100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
509 viewsPancreas
Pancreas
Uploaded by
Dr santoshThe pancreas is a mixed exocrine and endocrine gland located in the abdomen behind the stomach. It is roughly hammer shaped and measures 12-15 cm in length. The pancreas has a head, neck, body, and tail. It produces enzymes that are released into the small intestine to aid in digestion. The pancreas also contains clusters of cells called islets of Langerhans that secrete the hormones insulin and glucagon which regulate blood sugar levels. Disorders of the pancreas can include diabetes if insulin is deficient, digestive issues if pancreatic enzymes are lacking, and pancreatitis which is inflammation of the pancreas.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Pancreas
Pancreas
Uploaded by
Dr santosh100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
509 views8 pagesThe pancreas is a mixed exocrine and endocrine gland located in the abdomen behind the stomach. It is roughly hammer shaped and measures 12-15 cm in length. The pancreas has a head, neck, body, and tail. It produces enzymes that are released into the small intestine to aid in digestion. The pancreas also contains clusters of cells called islets of Langerhans that secrete the hormones insulin and glucagon which regulate blood sugar levels. Disorders of the pancreas can include diabetes if insulin is deficient, digestive issues if pancreatic enzymes are lacking, and pancreatitis which is inflammation of the pancreas.
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
The pancreas is a mixed exocrine and endocrine gland located in the abdomen behind the stomach. It is roughly hammer shaped and measures 12-15 cm in length. The pancreas has a head, neck, body, and tail. It produces enzymes that are released into the small intestine to aid in digestion. The pancreas also contains clusters of cells called islets of Langerhans that secrete the hormones insulin and glucagon which regulate blood sugar levels. Disorders of the pancreas can include diabetes if insulin is deficient, digestive issues if pancreatic enzymes are lacking, and pancreatitis which is inflammation of the pancreas.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
509 views8 pagesPancreas
Pancreas
Uploaded by
Dr santoshThe pancreas is a mixed exocrine and endocrine gland located in the abdomen behind the stomach. It is roughly hammer shaped and measures 12-15 cm in length. The pancreas has a head, neck, body, and tail. It produces enzymes that are released into the small intestine to aid in digestion. The pancreas also contains clusters of cells called islets of Langerhans that secrete the hormones insulin and glucagon which regulate blood sugar levels. Disorders of the pancreas can include diabetes if insulin is deficient, digestive issues if pancreatic enzymes are lacking, and pancreatitis which is inflammation of the pancreas.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 8
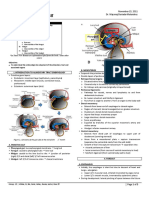
Pancreas
The name pancreas means all flesh
It is mixed gland having both exocrine & endocrine
secretions
Situation – it is situated in the ‘C’ it lies horizontal
or transverse in posterior abdominal wall behind
peritoneum
Extent - from umbilical region to Lt Hypochondriac
region
Shape – it is roughly hammer shape
Length - 12 to 15 cm
Breadth - 3-4 cm broad
Thickness – 1.5-2 cm
Weight - 90 Gms
Parts - it has following parts
Head, neck, body, & tail
Head – it is elongated Rt part of pancreas
It is situated in 1, 2 & 3rd part of duodenum
It has
Two surfaces – anterior & posterior
Four borders - superior inferior RT, Lt
One process- uncinate process
Uncinate process - it has two surfaces
Anterior - superior mesentric vessels
Posterior - aorta
Relations
Anterior surface - transverse colon, jejunum &
