0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 viewsWhat Is Solar System
What Is Solar System
Uploaded by
Anonymous Clyy9NThe Solar System consists of the Sun and everything that orbits it, including 8 planets that orbit directly as well as smaller objects like dwarf planets, asteroids, and comets. It formed 4.6 billion years ago from the collapse of a giant molecular cloud. The vast majority of its mass is contained in the Sun and Jupiter. The inner terrestrial planets are rocky, while the outer gas giants are massive and composed of hydrogen and helium or ices. The Solar System also contains regions populated by smaller objects like the asteroid belt and Kuiper Belt.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
What Is Solar System
What Is Solar System
Uploaded by
Anonymous Clyy9N0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views3 pagesThe Solar System consists of the Sun and everything that orbits it, including 8 planets that orbit directly as well as smaller objects like dwarf planets, asteroids, and comets. It formed 4.6 billion years ago from the collapse of a giant molecular cloud. The vast majority of its mass is contained in the Sun and Jupiter. The inner terrestrial planets are rocky, while the outer gas giants are massive and composed of hydrogen and helium or ices. The Solar System also contains regions populated by smaller objects like the asteroid belt and Kuiper Belt.
Original Description:
sfdsg
Original Title
What is Solar System
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
The Solar System consists of the Sun and everything that orbits it, including 8 planets that orbit directly as well as smaller objects like dwarf planets, asteroids, and comets. It formed 4.6 billion years ago from the collapse of a giant molecular cloud. The vast majority of its mass is contained in the Sun and Jupiter. The inner terrestrial planets are rocky, while the outer gas giants are massive and composed of hydrogen and helium or ices. The Solar System also contains regions populated by smaller objects like the asteroid belt and Kuiper Belt.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views3 pagesWhat Is Solar System
What Is Solar System
Uploaded by
Anonymous Clyy9NThe Solar System consists of the Sun and everything that orbits it, including 8 planets that orbit directly as well as smaller objects like dwarf planets, asteroids, and comets. It formed 4.6 billion years ago from the collapse of a giant molecular cloud. The vast majority of its mass is contained in the Sun and Jupiter. The inner terrestrial planets are rocky, while the outer gas giants are massive and composed of hydrogen and helium or ices. The Solar System also contains regions populated by smaller objects like the asteroid belt and Kuiper Belt.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
This article is about the Sun and its planetary system.
For other similar systems, see Star system
and Planetary system.
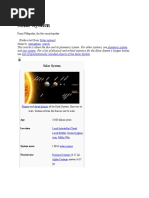
Solar System
The Sun and planets of the Solar System. Sizes but
not distances are to scale.
Age 4.568 billion years
Location
Local Interstellar
Cloud, Local Bubble,
OrionCygnus Arm,
Milky Way
System mass 1.0014 Solar masses
Nearest star
Proxima
Centauri (4.22 ly)
Alpha Centauri
system (4.37 ly)
Nearest known
planetary system
Alpha Centauri system (4.37
ly)
Planetary system
Semi-major axis of
outer planet
(Neptune)
30.10 AU (4.503 billion km)
Distance to Kuiper
cliff
50 AU
Populations
Stars 1 (Sun)
Planets
8 (Mercury
Venus
Earth
Mars
Jupiter
Saturn
Uranus
Neptune)
Known dwarf
planets
Possibly several hundred;
[1]
five currently recognized by
the IAU
(Ceres
Pluto
Haumea
Makemake
Eris)
Known natural
satellites
427
(170 planetary
[2]
257 minor planetary
[3]
)
Known minor
planets
644,275 (as of 2014-06-18)
[4]
Known comets 3,272 (as of 2014-06-18)
[4]
Identified rounded
satellites
19
Orbit about Galactic Center
Invariable-to-
galactic plane
inclination
60.198 (ecliptic)
Distance to Galactic
Center
27,000 1,000 ly
Orbital speed 220 km/s
Orbital period 225250 Myr
Star-related properties
Spectral type G2V
Frost line 5 AU
[5]
Distance to
heliopause
120 AU
Hill sphere radius 12 ly
The Solar System
[a]
comprises the Sun and the objects that orbit it, whether they orbit it directly
or by orbiting other objects that orbit it directly.
[b]
Of those objects that orbit the Sun directly, the
largest eight are the planets
[c]
that form the planetary system around it, while the remainder are
significantly smaller objects, such as dwarf planets and small Solar System bodies (SSSBs) such
as comets and asteroids.
