0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
343 viewsDrug Dilantin
Drug Dilantin
Uploaded by
SrkocherThis document provides information on the medication phenytoin (Dilantin) including its classification, dose, route, time/frequency of administration, pharmacokinetics, mechanism of action, indications, nursing implications, interactions, lab alterations, patient teaching points, and pre-administration assessment. Phenytoin is an antiarrhythmic and anticonvulsant prescribed for tic disorder. Nurses should monitor for signs of hypersensitivity, bradycardia, drug interactions that may increase phenytoin levels, and side effects involving the CNS, GI, dermatologic, and hematologic systems. The goal is to decrease signs of tic disorder while maintaining therapeutic drug levels through administration and ongoing assessment.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Drug Dilantin
Drug Dilantin
Uploaded by
Srkocher0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
343 views1 pageThis document provides information on the medication phenytoin (Dilantin) including its classification, dose, route, time/frequency of administration, pharmacokinetics, mechanism of action, indications, nursing implications, interactions, lab alterations, patient teaching points, and pre-administration assessment. Phenytoin is an antiarrhythmic and anticonvulsant prescribed for tic disorder. Nurses should monitor for signs of hypersensitivity, bradycardia, drug interactions that may increase phenytoin levels, and side effects involving the CNS, GI, dermatologic, and hematologic systems. The goal is to decrease signs of tic disorder while maintaining therapeutic drug levels through administration and ongoing assessment.
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
This document provides information on the medication phenytoin (Dilantin) including its classification, dose, route, time/frequency of administration, pharmacokinetics, mechanism of action, indications, nursing implications, interactions, lab alterations, patient teaching points, and pre-administration assessment. Phenytoin is an antiarrhythmic and anticonvulsant prescribed for tic disorder. Nurses should monitor for signs of hypersensitivity, bradycardia, drug interactions that may increase phenytoin levels, and side effects involving the CNS, GI, dermatologic, and hematologic systems. The goal is to decrease signs of tic disorder while maintaining therapeutic drug levels through administration and ongoing assessment.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
343 views1 pageDrug Dilantin
Drug Dilantin
Uploaded by
SrkocherThis document provides information on the medication phenytoin (Dilantin) including its classification, dose, route, time/frequency of administration, pharmacokinetics, mechanism of action, indications, nursing implications, interactions, lab alterations, patient teaching points, and pre-administration assessment. Phenytoin is an antiarrhythmic and anticonvulsant prescribed for tic disorder. Nurses should monitor for signs of hypersensitivity, bradycardia, drug interactions that may increase phenytoin levels, and side effects involving the CNS, GI, dermatologic, and hematologic systems. The goal is to decrease signs of tic disorder while maintaining therapeutic drug levels through administration and ongoing assessment.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
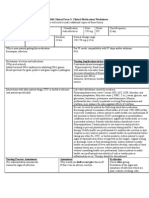
NURS 1556 Clinical Medication Worksheet Karen Nielsen
Generic Trade Name Classification Dose Route Time/frequency
Name Antiarrhythmic
Phenytoin Dilantin (group IB), 100 mg PO QD
anticonvulsant
Peak Onset Duration For IV meds, compatibility with IV drips and /or solutions
1.5-3 hr 2-24 hr 6-12 hr N/A but of note: use of IV phenytoin in geriatric pt may
increase risk of serious adverse effects.
Mechanism of action and indications: Nursing Implications (what to focus on)
(Why med ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactions-Hypersensitivity;
Sinus bradycardia, SA node block, 2nd or 3rd degree heart
Rx limits seizure propagation by altering ion transport, block. Caution in pt with severe cardiac or respiratory
may also decrease synaptic transmission. disease. Interacts with alcohol, gabapentin, omeprazole,
(may increase phenytoin drug levels). Antidepressants may
For Tic disorder. cause additive CNS depression.
Common side effects: CNS: ataxia, agitation, confusion,
drowsiness, dizziness, dysarthria, dyskinesia, extra
pyramidal syndrome, H/A, insomnia, weakness.EENT:
diplopia, nystagmus. CV: hypotension, tachycardia. GI:
gingival hyperplasia, N/V, constipation, drug-induced
hepatitis. Derm: hypertrichosis, rash, pruritis.
Hemat: Agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia, leukopenia,
megaloblastic anemia, thrombocytopenia. MS:
osteomalacia. Misc: allergic reactions including Stevens-
Johnson syndrome, fever, lymphadenopathy.
Interactions with other patient drugs, OTC or Lab value alterations caused by medicine:May increase
herbal medicines (ask patient specifically): serum alkaline phosphatase, GGT, and glucose levels.
Monitor serum folate concentrations periodically during
Gabapentin and omeprazole may increase drug levels. prolonged therapy.
