SHRM - HRM
SHRM - HRM
Uploaded by
sreelayaCopyright:
Available Formats
SHRM - HRM
SHRM - HRM
Uploaded by
sreelayaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
SHRM - HRM
SHRM - HRM
Uploaded by
sreelayaCopyright:
Available Formats
The Evolving Strategic Role of HRM
The Role of human resource management in organization has been evolving dramatically No more a personnel department HR is being seen as a strategic HR partner SHRM involves making the function of managing people the most important priority in the organization and integrating all HR programs and policies within the framework of a companys strategy
The Evolving Strategic Role of HRM
Strategic HRM realizes that people make or break an organization because all decisions made regarding finance, marketing, operations or technology are made by an organizations people Strategic HRM involves the development of a consistent, aligned collection of practices ,programs and policies to facilitate the achievement of the organizations strategic objectives
The Evolving Strategic Role of HRM
Strategic Human Resource Management is the process of linking the human resource function with the strategic objectives of the organization in order to improve performance Establishing a strong HR strategy that is clearly linked to the organizations strategy is not enough HR strategy needs to be communicated, practiced-spelled out and written down
Ulrich's Model of Human Resource Management
Strategic Focus Strategic partner Change Agent
Systems
People
Administrative Expert Operational
Employee Champion
Ulrich's Model of Human Resource Management
HR can be defined by what it does, or by what it delivers HR can perform 4 different Roles Strategic Partner: HR is responsible for the organizational architecture / structure; work with executive team to add value and achieve company objectives. Administrative Expert: HR makes sure that the work gets done effectively and efficiently; streamline and automate most operations
Ulrich's Model of Human Resource Management
Change Agent: HR helps the organization adopt and profit from change; helps plan for and overcome resistance to change. Employee Champion: Change Agent: HR responsible for motivating, advocating for, and representing the employees; work with and train line managers to achieve these goals
Strategic Human Resource Management
Strategic human resource management and traditional HR functions differ in several ways(adapted from Mellow 2003)
Traditional HRM Responsibility for HR programmes Focus of activities Staff personnel in the HR department Employees relations,motivation,productivity,c ompliance with laws Reactive and transactional SHRM Line managers,all managers responsible for people are HR managers Partnerships with internal and external customers Proactive and transformational,change leader Fast,flexible,systematic, change initiatives implemented in concert with other HR systems
Role of HR
Initiative for change
Slow,piecemeal,fragmented,not integrated with larger issues
Strategic Human Resource Management
Traditional HRM Time horizon Short term SHRM Consider various time frames as necessary (short,medium,or long) Organic control through flexibility as few restrictions on employee behaviour as possible Broad job design,flexibility,teams and groups and cross -training People and their knowledge,skills and abilities
Control
Bureaucratic control through rules ,procedures and policies
Job design
Focus on scientific management principles-division of labour,independence and specialization Capital ,products,technology and finance
Importance investments
Accountability
Cost centre
Investment centre
Strategic Human Resource Management
Difference between SHRM and HR Strategies(adapted from Armstrong 2000
SHRM HR Strategies A general approach to strategic management Outcome of the general SHRM approach of human resources Aligned with the organizational intention about its future direction Focus on long term people issue Defines the areas in which specific HR strategies need to be developed Focus on macro concerns such as structure culture Strategic HRM decisions are built into the strategic business plan Focus on specific organizational intentions about what needs to be done Focus on specific issues that facilitate the achievement of corporate strategy Human resource strategy decisions are derived from SHRM
Strategic Human Resource Management
Evolution of SHRM
PM 1930-1940
HRM Early 1970s
SHRM 1980 onwards
Strategic Human Resource Management
Myths about HR Professionals
Old Myth New Realities People go in for HR because they like people HR departments are not designed to provide corporate theraphy.HR professionals must create the practice that employees are more competitive, not more comfortable
Anyone can do HR
Hr activities are based on theory and research. HR professionals must muster both theory and practice
HR deals with soft side of business and therefore not accountable
The impact of HR practices on business results can and must be measured .HR professionals must learn how to translate their work into financial performance
Strategic Human Resource Management
Myths about HR Professionals
Old Myth HRs job is to be the policy police New Realities The HR function does not own compliancemanagers do.HR practices do not exist to make employees happy but to help them become comitted.HR professionals must help manager committed towards employees and administer policy
