0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
124 viewsValium
Valium
Uploaded by
Jess MatiasValium is a benzodiazepine that works by potentiating the effects of GABA to depress the central nervous system and suppress seizure activity. It is indicated for relief of anxiety, agitation, tension, and situational disturbances. Common side effects include drowsiness, tiredness, sleep problems, muscle weakness, lack of balance, slurred speech, nausea, vomiting, constipation, and headache. Nursing responsibilities include monitoring patients for dizziness, mental status changes, and falls as elderly patients are at higher risk. Patients should avoid activities requiring alertness until drug effects are known and avoid alcohol while taking Valium.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Valium
Valium
Uploaded by
Jess Matias0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
124 views1 pageValium is a benzodiazepine that works by potentiating the effects of GABA to depress the central nervous system and suppress seizure activity. It is indicated for relief of anxiety, agitation, tension, and situational disturbances. Common side effects include drowsiness, tiredness, sleep problems, muscle weakness, lack of balance, slurred speech, nausea, vomiting, constipation, and headache. Nursing responsibilities include monitoring patients for dizziness, mental status changes, and falls as elderly patients are at higher risk. Patients should avoid activities requiring alertness until drug effects are known and avoid alcohol while taking Valium.
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Valium is a benzodiazepine that works by potentiating the effects of GABA to depress the central nervous system and suppress seizure activity. It is indicated for relief of anxiety, agitation, tension, and situational disturbances. Common side effects include drowsiness, tiredness, sleep problems, muscle weakness, lack of balance, slurred speech, nausea, vomiting, constipation, and headache. Nursing responsibilities include monitoring patients for dizziness, mental status changes, and falls as elderly patients are at higher risk. Patients should avoid activities requiring alertness until drug effects are known and avoid alcohol while taking Valium.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
124 views1 pageValium
Valium
Uploaded by
Jess MatiasValium is a benzodiazepine that works by potentiating the effects of GABA to depress the central nervous system and suppress seizure activity. It is indicated for relief of anxiety, agitation, tension, and situational disturbances. Common side effects include drowsiness, tiredness, sleep problems, muscle weakness, lack of balance, slurred speech, nausea, vomiting, constipation, and headache. Nursing responsibilities include monitoring patients for dizziness, mental status changes, and falls as elderly patients are at higher risk. Patients should avoid activities requiring alertness until drug effects are known and avoid alcohol while taking Valium.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
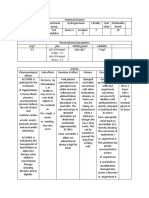
DRUG NAME MECHANISM OF INDICATION CONTRAINDICATIONS SIDE EFFECTS ADVERSE NURSING
ACTION EFFECTS RESPONSIBILITIES
VALIUM A benzodiazepine Symptomatic Contraindicated in drowsiness, tiredness Urinary retention. Monitor periodic hepatic, renal
that may potentiate relief of anxiety, pregnant women sleep problems Paradoxical and hematopoietic function
Generic name: Diazepam the effects of agitation and especially in first (insomnia); reactions. studies in patients receiving
GABA, depress tension due to trimester. muscle weakness, Dependence, repeated or prolonged therapy.
Available Forms: the CNS and psychoneurotic lack of balance or withdrawal
Injection 5mg/ml suppresses the states and Dependence on other coordination; symptoms. Monitor elderly patients for
Rectal gel twin packs spread of seizure transient substances including slurred speech; Jaundice. Tremors. dizziness, ataxia, and mental
Tablets 2 mg, 5 mg, 10 mg activity. situational alcohol except in nausea, vomiting, status changes. Patients are at
disturbances. management of acute constipation; an increased risk for falls.
For Anxiety: Adjunctively in withdrawal reactions. headache;
Adults: 2 to 10 mg PO bid major mental and drooling; skin rash; When using oral solution,
to qid. Or 2 to 10 mg IM or organic disorders. Patients with severe or loss of interest in dilute dose just before giving.
IV q 3 to 4 hours, prn Adjunct for the chronic hypercapnia, sex.
