E2 Lab 5 6 2
E2 Lab 5 6 2
Uploaded by
Ninja NuggetCopyright:
Available Formats
E2 Lab 5 6 2
E2 Lab 5 6 2
Uploaded by
Ninja NuggetOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
E2 Lab 5 6 2
E2 Lab 5 6 2
Uploaded by
Ninja NuggetCopyright:
Available Formats
Lab 5.6.
2: Challenge RIP Configuration
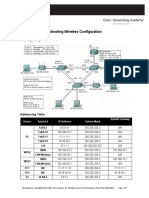
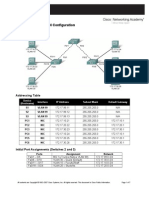
Topology Diagram
Addressing Table
Device BRANCH Interface Fa0/0 S0/0/0 Fa0/0 HQ S0/0/0 S0/0/1 ISP PC1 PC2 PC3 Fa0/0 S0/0/1 NIC NIC NIC IP Address 10.10.2.1 192.168.1.126 192.168.1.129 192.168.1.1 209.165.200.226 209.165.202.129 209.165.200.225 10.10.3.254 192.168.1.254 209.165.202.158 Subnet Mask 255.255.254.0 255.255.255.128 255.255.255.128 255.255.255.128 255.255.255.252 255.255.255.224 255.255.255.252 255.255.254.0 255.255.255.128 255.255.255.224 Default Gateway N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A 10.10.2.1 192.168.1.129 209.165.202.129
Learning Objectives
Upon completion of this lab, you will be able to: Subnet an address space given requirements. Assign appropriate addresses to interfaces and document them in the Addressing Table. Cable a network according to the Topology Diagram.
Page 1 of 7
All contents are Copyright 19922007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
CCNA Exploration Routing Protocols and Concepts: RIP version 1
Lab 5.6.2: Challenge RIP Configuration
Erase the startup configuration and reload a router to the default state.
All contents are Copyright 19922007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Page 2 of 7
CCNA Exploration Routing Protocols and Concepts: RIP version 1
Lab 5.6.2: Challenge RIP Configuration
Configure RIPv1 routing on all routers. Configure and propagate a static default route. Verify RIPv1 operation. Test and verify full connectivity. Reflect upon and document the network implementation.
Scenario
In this lab activity, you will be given a network address that must be subnetted to complete the addressing of the network shown in the Topology Diagram. A combination of RIPv1 and static routing will be required so that hosts on networks that are not directly connected will be able to communicate with each other.
Task 1: Subnet the Address Space.
Step 1: Examine the network requirements. The addressing for the network has the following requirements: The ISP LAN will use the 209.165.202.128/27 network. The link between the ISP router and the HQ router will use the 209.165.200.224/30 network. The 192.168.1.0/24 network must be subnetted for use in the HQ LAN and the link between the HQ and BRANCH routers. The HQ LAN will require 50 host IP addresses. The BRANCH LAN will use the 10.10.2.0/23 network.
(Note: Remember that the interfaces of network devices are also host IP addresses and are included in the above addressing requirements.) Step 2: Consider the following questions when creating your network design: How many subnets need to be created from the 192.168.1.0/24 network? 2 What is the subnet mask for this network in dotted decimal format? 255.255.255.128 What is the subnet mask for the network in slash format? 25 What are the network addresses of the subnets? Subnet 0: 192.168.1.0/25 Subnet 1: 192.168.1.128/25 How many usable host IP addresses are there per subnet? 128 How many usable hosts IP addresses are available in the BRANCH LAN? 512 Step 3: Assign subnetwork addresses to the Topology Diagram. 1. Assign subnet 1 in the 192.168.1.0 network to the WAN link between the HQ and BRANCH routers. 2. Assign subnet 2 in the 192.168.1.0 network to the LAN attached to the HQ router.
Task 2: Determine Interface Addresses.
Step 1: Assign appropriate addresses to the device interfaces. 1. Assign the first valid host address in the 209.165.202.128/27 network to the LAN interface on the ISP router.
All contents are Copyright 19922007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 3 of 7
CCNA Exploration Routing Protocols and Concepts: RIP version 1
Lab 5.6.2: Challenge RIP Configuration
2. Assign the last valid host address in the 209.165.202.128/27 network to PC3. 3. Assign the first valid host address in the 209.165.200.224/30 network to the WAN interface of the ISP router. 4. Assign the last valid host address in the 209.165.200.224/30 network to the Serial 0/0/1 interface of the HQ router. 5. Assign the first valid host address in the HQ LAN network to the LAN interface of the HQ router. 6. Assign the last valid host address in the HQ LAN network to PC 2. 7. Assign the first valid host address in the HQ/BRANCH WAN link to the Serial 0/0/0 interface of the HQ router. 8. Assign the last valid host address in the HQ/BRANCH WAN link to the Serial 0/0/0 interface of the BRANCH router. 9. Assign the first valid host address in the 10.10.2.0/23 network to the LAN interface on the BRANCH router. 10. Assign the last valid host address in the 10.10.2.0/23 network to PC1. Step 2: Document the addresses to be used in the table provided under the Topology Diagram.
