0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
47 viewsHoliday Shipping Wars
Holiday Shipping Wars
Uploaded by
Rajat RameshThis document discusses holiday shipping wars in India. It explains that with many festivals come many holidays in India, which are seen as opportunities by both buyers and sellers. This leads to "shipping wars" as companies try to fulfill increased demand for deliveries during holidays. Successful delivery is important to keep customers satisfied and meet commitments. The document outlines strategies that online retailers like Amazon and Flipkart use to improve their delivery performance during peak holiday periods through careful planning and monitoring of inventory, sales, and customer requirements.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Holiday Shipping Wars
Holiday Shipping Wars
Uploaded by
Rajat Ramesh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
47 views8 pagesThis document discusses holiday shipping wars in India. It explains that with many festivals come many holidays in India, which are seen as opportunities by both buyers and sellers. This leads to "shipping wars" as companies try to fulfill increased demand for deliveries during holidays. Successful delivery is important to keep customers satisfied and meet commitments. The document outlines strategies that online retailers like Amazon and Flipkart use to improve their delivery performance during peak holiday periods through careful planning and monitoring of inventory, sales, and customer requirements.
Original Description:
article
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
This document discusses holiday shipping wars in India. It explains that with many festivals come many holidays in India, which are seen as opportunities by both buyers and sellers. This leads to "shipping wars" as companies try to fulfill increased demand for deliveries during holidays. Successful delivery is important to keep customers satisfied and meet commitments. The document outlines strategies that online retailers like Amazon and Flipkart use to improve their delivery performance during peak holiday periods through careful planning and monitoring of inventory, sales, and customer requirements.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
47 views8 pagesHoliday Shipping Wars
Holiday Shipping Wars
Uploaded by
Rajat RameshThis document discusses holiday shipping wars in India. It explains that with many festivals come many holidays in India, which are seen as opportunities by both buyers and sellers. This leads to "shipping wars" as companies try to fulfill increased demand for deliveries during holidays. Successful delivery is important to keep customers satisfied and meet commitments. The document outlines strategies that online retailers like Amazon and Flipkart use to improve their delivery performance during peak holiday periods through careful planning and monitoring of inventory, sales, and customer requirements.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 8
PART-A
HOLIDAY SHIPPING WARS: COMMIT WITH CONFIDENCE
India is a country with a diversified population and a place where one could find a plethora of cultures.
With such a wide range of cultures come a wide range of festivals. But festivals means holidays! But
being in India, we get holidays for every festival. Every holiday is looked at as an opportunity from both,
the buyers as well as the sellers point of view. This leads to something which occurs
frequently.Shipping wars.
Before I proceed, it is important to lucidly understand the termShipping Wars. In a laymans language,
shipping wars means, literally, the wars that occur during the delivery of products. But, in a more
technical point of view, holiday shipping wars is a part of the supply chain management. Once upon a
time, shipping was viewed as a perk, but now its viewed as a requirement. Since the time shopping has
gone online, this concept has been even more talked about. The reason for this is that one part of sales
is to first come up with a concept but the other, and the more important part would be to live up to the
concept also to keep improvising them.
So what exactly is the war all about? In the simplest of terms, dont keep a kid waiting with empty socks
during Christmas when you have promised that it wouldnt be empty. Thats the reason why the term
commit with confidence is used. One first needs to set specific targets. But, he/she must also know
how to deliver when it matters.
Fig.1. Sales during holidays
Source: compete.com
Several corporate have come up with their online shipping facilities like PayPal, by Ebay, ShopRunner,
FlipKart.com, Amazon Prime etc. It is important to understand why and how these came up. Just a few
years ago, customers were apprehensive of online shipping as they were worried about the quality of
the products delivered and also the costs for shipping. However, times have drastically changed in the
last 5 years or so. The percentage of holiday shoppers who plan to shop online this year is expected to
reach almost 60% this year. Hence, to attack this segment of buyers requires careful strategy and
meticulous planning. The reason why planning becomes very important is that once the number of users
increase, the process of providing service also becomes increasingly complex. One needs to keep an
account of the stocks available and also keep a check of requirements. That is the reason why one needs
to commit with confidence. Setting realistic targets becomes vital here and estimating the number of
buyers becomes even more important. Hence, many organizations are aiming at bettering their
performances by spending more on Sales and Operations Planning.