The SSRI Zoloft may cause additive CNS depression
effects. Be sure to teach the patient the following about this
medication: Take with meals or right after to minimize GI
irritation. Chewable tablets must be crushed or chewed
well before swallowing. Take same time each day. May
cause drowsiness or dizziness. Maintain good oral hygiene.
Nursing Process- Assessment Assessment Evaluation
(Pre-administration assessment) Why would you hold or not give this Check after giving:
med?
Assess for phenytoin hypersensitivity Decrease in Tic disorder.
syndrome, (fever, skin rash, Signs of hypersensitivity, or Monitor serum phenytoin
lymphadenopathy). Vital signs. abnormally low heart rate, <50. levels routinely. Therapeutic
blood levels ( 10-20
mcg/ml).
You might also like
- Skin CareDocument49 pagesSkin CareDuong Cam100% (5)
- MKSAP Endocrinology and MetabolismDocument148 pagesMKSAP Endocrinology and MetabolismArthurHLima100% (2)
- Drug NeurontinDocument1 pageDrug NeurontinSrkocher100% (2)
- Drug TylenolDocument1 pageDrug TylenolSrkocherNo ratings yet
- Drug NeurontinDocument1 pageDrug NeurontinSrkocher100% (2)
- Fundamentals of Nursing Exam 3 (50 Items)Document16 pagesFundamentals of Nursing Exam 3 (50 Items)TamiyaPhil100% (1)
- Training Manual PDFDocument13 pagesTraining Manual PDFFitiwi Gnigus100% (2)
- Lopressor (Metoprolol) IVDocument2 pagesLopressor (Metoprolol) IVAdrianne Bazo100% (1)
- CholestyramineDocument1 pageCholestyramineKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- Lanoxin (Digoxin)Document3 pagesLanoxin (Digoxin)E100% (5)
- Ancef Drug CardDocument1 pageAncef Drug CardSheri490No ratings yet
- RisperdalDocument2 pagesRisperdalAdrianne Bazo100% (1)
- Drug Senna Drug CardDocument1 pageDrug Senna Drug CardSrkocher100% (2)
- CKD Case StudyDocument24 pagesCKD Case Studyapi-384366795No ratings yet
- Doreen's StoryDocument50 pagesDoreen's StoryLeonard Beddows50% (2)
- Critical Decisions in Periodontology - HallDocument378 pagesCritical Decisions in Periodontology - Halleili1100% (7)
- Lopressor (Metoprolol) 100mgDocument2 pagesLopressor (Metoprolol) 100mgAdrianne Bazo100% (2)
- LortabDocument1 pageLortabSheri490No ratings yet
- CarafateDocument1 pageCarafateAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Midazolam FinalDocument2 pagesMidazolam FinalAhmad AbqariNo ratings yet
- Drug Card Tricyclic DepressantsDocument2 pagesDrug Card Tricyclic DepressantsAaLona RobinsonNo ratings yet
- RocephinDocument1 pageRocephinCassieNo ratings yet
- Drug Card BenadrylDocument1 pageDrug Card BenadrylAdrianne Bazo100% (1)
- Drug CardsDocument2 pagesDrug CardsMichael LongsNo ratings yet
- Drug Cards BarryDocument6 pagesDrug Cards BarryJessica Lynn DyeNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyLouise Adrene SevillaNo ratings yet
- HPN Drug StudyDocument4 pagesHPN Drug StudyJohn Haider Colorado GamolNo ratings yet
- AmloDocument1 pageAmloamy navajaNo ratings yet
- Drug PrilosecDocument1 pageDrug PrilosecSrkocher100% (1)
- Colace Drug CardDocument1 pageColace Drug CardBenNo ratings yet
- Aerovent, Apovent Atronase, Ipraxa, Ipvent Rhinovent, Rinatecrinovagos, Atrovent, Atrovent HfaDocument4 pagesAerovent, Apovent Atronase, Ipraxa, Ipvent Rhinovent, Rinatecrinovagos, Atrovent, Atrovent HfaGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Plavix (Clopidogrel)Document1 pagePlavix (Clopidogrel)E50% (2)
- Medication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic UseDocument1 pageMedication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic UseAli GarciaNo ratings yet
- Drug OmeprazoleDocument1 pageDrug OmeprazoleSrkocherNo ratings yet
- Drug Cards Milk of MagnesiaDocument1 pageDrug Cards Milk of MagnesiaAdrianne Bazo100% (1)
- Metoclopramide (Reglan)Document1 pageMetoclopramide (Reglan)ENo ratings yet
- Adrenergic Blocking, Cholinergic, Sedatives and Hypnotic WORDDocument5 pagesAdrenergic Blocking, Cholinergic, Sedatives and Hypnotic WORDKeon RicoNo ratings yet
