351\225\277\344\270\212\345\215\207\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
+++ "b/problems/0300.\346\234\200\351\225\277\344\270\212\345\215\207\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0309.\346\234\200\344\275\263\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\346\227\266\346\234\272\345\220\253\345\206\267\345\206\273\346\234\237.md" "b/problems/0309.\346\234\200\344\275\263\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\346\227\266\346\234\272\345\220\253\345\206\267\345\206\273\346\234\237.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 0eb66fb543..d396e521b3
--- "a/problems/0309.\346\234\200\344\275\263\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\346\227\266\346\234\272\345\220\253\345\206\267\345\206\273\346\234\237.md"
+++ "b/problems/0309.\346\234\200\344\275\263\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\346\227\266\346\234\272\345\220\253\345\206\267\345\206\273\346\234\237.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0309.\346\234\200\344\275\263\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\346\227\266\346\234\272\345\220\253\345\206\267\345\206\273\346\234\237.md" "b/problems/0309.\346\234\200\344\275\263\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\346\227\266\346\234\272\345\220\253\345\206\267\345\206\273\346\234\237.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 0eb66fb543..d396e521b3
--- "a/problems/0309.\346\234\200\344\275\263\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\346\227\266\346\234\272\345\220\253\345\206\267\345\206\273\346\234\237.md"
+++ "b/problems/0309.\346\234\200\344\275\263\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\346\227\266\346\234\272\345\220\253\345\206\267\345\206\273\346\234\237.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0322.\351\233\266\351\222\261\345\205\221\346\215\242.md" "b/problems/0322.\351\233\266\351\222\261\345\205\221\346\215\242.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index eae4ab3ac0..f3a0a07dd9
--- "a/problems/0322.\351\233\266\351\222\261\345\205\221\346\215\242.md"
+++ "b/problems/0322.\351\233\266\351\222\261\345\205\221\346\215\242.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0322.\351\233\266\351\222\261\345\205\221\346\215\242.md" "b/problems/0322.\351\233\266\351\222\261\345\205\221\346\215\242.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index eae4ab3ac0..f3a0a07dd9
--- "a/problems/0322.\351\233\266\351\222\261\345\205\221\346\215\242.md"
+++ "b/problems/0322.\351\233\266\351\222\261\345\205\221\346\215\242.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
-
diff --git "a/problems/0332.\351\207\215\346\226\260\345\256\211\346\216\222\350\241\214\347\250\213.md" "b/problems/0332.\351\207\215\346\226\260\345\256\211\346\216\222\350\241\214\347\250\213.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 036cfc51b5..1168277a8d
--- "a/problems/0332.\351\207\215\346\226\260\345\256\211\346\216\222\350\241\214\347\250\213.md"
+++ "b/problems/0332.\351\207\215\346\226\260\345\256\211\346\216\222\350\241\214\347\250\213.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0332.\351\207\215\346\226\260\345\256\211\346\216\222\350\241\214\347\250\213.md" "b/problems/0332.\351\207\215\346\226\260\345\256\211\346\216\222\350\241\214\347\250\213.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 036cfc51b5..1168277a8d
--- "a/problems/0332.\351\207\215\346\226\260\345\256\211\346\216\222\350\241\214\347\250\213.md"
+++ "b/problems/0332.\351\207\215\346\226\260\345\256\211\346\216\222\350\241\214\347\250\213.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0337.\346\211\223\345\256\266\345\212\253\350\210\215III.md" "b/problems/0337.\346\211\223\345\256\266\345\212\253\350\210\215III.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index f616ec7417..44af86bb4c
--- "a/problems/0337.\346\211\223\345\256\266\345\212\253\350\210\215III.md"
+++ "b/problems/0337.\346\211\223\345\256\266\345\212\253\350\210\215III.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0337.\346\211\223\345\256\266\345\212\253\350\210\215III.md" "b/problems/0337.\346\211\223\345\256\266\345\212\253\350\210\215III.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index f616ec7417..44af86bb4c
--- "a/problems/0337.\346\211\223\345\256\266\345\212\253\350\210\215III.md"
+++ "b/problems/0337.\346\211\223\345\256\266\345\212\253\350\210\215III.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
-
diff --git "a/problems/0343.\346\225\264\346\225\260\346\213\206\345\210\206.md" "b/problems/0343.\346\225\264\346\225\260\346\213\206\345\210\206.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index bbbd5c6379..c9467e361f
--- "a/problems/0343.\346\225\264\346\225\260\346\213\206\345\210\206.md"
+++ "b/problems/0343.\346\225\264\346\225\260\346\213\206\345\210\206.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0343.\346\225\264\346\225\260\346\213\206\345\210\206.md" "b/problems/0343.\346\225\264\346\225\260\346\213\206\345\210\206.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index bbbd5c6379..c9467e361f
--- "a/problems/0343.\346\225\264\346\225\260\346\213\206\345\210\206.md"
+++ "b/problems/0343.\346\225\264\346\225\260\346\213\206\345\210\206.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0344.\345\217\215\350\275\254\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md" "b/problems/0344.\345\217\215\350\275\254\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 44184c53bc..cadb31c97b
--- "a/problems/0344.\345\217\215\350\275\254\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md"
+++ "b/problems/0344.\345\217\215\350\275\254\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0344.\345\217\215\350\275\254\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md" "b/problems/0344.\345\217\215\350\275\254\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 44184c53bc..cadb31c97b
--- "a/problems/0344.\345\217\215\350\275\254\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md"
+++ "b/problems/0344.\345\217\215\350\275\254\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0347.\345\211\215K\344\270\252\351\253\230\351\242\221\345\205\203\347\264\240.md" "b/problems/0347.\345\211\215K\344\270\252\351\253\230\351\242\221\345\205\203\347\264\240.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 93d605f5fe..fa7d6155a5
--- "a/problems/0347.\345\211\215K\344\270\252\351\253\230\351\242\221\345\205\203\347\264\240.md"
+++ "b/problems/0347.\345\211\215K\344\270\252\351\253\230\351\242\221\345\205\203\347\264\240.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0347.\345\211\215K\344\270\252\351\253\230\351\242\221\345\205\203\347\264\240.md" "b/problems/0347.\345\211\215K\344\270\252\351\253\230\351\242\221\345\205\203\347\264\240.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 93d605f5fe..fa7d6155a5
--- "a/problems/0347.\345\211\215K\344\270\252\351\253\230\351\242\221\345\205\203\347\264\240.md"
+++ "b/problems/0347.\345\211\215K\344\270\252\351\253\230\351\242\221\345\205\203\347\264\240.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
+
diff --git "a/problems/0349.\344\270\244\344\270\252\346\225\260\347\273\204\347\232\204\344\272\244\351\233\206.md" "b/problems/0349.\344\270\244\344\270\252\346\225\260\347\273\204\347\232\204\344\272\244\351\233\206.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 9902fff880..77e895da61
--- "a/problems/0349.\344\270\244\344\270\252\346\225\260\347\273\204\347\232\204\344\272\244\351\233\206.md"
+++ "b/problems/0349.\344\270\244\344\270\252\346\225\260\347\273\204\347\232\204\344\272\244\351\233\206.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+
diff --git "a/problems/0349.\344\270\244\344\270\252\346\225\260\347\273\204\347\232\204\344\272\244\351\233\206.md" "b/problems/0349.\344\270\244\344\270\252\346\225\260\347\273\204\347\232\204\344\272\244\351\233\206.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 9902fff880..77e895da61
--- "a/problems/0349.\344\270\244\344\270\252\346\225\260\347\273\204\347\232\204\344\272\244\351\233\206.md"
+++ "b/problems/0349.\344\270\244\344\270\252\346\225\260\347\273\204\347\232\204\344\272\244\351\233\206.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
+
diff --git "a/problems/0376.\346\221\206\345\212\250\345\272\217\345\210\227.md" "b/problems/0376.\346\221\206\345\212\250\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 5c2241c805..1be9cb4178
--- "a/problems/0376.\346\221\206\345\212\250\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
+++ "b/problems/0376.\346\221\206\345\212\250\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+
diff --git "a/problems/0376.\346\221\206\345\212\250\345\272\217\345\210\227.md" "b/problems/0376.\346\221\206\345\212\250\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 5c2241c805..1be9cb4178
--- "a/problems/0376.\346\221\206\345\212\250\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
+++ "b/problems/0376.\346\221\206\345\212\250\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0377.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214\342\205\243.md" "b/problems/0377.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214\342\205\243.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index a840ec9bcc..ab92f24aef
--- "a/problems/0377.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214\342\205\243.md"
+++ "b/problems/0377.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214\342\205\243.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0377.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214\342\205\243.md" "b/problems/0377.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214\342\205\243.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index a840ec9bcc..ab92f24aef
--- "a/problems/0377.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214\342\205\243.md"
+++ "b/problems/0377.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214\342\205\243.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
-
diff --git "a/problems/0383.\350\265\216\351\207\221\344\277\241.md" "b/problems/0383.\350\265\216\351\207\221\344\277\241.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index ff5aafed62..8a2f52ae42
--- "a/problems/0383.\350\265\216\351\207\221\344\277\241.md"
+++ "b/problems/0383.\350\265\216\351\207\221\344\277\241.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0383.\350\265\216\351\207\221\344\277\241.md" "b/problems/0383.\350\265\216\351\207\221\344\277\241.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index ff5aafed62..8a2f52ae42
--- "a/problems/0383.\350\265\216\351\207\221\344\277\241.md"
+++ "b/problems/0383.\350\265\216\351\207\221\344\277\241.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
+
diff --git "a/problems/0392.\345\210\244\346\226\255\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md" "b/problems/0392.\345\210\244\346\226\255\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index ebd567cbb7..bf2d959682
--- "a/problems/0392.\345\210\244\346\226\255\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
+++ "b/problems/0392.\345\210\244\346\226\255\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+
diff --git "a/problems/0392.\345\210\244\346\226\255\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md" "b/problems/0392.\345\210\244\346\226\255\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index ebd567cbb7..bf2d959682
--- "a/problems/0392.\345\210\244\346\226\255\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
