Non-Hydrocarbon - Esters: RCOOR Where R and R Represented The Same or Different Alkyl Groups
Non-Hydrocarbon - Esters: RCOOR Where R and R Represented The Same or Different Alkyl Groups
Uploaded by
cikgu ayuCopyright:
Available Formats
Non-Hydrocarbon - Esters: RCOOR Where R and R Represented The Same or Different Alkyl Groups
Non-Hydrocarbon - Esters: RCOOR Where R and R Represented The Same or Different Alkyl Groups
Uploaded by
cikgu ayuOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Non-Hydrocarbon - Esters: RCOOR Where R and R Represented The Same or Different Alkyl Groups
Non-Hydrocarbon - Esters: RCOOR Where R and R Represented The Same or Different Alkyl Groups
Uploaded by
cikgu ayuCopyright:
Available Formats
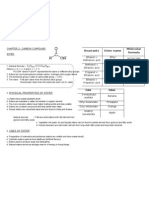
SPM Form 5 Terminology and Concepts: Carbon Compounds (Part 7)
Non-Hydrocarbon Esters
1. General formula: CnH2n+1COOCmH2m+1
Where n = 0, 1, 2, 3 and m = 1, 2, 3 (n and m = number of carbon)
RCOOR where R and R represented the same or different alkyl groups.
2. Esters are non-hydrocarbons which contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms.
3. The functional group in ester is carboxylate group, COO -.
CnH2n+1COOH + CmH2m+1OH > CnH2n+1COOCmH2m+1 + H2O
First part: taken from the alcohol (alkyl group)
Second part: taken from the carboxylic acid (-oic to -oate)
Name of ester
Ethyl methanoate
Methyl ethanoate
Propyl ethanoate
Ethyl propanoate
Molecular formula of
ester
HCOOC2H5
CH3COOCH3
CH3COOC3H7
C2H5COOC2H5
Prepared from
Ethanol + Methanoic acid
Methanol + Ethanoic acid
Propanol + Ethanoic acid
Ethanol + Propanoic acid
4. Physical properties of ester
Name
Odour
3-metylbutyl acetate Banana
Ethyl butanoate
Pineapple
Octyl ethanoate
Orange
Isoamyl isovalerate
Apple
Simple esters are colourless liquid and are found in fruits and flowers.
Esters have sweet pleasant smell.
Esters are covalent compounds.
Esters are insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvent.
Esters are less dense than water.
Esters are neutral and cannot conduct electricity.
The higher and more complex esters have higher boiling points and less volatile.
Natural sources:
Vegetable oils (palm oil) and liquids esters can be found in plants derived from
glycerol and fatty acids.
Fats are solid esters (milk fat) derived from glycerol and fatty acids.
Waxes (beewax) are solid ester derived from long-chain fatty acids and long-chain
alcohols.
5. Uses of Esters
Preparation of cosmetics and perfumes (esters are volatile and have sweet smell).
Synthetic esters used as food additives (artificial flavour).
Natural esters serves as storage reserve of energy in living things.
In plant, wax (esters) helps to prevent dehydration and attack of microorganisms.
Esters used as solvents for glue and varnishes.
Esters used to make plastics softer.
Esters used to produce polyester (threads and synthetics fabrics)
Esters used to produce soap and detergents.