HR is full of fads
HR practices has evolved over time.HR professionals must see their current work as part of an evolutionary chain and explain their work with less jargon and more authority
Strategic Human Resource Management
Myths about HR Professionals
Old Myth HR is staffed by nice people New Realities At times HR should force vigorous debates.HR professionals should be and challenging as well as supportive
HR is HRs job
HR work is important to line managers as are finance, strategy and other business domains. HR professionals should join with managers in championing HR issues Hr practices must create value by increasing the intellectual capital within the firm. HR professionals must add value not reduce costs
HR focuses on costs which must be controlled
Strategic Human Resource Management
Challenges for HR managers Globalization(1)
Effective global competition requires more than creating a product in a home market and shipping it as it is to the new market. It requires complex net work of global centres of excellence that draw on technologies invented in one locale and shared worldwide-rapid ideas around the world to meet local needs It needs local commitment(thinking globally but acting locally)
Strategic Human Resource Management
Challenges for HR managers
Value chain for business competitiveness and HR services(2) HR professionals and theorists have emphasized building HR practices within a form Refocusing HR practices more on the value chain(Suppliers and customers)and less on activities within the firm has profound implications The shift to a customer focus redirects attention from the firm to the value chain in which it is embedded This help the firm to be more customer responsive
Strategic Human Resource Management
Challenges for HR managers
Profitability through cost and growth (3) Cutting costs has been one of the means to become more profitable-It is however increasingly being realized that revenue growth is other means for increasing profits The point is not to replace cost with growth but to find ways to experience profitable growth by leveraging customers ,leveraging core organizational competencies and inorganic route to Mergers and acquisitions/joint ventures are the other means for profitable growth
Strategic Human Resource Management
Challenges for HR managers
Capability(4) 1.Building capabilities of confidence 2.Becoming boundary less, allowing flow of information and ideas across hierarchical ,horizontal and external boundaries 3.Achieving capacity for change, the flexibility and agility that allow constant innovation 4.Learning, attaining change that builds on and maintain itself HR managers have to constantly seek the capablities necessary for success
Strategic Human Resource Management
Challenges for HR managers
Capability(4) 1.Building capabilities of confidence 2.Becoming boundary less, allowing flow of information and ideas across hierarchical ,horizontal and external boundaries 3.Achieving capacity for change, the flexibility and agility that allow constant innovation 4.Learning, attaining change that builds on and maintain itself HR managers have to constantly seek the capabilities necessary for success
Strategic Human Resource Management
Challenges for HR managers
Change(5) Managers ,employees and Organizations must learn to change faster and more comfortably HR professionals need to help their organization change 1.How to unlearn what we have learnt 2.How to honour the past and adapt for the future 3.How to encourage risk taking necessary for change without putting the firm in jeopardy 4.How to determine which HR practices to change for transformation and which to leave for continuity
Strategic Human Resource Management
Challenges for HR managers
Technology(6) Technology has made our world smaller, closer and fasterideas and images spread quickly worldwide Technology will dramatically affect how and where work is done through teleconferencing, telecommunicating and shared data sources Proximity was critical when a firms boundaries were geographical HR Professionals will have to figure out how to make technology a viable and productive part of the setting
Strategic Human Resource Management
Challenges for HR managers
Attracting ,Retaining and measuring competence and intellectual capital(7) Sourcing and retaining talent has become the competitive battleground Sourcing intellectual capital means upgrading the leadership bench Leadership in the future will be team focused and shared rather than driven by single person The task of seeking intellectual capital will change a firms measurement process(vs profitability or financial performance etc) HR managers will have to seek, identify and use such measures
Strategic Human Resource Management
Challenges for HR managers
Turnaround(8) Turnaround is not transformation Turnaround so often seen in the corporate world is not transformation Transformation changes the fundamental image of the business as seen by customers and employees Transformation focuses on creating mind-share more than market share HR professionals who focus on transformation create fundamental change
Strategic Human Resource Management
Challenges for HR managers
Organizations have difficulty achieving their strategic objectives because employees do not really understand these or how their jobs contribute to overall organizational effectiveness Fewer than 50% employees understand their organization strategy Effective strategy management require not only that the organizations strategic objective be communicated to employees but that there is a link between employees productivity-relative to these objectives-and the organizations reward system
