Tutorial Chapter 4: Electronics: A. B. C. D. E
Uploaded by
Mohamad Rizal MukhtarTutorial Chapter 4: Electronics: A. B. C. D. E
Uploaded by
Mohamad Rizal MukhtarTUTORIAL CHAPTER 4 : ELECTRONICS
Part A: Objective questions
A.
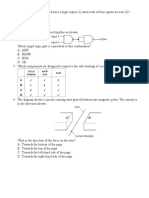
1. Which of the following is not a property
of cathode rays?
It is positively charged.
A.
It travels in a straight line.
B.
It can be deflected by magnetic field.
C.
It can be deflected by electric field.
D.
2.
Cathode rays consists of
Fluorescent particles
Light rays from a screen
B.
Beams of fast moving particles
C.
Light rays from hot filament
D.
A.
3. A beam of electrons is being deflected
due to a potential difference between
plates P and Q.
P
Figure 9.33
Q
Which of the following statements is not
true?
The potential at plate P is positive.
A.
The deflection would be greater if
B.
the potential difference is greater.
The deflection would be greater if
C.
the electrons are moving faster.
The electron beam will return to
D.
straight line if a suitable magnetic
field is applied between the plates.
4. The figure 9.34 shows the trace
displayed on a CRO with the Y-gain
control is turned to 3.75 V/div.
What is the maximum value of the
potential difference being measured?
Figure 9.34
Strive to A+
B.
C.
D.
E.
2.5 V
5.5 V
7.5 V
12.5 V
15.0 V
5. In p-type semiconductor
The number of holes are equal to the
A.
number of electrons.
The number of the holes are more
B.
than the number of electrons.
The number of the holes are less than
C.
the number of electrons.
6. Which of the following is not true about
diode?
It can be used to rectify alternating
A.
current.
It can only conduct electricity when
B.
it is connected in forward in forward
bias in a circuit.
It is formed by joining an n-type and
C.
a p-type semiconductor.
The majority charge carriers in the
D.
diode are electrons.
7. The figure 9. 35 shows the arrangement
of silicon atoms after an atom P is doped
to form an extrinsic semiconductor.
Figure 9.35
Which of the following is not true?
The conductivity of the
A.
semiconductor increases.
The semiconductor becomes an nB.
type.
The majority charge carrier is
C.
electron.
Atom P is a trivalent atom.
D.
Physics Unit 2011
TUTORIAL CHAPTER 4 : ELECTRONICS
8. The figure 9.36 shows a rectifier circuit.
Which of the following statements is
true?
P
Figure 9.36
B.
C.
D.
IC
Figure 9.40
A.
IB
A rectifier changes d.c to a.c.
Device P allows current to flow in
any directions.
Device Q acts as a rectifier.
The rectifier circuit would still work
if device P is reversed.
9. Which of the following statements about
a transistor is not true?
A transistor can act as an amplifier
A.
A transistor can act as a relay switch.
B.
The function of a transistor is the
C.
same as that of two diodes.
A transistor is a combination of two
D.
types of semiconductors.
Figure 9.39
10. What is the function of the transistor
circuit shown in figure 9.39?
As an amplifier
A.
As a rectifier
B.
As a switch device
C.
As a modulator
D.
11. The figure 9.40 shows a transistor being
used as a current amplifier.
Strive to A+
Which of the following is correct?
IB > I C
A.
IB = I C
B.
IB < I C
C.
12. The figure 9. 42 shows a transistor
circuit being used to amplify sound.
M- Microphone
C- Capacitor
S- Speaker
Figure 9.42
Which of the following is not correct
about the circuit?
T is an npn transistor
A.
The capasitor prevents d.c current
B.
but allows a.c current to pass through
it.
Speaker amplifies the sound.
C.
R1 and R2 act as potential divider.
D.
13. The figure 9.43 shows a logic gate
circuit with input signals, X and Y.
Figure 9.43
Which of the following is the output
signal?
Physics Unit 2011
TUTORIAL CHAPTER 4 : ELECTRONICS
14. The figure 9.44 shows a logic gate
circuit.
Figure 9.43
Which of the following is the output
signal Z?
0110
A.
1010
B.
1110
C.
0101
D.
15. The figure 9.44 shows the combination
of three logic gates.
Figure 9.44
The truth table for the combination of
tree logic gates is as follows.
What is gate X?
AND
A.
NOR
B.
OR
C.
NAND
D.
16. The figure 9. 45 shows a combination of
three logic gates in a logic circuit. When
inputs P and Q are both 1 output Y is 1.
J
K
Figure 9.45
Which of the following logic gates can
be used to represent J and K?
A.
B.
C.
D.
