Haz Id Poster1
Haz Id Poster1
Uploaded by
AmeenudeenCopyright:
Available Formats
Haz Id Poster1
Haz Id Poster1
Uploaded by
AmeenudeenCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Haz Id Poster1
Haz Id Poster1
Uploaded by
AmeenudeenCopyright:
Available Formats
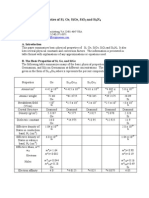
Hazard Identification Tool
Gravity Temperature
Gravitational energy is the force caused by the Temperature is the measurement of differences in the
attraction of all other masses to the mass of the thermal energy of objects or the environment, which
Earth.
M e c h a nic al the human body senses as either heat or cold.
n Ele
Examples: a falling object, a collapsing roof, a
i o ctr Examples: open flame and ignition sources, hot or
body tripping or falling ot ic cold surfaces, liquids or gases, friction, general envi-
M ronmental conditions, steam, extreme and changing
al
weather conditions
Motion
Pre
Chemical
it y
The change in position of objects or substances.
Grav
ssure
The energy present in chemicals that inherently,
See
Examples: vehicle, vessel or equipment move- or through reaction, has the potential to create a
ment, flowing water, wind, body positioning: lift- physical or health hazard to people, equipment,
ing, straining, or bending or the environment.
It!
Examples: flammable vapors, reactive hazards, car-
ature
cinogens or other toxic compounds, corrosives, pyro-
Soun
phorics, combustibles, inert gas, welding fumes, dusts
Mechanical
per
The energy of the components of a mechanical
d Biological
m
system, i.e., rotation, vibration, or motion within
Te
an otherwise stationary piece of equipment or
machinery. Living organisms that can present a hazard.
ad
R Examples: animals, bacteria, viruses, insects, blood-
ic
al
Examples: rotating equipment, compressed ia
springs, drive belts, conveyors, motors ti o e m
borne pathogens, improperly handled food, contami-
n C h nated water
Biolo gic al
Electrical Radiation
The presence and flow of an electric charge. The energy emitted from radioactive elements or
sources and naturally occurring radioactive materials.
Examples: power lines, transformers, static
charges, lightning, energized equipment, Hazard: Examples: Lighting issues, welding arc, X-rays, solar
rays, microwaves, naturally occurring radioactive ma-
wiring, batteries
terial (NORM) scale, or other non-ionizing sources
A condition or action that has the potential for an unplanned release
Pressure of, or unwanted contact with, an energy source that may result in
Sound
harm or injury to people, property, or the environment.
Energy applied by a liquid or gas which has been Sound is produced when a force causes an object or
compressed or is under a vacuum. Identify hazards at your workplace, analyzing each energy source substance to vibratethe energy is transferred
Examples: pressure piping, compressed cylin- through the substance in waves.
with the Hazard Identification Tool.
ders, control lines, vessels, tanks, hoses, pneu- Examples: impact noise, vibration, high-pressure
matic and hydraulic equipment relief, equipment noise
2008 Chevron Corporation. All rights reserved. CBRES/IDC Houston 064611 05/08
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6018)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1113)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (909)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (937)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (619)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (546)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (358)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (831)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (479)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (275)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (434)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2281)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (99)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (125)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (273)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (233)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (235)
- Hazard Prevention Through Effective Safety and Health Training - Table - ContentsDocument1 pageHazard Prevention Through Effective Safety and Health Training - Table - ContentsAmeenudeen0% (1)
- Conservation of MomentumDocument4 pagesConservation of MomentumEmme PullenNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (75)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Eid Prayers: Allaahu Alayhi Wa Sallam) Arrived in Madinah and The People There Had Two Days On Which TheyDocument4 pagesThe Eid Prayers: Allaahu Alayhi Wa Sallam) Arrived in Madinah and The People There Had Two Days On Which TheyAmeenudeenNo ratings yet
