Rancangan Pelajaran Tahunan 2014: RPT: Science Form 1
Rancangan Pelajaran Tahunan 2014: RPT: Science Form 1
Uploaded by
ssukgantiCopyright:
Available Formats
Rancangan Pelajaran Tahunan 2014: RPT: Science Form 1
Rancangan Pelajaran Tahunan 2014: RPT: Science Form 1
Uploaded by
ssukgantiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Rancangan Pelajaran Tahunan 2014: RPT: Science Form 1
Rancangan Pelajaran Tahunan 2014: RPT: Science Form 1
Uploaded by
ssukgantiCopyright:
Available Formats
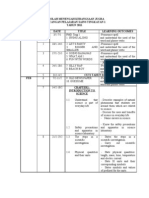
RPT: SCIENCE FORM 1
RANCANGAN PELAJARAN TAHUNAN 2014
SEKOLAH
MATA PELAJARAN
SAINS
TINGKATAN
SATU
MINGGU/
TARIKH
Week 1
(2 3 Jan)
Week 2
(6 10 Jan)
TAJUK
ISI KANDUNGAN
PEKA
-Taklimat
-Membuka fail PEKA
TARIKH
DISEMPURNAKAN
(Beri kenyataan
sekiranya lewat)
HASIL PEMBELAJARAN
INTRODUCING
SCIENCE
1.1 Understanding that A student is able to:
1.0 Introduction to science is part of - List what he sees around him that is related to
science
everyday life
science,
- Explain the importance of science in everyday life,
- Name some careers in science such as:
a) science teachers
b) doctors
c) engineers
d) environmental scientists
Week 3
(13-17 Jan)
1.2Understanding the A student is able to:
steps
in
scientific - State
the
steps
in
investigation.
investigation/experiment,
- Carry out a scientific investigation.
Week 4
(20-24 Jan)
1.3Knowing
physical A student is able to:
quantities and their - State the physical quantities length, mass, time,
units.
temperature and electric current,
- State the S.I. units and the corresponding symbols
for these physical quantities,
- State the symbols and values of prefixes for unit of
length and mass: milli-, centi-, and kilo-,
- Identify and use appropriate prefixes in the
measurement of length and mass.
1.4Understanding
A student is able to:
Week 5
scientific
RPT: SCIENCE FORM 1
(27-31 Jan)
the use of measuring
tools.
- Choose the right tool and measure length,
- Estimate the area of regular and irregular shapes
using graph paper,
- Choose the right tool and measure the volume of
liquid,
- Choose the right tool to measure the body
temperature and the temperature of a liquid,
- Determine the volume of solid using the water
displacement method
Week 6
(3-7 Feb)
1.5Understanding
the concept of mass.
A student is able to:
- Determine the weight of an object,
-Explain the concept of weight,
-Explain the concept of mass,
-Determine the mass of an object,
-Explain the difference between mass and weight,
-Apply the use of spring and beam/lever balance in
the context of an experiment.
Week 7
(10-14 Feb)
Week 8
(17-21 Feb)
1.6Realising the
importance of standard
units in everyday life.
A student is able to:
-Give examples of problems that may arise if
standard units are not used.
2.1 Understanding
cells.
A student is able to:
-Identify that cell is the basic unit of living things,
-Prepare slides following the proper procedure,
-Use a microscope properly,
-Identify the general structures of animal cells and
plant cells,
-Draw the general structure of an animal cell and a
plant cell,
-Label the general structure of an animal cell and a
plant cell,
-State the function of each cell structure,
-State the similarities and differences between an
MAN AND THE
VARIETY OF
LIVING THINGS
2. 0 Cell as a Unit
of Life
RPT: SCIENCE FORM 1
animal cell and a plant cell.
A student is able to:
-State the meaning of unicellular organism and
multicellular
organism,
-Give examples of unicellular organism and
multicellular
organism.
Week 9
(24-28 Feb)
2.2Understanding
unicellular
organism and
multicellular
organism.
Week 10
(3-7 Mar)
2.3Understanding
that cells form
tissues, organs
and systems in
the human
body
A student is able to:
-Name the different types of human cells,
-State the function of different types of human cells,
-Arrange sequentially cell organisation from simple
to complex using the terms cell, tissue, organ,
system and organism.
2.4Realising that
humans are
complex organisms.
