Pharmacology Trans ANS Drugs I
Pharmacology Trans ANS Drugs I
Uploaded by
Princess Mara DuranCopyright:
Available Formats
Pharmacology Trans ANS Drugs I
Pharmacology Trans ANS Drugs I
Uploaded by
Princess Mara DuranOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Pharmacology Trans ANS Drugs I
Pharmacology Trans ANS Drugs I
Uploaded by
Princess Mara DuranCopyright:
Available Formats
ACETYLCHOLINE
AUTONOMIC DRUGS
Dr. Paguirigan (August 23, 2019)
is a prototype of drug that acts directly at both
4 GROUPS: the muscarinic and nicotinic receptors
1. CHOLINOCEPTOR-ACTIVATING & spectrum of action: both Muscarinic and
CHOLINESTERASE INHIBITING DRUGS Nicotinic receptors
2. CHOLINOCEPTOR-BLOCKING DRUGS rapidly hydrolyzed by cholinesterase
3. ADRENOCEPTOR-AGONIST & duration of action: 5 - 30 seconds
SYMPATHOMIMETIC DRUGS METHACOLINE
4. ADRENOCEPTOR-ANTAGONIST DRUGS
acetyl-β-methylcholine
CHOLINOCEPTOR-ACTIVATING & pharmacologically similar to Acetylcholine
CHOLINESTERASE INHIBITING DRUGS
CARBACHOL
2 GROUPS:
spectrum of action: both Muscarinic and
1. DIRECT-ACTING CHOLINOCEPTOR Nicotinic
STIMULANTS resistant to cholinesterase
2. INDIRECT-ACTING CHOLINOMIMETICS/ orally active
CHOLINESTERASE INHIBITORS has poor lipid solubility
duration of action: 30 minutes – 2 hours
DIRECT-ACTING CHOLINOCEPTOR STIMULANTS
BETHANECOL
also called direct-acting cholinomimetic agents
they bind to and they activate the Muscarinic spectrum of action: both Muscarinic and
or Nicotinic receptors Nicotinic; but more on Muscarinic receptor
further subdivided into 2 subgroups: has the same pharmacologic feature as
Carbachol
CHOLINE ESTERS
o include: PILOCARPINE
Acetylcholine spectrum of action: Muscarinic
Methacoline- acetyl-β- not an ester; more of an alkaloid
methylcholine has a good lipid solubility
Carbachol- carbanoyl choline duration of action: 30 minutes – 2 hours
Bethanecol- carbanyl-β-
methylcholine NICOTINE
CHOLINOMIMETIC ALKALOIDS also acts on the Periperheral Nervous System
o either muscarinic or nicotinic there is an initial stimulation and
o include: subsequently there is a major persistent
Muscarine depression of all the autonomic ganglia
Pilocarpine also causes the release of cathecolamine in a
Nicotine number of isolated organs
Lobeline effects on the neuromuscular junction are
similar to those of the ganglia
also stimulates a number of sensory receptors
and this includes:
Acebedo, Cruz, Davis, Duran, Salucon, Uy 1
o Methanoreceptor- respond to stretch or if it is given via IV bolus injection it can cause
pressure on the skin, the mesentery in the transient bradycardia; otherwise it will
tongue, lungs, stomach produce reflex tachycardia
o Chemoreceptors- in the carotid body
o Thermal receptors- in the skin and tongue
and also some pain receptors INDIRECT-ACTING CHOLINOMIMETICS/
perfectly stimulates the Central Nervous CHOLINESTERASE INHIBITORS
Sytem (CNS)
on the Cardiovascular System, it increases the has primary effect at the active site of
heart rate and the blood pressure acetylcholinesterase while some ahve direct
on the Gastrointestinal Tract, it increases the actions at the Nicotinic receptors
tone and motor activity of the bowel drugs include:
in the exocrine glands, Nicotine has an initial Neostigmine
stimulation of the salivary and bronchial Physostigmine
secretion followed by inhibition Carbaryl
readily absorbed from the respiratory tract Edrophonium
(major source of Nicotine is cigarette) from the Ambenonium
buccal mucosa and skin Demecarium
about 80-90% of the Nicotine that we take in NEOSTIGMINE, PYRIDOSTIGMINE, and
is altered in the body mainly in the liver but AMBENONIUM
some are also metabolized in the kidney and o are standard anticholinesterase drugs that
lungs are used as symptomatic treatment for
half life after inhalation or parenteral “myasthenia gravis”; these are reversible
administration is about 2 hours anticholinesterase drugs
both Nicotine and its metabolite are rapidly o also used in the reversal of neuromuscular
eliminated by the kidney via renal elimination blocking
the rate of urinary secretion is dependent on o dosage:
the pH of the urine; there is decreased rate of Neostigmine = 7.5mg
elimination if the urine is alkaline Pyridostigmine = 30mg
the major metabolite of Nicotine are Cotinine Ambenonium = 2.5mg
and nicotine-N-oxide
Nicotinic toxicity: has 2 major chemical classes:
o stimulation of the CNS and ganglion
o neuromuscular end plate depolarization CARBAMIC ACID ESTERS/ CARBAMATES
which will lead to fasciculations and o prototype: NEOSTIGMINE
paralysis o are hydrolyzed; and the carbamate
Muscarinic Toxicity: residue is released by cholinesterase
o stimulation of CNS (uncommon) over a period of 2-8 hours
o produces myosis
o spasm of accommodation PHOSPHORIC ACID ESTERS/
o bronchoconstriction ORGANOPHOSPHATES
o increase GIT and urinary tract smooth o prototype: ECHOTHIOPHATE
muscle activity long acting cholinesterase inhibitors
o increase activity in the sweat glands, include:
airways and GIT ECHOTHIOPHATE
PARATHION
Acebedo, Cruz, Davis, Duran, Salucon, Uy 2
MALATHION PYRIDOSTIGMINE
SOMAN
PARAOXON use:
MALAOXON o for myasthenia gravis
form an extremely stable phosphate duration of action: 3-6 hrs
complex with the enzyme
released over a period of many days or CARBARYL
even weeks
effects: cause an increase in the used as an insecticide
concentration and half-life of acetylcholine
especially in the synapses where EDROPHONIUM
acetylcholine is realeased physiologically not an ester but an alcohol
these cholinesterase inhinbitors do not uses:
have therapeutic actions in parts of the o for the diagnosis of “myasthenia gravis”
body where acetylcholine is not normally o Ileus
released
o Arrhythmia
Other group: duration of action: 5-15 mins
ALCOHOL ECHOTHIOPHATE
o EDROPHONIUM
amplifies the effects of acetylcholine
use:
o anti-glaucoma drug
DRUGS USED AS CHOLINESTERASE INHIBITORS duration of action: 100 hours
NEOSTIGMINE MALATHION
is a typical ester is an insecticide but it is used as scabicide for
