0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 viewsTechnical Discussio1
Technical Discussio1
Uploaded by
Andreo Miguel H. ZamoraThe document discusses the construction of an on-off keying (OOK) transmitter circuit. OOK represents digital data as the presence or absence of a carrier wave. The circuit is tested and achieves the desired output of a sinusoidal waveform for a logic 1 pulse and a straight line for a logic 0 pulse, but initially had distortion. Changing the resistor value lessened the distortion in subsequent tests as seen in the cleaner waveform output.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Technical Discussio1
Technical Discussio1
Uploaded by
Andreo Miguel H. Zamora0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views2 pagesThe document discusses the construction of an on-off keying (OOK) transmitter circuit. OOK represents digital data as the presence or absence of a carrier wave. The circuit is tested and achieves the desired output of a sinusoidal waveform for a logic 1 pulse and a straight line for a logic 0 pulse, but initially had distortion. Changing the resistor value lessened the distortion in subsequent tests as seen in the cleaner waveform output.
Original Description:
gr
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
The document discusses the construction of an on-off keying (OOK) transmitter circuit. OOK represents digital data as the presence or absence of a carrier wave. The circuit is tested and achieves the desired output of a sinusoidal waveform for a logic 1 pulse and a straight line for a logic 0 pulse, but initially had distortion. Changing the resistor value lessened the distortion in subsequent tests as seen in the cleaner waveform output.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views2 pagesTechnical Discussio1
Technical Discussio1
Uploaded by
Andreo Miguel H. ZamoraThe document discusses the construction of an on-off keying (OOK) transmitter circuit. OOK represents digital data as the presence or absence of a carrier wave. The circuit is tested and achieves the desired output of a sinusoidal waveform for a logic 1 pulse and a straight line for a logic 0 pulse, but initially had distortion. Changing the resistor value lessened the distortion in subsequent tests as seen in the cleaner waveform output.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
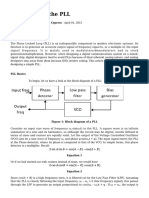
TECHNICAL DISCUSSION:
In the experiment we construct a circuit that deals
with OOK (on-off keying) transmitter circuit. On-off keying
denotes the simplest form of amplitude-shift keying (ASK)
modulation that represents digital data as the presence or
absence of a carrier wave. OOK is most commonly used to
transmit Morse code over radio frequencies, although in
principle any digital encoding scheme may be used. OOK is also
used in optical communication systems. The desire output that
we must get in the OOK circuit must have a waveform if our
pulse is in logic 0 (Low) the waveform must be straight (OFF
state) but if the pulse is in logic 1 (High) the waveform must be
a sinusoidal waveform (ON state).
As we test our circuit we achieved the desire output
of the circuit but have a distortion to lessen the distortion we
changed the value of our resistor. As we change the value of our
resistor and test again our circuit the waveform of our circuit
has less distortion different from our first try that have a
distortion. We can see in the waveform if we have a logic 1 in
our pulse we get a sinusoidal waveform but if we have a logic 0
in our pulse we get a straight line.
