Bloom's Taxonomy: Higher Order Questioning in The Context of Looking at Works of Art and Reading
Bloom's Taxonomy: Higher Order Questioning in The Context of Looking at Works of Art and Reading
Uploaded by
Bert EngCopyright:
Available Formats
Bloom's Taxonomy: Higher Order Questioning in The Context of Looking at Works of Art and Reading
Bloom's Taxonomy: Higher Order Questioning in The Context of Looking at Works of Art and Reading
Uploaded by
Bert EngOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Bloom's Taxonomy: Higher Order Questioning in The Context of Looking at Works of Art and Reading
Bloom's Taxonomy: Higher Order Questioning in The Context of Looking at Works of Art and Reading
Uploaded by
Bert EngCopyright:
Available Formats
Bloom's Taxonomy
Higher order questioning in the context of looking at works
of art and reading
In 1956, Benjamin Bloom headed a group of educational psychologists who developed a
classification of levels of intellectual behaviour important in learning. Bloom found that over 95
% of the test questions students encounter require them to think only at the lowest possible
level...the recall of information.
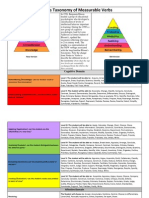
Bloom identified six levels within the cognitive domain, from the simple recall or recognition of
facts, as the lowest level, through increasingly more complex and abstract mental levels, to the
highest order, which is classified as evaluation. Verb examples that represent intellectual activity
on each level are listed below.
Creativity
Evaluation
Synthesis
Analysis
Application
Understanding
1
2
3
4
5
6
Knowledge: arrange, define, duplicate, label, list, memorize, name, order, recognize, relate,
Knowledge
recall, repeat, reproduce state.
Comprehension: classify, describe, discuss, explain, express, identify, indicate, locate,
recognize, report, restate, review, select, translate,
Application: apply, choose, demonstrate, dramatize, employ, illustrate, interpret, operate,
practice, schedule, sketch, solve, use, write.
Analysis: analyze, appraise, calculate, categorize, compare, contrast, criticize, differentiate,
discriminate, distinguish, examine, experiment, question, test.
Synthesis: arrange, assemble, collect, compose, construct, create, design, develop,
formulate, manage, organize, plan, prepare, propose, set up, write.
Evaluation: appraise, argue, assess, attach, choose compare, defend estimate, judge,
predict, rate, core, select, support, value, evaluate.
You might also like
- Metal StudDocument24 pagesMetal StudBert EngNo ratings yet
- Liquidation Report FormDocument42 pagesLiquidation Report FormBert Eng50% (2)
- Bloom 1Document2 pagesBloom 1Mac MacNo ratings yet
- Higher Order Thinking SkillsDocument9 pagesHigher Order Thinking SkillsAim Ben Aini100% (1)
- Presentation Taxonomy BloomDocument20 pagesPresentation Taxonomy Bloomhazreen othmanNo ratings yet
- Bloom Anderson's TaxonDocument2 pagesBloom Anderson's TaxonAnang TriyosoNo ratings yet
- Bloom's TaxonomyDocument3 pagesBloom's TaxonomymjacquinetNo ratings yet
- Readings 1Document3 pagesReadings 1Ramadhani Nesi RahmadhaniNo ratings yet
- Bloom's TaxonomyDocument9 pagesBloom's TaxonomyIsrahana Shahril100% (1)
- Bloom S TaxonomyDocument40 pagesBloom S TaxonomygauravNo ratings yet
- Facilitating Learning Written ReportDocument11 pagesFacilitating Learning Written ReportJohn Ace Revelo-JubayNo ratings yet
- 3 Types of Learning CognitiveFinalDocument23 pages3 Types of Learning CognitiveFinalAngel SangalangNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Learning in The Cognitive Domain Handout 3Document11 pagesAssessment of Learning in The Cognitive Domain Handout 3Rizaldy GarciaNo ratings yet
- BloomDocument12 pagesBloomjustin_1njpNo ratings yet
