1AD FTV Su DPF
1AD FTV Su DPF
Uploaded by
telebetaCopyright:
Available Formats
1AD FTV Su DPF
1AD FTV Su DPF
Uploaded by
telebetaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
1AD FTV Su DPF
1AD FTV Su DPF
Uploaded by
telebetaCopyright:
Available Formats
6
AVENSIS NEW FEATURES
NEW FEATURES
J1AD-FTV ENGINE (WITH DPF CATALYTIC CONVERTER)
1. Description
A DPF (Diesel Particulate Filter) catalytic converter has been added to the 1AD-FTV engine to improve its
exhaust gas cleaning performance.
Along with the provision of the DPF catalytic converter, an EGR bypass switching valve, exhaust fuel
addition injector, and catalyst support control have been added.
"
Engine Specification A
Model
With DPF
Without DPF
4-cylinder, In-line
16-valve DOHC,
Chain and Gear Drive
Direction Injection Type
Cross-flow
Common-rail Type
1998 (121.9)
86.0 x 86.0 (3.39 x 3.39)
Compression Ratio
16.8 : 1
Max. Output (EEC)
93 kW @ 3600 rpm
Max. Torque (EEC)
300 N.m @ 1800 2400 rpm
300 N.m @ 2000 2800 rpm
Open
2_ BTDC
Close
31_ ABDC
Open
51_ BBDC
Close
2_ ATDC
ACEA B1, C2 (Prefer)*1
G-DLD1 or ACEA B1,
API CF-4 or CF
1342
Fuel Cetane Number
48 or more
Emission Regulation
IV*2
No. of Cyls. & Arrangement
Valve Mechanism
Combustion Chamber
Manifolds
Fuel System
Displacement
cm3 (cu. in.)
Bore x Stroke
mm (in.)
Intake
Valve
Timing
Exhaust
Oil Grade
Firing Order
Engine Service Mass
(Reference)
EURO
kg (lb)
152 (335)
EURO IV
147 (324)
*1:When you use non-recommended oil such as API CF grade, you may need extra maintenance for DPF.
Recommended oil viscosity: 5W-30
*2: PM: 80% less than EURO IV regulations
AVENSIS NEW FEATURES
"
Valve Timing A
: IN Valve Opening Angle
: EX Valve Opening Angle
TDC
2_ 2_
51_
31_
BDC
288EG03Y
"
Performance Curve A
120
110
100
400
350
Torque
(N.m)
300
90
80
250
70
200
60
150
100
50
40
30
20
10
0
1000 2000
3000 4000
5000
Engine Speed (rpm)
02JEG22Y
Output
(kW)
AVENSIS NEW FEATURES
2. Features of 1AD-FTV Engine
The 1AD-FTV engine has achieved the following performance through the use of the items listed below.
(1) High performance and reliability
(2) Low noise and vibration
(3) Lightweight and compact design
(4) Good serviceability
(5) Clean emission and fuel economy
Item
Engine
Proper
Valve
V
l
Mechanism
Cooling
System
Intake and
Exhaust
System
With
DPF
Without
DPF
A cylinder head and cylinder block made of
aluminum alloy are used.
Piston provided with combustion chamber
is used in conjunction with the adoption of
direct injection.
Hydraulic lash adjuster is used.
f
f
f
A timing chain and chain tensioner are used.
Roller rocker arms are used.
Lubrication
System
(1) (2) (3) (4) (5)
An oil filter with a replaceable element is
used.
The water-cooled type oil cooler is used.
f
f
TOYOTA Genuine SLLC (Super Long Life
Coolant) is used.
A rotary solenoid type diesel throttle control
motor is used in the throttle body.
A linear solenoid type EGR valve is used.
A water-cooled type EGR cooler is used.
A water-cooled type EGR cooler with a
bypass is used.
The variable nozzle vane type turbocharger
is used.
The exhaust manifold converter uses
oxidation catalyst and DPF catalyst.
Fuel
System
A common-rail type fuel injection system is
used.
Solenoid type injectors on which
compensation value and QR code are
printed are used.
An exhaust fuel addition injector is used.
Charging
g g
System
A segment conductor type alternator is
used.
An alternator pulley with a one-way clutch
is used.
f
f
(Continued)
AVENSIS NEW FEATURES
Item
Serpentine
Belt Drive
System
A serpentine belt drive system is used.
A pilot injection control system is used.
Engine
Control
System
(1) (2) (3) (4) (5)
f
An oil maintenance management system is
used.
With
DPF
Without
DPF
A charging control system is used.
A catalyst support control is used.
3. Engine Proper
Cylinder Head
A hole for installing the exhaust fuel addition injector is located on the No. 4 exhaust port of the cylinder
head.
