5.1 Bilirubin Pathway
5.1 Bilirubin Pathway
Uploaded by
goku198Copyright:
Available Formats
5.1 Bilirubin Pathway
5.1 Bilirubin Pathway
Uploaded by
goku198Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
5.1 Bilirubin Pathway
5.1 Bilirubin Pathway
Uploaded by
goku198Copyright:
Available Formats
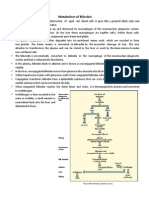
7. Pathway of bilirubin synthesis and breakdown? Causes of Jaundice?
• Bilirubin is a waste product excreted via bile, generated from the break-down
of worn out RBCs – more specifically, the degradation of heme (iron-
containing part of Hb). This bilirubin is extracted from the blood by
hepatocytes and excreted via bile.
• Most of the breakdown of bilirubin is from senescent erythrocytes (worn out
RBCs), but also from the turnover of hepatic hemoproteins from premature
destruction of newly formed erythrocytes in BM.
• The pathway involves: heme oxygenase oxidises heme to biliverdin which is
then reduced to biliverdin reductase. Bilirubin is formed outside the liver in
cells of mononuclear phagocytes/reticuloendothelial cells (such as in spleen,
macrophages etc) is released and bound to serum albumin. This bilirubin is
unconjugated and is not water soluble in the blood. Therefore purpose of liver
processes is conjugation to make it soluble in bile for excretion. Liver
processes includes;
1. carrier mediated uptake at the sinusoidal membrane (transport)
2. cytosolic protein binding and delivery to endoplasmic reticulum
(absorption, conversion)
3. conjugation with 1 or 2 molecules of glucoronic acid by bilirubin
uridine diphosphate-glucuronosyltransferase (conjugation – made
water soluble for bile)
4. Excretion of the water-soluble non-toxic bilirubin glucuronides into
bile.
5. gut bacteria deconjugates the bilirubin and degrade it to colourless
urobilinogens which is then excreted in urine. It is further oxidise to
form stercobilins which is excreted in feces. Feces darkens by
oxidation in air to give its proper colour…
• Bilirubin is a yellow pigment that gives bile its yellow colour. In gut though it
goes colourless due to bacteria, hence feces colour isn’t that yellowish
• A small amount is normally reabsorbed by the intestine back into the blood,
also excreted through urine and responsible for yellow colour. It can only be
excreted by kidneys after modification in liver and intestine.
• If bilirubin is formed more rapidly that it can be cleared, it accumulates in
body = jaundice – patients appear yellowish esp in whites of eyes (sclera).
Types and causes of Jaundice:
Types
• Prehepatic – or haemolytic – jaundice due 2 excessive breakdown of RBC,
liver’s capabilities stretched. Often medical treatment
• Hepatic – liver itself is diseased and cant deal with normal load
• Posthepatic – or obstructive, processing is fine, but elimination is hindered by
obstruction such as gallstone i.e. cant excrete in feces properly. Often surgical.
Causes
1. excessive production of bilirubin, normal is 0.2-0.3 g a day e.g. haemolytic
anaemia, internal haemorrhage
2. reduced hepatic uptake e.g. drug interference, viral hep
3. impaired conjugation e.g. newborns…
4. decreased hepatocellular excretion e.g. deficiency in transporters,
hepatocellular damage etc
5. impaired bile flow (intra and extra hepatic) e.g. obstruction
• 1-3 are called unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia (pre and hepatic), 4-5, are
conjugated hyperbilirubinemia – refers to post.
• Also inborn errors in metabolism – gilbert syndrome- inherited and dubin-
johnson syndrome – autosomal recessive defect. Both effect pathway at some
point.
