Journal Description
Hospitals
Hospitals
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on hospital management, services and policy published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- Rapid Publication: first decisions in 16 days; acceptance to publication in 5.8 days (median values for MDPI journals in the first half of 2024).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
Latest Articles
Does Hospital–Physician Integration Improve Hospital Performance? Results from a USA Longitudinal Study
Hospitals 2024, 1(2), 172-184; https://doi.org/10.3390/hospitals1020014 - 8 Oct 2024
Cited by 1
Abstract
►
Show Figures
In a dynamic healthcare industry, aligning the goals and objectives of hospitals and physicians through integration has been suggested to influence performance. Physicians’ leadership and active involvement in governance can direct resource usage, Electronic Health Record (EHR) implementation, price negotiation, better coordination, and
[...] Read more.
In a dynamic healthcare industry, aligning the goals and objectives of hospitals and physicians through integration has been suggested to influence performance. Physicians’ leadership and active involvement in governance can direct resource usage, Electronic Health Record (EHR) implementation, price negotiation, better coordination, and continuity of services for patients, thus affecting performance. This study aimed to examine the relationship between physician integration and hospital performance, investigating both financial and quality outcomes. We used a longitudinal study design. Our sample was hospital-level data from 2014 to 2019, which contained 6000 U.S. hospital-year observations. The dependent variables were quality outcomes (readmission rates) and financial outcomes (total and operating margins). The independent variable explored three dimensions of integration: high, low, and overall integration. Findings showed no impact of hospital–physician integration on quality outcomes and financial performance. High-integration hospitals did not show any significant relationships with quality outcomes and financial performance compared to hospitals that did not have high integration. Hospital–physician integration may have little potential to bring clinical integration even though vertical integration is present. A commitment to improving quality as a strategic priority may be vital in impacting quality outcomes, followed by financial performance.
Full article
Open AccessReview
European Nurses’ Burnout before and during the COVID-19 Pandemic and Its Impact on Patient Safety: A Scoping Review
by
Goitseone Mogomotsi and Jennifer Creese
Hospitals 2024, 1(2), 151-171; https://doi.org/10.3390/hospitals1020013 - 6 Oct 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Health systems around the world continue to experience healthcare workforce shortages, including shortages of nurses. This results in staff experiencing prolonged shifts and other stressors, which are linked to burnout, yet burned-out staff are then entrusted with the provision of patient care, despite
[...] Read more.
Health systems around the world continue to experience healthcare workforce shortages, including shortages of nurses. This results in staff experiencing prolonged shifts and other stressors, which are linked to burnout, yet burned-out staff are then entrusted with the provision of patient care, despite healthcare facilities being regarded as safety-critical areas. It is assumed that the situation may have been worsened by the COVID-19 pandemic. This scoping review aims to identify the prevalence of burnout among nurses in Europe before and during the pandemic, the factors associated with this burnout, and its impact on patient safety. A literature search was conducted in the MEDLINE database; search terms included Nurse and Burnout and Patient Safety and their synonyms. The search limits used were English language, 2013 to 2023 publication years, original published research only (excluding review papers, dissertations, and unpublished reports), and studies conducted in European countries. A total of 16 papers were included for analysis: four indicated burnout levels of study participants, while 11 gave scores for individual burnout symptoms. Almost all studies indicated factors that were linked to burnout or individual dimensions of burnout. A few papers touched on the implications of these factors on patient safety. The review findings concluded that the few studies providing burnout levels on study participants could not give a clear picture of the burnout prevalence among nurses across Europe, either in general, before, or during the pandemic; therefore, this objective was not achieved and more research is required to establish this. Several factors thematically classified as sociodemographic, personal, organizational, and patient/client-related were linked to burnout. However, there were some contradictions in sociodemographic factors. Low personal accomplishment was the most common symptom of burnout before the pandemic, followed by emotional exhaustion and lastly depersonalization. Emotional exhaustion took the lead during the COVID-19 pandemic, followed by low personal accomplishment, and depersonalization remained the least common. More research is needed to establish the relationship between burnout and these factors.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessEditorial
Redefining Hospital Excellence: Join the Conversation
by
Francisco Epelde
Hospitals 2024, 1(1), 149-150; https://doi.org/10.3390/hospitals1010012 - 5 Sep 2024
Abstract
Welcome to Hospitals, a journal dedicated to exploring the essential pillars that drive the success and evolution of hospitals in today’s world [...]