Strategic Human Resource Management The SHRM is rooted in manpower planning It was the work of influential management gurus(for example Ouchi, 1981; Peters & Waterman, 1982), - affirming the importance of the effective management of people as a source of competitive advantage This encouraged academics to develop frameworks emphasizing the strategic role of the HR function (for example Beer et al., 1985; Fombrun etal., 1984) -attaching the prefix strategic to the term human resource management
Strategic Human Resource Management
Fombrun ,Tichy and devana were the first to formulate the concept of strategic HRM in 1984 These researchers emphasize a strategic fit between HRM and corporate strategy
Fombrun Model Of HRM
HRD
Selection
Appraisal
Organisational effectiveness
Rewards
The Harvard Model of Human Resource Management
Guests Model of HRM
Guest
Warwick
Strategic Human Resource Management
Hendry and Pettigrew (1986) put forward four meanings of SHRM: 1.The use of planning in human resource management 2.An integrated approach to the design and implementation of HR systems 3.Matching HRM policies and activities with the business strategy of the organization 4.Viewing people as a strategic resource for the achievement of competitive advantage
Strategic Human Resource Management
Once the business strategy has been determined, an HR strategy is implemented to support the chosen competitive strategy. one-way downward from business- to functionallevel strategy. In this sense, a HR strategy is concerned with the challenge of matching the philosophy, policies, programmes, practices and processes the five Ps
Strategic Human Resource Management
The major objectives of SHRM are as follows: To ensure the availabilty of a skilled committed and highly motivated workforce in the organization to achieve sustained competitive advantage To provide direction to the organization so that both the business needs of the organization and the individual and collective needs of its workforce are met This is achieved by developing and implementing HR practices that are strategically aligned
Strategic Human Resource Management
The extent of application of SHRM within organizations as well as the form and content of SHRM vary from one organization to another HRM is practiced in only those organizations that have a clearly articulated corporate or business strategy Organizations who do not have a corporate plan cannot have SHRM In such organization HR personnel carry out the traditional administrative and service roles-not concerned with strategic business issues
Strategic Human Resource Management
Hendry and Pettigrew (1986) put forward four meanings of SHRM: 1.The use of planning in human resource management 2.An integrated approach to the design and implementation of HR systems 3.Matching HRM policies and activities with the business strategy of the organization 4.Viewing people as a strategic resource for the achievement of competitive advantage
Strategic Human Resource Management
Once the business strategy has been determined, an HR strategy is implemented to support the chosen competitive strategy. one-way downward from business- to functionallevel strategy. In this sense, a HR strategy is concerned with the challenge of matching the philosophy, policies, programmes, practices and processes the five Ps
Strategic Human Resource Management
The major objectives of SHRM are as follows: To ensure the availabilty of a skilled committed and highly motivated workforce in the organization to achieve sustained competitive advantage To provide direction to the organization so that both the business needs of the organization and the individual and collective needs of its workforce are met This is achieved by developing and implementing HR practices that are strategically aligned
Strategic Human Resource Management
The extent of application of SHRM within organizations as well as the form and content of SHRM vary from one organization to another HRM is practiced in only those organizations that have a clearly articulated corporate or business strategy Organizations who do not have a corporate plan cannot have SHRM In such organization HR personnel carry out the traditional administrative and service roles-not concerned with strategic business issues
Strategic Human Resource Management
(SHRM)Strategic human resource management deals with macro concerns such as quality Commitment performance culture management development It defines the areas in which specific HR strategies need to be developed
Strategic Human Resource Management
strategic HRM is an outcome: as organizational systems designed to achieve sustainable competitive advantage through people. For others, however, SHRM is viewed as a process, the process of linking HR practices to business strategy (Ulrich, 1997,)
Strategic Human Resource Management
Human resource strategies are concerned with ensuring Availability of an efficient workforce Training Rewards Good employee relations Human resource strategies are more specific and facilitate the successful achievement of the corporate objectives and goals According to Ulrich (1997, ) HR strategy is the outcome: the mission, vision and priorities of the HR function.