You might also like
- Cambridge Igcse Chemistry Revision Guide - Public PDFDocument50 pagesCambridge Igcse Chemistry Revision Guide - Public PDFMoarz Galaxy62% (13)
- Essential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilFrom EverandEssential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 05oxidationnum Half ReactionsDocument5 pages05oxidationnum Half ReactionsYesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 EsterDocument1 pageChapter 2 EsterfazdirNo ratings yet
- RCOOR Where R and R Represented The Same or Different Alkyl GroupsDocument6 pagesRCOOR Where R and R Represented The Same or Different Alkyl GroupsSharmini RajagopalNo ratings yet
- BlongDocument11 pagesBlongMeriza SagaNo ratings yet
- Science Ester Info 1Document10 pagesScience Ester Info 1Albert AntonioNo ratings yet
- Esters IntroductionDocument6 pagesEsters IntroductionAkshatNo ratings yet
- EstersDocument11 pagesEstersJasmine GalvanNo ratings yet
- EstersDocument33 pagesEsterssaifelwaayNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Ester.: by HenryDocument11 pagesPreparation of Ester.: by HenryHenery HeinNo ratings yet
- Carbon CompoundDocument16 pagesCarbon CompoundAidah AmirNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1-1Document26 pagesLecture 1-1kerolosshafek8No ratings yet
- Organic Compound - Part IIDocument4 pagesOrganic Compound - Part IITherese ClaireNo ratings yet
- ESTERSDocument36 pagesESTERSAbdihakemNo ratings yet
- Non-Hydrocarbon - Fats: SPM Form 5 - Terminology and Concepts: Carbon Compounds (Part 8)Document3 pagesNon-Hydrocarbon - Fats: SPM Form 5 - Terminology and Concepts: Carbon Compounds (Part 8)cikgu ayuNo ratings yet
- Non-Hydrocarbon - Fats: SPM Form 5 - Terminology and Concepts: Carbon Compounds (Part 8)Document4 pagesNon-Hydrocarbon - Fats: SPM Form 5 - Terminology and Concepts: Carbon Compounds (Part 8)cikgu ayuNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Natural Products PDFDocument21 pagesChemistry of Natural Products PDFhosseini_9864No ratings yet
- Chem 3Document14 pagesChem 3Rhea MandatoNo ratings yet
- Ether ProjectDocument22 pagesEther ProjectekojamichaelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Carbon Compounds: Carbon Mineral Carbonates, Natural Gas, Oil and Coal. Graphite Diamond. Allotrophy GraphiteDocument15 pagesChapter 4: Carbon Compounds: Carbon Mineral Carbonates, Natural Gas, Oil and Coal. Graphite Diamond. Allotrophy GraphiteLemathaNo ratings yet
- Presentation About NationDocument19 pagesPresentation About Nationq7fycw4vnqNo ratings yet
- Bautista, John Mhar M. (Experiment 7)Document4 pagesBautista, John Mhar M. (Experiment 7)2g8vdspqm5No ratings yet
- Las 8Document6 pagesLas 8Carl DoriaNo ratings yet
- Detregent 1Document48 pagesDetregent 1Rahmat Eko SanjayaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry - Esters Lab & Lab Report (Making Scents of Esters)Document7 pagesOrganic Chemistry - Esters Lab & Lab Report (Making Scents of Esters)Mark Riley86% (14)
- Lesson 42 Esters (Lesson 43)Document3 pagesLesson 42 Esters (Lesson 43)BradleyNo ratings yet
- LipidsDocument38 pagesLipidsDaly DaliaNo ratings yet
- Assignment On "Terpenoids": Name: Galib Abdullah Roll: 186 Year: Hons 3 Year Session: 2017-18Document13 pagesAssignment On "Terpenoids": Name: Galib Abdullah Roll: 186 Year: Hons 3 Year Session: 2017-18Galib AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Q2 Episode 8 SLMDocument4 pagesScience 9 Q2 Episode 8 SLMJunefer MalinisNo ratings yet
- GenChem Functional Groups 1Document28 pagesGenChem Functional Groups 1Fresco PlayzNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument100 pagesCarbon and Its Compoundsmrpulkit20No ratings yet
- S2 Q4: Organic Chemistry EsterDocument28 pagesS2 Q4: Organic Chemistry EsterMenaga A/P IlangkovanNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument6 pagesUntitledsam cuadraNo ratings yet
