FileOutputStream in Java
Last Updated :
25 Jun, 2021
FileOutputStream is an outputstream for writing data/streams of raw bytes to file or storing data to file. FileOutputStream is a subclass of OutputStream. To write primitive values into a file, we use FileOutputStream class. For writing byte-oriented and character-oriented data, we can use FileOutputStream but for writing character-oriented data, FileWriter is more preferred.
What is meant by storing data to files?
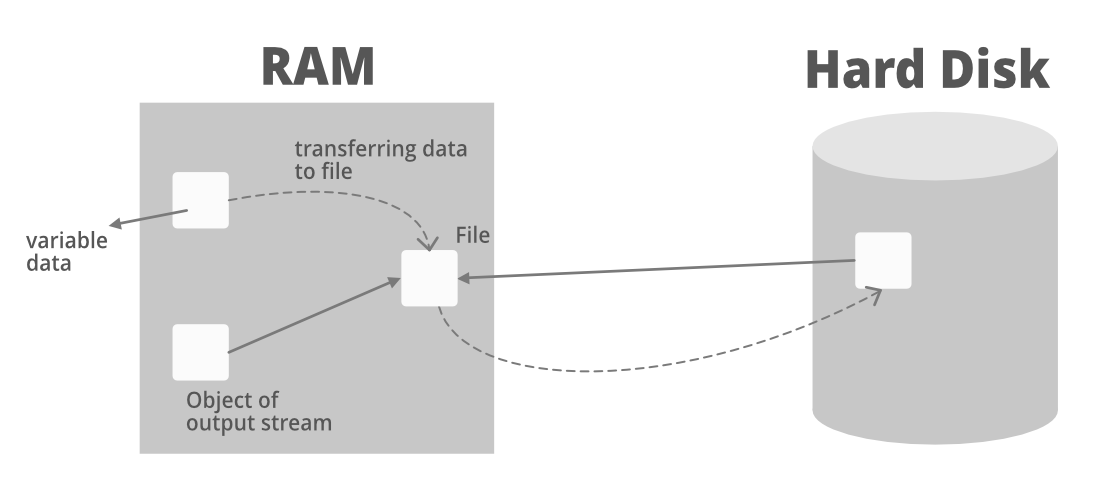
Through the above image, we can understand that when we run the java program, the data is stored in the RAM. Now, suppose the variable data stored in RAM, we want to access that data and bring it to a file in our hard disk. So, we will create an object of OutputStream in the RAM and that will point to a file referencing to hard disk.
Now, the data from the variable data file in the RAM will go to the referencing file (object of Output Stream) and from there will be transferred/stored in the file of the hard disk.
Hierarchy of FileOutputStream
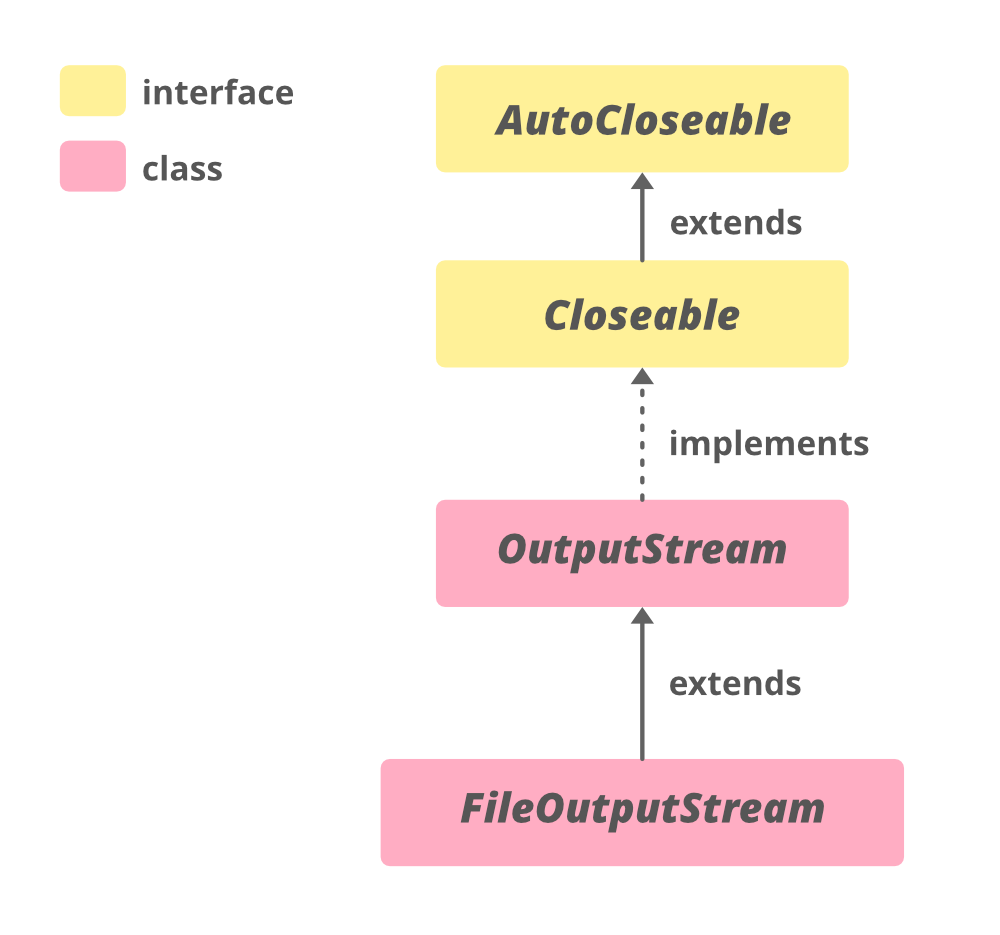
Constructors of FileOutputStream
1. FileOutputStream(File file): Creates a file output stream to write to the file represented by the specified File object.
FileOutputStream fout = new FileOutputStream(File file);
2. FileOutputStream( File file, boolean append): Creates a file output stream object represented by specified file object.
FileOutputStream fout = new FileOutputStream(File file, boolean append);
3. FileOutputStream(FileDescripter fdobj): Creates a file output stream for writing to the specified file descriptor, which represents an existing connection with the actual file in the file system.
FileOutputStream fout = new FileOutputStream(FileDescripter fdobj);
4. FileOutputStream( String name): Creates an object of file output stream to write to the file with the particular name mentioned.
FileOutputStream fout = new FileOutputStream( String name);
5. FileOutputStream( String name, boolean append): Creates an object of file output stream to write to the file with the specified name.
FileOutputStream fout = new FileOutputStream( String name, boolean append);
Declaration:
public class FileOutputStream extends OutputStream
Steps to write data to a file using FileOutputStream:
- First, attach a file path to a FileOutputStream as shown here:
FileOutputStream fout = new FileOutputStream(“file1.txt”);
- This will enable us to write data to the file. Then, to write data to the file, we should write data using the FileOutputStream as,
fout.write();
- Then we should call the close() method to close the fout file.
fout.close()
Example:
We need to import the java.io package to use FileOutputStream class.