amplifies the endogenous acetylcholine medical use (for scabies)
uses:
o post-operative and neurogenic ileus PARATHION
o urinary retention
one of the most toxic
o reversal of neuromuscular blocking
rapidly fatal if the exposure is not immediately
o Ileus
recognized and treated
o Myasthenia gravis
if there is an inadvertent exposure to this
duration of action: 30 min- 2 hrs
drug, treatment used is a Regenerator
PHYSOSTIGMINE Compound like PRALIDOXIME
o this can be used if given early
naturally-occurring carbamate signs and symptoms of toxicity are the same
amplifies the effects of acetylcholine as the toxicity during direct-acting drugs
use: except for the following: Parathion may cause
o for glaucoma o Vasodilation- late and uncommon
duration of action: 30 minutes- 2 hours o Bradycardia and CNS stimulation- more
common
Acebedo, Cruz, Davis, Duran, Salucon, Uy 3
METRIFONATE B. DIRECT-ACTING MUSCARINIC ALKALOIDS
(SYNTHETICS)
antihelminthic drug
PILOCARPINE
Effects of indirect-acting cholinomimetics/
cholinesterase inhibitors : like Bethanechol--partial agonist
D -diarrhea CEVIMELINE
U -urination synthetic M3 selective
similar to Pilocarpine
M - miosis
B - bronchoconstriction
C. DIRECT-ACTING NICOTINIC AGONISTS
E – excitation of skeletal muscles and CNS
NICOTINE
L - lacrimation
agonist of both Nn and Nm receptors
S - salivation
VARENICLINE
AMBENONIUM
selective partial agonist of both alpha-4 and
use: beta-2 nicotinic receptors
o Myasthenia gravis use: exclusively for smoking cessation
duration of action: 4-8 hours
DEMECARIUM
D. SHORT- ACTING CHOLINESTERASE INHIBITORS
use: (ALCOHOLS)
o Glaucoma
EDROPHONIUM
Duration of Action: 4-6 hrs
only drug under this category
DRUGS THAT ARE USED FOR CHOLINOMIMETIC
alcohol
EFFECTS
binds briefly to the active site of
A. DIRECT-ACTING CHOLINE ESTERS acetylcholinesterase and prevents the access
of acetylcholine
BETHANECHOL
muscarinic agonists
CARBACHOL
non-selective muscarinic and nicotinic agonist
Acebedo, Cruz, Davis, Duran, Salucon, Uy 4
E. INTERMEDIATE- ACTING CHOLINESTERASE CHOLINOCEPTOR BLOCKING DRUGS
INHIBITORS (CARBAMATES)
ANTIMUSCARNIC DRUGS
NEOSTIGMINE
ATROPINE
forms a covalent bond with
acetylcholinesterase but it is hydrolyzed and it prototype of naturally occurring compounds
is released with antimuscarinic effects
PYRIDOSTIGMINE PROPANTHELINE
like Neostigmine in pharmacologic action quaternary amine
but has longer action, longer-acting
PIRENZEPINE
duration of action: 4-6 hrs
use: for myasthenia gravis tertiary amine
use: peptic ulcer diseases
PHYSOSTIGMINE
TROPICAMIDE
like neostigmine but a natural alkaloid
a tertiary amine tertiary amine
enters the CNS use:
o mydriatic action
o cycloplegic action
F. LONG- ACTING CHOLINESTERASE INHIBITORS
GLYCOPYRROLATE
(ORGANOPHOSPHATES)
quaternary amine
ECHOTHIOPATE
DICYCLOMINE
like Neostigmine, but released more slowly
tertiary amine
MALATHION
use:
insecticide but relatively safe for mammals o peptic ulcer diseases
and birds o GI hypermotility
PARATHION TIOTROPIUM
insecticide and very dangerous to all animals quaternary amine
use: asthma
SARIN
BENZTROPINE
nerve gas
use: exclusively for warfare and terroristic tertiary amine
activities use: Parkinson’s disease
Acebedo, Cruz, Davis, Duran, Salucon, Uy 5
ANTIMUSCARINIC DRUGS USED IN MUSCARINIC ANTAGONISTS (MUSCARINIC
OPTHALMOLOGY BLOCKERS)
1. ATROPINE A. NON-SELECTIVE
2. SCOPOLAMINE a. ATROPINE – prototype
3. HOMATROPINE b. SCOPOLAMINE
4. CYCLOPENTOLATE c. GLYCOPYRROLATE
5. TROPICAMIDE d. IPRATROPIUM
e. CYCLOPENTOLATE
ANTIMUSCARINIC DRUGS USED IN
f. BENZTROPINE
GASTROINTESTINAL AND GENITOURINARY
g. HOMATROPINE
CONDITIONS
h. METHYLSCOPOLAMINE
A. QUATERNARY AMINES i. TROPICAMIDE
a. ANISOTROPINE B. M1 SELECTIVE
b. CLIDINIUM a. PIRENZEPINE
c. GLYCOPYRROLATE b. TELENZEPINE
d. ISOPROPAMIDE
ATROPINE
e. MEPENZOLATE
f. METHANTHELINE Prototype drug
g. METHYLSCOPOLAMINE alkaloid found in Atropa belladonna and many
h. OXYPHENONIUM other plants
i. PROPANTHELINE tertiary amine
j. TRIDIHEXETHYL relatively lipid-soluble
k. TROSPIUM readily crosses the membrane barrier
B. TERTIARY AMINES well distributed in the CNS and other organs
a. ATROPINE eliminated by hepatic or liver metabolism and
b. DARIFENACIN partly by renal excretion
c. DICYCLOMINE elimination half-life: about 2 hours
d. OXYBUTYNIN duration of action: 4-8 hours except in the
e. OXYPHENCYCLIMINE eyes where the action lasts for 72 hours or
f. PROPIVERINE longer
g. SCOPOLAMINE moa: muscarinic blocking drug that acts as a
h. SOLIFENACIN competitive(or surmountable) pharmacologic
i. TOLTERODINE antagonists
o blocking effect could be overcome by
GANGLION-BLOCKING DRUGS
increasing the concentration of
1. HEXAMETHONIUM muscarinic agonist
2. MECAMYLAMINE effects: same ocular, GI, genitourinary and
3. TETRAETHYLAMMONIUM secretory effects as cholinoceptor blocking
4. ACETYLCHOLINE drugs
Acebedo, Cruz, Davis, Duran, Salucon, Uy 6
CNS Sedation effects and very low/few
Amelioration of motion antimuscarinic effect
sickness outside the lungs
Reduction of signs of because it is poorly
Parkinsonism absorbed and is rapidly
CVS Initial bradycardia followed by metabolized
tachycardia
Reduction of AV conduction
time D. GENITOURINARY TRACT
EYES Cycloplegia
Mydriasis ATROPINE Reduce acid
LUNGS Bronchodilation METHSCOPOLAMINE secretion but less
SECRETIONS Reduction of salivation, PROPANTHELINE effective than
lacrimation, sweating and other H2 blockers
gastric secretion like Cimetidine
SKELETAL No effect PIRENZEPINE New muscarinic
MUSCLES drug
Selective
muscarinic blocker
CLINICAL USES OF MUSCARINE BLOCKERS Use: Peptic Ulcer
Diseases
A. CNS
SCOPOLAMINE Motion sickess E. GIT
BENZTROPINE Parkinsonism Muscarinic blocker that reduces cramping and
BIPERIDEN hypermotility in transient diarrhea but
TRIHEXYPHENIDYL DIPHENOXYLATE or LOMOTIL is more effective
BENZTROPINE (given Acute dystonic caused
parenterally) by antipsychotic F. BLADDER
medications
GLYCOPYRROLATE Reduce the
B. EYES OXYBUTYNIN urgency and
ATROPINE 72 hrs Dilate the METHYLSCOPOLAMINE mild cystitis
