0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
185 viewsAnalytic Trigonometry: Section 5.1 Using Fundamental Identities
Analytic Trigonometry: Section 5.1 Using Fundamental Identities
Uploaded by
sarasmile2009Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Analytic Trigonometry: Section 5.1 Using Fundamental Identities
Analytic Trigonometry: Section 5.1 Using Fundamental Identities
Uploaded by
sarasmile20090 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
185 views2 pagesOriginal Title
5-1
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
185 views2 pagesAnalytic Trigonometry: Section 5.1 Using Fundamental Identities
Analytic Trigonometry: Section 5.1 Using Fundamental Identities
Uploaded by
sarasmile2009Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Name______________________________________________
Chapter 5 Analytic Trigonometry
Section 5.1 Using Fundamental Identities
Objective: In this lesson you learned how to use fundamental
trigonometric identities to evaluate trigonometric functions
and simplify trigonometric expressions.
I. Introduction (Page 374) What you should learn
How to recognize and
Name four ways in which the fundamental trigonometric write the fundamental
identities can be used: trigonometric identities
1) to evaluate trigonometric functions
2) to simplify trigonometric expressions
3) to develop additional trigonometric identities
4) to solve trigonometric equations
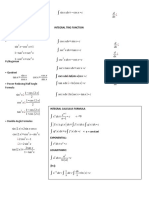
The Fundamental Trigonometric Identities
List six reciprocal identities: List six cofunction identities:
1) sin u = 1/(csc u) 1) sin(π/2 − u) = cos u
2) cos u = 1/(sec u) 2) cos(π/2 − u) = sin u
3) tan u = 1/(cot u) 3) tan(π/2 − u) = cot u
4) csc u = 1/(sin u) 4) cot(π/2 − u) = tan u
5) sec u = 1/(cos u) 5) sec(π/2 − u) = csc u
6) cot u = 1/(tan u) 6) csc(π/2 − u) = sec u
List two quotient identities: List six even/odd identities:
1) tan u = (sin u)/(cos u)
1) sin(− u) = − sin u
2) cot u = (cos u)/(sin u)
2) cos(− u) = cos u
List three Pythagorean identities:
3) tan(− u) = − tan u
2 2
1) sin u + cos u = 1
4) csc(− u) = − csc u
2 2
2) 1 + tan u = sec u
5) sec(− u) = sec u
2 2
3) 1 + cot u = csc u
6) cot(− u) = − cot u
Larson/Hostetler Precalculus/Precalculus with Limits Notetaking Guide IAE
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 99
100 Chapter 5 • Analytic Trigonometry
II. Using the Fundamental Identities (Pages 375−378)
What you should learn
Example 1: Explain how to use the fundamental trigonometric How to use the funda-
identities to find the value of tan u given that mental trigonometric
sec u = 2 . identities to evaluate
trigonometric functions,
simplify trigonometric
Use the Pythagorean identity 1 + tan2 u = sec2 u.
expressions, and rewrite
Substitute 2 for the value of sec u and solve for
trigonometric expressions
tan u.
Example 2: Explain how to use the fundamental trigonometric
identities to simplify sec x − tan x sin x .
Rewrite the expression in terms of sines and
cosines. Combine the resulting fractions to obtain
(1 − sin2 x)/(cos x). Using the Pythagorean identity
sin2 u + cos2 u = 1, replace the numerator with
cos2 x. Simplify the result to obtain cos x.
