100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
2K viewsRestrictions On Land Use
Restrictions On Land Use
Uploaded by
Brat WurstOwnership and control over property is considered the most important property right. Courts must protect property rights through remedies like injunctions and damages, as property rights are hollow without means to enforce them. There are different types of agreements between neighbors regarding land use, such as easements which allow use of another's land, and covenants which restrict land use. Zoning laws systematically organize incompatible land uses through regulations and districts. The government also has power of eminent domain to take private property for public use, but it must provide compensation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Restrictions On Land Use
Restrictions On Land Use
Uploaded by
Brat Wurst100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
2K views1 pageOwnership and control over property is considered the most important property right. Courts must protect property rights through remedies like injunctions and damages, as property rights are hollow without means to enforce them. There are different types of agreements between neighbors regarding land use, such as easements which allow use of another's land, and covenants which restrict land use. Zoning laws systematically organize incompatible land uses through regulations and districts. The government also has power of eminent domain to take private property for public use, but it must provide compensation.
Original Description:
1L Flow Charts by blondebarrister of reddit
Original Title
Restrictions on Land Use
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Ownership and control over property is considered the most important property right. Courts must protect property rights through remedies like injunctions and damages, as property rights are hollow without means to enforce them. There are different types of agreements between neighbors regarding land use, such as easements which allow use of another's land, and covenants which restrict land use. Zoning laws systematically organize incompatible land uses through regulations and districts. The government also has power of eminent domain to take private property for public use, but it must provide compensation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
2K views1 pageRestrictions On Land Use
Restrictions On Land Use
Uploaded by
Brat WurstOwnership and control over property is considered the most important property right. Courts must protect property rights through remedies like injunctions and damages, as property rights are hollow without means to enforce them. There are different types of agreements between neighbors regarding land use, such as easements which allow use of another's land, and covenants which restrict land use. Zoning laws systematically organize incompatible land uses through regulations and districts. The government also has power of eminent domain to take private property for public use, but it must provide compensation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
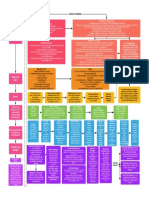
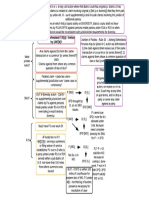
Ownership and Often seen as most important
Control Over the property right
Use of Property Courts have to protect - property
Involves two parcesl of land: dominant (derives
benefit) and servient (bears burden aka the land
rights hollow if there's insufficient
means to protect used). Can get via purchase, implied,
presription, estoppel
Not absolute - dominion over
Right to Exclude (trespass: property rights doesn't give dominion Easement Appurtenant: benefits easement
land invaded by physical over people on your property owner in the use of land belonging to that owner
object) (property described in location terms - church
purposes - not specific church) (PREFERRED
BY COURTS)
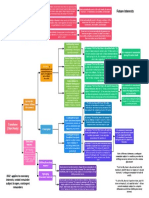
Private v. Public
Nuisance Law: provides a Easement in Gross: benefits easement owner
remedy for nonphysical personally rather than in connection with the
Remedies: Injunction, Damages
invasions to protect use and use of land (church example: want easement to
be with them specifically, not the land)
enjoyment of land
Coase: nuisance law forces
companies to take externality
(pollution) into account
Real Covenant (Damages):
4 requirements: writing, intend that it run with
Easement: a grant of interest in the land, touch and concern, privity of estate
Servitudes: agreements land that entitles a person to use
land possessed by another (just
between neighbors - land
about use - right of way is a
owned by one person subject common example) Equitable Servitude (Injunction)
to specified use by another 4 requirements: writing, intend that it run with
the land, touch and concern, NOTICE (not
Covenant: a right that arises from privity)
a promise respecting use of land
by one landowner to another (like
not to do something, for example) Termination: terminate based on changes
inside or outside the land - remember changed
circumstances rule!
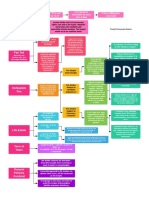
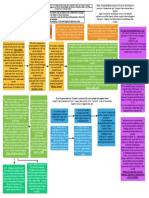
Euclidian Zoning: regulations on use,
height, area to regulate property. Districts
graded highest (single family homes) to lowest Variance: permits use of land in a way
(worst type of industry). Higher uses permitted
in areas zoned for lower uses, but not vice expressly prohibited. Two Rules:
versa (can have single family home in 1. Necessary to avoid undue hardship
apartment district; can't have commercial 2. Doesn't impinge on public good or
Zoning: systematic appraoch to business in residential district.