Full article
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
The TERCAP Tool: Investigation of Nursing Errors in Greek Hospitals
by
Despoina Pappa, Eleni Evangelou, Ioannis Koutelekos, Evangelos Dousis, Nikoletta Margari, Georgia Toulia, Areti Stavropoulou, Alexandra Koreli, Maria Theodoratou, Aggeliki Bilali, Konstantina Chasaki, Afroditi Zartaloudi and Chrysoula Dafogianni
Hospitals 2024, 1(1), 131-148; https://doi.org/10.3390/hospitals1010011 - 13 Aug 2024
Abstract
Background: Errors are a common occurrence in all healthcare settings, and the safety of patients is a critical concern that involves multiple factors, including the complex and demanding nature of nursing practice. Nurses, due to their continuous and direct patient care, play a
[...] Read more.
Background: Errors are a common occurrence in all healthcare settings, and the safety of patients is a critical concern that involves multiple factors, including the complex and demanding nature of nursing practice. Nurses, due to their continuous and direct patient care, play a pivotal role in ensuring patient safety. This cross-sectional study aimed to investigate the factors that contribute to errors from the perspectives of nurses in Greek hospitals, with a focus on understanding the challenges they face in their daily practice. Methods: Clinical nurses willingly and anonymously filled out a specific structured questionnaire, the Taxonomy of Error, Root Cause Analysis, and Practice-responsibility (TERCAP) tool that describes the conditions under which an error during clinical practice occurred. The study method included convenience sampling. After obtaining permission, questionnaires were distributed to hospital departments. To accommodate pandemic-related restrictions, an electronic version of the questionnaire was also created for distribution and collection. Analysis of data was accomplished via SPSS 26.0. Results: Five hundred and ninety-seven clinical nurses participated anonymously, reporting errors in almost seven out of ten cases, often attributing them to high workload and staff shortages. Errors were commonly reported during different shifts in this study. Factors such as assigning significant responsibilities to inexperienced staff and inadequate implementation guidelines were highlighted. Conclusions: The in-depth study of nursing errors provides a nuanced understanding of their causes by categorizing them based on various factors. It emphasizes the complexity of challenges and the need to integrate systemic, clinical, and individual factors into intervention strategies, including medication protocols, ongoing training, clear communication, administrative support, and fostering an open communication culture.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Comparing Healthcare Facilities to Demographic Standards in the Pakistani Rural Environment
by
Mir Aftab Hussain Talpur
Hospitals 2024, 1(1), 114-130; https://doi.org/10.3390/hospitals1010010 - 9 Aug 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The population of Pakistan is increasing, with approximately 2% growth. Over the years, the country’s healthcare system has struggled to meet the needs of the population. Nevertheless, because of shortages compared to population distribution, people are facing primary healthcare challenges, specifically in rural
[...] Read more.
The population of Pakistan is increasing, with approximately 2% growth. Over the years, the country’s healthcare system has struggled to meet the needs of the population. Nevertheless, because of shortages compared to population distribution, people are facing primary healthcare challenges, specifically in rural environments. Because of the absence of standard health services, the quality of the health sector deteriorated over time. Therefore, this study aims to compute the shortage of health facilities in Badin, Pakistan, per local health standards. The information related to available health institutes was obtained from the office of the Director-General Health Office with the help of a questionnaire. The current population was determined, and the same was projected up to the year 2035 with the help of a compound interest model. The linear model was executed and found to be significant, with the values of R = 0.996, R2 = 0.991, and Sig. F-change = 0.000. The Badin sub-region needed 201 basic health units, 37 rural health centers, and 746 dispensaries. The public health institutes were found unavailable as per demographic standards. This research set a platform for local authorities to take certain actions in framing essential policies to curtail the shortage of health institutions. This study is significant, as it confers existing and futuristic health institute demands. This research can serve as a model for remote sub-regions to address primary healthcare issues, including the fight against diseases and viruses. This research may also contribute to sustainable goal number 3, i.e., Good Health and Well-being.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Effectiveness of Multidisciplinary Pre-Discharge Conferences on Concordance Rate in Place of End-of-Life Care and Death: A Single-Center Retrospective Study
by
Hisayuki Miura and Yuko Goto
Hospitals 2024, 1(1), 104-113; https://doi.org/10.3390/hospitals1010009 - 1 Aug 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Backgrounds: The pre-discharge conference (PDC) is crucial for ensuring care continuity based on patients’ preferences and goals. However, there is no quantitative on its effectiveness. We investigated the effectiveness of multidisciplinary PDC on the concordance rate between the preferred (PPEoLC) and actual place
[...] Read more.
