Transporting Electricity Infosheet
Transporting Electricity Infosheet
Uploaded by
api-222959505Copyright:
Available Formats
Transporting Electricity Infosheet
Transporting Electricity Infosheet
Uploaded by
api-222959505Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Transporting Electricity Infosheet
Transporting Electricity Infosheet
Uploaded by
api-222959505Copyright:
Available Formats
Electricity
Secondary Energy Source
Electricity is different from primary sources of energy. Unlike coal,
petroleum, or solar energy, electricity is a secondary source of
energy. That means we must use other energy sources to make
electricity. It also means we cant classify electricity as renewable or
nonrenewable.
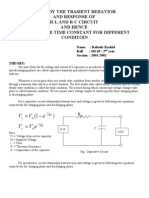
Lets follow the path of electricity from a power plant to a light bulb
in your home. First, the electricity is generated at a power plant. It
travels through a wire to a transformer that steps up the voltage.
Power plants step up the voltage because less electricity is lost along
the power lines when it is at higher voltage.
Coal, which is nonrenewable, can be used to make electricity. So can
hydropower, a renewable energy source. The energy source we use
can be renewable or nonrenewable, but electricity is neither.
The electricity is then sent to a nationwide network of transmission
lines. Transmission lines are the huge tower lines you see along the
highway. The transmission lines are interconnected, so if one line
fails, another can take over the load.
Generating Electricity
Most of the electricity we use in the United States is generated
by large power plants. These plants use many fuels to produce
electricity. Thermal power plants use coal, biomass, petroleum, or
natural gas to superheat water into steam, which powers a generator
to produce electricity. Nuclear power plants use fission to produce
the heat. Geothermal power plants use heat from inside the earth.
Wind farms use the kinetic energy in the wind to generate electricity,
while hydropower plants use the energy in moving water.
Moving Electricity
We use more electricity every year. One reason we use so much
electricity is that its easy to move from one place to another. It can
be made at a power plant and moved long distances before it is used.
There is also a standard system in place so that all of our machines
and appliances can operate on electricity. Electricity makes our lives
simpler and easier.
Step-down transformers, located at substations along the lines,
reduce the voltage from 350,000 volts to 12,000 volts. Substations
are small fenced-in buildings that contain transformers, switches,
and other electrical equipment.
The electricity is then carried over distribution lines that deliver
electricity to your home. These distribution lines can be located
overhead or underground. The overhead distribution lines are the
power lines you see along streets.
Before the electricity enters your house, the voltage is reduced again
at another transformer, usually a large gray metal box mounted on
an electric pole. This transformer reduces the electricity to the 120
volts that are used to operate the appliances in your home.
Electricity enters your home through a three-wire cable. Wires are
run from the circuit breaker or fuse box to outlets and wall switches
in your home. An electric meter measures how much electricity you
use so that the utility company can bill you.