Hole for Installing Exhaust Fuel
Addition Injector
Front
View from A
Cylinder Head
288EG73Y
10
AVENSIS NEW FEATURES
4. Intake and Exhaust System
General
D A bypass path with a switching valve is added to the EGR cooler.
D An oxidation catalyst and DPF catalyst are used in the exhaust manifold converter.
EGR Cooler
A bypass with an EGR cooler bypass switching valve is added to the EGR cooler.
D If EGR gas is cooled down in the EGR cooler with light engine load, compression air temperature
decreases. To prevent this, the EGR gas passage is switched by the EGR cooler bypass switching valve.
Water IN
Exhaust Gas IN
Exhaust Gas IN
Bypass Switching Valve
Water OUT
Water IN
A
Exhaust Gas
OUT
A
Bypass Path
Exhaust Gas
Outlet for
Cooler Side Gas
Water
Outlet for
Bypass Side Gas
Exhaust Gas OUT
EGR Cooler
A A Cross Section
Water OUT
02JEG23Y
Exhaust Manifold Converter
D The exhaust manifold converter consists of the oxidation catalyst and DPF catalyst.
D The DPF catalyst purifies the PM (Particulate Matter), HC, CO.
Exhaust Gas
PM
Oxidation Catalyst
Filter
DPF Catalyst
02JEG08Y
11
AVENSIS NEW FEATURES
5. Fuel System
General
D The fuel outlet for the exhaust fuel addition injector is added to the supply pump.
D The exhaust fuel addition injector is added for catalyst support control.
Supply Pump
Fuel Tank
Injector
EDU
Quick Connectors
Common-rail
D Fuel Pressure Sensor
Fuel Filter
Exhaust Fuel Addition Injector*
02JEG17Y
*: Only for DPF Models
12
AVENSIS NEW FEATURES
Common-rail System
1) General
In this system, the high pressurized fuel that is supplied by the supply pump is stored in the common-rail,
and the engine ECU sends signals to the injectors via the EDU (Electronic Driver Unit) in order to control
the injection timing and injection volume.
"
System Diagram A
Fuel Pressure Sensor
Pressure Limiter
Common-rail
Fuel Temperature Sensor
Supply
Pump
Exhaust Fuel
Addition Injector*
Fuel
Filter
Injector
EDU
Fuel Tank
Engine
ECU
02JEG11Y
*: Only for DPF Models
2) Supply Pump
The fuel outlet for the exhaust fuel addition injector is added.
Fuel Outlet
288EG101Y
13
AVENSIS NEW FEATURES
3) Exhaust Fuel Addition Injector
D An exhaust fuel addition injector is
installed on the No. 4 exhaust port of the
cylinder head. This injector supplies
additional fuel into the No. 4 exhaust
port, and maintains the proper catalyst
temperature for the purpose of PM
(Particulate Matter) recovery.
D An exhaust fuel addition injector consists
of a needle valve body, needle valve, and
solenoid valve.
Solenoid Valve
Needle Valve
Needle Valve Body
288EG89Y
14
AVENSIS NEW FEATURES
6. Engine Control System
General
The engine control system for the 1AD-FTV engine has following systems.
Outline
With
DPF
Without
DPF
j
Fuel Injection
Volume Control
Based on the signals received from the sensors, the
engine ECU determines the fuel injection volume in
accordance with the engine condition.
Fuel Injection
j
Timing Control
Based on the signals received from the sensors, the
engine ECU determines the fuel injection timing in
accordance with the engine condition.
Fuel Pressure
Control
Based on the signals received from the sensors, the
engine ECU controls fuel pressure using the SCV
according to engine conditions.
Pilot Injection
j
Control
Based on the signals received from the various sensors,
the engine
ECU determines ppilot injection
volume,
g
j
timing, and interval (between pilot injection and main
injection) in accordance with the engine condition.
Catalyst
y Support
pp
Control
(See page 24)
Based on the signals
g
received from the sensors,, the
engine ECU controls exhaust fuel addition injector to
purify PM.
Idle Speed Control
The engine ECU determines the idle speed in accordance
with the engine condition, and controls the fuel injection
volume in order to maintain the target idle speed.
Glow Plug Control
Controls the length of time when the current is applied
to the glow plugs, in accordance with water temperature.
Based on the signals received from the sensors, the
engine ECU determines the EGR volume via EGR valve
and diesel throttle control valve in accordance with the
engine condition.
Based on the signals received from the sensors, the
engine ECU determines the EGR volume via EGR valve,
EGR cooler bypass switching valve and diesel throttle
control valve in accordance with the engine condition.
Turbo Pressure
Control
Based on the signals received from the sensors, the
E VRV in
engine ECU controls the actuator via E-VRV
accordance with the engine condition.