Backgrounds: The pre-discharge conference (PDC) is crucial for ensuring care continuity based on patients’ preferences and goals. However, there is no quantitative on its effectiveness. We investigated the effectiveness of multidisciplinary PDC on the concordance rate between the preferred (PPEoLC) and actual place of end-of-life care and death. Methods: Overall, 551 older homebound patients (median age, 83.0 years; female, 49.4%; male, 50.6%) receiving continuous home medical care through clinics were enrolled in hospital ward admission from March 2011 to September 2018. Patient demographics, presence or absence of PDCs, statements from patients and their families regarding PPEoLC, and place of death of deceased patients were confirmed from the patients’ medical records, followed by concordance rate analyses between PPEoLC and place of death and a multivariate analysis of home mortality. We used the Mann–Whiney U test to assess attribute data, hypothesis testing to assess the difference in the population proportions, and binominal logistic regression analyses to evaluate the relationship between valuables. Results: In the conference group, the home mortality rate, patients’ and their families’ expression rates, and preferences for their home of PPEoLC were higher (p < 0.001) than those in the non-conference group. The place of death was significantly influenced by family preferences. Conclusions: PDC can affect the place of death of homebound patients, but family preferences rather than patient preferences influence the decision of the patient’s place of death. To better reflect the patient preferences, patient-centered decision support should be provided earlier in the disease process.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessFeature PaperReview
Transformational Leadership—Quality Achievements and Benefits for the Healthcare Organizations: A Scoping Review
by
Eleni Tsapnidou, Martha Kelesi, Michael Rovithis, Georgios Katharakis, Georgia Gerogianni, Chrysoula Dafogianni, Georgia Toylia, Georgia Fasoi and Areti Stavropoulou
Hospitals 2024, 1(1), 87-103; https://doi.org/10.3390/hospitals1010008 - 26 Jul 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Effective nursing leadership is critical for healthcare organizations’ sustainability as nurse leaders influence many organizational aspects, including staff retention, quality of care, resource management, and development. The aim of this study is to highlight the quality achievements and benefits that transformational leadership may
[...] Read more.
Effective nursing leadership is critical for healthcare organizations’ sustainability as nurse leaders influence many organizational aspects, including staff retention, quality of care, resource management, and development. The aim of this study is to highlight the quality achievements and benefits that transformational leadership may have for healthcare organizations. An extensive literature search has been conducted through MEDLINE and Scopus. The 6-stage framework proposed by Arksey and O’Malley was applied, guided the scoping review process. Data extracted from the included studies were systematically charted. This approach allowed for a comprehensive understanding of the advantages of transformational leadership in healthcare organizations. Of the 1245 searched articles, 26 encountered the study’s inclusion criteria. Analysis of the studies led to the formulation of two thematic categories, namely, (a) transformational leadership and human resources and (b) transformational leadership and healthcare delivery. Results indicated that transformational nursing leadership can benefit healthcare organizations in terms of effective resource management, high quality of care, and sustainability. Visionary leaders support staff retention, innovation, and research and promote organizational status and development. Through continuous support and training, transformational nurse leaders can ensure nurses’ job satisfaction and engagement, patients’ satisfaction, the best therapeutic outcomes, and high levels of organizational achievement.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Investigation of Nursing Errors in Greek Pediatric Hospitals
by
Despoina Pappa, Eleni Evangelou, Ioannis Koutelekos, Evangelos Dousis, Georgia Toulia, Areti Stavropoulou, Nikoletta Margari, Anna Giga, Eftychia Ferentinou, Konstantina Chasaki, Aggeliki Bilali, Afroditi Zartaloudi and Chrysoula Dafogianni
Hospitals 2024, 1(1), 75-86; https://doi.org/10.3390/hospitals1010007 - 3 Jul 2024
Cited by 1
Abstract
Background: Adverse events are a prevalent occurrence across pediatric healthcare environments, and patient safety is intricately tied to nursing errors due to nurses’ consistent presence and interaction with patients, which surpasses that of any other healthcare professional. This research sought to explore the
[...] Read more.
