100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
410 viewsProblem Set ForceAndAccelerationV01
1. The document contains 14 physics problems involving kinetics, forces, accelerations, friction, inclined planes, and pulley systems. The problems provide mass values, initial conditions, coefficients of friction, and ask solver to determine values like acceleration, tension, distance, speed, or time.
2. Common concepts assessed include determining acceleration from applied forces, effects of friction on motion, and analyzing pulley systems and inclined planes to solve for unknown values.
3. Problem solving requires applying Newton's laws of motion, equations for acceleration, and principles of forces, friction and pulleys.
Uploaded by
Benedick Jayson P. MartiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
410 viewsProblem Set ForceAndAccelerationV01
1. The document contains 14 physics problems involving kinetics, forces, accelerations, friction, inclined planes, and pulley systems. The problems provide mass values, initial conditions, coefficients of friction, and ask solver to determine values like acceleration, tension, distance, speed, or time.
2. Common concepts assessed include determining acceleration from applied forces, effects of friction on motion, and analyzing pulley systems and inclined planes to solve for unknown values.
3. Problem solving requires applying Newton's laws of motion, equations for acceleration, and principles of forces, friction and pulleys.
Uploaded by
Benedick Jayson P. MartiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
You are on page 1/ 2
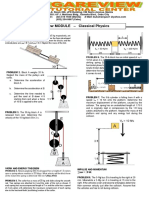
Problem Set No.
Kinetics : Force and Acceleration
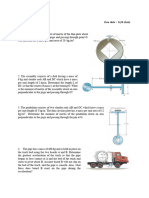
1 The casting has a mass of 4 Mg. Suspended in a
vertical position and initially at rest, it is given an
upward speed of 250 mm/ s in 0.4 s using a crane 4 The 3-Mg truck is traveling at 17 m /s when the
hook H. Determine the tension in cables AC and brakes on all its wheels are applied, causing it to
AB during this time interval if the acceleration is skid for a distance of 15 m before coming to rest.
constant. Determine the constant horizontal force developed
in the coupling C, and the frictional force developed
between the tires of the truck and the road during
this time. The total mass of the boat and trailer is 2
Mg.
5 If blocks A and B of mass 15 kg and 10 kg,
respectively, are placed on the inclined plane and
released, determine the force developed in the link.
The coefficients of kinetic friction between the
blocks and the inclined plane are A = 0.2 and B =
0.4. Neglect the mass of the link.
2 The 170-Mg train travels with a speed of 90 km/h
when it starts to climb the slope. If the engine
exerts a traction force F of 1/30 of the weight of the
train and the rolling resistance F D is equal to 1/600
of the weight of the train, determine the
deceleration of the train.
6 Motors A and B draw in the cable with the
accelerations shown. Determine the acceleration of
the 400-lb crate C and the tension developed in the
3 The 170-Mg train starts from rest and begins to cable. Neglect the mass of all the pulleys.
climb the slope as shown. If the engine exerts a
traction force F of 1/10 of the weight of the train,
determine the speed of the train when it has
traveled up the slope a distance of 1.2 km. Neglect
rolling resistance.
7 The van is traveling at 30 km h when the coupling
of the trailer at A fails. If the trailer has a mass of
350 kg and coasts 55 m before coming to rest,
determine the constant horizontal force F created
by rolling friction which causes
the trailer to stop.
12 The man pushes on the 60-lb crate with a force F.
The force is always directed down at 30 from the
horizontal as shown, and its magnitude is increased
8 If the 15-lb block A slides down the plane with a until the crate begins to slide. Determine the crates
constant velocity when = 40, determine the initial acceleration if the coefficient of static friction is
acceleration of the block when = 45. s = 0.7 and the coefficient of kinetic friction is k =
0.4.
9 Each of the three barges has a mass of 40 Mg,
whereas the tugboat has a mass of 14 Mg. As the
barges are being pulled forward with a constant
velocity of 5 m/s, the tugboat must overcome the 13 A force of F = 20 lb is applied to the cord.
frictional resistance of the water, which is 3 kN for Determine how high the 40-lb block A rises in 4 s
each barge and 2.5 kN for the tugboat. If the starting from rest. Neglect the weight of the pulleys
cable between A and B breaks, determine the and cord.
acceleration of the tugboat.
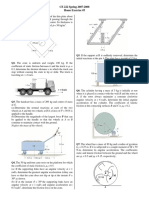
10 The crate has a mass of 90 kg and is being towed
by a chain which is always directed at 30 from the
horizontal as shown. If the magnitude of P is
increased until the crate begins to slide, determine
the crates initial acceleration if the coefficient of
static friction is s = 0.6 and the coefficient of
kinetic friction is k = 0.4. 14 The 70-kg crate shown below rests on a horizontal
surface for which the coefficient of kinetic friction is
k = 0.4. If the crate is subjected to a 400-N towing
force as shown, determine the velocity of the crate
in 3 s starting from rest.
11 Determine the acceleration of the system and the
tension in each cable. The inclined plane is
smooth, and the coefficient of kinetic friction
between the horizontal surface and block C is (k)C
= 0.3.