intent/purpose of zoning plane
organizing incompatible land uses -
zoning boards restrict certain areas Flexible Zoning
to certain purposes
Special Exception: puse permitted by
Aesthetic Zoning: restrictions on ordinance that's not necessarily incompatible,
apperance on property - valid if related but may cause harm if not watched. Two
to general welfare approaches:
1. Zoners use as discretionary device, only
Restrictions on Household approve if very general criteria met
Composition: okay for safety reasons, 2. Very detailed criteria, and if met, exception
but keep in mind FHA and discrimination granted
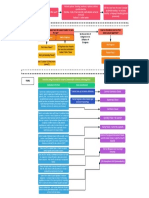
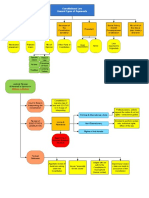
Physical Takings: physical takings Categorical Rules:
allowed for public use/public 1. Regulations that control nuisances or nuisance
like activity are not takings, gov. shouldn't have to
purpose - but always require
pay to regulate/protect people from nuisance.
compensation 2. Permanent physical occupation authorized by
government is always a taking (even if serves public
Eminent Domain interest - but has to be occupation by a third party).
(Takings): power of government 3. A regulation that denies owner of all economically
beneficial use is a taking (unless it was something
to take title to property against the government could regulate before)
owner's will Regulatory Takings: occurs when
government regulates the use of
property in a way that impacts Penn Central Test to Determine whether a
owners, but may or may not regulation is a taking
amount to a taking. Regulations 1. Economic impact of regulation
that go too far = takings; so has the (interfererence with investment backed
consequence of the regulation expectations, dimunition in value)
amounted to a taking? 2. Character of government action
(disproportionate affects, reciprocity of
advantage, is government abusing power?
You might also like
- ConLaw PreWrites 2018 PDFDocument12 pagesConLaw PreWrites 2018 PDFMaria M100% (1)
- ContractsDocument1 pageContractsBrat Wurst100% (2)
- ContractsDocument1 pageContractsBrat Wurst100% (2)
- Future Estates Flow ChartDocument1 pageFuture Estates Flow ChartKelsey100% (5)
- Negligence AnalysisDocument1 pageNegligence AnalysisBrat Wurst100% (3)
- Joinder DiagramsDocument1 pageJoinder DiagramsBrat Wurst100% (3)
- Negligence AnalysisDocument1 pageNegligence AnalysisBrat Wurst100% (3)
- Future InterestsDocument1 pageFuture InterestsBrat WurstNo ratings yet
- Ucc 2-207Document1 pageUcc 2-207Brat Wurst100% (1)
- Possessory Estates ChartDocument8 pagesPossessory Estates ChartJulia Bienstock100% (11)
- Ucc 2-207Document1 pageUcc 2-207Brat Wurst100% (1)
- July 2005 Motion To Change CustodyDocument5 pagesJuly 2005 Motion To Change CustodySilenceIsOppression100% (8)
- Property Present EstatesDocument1 pageProperty Present EstatesBrat Wurst100% (1)
- Con Law Master ChartDocument1 pageCon Law Master ChartBrat Wurst100% (1)
- Con Law Master ChartDocument1 pageCon Law Master ChartBrat Wurst100% (1)
- Gumamela As Alternative Dishwashing LiquidDocument30 pagesGumamela As Alternative Dishwashing LiquidJAMES ALDWIN ABENIS90% (39)
- Answering A Con Law QuestionDocument1 pageAnswering A Con Law QuestionBrat WurstNo ratings yet
- Civil Procedure - Erie EssayDocument2 pagesCivil Procedure - Erie Essayjustgottabezen100% (1)
- Criminal Law 1L Attack OutlineDocument4 pagesCriminal Law 1L Attack OutlineChris Loy100% (2)
- Civ Pro Flow ChartDocument8 pagesCiv Pro Flow Chartnhjefferson100% (2)
- Criminal Law MPC v. CL ChartDocument17 pagesCriminal Law MPC v. CL Charttgatga100% (8)
- Unit 12 Test PDFDocument2 pagesUnit 12 Test PDFValentina Nelkovska80% (5)
- Civ Pro Outline 2021Document71 pagesCiv Pro Outline 2021AmandaNo ratings yet
- 1st A - Speech Flowchart # CasesDocument2 pages1st A - Speech Flowchart # Casessmuldersam100% (1)
- Constitutional Law Essay Rules For Bar ExamDocument14 pagesConstitutional Law Essay Rules For Bar ExamT Sheth100% (6)
- Commerce Clause FlowchartDocument1 pageCommerce Clause FlowchartMark Adamson100% (1)
- Property 1L Outline - 2021Document67 pagesProperty 1L Outline - 2021AmandaNo ratings yet
