The Respiratory System
The Respiratory System
Uploaded by
api-271854549Copyright:
Available Formats
The Respiratory System
The Respiratory System
Uploaded by
api-271854549Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
The Respiratory System
The Respiratory System
Uploaded by
api-271854549Copyright:
Available Formats
The Human Respiratory System
Kaarle Comeau
Biology Fundamentals
BIO112- Section 01
Ms. Giardino
The Human Respiratory System
Part Two
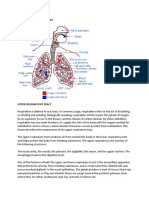
The main purpose of the respiratory system is to supply our bodies with oxygen so that we stay
healthy and functional. With the constant stream of oxygen, our bodys cells are absorbing the
oxygen while removing carbon dioxide. The first step to this complex system begins at the nasal
cavity. The nasal cavity is a hollow area within the nose that is lined with hair and mucous.
These features might not seem that important but they trap bacteria or impurities such as dust
and mold. The oral cavity is another way that oxygen gets into the body but isnt as affective for
filtering as the nasal cavity. The pharynx is a muscular tube that extends from the nasal cavity
to the esophagus. Once the oxygen travels through the pharynx it goes to the larynx. This is the
section of the airway that is connected to the trachea. The epiglottis is one of the many
cartilage areas of the larynx and is essential. This covers the larynx while swallowing to prevent
choking and promote the distribution of oxygen throughout the body. The trachea is a long
tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi and provides a clear airway to enter and exit the
lungs. Just like the nasal cavity, the trachea traps unwanted debris and stops it from going into
the lungs. The trachea also has cilia which move mucus so it can be swallowed and digested.
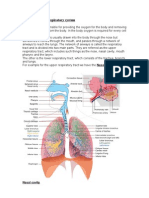
Once the trachea ends, the airway splits into two sections. These are known as the bronchi and
are split even more creating bronchioles. The bronchioles are located in the lungs and bring
oxygen to the alveoli. The lungs are a pair of spongy organs that have enough space to expand
and contract to get oxygen. In the interior of the lungs there are small sacs known as alveoli
which exchange gases with the blood passed through the capillaries. The diaphragm is a sheet
of muscles that lies across the bottom of the chest cavity. The diaphragm is responsible for
pumping the carbon dioxide out of the lungs and pulls the oxygen into the lungs. As the
The Human Respiratory System
diaphragm contracts and relaxes, breathing takes place. As the diaphragm contracts, oxygen is
pulled into the lungs. When the diaphragm relaxes, carbon dioxide is pumped out of the lungs.
You might also like
- Respiratory SystemDocument12 pagesRespiratory SystemLevita FelixNo ratings yet
- Parts and Functions of Respiratory System.Document3 pagesParts and Functions of Respiratory System.Alvin Patrick Colobong AsisNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer (MID)Document53 pagesScience Reviewer (MID)Francesca KatigbakNo ratings yet
- Human Respiratory System FunctionsDocument2 pagesHuman Respiratory System Functionsapi-169639475No ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument11 pagesAnatomy and Physiologyjawn09euclidNo ratings yet
- Human Respiratory System Aniket DasDocument11 pagesHuman Respiratory System Aniket DasChep KepNo ratings yet
- Human Respiratory SystemDocument7 pagesHuman Respiratory Systemshashwatdwivedi9000No ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument2 pagesRespiratory Systemayubanmaryjane382No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Respiratory SystemLyka100% (1)
- Respiratory System: Anatomy of The NoseDocument6 pagesRespiratory System: Anatomy of The NoseAlmira ColumbanoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology: Upper Respiratory TractDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology: Upper Respiratory TractAltea MartirezNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATORYDocument27 pagesRESPIRATORYAshyyNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument8 pagesThe Respiratory SystemDavid DanielNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesRespiratory SystemjoimaciascorreaNo ratings yet
- The Cells of The Human Body Require A Constant Stream of Oxygen To Stay AliveDocument14 pagesThe Cells of The Human Body Require A Constant Stream of Oxygen To Stay AlivePeperoniiNo ratings yet
- Respiration Is A Chemical Reaction That Happens in All Living CellsDocument3 pagesRespiration Is A Chemical Reaction That Happens in All Living CellsKani KurmanbekovaNo ratings yet