You might also like
- Physical Chemistry Board Exam Questions PDF100% (3)Physical Chemistry Board Exam Questions PDF10 pages
- Process Calculations 2nd Ed. - V. Venkataramani, N. Anantharaman & K.M. Meera Sheriffa Begum 2011 PDF100% (7)Process Calculations 2nd Ed. - V. Venkataramani, N. Anantharaman & K.M. Meera Sheriffa Begum 2011 PDF260 pages
- F at Each Wheel. Assume A Constant Deceleration For The 1500-kg CarNo ratings yetF at Each Wheel. Assume A Constant Deceleration For The 1500-kg Car12 pages
- Tut 9 - Kinetics - Linear Impulse and Mom and ConservationNo ratings yetTut 9 - Kinetics - Linear Impulse and Mom and Conservation4 pages
- Dynamics Tutorial Sheet 4 - Particle KineticsNo ratings yetDynamics Tutorial Sheet 4 - Particle Kinetics6 pages
- Constant Speed of 6 Ft/s. Determine How Fast The Boat Approaches The Pier at The Instant The Rope Length AB Is 50 FTNo ratings yetConstant Speed of 6 Ft/s. Determine How Fast The Boat Approaches The Pier at The Instant The Rope Length AB Is 50 FT6 pages
- Review Module 11 Classical Physics Part 2No ratings yetReview Module 11 Classical Physics Part 22 pages
- CE 222 Spring 2007-2008 Home Exercise #5: A. If The Rotor Always Maintains A Constant ClockwiseNo ratings yetCE 222 Spring 2007-2008 Home Exercise #5: A. If The Rotor Always Maintains A Constant Clockwise2 pages
- University of Bahrain Department of Mechanical Engineering MENG 263 TUTORIAL # 4 (Chapter 3)No ratings yetUniversity of Bahrain Department of Mechanical Engineering MENG 263 TUTORIAL # 4 (Chapter 3)5 pages
- Trabajo Energia en Una Partícula EjerciciosNo ratings yetTrabajo Energia en Una Partícula Ejercicios7 pages
- Tutorial 1: Energy and Momentum Methods of Particle: Applied Mechanics II, Ramesh Khanal, Nepal Engineering College, 2016No ratings yetTutorial 1: Energy and Momentum Methods of Particle: Applied Mechanics II, Ramesh Khanal, Nepal Engineering College, 20165 pages
- Instruction: Answer The Following Questions by Groups of 3, On Long Bond PaperNo ratings yetInstruction: Answer The Following Questions by Groups of 3, On Long Bond Paper2 pages
- Opción Múltiple: Ecuación de Movimiento Fuerza y AceleraciónNo ratings yetOpción Múltiple: Ecuación de Movimiento Fuerza y Aceleración11 pages
- Food Chemistry: Prof. DR - Fahim ShaltoutNo ratings yetFood Chemistry: Prof. DR - Fahim Shaltout29 pages
- Sales, Abipiel Regina I. Bsche Environmental Engineering ES21FB2No ratings yetSales, Abipiel Regina I. Bsche Environmental Engineering ES21FB241 pages
- Brian Tracy 18 Pasos para Programar La Mente para El ExitoNo ratings yetBrian Tracy 18 Pasos para Programar La Mente para El Exito19 pages
- Habitat The Place Where A Plant or Any Living Thing Lives Naturally AdaptationNo ratings yetHabitat The Place Where A Plant or Any Living Thing Lives Naturally Adaptation6 pages
- Transparent Governance in An Age of AbundanceNo ratings yetTransparent Governance in An Age of Abundance452 pages
- ANDUALEM DEMISSIE DEGU The Effect of Working Capital Management On The Profitability of Manufacturing Companies in Ethiopia100% (1)ANDUALEM DEMISSIE DEGU The Effect of Working Capital Management On The Profitability of Manufacturing Companies in Ethiopia78 pages
- Distance Learning and Effect On Practical Skills Courses in BTVTED of ZCSPCNo ratings yetDistance Learning and Effect On Practical Skills Courses in BTVTED of ZCSPC12 pages
- Components of The Smart Eye Glasses Price EstimationNo ratings yetComponents of The Smart Eye Glasses Price Estimation2 pages
- Analysis of Synchronous Generator Internal Insulation Failures100% (2)Analysis of Synchronous Generator Internal Insulation Failures5 pages
- Configuring Sequences With SFC: Simatic Pcs 7No ratings yetConfiguring Sequences With SFC: Simatic Pcs 720 pages
- Communication Skills Among University StudentsNo ratings yetCommunication Skills Among University Students6 pages
- The Management of Productivity and Technology in Manufacturing PDF100% (2)The Management of Productivity and Technology in Manufacturing PDF333 pages
- Earthworks: Theory and Practice of Surveying Review Innovations100% (1)Earthworks: Theory and Practice of Surveying Review Innovations50 pages
- Map Server For Visualizing Air Traffic Based On Data From A Remote Pseudo RadarNo ratings yetMap Server For Visualizing Air Traffic Based On Data From A Remote Pseudo Radar14 pages
- IMOmath - Functional Equations - Problems With SolutionsNo ratings yetIMOmath - Functional Equations - Problems With Solutions15 pages