- Six LevelsDocument10 pagesSix LevelsBlesilda MallillinNo ratings yet
- Bloom's Taxonomy: Note That The Top Two Levels Are Essentially Exchanged From The Traditional To The New VersionDocument1 pageBloom's Taxonomy: Note That The Top Two Levels Are Essentially Exchanged From The Traditional To The New VersionPolly AnnaNo ratings yet
- Bloom Educational ImplicationDocument4 pagesBloom Educational ImplicationBernard MartinNo ratings yet
- C Yyyyy Yyyy Yyy: Y'YyyyyyyyyyyyDocument7 pagesC Yyyyy Yyyy Yyy: Y'YyyyyyyyyyyyMaha AhmadNo ratings yet
- Bloom S TaxonomyDocument5 pagesBloom S TaxonomyIrshad AhmedNo ratings yet
- Domains of LearningDocument19 pagesDomains of LearningJoshua Olufemi100% (1)
- Butuan City: Saint Joseph Institute of TechnologyDocument7 pagesButuan City: Saint Joseph Institute of TechnologyNash Aguas IdolNo ratings yet
- Benjamin Bloom's Taxonomy of Educational ObjectivesDocument3 pagesBenjamin Bloom's Taxonomy of Educational ObjectivesHarshal VaidyaNo ratings yet
- What Is BloomDocument15 pagesWhat Is BloomPETER, JR. PAMANo ratings yet
- Developing Teaching CompetenciesDocument8 pagesDeveloping Teaching CompetenciesChristine Evan UndangNo ratings yet
- Bloom'S Taxonomy September 22, 2016 Ivan Teh - Runningman 0 CommentsDocument5 pagesBloom'S Taxonomy September 22, 2016 Ivan Teh - Runningman 0 CommentsDr. MURALI KRISHNA VELAVETINo ratings yet
- Bloom's Taxonomy - WikipediaDocument10 pagesBloom's Taxonomy - WikipediaHarshal VaidyaNo ratings yet
- The Three Types of LearningDocument5 pagesThe Three Types of LearningRegine QuijanoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To BloomDocument2 pagesIntroduction To BloomsalmaNo ratings yet
- TaxonomiesDocument25 pagesTaxonomiesMilagrosNo ratings yet
- Bloom's Taxonomy of Cognitive LevelsDocument14 pagesBloom's Taxonomy of Cognitive Levelserischolar2003No ratings yet
- Bloom TaxonomyDocument7 pagesBloom TaxonomyZohrahLiaqatNo ratings yet
- Bloom's Taxonomy of Learning DomainsDocument10 pagesBloom's Taxonomy of Learning DomainsJose JosephNo ratings yet
- Blooms Revised TaxonomyDocument11 pagesBlooms Revised Taxonomycleofasjoeann031401No ratings yet
- Bloom 2Document2 pagesBloom 2api-285834686No ratings yet
- Social Learning Theory (Bandura) : Key ConceptsDocument6 pagesSocial Learning Theory (Bandura) : Key ConceptsErica CaladcadanNo ratings yet
- Blooms Taxonomy and Learning ThoriesDocument15 pagesBlooms Taxonomy and Learning ThoriesMuneeb AnjumNo ratings yet
- Knowledge: Examples: Dates, Events, Places, Vocabulary, Key Ideas, Parts of Diagram, 5WsDocument1 pageKnowledge: Examples: Dates, Events, Places, Vocabulary, Key Ideas, Parts of Diagram, 5WsDessy RismayatiNo ratings yet
- DraftDocument9 pagesDraftMyra CeaNo ratings yet
- Bloom's Taxonomy: A New Look at An Old Standby: Designing Effective Projects: Thinking Skills FrameworksDocument5 pagesBloom's Taxonomy: A New Look at An Old Standby: Designing Effective Projects: Thinking Skills FrameworksElena PopaNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Learning DomainDocument2 pagesCognitive Learning DomainFheng UddinNo ratings yet
- BLOOM's TAXONOMY 6Document9 pagesBLOOM's TAXONOMY 6ZeeshanNo ratings yet
- Taxonomies of Thinking SkillsDocument9 pagesTaxonomies of Thinking Skillsmhel20010No ratings yet
- Topic 16 (Relova, Philippe D. & Lana, Jerome Maya)Document11 pagesTopic 16 (Relova, Philippe D. & Lana, Jerome Maya)Ryan Philippe RelovaNo ratings yet
- Benjamin Bloom: (Bloom, Englehart, Furst, Hill, & Krathwohl, 1956)Document7 pagesBenjamin Bloom: (Bloom, Englehart, Furst, Hill, & Krathwohl, 1956)Paula Tanseco SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Bloom's Taxonomy of Measurable Verbs: Cognitive DomainDocument3 pagesBloom's Taxonomy of Measurable Verbs: Cognitive Domainamnoman17No ratings yet