Fig 2: Holiday Budget
Source: tomsnewsletter.com
This was meant to get different stakeholders of an enterprise on the same front, which is still vital, but
the new norm is the timely and systemic involvement of the trading partners like the distributors,
customers, suppliers in this process as they have an important impact on the ability to execute to
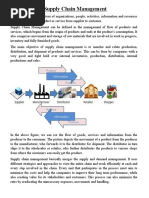
achieve the operational, commercial, and ultimately, the financial plan. The supply chain is nothing but
the movement of a product from the supplier to the consumer. The basic objective of a supply chain is
optimization of the chain in itself, thus making the process a better one. The Sales and Operations
Planning process and the integration of supply chain planning across the company were concurrently
the largest single opportunity for improvement. From the graph shown, we can clearly infer that sales
certainly depend a lot on the time of the selling.
Shipping in the real world scenario (not online) is probably a more arduous task as there is a direct
interaction with clients and to meet customer satisfaction is a huge challenge in itself. To come up with
specific plans might be a bad idea at times as flexibility is vital here. In India, electronics sell like hot
cakes in the festival season as the prices and offers are certainly more attractive. In fact, the system has
almost transformed into one in which both, the buyers as well as sellers wait for the festive season.
Hence, as a conclusion, one would say that there are two sides to the entire situation-one at the
supplier side and the other at the customer side. However, the suppliers performance is what finally
matters. The ability to sell a product strategically is extremely important. The holiday season just acts as
an opportunity to strike the iron when it is hot. But careful planning is required before the striking as the
process is difficult in itself. To be able to deliver and keep up promises and value orders is something not
every organization can achieve easily. So, the situation is nothing less than a war where confidence is
required before actually committing.
PART-C
1. LEAD TIME: It is the time required to meet a customers demand.
2. LITTLES LAW: It is the rate of inventory for a given flow time.
3. MUDA: It is the waste that is generated during the production and needs to be minimized
4. QUEUING: It is nothing but the formation of lines. It also deals with the formation and the variation of
the queues.
5. OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT: It refers to the coordination of business practices and has the objective
of creating the highest level of efficiency possible within an organization.
6. BLUE SKY: It refers to the goodwill associated with an asset of a company.
7. EBITDA: Earnings before taxes, depreciation etc
8. FILL RATE: Fraction of total demand satisfied by inventory on hand.
9. Labor productivity: The average output of each worker over a period of time - Current output /
number of workers
10. Merger: The joining of two businesses to create a new organization
11. Economies of scale: The reduction in average cost per unit
12. CRITICAL PATH: It is the path through an activity that has the longest flow time.
13. Subcontracting: Using the resources of another organization, or letting out the business's resources in
order to increase efficiency
14. FLOW SHOP: A flow shop is nothing but an operation which produces products in a continuous flow.
15. Overtime: Staff working beyond their contracted hours in exchange for a higher hourly wage
16. Total Quality Management: It is the approach to quality that aims to involve all employees in the
quality improvement process
17. Kaizen groups: They are formed to encourage new ideas from all workers as part of a continuous
improvement strategy
18. Downtime: It is the period when machinery is not being used. This could be either as a result of
maintenance or when parts of the machinery have to be adapted to produce a slightly different unit of
production
19. Supply chain: It is the chain where all the stages in the production process from obtaining raw
materials to selling to the consumer - from point of origin to point of consumption
20. Stock: It is nothing but the stored materials such as raw materials, work in progress or finished goods
21. Quality product: It is the product or service that meets customer' expectations
22. Quality control: It is the inspection of products to check they meet necessary standards.
23. Job production: It is the manufacture of one-off goods tailor made to meet the specifications
customers.