HOMATROPINE 24 hrs pupil
Reduce bladder
CYCLOPENTOLATE 2-12 hrs
spasm followed
TROPICAMIDE 30 min-4 hrs
by neurologic
surgery
C. BRONCHI
ATROPINE Reduce the airway
secretion especially Mnemonics for Atropine Toxicity:
during surgery
IPRATROPIUM Inhalation: reduce “Dry as a bone, red as a beet, mad as a hatter,
bronchoconstriction in blind as a bat”
asthma and COPD
Has less arrhythmic side
Acebedo, Cruz, Davis, Duran, Salucon, Uy 7
*These descriptions will reflect both predictable Classified into 2 groups:
antimuscarinic effect and some of the
unpredictable actions of Atropine” 1. Drugs that initially stimulate the ganglia by
ACh-like action then blocks the ganglia
The predictable toxic reactions are because of persistent depolarization
Eg. Nicotine – most popular drug that
Hyperthermia or atrophic fever because of the
gives this action
blockade of the thermoregulatory sweating
prolong application results in
mechanism. This effect can be fatal in infants.
desensitization of cholinergic
In adults, sweating salivation and lacrimation
receptor sites and there will be
are all significantly reduced or even stopped
continuous blockade
by Atropine
In the elderly, it can also produce acute angle drugs that do not involve prior ganglionic
glaucoma and urinary retention stimulation or change in the ganglionic potential
Constipation and blurred vision are seen in all
age groups 2. Drugs that impair transmission either by
competing with ACh or ganglionic
Other toxic reactions of Atropine cholinergic receptor sites or blocking the
channels when it is open (drugs that do not
A. CNS
involve prior ganglionic stimulation or
Sedation
change in the ganglionic potential)
Amnesia
Eg. Hexamethonium, Trimethaphan -
delirium or hallucination (“mad as a
prototypes
hatter”)
convulsions HEXAMETHONIUM & RELATED DRUGS
B. CVS
intraventricular conduction blockade Effects on CVS
dilation of the cutaneous blood vessels postural hypotention, sympathetically-
especially in the arm, head, neck and mediated vasomotor reflexes that are
trunk --Atropic flash (this sign may be inhibited and they also reduce the cold
diagnostic for overdose of Atropine); pressor response
“red as a beet” Mild tachycardia that accompanies
hypotension
Contraindication/Cautions Reduced cardiac output as a result of
diminished venous return due to
Infants – danger of hyperthermia
venous dilatation and peripheral
Patients with glaucoma (especially closed
pooling of blood
angle glaucoma)
In Hypotension – CO, SV and left
Men with Prostatic Hyperplasia
ventricular work are all diminished
Total systemic vascular resistance is
decreased but the blood flow and
NICOTINIC ANTAGONISTS vascular resistance (vascular beds are
variable)
Skin temperature is elevated mostly in
GANGLION BLOCKING DRUGS
head and feet
Impair the actions of primary nicotinic Blood flow into limbs is increased
receptors
Acebedo, Cruz, Davis, Duran, Salucon, Uy 8
Reduced cerebral blood flow – minimal NEUROMUSCULAR BLOCKING DRUGS
unless the mean systolic BP falls below
50-60 mmHg A. Non-depolarizing Group
Skeletal muscle blood flow is unaltered Includes Tubocurarine, Pancuronium,
Splanchnic and renal blood flow are Atrocurium – neuromuscular blocking
decreased drugs
Ganclion blocking drugs are not anymore
Renal vascular resistance is increased
clinically used because of severe serious
Glomerular filtration is decreased
side effects like:
Cyclopegia
severe constipation
Other effects reduced bladder contractility
GIT secretions are decreased impairment of erection and
Tone and motility of GIT are reduced ejaculation
Partial impairment of voiding and tachycardia
contraction of the urinary bladder reduced CO
Penile erection and ejaculation are reduced venous tone
impaired decreased BP
Mydriasis partial loss of orthostatic hypotension
accommodation reduced salivation
Sweating is reduced lacrimation
sweating
Clinical Uses GI secretion
Used as an emergency drug in
hypertensive crisis The neuromuscular blocking drugs are
Initial control of BP in acute dissecting important for producing complex skeletal
aortic aneurysm muscle relaxation especially during surgery
Production of controlled hypotension
Other drugs:
TRIMETHAPHAN Vecuronium
Gallamine
management of autonomic hyperreflexia
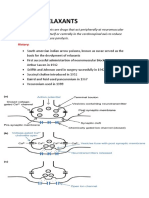
TUBOCURARINE
prototype
OTHER GANGLIONIC BLOCKING DRUGS
causes flaccid paralysis that can last for 30 – 60
minutes
1. Mecamylamine
2. Trimethaphan PANCURONIUM, ATROCURIUM, VECURONIUM
3. Pempidine
4. Pentolinium shorter acting non-depolarizing blockers
GALLAMINE
old drug that is now rarely used
Acebedo, Cruz, Davis, Duran, Salucon, Uy 9
B. Depolarizing Group Also classified according to MOA and spectrum
of activity
SUCCINYLCHOLINE
only member of the group that is used 1. ENDOGENOUS CATECHOLAMINES
clinically Epinephrine
produces fasciculations during induction of Norepinephrine
paralysis Dopamine
hydrolyzed by pseudocholinesterase or plasma
cholinesterases
Half life: few minutes 2. DIRECT – ACTING SYMPATHOMIMETICS
duration of action: may be prolonged in PHENYLEPHRINE
patients with genetically determined
abnormality in cholinesterase longer duration of action than the
catecholamines
Effective mydriatic and decongestant
In case of cholinesterase overdose, you can use a
cholinesterase regenerator: MIDODRINE
PRALIDOXIME prodrug
selective alpha-1 receptor agonist
prototype drug
Used in cholinesterase overdose METHOXAMINE
cholinesterase regenerators are not receptor
antagonist but are chemical antagonists predominantly direct-acting alpha-1 receptor
contain an “–oxime” group which has an agonist
extremely high affinity for phosphorous atom CLONIDINE, METHYLDOPA, GUANFACINE,
in organophosphate insecticides GUANABENZ
Because of high affinity for phosphorous
excess that of the enzyme active site, these alpha selective agonist
agents will be able to bind to inhibitor and used in treatment of hypertension
displace the enzyme – so the active enzyme
will be regenerated MOXONIDINE OR RILMENIDINE
also used for HTN