Children 6 months above: 1 relief of reflex myasthenia gravis, severe Warn patient to avoid activities
to 2.5 mg, 1 or 2 times daily muscle spasm due respiratory insufficiency, that require alertness and good
initially. Increase gradually to local trauma. severe hepatic coordination until effects of
as needed. To combat insufficiency, sleep apnea drug are known.
spasticity arising syndrome.
For Preoperative Sedation: from damage to Tell patient to avoid alcohol
10 mg IM or IV before spinal and Do not give this while taking drug.
surgery supraspinal medication to a child
interneurons. younger than 6 months Notify patient that smoking
old. may decrease drug’s
Basal sedation effectiveness.
before stressful
therapeutic Warn woman to avoid use
measures or during pregnancy.
interventions. For
pre-op medication
of anxious or
tense patients.
You might also like
- Dream Station Service Manual PDFDocument135 pagesDream Station Service Manual PDFSveto Sl100% (2)
- Gynecologist Career EssayDocument4 pagesGynecologist Career Essayapi-531232390No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - MCNDocument2 pagesChapter 6 - MCNPrincess Queenie OlarteNo ratings yet
- Checklist For Physical AssessmentDocument13 pagesChecklist For Physical AssessmentSharene Kate EribalNo ratings yet
- Post-Partum CareDocument4 pagesPost-Partum CarejoethemangoNo ratings yet
- Sleep Pattern DisturbanceDocument1 pageSleep Pattern DisturbanceNik Rose ElNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyNathalia CabalseNo ratings yet
- Community Teaching Plan and Evaluation Submission, Assignment Week 6Document10 pagesCommunity Teaching Plan and Evaluation Submission, Assignment Week 6taniaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyGlaiza M. BañaresNo ratings yet
- Immune FinalDocument53 pagesImmune FinalJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- Semifinals-Lesson 7-Enzymes and VitaminsDocument4 pagesSemifinals-Lesson 7-Enzymes and Vitaminsino zuii javierNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Classification and Mode of Action Adverse Effects/precautions Nursing ConsiderationsDocument3 pagesName of Drug Classification and Mode of Action Adverse Effects/precautions Nursing ConsiderationsDyanne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For SCIDocument10 pagesNursing Care Plan For SCINur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Health Care Ethics PRELIM ReviewerDocument11 pagesHealth Care Ethics PRELIM ReviewerVeejay CervantesNo ratings yet
- Bisacodyl DulcolaxDocument1 pageBisacodyl DulcolaxENo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway Clearance NCPDocument1 pageIneffective Airway Clearance NCPBenz ParCoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Magnesium Sulfate (MGSO4)Document2 pagesDrug Study - Magnesium Sulfate (MGSO4)Leslie LibrandoNo ratings yet
- NCP Acute PainDocument3 pagesNCP Acute PainSian Grace AsadaNo ratings yet
- Requirement in NCP 312 (Medical and Surgical Nursing) : Submitted By: Cadalin, Fremelen Rose CDocument4 pagesRequirement in NCP 312 (Medical and Surgical Nursing) : Submitted By: Cadalin, Fremelen Rose CFremelen Rose CadalinNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Week 7 - ProteinsDocument6 pagesBiochemistry Week 7 - ProteinsMicah JadeNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Adn Ncp-Case Pres.Document22 pagesDrug Study Adn Ncp-Case Pres.MaeNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Atracurium: RecommendedDocument5 pagesDrug Study: Atracurium: RecommendedShara Lailanie A. AzisNo ratings yet
- DRUG StudyDocument6 pagesDRUG StudyDonna ClaritoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyJay-ar Batara SorianoNo ratings yet
- Bucao - HOT SITZ BATHDocument4 pagesBucao - HOT SITZ BATHTrishaNo ratings yet