Additional notes
Homework Assignment
Page(s)
Exercises
Larson/Hostetler Precalculus/Precalculus with Limits Notetaking Guide IAE
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
You might also like
- Trigonometry Notes Grade-11Document10 pagesTrigonometry Notes Grade-11Kelvin Lai100% (7)
- Linearity of Power of A PointDocument8 pagesLinearity of Power of A PointStefy Stefan100% (2)
- Lect6 IdentitiesDocument38 pagesLect6 IdentitiessatyamkumarNo ratings yet
- 4 - Analytic TrigonometryDocument55 pages4 - Analytic Trigonometryธนเสฐฐ์ กิตติวรรธโนทัยNo ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument52 pagesTrigonometrychristiantc0000No ratings yet
- Simplifying and Proving Trig ExpressionsDocument3 pagesSimplifying and Proving Trig ExpressionsAndrea LacdaoNo ratings yet
- SLG M4 13 - 1 - 5Document4 pagesSLG M4 13 - 1 - 5fionakirstie27No ratings yet
- Trigonometric Identities: Peggy AdamsonDocument17 pagesTrigonometric Identities: Peggy AdamsonAbdul RahimNo ratings yet
- Lcture Topic 3 - NotesDocument2 pagesLcture Topic 3 - NotesAnthea ClarkeNo ratings yet
- TrigonometricIdentities - Grade 8 - LP - BenitezDocument12 pagesTrigonometricIdentities - Grade 8 - LP - BenitezAliyah Monique BenitezNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric IdentitiesDocument18 pagesTrigonometric IdentitiesJhunard Christian O. AsayasNo ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument44 pagesTrigonometrymistyyzxNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Identities and EquationsDocument9 pagesTrigonometric Identities and EquationsyankhodianachakwiyaNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document8 pagesModule 4Sumukh KiniNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6.1Document6 pagesLesson 6.1FS - John Nimar BaralNo ratings yet
- LAS - Trigonometric IdentitiesDocument2 pagesLAS - Trigonometric IdentitiesJERLYN MACADONo ratings yet
- Continuous Time Fourier Series - Practice Sheet 01Document7 pagesContinuous Time Fourier Series - Practice Sheet 01Sahil SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Module 8 Lesson 8 Trigo IdentitiesDocument5 pagesModule 8 Lesson 8 Trigo IdentitiesHilan Gel GulmaticoNo ratings yet
- b2 Module 2 Lesson 3Document10 pagesb2 Module 2 Lesson 3CYRELL JAY REBALDONo ratings yet
- 103 Sept 2000 SolutionDocument9 pages103 Sept 2000 SolutionKanika KanodiaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 (Trig IDs)Document5 pagesLesson 1 (Trig IDs)tokage cafeNo ratings yet
- Cot Pre Cal January 18,2023-1Document4 pagesCot Pre Cal January 18,2023-1jocelyn pataNo ratings yet
- Exercises From Linear Algebra, Signal Processing, and Wavelets. A Unified Approach. MATLAB VersionDocument71 pagesExercises From Linear Algebra, Signal Processing, and Wavelets. A Unified Approach. MATLAB VersionAfsaneh ShakeriNo ratings yet
- 109 Topic8Document12 pages109 Topic8vishal_bokaroNo ratings yet
- Graphs of Circular FunctionsDocument40 pagesGraphs of Circular FunctionsClain ManalastasNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mathematics Vol I by Rajesh Pandey (From WWW - Mathschoolinternational.com)Document377 pagesEngineering Mathematics Vol I by Rajesh Pandey (From WWW - Mathschoolinternational.com)JOSE BENAVENTENo ratings yet
- DAA QueBank123Document6 pagesDAA QueBank123Om BhaleraoNo ratings yet
- Fourierseries ProblemsDocument3 pagesFourierseries ProblemsEla TekanNo ratings yet
