0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
65 viewsSteel Piston PDF
Steel Piston PDF
Uploaded by
victoverCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Steel Piston PDF
Steel Piston PDF
Uploaded by
victover0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
65 views14 pagesOriginal Title
Steel Piston.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
65 views14 pagesSteel Piston PDF
Steel Piston PDF
Uploaded by
victoverCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 14
SERIES 60 SERVICE MANUAL
All information subject to change without notice.
6SE483 9610 1996 DETROIT DIESEL CORPORATION From Bulletin 19-60-98 1-275
1.18 PISTON AND CONNECTING ROD ASSEMBLY
Since the piston and connecting rod assembly is one unit made of two separate components, the
components will be addressed in separate sections.
For general piston information, refer to section 1.17.
For general connecting rod assembly information, refer to section 1.19.
1.18 PISTON AND CONNECTING ROD ASSEMBLY
All information subject to change without notice.
1-276 From Bulletin 19-60-98 6SE483 9610 1996 DETROIT DIESEL CORPORATION
1.18.1 Repair or Replacement of Piston and Connecting Rod
To determine if repair is possible or replacement is necessary, perform the following procedure.
See Figure 1-233.
Figure 1-233 Flowchart for Repair or Replacement of Piston and Connecting Rod
SERIES 60 SERVICE MANUAL
All information subject to change without notice.
6SE483 9610 1996 DETROIT DIESEL CORPORATION From Bulletin 19-60-98 1-277
1.18.2 Removal and Cleaning of Piston and Connecting Rod
Precleaning is not necessary.
Remove the piston and connecting rod assembly as follows:
1. Drain the engine cooling system. Refer to section 13.8.4.
2. Drain the engine oil. Refer to section 13.8.1.
3. Remove the oil pan. Refer to section 3.11.2.
4. For pre-1991 engines, disconnect and remove the lubricating oil pump inlet pipe and
screen assembly, oil pump outlet pipe and lubricating oil pump. Refer to section 3.2.2.
See Figure 1-234.
NOTE:
It is not necessary to remove the oil pump on 1991 and later model year engines.
Figure 1-234 Oil Pump Removal (Pre-1991 Engines)
5. Remove the cylinder head. Refer to section 1.2.2.
6. Use an emery cloth to remove any carbon deposits from the upper surface of the cylinder
liner.
1.18 PISTON AND CONNECTING ROD ASSEMBLY
All information subject to change without notice.
1-278 From Bulletin 19-60-98 6SE483 9610 1996 DETROIT DIESEL CORPORATION
NOTICE:
If installed, remove the piston cooling nozzles from the base of
the cylinder bores to prevent nozzle damage, during piston
removal.
7. Remove the bearing cap and lower bearing shell from the connecting rod.
8. Install connecting rod guides, J 35945 (or equivalent) for removing cast-iron pistons or
J 43661 (or equivalent) for removing forged steel pistons, to protect the crankshaft
journals.
9. Push the piston and rod assembly out through the top of the cylinder block.
NOTE:
The piston cannot be removed from the bottom of the cylinder block.
10. Assemble the bearing cap and lower bearing shell to the connecting rod after removal. If
not already marked, match-mark the rod and cap (on the tang side) with the cylinder
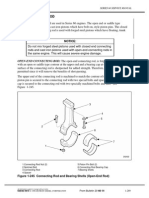
number from where they were removed. See Figure 1-235.
Figure 1-235 Connecting Rod and Cap Identification
NOTE:
When removed, the bearing cap and the bearing shell must be reinstalled on the
original connecting rod before another connecting rod bearing cap is removed.
SERIES 60 SERVICE MANUAL
All information subject to change without notice.
6SE483 9610 1996 DETROIT DIESEL CORPORATION From Bulletin 19-60-98 1-279
NOTE:
If removing the piston and connecting rod assembly to work on the cylinder liner, stop
here. Refer to section for cylinder liner removal procedure.
1.18.3 Disassembly of Piston and Connecting Rod Assembly
Piston assembly components should be segregated by cylinder and match-marked during
disassembly to ensure they are assembled in the same position and orientation.
NOTICE:
Stamping cylinder numbers on the piston assembly will damage
the components.
It is best to use a paint pencil. For cast iron pistons, mark the pin, skirt, bushing, and dome ear at
the front. For forged steel pistons, mark the pin, skirt, and dome.