Strategic Human Resource Management
Vision for Human Resources Business Partner -Aligned with line management -Integral member of management team Both at corporate and regional level Drive culture change to fit strategy and vision Do the basics (administrative tasks)well Organize flexibility around the work to be done
Strategic Human Resource Management
Human Resource Mission To provide high quality and cost effective processes, programs, and services to our associates throughout the world that align with companys overall business strategy
Strategic Human Resource Management
Strategic human resource management and traditional HR functions differ in several ways(adapted from Mellow 2003)
Traditional HRM Responsibility for HR programmes Focus of activities Staff personnel in the HR department Employees relations,motivation,productivity,c ompliance with laws Reactive and transactional SHRM Line managers,all managers responsible for people are HR managers Partnerships with internal and external customers Proactive and transformational,change leader Fast,flexible,systematic, change initiatives implemented in concert with other HR systems
Role of HR
Initiative for change
Slow,piecemeal,fragmented,not integrated with larger issues
Strategic Human Resource Management
Traditional HRM Time horizon Short term SHRM Consider various time frames as necessary (short,medium,or long) Organic control through flexibility as few restrictions on employee behaviour as possible Broad job design,flexibility,teams and groups and cross -training People and their knowledge,skills and abilities
Control
Bureaucratic control through rules ,procedures and policies
Job design
Focus on scientific management principles-division of labour,independence and specialization Capital ,products,technology and finance
Importance investments
Accountability
Cost centre
Investment centre
Strategic Human Resource Management
Difference between SHRM and HR Strategies(adapted from Armstrong 2000
SHRM HR Strategies A general approach to strategic management Outcome of the general SHRM approach of human resources Aligned with the organizational intention about its future direction Focus on long term people issue Defines the areas in which specific HR strategies need to be developed Focus on macro concerns such as structure culture Strategic HRM decisions are built into the strategic business plan Focus on specific organizational intentions about what needs to be done Focus on specific issues that facilitate the achievement of corporate strategy Human resource strategy decisions are derived from SHRM
Strategic Human Resource Management
Link between HR Strategy and Business Strategy The concept of SHRM is the idea of strategic fit In order to ensure that HR strategies facilitate the achievement of business strategies a strategic integration between the two is necessary A key factor that influences the linkage is organizations quest to attain Competitive advantage
Strategic Human Resource Management
Strategic Fit: A Conceptual Framework Organizations are often confronted with a dilemma Should they adopt business strategies that fit the available competencies and capabilities in the firm Should they first decide their business strategy and then stretch and modify their competencies and capabilities to fit the business strategy? The strategic fit proposes that if an organization seeks to maximise its competitive advantage Must match its internal resources and skills(organizational competencies)with the opportunities in external environment
Strategic Human Resource Management
Strategic Fit: A Conceptual Framework When Organization attempts to implement new strategies with outmoded or inappro-priate HR strategies it can face problems Strategic human resource management is largely about integration Guest (1989) emphasized that it is important to ensure that HRM is fully integrated to strategic planning In 1997Guest identified the following five types of fit:
Strategic Human Resource Management
Types of Fit between HR and Business Strategy
Fit as bundles(con figuration approach) Fit perspective
Fit as strategic interactio n best fit approach
Fit as gestalt
Fit as an ideal set of practices
Fit as contingency
Strategic Human Resource Management
Strategic Fit: A Conceptual Framework 1.Fit as strategic interaction(best fit approach)-HR practices linkage with external context 2.Fit as contingency-HR approaches to ensure that internal practices of the organization respond to external factors such as the nature of the market, skill availability 3.Fit as an ideal set of practices(best practice approach )there are best practices which all firm can adopt