- L1-The Respiratory SystemDocument40 pagesL1-The Respiratory SystemMary Ann FriasNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument5 pagesRespiratory Systemcharamina13No ratings yet
- Physiology L Homework 1Document3 pagesPhysiology L Homework 1qatawnehsojodNo ratings yet
- The Human Respiratory SystemDocument13 pagesThe Human Respiratory SystemKaavya Saraswathi SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System ApolinarDocument4 pagesRespiratory System ApolinarReysan Dela Peña ApolinarNo ratings yet
- RespiratoryDocument2 pagesRespiratoryalybalambanNo ratings yet
- Human Respiratory SystemDocument7 pagesHuman Respiratory Systemshamshad aliNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument13 pagesRespiratory SystemshnasrNo ratings yet
- Breathing Process PDFDocument3 pagesBreathing Process PDFDianeNo ratings yet
- Structure of The Respiratory System 2Document5 pagesStructure of The Respiratory System 2domhughes1093No ratings yet
- Lungs: Importance of The LungsDocument4 pagesLungs: Importance of The Lungsdg100% (1)
- Parts & Function of Respiratory SystemDocument4 pagesParts & Function of Respiratory SystemLucille Ballares86% (7)
- Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesRespiratory Systemๆรำำทแร หบหฝำมฟNo ratings yet
- The Main Structure of The Respiratory System Is The Nasal CavityDocument1 pageThe Main Structure of The Respiratory System Is The Nasal CavitykalabawNo ratings yet
- Transparency 2Document11 pagesTransparency 2nitesh tirkeyNo ratings yet
- ReproductiveDocument5 pagesReproductiveJason Vinluan CarinanNo ratings yet
- Parts and Functions of Respiratory SystemDocument18 pagesParts and Functions of Respiratory Systemjosephabram051590No ratings yet
- The Respiratory System PresentationDocument9 pagesThe Respiratory System Presentationgonzalesjohnkeneth5No ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument2 pagesUntitled DocumentetubabesNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument2 pagesThe Respiratory Systemgiulietta1231No ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument11 pagesThe Respiratory Systemfahimpatwary.fppNo ratings yet
- LumnsDocument10 pagesLumnsAdnan aliNo ratings yet
- Notes 1Document12 pagesNotes 1Muhammad TaimoorNo ratings yet
- Respiratory HandoutsDocument4 pagesRespiratory HandoutsEmmanuel AzoresNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATORY SYS-WPS OfficeDocument4 pagesRESPIRATORY SYS-WPS OfficeRina Catubo100% (1)
- The Respiratory System (Handouts)Document6 pagesThe Respiratory System (Handouts)EdNo ratings yet
- What Are The Parts of Respiratory System With FunctionsDocument3 pagesWhat Are The Parts of Respiratory System With FunctionsMelx UbaldeNo ratings yet
- LO4 - Respiratory SystemDocument10 pagesLO4 - Respiratory SystemCHR1555No ratings yet
- LO4 - Respiratory SystemDocument10 pagesLO4 - Respiratory SystemCHR1555No ratings yet
- Boundless Biology Respiratory SystemDocument7 pagesBoundless Biology Respiratory SystemZackary TsangNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Physiology - MelaneeDocument5 pagesAnatomy Physiology - MelaneeNikkoBacasonNo ratings yet
- DescriptionDocument2 pagesDescriptionGliane, Adrie Ann C.No ratings yet
- Q1 9 Science Respiratory SystemDocument14 pagesQ1 9 Science Respiratory SystemPatrick GarciaNo ratings yet
- human resourcesDocument12 pageshuman resourcesrazdaulayan7No ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument34 pagesRespiratory SystemumeazabashaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Respiratory SystemDocument21 pagesLesson 1 Respiratory SystemJohnNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: InhalationDocument2 pagesRespiratory System: InhalationBeverlyPeñaPinedaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System in Human BeingsDocument11 pagesRespiratory System in Human BeingsSarada KasyapNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument1 pageAnatomy and PhysiologyDian Rose Sebanes MamintaNo ratings yet
- Final PresentaionDocument30 pagesFinal Presentaionthapelomatlou959No ratings yet
- How Do Humans Breathe? Science Book Age 8 | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandHow Do Humans Breathe? Science Book Age 8 | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- Human Body Book | Introduction to the Respiratory System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionFrom EverandHuman Body Book | Introduction to the Respiratory System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionNo ratings yet