A student is able to:
-Explain why human beings are complex organisms.
3.1Understanding
that matter has
mass and occupies
space.
A student is able to:
-State that things have mass and occupy space,
-Explain what matter is,
-Relate things and matter,
-Carry out activities to show that air, water, soil and
living things have mass and occupy space.
Week 11
(10-14 Mar)
Week 12
(17-21 Mar)
MATTER IN
NATURE
3.0 Matter
Week 13
(24-28 Mar)
Week 14
(1-4 Apr)
CUTI PERTENGAHAN PENGGAL 1
3.2Understanding
the three states of
matter.
A student is able to:
-State that matter is made up of particles,
-State the three states of matter,
-State the arrangement of particles in the three
states of matter,
-State the differences in the movement of particles in
the three states of matter.
3
RPT: SCIENCE FORM 1
Week 15
(7-11 Apr)
3.3Understanding
the concept of
density.
PEKA 1
3.4Appreciating
the use of properties of
matter in everyday life.
Week 16
(14-18 Apr)
Week 17
(21-25 Apr)
A student is able to:
-Define density,
-Explain why some objects and liquids float,
-Solve simple problems related to density,
-Carry out activities to explore the densities of
objects and liquids.
A student is able to:
-Describe how man uses the different states of
matter,
-Describe how man applies the concept of density,
-Carry out an activity to explore the applications of
the concept of floating and sinking related to
density.
The Variety of
Resources
on
Earth
4.1Knowing
the A student is able to:
different resources on
-List the resources on earth needed to sustain life,
earth.
-List the resources on earth used in everyday life.
Week 18
(28-2 Mei)
4.2 Understanding
elements, compounds
and mixtures.
Week 19
(5-9 Mei)
4.3 Appreciating
the importance
of the variety
A student is able to:
-State what elements, compounds and mixtures are,
-Give examples of elements, compounds and
mixtures,
-State
the
differences
between
elements,
compounds and mixtures,
-Carry out activities to compare and contrast the
properties of different metals and non-metals,
-Classify elements as metals and non-metals based
on their characteristics,
-Give examples of metals and non-metals,
carry out activities to separate the components of a
mixture.
A student is able to:
-Explain the importance of variety of earths
resources to
4
RPT: SCIENCE FORM 1
of earths
resources to
man.
Week 20
(12-16 Mei)
man,
-State the meaning of the preservation and
conservation of resources on earth,
-State the importance of the preservation and
conservation of resources on earth,
-Practise reducing the use, reusing and recycling of
materials.
The Air Around
Us
5.1 Understanding
what air is made up of.
A student is able to:
-State what air is made up of,
-Explain why air is a mixture,
-State the percentage of nitrogen, oxygen and
carbon dioxide in air,
-Carry out activities to show:
a) the percentage of oxygen in air,
b) that air contains water vapour, microorganisms
and dust
PEPERIKSAAN PERTENGAHAN TAHUN
Week 21
(17-23 Mei)
Week 22-24
(27Mei13Jun )
CUTI PENGGAL 2
Week 25
(16-20 Jun)
5.2 Understanding
the properties
of oxygen and
carbon dioxide
A student is able to:
-List the properties of oxygen and carbon dioxide,
-Identify oxygen and carbon dioxide based on their
properties,
-Choose a suitable test for oxygen and carbon
dioxide
Week 26
(23- 27 Jun)
5.3 Understanding
that oxygen is
needed in
respiration.
A student is able to:
-State that energy, carbon dioxide and water vapour
are the products of respiration,
-Relate that living things use oxygen and give out
carbon dioxide during respiration,
-Compare and contrast the content of oxygen in
inhaled and exhaled air in humans,
-State that oxygen is needed for respiration,
5
RPT: SCIENCE FORM 1
-Carry out an experiment to show that living things
use oxygen and give out carbon dioxide during
Respiration
Week 27
(30 Jun- 4
Julai)
5.4 Understanding
that oxygen is
needed for
combustion
(burning).
A student is able to:
-State what combustion is,
-State that oxygen is needed for combustion,
-List the products of combustion,
-Carry out experiments to investigate combustion.
PEKA 2
Week 28
(7-11 Julai)
5.5 Analysing the
effects of air
pollution.