DEXMEDETOMIDINE
ADRENOCEPTOR ANTAGONISTS AND
SYMPATHOMIMETIC DRUGS produces sedation
initial sedation needed for intubated patients
Sympathomimetic drugs – these drugs mimic
or imitate stimulation of sympathetic ANS TIZAMIDINE
Classified as:
Endogenous Catecholamines central muscle relaxant
Direct – acting Sympathomimetics XYLOMETAZOLINE AND OXYMETAZOLINE
Mixed – acting Sympathomimetics
Indirect-acting sympathomimetics direct acting alpha agonist
Dopamine Agonists used only as topical decongestant
Acebedo, Cruz, Davis, Duran, Salucon, Uy 10
ISOPROTERENOL (ISOPRENALINE) Duloxetine
Milnasipram
very potent beta receptor agonist with very Cocaine
little effect on alpha agonist
DOBUTAMINE AND PRENALTEROL ATOMOXETINE
frequently seen to cause ORTHOSTATIC
Beta – 1 selective agonist (Prenalterol – partial TACHYCARDIA
agonist)
REBOXETINE
RITODRINE AND TERBUTALINE like Atomoxetine pharmacologically
Beta – 2 selective agonist
SIBUTRAMINE
used for the treatment of asthma
an APPETITE SUPPRESSANT
3. MIXED – ACTING SYMPATHOMIMETICS
DULOXETINE
Ephedrine
an ANTIDEPRESSANT
Pseudoephedrine
Phenylpropanolamine
MILNASIPRAM
used to RELIEVE PAIN in cases of
4. INDIRECT ACTING SYMPATHOMIMETICS
FIBROMYALGIA
Either: Amphetamine-like or
Catecholamine Reuptake Inhibitors
COCCAINE
mainly acts on CNS
AMPHETAMINE-LIKE
used to INHIBIT DOPAMINE REUPTAKE in the
SYMPATHOMIMETICS
neurons or more specifically the pleasure
Amphetamine
center of the brain
Methamphetamine
Phenmetrazine
5. DOPAMINE AGONISTS
Methylphenidate
Includes:
Modafinil
Levodopa
Tyramine
Dopamine agonists with central
action
AMPHETAMINE
has a very strong CNS STIMULANT effect like
LEVODOPA
Methamphetamine
is converted to Dopamine in the body
MODAFINIL
LEVODOPA AND DOPAMINE AGONISTS WITH
used for NARCOLEPSY
CENTRAL ACTION
used for Parkinson’s Disease and
TYRAMINE
prolactinemia
acts as Norepinephrine
Sympathomimetic drugs can also be classified
according to their MOA and spectrum of
CATECOLAMINE-REUPTAKE INHIBITORS
activity
Atomoxetine
Reboxetine
Sibutramine
Acebedo, Cruz, Davis, Duran, Salucon, Uy 11
ACCORDING TO MOA: ISOPROTERINOL
prototype for drugs that act on the beta
AMPHETAMINE can cause the release of receptors
DERIVATIVES stored catecholamines so
AND TYRAMINE they have an indirect DRUGS THAT ACT ON THE DOPAMINE RECEPTORS
action
I. CATECHOLAMINE
COCCAINE AND inhibit the uptake of Epinephrine
TRICYCLIC catecholamine by the Norepinephrine
ANTIDEPRESSA nerve terminals so they Isoproterinol
NTS increase the synaptic Dopamine
activity of the released Dobutamine
transmitter, so they also
have an indirect action II. NON-CATECHOLAMINE
Amphetamine
They can also act to block Ephedrine
the metabolism of the Mephentermine
drug like the blockade of Hydroxyamphetamine
catechol-O-methyl Metaraminol
transferase (COMT) and Phenylephrine
the monoamine oxidase Methoxamine
(MAO) Prenalterol
They have little direct
effect on the autonomic A. CATECHOLAMINE
activity but the bound (?)
inhibition will increase SELECTIVE BETA-1 AGONISTS
the stores of
catecholamine in the DOBUTAMINE
storage vesicles resembles dopamine chemically
a direct acting drug with the selectivity to beta
They can potentiate the 1 receptors
action of indirectly acting relatively more effective in enhancing the
sympathomimetics contractile force of the heart than increasing
the heart rate
it does not affect the atrial conduction velocity
ACCORDING TO SPECTRUM OF ACTION: but it augments the conduction velocity
through the AV node
EPINEPHRINE there is little or no effect on ventricular
the prototype for drugs that act on all impulse conduction
adrenoceptors does not produce renal vasodilation
plasma half life: approximately 2 mins only
PHENYLEPHRINE not effective orally
prototype for drugs that act on the alpha usual dose: 2.5-10 nanograms per kilogram
receptors body weight per minute
Acebedo, Cruz, Davis, Duran, Salucon, Uy 12
rapidly metabolized in the liver to an inactive tachycardia
conjugate with glucoronic acid and 3-O-methyl anginal pain
dobutamide arrhythmia
should not be used in patients with atrial headache
fibrillation hypertension
the less frequent SE: vasocontriction
nausea Contraindications: MAO inhibitors
headache
palpitation Therapeutic uses:
SOB treatment of some types of shock
anginal pain oliguria and those with low or normal
peripheral vascular resistance
Therapeutic Uses: cardiogenic and bacteremic shock and
Congestive heart failure profound hypertension following removal
Cardiogenic shock of pheochromocytoma
Contraindications:
Patients with marked obstruction to
cardiac ejection like in idiopathic B. NON CATECJHOLAMINES
hypertrophic subaortic stenosis
DOPAMINE AMPHETAMINE
is the immediate metabolic precursor of NE has a powerful CNS stimulant action in
and epinephrine addition to the peripheral alpha and beta
a central neurotransmitter actions that are common to indirect acting
possesses important intrinsic pharmacologic sympathomimetic drugs
properties effective for oral administration
a substrate for both MAO and COMT effect lasts for several hours
ineffective when administered orally the effects on the system raises both systolic
Cardiovascular effects: and diastolic BP
positive inotropic effect on myocardium heart rate is reflexly slow and cardiac
acting as an agonist at the beta-1 receptor arrhythmias can occur
capable of causing the release of NE from L-isomer is slightly more potent than D-isomer
nerve terminals preparation of amphetamine (as far as its
tachycardia is less compared to one that is cardiovascular action is concern)
produced by isoproterenol one of the most potent sympathomimetic
it can increase the systolic pressure and amines with respect to the stimulation of CNS
pulse pressure stimulates the medullary respiratory center
increases GFR, renal blood flow and and lessens the degree of central depression
sodium excretion caused by various drugs
depresses appetite, but found out that weight
Overdose: loss in obese patient treated with
attributable to the excessive amphetamine is almost entirely due to