24. Ombudsmen: They are independent organizations that police specific industries and investigate
complaints on behalf of customers
25. Warranties: It Similar to a guarantee, but normally the customer pays for the extra protection. They
are1 often known as extended warranties or insurance policies against repair and replacement costs
26. Guarantees: It is the official reassurance given free of charge by the manufacturer of a product to the
customer that if the product proves faulty within a specified period their money will be refunded.
27. Operational targets: Specific and measurable objectives set for each operations activity of a business
28. Sustainability: Sustainability is defined as the production systems that prevent waste by using the
minimum of non-renewable resources so that levels of production can be sustained in the future
29. Outsource: The contracting of an outside organization to provide a product or service that might be
too expensive, complicated or time-consuming for the business to do itself
30. Job production: The manufacture of one-off goods tailor made to meet the specifications of the
customer.
31. Rationalization: Reorganizing a business to reduce capacity and increase efficiency
32. Capital intensive
High proportion of capital (machinery) compared to labor
33. Labor intensive
When there is a high proportion of labor compared to capital
34. Flow/Mass production
It is the continuous movement of items through each stage of production
35. Batch production
It is the manufacturing of groups of products to meet a specific order. The products will move through the
stages of production at the same time.
36. Capacity: It is the maximum possible output that can be produced with the given resources
37. Capacity management
It refers to the planning and controlling the capacity of an organization to meet the demands of customers
38. Capacity utilization
The proportion of capacity used over a period of time: Current output / Maximum output x 100
39. Diseconomies of scale
Increase in average cost per unit
40. Unit cost
Average cost per unit of output:
41. Unit labor cost
The cost of labor needed to produce one unit of output
42. Efficiency
It is defined as the making the most of resources by maximizing the output from a given level of inputs.
Labor efficiency is output per worker.
43. Buffer stock
Stock kept in order that production can be increased to meet unexpected demand
44. Opportunity cost
The benefit lost from the next best alternative foregone.
45. Stock-out costs
It is the cost of lost production, lost sales and customer dissatisfaction when the business runs out of stock
46. Total Quality Management
It is an approach to quality that aims to involve all employees in the quality improvement process
47. Minimum efficient scale
The smallest output that a business can produce while making sure that its average costs are minimized
48. External growth
It is the expansion achieved through buying or merging with another business
49. Unit labor cost
It is the cost of labor needed to produce one unit of output
50. ISO 9000/9001
It is the internationally recognized certificate that acknowledges the existence of a quality procedure that
meets certain conditions
1.
You might also like
- Nissan Case StudyDocument11 pagesNissan Case Studysatishkamath33% (3)
- Wisdom of SolomonDocument47 pagesWisdom of Solomonesemilenio7693100% (7)
- Porter Diamond Theory On ChinaDocument5 pagesPorter Diamond Theory On Chinagauravbansall56760% (5)
- Module No. 1 - Introduction To Materials ManagementDocument32 pagesModule No. 1 - Introduction To Materials Managementgarciajeremiah070No ratings yet
