0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
48 viewsIJSO Part-14
IJSO Part-14
Uploaded by
SadguruThis document provides steps to solve problems involving objects that are accelerating. It first discusses a system with two masses connected by a string over a pulley. It then works through an example involving blocks attached by a rope where the net force, tension, and external force are calculated. Finally, it presents a problem about blocks on top of each other where the acceleration is to be found. The key steps outlined are: 1) drawing free body diagrams of individual objects, 2) labeling all external forces, 3) choosing a coordinate system, 4) writing force equations, and 5) solving equations to find unknown values.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
IJSO Part-14
IJSO Part-14
Uploaded by
Sadguru0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
48 views1 pageThis document provides steps to solve problems involving objects that are accelerating. It first discusses a system with two masses connected by a string over a pulley. It then works through an example involving blocks attached by a rope where the net force, tension, and external force are calculated. Finally, it presents a problem about blocks on top of each other where the acceleration is to be found. The key steps outlined are: 1) drawing free body diagrams of individual objects, 2) labeling all external forces, 3) choosing a coordinate system, 4) writing force equations, and 5) solving equations to find unknown values.
Original Description:
IJSO
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
This document provides steps to solve problems involving objects that are accelerating. It first discusses a system with two masses connected by a string over a pulley. It then works through an example involving blocks attached by a rope where the net force, tension, and external force are calculated. Finally, it presents a problem about blocks on top of each other where the acceleration is to be found. The key steps outlined are: 1) drawing free body diagrams of individual objects, 2) labeling all external forces, 3) choosing a coordinate system, 4) writing force equations, and 5) solving equations to find unknown values.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
48 views1 pageIJSO Part-14
IJSO Part-14
Uploaded by
SadguruThis document provides steps to solve problems involving objects that are accelerating. It first discusses a system with two masses connected by a string over a pulley. It then works through an example involving blocks attached by a rope where the net force, tension, and external force are calculated. Finally, it presents a problem about blocks on top of each other where the acceleration is to be found. The key steps outlined are: 1) drawing free body diagrams of individual objects, 2) labeling all external forces, 3) choosing a coordinate system, 4) writing force equations, and 5) solving equations to find unknown values.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
F x = max
Since string is massless, so tension in both sides
N = m2 . a
of string is same.
So magnitude of force exerted by string on pulley m2F F
N= sin ce a
m1 m2 m1 m 2
= 100 2 100 2 = 100 2 N
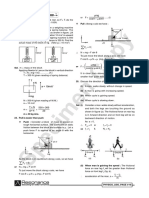
16. A 5 kg block has a rope of mass 2 kg attached to its
Note : Since pulley is in equilibrium position, so net underside and a 3 kg block is suspended from the other
forces on it is zero. end of the rope. The whole system is accelerated
(ii) Accelerating Objects : upward at 2 m/s2 by an external force F0.
(a) What is F0 ?
Steps to solve problems involving objects that are in
(b) What is the net force on rope ?
accelerated motion :
(c) What is the tension at middle point of the rope ?
Step 1 : Make a sketch of the problem. (g = 10 m/s2)
Step 2 : Isolate a single object and then draw the free
- body diagram for that object. Label all external forces
acting on it. Be sure to include all the forces acting on
the chosen body, but be equally careful not to include
any force exerted by the body on some other body.
Some of the forces may be unknown , label them with
algebraic symbols.
Step 3 : Choose a convenient coordinate system, show
Sol.For calculating the value of F0.
location of coordinate axis explicitly in the free - body
diagram, and then determine components of forces F.B.D of whole system
with reference to these axis and resolve all forces into
x and y components. F0
Step 4 : Apply the equations Fx = max & Fy = may.
2
Step 5 : Step 4 will give two equations with several (a) 2m/s
unknown quantities. If you have only two unknown 10 g = 100 N
quantities at this point, you can solve the two equations
for those unknown quantities.
F0 –100 = 10 × 2
Step 6 : If step 5 produces two equations with more
than two unknowns, go back to step 2 and select F0 = 120 N ........(1)
another object and repeat these steps. Eventually at
(b) According to Newton’s second law, net force on
step 5 you will have enough equations to solve for all
unknown quantities. rope.