- MathDocument20 pagesMathdeepteck000No ratings yet
- Find A Formula or Conjecture For Each of The Patterns Shown Below, and Give The Next Three Terms of Each PatternDocument48 pagesFind A Formula or Conjecture For Each of The Patterns Shown Below, and Give The Next Three Terms of Each PatternDineo MasipaNo ratings yet
- Test 1 - Mechanical Vibration 24.6.2020Document6 pagesTest 1 - Mechanical Vibration 24.6.2020Ateeq MalikNo ratings yet
- Pcal 11 q2 1302 FinalDocument25 pagesPcal 11 q2 1302 Finalblxx0981No ratings yet
- (2015) ADA-2nd internals-QN+Ans - KeyDocument4 pages(2015) ADA-2nd internals-QN+Ans - KeyNandulal KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Exercises From Linear Algebra, Signal Processing, and Wavelets. A Unified Approach. Python VersionDocument71 pagesExercises From Linear Algebra, Signal Processing, and Wavelets. A Unified Approach. Python VersionAfsaneh ShakeriNo ratings yet
- Pre Calculus ReviewDocument10 pagesPre Calculus ReviewRocket FireNo ratings yet
- Birla Institute of Technology and Science, PilaniDocument1 pageBirla Institute of Technology and Science, PilaniUtkarsh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Week 5 - Signal Representations Using Fourier Series Activities Part 2Document7 pagesWeek 5 - Signal Representations Using Fourier Series Activities Part 2siarwafaNo ratings yet
- 11 Dp Assignment ScienceDocument3 pages11 Dp Assignment Sciencekumarsuryansh700No ratings yet
- 12 ArcLengthandCurvatureDocument54 pages12 ArcLengthandCurvaturegomsonNo ratings yet
- LAS Q2 Trigonometry Week 1 - Trigonometric Identities Part 1Document6 pagesLAS Q2 Trigonometry Week 1 - Trigonometric Identities Part 1Flordemae Legaspi0% (1)
- SLG M4 13 - 1 - 3Document6 pagesSLG M4 13 - 1 - 3fionakirstie27No ratings yet
- Cartilla Modulo 4 RespuestasDocument11 pagesCartilla Modulo 4 Respuestasel manifestante revolucionarioNo ratings yet
- 9.4.6 Test (TST) - Working With Trigonometric Functions (Test) - 2Document20 pages9.4.6 Test (TST) - Working With Trigonometric Functions (Test) - 2amenfamily00No ratings yet
- 373 Assignment 1Document2 pages373 Assignment 1EnmuskNo ratings yet
- Maths 6Document50 pagesMaths 6Yoel SisayNo ratings yet
- Cal1(finals)Document18 pagesCal1(finals)Adalin Aldrin MicoNo ratings yet
- ECE633 Signals and Systems I, Fall 2009 - Homework 2 SolutionsDocument13 pagesECE633 Signals and Systems I, Fall 2009 - Homework 2 SolutionsGabrielPopoola13100% (2)
- Integration Using Trig Identities or A Trig SubstitutionDocument7 pagesIntegration Using Trig Identities or A Trig SubstitutionAniket SankpalNo ratings yet
- Fresnel Equation Optics-2Document7 pagesFresnel Equation Optics-2Yassin ChibraniNo ratings yet
- PC_Unit_4_Overview_24_25Document3 pagesPC_Unit_4_Overview_24_25asaxena773No ratings yet
- NCATM-17Proceeding_PaperDocument5 pagesNCATM-17Proceeding_Papermilanksv23No ratings yet
- 4 Trigonometric & Inverse Trigo Functions MabborangDocument23 pages4 Trigonometric & Inverse Trigo Functions MabboranglopomNo ratings yet
- Wa0005.Document2 pagesWa0005.MR GAMERNo ratings yet
- 103 Sept 2001 QuestionDocument7 pages103 Sept 2001 QuestionKanika KanodiaNo ratings yet
- PDE's For Dummies: CSE 260 - Introduction To Parallel ComputationDocument15 pagesPDE's For Dummies: CSE 260 - Introduction To Parallel ComputationBrahim MedjberNo ratings yet
