Ca Rxns I
Ca Rxns I
Uploaded by
api-465421809Copyright:
Available Formats
Ca Rxns I
Ca Rxns I
Uploaded by
api-465421809Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Ca Rxns I
Ca Rxns I
Uploaded by
api-465421809Copyright:
Available Formats
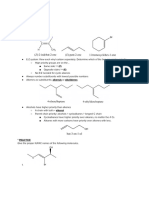
CARBOXYLIC ACID RXNS I Chemistry Specialist: Alicia Hart
UC Davis - SASC
a) Acyl Halide Synthesis
i) SOCl2
O O
SOCl2
R OH R Cl
- SN2 type mechanism
ii) PX3 or P, I2
O O
PX3
R OH R X
X = Cl or Br
b) Anhydride Synthesis
O O
O O
R O R
R OH R X
X = Halogen or OH
- Note that heat often acts merely as a catalyst.
c) Ester Synthesis
i) intermolecular O
O
R'OH, H+,
R OR'
R OH
O
ii) intramolecular
O
H+ O
HO OH
iii) via Substitution
O O O
NaOH R'X
R OH R O R OR'
- If R' is Me - 2 goes SN2 if R' is 3 goes SN1
d) Amide Synthesis
O O
NH3,
R OH R NH2
* must have heat to form amide; otherwise, this is a simple
acid-base rxn between the carboxylic acid and amine
- 1 and 2 amines work too
You might also like
- Guitar Department Exam Levels1 8 Proficiency BERKLEE PDFDocument12 pagesGuitar Department Exam Levels1 8 Proficiency BERKLEE PDFMelissa Moore100% (1)
- Organic Chemistry Reaction Summary SheetDocument30 pagesOrganic Chemistry Reaction Summary SheetKylo RenNo ratings yet
- Zinc FinalDocument12 pagesZinc Finalamanuel tafeseNo ratings yet
- CH 19Document68 pagesCH 19Britany DyerNo ratings yet
- 金属有机化学课件 PDFDocument408 pages金属有机化学课件 PDFmingNo ratings yet
- Ca SynthDocument1 pageCa Synthapi-465421809No ratings yet
- Ca SynthDocument1 pageCa Synthapi-465421809No ratings yet
- The Beautiful SouthDocument10 pagesThe Beautiful SouthAlonsso MiguelNo ratings yet
- Anhydride RxnsDocument1 pageAnhydride Rxnsapi-465421809No ratings yet
- Ester RxnsDocument1 pageEster Rxnsapi-465421809No ratings yet
- Phenol Rxns IDocument1 pagePhenol Rxns Iapi-465421809No ratings yet
- Chemistry 108B Exam #2 Cheat Sheet 2Document1 pageChemistry 108B Exam #2 Cheat Sheet 2雪郎かざきNo ratings yet
- Organic Reagents: 1. Alcoholic KOH 2. Aluminium EthoxideDocument9 pagesOrganic Reagents: 1. Alcoholic KOH 2. Aluminium EthoxideAarya Nandal100% (1)
- Benzene RxnsDocument1 pageBenzene Rxnsapi-465421809No ratings yet
- Amine SynthDocument1 pageAmine Synthapi-465421809No ratings yet
- Acyl Halide RxnsDocument1 pageAcyl Halide Rxnsapi-465421809No ratings yet
- Amide RxnsDocument1 pageAmide Rxnsapi-465421809No ratings yet
- Nitrile RxnsDocument1 pageNitrile Rxnsapi-465421809No ratings yet
- Ca RXN CheckDocument1 pageCa RXN Checkapi-4654218090% (1)
- Phenol SynthDocument1 pagePhenol Synthapi-465421809No ratings yet
- Roadmap Problem - 3Document1 pageRoadmap Problem - 3abhyudaipathwayNo ratings yet
- Road Maps Organic Chemistry Set 1Document82 pagesRoad Maps Organic Chemistry Set 1anshika.sawdekarNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon: Ashwani Tyagi Sir (Code: ATJEE)Document22 pagesHydrocarbon: Ashwani Tyagi Sir (Code: ATJEE)Prince DigvijayNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes1Document15 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloarenes1Poorni RenuNo ratings yet