F = ma = 2 × 2
15. A force F is applied horizontally on mass m1 as shown = 4N ............(2)
in figure. Find the contact force between m1 and m2.
(c) For calculating tension at the middle point we draw
F.B.D. of 3 kg block with half of the rope (mass 1
kg) as shown.
Sol.Considering both blocks as a system to find the
common acceleration.
Common acceleration
T–4g=4.2
F
a=
m1 m2 .......(1) T = 48 N
17. A block of mass 50 kg is kept on another block of mass
F m1 m2 a
1 kg as shown in figure. A horizontal force of 10 N is
applied on the 1Kg block. (All surface are smooth).
To find the contact force between ‘A’ and ‘B’ we draw Find : (g = 10 m/s2)
F.B.D. of mass m2.
F.B.D. of mass m2 (a) Acceleration of blocks A and B.
PHYSICS_IJSO_PAGE #13
13
You might also like
- Handling Notes Cessna 172: Singapore Flying CollegeDocument42 pagesHandling Notes Cessna 172: Singapore Flying CollegeEthan PoonNo ratings yet
- Toshiba Es4520c Service Hand BookDocument546 pagesToshiba Es4520c Service Hand BookMarco Delsalto100% (1)
- Newton'S Laws of MotionDocument21 pagesNewton'S Laws of MotionRagheb IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Dynamics Checked PDFDocument24 pagesChapter 3 Dynamics Checked PDFWan WenNo ratings yet
- e2ee220e-0e37-4aa8-95c1-d738cf047cc3_Laws of Motion and Friction - RaceDocument2 pagese2ee220e-0e37-4aa8-95c1-d738cf047cc3_Laws of Motion and Friction - RaceSam UkiyoNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 18 Sept 2022Document6 pagesAdobe Scan 18 Sept 2022Ajay AroraNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Homework Important Note About WebassignDocument10 pagesWeek 3 Homework Important Note About WebassignJB SibolinaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Dynamics: Force and Newton'S Laws of Motion: Net F Ma (63.0 KG) (4.20 M/s ) 265 NDocument15 pagesChapter 4: Dynamics: Force and Newton'S Laws of Motion: Net F Ma (63.0 KG) (4.20 M/s ) 265 NCedric KouakouNo ratings yet
- Iit Jee (Notes+questions+ Mains)Document35 pagesIit Jee (Notes+questions+ Mains)dinrajk2No ratings yet
- LOM FrictionDocument3 pagesLOM Frictiondakshbadgotya09No ratings yet
- Force and Newton's Laws of MotionDocument8 pagesForce and Newton's Laws of MotionUJJVAL GAHOINo ratings yet
- Newchapter 2 CstaticsofparticleDocument24 pagesNewchapter 2 Cstaticsofparticlehamizanafiq0809No ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument3 pagesAssignmentabdallah amrNo ratings yet
- Impo. NLMDocument31 pagesImpo. NLMChirayu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Lecture04 P1Document22 pagesLecture04 P1Cao Gia BảoNo ratings yet
- Lecture04-05-06 - P1 PhysicsDocument61 pagesLecture04-05-06 - P1 Physicsthuy36030No ratings yet
- NLM - 1Document6 pagesNLM - 1shridhanyaiitm26No ratings yet
- Answers & Solution - Major Test - 3 (ADV) DT. 27-03-2022Document29 pagesAnswers & Solution - Major Test - 3 (ADV) DT. 27-03-2022shehbazthakur123No ratings yet
- Dynamics: Newton's Laws of Motion: Phys101 Lectures 4 & 5Document27 pagesDynamics: Newton's Laws of Motion: Phys101 Lectures 4 & 5Phạm Bùi Quốc QuyềnNo ratings yet
- Lecture04 P1Document22 pagesLecture04 P1thanhgold1105No ratings yet
- Physics, Chemistry and MathematicsDocument10 pagesPhysics, Chemistry and Mathematicsarchit jain123No ratings yet