+++ "b/problems/0392.\345\210\244\346\226\255\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0404.\345\267\246\345\217\266\345\255\220\344\271\213\345\222\214.md" "b/problems/0404.\345\267\246\345\217\266\345\255\220\344\271\213\345\222\214.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 3d0f5a8abf..10b159b181
--- "a/problems/0404.\345\267\246\345\217\266\345\255\220\344\271\213\345\222\214.md"
+++ "b/problems/0404.\345\267\246\345\217\266\345\255\220\344\271\213\345\222\214.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0404.\345\267\246\345\217\266\345\255\220\344\271\213\345\222\214.md" "b/problems/0404.\345\267\246\345\217\266\345\255\220\344\271\213\345\222\214.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 3d0f5a8abf..10b159b181
--- "a/problems/0404.\345\267\246\345\217\266\345\255\220\344\271\213\345\222\214.md"
+++ "b/problems/0404.\345\267\246\345\217\266\345\255\220\344\271\213\345\222\214.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0406.\346\240\271\346\215\256\350\272\253\351\253\230\351\207\215\345\273\272\351\230\237\345\210\227.md" "b/problems/0406.\346\240\271\346\215\256\350\272\253\351\253\230\351\207\215\345\273\272\351\230\237\345\210\227.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index b0b02c1454..ce9d3bfb4e
--- "a/problems/0406.\346\240\271\346\215\256\350\272\253\351\253\230\351\207\215\345\273\272\351\230\237\345\210\227.md"
+++ "b/problems/0406.\346\240\271\346\215\256\350\272\253\351\253\230\351\207\215\345\273\272\351\230\237\345\210\227.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0406.\346\240\271\346\215\256\350\272\253\351\253\230\351\207\215\345\273\272\351\230\237\345\210\227.md" "b/problems/0406.\346\240\271\346\215\256\350\272\253\351\253\230\351\207\215\345\273\272\351\230\237\345\210\227.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index b0b02c1454..ce9d3bfb4e
--- "a/problems/0406.\346\240\271\346\215\256\350\272\253\351\253\230\351\207\215\345\273\272\351\230\237\345\210\227.md"
+++ "b/problems/0406.\346\240\271\346\215\256\350\272\253\351\253\230\351\207\215\345\273\272\351\230\237\345\210\227.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0416.\345\210\206\345\211\262\347\255\211\345\222\214\345\255\220\351\233\206.md" "b/problems/0416.\345\210\206\345\211\262\347\255\211\345\222\214\345\255\220\351\233\206.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 71e01ae392..75bc5d0e10
--- "a/problems/0416.\345\210\206\345\211\262\347\255\211\345\222\214\345\255\220\351\233\206.md"
+++ "b/problems/0416.\345\210\206\345\211\262\347\255\211\345\222\214\345\255\220\351\233\206.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0416.\345\210\206\345\211\262\347\255\211\345\222\214\345\255\220\351\233\206.md" "b/problems/0416.\345\210\206\345\211\262\347\255\211\345\222\214\345\255\220\351\233\206.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 71e01ae392..75bc5d0e10
--- "a/problems/0416.\345\210\206\345\211\262\347\255\211\345\222\214\345\255\220\351\233\206.md"
+++ "b/problems/0416.\345\210\206\345\211\262\347\255\211\345\222\214\345\255\220\351\233\206.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0417.\345\244\252\345\271\263\346\264\213\345\244\247\350\245\277\346\264\213\346\260\264\346\265\201\351\227\256\351\242\230.md" "b/problems/0417.\345\244\252\345\271\263\346\264\213\345\244\247\350\245\277\346\264\213\346\260\264\346\265\201\351\227\256\351\242\230.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 8fe0f1b426..c9494313a1
--- "a/problems/0417.\345\244\252\345\271\263\346\264\213\345\244\247\350\245\277\346\264\213\346\260\264\346\265\201\351\227\256\351\242\230.md"
+++ "b/problems/0417.\345\244\252\345\271\263\346\264\213\345\244\247\350\245\277\346\264\213\346\260\264\346\265\201\351\227\256\351\242\230.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0417.\345\244\252\345\271\263\346\264\213\345\244\247\350\245\277\346\264\213\346\260\264\346\265\201\351\227\256\351\242\230.md" "b/problems/0417.\345\244\252\345\271\263\346\264\213\345\244\247\350\245\277\346\264\213\346\260\264\346\265\201\351\227\256\351\242\230.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 8fe0f1b426..c9494313a1
--- "a/problems/0417.\345\244\252\345\271\263\346\264\213\345\244\247\350\245\277\346\264\213\346\260\264\346\265\201\351\227\256\351\242\230.md"
+++ "b/problems/0417.\345\244\252\345\271\263\346\264\213\345\244\247\350\245\277\346\264\213\346\260\264\346\265\201\351\227\256\351\242\230.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0435.\346\227\240\351\207\215\345\217\240\345\214\272\351\227\264.md" "b/problems/0435.\346\227\240\351\207\215\345\217\240\345\214\272\351\227\264.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index cf9996ddef..4231a8ee90
--- "a/problems/0435.\346\227\240\351\207\215\345\217\240\345\214\272\351\227\264.md"
+++ "b/problems/0435.\346\227\240\351\207\215\345\217\240\345\214\272\351\227\264.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0435.\346\227\240\351\207\215\345\217\240\345\214\272\351\227\264.md" "b/problems/0435.\346\227\240\351\207\215\345\217\240\345\214\272\351\227\264.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index cf9996ddef..4231a8ee90
--- "a/problems/0435.\346\227\240\351\207\215\345\217\240\345\214\272\351\227\264.md"
+++ "b/problems/0435.\346\227\240\351\207\215\345\217\240\345\214\272\351\227\264.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
+
diff --git "a/problems/0450.\345\210\240\351\231\244\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\350\212\202\347\202\271.md" "b/problems/0450.\345\210\240\351\231\244\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\350\212\202\347\202\271.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 8922a14e14..44575b8aff
--- "a/problems/0450.\345\210\240\351\231\244\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\350\212\202\347\202\271.md"
+++ "b/problems/0450.\345\210\240\351\231\244\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\350\212\202\347\202\271.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+
diff --git "a/problems/0450.\345\210\240\351\231\244\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\350\212\202\347\202\271.md" "b/problems/0450.\345\210\240\351\231\244\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\350\212\202\347\202\271.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 8922a14e14..44575b8aff
--- "a/problems/0450.\345\210\240\351\231\244\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\350\212\202\347\202\271.md"
+++ "b/problems/0450.\345\210\240\351\231\244\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\350\212\202\347\202\271.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
+### Ruby
+> 递归法:
+```ruby
+# @param {TreeNode} root
+# @param {Integer} key
+# @return {TreeNode}
+def delete_node(root, key)
+ return nil if root.nil?
+
+ right = root.right
+ left = root.left
+
+ if root.val == key
+ return right if left.nil?
+ return left if right.nil?
+
+ node = right
+ while node.left
+ node = node.left
+ end
+ node.left = left
+
+ return right
+ end
+
+ if root.val > key
+ root.left = delete_node(left, key)
+ else
+ root.right = delete_node(right, key)
+ end
+
+ return root
+end
+```
diff --git "a/problems/0452.\347\224\250\346\234\200\345\260\221\346\225\260\351\207\217\347\232\204\347\256\255\345\274\225\347\210\206\346\260\224\347\220\203.md" "b/problems/0452.\347\224\250\346\234\200\345\260\221\346\225\260\351\207\217\347\232\204\347\256\255\345\274\225\347\210\206\346\260\224\347\220\203.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index cd57f83b26..76de3f93a2
--- "a/problems/0452.\347\224\250\346\234\200\345\260\221\346\225\260\351\207\217\347\232\204\347\256\255\345\274\225\347\210\206\346\260\224\347\220\203.md"
+++ "b/problems/0452.\347\224\250\346\234\200\345\260\221\346\225\260\351\207\217\347\232\204\347\256\255\345\274\225\347\210\206\346\260\224\347\220\203.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+### Ruby
+> 递归法:
+```ruby
+# @param {TreeNode} root
+# @param {Integer} key
+# @return {TreeNode}
+def delete_node(root, key)
+ return nil if root.nil?
+
+ right = root.right
+ left = root.left
+
+ if root.val == key
+ return right if left.nil?
+ return left if right.nil?
+
+ node = right
+ while node.left
+ node = node.left
+ end
+ node.left = left
+
+ return right
+ end
+
+ if root.val > key
+ root.left = delete_node(left, key)
+ else
+ root.right = delete_node(right, key)
+ end
+
+ return root
+end
+```
diff --git "a/problems/0452.\347\224\250\346\234\200\345\260\221\346\225\260\351\207\217\347\232\204\347\256\255\345\274\225\347\210\206\346\260\224\347\220\203.md" "b/problems/0452.\347\224\250\346\234\200\345\260\221\346\225\260\351\207\217\347\232\204\347\256\255\345\274\225\347\210\206\346\260\224\347\220\203.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index cd57f83b26..76de3f93a2
--- "a/problems/0452.\347\224\250\346\234\200\345\260\221\346\225\260\351\207\217\347\232\204\347\256\255\345\274\225\347\210\206\346\260\224\347\220\203.md"
+++ "b/problems/0452.\347\224\250\346\234\200\345\260\221\346\225\260\351\207\217\347\232\204\347\256\255\345\274\225\347\210\206\346\260\224\347\220\203.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0454.\345\233\233\346\225\260\347\233\270\345\212\240II.md" "b/problems/0454.\345\233\233\346\225\260\347\233\270\345\212\240II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index a0bf84da83..a26071a1fa
--- "a/problems/0454.\345\233\233\346\225\260\347\233\270\345\212\240II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0454.\345\233\233\346\225\260\347\233\270\345\212\240II.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0454.\345\233\233\346\225\260\347\233\270\345\212\240II.md" "b/problems/0454.\345\233\233\346\225\260\347\233\270\345\212\240II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index a0bf84da83..a26071a1fa
--- "a/problems/0454.\345\233\233\346\225\260\347\233\270\345\212\240II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0454.\345\233\233\346\225\260\347\233\270\345\212\240II.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
+
+### Ruby:
+
+```ruby
+# @param {Integer[]} nums1
+# @param {Integer[]} nums2
+# @param {Integer[]} nums3
+# @param {Integer[]} nums4
+# @return {Integer}
+# 新思路:和版主的思路基本相同,只是对后面两个数组的二重循环,用一个方法调用外加一重循环替代,简化了一点。
+# 简单的说,就是把四数和变成了两个两数和的统计(结果放到两个 hash 中),然后再来一次两数和为0.
+# 把四个数分成两组两个数,然后分别计算每组可能的和情况,分别存入 hash 中,key 是 和,value 是 数量;
+# 最后,得到的两个 hash 只需要遍历一次,符合和为零的 value 相乘并加总。
+def four_sum_count(nums1, nums2, nums3, nums4)
+ num_to_count_1 = two_sum_mapping(nums1, nums2)
+ num_to_count_2 = two_sum_mapping(nums3, nums4)
+
+ count_sum = 0
+
+ num_to_count_1.each do |num, count|
+ count_sum += num_to_count_2[-num] * count # 反查另一个 hash,看有没有匹配的,没有的话,hash 默认值为 0,不影响加总;有匹配的,乘积就是可能的情况
+ end
+
+ count_sum
+end
+
+def two_sum_mapping(nums1, nums2)
+ num_to_count = Hash.new(0)
+
+ nums1.each do |num1|
+ nums2.each do |nums2|
+ num_to_count[num1 + nums2] += 1 # 统计和为 num1 + nums2 的有几个
+ end
+ end
+
+ num_to_count
+end
+```
diff --git "a/problems/0455.\345\210\206\345\217\221\351\245\274\345\271\262.md" "b/problems/0455.\345\210\206\345\217\221\351\245\274\345\271\262.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 6ae206dba2..2c38ab9ec1
--- "a/problems/0455.\345\210\206\345\217\221\351\245\274\345\271\262.md"
+++ "b/problems/0455.\345\210\206\345\217\221\351\245\274\345\271\262.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+
+### Ruby:
+
+```ruby
+# @param {Integer[]} nums1
+# @param {Integer[]} nums2
+# @param {Integer[]} nums3
+# @param {Integer[]} nums4
+# @return {Integer}
+# 新思路:和版主的思路基本相同,只是对后面两个数组的二重循环,用一个方法调用外加一重循环替代,简化了一点。
+# 简单的说,就是把四数和变成了两个两数和的统计(结果放到两个 hash 中),然后再来一次两数和为0.