[d]
The Solar System formed 4.6 billion years ago from the gravitational collapse of a giant
molecular cloud. The vast majority of the system's mass is in the Sun, with most of the remaining
mass contained in Jupiter. The four smaller inner planets, Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars, also
called the terrestrial planets, are primarily composed of rock and metal. The four outer planets,
called the gas giants, are substantially more massive than the terrestrials. The two largest, Jupiter
and Saturn, are composed mainly of hydrogen and helium; the two outermost planets, Uranus
and Neptune, are composed largely of substances with relatively high melting points (compared
with hydrogen and helium), called ices, such as water, ammonia and methane, and are often
referred to separately as "ice giants". All planets have almost circular orbits that lie within a
nearly flat disc called the ecliptic plane.
The Solar System also contains regions populated by smaller objects.
[d]
The asteroid belt, which
lies between Mars and Jupiter, mostly contains objects composed, like the terrestrial planets, of
rock and metal. Beyond Neptune's orbit lie the Kuiper belt and scattered disc, linked populations
of trans-Neptunian objects composed mostly of ices. Within these populations are several dozen
to more than ten thousand objects that may be large enough to have been rounded by their own
gravity.
[10]
Such objects are referred to as dwarf planets. Identified dwarf planets include the
asteroid Ceres and the trans-Neptunian objects Pluto and Eris.
[d]
In addition to these two regions,
various other small-body populations, including comets, centaurs and interplanetary dust, freely
travel between regions. Six of the planets, at least three of the dwarf planets, and many of the
smaller bodies are orbited by natural satellites,
[e]
usually termed "moons" after Earth's Moon.
Each of the outer planets is encircled by planetary rings of dust and other small objects.
The solar wind, a flow of plasma from the Sun, creates a bubble in the interstellar medium
known as the heliosphere, which extends out to the edge of the scattered disc. The Oort cloud,
which is believed to be the source for long-period comets, may also exist at a distance roughly a
thousand times further than the heliosphere. The heliopause is the point at which pressure from
the solar wind is equal to the opposing pressure of interstellar wind. The Solar System is located
in the Orion Arm, 26,000 light years from the center of the Milky Way.
You might also like
- Development of An Automated Impact Hammer For Modal Analysis of StructuresDocument33 pagesDevelopment of An Automated Impact Hammer For Modal Analysis of StructuresAnonymous Clyy9NNo ratings yet
- Kolob, The God StarDocument7 pagesKolob, The God StarAnthony E. Larson100% (2)
- Dane Rudhyar - Astrological TimingDocument77 pagesDane Rudhyar - Astrological Timingbosiok100% (3)
- Solar System: This Article Is About The Sun and Its Planetary System. For Other Systems, See andDocument5 pagesSolar System: This Article Is About The Sun and Its Planetary System. For Other Systems, See andDavy Jones Carausos RosellasNo ratings yet
- Solar System Navigation SearchDocument4 pagesSolar System Navigation Searchsumit guptaNo ratings yet
- Coleen MoreteDocument3 pagesColeen MoreteZie BeaNo ratings yet
- Solar SystemDocument12 pagesSolar SystemDeepak Lohar DLNo ratings yet
- Solar SystemDocument2 pagesSolar SystemSheetal ThoratNo ratings yet
- Solar System - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument24 pagesSolar System - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaAriana BalidoyNo ratings yet
- Objects in The Solar SystemDocument16 pagesObjects in The Solar Systemscribd_sandeepNo ratings yet