Intake Throttle
Control
D Based on the signals received from the various
sensors, the engine ECU determines throttle position
condition
in accordance with engine condition.
D Fully closes the diesel throttle control valve in order
to reduce the vibration when the engine is stopped.
System
EGR Control
(See page 25)
(Continued)
15
AVENSIS NEW FEATURES
Outline
With
DPF
Without
DPF
Charging Control
The engine ECU regulates the charging voltage of the
alternator in accordance with the driving conditions and
the charging state of the battery
Air-fuel Ratio Sensor
Heater Control
Maintains the temperature of the air-fuel ratio sensor at
an appropriate level to increase accuracy of detection of
the oxygen concentration in the exhaust gas.
Air Conditioner
Cut-off Control
By controlling the air conditioner compressor ON or
OFF in accordance with the engine condition, drivability
is maintained.
Engine
Immobilizer
Prohibits fuel injection if an attempt is made to start the
engine with an invalid ignition key.
Oil Maintenance
Management
System
When the engine ECU determines engine oil
deterioration, the engine oil change reminder light turns
ON to inform the driver.
Diagnosis
(See page 26)
When the engine ECU detects a malfunction, the engine
ECU diagnoses and memorizes the failed section.
Fail-safe
(See page 26)
When the engine ECU detects a malfunction, the engine
ECU stops or controls the engine according to the data
already stored in the memory.
System
16
AVENSIS NEW FEATURES
Construction
The configuration of the engine control system is as shown in the following chart.
SENSORS
AIR FLOW METER
ATMOSPHERIC
TEMPERATURE SENSOR
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE
SENSOR
ACTUATORS
#1
VG
#3
THA
#4
INJF
THIA
WATER TEMPERATURE SENSOR THW
CRANKSHAFT POSITION
SENSOR
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
DIESEL THROTTLE POSITION
SENSOR
VLU
FUEL TEMPERATURE SENSOR
THF
EGR VALVE POSITION SENSOR
DIFFERENTIAL PRESSURE
SENSOR*
PCR1
BATTERY CURRENT SENSOR
PCV
No. 3 INJECTOR
No. 4 INJECTOR
EDU RELAY
EXHAUST FUEL
ADDITION INJECTOR*
SUCTION CONTROL VALVE
INTAKE THROTTLE CONTROL
ENGINE
ECU
LUSL
DIESEL THROTTLE
CONTROL MOTOR
GLOW PLUG CONTROL
EGLS
GREL
GLOW PLUG RELAY
PEX
EXHAUST GAS TEMPERATURE THCO
SENSOR (LOWER SIDE)*
BATTERY TEMPERATURE
SENSOR
EDU
PIM
EXHAUST GAS TEMPERATURE THCI
SENSOR (UP SIDE)*
ALTERNATOR
FIV
G
VPA
VPA2
TURBO PRESSURE SENSOR
IREL
No. 2 INJECTOR
NE
ACCELERATOR PEDAL
POSITION SENSOR
FUEL PRESSURE SENSOR
No. 1 INJECTOR
#2
EGR CONTROL
EGRS
ECBV
EGR VALVE
VSV (FOR EGR COOLER
BYPASS SWITCHING VALVE)*
ALT
RL
THB
IB
TURBOCHARGER CONTROL
VN
E-VRV
(Continued)
*: Only for DPF Models
02JEG09Y
17
AVENSIS NEW FEATURES
CLUTCH SWITCH
CRUISE CONTROL SWITCH
SKID CONTROL ECU
AIR-FUEL RATIO SENSOR*
STOP LIGHT SWITCH
CLSW
CHARGING CONTROL
CCS
RLO
TRC
AF2
AIR-FUEL RATIO SENSOR
HEATER CONTROL*
STP
HAF2
POWER STEERING OIL
PRESSURE SENSOR
TAIL LAMP RELAY
PSP
ENGINE
ECU
COOLING FAN CONTROL
MPX2
FAN
IGNITION SWITCH
D Starter Signal
D Ignition Signal
COMBINATION METER
MREL
SPD
MAIN RELAY
+B
IMI
IMO
SIL, TC
DLC3
COOLING FAN RELAY
STA
IGSW
D Vehicle Speed Signal
TRANSPONDER KEY ECU
AIR-FUEL RATIO
SENSOR HEATER
ELS
PTC
AIR CONDITIONER ECU
ALTERNATOR
(IC REGULATOR)
WFSE
MPX1
W
COMBINATION METER
CHECK ENGINE
WARNING LIGHT
BATT
BATTERY
02JEG10Y
: BEAN
*: Only for DPF Models
18
AVENSIS NEW FEATURES
Engine Control System Diagram
Combination Meter
D Vehicle Speed Signal
D Check Engine Warning Light
D Glow Indicator Light
D Engine Oil Change Reminder Light
Accelerator Pedal
Position Sensor
Fuel Temperature
Sensor
BEAN
BEAN
Air Conditioner
ECU
Supply Pump
Alternator