- Materials Management - Ch1Document26 pagesMaterials Management - Ch1Rdon KhalidNo ratings yet
- SCM 301Document10 pagesSCM 301Manda simzNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Management - PresentationDocument6 pagesSupply Chain Management - Presentationjohnliston758No ratings yet
- Belen-Materials Management MidtermsDocument13 pagesBelen-Materials Management MidtermsChristian BelenNo ratings yet
- Department of CSE MG2452-Engineering Economics & Financial AccountingDocument5 pagesDepartment of CSE MG2452-Engineering Economics & Financial AccountingsridharanchandranNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Supply Chain ManagementDocument9 pagesChapter 10 Supply Chain ManagementarantonizhaNo ratings yet
- Materials ManagementDocument75 pagesMaterials Management22-33462No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 SCMDocument6 pagesChapter 2 SCMHM-1E Doroteo,MalvenNo ratings yet
- Production and Operation ManagementDocument8 pagesProduction and Operation ManagementBavya RajNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain ManagementDocument28 pagesSupply Chain ManagementCrispin MponjiNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Good and ServicesDocument9 pagesDifference Between Good and ServicesMahmudul HasanNo ratings yet
- Question 1. Outline Main Benefits of Supply Chain ManagementDocument5 pagesQuestion 1. Outline Main Benefits of Supply Chain ManagementMuhammad ZubairNo ratings yet
- Reporting ManagmentDocument12 pagesReporting ManagmentTuseef AhmedNo ratings yet
- Dbs PurchasingDocument67 pagesDbs PurchasingBenjamin Adelwini BugriNo ratings yet
- Jacobs2ce ISM Ch13Document11 pagesJacobs2ce ISM Ch13Fernando D'OriaNo ratings yet
- 24 72783errDocument2 pages24 72783errladu johnNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER-2 Supply ChainDocument16 pagesCHAPTER-2 Supply ChainChristian Steve TerencioNo ratings yet
- Supply-Chain Strateries: Suppliers Become Part of A Company CoalitionDocument4 pagesSupply-Chain Strateries: Suppliers Become Part of A Company CoalitionJezza Mae Gomba RegidorNo ratings yet
- C1 QDocument10 pagesC1 QTrang HoàngNo ratings yet
- SC MGT - Supply Chain Management in Hospitality Industry (PRELIM NOTES)Document13 pagesSC MGT - Supply Chain Management in Hospitality Industry (PRELIM NOTES)chloekent loreNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Notes - SCMDocument14 pagesChapter 3 Notes - SCMskill share premiumNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Operations and Supply Chain ManagemetDocument6 pagesChapter 10 Operations and Supply Chain ManagemetArturo QuiñonesNo ratings yet
- Report in Production ManagementDocument6 pagesReport in Production ManagementNheil Coping BeteNo ratings yet
- VMI in Apparel Manufacturing: Concept Note: 1Document6 pagesVMI in Apparel Manufacturing: Concept Note: 1Priyanka JanaNo ratings yet
- Om CH-2Document9 pagesOm CH-2Asiya HeyredinNo ratings yet
- Introduction To SCMDocument14 pagesIntroduction To SCMmridulchandraNo ratings yet
- SCM NotesDocument166 pagesSCM Notesnandini_mba4870100% (1)
- Capitolul 1Document89 pagesCapitolul 1lory172002No ratings yet
- Let's Know What Supply Chain IsDocument8 pagesLet's Know What Supply Chain IsRafia TasnimNo ratings yet
- Operations Management: Individual Assignment (20%)Document7 pagesOperations Management: Individual Assignment (20%)AddiNo ratings yet
- FM - UNIT 5Document3 pagesFM - UNIT 5swarajchhakkarNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Management Definition Scope and Risks - Dem - Ramos Unciano KristineDocument20 pagesSupply Chain Management Definition Scope and Risks - Dem - Ramos Unciano Kristinealan nebridaNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain TerminologyDocument5 pagesSupply Chain TerminologyMehroz KhanNo ratings yet