Sherwood, Robbins pathology
You might also like
- Diagnostic Atlas of Melanocytic PathologyDocument588 pagesDiagnostic Atlas of Melanocytic PathologyNyxa AbdullaNo ratings yet
- Bilirubin MetabolismDocument29 pagesBilirubin Metabolismzahra maulidaNo ratings yet
- Jaundice Biochemical ProfileDocument64 pagesJaundice Biochemical ProfileGhaidaa SadeqNo ratings yet
- Bilirubin MetabolismDocument5 pagesBilirubin Metabolismgugus aminaNo ratings yet
- JaundiceDocument4 pagesJaundiceShubhamNo ratings yet
- BiIirubin MetabolismDocument38 pagesBiIirubin Metabolismdejilo9839No ratings yet
- Liver Function Test (TSB)Document25 pagesLiver Function Test (TSB)shafyd ramdanNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry - LG 1 (Liver Function Tests) - Dr. SalarDocument28 pagesBiochemistry - LG 1 (Liver Function Tests) - Dr. Salargabi.g.wahbeNo ratings yet
- Heme DegradationDocument26 pagesHeme DegradationDerick SemNo ratings yet
- 212 Spring 2005 Heme DegradationDocument17 pages212 Spring 2005 Heme Degradationcockatoo_whiteNo ratings yet
- Catabolism of Heme 2024Document38 pagesCatabolism of Heme 2024Ayeza MazharNo ratings yet
- Metabolism of BilirubinDocument3 pagesMetabolism of BilirubinEris Abdul Aziz100% (1)
- Heme Degradation & HyperbilirubinemiasDocument30 pagesHeme Degradation & HyperbilirubinemiasSubhi MishraNo ratings yet
- Liver PathologyDocument35 pagesLiver Pathologynhgwdwffp2No ratings yet
- JAUNDICE. for undergraduate pptxDocument38 pagesJAUNDICE. for undergraduate pptxSurendar KesavanNo ratings yet
- Jaundice FinalDocument30 pagesJaundice FinalFrances GrefalNo ratings yet
- Heme DegradationDocument17 pagesHeme DegradationsarcaliNo ratings yet
- Liver Function TestsDocument26 pagesLiver Function TestsSadeq TalibNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of JaundiceDocument23 pagesPathophysiology of Jaundiceharshdadhich29No ratings yet
- Heme Degradation and Jaundice BSC NursingDocument6 pagesHeme Degradation and Jaundice BSC Nursingmadjoke0070No ratings yet
- JaundiceDocument56 pagesJaundicesohaNo ratings yet
- Heme DegradationDocument6 pagesHeme Degradationanshasm196No ratings yet
- Liver Function Test For CLMDocument43 pagesLiver Function Test For CLMassfawteklemariam17No ratings yet
- Liver Function Tests (LFTS)Document18 pagesLiver Function Tests (LFTS)farkad rawiNo ratings yet
- Bilirubin Metabolism and HyperbilirubinaemiasDocument35 pagesBilirubin Metabolism and HyperbilirubinaemiasEuphrasiaNo ratings yet
- Pathology of The Liver: Systems Pathology II-PA5402 Dr. Khan T-W-RDocument78 pagesPathology of The Liver: Systems Pathology II-PA5402 Dr. Khan T-W-RCrystal Lynn Keener SciariniNo ratings yet
- Transcutaneous Bilirubin DNB PDF 2023Document46 pagesTranscutaneous Bilirubin DNB PDF 2023Rishabh MasutaNo ratings yet
- JAUNDICE pptm-1Document29 pagesJAUNDICE pptm-1jismi vallachiraNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEM Jaundice FinalDocument54 pagesBIOCHEM Jaundice FinalJohnRobynDiezNo ratings yet
- Clinical ChemistryDocument3 pagesClinical ChemistryHazel Loren GrandeNo ratings yet
- JaundiceDocument24 pagesJaundicey . uNo ratings yet
- Jaundice ChoDocument30 pagesJaundice Chokamaramusa331No ratings yet
- Liver FunctionDocument45 pagesLiver Functionpuno ric100% (1)