- The P-Block Elements - Mind Maps - Lakshya JEE 2024Document1 pageThe P-Block Elements - Mind Maps - Lakshya JEE 2024librarybooks.tashiNo ratings yet
- Chem 212 Alkyl Halide Problems 2Document1 pageChem 212 Alkyl Halide Problems 2kevinamy100% (1)
- Heck - 3 20 17Document11 pagesHeck - 3 20 17Preeti YadavNo ratings yet
- Grignard Reagent Q.B.Document12 pagesGrignard Reagent Q.B.Aariya KumariNo ratings yet
- HYDROCARBONDocument31 pagesHYDROCARBONRaghav VohraNo ratings yet
- All Organic ReagentDocument13 pagesAll Organic Reagentsanjaykumarsaha507100% (1)
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Class Notes Manzil JEE 2025Document76 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloarenes Class Notes Manzil JEE 2025Vedant Vohra100% (2)
- Carbonyl Compounds 1654147338445Document33 pagesCarbonyl Compounds 1654147338445Harsh VardhanNo ratings yet
- Retrosynthesis Practice Problems: O O OR O N O O BR O O OR 1)Document10 pagesRetrosynthesis Practice Problems: O O OR O N O O BR O O OR 1)butko88No ratings yet
- CHAPTER25 HeterocyclesDocument44 pagesCHAPTER25 HeterocyclesRiyanto WidodoNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes & Haloarenes HandbookDocument3 pagesHaloalkanes & Haloarenes HandbookSuhani SubratNo ratings yet
- 3 Chemical KineticsDocument219 pages3 Chemical KineticsArkaNo ratings yet
- AIEEE Chemistry Quick ReviewDocument1 pageAIEEE Chemistry Quick ReviewYashwanth KalyanNo ratings yet
- Chapter36 - BiomoleculesDocument19 pagesChapter36 - BiomoleculesAkash GoelNo ratings yet
- Reagent Chemistry Jeet Sir FinalDocument217 pagesReagent Chemistry Jeet Sir Finalallenclass11workNo ratings yet
- Road Maps Organic Chemistry Set 4 Eklavya @JEEAdvanced - 2024Document13 pagesRoad Maps Organic Chemistry Set 4 Eklavya @JEEAdvanced - 2024puneethrgcNo ratings yet
- Synthesis 3 AnsDocument1 pageSynthesis 3 AnskevinamyNo ratings yet
- 04 Roadmap (Oc) StudentDocument1 page04 Roadmap (Oc) StudentShubham RajNo ratings yet
- S-Block ElementDocument31 pagesS-Block ElementSiva ChamlingNo ratings yet
- 02 Oc Roadmap Student Copy 1595063648 PDFDocument1 page02 Oc Roadmap Student Copy 1595063648 PDFsantosh tripathyNo ratings yet
- Day-2 Chemical BondingDocument4 pagesDay-2 Chemical BondingpriyanshuNo ratings yet
- Ciclos de Born HaberDocument4 pagesCiclos de Born HaberLeonardo Batista RibeiroNo ratings yet
- Conjugate AdditionDocument15 pagesConjugate AdditionNazifa. E. AzmanNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon: Target Iit Jee 2017 Xii (VS+VR)Document36 pagesHydrocarbon: Target Iit Jee 2017 Xii (VS+VR)Aariya KumariNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes MADDocument31 pagesHaloalkanes MADggdfjkkvvNo ratings yet
- 7 Coordination CompoundsDocument329 pages7 Coordination CompoundsArka100% (1)
