Two Methods of Planting Gr.5
Two Methods of Planting Gr.5
Uploaded by
abelCopyright:
Available Formats
Two Methods of Planting Gr.5
Two Methods of Planting Gr.5
Uploaded by
abelOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Two Methods of Planting Gr.5
Two Methods of Planting Gr.5
Uploaded by
abelCopyright:
Available Formats
Name: Grade and section:
Handout #2:
TWO METHODS of PLANTING
Vocabulary: English - Tagalog
1. plot – isang lagay ng lupa
1. Direct-seeding 2. hay – dayami
- method of planting seeds directly in the garden plot. 3. mulch – malts
4. seedling – punla
5. sheath – saha
Characteristics of seeds and plants: 6. sprout – usbong
big seeds 7. sow – ihasik ; ipunla
seeds that grow fast
seeds and plants that do not need extra care during the seedling stage.
seeds with delicate root system
Examples of seeds:
cucumber sitao
squash okra
kangkong radish
melon beans
watermelon carrot
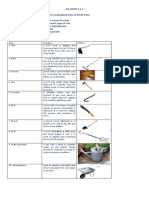
Steps in planting using the direct-seeding method
1. Prepare garden plots.
Ideal size is 2 to 3 feet.
2. Sterilize the garden plot.
Burn hays on the surface of the garden plot
Pour boiling water on the surface of the garden plot
3. Sow seeds on the ground and cover them with soil.
The depth of the hole should be twice or four times the diameter of the seed.
The spacing between the plants should be equal to the height of the plant
when it reaches maturity.
Plants which grow tall and slender like celery, green peas, bush lima and
onions can be planted nearer while plants which grow broader like kangkong,
broccoli and cabbage should be planted farther away each other.
4. Cover the soil with mulch.
Mulch – any organic material like grasses, lawn clippings that you put on the
surface of the soil to prevent water from evaporating.
Cover the soil with mulch and not the plants.
5. Water the plants and the soil.
6. Remove some seedlings once the true leaves have come out to maintain at least 5
centimeter distance between plants.
7. Cover the garden bed with nylon net once the seedling start to grow to protect plants
from too much heat of the sun and strong winds.
Two Methods of Planting Page 1
Name: Grade and section:
2. Transplanting
- method of planting seed in a seed box and later, when the seedlings are big
enough, (when they have two or four “ true” leaves) they are transplanted from
the seed box to the garden plot.
Characteristics of seeds and plants
small seeds
plants that need extra care during their seedling stage
Examples of seeds
tomato Eggplant
Mustard Pechay
Pepper
Steps in planting seeds in a seed box
1. Prepare the seed box using wooden box, plastic egg tray or metal cans.
2. Fill seed box with a good soil for sprouting seeds.
3. Sow the seeds and cover them with soil.
The depth of the hole should be twice or four times the diameter of the seed.
4. Water the soil using a sprinkler.
5. Cover the seed box with a plastic cover to protect seeds from direct heat of the sun.
6. Transplant the seedling once the “true leaves” have emerge.
Considerations when transplanting
Transplant seedlings in the afternoon to allow the roots to recover from
damage.
Do not transplant during rainy weather.
Bring the seed box near the garden plot.
Steps in transplanting
1. Remove the seedling from the seed box as gently as possible by digging 2 to 3
inches beneath the root system.
Pass a sharp knife or trowel in between the seedlings, much like cutting a
cake into smaller pieces.
2. Transplant the seedling in the prepared garden plot.
3. Cover the seedling and gently tamp the soil up to the first leaves.
4. Water each seedling soon after you have transferred it.
Do not wait until you have planted a row of seedling before watering.
5. Maintain at least 5-inch distance between seedlings.
6. Cover the seedling with saha to protect them from strong winds and too much
heat of the sun.