Tail Light Relay
Cooling Fan Relay
Stop Light Relay
Starter Relay
Ignition
Switch
Fuel Pressure Sensor
Main Relay
Battery Current Sensor
Battery Temperature Sensor
Battery
SCV
Engine
ECU
Common-rail
DLC3
Power Steering Oil Pressure Sensor
EDU Relay
EDU
Intake Air
Temperature
Sensor
Atmospheric Temperature
Sensor
Diesel Throttle
Control Motor
EGR Valve
Air Flow Meter
VSV (For EGR Cooler
Bypass Switching Valve)*
Injector
Actuator
Camshaft
Position
Sensor
E-VRV
(For Turbocharger Control)
Exhaust Temperature Sensor
(Up Side)*
Exhaust Temperature Sensor
(Lower Side)*
Exhaust Fuel
Addition
Injector*
Differential
Pressure Sensor*
Throttle
Position
Sensor
Turbo Pressure
Sensor
Glow
Plug
Water
Temperature
Sensor
Glow
Relay
Crankshaft Position
Sensor
Air-fuel Ratio Sensor*
02JEG13Y
*: Only for DPF Models
19
AVENSIS NEW FEATURES
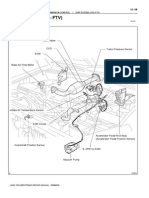
Layout of Main Components
Air Flow Meter
Battery Current Sensor
Differential
Pressure Sensor*
EDU
Intake Air Temperature
Sensor
Glow Plug Indicator
Engine Oil Change
Reminder Light
Air-fuel Ratio Sensor*
Battery Temperature Sensor
Check Engine
Warning Light
Engine ECU
DLC3
Accelerator Pedal
Position Sensor
02JEG19Y
*: Only for DPF Models
20
AVENSIS NEW FEATURES
Injector
Suction Control Valve
Glow Plug
Fuel Pressure Sensor
Fuel Temperature
Sensor
Exhaust Fuel
Addition Injector*
Water Temperature
Sensor
Turbo Pressure
Sensor
EGR Valve
Diesel Throttle Position Sensor
E-VRV
(For Turbocharger Control)
VSV (For EGR Cooler
Bypass Switching Valve)
Camshaft Position Sensor
Exhaust Temperature
Sensor (Up Side)*
Exhaust Temperature
Sensor (Lower Side)*
Crankshaft
Position Sensor
*: Only for DPF Models
02JEG20Y
21
AVENSIS NEW FEATURES
Main Component of Engine Control System
1) General
The main components of the 1AD-FTV engine control system are as follows:
Components
Engine ECU
EDU
Air Flow Meter
Crankshaft Position Sensor (Rotor Teeth)
Camshaft Position Sensor (Rotor Teeth)
Fuel Pressure Sensor
Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor
Diesel Throttle Position Sensor
Differential Pressure Sensor*
Exhaust Gas Temperature Sensor*
Up Side
Lower Side
Air-fuel Ratio Sensor*
Outline
Quantity
32-bit CPU
1
Including a built-in DC-DC converter
1
Hot-wire Type
1
Pick-up Coil Type (36 2)
1
Pick-up Coil Type (1)
1
Semiconductor Strain Gauge Type
1
(Two Circuits Type)
Linear (Non-contact) Type
1
Linear (Non-contact) Type
1
Semiconductor Strain Gauge Type
1
Thermistor Type
1 each
Type with heater (Planar Type)
*: Only for DPF Models
2) Differential Pressure Sensor
D The differential pressure sensor measures the pressure differences between front and back of the DPF
catalyst with PM in order to detect the clogging.
D The sensor is mounted on the cowl, where the effects of vibration are minimal. The DPF catalyst and
the sensor are connected with pipes and hoses.
Differential Pressure Sensor
02JEG25Y
(V)
4.65
Voltage
100
Pressure
(kPa)
02JEG24Y
02JEG26Y
22
AVENSIS NEW FEATURES
3) Exhaust Gas Temperature Sensor
The exhaust gas temperature sensor, which is a thermistor type, is installed in front and back of the DPF
catalyst, in order to detect the temperature of the catalyst.
106
105
Electric
Resistance 104
Value
()
103
102
100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900
Exhaust Gas Temperature (_C)
258AE40
258AE41
4) Air-fuel Ratio Sensor
a. General
D The planar type air-fuel ratio sensor is used.
D The planar type air-fuel ratio sensor uses alumina, which excels in heat conductivity and insulation,
to integrate a sensor element with a heater, thus improving the warm-up performance of the sensor.
