Drug Name
Drug Name
Uploaded by
Sarah Agudo FernandezCopyright:
Available Formats
Drug Name
Drug Name
Uploaded by
Sarah Agudo FernandezOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Drug Name
Drug Name
Uploaded by
Sarah Agudo FernandezCopyright:
Available Formats
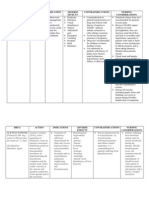
Drug Name Generic Name: Celocoxib Brand Name: Celebrex Stock dose: 100 or 200mg/ tab
Classific ation NSAID
Action Thought to inhibit prostaglandi n synthesis, impeding cyclooxygen ase- (COX2) to produce antiinflammator y, analgesic, and antipyretic effect.
Indication To relieve signs and symptoms of osteoarthritis To relieve signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis To relieve signs and symptoms of ankylosing spondylitis Adjunctive treatment for adenomatous polyposis to reduce the number of adematous colorectal polyps Acute pain and primary dysmenorrheal
Contraindication Contraindicated in patients hypersensitivity to drug, aspirin, sulfonamides, and other NSAIDs Contraindicated in those with severe hepatic impairment and in the treatment of perioperative pain after coronary artery bypass graft surgery Avoid use in the third trimester of pregnancy
Adverse Reaction CNS: dizziness, headache, insomnia CV: peripheral edema EENT: pharyngitis, rhinitis, sinusitis GI: abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, flatulence, dyspepsia Metabolic: nyperchloremia Musculoskeletal: back pain Respiratory: URTI Skin: rash, toxic eptdermal necrolysis, stevensJohnson syndrome, erythema multiforme, exfoliatve dermatitis Other: a ccidental injury
Nursing Considerations Ask patients allergic to or with a history of anaphylactic reaction to sulfonamides, aspirin, or other NSAIDs may be allergic to this drug Patient with history of ulcers or GI bleeding is at high risk for GI bleeding while taking NSAIDs, such as celecoxib. Other risk factors for GI bleeding include treatment with corticosteroids or anticoagulants, longer duration of NSAID treatment, smoking, alcoholism, older age and poor overall health NSAIDs may increase the risk of serious thrombotic events, MI, or stroke. The risk mat be greater with longer use or in patients with CV disease or risk factors for CV disease Although drug may be use with low aspirin dosages the combination may increase risk for GI bleeding Watch for signs and symptoms of overt and occult bleeding NSAIDs such as celecoxib can cause fluid retention, monitor patients with hypertension, edema or heart failure Assess patients with CV risk factor before therapy Drugs may be hepatotoxic, watch for sign and symptom of liver toxicity Before starting drug therapy, rehydrate dehydrated patient Drugs can be given without regard to meals, but food may decrease GI upset Dont confuse celecoxib with cerebyx or celexa Tell patient to report history of allergic reactions to sulfonamides, aspirin or other NSAIDs before starting therapy Instruct patient to promptly report signs of GI bleeding such as blood in vomit, urine or stool; or black, tarry stool Advise patient to immediately report ras, unexplained weight gain or swelling
Tell woman to notify prescriber if she becomes pregnant or is planning to become pregnant during drug therapy Instruct patient to take drug with meal if stomach upset occurs Teach patients that all NSAIDs including celecoxib, may harm the liver. Advise patient to stop therapy and notify prescriber immediately if he experiences signs and symptoms of liver toxicity, including nausea, fatigue, lethargy, itching, yellowing of skin or eyes, right upper quadrant tenderness, and flulike syndrome Inform patient it may take several days before he feels consistent pain relief Advise patient that using OTC NSAIDs with celecoxib may increase the risk of GI toxicity
You might also like
- Advantages of Voluntary Blood DonationDocument2 pagesAdvantages of Voluntary Blood DonationSarah Agudo FernandezNo ratings yet
- Felodipine CefuroximeDocument3 pagesFelodipine CefuroximecotyboyNo ratings yet
- ECLAMPSIA Drug StudyDocument10 pagesECLAMPSIA Drug Studyjessica_omegaNo ratings yet
- Cefuroxime Drug AnaDocument4 pagesCefuroxime Drug AnaCarpz DarpzNo ratings yet