- Planets Pt. 10Document5 pagesPlanets Pt. 10jpbalganion.fo2No ratings yet
- Solar System WikipediaDocument23 pagesSolar System WikipediamexcesNo ratings yet
- Planet 1Document7 pagesPlanet 1anwarNo ratings yet
- Universe and Solar System: GalaxyDocument6 pagesUniverse and Solar System: GalaxyGoutham ReddyNo ratings yet
- Solar SystemDocument5 pagesSolar SystemUNLA LA CORPORATIONNo ratings yet
- Solar SystemDocument47 pagesSolar SystemHarvey Villalobos100% (1)
- L-7 Solar SystemDocument5 pagesL-7 Solar SystemKhushi KotwaniNo ratings yet
- ASTRONOMYDocument18 pagesASTRONOMYrafihaaliu53No ratings yet
- AstronomyDocument3 pagesAstronomyStanleyNo ratings yet
- Planet Earth: Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune Mercury Mars VenusDocument2 pagesPlanet Earth: Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune Mercury Mars VenusMa Carlyn TerragoNo ratings yet
- Discussion About Solar SystemDocument8 pagesDiscussion About Solar SystemSancia JacintoNo ratings yet
- PlanetiaDocument49 pagesPlanetiahapiy50714No ratings yet
- The Solar SystemDocument4 pagesThe Solar SystemClaudine Manuel LibunaoNo ratings yet
- Planetary Science (Middle School) by NThomasDocument2 pagesPlanetary Science (Middle School) by NThomasNatalia TNo ratings yet
- Solar SystemDocument2 pagesSolar SystemKylliíanNo ratings yet
- Solar System - by Diffit (Printable)Document4 pagesSolar System - by Diffit (Printable)Linda HongNo ratings yet
- What Is The Solar SystemDocument4 pagesWhat Is The Solar SystemGRascia OnaNo ratings yet
- Solar System Facts - A Guide To Things Orbiting Our SunDocument12 pagesSolar System Facts - A Guide To Things Orbiting Our SunSrushti SawantNo ratings yet
- Our Solar SystemDocument50 pagesOur Solar SystemKashish GuptaNo ratings yet
- PlanetsDocument123 pagesPlanetsJam Uly GastyNo ratings yet
- GeographyDocument10 pagesGeographyhurairaNo ratings yet
- Igcse (9 - 1) Physics Unit 8: AstrophysicsDocument17 pagesIgcse (9 - 1) Physics Unit 8: AstrophysicsDraugerPlayzNo ratings yet
- MMP42Document3 pagesMMP42jafasoh293No ratings yet
- Unit Six 6. The Solar System 6.1. Family of The Solar System The Solar SystemDocument10 pagesUnit Six 6. The Solar System 6.1. Family of The Solar System The Solar Systemtsehay asratNo ratings yet
- Dwarf PlanetsDocument13 pagesDwarf PlanetsZiela RazalliNo ratings yet
- There Are Eight Planets in The Solar SystemDocument2 pagesThere Are Eight Planets in The Solar SystemVivialyn YumulNo ratings yet
- PlanetsDocument7 pagesPlanetsjpbalganion.fo2No ratings yet
- TOEFL iBT ReadingDocument5 pagesTOEFL iBT ReadingElisa RosasNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Geology PDFDocument15 pagesModule 1 Geology PDFARGENE CAHINDENo ratings yet
- CMP41Document2 pagesCMP41jafasoh293No ratings yet
- Nakshatras 20-12-15Document36 pagesNakshatras 20-12-15shunmugathasonNo ratings yet
- RGRFVFDocument6 pagesRGRFVFMega ShowsNo ratings yet
- GeographyDocument4 pagesGeographyAnu GangeleNo ratings yet
- Solar System in Depth 1Document4 pagesSolar System in Depth 1Vinayak rashinkarNo ratings yet
- Solar SystemDocument26 pagesSolar SystemyanjunNo ratings yet
- How Planets Are ClassifiedDocument4 pagesHow Planets Are ClassifiedEl LlacunaNo ratings yet
- MMP41Document3 pagesMMP41jafasoh293No ratings yet
- NHFTGBRTDocument6 pagesNHFTGBRTMega ShowsNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Geology AssignmentDocument52 pagesEarth Science Geology AssignmentChristine MaeNo ratings yet
- Space PhysicsDocument27 pagesSpace PhysicsNethil dulmiraNo ratings yet
- Solar SystemDocument21 pagesSolar Systemmystie100% (1)
- The Solar System Is A Vast System That Consists of The SunDocument2 pagesThe Solar System Is A Vast System That Consists of The Sunshubh cards bhilwara Wedding cardsNo ratings yet
