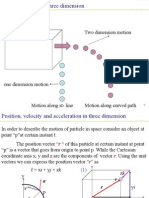
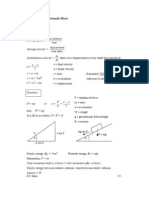
Physics Formulas
Uploaded by
Zahid MohammadPhysics Formulas
Uploaded by
Zahid Mohammadwww.educatalyst.
net Baaz Pathan IGCSE/ IB Tutors JUHU 9930758555
Useful Formulas for the IGCSE Physical Science Examinations General Physics Formula in Words speed = total distance / total time weight = mass x acceleration of gravity acceleration = change in speed / change in time density = mass / volume force = mass x acceleration extension = a constant x load work = force x distance potential energy = mass x acceleration of gravity x height kinetic energy = x mass x velocity squared energy efficiency = energy output / energy input x 100% energy used = work done energy of a nuclear reaction = mass x speed of light squared power = energy / time Physics of Waves Formula in Words speed of a wave = frequency x wavelength angle of incidence = angle of reflection index of refraction = sine of incident angle / sine of refracted angle Formula in Symbols v=d/t w=mxg a=v/t d=m/v F=mxa x=kxF W=Fxd p.e. = m x g x h 2 k.e. = x m x v e = Eout / Ein x 100% E=W 2 E=mxc P=E/t
Formula in Symbols c=fx i=r n = sin i / sin r
Electricity and Magnetism Formula in Symbols Formula in Words I=Q/t current = charge / time R=V/I resistance = potential difference / current R=kxl/A resistance = a constant x length / cross sectional area R = R1 + R2 resistances in series add together 1 / R = 1 / R 1 + 1 / R2 reciprocals of resistances in parallel add together I = I 1 + I2 currents in parallel add together Iin = Iout total current into a point = total current out of a point V = V 1 + V2 voltage of source = sum of all voltage drops in a circuit P=IxV power used in an electric circuit = current x voltage E=IxVxt energy used in an electric circuit = current x voltage x time Vp = N p voltage in primary coil = number of turns in primary coil Vs = N s voltage in secondary coil number of turns in secondary coil Vp x I p = V s x I s power in primary coil = power in secondary coil (for a perfect transformer) V = w/Q Q= It W=VxIxt P=VxI P = I2 x R P = V2 / R Sp Heat Capacity Q= mxc xt Pt =mxcxt VIt=mxcxt Thermal Capacity = m x C Or = Q / t
Sp Latent Heat of Fusion Q = m X Lf or P t = m x Lf VIt = m X Lf Sp Latent Heat of Vaporisation Q = m x Lv or Pt = m x Lv V I t = m x Lv
You might also like
- AP Physics Formulas (Kinematic) Cheat Sheet: by ViaNo ratings yetAP Physics Formulas (Kinematic) Cheat Sheet: by Via2 pages
- SCI 121 - Introduction To Physics & Chemistry Formula Sheet 1 KinematicsNo ratings yetSCI 121 - Introduction To Physics & Chemistry Formula Sheet 1 Kinematics10 pages
- Uniform and Non - Uniform Circular MotionNo ratings yetUniform and Non - Uniform Circular Motion4 pages
- Best Coaching Institute For Iit-Jee Booklet (Work, Energy and Power)No ratings yetBest Coaching Institute For Iit-Jee Booklet (Work, Energy and Power)50 pages
- CH 6 Momentum: Relationship Between Momentum & ForceNo ratings yetCH 6 Momentum: Relationship Between Momentum & Force2 pages
- Motion - Free Failing Bodies and Projectile MotionNo ratings yetMotion - Free Failing Bodies and Projectile Motion31 pages
- Angular Displacement, Velocity, AccelerationNo ratings yetAngular Displacement, Velocity, Acceleration3 pages
- Collisions: Previous Eamcet Questions Engineering100% (1)Collisions: Previous Eamcet Questions Engineering12 pages