Two Methods of Planting Page 2
You might also like
- CSEC Integrated Science Syllabus RevisedDocument198 pagesCSEC Integrated Science Syllabus RevisedNigella CampbellNo ratings yet
- Astm D2321 (2000) PDFDocument10 pagesAstm D2321 (2000) PDFMohammad Rawoof100% (1)
- Dpr-Srikanth Reddy - Polyhouse With SubsidyDocument23 pagesDpr-Srikanth Reddy - Polyhouse With SubsidyGenesisGenesis75% (4)
- TLE-Agriculture 9 Reviewer Q2Document4 pagesTLE-Agriculture 9 Reviewer Q2garciathomas0210No ratings yet
- Week 3-4 Methods and WAYS of PlantingDocument21 pagesWeek 3-4 Methods and WAYS of PlantingPen Molina de VeraNo ratings yet
- Planting A Home Vegetable Garden: Selecting SeedsDocument4 pagesPlanting A Home Vegetable Garden: Selecting SeedsthaturhannaNo ratings yet
- Module 4. Direct Planting and TransplantingDocument26 pagesModule 4. Direct Planting and TransplantingMayco CabildoNo ratings yet
- Elements To Be Observed in Planting TreesDocument18 pagesElements To Be Observed in Planting TreesDolores Dellosa Noga0% (1)
- Planting A Home Vegetable Garden: Preparing The SeedbedDocument4 pagesPlanting A Home Vegetable Garden: Preparing The Seedbedbya316No ratings yet
- Elements To Be Observed in Planting TreesDocument18 pagesElements To Be Observed in Planting TreesDolores Dellosa Noga85% (13)
- PM819 Vegetable GardeningDocument4 pagesPM819 Vegetable Gardeningdag57No ratings yet
- TRANSPLANTINGDocument54 pagesTRANSPLANTINGOwell Angeles FababierNo ratings yet
- Onahon (TLE - 2k Report)Document5 pagesOnahon (TLE - 2k Report)Sharmaine FabriaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document11 pagesLesson 2christopher palacioNo ratings yet
- TLE6-CapSLET AgriQ1 W2Document12 pagesTLE6-CapSLET AgriQ1 W2Gia AlvarezNo ratings yet
- 3rd Grading Module 4 Grade 11Document6 pages3rd Grading Module 4 Grade 11Jennifer DuranNo ratings yet
- TLE HO10 w5Document4 pagesTLE HO10 w5Argonaut DrakeNo ratings yet
- Epp 6 - Plant PropagationDocument20 pagesEpp 6 - Plant Propagationmarydcala24No ratings yet
- Worksheet in Tle 6 (Agriculture Week 2) : I. What I Need To KnowDocument18 pagesWorksheet in Tle 6 (Agriculture Week 2) : I. What I Need To Knowjaypee vargasNo ratings yet
- Gardening - Planting ManualDocument4 pagesGardening - Planting Manualcontadino_impazzitoNo ratings yet
- Tle Notes 1.2Document4 pagesTle Notes 1.2Keesha Athena Villamil - CabrerosNo ratings yet
- Sexual and Asexual Reproduction of PlantsDocument8 pagesSexual and Asexual Reproduction of Plantskangaro ossyNo ratings yet
- Collecting and Storing SeedsDocument2 pagesCollecting and Storing SeedsDragan SorinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document4 pagesChapter 3Rolan Domingo GalamayNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Elements To Be Observed in Planting Trees and FruitDocument4 pagesLesson 2 Elements To Be Observed in Planting Trees and FruitBimbo CuyangoanNo ratings yet
- Seeds. Starting Seeds Indoors 2Document2 pagesSeeds. Starting Seeds Indoors 2Sharad BhutoriaNo ratings yet
- Grade 4 - Q2 TVE LessonDocument14 pagesGrade 4 - Q2 TVE LessonHF ManigbasNo ratings yet
- Planting Woody OrnamentalsDocument8 pagesPlanting Woody OrnamentalsSharad BhutoriaNo ratings yet
- Agri Lesson 2 Elements To Be Observed in Planting Trees and Fruit Bearing TreesDocument21 pagesAgri Lesson 2 Elements To Be Observed in Planting Trees and Fruit Bearing TreesLady RuedaNo ratings yet
- Resource000844 Rep884Document4 pagesResource000844 Rep884NVAzirNo ratings yet