TRANSPORTING ELECTRICITY
Power plant
generates electricity
Transmission line
carries electricity
long distances
Transformer
steps up voltage
for transmission
36
Distribution line
carries electricity
to house
Neighborhood
transformer
steps down voltage
Transformer on pole
steps down voltage
before entering house
Intermediate Energy Infobook
You might also like
- Door Hinge CalculationDocument4 pagesDoor Hinge CalculationRamachandra Bhat HireNo ratings yet
- How Electricity Delivers EnergyDocument6 pagesHow Electricity Delivers EnergyAishwarya ChaudhryNo ratings yet
- Electricity PrintDocument14 pagesElectricity PrintSirna Santosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Electricity: Electricity at A Glance, 2009Document7 pagesElectricity: Electricity at A Glance, 2009Amos OkechNo ratings yet
- POWERPLANTDocument2 pagesPOWERPLANTHi HiNo ratings yet
- Power Plans and How Electrical FlowsDocument10 pagesPower Plans and How Electrical FlowsEugene OlidNo ratings yet
- Generation, Transmission and DistributionDocument8 pagesGeneration, Transmission and DistributionCesar García MataNo ratings yet
- Notes Introduction - To - ElectricityDocument3 pagesNotes Introduction - To - Electricitystacyjumpo1No ratings yet
- 1 Photovoltaics in The Electricity NetworkDocument4 pages1 Photovoltaics in The Electricity NetworkIsabel GuevaraNo ratings yet
- How Does A Hydro Plant WorkDocument2 pagesHow Does A Hydro Plant Worklaloo01No ratings yet
- Electric Power SystemsDocument9 pagesElectric Power SystemsAbdifatah mohamedNo ratings yet
- Generation and TransmissionDocument9 pagesGeneration and TransmissionAzat OnkolNo ratings yet
- Electrical, Home Inspection Course and ExamDocument40 pagesElectrical, Home Inspection Course and ExamAli Noroozi100% (2)
- Household CircuitDocument5 pagesHousehold Circuitdhakanem7739No ratings yet
- Resume of The Electrical Grid and Electricity Supply-Angeles SolorzanoDocument6 pagesResume of The Electrical Grid and Electricity Supply-Angeles Solorzanopedrossj163No ratings yet
- How Electricity WorksDocument1 pageHow Electricity WorksflourineairamNo ratings yet
- What Is Household CircuitDocument5 pagesWhat Is Household CircuitAten AzharNo ratings yet
- Electricity Research (Hady G9B)Document4 pagesElectricity Research (Hady G9B)Hady SalehNo ratings yet
- BL Week 8Document2 pagesBL Week 8Haikal ShhrmNo ratings yet
- Electricity-Transmission-and-Domestic-Electric-CircuitDocument9 pagesElectricity-Transmission-and-Domestic-Electric-Circuitkhizar20213No ratings yet
- How Electricity Is DistributedDocument1 pageHow Electricity Is DistributedArdhi YogaNo ratings yet
- How Do We Receive Electrical Power at Our Home or OfficeDocument2 pagesHow Do We Receive Electrical Power at Our Home or OfficeEr Arun KisharNo ratings yet
- BS Blended LearningDocument1 pageBS Blended LearningMohd Farhan MarjanNo ratings yet
- Workshop Technology (Electrical) 1Document39 pagesWorkshop Technology (Electrical) 1Tonny OkwiriNo ratings yet
- Epdu Assignment 2Document13 pagesEpdu Assignment 2pindi2197No ratings yet
- 85 Generation of Electricity 09Document10 pages85 Generation of Electricity 09Wong Yun LoongNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Magnetism: Remelyn Barte Rodel RopanDocument8 pagesElectricity and Magnetism: Remelyn Barte Rodel RopanLiana SalangoNo ratings yet
- Generation: The Power PlantDocument6 pagesGeneration: The Power PlantElkay Rebel-Ikons MillerNo ratings yet
- PHY1Document10 pagesPHY1malarvilisaravanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - ElectricDocument48 pagesChapter 12 - ElectricQuang LeNo ratings yet