sympathomimetic activity reduced food intake and only in small
encountered during dopamine infusion: measures due to increased metabolism
nausea
vomitting
Acebedo, Cruz, Davis, Duran, Salucon, Uy 13
EPHEDRINE the actions of this drug are similar to that of
Ephedrine except that the drug almost entirely
stimulates both alpha and beta receptors lacks a CNS stimulant activity
clinical uses are related to both its action on the only current clinical use of
alpha and beta receptors hydroxyamphetamine now is as a mydriatic
cardiovascular action persists 10x longer than (an agent that makes the pupil of the eye
that of Epinephrine dilate or open up)
the bronchial muscle relaxation that is
produced by Ephedrine is less prominent but METARAMINOL
is more sustained compared to that produced
by Epinephrine is used almost exclusively for the treatment of
mydriasis occurs after local application of the hypotension or hypotensive states
drug to the eyes it has both a direct and indirect action
activity of the human uterus is usually reduced its overall effects are similar to those of
by Ephedrine Norepinephrine but it is much less potent and
less effective than epinephrine in elevating the has a more prolonged action
concentration of glucose in the blood it does not have any CNS stimulant effect
CNS effect are similar to those Amphetamine it is absorbed after oral administration, but for
but are considerably less marked equal effects, the oral dose must be 5-6 times
Therapeutic uses: greater than the dose when you give it by IM
Bronchospasm or IV
Stoke Adams syndrome the pressor effect on an IM dose is 5 mg and it
Decongestant (Nasal decongestant) will last for 1 and a half hour
Allergic disorders the principal use clinically by Metaraminol is
Pressor agent during spinal anesthesia as a pressor agent in certain hypotensive
Central stimulant in cases of narcolepsy states.
MEPHENTERMINE PHENYLEPHRINE
used in various hypotensive conditon a powerful alpha-1 receptor stimulant with
prolonged duration of action, can be up to very little effect on the beta receptors of the
4hrs heart
cardiac contraction is enhanced its direct action on the receptors accounts for
cardiac output and the systolic and diastolic the greater part of its effect and only small
pressures are also increased part being due to its ability to release
there is a marked mucosal vasoconstriction if norepinephrine
applied locally however, the central stimulant effect on the
used mainly as pressor (producing an increase CNS is very minimal
in blood pressure by stimulating constriction of the responses to the drug persist for about 20
the blood vessels) drug in various hypotensive minutes after IV injection and it can persist for
states or conditions as long as 50 minutes after subcutaneous
injection.
HYDROXYAMPHETAMINE The effects of phenylephrine are:
marked reflex bradycardia
slight increase in the heart rate
slightly decreased cardiac output
Acebedo, Cruz, Davis, Duran, Salucon, Uy 14
peripheral resistance is considerably PRENALTEROL
increased
increased coronary blood flow a selective beta-1 adrenergic agonist
pulmonary blood vessels are constricted it is used as a cardiac stimulant
elevated pulmonary arterial pressure useful in the management of chronic
congestive heart failure
Therapeutic uses of phenylephrine:
as a nasal decongestant
used for hypotension TYPES OF ADRENOCEPTORS
used as a mydriatic
used as a local vasoconstrictor when given 1. alpha 1
together with a local anesthetic 2. alpha 2
used to relieve paroxysmal atrial 3. beta 1
tachycardia 4. beta 2
5. beta 3
6. dopamine 1
METHOXAMINE 7. dopamine 2
ORGAN SYSTEM EFFECTS OF STIMULATION OF
the pharmacologic properties of this drug are ADRENOCEPTORS
almost exclusively those that characterize an A. CNS
alpha receptor stimulant
it acts directly on the sit AMPHETAMINE can enter the CNS
the actions of methoxamine are similar to it starts its effect with a
those of Phenylephrine mild alerting effect
the outstanding effect of this drug is increased there is anorexia,
in the blood pressure due entirely to euphoria, and insomnia
vasoconstriction high doses of
there is no stimulant action on the heart and it amphetamine will cause
also lacks beta receptor action on smooth marked anxiety,
muscles aggressiveness, paranoia,
it does not have any CNS stimulation effect and sometimes
Reflex bradycardia is a prominent action so it convulsions (high doses)
is used clinically to relieve attacks of
paroxysmal atrial tachycardia B. EYES
it does not appear to precipitate cardiac
arrhythmia PHENYLEPHRINE cause mydriasis
it can prolong the ventricular muscle action & OTHER ALPHA- can reduce intraocular
potentials and the refractory period so it can AGONISTS pressure
slow the AV conduction time
C. BRONCHI
Therapeutic uses of methoxamine
a pressor agent in hypotensive states BETA-2 cause bronchodilation
used to end attacks of paroxysmal atrial AGONISTS
tachycardia
Acebedo, Cruz, Davis, Duran, Salucon, Uy 15
D. GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT Dopamine-1 receptor cause vasodilation
there will be an activation of the alpha agonist in the splanchnic
and beta receptors causing relaxation and renal vascular
of the smooth muscles bed but at higher
Alpha-2 agonists decrease salt and water doses beta
secretion in the GIT receptors are
activated and at
even higher doses
E. GENITOURINARY
alpha receptors are
also activated
ALPHA RECEPTORS cause contraction of
the urinary
G. HEART
sphincter
there will be an increased rate of
BETA-2 AGONISTS will cause significant
cardiac pacemaker
uterine relaxation in
the AV node conduction and the
women near term
cardiac force will be increased
on the other cardiovascular actions,
there is increased blood pressure and a
F. VASCULAR SYSTEM
reflex bradycardia because of increased
vagal outflow
PHENYLEPHRINE (alpha- constrict the skin
1 agonist) and splanchnic
H. METABOLIC AND HORMONAL EFFECTS
blood vessels and
increase the
Beta-1 agonists increase renin
peripheral vascular