gastroduodenal artery
Posterior - bile duct, IVC, RT crus of diaphragm,
terminal part of renal vein
Superior border – it is overlapped by 1st part of
duodenum superior pancreatico-duodenal artery
Inferior border – it is overlapped by 3rd part of
duodenum inferior pancreatico-duodenal artery
Neck - it is constricted part at the junction bet
head & body it lies in front of portal vein
It has two surfaces
Anterior - pylorus of stomach
Posterior - portal vein
Body - it is longest part of pancreas & extends
from neck to tail
Shape - triangular in cross section
It has three surfaces & three borders
Anterior surface – to form the part of stomach
bed
Posterior - it lies opposite the L1 & L2 vertebrae it
is related with
1. Aorta with SMA
2. Veretebral column
3. Lt Crus of diaphragm
4. Lt Psoas major
5. Lt Ureter
6. Lt Kidney & suprarenal gland
7. Lt testicular or ovarian vessels
Inferior surface – it is covered by peritoneum it
is related to
1. Duodeno-jejunal flexure
2. Coils of jejunum
3. Lt colic flexure
Superior border - it has
Tuber omentale - a conical projection at the RT
end
Rest of border is related to splenic artery
Anterior border – root of transverse colon
Inferior border - superior mesenteric vessels
Tail of pancreas - it is Lt Terminal part of
pancreas lying bet two layers of lieno-renal
ligament & extend up to Hilum of spleen
Relations -
In front - lesser sac with stomach
Behind - spleen & splenic vessels
Below – Lt Colic flexure
The tail of pancreas has maximum endocrine part
in it
Endocrinal part consists of
1. Islets of langerhans ( alpha & beta cells )
Alpha cell secretes glucagon
Beta cells secretes insulin
Glucagon & insulin both regulates blood sugar level
The pancreas develops from the site of junction of
foregut & mid gut
Foregut extends from oral cavity to 2nd part of
duodenum where the hepatopancreatic duct opens
Midgut extends from opening of hepatopancreatic
duct in duodenum up to junction of Rt 2/3rd & Lt
1/3rd of transverse colon
Hind gut extends from junction of Rt 2/3rd & Lt
1/3rd of transverse colon up to anal canal
Therefore it is supplied by both arteries of foregut
& Midgut i.e. coeliac trunk & superior mesenteric
artery
Blood supply - it is supplied by superior
pancreatico duodenal artery & inferior pancreatico
duodenal artery & branches of splenic artery there
are two branches 1. Arteria pancreatic magna –
supplies body & 2. Arteria caudac pancreatis –
supplies tail
Venous drainage - superior mesenteric vein,
splenic vein to portal vein
Lympathetic – pancreatico splenic group, superior
mesenteric group
Nerve supply - sympathetic through coeliac
plexus parasympathetic through vagus
Development - it develops from junction of
foregut & mid gut
It develops from two buds namely
1. Dorsal pancreatic bud
2. Ventral pancreatic bud
These buds enlarges because of rotation of gut &
differential growth of body wall
These two buds fuse with each other
Ventral pancreatic buds forms lower part of head &
uncinate process
Dorsal pancreatic buds forms rest of pancreas
Ducts of pancreas - it has two ducts in it
1. Main pancreatic duct –opens at major
duodenal papilla it lies near the post surface
& begins at tail & runs towards the head it
joins with bile ducts forms hepato-pancreatic
ampulla( ampulla of vater ) which opens at
the summit of major duodenal papilla
Lumen of duct is 3mm in diameter
2. Accessory pancreatic duct – opens at minor
duodenal papilla
Functions - exocrine part secretes pancreatic
juice which is used for digestion of fat
Endocrinal part secrets hormone namely glucagon
& insulin regulates blood sugar level
Applied anatomy -
1. Deficiency of insulin causes a condition called as
diabetes mellitus
2. Deficiency of pancreatic juice causes digestive
distubarance
3. Ca of head causes a condition called as
obstructive jaundice