Task 3: Prepare the Network.
Step 1: Cable a network that is similar to the one in the Topology Diagram. You can use any current router in your lab as long as it has the required interfaces shown in the topology. Note: If you use 1700, 2500, or 2600 routers, the router outputs and interface descriptions will appear different. Step 2: Clear any existing configurations on the routers.
Task 4: Perform Basic Router Configurations.
Perform basic configuration in the BRANCH, HQ, and ISP routers according to the following guidelines: 1. Configure the router hostname. 2. Disable DNS lookup. 3. Configure an EXEC mode password. 4. Configure a message-of-the-day banner. 5. Configure a password for console connections. 6. Configure a password for VTY connections. 7. Synchronize unsolicited messages and debug output with solicited output and prompts for the console and virtual terminal lines. 8. Configure an EXEC timeout of 15 minutes.
Task 5: Configure and Activate Serial and Ethernet Addresses.
Step 1: Configure the BRANCH, HQ, and ISP routers. Configure the interfaces on the BRANCH, HQ, and ISP routers with the IP addresses from the Addressing Table provided under the Topology Diagram.
All contents are Copyright 19922007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Page 4 of 7
CCNA Exploration Routing Protocols and Concepts: RIP version 1
Lab 5.6.2: Challenge RIP Configuration
When you have finished, be sure to save the running configuration to the NVRAM of the router. Step 2: Configure the Ethernet interfaces of PC1, PC2, and PC3. Configure the Ethernet interfaces of PC1, PC2, and PC3 with the IP addresses from the Addressing Table provided under the Topology Diagram.
Task 6: Verify Connectivity to Next-Hop Device.
You should not have connectivity between end devices yet. However, you can test connectivity between two routers and between an end device and its default gateway. Step 1: Verify BRANCH connectivity. Verify that BRANCH can ping across the WAN link to HQ and that HQ can ping across the WAN link it shares with ISP. Step 2: Verify Ethernet interface connectivity. Verify that PC1, PC2, and PC3 can ping their respective default gateways.
Task 7: Configure RIP Routing on the BRANCH Router.
Consider the networks that need to be included in the RIP updates that are sent out by the BRANCH router. What networks are currently present in the BRANCH routing table before RIP is configured? List the networks with slash notation. 10.0.0.0/23 192.168.1.0/25 What commands are required to enable RIP version 1 and include these networks in the routing updates? router rip network 10.0.0.0 network 192.168.1.0 Are there any router interfaces that do not need to have RIP updates sent out? yes What command is used to disable RIP updates on this interface? BRANCH(config-router)#passive-interface FastEthernet0/0
Task 8: Configure RIP and Static Routing on the HQ Router
Consider the type of static routing that is needed on HQ. What networks are present in the HQ routing table? List the networks with slash notation. 192.168.1.0/25 209.165.200.0/27
All contents are Copyright 19922007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Page 5 of 7
CCNA Exploration Routing Protocols and Concepts: RIP version 1
Lab 5.6.2: Challenge RIP Configuration
A static default route will need to be configured to send all packets with destination addresses that are not in the routing table to the ISP router. What command is needed to accomplish this? Use the appropriate exit interface on the HQ router in the command. HQ(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 Serial0/0/1 What commands are required to enable RIPv1 and include the LAN network in the routing updates? router rip network 192.168.1.0 Are there any router interfaces that do not need to have RIP updates sent out? yes What command is used to disable RIP updates on this interface? HQ(config-router)#passive-interface FastEthernet0/0 The HQ router needs to send the default route information to the BRANCH router in the RIP updates. What command is used to configure this? HQ(config-router)#default-information originate
Task 9: Configure Static Routing on the ISP Router
Static routes will need to be configured on the ISP router for all traffic that is destined for the RFC 1918 addresses that are used on the BRANCH LAN, HQ LAN, and the link between the BRANCH and HQ routers. What are the commands that will need to be configured on the ISP router to accomplish this? ISP(config)# ip route 10.10.2.0 255.255.254.0 Serial0/0/1 ISP(config)# ip route 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 Serial0/0/1
Task 10: Verify the Configurations
Answer the following questions to verify that the network is operating as expected. From PC2, is it possible to ping PC1? yes From PC2, is it possible to ping PC3? yes From PC1, is it possible to ping PC3? yes The answer to the above questions should be yes. If any of the above pings failed, check your physical connections and configurations. Refer to the basic troubleshooting techniques used in the Chapter 1 labs. What routes are present in the routing table of the BRANCH router? 10.0.0.0/23 192.168.1.0/25 0.0.0.0/0 What is the gateway of last resort in the routing table of the BRANCH router? 192.168.1.1 to network 0.0.0.0 What routes are present in the routing table of the HQ router? 10.0.0.0/8