- Teaching and Educational Development Institute Teaching and Educational Development Institute Bloom S Taxonomy of Educational ObjectivesDocument10 pagesTeaching and Educational Development Institute Teaching and Educational Development Institute Bloom S Taxonomy of Educational ObjectiveswiddyhidayahNo ratings yet
- Bloom Taxonomy: Rabiya KamranDocument7 pagesBloom Taxonomy: Rabiya KamranFahad Khan TareenNo ratings yet
- Blooms Richard CDocument2 pagesBlooms Richard Capi-224540514No ratings yet
- Blooms TaxonomyDocument39 pagesBlooms TaxonomyAnonymous cl6f9sZ100% (1)
- Blooms TaxonomyDocument2 pagesBlooms TaxonomydaisylodorNo ratings yet
- Bloom's Taxonomy ObjectivesDocument15 pagesBloom's Taxonomy Objectivesjemil l. candilada100% (1)
- New Blooms TaxonomyDocument5 pagesNew Blooms TaxonomyJohnnyboy SalemNo ratings yet
- Bloom's Taxonomy of Learning DomainsDocument8 pagesBloom's Taxonomy of Learning DomainsSakura MyristicNo ratings yet
- Bloom's Taxonom-WPS OfficeDocument12 pagesBloom's Taxonom-WPS OfficeYoyen macaranasNo ratings yet
- 4233-Article Text-12144-1-10-20180608Document6 pages4233-Article Text-12144-1-10-20180608Peter McManusNo ratings yet
- Bloom's Taxonomy: New Version Old Version: Can The Student Recall orDocument5 pagesBloom's Taxonomy: New Version Old Version: Can The Student Recall orCarlos CabreraNo ratings yet
- Bloom's Taxonomy of Learning DomainsDocument23 pagesBloom's Taxonomy of Learning DomainsKanwal IshaqNo ratings yet
- Bloom's Taxonomy of Learning DomainsDocument5 pagesBloom's Taxonomy of Learning Domainsthanu_2010No ratings yet
- Bloom TaxonomyDocument9 pagesBloom TaxonomyDr.Shimna PaulNo ratings yet
- Bloom's Taxonomy - WikipediaDocument7 pagesBloom's Taxonomy - Wikipediaglh00No ratings yet
- New Assignment Bloom's TaxonomyDocument12 pagesNew Assignment Bloom's Taxonomyshirazpasoon91No ratings yet
- Dma 30-Pueblo List of Customers Under Area-1-4-29-2021Document40 pagesDma 30-Pueblo List of Customers Under Area-1-4-29-2021Bert EngNo ratings yet
- 02a Biddocs Dotc Caraga Regnlannexbldg 2aDocument6 pages02a Biddocs Dotc Caraga Regnlannexbldg 2aBert EngNo ratings yet
- Brgy. Hall DesignDocument2 pagesBrgy. Hall DesignBert EngNo ratings yet
- MULTI-PURPOSE DepED PDFDocument8 pagesMULTI-PURPOSE DepED PDFRumylo AgustinNo ratings yet
- Pamucutan Intake No Correction2Document1 pagePamucutan Intake No Correction2Bert EngNo ratings yet
- Personal Data SheetDocument4 pagesPersonal Data SheetLeonil Estaño100% (7)
- Zamboanga City Water DistrictDocument10 pagesZamboanga City Water DistrictBert EngNo ratings yet
- Civil Service Commission Professional or SubDocument7 pagesCivil Service Commission Professional or SubBert EngNo ratings yet
- Edited - Rehab. Impvt. of Grandstand (8!1!15)Document570 pagesEdited - Rehab. Impvt. of Grandstand (8!1!15)Bert EngNo ratings yet
- The Art of Effective QuestioningDocument39 pagesThe Art of Effective QuestioningBert EngNo ratings yet
- Pressure VesselDocument2 pagesPressure VesselBert EngNo ratings yet
- ResumeDocument2 pagesResumeBert EngNo ratings yet
- Frequencies: Jonah Elbert RosarosoDocument2 pagesFrequencies: Jonah Elbert RosarosoBert EngNo ratings yet
- Effort Oriented-These Are Bosses Who Require Their Subordinates To AlwaysDocument1 pageEffort Oriented-These Are Bosses Who Require Their Subordinates To AlwaysBert EngNo ratings yet
- Zamboanga Ministers Fellowship May 9Document1 pageZamboanga Ministers Fellowship May 9Bert EngNo ratings yet
- What Is The Purpose of Literature ReviewDocument5 pagesWhat Is The Purpose of Literature ReviewBert EngNo ratings yet
- BA Estimating Worksheet 2015 2.1Document45 pagesBA Estimating Worksheet 2015 2.1Bert EngNo ratings yet
- CPM S Curve BroilerDocument4 pagesCPM S Curve BroilerBert EngNo ratings yet