J
AND
NAND
OR
NOR
Strive to A+
K
NOR
NOR
AND
AND
Physics Unit 2011
TUTORIAL CHAPTER 4 : ELECTRONICS
Part B: Structured Questions
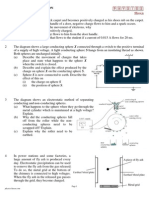
1. Figure 9.46 shows a trace obtained on an oscilloscope screen when an a.c voltage is
connected to the Y-plates of an oscilloscope.
Figure 9.46
Scale: 1 division = 1 cm
The Y-gain is set at 3 V/cm
The time base is set at 5 ms/cm
(a) Explain what is meant by thermionic emission.
Emission
of electrons from the surface of a metal by heat.
(b) Determine the peak voltage of a.c voltage.
2 x 3 = 6V
(c) Determine the time for one complete oscillation on the screen.
2 x 5 = 10 ms
(d) What is the frequency of the a.c voltage?
f
=1/T=50 Hz
(e) With the same a.c voltage applied to the oscilloscope, the time-base setting is altered to
2.5 ms/cm and the Y-gain setting is altered to 2 V/cm. On the space below, sketch the new
trace would appear on the oscilloscope.
2. Figure 9. 47 shows a full wave bridge rectifier. The a.c supply has a frequency of 50 Hz.
Figure 9.47
(a) When the polarity of the a.c supply voltage is positive at A, state the two diodes which are
forward biased.
D1
and D3
..
Strive to A+
Physics Unit 2011
TUTORIAL CHAPTER 4 : ELECTRONICS
(b) When the polarity of the a.c supply voltage is negative at A, state the two diodes which
are forward biased.
(c) Using the axes in figure 9.48, sketch the voltage-time graph across the resistor, R.
Voltage/V
Figure 9.48
Time/ms
(d) On the figure 9.49, sketch the voltage-time graph across the resistor if a capacitor is
connected across the resistor if a capacitor is connected across the resistor R parallel with
the resistor.
Voltage/V
Figure 9.49
Time/ms
(e) Explain how the capacitor causes the voltage across the resistor to vary with time in the
way that you have drawn.
3. A student wants to build a simple lift motor control system which operates using two buttons,
A and B for a two-storey building.
A: Up button
B: Down button
The lift motor only activates when someone presses any one of the buttons. Figure 9.50
shows the circuit that can be used to activate the motor.
12 V
Logic gate
A
X
Relay switch
0V
Keys:
Buttons A and B :
X Output
Strive to A+
Motor
Figure 9.50
When pressed,
Not pressed,
Motor is activated,
240 V
logic 1
logic 0
logic 1
Physics Unit 2011
TUTORIAL CHAPTER 4 : ELECTRONICS
(a) The truth table below shows the operations of the logic gates in a lift motor control
system.
Input
Output
(i)
Using the keys given,
A
B
X
complete the truth
0
0
0
table.
0
1
1
(ii)
Name the logic gate
1
0
1
in
the circuit in the
1
1
0
figure 9.50.
(iii)
In the space below, draw the logic gate symbol in 3(a)(ii).
Why is a relay switch needed in the circuit?
(b) The door of the lift is fitted with a light transmitter and a detector which is a light
dependent resistor, LDR. If the light dependent resistor detects light, the relay switch is
activated and the lift door will close. Figure 9.51 shows an electronic circuit for the
control system of the lift door.
240 V
Motor
Figure 9.51
(i)
State the relationship between the resistance and the intensity of light received
by the light dependent resistor, LDR.
Complete the circuit in figure 9.51 by drawing the resistor and the light
dependent resistor using the symbols given below.
(ii)
Resistor
(iii)
Light dependent resistor
Explain how the circuit functions.
Part C: Essay Questions
1.
Strive to A+
Physics Unit 2011
TUTORIAL CHAPTER 4 : ELECTRONICS
(a) The diode, bulb and battery in circuit X and circuit Y of figures 9.52 and 9.53 are
identical.
Figure 9.52
Figure 9.53
(i) What is meant by a direct current and an alternating current?
[2 marks]
(ii) Using Figures 9.52 and figure 9.53, compare the connection of the diodes and the conditions
of the bulbs. Relating the connection of the diodes and the conditions of the bulbs, deduce
the function of a diode.
[5 marks]
(iii) State the use of a diode.
[1 mark]
(b) A semiconductor diode is made by joining a p-type semiconductor with a n-type semiconductor.
Describe and explain the production and the characteristics of a p-type semiconductor and a ntype semiconductor.
[4 marks]
2. Figure 9.55 shows four circuits W, X, Y and Z, each has an ideal transformer and the circuit
are used for the purpose of rectification.
Circuit W
Circuit Y
Circuit X
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
Circuit Z
What is meant by rectification?
[1mark]
Explain the working principle of a transformer.
[3 marks]
You are asked to make a 12 V battery charger. Study the circuits W, X, Y and Z in figures 9.55
and consider the following aspects:
Type of transformer
The number of turns in the primary coil and in the secondary coil.