- Midterm Exam #2, Part ADocument6 pagesMidterm Exam #2, Part AhariNo ratings yet
- CH3 MergerDocument45 pagesCH3 MergerRuthNo ratings yet
- Sankalp - Phase Ii - Wep - 2Document4 pagesSankalp - Phase Ii - Wep - 2pryandeepNo ratings yet
- 11th JEE Advance Paper-1 Sol MT-02 DT 23-12-23Document18 pages11th JEE Advance Paper-1 Sol MT-02 DT 23-12-23shasumith12No ratings yet
- PHY131 hw6Document4 pagesPHY131 hw62kbymgm5zqNo ratings yet
- Tutorial: Theory and Applications of The Maxwell Stress TensorDocument5 pagesTutorial: Theory and Applications of The Maxwell Stress TensorimamuraNo ratings yet
- 11th - EM - JEE - J3 P+C+M 05 08 2023 - PAPER 1Document10 pages11th - EM - JEE - J3 P+C+M 05 08 2023 - PAPER 1ashmitaramoliya123No ratings yet
- Block on Block (two blocks) DPP_081305Document39 pagesBlock on Block (two blocks) DPP_081305skalampalli737No ratings yet
- y3uGbpQ53z4GI3JOLDV1Document7 pagesy3uGbpQ53z4GI3JOLDV1pv artsNo ratings yet
- DPPS Neet Disha Physics Original_Part13Document4 pagesDPPS Neet Disha Physics Original_Part13prakharNo ratings yet
- Laws of Motion: Contact Number: 9667591930 / 8527521718Document5 pagesLaws of Motion: Contact Number: 9667591930 / 8527521718ukneet8No ratings yet
- Unit 4: Dynamics: Newton's Laws of MotionDocument22 pagesUnit 4: Dynamics: Newton's Laws of MotionDandy H HerkoNo ratings yet
- L6Firction Forces (Unit II)Document48 pagesL6Firction Forces (Unit II)Jaanaki NishuNo ratings yet
- Race-02 - XI (Nurture) (IIT) - Physics (Friction) - Santosh Kumar Sir - On 05.07.2024 - FINALDocument5 pagesRace-02 - XI (Nurture) (IIT) - Physics (Friction) - Santosh Kumar Sir - On 05.07.2024 - FINALkrishnansu1234No ratings yet
- IJSO Part-19Document1 pageIJSO Part-19SadguruNo ratings yet
- Avitation TheoryDocument22 pagesAvitation TheoryArjun Narayanan SatchidanandamNo ratings yet
- Laws of MotionDocument35 pagesLaws of Motionparthbajajjan2008No ratings yet
- Gravitation Tutorial and Sol Q1 To 8 OnlyDocument11 pagesGravitation Tutorial and Sol Q1 To 8 OnlyJarrell YappNo ratings yet
- Exercise NLMDocument27 pagesExercise NLMparthbajajjan2008No ratings yet
- 4.1 Gravity Force LabDocument4 pages4.1 Gravity Force LabT. Danielle Dockery100% (1)
- CH 4Document3 pagesCH 4aliNo ratings yet
- FrictionDocument12 pagesFrictionKanuv SinghalNo ratings yet
- Introductory Problems: Problems I: Introductory Problems & Collisions in One DimensionDocument4 pagesIntroductory Problems: Problems I: Introductory Problems & Collisions in One DimensionDiego ForeroNo ratings yet
- Friction PDFDocument21 pagesFriction PDFPradeep SharmaNo ratings yet
- Science201 Act.3Document4 pagesScience201 Act.3Judy Ann CercadoNo ratings yet
- Law of MotionDocument19 pagesLaw of MotionEzhil MukilNo ratings yet
- Ch3-Forces DynamicsDocument42 pagesCh3-Forces DynamicsJimmy LauNo ratings yet
- Final1 PDFDocument10 pagesFinal1 PDFAngelica SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Example ProblemsDocument9 pagesLesson 6 Example ProblemsOksana MandrykNo ratings yet
- 4-Newton's Laws of Motion QuestionDocument4 pages4-Newton's Laws of Motion Questionsaravanasaravanan84487No ratings yet
- Physics DPP - 9Document4 pagesPhysics DPP - 9Hemant JasoriyaNo ratings yet