- Space ScienceDocument4 pagesSpace ScienceVerendraNo ratings yet
- The Solar SystemDocument28 pagesThe Solar SystemkiluNo ratings yet
- The Moon Is The EarthDocument2 pagesThe Moon Is The EarthNilda AdadNo ratings yet
- Answer SheetDocument2 pagesAnswer Sheetapi-240302279No ratings yet
- Facts About Solar System: Matthew E. Balatero Grade-IVDocument1 pageFacts About Solar System: Matthew E. Balatero Grade-IVGi SelleNo ratings yet
- Sistema SolarDocument2 pagesSistema SolarMejía Guzmán Fernanda SofíaNo ratings yet
- PlanetsDocument2 pagesPlanetsbliadzeirakli19No ratings yet
- Planets ResearchDocument6 pagesPlanets Researchnghabaotran88No ratings yet
- Solar System: Physical ScienceDocument9 pagesSolar System: Physical ScienceIrene JavierNo ratings yet
- FABRICATION OF AUTO ROTATING SOLAR PANEL 1st REVIEWDocument13 pagesFABRICATION OF AUTO ROTATING SOLAR PANEL 1st REVIEWAnonymous Clyy9NNo ratings yet
- FABRICATION OF PROPELLER SHAFT BICYCLE - 1st REVIEWDocument14 pagesFABRICATION OF PROPELLER SHAFT BICYCLE - 1st REVIEWAnonymous Clyy9NNo ratings yet
- FABRICATION OF BIO GAS PRODUCTION IN COLLEGE CANTEEN WASTE 1st REVIEWDocument13 pagesFABRICATION OF BIO GAS PRODUCTION IN COLLEGE CANTEEN WASTE 1st REVIEWAnonymous Clyy9NNo ratings yet
- FABRICATION OF SOLAR THERMAL BATTERY WATER DISTILLATION IN SALT WATER 2nd REVIEWDocument14 pagesFABRICATION OF SOLAR THERMAL BATTERY WATER DISTILLATION IN SALT WATER 2nd REVIEWAnonymous Clyy9NNo ratings yet
- Fabrication of Concentric Tube Heat Exchanger 1ST ReviewDocument14 pagesFabrication of Concentric Tube Heat Exchanger 1ST ReviewAnonymous Clyy9NNo ratings yet
- Finger Print Based Door Locking System - 1ST ReviewDocument15 pagesFinger Print Based Door Locking System - 1ST ReviewAnonymous Clyy9NNo ratings yet
- Coin Based Mobile Phone Charging System-ReviewDocument15 pagesCoin Based Mobile Phone Charging System-ReviewAnonymous Clyy9NNo ratings yet
- Arrangement of Evaporator Body - 09.02.2020 (Elevation) PDFDocument1 pageArrangement of Evaporator Body - 09.02.2020 (Elevation) PDFAnonymous Clyy9NNo ratings yet
- 10.FABRICATION OF GEO THERMAL HEATING AND COOLING SYSTEM 1st REVIEWDocument13 pages10.FABRICATION OF GEO THERMAL HEATING AND COOLING SYSTEM 1st REVIEWAnonymous Clyy9NNo ratings yet
- Lab ViewDocument4 pagesLab ViewAnonymous Clyy9NNo ratings yet
- Design and Fabrication of Leaf JigDocument9 pagesDesign and Fabrication of Leaf JigAnonymous Clyy9NNo ratings yet
- Arrangement of Evaporator Body - 09.02.2020 (Elevation) PDFDocument1 pageArrangement of Evaporator Body - 09.02.2020 (Elevation) PDFAnonymous Clyy9NNo ratings yet
- Remote Control Based Ac or DC Motor Speed Control System - 1ST ReviewDocument15 pagesRemote Control Based Ac or DC Motor Speed Control System - 1ST ReviewAnonymous Clyy9NNo ratings yet
- Fabrication of Wire Pealing Machine - SynopsisDocument2 pagesFabrication of Wire Pealing Machine - SynopsisAnonymous Clyy9NNo ratings yet
- SPT Attach MagDocument6 pagesSPT Attach MagAnonymous Clyy9NNo ratings yet
- Proposed Plan For Mr.K.GanaprakashamDocument1 pageProposed Plan For Mr.K.GanaprakashamAnonymous Clyy9NNo ratings yet
- Review On Fabrication of 3 Axis Spray Painting Machine Ijariie1981Document4 pagesReview On Fabrication of 3 Axis Spray Painting Machine Ijariie1981Anonymous Clyy9N100% (1)
- Variable Speed Drilling Machine Without Gearbox - AbstractDocument1 pageVariable Speed Drilling Machine Without Gearbox - AbstractAnonymous Clyy9NNo ratings yet
- Design and Fabrication of Vehicles Multi Wheel Nuts Tightner and RemoverDocument6 pagesDesign and Fabrication of Vehicles Multi Wheel Nuts Tightner and RemoverAnonymous Clyy9N100% (1)