4. Inflammation to pancreas called as pancreatitis
5. Congenital anomalies like annular pancreas
You might also like
- 4 Peritoneum PDFDocument64 pages4 Peritoneum PDFN ANo ratings yet
- Peritoneum and Peritoneal CavityDocument26 pagesPeritoneum and Peritoneal CavitytuhinsinghNo ratings yet
- Technical Delivery Condition: Applicable To Parts: Ring WCFN0055Document4 pagesTechnical Delivery Condition: Applicable To Parts: Ring WCFN0055Balram JiNo ratings yet
- Gravel/ Sand Filters: Irrigation Equipment LTDDocument24 pagesGravel/ Sand Filters: Irrigation Equipment LTDMerca RosalNo ratings yet
- PANCREAS - DR JNDocument57 pagesPANCREAS - DR JNPravesh AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Definition - It Is Muscular Bag Forming Widest &Document10 pagesDefinition - It Is Muscular Bag Forming Widest &Dr santosh100% (1)
- Anatomy of Small Intestine: Lecture-4Document23 pagesAnatomy of Small Intestine: Lecture-4Ahmed OudahNo ratings yet
- ACCESORY ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Contrast 1Document56 pagesACCESORY ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Contrast 1Rea FloresNo ratings yet
- Pankreas & LienDocument38 pagesPankreas & LienopimadridistaNo ratings yet
- Untitled PresentationDocument18 pagesUntitled Presentationpkakash1042004No ratings yet
- Peritoneum 2022Document86 pagesPeritoneum 2022Tayyib KhanNo ratings yet
- PancreaDocument21 pagesPancreasiddharth.roy26587No ratings yet
- 3protected DuodenumDocument29 pages3protected Duodenumrdxbeast777No ratings yet
- Anatomy of PancreasDocument51 pagesAnatomy of PancreaskarthickNo ratings yet
- Digestive System NotesDocument8 pagesDigestive System NotesAnurag JosephNo ratings yet
- Git AnatomyDocument62 pagesGit AnatomyBimo HarmajiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy: Know Your Abdomen: GlossaryDocument5 pagesAnatomy: Know Your Abdomen: GlossaryNaida KapetanovicNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Digestive SystemDocument20 pagesAnatomy of Digestive Systemolive jollyNo ratings yet
- Development of Digestive TractDocument14 pagesDevelopment of Digestive TractSulochan Ssplendid Splinterr LohaniNo ratings yet
- The GI SystemDocument5 pagesThe GI SystemJohn Zedric Villanueva ArciagaNo ratings yet
- Pancreas A PDFDocument36 pagesPancreas A PDFtjqch6r2x8No ratings yet
- Surgical Anatomy of Pancreas: DR GaneshDocument42 pagesSurgical Anatomy of Pancreas: DR GaneshGanesh MarutinathNo ratings yet
- Anatomy StomachDocument43 pagesAnatomy StomachBijo K BennyNo ratings yet
- Pancreas: Anatomy of The PancreasDocument11 pagesPancreas: Anatomy of The PancreasHart ElettNo ratings yet
- Histology and Gross Pancreas 2019Document59 pagesHistology and Gross Pancreas 2019Azwaah Hassan100% (1)
- Abdo. VisceraDocument123 pagesAbdo. VisceraDureti DuretiNo ratings yet
- 1 11857 AnatomyDocument5 pages1 11857 Anatomykalyan2k5No ratings yet
- AbdomenDocument142 pagesAbdomenleul TizazuNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology of The Digestive SystemDocument83 pagesAnatomy & Physiology of The Digestive SystemDuodu StevenNo ratings yet
- PancreasDocument35 pagesPancreasPaskalisNo ratings yet
- Extra Hepatic Biliary ApparatusDocument5 pagesExtra Hepatic Biliary ApparatusDr santosh100% (8)
- Development of Gut Tube Fore GutDocument52 pagesDevelopment of Gut Tube Fore GutSusan SarkerNo ratings yet
- 3 Stomach & Small Intestine Oct 2017Document50 pages3 Stomach & Small Intestine Oct 2017mayankNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Dr. Aguirre Pancreas: ND RDDocument3 pagesAnatomy Dr. Aguirre Pancreas: ND RDAlbert CorderoNo ratings yet
- Esophages and Stomach ...........Document65 pagesEsophages and Stomach ...........Gebrie DinkayehuNo ratings yet
- Peritoneum: Scarlet SinghDocument34 pagesPeritoneum: Scarlet Singhandrea titusNo ratings yet
