UNIT – I
CMOS TECHNOLOGY
List the advantages of CMOS technology over other technologies. [EC2354-Nov/Dec’12]
The advantages of CMOS technology over other technologies are,
Low power consumption
Scalable threshold voltage
High noise margin
Low output drive current
High performance
Give a short note on design rules. [080290038-Nov/Dec’12]
Design rules are the communication link between designer specifying requirements and the fabricator who materializes them. They represent geometric constraints on layout artwork so that patterns on the processed wafer will preserve the topology of the designs.
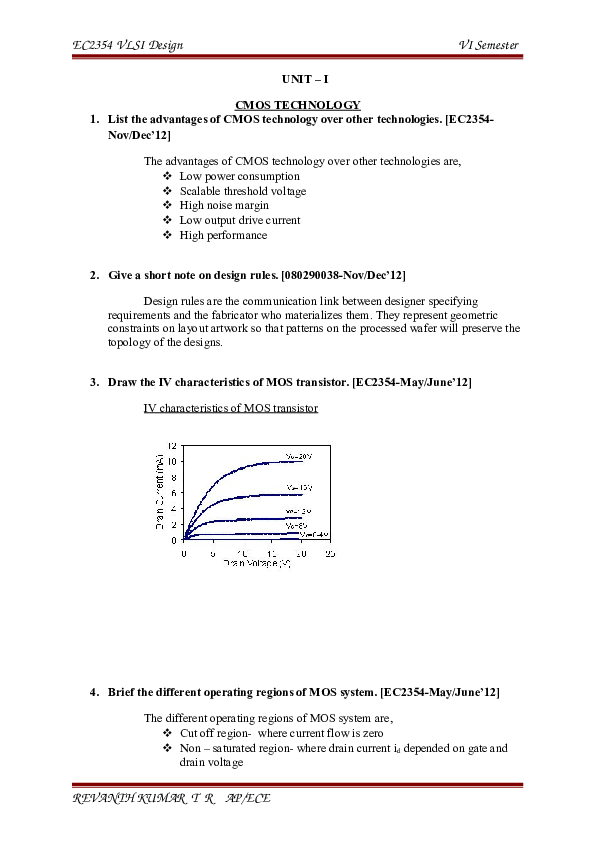
Draw the IV characteristics of MOS transistor. [EC2354-May/June’12]
IV characteristics of MOS transistor
Brief the different operating regions of MOS system. [EC2354-May/June’12]
The different operating regions of MOS system are,
Cut off region- where current flow is zero
Non – saturated region- where drain current id depended on gate and drain voltage
Saturated region –where drain current flow is ideally independent of drain-source voltage
Determine whether an NMOS transistor with a threshold voltage of 0.7 v is operating in the saturation region if VGS=2 V and VDS= 3 V[EC2354 Nov/Dec’11]
Given: VGS=2 V and VDS= 3 V
Vt =0.7 v
For saturation region, Vds > Vgs-Vt
i,e 3 > (2-0.7)
3 > 1.3
Therefore, the NMOS transistor is in saturation region.
What is body effect coefficient? [EC2354 Apr/May’11]
The substrate voltage vsb increases, with the increase in the width of channel substrate and thereby resulting in an increase in the density of trapped carriers in the depletion layer. This results in increase of channel-substrate junction potential and an overall effect in an increase in the threshold voltage. This is known as body effect coefficient and is given by,
where : Body effect coefficient
: Electric charge
: Permittivity of silicon = 1.06 x 10-12
: Density of the carriers in the doped semiconductor substrate
: Gate - oxide capacitance
Draw the energy band diagrams of the components that make up the MOS system. [EC2354 Apr/May’11]
Energy band diagrams of the MOS
where Eo : Free space
Ec : Conduction band
Ei : Intrinsic Fermi level
Ev : Valence band
EFp : Equilibrium Fermi level for p-type semiconductor
q : Electron affinity of silicon
qm : work function of an aluminium gate = 4.1eV
Fp : Fermi potential for p-type semiconductor
Write down the equation for describing the channel length modulation effect in NMOS transistors. [EC2354 Nov/Dec’11]
The channel length modulation effect in NMOS transistors is given by,
where : Drain - source current
: MOS transistor gain factor
: Gate – Source voltage
: Threshold voltage
: An Empirical channel length modulation factor
: Drain – Source voltage
Why the tunneling current is higher for NMOS transistors than PMOS transistors with silica gate? [EC2354 Nov/Dec’12]
The tunneling current is higher for nMOS transistors than pMOS transistors with silica gate because electrons tunnel from the conduction band while the holes tunnel from valence band and see a higher barrier.