Strategic Human Resource Management
4.Fit as gestalt-emphasizes the importance of finding an appropriate combination of practices 5.Fit as bundles (the configuration approach)-suggests a search for distinct configuration or bundles of HR practices that complement each other in order to determine which bundle is likely to be most effective
Strategic Human Resource Management
Three of the five types of fit provide the following possible approaches to SHRM: The best fit approach The HR bundles or configuration approach The best practice approach
Strategic Human Resource Management
The Best Fit Approach The focus of the best fit approach is on the linkage of HR strategies with business strategies Also referred to as external fit or vertical integration Best fit also means that HR strategies match the stages of development of the firm Start-up Maturity Decline/degeneration Regeneration or transformation Business strategies and HR strategies will differ between green field firm and one that is in the transformation stage
Strategic Human Resource Management
HR practices Corresponding to the stages of an Organizations life cycle(adapted from Armstrong)
Life Cycle Stages HR Practices
Start up
Flexible patterns of work Recruitment of highly motivated and committed employees Little formality No unions More sophisticated recruitment and selection Training and development Performance management processes Reward systems Focus on high commitment Developing stable employee relations Control compensation
Growth
Strategic Human Resource Management
HR practices Corresponding to the stages of an Organizations life cycle
Life Cycle Stages HR Practices
Maturity
Attention to the control of labour costs Focus on increasing productivity Strained employee relations Control compensation Emphasis on rationalization of workforce and downsizing Abandoning some longstanding practices to cut costs Trade unions have a marginalized role Retaining and career consulting services
Decline
Strategic Human Resource Management
The Best Fit Approach contd Bases of classification of HR Strategies: Beaumont (1992) three bases of classification of HR strategies: 1.Different types of business strategies- exampleorganization chooses strategy of low cost producer it adopts different HR approaches to compensation as compared to an organization which adopts a product innovation strategy Porter(1985) different business strategies will result in variation in HR practices
Strategic Human Resource Management
The Best Fit Approach contd 2.Stages in the business or product cycle HR practices are related to variations in the life cycle stages of a business-startup-growth-maturity-decline In the growth stage an organization recruits an adequate number and mix of qualified people In the maturity stage encourages sufficient turnover to minimize layoffs and facilitate reorganization Decline stage-plans and implements workforce reductions
Strategic Human Resource Management
The Best Fit Approach contd 3.Types and numbers of products-Fombrun et al.(1984)suggested that the strategy aimed at achieving variations in product focus -Single product strategy having a functional structure is likely to be subjective in selection/appraisal/rewards Organization that follows strategy of growth acquisition of unrelated business-criteria of selection will differ -performance appraisals and rewards are impersonal and based on ROI and profitability -Development is cross functional not cross business
Strategic Human Resource Management
Three types of business strategy that may be adopted by an organization Cost leadership Differentiation Focus According to Porter an organization may adopt any one of the three business strategies in order to compete successfully in a particular market and gain and sustain superior performance as well as an advantage over its competitors
Strategic Human Resource Management
HR strategy classification After discussing the bases of classification of HR strategy the most popular approach is the type of business strategy and adoption of complementary HR strategies Schuler and Jackson focused on Porter s classification of the three generic business strategies Cost Leadership Differentiation Focus They argued that the HR practices should be designed to reinforce the behavioural implication of these strategies
Strategic Human Resource Management
Linking Business Strategy and HR Strategy(ORiordon)
Business Strategy HR Strategy
Cost Leadership Suitable for repetitive and predictable behaviour Concerned with short term focus and quantities Result oriented Differentiation Long term focus Creative job behaviour Moderate concern for quality and quantity Focus High concern for quality Moderate concern for quality Long /medium term focus