+# 把四个数分成两组两个数,然后分别计算每组可能的和情况,分别存入 hash 中,key 是 和,value 是 数量;
+# 最后,得到的两个 hash 只需要遍历一次,符合和为零的 value 相乘并加总。
+def four_sum_count(nums1, nums2, nums3, nums4)
+ num_to_count_1 = two_sum_mapping(nums1, nums2)
+ num_to_count_2 = two_sum_mapping(nums3, nums4)
+
+ count_sum = 0
+
+ num_to_count_1.each do |num, count|
+ count_sum += num_to_count_2[-num] * count # 反查另一个 hash,看有没有匹配的,没有的话,hash 默认值为 0,不影响加总;有匹配的,乘积就是可能的情况
+ end
+
+ count_sum
+end
+
+def two_sum_mapping(nums1, nums2)
+ num_to_count = Hash.new(0)
+
+ nums1.each do |num1|
+ nums2.each do |nums2|
+ num_to_count[num1 + nums2] += 1 # 统计和为 num1 + nums2 的有几个
+ end
+ end
+
+ num_to_count
+end
+```
diff --git "a/problems/0455.\345\210\206\345\217\221\351\245\274\345\271\262.md" "b/problems/0455.\345\210\206\345\217\221\351\245\274\345\271\262.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 6ae206dba2..2c38ab9ec1
--- "a/problems/0455.\345\210\206\345\217\221\351\245\274\345\271\262.md"
+++ "b/problems/0455.\345\210\206\345\217\221\351\245\274\345\271\262.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0459.\351\207\215\345\244\215\347\232\204\345\255\220\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md" "b/problems/0459.\351\207\215\345\244\215\347\232\204\345\255\220\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 311e3a695e..d164277731
--- "a/problems/0459.\351\207\215\345\244\215\347\232\204\345\255\220\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md"
+++ "b/problems/0459.\351\207\215\345\244\215\347\232\204\345\255\220\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0459.\351\207\215\345\244\215\347\232\204\345\255\220\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md" "b/problems/0459.\351\207\215\345\244\215\347\232\204\345\255\220\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 311e3a695e..d164277731
--- "a/problems/0459.\351\207\215\345\244\215\347\232\204\345\255\220\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md"
+++ "b/problems/0459.\351\207\215\345\244\215\347\232\204\345\255\220\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0463.\345\262\233\345\261\277\347\232\204\345\221\250\351\225\277.md" "b/problems/0463.\345\262\233\345\261\277\347\232\204\345\221\250\351\225\277.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 2e954e30ad..ba60bc4564
--- "a/problems/0463.\345\262\233\345\261\277\347\232\204\345\221\250\351\225\277.md"
+++ "b/problems/0463.\345\262\233\345\261\277\347\232\204\345\221\250\351\225\277.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0463.\345\262\233\345\261\277\347\232\204\345\221\250\351\225\277.md" "b/problems/0463.\345\262\233\345\261\277\347\232\204\345\221\250\351\225\277.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 2e954e30ad..ba60bc4564
--- "a/problems/0463.\345\262\233\345\261\277\347\232\204\345\221\250\351\225\277.md"
+++ "b/problems/0463.\345\262\233\345\261\277\347\232\204\345\221\250\351\225\277.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- +
+ C++代码如下:(详细注释)
@@ -91,7 +89,7 @@ result = 岛屿数量 * 4 - cover * 2;
如图:
-
C++代码如下:(详细注释)
@@ -91,7 +89,7 @@ result = 岛屿数量 * 4 - cover * 2;
如图:
- +
+ C++代码如下:(详细注释)
@@ -432,8 +430,4 @@ function islandPerimeter(grid: number[][]): number {
}
```
-
C++代码如下:(详细注释)
@@ -432,8 +430,4 @@ function islandPerimeter(grid: number[][]): number {
}
```
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0474.\344\270\200\345\222\214\351\233\266.md" "b/problems/0474.\344\270\200\345\222\214\351\233\266.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 904d941e9d..750917de3e
--- "a/problems/0474.\344\270\200\345\222\214\351\233\266.md"
+++ "b/problems/0474.\344\270\200\345\222\214\351\233\266.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0474.\344\270\200\345\222\214\351\233\266.md" "b/problems/0474.\344\270\200\345\222\214\351\233\266.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 904d941e9d..750917de3e
--- "a/problems/0474.\344\270\200\345\222\214\351\233\266.md"
+++ "b/problems/0474.\344\270\200\345\222\214\351\233\266.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
+
diff --git "a/problems/0491.\351\200\222\345\242\236\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md" "b/problems/0491.\351\200\222\345\242\236\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 1aa69a3669..5d37737169
--- "a/problems/0491.\351\200\222\345\242\236\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
+++ "b/problems/0491.\351\200\222\345\242\236\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+
diff --git "a/problems/0491.\351\200\222\345\242\236\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md" "b/problems/0491.\351\200\222\345\242\236\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 1aa69a3669..5d37737169
--- "a/problems/0491.\351\200\222\345\242\236\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
+++ "b/problems/0491.\351\200\222\345\242\236\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0494.\347\233\256\346\240\207\345\222\214.md" "b/problems/0494.\347\233\256\346\240\207\345\222\214.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index e7a05d45c3..b161bc57a8
--- "a/problems/0494.\347\233\256\346\240\207\345\222\214.md"
+++ "b/problems/0494.\347\233\256\346\240\207\345\222\214.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0494.\347\233\256\346\240\207\345\222\214.md" "b/problems/0494.\347\233\256\346\240\207\345\222\214.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index e7a05d45c3..b161bc57a8
--- "a/problems/0494.\347\233\256\346\240\207\345\222\214.md"
+++ "b/problems/0494.\347\233\256\346\240\207\345\222\214.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
+
diff --git "a/problems/0496.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\233\264\345\244\247\345\205\203\347\264\240I.md" "b/problems/0496.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\233\264\345\244\247\345\205\203\347\264\240I.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index d97a3e8482..628149b75d
--- "a/problems/0496.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\233\264\345\244\247\345\205\203\347\264\240I.md"
+++ "b/problems/0496.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\233\264\345\244\247\345\205\203\347\264\240I.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+
diff --git "a/problems/0496.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\233\264\345\244\247\345\205\203\347\264\240I.md" "b/problems/0496.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\233\264\345\244\247\345\205\203\347\264\240I.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index d97a3e8482..628149b75d
--- "a/problems/0496.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\233\264\345\244\247\345\205\203\347\264\240I.md"
+++ "b/problems/0496.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\233\264\345\244\247\345\205\203\347\264\240I.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0501.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\344\274\227\346\225\260.md" "b/problems/0501.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\344\274\227\346\225\260.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 20627d1ad6..457fd61d24
--- "a/problems/0501.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\344\274\227\346\225\260.md"
+++ "b/problems/0501.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\344\274\227\346\225\260.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0501.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\344\274\227\346\225\260.md" "b/problems/0501.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\344\274\227\346\225\260.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 20627d1ad6..457fd61d24
--- "a/problems/0501.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\344\274\227\346\225\260.md"
+++ "b/problems/0501.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\344\274\227\346\225\260.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0503.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\233\264\345\244\247\345\205\203\347\264\240II.md" "b/problems/0503.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\233\264\345\244\247\345\205\203\347\264\240II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 6df83fb208..93924483f3
--- "a/problems/0503.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\233\264\345\244\247\345\205\203\347\264\240II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0503.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\233\264\345\244\247\345\205\203\347\264\240II.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0503.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\233\264\345\244\247\345\205\203\347\264\240II.md" "b/problems/0503.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\233\264\345\244\247\345\205\203\347\264\240II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 6df83fb208..93924483f3
--- "a/problems/0503.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\233\264\345\244\247\345\205\203\347\264\240II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0503.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\233\264\345\244\247\345\205\203\347\264\240II.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0509.\346\226\220\346\263\242\351\202\243\345\245\221\346\225\260.md" "b/problems/0509.\346\226\220\346\263\242\351\202\243\345\245\221\346\225\260.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 71c022bd34..b2e56a613c
--- "a/problems/0509.\346\226\220\346\263\242\351\202\243\345\245\221\346\225\260.md"
+++ "b/problems/0509.\346\226\220\346\263\242\351\202\243\345\245\221\346\225\260.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0509.\346\226\220\346\263\242\351\202\243\345\245\221\346\225\260.md" "b/problems/0509.\346\226\220\346\263\242\351\202\243\345\245\221\346\225\260.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 71c022bd34..b2e56a613c
--- "a/problems/0509.\346\226\220\346\263\242\351\202\243\345\245\221\346\225\260.md"
+++ "b/problems/0509.\346\226\220\346\263\242\351\202\243\345\245\221\346\225\260.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0513.\346\211\276\346\240\221\345\267\246\344\270\213\350\247\222\347\232\204\345\200\274.md" "b/problems/0513.\346\211\276\346\240\221\345\267\246\344\270\213\350\247\222\347\232\204\345\200\274.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index d897bba13a..03f076a2c9
--- "a/problems/0513.\346\211\276\346\240\221\345\267\246\344\270\213\350\247\222\347\232\204\345\200\274.md"
+++ "b/problems/0513.\346\211\276\346\240\221\345\267\246\344\270\213\350\247\222\347\232\204\345\200\274.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0513.\346\211\276\346\240\221\345\267\246\344\270\213\350\247\222\347\232\204\345\200\274.md" "b/problems/0513.\346\211\276\346\240\221\345\267\246\344\270\213\350\247\222\347\232\204\345\200\274.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index d897bba13a..03f076a2c9
--- "a/problems/0513.\346\211\276\346\240\221\345\267\246\344\270\213\350\247\222\347\232\204\345\200\274.md"
+++ "b/problems/0513.\346\211\276\346\240\221\345\267\246\344\270\213\350\247\222\347\232\204\345\200\274.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0516.\346\234\200\351\225\277\345\233\236\346\226\207\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md" "b/problems/0516.\346\234\200\351\225\277\345\233\236\346\226\207\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 44bdec1f19..882c36bb05