secretion
resistance and
venous pressure
Beta-2 agonists increase insulin
secretion
CLONIDINE (alpha-2 if given by IV or as
agonist) nasal spray, it will
cause they will also increase glycogenolysis in
vasoconstriction the liver and they can also stimulate
but if it is given lipolysis
orally, it will cause
reduced
sympathetic CLINICAL USES:
outflow and blood
pressure EPINEPHRINE
TERBUTALINE (beta-2 significantly reduce used in anaphylaxis, glaucoma, asthma, and as
agonist) the arteriolar tone a vasoconstrictor
in the skeletal
muscle vascular NOREPINEPHRINE
bed will cause vasoconstriction and hypotension
can reduce
peripheral vascular ISOPROTERENOL
resistance and used for asthma and AV block although it is
arterial blood rarely used
pressure
Acebedo, Cruz, Davis, Duran, Salucon, Uy 16
DOPAMINE small doses of these sympathomimetics can
for most type of shock and heart failure cause nervousness, anorexia, and insomnia
higher doses can cause anxiety, aggressiveness
DOBUTAMINE or paranoid behavior
also for shock and heart failure convulsions can also occur
ALPHA-1 AGONIST
AMPHETAMINE and PHENMETRAZINE can cause hypotension
for narcolepsy, obesity and for attention-
deficit disorder BETA-1 AGONIST
can cause sinus tachycardia and serious
EPHEDRINE cardiac arrhythmias
used for urinary incontinence and hypotension
BETA-2 AGONIST
can cause skeletal muscle tremor
PHENYLEPHRINE COCAINE
will cause mydriasis, vasoconstriction, and as a
can cause addiction, cardiac arrythmia,
decongestant
infarction, and convulsion
ALBUTEROL, METAPROTERENOL, and
TERBUTALINE SUBCLASSES OF SYMPATHOMIMETIC DRUGS
used in asthma
premature labor A. ALPHA-1 AGONISTS
OXYMETAZOLINE AND XYLOMETAZOLINE
MIDODRIN
used as long-acting nasal decongestant
activates phospholipase C resulting in the
COCAINE increase intracellular calcium and
will cause vasoconstriction vasoconstriction
used also as local anesthetic
PHENYLEPHRINE
TOXICITY when used by IV for short a term period, is
used to maintain BP for acute hypotension
CATHECOLAMINES – has little CNS toxicity
although they cause: intranasally as decongestant
o excessive vasoconstriction
o cardiac arrhythmias B. ALPHA-2 AGONISTS
o myocardial infarction Clonidine
o pulmonary edema Methyldopa
o hemorrhage Guanfacine
Guanabenz
OTHER SYMPATHOMIMETICS
Dexmedetomidine
PHENYLISOPROPYLAMINE Tizanidine
Apraclonidine
will cause light to moderate CNS toxicity Brimonidine
Acebedo, Cruz, Davis, Duran, Salucon, Uy 17
CLONIDINE
inhibit adenyl cyclase and interacts with other METHYLDOPA
intracellular pathways thus it lowers BP exerts its effect via central mechanism
antihypertensive agent that paradoxically, enters cns readily and is decarboxylated to α-
possesses primarily alpha-2 adrenergic methyldopamine and beta hydroxylated to α-
agonist properties methylnorepinephrine which occurs at the
owes its antihypertensive effect to a central adgrenergic neurons
predominant action on the CNS thus, a o α-methylnorepinephrine- is a potent
centrally acting antihypertensive agonist at alpha-2 receptors in the CNS
decreases the sympathetic outflow from the and like clonidine, it will inhibit central
brain sympathetic outflow; more potent
possible site of action on the nucleus tractus stimulator at the alpha-2 receptors
solitarius in the lower brainstem (region rich in than in the alpha-1 receptors
cell bodies and nerve terminals that contain alpha-methyldopa, marketed as Aldomet
epinephrine and norepinephrine) used mainly for pre-eclampsia
Possible SE: SE:
sedation sedation
rebound hypertension (especially when hemolytic anemia
withdrawn suddenly-taper the use positive Coomb’s test
before total discontinuation to avoid
this) APRACLONIDINE, BRIMONIDINE
dry mouth both sympathomimetics
**treatment for rebound hypertension, alpha-2 selective
due to inadvertently stopping the use of increase secretion of aqueous humor by
Clonidine, using PHENTOLAMINE activating the alpha-2 adrenergic receptors
for glaucoma
GUANFACINE & GUANABENZ SE: dry mouth
central sympatholytic; also act on CNS blurred visin
used for hypertension conjunctivitis
same pharmacologic properties as Clonidine
C. BETA-1 AGONIST
DEXMEDETOMEDINE
sedative effect DOBUTAMINE
adjunct for anesthesia activates adenyl cyclase
increase in myocardial contaractility
TIZANIDINE positive ionotropic effect
muscle relaxant
APRACLONIDINE & PRIMONIDINE
for glaucoma
Acebedo, Cruz, Davis, Duran, Salucon, Uy 18
D. BETA-2 AGONISTS used for treatment of reversible obstruction of
the airway
ALBUTEROL selective beta-2 agonist
activates adenyl cyclase causing bronchial not methylated by COMT
smooth muscle to dilate after a 5 mg dose- produce bronchodilation
used for asthma after 1 hour and lasts for 7 hours;
subcutaneous- effect starts within 5 minutes
METAPROTERENOL and lasts for 4 hours
chemically similar to Isoproterenol SE:
resistant to methylation by COMT Nervousness
effective orally muscle tremors
longer duration of action than Isoproterenol headache
primarily a beta-2 adrenergic agonist tachycardia
when administered by inhalation, it has little palpitation
effect on the beta-1 receptors in the heart drowsiness
after inhalation/ oral adminstration- there is nausea
an increased force expiratory volume (FEV) vomiting
and maximal rate of force expiratory flow sweating
(FEF) and decreased in airway resistance
after oral dose - improvement of airway used in children below 12yo is not
function will be demonstrable for a period of recommended
at least 4 hours subcutaneous dose: 0.25 mg
after inhalation - improved respiratory inhalation: 2 sprays every 4-6 hours;
function will be apparent for 3-4 hours tablet: 2.5 mg or 5 mg depending on body size;
approx. 40% of Metaproterenol will be injection: 1 mg (prep of 1mg/ml)
absorbed after oral dose aerosol: 0.2 mg per spray
excreted in the urine as a conjugate with
glucuronic acid ALBUTEROL
Adverse effects: selective beta-2 adrenergic agonist
tachycardia same pharmacologic properties and
hypertension therapeutic indications with Terbutaline