You might also like
- Figure 1: Output of IR Receiver Being Sent To PLLDocument2 pagesFigure 1: Output of IR Receiver Being Sent To PLLshychangNo ratings yet
- UIC BioE 431 Instrumentation LabDocument71 pagesUIC BioE 431 Instrumentation LabSimisola OludareNo ratings yet
- Digital ElectronicsDocument32 pagesDigital ElectronicsLakshmi CgNo ratings yet
- DLD Labrep 11Document2 pagesDLD Labrep 11hadeeda980No ratings yet
- Demystifying The PLLDocument14 pagesDemystifying The PLLgovindcoolNo ratings yet
- De Unit-3Document19 pagesDe Unit-3manojbotsa69No ratings yet
- Wireless Power TransmissionDocument15 pagesWireless Power TransmissionGabriel ObrikiNo ratings yet
- ASKDocument8 pagesASKShiela Monique Fajardo100% (1)
- RTL or NorDocument11 pagesRTL or Norمعتصم الكاملNo ratings yet
- Ultra-Fast Clock Recovery by All-Optical PLL: Tuy4 4:30Pm 4:45PmDocument2 pagesUltra-Fast Clock Recovery by All-Optical PLL: Tuy4 4:30Pm 4:45PmOPTICALMIMOOFDMNo ratings yet
- Oscillators: 4.6 Troubleshooting Tips For Oscillator CircuitsDocument5 pagesOscillators: 4.6 Troubleshooting Tips For Oscillator CircuitsElla Mae AbayNo ratings yet
- 225 - Lab 1 ReportDocument10 pages225 - Lab 1 Reportsyed IrvinNo ratings yet
- Project ReportDocument9 pagesProject ReportBinshi GopinadanNo ratings yet
- Automatic Street Light and Logic Gates .Document34 pagesAutomatic Street Light and Logic Gates .jeemains.last.opportunityNo ratings yet
- Bca 1 STDocument42 pagesBca 1 STTushar PatelNo ratings yet
- Combinational Logic CircuitsDocument6 pagesCombinational Logic CircuitsJohn Brix Balisteros100% (1)
- Buddy Activity Digitech MidtermDocument3 pagesBuddy Activity Digitech MidtermVictor John SalardaNo ratings yet
- Ch7-Basic Digital LogicsDocument35 pagesCh7-Basic Digital Logicsgebreyohansgebreyesus085No ratings yet
- An All Optical XOR Logic Gate For NRZ Based On TOAD: E E J J E EDocument5 pagesAn All Optical XOR Logic Gate For NRZ Based On TOAD: E E J J E EHimadri MandalNo ratings yet
- Pc-Eee-791 LabDocument26 pagesPc-Eee-791 Labca.ist.eeeNo ratings yet
- M2 DoneDocument29 pagesM2 Donesubhan ullahNo ratings yet
- Lecture4 DFDocument26 pagesLecture4 DFShimaa ZeinNo ratings yet
- Logic Gates and Boolean Algebra-OutlineDocument11 pagesLogic Gates and Boolean Algebra-OutlineSiddharajsinh GohilNo ratings yet
- Ece326 Lab 3 Exp 19Document8 pagesEce326 Lab 3 Exp 19max1039No ratings yet
- What Is An Op-Amp?Document10 pagesWhat Is An Op-Amp?BookMaggot100% (1)
- Experiment: Title:-IR BlockerDocument14 pagesExperiment: Title:-IR BlockerOisin MaguireNo ratings yet
- Combinational Logic CircuitDocument9 pagesCombinational Logic CircuitJiremy NoriegaNo ratings yet
- Pre-Lab Assignment: Read and Review Sections 2.4, 2.8.2, 9.9.3, 13.4, 13.5, and 13.9 inDocument11 pagesPre-Lab Assignment: Read and Review Sections 2.4, 2.8.2, 9.9.3, 13.4, 13.5, and 13.9 inThe_Dude1138No ratings yet
- Lecture 6: Time-Dependent Behaviour of Digital Circuits: Source Load DDocument5 pagesLecture 6: Time-Dependent Behaviour of Digital Circuits: Source Load DTaqi Shah100% (1)
- A Novel Frequency-Adaptive PLL For Single-Phase Grid-Connected ConvertersDocument6 pagesA Novel Frequency-Adaptive PLL For Single-Phase Grid-Connected ConvertersYubaraj KafleNo ratings yet
- Constant Gain MultiplierDocument7 pagesConstant Gain Multiplierchristian marananNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 4 Oscillators FinalizedDocument47 pagesChapter - 4 Oscillators FinalizednegussenoahNo ratings yet
- Percobaan I Parameter Gerbang Logika: Basry A Sihotang (14S16040)Document6 pagesPercobaan I Parameter Gerbang Logika: Basry A Sihotang (14S16040)Basry Answar SihotangNo ratings yet
- Laches y Flip FlopsDocument38 pagesLaches y Flip FlopsFernando RamirezNo ratings yet