If the second ring on the piston is a rectangular section, the engine should be fitted with the
current piston assemblies that contain a Second Keystone Ring (SKR) configuration. Former
piston rings must NOT be used in the SKR configuration.
Disassemble the cast iron piston and connecting rod assembly as follows:
1. Place the piston, dome down, on the round plate of the piston and connecting rod holding
fixture, J 36211 . See Figure 1-236.
Figure 1-236 Piston Connecting Rod Holding Fixture
1.18 PISTON AND CONNECTING ROD ASSEMBLY
All information subject to change without notice.
1-280 From Bulletin 19-60-98 6SE483 9610 1996 DETROIT DIESEL CORPORATION
2. Slide the movable portion of the fixture until it contacts the piston pin and tighten the
handle.
3. Loosen the two bolts that secure the connecting rod to the piston pin and remove the two
bolts and spacers.
4. Remove the connecting rod.
5. Remove the piston, pin and skirt from the holding fixture.
Disassemble the forged steel piston and connecting rod assembly as follows:
1. Using the required snap ring pliers, remove the circlip-type snap rings from the piston
skirt.
2. Slide out the piston pin and remove the rod from the piston.
3. Disassemble the piston dome from the skirt. Tool J 33048 may be used to aid in
separating these parts.
1.18.3.1 Inspection of Piston and Connecting Rod Assembly
Refer to section 1.17.3 for disassembly of the piston and piston rings.
Refer to section 1.17.3.1 for inspection of the piston and piston rings.
Refer to section 1.19.3 for disassembly of the connecting rod.
Refer to section 1.19.3.1 for inspection of the connecting rod.
1.18.4 Assembly of Piston and Connecting Rod Assembly
Assemble the cast iron piston and connecting rod assembly as follows:
NOTICE:
The connecting rod-to-piston pin attaching bolts and spacers are
specially designed components. No other bolts or spacers may
be used. Piston pin bolts are considered one-use items and
must be replaced with new bolts when removed for any
reason. Failure to observe this precaution may result in bolt
loosening or breaking during engine operation, which may cause
serious engine damage.
1. Discard used piston pin bolts and replace with new bolts.
2. Because of the low clearance fit between the piston pin and three-piece pin bearing, care
in handling and cleanliness of piston dome bore, bearings and, piston pin are important.
Otherwise, assembly may be impossible. The specifications on reusing piston assembly
components are listed in Table 1-16 and listed in Table 1-17.
3. The pin bore and bearing backs should be wiped clean prior to installation of the
bushings in the piston dome.
SERIES 60 SERVICE MANUAL
All information subject to change without notice.
6SE483 9610 1996 DETROIT DIESEL CORPORATION From Bulletin 19-60-98 1-281
4. Installing piston pin bearings (with the piston dome standing on the rim) requires the
upper bearing piece to be inserted through the end of the pin bore and dropped over the
retaining pin.
5. The lower bearing pieces are inserted flat side in by tilting the bearing at approximately a
30 angle from the vertical away from the dome ear.
6. Set the edge of the bearing parting line on the edge of the upper piece notch and rotate the
lower bushing up and into place. The lower bearing can then be pushed full into the bore
with the thumb.
7. Lubricate the piston pin bearings with clean engine oil. (Straight 30 weight oil is
recommended.)
8. Set the piston skirt on the piston dome.
9. Align the piston pin holes in the dome and skirt.
10. Check the piston pin for foreign matter in the bolt holes.
11. Lubricate the pin with clean engine oil and install in the bores with the bolt holes facing
the connecting rod, away from the dome.
NOTE:
The piston pin may feel considerably tighter than with conventional designs and
possibly may not be turned easily by hand. Proper pin and bearing installation should
result in a piston assembly in which the pin can be turned with the connecting rod while
the piston dome is standing on the rim and the piston skirt is held with the other hand.
12. Apply a small amount of International Compound #2, or equivalent, to the bolt threads
and bolt head contact surfaces and both ends of the spacers.
International Compound #2 is a trademark of IRMCO.
NOTICE:
The connecting rod-to-piston pin attaching bolts and spacers are
specially designed components. No other bolts or spacers may be
used. Piston pin bolts are considered one-time use items and
must be replaced with new bolts when removed for any reason.
Failure to observe this precaution may result in bolt loosening or
breakage during engine operation, which may cause serious
engine damage.