- Operations ManagementDocument6 pagesOperations ManagementAllen DimaculanganNo ratings yet
- Om 2022Document61 pagesOm 2022Rana SabryNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 SCMDocument93 pagesUnit 2 SCMsiddardhakvcNo ratings yet
- 2013duplex Flashcards Mod1Document28 pages2013duplex Flashcards Mod1moh247No ratings yet
- Guía de Administración de prodNOTASDocument13 pagesGuía de Administración de prodNOTASerikatri366No ratings yet
- Unidad IV Supplier Certification and DevelopmentDocument12 pagesUnidad IV Supplier Certification and DevelopmentCaptian BenettsNo ratings yet
- Industrial Operational ManagementDocument11 pagesIndustrial Operational ManagementAbu Al SaidNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Application of Lean Concept in Retail StoreDocument11 pagesThe Effects of Application of Lean Concept in Retail StoredrustagiNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Chapter No 2Document8 pagesSupply Chain Chapter No 2Simra SalmanNo ratings yet
- Life Cycle CostingDocument10 pagesLife Cycle Costingvicent laurianNo ratings yet
- TOMstudyDocument5 pagesTOMstudyImFree OfDebtNo ratings yet
- IBM Used Backward Placement To Improve Supply-Chain OperationsDocument16 pagesIBM Used Backward Placement To Improve Supply-Chain OperationsjonathanguntaraNo ratings yet
- Distribution & Logistics Management V3Document5 pagesDistribution & Logistics Management V3solvedcareNo ratings yet
- BUSINESS STRATEGIESDocument6 pagesBUSINESS STRATEGIEShakdoghakdog84No ratings yet
- 2nd QuarterDocument11 pages2nd Quarterchanchanmendez5No ratings yet
- Supply Chain ManagementDocument38 pagesSupply Chain Managementharish chandra75% (4)
- Lean Accounting, Costs of Quality & Target Costing: Oleh: Suyanto, MBA., Dipl. ResDocument47 pagesLean Accounting, Costs of Quality & Target Costing: Oleh: Suyanto, MBA., Dipl. ResrikiNo ratings yet
- 40 Best Manufacturing KPIs and Metric Examples For 2024 ReportingDocument15 pages40 Best Manufacturing KPIs and Metric Examples For 2024 Reportingsunnysam.8419No ratings yet
- Notes of POM Module 1 PDFDocument22 pagesNotes of POM Module 1 PDFRiyaNo ratings yet
- Las Entrep Q1 W5Document8 pagesLas Entrep Q1 W5AILEEN FENELLERENo ratings yet
- Assembly Line BalancingDocument5 pagesAssembly Line BalancingRajat ArroraNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Management: Dhwani MishraDocument42 pagesSupply Chain Management: Dhwani MishraKshitij MathurNo ratings yet
- SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT AdjustmentsDocument39 pagesSUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT Adjustmentsallanmsu2013No ratings yet
- Manufacturing Wastes Stream: Toyota Production System Lean Principles and ValuesFrom EverandManufacturing Wastes Stream: Toyota Production System Lean Principles and ValuesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Chapter 03Document26 pagesChapter 03Rajat RameshNo ratings yet
- Sketchup User GuideDocument887 pagesSketchup User GuideAdrian BrownNo ratings yet
- Foundation Verification ProblemsDocument62 pagesFoundation Verification ProblemsRajat RameshNo ratings yet
- WebinarQ A RBSDesignDocument3 pagesWebinarQ A RBSDesignRajat RameshNo ratings yet
- Design of Two Way Slab FCK 20 Fy 415 SL No Slab No Load S Span L Span Ly/lx Short-1 Short-2 Long-1 Long-2 D Dia D MSX Msy Msxhog Msyhog Asx AsyDocument3 pagesDesign of Two Way Slab FCK 20 Fy 415 SL No Slab No Load S Span L Span Ly/lx Short-1 Short-2 Long-1 Long-2 D Dia D MSX Msy Msxhog Msyhog Asx AsyRajat RameshNo ratings yet
