0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
829 viewsFocus Notes Psa 530
Focus Notes Psa 530
Uploaded by
Joyce Kay AzucenaThis document discusses audit sampling and other selective testing procedures. It defines key terms like audit sampling, anomalous error, population, sampling risk, non-sampling risk, sampling unit, statistical sampling, and stratification. It also discusses test of controls, substantive procedures, and appropriate procedures for obtaining evidence like inspection, observation, inquiry, confirmation, computation, and analytical procedures. The document provides guidance on selecting items for testing, including selecting all items, high value items, items over a certain amount, or using audit sampling. It also discusses selecting the sample, performing the audit procedure, and evaluating the nature and cause of any errors found.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Focus Notes Psa 530
Focus Notes Psa 530
Uploaded by
Joyce Kay Azucena0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
829 views1 pageThis document discusses audit sampling and other selective testing procedures. It defines key terms like audit sampling, anomalous error, population, sampling risk, non-sampling risk, sampling unit, statistical sampling, and stratification. It also discusses test of controls, substantive procedures, and appropriate procedures for obtaining evidence like inspection, observation, inquiry, confirmation, computation, and analytical procedures. The document provides guidance on selecting items for testing, including selecting all items, high value items, items over a certain amount, or using audit sampling. It also discusses selecting the sample, performing the audit procedure, and evaluating the nature and cause of any errors found.
Original Description:
auditing theory
Original Title
FOCUS NOTES PSA 530
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
This document discusses audit sampling and other selective testing procedures. It defines key terms like audit sampling, anomalous error, population, sampling risk, non-sampling risk, sampling unit, statistical sampling, and stratification. It also discusses test of controls, substantive procedures, and appropriate procedures for obtaining evidence like inspection, observation, inquiry, confirmation, computation, and analytical procedures. The document provides guidance on selecting items for testing, including selecting all items, high value items, items over a certain amount, or using audit sampling. It also discusses selecting the sample, performing the audit procedure, and evaluating the nature and cause of any errors found.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
829 views1 pageFocus Notes Psa 530
Focus Notes Psa 530
Uploaded by
Joyce Kay AzucenaThis document discusses audit sampling and other selective testing procedures. It defines key terms like audit sampling, anomalous error, population, sampling risk, non-sampling risk, sampling unit, statistical sampling, and stratification. It also discusses test of controls, substantive procedures, and appropriate procedures for obtaining evidence like inspection, observation, inquiry, confirmation, computation, and analytical procedures. The document provides guidance on selecting items for testing, including selecting all items, high value items, items over a certain amount, or using audit sampling. It also discusses selecting the sample, performing the audit procedure, and evaluating the nature and cause of any errors found.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
PSA 530 Audit Sampling and Other Selective
Testing Procedures
Audit Sampling involves the
application of audit procedures to
less than 100% of item which an
account balance or class of
transactions such that all sampling
units have a chance of selection.
Anomalous error error that
arises from an isolated event that
has not recurred other than on
specifically identifiable occasions
Population means that the entire
set of data from which a sample is
selected
Appropriate to the
objective of the sampling
procedure
Complete
Sampling Risk arises from the
possibility that the auditors
conclusion based on a sample may
be different from the conclusion
reached if the entire population
were subjected to the same audit
procedure.
Types:
a. Control risk is lower than it
actually is
b. Control risk higher than it
actually is
Non-sampling risk arises from
factors that cause the auditor to
reach an erroneous conclusion for
any reason not related to the size of
the sample.
Sampling unit individual items
constituting a population
Statistical Sampling random
selection of a sample; use of
probability theory to evaluate
sample results.
Stratification process of dividing
a population into subpopulations.
Test of Control performed if auditor
plans to assess control risk less than
high for a particular assertion
Substantive Procedures analytical
procedures and test of details of
transactions and balances; obtain
evidence to detect material
misstatements in FS
Procedures for Obtaining Evidence:
inspection, observation, inquiry and
confirmation, computation, and
analytical procedures
Appropriate means of selecting items
for testing:
a. Selecting all items (100%
examination)
b. Selecting specific items
High value or key items
All items over a certain
amount
Items to obtain information
Items to test procedures
c. Audit sampling using either
non-statistical or statistical
In
determining
sampling size,
sampling
methods
the auditor should consider
whether the sampling risk is
reduced to an acceptably low
level.
Selecting the sample:
The auditor should select items for the
sample with the expectation that all
sampling units in the population have
a
chance ofthe
selection.
Performing
audit procedure:
appropriate to the particular test
objective on each item selected.