- 3.digestive SystemDocument103 pages3.digestive Systemokoti.omutanyi22No ratings yet
- 9 DuodenumDocument22 pages9 DuodenumRashi ChamboleNo ratings yet
- Functions-Bile Secretion, Glycogen Synthesis and Storage, Urea Formation, PlasmaDocument2 pagesFunctions-Bile Secretion, Glycogen Synthesis and Storage, Urea Formation, PlasmaSanthosh.S.UNo ratings yet
- PancreasDocument2 pagesPancreasSam TagardaNo ratings yet
- The PancreasDocument31 pagesThe PancreasAryan DesaiNo ratings yet
- It Means Shield It Is Most Vascular GlandDocument9 pagesIt Means Shield It Is Most Vascular GlandDr santoshNo ratings yet
- LO1 Anatomy and Histology of Lower Gi TractDocument180 pagesLO1 Anatomy and Histology of Lower Gi TractIcarus WingsNo ratings yet
- GCP - Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument4 pagesGCP - Anatomy and PhysiologyKrishelle Kate PannigNo ratings yet
- Development of Gastrointestinal TractDocument28 pagesDevelopment of Gastrointestinal TractSaif100% (1)
- LESSON 9 Digestive SystemDocument13 pagesLESSON 9 Digestive Systemmaxveinblair26No ratings yet
- Anat 4.5 GIT Embryology MelendresDocument5 pagesAnat 4.5 GIT Embryology Melendreslovelots1234No ratings yet
- Esophagus & Stomach, Its Blood Supply& Development:: OesophagusDocument8 pagesEsophagus & Stomach, Its Blood Supply& Development:: OesophagusBoody KhalilNo ratings yet
- Endocrin System (Autosaved)Document100 pagesEndocrin System (Autosaved)syedarsl9No ratings yet
- PancreasDocument21 pagesPancreasshivamnamdeo758No ratings yet
- StomachDocument13 pagesStomachSemNo ratings yet
- Document - Merged ExportDocument24 pagesDocument - Merged ExportkmsvondezNo ratings yet
- General Arrangement of The Abdominal VisceraDocument30 pagesGeneral Arrangement of The Abdominal Visceraapi-249972919100% (2)
- Anatomy of PancreasDocument6 pagesAnatomy of PancreasNariska Cooper0% (1)
- 2 StomachDocument39 pages2 Stomachmikky8204No ratings yet
- Case Based Din DraDocument14 pagesCase Based Din DraSara JosephNo ratings yet
- PeritoneumDocument8 pagesPeritoneumDavid BadaruNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal System (Anatomy and Physiology For First Year Nursing Students)Document75 pagesGastrointestinal System (Anatomy and Physiology For First Year Nursing Students)Mary Grace MartinNo ratings yet
- Intestinal Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandIntestinal Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Pancreatic Islets, Functions, Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandPancreatic Islets, Functions, Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Pancreas, Functions, Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandPancreas, Functions, Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- HeartDocument12 pagesHeartDr santosh100% (1)
- Thoracic DuctDocument2 pagesThoracic DuctDr santosh100% (1)
- BreastDocument6 pagesBreastDr santoshNo ratings yet
- Azygos VeinDocument2 pagesAzygos VeinDr santoshNo ratings yet
- Angle of Louis or Sterna AngleDocument1 pageAngle of Louis or Sterna AngleDr santoshNo ratings yet
- CerebrumDocument12 pagesCerebrumDr santoshNo ratings yet
- Lateral Ventricle: Number - Two in Number One On Each SideDocument4 pagesLateral Ventricle: Number - Two in Number One On Each SideDr santoshNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous SystemDocument2 pagesCentral Nervous SystemDr santoshNo ratings yet
- Thalamus-: Disposition - It Lies Obliquely With Its Long AxisDocument8 pagesThalamus-: Disposition - It Lies Obliquely With Its Long AxisDr santoshNo ratings yet
- CerebellumDocument5 pagesCerebellumDr santoshNo ratings yet
- CardioDocument29 pagesCardioDr santoshNo ratings yet
- MusclesDocument3 pagesMusclesDr santoshNo ratings yet
- BoneDocument4 pagesBoneDr santoshNo ratings yet