- How Electricity Is ProducedDocument1 pageHow Electricity Is ProducedAbdoulaye Idriss AbakarNo ratings yet
- Module 7Document9 pagesModule 7suggondenutzNo ratings yet
- A Power PlantDocument7 pagesA Power PlantdevzaaraNo ratings yet
- How Power Stations Convert Coal Into ElectricityDocument2 pagesHow Power Stations Convert Coal Into Electricityeric12345678910ericNo ratings yet
- E-Note 19058 Content Attachment1 20240425024156PMDocument9 pagesE-Note 19058 Content Attachment1 20240425024156PMnidhidgowda185No ratings yet
- RECC-102 Unit-5Document6 pagesRECC-102 Unit-5Ashish PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Power Basic FundasDocument5 pagesPower Basic FundasLalit Kumar ChetaniNo ratings yet
- Ns and Tech PowerpointDocument24 pagesNs and Tech Powerpointsundusmain199No ratings yet
- Bigger Perspective Why Are Circuits Important?Document5 pagesBigger Perspective Why Are Circuits Important?Shaezer AlpayNo ratings yet
- Sem 5 Building Services II Electrical Class 2Document16 pagesSem 5 Building Services II Electrical Class 2Mounica Nanda KumarNo ratings yet
- EET301 - Module - 1bDocument116 pagesEET301 - Module - 1btarantinho308No ratings yet
- Case Study On 33 11KV Transmission SubstDocument36 pagesCase Study On 33 11KV Transmission SubstHareendralal A.G.No ratings yet
- Generation Transmission and DistributionDocument18 pagesGeneration Transmission and DistributionayazNo ratings yet
- AR 4.5 Building Services - IiDocument23 pagesAR 4.5 Building Services - IiDarshini AmalaNo ratings yet
- 6 Electricity - TransmissionDocument1 page6 Electricity - TransmissionMohamad IskandarNo ratings yet
- Electrical WiringDomest 8310585Document20 pagesElectrical WiringDomest 8310585Berry KasanNo ratings yet
- Plants DescrDocument4 pagesPlants Descrsnvasrk mallikarjunNo ratings yet
- FORCES AND ENERGY (ELECTRICITY AND ELECTRONICS) oriDocument6 pagesFORCES AND ENERGY (ELECTRICITY AND ELECTRONICS) oritailopezdarmoeNo ratings yet
- Indiction Generator TheoryDocument4 pagesIndiction Generator Theoryraghu_mnNo ratings yet
- Distribusi Tenaga ListrikDocument10 pagesDistribusi Tenaga ListrikSundara Sudibya JayaNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engineering-Unit - 3 - Generation, Electricty Bill CalculationsDocument35 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering-Unit - 3 - Generation, Electricty Bill CalculationsSAIPAVAN KUMAR NANDIGAMANo ratings yet
- Power PlantsDocument20 pagesPower Plantsjvharsha.sNo ratings yet
- M4 Ch2 Electric Power Generation PDFDocument5 pagesM4 Ch2 Electric Power Generation PDFMujeeb KhanNo ratings yet
- Electrical Installation and MaintenanceDocument1 pageElectrical Installation and MaintenanceEarl Cris RiggsNo ratings yet
- Electricity LessonDocument16 pagesElectricity LessonFelcher LayuganNo ratings yet
- Electrical System: Submitted By: Sumit Kumar 12BAC-022 Achal Gupta 12BAC043Document25 pagesElectrical System: Submitted By: Sumit Kumar 12BAC-022 Achal Gupta 12BAC043bharat vermaNo ratings yet
- 27 Electricity ProducedDocument3 pages27 Electricity ProducedSmart SarimNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Grade 9Document20 pagesScience 9 Grade 9c50799454No ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument4 pagesElectricityОленка КушнірNo ratings yet
- Modelling of Power System Component PDFDocument37 pagesModelling of Power System Component PDFSandeepKumarNo ratings yet
- A Guide to the Home Electric System: Home Guide Basics Series, #2From EverandA Guide to the Home Electric System: Home Guide Basics Series, #2No ratings yet
- DLP V Law of MotionDocument4 pagesDLP V Law of MotionNellen BastismoNo ratings yet