Type of rectification
Characteristics of output current
Explain the suitability of the above aspects and hence, determine the most suitable circuit to
make the battery charge.
[6 marks]
Strive to A+
Physics Unit 2011
TUTORIAL CHAPTER 4 : ELECTRONICS
3.
Figure 9.58 shows a microphone connected to a power amplifier. When the microphone
has detected a sound, an amplified sound is given out through the loudspeaker. The sound
becomes louder if the volume of the amplifier is turned on to increase the power.
Power amplifier
Loudspeaker
Volume control
Microphone
Figure 9.58
Using the information based on the observation of the brightness of the bulbs,
(a)
Make one suitable inference.
(b)
State one appropriate hypothesis that could be investigated.
(c)
Design an experiment to investigate the hypothesis stated in (b). Choose suitable
apparatus such as a diode, rheostat and others.
In your description, state clearly the following:
(i)
Aim of the experiment,
(ii)
Variables in the experiment,
(iii)
List of apparatus and materials,
(iv)
Arrangement of the apparatus,
(v)
The procedure of the experiment, which includes the method of controlling the
manipulated variable and the method of measuring the responding variable,
(vi)
The way you would tabulate the data,
(vii)
That way you would analyse the data.
Strive to A+
Physics Unit 2011
You might also like
- Useful Not True - Derek Sivers - 2024 - Anna's ArchiveNo ratings yetUseful Not True - Derek Sivers - 2024 - Anna's Archive138 pages
- Electric Circuits and Electron Devices Unit I Circuit Analysis Techniques Part-ANo ratings yetElectric Circuits and Electron Devices Unit I Circuit Analysis Techniques Part-A8 pages
- Electronics Revision Questions - 100741No ratings yetElectronics Revision Questions - 10074115 pages
- G-Cakna Kelantan 2015 - Physics Term 2 - Module 2No ratings yetG-Cakna Kelantan 2015 - Physics Term 2 - Module 212 pages
- 130901-2 Circuit & Networks Gtu 3rd Sem PaperNo ratings yet130901-2 Circuit & Networks Gtu 3rd Sem Paper2 pages
- EEE 2202 ANALOGUE ELECTRONICS I - July17 - ExamNo ratings yetEEE 2202 ANALOGUE ELECTRONICS I - July17 - Exam5 pages
- Previous Year Board Exam Questions (2007-2016) : Semiconductor DevicesNo ratings yetPrevious Year Board Exam Questions (2007-2016) : Semiconductor Devices13 pages
- Faculty of Electrical & Electronics Engineering Assignment Test 1No ratings yetFaculty of Electrical & Electronics Engineering Assignment Test 13 pages
- SPM Physics Summative Test 2 - Form 5 Chapter 2 and 30% (1)SPM Physics Summative Test 2 - Form 5 Chapter 2 and 38 pages
- Chapter 14 (Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits) UnsolvedNo ratings yetChapter 14 (Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits) Unsolved9 pages
- Contoh Soalan Final JJ102 Electrical TechnologyNo ratings yetContoh Soalan Final JJ102 Electrical Technology11 pages
- Physics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 03 For Board Exam 2024No ratings yetPhysics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 03 For Board Exam 20246 pages
- Soalan Peperiksaan Semester Disember 2008/2009: Fakultikejuruteraan Elektrik UTMNo ratings yetSoalan Peperiksaan Semester Disember 2008/2009: Fakultikejuruteraan Elektrik UTM442 pages
- Class 12 Cbse Physics Sample Paper 2013 Model 1No ratings yetClass 12 Cbse Physics Sample Paper 2013 Model 16 pages
- Structure Questions: 1. SPM 2013: QUESTION 3No ratings yetStructure Questions: 1. SPM 2013: QUESTION 322 pages
- Power System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)From EverandPower System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisFrom EverandElectromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS-P3@alinaimanarif (Electrical Electromagnetism)No ratings yetPHYSICS-P3@alinaimanarif (Electrical Electromagnetism)18 pages
- PHYSICS SPM DICTIONARY@alinaimanaarif PDFNo ratings yetPHYSICS SPM DICTIONARY@alinaimanaarif PDF25 pages
- Earth: Statements Surface Water / GroundwaterNo ratings yetEarth: Statements Surface Water / Groundwater2 pages
- Experiment & Project Based Learning (PBL)No ratings yetExperiment & Project Based Learning (PBL)5 pages
- Folio Technological Devices That Can Overcome The Limitations of Sight and HearingNo ratings yetFolio Technological Devices That Can Overcome The Limitations of Sight and Hearing19 pages
- Tender No: Indian Institute of Technology Madras Chennai 600 036No ratings yetTender No: Indian Institute of Technology Madras Chennai 600 0369 pages
- Sumara Gaspar - Co-Teaching With Fourth GradersNo ratings yetSumara Gaspar - Co-Teaching With Fourth Graders16 pages