Utilization HR Strategy HR Strategy focussed on short term performance measures results or outcomes Hierarchical pay ,few incentives Narrow career path ,limited training Facilitation HR strategy Broad career paths Extensive training Equal and fair pay/many incentives for creativity Accumulation HR Strategy Equal and fair pay with many incentives Hiring employees belonging to the new target market/High employee participation
Strategic Human Resource Management
The HR Bundles Approach Bundling refers to the development and implementation of several HR practices together so that they are interrelated and internally consistent Each HR practice complements and reinforces the other Flexible production techniques need to be supported by bundles of high commitment HR practices such as: Performance contingent pay Employment security etc -High involvement HR practice that is complementary to other HR practices is introduced in a firm -The new practice produces improvement in performance -Also has drawbacks
Strategic Human Resource Management
The best Practice Approach Superior management practices are readily identifiable and are transferable across organizations An organization should therefore identify any organization with reputation for excellence in some function and copy its practices in order to perform well Pleffers (1994) list of seven practices 1.Employment security 2.Selective hiring 3.Teamworking 4.High pay contingent on company performance 5.Extensive training/6.reduction of status differences/7.information sharing
Strategic Human Resource Management
Miles and Snows Classification of Business Strategy and HR Strategy
Dominant Culture of the organization (Business Strategy) Defenders Find change threatening HR Strategy Build HR Likely to emphasize training programmes and internal promotion Creative and flexible management style Have high quality HR Redeployment Acquire HR Emphasize recruitment, selection, performance based compensation Low levels of monitoring and coordination Buy and make Key HR Emphasize HR planning
Prospectors Thrive on change Favour strategies of product/market development Analyzers Seek to match new ventures with the present business set up Ventures not new to the market only new to the firm
You might also like
- Australian/New Zealand Standard: Structural Design Actions Part 0: General PrinciplesDocument8 pagesAustralian/New Zealand Standard: Structural Design Actions Part 0: General PrinciplesMikeChan0% (3)
- Strategic HR Vs Traditional HR: Role of HR Is Evolving in Recent YearsDocument18 pagesStrategic HR Vs Traditional HR: Role of HR Is Evolving in Recent YearsGangadhar MamadapurNo ratings yet
- Principles of HRMDocument22 pagesPrinciples of HRMSufyan Ranjha100% (1)
- 2 - Introduction To Strategic HRMDocument38 pages2 - Introduction To Strategic HRMfrio111180% (10)
- Strategic HRM EvolutionDocument59 pagesStrategic HRM EvolutionRmy Rjdrn100% (1)
- Session26 PPT SHRMDocument41 pagesSession26 PPT SHRMakansha bhatia100% (1)
- SHRMDocument27 pagesSHRMTaqdees Shaikh PawaskarNo ratings yet
- U1L3Document18 pagesU1L3Pushp ParagNo ratings yet
- SHRM Evolution PDFDocument65 pagesSHRM Evolution PDFdocsh100% (1)
- Chapter 1 SHRMDocument23 pagesChapter 1 SHRMAce NebulaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 and 2 SlidesDocument23 pagesLecture 1 and 2 SlidesKINZA ASHRAFNo ratings yet
- 304HRM-Strategic Human Resource ManagementDocument15 pages304HRM-Strategic Human Resource ManagementVandana MohantyNo ratings yet
- Strategic Human Resource ManagementDocument20 pagesStrategic Human Resource ManagementIshtiaq Hasnat Chowdhury Ratul100% (4)
- Human Resource ManagementDocument26 pagesHuman Resource ManagementSoma DonthuNo ratings yet
- SHRM Unit 1Document15 pagesSHRM Unit 1Jg VilashNo ratings yet
- SHRM Unit 1Document29 pagesSHRM Unit 1basrvsims21No ratings yet
- Human Resource ManagementDocument11 pagesHuman Resource ManagementNusrat IslamNo ratings yet
- Assignment TemplateDocument36 pagesAssignment TemplateSandi YukyawNo ratings yet
- EVOLUTION of SHRM, Traditionmodern HRM, Barriers, Role of SHRMDocument27 pagesEVOLUTION of SHRM, Traditionmodern HRM, Barriers, Role of SHRMDr. DhanabagiyamNo ratings yet
- HRM 23.08.2022Document32 pagesHRM 23.08.2022prabhat.kumarNo ratings yet
- HR AssignmentDocument18 pagesHR AssignmentFranklin NelsonNo ratings yet
- Human Capital ManagementDocument28 pagesHuman Capital ManagementRAJSHEKAR SNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - The Evolvingstrategic Role of A Human Resource ManagementDocument22 pagesChapter 4 - The Evolvingstrategic Role of A Human Resource ManagementNathalie G. CATALBASNo ratings yet