- L IssueDocument3 pagesL IssueSaur Maria Fitri SinambelaNo ratings yet
- Second Semester- Liver Function1-1 (1)Document35 pagesSecond Semester- Liver Function1-1 (1)Ameh FavourNo ratings yet
- 4-Rbc & Its DestructionDocument19 pages4-Rbc & Its Destructiongauravchetanjain124No ratings yet
- Liver Function TestDocument80 pagesLiver Function Testallenshanique1999No ratings yet
- cc2 Lectures AllDocument256 pagescc2 Lectures AllJayson Dagohoy SudioNo ratings yet
- Liver FunctionDocument6 pagesLiver Functionxp7wkzgcfgNo ratings yet
- Name of Test:-Serum Bilirubin Test: Tests For Liver FunctionDocument4 pagesName of Test:-Serum Bilirubin Test: Tests For Liver FunctionHiba EmadNo ratings yet
- JaundiceDocument12 pagesJaundicemk6523189No ratings yet
- Hemoglobin Catabolism and BilirubinDocument2 pagesHemoglobin Catabolism and BilirubinJacob MasikaNo ratings yet
- Metabolisme Bilirubin Blok 11 2016Document22 pagesMetabolisme Bilirubin Blok 11 2016Astri Hardianti RahimNo ratings yet
- Liver Function Test HandoutDocument14 pagesLiver Function Test HandoutKhisha RangasNo ratings yet
- JaundiceDocument5 pagesJaundiceAbinaya Hinaya HinayaNo ratings yet
- Liver Function TestDocument18 pagesLiver Function TestMuhammad Waqas MunirNo ratings yet
- 9.1 Liver Function TestsDocument8 pages9.1 Liver Function TestsGio Joaquin SantosNo ratings yet
- Metabolism of Bilirubin and Bile Salt SynthesisDocument34 pagesMetabolism of Bilirubin and Bile Salt SynthesisKumail LakraNo ratings yet
- The Biochemistry of JaundiceDocument29 pagesThe Biochemistry of JaundiceeminemizenNo ratings yet
- 8 BilirubinDocument25 pages8 BilirubinTagreed DerarNo ratings yet
- L6 - Bilirubin MetabolismDocument28 pagesL6 - Bilirubin Metabolismyouservezeropurpose113No ratings yet
- CLINICAL CHEMISTRY OF LIVER (New)Document18 pagesCLINICAL CHEMISTRY OF LIVER (New)haidernadhem57No ratings yet
- Bilirubin Metabolism: Hd. - Msc. (Biochemistry)Document18 pagesBilirubin Metabolism: Hd. - Msc. (Biochemistry)MuhamadMaruf100% (1)
- Obstructive JaundiceDocument53 pagesObstructive JaundiceAllan MakalaNo ratings yet
- 23.12.2022 - Metabolism of Heme and BilirubinDocument4 pages23.12.2022 - Metabolism of Heme and BilirubinMuhammed GaribovNo ratings yet
- Bilirubin Metabolism Jaundice PPP 9Document27 pagesBilirubin Metabolism Jaundice PPP 9Regina Marsha Xaveria100% (1)
- Chapter 4. JaundiceDocument29 pagesChapter 4. JaundiceShravan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ictericia Diagnostico Ravindran2020Document7 pagesIctericia Diagnostico Ravindran2020Francisco CarpioNo ratings yet
- Chem-Dr - Zainab-Bilirubin-Lab 2Document10 pagesChem-Dr - Zainab-Bilirubin-Lab 2gmpcbpzdysNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes: Clinical Chemistry of LiverDocument38 pagesLecture Notes: Clinical Chemistry of LivershehnilaNo ratings yet
- Jaundice, (Hyperbilirubinemia) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandJaundice, (Hyperbilirubinemia) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Epidemiological Study Designs: DR Saba Aijaz Msc. Clinical Research (Akuh)Document28 pagesEpidemiological Study Designs: DR Saba Aijaz Msc. Clinical Research (Akuh)sabaxlentNo ratings yet