What is the objective of layout rules? [EC2354 Nov/Dec’12]
The objective of layout rules is to describe how small features can be and how closely they can be packed in a particular manufacturing process. They are usually specified in microns.
UNIT – II
CIRCUIT CHARACTERIZATION AND SIMULATION
PART-A
1. Define: Body effect. [080290038-Nov/Dec’12]
The threshold voltage Vt is not constant with respect to voltage difference
between the substrate and the source of MOS transistor. This is known as body effect.
where γ : Body effect coefficient
εsi- : Dielectric constant of silicon dioxide
q : Charge of an electron
NA : Doping concentration density of substrate
Cox : Oxide capacitance
2. Express TPHL and TPLH in terms of Cload.[EC2354 Apr/May’11]
TPHL and TPLH in terms of Cload are expressed as,
TPHL in terms of Cload is defined as the time delay between the transition of the rising input voltage and the transition of the falling output voltage.
TPLH in terms of Cload is defined as the time delay between the transition of the falling input voltage and the transition of the rising output voltage.
TPHL = (RN1+RN2) Cload
TPLH = (RN1+RN2) Cload
TPHL : High-to-Low Propagation Delay
TPLH : Low-to-High Propagation Delay
Cload : Load capacitance
3. Write the expressions for the logical effort and parasitic delay of n input NOR gate.
[EC2354 Nov/Dec’11]
The expressions for the logical effort and parasitic delay of n input NOR gate is
Logical effort = (2n+1)/3
Parasitic delay = nPinv
where n :number of inputs
Pinv :Normalised parasitic delay
4. What are the factors that cause static power dissipation in CMOS family?
[EC2354-Nov/Dec’12]
The factors that cause static power dissipation in CMOS family are,
Sub-threshold conduction through OFF transistors
Tunnelling current through gate oxide
Leakage through reverse –biased diodes
Contention current in ratioed circuits.
5. What is meant by channel resistance? [EC2354-Nov/Dec’12]
The channel resistance of a MOS transistor in the linear region,
Rc = k (L/W)
where k = 1/μ Cox(Vgs-Vt)
6. Draw the equivalent circuit structure of the LEVEL 1 MOSFET model in SPICE.
[EC2354-May/June’12]
Equivalent circuit structure of the LEVEL 1 MOSFET model in SPICE.
7. Brief about the variation of the fringing field factor with the interconnect geometry.
[EC2354-May/June’12]
The variation of the fringing field factor is
FF = Ctotal / Cpp
where FF – fringing field factor
Ctotal – total capacitance
Cpp – parallel plate capacitance
The influence of fringing field increases with the decreasing (w/h) ratio.
(w-width of the wire and h-height of the wire)
The fringing field capacitance can be as much as 10-20 times larger than the parallel plate capacitance.
8. What is meant by design margin? [EC2354-May/June’13]
The aim of design margin is to design the circuit, which will reliably operate over all extremes of the three variables:
Supply Voltage
Operating temperature
Process variation
9. Define device modelling [EC2354-May/June’13]
Device modelling is defined as the circuit design to which a model is adopted,
which describes the behaviour of all components successfully. A model includes a set of
mathematical formulas, circuit representations, tables, reference standards etc.
10. What is the influence of voltage scaling on power and delay? [EC2354 Apr/May’11]
The influence of voltage scaling on power is that when VDD is kept constant ,
the device is scaled down by dimension α.
The influence of voltage scaling on delay is that when VDD is kept constant ,
the device is scaled down by dimension 1/α.
11. Give the effects of supply voltage and temperature variations on the CMOS system
performance. [EC2354-Nov/Dec’12]
The effects of supply voltage on the CMOS system vary due to tolerance of
voltage regulators, IR drop along the supply rail and di/dt noise.
The effects of temperature variations on the CMOS system is that when the
temperature is increased, the drain current is reduced for a given set of operating
conditions.
12. What is the influence of voltage scaling on power and delay? [EC2354 Apr/May’11]
The influence of voltage scaling on power is that when VDD is kept constant ,
the device is scaled down by dimension α.
The influence of voltage scaling on delay is that when VDD is kept constant ,
the device is scaled down by dimension 1/α.