D This sensor is based on a sensor that is developed for gasoline engines. Its cover is changed for diesel
engine applications in order to eliminate the influences of the sensor temperature and the PM. This
sensor, which is mounted after the DPF catalyst, detects the air-fuel ratio after the gases is reduced.
Alumina
Dilation Layer
Atmosphere
Alumina
Heater
Platinum
Electrode
Sensor Element (Zirconia)
288EG86Y
23
AVENSIS NEW FEATURES
b. Characteristics
The air-fuel ratio sensor and the heated oxygen sensor differ in output characteristics.
The air-fuel ratio sensor data is approximately proportionate to the existing air-fuel ratio. The air-fuel
ratio sensor converts the oxygen density to the current and sends it to the engine ECU.
As a result, the detection precision of the air-fuel ratio has been improved. The air-fuel ratio sensor data
is read out by an intelligent tester II.
4.2
(V)
Air-fuel Ratio Sensor Data
Displayed on Intelligent
Tester II
2.2
11 (Rich)
14.7
Air-fuel Ratio
19 (Lean)
258AE59
24
AVENSIS NEW FEATURES
Catalyst Support Control
1) General
The engine ECU judges manifold converter condition based on signals from the air flow meter, water
temperature sensor, two exhaust gas temperature sensors, differential pressure sensor, and air-fuel ratio
sensor to control the injectors and exhaust fuel addition injector for catalyst support control.
D The catalyst support control consists of the PM reduction control.
Injector
Exhaust Fuel Addition Injector
Water Temperature
Sensor
Air Flow Meter
Engine ECU
Exhaust Gas
Temperature
Sensors
Air-fuel Ratio
Sensor
Differential Pressure Sensor
288EG67C
2) PM Reduction Control
If the DPF catalyst temperature becomes low, catalyst performance decreases, resulting in an increase
of the amount of PM stuck in the filter substrate. When the engine ECU detects clogs in the filter substrate
by calculating the accumulated volume of PM discharged by engine, it operates the injectors and exhaust
fuel addition injector for PM reduction.
D At the same time, filter substrate temperature becomes high and PM reacts with active oxygen and
changes into CO2 for purification.
D Fuel efficiency drops during this control.
Service Tip
D When replacing the exhaust manifold converter with a new one, it is necessary to perform
initialization of the DPF catalyst deteriorate data history in the engine ECU by using the
intelligent tester II.
D When replacing the engine ECU with a new one, it is necessary to read DPF catalyst deteriorate
data history from the installed engine ECU and then transfer that data history to the new engine
ECU by using the intelligent tester II. When the DPF catalyst deteriorate data history is not
transferred, DTC (Diagnostic Trouble Code) P1601 is stored in the engine ECU, and the check
engine warning light comes on.
D When replacing both the exhaust manifold converter and the engine ECU, it is necessary to perform
initialization of the DPF catalyst deteriorate data history in the engine ECU using the intelligent
tester II. When DPF catalyst deteriorate history initialization is not performed, DTC (Diagnostic
Trouble Code) P1601 is stored in the engine ECU and the check engine warning light comes on.
For details, refer to the Avensis Repair Manual Supplement (Pub. No. RM02J1E).
25
AVENSIS NEW FEATURES
EGR Control
By sensing the engine driving conditions, the engine ECU operates the EGR valve, diesel throttle control
motor and VSV (for EGR cooler bypass switching valve) and regulates the amount of EGR gas.
Accelerator Pedal
Position Sensor
Crankshaft Position
Sensor
EGR Valve
Air Flow Meter
Engine
ECU
Water Temperature Sensor
Atmospheric Temperature
Sensor
EGR Cooler Bypass
Switching Valve
Turbo Pressure Sensor
EGR Cooler
To Turbocharger
Engine
Exhaust Gas
288EG103C
26
AVENSIS NEW FEATURES
Diagnosis
D The diagnosis uses the EURO-OBD (Europe On-Board Diagnosis) that complies with European
regulations.
D When the engine ECU detects a malfunction, the engine ECU makes a DTCs (Diagnostic Trouble Codes)
and memorizes the failed section. Furthermore, the check engine warning light in the combination meter
illuminates to inform the driver.
D The engine ECU will also store the DTCs (Diagnostic Trouble Codes) of the malfunctions. The DTC can
be accessed by using the intelligent tester II.
D For details, refer to the Avensis Repair Manual Supplement (Pub. No. RM02J1E).
Service Tip
To clear the DTC that is stored in the engine ECU, use an intelligent tester II, disconnect the battery
terminal or remove the EFI fuse for 1 minute or longer.