- Drugs Study For PneumoniaDocument5 pagesDrugs Study For PneumoniaLucelle ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument22 pagesDrug StudyColleen Fretzie Laguardia NavarroNo ratings yet
- NCP Drug StudyDocument3 pagesNCP Drug StudyArthadian De PeraltaNo ratings yet
- CelecoxibDocument2 pagesCelecoxibXtinegoNo ratings yet
- Mefenamic AcidDocument3 pagesMefenamic AcidAngelica Cassandra VillenaNo ratings yet
- Drugstudy Last DutyDocument5 pagesDrugstudy Last DutyJoeven HilarioNo ratings yet
- Alcofan: TabletsDocument2 pagesAlcofan: Tabletskokocodename47No ratings yet
- Drug Name Drug Class Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Reaction Nursing Responsibility Treatment of Urinary Tract InfectionDocument5 pagesDrug Name Drug Class Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Reaction Nursing Responsibility Treatment of Urinary Tract InfectionOamaga NajlaNo ratings yet
- DrugDocument2 pagesDrugMaryneth EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyMike Faustino SolangonNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyShiara Ruth EdrosoloNo ratings yet
- Drug Analysis (RN) - 3Document9 pagesDrug Analysis (RN) - 3Joannalyn Libo-on0% (1)
- ZolfinDocument3 pagesZolfinKhaled HasanNo ratings yet
- Ibuprofen Drug StudyDocument3 pagesIbuprofen Drug StudyEd King CubalanNo ratings yet
- GENERIC NAME: Celecoxib BRAND NAME: Celebrex: DRUG INTERACTIONS: Concomitant Use of Celecoxib WithDocument3 pagesGENERIC NAME: Celecoxib BRAND NAME: Celebrex: DRUG INTERACTIONS: Concomitant Use of Celecoxib Withrica13ableNo ratings yet
- Mefenamic Acid Indication, Dosage, Side Effect, Precaution MIMS MalaysiaDocument1 pageMefenamic Acid Indication, Dosage, Side Effect, Precaution MIMS MalaysianuruladyanisaifuzzamanNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENTDocument2 pagesASSIGNMENTMae MaricarNo ratings yet
- Drug OrderDocument3 pagesDrug OrderSaima BataloNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Indications Action Contraindication Side Effects Adverse Side Effects Nursing ManagementDocument3 pagesName of Drug Indications Action Contraindication Side Effects Adverse Side Effects Nursing Managementjhappo31No ratings yet
- Aceclofenac 100 MG Film-Coated Tablets - Summary of Product Characteristics (SMPC) - Print Friendly - (eMC) PDFDocument9 pagesAceclofenac 100 MG Film-Coated Tablets - Summary of Product Characteristics (SMPC) - Print Friendly - (eMC) PDFHabibNo ratings yet
- CVA Drug StudyDocument51 pagesCVA Drug StudyKarel LuNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - LeptospirosisDocument19 pagesDrug Study - LeptospirosisCamille PinedaNo ratings yet
- Case Pres PREECLAMPSIA Drugs NCPDocument12 pagesCase Pres PREECLAMPSIA Drugs NCPDanica May Galvez100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyMaye HerbitoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyNedemar OcampoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyKaloy KamaoNo ratings yet
- CHN Drug StudyDocument10 pagesCHN Drug StudyJoshua Cyryll ComiaNo ratings yet
- ASPIRIN Drug Study ERDocument1 pageASPIRIN Drug Study ERMargueretti Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- 2013 4 24 12 33 8Document2 pages2013 4 24 12 33 8Karim MohamedNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument19 pagesDrug StudyLovely EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Pedia Ward Drug Study...Document12 pagesPedia Ward Drug Study...Sheena Arnoco ToraynoNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument2 pagesDrugsShane CaltinoNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument6 pagesDrugsjesabel_caraigNo ratings yet
- Mefenamic AcidDocument2 pagesMefenamic AcidXtinego100% (1)
- Naproxen Sodium Drug StudyDocument3 pagesNaproxen Sodium Drug StudyEd King CubalanNo ratings yet
- Albuterol Drug StudyDocument7 pagesAlbuterol Drug StudyMaria Charlene OrpillaNo ratings yet
- DOLOSTAT-SP TabletsDocument15 pagesDOLOSTAT-SP TabletsVNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Classification and Mechanism of Action Indication/ Dosage/ Route Contraindicatio N Adverse Effects Nursing InterventionsDocument6 pagesDrug Name Classification and Mechanism of Action Indication/ Dosage/ Route Contraindicatio N Adverse Effects Nursing InterventionsVin LandichoNo ratings yet