13. Install the spacers on the two special connecting rod-to-piston attaching bolts.
14. After clamping the connecting rod in holding fixture, J 36211 , tighten each piston pin
bolt to 95-122 N m (70-90 lb ft) torque. See Figure 1-236.
15. Complete the process by tightening the bolts to 157 6.8 N m (115 5 lb ft) final
torque.
1.18 PISTON AND CONNECTING ROD ASSEMBLY
All information subject to change without notice.
1-282 From Bulletin 19-60-98 6SE483 9610 1996 DETROIT DIESEL CORPORATION
Assemble the forged steel piston and connecting rod assembly as follows:
1. Set the piston skirt on the piston dome.
2. Align the piston pin holes in the dome and skirt.
3. Position the end of the connecting rod inside the piston dome.
4. Lubricate the piston pin with clean engine oil and install into the pin bores.
5. Using the required snap ring pliers, install the circlip-type snap rings into the recesses in
the piston skirt to lock the pin in place. Orient the snap ring gap to either the 12 o'clock or
6 o'clock position.
1.18.5 Installation of Piston and Connecting Rod Assembly
To install the piston and connecting rod assembly to the engine, perform the following:
1. If the rings have been removed, install them onto the dome, refer to section . If the piston
rings are installed, proceed to step 2
2. Add clean engine oil to a clean pan at least 305 mm (12 in.) in diameter, until the level
reaches approximately 76 mm (3 in.).
3. Place the piston and connecting rod assembly into pan, with the dome of the piston on the
bottom of the pan. See Figure 1-237.
4. Coat the piston liberally with the engine oil, saturating the piston rings and lands.
Figure 1-237 Piston and Connecting Rod Assembly Lubrication
SERIES 60 SERVICE MANUAL
All information subject to change without notice.
6SE483 9610 1996 DETROIT DIESEL CORPORATION From Bulletin 19-60-98 1-283
5. Remove assembly from pan and position (stagger) the piston ring gaps properly on the
piston at 90 intervals. See Figure 1-238.
Figure 1-238 Figure Piston Ring Positioning
6. Place the piston, dome down, in the bottom of the pan. Center the dome of the piston
within the pan.
7. Coat the inside diameter of the ring compression tool, J 35598 liberally with clean
engine oil from the pan.
1.18 PISTON AND CONNECTING ROD ASSEMBLY
All information subject to change without notice.
1-284 From Bulletin 19-60-98 6SE483 9610 1996 DETROIT DIESEL CORPORATION
NOTICE:
Inspect the piston ring compressor for nicks or burrs, especially at
the non-tapered inside diameter end. Nicks or burrs on the inside
diameter of the ring compressor may result in damage to the
piston rings.
8. Install the tapered end of the piston ring compression tool over the end of the connecting
rod, and down onto the piston. As the compression tool slides down the piston to the
piston ring area, apply slow, even pressure on both sides of the compression tool to
compress the rings. See Figure 1-239.
Figure 1-239 Installing Piston and Connecting Rod Assembly into Ring
Compressor
9. Slide the compression tool down until it contacts the bottom of the drain pan.
10. Position the crankshaft so that the connecting rod journal for the cylinder being worked
on is at bottom-dead-center.
11. Remove the cap from the connecting rod.
SERIES 60 SERVICE MANUAL
All information subject to change without notice.
6SE483 9610 1996 DETROIT DIESEL CORPORATION From Bulletin 19-60-98 1-285
NOTICE:
Do not allow the connecting rod to contact the cylinder liner on
installation, or damage to the liner may occur. The numbers on
the side of the connecting rod and cap identify the rod with the
cap and indicate the particular cylinder in which they are used. If a
new service connecting rod is to be installed, the same
identification numbers must be stamped in the same location (on
the tang side of the rod and cap) as on the connecting rod that
was replaced.
12. Install the required connecting rod guide (J 35945for cast iron piston or J 43661 for
forged steel piston) over the ends of the connecting rod bolts to prevent damaging the
crankshaft journals or the joint face of the rod. The guides also prevent the connecting
rod from contacting the liner and damaging the surface. See Figure 1-240.
Figure 1-240 Connecting Rod Guides Installation
NOTE:
The connecting rod guides are threaded at the upper end and attach to the rod bolts.
1.18 PISTON AND CONNECTING ROD ASSEMBLY
All information subject to change without notice.
