100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
5K viewsDisturbed Sleep
Disturbed Sleep
Uploaded by
mawelThe patient was experiencing disturbed sleep patterns related to difficulty breathing from an underlying disease process. After 6-8 hours of nursing interventions including encouraging deep breathing exercises, adequate rest, and position changes, the patient was able to demonstrate an increased tolerance for activity without dyspnea or fatigue. The patient also identified and addressed negative factors affecting their activity tolerance and participated willingly in necessary activities. The nursing interventions aimed to promote optimal breathing and rest to facilitate healing and recovery.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Disturbed Sleep
Disturbed Sleep
Uploaded by
mawel100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
5K views1 pageThe patient was experiencing disturbed sleep patterns related to difficulty breathing from an underlying disease process. After 6-8 hours of nursing interventions including encouraging deep breathing exercises, adequate rest, and position changes, the patient was able to demonstrate an increased tolerance for activity without dyspnea or fatigue. The patient also identified and addressed negative factors affecting their activity tolerance and participated willingly in necessary activities. The nursing interventions aimed to promote optimal breathing and rest to facilitate healing and recovery.
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
The patient was experiencing disturbed sleep patterns related to difficulty breathing from an underlying disease process. After 6-8 hours of nursing interventions including encouraging deep breathing exercises, adequate rest, and position changes, the patient was able to demonstrate an increased tolerance for activity without dyspnea or fatigue. The patient also identified and addressed negative factors affecting their activity tolerance and participated willingly in necessary activities. The nursing interventions aimed to promote optimal breathing and rest to facilitate healing and recovery.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
5K views1 pageDisturbed Sleep
Disturbed Sleep
Uploaded by
mawelThe patient was experiencing disturbed sleep patterns related to difficulty breathing from an underlying disease process. After 6-8 hours of nursing interventions including encouraging deep breathing exercises, adequate rest, and position changes, the patient was able to demonstrate an increased tolerance for activity without dyspnea or fatigue. The patient also identified and addressed negative factors affecting their activity tolerance and participated willingly in necessary activities. The nursing interventions aimed to promote optimal breathing and rest to facilitate healing and recovery.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
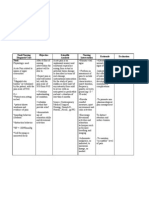
Need/Nursing Scientific Nursing Value
Objective Rationale Evaluation
Diagnosis/Cues Analysis Intervention Integration
Need: Sleep is required to After 6-8 hours Independent: After 6-8 hours
Physiologic need provide energy for of nursing of nursing
physical and mental intervention, the • Evaluate patient’s response • Establishes patient’s intervention, the
Nursing Diagnosis: activities. As persons patient will be to activity. capabilities or needs and patient was able
Disturbed sleep age the amount of able to: facilitates choice of interventions to:
pattern related to time spent in REM • Reduces stress and excess
difficulty or laboured sleep diminishes. The a. demonstrate a • Provide a quiet environment stimulation, promoting a. the patient was
breathing secondary to amount of sleep that measurable and limit visitors. rest. able to
disease process individuals require increase in demonstrate a
Cues: varies with age and tolerance in • Elevate head and encourage • These measures promote measurable
personal activity with frequent maximal inspiration. increase in
Subjective cues: characteristics. absence of position changes. tolerance in
“Dili ko katulog kay Disruption in the dyspnea and activity with
maglisod ko ug individual’s usual excessive • Encourage deep • Improve ventilation and absence of
ginhawa”, as diurnal pattern of fatigue. breathing exercise. promotes optimal chest dyspnea and
verbalized by the sleep and expansion. excessive fatigue.
patient. wakefulness may be b. Identify
temporary or chronic. negative factors • Encourage adequate rest • Facilitates healing process b. Identified
Such disruptions may affecting activity balanced with moderate and enhances natural negative factors
Objective cues: result in both tolerance and activity. Promote adequate resistance. affecting activity
• Frequent subjective distress eliminate or nutritional intake. tolerance and
yawning and apparent reduce their eliminate or
• Assist patient with self-care • Weakness may make
noticed impairment in effects when reduce their
needs. Keep bed in low activities of daily living
functional abilities. possible. effects when
position and assist and ambulation difficult,
• Fatigue possible.
with ambulation. further assistance is
c. Participate
needed.