Fail-safe
When a malfunction is detected by any of the sensors, there is a possibility of an engine or other malfunction
occurring if the engine ECU were to continue to control the engine control system in the normal way. To
prevent such a problem, the fail-safe function of the engine ECU either relies on the data stored in memory
to allow the engine control system to continue operating, or stops the engine if a hazard is anticipated. For
details, refer to the Avensis Repair Manual Supplement (Pub. No. RM02J1E).
You might also like
- VW Golf 7 Wiring Diagrams EngDocument1,698 pagesVW Golf 7 Wiring Diagrams EngExpress CarParts80% (5)
- Axd TimingDocument7 pagesAxd Timingdocrobb_75% (4)
- TOYOTA 1CD-FTV D4D Engine FuelDocument27 pagesTOYOTA 1CD-FTV D4D Engine FuelLuis Daniel Cortes100% (17)
- Rover 45Document409 pagesRover 45Daniel Card100% (1)
- ZX470-5G Workshop ManualDocument878 pagesZX470-5G Workshop Manualhydeer 13100% (13)
- New Holland t4030f t4040f t4050f Tractors Service ManualDocument20 pagesNew Holland t4030f t4040f t4050f Tractors Service Manualthomas98% (60)
- L200 VGT Setup ProcedureDocument7 pagesL200 VGT Setup ProcedureDraganKostovski100% (1)
- Reparatie 1.7dtiDocument6 pagesReparatie 1.7dtidaniel100% (2)
- Fuel Injector Removal - Installation (Skyactiv-D 2.2)Document9 pagesFuel Injector Removal - Installation (Skyactiv-D 2.2)Daniel Ungureanu100% (1)
- 1316146E EN Renault Master Opel Movano Nissan NV400 2010 D Evo AT-40Document32 pages1316146E EN Renault Master Opel Movano Nissan NV400 2010 D Evo AT-40Györök PeterNo ratings yet
- D4ga - Euro4 Engine - EGRDocument59 pagesD4ga - Euro4 Engine - EGRBigfair HD78100% (17)
- 3 Cylinders Engines For Skoda Cars (Engine Code AWY & AZQ)Document26 pages3 Cylinders Engines For Skoda Cars (Engine Code AWY & AZQ)kikouchaa100% (7)
- Toyota 4a-Fe Engine ReferenceDocument57 pagesToyota 4a-Fe Engine Referencecarmanpy88% (8)
- Toyota 1AZ-FSE Engine Repair Manual (RM1019E) - PDFs Free OnlineDocument5 pagesToyota 1AZ-FSE Engine Repair Manual (RM1019E) - PDFs Free OnlineMark Anthony Fletcher60% (5)
- Corsa D EPSDocument1 pageCorsa D EPScork_ie100% (1)
- 2015+Toyota+Tundra+Repair+Manual N7 PDFDocument9 pages2015+Toyota+Tundra+Repair+Manual N7 PDFAbbode HoraniNo ratings yet
- Conversion To Injection MantaDocument21 pagesConversion To Injection MantaMichael Mitchell100% (1)
- SSP 296 1.4 & 1.6 FSi EngineDocument24 pagesSSP 296 1.4 & 1.6 FSi Engineภูเก็ต เป็นเกาะ100% (3)
- 1kd FTVDocument2 pages1kd FTVGregory Ashley89% (18)
- SM Engine Fage y F4heDocument206 pagesSM Engine Fage y F4heJose Carmona100% (10)
- DTC P205C - 00 (MZR-CD 2.2)Document2 pagesDTC P205C - 00 (MZR-CD 2.2)asdfNo ratings yet
- VW Toureg 2003-2017 - Hybrid Electrical SystemDocument53 pagesVW Toureg 2003-2017 - Hybrid Electrical SystemChristian Linares Abreu100% (1)
- Toyota AD Series Diesel Engines PDFDocument15 pagesToyota AD Series Diesel Engines PDFKushtrim Mala100% (1)
- Common Rail System (CRS) SERVICE MANUAL: Operation: Toyota AvensisDocument55 pagesCommon Rail System (CRS) SERVICE MANUAL: Operation: Toyota Avensisjhonathan hernandez100% (2)
- Vito Part1Document97 pagesVito Part1Rezme Mbarek100% (1)
- En Us c5 2000Document259 pagesEn Us c5 2000Zoran Bozinovic75% (4)
- Toyota Avensis 2ad-Ftv FHV EngineDocument32 pagesToyota Avensis 2ad-Ftv FHV EngineGilbert Kamanzi100% (1)
- Volkswagen PASSAT 1.9 TDI 1995 Electrical Wiring DiagramDocument17 pagesVolkswagen PASSAT 1.9 TDI 1995 Electrical Wiring DiagramRicardo SanchezNo ratings yet