Week 29
(14-18 Julai)
5.6Realising the
A student is able to:
importance of keeping -Describe how life would be without clean air,
the air clean
-Suggest ways to keep the air clean,
-Practise habits that keep the air clean.
Week 30
(21- 25 Julai)
Week 31
(28 Julai - 1
Aug)
ENERGY
6.0 Sources
Energy
A student is able to:
-Explain what air pollution is,
-List examples of air pollutants,
-List the sources of air pollutants,
-Describe the effects of air pollution,
-Explain the steps needed to prevent and control air
pollution.
of 6.1Understanding
various forms
and sources of
energy.
A student is able to:
List the various forms of energy,
-List the various sources of energy,
-Identify energy changes,
-Identify the sun as the primary source of energy,
-Carry out an activity to investigate the change of
energy from potential to kinetic energy and vice
versa.
6.2 Understanding
renewable and
non-renewable
energy.
A student is able to:
-Define renewable and non-renewable sources of
energy,
-Group the various sources of energy into renewable
and non-renewable,
6
RPT: SCIENCE FORM 1
-Explain why we need to conserve energy,
-Suggest ways to use energy efficiently.
Week 32
(4-8 Ogos)
Week 33
( 11-15
Ogos)
Week 34
(18-22 Ogos)
Week 35
(25-29 Ogos)
Week 36
(1-5 Sept)
6.3Realising the
importance of
conserving energy
sources.
A student is able to:
-Describe the importance of conserving energy
sources,
-Explain the use and management of energy
sources
7.1Understanding
heat as a form
of energy.
A student is able to:
-State that the sun gives out heat,
-State other sources of heat,
-State that heat is a form of energy,
-Give examples of the uses of heat,
-State the meaning of temperature,
-State the difference between heat and temperature
7.2Understanding
heat flow and
its effect.
A student is able to:
-State that heat causes solids, liquids and gases to
expand and contract,
-State that heat flows in three different ways
(conduction, convection and radiation),
-State that heat flows from hot to cold,
-Give examples of heat flow in natural phenomena,
-State what a heat conductor is,
-State what a heat insulator is,
-List uses of heat conductors and heat insulators in
daily life,
-Carry out an experiment to investigate the use of
different materials as heat insulators
Heat
PENILAIAN AKADEMIK 3
7.3Analysing the
effect of heat on matter.
A student is able to:
-State the change in state of matter in physical
processes,
-Explain that change in state of matter involves the
absorption and release of heat,
-Give examples of daily change in state of matter.
7
RPT: SCIENCE FORM 1
Week 36
(8-12 Sept)
Week 37
(15-19 Sept)
Week 38
(22-26 Sept)
Week 39
(29Sept-3
Okt)
Week 40
(6-10 Okt)
Week 41
(13-17 Okt)
Week 42
(20-24 Okt)
Week 43 &
44
(27 Okt-7
Nov)
Week 45
(10-14 Nov)
Week 46
(17-21 Nov)
7.4 Applying the
principle of expansion
and contraction of
matter.
A student is able to:
-Explain with examples the use of expansion and
contraction of matter in daily life,
-Apply the principle of expansion and contraction of
matter in solving simple problems.
CUTI PERTENGAHAN PENGGAL 2/ HARI RAYA PUASA
7.5Understanding
that dark, dull
objects absorb
and give out
heat better.
A student is able to:
-State that dark, dull objects absorb heat better than
white, shiny objects,
-State that dark, dull objects give out heat better than
white, shiny objects,
-Carry out experiments to investigate heat
absorption and heat release.
7.6 Appreciating
the benefits of
heat flow.
PENTAKSIRAN PBS
A student is able to:
-Put into practice the principle of heat flow to provide
comfortable living.