- Asderrfuwdbc DFDCDDocument10 pagesAsderrfuwdbc DFDCDAnonymous Clyy9NNo ratings yet
- .Fabrication of Solar Air Cooler For Remote AreaDocument4 pages.Fabrication of Solar Air Cooler For Remote AreaAnonymous Clyy9NNo ratings yet
- Wear Testing of High-Alloy Carbon Steel Used in Mining ToolsDocument24 pagesWear Testing of High-Alloy Carbon Steel Used in Mining ToolsAnonymous Clyy9NNo ratings yet
- Design On Automatic Spraying Robot System Based On PC-PLC Network ControlDocument6 pagesDesign On Automatic Spraying Robot System Based On PC-PLC Network ControlAnonymous Clyy9NNo ratings yet
- D048021032 PDFDocument12 pagesD048021032 PDFAnonymous Clyy9NNo ratings yet
- Gears & Gear Manufacturing: Training ObjectiveDocument5 pagesGears & Gear Manufacturing: Training ObjectiveAnonymous Clyy9NNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Ansys SoftwareDocument49 pagesIntroduction To Ansys SoftwareAnonymous Clyy9NNo ratings yet
- Horton Hears A Who - PhilosophyDocument1 pageHorton Hears A Who - PhilosophyLove, Dream, HappinessNo ratings yet
- BaazigarDocument44 pagesBaazigarujjwal6396No ratings yet
- Marana Karaka SthanaDocument18 pagesMarana Karaka Sthanadavis mathewNo ratings yet
- AFERADocument19 pagesAFERAnedalinaNo ratings yet
- Formation of The Solar SystemDocument29 pagesFormation of The Solar SystemDarwin ValdezNo ratings yet
- Literary DevicesDocument97 pagesLiterary DevicesshypamaloyNo ratings yet
- Fix - Soal Lun Kelas Ix Pilihan GandaDocument4 pagesFix - Soal Lun Kelas Ix Pilihan GandaRida IllahiNo ratings yet
- Earth Moon Sun RelationshipDocument12 pagesEarth Moon Sun RelationshipMichelle Raquil100% (1)
- 200 More Puzzling Physics-AprofundamentoDocument21 pages200 More Puzzling Physics-AprofundamentoPaulo CesarNo ratings yet
- Brandi Jones-5e-Lesson-Plan 2Document3 pagesBrandi Jones-5e-Lesson-Plan 2api-491136095No ratings yet
- Space Physics: 6.1 Earth and The Solar System The EarthDocument4 pagesSpace Physics: 6.1 Earth and The Solar System The EarthRaahilNo ratings yet
- Korean Cottagecore Aesthetic MK CampaignDocument55 pagesKorean Cottagecore Aesthetic MK CampaignAline HerreraNo ratings yet
- Plotting Log Graphs of Planetary PatternsDocument11 pagesPlotting Log Graphs of Planetary Patternsavishik15No ratings yet
- Mars Habitation ColonyDocument213 pagesMars Habitation Colonycoolmania2k11100% (2)
- Earliest Cosmo Log 00 WarrDocument234 pagesEarliest Cosmo Log 00 WarrMarkus GrimmNo ratings yet
- Latihan PAS Kelas 6 Bahasa Inngris Semester 2Document4 pagesLatihan PAS Kelas 6 Bahasa Inngris Semester 2Prilia MaharaniNo ratings yet
- 5.2 (Gravity and Satellites)Document31 pages5.2 (Gravity and Satellites)mzsyedNo ratings yet
- The Earth in The Solar SystemDocument13 pagesThe Earth in The Solar SystemAyush BansalNo ratings yet
- NSTSE Power PackDocument10 pagesNSTSE Power Packpiyushprajapati0iyNo ratings yet
- Assess-Limitations of ModelsDocument2 pagesAssess-Limitations of Modelsmariella94No ratings yet
- Video Game Pitch Deck by SlidesgoDocument26 pagesVideo Game Pitch Deck by SlidesgoJunaid IqbalNo ratings yet
- Planets of Solar SystemDocument2 pagesPlanets of Solar SystemAhmad QureshiNo ratings yet
- Uranus, Neptune & PlutoDocument31 pagesUranus, Neptune & Plutozmajchek95% (19)
- The Nature of The True Religious Life - SWAMI KRISHNANANDADocument257 pagesThe Nature of The True Religious Life - SWAMI KRISHNANANDAvpharsora4205100% (1)
- Science Nat Parallel Test2Document11 pagesScience Nat Parallel Test2Kristine BarredoNo ratings yet
- Shadow Stick Astronomy CourseworkDocument6 pagesShadow Stick Astronomy Courseworkafiwjsazh100% (2)
- Space (Part 1)Document33 pagesSpace (Part 1)Murugan.SubramaniNo ratings yet
- Jstor Research PaperDocument10 pagesJstor Research Paperv devNo ratings yet