- Tle 6 Activity Sheets q1w7 1Document5 pagesTle 6 Activity Sheets q1w7 1jocelyn f. junioNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 LO5 - Lesson Information 5.1Document13 pagesLesson 6 LO5 - Lesson Information 5.1It's me zafra blogsNo ratings yet
- Asexual Propagation by Miming Momaming PDFDocument6 pagesAsexual Propagation by Miming Momaming PDFLebron DoggiNo ratings yet
- Module 3 OrnamentalsDocument14 pagesModule 3 OrnamentalssentlabanedavidNo ratings yet
- Week 2 TLEDocument14 pagesWeek 2 TLEQUENGELINE VILLARINNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6.4Document14 pagesLesson 6.4Binuri SandarekhaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 11Document7 pagesLesson 11Julianne Bea Notarte100% (1)
- Midterm FinalDocument31 pagesMidterm FinalMarie ShaneNo ratings yet
- Pot PlantsDocument5 pagesPot PlantsSirius blackNo ratings yet
- Class V Science Chapter 1 Long Answer Question SolutionDocument3 pagesClass V Science Chapter 1 Long Answer Question SolutionAnanya ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Agriculture Book2Document41 pagesAgriculture Book2tum chrisNo ratings yet
- 9 Leaf PotsDocument7 pages9 Leaf Potsadnhas100% (1)
- Module 4. (14pp) Direct Planting and TransplantingDocument14 pagesModule 4. (14pp) Direct Planting and TransplantingDimasalang Perez88% (8)
- Module 1 Vegetables.Document20 pagesModule 1 Vegetables.Regie MacayaNo ratings yet
- Commmunitiy Nursery PracticesDocument44 pagesCommmunitiy Nursery PracticesKonrad Neil III100% (1)
- AgricultureDocument2 pagesAgriculturevim09480No ratings yet
- Utah Native Plant Propagation HandbookDocument58 pagesUtah Native Plant Propagation HandbooksumfakNo ratings yet
- Grafting Procedure: For Sweet TamarindDocument41 pagesGrafting Procedure: For Sweet TamarindHermie LicuanNo ratings yet
- STD - Iii Sub - Science CH - Plants in Our SurroundingsDocument3 pagesSTD - Iii Sub - Science CH - Plants in Our SurroundingsSudip GhoshNo ratings yet
- Gardening For BeginnersDocument20 pagesGardening For Beginnersronalit malintadNo ratings yet
- Afa Agri-Crop 9 q2w3Document37 pagesAfa Agri-Crop 9 q2w3JMGNo ratings yet
- RAPE NurseryDocument4 pagesRAPE NurseryWellington KubaraNo ratings yet
- Agriculture HandoutsDocument3 pagesAgriculture HandoutsShella Mae AmperNo ratings yet
- Planting Trees and ShrubsDocument4 pagesPlanting Trees and ShrubsSharad BhutoriaNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document34 pagesModule 3REGIN VILLASISNo ratings yet
- Asexual PropagationDocument17 pagesAsexual PropagationOlive BautistaNo ratings yet
- Plant Parts RootsDocument6 pagesPlant Parts RootsavegailNo ratings yet
- Methods of Plant Propagation: Sexually and Asexually Propagating PlantsDocument30 pagesMethods of Plant Propagation: Sexually and Asexually Propagating PlantsCarrylle Janne NovalNo ratings yet
- Seed Propagation Techniques For The Home OwnerDocument16 pagesSeed Propagation Techniques For The Home OwnerVinny100% (4)
- "Beginners" Learn How to Grow Garden Vegetables: From the Dirt Up, #1From Everand"Beginners" Learn How to Grow Garden Vegetables: From the Dirt Up, #1No ratings yet
- UNIT-3 Index Properties of Soil: Er. Shatrudhan Prasad Yadav Constructor Instructor LTS, LahanDocument14 pagesUNIT-3 Index Properties of Soil: Er. Shatrudhan Prasad Yadav Constructor Instructor LTS, Lahanajai chyNo ratings yet
- Sprinkler DesignDocument125 pagesSprinkler DesignJames K. KirahukaNo ratings yet
- DDA JE Syllabus 2023Document3 pagesDDA JE Syllabus 2023Rahul ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Probiotics Farming Shrimp Intensively and SuccessfullyDocument12 pagesProbiotics Farming Shrimp Intensively and SuccessfullyChristine DaaeNo ratings yet
