Hamming Code
Uploaded by
Prabin RathHamming Code
Uploaded by
Prabin RathCalculating the Hamming Code http://www.cs.fiu.edu/~downeyt/cop3402/hamming.
html
Calculating the Hamming Code
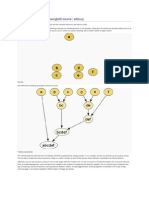
The key to the Hamming Code is the use of extra parity bits to allow the identification of a single error.
Create the code word as follows:
1. Mark all bit positions that are powers of two as parity bits. (positions 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, etc.)
2. All other bit positions are for the data to be encoded. (positions 3, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 17,
etc.)
3. Each parity bit calculates the parity for some of the bits in the code word. The position of the parity bit
determines the sequence of bits that it alternately checks and skips.
Position 1: check 1 bit, skip 1 bit, check 1 bit, skip 1 bit, etc. (1,3,5,7,9,11,13,15,...)
Position 2: check 2 bits, skip 2 bits, check 2 bits, skip 2 bits, etc. (2,3,6,7,10,11,14,15,...)
Position 4: check 4 bits, skip 4 bits, check 4 bits, skip 4 bits, etc. (4,5,6,7,12,13,14,15,20,21,22,23,...)
Position 8: check 8 bits, skip 8 bits, check 8 bits, skip 8 bits, etc. (8-15,24-31,40-47,...)
Position 16: check 16 bits, skip 16 bits, check 16 bits, skip 16 bits, etc. (16-31,48-63,80-95,...)
Position 32: check 32 bits, skip 32 bits, check 32 bits, skip 32 bits, etc. (32-63,96-127,160-191,...)
etc.
4. Set a parity bit to 1 if the total number of ones in the positions it checks is odd. Set a parity bit to 0 if
the total number of ones in the positions it checks is even.
Here is an example:
A byte of data: 10011010
Create the data word, leaving spaces for the parity bits: _ _ 1 _ 0 0 1 _ 1 0 1 0
Calculate the parity for each parity bit (a ? represents the bit position being set):
Position 1 checks bits 1,3,5,7,9,11:
? _ 1 _ 0 0 1 _ 1 0 1 0. Even parity so set position 1 to a 0: 0 _ 1 _ 0 0 1 _ 1 0 1 0
Position 2 checks bits 2,3,6,7,10,11:
0 ? 1 _ 0 0 1 _ 1 0 1 0. Odd parity so set position 2 to a 1: 0 1 1 _ 0 0 1 _ 1 0 1 0
Position 4 checks bits 4,5,6,7,12:
0 1 1 ? 0 0 1 _ 1 0 1 0. Odd parity so set position 4 to a 1: 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 _ 1 0 1 0
Position 8 checks bits 8,9,10,11,12:
0 1 1 1 0 0 1 ? 1 0 1 0. Even parity so set position 8 to a 0: 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0
Code word: 011100101010.
Finding and fixing a bad bit
The above example created a code word of 011100101010. Suppose the word that was received was
011100101110 instead. Then the receiver could calculate which bit was wrong and correct it. The method is
to verify each check bit. Write down all the incorrect parity bits. Doing so, you will discover that parity bits 2
and 8 are incorrect. It is not an accident that 2 + 8 = 10, and that bit position 10 is the location of the bad bit.
In general, check each parity bit, and add the positions that are wrong, this will give you the location of the
bad bit.
Try one yourself
Test if these code words are correct, assuming they were created using an even parity Hamming Code . If one
is incorrect, indicate what the correct code word should have been. Also, indicate what the original data was.
