Analyzing Learning FLows in Digital Learning Ecosystems
- 1. Analyzing Learning Flows in Digital Learning Ecosystems Maka Eradze, Kai Pata, and Mart Laanpere :: Tallinn University, Estonia
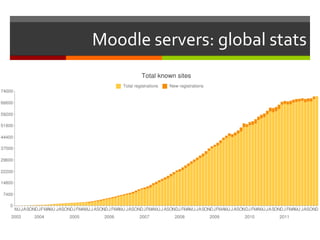
- 4. Moodle servers: global stats
- 5. Three generations ofTEL systems Dimension 1.generation 2.generation 3.generation Software architecture Educational software Course management systems Digital Learning Ecosystems Pedagogical foundation Bihaviorism Cognitivism Knowledge building, connectivism Content management Integrated with code Learning Objects, content packages Mash-up, remixed, user-generated Dominant affordances E-textbook, drill & practice, tests Sharing LO’s, forum discussions, quiz Reflections, collab. production, design Access Computer lab in school Home computer Everywhere – thanks to mobile devices Analytics Only feedback for learner Frequency-based usage statistics Interaction & uptake analytics
- 6. Digital Learning Ecosystem Ecosystem (biol.) is a community of living organisms (plants, animals and microbes) in conjunction with the nonliving components of their environment (e.g. air, water, light and soil), interacting as a system. DLE is an adaptive socio-technical system consisting of mutually interacting digital agents (tools, services, content used in learning process) and communities of users (learners, facilitators, trainers, developers) together with their social, economical and cultural environment.
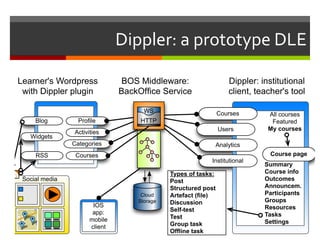
- 7. Dippler: a prototype DLE Social media Blog Profile Courses Activities RSS Users Analytics Courses Widgets Institutional BOS Middleware: BackOffice Service Cloud Storage HTTP WS Types of tasks: Post Structured post Artefact (file) Discussion Self-test Test Group task Offline task All courses Featured My courses Course page Summary Course info Outcomes Announcem. Participants Groups Resources Tasks Settings Categories Learner's Wordpress with Dippler plugin Dippler: institutional client, teacher's tool IOS app: mobile client
- 8. Learning interactions Wagner (1994): reciprocal events that require at least two objects and two actions. Interactions occur when these objects and events mutually influence each other Dyadic model of learning interactions (Moore, 1998): learner- learner, learner-teacher and learner-content Equivalence theorem by Anderson & Garrison (1998): reduction in one dyad can be compensated by increase in another Suthers (2011): interaction is fundamentally relational, so the most important unit of analysis is not isolated acts, but rather relationships between acts
- 9. Learning analytics: a critical view Most of the LA research is conducted in closed LMS context using frequency-based statistical analysis Only learner-content interactions are studied, not relations between the interactions Social Network Analysis (SNA) is focusing on teacher-learner and learner-learner interactions, but neglects the aspects of quality and dynamics in interactions Communities of Inquiry (CoI) approach focuses on quality and dynamics of learning interactions, but it is not scalable
- 10. Sequential analysis of learning flows In addition to frequency-based statistics, exploratory sequential data analysis is needed for analytics of learning flows in DLE In Dippler: extending Activity Streams (activitystrea.ms) vocabulary with pedagogical Action Verbs and Objects TinCan API or xAPI: specification for learning technology that makes it possible to collect data in a consistent format about the wide range of experiences a person has (online and offline) Uptake Framework (Suthers & Rosen, 2011): Uptake happens when a participant takes aspects of prior events as having relevance for ongoing activity; UF results with contingency graphs that can visualise media dependency, temporal proximity, spatial organization, semantic relatedness, inscriptional similarity
- 11. Sample scenario Collaborative concept mapping: identifying the core set of concepts for a given domain along with and their relations with each other, using a digital concept mapping tool Task is connected with some key concepts in domain ontology and also with a specific learning outcome Event transcript in activity stream: In Assignment 3, John adds a relation to conceptmap12 with CMapTool at 12:30 12-07-13. Results: contingency maps and uptake diagrams are created and fed back to learner and teacher, irregular patterns notified
- 12. Conclusions and future research Combining xAPI with Uptake Framework creates new opportunities for Learning Analytics and has several advantages: Recording interactions in dyadic events will encompass the processes, traces, domains; feedback loop for teachers & learners The relations with a domain will be identified and generalised through semantic annotation of events and artifacts Enables recording of the interactions that take place in distributed and partly user-defined digital ecosystem Advanced learning interaction analytics is automated and scalable Next steps: building xAPI Learning Record Store for Dippler and extending it to wider ecosystem, also to the physical world