- Tillage Equipment: PSAE Region IV - Agricultural Engineering I-20Document9 pagesTillage Equipment: PSAE Region IV - Agricultural Engineering I-20คาร่า วิสต้าNo ratings yet
- Clary Sage Production Guide 2012Document2 pagesClary Sage Production Guide 2012ScribidNo ratings yet
- Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology: K.N. Anith, S. Aswini, Shilpa Varkey, N.V. Radhakrishnan, Deepa S. NairDocument6 pagesBiocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology: K.N. Anith, S. Aswini, Shilpa Varkey, N.V. Radhakrishnan, Deepa S. Nairjdjo9505No ratings yet
- CPTu FormulasDocument4 pagesCPTu FormulasPieter OelofseNo ratings yet
- Nusrl PetitionDocument37 pagesNusrl PetitionAbhinavPrakashNo ratings yet
- (Q1) Pant2017Document10 pages(Q1) Pant2017Salma FahimaNo ratings yet
- Ringkasan Perbaikan Tanah: Dengan Berbagai MetodeDocument7 pagesRingkasan Perbaikan Tanah: Dengan Berbagai MetodeYasruddin MtNo ratings yet
- Heat and Mass Transfer Modeling GeostudioDocument80 pagesHeat and Mass Transfer Modeling GeostudiomrloadmovieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - WeatheringDocument18 pagesChapter 4 - WeatheringhasshosNo ratings yet
- Benefits of MSG in PlantingDocument23 pagesBenefits of MSG in Plantingnatnat.johnie.dave.andrianoNo ratings yet
- Flood Prevention and Mitigation Actions in Bangladesh The Sustainable Floodplain Development ApproachDocument25 pagesFlood Prevention and Mitigation Actions in Bangladesh The Sustainable Floodplain Development ApproachFaizur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Bengaluru - Citizenmatters - in - How To Make Mini Forest Miyawaki Method 34867 PDFDocument9 pagesBengaluru - Citizenmatters - in - How To Make Mini Forest Miyawaki Method 34867 PDFDebi GhoshNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 INTRODUCTION TO ECOLOGICAL SYSTEMSDocument72 pagesLesson 1 INTRODUCTION TO ECOLOGICAL SYSTEMSAnaliza Kitongan LantayanNo ratings yet
- Soil Investigation ReportDocument15 pagesSoil Investigation ReportShallborn PaulNo ratings yet
- Growing Fuchsias in The Ground-Barbara's Way: Soil and PositionDocument4 pagesGrowing Fuchsias in The Ground-Barbara's Way: Soil and PositionantonioforteseNo ratings yet
- TermiteDocument18 pagesTermiteGarima Mehta100% (1)
- Duckbill Ground Anchor Systems - Helical Anchors & Anchor Bolts (Feb 2010)Document12 pagesDuckbill Ground Anchor Systems - Helical Anchors & Anchor Bolts (Feb 2010)sandycastleNo ratings yet
- Executive Summary EIA Ladang Hutan Gunung BongsuDocument4 pagesExecutive Summary EIA Ladang Hutan Gunung BongsuSani PutraNo ratings yet
- Biodiversitynotes - Lecture Notes in Sts Biodiversitynotes - Lecture Notes in StsDocument5 pagesBiodiversitynotes - Lecture Notes in Sts Biodiversitynotes - Lecture Notes in Stsmariyha PalangganaNo ratings yet
- CEB-660 Pavement Material MonographDocument132 pagesCEB-660 Pavement Material MonographMANJUNo ratings yet
- Certificado de Acreditación Collaborative Testing Services IncDocument14 pagesCertificado de Acreditación Collaborative Testing Services IncJuan Pablo MarroquínNo ratings yet
- ForagingDocument10 pagesForagingCharmaine V. Bañes100% (1)
- A Critical Review of The Performance and Soil Biodegradability Profiles of Biobased Natural and Chemically Synthesized Polymers in Industrial ApplicationsDocument25 pagesA Critical Review of The Performance and Soil Biodegradability Profiles of Biobased Natural and Chemically Synthesized Polymers in Industrial Applicationslucas112358No ratings yet