- Air Material Wing Savings and Loan Association, Inc. v. NLRC Case DigestDocument2 pagesAir Material Wing Savings and Loan Association, Inc. v. NLRC Case DigestJazzy AlimNo ratings yet
- GOPAL DAIRY PROJECT MBA Project Report Prince DudhatraDocument68 pagesGOPAL DAIRY PROJECT MBA Project Report Prince DudhatrapRiNcE DuDhAtRa86% (7)
- Thesis Topics in HRM PDFDocument7 pagesThesis Topics in HRM PDFdwf6nx2z100% (2)
- CBR Stories From AfricaDocument71 pagesCBR Stories From AfricaOlmedo Zambrano Cordovez100% (1)
- Divinagracia Miguel Adam BSTM 4DDocument2 pagesDivinagracia Miguel Adam BSTM 4DRoxanne S. AyubanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14Document14 pagesChapter 14Mohammad A AlbadawyNo ratings yet
- BDO Credit Card Application FormDocument3 pagesBDO Credit Card Application FormAnna Fritz Sandoval100% (1)
- Sample PDF of STD 11th Secretarial Practice Smart Notes Book Commerce Maharashtra BoardDocument24 pagesSample PDF of STD 11th Secretarial Practice Smart Notes Book Commerce Maharashtra BoardAbhishek PanditNo ratings yet
- Business Ethics & Human ValuesDocument6 pagesBusiness Ethics & Human ValuesVikyath Ajjampur ShetruNo ratings yet
- Types of InsuranceDocument4 pagesTypes of InsuranceWael LotfyNo ratings yet
- Managing Early Growth of The New VentureDocument24 pagesManaging Early Growth of The New VentureZaryab Qurashi Xabi100% (1)
- For DefenseDocument31 pagesFor DefenseAmen MartzNo ratings yet
- HFS PHILIPPINES, INC., G.R. No. 168716 Ruben T. Del Rosario and Ium Shipmanagement As, Petitioners, Ronaldo R. Pilar, Respondent. PromulgatedDocument8 pagesHFS PHILIPPINES, INC., G.R. No. 168716 Ruben T. Del Rosario and Ium Shipmanagement As, Petitioners, Ronaldo R. Pilar, Respondent. PromulgateddanexrainierNo ratings yet
- Form PSC 38Document6 pagesForm PSC 38Ngetich KiplangatNo ratings yet
- Recommendation Letters (2024)Document6 pagesRecommendation Letters (2024)Sangram S KarandeNo ratings yet
- Sacom Att: Project Officer Debby Chan P.O. Box No. 79583 Mongkok Post Office Hong Kong Coca-Cola Complies With Labor Laws and Regulations in ChinaDocument10 pagesSacom Att: Project Officer Debby Chan P.O. Box No. 79583 Mongkok Post Office Hong Kong Coca-Cola Complies With Labor Laws and Regulations in Chinaming2899No ratings yet
- Suggested Answers Self-Review Questions (Chapters 1 and 2 Hilton and Platt)Document5 pagesSuggested Answers Self-Review Questions (Chapters 1 and 2 Hilton and Platt)kokomama231No ratings yet
- PD 424Document3 pagesPD 424givemeasign24No ratings yet
- Why Women Leave JournalismDocument14 pagesWhy Women Leave JournalismTracy EverbachNo ratings yet
- Role of Msmes in Indian Economy: Mea Project ReportDocument15 pagesRole of Msmes in Indian Economy: Mea Project Reportnishant singhalNo ratings yet
- POP-MART-report-edited (lacks source - phần TA)Document20 pagesPOP-MART-report-edited (lacks source - phần TA)Bùi Ngọc Khánh LinhNo ratings yet
- BEGINO v. ABS-CBNDocument3 pagesBEGINO v. ABS-CBNNorberto Sarigumba IIINo ratings yet
- Keeping 'Endo' Alive: DOLE's Department Order No. 174: Campaign Promise To End "Endo"Document7 pagesKeeping 'Endo' Alive: DOLE's Department Order No. 174: Campaign Promise To End "Endo"Kyle BanceNo ratings yet
- Group 3 Resesarch Manuscript 3Document22 pagesGroup 3 Resesarch Manuscript 3Rhealyn GajustaNo ratings yet
- BFWM Report - 251058Document19 pagesBFWM Report - 251058Shivangi GargNo ratings yet
- Appointment Letter Cimarex Energy CoDocument2 pagesAppointment Letter Cimarex Energy CoSaugat KarNo ratings yet
- ABSSafetyManualReedition 1Document73 pagesABSSafetyManualReedition 1Yilun MaoNo ratings yet
- UNIT 4 Topic 4 - JOB ANALYSISDocument12 pagesUNIT 4 Topic 4 - JOB ANALYSISshubhamNo ratings yet