- CONDITIONAL-CONTRADICTION-IDENTITYPYTHAGOREAN-IDENTITY (1)Document16 pagesCONDITIONAL-CONTRADICTION-IDENTITYPYTHAGOREAN-IDENTITY (1)Rence MasiNo ratings yet
- 2 - Week1 - ODL 1 - Chapter 1 - Classification of SignalsDocument16 pages2 - Week1 - ODL 1 - Chapter 1 - Classification of SignalsMuhammad MustaqimNo ratings yet
- General Useful Formulae: Complete Study Guide & Notes OnDocument5 pagesGeneral Useful Formulae: Complete Study Guide & Notes OnGauravAroraNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Identities and EquationsDocument22 pagesTrigonometric Identities and Equationsmihlemgoduka22No ratings yet
- 62 Trigonometric Ratio & Identity Part 1 of 2Document12 pages62 Trigonometric Ratio & Identity Part 1 of 2Samir RavalNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Section 12.4 Limits at Infinity and Limits of Sequences: NameDocument2 pagesSection 12.4 Limits at Infinity and Limits of Sequences: Namesarasmile2009No ratings yet
- Section 12.5 The Area Problem: NameDocument2 pagesSection 12.5 The Area Problem: Namesarasmile2009No ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry in Three Dimensions: Section 11.1 The Three-Dimensional Coordinate SystemDocument2 pagesAnalytic Geometry in Three Dimensions: Section 11.1 The Three-Dimensional Coordinate Systemsarasmile2009100% (1)
- Section 11.2 Vectors in Space: NameDocument2 pagesSection 11.2 Vectors in Space: Namesarasmile2009No ratings yet
- Section 12.3 The Tangent Line Problem: NameDocument2 pagesSection 12.3 The Tangent Line Problem: Namesarasmile2009No ratings yet
- Section 10.8 Graphs of Polar Equations: NameDocument2 pagesSection 10.8 Graphs of Polar Equations: Namesarasmile2009No ratings yet
- Section 11.3 The Cross Product of Two Vectors: NameDocument2 pagesSection 11.3 The Cross Product of Two Vectors: Namesarasmile2009No ratings yet
- Section 10.9 Polar Equations of Conics: NameDocument2 pagesSection 10.9 Polar Equations of Conics: Namesarasmile2009No ratings yet
- Section 10.6 Parametric Equations: NameDocument2 pagesSection 10.6 Parametric Equations: Namesarasmile2009No ratings yet
- Section 9.6 Counting Principles: NameDocument2 pagesSection 9.6 Counting Principles: Namesarasmile2009No ratings yet
- Section 10.5 Rotation of Conics: NameDocument2 pagesSection 10.5 Rotation of Conics: Namesarasmile2009No ratings yet
- Section 10.3 Ellipses: NameDocument2 pagesSection 10.3 Ellipses: Namesarasmile2009No ratings yet
- Section 9.5 The Binomial Theorem: NameDocument2 pagesSection 9.5 The Binomial Theorem: Namesarasmile2009No ratings yet
- Section 8.3 The Inverse of A Square Matrix: NameDocument2 pagesSection 8.3 The Inverse of A Square Matrix: Namesarasmile2009No ratings yet
- Section 8.4 The Determinant of A Square Matrix: NameDocument2 pagesSection 8.4 The Determinant of A Square Matrix: Namesarasmile2009No ratings yet
- Section 6.2 Law of Cosines: NameDocument2 pagesSection 6.2 Law of Cosines: Namesarasmile2009No ratings yet
- Section 7.1 Linear and Nonlinear Systems of EquationsDocument4 pagesSection 7.1 Linear and Nonlinear Systems of Equationssarasmile2009No ratings yet
- Section 5.5 Multiple-Angle and Product-to-Sum Formulas: NameDocument4 pagesSection 5.5 Multiple-Angle and Product-to-Sum Formulas: Namesarasmile2009No ratings yet
- Section 6.4 Vectors and Dot Products: NameDocument2 pagesSection 6.4 Vectors and Dot Products: Namesarasmile2009No ratings yet