Background: Adverse events are a prevalent occurrence across pediatric healthcare environments, and patient safety is intricately tied to nursing errors due to nurses’ consistent presence and interaction with patients, which surpasses that of any other healthcare professional. This research sought to explore the factors influencing errors as perceived by pediatric nurses in Greek hospital settings. Methods: Clinical pediatric nurses voluntarily and anonymously completed a specialized structured survey, utilizing the Taxonomy of Error, Root Cause Analysis, and Practice-responsibility (TERCAP) tool, which delineates the circumstances surrounding errors occurring during clinical practice. Results: Among the participants employed in the pediatric department, 80.8% (n = 84) reported experiencing an error at their workplace. Notably, in 48.7% (n = 38) of these instances, the error was attributed to themselves (personal responsibility), while in 78.9% (n = 56) of cases, it was linked to errors committed by other colleagues in the clinic. As reported by participants in pediatric departments, the primary factors contributing to potential error occurrence include the absence or inadequacy of orientation and training for new staff (43.2%), the absence of a standardized protocol for resolving disagreements (39%), insufficient ongoing training (38.3%), and breakdowns in interdisciplinary communication (21%). Conclusions: By classifying errors based on various criteria such as outcomes, processes, cognitive reasoning, ethical considerations, and importance, this study presents a holistic framework for examining pediatric nurses’ errors from diverse perspectives. Through this classification approach, the study establishes a foundation for tailored interventions targeting particular aspects of errors and their root causes in pediatric departments.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Impact of Program Region and Prestige on Industry Supplemental Earnings for Pediatric Orthopedic Surgery Fellowships in the United States: A Retrospective Analysis
by
Abhinav R. Balu, Anthony N. Baumann, Grayson M. Talaski, Faheem Pottayil, Kempland C. Walley, Albert T. Anastasio and Keith D. Baldwin
Hospitals 2024, 1(1), 65-74; https://doi.org/10.3390/hospitals1010006 - 4 Jun 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Introduction: With the passage of the Physician Payment Sunshine Act, there has been increased transparency regarding the industrial financial relations that physicians have. Orthopedic surgeons have been highly studied in this domain with approximately 50% of all orthopedic surgeons engaging in industrial financial
[...] Read more.
Introduction: With the passage of the Physician Payment Sunshine Act, there has been increased transparency regarding the industrial financial relations that physicians have. Orthopedic surgeons have been highly studied in this domain with approximately 50% of all orthopedic surgeons engaging in industrial financial relationships. Furthermore, an increasing number of orthopedic surgeons are seeking fellowship training with pediatric fellowship programs gaining popularity in recent years. The purpose of this study is to evaluate the impact various pediatric orthopedic fellowship programs have on industry earnings and academic productivity. Methods: Pediatric orthopedic fellowship programs were identified via the Orthopedic Society of North America (POSNA) website. Information on individual fellowship programs was obtained from their respective websites. Academic productivity was measured via an aggregate of all employed physicians’ H-index at a specific fellowship as found on the Scopus website. The Open Payments Database (OPD) website was used to assess lifetime industry earnings. Other variables such as Newsweek or Doximity ranking were taken directly from relevant websites. Statistical analysis was performed using a Kruskal–Wallis test with Bonferroni correction and Mann–Whitney U-test. Results: A total of 43 pediatric orthopedic surgery fellowships in the United States were identified with a total of 392 physicians as fellowship faculty. Complete OPD and H-index information were available for 336 of those physicians (85.7%). On average, there were 7.81 ± 5.18 physicians and 1.56 ± 0.93 fellows per program. The mean combined physician H-index was 117.23 ± 122.51, and the mean combined physician lifetime supplemental earnings in dollars was $646,684.37 ± $1,159,507.17. There was no significant relationship between region of pediatric orthopedic fellowship, Newsweek ranking of affiliated hospital, Doximity ranking of affiliated hospital, presence of MBA program, type of program (public, private, mixed), and the lifetime industry earnings or academic productivity of program graduates. Conclusions: Despite the observed lack of statistical significance, there were clear trends observed with fellowship programs in the northeast and west coast regions being the highest earning and fellowship programs with top 10 Newsweek ranking of affiliated hospital having by far the greatest industry earnings. Sample size limitations likely prevented the detection of statistical significance. Future studies should examine if any relation exists when accounting for type of industry payment received and case volume per fellowship program.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Confused about Rehabilitation? Multi-Faceted Approaches for Brain Injured Patients in a Confusional State
by
Jesper Fabricius, Anna Birthe Andersen, Gitte Lindegård Munk and Hanne Kaae Kristensen
Hospitals 2024, 1(1), 50-64; https://doi.org/10.3390/hospitals1010005 - 9 May 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Post-injury confusional state is a common phenomenon following acquired brain injury. A multi-faceted approach for decreasing confusion is recommended, but there is a paucity of research related to non-pharmacological management. The main objective was to present a conceptual model of multi-faceted approaches for
[...] Read more.