--- "a/problems/0516.\346\234\200\351\225\277\345\233\236\346\226\207\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
+++ "b/problems/0516.\346\234\200\351\225\277\345\233\236\346\226\207\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0516.\346\234\200\351\225\277\345\233\236\346\226\207\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md" "b/problems/0516.\346\234\200\351\225\277\345\233\236\346\226\207\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 44bdec1f19..882c36bb05
--- "a/problems/0516.\346\234\200\351\225\277\345\233\236\346\226\207\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
+++ "b/problems/0516.\346\234\200\351\225\277\345\233\236\346\226\207\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0518.\351\233\266\351\222\261\345\205\221\346\215\242II.md" "b/problems/0518.\351\233\266\351\222\261\345\205\221\346\215\242II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index da1c475565..7e4bbb9a81
--- "a/problems/0518.\351\233\266\351\222\261\345\205\221\346\215\242II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0518.\351\233\266\351\222\261\345\205\221\346\215\242II.md"
@@ -1,10 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0518.\351\233\266\351\222\261\345\205\221\346\215\242II.md" "b/problems/0518.\351\233\266\351\222\261\345\205\221\346\215\242II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index da1c475565..7e4bbb9a81
--- "a/problems/0518.\351\233\266\351\222\261\345\205\221\346\215\242II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0518.\351\233\266\351\222\261\345\205\221\346\215\242II.md"
@@ -1,10 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
+
diff --git "a/problems/0530.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\260\217\347\273\235\345\257\271\345\267\256.md" "b/problems/0530.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\260\217\347\273\235\345\257\271\345\267\256.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 82b3f5d4e9..a8eca862ef
--- "a/problems/0530.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\260\217\347\273\235\345\257\271\345\267\256.md"
+++ "b/problems/0530.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\260\217\347\273\235\345\257\271\345\267\256.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+
diff --git "a/problems/0530.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\260\217\347\273\235\345\257\271\345\267\256.md" "b/problems/0530.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\260\217\347\273\235\345\257\271\345\267\256.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 82b3f5d4e9..a8eca862ef
--- "a/problems/0530.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\260\217\347\273\235\345\257\271\345\267\256.md"
+++ "b/problems/0530.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\260\217\347\273\235\345\257\271\345\267\256.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
+
diff --git "a/problems/0538.\346\212\212\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\350\275\254\346\215\242\344\270\272\347\264\257\345\212\240\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0538.\346\212\212\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\350\275\254\346\215\242\344\270\272\347\264\257\345\212\240\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 7fcb5efd32..c4bfeae4b8
--- "a/problems/0538.\346\212\212\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\350\275\254\346\215\242\344\270\272\347\264\257\345\212\240\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0538.\346\212\212\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\350\275\254\346\215\242\344\270\272\347\264\257\345\212\240\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+
diff --git "a/problems/0538.\346\212\212\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\350\275\254\346\215\242\344\270\272\347\264\257\345\212\240\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0538.\346\212\212\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\350\275\254\346\215\242\344\270\272\347\264\257\345\212\240\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 7fcb5efd32..c4bfeae4b8
--- "a/problems/0538.\346\212\212\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\350\275\254\346\215\242\344\270\272\347\264\257\345\212\240\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0538.\346\212\212\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\350\275\254\346\215\242\344\270\272\347\264\257\345\212\240\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0541.\345\217\215\350\275\254\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262II.md" "b/problems/0541.\345\217\215\350\275\254\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 80e662f9dd..d5ad95c112
--- "a/problems/0541.\345\217\215\350\275\254\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0541.\345\217\215\350\275\254\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262II.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0541.\345\217\215\350\275\254\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262II.md" "b/problems/0541.\345\217\215\350\275\254\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 80e662f9dd..d5ad95c112
--- "a/problems/0541.\345\217\215\350\275\254\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0541.\345\217\215\350\275\254\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262II.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- +
+ 那么这里具体反转的逻辑我们要不要使用库函数呢,其实用不用都可以,使用reverse来实现反转也没毛病,毕竟不是解题关键部分。
@@ -282,7 +280,7 @@ class Solution:
return ''.join(res)
```
-### Python3 (v2):
+#### Python3 (v2):
```python
class Solution:
@@ -297,6 +295,21 @@ class Solution:
return s
```
+#### Python3 (v3):
+
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def reverseStr(self, s: str, k: int) -> str:
+ i = 0
+ chars = list(s)
+
+ while i < len(chars):
+ chars[i:i + k] = chars[i:i + k][::-1] # 反转后,更改原值为反转后值
+ i += k * 2
+
+ return ''.join(chars)
+```
+
### Go:
```go
@@ -501,7 +514,4 @@ impl Solution {
}
```
-
那么这里具体反转的逻辑我们要不要使用库函数呢,其实用不用都可以,使用reverse来实现反转也没毛病,毕竟不是解题关键部分。
@@ -282,7 +280,7 @@ class Solution:
return ''.join(res)
```
-### Python3 (v2):
+#### Python3 (v2):
```python
class Solution:
@@ -297,6 +295,21 @@ class Solution:
return s
```
+#### Python3 (v3):
+
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def reverseStr(self, s: str, k: int) -> str:
+ i = 0
+ chars = list(s)
+
+ while i < len(chars):
+ chars[i:i + k] = chars[i:i + k][::-1] # 反转后,更改原值为反转后值
+ i += k * 2
+
+ return ''.join(chars)
+```
+
### Go:
```go
@@ -501,7 +514,4 @@ impl Solution {
}
```
- -
+
diff --git "a/problems/0583.\344\270\244\344\270\252\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262\347\232\204\345\210\240\351\231\244\346\223\215\344\275\234.md" "b/problems/0583.\344\270\244\344\270\252\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262\347\232\204\345\210\240\351\231\244\346\223\215\344\275\234.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 7dbb8ef542..8208d9a1eb
--- "a/problems/0583.\344\270\244\344\270\252\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262\347\232\204\345\210\240\351\231\244\346\223\215\344\275\234.md"
+++ "b/problems/0583.\344\270\244\344\270\252\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262\347\232\204\345\210\240\351\231\244\346\223\215\344\275\234.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+
diff --git "a/problems/0583.\344\270\244\344\270\252\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262\347\232\204\345\210\240\351\231\244\346\223\215\344\275\234.md" "b/problems/0583.\344\270\244\344\270\252\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262\347\232\204\345\210\240\351\231\244\346\223\215\344\275\234.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 7dbb8ef542..8208d9a1eb
--- "a/problems/0583.\344\270\244\344\270\252\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262\347\232\204\345\210\240\351\231\244\346\223\215\344\275\234.md"
+++ "b/problems/0583.\344\270\244\344\270\252\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262\347\232\204\345\210\240\351\231\244\346\223\215\344\275\234.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0617.\345\220\210\345\271\266\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0617.\345\220\210\345\271\266\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 3478a2af5d..3ca5feb9da
--- "a/problems/0617.\345\220\210\345\271\266\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0617.\345\220\210\345\271\266\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0617.\345\220\210\345\271\266\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0617.\345\220\210\345\271\266\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 3478a2af5d..3ca5feb9da
--- "a/problems/0617.\345\220\210\345\271\266\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0617.\345\220\210\345\271\266\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0647.\345\233\236\346\226\207\345\255\220\344\270\262.md" "b/problems/0647.\345\233\236\346\226\207\345\255\220\344\270\262.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index d94d18c5c0..fd2ae43886
--- "a/problems/0647.\345\233\236\346\226\207\345\255\220\344\270\262.md"
+++ "b/problems/0647.\345\233\236\346\226\207\345\255\220\344\270\262.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0647.\345\233\236\346\226\207\345\255\220\344\270\262.md" "b/problems/0647.\345\233\236\346\226\207\345\255\220\344\270\262.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index d94d18c5c0..fd2ae43886
--- "a/problems/0647.\345\233\236\346\226\207\345\255\220\344\270\262.md"
+++ "b/problems/0647.\345\233\236\346\226\207\345\255\220\344\270\262.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0649.Dota2\345\217\202\350\256\256\351\231\242.md" "b/problems/0649.Dota2\345\217\202\350\256\256\351\231\242.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index db6b43df8e..e77070fcf8
--- "a/problems/0649.Dota2\345\217\202\350\256\256\351\231\242.md"
+++ "b/problems/0649.Dota2\345\217\202\350\256\256\351\231\242.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0649.Dota2\345\217\202\350\256\256\351\231\242.md" "b/problems/0649.Dota2\345\217\202\350\256\256\351\231\242.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index db6b43df8e..e77070fcf8
--- "a/problems/0649.Dota2\345\217\202\350\256\256\351\231\242.md"
+++ "b/problems/0649.Dota2\345\217\202\350\256\256\351\231\242.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0654.\346\234\200\345\244\247\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0654.\346\234\200\345\244\247\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index f54558a68c..49ccc9cdea
--- "a/problems/0654.\346\234\200\345\244\247\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0654.\346\234\200\345\244\247\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0654.\346\234\200\345\244\247\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0654.\346\234\200\345\244\247\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index f54558a68c..49ccc9cdea
--- "a/problems/0654.\346\234\200\345\244\247\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0654.\346\234\200\345\244\247\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0657.\346\234\272\345\231\250\344\272\272\350\203\275\345\220\246\350\277\224\345\233\236\345\216\237\347\202\271.md" "b/problems/0657.\346\234\272\345\231\250\344\272\272\350\203\275\345\220\246\350\277\224\345\233\236\345\216\237\347\202\271.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index ef58739122..c1706df4fa