- Strategic Human Resource ManagementDocument14 pagesStrategic Human Resource Management9934529377No ratings yet
- 6 Human Resource Management and Recruitment and Selection WS 17-18Document47 pages6 Human Resource Management and Recruitment and Selection WS 17-18Amr ElSananNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 SHRMDocument75 pagesUnit 1 SHRMpinky Nath100% (2)
- An Introduction To Human Resource ManagementDocument26 pagesAn Introduction To Human Resource Managementrohan_j_pNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Human Resource ManagementDocument29 pagesFundamentals of Human Resource ManagementAshNo ratings yet
- Module - 01Document33 pagesModule - 01neerajNo ratings yet
- Topic How Does Strategy Impacts The Human Resource Process of The Organisation?Document16 pagesTopic How Does Strategy Impacts The Human Resource Process of The Organisation?Ayush ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Session I - The HR FrameworkDocument50 pagesSession I - The HR Frameworkkusumawi2311100% (2)
- Strategic HRM:: Linking The People With The Strategic Needs of The BusinessDocument15 pagesStrategic HRM:: Linking The People With The Strategic Needs of The BusinessRitu MalikNo ratings yet
- HRM Unit1Document65 pagesHRM Unit1Suhani VermaNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management 1220350814078431 8Document144 pagesHuman Resource Management 1220350814078431 8Ariadi TjokrodiningratNo ratings yet
- Strategic Human Resource ManagementDocument13 pagesStrategic Human Resource ManagementPallavi PathakNo ratings yet
- SHRM - Aligning HR With StrategyDocument35 pagesSHRM - Aligning HR With Strategycygmaxmdu90% (29)
- There Will Be Quiz No. 1 TodayDocument36 pagesThere Will Be Quiz No. 1 TodayAbdur RehmanNo ratings yet
- HRM - 390 Case StudyDocument8 pagesHRM - 390 Case StudyTanvir HasanNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management: Dr. B.S.N.RAJU Associate Professor Department of MbaDocument42 pagesHuman Resource Management: Dr. B.S.N.RAJU Associate Professor Department of Mbasrikanthforever100% (1)
- Introduction To Human Resource ManagementDocument20 pagesIntroduction To Human Resource ManagementKathuria AmanNo ratings yet
- College Lectuer HRM Rect Perf TND Oc Od HRP SHRM To LectDocument168 pagesCollege Lectuer HRM Rect Perf TND Oc Od HRP SHRM To LectTushar KambleNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management: Dr. Hadia Hamdy Magda Hassan Yomna Samir Dina MehrezDocument144 pagesHuman Resource Management: Dr. Hadia Hamdy Magda Hassan Yomna Samir Dina MehrezBilal AsgharNo ratings yet
- HRMDocument11 pagesHRMshivanipandey2224No ratings yet
- 4 SHRMDocument29 pages4 SHRMbenu07No ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document32 pagesChapter 1NHI PHẠM YẾNNo ratings yet
- Strategic HRM: Conceptual Framework, Investment Perspective and Aligning People With Business StrategyDocument30 pagesStrategic HRM: Conceptual Framework, Investment Perspective and Aligning People With Business StrategyDaksh AnejaNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management (1) OneDocument148 pagesHuman Resource Management (1) OneMuhammad Anas KhanNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management MBSDocument43 pagesHuman Resource Management MBSRA T NA BCNo ratings yet
- Introduction To HRMDocument8 pagesIntroduction To HRMevelynkyazzeNo ratings yet
- HRM As A Value To ShareholderDocument32 pagesHRM As A Value To ShareholderLokesh Kumar MerugupalaNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management: FunctionsDocument19 pagesHuman Resource Management: FunctionsYatish BangeraNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept of HRMDocument30 pagesBasic Concept of HRMSuman PoudelNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management: Meera Mohan, Faculty Member, MSB, KochiDocument21 pagesHuman Resource Management: Meera Mohan, Faculty Member, MSB, KochiMr. Anu DevassyNo ratings yet
- HR MOdelsDocument16 pagesHR MOdelsLee CelNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management TrainingDocument13 pagesHuman Resource Management TrainingManagement Consultant100% (3)
- IHRMDocument22 pagesIHRMtannubana810No ratings yet
- Models of HRM Class Presentation OneDocument30 pagesModels of HRM Class Presentation OneRanjana KejariwalNo ratings yet
- SHRM - An IntroductionDocument25 pagesSHRM - An IntroductionShruti PillaiNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Perspectives in Organisation Strategy and Strategic Management Theory Universalistic TheoryDocument15 pagesTheoretical Perspectives in Organisation Strategy and Strategic Management Theory Universalistic TheorysreelayaNo ratings yet