1-286 From Bulletin 19-60-98 6SE483 9610 1996 DETROIT DIESEL CORPORATION
NOTICE:
Do not lift the assembly using the connecting rod guides. The
assembly could dislodge from the connecting rod guides and
could cause engine damage.
13. Grasp the connecting rod assembly with one hand, and the piston ring compressor with
the other. Lift the assembly out of the pan, and allow excess oil to drain back into the
pan.
NOTE:
Do not allow the piston to slide out of the bottom of the ring compressor.
14. With the crankshaft throw in the bottom position, being sure the number on the
connecting rod is towards the cooler side of the engine, place the ring compressor and the
piston and connecting rod assembly over the cylinder where it is to be installed. See
Figure 1-241.
Figure 1-241 Connecting Rod Indexing
NOTE:
There are orientation lugs cast into one side of the upper and lower sections of the
connecting rod. These orientation lugs face the front of the engine. See Figure 1-242.
SERIES 60 SERVICE MANUAL
All information subject to change without notice.
6SE483 9610 1996 DETROIT DIESEL CORPORATION From Bulletin 19-60-98 1-287
Figure 1-242 Orientation Lugs
NOTICE:
When installing a forged steel piston into the engine, care must be
taken to avoid damaging the piston cooling nozzle installed at the
base of the cylinder bore. Before loading the piston into the liner,
turn the connecting rod so that the bearing end is offset
approximately 1015 degrees and not perpendicular to the
crankshaft, as is the case with cast iron pistons. This will ensure
that the rod end does not strike the nozzle when the piston is
pushed in. Once the rod end is past the nozzle, turn the rod so
that the bearing end is perpendicular to the crankshaft journal.
NOTICE:
Failure to orient the piston connecting rod properly during forged
steel piston installation may result in the bearing end of the rod
striking the nozzle, causing damage to the nozzle or loosening it
from the block. A damaged or bent nozzle may cause a loss of
main gallery oil pressure. A loosened nozzle may cause a loss of
main gallery oil pressure. In either case, piston overheating or
lack of adequate lubrication may result in severe engine damage.
1.18 PISTON AND CONNECTING ROD ASSEMBLY
All information subject to change without notice.
1-288 From Bulletin 19-60-98 6SE483 9610 1996 DETROIT DIESEL CORPORATION
15. Position the ring compressor, with piston and connecting rod inside, into the proper
cylinder until the ring compressor is resting squarely on the cylinder liner. See
Figure 1-243.
Figure 1-243 Use of Ring Compressor
NOTICE:
Do NOT force the piston into the liner. The oil ring expander
applies considerable force on the oil ring. Therefore, care must be
taken during the loading operation to prevent ring breakage.
16. Push the piston and connecting rod assembly into the liner until the piston is free of the
ring compressor.
17. Remove the piston ring compressor.
18. Push or tap the piston and connecting rod assembly into the liner, turning the rod, if
necessary, until the upper bearing shell is firmly seated on the appropriate crankshaft
journal.
19. Remove the connecting rod guide from the ends of the connecting rod bolts.
NOTE:
Be sure the connecting rod bolts have not been unseated or turned and the bearing
locating tang is in its proper location.