- 2021 Property Attack OutlinesDocument32 pages2021 Property Attack OutlinesAmanda0% (1)
- Commerce ClauseDocument1 pageCommerce ClauseBrat WurstNo ratings yet
- SMJDocument1 pageSMJBrat WurstNo ratings yet
- Basic Commerce Clause FrameworkDocument1 pageBasic Commerce Clause FrameworkBrat WurstNo ratings yet
- DCCDocument1 pageDCCBrat WurstNo ratings yet
- Powers & Limitations of The Judiciary Step 1: Can/will The Supreme Court Hear The Case?Document1 pagePowers & Limitations of The Judiciary Step 1: Can/will The Supreme Court Hear The Case?Brat WurstNo ratings yet
- Takings FlowchartDocument1 pageTakings FlowchartAmanda100% (1)
- Dormant Commerce Clause FCDocument1 pageDormant Commerce Clause FCslbernstein100% (1)
- P JoiningDocument1 pageP JoiningBrat WurstNo ratings yet
- Contracts 1 - Quick Issue Spotting GuideDocument8 pagesContracts 1 - Quick Issue Spotting GuideVirginia Crowson100% (1)
- Crim Law ATK OutlineDocument10 pagesCrim Law ATK Outlinegialight100% (4)
- Defeasible Estates ChartDocument1 pageDefeasible Estates ChartMrsChuckBassNo ratings yet
- SSI Under 11thDocument1 pageSSI Under 11thBrat Wurst100% (1)
- SSI Under 11thDocument1 pageSSI Under 11thBrat Wurst100% (1)
- Basic Commerce Clause FrameworkDocument1 pageBasic Commerce Clause FrameworkBrat WurstNo ratings yet
- Cupid and Psyche SummaryDocument10 pagesCupid and Psyche SummaryLucila Gabuay50% (2)
- 06 Griswold Vs Connecticut - DIGESTDocument1 page06 Griswold Vs Connecticut - DIGESTKarez MartinNo ratings yet
- Present and Future Estates OutlineDocument4 pagesPresent and Future Estates OutlineTripp Rush100% (2)
- To The States, Are Reserved To The States Respectively, or To The People."Document1 pageTo The States, Are Reserved To The States Respectively, or To The People."Brat WurstNo ratings yet
- ENS CivPro Attack OutlineDocument4 pagesENS CivPro Attack OutlineseabreezeNo ratings yet
- Removal FlowchartDocument1 pageRemoval FlowchartAmandaNo ratings yet
- Supplemental Jurisdiction FlowchartDocument1 pageSupplemental Jurisdiction FlowchartAmandaNo ratings yet
- Impleader DiagramDocument1 pageImpleader DiagramBrat WurstNo ratings yet
- Allocation of Foreign Policy PowerDocument1 pageAllocation of Foreign Policy PowerBrat WurstNo ratings yet
- Property ChecklistDocument30 pagesProperty ChecklistHeather Kinsaul FosterNo ratings yet
- Executive Powers - Page 1Document1 pageExecutive Powers - Page 1Brat WurstNo ratings yet
- Criminal Law Pre-WritesDocument1 pageCriminal Law Pre-WritesAlex HardenNo ratings yet
- Con Law AttackDocument6 pagesCon Law Attackthisfadednight100% (2)
- Constitutional Law II Zietlow Outline VillanuevaDocument49 pagesConstitutional Law II Zietlow Outline VillanuevaCatNo ratings yet
- Intentional Torts OutlineDocument6 pagesIntentional Torts OutlineAmandaNo ratings yet
- Civil Procedure RoadmapsDocument15 pagesCivil Procedure RoadmapsCarolina JordanNo ratings yet
- Contracts Attack OutlineDocument6 pagesContracts Attack OutlineShannon LitvinNo ratings yet
- Civil War Enforcement PowersDocument1 pageCivil War Enforcement PowersBrat WurstNo ratings yet
- Joinder-Big Picture: R J I R Diver TyDocument1 pageJoinder-Big Picture: R J I R Diver Tysafkdjafgh leeeNo ratings yet
- P ReclusionDocument1 pageP ReclusionBrat WurstNo ratings yet
- Attack OutlineDocument3 pagesAttack OutlineSam Rodgers100% (2)
- Steel Seizure FrameworkDocument1 pageSteel Seizure FrameworkBrat WurstNo ratings yet
- Business Associations (Corporations) - Duty of Care FlowchartDocument1 pageBusiness Associations (Corporations) - Duty of Care FlowchartBill Brasky0% (2)
- Property Outline Fall 2020Document46 pagesProperty Outline Fall 2020Alyssa Morris100% (1)
- Erie Flow ChartDocument1 pageErie Flow ChartDhvanil Zaveri100% (2)
- Con Law Flow ChartsDocument6 pagesCon Law Flow ChartsBrady WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Law School Outline Keyed To Civil Procedure Freer 7th Ed - Wiki Law SchoolDocument39 pagesLaw School Outline Keyed To Civil Procedure Freer 7th Ed - Wiki Law SchoolACDCNo ratings yet