- PhysicsBowl 2007 Solutions PDFDocument6 pagesPhysicsBowl 2007 Solutions PDFElevenPlus ParentsNo ratings yet
- Physics101-Second Major-152-SolutionDocument9 pagesPhysics101-Second Major-152-SolutionAsrianorNo ratings yet
- 01 PT-01 - JEE-PHY - WE01 - Calc of WorkDocument6 pages01 PT-01 - JEE-PHY - WE01 - Calc of Workmangalsadan1967No ratings yet
- M22 Mazu0536 01 Ism C22Document20 pagesM22 Mazu0536 01 Ism C222836545No ratings yet
- NLM & Friction _ DPP 10 (Extra) __ NSEP Batch 2024Document5 pagesNLM & Friction _ DPP 10 (Extra) __ NSEP Batch 2024jatincomputer604No ratings yet
- WEPDCPDocument68 pagesWEPDCPAshwin AKNo ratings yet
- PPP0101 Principles of Physics Tutorial 3Document4 pagesPPP0101 Principles of Physics Tutorial 3TAN XIN YINo ratings yet
- F4 1920 Year-End TestDocument6 pagesF4 1920 Year-End Test5B04 CHOW HOI LAMNo ratings yet
- Problems in Quantum Mechanics: Third EditionFrom EverandProblems in Quantum Mechanics: Third EditionRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsNo ratings yet
- IJSO Part-17Document1 pageIJSO Part-17SadguruNo ratings yet
- IJSO Part-20Document1 pageIJSO Part-20SadguruNo ratings yet
- IJSO Part-16Document1 pageIJSO Part-16SadguruNo ratings yet
- (B) The Working of A Rocke T:: N' and MG Are Not Action - Reaction Pair. Since PairDocument1 page(B) The Working of A Rocke T:: N' and MG Are Not Action - Reaction Pair. Since PairSadguruNo ratings yet
- IJSO Part-13Document1 pageIJSO Part-13SadguruNo ratings yet
- IJSO Part-19Document1 pageIJSO Part-19SadguruNo ratings yet
- IJSO Part-15Document1 pageIJSO Part-15SadguruNo ratings yet
- Principle of Conservation of Linear Momentum: (A) Recoil of GunDocument1 pagePrinciple of Conservation of Linear Momentum: (A) Recoil of GunSadguruNo ratings yet
- Translatory Equilibrium: F F F MaDocument1 pageTranslatory Equilibrium: F F F MaSadguruNo ratings yet
- Impulse of Force: Demonstration-Newton's Third Law of MotionDocument1 pageImpulse of Force: Demonstration-Newton's Third Law of MotionSadguruNo ratings yet
- Newton'S First Law of Motion: (A) de Finition of Ine RtiaDocument1 pageNewton'S First Law of Motion: (A) de Finition of Ine RtiaSadguruNo ratings yet
- (B) Tension:: - KX K SpringDocument1 page(B) Tension:: - KX K SpringSadguruNo ratings yet
- (A) Conservative Force:: Galileo'S ExperimentsDocument1 page(A) Conservative Force:: Galileo'S ExperimentsSadguruNo ratings yet
- IJSO Part-8Document1 pageIJSO Part-8SadguruNo ratings yet
- (A) Normal Force (N) :: Detailed Analysis of Contact ForceDocument1 page(A) Normal Force (N) :: Detailed Analysis of Contact ForceSadguruNo ratings yet
- IJSO Part-2Document1 pageIJSO Part-2SadguruNo ratings yet
- Paper 1 CH 1 To 4Document4 pagesPaper 1 CH 1 To 4SadguruNo ratings yet
- Nso Set-B Class-12 UpdatedDocument1 pageNso Set-B Class-12 UpdatedSadguruNo ratings yet
- Empirical Formula and Molecular FormulaDocument20 pagesEmpirical Formula and Molecular FormulaShiela LumbagaNo ratings yet
- ElectroSmash - Dallas Rangemaster Treble Booster Circuit AnalysisDocument15 pagesElectroSmash - Dallas Rangemaster Treble Booster Circuit AnalysisChunxiao WeiNo ratings yet
- Kenil Rajodiya ResumeDocument1 pageKenil Rajodiya Resumekenilrajodiya5No ratings yet
- QGIS 3.22 ServerUserGuide enDocument108 pagesQGIS 3.22 ServerUserGuide enIQaba DyosiNo ratings yet