PENTAKSIRAN PBS
PENTAKSIRAN PBS
PEPERIKSAAN AKHIR TAHUN
MENGEMASKINI FAIL PEKA
You might also like
- Special Science Elementary SchoolDocument5 pagesSpecial Science Elementary SchoolRobbie Rose Lava100% (2)
- Energy WorksheetDocument4 pagesEnergy WorksheetAlyssa Cole100% (1)
- RPT Science FRM 1Document9 pagesRPT Science FRM 1Maslen DadeeNo ratings yet
- Rancangan Pelajaran Tahunan: RPT: Science Form 1Document9 pagesRancangan Pelajaran Tahunan: RPT: Science Form 1Mahfuzah AzmiNo ratings yet
- Rancangan Pelajaran Tahunan: RPT: Science Form 1Document9 pagesRancangan Pelajaran Tahunan: RPT: Science Form 1300664No ratings yet
- Rancangan Pelajaran Tahunan: RPT: Science Form 1Document9 pagesRancangan Pelajaran Tahunan: RPT: Science Form 1adleenshazNo ratings yet
- Rancangan Pelajaran Tahunan: RPT: Science Form 1Document9 pagesRancangan Pelajaran Tahunan: RPT: Science Form 1Choo Li MingNo ratings yet
- Rancangan Pelajaran Tahunan: RPT: Science Form 1Document9 pagesRancangan Pelajaran Tahunan: RPT: Science Form 1Nur Hayati YusofNo ratings yet
- RPT Sains Ting. 1Document10 pagesRPT Sains Ting. 1Norzaliatun RamliNo ratings yet
- Rancangan Pelajaran Tahunan 2014: RPT: Science F1Document9 pagesRancangan Pelajaran Tahunan 2014: RPT: Science F1Lydia HuangNo ratings yet
- Rancangan Pelajaran Tahunan: RPT: Science Form 1Document9 pagesRancangan Pelajaran Tahunan: RPT: Science Form 1Noralizah IsmadiNo ratings yet
- Yearly Lesson Plan Science Form 1 2015Document6 pagesYearly Lesson Plan Science Form 1 2015Muhd Mustaffa Kamal AbidinNo ratings yet
- Yearly Plan For Science Form 1Document27 pagesYearly Plan For Science Form 1Nor FaizahNo ratings yet
- Rancangan Pelajaran Tahunan Sains F1 2013Document8 pagesRancangan Pelajaran Tahunan Sains F1 2013mohd nazrul nizamNo ratings yet
- RPT SC F1 2016Document15 pagesRPT SC F1 2016amie1312No ratings yet
- Integrated Science Year 1Document45 pagesIntegrated Science Year 1Andre Swaggerific PickettNo ratings yet
- RPT Science FRM 2Document12 pagesRPT Science FRM 2reanizaNo ratings yet
- RPT Science FRM 1Document3 pagesRPT Science FRM 1Aniza Abu BakarNo ratings yet
- Yearly Teaching PlanDocument7 pagesYearly Teaching PlanrarmaaNo ratings yet
- Sekolah Menengah Kebangsaan JugraDocument7 pagesSekolah Menengah Kebangsaan JugraNoor FaralieyzaNo ratings yet
- Yearly Plan Form 1 EditedDocument15 pagesYearly Plan Form 1 EditedDianasalmie AhmadNo ratings yet
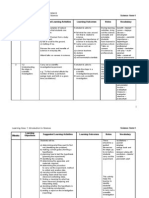
- Weeks: Science Form 1 Learning Objectives Suggested Learning Activities Learning Outcomes Notes VocabularyDocument23 pagesWeeks: Science Form 1 Learning Objectives Suggested Learning Activities Learning Outcomes Notes VocabularyAsmanura YahyaNo ratings yet
- Yearly Planning Science1 EditedDocument24 pagesYearly Planning Science1 Editedalena67No ratings yet
- DLL Science Grade9 Quarter1 Week2 (Palawan Division)Document5 pagesDLL Science Grade9 Quarter1 Week2 (Palawan Division)Cherry TamboongNo ratings yet
- Year Planner (f1) LatestDocument13 pagesYear Planner (f1) LatestNor ShakeelaNo ratings yet
- Week Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes Suggested Learning Activities NotesDocument15 pagesWeek Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes Suggested Learning Activities NoteswahyuniLoveSudirNo ratings yet
- Yearly Plan 2015 Science Form 2: SMK Menjalara Bandar Menjalara 52100 Kepong, Kuala LumpurDocument11 pagesYearly Plan 2015 Science Form 2: SMK Menjalara Bandar Menjalara 52100 Kepong, Kuala LumpurCheng Kai WahNo ratings yet