- CONTRACTS SHORT OUTLINE - HendersonDocument20 pagesCONTRACTS SHORT OUTLINE - HendersonSio Mo0% (1)
- Business Organizations: Outlines and Case Summaries: Law School Survival Guides, #10From EverandBusiness Organizations: Outlines and Case Summaries: Law School Survival Guides, #10No ratings yet
- Allocation of Foreign Policy PowerDocument1 pageAllocation of Foreign Policy PowerBrat WurstNo ratings yet
- To The States, Are Reserved To The States Respectively, or To The People."Document1 pageTo The States, Are Reserved To The States Respectively, or To The People."Brat WurstNo ratings yet
- Executive Powers - Page 1Document1 pageExecutive Powers - Page 1Brat WurstNo ratings yet
- Steel Seizure FrameworkDocument1 pageSteel Seizure FrameworkBrat WurstNo ratings yet
- Civil War Enforcement PowersDocument1 pageCivil War Enforcement PowersBrat WurstNo ratings yet
- Class Action - Rule 23 To Be Certified, Must Meet 23A Requirements & Fit Into A 23B - Not Class Action Until Court Certifies It As SuchDocument1 pageClass Action - Rule 23 To Be Certified, Must Meet 23A Requirements & Fit Into A 23B - Not Class Action Until Court Certifies It As SuchBrat Wurst100% (1)
- Chapter One Introduction To Operations ManagementDocument10 pagesChapter One Introduction To Operations ManagementWiz SantaNo ratings yet
- Organised Crime in IndiaDocument5 pagesOrganised Crime in Indiarahul singhNo ratings yet
- Physics Form 1 QuestionsDocument10 pagesPhysics Form 1 QuestionsOkumu KevinsNo ratings yet
- New Trend Maths ChapterDocument32 pagesNew Trend Maths ChapterAaron MokNo ratings yet
- The History of Discovery, Synthesis and Development of Testosterone For Clinical UseDocument12 pagesThe History of Discovery, Synthesis and Development of Testosterone For Clinical UseQuinn CRNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5: Selecting Event Venue and SiteDocument3 pagesLesson 5: Selecting Event Venue and SiteChavez RechelleNo ratings yet
- W: Jon P: Nydia Clip E: Behavior Behavior Percep-ons/A2ribu-ons Percep-ons/A2ribu-onsDocument2 pagesW: Jon P: Nydia Clip E: Behavior Behavior Percep-ons/A2ribu-ons Percep-ons/A2ribu-onsalina soareNo ratings yet
- Positive ReinforcementDocument7 pagesPositive ReinforcementfahimafridiNo ratings yet
- For More Important Questions Visit:: Matrices and DeterminantsDocument16 pagesFor More Important Questions Visit:: Matrices and Determinantsanon_462585635No ratings yet
- Come As You AreDocument1 pageCome As You AreBryan Varela GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Dobson Bay Club v. La Sonrisa de Siena LLC, Ariz. (2017)Document22 pagesDobson Bay Club v. La Sonrisa de Siena LLC, Ariz. (2017)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- R.A. No. 7716Document11 pagesR.A. No. 7716netortizNo ratings yet
- Ca 3 Lesson 2 Golden Era of PenologyDocument6 pagesCa 3 Lesson 2 Golden Era of PenologyChristian IlaganNo ratings yet
- Social Juistice and EquityDocument2 pagesSocial Juistice and EquityShreyash HemromNo ratings yet
- Murrey Math Is A Trading System For All EquitiesDocument27 pagesMurrey Math Is A Trading System For All Equitiesvito111100% (1)
- Taller 2Document4 pagesTaller 2CCJNo ratings yet
- 1757 08-10 Gelatamp ENDocument4 pages1757 08-10 Gelatamp ENStevishaNo ratings yet
- Alfozan Award Accessories Competition EnglishDocument5 pagesAlfozan Award Accessories Competition EnglishDasur 128No ratings yet
- Grammar Friends 3Document126 pagesGrammar Friends 3luu dinhNo ratings yet
- Six Sigma Glossary PDFDocument36 pagesSix Sigma Glossary PDFmancheung6429100% (1)
- Reflective Learning Journal (Teacher Guide) PDFDocument21 pagesReflective Learning Journal (Teacher Guide) PDFGary ZhaiNo ratings yet
- 2017 Safariland CatalogDocument76 pages2017 Safariland CatalogOld_RomadNo ratings yet
- LG g8 Thinq UgDocument202 pagesLG g8 Thinq UgMichael Eugene ChurchNo ratings yet
- Employment Contract: (Wide Range Digital Services) (The "Company")Document10 pagesEmployment Contract: (Wide Range Digital Services) (The "Company")Saifal Ahmed MughalNo ratings yet
- Unfair Labor PracticeDocument28 pagesUnfair Labor PracticeNicco AcaylarNo ratings yet