- Drugs and NCPDocument4 pagesDrugs and NCPApril Anne CostalesNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug Studyanne009No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Risk For Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Bleeding From Tonsillectomy Short TermDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Risk For Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Bleeding From Tonsillectomy Short TermErika Danalle ArceoNo ratings yet
- Drug TabulationDocument6 pagesDrug TabulationRosemarie Canete Delarita100% (1)
- Rectal and Vaginal Suppository InsertionDocument2 pagesRectal and Vaginal Suppository InsertionMariah Jane TaladuaNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 Computation 2021Document3 pagesNCM 112 Computation 2021Marie Kelsey Acena Macaraig100% (1)
- FNCPDocument7 pagesFNCPMaria Ivy Rochelle TanNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyJM AcNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: West Visayas State UniversityDocument2 pagesDrug Study: West Visayas State Universityw dNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology in NursingDocument1 pagePharmacology in NursingJessa Mae Barquilla100% (1)
- NCM 114 Care For Older Adults MODULE 7Document5 pagesNCM 114 Care For Older Adults MODULE 7Meryville JacildoNo ratings yet
- A Buddhist Perspective On Health and SpiritualityDocument3 pagesA Buddhist Perspective On Health and Spiritualityedi_wsNo ratings yet
- Sleeping DrugDocument9 pagesSleeping DrugNooratiekha Fazil IekhaNo ratings yet
- 11 - NCPsDocument6 pages11 - NCPsellian3leiNo ratings yet
- 3B Drug Study 2Document23 pages3B Drug Study 2Kristine Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Providing Steam InhalationDocument2 pagesProviding Steam InhalationJee MirasNo ratings yet
- IV Fluid ProtocolDocument4 pagesIV Fluid ProtocolAhmad AfghanNo ratings yet
- NUR 201 - Drug Study (Lanthanum Carbonate)Document1 pageNUR 201 - Drug Study (Lanthanum Carbonate)ReaNo ratings yet
- DRUG-STUDY OmeprazoleIV AngelicaRonquilloDocument4 pagesDRUG-STUDY OmeprazoleIV AngelicaRonquillokarl eiron delos santosNo ratings yet
- Assisting Delivery Name: Mary Grace G. Rivera Grade: - Year and Section:BSN-2D DateDocument3 pagesAssisting Delivery Name: Mary Grace G. Rivera Grade: - Year and Section:BSN-2D DateMary Grace RiveraNo ratings yet
- Case Study 4 Drug StudyDocument9 pagesCase Study 4 Drug StudyMontero, Ma. Cecilia - BSN 3-BNo ratings yet
- QUINAPRILDocument2 pagesQUINAPRILTazkiaNo ratings yet
- NOTE#4 - Effective Communication With Older AdultsDocument2 pagesNOTE#4 - Effective Communication With Older AdultsraaiNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Goal Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Goal Intervention Rationale EvaluationSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Assesment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Goal Nursing Intervention Rationale Actual EvaluationDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan Assesment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Goal Nursing Intervention Rationale Actual EvaluationFebee GeeNo ratings yet
- Guillain Barre Case StudyDocument18 pagesGuillain Barre Case Studymydnyt02No ratings yet
- DrugsDocument13 pagesDrugsJune DumdumayaNo ratings yet
- BisacodylDocument1 pageBisacodylJewel GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 1Document3 pagesDrug Study 1G4 AMOYO ANGELICA NICOLENo ratings yet
- Kee: Pharmacology, 6th Edition: Test Bank Chapter 4: Medications and Calculations Short AnswerDocument39 pagesKee: Pharmacology, 6th Edition: Test Bank Chapter 4: Medications and Calculations Short Answerthu_vu_2983% (6)
- The Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeFrom EverandThe Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Risperidone Drug StudyDocument2 pagesRisperidone Drug StudyLanzen DragneelNo ratings yet
- DORMICUMDocument1 pageDORMICUMArian Rose100% (1)
- Risperidone Drug StudyDocument2 pagesRisperidone Drug StudyBasema HashhashNo ratings yet
- DiazepamDocument2 pagesDiazepamBIRIN, JEHAN KAYLE T.No ratings yet