- Alcohol, Ether & Phenol: Chapter Practice ProblemsDocument6 pagesAlcohol, Ether & Phenol: Chapter Practice ProblemsAtharva GanjuNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 6941, Fall 2007 Synthesis Problems I - Key Dr. Peter NorrisDocument9 pagesChemistry 6941, Fall 2007 Synthesis Problems I - Key Dr. Peter NorrisQuốc NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Full Chemistry 2024Document601 pagesFull Chemistry 2024Nimit Khattar100% (1)
- original (2)Document108 pagesoriginal (2)Archana Nikam100% (1)
- original (3)Document287 pagesoriginal (3)Archana Nikam100% (1)
- Document From P. Suraj KumarDocument123 pagesDocument From P. Suraj KumarsuryavamshigajapatiNo ratings yet
- NEO - JEE-NEET - 12 - P1 - CHE - E - Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers. - S6 - 53Document193 pagesNEO - JEE-NEET - 12 - P1 - CHE - E - Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers. - S6 - 53NARRAYANAN ARNo ratings yet
- Conversion Chart Organic ChemistryDocument1 pageConversion Chart Organic ChemistryVishakha0% (1)
- Sergeev 2020Document38 pagesSergeev 2020Diana DascaluNo ratings yet
- DPP 1, 2, 3 (Goc)Document10 pagesDPP 1, 2, 3 (Goc)Nikhil RajNo ratings yet
- Amine - DPPDocument9 pagesAmine - DPPIs IsNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl Compounds and Carboxylic Acid - Med Easy - Yakeen 2.0 2024 (Legend)Document12 pagesCarbonyl Compounds and Carboxylic Acid - Med Easy - Yakeen 2.0 2024 (Legend)agrawaltwinkle2005No ratings yet
- Reactions of Alcohols I: Fill in The Appropriate Blanks: Na CR O H ODocument1 pageReactions of Alcohols I: Fill in The Appropriate Blanks: Na CR O H Obella33% (3)
- Advanced Organic Reactions 2000 - WarrenDocument174 pagesAdvanced Organic Reactions 2000 - Warrenshiv57100% (3)
- 118c Practice Synthesis KeyDocument18 pages118c Practice Synthesis Keyapi-465421809No ratings yet
- 118c Practice Synthesis KeyDocument18 pages118c Practice Synthesis Keyapi-465421809No ratings yet
- Benzene RxnsDocument1 pageBenzene Rxnsapi-465421809No ratings yet
- Amide RxnsDocument1 pageAmide Rxnsapi-465421809No ratings yet
- Amine SynthDocument1 pageAmine Synthapi-465421809No ratings yet
- Phenol SynthDocument1 pagePhenol Synthapi-465421809No ratings yet
- Nitrile RxnsDocument1 pageNitrile Rxnsapi-465421809No ratings yet
- CH 17: Aldehydes and Ketones: Nasiri CHE118B Final Study Guide Spring 2019 - S. Ly Sdly@ucdavis - EduDocument17 pagesCH 17: Aldehydes and Ketones: Nasiri CHE118B Final Study Guide Spring 2019 - S. Ly Sdly@ucdavis - Eduapi-465421809No ratings yet
- Acyl Halide RxnsDocument1 pageAcyl Halide Rxnsapi-465421809No ratings yet
- Ca RXN CheckDocument1 pageCa RXN Checkapi-4654218090% (1)
- ch17 SummaryDocument1 pagech17 Summaryapi-465421809No ratings yet
- 118b mt1 Study Guide 2Document21 pages118b mt1 Study Guide 2api-465421809No ratings yet
- ch15-16 SummaryDocument1 pagech15-16 Summaryapi-465421809No ratings yet
- ch18 SummaryDocument1 pagech18 Summaryapi-465421809No ratings yet
- Bond LinesDocument5 pagesBond Linesapi-465421809No ratings yet
- RevisiDocument40 pagesRevisiQinham NQmah GloodaxzNo ratings yet