You might also like
- Harley Davidson 250 and 350 SprintDocument8 pagesHarley Davidson 250 and 350 SprintElan Mutt Schwartz75% (4)
- 1971 Johnson 60HP Outboards Service Manual PDFDocument5 pages1971 Johnson 60HP Outboards Service Manual PDFChrisStainton0% (1)
- Camry Solara SEV6Document13 pagesCamry Solara SEV6arturmikieNo ratings yet
- SECTION 303-01B: Engine - 4.6L and 5.4L 2000 F-150 Workshop Manual AssemblyDocument35 pagesSECTION 303-01B: Engine - 4.6L and 5.4L 2000 F-150 Workshop Manual AssemblyHassan Vela VenegasNo ratings yet
- Cylinder Head Gasket - Installation (01 - 2010 - ) (Cylinder Head Assembly) - ALLDATA Repair Toyota Camry 2.5LtsDocument17 pagesCylinder Head Gasket - Installation (01 - 2010 - ) (Cylinder Head Assembly) - ALLDATA Repair Toyota Camry 2.5LtsFran SanchezNo ratings yet
- GM Engines v-6, V-8Document23 pagesGM Engines v-6, V-8jads301179No ratings yet
- Chevy Optra 2 0 PDFDocument91 pagesChevy Optra 2 0 PDFguillermoal539No ratings yet
- Ajuste de Valvulas PDFDocument8 pagesAjuste de Valvulas PDFRoberto Rincon Robles100% (1)
- Article Engine Cylinder Block DisassemblyDocument17 pagesArticle Engine Cylinder Block Disassembly94738183No ratings yet
- Forged Steel Piston PDFDocument14 pagesForged Steel Piston PDFvictoverNo ratings yet
- 3Document6 pages3George GuerreroNo ratings yet
- 3304-3306 Medidas de Bielas y BancadasDocument3 pages3304-3306 Medidas de Bielas y BancadasJuan Carlos RivasNo ratings yet
- Engine AssemblyDocument13 pagesEngine AssemblyJacob SilverstielkNo ratings yet
- Connecting Rod PDFDocument9 pagesConnecting Rod PDFvictoverNo ratings yet
- คู่มือบำรุงรักษา root blowerDocument17 pagesคู่มือบำรุงรักษา root blowervarayutjNo ratings yet
- Remove & Install Connecting Rod BearingsDocument4 pagesRemove & Install Connecting Rod BearingsRichard ChuaNo ratings yet
- One Cylinder ModelsDocument4 pagesOne Cylinder ModelsPaul MartinNo ratings yet
- Plymouth and Chrysler-built cars Complete Owner's Handbook of Repair and MaintenanceFrom EverandPlymouth and Chrysler-built cars Complete Owner's Handbook of Repair and MaintenanceNo ratings yet
- Clutch ManualDocument16 pagesClutch ManualCO BDNo ratings yet
- Connecting Rod BearingsDocument4 pagesConnecting Rod BearingsjonNo ratings yet
- Manual: 292 Engine Kt-150 SeriesDocument20 pagesManual: 292 Engine Kt-150 SeriesSuwan Noo ThomsonNo ratings yet
- Corolla LE Sedan RepairDocument17 pagesCorolla LE Sedan RepairmaximlevNo ratings yet
- Remove and Install Crankshaft Main BearingsDocument5 pagesRemove and Install Crankshaft Main BearingsBuku DigitalNo ratings yet
- Pistons and Connecting RodsDocument6 pagesPistons and Connecting Rodsma.powersourceNo ratings yet
- CS 533 ManualDocument9 pagesCS 533 ManualbagoesNo ratings yet
- CM6D28 Manual BookDocument26 pagesCM6D28 Manual BookNut Chen Li Jun100% (1)
- Orbit RolDocument12 pagesOrbit RolFabio MartinsNo ratings yet
- Instructions On Installation Operation and Maintenance For Kirloskar PumpDocument23 pagesInstructions On Installation Operation and Maintenance For Kirloskar Pumpmonuaspire4No ratings yet
- Pistons and Connecting Rods - InstallDocument3 pagesPistons and Connecting Rods - Installsergio blandon lNo ratings yet
- QSB-6.7 BielaDocument4 pagesQSB-6.7 BielaCHEMA BASANNo ratings yet
- 3013C Pistons and Connecting Rods - Install - PDF Version 1 PDFDocument4 pages3013C Pistons and Connecting Rods - Install - PDF Version 1 PDFJaime Herrera LaraNo ratings yet
- TA30 A894 Parte C PDFDocument148 pagesTA30 A894 Parte C PDFoctavio hernandezNo ratings yet
- Timing Belt: 2000 Acura Integra GS Coupe L4 1.8L Dohc MfiDocument10 pagesTiming Belt: 2000 Acura Integra GS Coupe L4 1.8L Dohc MfiVicctor PiñaNo ratings yet
- Crankshaft Main BearingsDocument5 pagesCrankshaft Main BearingsjonNo ratings yet
- Pistons and Connecting Rods - DisassembleDocument4 pagesPistons and Connecting Rods - Disassembleeshopmanual limaNo ratings yet