• Weak-looking willingly in c. Participated
necessary /
Dependent: • Aids in reduction of willingly in
desired • Provide supplemental shortness of breathe and necessary /
• Dyspnea oxygen via nasal cannula as prevent hyperventilation.
activities. desired activities.
ordered by the physician.
• Use of
accessory
muscles in
breathing
• Restlessness
• Number of
hours of
sleeping = 5
hours.
You might also like
- NCP - Risk For InfectionDocument2 pagesNCP - Risk For InfectionJet Bautista100% (1)
- Activity Intolerance Related To Decrease Blood FlowDocument3 pagesActivity Intolerance Related To Decrease Blood FlowDarkCeades100% (3)
- Disturbed Sleeping PatternDocument3 pagesDisturbed Sleeping Patternprickybiik50% (2)
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument3 pagesAssessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDanica Kate GalleonNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology-LiverDocument2 pagesAnatomy and Physiology-Livermawel100% (1)
- NCP - Acute Pain - FractureDocument1 pageNCP - Acute Pain - Fracturemawel74% (23)
- NCP Acute PainDocument1 pageNCP Acute Painmawel93% (30)
- LacerationsDocument8 pagesLacerationsmawelNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology-LiverDocument2 pagesAnatomy and Physiology-Livermawel100% (1)
- PNGIMR 40th Anniversary and ColloquiumDocument116 pagesPNGIMR 40th Anniversary and ColloquiumJamie CrossNo ratings yet
- NCP Acute Pain RT CancerDocument3 pagesNCP Acute Pain RT CancerCharissa Magistrado De LeonNo ratings yet
- Ncp-For-Sle-Fatigue-And-Pain EDITEDDocument4 pagesNcp-For-Sle-Fatigue-And-Pain EDITEDJordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- Disturbed Sleep Pattern Related To Environmental FactorsDocument9 pagesDisturbed Sleep Pattern Related To Environmental Factorsalaisah dimaporoNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument5 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationArian May MarcosNo ratings yet
- Chemo NCPDocument2 pagesChemo NCPJustin Eduardo100% (1)
- NCP AlteredDocument3 pagesNCP AlteredShaira TillahNo ratings yet
- FATIGUE NCP Que Fransis A.Document4 pagesFATIGUE NCP Que Fransis A.Irene Grace BalcuevaNo ratings yet
- Drug NameDocument4 pagesDrug Namecheanne003No ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPAlyanna Peñaflorida100% (2)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesNursing Care PlanAldrein GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan (Acute Pain)Document1 pageNursing Care Plan (Acute Pain)kyaw100% (3)
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPJhel NabosNo ratings yet
- Risk For InjuryDocument5 pagesRisk For InjuryAllene PaderangaNo ratings yet
- Activity IntoleranceDocument1 pageActivity IntoleranceAdrian MallarNo ratings yet
- NCP Disturbed Body ImageDocument2 pagesNCP Disturbed Body ImageDoneva Lyn MedinaNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPMichelleNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument6 pagesNCPKyla Carbonel100% (2)
- Chinese General Hospital College of Nursing Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesChinese General Hospital College of Nursing Nursing Care PlanKenji ToleroNo ratings yet
- N C P For Perioperative Pts.Document4 pagesN C P For Perioperative Pts.Daisy Palisoc100% (2)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument20 pagesNursing Care PlanZamranosNo ratings yet
- Self-Care DeficitDocument2 pagesSelf-Care DeficitNDJNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPsphinx809100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan For A Patient With Pleural EffusionDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan For A Patient With Pleural EffusionTrixie Anne GamotinNo ratings yet
- NCP sLEEP DEPRIVATIONDocument4 pagesNCP sLEEP DEPRIVATIONArianna MabungaNo ratings yet
- NCP Knowledge DeficitDocument1 pageNCP Knowledge Deficittspears82100% (2)
- Activity IntoleranceDocument2 pagesActivity IntoleranceSenyorita KHaye100% (4)
- NCP Close Complete Fracture Knowledge DeficitDocument2 pagesNCP Close Complete Fracture Knowledge DeficitArt Christian Ramos0% (1)
- Impaired Verbal CommDocument3 pagesImpaired Verbal CommKM100% (2)