- EnalaprilDocument2 pagesEnalaprilAyah PaasaNo ratings yet
- NUR 201 - Drug Study (Lanthanum Carbonate)Document1 pageNUR 201 - Drug Study (Lanthanum Carbonate)ReaNo ratings yet
- Zyloprim Drug CardDocument1 pageZyloprim Drug CardSheri490No ratings yet
- Drug Study: ER DrugsDocument5 pagesDrug Study: ER Drugsmaeca101No ratings yet
- FlagylDocument3 pagesFlagylAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Patient: B.V Age: 58y/oDocument2 pagesDrug Study: Patient: B.V Age: 58y/oAndrea Sibayan SorianoNo ratings yet
- DRUGSDocument5 pagesDRUGSDanica EspejoNo ratings yet
- Anes Drugs TableDocument20 pagesAnes Drugs TableKathleen Grace ManiagoNo ratings yet
- Ciprofloxacin CiproDocument1 pageCiprofloxacin CiproKristi WrayNo ratings yet
- Amitriptyline PDFDocument3 pagesAmitriptyline PDFscribdseewalNo ratings yet
- Xylocard PiDocument11 pagesXylocard PiRamakant SharmaNo ratings yet
- Drug Card SennaDocument1 pageDrug Card SennaAdrianne Bazo100% (1)
- Epinephrine DrugStudy WWW Rnpedia ComDocument4 pagesEpinephrine DrugStudy WWW Rnpedia ComIrish LigayaNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: BudesonideDocument8 pagesGeneric Name: BudesonidemeangelmeNo ratings yet
- DS FormoterolDocument2 pagesDS FormoterolPang Project100% (1)
- PrevacidDocument1 pagePrevacidAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Serratiopeptidase Is An Enzyme Having AntiDocument12 pagesSerratiopeptidase Is An Enzyme Having Antidracula386No ratings yet
- Drug Study (Capitol)Document8 pagesDrug Study (Capitol)Joy CalmerinNo ratings yet
- Metformin GlucophageDocument1 pageMetformin GlucophageENo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Hypothermia - Principles, Indications, Practical ApplicationFrom EverandTherapeutic Hypothermia - Principles, Indications, Practical ApplicationNo ratings yet
- Atenolol2Document1 pageAtenolol2Christine Pialan SalimbagatNo ratings yet
- Drug Analysis in PsychDocument3 pagesDrug Analysis in PsychBryan Andrew GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Catapres (Clonidine)Document2 pagesCatapres (Clonidine)Adrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- PhenerganDocument2 pagesPhenerganKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- Drug Study JrodDocument8 pagesDrug Study JrodGaez ﭢ UlpindoNo ratings yet
- Drug LopressorDocument1 pageDrug LopressorSrkocherNo ratings yet
- Drug CiproDocument1 pageDrug CiproSrkocherNo ratings yet
- PropanolDocument8 pagesPropanolStacey CamilleNo ratings yet
- Risperdone and Lithium CarbonateDocument4 pagesRisperdone and Lithium CarbonateFionah RetuyaNo ratings yet
- For MaDocument9 pagesFor MaKathrina TumbagaNo ratings yet
- Propylthiouracil Drug StudyDocument7 pagesPropylthiouracil Drug StudyAlexandrea MayNo ratings yet
- Propylthiouracil DSDocument7 pagesPropylthiouracil DSAlexandrea MayNo ratings yet
- Lisinopril Prinivil Zestril)Document1 pageLisinopril Prinivil Zestril)ENo ratings yet
- Code of Ethics Provision 4Document5 pagesCode of Ethics Provision 4SrkocherNo ratings yet
- Albuterol SulfateDocument4 pagesAlbuterol Sulfateapi-3797941No ratings yet
- BactobanDocument1 pageBactobanSrkocherNo ratings yet
- LovenoxDocument1 pageLovenoxSrkocherNo ratings yet
- Drug ZofranDocument1 pageDrug ZofranSrkocherNo ratings yet
- LovenoxDocument1 pageLovenoxSrkocherNo ratings yet
- Breast FeedingDocument1 pageBreast FeedingSrkocherNo ratings yet
- Levaquin Drug CardDocument1 pageLevaquin Drug CardSheri490100% (1)
- Drug PhenerganDocument1 pageDrug PhenerganSrkocherNo ratings yet
- What Is A Team Leader in NursingDocument2 pagesWhat Is A Team Leader in NursingSrkocher100% (2)
- Drug PhenerganDocument1 pageDrug PhenerganSrkocherNo ratings yet
- Drug Rewetting Drops, Artificial TearsDocument1 pageDrug Rewetting Drops, Artificial TearsSrkocherNo ratings yet
- Drug LopressorDocument1 pageDrug LopressorSrkocherNo ratings yet