13. What are the factors that cause static power dissipation in CMOS circuits?
[EC2354-Nov/Dec’12]
The factors that cause static power dissipation in CMOS circuits are,
Sub-threshold conduction through OFF transistors
Tunneling current through gate oxide
Leakage through through reverse-biased diodes
Contention current in ratioed circuits
�UNIT-III
COMBINATIONAL AND SEQUENTIAL CIRCUIT DESIGN
1. State the advantages of static CMOS circuits?
The advantages of static CMOS circuits are,
Good noise margin
Fast
Low power
Intensive to device variations
Easy to design
Widely supported by CAD tools
Readily available in standard cell libraries
2. Write the commonly used logic families alternative to complementary CMOS?
The commonly used alternatives to complementary CMOS are,
Domino
Pseudo-nMOS
Pass transistor logic
3. What is meant by pass transistor logic? [EC2354-Nov/Dec’12]
It is the MOS transistor, in which a gate is driven by a control signal.When the control signal is high, input is passed to the output and when the control signal is low, the output is floating such topology circuit is called pass transistor.
4. What is a pseudo-nMOS logic gate? . Draw a pseudo NMOS inverter . [EC2354 Nov/Dec’11]
Pseudo NMOS ierter:
A pseudo-nMOS logic gate is the common form of CMOS ratioed circuits in which the pull-down network is like that of a static gate, and the pull-up network is replaced with a single pMOS transistor that is grounded so it is always ON.
5. What are the disadvantages of using a pseudo n MOS gate instead of a full CMOS
gate? [EC2354-May/June’12]
The disadvantages of using a pseudo nMOS gate instead of a full CMOS gate are
Slow rising transistors
Contention on the falling transistors
Static power dissipation that occurs whenever the pull-down is turned on.
Reduced output voltage swing and gain , which makes the gate more susceptible to noise
6. What is CVSL? State the reasons for the speed advantage of CVSL family.
[EC2354-Nov/Dec’12]
CVSL (Cascode Voltage Switch Logic) is a gate which performs like the of ratioed circuits but without the static power consumption. It has the following advantages
Quite fast - since the positive feed-back of the two PMOS accelerates the switching of the gate
Very good noise margins.
7. What are the disadvantages of CVSL gate?
The disadvantages of CVSL gate are,
CVSL gate requires both the low- and high-going transitions, adding more delay.
Contention current during the switching period increases power consumption.
It also requires more area.
8. What is monotonicity problem?
In the evaluating phase of a dynamic gate, the inputs must be monotonically rising. The output of a dynamic gate begins HIGH and monotonically falls LOW which is not a suitable input to a second dynamic gate expecting montonically rising signals. This is called as monotonicity problem.
9. How can monotonicity problem be solved?
The monotonicity problem can be solved by placing a static CMOS inverter between dynamic gates which converts the monotonically falling output into a monotonically rising signal suitable for the next gate.
10. What are called transmission gates? (or)
Write a note on CMOS transmission gate logic. [EC2354 Apr/May’11]
�
A transmission gate is an electronic element. It is made by the parallel combination of an nMOS and pMOS transistor with the input at the gate of one transistor being complementary to the input at the gate of the other . It is also known as an analog gate, analogue switch or electronic relay depending on its use.
11. What are sense amplifier circuits?
Sense amplifier circuits are circuits which magnify small differential input voltages into larger output voltages. They are commonly used in memories in which differential bitlines have enormous capacitive loads.
12. What are called BICMOS circuits?
Gates comprising both bipolar and CMOS transistors are called BICMOS. They are used to build logic gates with low logical effort and are good for driving large capacitive loads.
13. Draw the circuit diagram of a CMOS bistable element and its time domain behavior. [EC2354 Apr/May’11]
The circuit diagram of a CMOS bistable element and its time domain behaviour is shown below
�
14. What are called sequencing elements?
The elements which is not really memory, instead it enforce sequence to distinguish the current data or token from the previous or next token are called sequencing elements.
15. List some of the sequencing elements for static circuits.
Some of the sequencing elements for static circuits are,
Flip-flops
2-phase transparent latches
Pulsed latches
16. What are the advantages of sequencing methodology?
The advantages of sequencing methodology are,
No sequencing overhead.
Allows sequencing elements back-to-back with no logic in between.
Grant the designer flexibility in balancing the amount of logic in each clock cycle.
Tolerate moderate amounts of clock skew without degrading performance.
Consumes zero area and power.
17. What are the sequencing methods applied for sequencing blocks of
combinational logic?