- BEE SafetyManualDocument196 pagesBEE SafetyManualAmeenudeenNo ratings yet
- Odalog L2 1407995247 LDocument2 pagesOdalog L2 1407995247 LAmeenudeenNo ratings yet
- HSES HandbookDocument48 pagesHSES HandbookNorman Ainomugisha100% (1)
- Hot Work QuizDocument1 pageHot Work QuizAmeenudeenNo ratings yet
- Topic 9 Safety and Risk Management in Oil and Gas IndustryDocument108 pagesTopic 9 Safety and Risk Management in Oil and Gas IndustryAmeenudeenNo ratings yet
- Heat StressDocument29 pagesHeat StressAmeenudeenNo ratings yet
- Forty Hadith: "Qudsi"Document23 pagesForty Hadith: "Qudsi"AmeenudeenNo ratings yet
- H2S AwarenessDocument15 pagesH2S AwarenessAmeenudeen100% (1)
- Building and Working With Effective Work Teams: FacilitatorDocument46 pagesBuilding and Working With Effective Work Teams: FacilitatorAmeenudeenNo ratings yet
- Lesson 14 - Emergency PreparednessDocument26 pagesLesson 14 - Emergency PreparednessAmeenudeenNo ratings yet
- The General Properties of Si, Ge, SiGe, SiO2 and Si3N4Document5 pagesThe General Properties of Si, Ge, SiGe, SiO2 and Si3N4AlaSamSomNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam Routine - Spring 2020Document4 pagesMidterm Exam Routine - Spring 2020Saim MollahNo ratings yet
- Inductance Part 2 - MowryDocument6 pagesInductance Part 2 - MowryJacky FanNo ratings yet
- A Model For Cutting Forces Generated During Machining With Self-Propelled Rotary ToolsDocument7 pagesA Model For Cutting Forces Generated During Machining With Self-Propelled Rotary ToolsYashwanth ReddyNo ratings yet
- Problem Set B Sinusoids and Phasors: John Alfred A. Ceniza BSME-5Document5 pagesProblem Set B Sinusoids and Phasors: John Alfred A. Ceniza BSME-5John A. CenizaNo ratings yet
- General Physics 2 Module 1Document32 pagesGeneral Physics 2 Module 1GNC Tricia Faye DeleonNo ratings yet
- AXXXCDocument9 pagesAXXXCAshwin MinzNo ratings yet
- Thb1355yxa PDFDocument3 pagesThb1355yxa PDFugano529510No ratings yet
- Solutions To Feynman-Hibbs Classical Action ProblemsDocument15 pagesSolutions To Feynman-Hibbs Classical Action ProblemsPamela Catalan ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Motivation LetterDocument2 pagesMotivation Letterapi-372390395% (39)
- CH 3 Design of Bolts in ConnectionsPartADocument22 pagesCH 3 Design of Bolts in ConnectionsPartAJakesNo ratings yet
- Fluent - 14.0 UdfDocument31 pagesFluent - 14.0 UdfvahidssNo ratings yet
- Wave Energy Conversion SystemsDocument14 pagesWave Energy Conversion SystemsYAGNESH DIVYANo ratings yet
- Transformer Basics and Transformer Principles of OperationDocument14 pagesTransformer Basics and Transformer Principles of Operationengsamir296No ratings yet
- 19 - Bearing Capacity - Eccentric LoadingDocument5 pages19 - Bearing Capacity - Eccentric LoadinghiyeonNo ratings yet
- Seismic Performance of A Laminated Rubber Bearing Under Tensile Axial LoadingDocument9 pagesSeismic Performance of A Laminated Rubber Bearing Under Tensile Axial LoadingIgor GjorgjievNo ratings yet
- CUET 2023 Physics Question Paper 1Document8 pagesCUET 2023 Physics Question Paper 1snehawasthi222No ratings yet
- Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy H - NMRDocument61 pagesProton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy H - NMRchemist100% (2)
- Belt Drive ExperimentDocument6 pagesBelt Drive ExperimentZeeshan HaiderNo ratings yet
- Types of Cam and FollowerDocument28 pagesTypes of Cam and Followersainathpedakanti1No ratings yet
- 28 Flow Through A Venturi Flume Slice Gate 374s18Document5 pages28 Flow Through A Venturi Flume Slice Gate 374s18Ekala XuhalxNo ratings yet
- Friction Head Loss in PipesDocument9 pagesFriction Head Loss in PipesnattydreadfathelahNo ratings yet
- Kinematics-03-Subjective SolvedDocument11 pagesKinematics-03-Subjective SolvedRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- HMWK5 SolutionsDocument4 pagesHMWK5 SolutionsWana BilaNo ratings yet
- Set 4 Heat Transfer Fin Analysis2Document54 pagesSet 4 Heat Transfer Fin Analysis2ndishematengeNo ratings yet
- Coefficient "A": Variation TypeDocument3 pagesCoefficient "A": Variation TypePrinceNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips Etabs-Checklist PDFDocument3 pagesDokumen - Tips Etabs-Checklist PDFMasud AlamNo ratings yet
- Wannier FlowDocument69 pagesWannier FlowRennie PhilipNo ratings yet
- Student's Guide To Year 9 and 10 Science (Stage 5)Document38 pagesStudent's Guide To Year 9 and 10 Science (Stage 5)dan964100% (1)