Post-injury confusional state is a common phenomenon following acquired brain injury. A multi-faceted approach for decreasing confusion is recommended, but there is a paucity of research related to non-pharmacological management. The main objective was to present a conceptual model of multi-faceted approaches for confusion, and secondly to investigate the rehabilitation outcome following these approaches. The setting is a specialized ward for rehabilitation of patients with severe cognitive difficulties following acquired brain injury. The conceptual model encompasses neurobehavioral strategies, pharmacological treatment, engagement in meaningful occupations, next of kin involvement, organizational demands, the physical environment, along with differential diagnostics. Patient cases are provided to illustrate the impact of each approach. A total of 141 of 281 patients were in a confusional state at admission. At discharge, 62% had emerged from the confusional state. Patients in a confusional state due to traumatic brain injury and subarachnoid hemorrhage had clinically important differences of >22 points in the functional independence measure from admission to discharge, following rehabilitation efforts based on the conceptual model. No clinically important difference was seen in patients with non-SAH stroke and patients with other types of brain injuries. The proposed conceptual model should be further evaluated in complex intervention studies.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Intermediate Care for Patient-Centered Care, Shared Decision Making, and Hospital Discharge Support in a Japanese Acute Care Hospital: A Cross-Sectional Study
by
Yuko Goto and Hisayuki Miura
Hospitals 2024, 1(1), 32-49; https://doi.org/10.3390/hospitals1010004 - 1 May 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
[Background] Intermediate care is a limited-time service founded on patient-centered care (PCC) that ensures continuity and quality of care during the transition between home and acute care services, promotes recovery, and restores independence and confidence. In Japan, systematic education on intermediate care for
[...] Read more.
[Background] Intermediate care is a limited-time service founded on patient-centered care (PCC) that ensures continuity and quality of care during the transition between home and acute care services, promotes recovery, and restores independence and confidence. In Japan, systematic education on intermediate care for care providers is lacking. [Method] The present study explored the relationship between a Japanese scale used to evaluate individualized discharge support skills, a Japanese version of a tool for evaluating intermediate care based on PCC, and a tool that measures the shared decision making of care providers, which is the pinnacle of PCC. [Results] Clear correlations were found between the concepts evaluated using these three tools. Some concepts were not correlated between the Japanese scale that evaluated individualized discharge support skills and intermediate care based on PCC. [Conclusions] Elucidating the perspectives that help expand discharge care to intermediate care based on PCC will contribute to future education on intermediate care for Japanese care providers and to enriching patient-centered intermediate care.