tremor inhalation: effect starts after 15 mintes and
palpitation lasts for 3-4 hours
nervousness preparations available:
nausea and vomiting o 2mg tab and 4mg tab for oral use,
therapeutic use: as a bronchodilator o aerosol preparation also available,
initial dose: 2-4 mg 3x or 4x a day
TERBUTALINE Total daily dose of 32 mg should not be
synthetic sympathomimetic drug exceeded
routes: oral, subcutaneous, inhalation
Acebedo, Cruz, Davis, Duran, Salucon, Uy 19
RITODRINE
selective beta-2 adrenergic agonist
used to delay or prevent premature
parturition
rapidly but incompletely absorbed (30%)
following oral dose
o 90% excreted in the urine as inactive
conjugate
o 50% excreted unchanged after IV
administration
Acebedo, Cruz, Davis, Duran, Salucon, Uy 20
You might also like
- Cholinergic DrugsDocument15 pagesCholinergic DrugsChris Girgis100% (1)
- Intensive Nursing Practicum: Bachelor of Science in NursingDocument11 pagesIntensive Nursing Practicum: Bachelor of Science in NursingMichelle Gliselle Guinto Mallare100% (1)
- Week 6 - Autonomic PharmacologyDocument19 pagesWeek 6 - Autonomic PharmacologyJayla Marie100% (1)
- Cholinergic and AnticholinergicDocument77 pagesCholinergic and Anticholinergicsweta sumanNo ratings yet
- Cholinergic System and DrugsDocument42 pagesCholinergic System and DrugsIgnatius MicahelNo ratings yet
- Cholinergic ReceptorsDocument67 pagesCholinergic ReceptorsShynne RPhNo ratings yet
- Pharma TosDocument64 pagesPharma Tossaaad javidNo ratings yet
- Topic 2. Pharmacology For Pain and Inflammation RDocument52 pagesTopic 2. Pharmacology For Pain and Inflammation RKendrick GalosoNo ratings yet
- Cholinergic Agonists/ Cholinomimetic Agents: Dr. Kyi Kyi Tha Basic Medical Sciences Kulliyyah of Pharmacy IiumDocument21 pagesCholinergic Agonists/ Cholinomimetic Agents: Dr. Kyi Kyi Tha Basic Medical Sciences Kulliyyah of Pharmacy IiumZhuan AhmadNo ratings yet
- CNS Pharmacology: Abebe Ejigu Departmenet of PharmacologyDocument358 pagesCNS Pharmacology: Abebe Ejigu Departmenet of PharmacologyMulugeta TesfayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Introduction To Autonomic PharmacologyDocument30 pagesChapter 6 Introduction To Autonomic PharmacologyImrana AamirNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic Drugs: Pharmacological Department Medical School - UNPAD Ike HusenDocument33 pagesAdrenergic Drugs: Pharmacological Department Medical School - UNPAD Ike HusenHendra EfendiNo ratings yet
- Autacoids Analgesics DR H AboshoushaDocument7 pagesAutacoids Analgesics DR H AboshoushaMoustafa HazzaaNo ratings yet
- PARASYMPATHOMIMETICS 201st 20yearDocument26 pagesPARASYMPATHOMIMETICS 201st 20yearFlorenz GatchalianNo ratings yet
- Cholinergic ReceptorsDocument121 pagesCholinergic ReceptorsambroceNo ratings yet
- Transes PharmacodynamicsDocument36 pagesTranses PharmacodynamicsGwyneth Koleen Lopez100% (1)
- Autacoids: Group No. 1Document92 pagesAutacoids: Group No. 1Rohan Pal100% (1)
- Adrenergic Receptor AntagonistsDocument9 pagesAdrenergic Receptor AntagonistsPatterson MachariaNo ratings yet
- Autacoids For Med.Document140 pagesAutacoids For Med.Feysal AhmedNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Notes (Chapter 20 and 21)Document2 pagesPharmacology Notes (Chapter 20 and 21)graycorypNo ratings yet
- 6 Beta Adrenergic BlockersDocument19 pages6 Beta Adrenergic Blockersmatchees-gone rogue100% (1)
- Endocrine System Short Answer Questions - LA - AnswersDocument2 pagesEndocrine System Short Answer Questions - LA - AnswersVasantha SantaNo ratings yet
- Cholinergic Agents PPDocument13 pagesCholinergic Agents PPمحمد علي حميدNo ratings yet
- MCQDocument17 pagesMCQpradeephdNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Pharmacology PDFDocument85 pagesCardiovascular Pharmacology PDFAhmed Shihab AhmedNo ratings yet
- AutacoidsDocument32 pagesAutacoidsRenellie TrimidalNo ratings yet
- Pharma CNSDocument20 pagesPharma CNSIbrahem AlNo ratings yet
- 7 - Cholinomimetic DrugsDocument50 pages7 - Cholinomimetic DrugslalitrajindoliaNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Practice Questions MEDPHARM 501/801 FALL, 2004Document16 pagesAutonomic Practice Questions MEDPHARM 501/801 FALL, 2004suresh yadavNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes: Introduction To Ocular Pharmacology, Ocular Route of Drug Administration, Chemotherapy, Antibiotics, Antiviral and Antifungal DrugsDocument8 pagesLecture Notes: Introduction To Ocular Pharmacology, Ocular Route of Drug Administration, Chemotherapy, Antibiotics, Antiviral and Antifungal Drugskûrñï såñskrùthîNo ratings yet
- Muscarinic and Anti-MuscarinicsDocument3 pagesMuscarinic and Anti-MuscarinicsElleJBNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting The Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)Document40 pagesDrugs Affecting The Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)HiwaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Prof PlevkovaDocument414 pagesPathophysiology Prof PlevkovaPrince XavierNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Mannual 2014Document43 pagesPharmacology Mannual 2014Surulivel MkmNo ratings yet
- Antiepileptic Drugs HandoutDocument16 pagesAntiepileptic Drugs HandoutElizabeth Ivory ChuaNo ratings yet
- General Anaesthesia: I Made Agus Kresna SucandraDocument37 pagesGeneral Anaesthesia: I Made Agus Kresna SucandraBakingpancakesNo ratings yet
- Pharma MCQS PointsDocument9 pagesPharma MCQS PointsNajeeb Ullah Qadir via GTXNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Review Questions For QuizDocument14 pagesPharmacology Review Questions For QuizusedforfunplocNo ratings yet
- Basic Pharmacology of Antipsychotic AgentsDocument29 pagesBasic Pharmacology of Antipsychotic AgentsZane PhillipNo ratings yet
- Anti-Cholinergic Drugs and Cholinesterase InhibitorsDocument24 pagesAnti-Cholinergic Drugs and Cholinesterase InhibitorsKhalid I. Abdullah100% (1)
- Antimalarial, Antiprotozoal, and Antihelmintic AgentsDocument37 pagesAntimalarial, Antiprotozoal, and Antihelmintic AgentsQuolette ConstanteNo ratings yet