- Medication Classificatio N Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Intervention Generic Name: CNS: GIDocument4 pagesMedication Classificatio N Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Intervention Generic Name: CNS: GIKathleenDawalNo ratings yet
- Final Drug StudyDocument22 pagesFinal Drug StudyPaula Xavier AlfalahiNo ratings yet
- PIL_MA685 01001Document12 pagesPIL_MA685 01001WissamNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug Studyjeanylou chachi coronadoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study AtrovastatinDocument2 pagesDrug Study AtrovastatinRez Apego100% (4)
- Effects On Lab Test ResultsDocument18 pagesEffects On Lab Test Resultsjay5ar5jamorabon5torNo ratings yet
- Drug 1Document5 pagesDrug 1Jesamine MayNo ratings yet
- Voltfast-Sep 2022.SIN-app260123 PDFDocument14 pagesVoltfast-Sep 2022.SIN-app260123 PDFChelang AbdulkareemNo ratings yet
- Drug-Study-Po (1) EwesdfdsfdsfsddsfdsfdsDocument14 pagesDrug-Study-Po (1) EwesdfdsfdsfsddsfdsfdsIbrahim RegachoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyZaira BataloNo ratings yet
- Drug StuyJJASGHDocument7 pagesDrug StuyJJASGHJan Pierre RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Drug Action Indication Adverse Effects Contraindications Nursing Considerations Ketorolac TromethamineDocument8 pagesDrug Action Indication Adverse Effects Contraindications Nursing Considerations Ketorolac TromethamineAiryn CanonNo ratings yet
- Cataflam: (Diclofenac Potassium)Document10 pagesCataflam: (Diclofenac Potassium)ddandan_2No ratings yet
- Drug Study (Mefenamic Acid, Beetab, Esomeprazole Aspirin, Citicoline Plavix)Document6 pagesDrug Study (Mefenamic Acid, Beetab, Esomeprazole Aspirin, Citicoline Plavix)Patricia LuceroNo ratings yet
- Constipation: How To Treat Constipation: How To Prevent Constipation: Along With Nutrition, Diet, And Exercise For ConstipationFrom EverandConstipation: How To Treat Constipation: How To Prevent Constipation: Along With Nutrition, Diet, And Exercise For ConstipationNo ratings yet
- Compilation of ProblemsDocument39 pagesCompilation of ProblemsSarah Agudo FernandezNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in ENGLISH Kindergarten 2 I. ObjectivesDocument8 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in ENGLISH Kindergarten 2 I. ObjectivesSarah Agudo FernandezNo ratings yet
- Storyytelling - Doc FinalDocument12 pagesStoryytelling - Doc FinalSarah Agudo FernandezNo ratings yet
- School Based First Aid Training: Learning Material ForDocument79 pagesSchool Based First Aid Training: Learning Material ForSarah Agudo FernandezNo ratings yet
- PHC 202 Three Year Strategic PlanDocument14 pagesPHC 202 Three Year Strategic PlanSarah Agudo FernandezNo ratings yet
- School of Health & Natural Sciences: Saint Mary's University Bayombong, Nueva VizcayaDocument5 pagesSchool of Health & Natural Sciences: Saint Mary's University Bayombong, Nueva VizcayaSarah Agudo FernandezNo ratings yet
- Proposal For Improving Records Management PracticeDocument24 pagesProposal For Improving Records Management PracticeSarah Agudo FernandezNo ratings yet
- QACHS School Wellness Action PlanDocument12 pagesQACHS School Wellness Action PlanSarah Agudo FernandezNo ratings yet
- EBP SAMPLE Program PlanDocument6 pagesEBP SAMPLE Program PlanSarah Agudo FernandezNo ratings yet
- Health Declaration Form DraftDocument1 pageHealth Declaration Form DraftSarah Agudo FernandezNo ratings yet
- Struggling To Manage Your School Finances EffectivelyDocument3 pagesStruggling To Manage Your School Finances EffectivelySarah Agudo FernandezNo ratings yet
- 9 Elemets: Shadow Texture SizeDocument1 page9 Elemets: Shadow Texture SizeSarah Agudo FernandezNo ratings yet
- Coronaviruses Are A Large Family of Viruses Which May Cause Illness in Animals or HumansDocument3 pagesCoronaviruses Are A Large Family of Viruses Which May Cause Illness in Animals or HumansSarah Agudo FernandezNo ratings yet
- Master of Science in Nursing (Adult Health)Document8 pagesMaster of Science in Nursing (Adult Health)Sarah Agudo FernandezNo ratings yet