The sequencing methods applied for sequencing blocks of combinational
logic are,
2-phase system
Pulsed system
Flip-flop based system
18. What is called a race condition?
Data incorrectly propagate through two successive elements on one clock edge. This is due to the holding time is large and the contamination delay is small thus corrupting the state of the system. This is called a race condition, hold time failure, or min-delay failure.
19. What is called setup time failure and can it be reduced?
The receiving element of the combinational logic miss its setup time and sample the wrong value, if the combinational logic delay is more. This is called setup time failure or max-delay failure.
The problem of setup time can be solved by redesigning the logic to be faster or by increasing the clock period.
20. What is time borrowing?
The technique of borrowing time from the shorter paths of the subsequent logic stages to the longer path in a logical circuit is called time borrowing or cycle stealing
21. What are the schemes of time borrowing for the system designer?
The schemes of time borrowing for the system designer are,
Intentional time borrowing
Opportunistic time borrowing
22. What are conventional CMOS latches?
Conventional CMOS latches are circuits which are built using pass transistors or tristate buffers. These latches pass data when the latch is transparent and has feedback to hold the data when the latch is opaque.
23. What is a synchronizer? Write its common application.
A synchronizer is a circuit that accepts an input that change at arbitrary times and
produces an output aligned to the synchronizer’s clock.
The common application of synchronizers is to communicate between asynchronous clock domains, i,e., blocks of circuits that do not share a common clock.
UNIT-IV
CMOS TESTING
What is the need for testing?
Testing is the process of identifying the fault in the design process or IC. The role of testing is to detect whether something went wrong in the design process.
What are the objectives of functionality test? (Nov/Dec 2011)
The objective of functionality test is, to test the functions of the design by giving them the inputs and examining the outputs.
Distinguish between testers and test fixtures. (Nov/Dec 2012)
TESTERS
TEST FIXTURES
A tester is a device which is used to drive the inputs and to monitor the outputs of a device under test.
A test fixture is a socket for transmitting electrical signals from the test signal generation to an IC device under test.
What are the stages at which a chip can be tested? (Nov/Dec 2012)
A chip can be tested at the following stages
a) At the wafer level
b) At the packaged chip level
c) At the system level
d) At the board level
e) In the field
What are the advantages of single stuck at fault? (Apr/May 2012)
The advantages of single stuck at fault are
a) Stuck at fault can be applied at the logic level or module level.
b) Algorithms for ATPG and fault simulation are well developed.
c) Other fault models such as stuck open and bridging fault can be
mapped into stuck at fault.
List the basic types of CMOS testing. (May/June 2013)
The basic types of CMOS testing are
a) Production test
b) Burn-in test
c) Incoming Inspection test
d) Characterization test
What is meant by logic verification? (May/June 2013)
Logic verification is a method of checking the functionality of a circuit by giving inputs and checking the outputs.
What is controllability and observability?
Controllability for a digital circuit is defined as the difficulty of setting a particular logic signal to a 0 or a 1.
Observability for a digital circuit is defined as the difficulty of observing the state of logic signal.
What is ATPG?
Automatic Test Pattern Generation is algorithm that injects a fault into a circuit, and then uses a variety of mechanisms to activate the fault and causes its effect to propagate through the hardware and manifest itself at a circuit output. The output signal changes from the value expected for the fault-free circuit, and this causes the fault to be detected.
What is PODEM algorithm?
The Path-Oriented Decision Making algorithm solves the problem of reconvergent fanout and allows multipath sensitization.
What is stuck at fault?
The fault at the interconnection of gates is called stuck-at fault. This fault is modeled by assigning a fixed 0 or 1 value to a signal line in the circuit.
What is Ad-Hoc testing? (Nov/Dec 2009)
Ad-hoc testing is one of the DFT methods for testing the design.
The main objective of Ad-Hoc testing is
a) Avoid asynchronous logic feedbacks
b) Avoid gates with a large fan-in
What are the classifications of fault simulation?
The classifications of fault simulations are
a) Serial fault simulation
b) Parallel fault simulation
c) Concurrent fault simulation
d) Non-deterministic fault simulation
Define RTL
Register Transfer Level-a text-based design description where the behaviour of a circuit is modelled as dataflow and control from register to register in reference to an applied clock, clocks or other synchronizing signals.
Define test vectors
Test vectors are the binary input bit patterns used to verify the functionality of the device under test.
What are the different formats of test data?
The different formats of test data are
Non-Return to zero
Return to zero
Surrounding by complement
Define Bridging Faults
The short-circuit faults occur in interconnect of groups of signals is called bridging faults. In bridging faults the logic value of the shorted net may be modeled as 1-dominant or 0-dominant.