- Obturator NerveDocument3 pagesObturator NerveDr santoshNo ratings yet
- Muscles of MasticationDocument2 pagesMuscles of MasticationDr santoshNo ratings yet
- PONSDocument1 pagePONSDr santoshNo ratings yet
- Paper Pattern of 1st Year BHMSDocument3 pagesPaper Pattern of 1st Year BHMSDr santosh100% (2)
- The Spirit of Regeneration Andean Culture Confronting Western Notions of DevelopmentDocument2 pagesThe Spirit of Regeneration Andean Culture Confronting Western Notions of DevelopmentJavier UgazNo ratings yet
- Believe in YourselfDocument3 pagesBelieve in Yourselfsoumitra paulNo ratings yet
- ch3 Fin Service CustDocument15 pagesch3 Fin Service CustPeiSanNo ratings yet
- Max Grin ResumeDocument6 pagesMax Grin ResumeAnvesh ,No ratings yet
- Food AdditiveDocument14 pagesFood AdditiveHarish SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Power Metering Ics: Definition of Quadrants Application NoteDocument3 pagesPower Metering Ics: Definition of Quadrants Application NoteIrfan UllahNo ratings yet
- S.N. Uni. Roll No. Name of Student Current CourseDocument8 pagesS.N. Uni. Roll No. Name of Student Current Coursejust another hoomanNo ratings yet
- PLURONIC PE Types - BASFDocument16 pagesPLURONIC PE Types - BASFJavier Miranda RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Kresta Catalogue 2013Document24 pagesKresta Catalogue 2013KrestaNo ratings yet
- Komatsu PC200-6 Shop ManualDocument711 pagesKomatsu PC200-6 Shop ManualMạnh Dũng100% (1)
- Introduction To Elementary StatisticsDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Elementary StatisticsMartin AlboresNo ratings yet
- Cordaflex (SMK) - V (N) Shtoeu EnglDocument3 pagesCordaflex (SMK) - V (N) Shtoeu EnglrachidNo ratings yet
- Explain Emotional Intelligence and The Importance of This Characteristic at WorkDocument4 pagesExplain Emotional Intelligence and The Importance of This Characteristic at WorkvncenttanNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE ™: Biology 0610/43Document15 pagesCambridge IGCSE ™: Biology 0610/43shabanaNo ratings yet
- Intro To Buddhist Path - The Five PathsDocument3 pagesIntro To Buddhist Path - The Five Pathsalbertmelondi100% (1)
- Seht Card Hospital ListDocument33 pagesSeht Card Hospital Listlucky xenNo ratings yet
- cMT3103 Wifi Setting UserManual enDocument11 pagescMT3103 Wifi Setting UserManual enShahzad NaveedNo ratings yet
- Viral PathogenesisDocument8 pagesViral PathogenesisBiofilm NSTUNo ratings yet
- Robert Ezra ParkDocument3 pagesRobert Ezra ParkrrpriasNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness and Efficiency of E-Recruitment in Public Organizations: A Case of Tanzania National Parks (Tanapa)Document7 pagesEffectiveness and Efficiency of E-Recruitment in Public Organizations: A Case of Tanzania National Parks (Tanapa)vinay kumarNo ratings yet
- Brijesh KumarDocument4 pagesBrijesh KumarmedhahrcNo ratings yet
- (Robert Rabil) Salafism in Lebanon From ApoliticiDocument298 pages(Robert Rabil) Salafism in Lebanon From Apoliticifafa_hayNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Grade & Section Advanced StrugllingDocument4 pagesDepartment of Education: Grade & Section Advanced StrugllingEvangeline San JoseNo ratings yet
- Indian Institute of Planning and Management, NewDocument74 pagesIndian Institute of Planning and Management, NewChetan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Confluent ComponentsDocument68 pagesIntroduction To Confluent ComponentsEdward LumentaNo ratings yet
- HONDA Pilot Owner's ManualDocument324 pagesHONDA Pilot Owner's ManualJoshua SvNo ratings yet
- Solid-State Level Sensors: User ManualDocument20 pagesSolid-State Level Sensors: User ManualGilbertNo ratings yet
- An Analysis of Historic Production Trends in AustralianDocument35 pagesAn Analysis of Historic Production Trends in AustralianAdrian KarimNo ratings yet