- Drug AtivanDocument1 pageDrug AtivanSrkocherNo ratings yet
- Drug ZoloftDocument1 pageDrug ZoloftSrkocherNo ratings yet
- AtivanDocument1 pageAtivanSheri490No ratings yet
- Drug Timoptic Eye DropsDocument1 pageDrug Timoptic Eye DropsSrkocherNo ratings yet
- Drug PepcidDocument2 pagesDrug PepcidSrkocher0% (1)
- Drug SynthroidDocument1 pageDrug SynthroidSrkocherNo ratings yet
- Drug NorvascDocument1 pageDrug NorvascSrkocherNo ratings yet
- Drug OmeprazoleDocument1 pageDrug OmeprazoleSrkocherNo ratings yet
- Drug NystatinDocument1 pageDrug NystatinSrkocherNo ratings yet
- Drug PercocetDocument1 pageDrug PercocetSrkocherNo ratings yet
- Drug LopressorDocument1 pageDrug LopressorSrkocherNo ratings yet
- Drug LovenoxDocument2 pagesDrug LovenoxSrkocherNo ratings yet
- Drug LopressorDocument1 pageDrug LopressorSrkocherNo ratings yet
- Drug MetronidazoleDocument1 pageDrug MetronidazoleSrkocherNo ratings yet
- NLP Trauma Recovery Manual 2011Document49 pagesNLP Trauma Recovery Manual 2011Francesco Fiorello100% (1)
- Pink Panther - Diabetes Management - Chapter 2Document6 pagesPink Panther - Diabetes Management - Chapter 2jennmoyerNo ratings yet
- JJ - Rules - 2017 Rule 34Document2 pagesJJ - Rules - 2017 Rule 34Anish DebNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound Thesis TopicsDocument6 pagesUltrasound Thesis Topicsdw9x1bxb100% (2)
- Removing Indwelling CatheterDocument1 pageRemoving Indwelling CatheterAngelie PantajoNo ratings yet
- Syringe DriverDocument2 pagesSyringe DriverMohd NizamNo ratings yet
- Cervical CancerDocument7 pagesCervical CancerTANMOY69100% (1)
- Gadsden Water Works and Sewer Board LawsuitDocument16 pagesGadsden Water Works and Sewer Board LawsuitBen CulpepperNo ratings yet
- Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy For Sacroiliac Joint Pain: A Prospective, Randomized, Sham-Controlled Short-Term TrialDocument7 pagesExtracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy For Sacroiliac Joint Pain: A Prospective, Randomized, Sham-Controlled Short-Term TrialLizeth Tatiana Ortiz PalominoNo ratings yet
- Information For Potential Participants in "Autism: Beliefs and Cures" StudyDocument1 pageInformation For Potential Participants in "Autism: Beliefs and Cures" StudyHelenEllsworthNo ratings yet
- Q and A On Vent Settings PandemicDocument6 pagesQ and A On Vent Settings PandemicChris Martin100% (1)
- British Hypnosis CoursesDocument12 pagesBritish Hypnosis CoursesykrisnanegaraNo ratings yet
- Case Study-Tb MeningitisDocument41 pagesCase Study-Tb Meningitislhan alvin83% (6)
- Serial Extraction PedoDocument23 pagesSerial Extraction PedoSelim BaftiuNo ratings yet
- Rptabstracts in Presentation Order 2013 PDFDocument283 pagesRptabstracts in Presentation Order 2013 PDFgod4alllNo ratings yet
- Cytotoxic Effects of Ultra-Diluted Remedies On Breast Cancer CellsDocument9 pagesCytotoxic Effects of Ultra-Diluted Remedies On Breast Cancer CellsAPH - Associação Portuguesa de Homeopatia (repositório 2008-15)100% (4)
- Emergency Psychiatry Other Than Suicide: Dr. Pooja Singh, MD Assistant ProfessorDocument45 pagesEmergency Psychiatry Other Than Suicide: Dr. Pooja Singh, MD Assistant Professorpooja singhNo ratings yet
- Electroencephalography (Eeg)Document13 pagesElectroencephalography (Eeg)Shelten GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Traumatic Hyphema: Clinical Features and DiagnosisDocument3 pagesTraumatic Hyphema: Clinical Features and DiagnosisSheira T. TayebNo ratings yet
- Tool Therapeutic JournalingDocument5 pagesTool Therapeutic Journalinggabsegura23No ratings yet
- Autogenic TrainingDocument243 pagesAutogenic TrainingDemosten100% (6)
- Antibiotic Use For Surgical Prophylaxis CAPADocument20 pagesAntibiotic Use For Surgical Prophylaxis CAPAمحمود رضاNo ratings yet
- Pyelonephritits in PregnancyDocument2 pagesPyelonephritits in PregnancyRia NicoleNo ratings yet