- Modes HandoutDocument4 pagesModes HandoutMúsico de SáNo ratings yet
- Buddy Guy Featuring MorelandDocument2 pagesBuddy Guy Featuring MorelandShane BentleyNo ratings yet
- His Theme - Undertale OSTDocument1 pageHis Theme - Undertale OSTIvoAlvesNo ratings yet
- KTRU Spring 2008 FolioDocument12 pagesKTRU Spring 2008 FolioktruhistoryNo ratings yet
- NightlifeDocument1 pageNightlifeLaurie HeustonNo ratings yet
- Steve Smith Guide PDF FreeDocument11 pagesSteve Smith Guide PDF FreePetr FlekNo ratings yet
- Pat Metheny Track-By-Track: What's It All AboutDocument3 pagesPat Metheny Track-By-Track: What's It All AboutКондратьев МихаилNo ratings yet
- MUH 2512 Dr. Bakan Exam 1 Study Guide Format: This Is A Multiple-Choice Exam. It Will Include at Least 100 Questions (No MoreDocument5 pagesMUH 2512 Dr. Bakan Exam 1 Study Guide Format: This Is A Multiple-Choice Exam. It Will Include at Least 100 Questions (No MoreidkwhattodoanymoreNo ratings yet
- Mateo Alejandro Castelblanco García Sixth Grade Angie Xiomara Pinto Cambridge SchoolDocument10 pagesMateo Alejandro Castelblanco García Sixth Grade Angie Xiomara Pinto Cambridge SchoolMariaGarciaNo ratings yet
- Pe Module 4 ReviewerDocument5 pagesPe Module 4 ReviewerjohnlloydrocasNo ratings yet
- 5 Beats To Play 5 Million Songs 2Document9 pages5 Beats To Play 5 Million Songs 2numaNo ratings yet
- Roaring 20s Webquest-Answer KeyDocument3 pagesRoaring 20s Webquest-Answer KeyMichelle Lucio100% (2)
- 68 Show Cue SheetDocument5 pages68 Show Cue SheetalexkelleybassNo ratings yet
- 8.572505 SungtextDocument9 pages8.572505 SungtextAlberto JorgeNo ratings yet
- Lute Suite in E Minor, BWV 996Document2 pagesLute Suite in E Minor, BWV 996hnjgqtyruky50% (4)
- Jazz Chord Essentials Drop 2 Voicings Part 1 PDFDocument2 pagesJazz Chord Essentials Drop 2 Voicings Part 1 PDFssno1100% (2)
- Zin31 Choreo NotesDocument21 pagesZin31 Choreo NotesElisa CorreaNo ratings yet
- Interview Roy HargroveDocument2 pagesInterview Roy HargroveDominik BorekNo ratings yet
- Copland Clarinet Concerto Piano Reduction PDF - Google SearchDocument2 pagesCopland Clarinet Concerto Piano Reduction PDF - Google Searchgwteng8% (13)
- Sultans of SwingDocument22 pagesSultans of Swingpaco jonesNo ratings yet
- Stephen Hus ArikDocument4 pagesStephen Hus Arik'-Pedro Emmanuel El KrackNo ratings yet
- Latin Chord E-Book: by Sergio ErcoleDocument18 pagesLatin Chord E-Book: by Sergio ErcoleCorkscrewNo ratings yet
- 4_5985592880427702189Document19 pages4_59855928804277021899g4jpdpyjkNo ratings yet
- Ice Cream SongDocument4 pagesIce Cream SongChristian Anthony MaillouxNo ratings yet
- Led ZeppelinDocument10 pagesLed Zeppelinapi-3802935No ratings yet
- Centro de Línguas Municipal Antonio Houaiss - Projeto Cinema - Maio - 2017Document2 pagesCentro de Línguas Municipal Antonio Houaiss - Projeto Cinema - Maio - 2017Mara Silveira DiasNo ratings yet
- Resume For Grace Elisabeth Ann SedgwickDocument2 pagesResume For Grace Elisabeth Ann Sedgwickapi-250171045No ratings yet