Full article
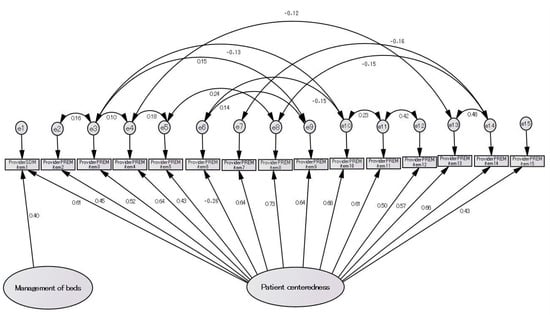
Figure 1
Open AccessOpinion
A Molecule from Madness: An Exploration into Patients’ Illnesses through West Texas Polio
by
Jonathan Kopel
Hospitals 2024, 1(1), 16-31; https://doi.org/10.3390/hospitals1010003 - 16 Jul 2023
Abstract
Neurology holds a unique perspective that embodies the art of capturing a patient’s story. Despite medical advancements, many neurological conditions leave patients permanently impaired. This sudden loss of independence can be demoralizing and, in most cases, directly changes a person’s identity. It is
[...] Read more.
Neurology holds a unique perspective that embodies the art of capturing a patient’s story. Despite medical advancements, many neurological conditions leave patients permanently impaired. This sudden loss of independence can be demoralizing and, in most cases, directly changes a person’s identity. It is therefore a necessary part of a neurologist’s trade to know their patient’s history—their story. Their tales reveal intimate details of their personality changes, memory loss, sensory deprivation, and movement disorders. A true neurologist is a person that remains vulnerable through their willingness to take a history—the story of their patient—and remain curious, vulnerable, and compassionate through their journey to heal and comfort the patient. To understand the patient’s illness experience in neurology, the underlying themes of patient recovery (compassion, determination, and patience) are explored with regard to the neurological patient’s experience. These themes are then expanded to include the neurology patient’s mental perceptions of themselves, and their illness’ influences over their identity, recovery, and daily life. In addition to the patient’s experience, the neurologist’s awareness and emotional response to the patient’s illness experience can provide an opportunity to develop a strong therapeutic bond with their patient and improve patient outcomes. Given that their neurological impairment causes a loss of independence and control over their identity and self-worth, neurologists can incorporate the patient’s experience into their management and treatment, to better address their emotional and spiritual needs as they come to terms with their identity.
Full article
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Obstetric Violence in Italy
by
Marina Di Lello Finuoli
Hospitals 2024, 1(1), 3-15; https://doi.org/10.3390/hospitals1010002 - 29 Jun 2023
Cited by 1
Abstract
This essay focuses on so-called obstetric violence, i.e., the medical malpractice consisting of disrespect and/or abuses to the detriment of women during their labor or when they give birth, as well as during health care services concerning the sexual and reproductive sphere. The
[...] Read more.
This essay focuses on so-called obstetric violence, i.e., the medical malpractice consisting of disrespect and/or abuses to the detriment of women during their labor or when they give birth, as well as during health care services concerning the sexual and reproductive sphere. The main goal is to start a debate on a topic already considered by foreign lawmakers, also for punishment purposes. After an empirical-criminological survey of the cases and the misconduct to be labelled as “obstetric violence”, this essay analyses the legal tools available in Italy. From a law reform perspective, the author reflects on the (non-criminal) strategies to prevent distortions of the doctor–patient relationship as well as on the harm to women’s self-determination and dignity, particularly in respect of the rules on informed consent.
Full article
Open AccessEditorial
Hospitals: A Journal Title with Many Meanings and One Vision
by
Antonio Oliva, Al Ozonoff, Matteo Caputo and Simone Grassi
Hospitals 2024, 1(1), 1-2; https://doi.org/10.3390/hospitals1010001 - 9 Nov 2022
Abstract
“Hospitals” as a name for a journal might appear simply as an umbrella term for healthcare-relevant research [...]
Full article
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Healthcare, IJERPH, Nursing Reports, Trauma Care, Hospitals
Integrated Health Services across Different Levels: Worldwide Experiences
Topic Editors: Alexandre Morais Nunes, Diogo Cunha FerreiraDeadline: 28 February 2025
Topic in
IJERPH, JCM, Medicina, Hospitals, Healthcare
The Imperative of Patient Safety and Safety Culture in Contemporary Healthcare
Topic Editors: Hana Brborović, Ognjen Brborovic, Reinhard StrametzDeadline: 25 December 2025

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Hospitals
AI in Hospitals: Present and Future
Guest Editor: Francisco EpeldeDeadline: 31 July 2025