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageIneffective Breathing Pattern Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanJasonlee Baluyot100% (1)
- NCP Activity IntoleranceDocument5 pagesNCP Activity IntoleranceRea HashimNo ratings yet
- NCP Impaired Skin IntegrityDocument1 pageNCP Impaired Skin Integritysinister17No ratings yet
- TB, Ineffectivbe Breathing PatternsDocument1 pageTB, Ineffectivbe Breathing PatternsnikkilyceeNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Subjective DataDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Subjective DataAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument5 pagesNursing Care Planseanamir100% (5)
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPkatrina_velasco_1No ratings yet
- NCP Sleep DisturbanceDocument1 pageNCP Sleep DisturbanceIsrael Soria EsperoNo ratings yet
- NCP RiskDocument3 pagesNCP RiskMaricar Azolae MascualNo ratings yet
- Imbalance Nutrition Lass Than Body Requirements Related To Loss of Appetite Due To Aging 2Document2 pagesImbalance Nutrition Lass Than Body Requirements Related To Loss of Appetite Due To Aging 2Senyorita KHaye100% (1)
- NURSING CARE PLAN Problem Body Weakness Nursing Diagnosis Impaired PhysicalDocument1 pageNURSING CARE PLAN Problem Body Weakness Nursing Diagnosis Impaired Physicalmitchie rivera100% (1)
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument7 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternJanmae JivNo ratings yet
- Prostate Cancer NCPDocument1 pageProstate Cancer NCPKathleen Dimacali0% (1)
- NCP - AnxietyDocument1 pageNCP - AnxietyNovie Carla100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan SeizureDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan SeizureTeresa JunioNo ratings yet
- NCP: Acute GastroenteritisDocument3 pagesNCP: Acute GastroenteritishauteanicoleNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationMyrien BanaagNo ratings yet
- NCP - Impaired Skin IntegrityDocument4 pagesNCP - Impaired Skin IntegrityColette Marie PerezNo ratings yet
- Disturbed SleepDocument3 pagesDisturbed SleepNicole MapiliNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN-Impired Physical MobilityDocument5 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN-Impired Physical MobilityKathleen Leana Viray JeanjaquetNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plankehyrie100% (2)
- NCP FormDocument3 pagesNCP FormJasmine diokNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument18 pagesNursing Care PlanElla Grace PradoNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN - SuicidalactDocument4 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN - SuicidalactJennifer ArdeNo ratings yet
- NCP Kuya TedDocument3 pagesNCP Kuya TedBenjie DimayacyacNo ratings yet
- NCP StrokeDocument6 pagesNCP StrokeIrish TatelNo ratings yet
- Nursing Problem Explanation Goal Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument2 pagesNursing Problem Explanation Goal Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveZed P. EstalillaNo ratings yet
- Estoya, Gen Paulo C. - Heart Failure NCP - NCM 112 LecDocument4 pagesEstoya, Gen Paulo C. - Heart Failure NCP - NCM 112 LecGen Paulo EstoyaNo ratings yet
- Special SensesDocument29 pagesSpecial Sensesmawel100% (2)
- PRC-Assisted Delivery 2010Document1 pagePRC-Assisted Delivery 2010mawelNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Imbalance NCPDocument1 pageNutrition Imbalance NCPmawelNo ratings yet
- DIAGNOSIS Hyperthermia Related To Increased Metabolic Rate, Illness. ASSESSMENT SubjectiveDocument1 pageDIAGNOSIS Hyperthermia Related To Increased Metabolic Rate, Illness. ASSESSMENT Subjectivemawel100% (1)
- NCP FractureDocument2 pagesNCP Fracturemawel50% (2)
- Need/Nursing Diagnosis/Cues Need: Physiologic Need Nursing Diagnosis: - Nutrition ImbalancedDocument1 pageNeed/Nursing Diagnosis/Cues Need: Physiologic Need Nursing Diagnosis: - Nutrition ImbalancedmawelNo ratings yet
- Hexetidine (Latin: Hexetidinum) Is An Anti-Bacterial and Anti-Fungal Agent CommonlyDocument1 pageHexetidine (Latin: Hexetidinum) Is An Anti-Bacterial and Anti-Fungal Agent CommonlymawelNo ratings yet
- Difficulty in SwallowingDocument1 pageDifficulty in SwallowingmawelNo ratings yet