- Talent Management: Issues of Focus and Fit: Valerie Garrow and Wendy Hirsh, Institute For Employment StudiesDocument14 pagesTalent Management: Issues of Focus and Fit: Valerie Garrow and Wendy Hirsh, Institute For Employment StudiessreelayaNo ratings yet
- Business EtiquetteDocument36 pagesBusiness Etiquettebs4472@gmail.com100% (1)
- Business QuizDocument318 pagesBusiness QuizsreelayaNo ratings yet
- Non-Verbal Communication - Body Language: Maya. M, Lecturer, MBA Department, Sathyabama UniversityDocument12 pagesNon-Verbal Communication - Body Language: Maya. M, Lecturer, MBA Department, Sathyabama UniversitysreelayaNo ratings yet
- Mixed Veg Oats Dosa Recipe: IngredientsDocument91 pagesMixed Veg Oats Dosa Recipe: Ingredientssreelaya100% (1)
- PHYS 2214 Assignment 4 Fall 2010Document4 pagesPHYS 2214 Assignment 4 Fall 2010Kira GidronNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Map: First Quarter-Earth and Space Key Stage StandarsDocument13 pagesCurriculum Map: First Quarter-Earth and Space Key Stage StandarsLeendeen Grace Solis SesdoyroNo ratings yet
- Faculty ApswreisDocument3 pagesFaculty ApswreisrajavikramarkaNo ratings yet
- Lord Kuthumi - 8:8:8 Lion's Gate 1 Prosperity Christ Grids Anchoring ChannellingDocument9 pagesLord Kuthumi - 8:8:8 Lion's Gate 1 Prosperity Christ Grids Anchoring ChannellingEmeraldRayNo ratings yet
- Natural Selection PhET SimulationDocument4 pagesNatural Selection PhET SimulationChris WalczakNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4 (Recrystallization) PDFDocument7 pagesExperiment 4 (Recrystallization) PDFanon_733744716No ratings yet
- EHS Fiori APPS For SAP S4 HANA Downloaded On 2024-05-14 Concise InfoDocument4 pagesEHS Fiori APPS For SAP S4 HANA Downloaded On 2024-05-14 Concise InfodineshNo ratings yet
- Breif History of RoboticsDocument3 pagesBreif History of Roboticsapi-253221137No ratings yet
- ADOPT UT EssHumanAnatPhys Plus Coloring Book Marieb 9th 2009 FINALDocument13 pagesADOPT UT EssHumanAnatPhys Plus Coloring Book Marieb 9th 2009 FINALJehan Majid MohammadNo ratings yet
- How To Take Care of An Egg Baby ProjectDocument3 pagesHow To Take Care of An Egg Baby Projectzzaentz0% (1)
- BESSELDocument5 pagesBESSELLinearNo ratings yet
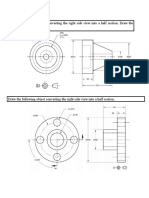
- Draw The Following Object Converting The Right Side View Into A Half Section. Draw The Appropriate Cutting Plane LineDocument2 pagesDraw The Following Object Converting The Right Side View Into A Half Section. Draw The Appropriate Cutting Plane LineAliceAlormenuNo ratings yet
- 1 IntroductionDocument24 pages1 IntroductionJiov AnniNo ratings yet
- Post Graduate - 17 November 2015Document20 pagesPost Graduate - 17 November 2015Times MediaNo ratings yet
- Intermediate LanguageDocument372 pagesIntermediate Languagevs_crni100% (1)
- Kahneman PsychologyPreferences 1982Document15 pagesKahneman PsychologyPreferences 1982m.altmeppen12No ratings yet
- Section 1 - Number Theory NotesDocument5 pagesSection 1 - Number Theory NotesEMMA SLAYNo ratings yet
- Sound 3-4 QR Usingechoestosee - HighDocument1 pageSound 3-4 QR Usingechoestosee - HighLola LolaNo ratings yet
- Audio Anti-Spoofing Detection: A Survey: Menglu Li, Yasaman Ahmadiadli, and Xiao-Ping ZhangDocument43 pagesAudio Anti-Spoofing Detection: A Survey: Menglu Li, Yasaman Ahmadiadli, and Xiao-Ping ZhangArnold SchwarzeneggerNo ratings yet
- Acjc h2 Maths p2 QN PaperDocument8 pagesAcjc h2 Maths p2 QN Papervincesee85No ratings yet
- Social Justice ARTifaritiDocument12 pagesSocial Justice ARTifaritiFederico GuzmánNo ratings yet
- LP Day 4 (Figure of Speech)Document6 pagesLP Day 4 (Figure of Speech)BelmerDagdagNo ratings yet
- Aero CollegesDocument3 pagesAero CollegesRohit MunaNo ratings yet
- Hydrogels in A Historical Perspective - From Simple Networks To Smart MaterialsDocument20 pagesHydrogels in A Historical Perspective - From Simple Networks To Smart Materialsalchemik1515No ratings yet
- Unlock-The Petrophysics of Problematic ReservoirsDocument9 pagesUnlock-The Petrophysics of Problematic ReservoirsJose BarreroNo ratings yet
- Display PDF PDFDocument128 pagesDisplay PDF PDFविरमपुर बनासकांठा गुजरात ईश्वरNo ratings yet
- Research Methods & Techniques (524) First Assignment: Ejaz Alam Khan - H 5279752Document23 pagesResearch Methods & Techniques (524) First Assignment: Ejaz Alam Khan - H 5279752NanaBearNo ratings yet
- Provide First AidDocument23 pagesProvide First AidKenard100% (6)
- Activity 2-Administrative & Supervisory Problem of Core CurriculumDocument3 pagesActivity 2-Administrative & Supervisory Problem of Core CurriculumAGAPE HUIDEMNo ratings yet