--- "a/problems/0657.\346\234\272\345\231\250\344\272\272\350\203\275\345\220\246\350\277\224\345\233\236\345\216\237\347\202\271.md"
+++ "b/problems/0657.\346\234\272\345\231\250\344\272\272\350\203\275\345\220\246\350\277\224\345\233\236\345\216\237\347\202\271.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0657.\346\234\272\345\231\250\344\272\272\350\203\275\345\220\246\350\277\224\345\233\236\345\216\237\347\202\271.md" "b/problems/0657.\346\234\272\345\231\250\344\272\272\350\203\275\345\220\246\350\277\224\345\233\236\345\216\237\347\202\271.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index ef58739122..c1706df4fa
--- "a/problems/0657.\346\234\272\345\231\250\344\272\272\350\203\275\345\220\246\350\277\224\345\233\236\345\216\237\347\202\271.md"
+++ "b/problems/0657.\346\234\272\345\231\250\344\272\272\350\203\275\345\220\246\350\277\224\345\233\236\345\216\237\347\202\271.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- +
+ C++代码如下:
@@ -181,8 +179,4 @@ var judgeCircle = function (moves) {
```
-
C++代码如下:
@@ -181,8 +179,4 @@ var judgeCircle = function (moves) {
```
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0669.\344\277\256\345\211\252\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0669.\344\277\256\345\211\252\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 916013c52c..dbcc6ed63d
--- "a/problems/0669.\344\277\256\345\211\252\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0669.\344\277\256\345\211\252\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0669.\344\277\256\345\211\252\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0669.\344\277\256\345\211\252\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 916013c52c..dbcc6ed63d
--- "a/problems/0669.\344\277\256\345\211\252\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0669.\344\277\256\345\211\252\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0673.\346\234\200\351\225\277\351\200\222\345\242\236\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227\347\232\204\344\270\252\346\225\260.md" "b/problems/0673.\346\234\200\351\225\277\351\200\222\345\242\236\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227\347\232\204\344\270\252\346\225\260.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 0277f24989..9e61229abb
--- "a/problems/0673.\346\234\200\351\225\277\351\200\222\345\242\236\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227\347\232\204\344\270\252\346\225\260.md"
+++ "b/problems/0673.\346\234\200\351\225\277\351\200\222\345\242\236\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227\347\232\204\344\270\252\346\225\260.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0673.\346\234\200\351\225\277\351\200\222\345\242\236\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227\347\232\204\344\270\252\346\225\260.md" "b/problems/0673.\346\234\200\351\225\277\351\200\222\345\242\236\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227\347\232\204\344\270\252\346\225\260.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 0277f24989..9e61229abb
--- "a/problems/0673.\346\234\200\351\225\277\351\200\222\345\242\236\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227\347\232\204\344\270\252\346\225\260.md"
+++ "b/problems/0673.\346\234\200\351\225\277\351\200\222\345\242\236\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227\347\232\204\344\270\252\346\225\260.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0674.\346\234\200\351\225\277\350\277\236\347\273\255\351\200\222\345\242\236\345\272\217\345\210\227.md" "b/problems/0674.\346\234\200\351\225\277\350\277\236\347\273\255\351\200\222\345\242\236\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 485e321c99..dae64a11ac
--- "a/problems/0674.\346\234\200\351\225\277\350\277\236\347\273\255\351\200\222\345\242\236\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
+++ "b/problems/0674.\346\234\200\351\225\277\350\277\236\347\273\255\351\200\222\345\242\236\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0674.\346\234\200\351\225\277\350\277\236\347\273\255\351\200\222\345\242\236\345\272\217\345\210\227.md" "b/problems/0674.\346\234\200\351\225\277\350\277\236\347\273\255\351\200\222\345\242\236\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 485e321c99..dae64a11ac
--- "a/problems/0674.\346\234\200\351\225\277\350\277\236\347\273\255\351\200\222\345\242\236\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
+++ "b/problems/0674.\346\234\200\351\225\277\350\277\236\347\273\255\351\200\222\345\242\236\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0684.\345\206\227\344\275\231\350\277\236\346\216\245.md" "b/problems/0684.\345\206\227\344\275\231\350\277\236\346\216\245.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index f5e84223b1..2f939d0827
--- "a/problems/0684.\345\206\227\344\275\231\350\277\236\346\216\245.md"
+++ "b/problems/0684.\345\206\227\344\275\231\350\277\236\346\216\245.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0684.\345\206\227\344\275\231\350\277\236\346\216\245.md" "b/problems/0684.\345\206\227\344\275\231\350\277\236\346\216\245.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index f5e84223b1..2f939d0827
--- "a/problems/0684.\345\206\227\344\275\231\350\277\236\346\216\245.md"
+++ "b/problems/0684.\345\206\227\344\275\231\350\277\236\346\216\245.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0685.\345\206\227\344\275\231\350\277\236\346\216\245II.md" "b/problems/0685.\345\206\227\344\275\231\350\277\236\346\216\245II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 0cad5ad581..27161d174c
--- "a/problems/0685.\345\206\227\344\275\231\350\277\236\346\216\245II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0685.\345\206\227\344\275\231\350\277\236\346\216\245II.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0685.\345\206\227\344\275\231\350\277\236\346\216\245II.md" "b/problems/0685.\345\206\227\344\275\231\350\277\236\346\216\245II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 0cad5ad581..27161d174c
--- "a/problems/0685.\345\206\227\344\275\231\350\277\236\346\216\245II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0685.\345\206\227\344\275\231\350\277\236\346\216\245II.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- +
+ 且只有一个节点入度为2,为什么不看出度呢,出度没有意义,一棵树中随便一个父节点就有多个出度。
@@ -48,7 +46,7 @@
如图:
-
且只有一个节点入度为2,为什么不看出度呢,出度没有意义,一棵树中随便一个父节点就有多个出度。
@@ -48,7 +46,7 @@
如图:
- +
+ 首先先计算节点的入度,这里不少录友在计算入度的时候就搞蒙了,分不清 edges[i][j] 表示的都是什么。
@@ -69,7 +67,7 @@ edges[2][0] = 2,edges[2][1] = 3,
搞清楚之后,我们如何统计入度呢?
-即 edges[i][1] 表示的节点都是 箭头指向的节点,即这个几点有一个入度! (如果想统计出度,那么就是 edges[i][0])。
+即 edges[i][1] 表示的节点都是 箭头指向的节点,即这个节点有一个入度! (如果想统计出度,那么就是 edges[i][0])。
所以,统计入度的代码如下:
@@ -108,7 +106,7 @@ if (vec.size() > 0) {
可以定义一个函数,代码如下:
-```
+```cpp
// 在有向图里找到删除的那条边,使其变成树,返回值就是要删除的边
vector
首先先计算节点的入度,这里不少录友在计算入度的时候就搞蒙了,分不清 edges[i][j] 表示的都是什么。
@@ -69,7 +67,7 @@ edges[2][0] = 2,edges[2][1] = 3,
搞清楚之后,我们如何统计入度呢?
-即 edges[i][1] 表示的节点都是 箭头指向的节点,即这个几点有一个入度! (如果想统计出度,那么就是 edges[i][0])。
+即 edges[i][1] 表示的节点都是 箭头指向的节点,即这个节点有一个入度! (如果想统计出度,那么就是 edges[i][0])。
所以,统计入度的代码如下:
@@ -108,7 +106,7 @@ if (vec.size() > 0) {
可以定义一个函数,代码如下:
-```
+```cpp
// 在有向图里找到删除的那条边,使其变成树,返回值就是要删除的边
vector -
diff --git "a/problems/0695.\345\262\233\345\261\277\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\244\247\351\235\242\347\247\257.md" "b/problems/0695.\345\262\233\345\261\277\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\244\247\351\235\242\347\247\257.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 87b1b5bbbb..a63d2b0e06
--- "a/problems/0695.\345\262\233\345\261\277\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\244\247\351\235\242\347\247\257.md"
+++ "b/problems/0695.\345\262\233\345\261\277\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\244\247\351\235\242\347\247\257.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0695.\345\262\233\345\261\277\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\244\247\351\235\242\347\247\257.md" "b/problems/0695.\345\262\233\345\261\277\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\244\247\351\235\242\347\247\257.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 87b1b5bbbb..a63d2b0e06
--- "a/problems/0695.\345\262\233\345\261\277\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\244\247\351\235\242\347\247\257.md"
+++ "b/problems/0695.\345\262\233\345\261\277\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\244\247\351\235\242\347\247\257.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0700.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\346\220\234\347\264\242.md" "b/problems/0700.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\346\220\234\347\264\242.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 9efb1e0519..40777a67a2
--- "a/problems/0700.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\346\220\234\347\264\242.md"
+++ "b/problems/0700.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\346\220\234\347\264\242.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0700.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\346\220\234\347\264\242.md" "b/problems/0700.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\346\220\234\347\264\242.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 9efb1e0519..40777a67a2
--- "a/problems/0700.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\346\220\234\347\264\242.md"
+++ "b/problems/0700.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\346\220\234\347\264\242.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0701.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\346\217\222\345\205\245\346\223\215\344\275\234.md" "b/problems/0701.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\346\217\222\345\205\245\346\223\215\344\275\234.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 98e60d5f5f..fec287449c
--- "a/problems/0701.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\346\217\222\345\205\245\346\223\215\344\275\234.md"
+++ "b/problems/0701.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\346\217\222\345\205\245\346\223\215\344\275\234.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0701.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\346\217\222\345\205\245\346\223\215\344\275\234.md" "b/problems/0701.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\346\217\222\345\205\245\346\223\215\344\275\234.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 98e60d5f5f..fec287449c
--- "a/problems/0701.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\346\217\222\345\205\245\346\223\215\344\275\234.md"
+++ "b/problems/0701.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221\344\270\255\347\232\204\346\217\222\345\205\245\346\223\215\344\275\234.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0704.\344\272\214\345\210\206\346\237\245\346\211\276.md" "b/problems/0704.\344\272\214\345\210\206\346\237\245\346\211\276.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 31e89ae344..e529629492
--- "a/problems/0704.\344\272\214\345\210\206\346\237\245\346\211\276.md"
+++ "b/problems/0704.\344\272\214\345\210\206\346\237\245\346\211\276.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0704.\344\272\214\345\210\206\346\237\245\346\211\276.md" "b/problems/0704.\344\272\214\345\210\206\346\237\245\346\211\276.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 31e89ae344..e529629492