- Electronics 2 Lab - Dela Cruz, Ashley Anne C.Document7 pagesElectronics 2 Lab - Dela Cruz, Ashley Anne C.Ashley De LeonNo ratings yet
- PLL DesignDocument6 pagesPLL DesignMohamedElsawiNo ratings yet
- Lecroy Probing Tutorial Appnote016Document12 pagesLecroy Probing Tutorial Appnote016Skate38No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 Superposition AnalysisDocument24 pagesCHAPTER 3 Superposition Analysisnurul najwaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3 Vco / PLL: 3.1 ObjectiveDocument7 pagesExperiment 3 Vco / PLL: 3.1 ObjectiveRajiv RanjanNo ratings yet
- Latches&FlipflopsDocument20 pagesLatches&FlipflopsAjay G Bellam100% (1)
- A Software Defined Radio ReceiverDocument24 pagesA Software Defined Radio ReceiverAntonis KanavourasNo ratings yet
- TD1 SALC GabourDocument2 pagesTD1 SALC Gabourachelirayane7No ratings yet
- Logic Gates Gr11eDocument25 pagesLogic Gates Gr11emarijasajatovic370 sajatovicNo ratings yet
- LachesDocument38 pagesLachesFernando RamirezNo ratings yet
- Experiment - Amplitude Shift KeyingDocument3 pagesExperiment - Amplitude Shift KeyingRaunaq Kalia75% (4)
- 32792222Document193 pages32792222ajit704687No ratings yet
- Digital Communications Project ReportDocument14 pagesDigital Communications Project ReportSonal Pinto0% (1)
- Ece 334 Lecture 37 EclDocument21 pagesEce 334 Lecture 37 EcladeeysfNo ratings yet
- Portfolio in Electronics Technology 1 (Cacho, Kathleenjoyc.)Document25 pagesPortfolio in Electronics Technology 1 (Cacho, Kathleenjoyc.)KATHLEEN JOY CACHONo ratings yet
- EE133 - Prelab 4 FM Demodulation: Transmitter ReceiverDocument3 pagesEE133 - Prelab 4 FM Demodulation: Transmitter ReceiverMahadevNo ratings yet
- RME 2102 Lec 3Document62 pagesRME 2102 Lec 3asraful islamNo ratings yet
- Phy InvestigatorynxDocument6 pagesPhy InvestigatorynxOMM PRASAD DASNo ratings yet
- Lica Tut1 24Document2 pagesLica Tut1 24hannivas329No ratings yet
- Experiment 3Document6 pagesExperiment 3কাওমিউজ্জামান কাব্যNo ratings yet
- Digital Comunication 7uiyiyDocument14 pagesDigital Comunication 7uiyiykasoNo ratings yet
- LM 339 ComparatorDocument7 pagesLM 339 ComparatorMark YulyNo ratings yet
- Design An Amplifier With A Gain of - 10 and Input Resistance of 10k . Ri 10k Av - Rf/Ri - 10 - Rf/10k RF 10 X 10 K 100 KDocument21 pagesDesign An Amplifier With A Gain of - 10 and Input Resistance of 10k . Ri 10k Av - Rf/Ri - 10 - Rf/10k RF 10 X 10 K 100 KMangaiyarkarasi VengatachalamNo ratings yet
- Digital Final 1Document3 pagesDigital Final 1Azelle BatallaNo ratings yet
- Geography 4: Test I: IdentificationDocument3 pagesGeography 4: Test I: IdentificationAndreo Miguel H. ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Crime MCQDocument6 pagesCrime MCQAndreo Miguel H. ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Medic Practitioner CasesDocument49 pagesMedic Practitioner CasesAndreo Miguel H. ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Medic Practitioner CasesDocument49 pagesMedic Practitioner CasesAndreo Miguel H. ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Digest Civ 2Document17 pagesDigest Civ 2Andreo Miguel H. ZamoraNo ratings yet
- History of Silicon DiodeDocument7 pagesHistory of Silicon DiodeAndreo Miguel H. ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Republic vs. Crasus IyoyDocument3 pagesRepublic vs. Crasus IyoyAndreo Miguel H. Zamora100% (1)
- Action de in Rem Verso Is An Action For Unjust EnrichmentDocument2 pagesAction de in Rem Verso Is An Action For Unjust EnrichmentAndreo Miguel H. ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Edith Windsor and Thea Spyer Married in Toronto in 2007 Where SameDocument9 pagesEdith Windsor and Thea Spyer Married in Toronto in 2007 Where SameAndreo Miguel H. ZamoraNo ratings yet
- ComplaintDocument2 pagesComplaintAndreo Miguel H. Zamora100% (1)