- Table of Content: Organic Synthesis: Formation of An Ester Lab ReportDocument11 pagesTable of Content: Organic Synthesis: Formation of An Ester Lab ReportMuhammad Irfan Malik100% (1)
- Ester FormationDocument6 pagesEster Formationkriss Wong100% (1)
- Minyak Atsiri: Benbasyar E., S.Farm, AptDocument60 pagesMinyak Atsiri: Benbasyar E., S.Farm, AptarifNo ratings yet
- EstersDocument3 pagesEstersmohammadrefaat26No ratings yet
- Lipid ChemistryDocument93 pagesLipid ChemistrySanreet RandhawaNo ratings yet
- Properties and General Classes of Organics CompoundsDocument19 pagesProperties and General Classes of Organics Compounds渡辺正平No ratings yet
- Bio Synthesis of Volatile OilsDocument27 pagesBio Synthesis of Volatile Oilsmekky990yahoocom100% (1)
- Lipids Revised 02-10-2021-1Document42 pagesLipids Revised 02-10-2021-1Niruta NepaliNo ratings yet
- Commonly Encountered Alcohols Methyl Alcohol (Methanol)Document4 pagesCommonly Encountered Alcohols Methyl Alcohol (Methanol)Peanut DucNo ratings yet
- Capitulo 04 PDFDocument14 pagesCapitulo 04 PDFAlejandro BoteroNo ratings yet
- LIPIDSDocument47 pagesLIPIDSMarialNo ratings yet
- Terpenoids Notes FinalDocument14 pagesTerpenoids Notes Finaldcba9812No ratings yet
- Module 7 Functional GroupsDocument56 pagesModule 7 Functional GroupsAlyza Wynn C.ThompsonNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument8 pagesUntitledsam cuadraNo ratings yet
- Humaira Jamil TerpenesDocument16 pagesHumaira Jamil TerpenesBisma KhanNo ratings yet
- Lipid Metabolism - I: Chemistry, Digestion and Absorption of LipidsDocument38 pagesLipid Metabolism - I: Chemistry, Digestion and Absorption of LipidscheckmateNo ratings yet
- Ethiopia Institute of Biotechnology: Table: A Comparison of Elements Present in Non-Living and Living MatterDocument25 pagesEthiopia Institute of Biotechnology: Table: A Comparison of Elements Present in Non-Living and Living Mattergebremeskel hagosNo ratings yet
- Lipid UpdateDocument50 pagesLipid UpdateIlmi Dewi ANo ratings yet
- Chemistry AssignmentDocument14 pagesChemistry AssignmentWasle YarNo ratings yet
- LipidsDocument9 pagesLipidsaumaruth013No ratings yet
- Terpineods Unit IvDocument52 pagesTerpineods Unit Ivsanjay sNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Module 9Document4 pagesChemistry Module 9angelo aquinoNo ratings yet
- HSC Chemistry Lesson Plan 19Document5 pagesHSC Chemistry Lesson Plan 19Ali HaidarNo ratings yet
- TriterpenoidDocument38 pagesTriterpenoidMitul ShahNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Organic ChemistryFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Organic ChemistryRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- What is Organic Chemistry? Chemistry Book 4th Grade | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandWhat is Organic Chemistry? Chemistry Book 4th Grade | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Organic Chemistry with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Organic Chemistry with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Atom of The Same Element: Bubble MAP Peta BuihDocument1 pageAtom of The Same Element: Bubble MAP Peta Buihcikgu ayuNo ratings yet
- 3 States of Matter-Tree MapDocument1 page3 States of Matter-Tree Mapcikgu ayuNo ratings yet
- Non-Hydrocarbon - Fats: SPM Form 5 - Terminology and Concepts: Carbon Compounds (Part 8)Document4 pagesNon-Hydrocarbon - Fats: SPM Form 5 - Terminology and Concepts: Carbon Compounds (Part 8)cikgu ayuNo ratings yet
- Non-Hydrocarbon - Fats: SPM Form 5 - Terminology and Concepts: Carbon Compounds (Part 8)Document3 pagesNon-Hydrocarbon - Fats: SPM Form 5 - Terminology and Concepts: Carbon Compounds (Part 8)cikgu ayuNo ratings yet
- Physical Properties Alkanes Alkenes: SPM Form 5 - Terminology and Concepts: Carbon CompoundsDocument2 pagesPhysical Properties Alkanes Alkenes: SPM Form 5 - Terminology and Concepts: Carbon Compoundscikgu ayuNo ratings yet