- Physiology Past SAQsDocument29 pagesPhysiology Past SAQsMatthew HoNo ratings yet
- L-19 Skeletal Muscle RelaxantDocument26 pagesL-19 Skeletal Muscle RelaxantZakiyahulfahdwNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology FirecrackerDocument37 pagesPharmacology FirecrackerRehan Usman100% (1)
- Revellionz'19 - Second Year Question BankDocument114 pagesRevellionz'19 - Second Year Question BankRamNo ratings yet
- Antiplatelet and Thrombolytic DrugsDocument48 pagesAntiplatelet and Thrombolytic DrugsNofa PuspitaNo ratings yet
- Adrenoreceptor Antagonist: Leida Marie P. Alarcon, MD, FPAFPDocument23 pagesAdrenoreceptor Antagonist: Leida Marie P. Alarcon, MD, FPAFPKenneth NuñezNo ratings yet
- Antiarrhythmic Drugs-Test-2-QuestionsDocument7 pagesAntiarrhythmic Drugs-Test-2-QuestionsDrishya BioplannetNo ratings yet
- PharmacologyDocument25 pagesPharmacologygregNo ratings yet
- Intro + Pharmacodynamics 2Document46 pagesIntro + Pharmacodynamics 2Dana E AbuqaudNo ratings yet
- Diuretics: By: Prof. A. AlhaiderDocument33 pagesDiuretics: By: Prof. A. AlhaiderNina Keraf100% (1)
- Drug Interactions Lecture Pre-ReadingDocument12 pagesDrug Interactions Lecture Pre-ReadingGregNo ratings yet
- MCQs On HypertensionDocument5 pagesMCQs On HypertensionDoctor RohailNo ratings yet
- Autacoids Related DrugsDocument74 pagesAutacoids Related DrugsVikash KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Peripheral Nervous System Pharmacology: Dr. M. IchwanDocument85 pagesIntroduction To Peripheral Nervous System Pharmacology: Dr. M. IchwanGarry B GunawanNo ratings yet
- 19 - ChemotherapyDocument38 pages19 - ChemotherapymeshoshalabyNo ratings yet
- The Anatomical Foundations of Regional Anesthesia and Acute Pain MedicineFrom EverandThe Anatomical Foundations of Regional Anesthesia and Acute Pain MedicineNo ratings yet
- Cholinoceptor-Activating, Cholinesterase-Inhibiting Drugs and Cholinoceptor-Blocking DrugsDocument6 pagesCholinoceptor-Activating, Cholinesterase-Inhibiting Drugs and Cholinoceptor-Blocking DrugsCarlos NiñoNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology I Cholinoceptor-Activating & Cholinesterase-Inhibiting DrugsDocument20 pagesPharmacology I Cholinoceptor-Activating & Cholinesterase-Inhibiting Drugsraafat mohammedNo ratings yet
- Autonomic DrugsDocument57 pagesAutonomic DrugsTykee OkonkwoNo ratings yet
- Skeletal Muscle Relaxants 1Document21 pagesSkeletal Muscle Relaxants 1pooja sureshNo ratings yet
- Performance of Clinical SignsDocument4 pagesPerformance of Clinical SignsDina AryaniNo ratings yet
- Chest PainDocument9 pagesChest PainIlyes FerenczNo ratings yet
- Claw Hand: Diagnosis and ManagementDocument25 pagesClaw Hand: Diagnosis and ManagementAditya Pratama SaaninNo ratings yet
- History ChecklistDocument5 pagesHistory ChecklistDianeNo ratings yet
- Communicable DiseasesDocument17 pagesCommunicable DiseasesKriska NoelleNo ratings yet
- REACTION-PAPERDocument1 pageREACTION-PAPERPaulineNicole MacanasNo ratings yet
- Faraz Pearls MRCP Part 2 by Faraz Ahmed YnzDocument466 pagesFaraz Pearls MRCP Part 2 by Faraz Ahmed Ynzashwini dhote100% (1)
- A Childbirth Cheat Sheet For Dads-To-be - Baby CenterDocument3 pagesA Childbirth Cheat Sheet For Dads-To-be - Baby CenterDrhtrth AsdfghsfgNo ratings yet
- Caso 1Document14 pagesCaso 1Luanna DávilaNo ratings yet
- Ambulance Nurse Call For ApplicationsDocument2 pagesAmbulance Nurse Call For ApplicationschelseapasiahNo ratings yet
- Emerging Dimensions in Artificial Intelligence in Medical Diagnosis and Health CareDocument10 pagesEmerging Dimensions in Artificial Intelligence in Medical Diagnosis and Health CareGracy SinghNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2 UNIT 1 Introduction To PathologyDocument61 pagesMODULE 2 UNIT 1 Introduction To PathologyICE ADRIENNE OCAMPONo ratings yet
- Head and Neck TumoursDocument50 pagesHead and Neck Tumoursene.dubemNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Palsy AnatomyDocument5 pagesCerebral Palsy AnatomyIoana irimiaNo ratings yet
- Depression in Older AdultsDocument5 pagesDepression in Older AdultsC Hendra WijayaNo ratings yet
- Pakpak LawinDocument16 pagesPakpak Lawinmaylene estoque0% (1)
- Oxygen Concentrator - Rapid Construction of Oxygen Concentrators With Minimal Technical RequirementsDocument2 pagesOxygen Concentrator - Rapid Construction of Oxygen Concentrators With Minimal Technical RequirementsleandroniedbalskiNo ratings yet
- Drugs AddictionDocument25 pagesDrugs AddictionReader67% (3)
- Daftar Pustaka: Affect Disord. 2003 73 (1-2) :123-31Document2 pagesDaftar Pustaka: Affect Disord. 2003 73 (1-2) :123-31Jumria Tandi PanggaloNo ratings yet
- Nerve Conduction Study - WikipediaDocument24 pagesNerve Conduction Study - WikipediaAravind Mohanan100% (1)
- Hiv Education Prevention ProgramDocument16 pagesHiv Education Prevention ProgramGelvia Awaeh0% (1)
- Peptic UlcerDocument23 pagesPeptic UlcerRomarie Salvador-CastilloNo ratings yet
- Faculties of GMERS Medical College, GandhinagarDocument36 pagesFaculties of GMERS Medical College, GandhinagarSmitaNo ratings yet
- Case Study Vital Pulp Therapy 5Document1 pageCase Study Vital Pulp Therapy 5chen danielNo ratings yet
- Cholinomimetic Drugs: (Parasympathomimetic DrugDocument60 pagesCholinomimetic Drugs: (Parasympathomimetic DrugGodishala Purna ChandrakalaNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae: More Than 2 Years Job ExperienceDocument4 pagesCurriculum Vitae: More Than 2 Years Job ExperienceDr. Uzair HamidNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology The Foundation of Public Health PDFDocument34 pagesEpidemiology The Foundation of Public Health PDFgabe18No ratings yet
- Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Pathophysiology DiagramDocument3 pagesAcute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Pathophysiology DiagrammonishaNo ratings yet
- Roles of Laboratory ProfessionalsDocument14 pagesRoles of Laboratory ProfessionalsOsama BakheetNo ratings yet