- Nats (Nissan Anti-Theft System) Nats (Nissan Anti-Theft System) Component Parts and Harness Connector LocationDocument21 pagesNats (Nissan Anti-Theft System) Nats (Nissan Anti-Theft System) Component Parts and Harness Connector Locationkrakhos100% (1)
- Toyota AD Series Diesel EnginesDocument1 pageToyota AD Series Diesel EnginesIohan DochevNo ratings yet
- Toyot Common Rail System-2AD Denso For Avensis Service Manual PDFDocument32 pagesToyot Common Rail System-2AD Denso For Avensis Service Manual PDFNery CastellanosNo ratings yet
- How To Read Simtec 56Document4 pagesHow To Read Simtec 56it_ady79No ratings yet
- Timing Setting The Valve Timing Without Removal - EP Engine Direct InjectionDocument11 pagesTiming Setting The Valve Timing Without Removal - EP Engine Direct InjectionDong HungNo ratings yet
- 4-Cylinder Diesel Engine (1.9 L Engine) - 1-145Document145 pages4-Cylinder Diesel Engine (1.9 L Engine) - 1-145Iago LeoteNo ratings yet
- When Using An OBD II Scan Tool Other Than TOYOTA Hand-Held Tester, Check All The Steps. - When Using TOYOTA Hand-Held Tester, Confirm The Information Code and Check It.Document2 pagesWhen Using An OBD II Scan Tool Other Than TOYOTA Hand-Held Tester, Check All The Steps. - When Using TOYOTA Hand-Held Tester, Confirm The Information Code and Check It.Nbeel AbdoNo ratings yet
- Fault Finding Immobiliser: N.T. 3532A Xb0XDocument19 pagesFault Finding Immobiliser: N.T. 3532A Xb0Xsantia6768No ratings yet
- OpelDocument17 pagesOpelMotor Csillag50% (2)
- 428L2 PDFDocument13 pages428L2 PDFesquisofNo ratings yet
- BMW Ews Immo Emulator User ManualDocument4 pagesBMW Ews Immo Emulator User ManualMantasPuskorius100% (1)
- MR415LAGUNA8 Electrical EquipmentDocument404 pagesMR415LAGUNA8 Electrical EquipmentValentin Lucian Chircu100% (1)
- Toyota Avensis Hamulec Ręczny EPBDocument1 pageToyota Avensis Hamulec Ręczny EPBlukasz_b7No ratings yet
- Water Heater: Thermo Top C Motorcaravan Parking HeaterDocument29 pagesWater Heater: Thermo Top C Motorcaravan Parking HeaterMarco CorreiaNo ratings yet
- Toyota Land Cruiser PDFDocument10 pagesToyota Land Cruiser PDFVelasquez Javier75% (4)
- Vigo Elec Wiring DiagramDocument18 pagesVigo Elec Wiring DiagramVinh Phạm100% (1)
- DFM Explanation: Pos Service HollandDocument4 pagesDFM Explanation: Pos Service HollandJhonny Eduardo Suarez GretaNo ratings yet
- DTC P0340/12 Engine Speed Sensor Circuit 1 (TDC or G1 Circuit)Document2 pagesDTC P0340/12 Engine Speed Sensor Circuit 1 (TDC or G1 Circuit)Andi Ka100% (1)
- Golf 2010 2.0LDocument162 pagesGolf 2010 2.0LJorge MorochoNo ratings yet
- Turbo Daily Fuel SystemDocument49 pagesTurbo Daily Fuel SystemMurdock67% (3)
- Toyota 1GR FE Engine - New Engine FeaturesDocument36 pagesToyota 1GR FE Engine - New Engine FeaturesJason100% (1)
- HiluxDocument11 pagesHiluxCarlos Eduardo Zelidon100% (3)
- Exhaust System Overview ISL9 CM2350Document34 pagesExhaust System Overview ISL9 CM2350jonNo ratings yet
- Engine Emission Control - 6.7l Power Stroke DieselDocument93 pagesEngine Emission Control - 6.7l Power Stroke DieselpowerlabdieselsolutionsNo ratings yet
- Tigercat Tier 4Document4 pagesTigercat Tier 4deroryNo ratings yet
- Interject KJetronicDocument7 pagesInterject KJetronicccumali100% (1)
- Model JP1 EFI Kit For JEEP 258 CID 4.2 6 CylinderDocument14 pagesModel JP1 EFI Kit For JEEP 258 CID 4.2 6 CylinderMildo BurgosNo ratings yet
- I Nstallati On: HowellDocument20 pagesI Nstallati On: HowellBrian DonovanNo ratings yet