- 06 Co-Pyrolysis of Hami Coal and Mixed Plastic - An Interaction Between Primary Volatiles Study Via In-Situ Py-TOF-MSDocument13 pages06 Co-Pyrolysis of Hami Coal and Mixed Plastic - An Interaction Between Primary Volatiles Study Via In-Situ Py-TOF-MSbambang.teknikkimia2022No ratings yet
- Masonry Building Tech NotesDocument13 pagesMasonry Building Tech Notescorazon phil100% (1)
- Dorian Tool TurningTools CarbideInserts PDFDocument168 pagesDorian Tool TurningTools CarbideInserts PDFRanjeet SinghNo ratings yet
- ITB - Failure in Boiler System 27 Oct 19Document65 pagesITB - Failure in Boiler System 27 Oct 19Steve WanNo ratings yet
- Resistência Da Cor Ao Calor Prensagem A Quente - AATCC 133-2010Document2 pagesResistência Da Cor Ao Calor Prensagem A Quente - AATCC 133-2010raissaNo ratings yet
- Market Trends and Customers' Preference ProductsDocument3 pagesMarket Trends and Customers' Preference ProductsANGIELICA DELIZONo ratings yet
- Chapter: 1: Chemical Reactions and Equations Lesson-1 NotesDocument2 pagesChapter: 1: Chemical Reactions and Equations Lesson-1 NotesAnsh TomarNo ratings yet
- Rope Materials in Chronological OrderDocument5 pagesRope Materials in Chronological Ordermick.pride81No ratings yet
- Chapter 18 ElectrochemistryDocument49 pagesChapter 18 ElectrochemistryDwivelia AftikaNo ratings yet
- Din Equivalent MaterialsDocument3 pagesDin Equivalent Materialspadmgovi23No ratings yet
- Pp Hdpe Ldpe Lldpe最终 1Document13 pagesPp Hdpe Ldpe Lldpe最终 1abdalla askarNo ratings yet
- Msds Mepoxe M GhsDocument5 pagesMsds Mepoxe M Ghssahluri sNo ratings yet
- Tetratex PTFE Membrane: Filter Bag Media For Torit Baghouse Dust CollectorsDocument2 pagesTetratex PTFE Membrane: Filter Bag Media For Torit Baghouse Dust CollectorsSantiago PENo ratings yet
- Anode Material For High Performance Li-Ion BatteryDocument10 pagesAnode Material For High Performance Li-Ion Batterymigman99No ratings yet
- LIST of APPROVED PRODUCTS For Use in Public Water Supply in The United KingdomDocument78 pagesLIST of APPROVED PRODUCTS For Use in Public Water Supply in The United Kingdomdeaji SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Px3 Lubrication: Wire Rope GreaseDocument1 pagePx3 Lubrication: Wire Rope GreaseEhsan AhmadiNo ratings yet
- Division 3: Concrete SpecificationsDocument12 pagesDivision 3: Concrete SpecificationsKae MoNo ratings yet
- List of Requirement of Stationary and Other Items For Six MonthsDocument16 pagesList of Requirement of Stationary and Other Items For Six Monthsnishant sinhaNo ratings yet
- Elemental Composition of Commercial SeasaltsDocument5 pagesElemental Composition of Commercial Seasaltsabhijeet_khairnarNo ratings yet
- HovedkatalogccDocument352 pagesHovedkatalogccibraheemNo ratings yet
- Full Scale Application of An Electrochemical Disinfection Solution in A Municipal Drinking Water Treatment PlantDocument10 pagesFull Scale Application of An Electrochemical Disinfection Solution in A Municipal Drinking Water Treatment PlantJessica CamilaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level: Chemistry 3173/12Document16 pagesCambridge O Level: Chemistry 3173/12Jack DoeNo ratings yet
- Mechster 1110W MSDS 2Document4 pagesMechster 1110W MSDS 2Nithin MathaiNo ratings yet
- DLL G6 Q4 WEEK 2 ALL SUBJECTS (Mam Inkay Peralta)Document68 pagesDLL G6 Q4 WEEK 2 ALL SUBJECTS (Mam Inkay Peralta)Elna Nuguit InfanteNo ratings yet
- Pureit Classic Ro MF ManualDocument17 pagesPureit Classic Ro MF ManualShyam0% (1)
- Tambobong National High SchoolDocument3 pagesTambobong National High Schoolkathryn soriano0% (1)
- Analysis of Contact Problems in Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Stacks Arising From Differences in Thermal Expansion CoefficientsDocument9 pagesAnalysis of Contact Problems in Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Stacks Arising From Differences in Thermal Expansion Coefficientsal-masriNo ratings yet
- Boq NewDocument18 pagesBoq NewPawan SutharNo ratings yet