- Section 7.6 Linear Programming: NameDocument2 pagesSection 7.6 Linear Programming: Namesarasmile2009No ratings yet
- Section 5.4 Sum and Difference Formulas: NameDocument2 pagesSection 5.4 Sum and Difference Formulas: Namesarasmile2009No ratings yet
- Section 5.2 Verifying Trigonometric Identities: NameDocument2 pagesSection 5.2 Verifying Trigonometric Identities: Namesarasmile2009No ratings yet
- Section 4.8 Applications and Models: NameDocument2 pagesSection 4.8 Applications and Models: Namesarasmile2009No ratings yet
- Calculus FormulaDocument2 pagesCalculus FormulaGeramagliquiangNo ratings yet
- Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics Grade 9: I. Learning ObjectivesDocument4 pagesSemi-Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics Grade 9: I. Learning ObjectivesKathy Agader CunanNo ratings yet
- Revision Math p2Document50 pagesRevision Math p2priorityk2006No ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument29 pagesTrigonometryKhyana Whitmore100% (1)
- ClassX H.H.mathsDocument21 pagesClassX H.H.mathsPranav ShahNo ratings yet
- 5 4Document17 pages5 4Seeta Anne0% (1)
- LeaP Math G4 Week 3 Q3Document4 pagesLeaP Math G4 Week 3 Q3Kimttrix WeizsNo ratings yet
- Math 224 - FormulaDocument3 pagesMath 224 - FormulaMau Camayra Jr.No ratings yet
- Pythagoras TheoremDocument23 pagesPythagoras Theoremsakti_badalaNo ratings yet
- I DunnoDocument71 pagesI DunnoJulius Patrick MallanaoNo ratings yet
- LP 2 Six TrigonometryDocument7 pagesLP 2 Six TrigonometryNoviemar UrsalNo ratings yet
- Similar Triangles PPT and ExamplesDocument38 pagesSimilar Triangles PPT and ExamplesKier Abejuela Acut100% (1)
- Trigonometric Identities Last PushDocument14 pagesTrigonometric Identities Last Pushpatiencemampane962No ratings yet
- Evaluation ExamDocument3 pagesEvaluation ExamEmileandro Perito QuindiaganNo ratings yet
- Math9 - Q4 - Mod8-10 - Wk8-10 - Application of Law of Sines and Cosines - v5Document37 pagesMath9 - Q4 - Mod8-10 - Wk8-10 - Application of Law of Sines and Cosines - v5Sam dela CernaNo ratings yet
- PRECALCULUS Module 4 10 12Document56 pagesPRECALCULUS Module 4 10 12emNo ratings yet
- Classification of Triangle1Document48 pagesClassification of Triangle1calebredondo1No ratings yet
- Trigonometry and The Area of A Triangle: Course ActivityDocument9 pagesTrigonometry and The Area of A Triangle: Course ActivityAdroit Writer100% (1)
- Special Topics Exam 2 - TrigonometryDocument2 pagesSpecial Topics Exam 2 - Trigonometryalvin bautistaNo ratings yet
- Maths Model Exam Grade 8 @ethiostudenteDocument14 pagesMaths Model Exam Grade 8 @ethiostudenteBahar Abdurahman93% (28)
- SimilarityDocument4 pagesSimilarityrandomuser8390No ratings yet
- MATHS Answer Key Batch - IIDocument6 pagesMATHS Answer Key Batch - IIvijayakumar11880No ratings yet
- 8-The Pythagorean Theorem and Its ConverseDocument4 pages8-The Pythagorean Theorem and Its ConverseAlejandro FelizNo ratings yet
- Pythagorean Theorem Math PDFDocument2 pagesPythagorean Theorem Math PDFapi-201420601No ratings yet
- Pythagoras TheoremDocument15 pagesPythagoras TheoremShikha AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Q4 - WEEK1 - WW For G9Document3 pagesQ4 - WEEK1 - WW For G9RC FerrerNo ratings yet
- Integrated DLP Math G-4Document4 pagesIntegrated DLP Math G-4Jeferson Eborda RoselNo ratings yet
- GeometryDocument370 pagesGeometryArkaprabha Chakraborty100% (9)