UNIT V
SPECIFICATONS USING VERILOG HDL
State the comparison between behavioral and Data flow level modeling
(May/June 2013)
Behavioral modeling represents digital circuits at a functional and algorithmic level. Behavioral description uses the keyword always and initial followed by a list of procedural assignment statements.
Dataflow modeling represents digital circuits by their function rather than by their
gate structure. Dataflow description uses continuous assignment statements.
What are gate primitives (May/June 2013)
Gate primitives are generalized modules that already exist in verilog. They can be
instantiated directly in other modules.
Write the verilog module for a 1-bit full adder. (Nov/Dec 2012)
module full_adder(a,b,c, sum,carry);
output sum,carry
input a;b,c;
wire w1,w2,w3;
xor (sum,a,b,c);
and(w1,a,b);
and(w2,b,c);
and(w3,c,a);
or(carry,w1,w2,w3);
endmodule
Give an example for implicit continuous assignment. (Nov/Dec 2012)
Regular continuous assignment
wire c,a,b;
assign c=a & b;
Implicit continuous assignment
wire c= a & b;
What is transport delay? (Apr/May 2011)
Transport delay is the delay caused by the wires connecting the gates. Wire do delay the signal they carry, this is due to the wire resistance, capacitance, and inductance. Simply transport delay is propagation delay on a wire. In verilog transport delay is modeled as follows: a <= #10 b.
What is subprogram overloading (Apr/May 2011)
Subprogram overloading is a process of using the same (function) name for many subprograms. The overloaded subprograms may differ in the number, type or order of its parameters.
Write the verilog module for an half adder (Nov/Dec 2011)
module halfadder(sum,carry,a,b);
output sum, carry;
input a,b;
xor(a,b,sum);
and (carry,a,b);
endmodule
What are the delays available in verilog HDL (Nov/Dec 2011)
The delays available in verilog HDL are
a) Regular Assignment Delay
b) Implicit Continuous Assignment Delay
c) Net Declaration Delay
Distinguish between task and function (Nov/Dec2009)
FUNCTION
TASK
A function can enable another function but not another task
A task can anable other tasks and functions
Function always execute in 0 simulation time
Tasks may execute in non-zero simulation time
Functions must not contain any delay, event, or timing control statements.
Tasks may contain delay, event, or timing control statements
Functions must have at least one input argument. They can have more than one input
Tasks may have zero or more arguments of type input, output, or inout.
What is the difference between = = = and = =? (Nov/Dec 2009)
= = Logical equality
Example:
If a=4; b=3;
Then a= =b Results in logical 0
= = = Case equality
Example:
If a= 4’b1xxz; b=4’b1xxz
Then a=b Results in logical 1.
What is CBIC ? (Nov/Dec 2009)
A cell based ASIC uses predesigned logic cells, known as standard cells. The standard
cell areas in a CBIC are built of rows of standard cell like a wall built of bricks.
Write a verilog code for D latch (Nov/Dec 2009)
module d_latch(q,qbar,d,c);
output q,qbar;
input d,c;
wire x1, x2, x3;
not g1(x1,d);
nand g2(x2,d,c);
nand g3(x3,x1,c);
nand g4(q,x2,qbar);
nand q5(qbar,x3,q); endmodule
What are the three types of gate delays?
The three types of gate delays are
a) Rise Delay
b) Fall delay
c) Turn-off delay
What are the different types of operators used in verilog?
The different types of operators used in verilog
a) Arithmetic
b) Logical
c) Relational
d) Equality
e) Bitwise
f) Reduction
g) Shift
h) Conditional
What is compiler directive?
A compiler directive when compiled remains in effect through the entire compilation process until a different compiler directive specifies otherwise.
16. Write a verilog module for CMOS inverter using switch level modelling.
module cmos_inverter(out,in);
output out;
input in;
supply1 pwr;
supply0 gnd;
pmos u1(out,pwr,in);
nmos u2(out,gnd,in);
endmodule
17. What are the conditional statements of verilog HDL?
The conditional statements of verilog HDL are
a) If statement
b) Case statement
c) Loop statement
Forever loop
Repeat loop
While loop
For loop
18. List the types of Design Methodology
The types of design methodology are
a) Top-Down methodology
b) Bottom-up methodology
C2354 VLSI Design VI Semester
REVANTH KUMAR T R AP/ECE

 Revanth Kumar Radhakrishnan
Revanth Kumar Radhakrishnan