- Speech To Entertain: A Guide: Joann BabinDocument16 pagesSpeech To Entertain: A Guide: Joann BabinSarah Agudo Fernandez100% (1)
- Training and Development: Strategic Directions 2013-2015Document7 pagesTraining and Development: Strategic Directions 2013-2015Sarah Agudo FernandezNo ratings yet
- NutritionDocument4 pagesNutritionSarah Agudo FernandezNo ratings yet
- Manual Book Autoclave Yamato SE510Document38 pagesManual Book Autoclave Yamato SE510ahmad sofwan mulyawanNo ratings yet
- MW CP CV CP CV R R GAS Lb/pmole Btu/lbDocument10 pagesMW CP CV CP CV R R GAS Lb/pmole Btu/lbme coowNo ratings yet
- Criminology: Vice & Drug Education and ControlDocument17 pagesCriminology: Vice & Drug Education and Controldynamic_edgeNo ratings yet
- WJMB - ReviewDocument11 pagesWJMB - ReviewDaniel González RegueroNo ratings yet
- The Fiberbond Fittings GuideDocument23 pagesThe Fiberbond Fittings GuideANDERSON NERESNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 - Thermodynamics Important Questions 2024-25Document15 pagesCBSE Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 - Thermodynamics Important Questions 2024-25sammisharma27No ratings yet
- Superthermolay App PL / MT: DescriptionDocument3 pagesSuperthermolay App PL / MT: DescriptionPrashantBaruaNo ratings yet
- Mola LarDocument2 pagesMola LarAshletyBultonNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Chapter 8 Manufactured Substances in IndustryDocument24 pagesChemistry Chapter 8 Manufactured Substances in Industrym-9575525No ratings yet
- Elval Colour Cladding Etalbond Pe and Etalbond FR PVDF Coated Composite Aluminium Cladding PanelsDocument11 pagesElval Colour Cladding Etalbond Pe and Etalbond FR PVDF Coated Composite Aluminium Cladding PanelsIvo AntonijevicNo ratings yet
- Class X Foundation NTSEDocument294 pagesClass X Foundation NTSEPankaj Kumar Sahu0% (1)
- Siege Weapon Craft SheetDocument4 pagesSiege Weapon Craft SheetMichelle WellsNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table Trends PDFDocument19 pagesPeriodic Table Trends PDFGhienel Surla NaguitNo ratings yet
- JJ308 REPORT Layout and Piping of The Steam Power Plant SystemDocument9 pagesJJ308 REPORT Layout and Piping of The Steam Power Plant SystemAh Tiang86% (7)
- Fibroid in WomenDocument13 pagesFibroid in Womentnemwill1889% (9)
- Mastering Data Visualization Techniques (Part 1)Document20 pagesMastering Data Visualization Techniques (Part 1)balu810No ratings yet
- Process For Manufacturing Low Alkali CementsDocument2 pagesProcess For Manufacturing Low Alkali CementsfaheemqcNo ratings yet
- Ecigarette or Vaping Products Visual Dictionary 508Document25 pagesEcigarette or Vaping Products Visual Dictionary 508James Harrill Laydea100% (1)
- Detailed Lesson Plan Substance and MixturesDocument17 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan Substance and MixturesNonie Beth Cervantes100% (3)
- Nursing Diagnosis: Acute Pain: NANDA Definition: Pain Is Whatever The ExperiencingDocument13 pagesNursing Diagnosis: Acute Pain: NANDA Definition: Pain Is Whatever The Experiencingasmika danaNo ratings yet
- Push-In Hose SystemDocument68 pagesPush-In Hose Systemhebert perezNo ratings yet
- Purification of BiogasDocument15 pagesPurification of BiogasHedi Ben MohamedNo ratings yet
- Natural Materials - Jean Frances PDFDocument223 pagesNatural Materials - Jean Frances PDFleon155No ratings yet
- Applications of Chemical ReactionsDocument7 pagesApplications of Chemical ReactionsPEWDIEPIE PEWNo ratings yet
- Scm2000xr ManualDocument23 pagesScm2000xr ManualPopo GisbertNo ratings yet
- Sun Micron Mesh BagsDocument1 pageSun Micron Mesh BagsOmar Escalante RomeroNo ratings yet
- Crystal Reiki Master Certification Manual: Lisa PowersDocument86 pagesCrystal Reiki Master Certification Manual: Lisa PowerslunaNo ratings yet
- Guangdong Fenghua Advanced Tech 0805CG220J500NT C24658Document27 pagesGuangdong Fenghua Advanced Tech 0805CG220J500NT C24658ramsringarNo ratings yet
- E Ffects of Operating Conditions During Low-Alcohol Beer Production by Osmotic DistillationDocument8 pagesE Ffects of Operating Conditions During Low-Alcohol Beer Production by Osmotic DistillationMarina ButuceaNo ratings yet
- Sweet HamDocument2 pagesSweet HamBryan CapulongNo ratings yet