Django Form
What is a HTML form? What kind of use cases does it have?
A webform, web form or HTML form on a web page allows a user to enter data that is sent to a server for processing. Forms can resemble paper or database forms because web users fill out the forms using checkboxes, radio buttons, or text fields. For example, forms can be used to enter shipping or credit card data to order a product, or can be used to retrieve search results from a search engine.
A HTML form is the most common way to send data from a client application to a server. In this article, we are going to learn how to use Django's Form library to handle HTML forms.
Benefits of Using Django's Form Library
In one of the previous articles, Writing Views to Upload Posts for Your First Python Django Application, we learned how to use request.POST variable to retrieve data from a HTML form. However, simply retrieving data is not enough because we would probably want to handle data validation and avoid writing the HTML form manually in a template.
Luckily, Django's form library is designed to provide the following benefits:
- Auto-generate a HTML form from a form widget.
- Validate submitted data against a set of rules.
- Redisplay the HTML form with errors if there's any.
- Convert submitted data into Python compatible types.
Basic Concepts
Before we dive into the details about writing a form, we need to know the following concepts:
- Widget: A Python class that renders itself into an HTML form.
- Field: A Python class that validates the data, e.g. a
CharFieldthat limits the number of maximum characters. - Form: A collection of fields.
- Form Assets: CSS and Javascript associated with rendering a form.
Designed correctly, the Form library is decoupled from other Django components, such as the database layer and even templates. By separating the Form library from the rest of Django, we can write and test forms independently from the rest of our application, which increases the maintainability of our application.
Forms and Views
Now let's go ahead and create a form object that represents a Post in myblog/forms.py.
[python]
from django import forms
class PostForm(forms.Form):
content = forms.CharField(max_length=256)
created_at = forms.DateTimeField()
[/python]
Then we create a new view that returns our form in the context.
[python]
from myblog.forms import PostForm
def post_form_upload(request):
if request.method == 'GET':
form = PostForm()
else:
# A POST request: Handle Form Upload
form = PostForm(request.POST) # Bind data from request.POST into a PostForm
# If data is valid, proceeds to create a new post and redirect the user
if form.is_valid():
content = form.cleaned_data['content']
created_at = form.cleaned_data['created_at']
post = m.Post.objects.create(content=content,
created_at=created_at)
return HttpResponseRedirect(reverse('post_detail',
kwargs={'post_id': post.id}))
return render(request, 'post/post_form_upload.html', {
'form': form,
})
[/python]
Then we create a new template that renders our form inside an HTML page in myblog/templates/post_form_upload.html.
[python]
<form action='/post/form_upload.html' method='post'>{% csrf_token %}
{{ form.as_p }}
<input type='submit' value='Submit' />
</form>
[/python]
Finally, we modify myblog/urls.py to append the following entry:
[python]
urlpatterns = patterns('',
...
url(r'^post/form_upload.html$',
'myblog.views.post_form_upload', name='post_form_upload'),
...
)
[/python]
Now we can access the URL http://localhost:8000/post/form_upload.html to take a look at our new post form page:
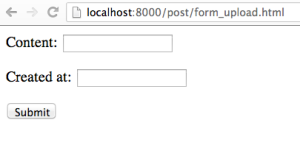
Our empty form page.
Filling out the form and clicking "submit" redirect you to the new post's detail page:
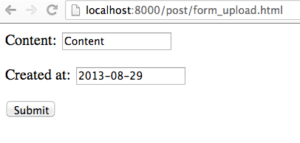
Our form filled in.
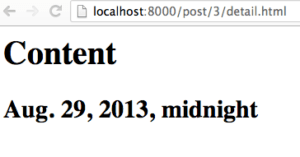
Our page after being submitted.
Since both the "content" and "created at" fields are required, you will get an error when you try to upload an empty field.
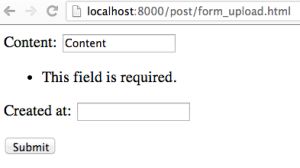
Required input error..
Summary and Tips
In this article, we learned how to use Django's form library to handle HTML forms. While it's common practice to create an HTML form by hand, creating Django's form objects provides better maintainability, readability and functionality. In the next article, we are going to learn how to use Django's ModelForm to auto-generate forms from models.