- RPT: Science Form 4 Rancangan Pelajaran TahunanDocument21 pagesRPT: Science Form 4 Rancangan Pelajaran TahunanChuah Siew HoonNo ratings yet
- RPT: Science Form 3Document15 pagesRPT: Science Form 3Ani AhwaiNo ratings yet
- Science Yearly Lesson Plan: Year 5Document8 pagesScience Yearly Lesson Plan: Year 5Muhammad FarisNo ratings yet
- R PT Science FRM 12013Document9 pagesR PT Science FRM 12013bartNo ratings yet
- RPT SC Form 1Document22 pagesRPT SC Form 1Norhidayah Binti PazilNo ratings yet
- SMK Tanjong Bunga Rancangan Tahunan Mengajar Sains Tingkatan 1Document20 pagesSMK Tanjong Bunga Rancangan Tahunan Mengajar Sains Tingkatan 1riyashreeNo ratings yet
- Yearly Plan Form 4 2013 CompleteDocument15 pagesYearly Plan Form 4 2013 Completemaisarah_mustapa_1No ratings yet
- What Is Causing Global Warming?: SubjectDocument3 pagesWhat Is Causing Global Warming?: SubjectJeric MaribaoNo ratings yet
- Sekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Sultan Badlishah Annual Lesson Plan Biology Form 4 (2016)Document30 pagesSekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Sultan Badlishah Annual Lesson Plan Biology Form 4 (2016)wienna1987No ratings yet
- SHS Core - Physical Science CG - With Tagged Sci EquipmentDocument17 pagesSHS Core - Physical Science CG - With Tagged Sci EquipmentBunso A. LorestoNo ratings yet
- f4 Yearly Plan 2011Document18 pagesf4 Yearly Plan 2011Zuraida Bt Zainol AbidinNo ratings yet
- Science f1 Lesson Plan Lates 09tDocument26 pagesScience f1 Lesson Plan Lates 09tSahrulRashidNo ratings yet
- Yearly Lesson Plan 2017 SC F2Document11 pagesYearly Lesson Plan 2017 SC F2Aisya OmeiraNo ratings yet
- RPT SN THN5Document10 pagesRPT SN THN5Jhoster YulongNo ratings yet
- Orientation Programme For Form 1 StudentsDocument24 pagesOrientation Programme For Form 1 StudentsVictor ManivelNo ratings yet
- Science f1 Yearly PlanDocument39 pagesScience f1 Yearly PlanCt NoraNo ratings yet
- Course Outline - Science 8Document3 pagesCourse Outline - Science 8api-336712848No ratings yet
- Yearly Plan For Science Form 1Document9 pagesYearly Plan For Science Form 1untatahiNo ratings yet
- Sekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Bukit Guntong Subject: Science Form: 1Document9 pagesSekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Bukit Guntong Subject: Science Form: 1Santhiya MadhavanNo ratings yet
- RPT Form 2Document8 pagesRPT Form 2Aidatul Shima IsmailNo ratings yet
- Ap Biology Daily ScheduleDocument22 pagesAp Biology Daily Scheduleapi-2592017970% (1)
- PBL Lesson PlansDocument48 pagesPBL Lesson PlansAmit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY YEAR 7 1st TERM LESSON PLAN (WEEK 1,2,3) AND SCHEME OF WORKDocument21 pagesCHEMISTRY YEAR 7 1st TERM LESSON PLAN (WEEK 1,2,3) AND SCHEME OF WORKewejeoadeniyiNo ratings yet
- Formative Crit D Poster Making-26-8-15Document3 pagesFormative Crit D Poster Making-26-8-15Seema ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Bio Supplement eDocument52 pagesBio Supplement eTom ChanNo ratings yet
- RPT Sains Ting. 3 2016Document20 pagesRPT Sains Ting. 3 2016NorSafarien RahimNo ratings yet
- Class 9th SyllabusDocument23 pagesClass 9th Syllabussanjeev kumarNo ratings yet
- Budget of Work (Sci.7)Document6 pagesBudget of Work (Sci.7)Mariah ThezNo ratings yet
- RPT: Science Form 2Document12 pagesRPT: Science Form 2Emmy MasturaNo ratings yet
- RPT Biology Form4Document50 pagesRPT Biology Form4Nadiah BorhanNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Work Senior Six Physical Chemistry Term Two 2012 Mr. Ndawula SolomonDocument6 pagesScheme of Work Senior Six Physical Chemistry Term Two 2012 Mr. Ndawula SolomonsololexzibNo ratings yet