- Motore d20dt d27dt Rexton EnginesDocument53 pagesMotore d20dt d27dt Rexton EnginescxNo ratings yet
- 9913 Ap 34Document108 pages9913 Ap 34احمدميدوNo ratings yet
- Toyota - Paseo - Workshop Manual - 1990 - 1991Document3,179 pagesToyota - Paseo - Workshop Manual - 1990 - 1991cginternet.ofcNo ratings yet
- Service - Service Manual Code 950 - 994 - 653Document30 pagesService - Service Manual Code 950 - 994 - 653Victor UribeNo ratings yet
- MR325KANGOO1Document208 pagesMR325KANGOO1Jumbosize100% (1)
- Ad Dit LC B Ti E I Advanced Internal Combustion Engines Mae 589V (Spring 2009)Document15 pagesAd Dit LC B Ti E I Advanced Internal Combustion Engines Mae 589V (Spring 2009)snmathad2No ratings yet
- PV776 20038171Document6 pagesPV776 20038171이종욱No ratings yet
- Nissan GTR R32 Service ManualDocument804 pagesNissan GTR R32 Service ManualGorkandMork67% (6)
- Ssang Yong ActyonDocument31 pagesSsang Yong Actyonlinx_bvNo ratings yet
- Rat - RP - 261Document5 pagesRat - RP - 261UNITED CADDNo ratings yet
- 2007 Mack Engine: Tune-UpDocument92 pages2007 Mack Engine: Tune-UpEduardo Torres100% (1)
- Release NewsDocument205 pagesRelease NewsLucian Ionut MihalacheNo ratings yet
- Chrysler Dakota Part10Document32 pagesChrysler Dakota Part10Sašo Brunšek-BrunoNo ratings yet
- SK 235 SR 2Document308 pagesSK 235 SR 2Bilal VURAL50% (2)
- HD 85 Engine Service ManualDocument77 pagesHD 85 Engine Service Manualcarlostapie.econovoNo ratings yet
- Ice Handout2Document17 pagesIce Handout2Camilo Jose100% (2)
- 016 1.9 TDI EngineDocument58 pages016 1.9 TDI EngineRicardo J. PintoNo ratings yet
- Audi Q3Document81 pagesAudi Q3mojbar0% (1)
- ENG0001 DL DV Common Rail EngineDocument24 pagesENG0001 DL DV Common Rail Enginedaniel alberto galvis jaimes100% (1)
- A0059192920-TDI Injection and Glow Plug System (4-Cyl 2 0 LTR Unit Injector 4-Valve)Document51 pagesA0059192920-TDI Injection and Glow Plug System (4-Cyl 2 0 LTR Unit Injector 4-Valve)suprorelNo ratings yet
- 8 CD Adapco 2005 ZellatDocument6 pages8 CD Adapco 2005 ZellatGlen YNo ratings yet
- Extended Abstract For Diesel CombustionDocument8 pagesExtended Abstract For Diesel CombustionGaurav TehlanNo ratings yet
- Toyota U240E Automatic Transaxle Repair Manual RM740UDocument136 pagesToyota U240E Automatic Transaxle Repair Manual RM740Ustephany castro100% (1)
- CASE IH FARMALL 115U EP Tractor With 16x16 Semi-Powershift Transmission Service Repair ManualDocument32 pagesCASE IH FARMALL 115U EP Tractor With 16x16 Semi-Powershift Transmission Service Repair Manualejky93201573No ratings yet
- 2021-Scheme-6th Sem ECE - OEDocument12 pages2021-Scheme-6th Sem ECE - OEbibliophileonthesamepageNo ratings yet
- Eges2701 DTCDocument5 pagesEges2701 DTCeng_hamada_4uNo ratings yet
- Posted January 15Document16 pagesPosted January 15Bigshow MeyerNo ratings yet
- Engine CNH Trainee MPTS ™Document154 pagesEngine CNH Trainee MPTS ™Luis Miguel Echevarria Quispe100% (4)
- Delmag RH Reihe enDocument20 pagesDelmag RH Reihe enIvanNo ratings yet
- Handy Abbreviations and Acronyms For Automotive Scantool ReferenceDocument5 pagesHandy Abbreviations and Acronyms For Automotive Scantool ReferenceSulaiman KhanNo ratings yet
- 114E-5 Series (JPN) SEN05537-03 Shop ManualDocument322 pages114E-5 Series (JPN) SEN05537-03 Shop Manualkhanh HiệpNo ratings yet
- SAE Automobile Heat Transfer 2Document281 pagesSAE Automobile Heat Transfer 2sardhan.rajender84100% (1)
- Specificatii Tehnice Excavatoare Pe Senile Komatsu PC210Document24 pagesSpecificatii Tehnice Excavatoare Pe Senile Komatsu PC210Cosmin Tataru100% (2)