Nature and Cause of Error
a. Direct effect of identified errors
on the FS
b. Effectiveness of accounting and
internal control systems and
their effect on the audit
procedure
You might also like
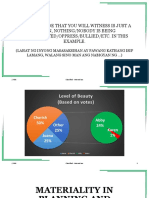
- Test Bank Law 1 CparDocument26 pagesTest Bank Law 1 CparJoyce Kay Azucena73% (22)
- AT Quiz 2 - B1Document3 pagesAT Quiz 2 - B1AMNo ratings yet
- Items 1Document7 pagesItems 1RYANNo ratings yet
- PSA 210 Terms of Audit Engagement SummaryDocument3 pagesPSA 210 Terms of Audit Engagement SummaryAbraham ChinNo ratings yet
- EDP Auditing SemiFinalDocument4 pagesEDP Auditing SemiFinalErwin Labayog MedinaNo ratings yet
- PSA 501: Audit Evidence - Specific Consideration For Selected Items InventoryDocument3 pagesPSA 501: Audit Evidence - Specific Consideration For Selected Items InventoryhanselNo ratings yet
- PSA 540: Auditing Accounting Estimates, Including Fair Value Accounting Estimates, and Related Disclosures ScopeDocument2 pagesPSA 540: Auditing Accounting Estimates, Including Fair Value Accounting Estimates, and Related Disclosures ScopeRam100% (1)
- Chapter 13Document25 pagesChapter 13Clarize R. Mabiog50% (2)
- QUIZ-Audit Evidence and Audit ProgramsDocument12 pagesQUIZ-Audit Evidence and Audit ProgramsKathleenNo ratings yet
- CH 09Document10 pagesCH 09Ali Abed0No ratings yet
- PSA 210 NotesDocument2 pagesPSA 210 NotesKhayceePadilla100% (2)
- LagunaDocument8 pagesLagunarandom17341No ratings yet
- Define Fraud, and Explain The Two Types of Misstatements That Are Relevant To Auditors' Consideration of FraudDocument3 pagesDefine Fraud, and Explain The Two Types of Misstatements That Are Relevant To Auditors' Consideration of FraudSomething ChicNo ratings yet
- Bigger Is Stronger? Case Study On The AOL Time Warner MergerDocument56 pagesBigger Is Stronger? Case Study On The AOL Time Warner MergerFiona QinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 MultiDocument3 pagesChapter 3 MultiJose Mari M. NavaseroNo ratings yet
- Psa 320Document18 pagesPsa 320Joanna CaballeroNo ratings yet
- AMERIL Chapter 1 (Pp.1-17)Document6 pagesAMERIL Chapter 1 (Pp.1-17)Nairah M. TambieNo ratings yet
- Financial Accountinng 3Document10 pagesFinancial Accountinng 3Nami2mititNo ratings yet
- CERTS - Revenue CycleDocument8 pagesCERTS - Revenue CycleralphalonzoNo ratings yet
- Psa 550 PDFDocument9 pagesPsa 550 PDFLen AlairNo ratings yet
- Instructions D. Advanced Financial Accounting and Reporting AFAR.3101 Partnership DrillDocument1 pageInstructions D. Advanced Financial Accounting and Reporting AFAR.3101 Partnership Drillvane rondinaNo ratings yet
- DocxDocument3 pagesDocxyvonneberdosNo ratings yet
- Mancon Quiz 4Document32 pagesMancon Quiz 4Quendrick SurbanNo ratings yet
- Ira Shalini M. YbañezDocument5 pagesIra Shalini M. YbañezIra YbanezNo ratings yet
- AT Quiz 1 (B44)Document8 pagesAT Quiz 1 (B44)chandria bernardoNo ratings yet
- XX AT.06.09-Evidence-and-Performance-of-Substantive-TestingDocument4 pagesXX AT.06.09-Evidence-and-Performance-of-Substantive-TestingMaydet MalapitNo ratings yet
- (REPORT) CHAPTER 9 - Risk Assessment Part 1Document12 pages(REPORT) CHAPTER 9 - Risk Assessment Part 1Jnn Cyc100% (1)
- 3 4Document5 pages3 4RenNo ratings yet
- AC - Acctg Gov Quiz 01Document2 pagesAC - Acctg Gov Quiz 01Erjohn PapaNo ratings yet
- Fedillaga Case13Document19 pagesFedillaga Case13Luke Ysmael FedillagaNo ratings yet
- Excel Professional Services, Inc.: Discussion QuestionsDocument7 pagesExcel Professional Services, Inc.: Discussion QuestionskæsiiiNo ratings yet
- Other PSAs and PAPSsDocument7 pagesOther PSAs and PAPSsnikNo ratings yet
- Psa 610Document9 pagesPsa 610shambiruarNo ratings yet
- Assumptions of AuditingDocument8 pagesAssumptions of Auditinggandhunk0% (1)
- Rmbe FarDocument15 pagesRmbe FarMiss Fermia0% (1)
- Auditing Theory Chapter 5Document13 pagesAuditing Theory Chapter 5Almira BesoniaNo ratings yet