- Advanced Management Science: Quantitative Approaches To Decision MakingNo ratings yetAdvanced Management Science: Quantitative Approaches To Decision Making69 pages
- Peter M. Mcisaac Museums of The Mind German Modernity and The Dynamics of Collecting 2007No ratings yetPeter M. Mcisaac Museums of The Mind German Modernity and The Dynamics of Collecting 2007338 pages
- B31 Willaware Products Corporation v. Jesichris Manufacturing Corporation, GR 195549, 3 September 2014, Third Division, Peralta (J) - EVANGELISTA PDFNo ratings yetB31 Willaware Products Corporation v. Jesichris Manufacturing Corporation, GR 195549, 3 September 2014, Third Division, Peralta (J) - EVANGELISTA PDF2 pages
- NCERT - Class11 - Polity - Notes-Political TheoryNo ratings yetNCERT - Class11 - Polity - Notes-Political Theory9 pages
- Republic of The Philippines Professional Regulation Commission ManilaNo ratings yetRepublic of The Philippines Professional Regulation Commission Manila4 pages
- Defining A Mentoring Relationship New MenteesNo ratings yetDefining A Mentoring Relationship New Mentees3 pages
- 22CS 1st Semester Tabulation Sheet May 2023No ratings yet22CS 1st Semester Tabulation Sheet May 202312 pages
- Wake County Schools IEP Document: C: EC File, Parent/Guardian Student UID#: 9294965, Page: 1No ratings yetWake County Schools IEP Document: C: EC File, Parent/Guardian Student UID#: 9294965, Page: 110 pages
- I Analysis of Statistics: Zantel (T) Radio Network Optimization GuidelineNo ratings yetI Analysis of Statistics: Zantel (T) Radio Network Optimization Guideline12 pages
- Useful Not True - Derek Sivers - 2024 - Anna's ArchiveUseful Not True - Derek Sivers - 2024 - Anna's Archive
- Electric Circuits and Electron Devices Unit I Circuit Analysis Techniques Part-AElectric Circuits and Electron Devices Unit I Circuit Analysis Techniques Part-A
- Previous Year Board Exam Questions (2007-2016) : Semiconductor DevicesPrevious Year Board Exam Questions (2007-2016) : Semiconductor Devices
- Faculty of Electrical & Electronics Engineering Assignment Test 1Faculty of Electrical & Electronics Engineering Assignment Test 1
- SPM Physics Summative Test 2 - Form 5 Chapter 2 and 3SPM Physics Summative Test 2 - Form 5 Chapter 2 and 3
- Chapter 14 (Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits) UnsolvedChapter 14 (Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits) Unsolved
- Physics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 03 For Board Exam 2024Physics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 03 For Board Exam 2024
- Soalan Peperiksaan Semester Disember 2008/2009: Fakultikejuruteraan Elektrik UTMSoalan Peperiksaan Semester Disember 2008/2009: Fakultikejuruteraan Elektrik UTM
- Power System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)From EverandPower System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)
- Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisFrom EverandElectromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case Analysis
- PHYSICS-P3@alinaimanarif (Electrical Electromagnetism)PHYSICS-P3@alinaimanarif (Electrical Electromagnetism)
- Folio Technological Devices That Can Overcome The Limitations of Sight and HearingFolio Technological Devices That Can Overcome The Limitations of Sight and Hearing
- Tender No: Indian Institute of Technology Madras Chennai 600 036Tender No: Indian Institute of Technology Madras Chennai 600 036
- Advanced Management Science: Quantitative Approaches To Decision MakingAdvanced Management Science: Quantitative Approaches To Decision Making
- Peter M. Mcisaac Museums of The Mind German Modernity and The Dynamics of Collecting 2007Peter M. Mcisaac Museums of The Mind German Modernity and The Dynamics of Collecting 2007
- B31 Willaware Products Corporation v. Jesichris Manufacturing Corporation, GR 195549, 3 September 2014, Third Division, Peralta (J) - EVANGELISTA PDFB31 Willaware Products Corporation v. Jesichris Manufacturing Corporation, GR 195549, 3 September 2014, Third Division, Peralta (J) - EVANGELISTA PDF
- Republic of The Philippines Professional Regulation Commission ManilaRepublic of The Philippines Professional Regulation Commission Manila
- Wake County Schools IEP Document: C: EC File, Parent/Guardian Student UID#: 9294965, Page: 1Wake County Schools IEP Document: C: EC File, Parent/Guardian Student UID#: 9294965, Page: 1
- I Analysis of Statistics: Zantel (T) Radio Network Optimization GuidelineI Analysis of Statistics: Zantel (T) Radio Network Optimization Guideline