The NIH HPC group plans, manages and supports
high-performance computing systems specifically for use by the
intramural NIH community. These systems include
Biowulf,
a 105,000+ processor
Linux cluster;
Helix, an interactive system for
file transfer and management, and
Helixweb, which provides a number of web-based
scientific tools. We provide access to a wide range of computational
applications for genomics, molecular and structural biology, mathematical and
graphical analysis, image analysis, and other scientific fields.
The continued growth and support of NIH's Biowulf cluster is dependent upon
its demonstrable value to the NIH Intramural Research Program. If you publish
research that involved significant use of Biowulf, please cite the cluster.
Suggested citation text:
This work utilized the computational resources of the NIH HPC Biowulf cluster (https://hpc.nih.gov).
|
Quick Links
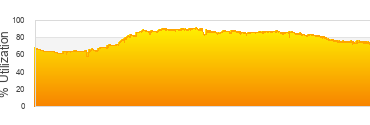
Biowulf Utilization
Saturday, November 16th, 2024
|
Last 24 hrs
|
|
116,891 jobs submitted
74,125 jobs completed
3,716,815 CPU hrs used
|
24 NIH Institutes
295 Principal Investigators
673 users
|
Announcements
|
Recent Papers that used Biowulf & HPC Resources
|
RNA helicase D1PAS1 resolves R-loops and forms a complex for mouse pachytene piRNA biogenesis required for male fertility
Choi, H; Zhou, L; Zhao, Y; Dean, J; ,
Nucleic Acids Res
, DOI://10.1093/nar/gkae712 (2024)
 Cryo-EM structure of a natural prion: chronic wasting disease fibrils from deer
Cryo-EM structure of a natural prion: chronic wasting disease fibrils from deer
Alam, P; Hoyt, F; Artikis, E et al.
Acta Neuropathol
, DOI://10.1007/s00401-024-02813-y (2024)
 The Bor1 elevator transport cycle is subject to autoinhibition and activation
The Bor1 elevator transport cycle is subject to autoinhibition and activation
Jiang, Y; Jiang, J; ,
Nat Commun
, DOI://10.1038/s41467-024-53411-1 (2024)
 MYB/MYBL1-altered gliomas frequently harbor truncations and non-productive fusions in the MYB and MYBL1 genes
MYB/MYBL1-altered gliomas frequently harbor truncations and non-productive fusions in the MYB and MYBL1 genes
Chung, HJ; Rajan, S; Wu, Z et al.
Acta Neuropathol
, DOI://10.1007/s00401-024-02803-0 (2024)
 Altruistic feeding and cell-cell signaling during bacterial differentiation actively enhance phenotypic heterogeneity
Altruistic feeding and cell-cell signaling during bacterial differentiation actively enhance phenotypic heterogeneity
Updegrove, TB; Delerue, T; Anantharaman, V et al.
Sci Adv
, DOI://10.1126/sciadv.adq0791 (2024)
The Myc-associated zinc finger protein epigenetically controls expression of interferon-γ-stimulated genes by recruiting STAT1 to chromatin
Xiao, T; Li, X; Felsenfeld, G; ,
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A
, DOI://10.1073/pnas.2320938121 (2024)
Targeting SWI/SNF ATPases reduces neuroblastoma cell plasticity
Xu, M; Hong, JJ; Zhang, X et al.
EMBO J
, DOI://10.1038/s44318-024-00206-1 (2024)
A machine learning model reveals expansive downregulation of ligand-receptor interactions that enhance lymphocyte infiltration in melanoma with developed resistance to immune checkpoint blockade
Sahni, S; Wang, B; Wu, D et al.
Nat Commun
, DOI://10.1038/s41467-024-52555-4 (2024)
|
|
 All Services Operational
All Services Operational