Java
import java.io.*;
class FileExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
throws IOException
{
int i;
FileOutputStream fout = new FileOutputStream("../files/name3.txt",
true);
String st = "TATA";
char ch[] = st.toCharArray();
for (i = 0; i < st.length(); i++) {
fout.write(ch[i]);
}
fout.close();
}
}
|
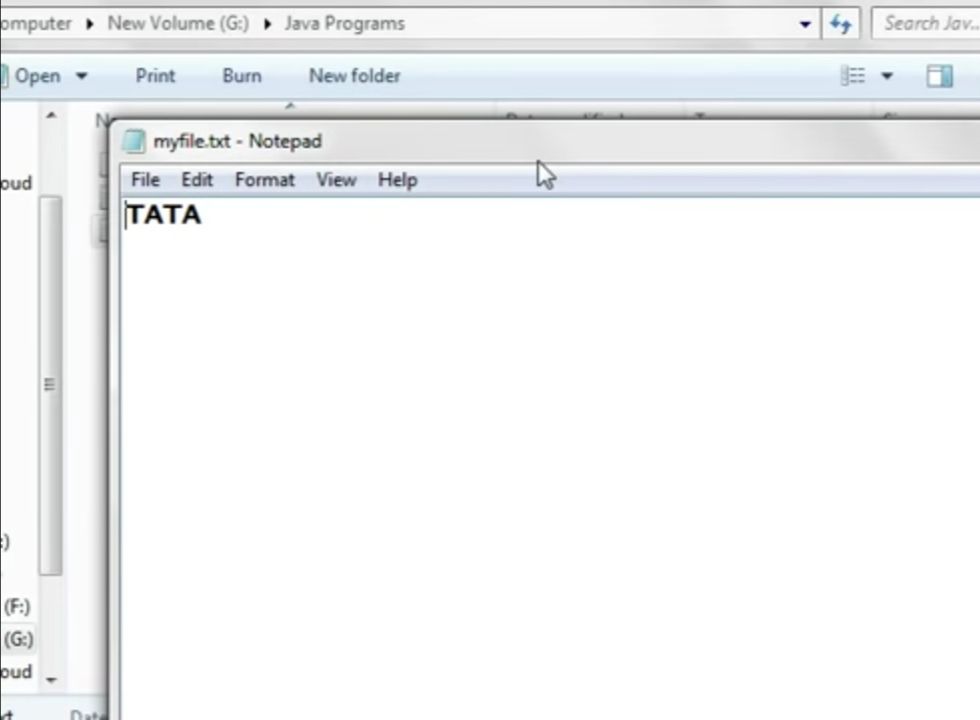
The data (i.e the string TATA will be transferred to file.
Before running the program
After running the program
myfile.txt file is created and the text “TATA” is saved in the file.
Some important Methods
1. Write() Method:
- write(): this writes the single byte to the file output stream.
- write(byte[] array): this writes the specified array’s bytes to the output stream.
- write(byte[] array, int start, int length): this writes the number of bytes equal to length to the output stream from an array starting from the position start.
Example:
Java
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String data = "Welcome to GfG";
try {
FileOutputStream output
= new FileOutputStream("output.txt");
byte[] array = data.getBytes();
output.write(array);
output.close();
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.getStackTrace();
}
}
}
|
When we run the program, the "Welcome to GfG" line is copied to output.txt file.
2. flush():
For clearing the OutputStream, we use the flush() method. This method forces all the data to get stored to its destination.
Example:
Java
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args)
throws IOException
{
FileOutputStream out = null;
String data = "Welcome to GfG";
try {
out = new FileOutputStream(" flush.txt");
out.write(data.getBytes());
out.flush();
out.close();
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.getStackTrace();
}
}
}
|
If, we run the program, the file flush.txt is filled with the text of the string"Welcome to GfG"
3. close() method:
This method closes the file OutputStream. Once it is called, we cannot use other methods.
Methods of fileOutputStream
| Method |
Description |
| void close() |
It closes the file output stream. |
| protected void finalize() |
It is used to clean up all the connection with the file output stream and finalize the data. |
| FileChannel getChannel() |
Returns the unique FileChannel object associated with this file output stream. |
| FileDescriptor getFD() |
It returns the file descriptor associated with the stream. |
| void write(int b) |
It is used to write the specified byte to the file output stream. |
| void write(byte[] arr) |
It is used to write data in bytes of arr[] to file output stream. |
| void write(byte[] ary, int off, int len) |
It is used to write the number of bytes equal to length to the output stream from an array starting from the position start. |
Methods declared in OutputStream class
| Method |
Description |
| flush() |
this method forces to write all data present in the output stream to the destination(hard disk). |
| nullOutputStream() |
this method returns a new OutputStream which discards all bytes. The stream returned is initially open. |
Reference: https://docs.oracle.com/en/java/javase/11/docs/api/java.base/java/io/FileOutputStream.html
Please Login to comment...