- Topographic Map of Willow CreekDocument1 pageTopographic Map of Willow CreekHistoricalMapsNo ratings yet
- Acr122U NFC Reader: Technical SpecificationsDocument6 pagesAcr122U NFC Reader: Technical SpecificationsAbdi Ayanda SinulinggaNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Activity Sheets Quarter 1 Week 1Document9 pagesGrade 10 Activity Sheets Quarter 1 Week 1Andrea Cristy Lañas DeiparineNo ratings yet
- Quantum Mechanics Fall 2003-Homework Set 2: Additional ProblemsDocument2 pagesQuantum Mechanics Fall 2003-Homework Set 2: Additional ProblemsLuis Fernando AlcerroNo ratings yet
- AVR Operation For Three Transformers - MJECDocument11 pagesAVR Operation For Three Transformers - MJECSiva NandhamNo ratings yet
- Safety and Reliability - Finite Element Methods For The Structural Analysis of Tension Leg Platforms For Floating Wind TurbinesDocument11 pagesSafety and Reliability - Finite Element Methods For The Structural Analysis of Tension Leg Platforms For Floating Wind TurbinesStevenNo ratings yet
- Caltech HW 2 Solutions Abstract AlgebraDocument2 pagesCaltech HW 2 Solutions Abstract AlgebraclulessNo ratings yet
- Pear™ S5591I: Outdoor/In-Building Directional Antenna (380-470/698-960/1695-2700 MHZ)Document3 pagesPear™ S5591I: Outdoor/In-Building Directional Antenna (380-470/698-960/1695-2700 MHZ)faster72hectorNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - ITCSDocument52 pagesUnit 4 - ITCSAnjani KumariNo ratings yet
- Principles of Radiation (POI)Document68 pagesPrinciples of Radiation (POI)JPIA LOANo ratings yet
- Brochure - Tewameter TMHexDocument2 pagesBrochure - Tewameter TMHexSanggari MogarajaNo ratings yet
- PID Tuning Assignment: Sir Dr. Ali MughalDocument7 pagesPID Tuning Assignment: Sir Dr. Ali MughalHaseeb TariqNo ratings yet
- LPO / Low Power ObjectiveDocument2 pagesLPO / Low Power ObjectiveFor AstroNo ratings yet
- Researchdemo 1Document11 pagesResearchdemo 1devika NairNo ratings yet
- Types of Materials: - Sound Absorbers - Sound Diffusers - Noise Barriers - Sound ReflectorsDocument11 pagesTypes of Materials: - Sound Absorbers - Sound Diffusers - Noise Barriers - Sound ReflectorsrahsanjiNo ratings yet
- Forecast Pro V8 Statistical Reference ManualDocument62 pagesForecast Pro V8 Statistical Reference Manualgacastroh81No ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Theory of Steady State Reactive Power Compensation in Electric TransmissionDocument45 pagesUnit 2 - Theory of Steady State Reactive Power Compensation in Electric TransmissionJagdeep Singh67% (3)
- Asme b16.36Document0 pagesAsme b16.36IPINo ratings yet
- Optimizing Cement Strength ZKG GermanyDocument5 pagesOptimizing Cement Strength ZKG GermanySarbaz BanozaiNo ratings yet
- Teddlie - Mixed Methods Sampling - A Typology With Examples PDFDocument25 pagesTeddlie - Mixed Methods Sampling - A Typology With Examples PDFFen LeeNo ratings yet
- Rapid ToolingDocument17 pagesRapid Toolinggowrisankar32No ratings yet
- General Additive Model - Michael ClarkDocument31 pagesGeneral Additive Model - Michael ClarkMohammad Azmain Iktidar 2035598680No ratings yet
- Introductiontohumanphysiology PDFDocument30 pagesIntroductiontohumanphysiology PDFkrishna baithaNo ratings yet
- A 5Document10 pagesA 5mert_atasoyNo ratings yet