- Teaching of G ScienceDocument9 pagesTeaching of G Scienceapi-2315168790% (1)
- Science Y7Document1 pageScience Y7api-296654747No ratings yet
- GOD and Quantum Physics PDFDocument19 pagesGOD and Quantum Physics PDFsamu2-4uNo ratings yet
- Ancillary Service Procurement Plan 2011Document63 pagesAncillary Service Procurement Plan 2011Raphael Sumalinog100% (1)
- Physics 11 - Work, Power, Energy WorksheetDocument4 pagesPhysics 11 - Work, Power, Energy Worksheetfazeelm24No ratings yet
- Structure of Atom MAster Explanation PRESS4Document105 pagesStructure of Atom MAster Explanation PRESS4Chad Ashley VandenbergNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 - Past Year Questions April 2011Document3 pagesAssignment 1 - Past Year Questions April 2011aiman_safianNo ratings yet
- Criticisms To General Relativity - Critiche Alla Relativita' GeneraleDocument79 pagesCriticisms To General Relativity - Critiche Alla Relativita' GeneraleLeonardo RubinoNo ratings yet
- TES Without Ice: by Daniel Pare, P.E., Associate Member ASHRAE and Stephane Bilodeau, PH.D., P.E., Member ASHRAEDocument4 pagesTES Without Ice: by Daniel Pare, P.E., Associate Member ASHRAE and Stephane Bilodeau, PH.D., P.E., Member ASHRAEPranay SawantNo ratings yet
- Leonics 2 MW Stand Alone PV Diesel Generator001Document2 pagesLeonics 2 MW Stand Alone PV Diesel Generator001Noel Gregorio SantosNo ratings yet
- Solar Pond ReportDocument40 pagesSolar Pond ReportSeena Raj100% (2)
- Neet - 2017 Test Series Two Dimensional Motion & Work Power EnergyDocument4 pagesNeet - 2017 Test Series Two Dimensional Motion & Work Power Energyumved singh yadav100% (1)
- Atomic Energy PresentstionDocument37 pagesAtomic Energy PresentstionM Salman RyanNo ratings yet
- 2 Hydro Power L2Document76 pages2 Hydro Power L2Yared TassewNo ratings yet
- G484 Module 1 Newtons Laws and Momentum Questions MSDocument3 pagesG484 Module 1 Newtons Laws and Momentum Questions MSTrishnee MunusamiNo ratings yet
- What Are The Factors That Affect DensityDocument14 pagesWhat Are The Factors That Affect DensitySatria Muliya PutraNo ratings yet
- 09 Science Notes Ch10 GravitationDocument4 pages09 Science Notes Ch10 Gravitationdvrao_chowdary100% (1)
- Physics - Reflection PaperDocument5 pagesPhysics - Reflection PaperDaniele Talens CaguiatNo ratings yet
- Working Principle of Solar PVDocument5 pagesWorking Principle of Solar PVkarthikgoldenrock100% (4)
- DPP WpeDocument6 pagesDPP WpeMohammed Aftab AhmedNo ratings yet
- Brochure Aquion Telecom PrintDocument2 pagesBrochure Aquion Telecom Printapi-223630583No ratings yet
- Nuclear Power PresentationDocument16 pagesNuclear Power Presentationdinesh1625No ratings yet
- The Life Cycle of StarsDocument11 pagesThe Life Cycle of StarsJake Bennett-WoolfNo ratings yet
- WINDPOWERDocument18 pagesWINDPOWERChanning TatumNo ratings yet
- Performance Evaluation of Egbin Thermal StationDocument12 pagesPerformance Evaluation of Egbin Thermal StationWisnu Yoga PrasetyaNo ratings yet
- Gas Turbines Technical PerformanceDocument2 pagesGas Turbines Technical PerformanceRoozbeh P100% (1)
- Chapt 19Document11 pagesChapt 19Rebecca Es100% (2)
- ABB Review 2-2015 - 72dpiDocument76 pagesABB Review 2-2015 - 72dpiasnawisulong mohdNo ratings yet
- Biological Effects of Radiation & Safety ConsiderationDocument21 pagesBiological Effects of Radiation & Safety ConsiderationTareq AzizNo ratings yet
- 10.1.10.SHM - Hookes LAW. Spring Practice Problems - KeyDocument3 pages10.1.10.SHM - Hookes LAW. Spring Practice Problems - KeyJose Barrera GaleraNo ratings yet