- National Vector Borne Disease Control Programme Malaria, Dengue, Chikungunya, Kala Azar and JEDocument31 pagesNational Vector Borne Disease Control Programme Malaria, Dengue, Chikungunya, Kala Azar and JEArushiNo ratings yet
- BegayDocument3 pagesBegayapi-549236958No ratings yet
- Children 10 00695Document16 pagesChildren 10 00695BBD BBDNo ratings yet
- Preventive DentistryDocument14 pagesPreventive DentistryatikramadhaniNo ratings yet
- Hematology - KitProtocol - List of TIC KitsDocument3 pagesHematology - KitProtocol - List of TIC Kitsuzair.narcNo ratings yet
- (Formerly NCCLS) Providing NCCLS Standards and Guidelines, ISO/TC 212 Standards, and ISO/TC 76 StandardsDocument28 pages(Formerly NCCLS) Providing NCCLS Standards and Guidelines, ISO/TC 212 Standards, and ISO/TC 76 StandardsErick RiveraNo ratings yet
- 1 Products of Conception - Libre PathologyDocument8 pages1 Products of Conception - Libre PathologyfadoNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume DeficitDocument3 pagesFluid Volume DeficitDan Gerald Alcido SalungaNo ratings yet
- CVS Module 4 Guideines by MBBS CafeteriaDocument33 pagesCVS Module 4 Guideines by MBBS CafeteriaKashaf KhanNo ratings yet
- PedoDocument14 pagesPedoHarjotBrarNo ratings yet
- A Review of Herbal and Pharmaceutical Galactagogues For Breast-FeedingDocument14 pagesA Review of Herbal and Pharmaceutical Galactagogues For Breast-FeedingKhoirotul HidayahNo ratings yet
- Varilrix Detail Aid DraftDocument5 pagesVarilrix Detail Aid DraftpheverishNo ratings yet
- Lexicometric and Sentiment Analysis of News in The Spanish Press Regarding Hiv and PrisonDocument6 pagesLexicometric and Sentiment Analysis of News in The Spanish Press Regarding Hiv and PrisonHerald Scholarly Open AccessNo ratings yet
- Mitral StenosisDocument67 pagesMitral StenosisNamithaNo ratings yet
- BAB II (McCracken's Removable Partial Prostodontics)Document3 pagesBAB II (McCracken's Removable Partial Prostodontics)Cattleya TanosseloNo ratings yet
- Assignment: Riphah International University (Faisalabad Campus)Document5 pagesAssignment: Riphah International University (Faisalabad Campus)Muhammad Uzair GujjarNo ratings yet
- FP Form1 V3.0 2016Document3 pagesFP Form1 V3.0 2016Lorenz Joey Ricarte100% (2)
- Theory and Science Specimen PaperDocument12 pagesTheory and Science Specimen PaperAhmed Yousef100% (3)
- Acute PyelonephritisDocument53 pagesAcute Pyelonephritiseeymee100% (1)
- Attending Physicians Statement Crisis Cover Renal Failure - 041222Document2 pagesAttending Physicians Statement Crisis Cover Renal Failure - 041222max leeNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Cell AppendagesDocument50 pagesBacterial Cell AppendagesNeha Samal100% (1)
- Jerd 12812Document15 pagesJerd 12812snkidNo ratings yet
- AdrenalDocument9 pagesAdrenalNada MuchNo ratings yet
- About Myelodysplastic Syndromes: Overview and TypesDocument12 pagesAbout Myelodysplastic Syndromes: Overview and TypesAulya ArchuletaNo ratings yet
- Candida EczemaDocument1 pageCandida EczemaVarun Singh ChandelNo ratings yet
- Hospital La Comunidad de Santa Rosa: Chapter I: Problem and Its SettingsDocument15 pagesHospital La Comunidad de Santa Rosa: Chapter I: Problem and Its SettingsMeynard MagsinoNo ratings yet
- Alternative System of MedicineDocument13 pagesAlternative System of MedicineDebipriya Mistry100% (2)
- AyuDocument3 pagesAyuDira RahmiNo ratings yet