- Volvo D13H Shop Armed Vol2Document34 pagesVolvo D13H Shop Armed Vol2Juan José AldanaNo ratings yet
- Ac Compressor ServicingDocument25 pagesAc Compressor Servicingsonny1234100% (1)
- CrankshaftDocument8 pagesCrankshaftma.powersourceNo ratings yet
- MC 10245814 9999Document10 pagesMC 10245814 9999abdatmeh99No ratings yet
- 07-124 Motor CharlynDocument12 pages07-124 Motor CharlynMiguel Angel Santos Pintado100% (2)
- Cams Andrews 99 Gear-01Document4 pagesCams Andrews 99 Gear-01dsgoodrichNo ratings yet
- Crankshaft Main BearingsDocument5 pagesCrankshaft Main Bearingsma.powersourceNo ratings yet
- Toyota MR2 Spyder L4-1.8L (1ZZ-FE) 2001: Timing Chain: Service and RepairDocument18 pagesToyota MR2 Spyder L4-1.8L (1ZZ-FE) 2001: Timing Chain: Service and RepairROSA GIMENEZNo ratings yet
- Pistons and Connecting Rods - Install: Desmontagem e MontagemDocument3 pagesPistons and Connecting Rods - Install: Desmontagem e MontagemJefferson SilvaNo ratings yet
- Timing Chain Components & Instalation Toyota Hilux 22R-E: Preparation of RemovalDocument7 pagesTiming Chain Components & Instalation Toyota Hilux 22R-E: Preparation of RemovalPablo FernandezNo ratings yet
- Remove and Install Crankshaft Main BearingsDocument4 pagesRemove and Install Crankshaft Main BearingsMax Will Carrasco SantiNo ratings yet
- Remove and Install Crankshaft Main BearingsDocument4 pagesRemove and Install Crankshaft Main BearingsMayumi Lizarme BuezoNo ratings yet
- Rod Install PDFDocument8 pagesRod Install PDFVeterano del Camino100% (2)
- Connecting Rod ReplacementDocument11 pagesConnecting Rod Replacementfjafarvand100% (1)
- 3.3L 6-Cyl VinDocument28 pages3.3L 6-Cyl VingypsyshortNo ratings yet
- AC Compressor ServicingDocument28 pagesAC Compressor Servicinggentiles mdqNo ratings yet
- Maico-MC 250 400 501 Square Barrel-68 71-Service Manual EngineDocument29 pagesMaico-MC 250 400 501 Square Barrel-68 71-Service Manual EngineducmansNo ratings yet
- Caterpillar Cat M318 Excavator (Prefix 8SS) Service Repair Manual Instant DownloadDocument29 pagesCaterpillar Cat M318 Excavator (Prefix 8SS) Service Repair Manual Instant Downloadmerylclark17No ratings yet
- S-1 Disassembly and Installation of Starter Motor AssemblyDocument19 pagesS-1 Disassembly and Installation of Starter Motor AssemblyLinzaw WinNo ratings yet
- G3406 Connecting Rod BearingsDocument4 pagesG3406 Connecting Rod BearingsnobodymagdesignNo ratings yet
- Sistema de TransmisionDocument239 pagesSistema de TransmisionCez Lopez BañezNo ratings yet
- The Book of the Singer Junior - Written by an Owner-Driver for Owners and Prospective Owners of the Car - Including the 1931 SupplementFrom EverandThe Book of the Singer Junior - Written by an Owner-Driver for Owners and Prospective Owners of the Car - Including the 1931 SupplementNo ratings yet
- A DIY'ers Definitive Guide to Building a Custom Volkswagen TrikeFrom EverandA DIY'ers Definitive Guide to Building a Custom Volkswagen TrikeNo ratings yet
- Installation and Operation Instructions For Custom Mark III CP Series Oil Fired UnitFrom EverandInstallation and Operation Instructions For Custom Mark III CP Series Oil Fired UnitNo ratings yet
- Water Pump PDFDocument2 pagesWater Pump PDFvictoverNo ratings yet
- Two-Bolt Camshaft PDFDocument7 pagesTwo-Bolt Camshaft PDFvictoverNo ratings yet
- 8.2.3.2 Checking 12-Rib Poly-Vee Belt-Driven 50 DN Alternator Belt TensionDocument2 pages8.2.3.2 Checking 12-Rib Poly-Vee Belt-Driven 50 DN Alternator Belt TensionvictoverNo ratings yet
- 1.16.1 Repair or Replacement of Flywheel HousingDocument2 pages1.16.1 Repair or Replacement of Flywheel HousingvictoverNo ratings yet
- Engine Coolant 2 PDFDocument3 pagesEngine Coolant 2 PDFvictoverNo ratings yet
- Connecting Rod PDFDocument9 pagesConnecting Rod PDFvictoverNo ratings yet