- Hella HINC Electrics CatalogDocument100 pagesHella HINC Electrics CatalogSteveNo ratings yet
- User Manual Product Description Static Switch SSW 7500A/30000A-230Document18 pagesUser Manual Product Description Static Switch SSW 7500A/30000A-230moumen BoughraraNo ratings yet
- Manipal Institute of Technology, ManipalDocument4 pagesManipal Institute of Technology, Manipaldon karthikeyaNo ratings yet
- Transformer Inrush CurrentDocument32 pagesTransformer Inrush CurrentD Avi Na ShNo ratings yet
- Mechanics For IIT-JEE/AIEEE/AIPMT by Sanjay PandeyDocument35 pagesMechanics For IIT-JEE/AIEEE/AIPMT by Sanjay PandeySanjay Pandey50% (2)
- Typical 61850 Signal List Micom P143Document1 pageTypical 61850 Signal List Micom P143swagata12345No ratings yet
- Lecture 10 An Not atDocument20 pagesLecture 10 An Not atapi-3721075No ratings yet
- The Crossed Field Antenna - Analyzed by Simulation and ExperimentDocument4 pagesThe Crossed Field Antenna - Analyzed by Simulation and ExperimentAnonymous 0qYv7WpgNo ratings yet
- 1.V4 Kombi Final Manual Balancing Valve F.endDocument13 pages1.V4 Kombi Final Manual Balancing Valve F.endKurkuma PlusNo ratings yet
- RU3AMDocument3 pagesRU3AMqaisermushtaq1981No ratings yet
- Pililla Wind FarmDocument7 pagesPililla Wind FarmASTIG TVNo ratings yet
- EI - 30 - Englisch Mini Board TransformerDocument8 pagesEI - 30 - Englisch Mini Board TransformerEduardo Arriagada MartinezNo ratings yet
- Added MassDocument3 pagesAdded MassAli PungaNo ratings yet
- Radiation Physics IDocument73 pagesRadiation Physics IYustia FardaNo ratings yet
- Zhang 2004 DattaDocument28 pagesZhang 2004 Dattaabdellaoui.mabrouka abdellaoui.mabroukaNo ratings yet
- Thermo 1 Exam 4Document1 pageThermo 1 Exam 4Juan KakakaNo ratings yet
- ABS-C0018, Left Rear ABS Inlet ValveDocument2 pagesABS-C0018, Left Rear ABS Inlet ValveBùi Xuân ĐứcNo ratings yet
- Boiler Operation Incl Emergency OperationDocument212 pagesBoiler Operation Incl Emergency Operationguddu yadavNo ratings yet
- T.umeda Y.omura, T.tominaga, H.matsumoto.a New Charge Conservation Method in Electromagnetic Particle-In-cell SimulationsDocument13 pagesT.umeda Y.omura, T.tominaga, H.matsumoto.a New Charge Conservation Method in Electromagnetic Particle-In-cell SimulationsyuratolNo ratings yet
- K23900 - Kinematic Viscosity Bath - Technical DatasheetDocument1 pageK23900 - Kinematic Viscosity Bath - Technical Datasheetmoh_ichwanuddinNo ratings yet
- Ecs Txo 2520Document2 pagesEcs Txo 2520miri10861No ratings yet
- R-L & R-C CircuitsDocument41 pagesR-L & R-C CircuitsAlamgir Kabir ShuvoNo ratings yet
- 05-01-2023 - SR - Super60 - NUCLEUS & ALL - BT - Jee-Main-GTM-02-First Year Syllabus - Q.PAPERDocument18 pages05-01-2023 - SR - Super60 - NUCLEUS & ALL - BT - Jee-Main-GTM-02-First Year Syllabus - Q.PAPERVatsa RachuriNo ratings yet
- SOP Simulation Generator SetDocument9 pagesSOP Simulation Generator SetAdenSalahuddinNo ratings yet
- Ultralow Offset Voltage Operational Amplifier: Data SheetDocument16 pagesUltralow Offset Voltage Operational Amplifier: Data Sheetjohn hilbertNo ratings yet
- Theory of Solutions DPP-2 (Questions) PDFDocument4 pagesTheory of Solutions DPP-2 (Questions) PDFHarshjeetNo ratings yet
- How Much Ac Ripple in A DC Power Supply Is Too Much?: Editor'S Note: Pdfs of This Article AreDocument2 pagesHow Much Ac Ripple in A DC Power Supply Is Too Much?: Editor'S Note: Pdfs of This Article Areparvinder ranaNo ratings yet
- Madhayanchal Vidhyut Vitran Nigam LTD.: Bill-Cum Disconnection Notice For The Month ofDocument3 pagesMadhayanchal Vidhyut Vitran Nigam LTD.: Bill-Cum Disconnection Notice For The Month ofdeepkamal_jaiswalNo ratings yet