- Hematologic DisorderDocument7 pagesHematologic Disordermawel100% (2)
- Constipation LeukemiaDocument1 pageConstipation LeukemiamawelNo ratings yet
- Molar PregnancyDocument1 pageMolar Pregnancymawel100% (1)
- Mechanism of HealingDocument1 pageMechanism of HealingmawelNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Imbalance NCPDocument1 pageNutrition Imbalance NCPmawelNo ratings yet
- PRC Form (Minor Operation)Document1 pagePRC Form (Minor Operation)mawelNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - DigoxinDocument2 pagesDrug Study - DigoxinDanielle AglusolosNo ratings yet
- Guideline Implementation Local AnesthesiaDocument12 pagesGuideline Implementation Local Anesthesiasandi kaputraNo ratings yet
- For COT 4th QDocument12 pagesFor COT 4th QMelbourneSinisinNo ratings yet
- Hpa HptaxeschartDocument2 pagesHpa Hptaxeschartdikadika_tansNo ratings yet
- Modalities of DiagnosisDocument5 pagesModalities of Diagnosismadhu.BNo ratings yet
- FORENSIC - Term 2 - MS'3 '26 (2023-10-02)Document51 pagesFORENSIC - Term 2 - MS'3 '26 (2023-10-02)Wajiha MughalNo ratings yet
- JOURNALDocument4 pagesJOURNALANGELIE CRISTINE POMADONo ratings yet
- CN1. Olfactory DisordersDocument2 pagesCN1. Olfactory DisordersKrishna KanthNo ratings yet
- Preanaesthetic Medication Anaesthetic AgentsDocument35 pagesPreanaesthetic Medication Anaesthetic AgentsSubhash BeraNo ratings yet
- Pain Management For Clinicians A Guide To Assessment and Treatment Carl Edward Noe 2024 Scribd DownloadDocument49 pagesPain Management For Clinicians A Guide To Assessment and Treatment Carl Edward Noe 2024 Scribd Downloadgessiwannah100% (3)
- Structuring Interdisciplinary Learning Using TBL Through PBL in Cardiovascular Diseases Case University of Algiers PDFDocument18 pagesStructuring Interdisciplinary Learning Using TBL Through PBL in Cardiovascular Diseases Case University of Algiers PDFGlobal Research and Development ServicesNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 - A Study PDFDocument4 pagesCOVID-19 - A Study PDFInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Ipcr - July-December, 2024Document3 pagesIpcr - July-December, 2024Dechy Lyn PalmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter TwoDocument12 pagesChapter TwoMuhd SaniNo ratings yet
- Final File 5a7d425b07f7c4.14364665Document4 pagesFinal File 5a7d425b07f7c4.14364665AmadeaNo ratings yet
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY-PTB - FinalDocument1 pagePATHOPHYSIOLOGY-PTB - FinaliamMye100% (1)
- Proximal Humeral Fractures: Current Controversies: Herbert Resch, MDDocument6 pagesProximal Humeral Fractures: Current Controversies: Herbert Resch, MDmichellmariottiNo ratings yet
- Liver Disorders-II Jaundice 3Document14 pagesLiver Disorders-II Jaundice 3Daksh SabharwalNo ratings yet
- The Root Canal MorphologyDocument622 pagesThe Root Canal MorphologyZdrenghea AngeloNo ratings yet
- Cryptorchidism PDFDocument44 pagesCryptorchidism PDFKrishna Oochit100% (1)
- The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses: Elaine N. MariebDocument75 pagesThe Lymphatic System and Body Defenses: Elaine N. MariebReysa Manulat100% (1)
- Sehteq CARE and CARE PLUS RN3 Network - May 2021Document87 pagesSehteq CARE and CARE PLUS RN3 Network - May 2021cmthebossNo ratings yet
- Structural Disorders of The SpineDocument6 pagesStructural Disorders of The SpineRod Reynon BorceNo ratings yet
- To Determine The Symptoms, Predisposing Factors and Causative Organisms of OtomycosisDocument3 pagesTo Determine The Symptoms, Predisposing Factors and Causative Organisms of OtomycosisAnonymous lAfk9gNPNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Deficiency DiseasesDocument2 pagesCarbohydrate Deficiency DiseasesMesoma100% (10)
- Penelitian Epidemiologi Untuk Program Pencegahan Kanker ServiksDocument73 pagesPenelitian Epidemiologi Untuk Program Pencegahan Kanker ServiksIndonesian Journal of Cancer100% (1)
- Essay FinalDocument4 pagesEssay FinalKalpanaNo ratings yet
- Skill 11 (1) ..Collection of Stool SpecimenDocument1 pageSkill 11 (1) ..Collection of Stool SpecimennetsquadNo ratings yet
- Orthodontic ApplianceDocument81 pagesOrthodontic AppliancemustahsinNo ratings yet