All contents are Copyright 19922007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 6 of 7
CCNA Exploration Routing Protocols and Concepts: RIP version 1
Lab 5.6.2: Challenge RIP Configuration
192.168.1.0/25 209.165.200.0/27 0.0.0.0/0
What networks are present in the routing table of the ISP router? 10.0.0.0/23 192.168.1.0/24 209.165.200.0/27 209.165.202.0/27
What networks, including the metric, are present in the RIP updates sent from the HQ router? network 0.0.0.0 metric 1 network 192.168.1.128 metric 1 What networks, including the metric, are present in the RIP updates sent from the BRANCH router? network 10.0.0.0 metric 1
Task 11: Reflection
If static routing were used instead of RIP on the BRANCH router, how many individual static routes would be needed for hosts on the BRANCH LAN to communicate with all of the networks in the Topology Diagram? Three
Task 12: Document the Router Configurations
On each router, capture the following command output to a text file and save for future reference: Running configuration Routing table Interface summarization
Task 13: Clean Up
Erase the configurations and reload the routers. Disconnect and store the cabling. For PC hosts that are normally connected to other networks (such as the school LAN or to the Internet), reconnect the appropriate cabling and restore the TCP/IP settings.
All contents are Copyright 19922007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Page 7 of 7
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good Life4/5 (6052)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You Are4/5 (1142)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On It4.5/5 (916)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space Race4/5 (946)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy Answers4.5/5 (360)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New America4.5/5 (273)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first Century3.5/5 (2283)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True Story3.5/5 (233)
- The Tutorial of Laser Engraving Software ManualNo ratings yetThe Tutorial of Laser Engraving Software Manual65 pages
- Lab 7.5.3: Troubleshooting Wireless Configuration: Topology DiagramNo ratings yetLab 7.5.3: Troubleshooting Wireless Configuration: Topology Diagram5 pages
- IBM 3650 M3 Problem Determination Guide - 00d3150No ratings yetIBM 3650 M3 Problem Determination Guide - 00d3150314 pages
- Blockchain-Based Internet of Vehicles: Distributed Network Architecture and Performance AnalysisNo ratings yetBlockchain-Based Internet of Vehicles: Distributed Network Architecture and Performance Analysis10 pages
- Executive Summary: Office of The District EngineerNo ratings yetExecutive Summary: Office of The District Engineer25 pages
- Windows 11 Discover From Beginner To Expert - Mike WangNo ratings yetWindows 11 Discover From Beginner To Expert - Mike Wang352 pages
- Ntdroid: Android Malware Detection Using Network Traffic: FeaturesNo ratings yetNtdroid: Android Malware Detection Using Network Traffic: Features12 pages
- Manual de Configuracion (Siemens - Ref RUGGEDCOM RST916C)No ratings yetManual de Configuracion (Siemens - Ref RUGGEDCOM RST916C)452 pages
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good Life
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You Are
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On It
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space Race
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy Answers
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic Future
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of Cancer
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy Living
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New America
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first Century
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True Story
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham Lincoln
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New Deal
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New America
- Lab 7.5.3: Troubleshooting Wireless Configuration: Topology DiagramLab 7.5.3: Troubleshooting Wireless Configuration: Topology Diagram
- Blockchain-Based Internet of Vehicles: Distributed Network Architecture and Performance AnalysisBlockchain-Based Internet of Vehicles: Distributed Network Architecture and Performance Analysis
- Executive Summary: Office of The District EngineerExecutive Summary: Office of The District Engineer
- Windows 11 Discover From Beginner To Expert - Mike WangWindows 11 Discover From Beginner To Expert - Mike Wang
- Ntdroid: Android Malware Detection Using Network Traffic: FeaturesNtdroid: Android Malware Detection Using Network Traffic: Features
- Manual de Configuracion (Siemens - Ref RUGGEDCOM RST916C)Manual de Configuracion (Siemens - Ref RUGGEDCOM RST916C)