--- "a/problems/0704.\344\272\214\345\210\206\346\237\245\346\211\276.md"
+++ "b/problems/0704.\344\272\214\345\210\206\346\237\245\346\211\276.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0707.\350\256\276\350\256\241\351\223\276\350\241\250.md" "b/problems/0707.\350\256\276\350\256\241\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index fecdbc3cad..72e35f430f
--- "a/problems/0707.\350\256\276\350\256\241\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
+++ "b/problems/0707.\350\256\276\350\256\241\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0707.\350\256\276\350\256\241\351\223\276\350\241\250.md" "b/problems/0707.\350\256\276\350\256\241\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index fecdbc3cad..72e35f430f
--- "a/problems/0707.\350\256\276\350\256\241\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
+++ "b/problems/0707.\350\256\276\350\256\241\351\223\276\350\241\250.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
+
diff --git "a/problems/0714.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272\345\220\253\346\211\213\347\273\255\350\264\271.md" "b/problems/0714.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272\345\220\253\346\211\213\347\273\255\350\264\271.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index db39864908..fb095d7518
--- "a/problems/0714.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272\345\220\253\346\211\213\347\273\255\350\264\271.md"
+++ "b/problems/0714.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272\345\220\253\346\211\213\347\273\255\350\264\271.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+
diff --git "a/problems/0714.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272\345\220\253\346\211\213\347\273\255\350\264\271.md" "b/problems/0714.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272\345\220\253\346\211\213\347\273\255\350\264\271.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index db39864908..fb095d7518
--- "a/problems/0714.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272\345\220\253\346\211\213\347\273\255\350\264\271.md"
+++ "b/problems/0714.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272\345\220\253\346\211\213\347\273\255\350\264\271.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0714.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272\345\220\253\346\211\213\347\273\255\350\264\271\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md" "b/problems/0714.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272\345\220\253\346\211\213\347\273\255\350\264\271\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 7e8e3d7c61..ebed4a0b30
--- "a/problems/0714.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272\345\220\253\346\211\213\347\273\255\350\264\271\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md"
+++ "b/problems/0714.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272\345\220\253\346\211\213\347\273\255\350\264\271\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0714.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272\345\220\253\346\211\213\347\273\255\350\264\271\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md" "b/problems/0714.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272\345\220\253\346\211\213\347\273\255\350\264\271\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 7e8e3d7c61..ebed4a0b30
--- "a/problems/0714.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272\345\220\253\346\211\213\347\273\255\350\264\271\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md"
+++ "b/problems/0714.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272\345\220\253\346\211\213\347\273\255\350\264\271\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
+
diff --git "a/problems/0718.\346\234\200\351\225\277\351\207\215\345\244\215\345\255\220\346\225\260\347\273\204.md" "b/problems/0718.\346\234\200\351\225\277\351\207\215\345\244\215\345\255\220\346\225\260\347\273\204.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 272cf2b2a4..12384a57a7
--- "a/problems/0718.\346\234\200\351\225\277\351\207\215\345\244\215\345\255\220\346\225\260\347\273\204.md"
+++ "b/problems/0718.\346\234\200\351\225\277\351\207\215\345\244\215\345\255\220\346\225\260\347\273\204.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+
diff --git "a/problems/0718.\346\234\200\351\225\277\351\207\215\345\244\215\345\255\220\346\225\260\347\273\204.md" "b/problems/0718.\346\234\200\351\225\277\351\207\215\345\244\215\345\255\220\346\225\260\347\273\204.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 272cf2b2a4..12384a57a7
--- "a/problems/0718.\346\234\200\351\225\277\351\207\215\345\244\215\345\255\220\346\225\260\347\273\204.md"
+++ "b/problems/0718.\346\234\200\351\225\277\351\207\215\345\244\215\345\255\220\346\225\260\347\273\204.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0724.\345\257\273\346\211\276\346\225\260\347\273\204\347\232\204\344\270\255\345\277\203\347\264\242\345\274\225.md" "b/problems/0724.\345\257\273\346\211\276\346\225\260\347\273\204\347\232\204\344\270\255\345\277\203\347\264\242\345\274\225.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 9ed8535e0d..bccca4f2d4
--- "a/problems/0724.\345\257\273\346\211\276\346\225\260\347\273\204\347\232\204\344\270\255\345\277\203\347\264\242\345\274\225.md"
+++ "b/problems/0724.\345\257\273\346\211\276\346\225\260\347\273\204\347\232\204\344\270\255\345\277\203\347\264\242\345\274\225.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0724.\345\257\273\346\211\276\346\225\260\347\273\204\347\232\204\344\270\255\345\277\203\347\264\242\345\274\225.md" "b/problems/0724.\345\257\273\346\211\276\346\225\260\347\273\204\347\232\204\344\270\255\345\277\203\347\264\242\345\274\225.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 9ed8535e0d..bccca4f2d4
--- "a/problems/0724.\345\257\273\346\211\276\346\225\260\347\273\204\347\232\204\344\270\255\345\277\203\347\264\242\345\274\225.md"
+++ "b/problems/0724.\345\257\273\346\211\276\346\225\260\347\273\204\347\232\204\344\270\255\345\277\203\347\264\242\345\274\225.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0738.\345\215\225\350\260\203\351\200\222\345\242\236\347\232\204\346\225\260\345\255\227.md" "b/problems/0738.\345\215\225\350\260\203\351\200\222\345\242\236\347\232\204\346\225\260\345\255\227.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 400dc90daa..17182778ae
--- "a/problems/0738.\345\215\225\350\260\203\351\200\222\345\242\236\347\232\204\346\225\260\345\255\227.md"
+++ "b/problems/0738.\345\215\225\350\260\203\351\200\222\345\242\236\347\232\204\346\225\260\345\255\227.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0738.\345\215\225\350\260\203\351\200\222\345\242\236\347\232\204\346\225\260\345\255\227.md" "b/problems/0738.\345\215\225\350\260\203\351\200\222\345\242\236\347\232\204\346\225\260\345\255\227.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 400dc90daa..17182778ae
--- "a/problems/0738.\345\215\225\350\260\203\351\200\222\345\242\236\347\232\204\346\225\260\345\255\227.md"
+++ "b/problems/0738.\345\215\225\350\260\203\351\200\222\345\242\236\347\232\204\346\225\260\345\255\227.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0739.\346\257\217\346\227\245\346\270\251\345\272\246.md" "b/problems/0739.\346\257\217\346\227\245\346\270\251\345\272\246.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index fdb11c63e3..2ad7e6b79b
--- "a/problems/0739.\346\257\217\346\227\245\346\270\251\345\272\246.md"
+++ "b/problems/0739.\346\257\217\346\227\245\346\270\251\345\272\246.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0739.\346\257\217\346\227\245\346\270\251\345\272\246.md" "b/problems/0739.\346\257\217\346\227\245\346\270\251\345\272\246.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index fdb11c63e3..2ad7e6b79b
--- "a/problems/0739.\346\257\217\346\227\245\346\270\251\345\272\246.md"
+++ "b/problems/0739.\346\257\217\346\227\245\346\270\251\345\272\246.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0743.\347\275\221\347\273\234\345\273\266\350\277\237\346\227\266\351\227\264.md" "b/problems/0743.\347\275\221\347\273\234\345\273\266\350\277\237\346\227\266\351\227\264.md"
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..40b699c18f
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/problems/0743.\347\275\221\347\273\234\345\273\266\350\277\237\346\227\266\351\227\264.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,1230 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
+
+# 743.网络延迟时间
+
+https://leetcode.cn/problems/network-delay-time/description/
+
+
+有 n 个网络节点,标记为 1 到 n。
+
+给你一个列表 times,表示信号经过 有向 边的传递时间。 times[i] = (ui, vi, wi),其中 ui 是源节点,vi 是目标节点, wi 是一个信号从源节点传递到目标节点的时间。
+
+现在,从某个节点 K 发出一个信号。需要多久才能使所有节点都收到信号?如果不能使所有节点收到信号,返回 -1 。
+
+
+
+提示:
+
+* 1 <= k <= n <= 100
+* 1 <= times.length <= 6000
+* times[i].length == 3
+* 1 <= ui, vi <= n
+* ui != vi
+* 0 <= wi <= 100
+* 所有 (ui, vi) 对都 互不相同(即,不含重复边)
+
+# dijkstra 精讲
+
+本题就是求最短路,最短路是图论中的经典问题即:给出一个有向图,一个起点,一个终点,问起点到终点的最短路径。
+
+接下来,我们来详细讲解最短路算法中的 dijkstra 算法。
+
+dijkstra算法:在有权图(权值非负数)中求从起点到其他节点的最短路径算法。
+
+需要注意两点:
+
+* dijkstra 算法可以同时求 起点到所有节点的最短路径
+* 权值不能为负数
+
+(这两点后面我们会讲到)
+
+如本题示例中的图:
+
+
+
+起点(节点1)到终点(节点7) 的最短路径是 图中 标记绿线的部分。
+
+最短路径的权值为12。
+
+其实 dijkstra 算法 和 我们之前讲解的prim算法思路非常接近,如果大家认真学过[prim算法](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/yX936hHC6Z10K36Vm1Wl9w),那么理解 Dijkstra 算法会相对容易很多。(这也是我要先讲prim再讲dijkstra的原因)
+
+dijkstra 算法 同样是贪心的思路,不断寻找距离 源点最近的没有访问过的节点。
+
+这里我也给出 **dijkstra三部曲**:
+
+1. 第一步,选源点到哪个节点近且该节点未被访问过
+2. 第二步,该最近节点被标记访问过
+3. 第三步,更新非访问节点到源点的距离(即更新minDist数组)
+
+大家此时已经会发现,这和prim算法 怎么这么像呢。
+
+我在[prim算法](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/yX936hHC6Z10K36Vm1Wl9w)讲解中也给出了三部曲。 prim 和 dijkstra 确实很像,思路也是类似的,这一点我在后面还会详细来讲。
+
+在dijkstra算法中,同样有一个数组很重要,起名为:minDist。
+
+**minDist数组 用来记录 每一个节点距离源点的最小距离**。
+
+理解这一点很重要,也是理解 dijkstra 算法的核心所在。
+
+大家现在看着可能有点懵,不知道什么意思。
+
+没关系,先让大家有一个印象,对理解后面讲解有帮助。
+
+我们先来画图看一下 dijkstra 的工作过程,以本题示例为例: (以下为朴素版dijkstra的思路)
+
+(**示例中节点编号是从1开始,所以为了让大家看的不晕,minDist数组下标我也从 1 开始计数,下标0 就不使用了,这样 下标和节点标号就可以对应上了,避免大家搞混**)
+
+## 朴素版dijkstra
+
+### 模拟过程
+
+-----------
+
+0、初始化
+
+minDist数组数值初始化为int最大值。
+
+这里在强点一下 **minDist数组的含义:记录所有节点到源点的最短路径**,那么初始化的时候就应该初始为最大值,这样才能在后续出现最短路径的时候及时更新。
+
+
+
+(图中,max 表示默认值,节点0 不做处理,统一从下标1 开始计算,这样下标和节点数值统一, 方便大家理解,避免搞混)
+
+源点(节点1) 到自己的距离为0,所以 minDist[1] = 0
+
+此时所有节点都没有被访问过,所以 visited数组都为0
+
+---------------
+
+以下为dijkstra 三部曲
+
+1、选源点到哪个节点近且该节点未被访问过
+
+源点距离源点最近,距离为0,且未被访问。
+
+2、该最近节点被标记访问过
+
+标记源点访问过
+
+3、更新非访问节点到源点的距离(即更新minDist数组) ,如图:
+
+
+
+
+更新 minDist数组,即:源点(节点1) 到 节点2 和 节点3的距离。
+
+* 源点到节点2的最短距离为1,小于原minDist[2]的数值max,更新minDist[2] = 1
+* 源点到节点3的最短距离为4,小于原minDist[3]的数值max,更新minDist[4] = 4
+
+可能有录友问:为啥和 minDist[2] 比较?
+
+再强调一下 minDist[2] 的含义,它表示源点到节点2的最短距离,那么目前我们得到了 源点到节点2的最短距离为1,小于默认值max,所以更新。 minDist[3]的更新同理
+
+
+-------------
+
+1、选源点到哪个节点近且该节点未被访问过
+
+未访问过的节点中,源点到节点2距离最近,选节点2
+
+2、该最近节点被标记访问过
+
+节点2被标记访问过
+
+3、更新非访问节点到源点的距离(即更新minDist数组) ,如图:
+
+
+
+
+更新 minDist数组,即:源点(节点1) 到 节点6 、 节点3 和 节点4的距离。
+
+**为什么更新这些节点呢? 怎么不更新其他节点呢**?
+
+因为 源点(节点1)通过 已经计算过的节点(节点2) 可以链接到的节点 有 节点3,节点4和节点6.
+
+
+更新 minDist数组:
+
+* 源点到节点6的最短距离为5,小于原minDist[6]的数值max,更新minDist[6] = 5
+* 源点到节点3的最短距离为3,小于原minDist[3]的数值4,更新minDist[3] = 3
+* 源点到节点4的最短距离为6,小于原minDist[4]的数值max,更新minDist[4] = 6
+
+
+
+-------------------
+
+1、选源点到哪个节点近且该节点未被访问过
+
+未访问过的节点中,源点距离哪些节点最近,怎么算的?