- Age Changes in Oral TissueDocument34 pagesAge Changes in Oral TissueAiswarya MishraNo ratings yet
- Dissociative Identity DisorderDocument66 pagesDissociative Identity DisorderTemesgen Endalew100% (1)
- Family Case StudyDocument13 pagesFamily Case StudyKathleen Joy Costales MagtanongNo ratings yet
- Questions and Answers On Module 1Document3 pagesQuestions and Answers On Module 1nitinNo ratings yet
- Land Snakes of Medical Significance in Malaysia. 3rd Edition (2022)Document98 pagesLand Snakes of Medical Significance in Malaysia. 3rd Edition (2022)Nabilah SufianNo ratings yet
- Chemical Plaque Control - 2Document44 pagesChemical Plaque Control - 2Mahnoor MustafaNo ratings yet
- PG Rotation Overview 2009Document3 pagesPG Rotation Overview 2009bestgraNo ratings yet
- Case Report Atrial Myxomas DR BayuDocument5 pagesCase Report Atrial Myxomas DR BayuKusmawan IdNo ratings yet
- 3-Unstratified Epithelium. Definitions and Examples of Squamous, Columnar (Simple, Ciliated, Microvilli, Secretory) and CuboidalDocument2 pages3-Unstratified Epithelium. Definitions and Examples of Squamous, Columnar (Simple, Ciliated, Microvilli, Secretory) and CuboidalAris PaparisNo ratings yet
- Biomedical Digital Signal Processing - TompkinsDocument378 pagesBiomedical Digital Signal Processing - TompkinsBeejesh AgNo ratings yet
- Ijmrhs Vol 2 Issue 4Document321 pagesIjmrhs Vol 2 Issue 4editorijmrhsNo ratings yet
- Opioid Analgesics and AntagonistsDocument8 pagesOpioid Analgesics and AntagonistsNishant KatiyarNo ratings yet
- Ex-NUS Professor in Resume Fraud Scandal in US 2014 - The Straits TimesDocument3 pagesEx-NUS Professor in Resume Fraud Scandal in US 2014 - The Straits TimesbismarckNo ratings yet
- Neonatal SepsisDocument39 pagesNeonatal SepsisBryan KernsNo ratings yet
- 4 - Factors To Consider Regarding The Effectiveness ofDocument6 pages4 - Factors To Consider Regarding The Effectiveness ofapi-241585431No ratings yet
- Ventilation Techniques Chris ThompsonDocument3 pagesVentilation Techniques Chris Thompsonfalcone87No ratings yet
- ATMR-201 : Application For Trans Tasman Mutual RecognitionDocument9 pagesATMR-201 : Application For Trans Tasman Mutual RecognitionFelix RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Survey of MCCQE Part II Examinees Reveals Limited Utility and Negative Impact of The ExamDocument21 pagesSurvey of MCCQE Part II Examinees Reveals Limited Utility and Negative Impact of The ExamAnonymousNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan DraftDocument2 pagesLesson Plan Draftapi-35520721250% (2)
- Bio-Chemistry Report:: Lahore: 10 Jail Road, Main Gulberg - Karachi: Al Khaleej Plaza, Shaheed-e-Millat RoadDocument3 pagesBio-Chemistry Report:: Lahore: 10 Jail Road, Main Gulberg - Karachi: Al Khaleej Plaza, Shaheed-e-Millat RoadHamza NajamNo ratings yet
- A A Allen - How To Have Freedom From Fear, Worry, and Your Case of NervesDocument75 pagesA A Allen - How To Have Freedom From Fear, Worry, and Your Case of NervesDaniel AbrahamNo ratings yet
- NorthShore100 2009Document68 pagesNorthShore100 2009Salem NewsNo ratings yet
- Shargel 8e AppCDocument60 pagesShargel 8e AppCdhanushNo ratings yet
- How To Apply ICF in Rehabilitation PDFDocument14 pagesHow To Apply ICF in Rehabilitation PDFCyndi MenesesNo ratings yet
- What Is Extracorporeal Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation?: Federico Pappalardo, Andrea MontisciDocument5 pagesWhat Is Extracorporeal Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation?: Federico Pappalardo, Andrea MontisciPrajogo KusumaNo ratings yet
- Drug-Induced Psoriasis DermNetDocument1 pageDrug-Induced Psoriasis DermNetZhouQian SophieNo ratings yet
- DR Narendranatha Reddy Profile 15 April 2018 PDFDocument5 pagesDR Narendranatha Reddy Profile 15 April 2018 PDFDr P N N ReddyNo ratings yet
- Jurnal AsliDocument10 pagesJurnal AsliNurulwidia SariNo ratings yet
- BevacizumabDocument8 pagesBevacizumabHitesh SharmaNo ratings yet