010101100011
111110001100
000010001010
1 of 1 03/14/2005 04:30 PM
You might also like
- cheatsheet-transformers-large-language-modelsNo ratings yetcheatsheet-transformers-large-language-models4 pages
- Unit10 - Hamming Code With Exercises ConditionalsNo ratings yetUnit10 - Hamming Code With Exercises Conditionals10 pages
- DE-Unit - 1 Error Detection & Correction Code, Parity Bit, Hamming CodeNo ratings yetDE-Unit - 1 Error Detection & Correction Code, Parity Bit, Hamming Code5 pages
- Hamming Code in Computer Network - GeeksforGeeksNo ratings yetHamming Code in Computer Network - GeeksforGeeks16 pages
- Error Detection and Correction: CIT 595 Spring 2008No ratings yetError Detection and Correction: CIT 595 Spring 20087 pages
- Error Detection / Correction: Computer Organization & ArchitectureNo ratings yetError Detection / Correction: Computer Organization & Architecture18 pages
- Error Detection / Correction: Computer Organization & ArchitectureNo ratings yetError Detection / Correction: Computer Organization & Architecture18 pages
- Error Correcting Codes: 15-1 IntroductionNo ratings yetError Correcting Codes: 15-1 Introduction27 pages
- 9-Error Detection and Correction-21!01!2022 (21-Jan-2022) Material I 21-01-2022 Error Detection - Correction-UpNo ratings yet9-Error Detection and Correction-21!01!2022 (21-Jan-2022) Material I 21-01-2022 Error Detection - Correction-Up56 pages
- 9-Error Detection and Correction-21!01!2022 (21-Jan-2022) Material I 21-01-2022 Error Detection - Correction-UpNo ratings yet9-Error Detection and Correction-21!01!2022 (21-Jan-2022) Material I 21-01-2022 Error Detection - Correction-Up56 pages
- Improved Hamming Code For Error Detection and Correction: U. K. Kumar, Member, IEEE, and B. S. UmashankarNo ratings yetImproved Hamming Code For Error Detection and Correction: U. K. Kumar, Member, IEEE, and B. S. Umashankar3 pages
- Experiment No.: 2: AIM: To Perform Encoding and Decoding For Hamming Code. APPARATUS: Scilab. TheoryNo ratings yetExperiment No.: 2: AIM: To Perform Encoding and Decoding For Hamming Code. APPARATUS: Scilab. Theory4 pages
- Binary, Error Detection & Correction Codes - Logic GatesNo ratings yetBinary, Error Detection & Correction Codes - Logic Gates8 pages
- Experiment No.: 2: AIM: To Perform Encoding and Decoding For Hamming Code. APPARATUS: Scilab. TheoryNo ratings yetExperiment No.: 2: AIM: To Perform Encoding and Decoding For Hamming Code. APPARATUS: Scilab. Theory4 pages
- IT-2205 Lec 04 Error Detection & Correction-2No ratings yetIT-2205 Lec 04 Error Detection & Correction-235 pages
- Lecture14 Hash Based Indexing and Sorting MHH 18oct 2016No ratings yetLecture14 Hash Based Indexing and Sorting MHH 18oct 201671 pages
- (Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing 358) Hoai an Le Thi, Ngoc Thanh Nguyen, Tien Van Do (Eds.)-Advanced Computational Methods for Knowledge Engineering_ Proceedings of 3rd International ConNo ratings yet(Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing 358) Hoai an Le Thi, Ngoc Thanh Nguyen, Tien Van Do (Eds.)-Advanced Computational Methods for Knowledge Engineering_ Proceedings of 3rd International Con416 pages
- Numerical Methods and Optimization An IntroductionNo ratings yetNumerical Methods and Optimization An Introduction408 pages
- Complete Download Image Processing The Fundamentals Second Edition Maria Petrou PDF All Chapters100% (1)Complete Download Image Processing The Fundamentals Second Edition Maria Petrou PDF All Chapters67 pages
- Modul 11 Siskom1 Base Band TransmissionNo ratings yetModul 11 Siskom1 Base Band Transmission16 pages
- Learn X in Y Minutes - Scenic Programming Language ToursNo ratings yetLearn X in Y Minutes - Scenic Programming Language Tours7 pages
- Apache Spark with Scala - cheatsheet (1) (1)No ratings yetApache Spark with Scala - cheatsheet (1) (1)7 pages
- Contents:: CS-201 Lab Manual Lab 4: Sorting: Insertion SortNo ratings yetContents:: CS-201 Lab Manual Lab 4: Sorting: Insertion Sort5 pages
- Calc BC Limits and Continuity Exam (Unit 1)No ratings yetCalc BC Limits and Continuity Exam (Unit 1)5 pages
- Scheduling Algorithms (SRTF, RR, Priority) : Nisha SinghNo ratings yetScheduling Algorithms (SRTF, RR, Priority) : Nisha Singh27 pages
- Lec-13.SS (3150912) Convolution Integral and SumNo ratings yetLec-13.SS (3150912) Convolution Integral and Sum32 pages