+
+其实就是看 minDist数组里的数值,minDist 记录了 源点到所有节点的最近距离,结合visited数组筛选出未访问的节点就好。
+
+从 上面的图,或者 从minDist数组中,我们都能看出 未访问过的节点中,源点(节点1)到节点3距离最近。
+
+
+2、该最近节点被标记访问过
+
+节点3被标记访问过
+
+3、更新非访问节点到源点的距离(即更新minDist数组) ,如图:
+
+
+
+由于节点3的加入,那么源点可以有新的路径链接到节点4 所以更新minDist数组:
+
+更新 minDist数组:
+
+* 源点到节点4的最短距离为5,小于原minDist[4]的数值6,更新minDist[4] = 5
+
+------------------
+
+1、选源点到哪个节点近且该节点未被访问过
+
+距离源点最近且没有被访问过的节点,有节点4 和 节点6,距离源点距离都是 5 (minDist[4] = 5,minDist[6] = 5) ,选哪个节点都可以。
+
+2、该最近节点被标记访问过
+
+节点4被标记访问过
+
+3、更新非访问节点到源点的距离(即更新minDist数组) ,如图:
+
+
+
+由于节点4的加入,那么源点可以链接到节点5 所以更新minDist数组:
+
+* 源点到节点5的最短距离为8,小于原minDist[5]的数值max,更新minDist[5] = 8
+
+--------------
+
+1、选源点到哪个节点近且该节点未被访问过
+
+距离源点最近且没有被访问过的节点,是节点6,距离源点距离是 5 (minDist[6] = 5)
+
+
+2、该最近节点被标记访问过
+
+节点6 被标记访问过
+
+
+3、更新非访问节点到源点的距离(即更新minDist数组) ,如图:
+
+
+
+由于节点6的加入,那么源点可以链接到节点7 所以 更新minDist数组:
+
+* 源点到节点7的最短距离为14,小于原minDist[7]的数值max,更新minDist[7] = 14
+
+
+
+-------------------
+
+1、选源点到哪个节点近且该节点未被访问过
+
+距离源点最近且没有被访问过的节点,是节点5,距离源点距离是 8 (minDist[5] = 8)
+
+2、该最近节点被标记访问过
+
+节点5 被标记访问过
+
+3、更新非访问节点到源点的距离(即更新minDist数组) ,如图:
+
+
+
+由于节点5的加入,那么源点有新的路径可以链接到节点7 所以 更新minDist数组:
+
+* 源点到节点7的最短距离为12,小于原minDist[7]的数值14,更新minDist[7] = 12
+
+-----------------
+
+1、选源点到哪个节点近且该节点未被访问过
+
+距离源点最近且没有被访问过的节点,是节点7(终点),距离源点距离是 12 (minDist[7] = 12)
+
+2、该最近节点被标记访问过
+
+节点7 被标记访问过
+
+3、更新非访问节点到源点的距离(即更新minDist数组) ,如图:
+
+
+
+节点7加入,但节点7到节点7的距离为0,所以 不用更新minDist数组
+
+--------------------
+
+最后我们要求起点(节点1) 到终点 (节点7)的距离。
+
+再来回顾一下minDist数组的含义:记录 每一个节点距离源点的最小距离。
+
+那么起到(节点1)到终点(节点7)的最短距离就是 minDist[7] ,按上面举例讲解来说,minDist[7] = 12,节点1 到节点7的最短路径为 12。
+
+路径如图:
+
+
+
+在上面的讲解中,每一步 我都是按照 dijkstra 三部曲来讲解的,理解了这三部曲,代码也就好懂的。
+
+### 代码实现
+
+本题代码如下,里面的 三部曲 我都做了注释,大家按照我上面的讲解 来看如下代码:
+
+```CPP
+class Solution {
+public:
+ int networkDelayTime(vector
-
diff --git "a/problems/0743.\347\275\221\347\273\234\345\273\266\350\277\237\346\227\266\351\227\264.md" "b/problems/0743.\347\275\221\347\273\234\345\273\266\350\277\237\346\227\266\351\227\264.md"
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..40b699c18f
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/problems/0743.\347\275\221\347\273\234\345\273\266\350\277\237\346\227\266\351\227\264.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,1230 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
+
+# 743.网络延迟时间
+
+https://leetcode.cn/problems/network-delay-time/description/
+
+
+有 n 个网络节点,标记为 1 到 n。
+
+给你一个列表 times,表示信号经过 有向 边的传递时间。 times[i] = (ui, vi, wi),其中 ui 是源节点,vi 是目标节点, wi 是一个信号从源节点传递到目标节点的时间。
+
+现在,从某个节点 K 发出一个信号。需要多久才能使所有节点都收到信号?如果不能使所有节点收到信号,返回 -1 。
+
+
+
+提示:
+
+* 1 <= k <= n <= 100
+* 1 <= times.length <= 6000
+* times[i].length == 3
+* 1 <= ui, vi <= n
+* ui != vi
+* 0 <= wi <= 100
+* 所有 (ui, vi) 对都 互不相同(即,不含重复边)
+
+# dijkstra 精讲
+
+本题就是求最短路,最短路是图论中的经典问题即:给出一个有向图,一个起点,一个终点,问起点到终点的最短路径。
+
+接下来,我们来详细讲解最短路算法中的 dijkstra 算法。
+
+dijkstra算法:在有权图(权值非负数)中求从起点到其他节点的最短路径算法。
+
+需要注意两点:
+
+* dijkstra 算法可以同时求 起点到所有节点的最短路径
+* 权值不能为负数
+
+(这两点后面我们会讲到)
+
+如本题示例中的图:
+
+
+
+起点(节点1)到终点(节点7) 的最短路径是 图中 标记绿线的部分。
+
+最短路径的权值为12。
+
+其实 dijkstra 算法 和 我们之前讲解的prim算法思路非常接近,如果大家认真学过[prim算法](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/yX936hHC6Z10K36Vm1Wl9w),那么理解 Dijkstra 算法会相对容易很多。(这也是我要先讲prim再讲dijkstra的原因)
+
+dijkstra 算法 同样是贪心的思路,不断寻找距离 源点最近的没有访问过的节点。
+
+这里我也给出 **dijkstra三部曲**:
+
+1. 第一步,选源点到哪个节点近且该节点未被访问过
+2. 第二步,该最近节点被标记访问过
+3. 第三步,更新非访问节点到源点的距离(即更新minDist数组)
+
+大家此时已经会发现,这和prim算法 怎么这么像呢。
+
+我在[prim算法](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/yX936hHC6Z10K36Vm1Wl9w)讲解中也给出了三部曲。 prim 和 dijkstra 确实很像,思路也是类似的,这一点我在后面还会详细来讲。
+
+在dijkstra算法中,同样有一个数组很重要,起名为:minDist。
+
+**minDist数组 用来记录 每一个节点距离源点的最小距离**。
+
+理解这一点很重要,也是理解 dijkstra 算法的核心所在。
+
+大家现在看着可能有点懵,不知道什么意思。
+
+没关系,先让大家有一个印象,对理解后面讲解有帮助。
+
+我们先来画图看一下 dijkstra 的工作过程,以本题示例为例: (以下为朴素版dijkstra的思路)
+
+(**示例中节点编号是从1开始,所以为了让大家看的不晕,minDist数组下标我也从 1 开始计数,下标0 就不使用了,这样 下标和节点标号就可以对应上了,避免大家搞混**)
+
+## 朴素版dijkstra
+
+### 模拟过程
+
+-----------
+
+0、初始化
+
+minDist数组数值初始化为int最大值。
+
+这里在强点一下 **minDist数组的含义:记录所有节点到源点的最短路径**,那么初始化的时候就应该初始为最大值,这样才能在后续出现最短路径的时候及时更新。
+
+
+
+(图中,max 表示默认值,节点0 不做处理,统一从下标1 开始计算,这样下标和节点数值统一, 方便大家理解,避免搞混)
+
+源点(节点1) 到自己的距离为0,所以 minDist[1] = 0
+
+此时所有节点都没有被访问过,所以 visited数组都为0
+
+---------------
+
+以下为dijkstra 三部曲
+
+1、选源点到哪个节点近且该节点未被访问过
+
+源点距离源点最近,距离为0,且未被访问。
+
+2、该最近节点被标记访问过
+
+标记源点访问过
+
+3、更新非访问节点到源点的距离(即更新minDist数组) ,如图:
+
+
+
+
+更新 minDist数组,即:源点(节点1) 到 节点2 和 节点3的距离。
+
+* 源点到节点2的最短距离为1,小于原minDist[2]的数值max,更新minDist[2] = 1
+* 源点到节点3的最短距离为4,小于原minDist[3]的数值max,更新minDist[4] = 4
+
+可能有录友问:为啥和 minDist[2] 比较?
+
+再强调一下 minDist[2] 的含义,它表示源点到节点2的最短距离,那么目前我们得到了 源点到节点2的最短距离为1,小于默认值max,所以更新。 minDist[3]的更新同理
+
+
+-------------
+
+1、选源点到哪个节点近且该节点未被访问过
+
+未访问过的节点中,源点到节点2距离最近,选节点2
+
+2、该最近节点被标记访问过
+
+节点2被标记访问过
+
+3、更新非访问节点到源点的距离(即更新minDist数组) ,如图:
+
+
+
+
+更新 minDist数组,即:源点(节点1) 到 节点6 、 节点3 和 节点4的距离。
+
+**为什么更新这些节点呢? 怎么不更新其他节点呢**?
+
+因为 源点(节点1)通过 已经计算过的节点(节点2) 可以链接到的节点 有 节点3,节点4和节点6.
+
+
+更新 minDist数组:
+
+* 源点到节点6的最短距离为5,小于原minDist[6]的数值max,更新minDist[6] = 5
+* 源点到节点3的最短距离为3,小于原minDist[3]的数值4,更新minDist[3] = 3
+* 源点到节点4的最短距离为6,小于原minDist[4]的数值max,更新minDist[4] = 6
+
+
+
+-------------------
+
+1、选源点到哪个节点近且该节点未被访问过
+
+未访问过的节点中,源点距离哪些节点最近,怎么算的?