- Auditing Reviewer 3Document3 pagesAuditing Reviewer 3Sheena ClataNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Assurance Services - Docx'Document8 pagesFundamentals of Assurance Services - Docx'jhell dela cruzNo ratings yet
- Personal Factors CPALEDocument113 pagesPersonal Factors CPALEGrashiela CalimlimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Auditing Theory 15 16 RoqueDocument34 pagesChapter 3 Auditing Theory 15 16 RoqueDarlene Ventura0% (1)
- Tax6 12Document182 pagesTax6 12Kaizu KunNo ratings yet
- CH 08Document22 pagesCH 08xxxxxxxxxNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2 Finals Acctng 411N Sampling and Substantive TestsDocument5 pagesQuiz 2 Finals Acctng 411N Sampling and Substantive TestsJunhui WenNo ratings yet
- De Guzman Module 7Document9 pagesDe Guzman Module 7Ma Ruby II SantosNo ratings yet
- Auditor's Cup Questions-2Document8 pagesAuditor's Cup Questions-2francesNo ratings yet
- 1st Assignment - FinalDocument13 pages1st Assignment - FinalJeane Mae BooNo ratings yet
- Chapter 05 AnsDocument12 pagesChapter 05 AnsDave Manalo100% (1)
- ACC 139 SAS Day 26 1152021 JLMD - Docx-1Document18 pagesACC 139 SAS Day 26 1152021 JLMD - Docx-1Aldrin Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Differentiate Confirmation and InquiryDocument3 pagesDifferentiate Confirmation and InquiryJasmine LimNo ratings yet
- Lesson H - 1 Ch10 Exp. Cycle Act. Tech.Document57 pagesLesson H - 1 Ch10 Exp. Cycle Act. Tech.Blacky PinkyNo ratings yet
- Audit of InvestmentsDocument3 pagesAudit of InvestmentsJasmine Marie Ng Cheong50% (2)
- Evidence and Performance of Substantive TestingDocument49 pagesEvidence and Performance of Substantive Testing2019-202518No ratings yet
- Substantive Tests of Receivables and SalesDocument5 pagesSubstantive Tests of Receivables and SalesEricaNo ratings yet
- SCM Finals - Extra CreditDocument16 pagesSCM Finals - Extra CreditEnola HolmesNo ratings yet
- Exercise 4 CashDocument4 pagesExercise 4 CashYeyebonl100% (1)
- Chapter 04 AnsDocument4 pagesChapter 04 AnsDave Manalo100% (1)
- Audit Program For EquityDocument12 pagesAudit Program For EquityIra Jean DaganzoNo ratings yet
- Audit SamplingDocument9 pagesAudit Samplingemc2_mcv100% (3)
- Audit SamplingDocument10 pagesAudit SamplingJayson Manalo GañaNo ratings yet
- RED - Audit SamplingDocument10 pagesRED - Audit SamplingClyde RamosNo ratings yet
- Corrective Action and Preventive Action (CAPA) in Pharmaceutical IndustryFrom EverandCorrective Action and Preventive Action (CAPA) in Pharmaceutical IndustryNo ratings yet
- Ap 8503Document6 pagesAp 8503Joyce Kay AzucenaNo ratings yet
- Tx-Drills-101a 101B 101C PDFDocument6 pagesTx-Drills-101a 101B 101C PDFJoyce Kay AzucenaNo ratings yet
- Bible Preacher Youth Conference Spiritual Leadership Conference TwitterDocument3 pagesBible Preacher Youth Conference Spiritual Leadership Conference TwitterJoyce Kay AzucenaNo ratings yet
- Full Text GBL CasesDocument102 pagesFull Text GBL CasesJoyce Kay AzucenaNo ratings yet
- Organizational JusticeDocument4 pagesOrganizational JusticeJoyce Kay AzucenaNo ratings yet
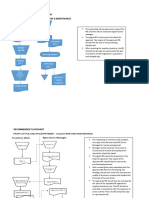
- Recommended Flowchart For DisposalDocument3 pagesRecommended Flowchart For DisposalJoyce Kay AzucenaNo ratings yet
- Tentative Description of The Nature o F Management Advisory Services by Independent Accounting FirmsDocument1 pageTentative Description of The Nature o F Management Advisory Services by Independent Accounting FirmsJoyce Kay AzucenaNo ratings yet
- Assessment of CG in The Phil PDFDocument34 pagesAssessment of CG in The Phil PDFJoyce Kay AzucenaNo ratings yet
- Group 6Document27 pagesGroup 6Joyce Kay AzucenaNo ratings yet
- Psa 520 Focus NotesDocument1 pagePsa 520 Focus NotesJoyce Kay AzucenaNo ratings yet
- Channel Management DecisionsDocument7 pagesChannel Management DecisionsJoyce Kay Azucena100% (2)
- Organization of MAS PracticeDocument3 pagesOrganization of MAS PracticeJoyce Kay AzucenaNo ratings yet
- Practical Accounting 2 With AnswersDocument11 pagesPractical Accounting 2 With Answerskidrauhl0767% (6)