+
+其实就是看 minDist数组里的数值,minDist 记录了 源点到所有节点的最近距离,结合visited数组筛选出未访问的节点就好。
+
+从 上面的图,或者 从minDist数组中,我们都能看出 未访问过的节点中,源点(节点1)到节点3距离最近。
+
+
+2、该最近节点被标记访问过
+
+节点3被标记访问过
+
+3、更新非访问节点到源点的距离(即更新minDist数组) ,如图:
+
+
+
+由于节点3的加入,那么源点可以有新的路径链接到节点4 所以更新minDist数组:
+
+更新 minDist数组:
+
+* 源点到节点4的最短距离为5,小于原minDist[4]的数值6,更新minDist[4] = 5
+
+------------------
+
+1、选源点到哪个节点近且该节点未被访问过
+
+距离源点最近且没有被访问过的节点,有节点4 和 节点6,距离源点距离都是 5 (minDist[4] = 5,minDist[6] = 5) ,选哪个节点都可以。
+
+2、该最近节点被标记访问过
+
+节点4被标记访问过
+
+3、更新非访问节点到源点的距离(即更新minDist数组) ,如图:
+
+
+
+由于节点4的加入,那么源点可以链接到节点5 所以更新minDist数组:
+
+* 源点到节点5的最短距离为8,小于原minDist[5]的数值max,更新minDist[5] = 8
+
+--------------
+
+1、选源点到哪个节点近且该节点未被访问过
+
+距离源点最近且没有被访问过的节点,是节点6,距离源点距离是 5 (minDist[6] = 5)
+
+
+2、该最近节点被标记访问过
+
+节点6 被标记访问过
+
+
+3、更新非访问节点到源点的距离(即更新minDist数组) ,如图:
+
+
+
+由于节点6的加入,那么源点可以链接到节点7 所以 更新minDist数组:
+
+* 源点到节点7的最短距离为14,小于原minDist[7]的数值max,更新minDist[7] = 14
+
+
+
+-------------------
+
+1、选源点到哪个节点近且该节点未被访问过
+
+距离源点最近且没有被访问过的节点,是节点5,距离源点距离是 8 (minDist[5] = 8)
+
+2、该最近节点被标记访问过
+
+节点5 被标记访问过
+
+3、更新非访问节点到源点的距离(即更新minDist数组) ,如图:
+
+
+
+由于节点5的加入,那么源点有新的路径可以链接到节点7 所以 更新minDist数组:
+
+* 源点到节点7的最短距离为12,小于原minDist[7]的数值14,更新minDist[7] = 12
+
+-----------------
+
+1、选源点到哪个节点近且该节点未被访问过
+
+距离源点最近且没有被访问过的节点,是节点7(终点),距离源点距离是 12 (minDist[7] = 12)
+
+2、该最近节点被标记访问过
+
+节点7 被标记访问过
+
+3、更新非访问节点到源点的距离(即更新minDist数组) ,如图:
+
+
+
+节点7加入,但节点7到节点7的距离为0,所以 不用更新minDist数组
+
+--------------------
+
+最后我们要求起点(节点1) 到终点 (节点7)的距离。
+
+再来回顾一下minDist数组的含义:记录 每一个节点距离源点的最小距离。
+
+那么起到(节点1)到终点(节点7)的最短距离就是 minDist[7] ,按上面举例讲解来说,minDist[7] = 12,节点1 到节点7的最短路径为 12。
+
+路径如图:
+
+
+
+在上面的讲解中,每一步 我都是按照 dijkstra 三部曲来讲解的,理解了这三部曲,代码也就好懂的。
+
+### 代码实现
+
+本题代码如下,里面的 三部曲 我都做了注释,大家按照我上面的讲解 来看如下代码:
+
+```CPP
+class Solution {
+public:
+ int networkDelayTime(vector -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0763.\345\210\222\345\210\206\345\255\227\346\257\215\345\214\272\351\227\264.md" "b/problems/0763.\345\210\222\345\210\206\345\255\227\346\257\215\345\214\272\351\227\264.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 4e9ec578bc..d17878381f
--- "a/problems/0763.\345\210\222\345\210\206\345\255\227\346\257\215\345\214\272\351\227\264.md"
+++ "b/problems/0763.\345\210\222\345\210\206\345\255\227\346\257\215\345\214\272\351\227\264.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0763.\345\210\222\345\210\206\345\255\227\346\257\215\345\214\272\351\227\264.md" "b/problems/0763.\345\210\222\345\210\206\345\255\227\346\257\215\345\214\272\351\227\264.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 4e9ec578bc..d17878381f
--- "a/problems/0763.\345\210\222\345\210\206\345\255\227\346\257\215\345\214\272\351\227\264.md"
+++ "b/problems/0763.\345\210\222\345\210\206\345\255\227\346\257\215\345\214\272\351\227\264.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
-
diff --git "a/problems/0787.K\347\253\231\344\270\255\350\275\254\345\206\205\346\234\200\344\276\277\345\256\234\347\232\204\350\210\252\347\217\255.md" "b/problems/0787.K\347\253\231\344\270\255\350\275\254\345\206\205\346\234\200\344\276\277\345\256\234\347\232\204\350\210\252\347\217\255.md"
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..fb58c14816
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/problems/0787.K\347\253\231\344\270\255\350\275\254\345\206\205\346\234\200\344\276\277\345\256\234\347\232\204\350\210\252\347\217\255.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,180 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
+
+# 787. K 站中转内最便宜的航班
+
+有 n 个城市通过一些航班连接。给你一个数组 flights ,其中 flights[i] = [fromi, toi, pricei] ,表示该航班都从城市 fromi 开始,以价格 pricei 抵达 toi。
+
+现在给定所有的城市和航班,以及出发城市 src 和目的地 dst,你的任务是找到出一条最多经过 k 站中转的路线,使得从 src 到 dst 的 价格最便宜 ,并返回该价格。 如果不存在这样的路线,则输出 -1。
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+## 思路
+
+
+
+```CPP
+class Solution {
+public:
+ int findCheapestPrice(int n, vector
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0787.K\347\253\231\344\270\255\350\275\254\345\206\205\346\234\200\344\276\277\345\256\234\347\232\204\350\210\252\347\217\255.md" "b/problems/0787.K\347\253\231\344\270\255\350\275\254\345\206\205\346\234\200\344\276\277\345\256\234\347\232\204\350\210\252\347\217\255.md"
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..fb58c14816
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/problems/0787.K\347\253\231\344\270\255\350\275\254\345\206\205\346\234\200\344\276\277\345\256\234\347\232\204\350\210\252\347\217\255.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,180 @@
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
+
+# 787. K 站中转内最便宜的航班
+
+有 n 个城市通过一些航班连接。给你一个数组 flights ,其中 flights[i] = [fromi, toi, pricei] ,表示该航班都从城市 fromi 开始,以价格 pricei 抵达 toi。
+
+现在给定所有的城市和航班,以及出发城市 src 和目的地 dst,你的任务是找到出一条最多经过 k 站中转的路线,使得从 src 到 dst 的 价格最便宜 ,并返回该价格。 如果不存在这样的路线,则输出 -1。
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+## 思路
+
+
+
+```CPP
+class Solution {
+public:
+ int findCheapestPrice(int n, vector -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0827.\346\234\200\345\244\247\344\272\272\345\267\245\345\262\233.md" "b/problems/0827.\346\234\200\345\244\247\344\272\272\345\267\245\345\262\233.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 3f32dd7aa1..118735e943
--- "a/problems/0827.\346\234\200\345\244\247\344\272\272\345\267\245\345\262\233.md"
+++ "b/problems/0827.\346\234\200\345\244\247\344\272\272\345\267\245\345\262\233.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0827.\346\234\200\345\244\247\344\272\272\345\267\245\345\262\233.md" "b/problems/0827.\346\234\200\345\244\247\344\272\272\345\267\245\345\262\233.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 3f32dd7aa1..118735e943
--- "a/problems/0827.\346\234\200\345\244\247\344\272\272\345\267\245\345\262\233.md"
+++ "b/problems/0827.\346\234\200\345\244\247\344\272\272\345\267\245\345\262\233.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0841.\351\222\245\345\214\231\345\222\214\346\210\277\351\227\264.md" "b/problems/0841.\351\222\245\345\214\231\345\222\214\346\210\277\351\227\264.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index b4785d1b02..ffcf2fb919
--- "a/problems/0841.\351\222\245\345\214\231\345\222\214\346\210\277\351\227\264.md"
+++ "b/problems/0841.\351\222\245\345\214\231\345\222\214\346\210\277\351\227\264.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0841.\351\222\245\345\214\231\345\222\214\346\210\277\351\227\264.md" "b/problems/0841.\351\222\245\345\214\231\345\222\214\346\210\277\351\227\264.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index b4785d1b02..ffcf2fb919
--- "a/problems/0841.\351\222\245\345\214\231\345\222\214\346\210\277\351\227\264.md"
+++ "b/problems/0841.\351\222\245\345\214\231\345\222\214\346\210\277\351\227\264.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0844.\346\257\224\350\276\203\345\220\253\351\200\200\346\240\274\347\232\204\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md" "b/problems/0844.\346\257\224\350\276\203\345\220\253\351\200\200\346\240\274\347\232\204\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index c7f5220288..6d0cd68578
--- "a/problems/0844.\346\257\224\350\276\203\345\220\253\351\200\200\346\240\274\347\232\204\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md"
+++ "b/problems/0844.\346\257\224\350\276\203\345\220\253\351\200\200\346\240\274\347\232\204\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0844.\346\257\224\350\276\203\345\220\253\351\200\200\346\240\274\347\232\204\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md" "b/problems/0844.\346\257\224\350\276\203\345\220\253\351\200\200\346\240\274\347\232\204\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index c7f5220288..6d0cd68578
--- "a/problems/0844.\346\257\224\350\276\203\345\220\253\351\200\200\346\240\274\347\232\204\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md"
+++ "b/problems/0844.\346\257\224\350\276\203\345\220\253\351\200\200\346\240\274\347\232\204\345\255\227\347\254\246\344\270\262.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- +
+ 如果S[i]和S[j]不相同返回false,如果有一个指针(i或者j)先走到的字符串头部位置,也返回false。
@@ -587,8 +585,4 @@ impl Solution {
}
```
-
如果S[i]和S[j]不相同返回false,如果有一个指针(i或者j)先走到的字符串头部位置,也返回false。
@@ -587,8 +585,4 @@ impl Solution {
}
```
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0860.\346\237\240\346\252\254\346\260\264\346\211\276\351\233\266.md" "b/problems/0860.\346\237\240\346\252\254\346\260\264\346\211\276\351\233\266.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index db70112d8f..aeb470fe5a
--- "a/problems/0860.\346\237\240\346\252\254\346\260\264\346\211\276\351\233\266.md"
+++ "b/problems/0860.\346\237\240\346\252\254\346\260\264\346\211\276\351\233\266.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0860.\346\237\240\346\252\254\346\260\264\346\211\276\351\233\266.md" "b/problems/0860.\346\237\240\346\252\254\346\260\264\346\211\276\351\233\266.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index db70112d8f..aeb470fe5a
--- "a/problems/0860.\346\237\240\346\252\254\346\260\264\346\211\276\351\233\266.md"
+++ "b/problems/0860.\346\237\240\346\252\254\346\260\264\346\211\276\351\233\266.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0922.\346\214\211\345\245\207\345\201\266\346\216\222\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204II.md" "b/problems/0922.\346\214\211\345\245\207\345\201\266\346\216\222\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 72be8fa732..484099f89f
--- "a/problems/0922.\346\214\211\345\245\207\345\201\266\346\216\222\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0922.\346\214\211\345\245\207\345\201\266\346\216\222\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204II.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0922.\346\214\211\345\245\207\345\201\266\346\216\222\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204II.md" "b/problems/0922.\346\214\211\345\245\207\345\201\266\346\216\222\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 72be8fa732..484099f89f
--- "a/problems/0922.\346\214\211\345\245\207\345\201\266\346\216\222\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0922.\346\214\211\345\245\207\345\201\266\346\216\222\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204II.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
-